Linksys SPA2102 User Manual

Your Internet Telephone Company
offering you more - connecting you for less
Phone Adapter with Router
User Guide
Voice
Model No. SPA2102

Phone Adapter with Router
Copyright and Trademarks
Specifications are subject to change without notice. Linksys is a registered trademark or trademark of Cisco Systems, Inc. and/or its affiliates in the U.S. and certain other countries. Copyright © 2006 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Other brands and product names are trademarks or registered trademarks of their respective holders.
WARNING: This product contains chemicals, including lead, known to the State of California to cause cancer, and birth defects or other reproductive harm. Wash hands after handling.
How to Use this Guide
Your guide to the Phone Adapter with Router has been designed to make understanding networking with the
Phone Adapter easier than ever. Look for the following items when reading this guide:
This exclamation point means there is a caution or warning and is something that could damage your property or the Phone Adapter.
This question mark provides you with a reminder about something you might need to do while using the Phone Adapter.
This checkmark means there is a note of interest and is something you should pay special attention to while using the Phone Adapter.
In addition to these symbols, there are definitions for technical terms that are presented like this:
word: definition.
Also, each figure (diagram, screenshot, or other image) is provided with a figure number and description, like this:
Figure numbers and descriptions can also be found in the “List of Figures” section.
SPA2102-UG-60613A DF
Phone Adapter with Router
Table of Contents
Phone Adapter with Router
Chapter 1: Introduction |
1 |
Welcome |
1 |
What’s in this Guide? |
2 |
Chapter 2: Networking Basics |
5 |
An Introduction to Local Area Networks |
5 |
The Use of IP Addresses |
5 |
Chapter 3: Getting to Know the Phone Adapter |
7 |
The Back Panel |
7 |
The Front Panel |
8 |
Chapter 4: Getting Started |
9 |
Before You Begin |
9 |
Connecting the Phone Adapter |
9 |
Configuring the Phone Adapter |
11 |
Placing the Phone Adapter |
13 |
Chapter 5: Using the Interactive Voice Response Menu |
15 |
Overview |
15 |
Accessing the Interactive Voice Response Menu |
15 |
Using the Interactive Voice Response Menu |
16 |
Entering a Password |
21 |
Configuring the Settings for your babyTEL Service |
22 |
Chapter 6: Using the Web-based Utility |
23 |
Overview |
23 |
How to Access the Web-based Utility |
24 |
The Router Tab |
25 |
The Voice Tab |
34 |
Phone Adapter with Router
Appendix A: Troubleshooting |
45 |
Common Problems and Solutions |
45 |
Frequently Asked Questions |
56 |
Appendix B: Finding the MAC Address and IP Address for Your Ethernet Adapter |
61 |
Windows 98 or Me Instructions |
61 |
Windows 2000 or XP Instructions |
62 |
For the Phone Adapter’s Web-based Utility |
62 |
Appendix C: Windows Help |
63 |
Appendix D: Glossary |
65 |
Appendix E: Specifications |
69 |
Appendix F: Warranty Information |
75 |
Appendix G: Regulatory Information |
77 |
Appendix H: Contact Information |
85 |
babyTEL |
85 |
Linksys |
85 |
List of Figures
Phone Adapter with Router
Figure 3-1: Back Panel |
7 |
Figure 3-2: Front Panel |
8 |
Figure 4-1: Connect a Telephone |
9 |
Figure 4-2: Connect a PC |
10 |
Figure 4-3: Connect to the Modem |
10 |
Figure 4-4: Connect Power |
10 |
Figure 4-5: Login Screen |
11 |
Figure 4-6: Router - WAN Setup Screen |
11 |
Figure 4-7: MAC Clone Settings |
11 |
Figure 4-8: Static IP Settings |
12 |
Figure 4-9: PPPoE Settings |
12 |
Figure 4-10: Measurement between |
|
Wall-Mount Slots |
13 |
Figure 6-1: Login Screen |
24 |
Figure 6-2: Router - Status Screen |
25 |
Figure 6-3: Router - WAN Setup Screen |
27 |
Figure 6-4: Static IP Settings |
27 |
Figure 6-5: PPPoE Settings |
27 |
Figure 6-6: Router - LAN Setup Screen |
30 |
Figure 6-7: Router - Application Screen |
32 |
