Ivoclar Vivadent SR Vivo TAC User Manual [en, de, fr, it, es]

SR |
VivoTAC / |
SR |
|
|
Instructions for Use
OrthoTAC
Page 2
Verarbeitungsanleitung
Seite 12
Mode d’emploi
Page 22
Istruzioni d’uso
Pagina 32
Instrucciones de uso
Pagina 42
Instruções de Uso
Página 52

Instructions for Use
Introduction
Please read these Instructions for Use carefully and familiarize yourself with the application techniques.
The prefabricated SR Vivo TAC / SR Ortho TAC tooth line is a diagnostic, radiopaque tool that is designed to help dental technicians fabricate implant-supported restorations. Because of their special composition, these teeth are radiopaque.
Advantages
–A defined radiopacity achieved through industrial fabrication
–Moulds corresponding to those of the popular SR Vivodent / SR Orthotyp and SR Vivodent PE / SR Orthotyp PE tooth lines
–Easily prepared diagnostic aid
–The shape of radiopaque teeth can be modified with radiopaque monomers and polymers
–Strong bond with heat-curing as well as cold-curing polymers
–Prefabricated radiopaque teeth save time in the fabrication of stents
–The teeth ensure the accurate placement of dental implants during the planning phase
–Homogeneous dispersion of the radiopaque material in the teeth
Composition
The resin teeth are composed of the following ingredients:
Polymethyl methacrylate and barium sulphate 66–67 wt%
Methyl methacrylate and dimethacrylate 33–34 wt% Additional components: catalysts and stabilizers
0.5 wt%
Modifier Monomer:
Methyl methacrylate and dimethacrylate 99 wt% Catalysts and stabilizers 1 wt%
Modifier Polymer:
Polymethyl methacrylate and barium sulphate > 99 wt%
Catalyst < 1 wt%
Indication
For the fabrication of fixed and removable implantsupported dental restorations in situations where the set-up of teeth is beneficial to the pre-surgical radiological diagnosis (CT, teleradiography as well as OPG), eg:
–severe dysgnathia
–severe atrophy of the alveolar ridge
–reconstructive surgery of the mouth, jaw or face
Pre-surgical planning of the restoration enables the ideal placement, location and angulation of the implant to be established.
Contraindication
The product is contraindicated for all the applications that are not specifically recommend by Ivoclar Vivadent as well as for permanent restorations in the mouth of patients.
In case of fixed metal prosthetics, metal fillings or metal osteosynthetic materials, the image quality of the CT and thus the recognizability of the radiopaque tooth may be impaired.
Side effects
To date, no systemic side effects are known. In rare cases, allergic reactions have been reported in conjunction with methyl methacrylate and polymethyl methacrylate materials. Do not use SR Vivo TAC / SR Ortho TAC or Modifier Polymer and Monomer if a patient is known to be allergic to any of the products’ ingredients.
2

Processing
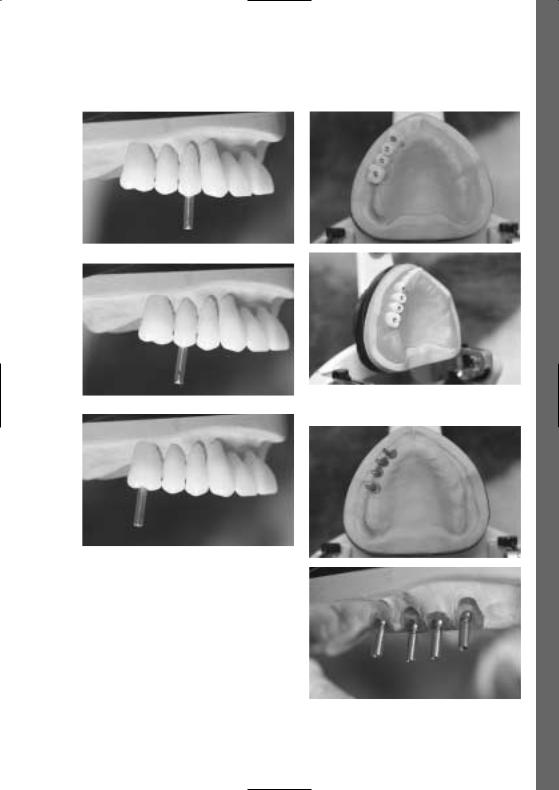
The radiopaque teeth SR Vivo TAC / SR Ortho TAC are set up according to conventional principles. The moulds of the radiopaque teeth are identical to those of the SR Vivodent / SR Orthotyp tooth line. SR Vivo TAC /
SR Ortho TAC exhibit excellent, consistent radiopacity. Consequently, the two and three-dimensional relationship between the position of the implant and that of the subsequent superstructure can be established.
Fabrication of diagnostic stents
1. Laboratory
Diagnostic stents are fabricated to allow the implantsupported complete denture to be set up according to the instructions of the dentist, taking aesthetic, phonetic and functional aspects into account. In the process,
SR Vivo TAC / SR Ortho TAC are used like conventional denture teeth.
