Honeywell MS9520 User Manual

MetroSelect®
Single-Line Scanner
Configuration Guide

Disclaimer
Honeywell International Inc. (“HII”) reserves the right to make changes in specifications and other information contained in this document without prior notice, and the reader should in all cases consult HII to determine whether any such changes have been made. The information in this publication does not represent a commitment on the part of HII.
HII shall not be liable for technical or editorial errors or omissions contained herein: nor for incidental or consequential damages resulting from the furnishing, performance, or use of this manual.
This document contains propriety information that is protected by copyright. All rights reserved. No part of this document may be photocopied, reproduced, or translated into another language without the prior written consent of HII.
© 2000 – 2011 Honeywell International Inc. All rights reserved.
Web Address: www.honeywellaidc.com
Trademarks
Omniplanar, MetroSet2, Metrologic, MetroSelect, RangeGate, CodeGate, CodeSelect, Voyager, VoyagerCG, VoyagerBT and Focus are trademarks or registered trademarks of Metrologic Instruments, Inc. or Honeywell International Inc.
Microsoft and Windows are trademarks or registered trademarks of Microsoft Corporation.
IBM is a trademark of International Business Machines Corporation.
The Bluetooth word mark is owned by the Bluetooth SIG, Inc. and any use of such marks by Honeywell International Inc. is under license.
Other product names mentioned in this manual may be trademarks or registered trademarks of their respective companies and are the property of their respective owners.

 Table of Contents
Table of Contents
Introduction
Bar Code Configuration Methods.............................................................. |
1–1 |
Single-Code Method.............................................................................. |
1–1 |
Multi-Code Method ................................................................................ |
1–1 |
Need to Start Over?.................................................................................. |
1–2 |
Code Types and Decode Rules
UPC/EAN.................................................................................................. |
2–1 |
Code 128 .................................................................................................. |
2–2 |
Code 39 .................................................................................................... |
2–2 |
2 of 5 Codes ............................................................................................. |
2–4 |
Codabar.................................................................................................... |
2–6 |
Code 93 .................................................................................................... |
2–6 |
Code 11 .................................................................................................... |
2–6 |
Telepen..................................................................................................... |
2–7 |
Plessey Codes.......................................................................................... |
2–7 |
Additional Decode Features...................................................................... |
2–8 |
Configurable Code Lengths ...................................................................... |
2–9 |
Supplements .................................................................................... |
3–1 |
GS1 Databar ..................................................................................... |
4–1 |
GS1 Databar Limited ................................................................................ |
4–2 |
GS1 Databar Expanded............................................................................ |
4–2 |
ISBT Code 128 Implementation |
|
Configuration Mode .................................................................................. |
5–1 |
Concatenation Configuration Mode .......................................................... |
5–2 |
Pre-Defined Concatenation Configuration Mode ...................................... |
5–2 |
User-Defined Concatenation Configuration Mode .................................... |
5–3 |
Communications.............................................................................. |
6–1 |
iii

Scanner Operation
Configuration Mode Options...................................................................... |
7–1 |
Scan Buffers.............................................................................................. |
7–1 |
Redundant Scans...................................................................................... |
7–2 |
Miscellaneous Decode Features ............................................................... |
7–2 |
Same Symbol Timeouts ............................................................................ |
7–3 |
LED Options .............................................................................................. |
7–3 |
Beeper Options ......................................................................................... |
7–4 |
Data Transmission Delays......................................................................... |
7–6 |
Communication Timeout Options .............................................................. |
7–7 |
Host Scanner Commands ......................................................................... |
7–8 |
Test Modes.............................................................................................. |
7–10 |
Prefixes/Suffixes
User Configurable Prefixes, All Data ......................................................... |
8–1 |
User Configurable ID Characters, Code Specific ...................................... |
8–2 |
Standard Prefix Characters ....................................................................... |
8–4 |
Standard Suffix Characters ....................................................................... |
8–6 |
Longitudinal Redundancy Check............................................................... |
8–7 |
Block Check Character.............................................................................. |
8–7 |
Character Replacements........................................................................... |
8–8 |
User Configurable Suffixes, All Data ......................................................... |
8–9 |
Special Formats ...................................................................................... |
8–10 |
Code Formatting
UPC/EAN Formatting ................................................................................ |
9–1 |
Codabar Formatting .................................................................................. |
9–3 |
Code 39 Formatting................................................................................... |
9–4 |
Code 11 Formatting................................................................................... |
9–4 |
Telepen ..................................................................................................... |
9–4 |
Plessey...................................................................................................... |
9–5 |
2 of 5 Code Formatting.............................................................................. |
9–5 |
iv

RS232
Parity Features ....................................................................................... |
10–1 |
Baud Rate............................................................................................... |
10–1 |
Data/Stop Bits......................................................................................... |
10–2 |
Hardware Handshaking .......................................................................... |
10–2 |
Software Handshaking............................................................................ |
10–4 |
Miscellaneous ......................................................................................... |
10–5 |
Keyboard
Enable Keyboard Emulation ................................................................... |
11–1 |
Country/Scan Code Table Selects.......................................................... |
11–1 |
Keyboard/System Type........................................................................... |
11–2 |
’Dumb’ Terminal Selections .................................................................... |
11–3 |
Special Keyboard Features..................................................................... |
11–4 |
InterScan Code Delays........................................................................... |
11–6 |
Control Sets ............................................................................................ |
11–7 |
OCIA ................................................................................................ |
12–1 |
Light Pen Parameters .................................................................... |
13–1 |
Set Narrow Element Width...................................................................... |
13–2 |
RS485 Configuration |
|
IBM Port.................................................................................................. |
14–1 |
IBM Reserve Codes................................................................................ |
14–1 |
USB.................................................................................................. |
15–1 |
Code Bytes Usage |
|
Code Bytes 0-9 ....................................................................................... |
16–1 |
Reserved Codes ..................................................................................... |
16–2 |
Code Type Table .................................................................................... |
16–2 |
ASCII Reference Table........................................................................... |
16–3 |
Extended Key Code Reference Table..................................................... |
16–7 |
v

