Sharp LH540204U-50, LH540204U-35, LH540204U-25, LH540204K-50, LH540204K-35 Datasheet
...
LH540204 |
CMOS 4096 × 9 Asynchronous FIFO |
FEATURES
∙Fast Access Times: 20/25/35/50 ns
∙Fast-Fall-Through Time Architecture Based on CMOS Dual-Port SRAM Technology
∙Input Port and Output Port Have Entirely Independent Timing
∙Expandable in Width and Depth
∙Full, Half-Full, and Empty Status Flags
∙Data Retransmission Capability
∙TTL-Compatible I/O
∙Pin and Functionally Compatible with Sharp LH5499 and with Am/IDT/MS7204
∙Control Signals Assertive-LOW for Noise Immunity
∙Packages:
28-Pin, 300-mil PDIP
28-Pin, 300-mil SOJ *
32-Pin PLCC
FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION
The LH540204 is a FIFO (First-In, First-Out) memory device, based on fully-static CMOS dual-portSRAMtech- nology, capable of storing up to 4096 nine-bit words. It follows the industry-standard architecture and package pinouts for nine-bit asynchronous FIFOs. Each nine-bit LH540204 word may consist of a standard eight-bit byte, together with a parity bit or a block-marking/framing bit.
The input and output ports operate entirely independently of each other, unless the LH540204 becomes either totally full or else totally empty. Data flow at a port is initiated by asserting either of two asynchronous, as- sertive-LOW control inputs: Write (W) for data entry at the input port, or Read (R) for data retrieval at the output port.
Full, Half-Full, and Empty status flags monitor the extent to which the internal memory has been filled. The system may make use of these status outputs to avoid the risk of data loss, which otherwise might occur either by attempting to write additional words into an already-full LH540204, or by attempting to read additional words from an already-empty LH540204. When an LH540204 is operating in a depth-cascaded configuration,the Half-Full Flag is not available.
PIN CONNECTIONS
28-PIN PDIP |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
TOP VIEW |
28-PIN SOJ * |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
28 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
W |
|
1 |
|
|
VCC |
|||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|
D8 |
|
|
|
2 |
27 |
|
D4 |
|||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||
|
|
D3 |
|
|
3 |
26 |
|
D5 |
||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||
|
|
D2 |
|
4 |
25 |
|
D6 |
|||||||||||||
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
|
D1 |
|
5 |
24 |
|
D7 |
|||||||||||||
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
23 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
D0 |
|
6 |
|
|
FL/RT |
|||||||||||||
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
22 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
XI |
|
|
7 |
|
RS |
||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
21 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
8 |
|
EF |
|||||||
|
|
FF |
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
9 |
20 |
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
Q0 |
|
|
|
XO/HF |
||||||||||||||
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
|
Q1 |
|
|
|
10 |
19 |
|
Q7 |
|||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||
|
Q2 |
|
11 |
18 |
|
Q6 |
||||||||||||||
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
Q3 |
|
12 |
17 |
|
Q5 |
||||||||||||||
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
Q8 |
|
|
|
13 |
16 |
|
Q4 |
||||||||||||
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
14 |
15 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
VSS |
|
|
R |
||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
540204-2D |
Figure 1. Pin Connections for PDIP and SOJ * Packages
32-PIN PLCC |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* |
|
|
|
CC |
4 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
TOP VIEW |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
3 |
8 |
|
W |
|
|
NC |
|
|
|
5 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
D |
|
|
D |
|
|
|
|
|
V |
|
|
D |
|
|
D |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
4 |
3 |
2 |
1 |
32 |
31 |
30 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
D2 |
|
|
|
|
|
5 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
29 |
|
|
D6 |
|||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
D1 |
|
|
|
|
|
6 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
28 |
|
|
D7 |
|||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
D0 |
|
|
|
|
|
7 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
27 |
|
|
NC |
|||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
8 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
|
|
XI |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
26 |
|
|
|
FL/RT |
||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
FF |
|
|
|
|
9 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
25 |
|
|
RS |
|||||||||||||||||||||||
Q0 |
|
|
|
|
|
10 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
24 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
EF |
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
Q1 |
|
|
|
|
11 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
23 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
XO/HF |
|||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
NC |
|
|
|
12 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
22 |
|
|
Q7 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Q2 |
|
|
|
13 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
21 |
|
|
Q6 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
14 |
|
15 |
|
16 |
|
17 |
|
18 |
|
|
19 |
20 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Q |
|
Q |
|
V |
|
NC* |
|
R |
|
Q |
|
Q |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
3 |
8 |
|
SS |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
4 |
5 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
NOTE: * = No external electrical connections are allowed.