The use of set-up aids such as the 2D/3D setting up template (Ivoclar Vivadent AG) is recommended.
Suggested procedure
Once the radiopaque teeth have been set up in wax, excess wax in the vestibular region is removed to lengthen the cervical region with the Monomer/Polymer Modifier until the base of the tooth rests on the model. Consequently, the entire length of the tooth is made of radiopaque material.
Wax model with lengthened cervical regions
English
3
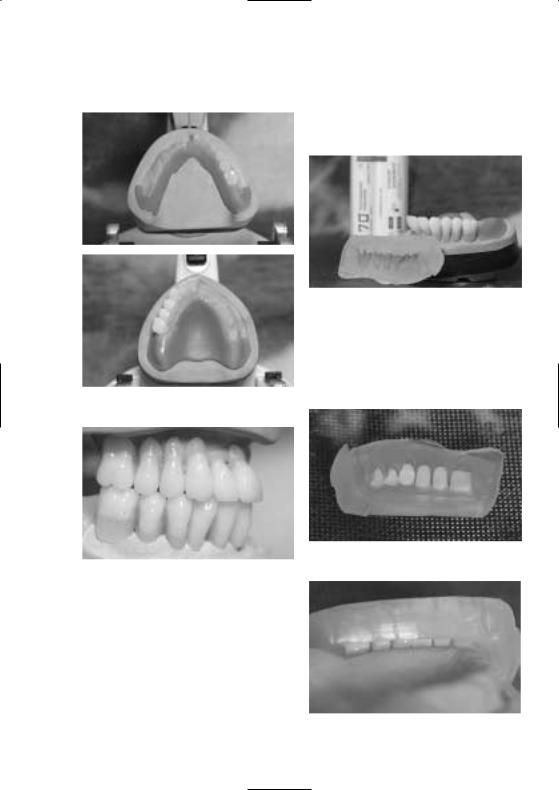
Adjustment of shape
– Following the set-up and wax-up procedures, a key is fabricated using silicone or plaster.
Key of teeth set up in wax
– Remove wax from the model and teeth without leaving any residue. If a plaster key is used, the model and the key have to be isolated with Ivoclar Vivadent Separating Fluid. In addition, the tooth surfaces requiring adjustments must be roughened.
Completed wax model
Reposition the teeth in the key
Completed model with lengthened cervical regions
Check the accuracy of fit
4
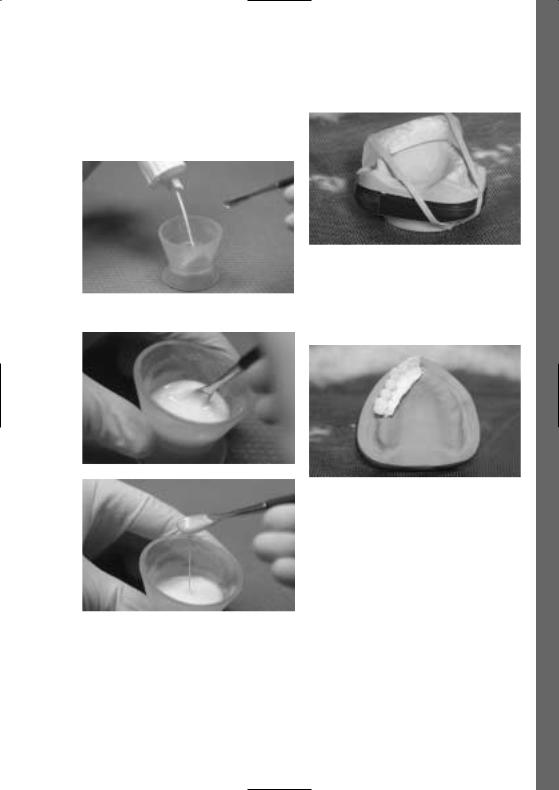
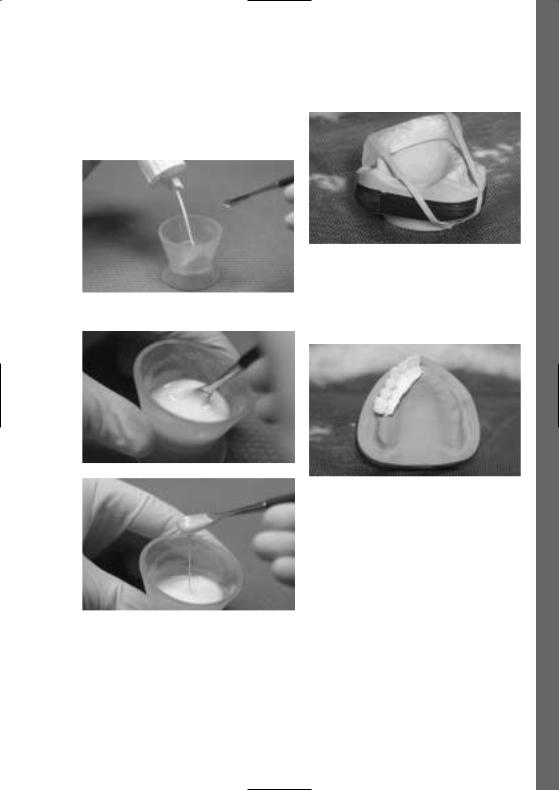
–Mix the Polymer and Monomer Modifier in a 1.3 : 1 ratio and leave to rest uncovered for 2–3 minutes.
