Schneider Electric AP9635 User Manual
User’s Guide
AP9635
Network
Management Card

This manual is available in English on the enclosed CD.
Dieses Handbuch ist in Deutsch auf der beiliegenden CD-ROM verfügbar.
Este manual está disponible en español en el CD-ROM adjunto.
Questo manuale è disponibile in italiano nel CD-ROM allegato.
동봉된 CD 안에 한국어 매뉴얼이 있습니다 .
Instrukcja obsługi w języku polskim jest dostępna na CD.
O manual em Português está disponível no CD-ROM em anexo.
您可以从包含的 CD 上获得本手册的中文版本。
您可以从付属的CD上获得本手册的中文版本。

Contents
Introduction ..................................................................... 1
Product Description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1
Features . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1
Initial setup . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2
Network management features . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2
Internal Management Features . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2
Overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2
Access priority for logging on . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3
Types of user accounts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3
How to Recover from a Lost Password . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .4
Front Panel . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .5
Features . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
Status LED . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
Link-RX/TX (10/100) LED . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
Watchdog Features. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
Overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
Network interface watchdog mechanism . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
Resetting the network timer . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
Command Line Interface ................................................ 8
How To Log On . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
Overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
Remote access to the command line interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
Main Screen. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
Sample main screen . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
Information and status fields . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
Using the Command Line Interface. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
Overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
Entering commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
Command syntax . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
Syntax examples . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
Command Response Codes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .12
Network Management Card User’s Guide
i

Command Descriptions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
? . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
about . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
alarmcount . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
boot . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
cd . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
console . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
date . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
delete . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
dir . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
dns . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
eventlog . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
exit . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
format . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
ftp . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
help . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
modbus . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
netstat . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
ntp . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
ping . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
portSpeed . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
prompt . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
quit . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
radius . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
reboot . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
resetToDef . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
snmp, snmp3 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
system . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
tcpip . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
tcpip6 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
tls . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24
uio . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
ups . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
user . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
web . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27
xferINI . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27
xferStatus . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27
Web Interface................................................................. 28
Introduction. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28
Overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28
Supported Web browsers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28
How to Log On . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28
Overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28
URL address formats . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
ii
Network Management Card User’s Guide

Home Page . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .30
Overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30
Quick status icons . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30
Recent Device Events . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30
How to Use the Tabs, Menus, and Links . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .31
Tabs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31
Menus . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31
Quick Links . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31
Monitor the UPS and Configure Shutdowns ............... 32
Overview Page. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .32
Operating state . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 32
Quick Status . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 32
Recent UPS Events . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 33
Status Page . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .33
Model-specific status displayed . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 33
The PowerChute Option . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .34
PowerChute Network Shutdown clients . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 34
PowerChute Network Shutdown configuration parameters . . . . . 35
The About Option . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .36
Environmental Monitoring ............................................37
Overview Page. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .37
Temperature and Humidity Page . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .38
Brief status . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 38
Detailed status and configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 38
Input Contacts Page . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .40
Brief status . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 40
Detailed status and configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 40
Output Relay Page. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .41
About Page. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .41
Configuring the Control Policy . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .42
Configuring an output to respond to an event . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 42
Configuring the UPS or output to respond to an input alarm . . . . 42
Network Management Card User’s Guide
iii

Logs................................................................................ 43
Use the Event and Data Logs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 43
Event log . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 43
Data log . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 44
How to use FTP or SCP to retrieve log files . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 47
Syslog servers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 49
Administration: Security............................................... 50
Local Users . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 50
Setting user access . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 50
Remote Users . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 50
Authentication . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 50
RADIUS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 51
Configuring the RADIUS Server . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 52
Summary of the configuration procedure . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 52
Configuring a RADIUS server on UNIX® with shadow passwords 52
Supported RADIUS servers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 52
Inactivity Timeout . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 53
Administration: Network Features............................... 54
TCP/IP and Communication Settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 54
TCP/IP settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 54
DHCP response options . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 55
Ping Response . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 56
Port Speed. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 57
DNS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 57
Web . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 59
Console . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 60
SNMP . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 61
SNMPv1 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 61
SNMPv3 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 62
Modbus . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 63
iv
Network Management Card User’s Guide

FTP Server . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .64
Administration: Notification .........................................65
Event Actions. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .65
Types of notification . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 65
Configuring event actions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 65
Active, Automatic, Direct Notification . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .67
E-mail notification . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 67
SNMP traps . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 69
SNMP Trap Test . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 69
Remote Monitoring Service . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 70
Syslog . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 70
Administration: General Options .................................72
Identification . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .72
Set the Date and Time . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .72
Method . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 72
Daylight saving . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 73
Format . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 73
Use an .ini File . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .73
Event Log, Temperature Units, and Log-In Page . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .74
Color-code event log text . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 74
Change the default temperature scale . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 74
Specify the UI language . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 74
Specify a default login page . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 74
Reset the Management Card . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .75
Configure Links . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .75
About the Management Card . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .75
Device IP Configuration Wizard ...................................76
Capabilities, Requirements, and Installation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .76
How to use the Wizard to configure TCP/IP settings . . . . . . . . . . . 76
System requirements . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 76
Installation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 76
Network Management Card User’s Guide
v

