HP 260 G1 Mini Maintenance and Service Guide

Maintenance and Service Guide
HP 260 G1 Desktop Mini PC
© Copyright 2015 Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P. The information contained herein is subject to change without notice.
Intel and Pentium are trademarks of Intel Corporation in the U.S. and other countries. Bluetooth is a trademark owned by its proprietor and used by Hewlett-Packard Company under license. Microsoft, Windows, Windows 7, and Windows 8.1 are U.S. registered trademarks of the Microsoft group of companies. SD Logo is a trademark of its proprietor.
The only warranties for HP products and services are set forth in the express warranty statements accompanying such products and services. Nothing herein should be construed as constituting an additional warranty. HP shall not be liable for technical or editorial errors or omissions contained herein.
This document contains proprietary information that is protected by copyright. No part of this document may be photocopied, reproduced, or translated to another language without the prior written consent of HewlettPackard Company.
First Edition (February 2015)
Document Part Number: 790975-001
Product notice
This guide describes features that are common to most models. Some features may not be available on your computer.
Not all features are available on all editions of Windows 8.1. This computer may require upgraded and/or separately purchased hardware, drivers, and/or software to take full advantage of Windows 8.1 functionality. See http://www.microsoft.com for details.
This computer may require upgraded and/ or separately purchased hardware and/or a DVD drive to install the Windows 7 software and take full advantage of Windows 7 functionality. See http://windows.microsoft.com/en-us/ windows7/get-know-windows-7 for details.

Safety warning notice
 WARNING! To reduce the possibility of heat-related injuries or of overheating the device, do not place
WARNING! To reduce the possibility of heat-related injuries or of overheating the device, do not place
the device directly on your lap or obstruct the device air vents. Use the device only on a hard, flat surface. Do not allow another hard surface, such as an adjoining optional printer, or a soft surface, such as pillows or rugs or clothing, to block airflow. Also, do not allow the AC adapter to contact the skin or a soft surface, such as pillows or rugs or clothing, during operation. The device and the AC adapter comply with the useraccessible surface temperature limits defined by the International Standard for Safety of Information Technology Equipment (IEC 60950).
iii
iv Safety warning notice