Secure the key
– Polymerization is conducted in a pressure device or in Mix the Monomer and Polymer Modifier a heat/pressure polymerization unit (eg Ivomat),
15 minutes at 40–50 °C / 104–122 °F and 2–6 bar pressure.
After polymerization
If necessary, radiographic balls or similar aids may be integrated into the diagnostic stents where they are needed.
Pour the liquid material into the key
English
5
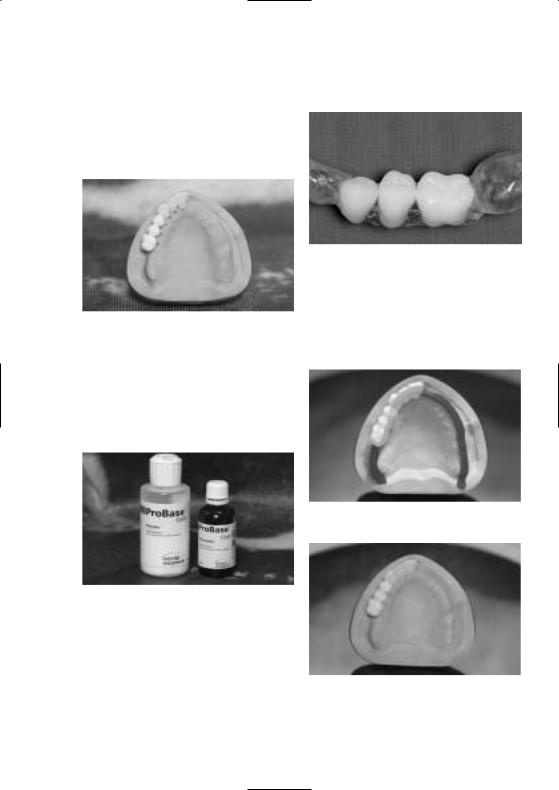
Finishing
Conventional finishing and polishing instruments are used for finishing (according to the conventional PMMA working techniques).
After finishing
Fabrication of base plates
In order to reinforce or stabilize the diagnostic stents, a base plate is fabricated for the palatal or lingual region. It is made of clear or pink denture base material (eg ProBase Cold pink/clear) or a heat-curing polymer (eg ProBase Hot pink/clear).
Stent design for gaps
If requested by the dentist, a radiopaque alveolar ridge with mucosa can be created by coating this area with the Monomer/Polymer Modifier.
Space retainer for radiopaque Modifier material
ProBase Cold clear (also available in pink)
When fixed restorations are planned (eg with an interdental gap), the base plate rests on the mesial or distal remaining dentition to stabilize and position the restoration.
Polymerized stents
6

Polishing
As the stents are used as a diagnostic tool and/or an aid during the surgical intervention, thorough prepolishing with goat’s hair brushes and pumice as well as high gloss polishing with cotton buffers and polishing paste (Universal Polishing Paste from Ivoclar Vivadent) is recommended.
Finished diagnostic stent
Option
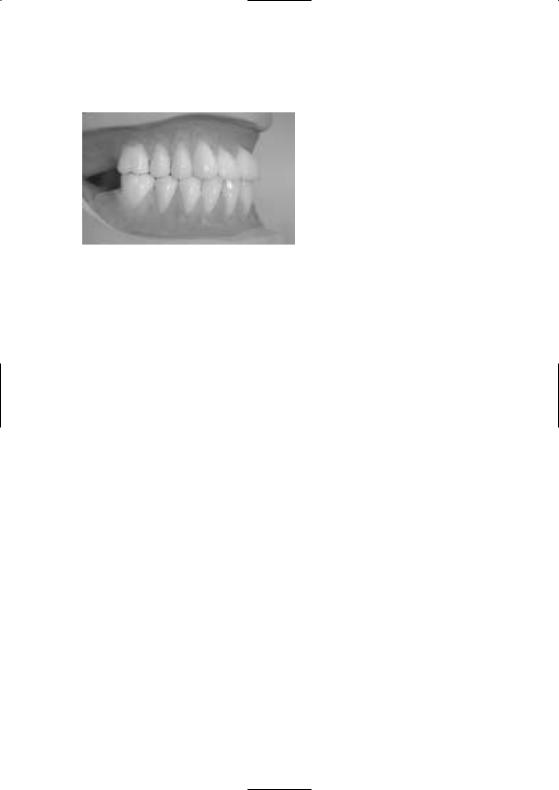
Diagnostic stent for complete maxillary denture
Check the occlusion
English
7
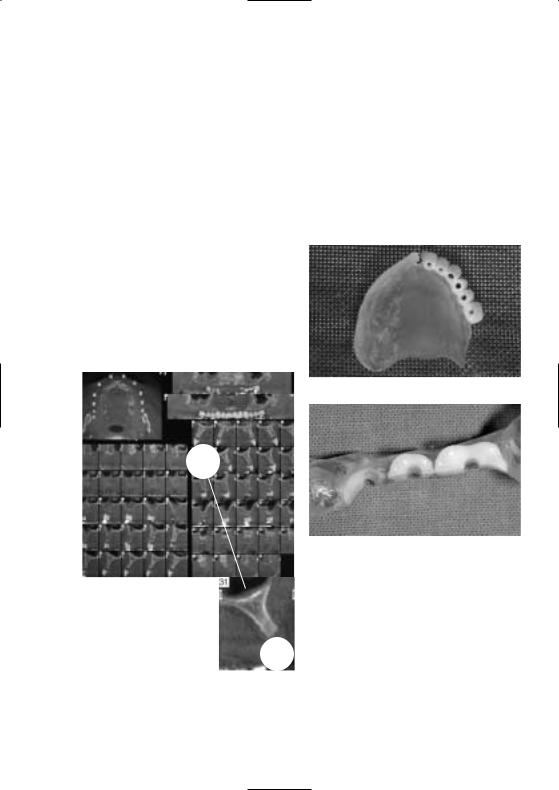
Transformation of the diagnostic stent into a surgical stent
Practice/Laboratory
When the dentist receives the stent from the laboratory, he or she can conduct a try-in to examine the aesthetics, phonetics and function of the planned dental restoration. It is advisable to make any necessary adjustments before the radiographic examination.
The radiograph serves as an additional treatment planning instrument. It enables the dental professional to establish the location and angulation of the implants, taking the bone substance and functional requirements of the future restoration into consideration.
(If necessary, radiographic balls or hollow titanium cylinders may be used with the stent.)
Application
In order to create guide channels prior to the surgical part of the treatment, the dentist (or dental technician) drills through the radiopaque teeth. These channels assist the clinician during the surgical intervention. In order to establish ideal prerequisites for the subsequent fabrication of the superstructure, the angles of the implant axes must be as parallel as possible.