Figure 6-8: Voice - Info Screen |
34 |
Figure 6-9: Line 1 Status |
35 |
Figure 6-10: Voice - System Screen |
38 |
Phone Adapter with Router |
|
Figure 6-11: Voice - User 1 Screen |
39 |
Figure 6-12: Speed Dial and Supplementary Service Settings |
41 |
Figure 6-13: Distinctive Ring and Ring Settings |
42 |
Figure B-1: IP Configuration Screen |
61 |
Figure B-2: MAC/Adapter Address |
61 |
Figure B-3: MAC/Physical Address |
62 |
Figure B-4: MAC Address Cloning |
62 |
Chapter 1: Introduction
Phone Adapter with Router
Welcome
Thank you for choosing the Phone Adapter with Router. This Phone Adapter will allow your computers to share a
high-speed Internet connection as well as resources, including files and printers. And after you have set up your babyTEL service, you will be able to make phone or fax calls using the Internet.
How does the Phone Adapter do all of this? By connecting your computers and peripherals, including phones or fax machines, to the Phone Adapter and connecting the Phone Adapter to your cable or DSL modem, then the Phone Adapter can direct and control communications for your network. Each of the Phone Adapter’s two telephone jacks can operate independently, with separate phone service and phone numbers, so you can have up to two Internet phone lines per Adapter.
But what does all of this mean?
Networks are useful tools for sharing Internet access and computer resources. Multiple computers can share Internet access, so you don’t need more than one high-speed Internet connection. With the babyTEL service,
your Internet access can now be shared by your phones or fax machines as well. You will be able to make phone calls using the account you set up with babyTEL, even while you are surfing the Internet.
Plus, you can access one printer from different computers and access data located on another
computer’s hard drive. Networks are even used for playing multiplayer video games. So, networks not only are useful in homes and offices, but also can be fun.
PCs on a wired network create a LAN, or Local Area Network. They are connected with Ethernet cables, which is why the network is called “wired”.
network: a series of computers or devices connected for the purpose of data sharing, storage, and/or transmission between users.
lan (local area network): the computers and networking products that make up the network in your home or office.
ethernet: an IEEE standard network protocol that specifies how data is placed on and retrieved from a common transmission medium.
Chapter 1: Introduction |
1 |
Welcome
Phone Adapter with Router
To create your network, install and set up the Phone Adapter. To guide you through the process, use the instructions in the Quick Installation or this User Guide to help you. These instructions should be all you need to get the most out of the Phone Adapter with Router.
What’s in this Guide?
This guide covers the basic steps for setting up a network with the Phone Adapter. After going through “Chapter 3: Getting to Know the Phone Adapter,” most users will only need to use the following chapters:
•Chapter 4: Getting Started
This chapter instructs you on how to connect and set up the Phone Adapter.
•Chapter 6: Using the Web-based Utility
This chapter explains how to configure the Phone Adapter using your web browser and the Phone Adapter’s Web-based Utility. You will configure the Phone Adapter using the settings provided by your ISP.
When you’re finished with the basic steps, then you are ready to connect to the Internet.
You also have other chapters available for reference:
•Chapter 1: Introduction
This chapter describes the Phone Adapter’s applications and this User Guide.
•Chapter 2: Networking Basics
This chapter briefly explains how a network functions.
•Chapter 5: Using the Interactive Voice Response Menu
This chapter explains how to configure the Phone Adapter’s network settings when you use its Interactive Voice Response Menu.
2
Chapter 1: Introduction
What’s in this Guide?
