Intel CORE I7-900, CORE I7-900 EXTREME Manual

Intel® Core™ i7-900 Desktop
Processor Extreme Edition Series
and Intel® Core™ i7-900 Desktop
Processor Series
Specification Update
April 2010
Notice: Intel® Core™ i7-900 Desktop Processor Extreme Edition Series and Intel® Core™ i7900 Desktop Processor Series may contain design defects or errors known as errata which may cause the product to deviate from published specifications. Current characterized errata are documented in this Specification Update.
Document Number: 320836-015

INFORMATION IN THIS DOCUMENT IS PROVIDED IN CONNECTION WITH INTEL® PRODUCTS. NO LICENSE, EXPRESS OR IMPLIED, BY ESTOPPEL OR OTHERWISE, TO ANY INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY RIGHTS IS GRANTED BY THIS DOCUMENT. EXCEPT AS PROVIDED IN INTEL’S TERMS AND CONDITIONS OF SALE FOR SUCH PRODUCTS, INTEL ASSUMES NO LIABILITY WHATSOEVER, AND INTEL DISCLAIMS ANY EXPRESS OR IMPLIED WARRANTY, RELATING TO SALE AND/OR USE OF INTEL PRODUCTS INCLUDING LIABILITY OR WARRANTIES RELATING TO FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE, MERCHANTABILITY, OR INFRINGEMENT OF ANY PATENT, COPYRIGHT OR OTHER INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY RIGHT.
UNLESS OTHERWISE AGREED IN WRITING BY INTEL, THE INTEL PRODUCTS ARE NOT DESIGNED NOR INTENDED FOR ANY APPLICATION IN WHICH THE FAILURE OF THE INTEL PRODUCT COULD CREATE A SITUATION WHERE PERSONAL INJURY OR DEATH MAY OCCUR.
Intel products are not intended for use in medical, life saving, or life sustaining applications. Intel may make changes to specifications and product descriptions at any time, without notice .
Designers must not rely on the absence or characteristics of any features or instructions marked “reserved” or “undefined.” Intel reserves these for future definition and shall have no responsibility whatsoever for conflicts or incompatibilities arising from future changes to them.
Intel processor numbers are not a measure of performance. Processor numbers differentiate features within each processor family, not across different processor families. See http://www.intel.com/products/processor_number for details.
Intel® Core™ i7-900 Desktop Processor Extreme Edition Series and Intel® Core™ i7-900 Desktop Processor Series may contain design defects or errors known as errata which may cause the product to deviate from published specifications. Current characterized errata are available on request.
Intel, the Intel logo, Celeron, Pentium, Xeon, Intel SpeedStep, Intel Core, and Core Inside are trademarks or registered trademarks of Intel Corporation or its subsidiaries in the United States and other countries.
*Other names and brands may be claimed as the property of others. Copyright © 2008-2010, Intel Corporation. All rights reserved.
Intel® Core™ i7 processor
Specification Update

Contents |
|
Preface................................................................................................................................. |
5 |
Summary Tables of Changes ................................................................................................... |
7 |
Identification Information ...................................................................................................... |
17 |
Errata.................................................................................................................................. |
19 |
Specification Changes ........................................................................................................... |
66 |
Specification Clarifications ..................................................................................................... |
67 |
Documentation Changes ........................................................................................................ |
68 |
Intel® Core™ i7 processor |
|
Specification Update |
3 |

Revision History
Revision |
|
Description |
Date |
|
|
|
|
|
|
-001 |
• |
Initial Release |
November 2008 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
-002 |
• |
Updated Specification Clarification AAJ1. |
January 2009 |
|
• |
Added Erratum AAJ89 |
|||
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
-003 |
• |
Updated Errata AAJ21, AAJ69 |
March 11th 2009 |
|
• |
Added Errata AAJ90-AAJ105 |
|||
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
• |
Added D0 stepping information |
|
|
-004 |
• |
Included i7-920 processor conversion to D0 step |
May 13th 2009 |
|
• |
Deleted Erratum AAJ105 and replaced with new erratum |
|||
|
|
|||
|
• |
Added Errata AAJ106-AAJ108 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
-005 |
• |
Included Intel® Core™ i7-975 processor Extreme Edition and |
June 3rd 2009 |
|
|
|
Intel® Core™ i7-950 processor |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
-006 |
• |
Added Errata AAJ109 - AAJ117 |
July 15th 2009 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
-007 |
• |
Added Errata AAJ118 - AAJ124 |
Aug 12th 2009 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
-008 |
• |
Added Errata AAJ125 and AAJ126 |
September 9th 2009 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
-009 |
• |
Added Errata AAJ127 - AAJ132 |
October 12th, 2009 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
-010 |
• |
Added Intel® Core™ i7-960 information |
October 19th, 2009 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
-011 |
• |
Added Errata AAJ133 - AAJ136 |
November 9th , 2009 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
-012 |
• |
Updated Errata AAJ121 and AAJ126 |
January, 2010 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
-013 |
• |
Added Errata AAJ137 |
February 7th, 2010 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
-014 |
• |
Added Intel® Core™ i7-930 information |
February 28th, 2010 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
-015 |
• |
Added Errata AAJ 138 |
March 16th, 2010 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
-016 |
• |
Added Errata AAJ 139 |
April 13th, 2010 |
|
|
|
|
|
§
Intel® Core™ i7 processor
Specification Update

Preface
Preface
This document is an update to the specifications contained in the Affected Documents table below. This document is a compilation of device and documentation errata, specification clarifications and changes. It is intended for hardware system manufacturers and software developers of applications, operating systems, or tools.
Information types defined in the Nomenclature section are consolidated into the specification update and are no longer published in other documents.
This document may also contain information that was not previously published.
Affected Documents
Document Title |
Document |
|
Number/Location |
|
|
Intel® Core™ i7-900 Desktop Processor Extreme Edition Series and |
http://download.intel.com |
Intel® Core™ i7-900 Desktop Processor Series Datasheet Volume 1 |
/design/processor/datash |
|
ts/320834.pdf |
Intel® Core™ i7-900 Desktop Processor Extreme Edition Series and |
http://download.intel.com |
Intel® Core™ i7-900 Desktop Processor Series Datasheet Volume 2 |
/design/processor/datash |
|
ts/320835.pdf |
Related Documents
Document Title |
Document |
|
|
Number/Location |
|
|
|
|
AP-485, Intel® Processor Identification and the CPUID Instruction |
http://www.intel.com/des |
|
|
ign/processor/applnots/2 |
|
|
41618.htm |
|
|
|
|
Intel® 64 and IA-32 Architectures Software Developer’s Manual |
http://www.intel.com/des |
|
Documentation Changes |
ign/processor/specupdt/2 |
|
52046.htm |
||
|
||
|
|
|
ACPI Specifications |
www.acpi.info |
|
|
|
Intel® Core™ i7 processor |
|
Specification Update |
5 |