Use the Wizard . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 77
Configure the basic TCP/IP settings remotely . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 77
Configure or reconfigure the TCP/IP settings locally . . . . . . . . . . 78
How to Export Configuration Settings ........................ 79
Retrieving and Exporting the .ini File . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 79
Summary of the procedure . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 79
Contents of the .ini file . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 79
Detailed procedures . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 79
The Upload Event and Error Messages . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 81
The event and its error messages . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 81
Messages in config.ini . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 81
Errors generated by overridden values . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 81
Related Topics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 82
File Transfers................................................................. 83
How to Upgrade Firmware . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 83
Benefits of upgrading firmware . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 83
Firmware files (Network Management Card) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 83
Obtain the latest firmware version . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 83
Firmware File Transfer Methods . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 84
Use FTP or SCP to upgrade one Management Card . . . . . . . . . . . 84
How to upgrade multiple Management Cards . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 85
Using the NMC2 Firmware Upgrade Utility for multiple upgrades 86
Use XMODEM to upgrade one Management Card . . . . . . . . . . . . . 86
Use a USB drive to transfer the files . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 87
Verifying Upgrades and Updates . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 87
Verify the success or failure of the transfer . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 87
Last Transfer Result codes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 87
Verify the version numbers of installed firmware. . . . . . . . . . . . . . 87
Adding and Changing Language Packs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 88
Troubleshooting ............................................................ 89
Management Card Access Problems . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 89
SNMP Issues . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 90
vi
Network Management Card User’s Guide

Appendix A: List of Supported Commands ................ 91
Two-Year Factory Warranty . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .94
Terms of warranty . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 94
Non-transferable warranty . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 94
Exclusions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 94
Warranty claims . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 95
Network Management Card User’s Guide
vii

Introduction
Product Description
Features
The American Power Conversion Network Management Card (AP9635) is a Web-based product that
manages supported devices using multiple, open standards such as Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP),
Telnet, Hypertext Transfer Protocol over Secure Sockets Layer (HTTPS), Secure SHell (SSH), Simple
Network Management Protocol (SNMP), File Transfer Protocol (FTP), and Secure CoPy (SCP). The
Network Management Card:
• Provides data and event logs
• Provides support for the PowerChute
• Supports using a Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) or BOOTstrap Protocol
(BOOTP) server to provide the network (TCP/IP) values of the Management Card
• Supports using the Remote Monitoring Service (RMS)
• Supports remote monitoring over modem using Tele Service Connect (TLS) (MGE
and MGE Galaxy 7000 only). Contact APC Support for information.
• Enables you to configure notification through event logging (by the Management Card and
Syslog), e-mail, and SNMP traps. You can configure notification for single events or groups of
events, based on the severity level or category of events
®
Network Shutdown utility
®
Galaxy® 300
• Provides the ability to export a user configuration (.ini) file from a configured card to one or more
unconfigured cards without converting the file to a binary file
• Provides a selection of security protocols for authentication and encryption
• Communicates with InfraStruxure
• Supports Modbus RTU over a serial RS485 port
• Supports Modbus over TCP (Symmetra
Devices in which you can install the Management Card. The AP9635 Network Management Card
can be installed into the Symmetra PX 250, Symmetra PX 500, MGE Galaxy 300, and MGE Galaxy
7000 UPS devices.
Note: The Network Management Card ships with the firmware for the MGE Galaxy 300 and
MGE Galaxy 7000 already installed. If you are ordering the card as a replacement part for a
Symmetra PX 250 or Symmetra PX 500, you will need to install the Symmetra-specific
firmware. Contact APC Worldwide Customer Support for more information. See “APC
Worldwide Customer Support” on page 96.
®
Central
®
PX 250 and 500 only)
Network Management Card User’s Guide1

Initial setup
You must define three TCP/IP settings for the Network Management Card before it can operate on the
network:
• IP address of the Management Card
• Subnet mask
• IP address of the default gateway
Caution: Do not use the loopback address (127.0.0.1) as the default gateway. Doing
so disables the card. You must then log on using a serial connection and reset TCP/IP
settings to their defaults.
To configure the TCP/IP settings, see the Network Management Card Installation
Manual, available on the Network Management Card Utility CD and in
printed form.
For detailed information on how to use a DHCP server to configure the TCP/IP
settings at a Management Card, see “TCP/IP and Communication Settings” on
page 54.
Network management features
These applications and utilities work with a UPS that connects to the network through a Network
Management Card.
• PowerChute Network Shutdown—Provide unattended remote graceful shutdown of computers
that are connected to American Power Conversion UPS devices.
• PowerNet
SETs and GETs and to use SNMP traps.
• InfraStruxure Central—Provide enterprise-level power management and management of
Amercian Power Conversion agents, UPS devices, and environmental monitors.
• Device IP Configuration Wizard—Configure the basic settings of one or more Network
Management Cards over the network.
• Security Wizard—Create components needed for high security for the Network Management
Card when you are using Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) and related protocols and encryption
routines.
®
Management Information Base (MIB) with a standard MIB browser—Perform SNMP
Internal Management Features
Overview
Use the Web interface or the command line interface to view the status of the UPS and manage the
Management Card.
For more information about the internal user interfaces, see “Web Interface” on page 28 and
“Command Line Interface” on page 8.
2Network Management Card User’s Guide