Phone Adapter with Router
•Appendix A: Troubleshooting
This appendix describes some possible problems and solutions, as well as frequently asked questions, regarding installation and use of the Phone Adapter.
•Appendix B: Finding the MAC Address and IP Address for Your Ethernet Adapter
This appendix instructs you on how to find the MAC address or Ethernet address of your PC’s Ethernet network adapter.
•Appendix C: Windows Help
This appendix describes how you can use Windows Help for instructions about networking, such as installing the TCP/IP protocol.
•Appendix D: Glossary
This appendix gives a brief glossary of terms frequently used in networking.
•Appendix E: Specifications
This appendix provides the technical specifications for the Phone Adapter.
•Appendix F: Warranty Information
This appendix supplies the warranty information for the Phone Adapter.
•Appendix G: Regulatory Information
This appendix supplies the regulatory information regarding the Phone Adapter.
•Appendix H: Contact Information
This appendix provides contact information for a variety of Linksys resources, including Technical Support.
Chapter 1: Introduction |
3 |
What’s in this Guide?
Phone Adapter with Router
4 |
Chapter 1: Introduction |
|
What’s in this Guide? |
Chapter 2: Networking Basics
Phone Adapter with Router
An Introduction to Local Area Networks
Simply put, a router is a network device that connects two networks together.
The Phone Adapter connects your local area network (LAN), or the group of PCs in your home or office, to the Internet. The Phone Adapter processes and regulates the data that travels between these two networks.
The Phone Adapter’s Network Address Translation (NAT) technology protects your network of PCs so users on the Internet cannot “see” your PCs. This is how your LAN remains private. The Phone Adapter protects your network by inspecting the first packet coming in through the Internet port before delivery to the final destination on one of the Ethernet ports. The Phone Adapter inspects Internet port services like the web server, ftp server, or other Internet applications, and, if allowed, it will forward the packet to the appropriate PC on the LAN side.
nat (network address translation): NAT technology translates IP addresses of a local area network to a different IP address for the Internet.
The Use of IP Addresses
IP stands for Internet Protocol. Every device in an IP-based network, including PCs, print servers, and routers, requires an IP address to identify its location, or address, on the network. This applies to both the Internet and LAN connections.
There are two ways of assigning IP addresses to your network devices.
A static IP address is a fixed IP address that you assign manually to a PC or other device on the network. Since a static IP address remains valid until you disable it, static IP addressing ensures that the device assigned it will always have that same IP address until you change it. Static IP addresses are commonly used with network devices such as server PCs or print servers.
ip (internet protocol): a protocol used to send data over a network.
ip address: the address used to identify a computer or device on a network.
static ip address: a fixed address assigned to a computer or device that is connected to a network.
Chapter 2: Networking Basics |
5 |
An Introduction to Local Area Networks
Phone Adapter with Router
If you use the Phone Adapter to share your cable or DSL Internet connection, contact your ISP to find out if they have assigned a static IP address to your account. If so, you will need that static IP address when configuring the Phone Adapter. You can get the information from your ISP.
A dynamic IP address is automatically assigned to a device on the network. These IP addresses are called dynamic because they are only temporarily assigned to the PC or other device. After a certain time period, they expire and may change. If a PC logs onto the network (or the Internet) and its dynamic IP address has expired, the DHCP server will assign it a new dynamic IP address.
A DHCP server can either be a designated PC on the network or another network device, such as the Phone Adapter. By default, the Phone Adapter’s Internet Connection Type is DHCP (obtain an IP address automatically).
The PC or network device obtaining an IP address is called the DHCP client. DHCP frees you from having to assign IP addresses manually every time a new user is added to your network.
For DSL users, many ISPs may require you to log on with a user name and password to gain access to the Internet. This is a dedicated, high-speed connection type called Point to Point Protocol over Ethernet (PPPoE). PPPoE is similar to a dial-up connection, but PPPoE does not dial a phone number when establishing a connection. It also will provide the Phone Adapter with a dynamic IP address to establish a connection to the Internet.