Preface
Document Title |
Document |
|
Number/Location |
|
|
Intel® 64 and IA-32 Architectures Software Developer’s Manual, |
http://www.intel.com/pro |
Volume 1: Basic Architecture |
ducts/processor/manuals/ |
Intel® 64 and IA-32 Architectures Software Developer’s Manual, |
index.htm |
|
|
Volume 2A: Instruction Set Reference Manual A-M |
|
Intel® 64 and IA-32 Architectures Software Developer’s Manual, |
|
Volume 2B: Instruction Set Reference Manual N-Z |
|
Intel® 64 and IA-32 Architectures Software Developer’s Manual, |
|
Volume 3A: System Programming Guide |
|
Intel® 64 and IA-32 Architectures Software Developer’s Manual, |
|
Volume 3B: System Programming Guide |
|
Intel® 64 and IA-32 Intel Architecture Optimization Reference Manual |
|
Nomenclature
Errata are design defects or errors. These may cause the Intel® Core™ i7 processor Extreme Edition and Intel® Core™ i7 processor behavior to deviate from published specifications. Hardware and software designed to be used with any given stepping must assume that all errata documented for that stepping are present on all devices.
S-Spec Number is a five-digit code used to identify products. Products are differentiated by their unique characteristics, e.g., core speed, L2 cache size, package type, etc. as described in the processor identification information table. Read all notes associated with each S-Spec number.
Specification Changes are modifications to the current published specifications. These changes will be incorporated in any new release of the specification.
Specification Clarifications describe a specification in greater detail or further highlight a specification’s impact to a complex design situation. These clarifications will be incorporated in any new release of the specification.
Documentation Changes include typos, errors, or omissions from the current published specifications. These will be incorporated in any new release of the specification.
Note: Errata remain in the specification update throughout the product’s lifecycle, or until a particular stepping is no longer commercially available. Under these circumstances, errata removed from the specification update are archived and available upon request. Specification changes, specification clarifications and documentation changes are removed from the specification update when the appropriate changes are made to the appropriate product specification or user documentation (datasheets, manuals, etc.).
Intel® Core™ i7 processor
Specification Update

Summary Tables of Changes
Summary Tables of Changes
The following tables indicate the errata, specification changes, specification clarifications, or documentation changes which apply to the Intel® Core™ i7 processor extreme edition and Intel® Core™ i7 desktop processor product. Intel may fix some of the errata in a future stepping of the component, and account for the other outstanding issues through documentation or specification changes as noted. These tables uses the following notations:
Codes Used in Summary Tables
Stepping
X: |
Errata exists in the stepping indicated. Specification Change or |
|
Clarification that applies to this stepping. |
(No mark) |
|
or (Blank box): |
This erratum is fixed in listed stepping or specification change |
|
does not apply to listed stepping. |
Page
(Page): Page location of item in this document.
Status
Doc: |
Document change or update will be implemented. |
Plan Fix: |
This erratum may be fixed in a future stepping of the product. |
Fixed: |
This erratum has been previously fixed. |
No Fix: |
There are no plans to fix this erratum. |
Row
Change bar to left of table row indicates this erratum is either new or modified from the previous version of the document.
Each Specification Update item is prefixed with a capital letter to distinguish the product. The key below details the letters that are used in Intel’s microprocessor Specification Updates:
Intel® Core™ i7 processor |
|
Specification Update |
7 |

Summary Tables of Changes
A = |
Dual-Core Intel® Xeon® processor 7000 sequence |
C = |
Intel® Celeron® processor |
D = |
Dual-Core Intel® Xeon® processor 2.80 GHz |
E = |
Intel® Pentium® III processor |
F = |
Intel® Pentium® processor Extreme Edition and Intel® Pentium® D processor |
I = |
Dual-Core Intel® Xeon® processor 5000 series |
J = |
64-bit Intel® Xeon® processor MP with 1MB L2 cache |
K = |
Mobile Intel® Pentium® III processor |
L = |
Intel® Celeron® D processor |
M = |
Mobile Intel® Celeron® processor |
N = |
Intel® Pentium® 4 processor |
O = |
Intel® Xeon® processor MP |
P = |
Intel® Xeon® processor |
Q = |
Mobile Intel® Pentium® 4 processor supporting Hyper-Threading technology |
|
on 90-nm process technology |
R = |
Intel® Pentium® 4 processor on 90 nm process |
S = |
64-bit Intel® Xeon® processor with 800 MHz system bus (1 MB and 2 MB L2 |
|
cache versions) |
T = |
Mobile Intel® Pentium® 4 processor-M |
U = |
64-bit Intel® Xeon® processor MP with up to 8MB L3 cache |
V = |
Mobile Intel® Celeron® processor on .13 micron process in Micro-FCPGA |
|
package |
W= |
Intel® Celeron® M processor |
X = |
Intel® Pentium® M processor on 90nm process with 2-MB L2 cache and |
|
Intel® processor A100 and A110 with 512-KB L2 cache |
Y = |
Intel® Pentium® M processor |
Z = |
Mobile Intel® Pentium® 4 processor with 533 MHz system bus |
AA= Intel® Pentium® D processor 900 sequence and Intel® Pentium® processor Extreme Edition 955, 965
AB = Intel® Pentium® 4 processor 6x1 sequence AC = Intel® Celeron® processor in 478 pin package AD = Intel® Celeron® D processor on 65nm process
AE = Intel® Core™ Duo processor and Intel® Core™ Solo processor on 65nm process
AF = Dual-Core Intel® Xeon® processor LV
AG = Dual-Core Intel® Xeon® processor 5100 series
AH = Intel® Core™2 Duo/Solo Processor for Intel® Centrino® Duo Processor Technology
Intel® Core™ i7 processor
Specification Update