CT image
Creation of guide channels
Reduced teeth as an alternative
The surgical stents are used according to the preferred method of the user with the customary materials.
8
English
Completed surgical stent
Tooth and implant axes
Implant axes on the model
9
Completed acrylic resin denture
Additional applications
–Insertion of metal guide channels
–Sagittal reduction of the vestibular or oral region of the guide channel up to the first half of the drill holes.
Source:
Pictures courtesy of M Nanni, Dr A Fanti, P Miceli, Italy
Warnings
–The inhalation of grinding dust must be avoided.
–Mucous membranes must not come into contact with uncured material.
–Prolonged or repeated skin contact with the monomer and uncured material may cause irritation and sensitivity to methacrylates.
–The Modifier Monomer contains methyl methacrylate.
–MMA is easily flammable and irritating (flash point +10 °C / 50 °F).
–Irritating to the eyes, skin and respiratory organs.
–Do not inhale vapours.
–May cause sensitization by skin contact.
–Keep away from ignition sources. Do not smoke.
–Do not empty in drains.
Storage of the Modifier Monomer /
Modifier Polymer
–Store in a cool, dark place.
–Storage temperature: 12–28 °C / 54–82 °F
–See secondary packaging for storage instructions and expiry date.
–Do not use the product after the indicated date of expiration.
–Keep out of the reach of children.
Delivery form
Basic Kit
1x SR Vivo TAC upper anterior teeth in moulds A15, A24B, A25, A27
1x SR Vivo TAC lower anterior teeth in moulds A4, A8, A9
1x SR Ortho TAC upper posterior teeth in moulds N2, N6
1x SR Ortho TAC lower posterior teeth in moulds N2, N6
Modifier Kit (1 Monomer 30 ml, 1 Polymer 30 g) Instructions for Use
Refills
–SR Vivo TAC A15, A24B, A25, A27, A4, A8, A9
–SR Ortho TAC N2, N6 upper and lower
–Polymer Modifier 30 ml
–Monomer Modifier 30 g
10

This product has been developed solely for use in dentistry. Processing should be carried out strictly according to the Instructions for Use. Liability cannot be accepted for damages resulting from failure to observe the Instructions or the stipulated area of application. The user is responsible for testing the materials for their suitability and use for any purpose not explicitly stated in the Instructions. Descriptions and data constitute no warranty of attributes and are not binding.
Date information prepared
03/2004
Ivoclar Vivadent AG
FL-9494 Schaan / Liechtenstein
English
11

Verarbeitungsanleitung
Prämisse
Bitte lesen Sie diese Verabeitungsanleitung aufmerksam durch und machen Sie sich mit der Anwendung vertraut.