Access priority for logging on
Only one user at a time can log on to the Management Card. The priority for access, beginning with the
highest priority, is as follows:
• Local access to the command line interface from a computer with a direct serial connection to the
Management Card
• Telnet or SSH access to the command line interface from a remote computer
• Web access, either directly or through InfraStruXure Central
Note: SNMP has Write + and Write access. Write + has top access and enables logging on
when another user is already logged on. Write access is equivalent to Web access.
See “SNMP” on page 61 for information about how SNMP access to the Management
Card is controlled.
Types of user accounts
The Management Card has three levels of access (Administrator, Device User, and Read-Only User),
which are protected by user name and password requirements.
• An Administrator can use all the menus in the Web interface and all of the commands in the
command line interface. The default user name and password are both apc.
• A Device User can access only the following:
– In the Web interface, the menus on the UPS tab and the event and data logs, accessible under
the Events and Data headings on the left navigation menu of the Logs tab.The event and data
logs display no button to clear the log.
– In the command line interface, the equivalent features and options.
The default user name is device, and the default password is apc.
• A Read-Only User has the following restricted access:
– Access through the Web interface only.
– Access to the same tabs and menus as a Device User, but without the capability to delete data
or use file transfer options. The event and data logs display no button to clear the log.
The default user name is readonly, and the default password is apc.
To set User Name and Password values for the three account types, see “Setting
user access” on page 50.
Network Management Card User’s Guide3