540204-3D
Figure 2. Pin Connections for PLCC Package
* This is a final data sheet; except that all references to the SOJ package have Advance Information status.
1

LH540204 |
CMOS 4096 × 9 Asynchronous FIFO |
|
|
FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION (cont’d)
Data words are read out from the LH540204’s output port in precisely the same order that they were written in at its input port; that is, according to a First-In, First Out (FIFO) queue discipline. Since the addressing sequence for a FIFO device’s memory is internally predefined, no external addressing information is required for the operation of the LH540204 device.
Drop-in-replacement compatibility is maintained with both larger sizes and smaller sizes of industry-standard nine-bit asynchronous FIFOs. The only change is in the number of internally-stored data words implied by the states of the Full Flag and the Half-Full Flag.
The Retransmit (RT) control signal causes the internal FIFO-memory-array read-address pointer to be set back to zero, to point to the LH540204’s first physical memory location, without affecting the internal FIFO-memory- array write-address pointer. Thus, the Retransmit control signal provides a mechanism whereby a block of data, delimited by the zero physical address and the current write-address-pointer value, may be read out repeatedly an arbitrary number of times. The only restrictions are that neither the read-address pointer nor the write-address pointer may ‘wrap around’ during this entire process, i.e., advance past physical location zero after traversing the entire memory. The retransmit facility is not available when an LH540204 is operating in a depth-expanded configuration.
The Reset (RS) control signal returns the LH540204 to an initial state, empty and ready to be filled. An LH540204 should be reset during every system power-up sequence. A reset operation causes the internal FIFO- memory-array write-address pointer, as well as the readaddress pointer, to be set back to zero, to point to the LH540204’s first physical memory location. Any information which previously had been stored within the LH540204 is not recoverable after a reset operation.
Acascading (depth-expansion) scheme may be implemented by using the Expansion In (XI) input signal and the Expansion Out (XO/HF) output signal. This allows a deeper ‘effective FIFO’ to be implemented by using two or more LH540204 devices, without incurring additional latency (‘fallthrough’ or ‘bubblethrough’) delays, and without the necessity of storing and retrieving any given data word more than once. In this cascaded operating mode, one LH540204 device must be designated as the ‘firstload’ or ‘master’ device, by grounding its First-Load (FL/RT) control input; the remaining LH540204 devices are designated as ‘slaves,’ by tying theirFL/RT inputs HIGH. Because of the need to share control signals on pins, the Half-Full Flag and the retransmission capability are not available for either ‘master’ or ‘slave’ LH540204 devices operating in cascaded mode.