Summary Tables of Changes
AI = |
Intel® Core™2 Extreme processor X6800 and Intel® Core™2 Duo desktop |
|
processor E6000 and E4000 sequence |
AJ = |
Quad-Core Intel® Xeon® processor 5300 series |
AK = |
Intel® Core™2 Extreme quad-core processor QX6000 sequence and Intel® |
|
Core™2 Quad processor Q6000 sequence |
AL = |
Dual-Core Intel® Xeon® processor 7100 series |
AM = |
Intel® Celeron® processor 400 sequence |
AN = |
Intel® Pentium® dual-core processor |
AO = |
Quad-Core Intel® Xeon® processor 3200 series |
AP = |
Dual-Core Intel® Xeon® processor 3000 series |
AQ = |
Intel® Pentium® dual-core desktop processor E2000 sequence |
AR = |
Intel® Celeron® processor 500 series |
AS = |
Intel® Xeon® processor 7200, 7300 series |
AT = |
Intel® Celeron® processor 200 series |
AU = |
Intel® Celeron® Dual Core processor T1400 |
AV = |
Intel® Core™2 Extreme processor QX9650 and Intel® Core™2 Quad |
|
processor Q9000 series |
AW = |
Intel® Core™ 2 Duo processor E8000 series and E7000 series |
AX = |
Quad-Core Intel® Xeon® processor 5400 series |
AY = |
Dual-Core Intel® Xeon® processor 5200 series |
AZ= |
Intel® Core™2 Duo processor and Intel® Core™2 Extreme processor on 45- |
|
nm process |
AAA= |
Quad-Core Intel® Xeon® processor 3300 series |
AAB= |
Dual-Core Intel® Xeon® E3110 processor |
AAC= |
Intel® Celeron® dual-core processor E1000 series |
AAD = |
Intel® Core™2 Extreme processor QX9775 |
AAE = |
Intel® Atom™ processor Z5xx series |
AAF = |
Intel® Atom™ processor 200 series |
AAG = |
Intel® Atom™ processor N series |
AAH = |
Intel® Atom™ processor 300 series |
AAI = |
Intel® Xeon® Processor 7400 Series |
AAJ = |
Intel® Core™ i7-900 Desktop Processor Extreme Edition Series and Intel® |
|
Core™ i7-900 Desktop Processor Series |
AAL = |
Intel® Pentium Dual-Core Processor E5000 Series |
Intel® Core™ i7 processor |
|
Specification Update |
9 |

Summary Tables of Changes
No |
C-0 |
D-0 |
Status |
ERRATA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
AAJ1 |
X |
X |
No Fix |
MCi_Status Overflow Bit May Be Incorrectly Set on a Single Instance of a |
|
DTLB Error |
|||||
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
AAJ2 |
X |
X |
No Fix |
Debug Exception Flags DR6.B0-B3 Flags May be Incorrect for Disabled |
|
Breakpoints |
|||||
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
AAJ3 |
X |
X |
No Fix |
MONITOR or CLFLUSH on the Local XAPIC's Address Space Results in Hang |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
AAJ4 |
X |
X |
No Fix |
Corruption of CS Segment Register During RSM While Transitioning From |
|
Real Mode to Protected Mode |
|||||
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
AAJ5 |
X |
X |
No Fix |
The Processor May Report a #TS Instead of a #GP Fault |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
REP MOVS/STOS Executing with Fast Strings Enabled and Crossing Page |
|
AAJ6 |
X |
X |
No Fix |
Boundaries with Inconsistent Memory Types may use an Incorrect Data |
|
|
|
|
|
Size or Lead to Memory-Ordering Violations |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Code Segment Limit/Canonical Faults on RSM May be Serviced before |
|
AAJ7 |
X |
X |
No Fix |
Higher Priority Interrupts/Exceptions and May Push the Wrong Address |
|
|
|
|
|
Onto the Stack |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
AAJ8 |
X |
X |
No Fix |
Performance Monitor SSE Retired Instructions May Return Incorrect Values |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
AAJ9 |
X |
X |
No Fix |
Premature Execution of a Load Operation Prior to Exception Handler |
|
Invocation |
|||||
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
AAJ10 |
X |
X |
No Fix |
MOV To/From Debug Registers Causes Debug Exception |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
AAJ11 |
X |
X |
No Fix |
Incorrect Address Computed For Last Byte of FXSAVE/FXRSTOR Image |
|
Leads to Partial Memory Update |
|||||
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
AAJ12 |
X |
X |
No Fix |
Values for LBR/BTS/BTM will be Incorrect after an Exit from SMM |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
AAJ13 |
X |
X |
No Fix |
Single Step Interrupts with Floating Point Exception Pending May Be |
|
Mishandled |
|||||
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
AAJ14 |
X |
X |
No Fix |
Fault on ENTER Instruction May Result in Unexpected Values on Stack |
|
Frame |
|||||
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
AAJ15 |
X |
X |
No Fix |
IRET under Certain Conditions May Cause an Unexpected Alignment Check |
|
Exception |
|||||
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
AAJ16 |
X |
X |
No Fix |
General Protection Fault (#GP) for Instructions Greater than 15 Bytes May |
|
be Preempted |
|||||
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
AAJ17 |
X |
X |
No Fix |
General Protection (#GP) Fault May Not Be Signaled on Data Segment |
|
Limit Violation above 4-G Limit |
|||||
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
AAJ18 |
X |
X |
No Fix |
LBR, BTS, BTM May Report a Wrong Address when an Exception/Interrupt |
|
Occurs in 64-bit Mode |
|||||
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
AAJ19 |
X |
X |
No Fix |
Performance Monitoring Events for Read Miss to Level 3 Cache Fill |
|
Occupancy Counter may be Incorrect |
|||||
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
AAJ20 |
X |
X |
No Fix |
A VM Exit on MWAIT May Incorrectly Report the Monitoring Hardware as |
|
Armed |
|||||
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
AAJ21 |
X |
X |
No Fix |
Memory Aliasing of Code Pages May Cause Unpredictable System Behavior |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
AAJ22 |
X |
X |
No Fix |
Delivery Status of the LINT0 Register of the Local Vector Table May be Lost |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
AAJ23 |
X |
X |
No Fix |
Performance Monitor Event SEGMENT_REG_LOADS Counts Inaccurately |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Intel® Core™ i7 processor
Specification Update