Die präfabrizierten Zähne SR Vivo TAC / SR Ortho TAC stellen ein diagnostisches röntgenopaques Instrument dar, welches der Zahntechniker zur Unterstützung bei der nachfolgenden Realisierung von implantatgetragenen Restaurationen verwenden kann.
Dank der besonderen Zusammensetzung besitzen diese Zähne eine röntgenopaque Wirkung.
Vorteile:
–Die industrielle Herstellung ermöglicht eine definierte Röntgenopazität
–Die Formen entsprechen den bekannten Zahnlinien SR Vivodent / SR Orthotyp oder SR Vivodent PE / SR Orthotyp PE
–Einfaches Erstellen eines diagnostischen Hilfsmittels
–Formveränderungen der röntgenopaquen Zähne mittels röntgenopaquem Polymer und Monomer möglich
–Hoher Verbund sowohl mit Heisspolymerisat als auch mit Kaltpolymerisat
–Zeitersparnis bei der Herstellung von Bohrschienen durch präfabrizierte, röntgenopaque Zähne
–Dient der gezielten Positionsbestimmung dentaler Implantate während der Planungsphase für dentale, implantologische Rekonstruktionen
–Homogene Durchmischung der Zähne mit Röntgenkontrastmittel
Zusammensetzung:
Die Kunststoffzähne bestehen aus folgenden Inhaltsstoffen:
Polymethylmethacrylat und Bariumsulfat 66–67 Gew.%; Methylmethacrylat und Dimethacrylat 33–34 Gew.%. Zusätzlich enthalten sind Katalysator und Stabilisatoren 0.5 Gew.%.
Modifier Monomer:
Methylmethacrylat und Dimethacrylat 99 Gew.%: Katalysator und Stabilisatoren 1 Gew.%.
Modifier Polymer:
Polymethylmethacrylat und Bariumsulfat > 99 Gew.%: Katalysator < 1 Gew.%
Indikation:
Zur Anfertigung von festsitzendem und abnehmbarem implantatgetragenen Zahnersatz, bei dem zur präoperativen, radiologischen Diagnostik (CT, Fernröntgen aber auch OPG möglich) Zahnaufstellungen von Vorteil sind, wie z.B. bei:
–ausgeprägter Dysgnathie
–ausgeprägter Alveolarkammatrophie
–mund-, kieferund gesichtschirurgischen Korrekturen und Rekonstruktionen
Durch die präoperative Diagnostik der geplanten Versorgung kann eine ideale Implantatposition ermittelt und festgelegt werden.
Kontraindikation:
Für alle Indikationen, die nicht ausdrücklich von Ivoclar Vivadent empfohlen werden und für die Verwendung als im Mund des Patienten permanent verbleibenden Zahnersatz.
Beim Vorliegen von festsitzendem, metallischen Zahnersatz, metallischen Füllungen oder metallischen Osteosynthesematerial kann die Bildqualität des CT und damit die Erkennbarkeit des röntgenopaquen Zahnes beeinträchtigt werden.
Nebenwirkungen:
Systemische Nebenwirkungen sind bisher keine bekannt. In Einzelfällen wurden bei Methylmethacrylatund Polymethylmethacrylat-Materialien allergische Reaktionen beschrieben. Bei erwiesener Allergie auf Bestandteile von SR Vivo TAC / SR Ortho TAC und Modifier Polymer wie Monomer auf die Anwendung verzichten.
12
Verarbeitung
Die Anwendung der röntgenopaquen Zähne SR Vivo TAC / SR Ortho TAC erfolgt analog den üblichen Aufstellprinzipien. Die röntgenopaquen Zahnformen sind mit den entsprechenden Zähnen der SR Vivodent /
SR Orthotyp Zahnlinie formenidentisch. SR Vivo TAC / SR Ortho TAC besitzen eine ausgezeichnete, konstante Radiopazität. Somit kann der 2- bzw. 3-dimensionale Bezug zwischen der Implantatposition und der Position der späteren Suprakonstruktion hergestellt werden.
Herstellung der diagnostischen Bohrschiene
1. Labor
Bei der Herstellung einer diagnostischen Bohrschiene zur späteren Herstellung einer implantat-
getragenen Restauration kann anhand der Angaben des Zahnarztes eine entsprechende Aufstellung unter Berücksichtigung von Ästhetik, Phonetik und Funktion erstellt werden. Dabei wird SR Vivo TAC / SR Ortho TAC wie ein konventioneller Prothesenzahn angewendet. Die Anwendung von Aufstellhilfen wie z.B. 2D/3DAufstellkalotten (Ivoclar Vivadent AG) ist empfehlenswert.
Mögliche Vorgehensweise
Nach der Aufstellung der röntgenopaquen Zähne in Wachs wird überschüssige, vestibuläre Wachsmodellation entfernt, um den Zahnhals mit Monomer/Polymer Modifier so zu verlängern, dass die Zahnbasis auf dem Modell zu liegen kommt. Somit ist die spätere gesamte Zahnlänge aus röntgenopaquem Material gefertigt.