RS |
RESET |
|
DATA INPUTS |
|
|
|
D0 - D8 |
|
|
||
LOGIC |
|
|
|
||
|
INPUT |
|
|
OUTPUT |
R |
W |
PORT |
|
|
PORT |
|
|
CONTROL |
|
DUAL-PORT |
CONTROL |
|
|
|
WRITE |
RAM |
READ |
|
|
|
ARRAY |
|
||
|
|
POINTER |
POINTER |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
4096 x 9 |
|
|
|
|
|
. . . |
|
|
|
|
|
DATA OUTPUTS |
|
|
|
|
|
Q0 - Q8 |
|
|
|
|
|
FLAG |
EF |
|
|
|
|
LOGIC |
FF |
|
|
|
FL/RT |
EXPANSION |
|
|
|
|
LOGIC |
XO/HF |
|
|
|
|
XI |
|
||
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
540204-1 |
Figure 3. LH540204 Block Diagram
2

CMOS 4096 × 9 Asynchronous FIFO |
LH540204 |
|
|
PIN DESCRIPTIONS
|
|
|
PIN |
PIN TYPE 1 |
DESCRIPTION |
|
|
|
|
PIN |
PIN TYPE 1 |
DESCRIPTION |
||||
D0 – D8 |
I |
Input Data Bus |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
O |
Expansion Out/Half-Full Flag |
||||
XO/HF |
||||||||||||||||
Q0 – Q8 |
O/Z |
Output Data Bus |
|
|
|
|
|
I |
Expansion In |
|||||||
XI |
||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
I |
Write Request |
|
|
|
|
|
I |
First Load/Retransmit |
|||
W |
FL/RT |
|||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
I |
Read Request |
|
|
|
I |
Reset |
||||||
R |
RS |
|||||||||||||||
|
|
|
O |
Empty Flag |
VCC |
V |
Positive Power Supply |
|||||||||
EF |
||||||||||||||||
|
|
O |
Full Flag |
VSS |
V |
Ground |
||||||||||
FF |
||||||||||||||||
NOTE:
1. I = Input, O = Output, Z = High-Impedance, V = Power Voltage Level
OPERATIONAL DESCRIPTION
Reset
The LH540204 is reset whenever the Reset input (RS) is taken LOW. A reset operation initializes both the readaddress pointer and the write-address pointer to point to location zero, the first physical memory location. During a reset operation, the state of the XI and FL/RT inputs determines whether the device is in standalone mode or in depth-cascaded mode. (See Tables 1 and 2.) The reset operation forces the Empty Flag EF to be asserted (EF = LOW), and the Half-Full Flag HF and the Full Flag FF to be deasserted (HF = FF = HIGH); the Data Out pins (D0 – D8) are forced into a high-impedance state.
A reset operation is required whenever the LH540204 first is powered up. The Read (R) and Write (W) inputs may be in any state when the reset operation is initiated; but they must be HIGH, before the reset operation is terminated by a rising edge of RS, by a time tRRSS (for Read) or tWRSS (for Write) respectively. (See Figure 10.)
Write
A write cycle is initiated by a falling edge of the Write
(W) control input. Data setup times and hold times must be observed for the data inputs (D0 – D8). Write operations may occur independently of any ongoing read operations. However, a write operation is possible only if the FIFO is not full, (i.e., if the Full Flag FF is HIGH).
At the falling edge of W for the first write operation after the memory is half filled, the Half-Full Flag is asserted (HF = LOW). It remains asserted until the difference between the write pointer and the read pointer indicates that the data words remaining in the LH540204 are filling the FIFO memory to less than or equal to one-half of its total capacity. The Half-Full Flag is deasserted (HF = HIGH) by the appropriate rising edge of R. (See Table 3.)
The Full Flag is asserted (FF = LOW)at the falling edge of W for the write operation which fills the last available location in the FIFO memory array. FF = LOW inhibits further write operations until FF is cleared by a valid read
operation. The Full Flag is deasserted (FF = HIGH) after
the next rising edge of R releases another memory location. (See Table 3.)
Read
A read cycle is initiated by a falling edge of the Read
(R) control input. Read data becomes valid at the data outputs (Q0 – Q8) after a time tA from the falling edge of
R. After R goes HIGH, the data outputs return to a high-impedance state. Read operations may occur independently of any ongoing write operations. However, a read operation is possible only if the FIFO is not empty (i.e., if the Empty Flag EF is HIGH).
The LH540204’s internal read-address and writeaddress pointers operate in such a way that consecutive read operations always access data words in the same order that they were written. The Empty Flag is asserted (EF = LOW) after that falling edge of R which accesses
the last available data word in the FIFO memory. EF is deasserted (EF = HIGH) after the next rising edge of W loads another valid data word. (See Table 3.)
Data Flow-Through
Read-data flow-through mode occurs when the Read
(R) control input is brought LOW while the FIFO is empty, and is held LOW in anticipation of a write cycle. At the end of the next write cycle, the Empty Flag EF momentarily is deasserted, and the data word just written becomes available at the data outputs (Q0 – Q8) after a maximum timeoftWEF + tA.Additional write operationsmayoccur
while the R input remains LOW; but only data from the first write operation flows through to the data outputs. Additional data words, if any, may be accessed only by toggling R.
