HP 30B User Manual

i
HP 20b Business Consultant
HP 30b Business Professional
Financial Calculator User’s Guide
HP Part Number: NW238-90001
Edition 1, December 2009

ii
Legal Notice
This manual and any examples contained herein are provided "as is" and are subject to
change without notice. Hewlett-Packard Company makes no warranty of any kind with regard
to this manual, including, but not limited to, the implied warranties of merchantability, non-
infringement and fitness for a particular purpose. In this regard, HP shall not be liable for
technical or editorial errors or omissions contained in the manual.
Hewlett-Packard Company shall not be liable for any errors or for incidental or consequential
damages in connection with the furnishing, performance, or use of this manual or the
examples contained herein.
Copyright © 2009 Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P.
Reproduction, adaptation, or translation of this manual is prohibited without prior written
permission of Hewlett-Packard Company, except as allowed under the copyright laws.
Hewlett-Packard Company
16399 West Bernardo Drive
MS 66M-785
San Diego, CA 92127-1899
USA

iii
HP 20b Business Consultant

iv
HP 30b Business Professional

v
Keyboard Map Legend
* Only applies to HP 30b.
**Does not apply to the HP 20b.
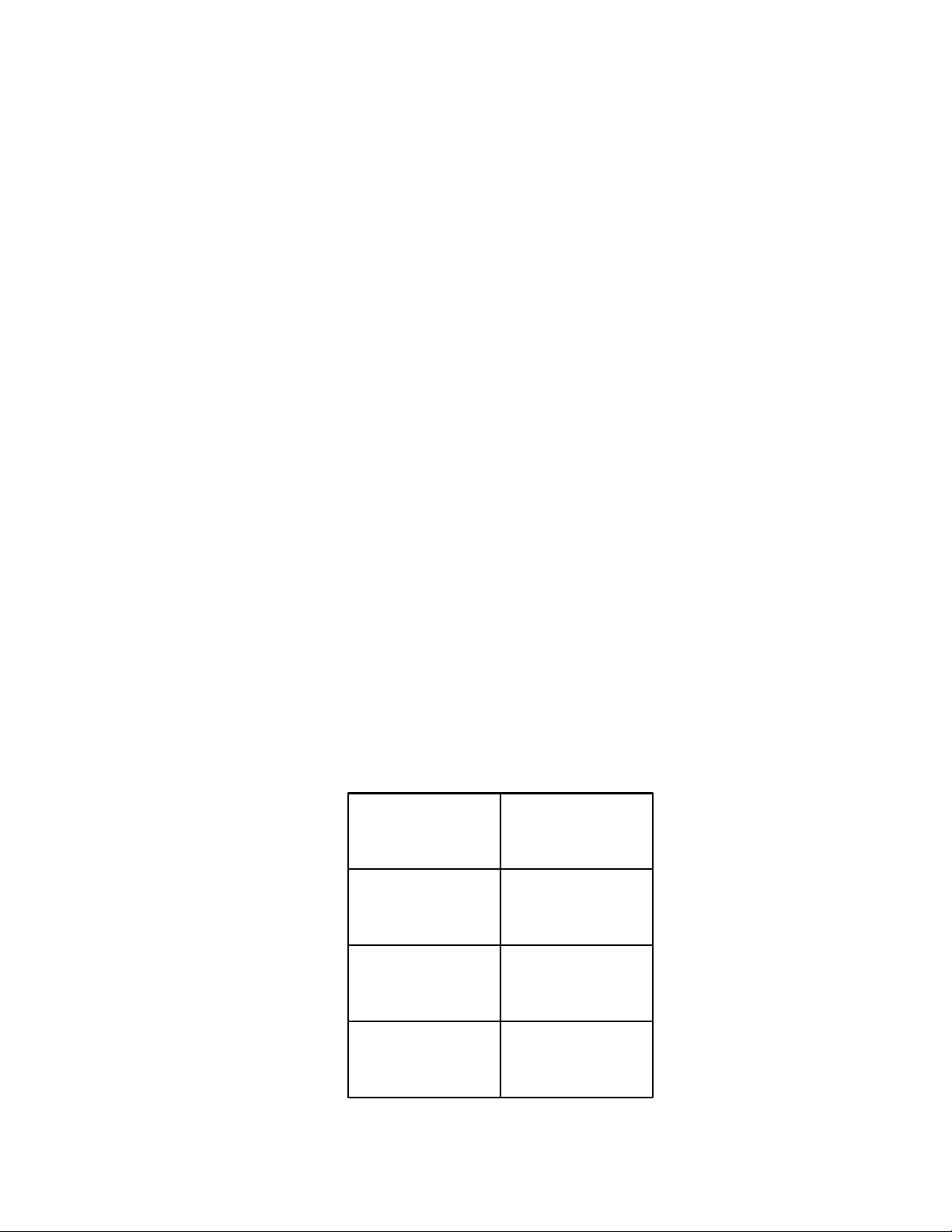
Number Feature Number Feature
1 2-line, alphanumeric scrolling
display screen
9 Common Mathematical
functions and Math (Math)
menu
2 Time Value of Money keys
(TVM)
10 Program menu*
RPN Swap/Close parenthesis
3 Cash Flow, IRR and NPV keys 11 Backspace key/Reset menu
4 Data and Statistics menus 12 Percent/Percent calculation
(business) and Date menus
5 Input key and Memory menu 13 Recall and Store
6 Insert and Delete/scroll (up
and down)
14 Black-Scholes** and Bond
menus
7 Shift key 15 Amortization/Depreciation
menus
8 On/Off/Cancel 16 Annunciators

vi

i
Table of Contents
Legal Notice.............................................................................................................ii
HP 20b Business Consultant ......................................................................................iii
HP 30b Business Professional .................................................................................... iv
Keyboard Map Legend.............................................................................................. v
1 Basic Features ......................................................................................................... 1
Welcome to your new HP Financial Calculator .............................................................1
Turning the Calculator On and Off..............................................................................1
Selecting a Language ................................................................................................1
Adjusting the Display Contrast ....................................................................................1
Cursor .....................................................................................................................2
Two Line Display.......................................................................................................2
The Mode Menu: Setting Preferences...........................................................................2
Changing the Calculation Mode .................................................................................4
Key Presses, the Shift Key, Secondary, and Tertiary Functions*.......................................4
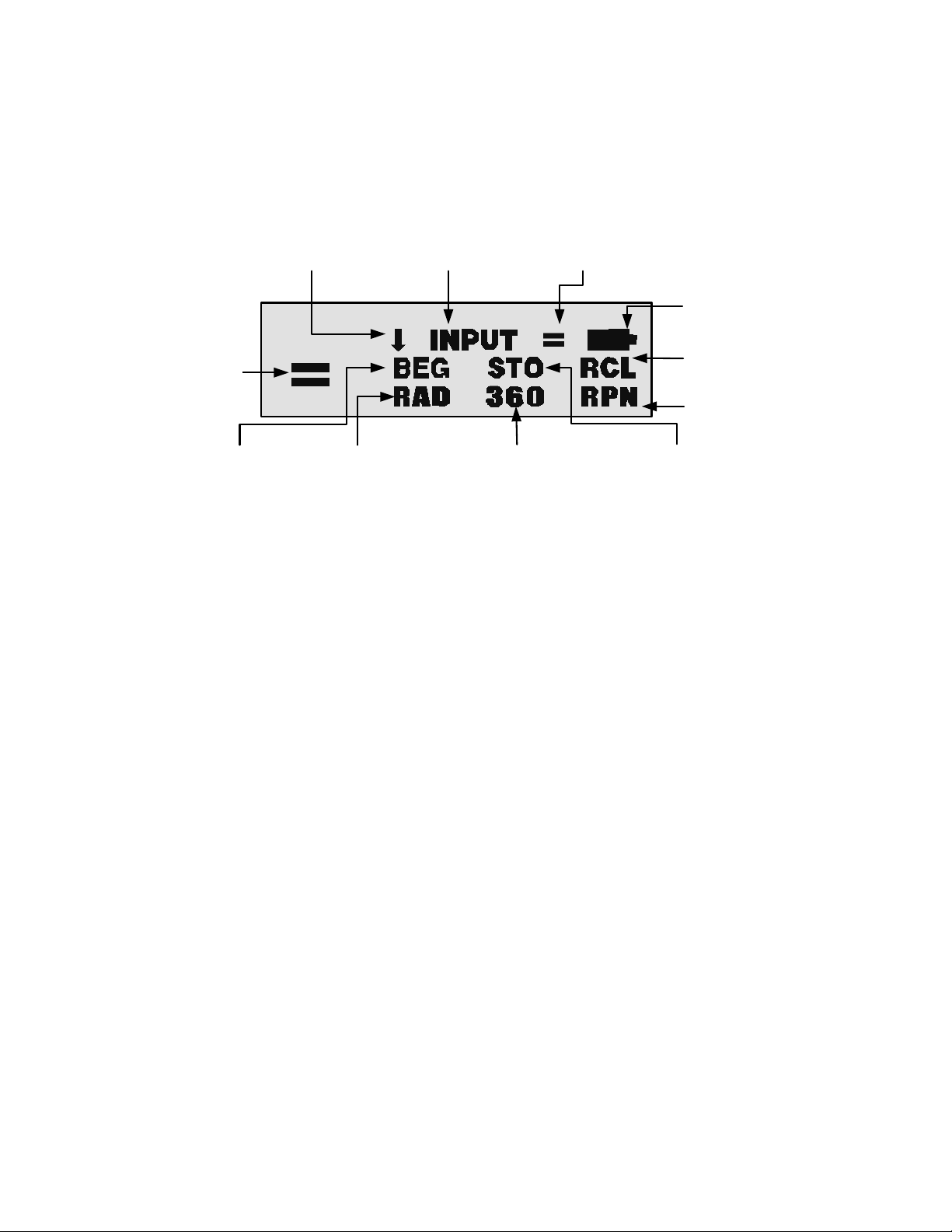
Annunciators ............................................................................................................6
The Input Key ...........................................................................................................6
The Equals Key .........................................................................................................6
Using the Input and Equals Keys .................................................................................6
Editing and Clearing Entries .......................................................................................7
The On/CE Key........................................................................................................7
The Reset Menu ........................................................................................................7
Notes about Special Menus .......................................................................................8
Memory and the Memory Menu..................................................................................8
Accessing Menus and Menu Maps..............................................................................8
2 Mathematical Calculations ..................................................................................... 11
Mathematical Functions ...........................................................................................11
Number Entry and Display.......................................................................................11
Chain Mode...........................................................................................................12
Algebraic Mode .....................................................................................................12
Reverse Polish Notation (RPN) Mode .........................................................................13
The RPN Stack........................................................................................................13
Last Number...........................................................................................................14
One-Number Functions and the Math Menu ...............................................................18
Random number .....................................................................................................19
The Math Menu ......................................................................................................19
The Probability Sub-menu.........................................................................................21
Binomial Functions ..................................................................................................23
Two-Number Functions ............................................................................................23
Storing and Recalling Numbers ................................................................................24
Recall Arithmetic .....................................................................................................24
Storing and Recalling with Time Value of Money (TVM) Keys .......................................24
Recalling a Menu Item Value in a Menu.....................................................................25
Recalling and Storing Values in the Data and Cash Flow Menus...................................25
Rounding Numbers .................................................................................................25
Percentages............................................................................................................25
3 Time Value of Money............................................................................................. 27
Time Value of Money (TVM) Keys..............................................................................27