MS9520 Voyager® and MS9540 VoyagerCG® Series
Activation Range ..................................................................................... |
17–1 |
Stand Scan Modes .................................................................................. |
17–1 |
CodeGate® Status .................................................................................. |
17–1 |
Laser/Scan Modes .................................................................................. |
17–2 |
Same Symbol Time Outs......................................................................... |
17–3 |
MS9520/9540-00 Laser Emulation Mode ................................................ |
17–4 |
MS9524 and MS9544 VoyagerPDF® Series
PDF CodeGate Status............................................................................. |
18–1 |
MicroPDF and Composite Code Handling............................................... |
18–1 |
MS9535 VoyagerBT ....................................................................... |
19–1 |
MS9535-5M VoyagerBT.................................................................. |
20–1 |
Inventory Quantity Bar Codes ................................................................. |
20–3 |
IS4125 and IS4225 Scan Engines ................................................. |
21–1 |
IS4823 and IS4825 Scan Engines ................................................. |
22–1 |
Operating Modes..................................................................................... |
22–1 |
Miscellaneous Features |
|
Custom Defaults...................................................................................... |
23–1 |
Serial Program Mode .............................................................................. |
23–2 |
Customer Support.......................................................................... |
24–1 |
Technical Assistance............................................................................... |
24–1 |
Product Service and Repair..................................................................... |
24–2 |
vi

1
Introduction
Your new scanner has been factory configured with a set of default parameters. Since many host systems have unique formats and protocol requirements, Honeywell provides a wide range of configurable features that may be selected using this bar code based configuration tool. Once the configuration is completed, the scanner stores the settings in nonvolatile memory (NOVRAM). NOVRAM saves the settings when the power is off.
Note: Bar code descriptions marked with an asterisk ( * ) define a feature that is a factory default. Bar codes marked with a tilde ( ~ ) require the Multi-Code configuration method.
Bar Code Configuration Methods
The MetroSelect class of scanners can be bar code configured in two ways: the Single-Code Method and the Multi-Code Method.
Note: To properly configure an MS9540 scanner, all configuration codes must be scanned using the CodeGate® option.
Single-Code Method
Most features can be enabled or disabled using the Single-Code Method.
1.Power-up the scanner.
2.Scan the bar code for the desired feature.
3.The scanner will emit a multi-toned beep to indicate the configuration has been saved to NOVRAM.
Multi-Code Method
All features can be enabled or disabled using the Multi-Code Method. A feature marked with a tilde ( ~ ) requires the Multi-Code Method.
1.Power-up the scanner.
2.Scan the enter/exit configuration mode bar code (3 beeps).
3.Scan the bar code for the desired feature (1 beep). Multiple features can be enabled/disabled before scanning the enter/exit configuration mode bar code.
4.Scan the enter/exit configuration mode bar code (3 beeps) and save the new configuration. To abort a configuration change, power off the scanner before scanning the enter/exit code.
Enter/Exit Configuration Mode
³ |
9 |
9 |
9 |
9 |
9 |
9 |
1–1

Need To Start Over?
Scan the Recall Defaults bar code to erase all previous settings and return the scanner to its factory default communication protocol. Keyboard Wedge interface scanners will load keyboard wedge defaults. All other scanners load RS232 defaults.
Note: Honeywell manufactures several products for OEM applications. These OEM products are configured with custom OEM defaults, which may use a different set of defaults than the standard set of factory defaults. See page 23–1 for additional information on custom defaults and how they affect factory defaults.
Recall Defaults
³ |
9 |
9 |
9 |
9 |
9 |
8 |
1–2

2
Code Types and Decode Rules
Bar code descriptions marked with an asterisk ( * ) define a feature that is a factory default. Bar codes marked with a tilde ( ~ ) require the Multi-Code configuration method.
UPC/EAN
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Enable UPC/EAN |
³ |
1 |
0 |
0 |
1 |
1 |
6 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Disable UPC/EAN |
³ |
1 |
0 |
0 |
1 |
0 |
6 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Enable UPC-A |
³ |
1 |
0 |
0 |
2 |
1 |
6 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Disable UPC-A |
³ |
1 |
0 |
0 |
2 |
0 |
6 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Enable UPC-E |
³ |
1 |
0 |
0 |
2 |
1 |
0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Disable UPC-E |
³ |
1 |
0 |
0 |
2 |
0 |
0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Enable EAN-13 |
³ |
1 |
0 |
0 |
2 |
1 |
1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Disable EAN-13 |
³ |
1 |
0 |
0 |
2 |
0 |
1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Enable EAN-8 |
³ |
1 |
0 |
0 |
2 |
1 |
4 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Disable EAN-8 |
³ |
1 |
0 |
0 |
2 |
0 |
4 |
2–1