Table of contents
1 Product features ........................................................................................................................................... |
1 |
Standard configuration features ........................................................................................................................... |
1 |
Front panel components ....................................................................................................................................... |
2 |
Rear panel components ......................................................................................................................................... |
3 |
Serial number location .......................................................................................................................................... |
4 |
2 Illustrated parts catalog ................................................................................................................................ |
5 |
Chassis spare parts ................................................................................................................................................ |
5 |
Computer major components ............................................................................................................. |
5 |
Drives ................................................................................................................................................... |
7 |
Misc parts ............................................................................................................................................. |
8 |
3 Routine care, SATA drive guidelines, and disassembly preparation .................................................................. |
10 |
Electrostatic discharge information ................................................................................................................... |
10 |
Generating static ............................................................................................................................... |
10 |
Preventing electrostatic damage to equipment .............................................................................. |
11 |
Personal grounding methods and equipment .................................................................................. |
11 |
Grounding the work area .................................................................................................................. |
11 |
Recommended materials and equipment ........................................................................................ |
12 |
Operating guidelines ........................................................................................................................................... |
12 |
Routine care ......................................................................................................................................................... |
13 |
General cleaning safety precautions ................................................................................................ |
13 |
Cleaning the Computer Case ............................................................................................................. |
13 |
Cleaning the keyboard ...................................................................................................................... |
13 |
Cleaning the monitor ......................................................................................................................... |
14 |
Cleaning the mouse ........................................................................................................................... |
14 |
Service considerations ........................................................................................................................................ |
14 |
Tools and software requirements .................................................................................................... |
14 |
Screws ............................................................................................................................................... |
14 |
Cables and connectors ...................................................................................................................... |
14 |
Hard Drives ........................................................................................................................................ |
15 |
Lithium coin cell battery ................................................................................................................... |
15 |
SATA hard drives .................................................................................................................................................. |
16 |
SATA hard drive cables ........................................................................................................................................ |
16 |
SATA data cable ................................................................................................................................. |
16 |
SMART ATA drives ................................................................................................................................................ |
16 |
v
Cable management .............................................................................................................................................. |
16 |
4 Removal and replacement procedures ........................................................................................................... |
17 |
Preparation for disassembly ............................................................................................................................... |
17 |
Access panel ........................................................................................................................................................ |
18 |
Hard drive ............................................................................................................................................................ |
19 |
Memory ................................................................................................................................................................ |
21 |
SODIMMs ............................................................................................................................................ |
21 |
DDR3L-SDRAM SODIMMs .................................................................................................................. |
21 |
Populating SODIMM sockets ............................................................................................................. |
22 |
Replacing SODIMMs ........................................................................................................................... |
23 |
Replacing the battery .......................................................................................................................................... |
26 |
Speaker ................................................................................................................................................................ |
28 |
Fan ....................................................................................................................................................................... |
30 |
Heat sink .............................................................................................................................................................. |
31 |
Drive cage and drive cable ................................................................................................................................... |
32 |
WLAN module ...................................................................................................................................................... |
35 |
M.2 solid-state drive ............................................................................................................................................ |
37 |
System board ....................................................................................................................................................... |
39 |
System board callouts ...................................................................................................................... |
42 |
WLAN antennas .................................................................................................................................................... |
43 |
Changing from desktop to tower configuration ................................................................................................. |
46 |
5 Computer Setup (F10) Utility ........................................................................................................................ |
47 |
Computer Setup (F10) Utilities ............................................................................................................................ |
47 |
Using Computer Setup (F10) Utilities ............................................................................................... |
48 |
Computer Setup—File ...................................................................................................................... |
49 |
Computer Setup—Storage ............................................................................................................... |
50 |