ii
Amortization.......................................................................................................... 29
Interest Conversion Menu ........................................................................................ 33
4 Canadian Mortgages: TVM Canada........................................................................35
Canadian Mortgage Example.................................................................................. 36
5 Cash Flows ............................................................................................................37
Cash Flow Example ................................................................................................ 38
Sample Cash Flow Diagrams ................................................................................... 46
6 Bonds....................................................................................................................47
The Bond Menu...................................................................................................... 48
7 Black-Scholes Calculation Menu* ............................................................................51
The Black-Scholes Menu ..........................................................................................52
8 Date Calculation ....................................................................................................57
The Date Calculation Menu...................................................................................... 57
9 Break-even ............................................................................................................59
The Break-even Menu..............................................................................................59
10 Business Problems................................................................................................61
The Percent Calculation Menu.................................................................................. 61
11 Depreciation ........................................................................................................65
The Depreciation Menu ........................................................................................... 66
12 Statistical Operations ...........................................................................................69
The Data and Stats Menus ....................................................................................... 70
13 Programming.......................................................................................................75
Programming the HP 30b ........................................................................................ 75
Key Presses for Program Instructions.......................................................................... 75
Programming Example ............................................................................................ 77
Program Step 0...................................................................................................... 78
Reassigning Menu Functions ....................................................................................79
The Program Menu and Program Editing ................................................................... 80
Tests and Jump Functions......................................................................................... 81
Long Programs and Battery Life ................................................................................ 82
Sub-Function Call.................................................................................................... 82
Other Programming Functions .................................................................................. 83
Messages..............................................................................................................84
Debugging a Program.............................................................................................85
Saving, Restoring, and Modifying Mode Settings ....................................................... 86
Solve .................................................................................................................... 87
14 Error Messages ....................................................................................................89
Error Messages and Calculator Status ....................................................................... 89
15 Warranty, Regulatory, and Contact Information ....................................................91
Replacing the Batteries............................................................................................91
HP Limited Hardware Warranty and Customer Care................................................... 91
Contact Information ................................................................................................ 95

Basic Features
1
1Basic Features
Welcome to your new HP Financial Calculator
This manual is designed to familiarize you with the many features available on your new HP
Business and Financial calculators. It includes menu maps, cash flow diagrams, and example
problems and solutions with key presses and screen shots. Also included are sections which
list the error messages, a chapter about programming, and an explanation of how Reverse
Polish Notation (RPN) works. Refer to the Table of Contents for quick access to various topics.
If you need more information about your calculator or calculator operation, please refer to the
training materials available at: www.hp.com/calculators.
This manual describes in detail the features available on both the HP 20b and the HP 30b
calculators. In addition to all of the features found on the HP 20b, the HP 30b includes the
Black-Scholes option pricing model, Modified Internal Rate of Return (MIRR), Financial
Management Rate of Return (FMRR), and programming capabilities. When features apply
only to a particular model, they will be identified throughout the manual with an asterisk*.
Turning the Calculator On and Off
To turn on your calculator, press O. To turn it off, press :a.
Turning the calculator off does not erase any data. The calculator automatically turns itself off
after approximately five minutes to conserve energy. If you see the low battery symbol ( )
in the display, replace the batteries. See the Chapter 15, Warranty, Regulatory, and Contact
Information for instructions on replacing the batteries.
Selecting a Language
English is the default language for messages displayed on the screen. To select a language
other than English:
1. P r e s s
:u to access the Mode menu. FIX displays on the top line of the screen.
2. Press
<
repeatedly until English displays on the screen.
3. Press
I until the desired language is displayed. The displayed language is the
active setting.
4. Press O to return to the default calculator screen.
5. For more information on accessing menus and changing calculator settings, refer to the
section below titled, The Mode Menu: Setting Preferences.
Adjusting the Display Contrast
To adjust the contrast of the display, press and hold O while pressing the + or -
keys. Each press of the + or - keys slightly increases or decreases the contrast of the
display.

Basic Features2
Cursor
When you enter a number, the cursor (_) blinks in the display and indicates you are in number
entry mode.
Two Line Display
There are two lines in the display screen as shown in Figure 1.
Figure 1 Display Screen
The top line of the screen displays operation status, operator symbols, annunciators, and
abbreviations of the variables and menu names. Throughout this manual, this line is referred
to as the top line. In Figure 1, SIN is on the top line. The bottom line displays numbers you
have entered, or results. Throughout this manual, this line is referred to as the bottom line.
When no operations have been entered and no operations are pending, the bottom line of
the screen displays 0.00. This state of the calculator is referred to as the default calculator
screen.
The Mode Menu: Setting Preferences
The Mode menu allows you to customize the calculator. To access the Mode menu, press
:u. Press < or > repeatedly to scroll through the menu starting with FIX=2
(the number of digits displayed to the right of the decimal point). Once an item is displayed,
press I to cycle through the other options for that setting. To exit the Mode menu,
press O. Table 1-1 lists the items in the Mode menu.

Basic Features
3
Table 1-1 Mode Menu Settings
Setting (top line) Description
FIX= 2 Display precision (number of digits displayed to the right of the decimal point).
Default is 2.
Key in the number of digits you want and press I, or press = until the
number of digits you want is displayed.
The display precision can be any number from 0-11. If you specify –1, the calculator
displays numbers with the most appropriate number of digits after the decimal point.
If you find you need to change the FIX setting often, use the following shortcut:
1. P r e s s
: and release it. Check that the secondary function indicator is displayed.
2. Press : again, and, without releasing it, press a key, 0 through 9 that
corresponds to the desired FIX setting. FIX settings for 10 and 11 are not available using
this shortcut. If you press
. instead of a numbered key, FIX= –1 is selected.
Degree or Radian Angular mode in degrees or radians for trigonometric functions.
Default is Degree.
Pressing I toggles between these options.
Date:
mm.ddyyyy or
dd.mmyyyy
Format for dates. December 3, 2010 is entered as 12 .0 32 010 in mm.ddyyyy format, or
3.122010 in dd.mmyyyy format. Note the (.) in both formats separating the first and second
groups. The valid range of dates is October 15, 1582 to December 31, 9999.
Default is mm.ddyyyy format.
Pressing
I toggles between these options.
Note that when a date is displayed, a number between 1 and 7 also displays at the right of
the screen. This number indicates the day of the week corresponding to that date. Monday
is 1, and Sunday is 7.
NOTE: in 360-day calendar mode (Cal.360), days of the week are displayed only if the
date is valid.
1. 23 or 1,2 3 Selects point or comma as decimal separator.
Default is decimal point, 1.23 .
Pressing
I toggles between these options.
1000.00, 1,000.00,
1000,00 or 1.000,00
Selects thousands separator.
Default is none, 1000 .00
Pressing I toggles between these options.
NOTE: the 1000.00 and 1,000.00 options are only available if the decimal separator is
set for point (.); 1000,00 and 1.000,00 are available only if the decimal separator is set
for comma (,).
Chain, Algebraic, or RPN Calculation mode. For more information, refer to Chapter 2, Mathematical Calculations.
Pressing
I cycles through these options.
English, Français,
Deutch, or Español
Language setting for the messages displayed on the screen.
Default is English.
Pressing
I cycles through these options.