Code 128
³ |
1 |
0 |
0 |
1 |
1 |
3 |
³ |
1 |
0 |
0 |
1 |
0 |
3 |
³ |
1 |
0 |
0 |
3 |
1 |
4 |
³ |
1 |
0 |
0 |
3 |
0 |
4 |
³ |
1 |
0 |
0 |
7 |
1 |
1 |
³ |
1 |
0 |
0 |
7 |
0 |
1 |
*Enable Code 128
Disable Code 128
Enable UCC/EAN-128 ‘]C1’ Code Formatting –
For Coupon Code 128, see page 3–3.
*Disable UCC/EAN-128 ‘]C1’ Code Formatting
Ignore <FNC4> Code 128 Characters
*Use <FNC4> to Determine Extended ASCII
Characters
Code 39
³ |
1 |
0 |
0 |
1 |
1 |
1 |
³ |
1 |
0 |
0 |
1 |
0 |
1 |
³ |
1 |
0 |
0 |
2 |
1 |
3 |
³ |
1 |
0 |
0 |
2 |
0 |
3 |
³ |
1 |
0 |
0 |
2 |
1 |
7 |
³ |
1 |
0 |
0 |
2 |
0 |
7 |
*Enable Code 39
Disable Code 39
Enable MOD 43 Check Digit on Code 39 – The scanner only scans Code 39 bar codes that have a valid Modulo 43 check digit.
*Disable MOD 43 Check Digit on Code 39
Enable Full ASCII Code 39
*Disable Full ASCII Code 39
2–2

³ |
1 |
0 |
0 |
2 |
1 |
5 |
³ |
1 |
0 |
0 |
2 |
0 |
5 |
³ |
1 |
0 |
0 |
3 |
0 |
7 |
³ |
1 |
0 |
0 |
3 |
1 |
7 |
³ |
1 |
0 |
0 |
3 |
1 |
2 |
³ |
1 |
0 |
0 |
3 |
0 |
2 |
³ |
1 |
0 |
0 |
7 |
0 |
2 |
³ |
1 |
0 |
0 |
7 |
1 |
2 |
³ |
1 |
0 |
0 |
4 |
1 |
6 |
³ |
1 |
0 |
0 |
4 |
0 |
6 |
³ |
1 |
0 |
0 |
9 |
1 |
4 |
³ |
1 |
0 |
0 |
9 |
0 |
4 |
³ |
1 |
0 |
7 |
7 |
1 |
5 |
³ |
1 |
0 |
7 |
7 |
0 |
5 |
Enable PARAF (Italian Pharmaceutical Codes)
Support – Code 39 bar codes are converted to PARAF format.
*Disable PARAF Support
*Allow PARAF Codes Only
Allow Non-PARAF Codes
Enable TRI-OPTIC Code
*Disable TRI-OPTIC Code
*Use Standard Code 39 Framing
Try Code 39 Codes Without 5 Bar Multiples Enable ITF/Code 39 Filters
*Disable ITF/Code 39 Filters
Enable Self-Service Library Code 39
*Disable Self-Service Library Code 39
Transmit MOD 43 Check Digit – with Self
Service Library Code 39
*Do Not Transmit MOD 43 Check Digit – with
Self Service Library Code 39
2–3

³ |
1 |
1 |
5 |
4 |
1 |
3 |
³ |
1 |
1 |
5 |
4 |
0 |
3 |
Enable Alternate Code 39 Reference
Comparison Check – assists with elements that are below the 2 to 1 (wide to narrow) element width requirement.
*Normal Code 39 Reference Comparison
Check
2 OF 5 CODES
³ |
1 |
0 |
0 |
1 |
1 |
5 |
³ |
1 |
0 |
0 |
1 |
0 |
5 |
³ |
1 |
0 |
0 |
3 |
1 |
0 |
³ |
1 |
0 |
0 |
3 |
0 |
0 |
³ |
1 |
0 |
7 |
8 |
1 |
7 |
³ |
1 |
0 |
7 |
8 |
0 |
7 |
³ |
9 |
0 |
1 |
6 |
0 |
0 |
³ |
9 |
0 |
1 |
7 |
0 |
0 |
³ |
9 |
0 |
3 |
4 |
0 |
0 |
*Enable Interleaved 2 of 5 (ITF)
Disable Interleaved 2 of 5 (ITF)
Enable MOD 10 Check on ITF – The scanner will only scan Interleaved 2 of 5 (ITF) bar codes that have a Modulo 10 check digit.
*Disable MOD 10 Check on ITF
Allow ITF Null Characters
*Do Not Allow ITF Null Characters
~ITF Symbol Length Lock 1 – To specify a first
ITF symbol length lock, scan this bar code and the appropriate code byte sequence located on page 16–1.
~ITF Symbol Length Lock 2 – To specify a second
ITF symbol length lock, scan this bar code and the appropriate code byte sequence located
on page 16–1.
~ITF Minimum Symbol Length – To specify a minimum number of ITF characters to be decoded, scan the appropriate code byte sequence located on page 16–1.
2–4