By default, a DHCP server (on the LAN side) is enabled on the Phone Adapter. If you already have a DHCP server running on your network, you MUST disable one of the two DHCP servers. If you run more than one DHCP server on your network, you will experience network errors, such as conflicting IP addresses. To disable DHCP on the Phone Adapter, see the Router - LAN Setup section in “Chapter 5: Using the Web-based Utility.”
dynamic ip address: a temporary IP address assigned by a DHCP server.
dhcp (dynamic host configuration protocol): a protocol that lets one device on a local network, known as a DHCP server, assign temporary IP addresses to the other network devices, typically computers.
6 |
Chapter 2: Networking Basics |
|
The Use of IP Addresses |

Chapter 3: Getting to Know the Phone Adapter Phone Adapter with Router
The Back Panel
The Phone Adapter’s ports are located on the back panel.
|
Figure 3-1: Back Panel |
|
PHONE 1/2 |
Use this port to connect an analog phone (or fax machine) with an RJ-11 telephone cable. |
|
ETHERNET |
The ETHERNET port connects to a network device, such as a PC or a switch, with an |
|
|
Ethernet network cable. |
|
INTERNET |
The INTERNET port connects to your cable or DSL modem. |
|
Power |
The Power port is where you will connect the power adapter. |
|
Chapter 3: Getting to Know the Phone Adapter |
7 |
|
The Back Panel

Phone Adapter with Router
The Front Panel
The Phone Adapter’s LEDs, which inform you about network activities, are located on the front panel.
|
Figure 3-2: Front Panel |
Power |
Green. The Power LED lights up when the Phone Adapter is powered on and connected to |
|
the Internet. It flashes when the Phone Adapter is not connected to the Internet. The LED |
|
also flashes when the Phone Adapter is booting up or upgrading its firmware. |
INTERNET |
Green. The INTERNET LED lights up when there is an active connection through the port. If |
|
the LED is flashing, then there is traffic moving through that port. |
PHONE 1/2 |
Green. The PHONE LED is solidly lit when a telephone or fax machine has an active or |
|
registered connection to babyTEL through the corresponding port. It flashes when the |
|
phone is being used or is off the hook. |
|
Proceed to “Chapter 4: Getting Started.” |
8 |
Chapter 3: Getting to Know the Phone Adapter |
|
The Front Panel |

Chapter 4: Getting Started
Before You Begin
Make sure you have the following:
•An active Internet connection
•An active babyTEL service account and its settings
•cable/DSL modem
•One computer for configuration of the Phone Adapter
•Analog telephone or fax machine with an RJ-11 phone cable
Connecting the Phone Adapter
1.Power off your network devices, including your modem and PC.
2.Connect the RJ-11 phone cable to the Phone Adapter’s PHONE 1 port. Connect the other end to your analog telephone or fax machine.
IMPORTANT: Do not connect the PHONE port to a telephone wall jack. Make sure you only connect a telephone or fax machine to the PHONE port. Otherwise, the Phone Adapter or the telephone wiring in your home or office may be damaged.
3. Repeat step 2 with the PHONE 2 port.
Chapter 4: Getting Started
Phone Adapter with Router
Figure 4-1: Connect a Telephone
9
Before You Begin

Phone Adapter with Router
4.Connect one end of an Ethernet network cable (included) to the ETHERNET port of the Phone Adapter. Connect the other end to the Ethernet port of your PC.
5.Connect one end of a different Ethernet network cable to the INTERNET port of the Phone Adapter. Connect the other end to your cable/DSL modem.
6.Power on the broadband modem.
Figure 4-2: Connect a PC
7.Connect the included power adapter to the Phone Adapter’s power port, and then plug the power adapter into an electrical outlet. The power LED on the front panel will light up as soon as the Phone Adapter powers on.
8.Power on your PC.