Basic Features4
Changing the Calculation Mode
After viewing the default settings, suppose you want to change the calculation mode from
Chain to RPN. See Table 1-2.
Key Presses, the Shift Key, Secondary, and Tertiary Functions*
To execute the function associated with a key, press and release the desired key. However,
most of the calculators’ keys have more than one function: the first, or primary function, the
shifted, or secondary function, and, in some cases, a third, or tertiary function (see Figure 2).
* Tertiary functions do not apply to the HP 20b.
Actual or Cal.360 Calendar options for bonds and date calculations.
Default is Actual.
Pressing I toggles between these options.
Annual or Semiannual Bond type.
Default is Annual.
Pressing
I toggles between these options.
TVM Standard or TVM
Canada
Activate or deactivate the compounding per year (C/YR) option in time value of money
(TVM) calculations. This option is primarily used for Canadian mortgage calculations. See
Chapter 4, Canadian Mortgages: TVM Canada for more information.
Pressing
I toggles between these options.
Table 1-1 Mode Menu Settings
Setting (top line) Description
Table 1-2 Changing the Calculation Mode
Keys Display Description
:u
Opens the Mode menu, starting with first setting
option, FIX, the number of digits displayed to the
right of the decimal point.
<<<
<<
(Press five times)
Scrolls to the current setting for the calculation
mode, Chain.
II
(Press two times)
Selects RPN as the active setting. Note the RPN
annunciator to the right.
O
Exits the Mode menu and returns you to the
default calculator screen.

Basic Features
5
• The primary function is printed on the top of the key.
• The secondary function is printed on the bevel of the key. To activate the secondary function of a key,
press and release
: followed by the key with the secondary function printed on the bevel.
• The third, or tertiary functions are printed above specific keys on the keyboard. To activate the
tertiary function of a key, press and hold
: and simultaneously press the key below the printed
function. Release both keys.
Figure 2 Primary, Secondary, and Tertiary Key Functions
In this manual, key symbols of the commands are provided throughout the manual so you can
follow along with the examples.
• The primary functions are represented by the key symbol with the primary function.
• The secondary key functions are represented by the shift key symbol,
:, followed by the key
with the secondary function. For example, to execute sine, press
:p. Note how the SIN
portion of the key is highlighted, while the
7 is grayed out. This highlighting focuses on the function
of the key that will be activated in a given command.
• Commands with a tertiary function are represented by the shift key symbol,
:, followed by the
term (HOLD), followed by the key with the tertiary function. For example, to activate the Black-Scholes
feature shown above, press
:(HOLD) B*.
When : is active, the down arrow annunciator appears on screen, indicating that the
next key pressed will execute the secondary function of the key. To cancel an accidental press
of :, simply press : a second time.
Key commands for example problems are provided throughout the text and in tables. Key
symbols are placed in the order they are to be pressed, from left to right.
* Does not apply to the HP 20b.
B
Primary
Function
Shifted
(secondary)
Function
Black S
Tertiary function:
(press SHIFT and
the function key
simultaneously)
Basic Features6
Annunciators
Annunciators are symbols that appear in the display as messages, or after certain keys or key
combinations have been pressed. Annunciators are special symbols indicating a specific
status in the calculator. Figure 3 illustrates the annunciator symbols in the display.
Figure 3 Annunciator Symbols in the Screen Display
The Input Key
The I key is used to input values for variables and execute menu items.
The I key is also used in Reverse Polish Notation (RPN) mode to enter a number on
the stack or duplicate it.
The Equals Key
The = key is used at the end of a mathematical operation to calculate the final result. For
example, 1+2= returns a final result of 3.
The
= key, when pressed outside of a mathematical operation, also allows you to request
a calculation for the value of an item. This request only applies to items that can be calculated.
Using the Input and Equals Keys
Suppose you wanted to calculate the effective interest rate for a 12% nominal interest rate with
12 payments per year in the Interest Conversion (IConv) menu. To open the IConv menu, press
:&. Nom %= displays on the top line, and the current value assigned to the nominal
Valid item for the
Input
key
Secondary
function active
Valid item for
the Equals
key
RPN mode
active
Number recall
active
Low batteries
Radians active
Begin mode
active
Number storage
active
360 day-count calendar active
Assigned value

Basic Features
7
interest rate is displayed on the bottom line. With this screen displayed, press
12I to input a new value for the nominal rate. Press < followed by
= to calculate the value for the effective rate. See Figure 4.
Figure 4
When an item for which the = key is valid displays, the small annunciator (=) is displayed
on the top line at the right of the screen. Do not confuse this small annunciator (=) with the
larger annunciator (
=
) found to the right of a variable.
When an item for which the I key is valid displays, the INPUT annunciator is
displayed on the top line at the right of the screen.
Editing and Clearing Entries
The On/CE Key
Pressing O one time cancels current number entries, mathematical operations, or a menu
selection, in that order.
Pressing O repeatedly when performing multiple operations cancels one operation at a
time, from the latest to the earliest.
The Reset Menu
The Reset menu allows you to reset some, or all, of the menu items, variables, and registers to
their default values.
To open the Reset menu, press :x. TVM displays on the top line. Press < or >
repeatedly to scroll to a specific item. To validate a choice and reset the selected items, press
I. Press O to cancel. If you select the command to reset the cash flow (Cash Flow),
statistics (Stats ), programs (Prgm)* or all values (All ) items, you will be prompted to confirm
your choice. At the Del. All?, Del. Data?, Del. Prgm?*, and Del. CF? prompts, press
I
again to confirm the reset, or
O to cancel. While working within a specific menu, pressing
:x takes you directly to the item of the Reset menu that allows you to reset that specific
menu. For example, if you are working in the Bond menu and you wish to reset all your entries
in the Bond menu, with any item of the Bond menu displayed, press
:x. Bond displays
on screen. At this prompt, pressing
I resets the Bond menu and returns you to the last
item you were working with in the Bond menu.
* Only applies to the HP 30b.