Computer Setup—Security ............................................................................................................... |
51 |
Computer Setup—Power .................................................................................................................. |
53 |
Computer Setup—Advanced ............................................................................................................ |
53 |
Recovering the Configuration Settings ............................................................................................................... |
54 |
6 Troubleshooting without diagnostics ............................................................................................................ |
55 |
Safety and comfort .............................................................................................................................................. |
55 |
Before you call for technical support .................................................................................................................. |
55 |
Helpful hints ........................................................................................................................................................ |
56 |
Solving general problems ................................................................................................................................... |
57 |
Solving hard drive problems ............................................................................................................................... |
60 |
Solving display problems .................................................................................................................................... |
62 |
vi
Solving audio problems ....................................................................................................................................... |
66 |
Solving printer problems ..................................................................................................................................... |
68 |
Solving keyboard and mouse problems ............................................................................................................. |
69 |
Solving Hardware Installation Problems ............................................................................................................ |
70 |
Solving Network Problems .................................................................................................................................. |
72 |
Solving memory problems .................................................................................................................................. |
75 |
Solving USB flash drive problems ....................................................................................................................... |
76 |
Solving Internet access problems ....................................................................................................................... |
77 |
Solving software problems ................................................................................................................................. |
78 |
7 POST error messages ................................................................................................................................... |
80 |
POST numeric codes and text messages ............................................................................................................ |
80 |
Interpreting POST diagnostic front panel LEDs and audible codes .................................................................... |
84 |
8 Password security and resetting CMOS .......................................................................................................... |
86 |
Resetting the password jumper .......................................................................................................................... |
86 |
Changing a Setup or Power-On password .......................................................................................................... |
87 |
Deleting a Setup or Power-On password ............................................................................................................ |
88 |
Clearing and resetting the CMOS ......................................................................................................................... |
88 |
9 HP PC Hardware Diagnostics ......................................................................................................................... |
90 |
Why run HP PC Hardware Diagnostics ................................................................................................................. |
90 |
How to access and run HP PC Hardware Diagnostics ......................................................................................... |
90 |
Downloading HP PC Hardware Diagnostics (UEFI) to a USB device .................................................................... |
91 |
10 System backup and recovery ...................................................................................................................... |
92 |
Backing up, restoring, and recovering in Windows 8.1 or Windows 8 ................................................................ |
92 |
Creating recovery media and backups .............................................................................................. |
92 |
Restoring and recovering using Windows tools ............................................................................... |
92 |
Using Reset when the system is not responding ........................................................... |
93 |
Recovery using the Windows recovery USB flash drive ................................................. |
93 |
Recovery using Windows operating system media (purchased separately) ................ |
94 |
Backing up, restoring, and recovering in Windows 7 .......................................................................................... |
94 |
Creating recovery media ................................................................................................................... |
95 |
Creating recovery media using HP Recovery Manager (select models only) ................ |
95 |
Creating recovery discs with HP Recovery Disc Creator (select models only) .............. |
96 |
Creating recovery discs ................................................................................ |
96 |
Backing up your information .......................................................................................... |
97 |
System Restore ................................................................................................................................. |
97 |
System Recovery ............................................................................................................................... |
98 |
vii
System Recovery when Windows is responding ............................................................ |
98 |
System Recovery when Windows is not responding ..................................................... |
99 |
System Recovery using recovery media (select models only) ...................................... |
99 |
Using HP Recovery Disc operating system discs (select models only) ....................... |
100 |
Appendix A Power Cord Set Requirements ...................................................................................................... |
102 |
General Requirements ....................................................................................................................................... |
102 |
Japanese Power Cord Requirements ................................................................................................................ |
102 |
Country-Specific Requirements ........................................................................................................................ |
103 |
Appendix B Statement of Volatility ................................................................................................................ |
104 |
Appendix C Specifications ............................................................................................................................. |
106 |
Index ........................................................................................................................................................... |
107 |
viii
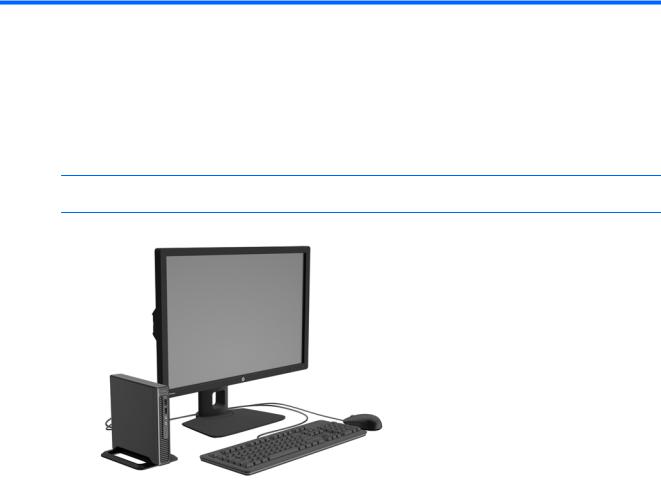
1 Product features
Standard configuration features
Features may vary depending on the model. For a complete listing of the hardware and software installed in the computer, run the diagnostic utility (included on some computer models only).
 NOTE: This computer model can be used in a tower orientation or a desktop orientation. The tower stand is sold separately.
NOTE: This computer model can be used in a tower orientation or a desktop orientation. The tower stand is sold separately.
Standard configuration features |
1 |
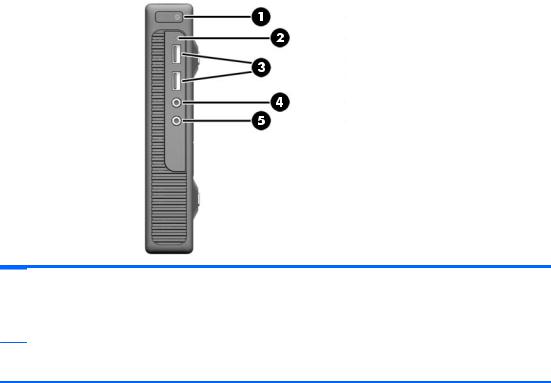
Front panel components
Drive configuration may vary by model.
1 |
Dual-State Power Button |
4 |
Microphone Connector |
|
|
|
|
2 |
Hard Drive Activity Light |
5 |
Headphone Connector |
|
|
|
|
3 |
USB 3.0 Ports |
|
|
NOTE: The Power On Light is normally white when the power is on. If it is flashing red, there is a problem with the computer and it is displaying a diagnostic code. Refer to the Maintenance and Service Guide to interpret the code.
2 Chapter 1 Product features

