Fairchild FAN6300, FAN6300A, FAN6300H service manual

www.fairchildsemi.com
AN-6300
FAN6300 / FAN6300A / FAN6300H
Highly Integrated Quasi-Resonant PWM Controller
Abstract
This application note describes a detailed design strategy for higher-power conversion efficiency and better EMI using a Quasi-Resonant PWM controller compared to the conventional, hard-switched converter with a fixed switching frequency. Based on the proposed design guideline, a design example with detailed parameters demonstrates the performance of the controller.
Introduction
The highly integrated FAN6300/A/H PWM controller provides several features to enhance the performance of flyback converters. FAN6300/A are applied on QuasiResonant flyback converter where maximum operating frequency is below 100kHz and FAN6300H is suitable for high frequency operation that is around 190kHz. A built-in High Voltage (HV) startup circuit can provide more startup current to reduce the startup time of the controller. Once the VDD voltage exceeds the turn-on threshold voltage, the HV startup function is disabled immediately to reduce power consumption. An internal valley voltage detector ensures power system operates in quasi-resonant operation in wide-
range line voltage and reduces switching loss to minimize switching voltage on drain of the power MOSFET.
To minimize standby power consumption and improve lightload efficiency, a proprietary green-mode function provides off-time modulation to decrease switching frequency and perform extended valley voltage switching to keep to a minimum switching voltage.
FAN6300/A/H controller provides many protection functions. Pulse-by-pulse current limiting ensures the fixed peak current limit level, even when short-circuit occurs. Once an open-circuit failure occurs in the feedback loop, the internal protection circuit disables PWM output immediately. As long as VDD drops below the turn-off threshold voltage, the controller also disables the PWM output. The gate output is clamped at 18V to protect the power MOS from high gate-source voltage conditions. The minimum tOFF time limit prevents the system frequency from being too high. If the DET pin reaches OVP level, internal OTP is triggered, and the power system enters latch-mode until AC power is removed.
© 2009 Fairchild Semiconductor Corporation |
www.fairchildsemi.com |
Rev. 1.0.2 • 5/21/10 |
|
AN-6300 |
|
|
|
APPLICATION NOTE |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
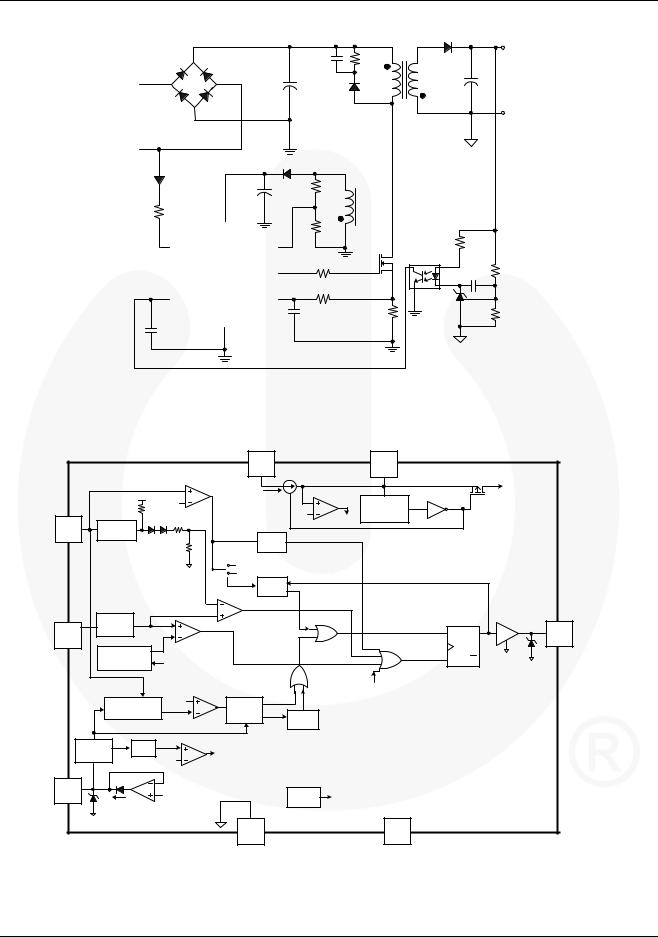
Figure 1. Basic Quasi-Resonant Converter
FB 2
CS 3
|
|
|
|
HV |
|
|
VDD |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
8 |
|
|
6 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Internal |
|
|
|
|
|
IHV |
|
OVP |
|
|
Bias |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Two Steps |
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
4.2V |
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
UVLO |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
27V |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2R |
|
Latched |
16V/10V/8V |
|
|
|
|
|
Soft-Start |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
5ms |
|
Timer |
FB OLP |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
R |
55ms |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2ms |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
30µs |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Starter |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Blanking |