Basic Features8
Notes about Special Menus
The Mode, Memory, Math and Reset menus are unique menus; they allow you to work in
another menu simultaneously without having to exit. For example, if you were working in the
Bond menu prior to entering one of these menus, pressing O to exit returns you to your
previous work in the Bond menu.
Memory and the Memory Menu
The Memory menu contains the following items: memories 1–9 (Mem 1–9) and 0 (Mem 0),
Cash Flow, Statistics (Stats), programs (Prgm)*, and Memory. To enter the menu, press
:t. Press < or > repeatedly to scroll through the items starting with
memory 1 (Mem 1).
When a memory item is displayed, you can key in a new number and modify the value of
the memory by pressing
I.
For more information about storing and recalling numbers, refer to the section titled, Storing
and Recalling Numbers in Chapter 2.
The Cash Flow and Statistics data share the same memory and are limited to a combined total
of 50 memory slots. The number displayed with Memory refers to the number of remaining
memory slots. When the cash flow or statistics items are displayed, a number also appears
on the bottom line. This number indicates the number of memory slots used by the cash flow
or statistical data.
290 bytes are available for programs. The Prgm* menu item displays the number of bytes
used.
Press I on the Cash Flow, Statistic, or Prgm* menu item to erase the associated data.
Since entering data in these menus can represent a significant amount of work, you will be
asked to confirm your choice. At the Del.Data?, Del. Prgm?*, or Del.CF? prompts, press
I to confirm, or O to cancel.
Accessing Menus and Menu Maps
Many of the calculator's functions are located within menus. To access a menu, press the key,
or secondary-function, key combination for the menu in which you wish to work. To exit a
menu, press
O.
For example, to access the Break-even menu, press : .
* Only applies to the HP 30b.
Basic Features
9
Once opened, you can scroll through the items in the menu by pressing < or >
repeatedly. In most menus, when you arrive at the last item in a menu, pressing < returns
you to the first item. Similarly, pressing > once on the first menu item scrolls to the last
item in the menu.
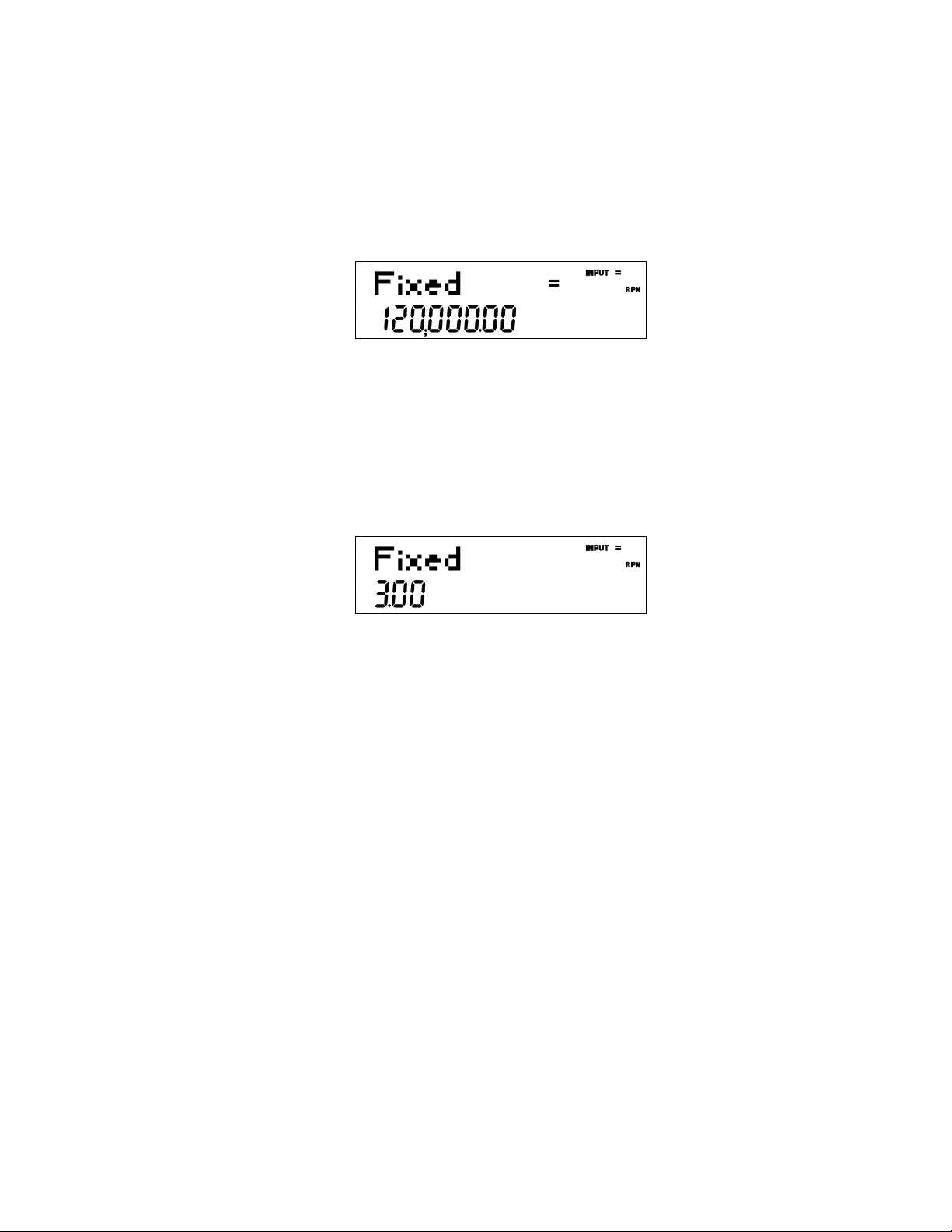
Most items consist of two parts: a name and an associated number. For example, the Fixed
item in the Break-even menu (Figure 7) is displayed in Figure 5.
Figure 5
The large (=) annunciator shows that the value assigned to Fixed is 120,000. For example, if
you perform a calculation with the operating mode set to RPN with this item displayed by
pressing 1I2+, Fixed is still selected as the current item, but the large
(=) annunciator is now turned off, indicating that the 3 is not the value assigned to Fixed (see
Figure 6).
Figure 6
At this point, to return to the display of the Fixed menu item shown in Figure 5, press O.
Some menus have sub-menus. If an item represents a sub-menu, pressing I with that
menu item displayed opens the sub-menu. Once the menu sub-menu is open, use
> and
< to navigate through the items of the sub-menu, unless otherwise directed.
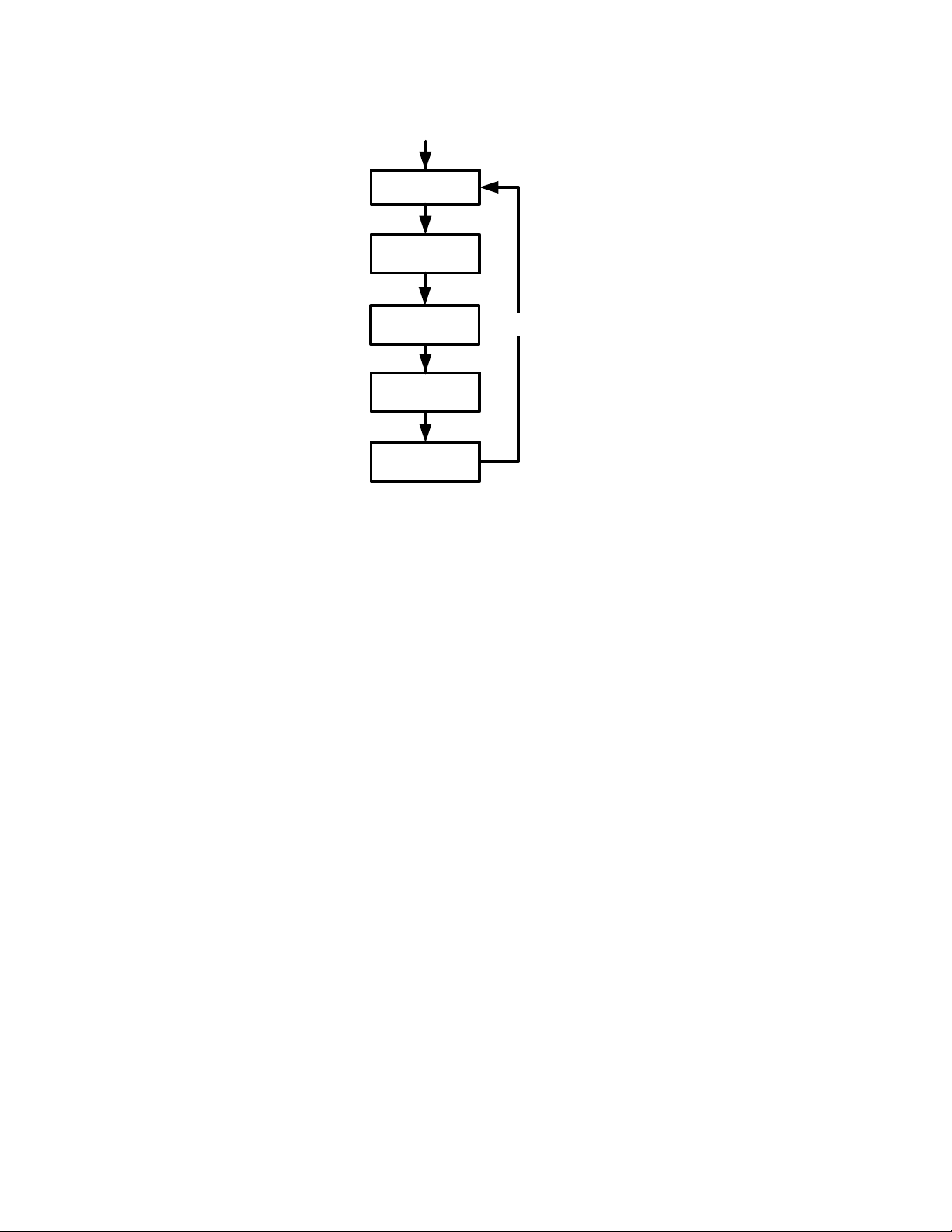
In this manual, diagrams called Menu Maps are included at the beginning of each section to
assist you with navigating through the menus described in that section. For an example of a
menu map, see Figure 7 below. Once opened, use the
> and < keys to navigate
through the menu items of the Break-even menu. The downward arrows in the map indicate
you press
< to scroll to the next item. If a press of the I key is required to open
a sub-menu, the word INPUT appears in the arrow(s). For examples of menu maps with sub-
menus, see chapters 10-12. The return arrows direct you to the next item displayed after the
last item in a menu. For example, in Figure 7, pressing
< on the last item in the menu
returns you to the FIXED item.
Basic Features10
Figure 7 Menu Map of the Break-even menu
There are four types of menu items:
1. Read/write. Read/write menu items, such as Fixed in the Break-even menu shown
above, are easily recognizable, because when they are selected, both the INPUT and
small (=) annunciators are lit. When lit, these annunciators indicate that keying in a
number and pressing I will store the entered number in the displayed menu
item. Pressing = (outside of a mathematical operation) calculates the value for that
item based on available data.
2. Read-only. Read-only items such as Internal Rate of Return (IRR% ) in the IRR menu are
display-only; they are values computed internally by the calculator.
3. Write-only. Write-only items, such as investment interest rate (Inv. I% ) in the Net Present
Value (NPV) menu, are similar to read/write items in that the INPUT annunciator is lit
when these items are selected, indicating that keying in a number and pressing
I stores that number in that menu item. However, the = key does not
calculate a value for that item.
4. Special items. Special items, such as the Degree/Radian option in the Mode menu, the
items of the Reset menu, and the items of the Percent Calculation (%calc ) menu perform
an action when I is pressed. Depending on the menu, this action can be the
selection of a sub-menu (%calc), changing a mode or setting (Mode menu), or erasing
data (Reset menu)
:P
Fixed
DWN
Cost
Price
Profit
Quantity