How to Recover from a Lost Password
You can use a local computer that connects to the Management Card through the serial port to access the
command line interface.
1. Select a serial port at the local computer, and disable any service that uses that port.
2. Connect the provided serial cable (part number 940-0299) to the selected port at the computer
and to the configuration port at the Management Card.
3. Run a terminal program (such as HyperTerminal
8 data bits, no parity, 1 stop bit, and no flow control.
®
) and configure the selected port for 9600 bps,
4. Press
ENTER, repeatedly if necessary, to display the User Name prompt. If you are unable to
display the User Name prompt, verify the following:
– The serial port is not in use by another application.
– The terminal settings are correct as specified in step 3.
– The correct cable is being used as specified in step 2.
5. Press the Reset button. The Status LED will flash alternately orange and green. Press the Reset
button a second time immediately while the LED is flashing to reset the user name and password
to their defaults temporarily.
6. Press
ENTER, repeatedly if necessary, to display the User Name prompt again, then use the
default, apc, for the user name and password. (If you take longer than 30 seconds to log on after
the User Name prompt is redisplayed, you must repeat step 5 and log on again.)
7. At the command line interface, use the following commands to change the User Name and
Password settings, both of which are now apc:
user -an yourAdministratorName
user -ap yourAdministratorPassword
For example, to change the Administrator user name to Admin, type:
user -an Admin
8. Type quit or exit to log off, reconnect any serial cable you disconnected, and restart any
service you disabled.
4Network Management Card User’s Guide
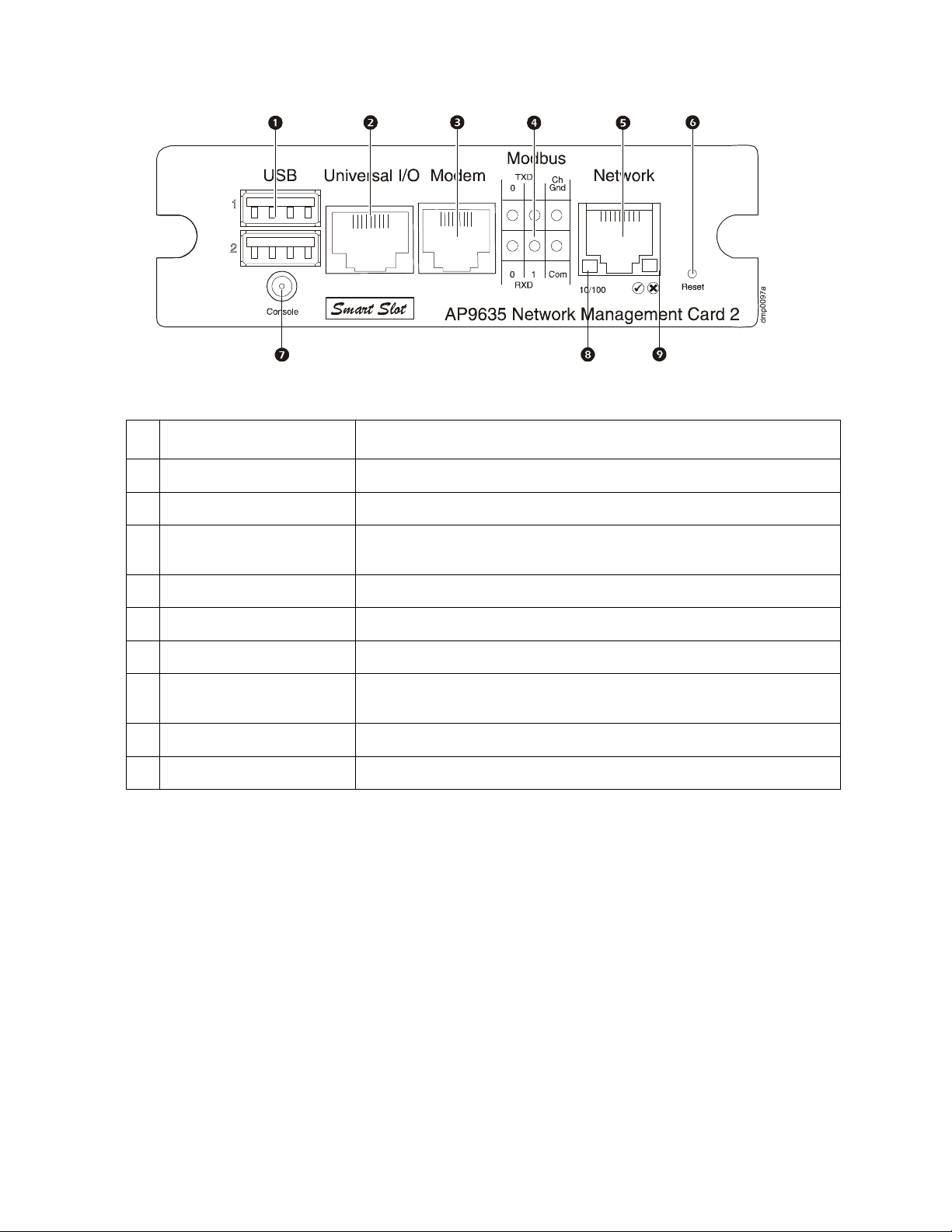
Front Panel
Features
Item Description
USB ports Reserved for future use.
1
Universal I/O sensor port Connects external sensors to the Network Management Card. (
2
Modem port Used for Tele Service Connect (TLS) (MGE Galaxy 300 and MGE Galaxy
3
Modbus connector Connects the Management Card to a Building Management System (BMS)
4
10/100 Base-T connector Connects the Management Card to the Ethernet network.
5
Reset button Resets the Management Card while power remains on.
6
Serial configuration port Connects the Management Card to a local computer to configure initial
7
Link-RX/TX (10/100) LED See “Link-RX/TX (10/100) LED” on page 6.
8
Status LED See “Status LED” on page 6.
9
7000 only).
network settings or access the command line interface.
Network Management Card User’s Guide5
Status LED
This LED indicates the status of the Management Card.
Condition Description
Off One of the following situations exists:
• The Management Card is not receiving input power.
• The Management Card is not operating properly. It may need to be repaired or
replaced. Contact APC Worldwide Customer Support. See “APC Worldwide
Customer Support” on page 96.
Solid green The Management Card has valid TCP/IP settings.
Solid orange A hardware failure has been detected in the Management Card. Contact APC
Worldwide Customer Support. See “APC Worldwide Customer Support” on page 96.
Flashing green The Management Card does not have valid TCP/IP settings.
Flashing orange The Management Card is making BOOTP requests.
1
1
Alternately flashing
green and orange
If the LED is alternately flashing slowly, the Management Card is making DHCP2
requests.
If the LED is alternately flashing rapidly, the Management Card is starting up.
1. If you do not use a BOOTP or DHCP server, see the Network Management Card Installation and Quick Start
Manual provided in printed format and on the Network Management Card Utility CD to configure the
TCP/IP settings of the Management Card manually.
2. To use a DHCP server, see “TCP/IP and Communication Settings” on page 54.
Link-RX/TX (10/100) LED
This LED indicates the network status.
Condition Description
Off One or more of the following situations exist:
• The Management Card is not receiving input power.
• The cable that connects the Management Card to the network is disconnected or defective.
• The device that connects the Management Card to the network is turned off or not
operating correctly.
• The Management Card itself is not operating properly. It may need to be repaired or
replaced. Contact APC Worldwide Customer Support
Support” on page 96.
1
. See “APC Worldwide Customer
Solid green The Management Card is connected to a network operating at 10 Megabits per second
(Mbps).
Solid orange The Management Card is connected to a network operating at 100 Mbps.
Flashing green The Management Card is receiving or transmitting data packets at 10 Mbps.
Flashing orange The Management Card is receiving or transmitting data packets at 100 Mbps.
6Network Management Card User’s Guide