Rear panel components
1 |
AC Power Cord Connector |
6 |
Line-Out Connector for powered audio |
|
|
|
devices (green) |
|
|
|
|
2 |
DisplayPort Monitor Connector |
7 |
USB 2.0 Ports (black) with keyboard |
|
|
|
wakeup function |
|
|
|
|
3 |
RJ-45 (network) Jack |
8 |
USB 3.0 Ports (blue) |
|
|
|
|
4 |
Power Cord Retainer Clip |
9 |
Cable lock slot |
|
|
|
|
5 |
VGA Monitor Connector (blue) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Rear panel components |
3 |
Serial number location
Each computer has a unique serial number and a product ID number that are located on the exterior of the computer. Keep these numbers available for use when contacting customer service for assistance.
4 Chapter 1 Product features

2 Illustrated parts catalog
Chassis spare parts
 NOTE: HP continually improves and changes product parts. For complete and current information on supported parts for your computer, go to http://partsurfer.hp.com, select your country or region, and then follow the on-screen instructions.
NOTE: HP continually improves and changes product parts. For complete and current information on supported parts for your computer, go to http://partsurfer.hp.com, select your country or region, and then follow the on-screen instructions.
Computer major components
Item |
Description |
|
|
|
|
(1) |
Access panel |
|
|
|
|
(2) |
Base enclosure |
|
|
|
|
(3) |
System board with embedded processor (includes replacement thermal material) |
|
|
|
|
|
Intel Core i5-4210U processor: |
|
|
|
|
|
● |
Without Windows operating system |
|
|
|
|
● |
Windows 8.1 Standard |
|
|
|
Chassis spare parts |
5 |

Item Description
●Windows 8.1 Professional
●NetClone
Intel Core i3-4030U processor:
●Without Windows operating system
●Windows 8.1 Standard
●Windows 8.1 Professional
●NetClone
Intel Pentium 3558U processor:
●Without Windows operating system
●Windows 8.1 Standard
●Windows 8.1 Professional
●NetClone
Intel Celeron 2957U processor:
●Without Windows operating system
●Windows 8.1 Standard
●Windows 8.1 Professional
●NetClone
6 Chapter 2 Illustrated parts catalog

Drives
Item Description
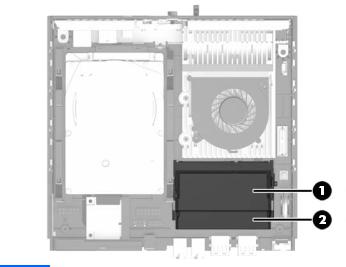
(1)Hard drive:
500 GB, 7200 rpm hard drive, 2.5-inch
(2)Solid state drives:
256 GB, self-encrypting (SED), OPAL 2.0
128 GB
(3)M.2 solid state drive:
32 GB, M.2 2242DS
Grommet, hard drive (not illustrated)
Chassis spare parts |
7 |

Misc parts
Item Description
(1)Heat sink
(2)Fan
(3)Speaker
(4)Hard drive connector and cable
(5)Hard drive cage
(6)Antennas and transceivers
(7)WLAN module (Realtek RTL8188EE 802.11b/g/n Wireless LAN Driver)
Rubber screw covers
Power supply, 65W, 89% efficiency
Memory modules (SODIMM, PC3-12800)
8 Chapter 2 Illustrated parts catalog