Wachsaufstellung mit verlängerten Zahnhälsen
Deutsch
13

Formänderung
– Nach dem Aufstellen und dem Wax-up, wird ein Schlüssel in Silikon oder Gips erstellt.
Schlüssel der Wachsaufstellung
– Wachs rückstandslos von Modell und Zähnen entfernen. Bei Verwendung von Gipsschlüsseln, das Modell sowie den Schlüssel mit Ivoclar Vivadent Separating Fluid isolieren und die Zähne an den zu ergänzenden Flächen anrauhen.
Komplette Wachsaufstellung
Repositionierung der Zähne im Schlüssel
Komplette Wachsmodellation mit verlängerten Zahnhälsen
Überprüfung der Passgenauigkeit
14
–Polymer und Monomer Modifier im Verhältnis 1,3:1 anmischen und 2–3 Minuten abgedeckt ruhen lassen.
Schlüssel fixieren
– Die Polymerisation erfolgt im Drucktopf oder im Anmischen von Polymer und Monomer Modifier Druck- /Hitze-Polymerisationsgerät (z.B. Ivomat),
15 Min. bei 40–50 °C und 2–6 bar Druck.
Nach der Polymerisation
Bei Bedarf können in die diagnostische Bohrschiene Röntgenmesskugeln oder ähnliche Hilfsmittel an geeigneter Stelle integriert werden.
Die noch flüssige Masse in den Schlüssel einfliessen lassen
Deutsch
15
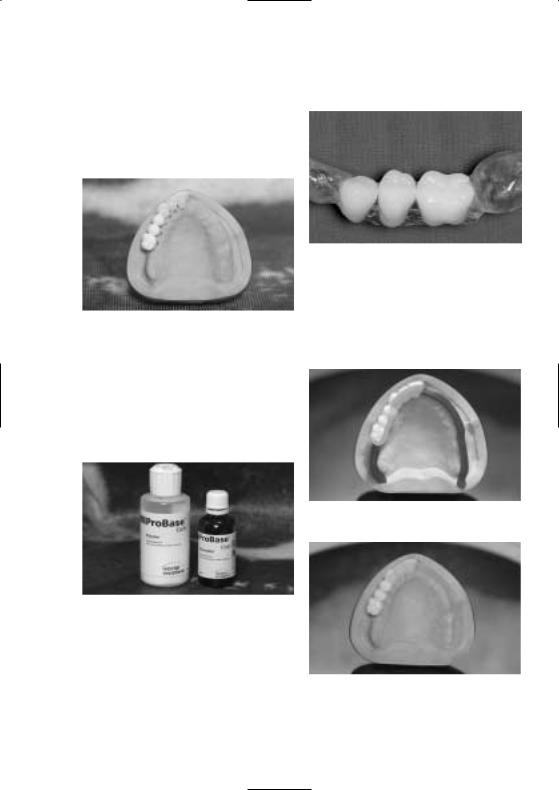
Ausarbeitung
Die Ausarbeitung erfolgt mit üblichen Schleifund Polierkörpern (analog der branchenüblichen PMMA Verarbeitung).
Nach der Ausarbeitung
Fertigung der Basisplatten
Zur Verstärkung bzw. Stabilisierung der diagnostischen Bohrschiene wird im palatinalen oder lingualen Bereich eine Basisplatte aus transparentem oder rosa Prothesenbasis-Kunststoff (z.B. ProBase Cold pink/clear) oder Heisspolymerisat (z.B. ProBase Hot pink/clear) hergestellt.
Bohrschienendesign bei Schaltlücken
Um dem Wunsch eines Zahnarztkunden gerecht zu werden, den Verlauf des Kieferkammes mit Schleimhaut röntgenopaque darzustellen, kann dieser Bereich ebenfalls mit dem Monomer/ Polymer Modifier bedeckt werden.
Platzhalter für röntgenopaques Modifier Material
ProBase Cold clear (auch in pink erhältlich)
Bei der Planung von festsitzenden Versorgungen (mit z.B. Schaltlücke) wird die Basisplatte zur Stabilisierung und Positionierung auf der mesialen bzw. distalen Rest-
bezahnung abgestützt.