³ |
1 |
0 |
0 |
9 |
1 |
3 |
³ |
1 |
0 |
0 |
9 |
0 |
3 |
³ |
1 |
0 |
0 |
1 |
1 |
0 |
³ |
1 |
0 |
0 |
1 |
0 |
0 |
³ |
9 |
0 |
1 |
5 |
0 |
0 |
³ |
1 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
1 |
5 |
³ |
1 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
5 |
³ |
1 |
0 |
0 |
5 |
0 |
7 |
³ |
1 |
0 |
0 |
5 |
1 |
7 |
³ |
1 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
1 |
4 |
³ |
1 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
4 |
³ |
1 |
0 |
0 |
3 |
1 |
3 |
³ |
1 |
0 |
0 |
3 |
0 |
3 |
Alternative ITF first Bar Reference
*Normal ITF first Bar Reference
Enable Standard 2 of 5
*Disable Standard 2 of 5
~Standard 2 of 5 Symbol Length – To specify the number of characters to be decoded, scan this bar code and the appropriate code byte sequence located on page 16–1.
Enable Matrix 2 of 5
*Disable Matrix 2 of 5
*Enable Matrix 2 of 5 Check Digit Requirement
Disable Matrix 2 of 5 Check Digit Requirement
Enable 15 Digit Airline 2 of 5
*Disable 15 Digit Airline 2 of 5
Enable 13 Digit Airline 2 of 5
*Disable 13 Digit Airline 2 of 5
2–5

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Enable Hong Kong 2 of 5 |
³ |
1 |
0 |
0 |
3 |
1 |
6 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* |
Disable Hong Kong 2 of 5 |
³ |
1 |
0 |
0 |
3 |
0 |
6 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Enable Follett ITF |
³ |
1 |
1 |
5 |
4 |
1 |
1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* |
Disable Follett ITF |
³1 1 5 4 0 1
Codabar
|
|
|
|
|
|
* |
Enable Codabar |
³ |
1 |
0 |
0 |
1 |
1 |
4 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Disable Codabar |
³ |
1 |
0 |
0 |
1 |
0 |
4 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Enable Dual Field Codabar |
³ |
1 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
1 |
2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* |
Disable Dual Field Codabar |
³1 0 0 0 0 2
Code 93
* Enable Code 93
³ |
1 |
0 |
0 |
1 |
1 |
2 |
Disable Code 93
³1 0 0 1 0 2
Code 11
Enable Code 11
³ |
1 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
1 |
3 |
2–6

|
|
|
|
|
|
* |
Disable Code 11 |
|
³ |
1 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
3 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* |
Check for 1 Code 11 |
Check Digit |
³ |
1 |
0 |
8 |
0 |
0 |
5 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Check for 2 Code 11 |
Check Digits |
³ |
1 |
0 |
8 |
0 |
1 |
5 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* |
Do Not Check for 2 Code 11 Check Digits |
|
³ |
1 |
0 |
8 |
0 |
0 |
4 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Check for 2 Code 11 |
Check Digits if Code |
³1 0 8 0 1 4 Length is Greater Than 10 Characters
Telepen
|
|
|
|
|
|
Enable Telepen |
³ |
1 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
1 |
7 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Disable Telepen |
³ |
1 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
7 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Enable ALPHA Telepen |
³ |
1 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
1 |
6 |
* Disable ALPHA Telepen
³1 0 0 0 0 6
Plessey Codes
³ |
1 |
0 |
0 |
2 |
1 |
2 |
³ |
1 |
0 |
0 |
2 |
0 |
2 |
³ |
2 |
0 |
0 |
7 |
0 |
4 |
Enable MSI Plessey
*Disable MSI Plessey
*No MSI Plessey Check Digit – Plessey bar codes will not be tested for a check digit.
2–7

³ |
2 |
0 |
0 |
7 |
3 |
4 |
³ |
2 |
0 |
0 |
7 |
2 |
4 |
³ |
1 |
0 |
0 |
1 |
1 |
7 |
³ |
1 |
0 |
0 |
1 |
0 |
7 |
³ |
1 |
0 |
0 |
7 |
1 |
6 |
³ |
1 |
0 |
0 |
7 |
0 |
6 |
³ |
1 |
0 |
8 |
0 |
0 |
3 |
³ |
1 |
0 |
8 |
0 |
1 |
3 |
Enable MSI Plessey MOD 10/10 Check Digit –
Test MSI Plessey bar codes for a 2 digit Modulo 10 check digit.
*Enable MSI Plessey MOD 10 Check Digit –
Test MSI Plessey bar codes for a 1 digit Modulo 10 check digit.
Enable UK Plessey
*Disable UK Plessey
Enabled UK Plessey A to X Conversion
*Disabled UK Plessey A to X Conversion
*Standard Plessey Stop Characters
Accept Bad Plessey Stop Characters
Additional Decode Features
³ |
1 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
1 |
1 |
³ |
1 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
1 |
³ |
1 |
0 |
1 |
1 |
1 |
5 |
³ |
1 |
0 |
1 |
1 |
0 |
5 |
Enable Double Border Required / Large
Intercharacter Space
*Disable Double Border Required / Large
Intercharacter Space
Enable Small Border Required
*Disable Small Border
2–8