|
|
|
|
|
|
DRV |
|
|
|
Circuit |
|
|
|
|
S SET |
Q |
5 |
GATE |
|
|
|
|
PWM |
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
18V |
|
|
|
|
Over-Power |
Current Limit |
|
|
|
R CLR |
Q |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
Compensation |
IDET |
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(3µs/13µs) |
|
|
|
|
Latched |
|
|
|
|
for H version |
0.3V |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
tOFF-MIN |
Valley |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
(8µs/38µs) |
VDET |
Detector |
tOFF-MIN |
tOFF-MIN +5µs |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1st |
+9µs |
for H version |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
Valley |
|
|
|
|
|
|
tOFF |
|
S/H |
VDET |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Blanking |
|
Latched |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
(4µs) |
|
|
2.5V |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
(1.5µs) for H version |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
DET OVP |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
DET 1 |
0.3V |
Internal |
Latched |
5V |
IDET |
OTP |
|
|
|
||
|
4 |
|
7 |
|
GND |
|
NC |
Figure 2. Functional Block Diagram
© 2009 Fairchild Semiconductor Corporation |
www.fairchildsemi.com |
Rev. 1.0.2 • 5/21/10 |
2 |

AN-6300 |
APPLICATION NOTE |
Design Procedure for the Primary-Side Inductance of Transformer
In this section, a design procedure is described using the schematic of Figure 1 as a reference.
[a] Define the System Specifications
Line voltage range (Vin,min and Vin,max)
Maximum output power (Po).
Output voltage (Vo) and maximum output current (Io)
Estimated efficiency (η)
The power conversion efficiency must be estimated to calculate the maximum input power. In the case of NB adaptor applications, the typical efficiency is 85%~90%.
With the estimated efficiency, the maximum input power is given by:
Pin = |
Po |
(1) |
|
η |
|||
|
[b] Estimate Reflected Output Voltage
Figure 3 shows the typical waveforms of the drain voltage of quasi-resonant flyback converter. When the MOSFET is turned off, the DC link voltage (Vo), together with the output voltage (Vo) and the forward voltage drop of the Schottky diode (Vd) reflected to the primary, are imposed on the MOSFET. The maximum nominal voltage across the MOSFET (Vds) is:
Vds,max = Vin,max + n(Vo +Vd ) |
(2) |
where the turns ratio of primary to secondary side of transformer is defined as n and Vds is as specified in Equation 2.
By increasing n, the capacitive switching loss and conduction loss of the MOSFET is reduced. However, this increases the voltage stress on the MOSFET as shown in Figure 3. Therefore, determine n by a trade-off between the voltage margin of the MOSFET and the efficiency. Typically, a turn-off voltage spike of Vds is considered as
100V, thus Vds,max is designed around 490~550V (75~85% of MOSFET rated voltage).
[c] Determine the Transformer Primary-side Inductance (LP)
Figure 4 shows the typical waveforms of MOSFET drain current (Ids), secondary diode current (Id), and the MOSFET drain voltage (Vds) of a QR converter. During tOFF, the current flows through the secondary side rectifier diode. When Id reduces to zero, Vds begins to drop by the resonance between the effective output capacitor of the MOSFET and the primary-side inductance (LP). To minimize the switching loss, the FAN6300/A/H is
designed to turn on the MOSFET when Vds reaches its minimum voltage Vin-n(Vo+Vd).