Mathematical Calculations
11
2 Mathematical Calculations
Mathematical Functions
Mathematical functions are located:
• On keys, such as, +-*/, etc.
• On shifted, or secondary functions, such as,
:p
• In the Math menu, :s
Number Entry and Display
Numbers are entered by pressing:
• Numbered keys, 0–9
• The decimal point .
•The } key
•The
:w keys
To correct a number entry, press the backspace key, {. Each press of { erases the last
digit or symbol you entered.
To enter a number in the display, press the number digits successively. A number can have up
to 12 digits.
To change the sign of a number from positive to negative, press }.
Use scientific notation to enter very large and very small numbers. For example, to enter the
number 1.23x 10
127
in scientific notation, first enter the mantissa (1.2 3) and then press
:w and enter the number (127 ) representing the exponent. The exponent must have a
value between –499 and +499. If an expression has more than 12 digits, or if an operation
returns a result with more than 12 digits, the calculator automatically displays scientific
notation.
Figure 1 Scientific Notation in FIX=2 Mode
Mathematical Calculations12
Chain Mode
Calculations in Chain mode are interpreted in the order in which they are entered. For
example, entering the following numbers and operations as written from left to right,
1+2*3=, returns 9. See Figure 2.
Figure 2 Calculation in Chain Mode
NOTE: if you press an operator key, +-*/, after =, the calculation is
continued using the currently displayed value.
In Chain mode, if you wish to override the left to right order of entry, use parentheses
(D to prioritize operations.
For example, to calculate 1 + (2 x 3), you may enter the problem as written from left to right,
with parentheses to prioritize the multiplication operation. See Table 2-1 below.
Algebraic Mode
To set the calculator in Algebraic mode, refer to the section titled, The Mode Menu: Setting
Preferences in Chapter 1.
In Algebraic mode, multiplication and division have a higher priority than addition and
subtraction. For example, in Algebraic mode, pressing
1+2*3=
returns a result of 7.0 0. In Chain mode, the same key presses return a result of 9.00.
In Algebraic mode, operations between two numbers have the following priority:
• Highest priority: the power function ( y
x
)
• Second priority: combinations and permutations
• Third priority: multiplication and division
• Lowest priority: addition and subtraction
Table 2-1 Simple Arithmetic Calculations in Chain Mode
Keys Display Description
1+
(2*3D
Sets operational priority, inputs numbers,
and multiplies 2 and 3.
=
Adds 1 to 6 and returns 7.0 0 on the bottom
line as the final result.
Mathematical Calculations
13
For example, key in 1 + 2 x 5 nPr 2
2
in Algebraic mode by pressing:
1+2*5:b2:m=. The result is 241.
NOTE: the calculator is limited to 12 pending operations. An operation is pending when it
is waiting for the input of a number or the result of an operation of higher priority.
Reverse Polish Notation (RPN) Mode
To set the calculator in RPN mode, refer to the section titled, The Mode Menu: Setting
Preferences in Chapter 1. In RPN mode, numbers are keyed in first, separated by pressing
I or =, followed by an operation key.
NOTE: pressing I or = is optional after keying in a number, if the next key
pressed is an operation.
Each time you press an operation or function key in RPN, the answer is calculated immediately
and displayed. For example, suppose you wanted to add two numbers in RPN, 1 and 2. Press
1I2+. The result, 3.00, is calculated and displayed immediately on the
bottom line along with the (+) symbol on the top line.
NOTE: in RPN mode, when you are in a menu for which I or = are valid,
pressing these keys enters the number, but it also performs the action associated with the key
for the menu item, which is generally saving the number in the variable or calculating the
item's value.
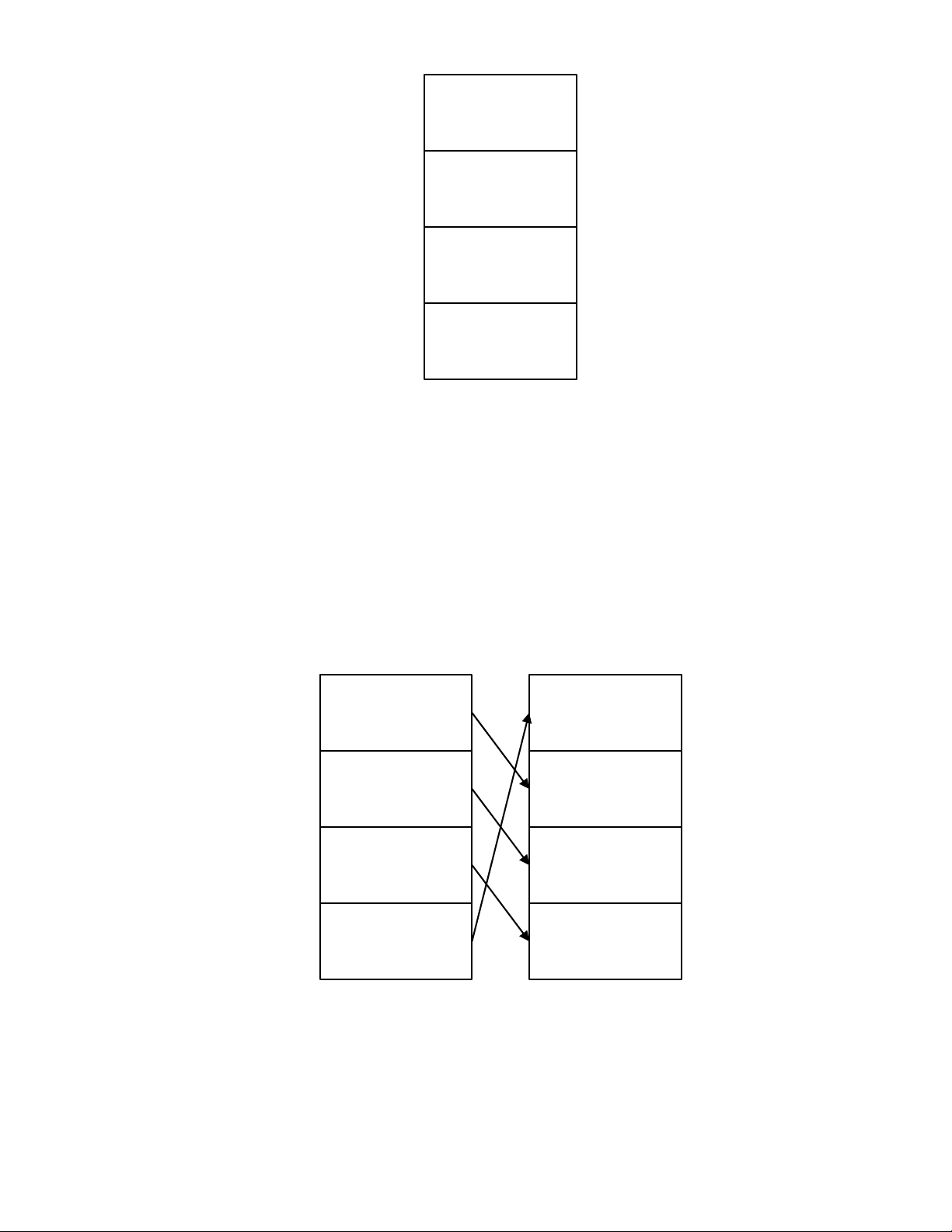
The RPN Stack
RPN works by placing numbers in storage registers called the stack. The RPN stack has four
levels numbered 1– 4. The levels are stacked on top of one another. See Figure 3.
Figure 3 The RPN Stack
Stack Level 4
Stack Level 1
Stack Level 3
-15
12
Stack Level 2 41
23
Mathematical Calculations14
In Figure 3, the stack contains four numbers, 23, 41, 12, and –15. Each level (1– 4) contains
one number. When a number is typed and entered into the stack by pressing I, this
new number is "pushed" into level one of the stack, and each number already in the stack
moves up one level. The number in Level 4, –15, is pushed out and is lost.
When an operation is performed on the stack, addition
(+) for instance, the calculator
"pops" or moves the two numbers from the bottom levels (Levels 1 and 2) out of the stack,
performs the operation, and "pushes" the results back into the stack.
With the numbers entered into the stack as shown in Figure 3, pressing