Polymerisierte Bohrschienen
16
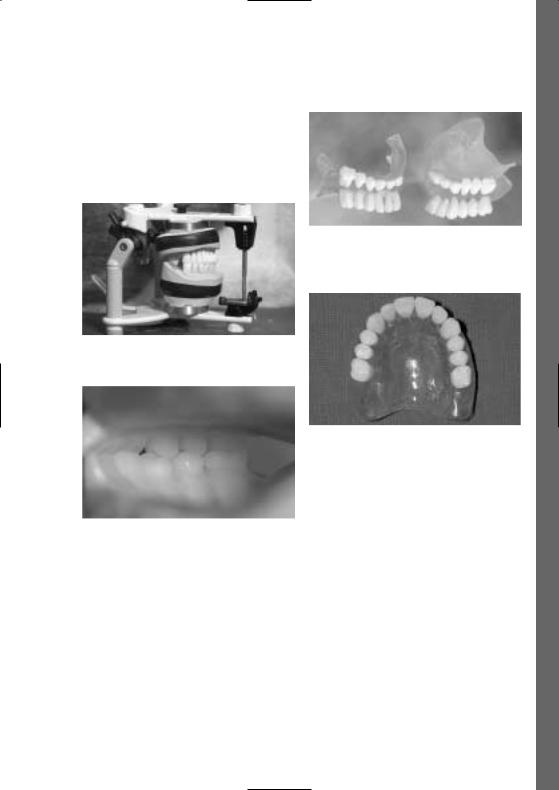
Politur
Da die Bohrschiene zur Diagnose und/oder als Hilfsmittel während des chirurgischen Eingriffs dient, wird eine gute Vorpolitur mit Ziegenhaarbürste, Bimsstein und eine Hochglanzpolitur mit Baumwollschwabbel und Polierpaste (Ivoclar Vivadent Universal Polierpaste) empfohlen.
Fertige diagnostische Bohrschiene
Variante
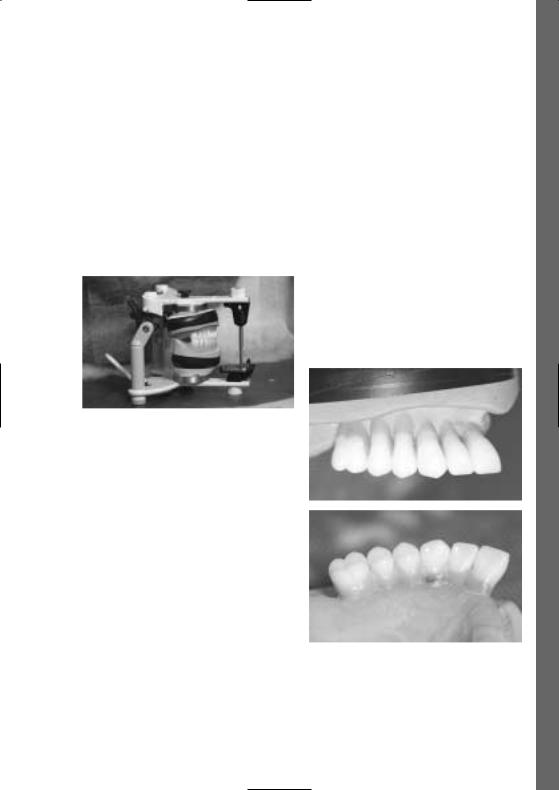
Diagnostische Bohrschiene im Artikulator
Diagnostische Bohrschiene für OK-Totale
Kontrolle der Okklusion
Deutsch
17
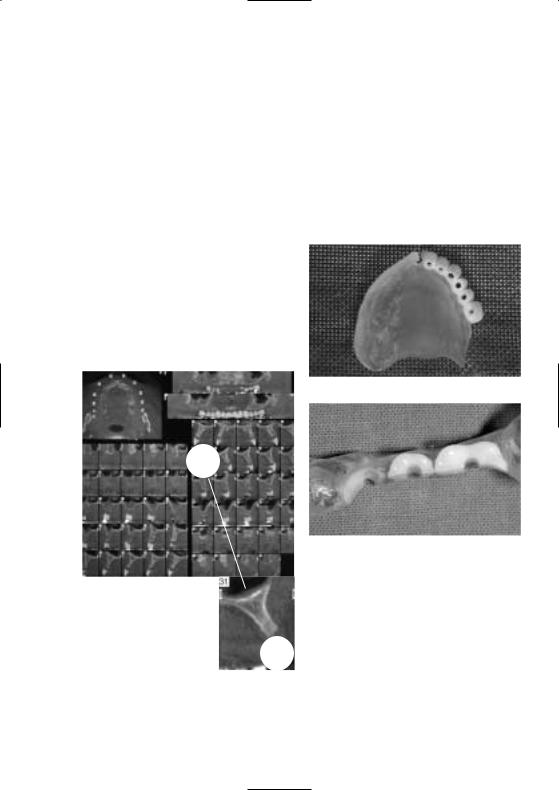
Umwandlung des diagnostischen Instruments in eine chirurgische Bohrschiene
Praxis/Labor
Beim Erhalt der Bohrschiene aus dem Labor kann der Zahnarzt eine Einprobe durchführen, um die Ästhetik, Phonetik und Funktion des geplanten Zahnersatzes zu beurteilen. Bevor die Röntgenaufnahme durchgeführt wird, empfiehlt es sich, notwendige Korrekturen umzusetzen.