Summary Tables of Changes
No |
C-0 |
|
D-0 |
Status |
ERRATA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
AAJ24 |
X |
|
X |
No Fix |
#GP on Segment Selector Descriptor that Straddles Canonical Boundary |
|
May Not Provide Correct Exception Error Code |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
AAJ25 |
X |
|
X |
No Fix |
Improper Parity Error Signaled in the IQ Following Reset When a Code |
|
Breakpoint is Set on a #GP Instruction |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
An Enabled Debug Breakpoint or Single Step Trap May Be Taken after MOV |
AAJ26 |
X |
|
X |
No Fix |
SS/POP SS Instruction if it is Followed by an Instruction That Signals a |
|
|
|
|
|
Floating Point Exception |
|
|
|
|
|
|
AAJ27 |
X |
|
X |
No Fix |
IA32_MPERF Counter Stops Counting During On-Demand TM1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
AAJ28 |
X |
|
X |
No Fix |
Intel® QuickPath Memory Controller tTHROT_OPREF Timings May be |
|
Violated During Self Refresh Entry |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
AAJ29 |
X |
|
X |
No Fix |
Processor May Over Count Correctable Cache MESI State Errors |
|
|
|
|
|
|
AAJ30 |
X |
|
X |
No Fix |
Synchronous Reset of IA32_APERF/IA32_MPERF Counters on Overflow |
|
Does Not Work |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
AAJ31 |
X |
|
X |
No Fix |
Disabling Thermal Monitor While Processor is Hot, Then Re-enabling, May |
|
Result in Stuck Core Operating Ratio |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
AAJ32 |
X |
|
|
Fixed |
The PECI Throttling Counter May Not be Accurate |
|
|
|
|
|
|
AAJ33 |
X |
|
X |
No Fix |
PECI Does Not Support PCI Configuration Reads/Writes to Misaligned |
|
Addresses |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
AAJ34 |
X |
|
X |
No Fix |
OVER Bit for IA32_MCi_STATUS Register May Get Set on Specific lnternal |
|
Error |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
AAJ35 |
X |
|
X |
No Fix |
Writing the Local Vector Table (LVT) when an Interrupt is Pending May |
|
Cause an Unexpected Interrupt |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
AAJ36 |
X |
|
|
Fixed |
A Processor Core May Not Wake Up from S1 State |
|
|
|
|
|
|
AAJ37 |
X |
|
X |
No Fix |
Reading Reserved APIC Registers May Not Signal an APIC Error |
|
|
|
|
|
|
AAJ38 |
X |
|
|
Fixed |
A Logical Processor Receiving a SIPI After a VM Entry Into WFS State May |
|
|
Become Unresponsive |
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
AAJ39 |
X |
|
X |
No Fix |
Memory Controller May Deliver Incorrect Data When Memory Ranks Are In |
|
Power-Down |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
AAJ40 |
X |
|
X |
No Fix |
Faulting MMX Instruction May Incorrectly Update x87 FPU Tag Word |
|
|
|
|
|
|
AAJ41 |
X |
|
|
Fixed |
A Floating-Point Store Instruction May Cause an Unexpected x87 FPU |
|
|
Floating-Point Error (#MF) |
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
AAJ42 |
X |
|
|
Fixed |
Incorrect TLB Translation May Occur After Exit From C6 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
AAJ43 |
X |
|
|
Fixed |
USB 1.1 ISOCH Audio Glitches with Intel® QuickPath Interconnect Locks |
|
|
and Deep C-States |
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
AAJ44 |
X |
|
|
Fixed |
Stack Pointer May Become Incorrect In Loops With Unbalanced Push and |
|
|
Pop Operations |
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
AAJ45 |
X |
|
X |
No Fix |
A P-state Change While Another Core is in C6 May Prevent Further C-state |
|
and P-state Transitions |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
AAJ46 |
X |
|
X |
No Fix |
Certain Store Parity Errors May Not Log Correct Address in |
|
IA32_MCi_ADDR |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Intel® Core™ i7 processor |
|
|
|||
Specification Update |
|
|
11 |
||

Summary Tables of Changes
No |
C-0 |
D-0 |
Status |
ERRATA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
AAJ47 |
X |
X |
No Fix |
xAPIC Timer May Decrement Too Quickly Following an Automatic Reload |
|
While in Periodic Mode |
|||||
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
AAJ48 |
X |
X |
No Fix |
Certain Undefined Opcodes Crossing a Segment Limit May Result in #UD |
|
Instead of #GP Exception |
|||||
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
AAJ49 |
X |
X |
No Fix |
Indication of A20M Support is Inverted |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
AAJ50 |
X |
X |
No Fix |
Reported Memory Type May Not Be Used to Access the VMCS and |
|
Referenced Data Structures |
|||||
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
AAJ51 |
X |
|
Fixed |
After VM Entry, Instructions May Incorrectly Operate as if CS.D=0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
AAJ52 |
X |
|
Fixed |
Spurious Machine Check Error May Occur When Logical Processor is Woken |
|
|
Up |
||||
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
AAJ53 |
X |
X |
No Fix |
B0-B3 Bits in DR6 For Non-Enabled Breakpoints May be Incorrectly Set |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
AAJ54 |
X |
X |
No Fix |
Core C6 May Clear Previously Logged TLB Errors |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
AAJ55 |
X |
X |
No Fix |
Processor May Hang When Two Logical Processors Are in Specific Low |
|
Power States |
|||||
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
AAJ56 |
X |
X |
No Fix |
MOVNTDQA From WC Memory May Pass Earlier Locked Instructions |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
AAJ57 |
X |
X |
No Fix |
Performance Monitor Event MISALIGN_MEM_REF May Over Count |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
AAJ58 |
X |
X |
No Fix |
Changing the Memory Type for an In-Use Page Translation May Lead to |
|
Memory-Ordering Violations |
|||||
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
AAJ59 |
X |
|
Fixed |
Writes to IA32_CR_PAT or IA32_EFER MSR May Cause an Incorrect ITLB |
|
|
Translation |
||||
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
AAJ60 |
X |
|
Fixed |
The "Virtualize APIC Accesses" VM-Execution Control May be Ignored |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
AAJ61 |
X |
|
Fixed |
C6 Transitions May Cause Spurious Updates to the xAPIC Error Status |
|
|
Register |
||||
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
AAJ62 |
X |
|
Fixed |
Critical ISOCH Traffic May Cause Unpredictable System Behavior When |
|
|
Write Major Mode Enabled |
||||
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
AAJ63 |
X |
X |
No Fix |
Running with Write Major Mode Disabled May Lead to a System Hang |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
AAJ64 |
X |
X |
No Fix |
Memory Controller Address Parity Error Injection Does Not Work Correctly |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
AAJ65 |
X |
X |
No Fix |
Memory Controller Opportunistic Refreshes Might be Missed |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
AAJ66 |
X |
X |
No Fix |
Delivery of Certain Events Immediately Following a VM Exit May Push a |
|
Corrupted RIP Onto The Stack |
|||||
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
AAJ67 |
X |
X |
No Fix |
The Combination of a Bus Lock and a Data Access That is Split Across Page |
|
Boundaries May Lead to Processor Livelock |
|||||
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
AAJ68 |
X |
X |
No Fix |
CPUID Instruction Returns Incorrect Brand String |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
AAJ69 |
X |
X |
No Fix |
An Unexpected Page Fault May Occur Following the Unmapping and Re- |
|
mapping of a Page |
|||||
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
AAJ70 |
X |
X |
No Fix |
Infinite Stream of Interrupts May Occur if an ExtINT Delivery Mode |
|
Interrupt is Received while All Cores in C6 |
|||||
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
AAJ71 |
X |
X |
No Fix |
Two xAPIC Timer Event Interrupts May Unexpectedly Occur |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Intel® Core™ i7 processor
Specification Update