Write-data flow-through mode occurs when the Write
(W) input is brought LOW while the FIFO is full, and is held LOW in anticipation of a read cycle. At the end of the read cycle, the Full Flag momentarily is deasserted, but then immediately is reasserted in response to W being held LOW. A data word is written into the FIFO on the rising edge of W, which may occur no sooner than tRFF + tWPW after the read operation.
3

LH540204 |
CMOS 4096 × 9 Asynchronous FIFO |
|
|
OPERATIONAL DESCRIPTION (cont’d)
Retransmit
The FIFO can be made to reread previously-read data by means of the Retransmit function. A retransmit operation is initiated by pulsing the RT input LOW. Both R and W must be deasserted (HIGH) for the duration of the retransmit pulse. The FIFO’s internal read-address pointer is reset to point to location zero, the first physical memory location, while the internal write-address pointer remains unchanged.
After a retransmit operation, those data words in the region in between the read-address pointer and the write-address pointer may be reaccessed by subsequent read operations. A retransmit operation may affect the state of the status flags FF, HF, and EF, depending on the relocation of the read-address pointer. There is no restriction on the number of times that a block of data within an LH540204 may be read out, by repeating the retransmit operation and the subsequent read operations.
The maximum length of a data block which may be retransmitted is 4096 words. Note that if the write-address pointer ever ‘wraps around’ (i.e., passes location zero more than once) during a sequence of retransmit operations, some data words will be lost.
The Retransmit function is not available when the LH540204 is operating in depth-cascaded mode, because the FL/RT control pin must be used for first-load selection rather than for retransmission control.
Table 1. Grouping-Mode Determination
During a Reset Operation
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
FL/ |
|
MODE |
XO/HF |
|
XI |
|
FL/RT |
|||||||||||||||||
XI |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
RT |
|
USAGE |
USAGE |
USAGE |
|||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
H 1 |
|
|
|
|
Cascaded |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
H |
|
|
|
XO |
XI |
|
|
FL |
|||||||||||||||||||
|
|
Slave |
2 |
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
H 1 |
|
|
|
|
Cascaded |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
L |
|
|
|
XO |
XI |
|
|
FL |
|||||||||||||||||||
|
|
Master |
2 |
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
L |
|
X |
|
Standalone |
|
|
|
(none) |
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
HF |
|
|
|
RT |
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
NOTES:
1.A reset operation forces XO HIGH for the nth FIFO, thus forcing XI HIGH for the (n+1)st FIFO.
2.The terms ‘master’ and ‘slave’ refer to operation in depth-cas- caded grouping mode.
3.H = HIGH; L = LOW; X = Don’t Care.
Table 2. Expansion-Pin Usage According to Grouping Mode
I/O |
|
|
PIN |
|
|
STANDALONE |
CASCADED |
|
CASCADED |
|||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
MASTER |
|
|
SLAVE |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