³ |
9 |
0 |
1 |
8 |
0 |
0 |
³ |
9 |
0 |
1 |
9 |
0 |
0 |
³ |
1 |
1 |
9 |
4 |
1 |
7 |
³ |
1 |
1 |
9 |
4 |
0 |
7 |
³ |
1 |
0 |
0 |
7 |
1 |
2 |
³ |
1 |
0 |
0 |
7 |
0 |
2 |
~Minimum Symbol Length – Single-line default
is 3. Combine this code with the proper code bytes (on page 16–1), to specify the minimum number of characters in all non-UPC/EAN bar codes.
~Symbol Length Lock – Combine this code with the proper code bytes, to lock the bar code’s length into place.
Enable Modulus 8 Filter on Bar & Space
Counts
*Disable Modulus 8 Filter on Bar & Space
Counts
Handle Code 39 Bad Border
*Disable Code 39 Bad Border
Configurable Code Lengths
There are seven bar code lock lengths available. Specific code types can be assigned to a lock length.
While in configuration mode:
1.Scan the code length lock #1 bar code (below).
2.Scan the three code bytes that represent the code length (on page 16–1).
3.Scan the matching code type lock #1 bar code (below).
4.Scan the three code bytes that represent the code type (on page 16–1).
This process can be repeated for lock lengths 2 through 7.
³ |
9 |
0 |
2 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
³ |
9 |
0 |
2 |
1 |
0 |
0 |
~Code Length Lock #1
~Code Type Lock #1
2–9

|
|
|
|
|
|
~ Code Length Lock #2 |
³ |
9 |
0 |
2 |
2 |
0 |
0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
~ Code Type Lock #2 |
³ |
9 |
0 |
2 |
3 |
0 |
0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
~ Code Length Lock #3 |
³ |
9 |
0 |
2 |
4 |
0 |
0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
~ Code Type Lock #3 |
³ |
9 |
0 |
2 |
5 |
0 |
0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
~ Code Length Lock #4 |
³ |
9 |
0 |
2 |
6 |
0 |
0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
~ Code Type Lock #4 |
³ |
9 |
0 |
2 |
7 |
0 |
0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
~ Code Length Lock #5 |
³ |
9 |
0 |
2 |
8 |
0 |
0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
~ Code Type Lock #5 |
³ |
9 |
0 |
2 |
9 |
0 |
0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
~ Code Length Lock #6 |
³ |
9 |
0 |
3 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
~ Code Type Lock #6 |
³ |
9 |
0 |
3 |
1 |
0 |
0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
~ Code Length Lock #7. |
³ |
9 |
0 |
3 |
2 |
0 |
0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
~ Code Type Lock #7. |
³ |
9 |
0 |
3 |
3 |
0 |
0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Enable Japanese Multi-Field |
³ |
1 |
2 |
4 |
7 |
1 |
3 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Disable Japanese Multi-Field |
³ |
1 |
2 |
4 |
7 |
0 |
3 |
2–10

3
Supplements
³ |
1 |
0 |
1 |
2 |
1 |
7 |
³ |
1 |
0 |
1 |
2 |
0 |
7 |
³ |
1 |
0 |
1 |
2 |
1 |
2 |
³ |
1 |
0 |
1 |
2 |
0 |
2 |
³ |
1 |
0 |
1 |
2 |
1 |
6 |
³ |
1 |
0 |
1 |
2 |
0 |
6 |
³ |
1 |
0 |
1 |
2 |
1 |
1 |
³ |
1 |
0 |
1 |
2 |
0 |
1 |
³ |
1 |
0 |
1 |
2 |
1 |
3 |
³ |
1 |
0 |
1 |
2 |
0 |
3 |
³ |
1 |
0 |
1 |
4 |
1 |
6 |
³ |
1 |
0 |
1 |
4 |
0 |
6 |
³ |
1 |
2 |
5 |
1 |
1 |
4 |
³ |
1 |
2 |
5 |
1 |
0 |
4 |
Enable Two Digit Supplements
*Disable Two Digit Supplements
*Enable Two Digit Redundancies – The scanner will scan the bar code plus the 2 digit add on twice before accepting data.
Disable Two Digit Redundancies
Enable Five Digit Supplements
*Disable Five Digit Supplements
Enable Five Digit Redundancies – The scanner will scan the bar code plus the 5 digit add on twice before accepting data.
*Disable Five Digit Redundancies
Supplements are Required – All UPC/EAN labels that are scanned must have a supplement.
*Supplements are Not Required
Enable Remote Supplement Required –
MS9500 & MS6200 not supported.
*Disable Remote Supplement Required –
MS9500 & MS6200 not supported.
Enable Bookland (979) Supplement Required
*Disable Bookland (979) Supplement Required
3–1

³ |
1 |
0 |
1 |
4 |
1 |
7 |
³ |
1 |
0 |
1 |
4 |
0 |
7 |
³ |
1 |
0 |
1 |
3 |
1 |
4 |
³ |
1 |
0 |
1 |
3 |
0 |
4 |
³ |
1 |
0 |
1 |
3 |
1 |
3 |
³ |
1 |
0 |
1 |
3 |
0 |
3 |
³ |
1 |
0 |
1 |
4 |
1 |
3 |
³ |
1 |
0 |
1 |
4 |
0 |
3 |
³ |
1 |
0 |
1 |
4 |
1 |
5 |
³ |
1 |
0 |
1 |
4 |
0 |
5 |
³ |
1 |
0 |
1 |
4 |
1 |
2 |
³ |
1 |
0 |
1 |
4 |
0 |
2 |
³ |
1 |
0 |
1 |
2 |
1 |
5 |
³ |
1 |
0 |
1 |
2 |
0 |
5 |
Enable Bookland (978) Supplement Required
*Disable Bookland (978) Supplement Required
Enable 977 (2 Digit) Supplement Required –
The scanner will require a 2 digit supplement to be scanned when an EAN-13 code begins with 977.
*Disable 977 (2 Digit) Supplement Required
Enable 378/379 French Supplement Required
*Disable 378/379 French Supplement Required
Enable 414/419 German Bookland
Supplement Required
*Disable 414/419 German Bookland
Supplement Required
Enable 434/439 German Supplement Required
*Disable 434/439 German Supplement
Required
Enable # System 2 Requires Supplements
*Disable # System 2 Requires Supplements
Enable UPC # System 5 Requires
Supplements
*Disable UPC # System 5 Requires
Supplements
3–2