+ changes the
stack as shown in Figure 4. Note that when the numbers are "popped" out to add 23 and 41,
Level 4 of the stack remains unchanged.
Figure 4 The RPN Stack of Figure 3 Shown After the Addition Operation
Last Number
Each time you perform a mathematical operation, the content of Level 1 of the stack is saved.
Pressing
:d recalls that number. This functionality can be used to undo an erroneous
key press, or if you want to reuse a number, such as 56.123 in the expression:
See Table 2-2 for an example using the last number function.
-15
-15
12
64
1.23 56.123+()
56.123()
--------------------------------------
Mathematical Calculations
15
For more complex problems requiring two or more operations, you do not need to enter
parentheses to set operational priority. Key in numbers and operations inside the parentheses
first, followed by those outside of the parentheses. If a problem has more than one set of
parentheses, start by working with the operations and numbers in the innermost parentheses
and work out. For example, calculate:
(3 + 4) x (5 + 6)
One way to calculate this problem is to key in the numbers and operations within the
parentheses first, followed by the operation outside of the parentheses. See Table 2-3.
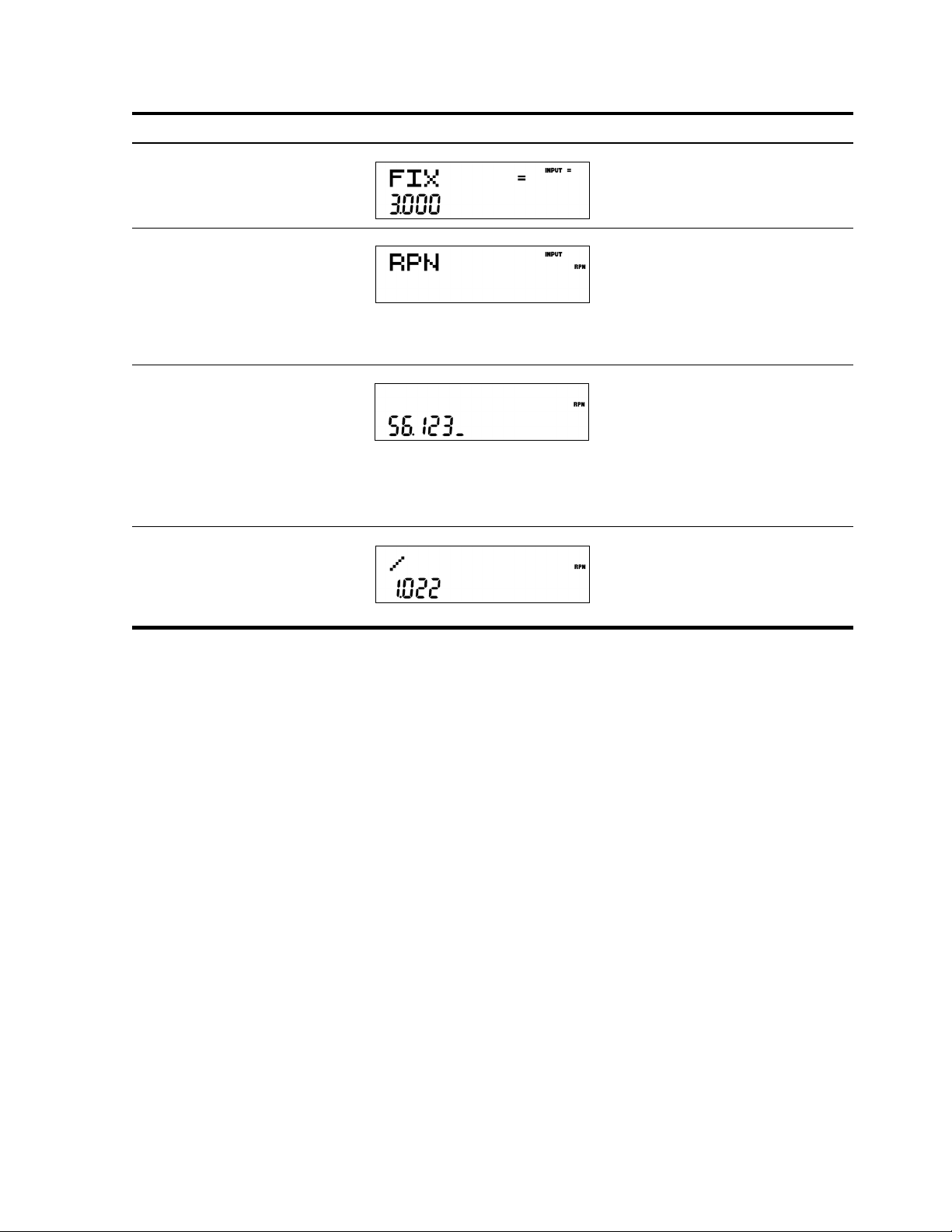
Table 2-2 Last Number
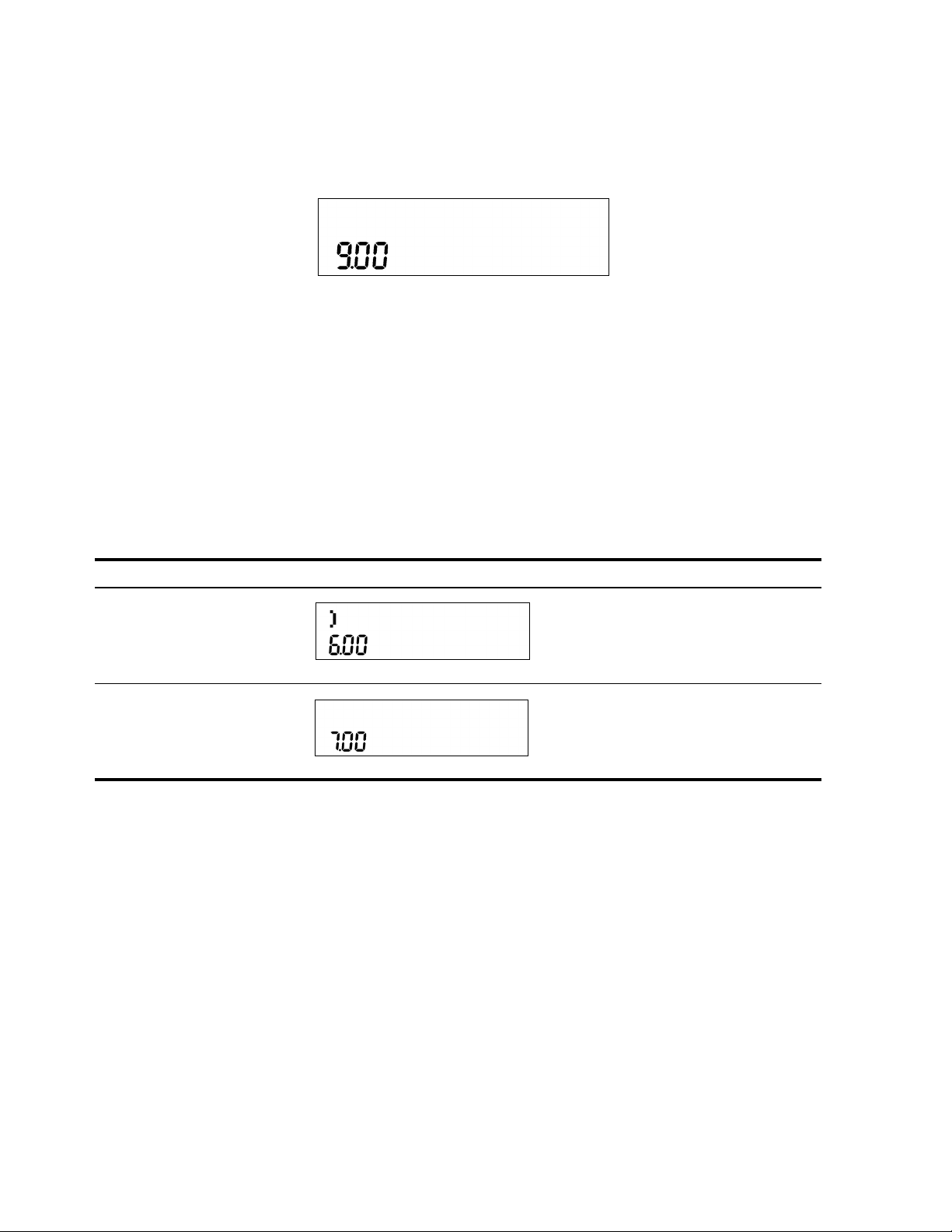
Keys Display Description
:u3I
Sets FIX= to 3.000
<<<<
<
II
Selects RPN as the operating mode.
O1c23
I56c
1
23
Inputs 1.23 and 56.123
+:d/
Adds 1.23 and 56.123, then divides
the sum by the last number, 56.123.
Returns results in the selected display
format.
Mathematical Calculations16
Pressing I or = when you are not entering a number duplicates the number on
Level 1. That is, the number on Level 1 is pushed on the stack, making Levels 1 and 2 equal.
In the example above, pressing
I after * duplicates 77 on the stack, making
Levels 1 and 2 equal. See Figure 5.
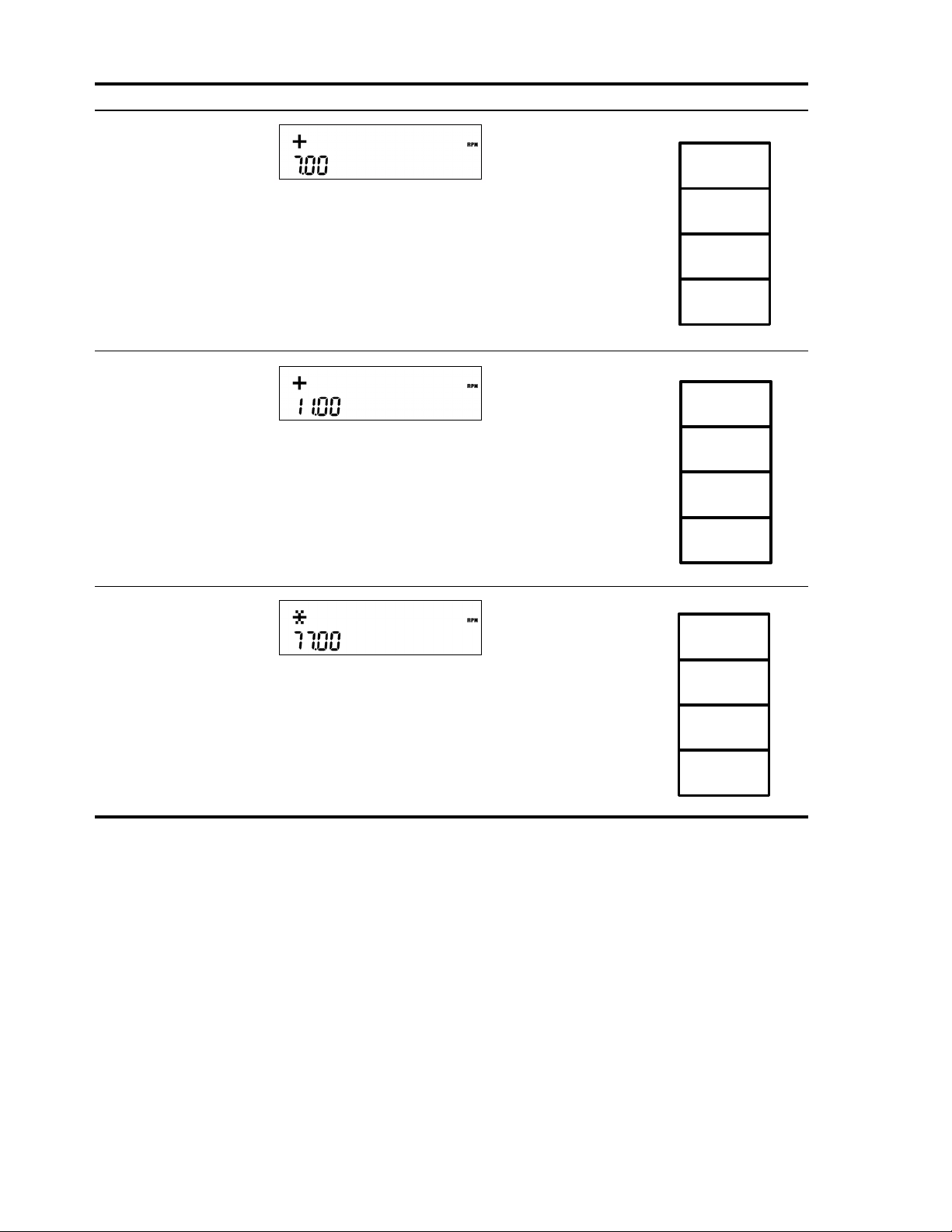
Table 2-3 Simple Arithmetic Calculations in RPN Mode
Keys Display Description RPN Stack
3I4
+
Inputs the numbers and the
operation in the first set of
parentheses. Intermediate
results are displayed. Note
the (+) and (RPN)
annunciators.
5I6
+
Inputs the numbers and the
operation in the second set
of parentheses.
Intermediate results are
displayed. Note the (+)
annunciator.
*
Finishes the operation and
displays the results.
Previous
Value
Previous
Value
Previous
Value
7
Previous
Value
Previous
Value
7
11
Previous
Value
Previous
Value
Previous
Value
77
Mathematical Calculations
17
Figure 5 Duplicating a Number on the Stack
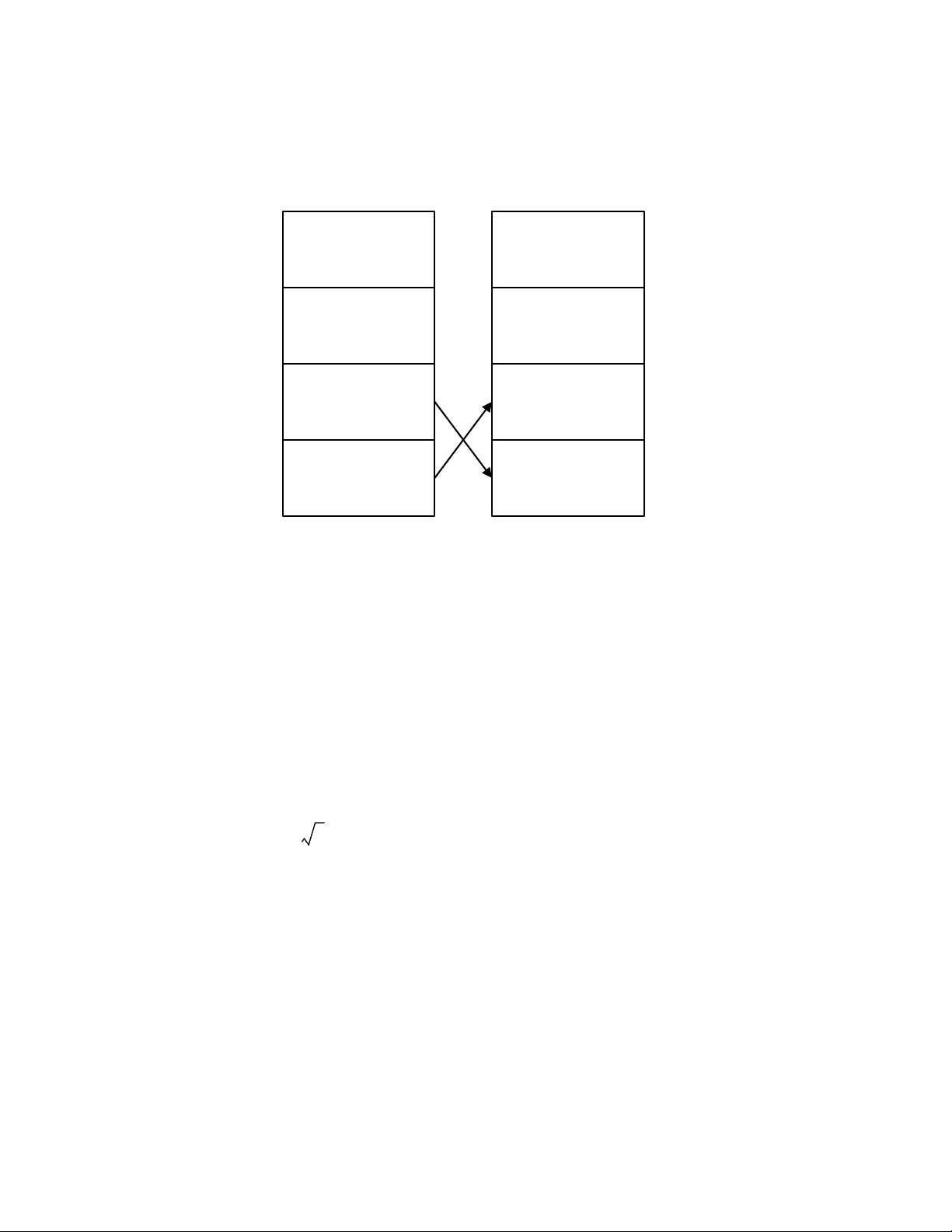
In RPN, the parentheses keys (D manipulate the stack. Pressing ( performs a roll
down of the stack. A roll down causes the stack to roll towards the bottom of the stack, during
which the number in Level 2 to moves down to Level 1, the number in Level 3 to moves down
to Level 2, the number in Level 4 to moves down to Level 3, and the number of Level 1 to moves
up to Level 4. The ( key has a small down arrow on it to indicate the roll down feature.
With the numbers entered into the stack shown in the left column in Figure 6, pressing (
performs the roll down of the stack shown in the right column.
Figure 6 The RPN Stack and the Roll Down Operation
Previous Value
Previous Value
77
77
-15
12
41
23
23
-15
12
41
Mathematical Calculations18
Pressing D performs a swap. A swap operation exchanges the numbers on Levels 1 and 2
of the stack. The
D key has a small symbol to the right of the parenthesis symbol to indicate
the swap feature. With the numbers entered into the stack shown in the left column in Figure 7,
pressing D performs a swap to the stack as shown in the right column.
Figure 7 The RPN Stack and the Swap Operation
NOTE: when no menu is selected, the < key performs the same function as the ( key.
The > key performs the inverse operation called, roll up.
One-Number Functions and the Math Menu
The key presses for the one-number mathematical functions listed in Table 2-4 below apply to
all modes, Chain, Algebraic, and RPN. To execute one-number functions, with a number
displayed, press the key or key combination corresponding to the operation you wish to
execute. The result is displayed on the bottom line.
For example, to calculate , press 6:n. The result of 2.45 is calculated
immediately and displayed on the bottom line. Note the square root symbol appears on the
top line.
NOTE: before doing any trigonometric calculations in the Math menu, check whether the
angle mode is set for degrees (Degree) or radians (Radian). You will need to change the
setting if the active mode is not what your problem requires. For more information on the
Mode menu and calculator settings, refer to the section titled, The Mode Menu: Setting
Preferences in Chapter 1. Table 2-4 lists one-number functions along with their corresponding
keys.
-15
-15
23
41
-15
12
41
23
6