Watchdog Features
Overview
To detect internal problems and recover from unanticipated inputs, the Management Card uses internal,
system-wide watchdog mechanisms. When it restarts to recover from an internal problem, a System:
Warmstart event is recorded in the event log.
Network interface watchdog mechanism
The Management Card implements internal watchdog mechanisms to protect itself from becoming
inaccessible over the network. For example, if the Management Card does not receive any network
traffic for 9.5 minutes (either direct traffic, such as SNMP, or broadcast traffic, such as an Address
Resolution Protocol [ARP] request), it assumes that there is a problem with its network interface and
restarts.
Resetting the network timer
To ensure that the Management Card does not restart if the network is quiet for 9.5 minutes, the
Management Card attempts to contact the default gateway every 4.5 minutes. If the gateway is present, it
responds to the Management Card, and that response restarts the 9.5-minute timer. If your application
does not require or have a gateway, specify the IP address of a computer that is running on the network
most of the time and is on the same subnet. The network traffic of that computer will restart the 9.5minute timer frequently enough to prevent the Management Card from restarting.
Network Management Card User’s Guide7

Command Line Interface
How To Log On
Overview
You can use either a local (serial) connection, or a remote (Telnet or SSH) connection with a computer
on the same network as the Network Management Card to access the command line interface.
Use case-sensitive user name and password entries to log on (by default, apc and apc for an
Administrator, or device and apc for a Device User). A Read-Only User cannot access the command line
interface.
If you cannot remember your user name or password, see “How to Recover from a Lost
Password” on page 4.
Note: The command line interface does not display information about the Symmetra PX 250
or Symmetra PX 500 UPS.
Remote access to the command line interface
You can access the command line interface through Telnet or SSH. Telnet is enabled by default. Enabling
SSH disables Telnet.
To enable or disable these access methods, use the Web interface. On the Administration tab, select
Network on the top menu bar, and then the access option under Console on the left navigation menu.
Telnet for basic access. Telnet provides the basic security of authentication by user name and
password, but not the high-security benefits of encryption.
To use Telnet to access the command line interface:
1. From a computer that has access to network on which the Management Card is installed, at a
command prompt, type
telnet 139.225.6.133, when the Management Card uses the default Telnet port of 23), and
ENTER.
press
If the Management Card uses a non-default port number (from 5000 to 32768), you must
include a colon or a space, depending on your Telnet client, between the IP address (or DNS
name) and the port number. (These are commands for general usage: some clients don’t allow
you to specify the port as an argument and some types of Linux might want extra commands).
2. Enter the user name and password (by default, apc and apc for an Administrator, or device and
apc for a Device User).
SSH for high-security access. If you use the high security of SSL for the Web interface, use SSH for
access to the command line interface. SSH encrypts user names, passwords, and transmitted data. The
interface, user accounts, and user access rights are the same whether you access the command line
interface through SSH or Telnet, but to use SSH, you must first configure SSH and have an SSH client
program installed on your computer.
telnet and the IP address for the Management Card (for example,
8Network Management Card User’s Guide
Local access to the command line interface. For local access, use a computer that connects to the
American Power Conversion Network Management Card AOS vx.x.x
(c)Copyright 2008 All Rights Reserved Symmetra PX APP vx.x.x
------------------------------------------------------------------------- Name : Test Lab Date : 03/30/2009
Contact : Don Adams Time : 5:58:30
Location : Building 3 User : Administrator
Up Time : 0 Days, 21 Hours, 21 Minutes Stat : P+ N+ A+
APC>
Management Card through the serial port to access the command line interface:
1. Select a serial port at the computer and disable any service that uses the port.
2. Connect the provided serial cable (part number 940-0299) from the selected port on the computer
to the configuration port at the Management Card.
3. Run a terminal program (e.g., HyperTerminal), and configure the selected port for 9600 bps, 8
data bits, no parity, 1 stop bit, and no flow control.
4. Press
ENTER twice. At the prompts, enter your user name and password.
Main Screen
Sample main screen
Following is an example of the screen displayed when you log on to the command line interface at the
Management Card.
Information and status fields
Main screen information fields.
• Two fields identify the APC operating system (AOS) and application (APP) firmware versions.
The application firmware name identifies the device that connects to the network through this
Management Card. In the example above, the Management Card uses the application firmware for
a Symmetra PX UPS.
Network Management Card AOS vx.x.x
Symmetra PX APP vx.x.x
• Three fields identify the system name, contact person, and location of the Management Card. (In
the Web interface, select the Administration tab, General in the top menu bar, and
Identification in the left navigation menu to set these values.)
Name : Test Lab
Contact : Don Adams
Location: Building 3
• The Up Time field reports how long the Management Card has been running since it was last
turned on or reset.
Network Management Card User’s Guide9