From |
|
|
|
|
|
From |
|
|
|
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
XO |
|
|
XO |
||||||||||||||
I |
|
XI |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Grounded |
(n-1st |
|
|
(n-1st |
|||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
FIFO) |
|
|
FIFO) |
||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
To |
|
|
|
|
|
|
To |
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Becomes |
XI |
|
|
XI |
|||||||||||||||||
O |
|
XO/HF |
|
|
(n+1st |
|
|
(n+1st |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
HF |
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
FIFO) |
|
|
FIFO) |
||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Becomes |
Grounded |
|
Logic |
||||||||||||||||||
I |
|
FL/RT |
|
|
(Logic |
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
RT |
|
|
HIGH |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
LOW) |
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Table 3. Status Flags |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||
NUMBER OF UNREAD DATA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
WORDS PRESENT WITHIN |
|
|
FF |
|
|
|
HF |
|
|
|
|
EF |
|
|||||||||||||||||||
|
|
4096 × 9 FIFO |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
H |
|
|
H |
|
|
|
|
|
L |
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
1 to 2048 |
|
|
H |
|
|
H |
|
|
|
|
H |
|||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
|
2049 to 4095 |
|
|
H |
|
|
L |
|
|
|
|
H |
|||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||
|
4096 |
|
|
|
|
L |
|
|
L |
|
|
|
|
H |
||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
4
CMOS 4096 × 9 Asynchronous FIFO |
LH540204 |
|
|
OPERATIONAL MODES |
Width Expansion |
|||
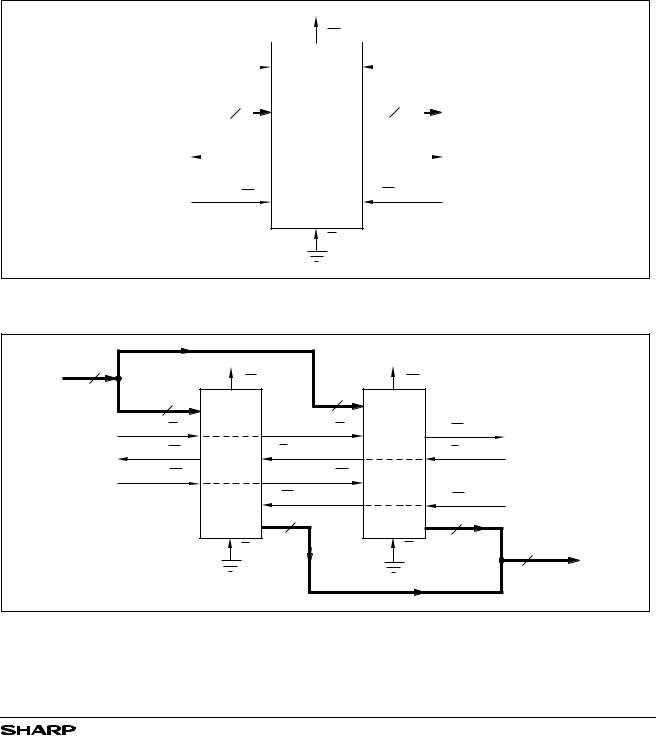
Standalone Configuration |
Word-width expansion is implemented by placing mul- |
|||
tiple LH540204 devices in parallel. Each LH540204 |
||||
When depth cascading is not required for a given |
||||
should be configured for standalone mode. In this ar- |
||||
application, the LH540204 is placed in standalone mode |
||||
rangement, the behavior of the status flags is identical for |
||||
|
|
|
||
by tying the Expansion In input (XI) to ground. This |
||||
all devices; so, in principle, a representative value for |
||||
input is internally sampled during a reset operation. (See |
||||
each of these flags could be derived from any one device. |
||||
Table 1.) |
||||
In practice, it is better to derive ‘composite’ flag values |
||||
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
using external logic, since there may be minor speed |
|
|
|
|
variations between different actual devices. (See Figures |
|
|
|
|
4, 5, and 6.) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
HF |
|
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
R |
|
||||
WRITE |
|
|
W |
|
|
|
|
READ |
||||||||||
|
9 |
|
|
|
|
|
9 |
|
|
|
||||||||
DATA IN |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
DATA OUT |
||||||||||
D0 - D8 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
LH540204 |
|
|
Q0 - Q8 |
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
FULL FLAG |
|
|
|
FF |
|
|
|
|
EF |
EMPTY FLAG |