Summary Tables of Changes
No |
C-0 |
|
D-0 |
Status |
ERRATA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
AAJ72 |
X |
|
X |
No Fix |
EOI Transaction May Not be Sent if Software Enters Core C6 During an |
|
Interrupt Service Routine |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
AAJ73 |
X |
|
X |
No Fix |
FREEZE_WHILE_SMM Does Not Prevent Event From Pending PEBS During |
|
SMM |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
AAJ74 |
X |
|
X |
No Fix |
PEBS Records For Load Latency Monitoring May Contain an Incorrect Linear |
|
Address |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
AAJ75 |
X |
|
X |
No Fix |
PEBS Field “Data Linear Address” is Not Sign Extended to 64 Bits |
|
|
|
|
|
|
AAJ76 |
X |
|
X |
No Fix |
Core C6 May Not Operate Correctly in the Presence of Bus Locks |
|
|
|
|
|
|
AAJ77 |
X |
|
X |
No Fix |
Intel® Turbo Boost Technology May be Limited Immediately After Package |
|
C-state Exit with QPI L1 Mode Disabled |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
AAJ78 |
X |
|
X |
No Fix |
APIC Error “Received Illegal Vector” May be Lost |
|
|
|
|
|
|
AAJ79 |
X |
|
X |
No Fix |
CPUID Incorrectly Indicates the UnHalted Reference Cycle Architectural |
|
Event is Supported |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
AAJ80 |
X |
|
|
Fixed |
Architectural Performance Monitor Event ‘Branch Misses Retired’ is Counted |
|
|
Incorrectly |
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
AAJ81 |
X |
|
X |
No Fix |
DR6 May Contain Incorrect Information When the First Instruction After a |
|
MOV SS,r/m or POP SS is a Store |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
AAJ82 |
X |
|
X |
No Fix |
An Uncorrectable Error Logged in IA32_CR_MC2_STATUS May also Result |
|
in a System Hang |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
AAJ83 |
X |
|
X |
No Fix |
IA32_PERF_GLOBAL_CTRL MSR May be Incorrectly Initialized |
|
|
|
|
|
|
AAJ84 |
X |
|
X |
No Fix |
Performance Monitor Interrupts Generated From Uncore Fixed Counters |
|
(394H) May be Ignored |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
AAJ85 |
X |
|
X |
No Fix |
Processors with SMT May Hang on P-State Transition or ACPI Clock |
|
Modulation Throttling |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
AAJ86 |
X |
|
X |
No Fix |
Performance Monitor Counter INST_RETIRED.STORES May Count Higher |
|
than Expected |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
AAJ87 |
X |
|
X |
No Fix |
Sleeping Cores May Not be Woken Up on Logical Cluster Mode Broadcast |
|
IPI Using Destination Field Instead of Shorthand |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
AAJ88 |
X |
|
X |
No Fix |
Faulting Executions of FXRSTOR May Update State Inconsistently |
|
|
|
|
|
|
AAJ89 |
X |
|
X |
No Fix |
Unexpected QPI Link Behavior May Occur When a CRC Error Happens |
|
During L0s |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
AAJ90 |
X |
|
X |
No Fix |
Performance Monitor Event EPT.EPDPE_MISS May be Counted While EPT is |
|
Disabled |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
AAJ91 |
X |
|
X |
No Fix |
Performance Monitor Counters May Count Incorrectly |
|
|
|
|
|
|
AAJ92 |
X |
|
X |
No Fix |
Processor Forward Progress Mechanism Interacting With Certain MSR/CSR |
|
Writes May Cause Unpredictable System Behavior |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
AAJ93 |
X |
|
|
Fixed |
USB 1.1 Isoch Memory Latencies May Increase During Package C3/C6 |
|
|
Transitions |
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
AAJ94 |
X |
|
X |
No Fix |
Processor May Incorrectly Demote Processor C6 State to a C3 State |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Intel® Core™ i7 processor |
|
|
|||
Specification Update |
|
|
13 |
||