Mit dieser Röntgenaufnahme als unterstützendes Instrument für die therapeutische Planung kann der Zahnarzt die Position der Implantate unter Berücksichtigung von Knochensubstanz und funktionellen Anforderungen der späteren Restauration festlegen (bei Bedarf kann die Bohrschiene mit metallischen
Röntgenmesskugeln oder Titanhülsen versehen werden.)
CT Aufnahme
Anwendungsmöglichkeit
Zur Schaffung von Führungskanälen vor dem chirurgischen Teil wird der Zahnarzt (oder Zahntechniker) die röntgenopaquen Zähne durchbohren, sodass die Führungskanäle den Kliniker während dem chirurgischen Eingriff unterstützen. Dazu ist, um ideale Voraussetzungen für die spätere Erstellung der Suprastruktur zu schaffen, eine möglichst parallele Position der Implantat-Angulation zu definieren.
Umsetzung der Führungskanäle
Reduzierte Zähne als Variante
Die Anwendung chirurgischer Bohrschienen erfolgt grundsätzlich in der vom Anwender gewohnten Weise unter Verwendung der gewohnten Materialien.
18
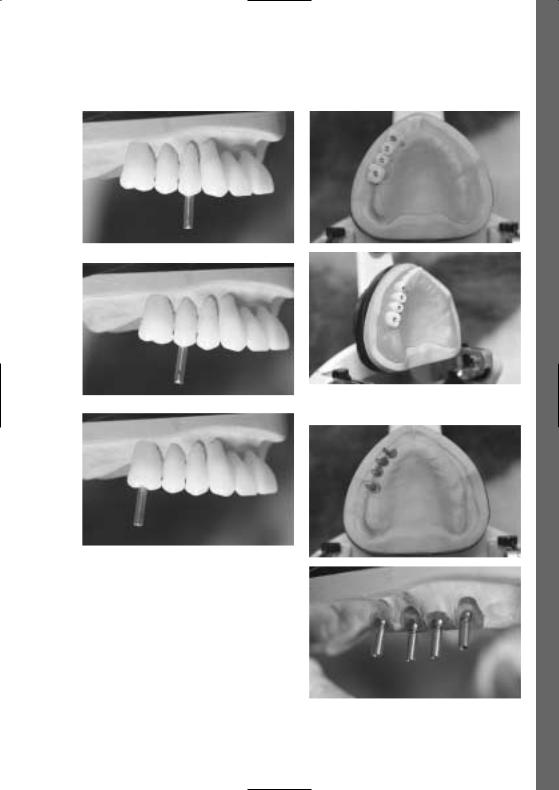
Deutsch
Fertige chirurgische Bohrschienen
Zahnund Implantat-Achsen
Implantat-Achsen auf dem Modell
19

Umsetzung in Kunststoff
Weitere Anwendungsvarianten
–Einbringung von metallischen Führungshülsen als Bohrlehre
–Sagittale Reduktion des vestibulären oder oralen Bereichs der Bohrlehre bis zu den hälftigen Bohrlöchern
Quelle:
Bildmaterial M. Nanni, Dr. A. Fanti, P. Miceli, Italien
Gefahrenhinweise
–Generell das Inhalieren von Schleifstaub vermeiden
–Schleimhautkontakt mit unpolymerisiertem Material unbedingt vermeiden.
–Längerer oder oft wiederholter Hautkontakt mit Monomer und unausgehärtetem Material kann reizend wirken und zu einer Sensibilisierung auf Methylacrylate führen.
–Das Modifier Monomer enthält Methylmethacrylat
–MMA ist leicht entzündlich und reizend (Flammpunkt +10 °C).
–Reizt die Augen, Atmungsorgane und die Haut
–Dämpfe nicht einatmen.
–Sensibilisierung durch Hautkontakt möglich.
–Von Zündquellen fernhalten. Nicht rauchen.
–Nicht in die Kanalisation gelangen lassen.
Lagerungshinweise Modifier Monomer /
Modifier Polymer
–Kühl, trocken und vor Licht geschützt aufbewahren.
–Lagertemperatur 12–28 °C.
–Lagerhinweise und Verfallsdatum auf der Sekundärpackung beachten.
–Produkte nach Ablauf des Verfalldatums nicht mehr verwenden.
–Für Kinder unzugänglich aufbewahren.
Lieferform
Basic Kit
1 x SR Vivo TAC Frontzähne Oberkiefer in den Formen A15, A24B, A25, A27
1 x SR Vivo TAC Frontzähne Unterkiefer in den Formen A4, A8, A9
1x SR Ortho TAC Backenzähne Oberkiefer in den Formen N2, N6
1 x SR Ortho TAC Backenzähne Unterkiefer in den Formen N2, N6
Modifier Kit (1 Monomer 30 ml, 1 Polymer 30 g) Verarbeitungsanleitung
Nachfüllpackungen
–SR Vivo TAC A15, A24B, A25, A27, A4, A8, A9
–SR Ortho TAC N2, N6 obere und untere
–Polymer Modifier 30 g
–Monomer Modifier 30 ml
20
 Loading...
Loading...