Olson Technology OTD-3000-DC User Manual

OTD-3000-DC
FREQUENCY AGILE
TELEVISION DEMODULATOR
PAL-D (China) STANDARD
INSTRUCTION MANUAL
Phone:
E-Mail: salessupport@olsontech.com
025-000105 REV B 8/23/01
(209) 586-1022
(800) 545-1022
Fax:
(209) 586-1026
www.olsontech.com
1) INTRODUCTION
The OTM-3000 DC is a frequency agile television modulator with an output frequency range of 48.25MHz
through 450.00MHz. All channels are selectable by front panel DIP switches in .25MHz increments.
The OTM-3000 DC offers high output level, typically +60dBmV. This unit has a very high out-of-band carrier
to noise ratio (>80dB) and uses SA W I.F . filtering, which allows virtually an unlimited number of modulators to
be combined without the need for external bandpass filters. The OTM-3000 DC has low power consumption
(typically 12 watts @ 220 VAC) for reliable long term operation.
2) CHANNEL SELECTION
Output frequency selection is made by properly setting the two 8-position DIP switches SW1 and SW2 which
are located behind the small cover plate on the front panel.
OTM-3000 DC
FREQUENCY AGILE PAL D
TELEVISION MODULA TOR
Refer to T able 1 to determine the proper switch settings for various P AL D China channels. Set the
switches from left to right as shown in T able 1.
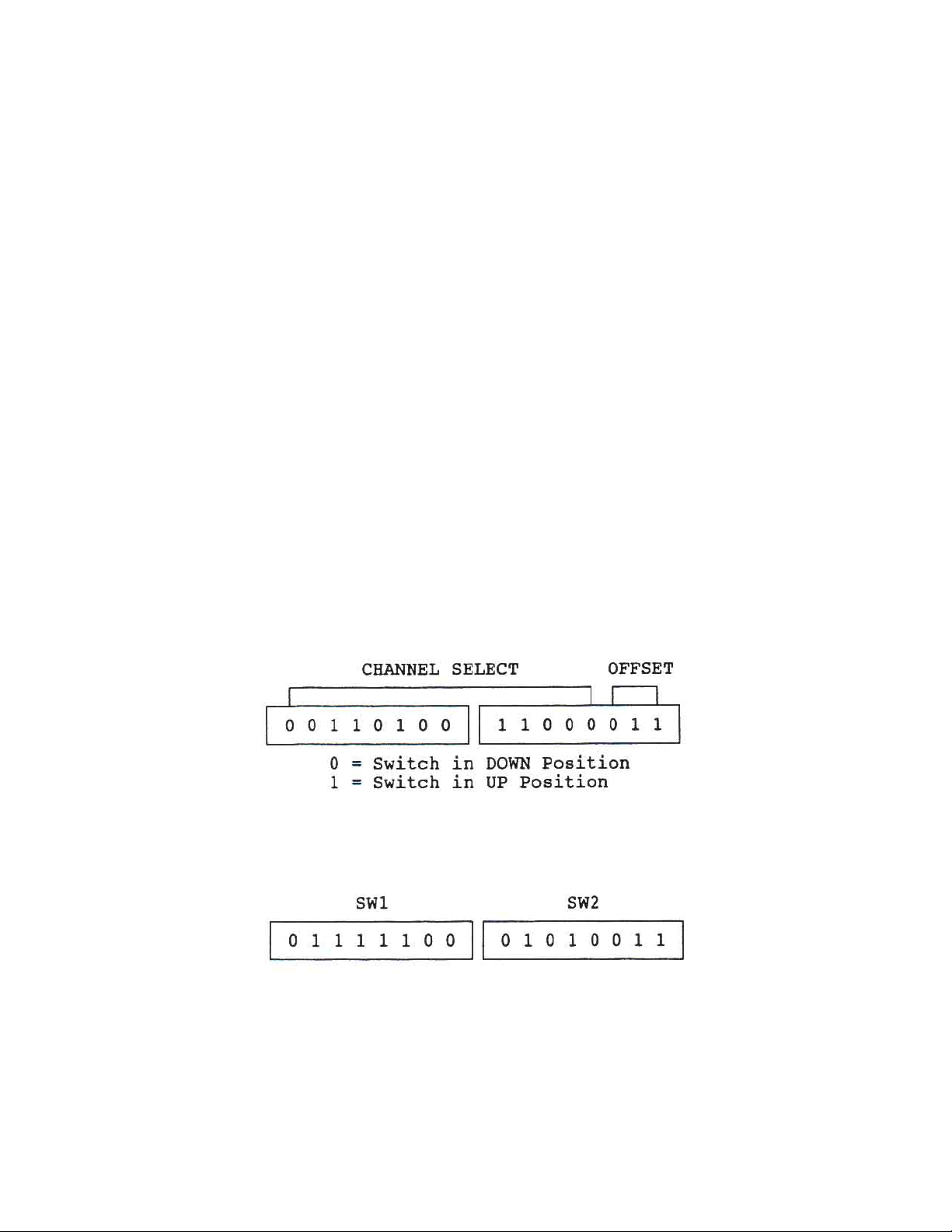
Figure 1 - SW1, SW2 Switch Functions
For example, if 49.75MHz is desired, the DIP switches would be positioned as follows:
025-000128 REV B
Page 2
3) SELECTION OF NON-ST ANDARD OUTPUT FREQUENCIES
Refer to the following paragraphs if you need to set the switches for non- standard assignments.