Summary Tables of Changes
No |
C-0 |
D-0 |
Status |
ERRATA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
AAJ95 |
X |
X |
No Fix |
Performance Monitor Event Offcore_response_0 (B7H) Does Not Count NT |
|
Stores to Local DRAM Correctly |
|||||
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
AAJ96 |
X |
X |
No Fix |
EFLAGS Discrepancy on Page Faults and on EPT-Induced VM Exits after a |
|
Translation Change |
|||||
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
System May Hang if |
|
AAJ97 |
X |
X |
No Fix |
MC_CHANNEL_{0,1,2}_MC_DIMM_INIT_CMD.DO_ZQCL Commands Are |
|
|
|
|
|
Not Issued in Increasing Populated DDR3 Rank Order |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
AAJ98 |
X |
X |
No Fix |
LER and LBR MSRs May Be Incorrectly Updated During a Task Switch |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
AAJ99 |
X |
|
Fixed |
Virtualized WRMSR to the IA32_EXT_XAPIC_TPR MSR Uses Incorrect Value |
|
|
for TPR Threshold |
||||
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
AAJ100 |
X |
X |
No Fix |
Back to Back Uncorrected Machine Check Errors May Overwrite |
|
IA32_MC3_STATUS.MSCOD |
|||||
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
AAJ101 |
X |
X |
No Fix |
Memory Intensive Workloads with Core C6 Transitions May Cause System |
|
Hang |
|||||
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
AAJ102 |
X |
X |
No Fix |
Corrected Errors With a Yellow Error Indication May be Overwritten by |
|
Other Corrected Errors |
|||||
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
AAJ103 |
X |
X |
No Fix |
PSI# Signal May Incorrectly be Left Asserted |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
AAJ104 |
X |
X |
No Fix |
A String Instruction that Re-maps a Page May Encounter an Unexpected |
|
Page Fault |
|||||
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
AAJ105 |
X |
X |
No Fix |
Performance Monitor Events DCACHE_CACHE_LD and DCACHE_CACHE_ST |
|
May Overcount |
|||||
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
AAJ106 |
X |
X |
No Fix |
Rapid Core C3/C6 Transition May Cause Unpredictable System Behavior |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
AAJ107 |
X |
X |
No Fix |
Performance Monitor Events INSTR_RETIRED and MEM_INST_RETIRED |
|
May Count Inaccurately |
|||||
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
AAJ108 |
X |
X |
No Fix |
A Page Fault May Not be Generated When the PS bit is set to "1" in a |
|
PML4E or PDPTE |
|||||
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
AAJ109 |
X |
X |
Plan Fix |
tRP Timing Violations May be Observed Near a Self Refresh Entry |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
System May Hang if |
|
AAJ110 |
X |
X |
No Fix |
MC_CHANNEL_{0,1,2}_MC_DIMM_INIT_CMD.DO_ZQCL Commands Are |
|
|
|
|
|
Not Issued in Increasing Populated DDR3 Rank Order |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
AAJ111 |
X |
X |
No Fix |
Concurrent Updates to a Segment Descriptor May be Lost |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Processor May Incorrectly Demote Processor C6 State to a C3 State |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
AAJ112 |
X |
X |
No Fix |
Memory Controller Clock Circuits May Show a Temperature Sensitive |
|
Dependence on Power-On Conditions |
|||||
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
AAJ113 |
X |
X |
No Fix |
PMIs May be Lost During Core C6 Transitions |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
AAJ114 |
X |
X |
No Fix |
Uncacheable Access to a Monitored Address Range May Prevent Future |
|
Triggering of the Monitor Hardware |
|||||
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
AAJ115 |
X |
X |
No Fix |
BIST Results May be Additionally Reported After a GETSEC[WAKEUP] or |
|
INIT-SIPI Sequence |
|||||
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
AAJ116 |
X |
X |
No Fix |
Pending x87 FPU Exceptions (#MF) May be Signaled Earlier Than Expected |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Intel® Core™ i7 processor
Specification Update

Summary Tables of Changes
No |
C-0 |
D-0 |
Status |
ERRATA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
AAJ117 |
X |
X |
No Fix |
VM Exits Due to “NMI-Window Exiting” May Be Delayed by One Instruction |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
AAJ118 |
X |
X |
No Fix |
VM Exits Due to EPT Violations Do Not Record Information About Pre-IRET |
|
NMI Blocking |
|||||
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
AAJ119 |
X |
X |
No Fix |
Multiple Performance Monitor Interrupts are Possible on Overflow of |
|
IA32_FIXED_CTR2 |
|||||
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
AAJ120 |
X |
X |
No Fix |
LBRs May Not be Initialized During Power-On Reset of the Processor |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
AAJ121 |
X |
X |
No Fix |
Unexpected Interrupts May Occur on C6 Exit If Using APIC Timer to |
|
Generate Interrupts |
|||||
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
LBR, BTM or BTS Records May have Incorrect Branch From |
|
AAJ122 |
X |
X |
No Fix |
Information After an EIST Transition, T-states, C1E, or Adaptive Thermal |
|
|
|
|
|
Throttling |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
AAJ123 |
X |
X |
No Fix |
Redirection to Probe Mode May be delayed beyond Intended Instruction |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
AAJ124 |
X |
X |
No Fix |
VMX-Preemption Timer Does Not Count Down at the Rate Specified |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
AAJ125 |
X |
X |
No Fix |
Multiple Performance Monitor Interrupts are Possible on Overflow of Fixed |
|
Counter 0 |
|||||
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
AAJ126 |
X |
X |
No Fix |
VM Exits Due to LIDT/LGDT/SIDT/SGDT Do Not Report Operand Size |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
AAJ127 |
X |
|
No Fix |
Performance Monitoring Events STORE_BLOCKS.NOT_STA and |
|
|
STORE_BLOCKS.STA May Not Count Events Correctly |
||||
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
AAJ128 |
X |
X |
No Fix |
Storage of PEBS Record Delayed Following Execution of MOV SS or STI |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
AAJ129 |
X |
X |
No Fix |
Performance Monitoring Event FP_MMX_TRANS_TO_MMX May Not Count |
|
Some Transitions |
|||||
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
AAJ130 |
X |
X |
Plan Fix |
INVLPG Following INVEPT or INVVPID May Fail to Flush All Translations for |
|
a Large Page |
|||||
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
AAJ131 |
X |
X |
No Fix |
The PECI Bus May be Tri-stated After System Reset |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
AAJ132 |
X |
X |
No Fix |
LER MSRs May Be Unreliable |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
AAJ133 |
X |
X |
No Fix |
An Exit From the Core C6-state May Result in the Dropping of an Interrupt |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
AAJ134 |
X |
X |
No Fix |
PMIs During Core C6 Transitions May Cause the System to Hang |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
AAJ135 |
X |
X |
No Fix |
2MB Page Split Lock Accesses Combined With Complex Internal Events |
|
May Cause Unpredictable System Behavior |
|||||
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
AAJ136 |
X |
X |
No Fix |
IA32_MC8_CTL2 MSR is Not Cleared on Processor Warm Reset |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
AAJ137 |
X |
X |
No Fix |
The Combination of a Page-Split Lock Access And Data Accesses That Are |
|
Split Across Cacheline Boundaries May Lead to Processor Livelock |
|||||
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
FP Data Operand Pointer May Be Incorrectly Calculated After an FP Access |
|
AAJ138 |
X |
X |
No Fix |
Which Wraps a 4-Gbyte Boundary in Code That Uses 32-Bit Address Size in |
|
|
|
|
|
64-bit Mode |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
AAJ139 |
X |
X |
No Fix |
IO_SMI Indication in SMRAM State Save Area May Be Lost |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Intel® Core™ i7 processor |
|
Specification Update |
15 |