Item Description
8-GB
4-GB
2-GB
Stand
HP Ultraslim Keyed Cable Lock
Grommet, hard drive
Adapters:
DisplayPort to HDMI 1.4
DisplayPort to VGA
DisplayPort to DVI
DisplayPort cable
Mouse, USB, optical
Keyboard, USB
Chassis spare parts |
9 |

3Routine care, SATA drive guidelines, and disassembly preparation
This chapter provides general service information for the computer. Adherence to the procedures and precautions described in this chapter is essential for proper service.
 CAUTION: When the computer is plugged into an AC power source, voltage is always applied to the system board. You must disconnect the power cord from the power source before opening the computer to prevent system board or component damage.
CAUTION: When the computer is plugged into an AC power source, voltage is always applied to the system board. You must disconnect the power cord from the power source before opening the computer to prevent system board or component damage.
Electrostatic discharge information
A sudden discharge of static electricity from your finger or other conductor can destroy static-sensitive devices or microcircuitry. Often the spark is neither felt nor heard, but damage occurs. An electronic device exposed to electrostatic discharge (ESD) may not appear to be affected at all and can work perfectly throughout a normal cycle. The device may function normally for a while, but it has been degraded in the internal layers, reducing its life expectancy.
Networks built into many integrated circuits provide some protection, but in many cases, the discharge contains enough power to alter device parameters or melt silicon junctions.
Generating static
The following table shows that:
●Different activities generate different amounts of static electricity.
●Static electricity increases as humidity decreases.
|
|
Relative Humidity |
|
|
|
|
|
Event |
55% |
40% |
10% |
|
|
|
|
Walking across carpet |
7,500 V |
15,000 V |
35,000 V |
Walking across vinyl floor |
3,000 V |
5,000 V |
12,000 V |
Motions of bench worker |
400 V |
800 V |
6,000 V |
Removing DIPs from plastic tube |
400 V |
700 V |
2,000 V |
|
|
|
|
Removing DIPs from vinyl tray |
2,000 V |
4,000 V |
11,500 V |
Removing DIPs from Styrofoam |
3,500 V |
5,000 V |
14,500 V |
Removing bubble pack from PCB |
7,000 V |
20,000 V |
26,500 V |
Packing PCBs in foam-lined box |
5,000 V |
11,000 V |
21,000 V |
These are then multi-packaged inside plastic tubes, trays, or Styrofoam.
 NOTE: 700 volts can degrade a product.
NOTE: 700 volts can degrade a product.
10 Chapter 3 Routine care, SATA drive guidelines, and disassembly preparation