Up Time: 0 Days 21 Hours 21 Minutes
• Two fields report when you logged in, by date and time.
Date : 03/30/2009
Time : 5:58:30
• The User field reports whether you logged in through the Administrator or Device Manager
account. (The Read Only User account cannot access the command line interface.)
When you log on as Device Manager (equivalent to Device User in the Web interface), you can
access the event log and view the number of active alarms.
User : Administrator
Main screen status fields.
• The Stat field reports the Management Card status.
Stat : P+ N+ A+
P+ The operating system (AOS) is functioning properly.
N+ The network is functioning properly.
N? A BOOTP request cycle is in progress.
N– The Management Card failed to connect to the network.
N! Another device is using the IP address of the Management Card.
A+ The application is functioning properly.
A– The application has a bad checksum.
A? The application is initializing.
A! The application is not compatible with the AOS.
If P+ is not displayed, contact APC Customer Support. See “APC Worldwide Customer
Support” on page 96.
To view the status of the UPS, you must access the Web interface of the Management Card.
For more information, see “Web Interface” on page 28.
10Network Management Card User’s Guide
Using the Command Line Interface
Overview
The command line interface provides options to configure the network settings and monitor the
Management Card.
To view the status of the UPS, you must access the Web interface of the Management Card.
For more information, see “Web Interface” on page 28.
Entering commands
At the command line interface, use commands to configure the Management Card. To use a command,
type the command and press
mixed case. Options are case-sensitive.
At the command line interface, you can also use these keyboard shortcuts:
ENTER. Commands and arguments are valid in lowercase, uppercase, or
• Type
? and press ENTER to view a list of available commands, based on your account type.
To obtain information about the purpose and syntax of a specified command, type the
command, a space, and
options, type:
radius ?
or
radius help
• Press the UP arrow key to view the command that was entered most recently in the session. Use
UP and DOWN arrow keys to scroll through a list of up to ten previous commands.
the
• Type at least one letter of a command, then press the
commands that match the text you typed in the command line.
• Type
exit or quit to close the connection to the command line interface.
Command syntax
Item Description
- Options are preceded by a hyphen.
< > Definitions of options are enclosed in angle brackets. For example:
-dp <device password>
? or the word help. For example, to view RADIUS configuration
TAB key to scroll through a list of valid
[ ] If a command accepts multiple options or an option accepts mutually exclusive arguments, the
values may be enclosed in brackets.
| A vertical line between items enclosed in brackets or angle brackets indicates that the items are
mutually exclusive. You must use one of the items.
Network Management Card User’s Guide11