NOTE: Make sure your PC’s Ethernet adapter is set to obtain an IP address automatically. For more information, refer to Windows Help.
Figure 4-3: Connect to the Modem
Proceed to the next section.
Figure 4-4: Connect Power
10 |
Chapter 4: Getting Started |
|
Connecting the Phone Adapter |
Phone Adapter with Router
Configuring the Phone Adapter
1.Launch the web browser on the PC.
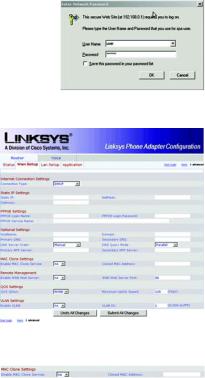
2.Enter 192.168.0.1/advanced in the Address field (192.168.0.1 is the default local IP address of the Phone Adapter). Then press the Enter key.
3.If babyTEL did not supply a password, you will not see a login screen.
Proceed to step 4.
If babyTEL supplied a password, you will see a login screen. In the User Name field, enter user, the default user name for user access (this cannot be changed). Then enter the user password supplied by babyTEL.
4.The Router - Status screen will appear. Click the WAN Setup tab.
5.Proceed to the appropriate instructions for your Internet Connection Type.
DHCP
a.Select DHCP from the Connection Type drop-down menu.
b.If you use a cable modem, you may need to configure the MAC Clone Settings. (Contact your ISP for more information.)
Enable MAC Clone Service. If your service uses a specific PC MAC address, then select yes from the Enable MAC Clone Service setting. Then enter the PC’s MAC address in the Cloned MAC Address field.
c.Click the Submit All Changes button.
Chapter 4: Getting Started
Figure 4-5: Login Screen
Figure 4-6: Router - WAN Setup Screen
Figure 4-7: MAC Clone Settings
11
Configuring the Phone Adapter

Phone Adapter with Router
Static IP
a.Select Static IP from the Connection Type drop-down menu.
b.In the Static IP Settings section, enter the IP address in the Static IP field, the subnet mask in the NetMask field, and the default gateway IP address in the Gateway field.
c.In the Optional Settings section, enter the DNS server address(es) in the Primary DNS and optional
Secondary DNS fields.
d.Click the Submit All Changes button.
PPPoE (most DSL users)
a.Select PPPoE from the Connection Type drop-down menu.
b.Enter the user name in the PPPoE Login Name field, and enter the password in the PPPoE Login Password field.
c.Click the Submit All Changes button.
6.If the Phone Adapter is pre-configured by babyTEL, then you do not need to change any of the default voice settings. Refer to the documentation supplied by babyTEL for more information. If you need to configure additional settings, refer to “Chapter 6: Using the Web-based Utility” for instructions.
Proceed to the next section, “Placing the Phone Adapter.”
12
Figure 4-8: Static IP Settings
static ip address: a fixed address assigned to a computer or device connected to a network.
subnet mask: an address code that determines the size of the network.
default gateway: a device that forwards Internet traffic from your local area network.
Figure 4-9: PPPoE Settings
pppoe: a type of broadband connection that provides authentication (username and password) in addition to data transport.
Chapter 4: Getting Started
Configuring the Phone Adapter

Phone Adapter with Router
Placing the Phone Adapter
There are two ways to place the Phone Adapter. The first way is to place the Phone Adapter horizontally on a surface. The second way is to mount the Phone Adapter on a wall. The wall-mount option is explained in further detail below.
Wall-Mount Option
The Phone Adapter has two wall-mount slots on its back panel. The distance between the two slots is 58 mm (2.28 inches).
1.Determine where you want to mount the Phone Adapter.
2.Drill two holes into the wall. Make sure the holes are 58 mm (2.28 inches) apart.
3.Insert a screw into each hole, and leave 5 mm (0.2 inches) of its head exposed.
4.Maneuver the Phone Adapter so the wall-mount slots line up with the two screws.