³ |
1 |
0 |
1 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
³ |
1 |
0 |
1 |
0 |
1 |
0 |
³ |
1 |
0 |
1 |
0 |
0 |
1 |
³ |
1 |
0 |
1 |
0 |
1 |
1 |
³ |
1 |
0 |
0 |
3 |
1 |
5 |
³ |
1 |
0 |
0 |
3 |
0 |
5 |
³ |
1 |
0 |
1 |
4 |
1 |
1 |
³ |
1 |
0 |
1 |
4 |
0 |
1 |
³ |
1 |
0 |
1 |
4 |
1 |
4 |
³ |
1 |
0 |
1 |
4 |
0 |
4 |
³ |
3 |
0 |
1 |
3 |
4 |
0 |
³ |
3 |
0 |
1 |
3 |
2 |
0 |
³ |
3 |
0 |
1 |
3 |
1 |
0 |
*Enable 2 Digit Supplements with 37x, 43x, or
UPC # System 5
Disable 2 Digit Supplements with 37x, 43x, or
UPC # System 5
*Enable 5 Digit Supplements with 37x, 43x, or
UPC # System 5
Disable 5 Digit Supplements with 37x, 43x, or
UPC # System 5
Enable Coupon Code 128
*Disable Coupon Code 128
Enable Code 128 ‘]C1’ Extended Code Format
–The scanner transmits a ‘]C1’ at the beginning of the Code 128 portion of the coupon code.
*Disable Code 128 ‘]C1’ Extended Code
Format.
*Enable Code 128 Group Separators – A “GS” (1DH) character will be transmitted with coupon Code 128 codes.
Disable Code 128 Group Separators
400 msec to Find Supplemental – The scanner will allot 400 milliseconds to find an add on after a main UPC/EAN bar code has been scanned.
200 msec to Find Supplemental – The scanner will allot 200 milliseconds to find an add on after a main UPC/EAN bar code has been scanned.
*100 msec to Find Supplemental – The scanner will allot 100 milliseconds to find an add on after a main UPC/EAN bar code has been scanned.
3–3

³ |
1 |
0 |
1 |
2 |
1 |
4 |
³ |
1 |
0 |
1 |
2 |
0 |
4 |
³ |
1 |
1 |
8 |
4 |
0 |
6 |
³ |
1 |
1 |
8 |
4 |
1 |
6 |
³ |
1 |
0 |
1 |
3 |
1 |
5 |
³ |
1 |
0 |
1 |
3 |
0 |
5 |
³ |
1 |
0 |
1 |
3 |
1 |
7 |
³ |
1 |
0 |
1 |
3 |
0 |
7 |
³ |
1 |
0 |
1 |
3 |
1 |
6 |
³ |
1 |
0 |
1 |
3 |
0 |
6 |
³ |
1 |
2 |
5 |
1 |
1 |
5 |
³ |
1 |
2 |
5 |
1 |
0 |
5 |
³ |
1 |
2 |
5 |
1 |
0 |
6 |
³ |
1 |
2 |
5 |
1 |
1 |
6 |
Enable Code ID’s with Supplements
*Disable Code ID’s with Supplements
*Beep Once on Supplements
Beep Twice on Supplements
Enable ISBN Check Digit Transmission – Not available with all models.
Disable ISBN Check Digit Transmission
Enable Bookland to ISBN Conversion – Not available with all models.
*Disable Bookland to ISBN Conversion
Enable ISBN Re-Formatting
*Disable ISBN Re-Formatting
Enable Bookland to ISBN 979 Conversion
*Disable Bookland to ISBN 979 Conversion
*Normal ISBN Re-Formatting
13 Digit ISBN Re-Formatting
3–4

³ |
1 |
0 |
1 |
2 |
1 |
0 |
³ |
1 |
0 |
1 |
2 |
0 |
0 |
³ |
1 |
2 |
5 |
0 |
1 |
7 |
³ |
1 |
2 |
5 |
0 |
0 |
7 |
Disable Supplemental when CodeGate Button is Pressed – Available for MS9540 scanners only. Requires standard Code Gate be inactive in and out of stand.
*CodeGate Does Not Affect Supplemental
Scanning – Available for MS9540 scanners only.
No Supplement Checking if EAN-13 Code is just scanned
*Normal Supplement Checking
3–5

3–6

4
GS1 DataBar
Honeywell’s MS9520 Voyager® and MS9540 VoyagerCG® scanners with software #14810 and higher can be configured to scan GS1 DataBar type bar codes.
Double Border Required – Due to the large
³1 0 0 0 1 1 spaces commonly found in GS1 DataBar
³ |
1 |
0 |
0 |
4 |
1 |
3 |
³ |
1 |
0 |
0 |
4 |
0 |
3 |
³ |
1 |
1 |
4 |
9 |
0 |
0 |
³ |
1 |
1 |
4 |
9 |
1 |
0 |
³ |
1 |
1 |
4 |
9 |
0 |
1 |
³ |
1 |
1 |
4 |
9 |
1 |
1 |
³ |
1 |
1 |
4 |
9 |
0 |
2 |
³ |
1 |
1 |
4 |
9 |
1 |
2 |
symbologies, Honeywell recommends double border requirements be enabled when scanning GS1 DataBar code type symbologies.
Enable GS1 DataBar 14
*Disable GS1 DataBar 14
*Transmit GS1 DataBar 14 Check Digit
Do Not Transmit GS1 DataBar 14 Check Digit
*Transmit GS1 DataBar 14 Application ID –
Application Identifier “01” is transmitted by default.
Do Not Transmit GS1 DataBar 14
Application ID
*Transmit GS1 DataBar 14 Symbology ID –
Symbology Identifier “]e0” is transmitted by default.
Do Not Transmit GS1 DataBar 14 Symbology
4–1