Each of the switches has a weighted value as indicated in Figure 2. The switches are either
UP = OFF = (value) or are DOWN = ON = 0.
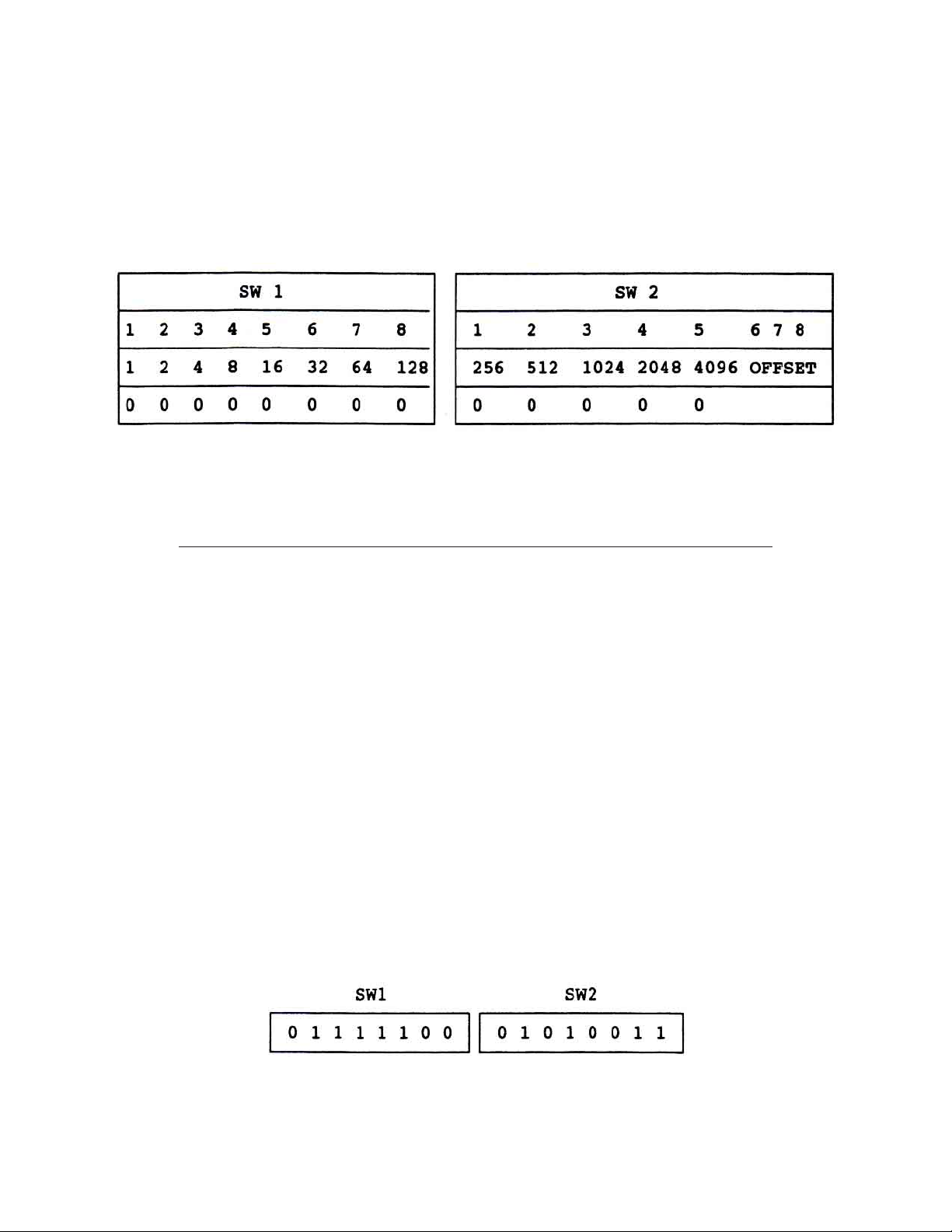
Figure 2 - SW1/SW2 Switch V alues
The selected video carrier frequency may be any frequency within the 48 to 450MHz band providing the selected
frequency (+) 605.75 is evenly divisible by .25. The procedure is as follows:
COMPUTING SWITCH SETTINGS FOR NON-ST ANDARD FREQUENCIES
A) Decide on the required frequency and check that it is evenly divisible by .25 (answer must end in .00).
B) Compute the total weighted switch value required.
C) Set the DIP switches to equal the total weighted value.
EXAMPLE:
If X is the required frequency in MHz and Y is the total weighted value of the switch settings, then (X + 605.75)
divided by .25 = Y.
T o illustrate: If the desired frequency is 49.75.
Y = (49.75 + 605.75) divided by .25 = 2622
Refer to Figure 2 and compute which switch positions must be moved UP so their total value = 2622. This would
yield switch settings of:
025-000128 REV B
Figure 3 - Example of settings for 49.75MHz.
Page 3