Mathematical Calculations
19
Random number
Press :f to generate a randomly distributed number between 0 and 1.
Type a number and press
:$:f to store a new seed for random number
generation.
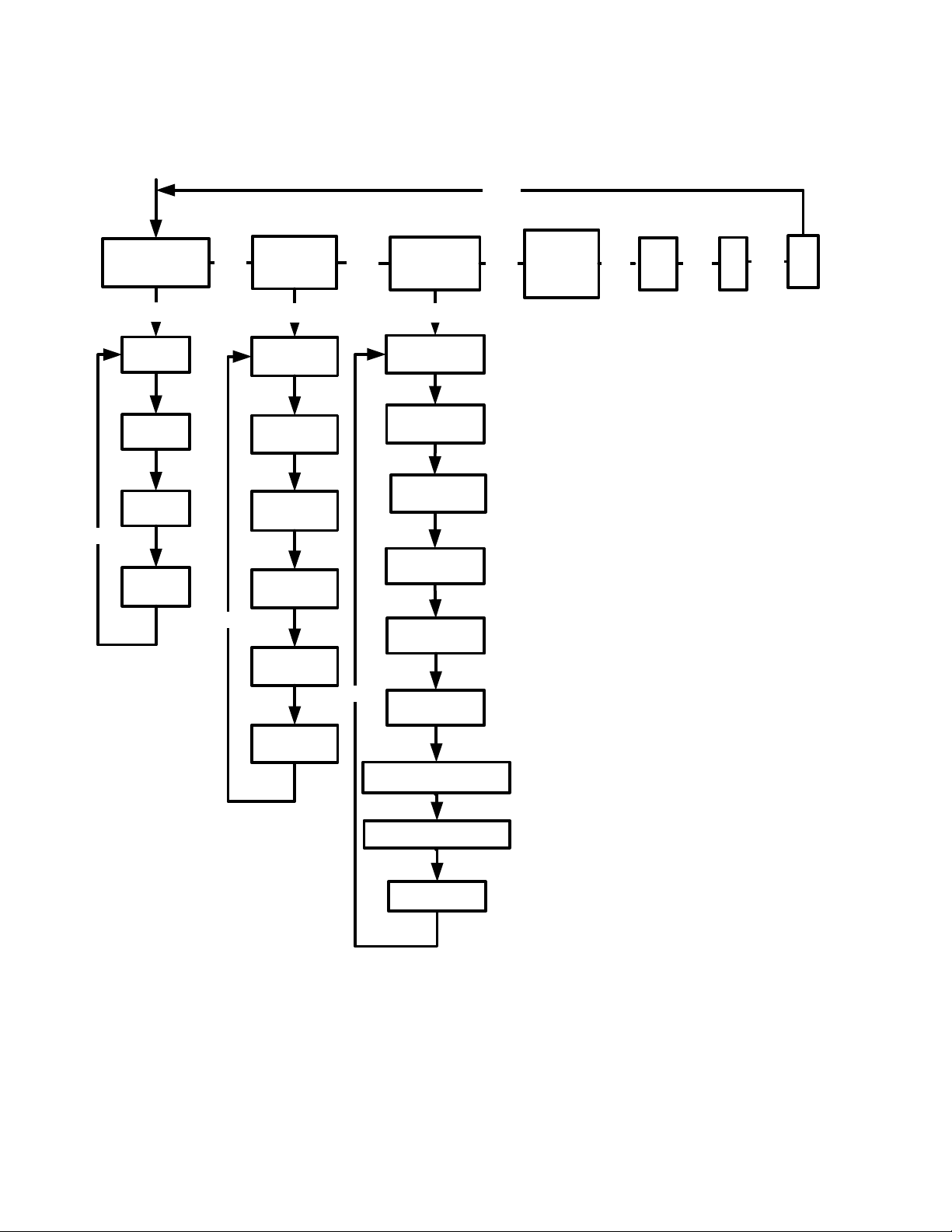
The Math Menu
There are additional functions available in the Math menu. To open the Math menu, press
:s. See Figure 8 for the menu map of the Math menu.
Table 2-4 Shifted Function Mathematical Operations
Keys Description
:p
Calculates sine.
:q
Calculates cosine.
:r
Calculates tangent.
:k
Calculates natural log.
:l
Calculates natural exponent to the power of x.
:m
Calculates square of x.
:n
Calculates square root.
:f
Executes the Random function. Returns a random number in the range 0
<
x
<
1.
:g
Calculates factorial of x (where –253
<
x
<
253). The Gamma function is used to
calculate x! for non-integers or negative numbers.
:i
Calculates the reciprocal.
:d
In Chain or Algebraic mode, recalls the result of the last operation. In RPN mode,
returns the content of the Last Number variable.
:e
Rounds x to the number specified by the display format.
Mathematical Calculations20
Figure 8 The Menu Map for the Math Menu
Press < to scroll through the menu items, starting with Trigonometry. The Trigonometry,
Hyperbolic, and Probability items have sub-menus. Press
I on any of these items to
access the functions within the sub menus. Press < to scroll through the functions.
* IP and FP functions are not available on the HP 20b.
DWN
DWN
INPUT
:s
Trigonometry
Hyperbolic
Probability
ABS
(Absolute
Value)
PI
SIN
-1
SINH
COSH
TANH
LTND
LTND
-1
LOG
INPUT
DWN
COS
-1
DWN
TAN
-1
TANH
-1
SINH
-1
COSH
-1
DWN
DWN
INPUT
DWN
Student
Student
-1
Chi
2
Chi
2-1
F—Distribution
F
-1
—Distribution
DWN
Binomial
IP
*
DWN
FP
*
DWN