GS1 DataBar Limited
³ |
1 |
0 |
0 |
4 |
1 |
4 |
³ |
1 |
0 |
0 |
4 |
0 |
4 |
³ |
1 |
1 |
4 |
9 |
0 |
3 |
³ |
1 |
1 |
4 |
9 |
1 |
3 |
³ |
1 |
1 |
4 |
9 |
0 |
4 |
³ |
1 |
1 |
4 |
9 |
1 |
4 |
³ |
1 |
1 |
4 |
9 |
0 |
5 |
³ |
1 |
1 |
4 |
9 |
1 |
5 |
Enable GS1 DataBar Limited
*Disable GS1 DataBar Limited
*Transmit GS1 DataBar Limited CD
Do Not Transmit GS1 DataBar Limited CD
*Transmit GS1 DataBar Limited Application ID –
Application identifier “01” is transmitted by default.
Do Not Transmit GS1 DataBar Limited
Application ID
*Transmit GS1 DataBar Limited Symbology ID –
Symbology identifier “]e0” is transmitted by default.
Do Not Transmit GS1 DataBar Limited
Symbology ID
GS1 DataBar Expanded
³ |
1 |
0 |
0 |
4 |
1 |
5 |
³ |
1 |
0 |
0 |
4 |
0 |
5 |
³ |
1 |
1 |
4 |
9 |
0 |
6 |
³ |
1 |
1 |
4 |
9 |
1 |
6 |
Enable GS1 DataBar Expanded
*Disable GS1 DataBar Expanded
*Transmit GS1 DataBar Expanded Symbol ID –
Symbology identifier “]e0” is transmitted by default.
Do Not Transmit GS1 DataBar Expanded
Symbol ID
4–2

5
ISBT Code 128 Implementation
Configuration Mode
Enable ISBT Code 128
³ |
1 |
3 |
8 |
4 |
1 |
7 |
³ |
1 |
3 |
8 |
4 |
0 |
7 |
Disable ISBT Code 128
The bar codes below enable or disable a special transmit mode as outlined in section 3.5.2 of the ISBT-128 Specification. This output method allows the user to confirm independently the accuracy of the Code-128 check digit.
Enable ISBT Special Transmit
³ |
1 |
3 |
8 |
4 |
1 |
6 |
³ |
1 |
3 |
8 |
4 |
0 |
6 |
Disable ISBT Special Transmit
The bar codes below enable or disable the transmission of the ISBT Code 128 data identifiers. When this option is enabled, the first two data characters
are removed from the data stream (ID characters) unless the ISBT bar code scanned contains Donation Identification Number identifiers. If Donation Identification Number identifiers are present, only the first ID character is removed from the Donation ID Number. The second is regarded as
normal data.
Don’t Transmit ISBT ID’s
³ |
1 |
3 |
8 |
4 |
1 |
5 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
* |
Transmit ISBT Identifiers |
³ |
1 |
3 |
8 |
4 |
0 |
5 |
|
The bar codes below convert and transmit the Mode 37, 2 check digit from the flag digits of the Donation Identification Number provided the check digit is contained in the flag digits. Transmission of the Donation Identification number will be the same except for the last two digits, which are converted into a single check sum character.
|
|
|
|
|
|
Convert Flag Digits to Mod 37, 2 CD |
³ |
1 |
3 |
8 |
5 |
1 |
0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Normal Flag Digit Transmission |
³ |
1 |
3 |
8 |
5 |
0 |
0 |
5–1

Concatenation Configuration Mode†
The following bar codes are used to configure variable time requirements used to find the second bar code of the ISBT concatenation sequence.
|
|
|
|
|
|
100 msec to Find Concatenation Sequence |
³ |
3 |
0 |
1 |
3 |
1 |
0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
200 msec to Find Concatenation Sequence |
³ |
3 |
0 |
1 |
3 |
2 |
0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
300 msec to Find Concatenation Sequence |
³ |
3 |
0 |
1 |
3 |
3 |
0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
400 msec to Find Concatenation Sequence |
³ |
3 |
0 |
1 |
3 |
4 |
0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
500 msec to Find Concatenation Sequence |
³ |
3 |
0 |
1 |
3 |
5 |
0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
600 msec to Find Concatenation, Sequence |
³ |
3 |
0 |
1 |
3 |
6 |
0 |
700 msec to Find Concatenation Sequence
³3 0 1 3 7 0
Pre-Defined Concatenation Configuration Mode†
The first two bar codes below enable or disable pre-defined concatenation sequences. The remaining bar codes enable the specific pre-defined concatenation sequence shown, but are not needed to enable concatenation. They can be used to disable or re-enable any selected pre-defined concatenation sequence.
|
|
|
|
|
|
Enable Pre-Defined Concatenation Sequence |
³ |
1 |
3 |
8 |
4 |
1 |
3 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Disable Pre-Defined Concatenation Sequence |
³ |
1 |
3 |
8 |
4 |
0 |
3 |
³ |
4 |
3 |
8 |
4 |
8 |
0 |
Donation Identification Number + AB0/Rh (D) Blood Groups =á + =% Concatenation
† This feature is only supported in the MS9500 Voyager product series.
5–2