Syntax examples
A command that supports multiple options:
user [-an <admin name>] [-ap <admin password>]
In the preceding example, the user command accepts the option -an, which defines the Administrator
user name, and the option
-ap, which defines the Administrator password. To change the Administrator
user name and password to XYZ:
1. Type the
user -ap XYZ
user command, one option, and the argument XYZ:
2. After the first command succeeds, type the user command, the second option, and the argument
XYZ:
user -an XYZ
A command that accepts mutually exclusive arguments for an option:
alarmcount -p [all | warning | critical]
In the preceding example, the option -p accepts only three arguments: all, warning, or critical.
For example, to view the number of active critical alarms, type:
alarmcount -p critical
The command will fail if you type an argument that is not specified.
Command Response Codes
The command response codes enable scripted operations to detect error conditions reliably without
having to match error message text.
The CLI reports all command operations with the following format:
E [0–9][0–9][0–9]: Error message
Code Error message
E000 Success
E100 Command failed
E101 Command not found
E102 Reserved
E103 Reserved
E104 Reserved
E200 Reserved
12Network Management Card User’s Guide
Command Descriptions
?
Access: Administrator, Device User
Description: View a list of all the CLI commands available to your account type. To view help text for
a specific command, type the command followed by a question mark.
Example: To view a list of options that are accepted by the alarmcount command, type:
alarmcount ?
about
Access: Administrator, Device User
Description: View hardware and firmware information. This information is useful in troubleshooting
and enables you to determine if updated firmware is available at the APC Web site, www.apc.com/tools/
download.
alarmcount
Access: Administrator, Device User
Description:
Option Arguments Description
-p all View the number of active alarms reported by the Management Card.
Information about the alarms is provided in the event log.
warning View the number of active warning alarms.
critical View the number of active critical alarms.
Example:
alarmcount -p warning
To view all active warning alarms, type:
Network Management Card User’s Guide13
boot
Access: Administrator only
Description: Define how the Management Card will obtain its network settings, including the IP
address, subnet mask, and default gateway. Then configure the BOOTP or DHCP server settings.
Option Argument Description
-b
<boot
mode>
-c enable | disable dhcp boot mode only. Enable or disable the requirement that the
The default values for these three settings generally do not need to be changed:
-v <vendor class>: APC
-i <client id>: The MAC address of the Network Management Card, which uniquely identifies it on the
local area network (LAN)
-u <user class>: The name of the application firmware module
dhcp | bootp | manual Define how the TCP/IP settings will be configured when the
Management Card turns on, resets, or restarts. The default setting is
dhcp. See “TCP/IP and Communication Settings” on page 54 for
information about each boot mode setting.
DHCP server provide the APC cookie.
Example: To use a DHCP server to obtain network settings:
1. Define the boot mode setting.
boot -b dhcp
2. Enable the requirement that the DHCP server provide the APC cookie.
boot -c enable
cd
Access: Administrator, Device User
Description: Navigate to a folder in the directory structure of the Network Management Card.
Example 1: To change to the ssh folder and confirm that an SSH security certificate was uploaded to
the Management Card:
1. Type
2. Type
cd ssh and press ENTER.
dir and press ENTER to list the files stored in the SSH folder.
Example 2: To return to the main directory folder, type:
cd ..
14Network Management Card User’s Guide
console
Access: Administrator only
Description: Define whether users can access the command line interface using Telnet, which is
enabled by default, or Secure SHell (SSH), which provides protection by transmitting user names,
passwords, and data in encrypted form. You can change the Telnet or SSH port setting for additional
security. Alternately, disable network access to the command line interface.
Option Argument Description
-S disable | telnet | ssh Configure access to the command line interface, or use the disable
command to prevent access.. Enabling SSH enables SCP and disables
Telnet.
-pt <telnet port n> Define the Telnet port used to communicate with the Management Card (23
by default).
-ps <SSH port n> Define the SSH port used to communicate with the Management Card (22 by
default).
-b 2400 | 9600 |
19200 | 38400
Configure the speed of the serial port connection (9600 bps by default).
Example 1: To enable SSH access to the command line interface, type:
console -S ssh
Example 2: To change the Telnet port to 5000, type:
console -pt 5000
date
Access: Administrator only
Definition: To configure an NTP server to define the date and time for the Management Card, see “Set
the Date and Time” on page 72.
Option Argument Description
-d <“datestring”> Configure the date used by the Management Card. Use the date format specified
by the date -f command.
-t <00:00:00> Configure the current time, in hours, minutes, and seconds. Use the 24-hour
clock format.
-f mm/dd/yy |
dd.mm.yyyy |
mmm-dd-yy |
dd-mmm-yy |
yyyy-mm-dd
Select the format in which to display all dates in this user interface. Each letter
m (for month), d (for day), and y (for year) represents one digit. Single-digit
days and months are displayed with a leading zero. The format mmm represents a
three-letter month name.
-z <time zone
offset>
Set the difference with GMT in order to specify your time zone. This enables
you to synchonize with other people in different time zones.
Example 1: To display the date using the format yyyy-mm-dd, type:
date -f yyyy-mm-dd
Network Management Card User’s Guide15
Example 2: To define the date as October 30, 2010, using the format configured in the preceding
example, type:
date -d “2010-10-30”
Example 3: To define the time as 5:21:03 p.m., type:
date -t 17:21:03
delete
Access: Administrator only
Description: Delete the event or data log, or delete a file in the file system.
Argument Description
<file name> Type the name of the file to delete.
Example:
1. Navigate to the folder that contains the file to delete. For example, to delete the event log, type
this command to navigate to the
logs folder:
cd logs
2. To view the files in the
dir
logs folder, type:
The file event.txt is listed.
3. Type
delete event.txt.
dir
Access: Administrator, Device User
Description: View the files and folders stored on the Management Card.
dns
Access: Administrator
Description: Configure the manual Domain Name System (DNS) settings.
Parameter Argument Description
-OM enable | disable
-p <primary DNS server> Set the primary DNS server.
Override the manual DNS.
-s <secondary DNS server> Set the secondary DNS server.
-d <domain name> Set the domain name.
-n <domain name IPv6> Set the domain name IPv6.
-h <host name> Set the host name.
16Network Management Card User’s Guide
eventlog
Access: Administrator, Device User
Description: View the date and time you retrieved the event log, the status of the UPS, and the status of
sensors connected to the Management Card. View the most recent device events, and the date and time