Mathematical Calculations
21
Press O to cancel the Math menu and return to current work. Press :s to return
to the top of the Math menu.
For example, using the math menu calculate Sin
–1
(0.5), see Table 2-5.
In the Math menu, PI does not perform calculations; it enters PI for calculations. You may start
an operation, use the Math menu to execute a function, and continue calculating with your
original operation without losing your work.
The Probability Sub-menu
Lower Tail Normal Distribution (LTND) calculates the probability for a normally distributed,
random variable to be less than the input.
Inverse Lower Tail Normal Distribution (LTND
-1
) is the inverse function for LTND; it calculates
the value (V) for which the probability of a normally distributed, random variable to be less
than V is the given input. Student, Inverse Student, Chi
2
(
2
), Inverse Chi
2
, F-Distribution and
Inverse F-Distribution perform similar operations for Student, Chi
2
, and F-Distributions.
Student, Chi
2
, and F-Distribution and their inverse operations are special cases, as they
require more than one number as input. Student and Chi
2
require (N), the number of degrees
of freedom, and F-Distribution requires (N1) and (N2), two degrees of freedom.
To perform Student and Chi
2
operations or their inverse:
1. Enter the number of degree(s) of freedom by typing the number and pressing I
or =.
2. Type the number for which you want to calculate the probability, or, for the inverse, the
probability for which you want the number.
3. Navigate to the appropriate function in the Probability sub-menu of the Math menu.
To perform F-Distribution operations or their inverse:
Table 2-5 Math Menu Example
Keys Display Description
.5I
:s
Enters 0.5 and opens the Math menu starting
with Trigonometry.
I<
Selects the Trigonometry sub-menu and scrolls to
Sin
-1
. Note the value for Sin
-1
is calculated
immediately and displayed.
I or =
Validates the result.
χ
Mathematical Calculations22
1. Enter the two degrees of freedom by typing each number followed by I or
=.
2. Type the number for which you want to calculate the probability, or, for the inverse, the
probability for which you want the number.
3. Navigate to the appropriate function in the Probability sub-menu of the Math menu. See
Table 2-6. Note: the examples below are calculated with Chain set as the operating
mode.
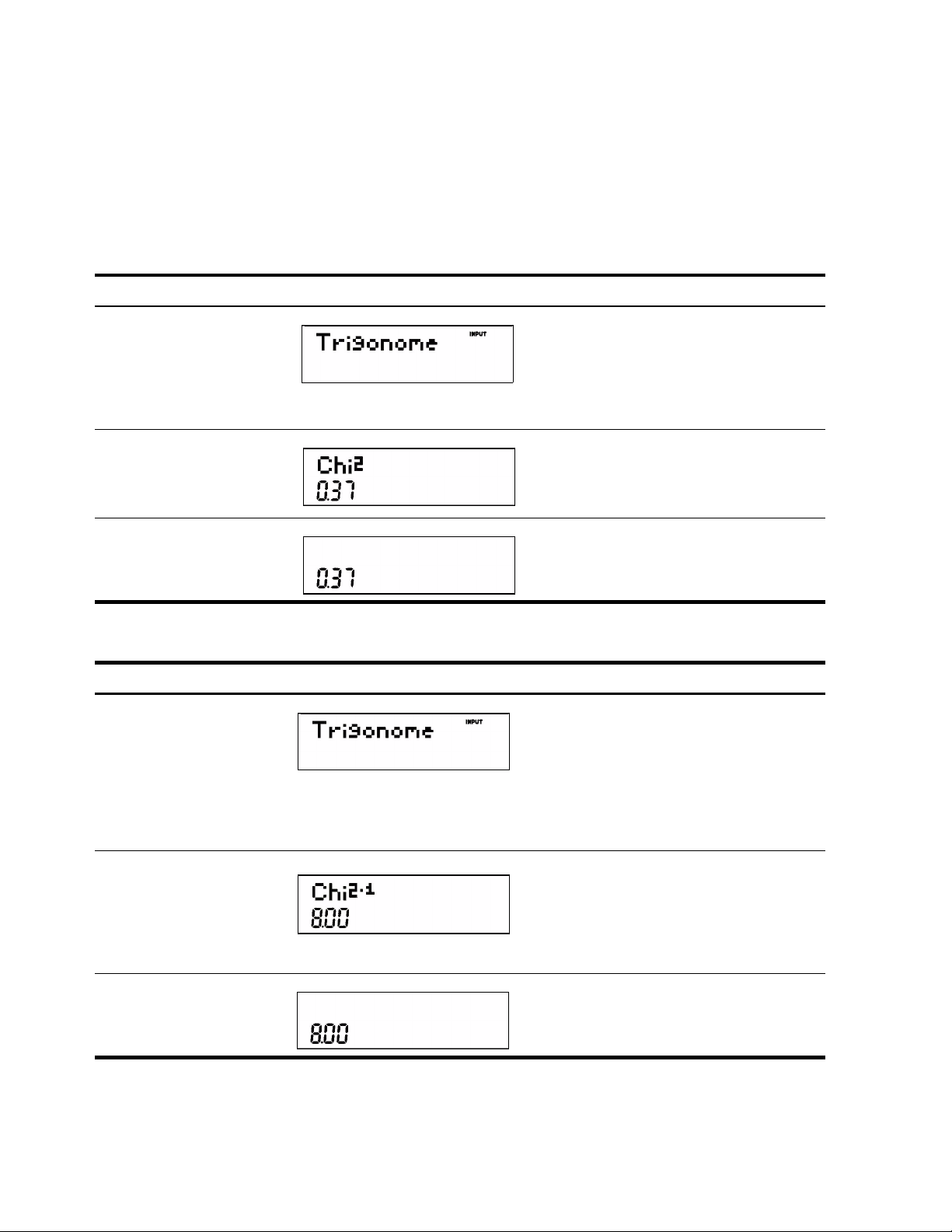
Table 2-6 Probability Example
Keys Display Description
10I
8I
:s
Enters 10 degrees of freedom and the number
for which probability is to be calculated.
Opens the Math menu.
<<I
<<<<
Selects the Probability menu item and scrolls to
Chi
2.
.
I or =
Validates the result.
Table 2-7 Inverse Probability Example
Keys Display Description
10I
0.37
12I
:s
Enters 10 degrees of freedom and the
probability. Opens the Math menu.
<<I
<<<<
<
Selects the Probability menu item. Scrolls to
Chi
2-1
.
I or =
Validates the result.
 Loading...
Loading...