5.Place the wall-mount slots over the screws and slide the Phone Adapter down until the screws fit snugly into the wall-mount slots.
Congratulations! The installation of the Phone Adapter is complete.
Chapter 4: Getting Started
Figure 4-10: Measurement between Wall-Mount Slots
13
Placing the Phone Adapter
Phone Adapter with Router
14 |
Chapter 4: Getting Started |
|
Placing the Phone Adapter |

Phone Adapter with Router
Chapter 5: Using the Interactive Voice Response Menu
Overview
NOTE: If babyTEL sent you the Phone Adapter, then it may be pre-configured for you, and you do not need to change any settings. Refer to the instructions supplied by babyTEL for more information.
You may need to manually configure the Phone Adapter by entering the settings provided by babyTEL. This chapter explains how to use the Interactive Voice Response Menu to configure the Phone Adapter's network settings. You will use the telephone’s keypad to enter your commands and select choices,
and the Phone Adapter will use voice responses.
For more advanced configuration, refer to “Chapter 6: Using the Web-based Utility.”
Accessing the Interactive Voice Response Menu
1.Use a telephone connected to one of the Phone Adapter’s PHONE ports. (You can only access the Interactive Voice Response Menu through an analog telephone, not any of the Internet phones.)
2.Press **** (in other words, press the star key four times).
3.Wait until you hear “Linksys configuration menu. Please enter the option followed by the # (pound) key or hang up to exit.”
4.Refer to the following table that lists actions, commands, menu choices, and descriptions. After you select an option, press the # (pound) key. To exit the menu, hang up the telephone.
Chapter 5: Using the Interactive Voice Response Menu |
15 |
Overview
Phone Adapter with Router
Using the Interactive Voice Response Menu
While entering a value, such as an IP address, you may exit without entering any changes. Press the * (star) key twice within half a second. Otherwise, the * will be treated as a decimal point or dot.
After entering a value, such as an IP address, press the # (pound) key to indicate you have finished your selection. To save the new setting, press 1. To review the new setting, press 2. To re-enter the new setting, press 3. To cancel your entry and return to the main menu, press * (star).
For example, to enter the IP address 191.168.1.105 by keypad, press these keys: 191*168*1*105. Press the # (pound) key to indicate that you have finished entering the IP address. Then press 1 to save the IP address or press the * (star) key to cancel your entry and return to the main menu.
If the menu is inactive for more than one minute, the Phone Adapter will time out. You will need to re-enter the menu by pressing ****.
16 |
Chapter 5: Using the Interactive Voice Response Menu |
|
Using the Interactive Voice Response Menu |
Phone Adapter with Router
The settings you have saved will take effect after you have hung up the telephone. The Phone Adapter may reboot at this time.
Interactive Voice Response Menu
Action |
Command |
Choices |
Description |
|
(press these |
|
|
|
keys on the |
|
|
|
telephone) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Enter Interactive Voice |
**** |
|
Use this command to enter the Interactive |
Response Menu |
|
|
Voice Response Menu. Do not press any |
|
|
|
other keys until you hear, “Linksys |
|
|
|
configuration menu. Please enter the option |
|
|
|
followed by the # (pound) key or hang up to |
|
|
|
exit.” |
|
|
|
|
Check Internet |
100 |
|
Hear the Internet connection type of the |
Connection Type |
|
|
Phone Adapter. |
|
|
|
|
Check Internet IP |
110 |
|
Hear the IP address assigned to the Phone |
Address |
|
|
Adapter’s Internet (external) interface. |
|
|
|
|
Check Network Mask |
120 |
|
Hear the network or subnet mask assigned to |
(or Subnet Mask) |
|
|
the Phone Adapter. |
|
|
|
|
Check Gateway IP |
130 |
|
Hear the IP address of the Phone Adapter |
Address |
|
|
(usually the network router). |
|
|
|
|
Check MAC Address |
140 |
|
Hear the MAC address of the Phone Adapter |
|
|
|
in hexadecimal string format. |
|
|
|
|
Chapter 5: Using the Interactive Voice Response Menu |
|
||
ip (internet protocol): a protocol used to send data over a network.
ip address: the address used to identify a computer or device on a network. subnet mask: an address code that determines the size of the network.
gateway: a device that forwards Internet traffic from your local area network. mac address: the unique address that a manufacturer assigns to each networking device.