Donation Identification Number + Donor
³4 3 8 4 9 0 Identification Number =á + &; Concatenation
³ |
4 |
3 |
8 |
4 |
1 |
0 |
0 |
³ |
4 |
3 |
8 |
4 |
1 |
1 |
0 |
³ |
4 |
3 |
8 |
4 |
1 |
2 |
0 |
³ |
4 |
3 |
8 |
4 |
1 |
3 |
0 |
³ |
4 |
3 |
8 |
4 |
1 |
4 |
0 |
Donation Identification Number + Confidential Unit Exclusion Status =á + &! Concatenation
Product Code + Expiration Date (Form 1) =< + =>Concatenation
Product Code + Expiration Date (Form 2) =< + &> Concatenation
Product Code + Expiration Date (Form 3) &< + => Concatenation
Product Code + Expiration Date (Form 4) &< + &> Concatenation
User-Defined Concatenation Configuration Mode
The first two bar codes shown below can be used to enable or disable userdefined concatenation sequences. The remaining bar codes are used to enter the user-defined identifiers used in the concatenation sequence. First enter configuration mode then scan the one of the identifier codes, followed by the code byte sequence or the desired identifiers.
|
|
|
|
|
|
Enable User-Defined Sequences |
³ |
1 |
3 |
8 |
4 |
1 |
4 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Disable User-Defined Sequences |
³ |
1 |
3 |
8 |
4 |
0 |
4 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
1st Left Identifier |
³ |
9 |
3 |
8 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
2nd Left Identifier
³ |
9 |
3 |
8 |
1 |
0 |
0 |
³ |
9 |
3 |
8 |
2 |
0 |
0 |
³ |
9 |
3 |
8 |
3 |
0 |
0 |
1st Right Identifier
2nd Right Identifier
† This feature is only supported in the MS9500 Voyager product series.
5–3
The following example demonstrates how to configure the User-Defined ISBT identifiers:
Assume the left-hand identifiers are the ISBT defined donation identification number: “=G”; and the right hand identifiers are country specific identifiers “&a”.
1.Scan the ENTER/EXIT configuration mode bar code.
2.Scan the 1st Left Identifier configuration mode bar code.
3.Scan (Code Byte 0) + (Code Byte 6) + (Code Byte 1).
4.Scan the 2nd Left Identifier configuration mode bar code.
5.Scan (Code Byte 0) + (Code Byte 7) + (Code Byte 1).
6.Scan the 1st Right Identifier configuration mode bar code.
7.Scan (Code Byte 0) + (Code Byte 3) + (Code Byte 8).
8.Scan the 2nd Right Identifier configuration mode bar code.
9.Scan (Code Byte 0) + (Code Byte 9) + (Code Byte 7).
10.Scan the Enable User-Defined Sequence bar Code.
11.Scan the Enable ISBT bar code.
12.Scan the ENTER/EXIT configuration mode bar code.
The scanner is now configured with the appropriate identifiers. Since both ISBT and User-defined Concatenation are enabled, ISBT 128 bar codes scanned successively that contain these identifiers will be concatenated.
An alternate method of the type found in section 4.8.1 of the ISBT specifications can be used for configuring user-defined concatenation sequences. Using the previous example, the identifiers can be configured into a single configuration mode bar code. The following bar codes can be used to enable and disable the user-defined concatenation.
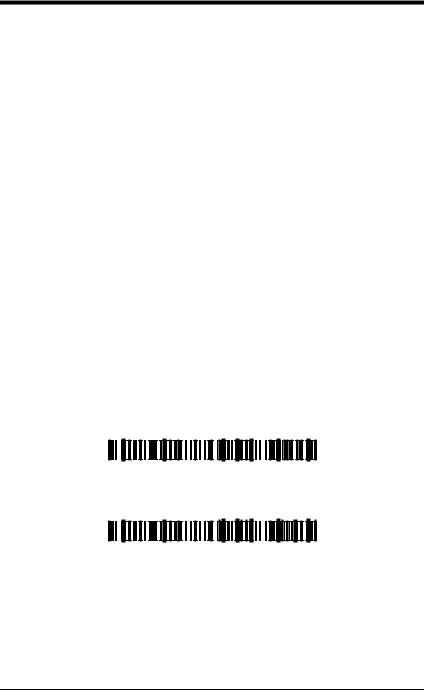
Enable (Left, =G) + (Right, &a)
= & |
³ |
= G & |
a |
5 |
0 |
5 |
d |
1 |
Disable (Left, =G) + (Right, &a)
= & |
³ |
= G & |
a |
5 |
0 |
5 |
d |
0 |
Note: These configuration bar codes require Single-Code configuration mode. These bar codes are not recognized in Multi-Code configuration mode.
Two forms of concatenation can be enabled at any given time, one pre-defined sequence and the user-defined sequence. Code selects and ISBT Code-128 concatenation cannot be used simultaneously. Both functions use the same internal resources so they must remain mutually exclusive.
5–4
 Loading...
Loading...