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
RESET |
RS |
RT |
RETRANSMIT |
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
XI |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
540204-17 |
|
|
Figure 4. Standalone FIFO (4096 × 9) |
|
|
|
DATA IN |
18 |
HF |
HF |
|
|
D0 - D17 |
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
9 |
|
9 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
W |
|
W |
EF |
|
|
WRITE |
|
LH540204 |
EMPTY FLAG |
|
|
FF |
R |
R |
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
FULL FLAG |
LH540204 |
|
READ |
|
|
RS |
|
RS |
|
|
|
RESET |
|
|
|
|
|
|
RT |
|
RT |
|
|
|
|
|
RETRANSMIT |
|
|
|
9 |
|
9 |
|
|
|
XI |
XI |
18 |
DATA OUT |
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
Q0 - Q17 |
|
|
|
|
|
540204-18 |
Figure 5. FIFO Word-Width Expansion (4096 × 18)
5
LH540204 |
CMOS 4096 × 9 Asynchronous FIFO |
|
|
OPERATIONAL MODES (cont’d)
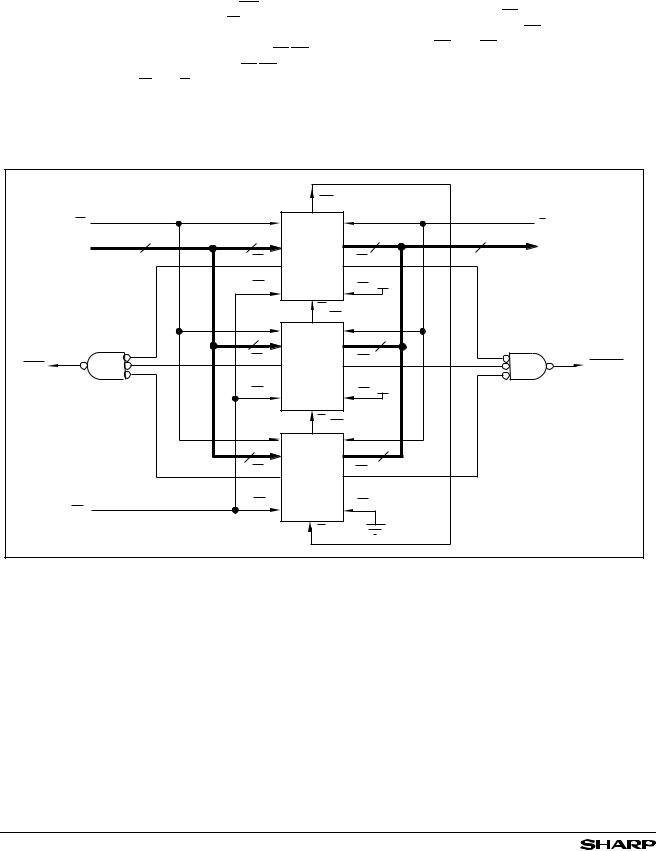
Depth Cascading
Depth cascading is implemented by configuring the required number of LH540204s in depth-cascaded mode. In this arrangement, the FIFOs are connected in a circular fashion, with the Expansion Out output (XO) of each device tied to the Expansion In input (XI) of the next device. One FIFO in the cascade must be designated as the ‘first-oad’l device, by tying its First Load input (FL/RT) to ground. All other devices must have their FL/RT inputs tied HIGH. In this mode, W and R signals are shared by all devices, while logic within each LH540204 controls the steering of data. Only one LH540204 is enabled during any given write cycle; thus, the common Data In inputs of
all devices are tied together. Likewise, only one LH540204 is enabled during any given read cycle; thus, the common Data Out outputs of all devices are wireORed together.
In depth-cascaded mode, external logic should be used to generate a composite Full Flag and a composite Empty Flag, by ANDing the FF outputs of all LH540204 devicestogetherand ANDing the EF outputs ofall devices together. Since FF and EF are assertive-LOW signals, this ‘ANDing’ actually is implemented using an assertiveHIGH physical OR gate. The Half-Full Flag and the Retransmit function are not available in depth-cas- caded mode.
|
|
|
|
|
|
XO |
|
|
|
|
|
W |
|
|
|
|
|
R |
|
DATA IN |
9 |
9 |
LH540204 |
9 |
9 |
DATA OUT |
|||
D |
0 |
- D |
8 |
|
FF |
EF |
|
Q0 - Q8 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
RS |
|
FL Vcc |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
XI |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
XO |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
9 |
|
9 |
|
|
FULL |
|
|
|
|
FF |
LH540204 |
EF |
|
EMPTY |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
RS |
|
FL Vcc |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
XI XO |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
9 |
|
9 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
FF |
LH540204 |
EF |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
RS |
|
RS |
|
FL |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
XI |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
540204-19 |
Figure 6. FIFO Depth Cascading (12288 × 9)
6
 Loading...
Loading...