17
Using the Interactive Voice Response Menu
Phone Adapter with Router
Interactive Voice Response Menu
Action |
Command |
Choices |
Description |
|
(press these |
|
|
|
keys on the |
|
|
|
telephone) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Check Firmware |
150 |
|
Hear the version number of the firmware |
Version |
|
|
currently running on the Phone Adapter. |
|
|
|
|
Check Primary DNS |
160 |
|
Hear the IP address of the primary DNS |
Server IP Address |
|
|
(Domain Name Service) server. |
|
|
|
|
Check Internet Web |
170 |
|
Hear the port number of the Internet Web |
Server Port |
|
|
server used for the Web-based Utility. |
|
|
|
|
Check Local IP |
210 |
|
Hear the local IP address of the Phone |
Address |
|
|
Adapter. |
|
|
|
|
Set Internet |
101 |
Press 0 to use DHCP. |
Select the type of Internet connection you are |
Connection Type |
|
Press 1 to use a static IP |
using. Refer to the documentation supplied |
|
|
address. |
by your Internet Service Provider (ISP). |
|
|
Press 2 to use PPPoE. |
|
|
|
|
|
Set Static IP Address |
111 |
Enter the IP address using |
First, set the Internet Connection Type to |
|
|
numbers on the telephone |
static IP address; otherwise, you will hear, |
|
|
keypad. Use the * (star) |
“Invalid Option,” if you try to set the static IP |
|
|
key when entering a |
address. |
|
|
decimal point. |
|
|
|
|
|
firmware: the programming code that runs a networking device.
dhcp (dynamic host configuration protocol): a protocol that lets one device on a local network, known as a DHCP server, assign temporary IP addresses to the other network devices, typically computers.
static ip address: a fixed address assigned to a computer or device that is connected to a network.
pppoe: a type of broadband connection that provides authentication (username and password) in addition to data transport.
18 |
Chapter 5: Using the Interactive Voice Response Menu |
|
Using the Interactive Voice Response Menu |
Phone Adapter with Router
Interactive Voice Response Menu
Action |
Command |
Choices |
Description |
|
(press these |
|
|
|
keys on the |
|
|
|
telephone) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Set Network (or |
121 |
Enter the network or |
First, set the Internet Connection Type to |
Subnet) Mask |
|
subnet mask using |
static IP address; otherwise, you will hear, |
|
|
numbers on the telephone |
“Invalid Option,” if you try to set the network |
|
|
keypad. Use the * (star) |
or subnet mask. |
|
|
key when entering a |
|
|
|
decimal point. |
|
|
|
|
|
Set Gateway IP |
131 |
Enter the IP address using |
First, set the Internet Connection Type to |
Address |
|
numbers on the telephone |
static IP address; otherwise, you will hear, |
|
|
keypad. Use the * (star) |
“Invalid Option,” if you try to set the gateway |
|
|
key when entering a |
IP address. |
|
|
decimal point. |
|
|
|
|
|
Set Primary DNS |
161 |
Enter the IP address using |
First, set the Internet Connection Type to |
Server IP Address |
|
numbers on the telephone |
static IP address; otherwise, you will hear, |
|
|
keypad. Use the * (star) |
“Invalid Option,” if you try to set the IP |
|
|
key when entering a |
address of the primary DNS server. |
|
|
decimal point. |
|
|
|
|
|
Chapter 5: Using the Interactive Voice Response Menu |
19 |
Using the Interactive Voice Response Menu
 Loading...
Loading...