|
|
n:1 |
|
+ |
- |
|
+ |
|
+ Vd - |
||
Vin |
|
|
|
n(Vo+Vd) |
|
|
|
|
|
Vo |
|
- |
+ |
|
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
+ |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Coss |
Vds |
|
|
|
- |
|
Vds |
|
|
n(Vo+Vd) |
|
|
|
|
n(Vo+Vd) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
Vds |
|
|||
|
|
|
n(Vo+Vd) |
|
|
|
|
n(Vo+Vd) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
Vin,max |
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0V
Figure 3. Typical Waveform of MOSFET Drain Voltage for QR Operation
Ids
Iin 
 Idspk
Idspk
Id DTs
Vds
Vin+n(Vo+Vd)
|
n(Vo+Vd) |
|
Vin |
n(Vo+Vd) |
|
Vin-n(Vo+Vd) |
||
|
tON |
tOFF |
tF |
|
TS |
|
Figure 4. Typical Waveform of QR Operation
© 2009 Fairchild Semiconductor Corporation |
www.fairchildsemi.com |
Rev. 1.0.2 • 5/21/10 |
3 |

AN-6300 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
APPLICATION NOTE |
||||
To determine the primary-side inductance (LP), the |
[d] Determine the Proper Core and the |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
following variables should be determined beforehand: |
Minimum Primary Turns |
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
The minimum switching frequency (fs,min): The |
When designing the transformer, consider the maximum |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
maximum average input current occurs at the |
flux density swing in normal operation (Bmax). The |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
minimum input voltage and full-load condition. |
maximum flux density swing in normal operation is |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Meanwhile, the switching frequency is at minimum |
related to the hysteresis loss in the core, while the |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
value during QR operation. |
|
|
|
maximum flux density in transient is related to the core |
||||||||||||||||||||||
The falling time of the MOSFET drain voltage (tf): |
saturation. |
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
From Faraday’s law, the minimum number of turns for the |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
As shown in Figure 4, the falling time of MOSFET |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
drain voltage is half of the resonant period of the |
transformer primary side is given by: |
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||
|
MOSFET effective output capacitance and primary- |
|
|
|
LP Ids,max |
pk |
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
side inductance. If a resonant capacitor is added to be |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
NP,min |
= |
|
×106 |
|
|
(9) |
||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
paralleled with Coss, tf can be increased and EMI can |
|
|
|
Bmax Ae |
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
|
be |
reduced. However, |
this |
forces |
a |
switching loss |
where: |
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||
|
increase. |
The |
typical |
value |
of tf |
for NB adaptor |
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||
|
LP |
|
|
is |
specified |
in |
Equation |
7; |
|||||||||||||||||||
|
application is about 0.5~1μs. |
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
Ids,maxpk is the peak drain current specified in Equation 6; |
|||||||||||||||||||||||
After determining fs,min and tf, the maximum duty cycle is |
Ae is |
|
the cross-sectional area of the |
core in mm2; |
and |
||||||||||||||||||||||
calculated as: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Bmax |
is the maximum flux density swing in tesla. |
|
|||||||||||||||
|
Dmax |
= |
|
|
n(Vo +Vd ) |
×(1 - fs,min ×tf ) |
|
(3) |
Generally, it is possible to use Bmax =0.25~0.30 T. |
|
|||||||||||||||||
|
n(Vo +Vd |
)+Vin |
|
Determine the Number of Turns for Auxiliary |
|||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||
where |
Vin,min |
|
is |
specified |
at low-line |
and full-load. |
|||||||||||||||||||||
|
Winding |
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
According to Equation 1, the maximum average input |
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
The number of turns for auxiliary winding (Na) can be |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
current Iin,max is determined as |
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
VoIo |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
obtained by: |
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
Iin,max |
= |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(4) |
Na = |
VDD +VD1 |
|
|
|
|
|
(10) |
|||||||
|
Vin,min η |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Vo +Vd |
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||
According to Figure 3, Iin,max can be obtained as: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||
where: |
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
= |
1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
VDD |
|
is the |
operating |
voltage |
for VDD |
pin; |
|||||||
I |
|
D |
I |
|
|
pk |
|
|
|
|
(5) |
VD1 is the forward voltage drop of D1 in Figure 5; and |
|||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
|
in,max |
|
2 |
max |
|
ds,max |
|
|
|
|
|
Vo and Vd as determined in Equation 2. |
|
|
|||||||||||||
Ids,maxpk can be determined as:
Ids,max pk = |
Vin,min Dmax |
(6) |
|
Lmfs,min |
|||
|
|
In Equation 5, replace Ids,maxpk by Equation 6, then combine Equations 4 and 5 to obtain LP:
LP |
= |
(Vin,min Dmax |
)2 |
(7) |
2Pin fs,min |
|
|||
|
|
|
|
where Pin, and Dmax are specified in Equations 1 and 3, respectively, and fs,min is the minimum switching
frequency.
Once LP is determined, the RMS current of the MOSFET in normal operation are obtained as:
rms |
Dmax |
peak |
|
|
Ids,max = |
|
Ids,max |
(8) |
|
3 |
||||
|
© 2009 Fairchild Semiconductor Corporation |
www.fairchildsemi.com |
Rev. 1.0.2 • 5/21/10 |
4 |
 Loading...
Loading...