Summary Tables of Changes
No |
SPECIFICATION CHANGES |
-There are no Specification Changes in this Specification Update revision.
No |
SPECIFICATION CLARIFICATIONS |
|
|
AAJ1 |
Clarification of TRANSLATION LOOKASIDE BUFFERS (TLBS) Invalidation |
|
|
|
|
No |
DOCUMENTATION CHANGES |
-There are no Documentation Changes in this Specification Update revision.
Intel® Core™ i7 processor
Specification Update

Identification Information
Identification Information
Component Identification via Programming Interface
The Intel® Core™ i7 processor extreme edition and Intel® Core™ i7 processor stepping can be identified by the following register contents:
Reser |
Extended |
Extended |
Reserv |
Process |
Family |
Model |
Stepping |
ved |
Family1 |
Model2 |
ed |
or Type3 |
Code4 |
Number5 |
ID6 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
31:28 |
27:20 |
19:16 |
15:14 |
13:12 |
11:8 |
7:4 |
3:0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
00000000b |
0001b |
|
00b |
0110 |
1010b |
xxxxb |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
NOTES:
1.The Extended Family, bits [27:20] are used in conjunction with the Family Code, specified in bits [11:8], to indicate whether the processor belongs to the Intel386, Intel486, Pentium, Pentium Pro, Pentium 4, Intel® Core™ processor family or Intel® Core i7 family.
2.The Extended Model, bits [19:16] in conjunction with the Model Number, specified in bits [7:4], are used to identify the model of the processor within the processor’s family.
3.The Processor Type, specified in bits [13:12] indicates whether the processor is an original OEM processor, an OverDrive processor, or a dual processor (capable of being used in a dual processor system).
4.The Family Code corresponds to bits [11:8] of the EDX register after RESET, bits [11:8] of the EAX register after the CPUID instruction is executed with a 1 in the EAX register, and the generation field of the Device ID register accessible through Boundary Scan.
5.The Model Number corresponds to bits [7:4] of the EDX register after RESET, bits [7:4] of the EAX register after the CPUID instruction is executed with a 1 in the EAX register, and the model field of the Device ID register accessible through Boundary Scan.
6.The Stepping ID in bits [3:0] indicates the revision number of that model. See Table 1 for the processor stepping ID number in the CPUID information.
When EAX is initialized to a value of ‘1’, the CPUID instruction returns the Extended Family, Extended Model, Processor Type, Family Code, Model Number and Stepping ID value in the EAX register. Note that the EDX processor signature value after reset is equivalent to the processor signature output value in the EAX register.
Cache and TLB descriptor parameters are provided in the EAX, EBX, ECX and EDX registers after the CPUID instruction is executed with a 2 in the EAX register.
Intel® Core™ i7 processor |
|
Specification Update |
17 |
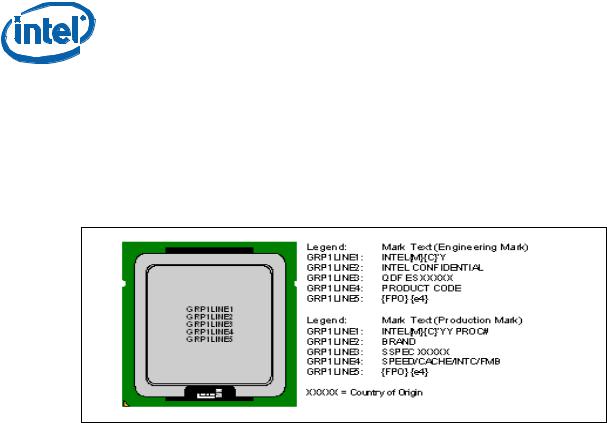
Identification Information
Component Marking Information
The Intel® Core™ i7 processor extreme edition and Intel® Core™ i7 processor stepping can be identified by the following component markings:
Figure 1. Processor Top-side Markings (Example)
Table 1. Intel® Core™ i7 Processor Information
QDF/ |
Step |
Processor |
Processor |
Core Frequency |
Available |
Cache |
Notes |
S- |
ping |
Number |
Signature |
(GHz) / |
bins of |
Size |
|
Spec |
|
|
|
Intel QuickPath |
Intel® Turbo |
(MB) |
|
|
|
|
|
Interconnect |
Boost |
|
|
|
|
|
|
(GT/s) / |
Technology2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
DDR3 (MHz) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
SLBCJ |
C-0 |
i7-965 |
0x000106A4 |
3.20 / 6.40/ 1066 |
1/1/1/2 |
8 |
1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
SLBCK |
C-0 |
i7-940 |
0x000106A4 |
2.93 / 4.80/ 1066 |
1/1/1/2 |
8 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
SLBCH |
C-0 |
i7-920 |
0x000106A4 |
2.66 / 4.80/ 1066 |
1/1/1/2 |
8 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
SLBEQ |
D-0 |
i7-975 |
0x000106A5 |
3.33 / 6.40/ 1066 |
1/1/1/2 |
8 |
1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
SLBEU |
D-0 |
i7-960 |
0x000106A5 |
3.20 / 4.80/ 1066 |
1/1/1/2 |
8 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
SLBEN |
D-0 |
i7-950 |
0x000106A5 |
3.06 / 4.80/ 1066 |
1/1/1/2 |
8 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
SLBKP |
D-0 |
i7-930 |
0x000106A5 |
2.80 / 4.80/ 1066 |
1/1/1/2 |
8 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
SLBEJ |
D-0 |
i7-920 |
0x000106A5 |
2.66 / 4.80/ 1066 |
1/1/1/2 |
8 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
NOTES:
1.Although these units are factory-configured for 1333 MHz integrated memory controller frequency, Intel does not support operation beyond 1066 MHz; however, this processor has additional support to override the integrated memory controller frequency.
2.Column indicates the number of frequency bins (133.33 MHz) of Intel® Turbo Boost Technology that are available for 4, 3, 2, or 1 cores active respectively.
§
Intel® Core™ i7 processor
Specification Update