they occurred. Use the following keys to navigate the event log:
Key Description
ESC
ENTER
SPACEBAR
B View the preceding page of the event log. This command is not available at the main page of the
D Delete the event log. Follow the prompts to confirm or deny the deletion. Deleted events cannot
Close the event log and return to the command line interface.
Update the log. Use this command to view events that were recorded after you last retrieved the
log.
View the next page of the event log.
event log.
be retrieved.
exit
Access: Administrator, Device User
Description: Exit from the command line interface session.
format
Access: Administrator only
Description: Reformat the file system of the Management Card and erase all security certificates,
encryption keys, configuration settings, and the event and data logs.
Warning: Use caution when issuing the format command. This command reformats the file
system of the Management Card, deleting all security certificates, encryption keys,
configuration settings, and the event and data logs.
Note: To reset the Management Card to its default configuration, use the
resetToDef
command.
Network Management Card User’s Guide17
ftp
Access: Administrator only
Description: Enable or disable access to the FTP server. Optionally, change the port setting to the
number of any unused port from 5001 to 32768 for added security.
Option Argument Definition
-p <port number> Define the TCP/IP port that the FTP server uses to communicate with the
Management Card (21 by default). The FTP server uses both the specified
port and the port one number lower than the specified port.
-S enable | disable Configure access to the FTP server.
Example: To change the TCP/IP port to 5001, type:
ftp -p 5001
help
Access: Administrator, Device User
Description: View a list of all the CLI commands available to your account type. To view help text for
a specific command, type the command followed by the
help command: user help
Example 1: To view a list of commands available to a Device User, type:
help
Example 2: To view a list of options that are accepted by the alarmcount command, type:
alarmcount ?
modbus
Access: Administrator only
Description: Manually configure these Modbus settings for the Management Card:
Option Argument Description
-p Display the configured Modbus parameters.
-a enable | disable Enable or disable the Modbus feature.
-br 9600 | 19200 Set the baud rate.
-pr even | odd | none Set the parity bit.
-s <slave # in hex> Set the Modbus slave address.
-o master | slave Define the mode of operation for the Modbus feature. (MGE Galaxy
models only)
-rt <timeout in mSec> Set the response timeout in milliseconds for query packets in Master
mode. (MGE Galaxy models only)
18Network Management Card User’s Guide
Option Argument Description
-sr <scan rate in mSec> Set the scan rate for query packets in Master mode. (MGE Galaxy
models only)
-rep <# of repetitions> Set the number of repetitions for query packets in Master mode. (MGE
Galaxy models only)
-ResetToDef Reset the modbus settings to their default values.
netstat
Access: Administrator, Device User
Description: View the status of the network and all active IPv4 and IPv6 addresses.
ntp
Access: Administrator
Description: View and configure the network time protocol parameters.
Option Argument Definition
-OM enable | disable
-p <primary NTP server> Specify the primary server.
-s <secondary NTP server> Specify the secondary server.
Override the manual settings.
Example 1: To enable the override of manual setting, type:
ntp -OM enable
Example 2: To specify the primary NTP server, type:
ntp -p 150.250.6.10
ping
Access: Administrator, Device User
Description: Determine whether the device with the IP address or DNS name you specify is connected
to the network. Four inquiries are sent to the address.
Argument Description
<IP address or DNS name> Type an IP address with the format xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx, or the DNS
name configured by the DNS server.
Example: To determine whether a device with an IP address of 150.250.6.10 is connected to the
network, type:
ping 150.250.6.10
Network Management Card User’s Guide19
portSpeed
Access: Administrator
Description:
Option Arguments Description
-s auto | 10H | 10F |
100H | 100F
Example:
To configure the TCP/IP port to communicate using 100 Mbps with half-duplex
Define the communication speed of the Ethernet port. The auto command
enables the Ethernet devices to negotiate to transmit at the highest possible
speed. See “Port Speed” on page 57 for more information about the port speed
settings.
communication (communication in only one direction at a time), type:
portspeed -s 100H
prompt
Access: Administrator, Device User
Description: Configure the command line interface prompt to include or exclude the account type of
the currently logged-in user. Any user can change this setting; all user accounts will be updated to use the
new setting.
Option Argument Description
-s long The prompt includes the account type of the currently logged-in user.
short The default setting. The prompt is four characters long: APC>
Example: To include the account type of the currently logged-in user in the command prompt, type:
prompt -s long
quit
Access: Administrator, Device User
Description: Exit from the command line interface session.
20Network Management Card User’s Guide
radius
Access: Administrator only
Description: View the existing RADIUS settings, enable or disable RADIUS authentication, and
configure basic authentication parameters for up to two RADIUS servers.
For a summary of RADIUS server configuration and a list of supported RADIUS servers, see
“Configuring the RADIUS Server” on page 52.
Additional authentication parameters for RADIUS servers are available at the Web interface
of the Management Card. See “RADIUS” on page 51 for more information.
For detailed information about configuring your RADIUS server, see the Security Handbook,
available on the Network Management Card Utility CD and at the APC Web site,
www.apc.com.
Option Argument Description
-a local |
radiusLocal |
radius
-p1
-p2
-s1
-s2
-t1
-t2
<server IP> The server name or IP address of the primary or secondary RADIUS server.
<server
secret>
<server
timeout>
Configure RADIUS authentication:
• local—RADIUS is disabled. Local authentication is enabled.
• radiusLocal—RADIUS, then Local Authentication. RADIUS and local
authentication are enabled. Authentication is requested from the RADIUS
server first. If the RADIUS server fails to respond, local authentication is used.
• radius—RADIUS is enabled. Local authentication is disabled.
N
OTE: RADIUS servers use port 1812 by default to authenticate users. To use a
different port, add a colon followed by the new port number to the end of the
RADIUS server name or IP address.
The shared secret between the primary or secondary RADIUS server and the
Management Card.
The time in seconds that the Management Card waits for a response from the
primary or secondary RADIUS server.
Example 1: To view the existing RADIUS settings for the Management Card, type radius and press
NTER.
E
Example 2: To enable RADIUS and local authentication, type:
radius -a radiusLocal
Example 3: To configure a 10-second timeout for a secondary RADIUS server, type:
radius -t2 10
reboot
Access: Administrator
Description: Resets the Management Card.
Network Management Card User’s Guide21
 Loading...
Loading...