Errata
Errata
AAJ1. |
MCi_Status Overflow Bit May Be Incorrectly Set on a Single Instance |
|
of a DTLB Error |
Problem: |
A single Data Translation Look Aside Buffer (DTLB) error can incorrectly set |
|
the Overflow (bit [62]) in the MCi_Status register. A DTLB error is indicated |
|
by MCA error code (bits [15:0]) appearing as binary value, 000x 0000 0001 |
|
0100, in the MCi_Status register. |
|
Implication: Due to this erratum, the Overflow bit in the MCi_Status register |
|
may not be an accurate indication of multiple occurrences of DTLB errors. |
|
There is no other impact to normal processor functionality. |
Workaround: None identified.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Table of Changes.
AAJ2. Debug Exception Flags DR6.B0-B3 Flags May be Incorrect for Disabled Breakpoints
Problem: When a debug exception is signaled on a load that crosses cache lines with data forwarded from a store and whose corresponding breakpoint enable flags are disabled (DR7.G0-G3 and DR7.L0-L3), the DR6.B0-B3 flags may be incorrect.
Implication: The debug exception DR6.B0-B3 flags may be incorrect for the load if the corresponding breakpoint enable flag in DR7 is disabled.
Workaround: None identified.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Table of Changes.
AAJ3. MONITOR or CLFLUSH on the Local XAPIC's Address Space Results in Hang
Problem: If the target linear address range for a MONITOR or CLFLUSH is mapped to the local xAPIC's address space, the processor will hang.
Implication: When this erratum occurs, the processor will hang. The local xAPIC's address space must be uncached. The MONITOR instruction only functions correctly if the specified linear address range is of the type writeback. CLFLUSH flushes data from the cache. Intel has not observed this erratum with any commercially available software.
Workaround: Do not execute MONITOR or CLFLUSH instructions on the local xAPIC address space.
Intel® Core™ i7 processor |
|
Specification Update |
19 |

Errata
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Table of Changes.
AAJ4. Corruption of CS Segment Register During RSM While Transitioning From Real Mode to Protected Mode
Problem: During the transition from real mode to protected mode, if an SMI (System Management Interrupt) occurs between the MOV to CR0 that sets PE (Protection Enable, bit 0) and the first FAR JMP, the subsequent RSM (Resume from System Management Mode) may cause the lower two bits of CS segment register to be corrupted.
Implication: The corruption of the bottom two bits of the CS segment register will have no impact unless software explicitly examines the CS segment register between enabling protected mode and the first FAR JMP. Intel® 64 and IA-32 Architectures Software Developer’s Manual Volume 3A: System Programming Guide, Part 1, in the section titled "Switching to Protected Mode" recommends the FAR JMP immediately follows the write to CR0 to enable protected mode. Intel has not observed this erratum with any commercially available software.
Workaround: None identified.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Table of Changes.
AAJ5. The Processor May Report a #TS Instead of a #GP Fault
Problem: A jump to a busy TSS (Task-State Segment) may cause a #TS (invalid TSS exception) instead of a #GP fault (general protection exception).
Implication: Operation systems that access a busy TSS may get invalid TSS fault instead of a #GP fault. Intel has not observed this erratum with any commercially available software.
Workaround: None identified.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Table of Changes.
AAJ6. REP MOVS/STOS Executing with Fast Strings Enabled and Crossing Page Boundaries with Inconsistent Memory Types may use an Incorrect Data Size or Lead to Memory-Ordering Violations
Problem: Under certain conditions as described in the Software Developers Manual section "Out-of-Order Stores For String Operations in Pentium 4, Intel Xeon, and P6 Family Processors" the processor performs REP MOVS or REP STOS as fast strings. Due to this erratum fast string REP MOVS/REP STOS instructions that cross page boundaries from WB/WC memory types to UC/WP/WT memory types, may start using an incorrect data size or may observe memory ordering violations.
Implication: Upon crossing the page boundary the following may occur, dependent on the new page memory type:
Intel® Core™ i7 processor Specification Update

Errata
•UC the data size of each write will now always be 8 bytes, as opposed to the original data size.
•WP the data size of each write will now always be 8 bytes, as opposed to the original data size and there may be a memory ordering violation.
•WT there may be a memory ordering violation.
Workaround: Software should avoid crossing page boundaries from WB or WC memory type to UC, WP or WT memory type within a single REP MOVS or REP STOS instruction that will execute with fast strings enabled.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Table of Changes.
AAJ7. Code Segment Limit/Canonical Faults on RSM May be Serviced before Higher Priority Interrupts/Exceptions and May Push the Wrong Address Onto the Stack
Problem: Normally, when the processor encounters a Segment Limit or Canonical Fault due to code execution, a #GP (General Protection Exception) fault is generated after all higher priority Interrupts and exceptions are serviced. Due to this erratum, if RSM (Resume from System Management Mode) returns to execution flow that results in a Code Segment Limit or Canonical Fault, the #GP fault may be serviced before a higher priority Interrupt or Exception (e.g. NMI (Non-Maskable Interrupt), Debug break(#DB), Machine Check (#MC), etc.). If the RSM attempts to return to a non-canonical address, the address pushed onto the stack for this #GP fault may not match the non-canonical address that caused the fault.
Implication: Operating systems may observe a #GP fault being serviced before higher priority Interrupts and Exceptions. Intel has not observed this erratum on any commercially available software.
Workaround: None identified.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Table of Changes.
AAJ8. Performance Monitor SSE Retired Instructions May Return Incorrect
Values
Problem: Performance Monitoring counter SIMD_INST_RETIRED (Event: C7H) is used to track retired SSE instructions. Due to this erratum, the processor may also count other types of instructions resulting in higher than expected values.
Implication: Performance Monitoring counter SIMD_INST_RETIRED may report count higher than expected.
Workaround: None identified.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Table of Changes.
Intel® Core™ i7 processor |
|
Specification Update |
21 |
 Loading...
Loading...