Preventing electrostatic damage to equipment
Many electronic components are sensitive to ESD. Circuitry design and structure determine the degree of sensitivity. The following packaging and grounding precautions are necessary to prevent damage to electric components and accessories.
●To avoid hand contact, transport products in static-safe containers such as tubes, bags, or boxes.
●Protect all electrostatic parts and assemblies with conductive or approved containers or packaging.
●Keep electrostatic sensitive parts in their containers until they arrive at static-free stations.
●Place items on a grounded surface before removing them from their container.
●Always be properly grounded when touching a sensitive component or assembly.
●Avoid contact with pins, leads, or circuitry.
●Place reusable electrostatic-sensitive parts from assemblies in protective packaging or conductive foam.
Personal grounding methods and equipment
Use the following equipment to prevent static electricity damage to equipment:
●Wrist straps are flexible straps with a maximum of one-megohm ± 10% resistance in the ground cords. To provide proper ground, a strap must be worn snug against bare skin. The ground cord must be connected and fit snugly into the banana plug connector on the grounding mat or workstation.
●Heel straps/Toe straps/Boot straps can be used at standing workstations and are compatible with most types of shoes or boots. On conductive floors or dissipative floor mats, use them on both feet with a maximum of one-megohm ± 10% resistance between the operator and ground.
|
Static Shielding Protection Levels |
|
|
Method |
Voltage |
|
|
Antistatic plastic |
1,500 |
Carbon-loaded plastic |
7,500 |
Metallized laminate |
15,000 |
|
|
Grounding the work area
To prevent static damage at the work area, use the following precautions:
●Cover the work surface with approved static-dissipative material. Provide a wrist strap connected to the work surface and properly grounded tools and equipment.
●Use static-dissipative mats, foot straps, or air ionizers to give added protection.
●Handle electrostatic sensitive components, parts, and assemblies by the case or PCB laminate. Handle them only at static-free work areas.
●Turn off power and input signals before inserting and removing connectors or test equipment.
●Use fixtures made of static-safe materials when fixtures must directly contact dissipative surfaces.
●Keep work area free of nonconductive materials such as ordinary plastic assembly aids and Styrofoam.
●Use field service tools, such as cutters, screwdrivers, and vacuums, that are conductive.
Electrostatic discharge information 11
Recommended materials and equipment
Materials and equipment that are recommended for use in preventing static electricity include:
●Antistatic tape
●Antistatic smocks, aprons, or sleeve protectors
●Conductive bins and other assembly or soldering aids
●Conductive foam
●Conductive tabletop workstations with ground cord of one-megohm +/- 10% resistance
●Static-dissipative table or floor mats with hard tie to ground
●Field service kits
●Static awareness labels
●Wrist straps and footwear straps providing one-megohm +/- 10% resistance
●Material handling packages
●Conductive plastic bags
●Conductive plastic tubes
●Conductive tote boxes
●Opaque shielding bags
●Transparent metallized shielding bags
●Transparent shielding tubes
Operating guidelines
To prevent overheating and to help prolong the life of the computer:
●Keep the computer away from excessive moisture, direct sunlight, and extremes of heat and cold.
●Operate the computer on a sturdy, level surface. Leave a 10.2-cm (4-inch) clearance on all vented sides of the computer and above the monitor to permit the required airflow.
●Never restrict the airflow into the computer by blocking any vents or air intakes. Do not place the keyboard, with the keyboard feet down, directly against the front of the desktop unit as this also restricts airflow.
●Occasionally clean the air vents on all vented sides of the computer. Lint, dust, and other foreign matter can block the vents and limit the airflow. Be sure to unplug the computer before cleaning the air vents.
●Never operate the computer with the cover or side panel removed.
●Do not stack computers on top of each other or place computers so near each other that they are subject to each other’s re-circulated or preheated air.
●If the computer is to be operated within a separate enclosure, intake and exhaust ventilation must be provided on the enclosure, and the same operating guidelines listed above will still apply.
●Keep liquids away from the computer and keyboard.
12 Chapter 3 Routine care, SATA drive guidelines, and disassembly preparation

●Never cover the ventilation slots on the monitor with any type of material.
●Install or enable power management functions of the operating system or other software, including sleep states.
Routine care
General cleaning safety precautions
1.Never use solvents or flammable solutions to clean the computer.
2.Never immerse any parts in water or cleaning solutions; apply any liquids to a clean cloth and then use the cloth on the component.
3.Always unplug the computer when cleaning with liquids or damp cloths.
4.Always unplug the computer before cleaning the keyboard, mouse, or air vents.
5.Disconnect the keyboard before cleaning it.
6.Wear safety glasses equipped with side shields when cleaning the keyboard.
Cleaning the Computer Case
Follow all safety precautions in General cleaning safety precautions on page 13 before cleaning the computer.
To clean the computer case, follow the procedures described below:
●To remove light stains or dirt, use plain water with a clean, lint-free cloth or swab.
●For stronger stains, use a mild dishwashing liquid diluted with water. Rinse well by wiping it with a cloth or swab dampened with clear water.
●For stubborn stains, use isopropyl (rubbing) alcohol. No rinsing is needed as the alcohol will evaporate quickly and not leave a residue.
●After cleaning, always wipe the unit with a clean, lint-free cloth.
●Occasionally clean the air vents on the computer. Lint and other foreign matter can block the vents and limit the airflow.
Cleaning the keyboard
Follow all safety precautions in General cleaning safety precautions on page 13 before cleaning the keyboard.
To clean the tops of the keys or the keyboard body, follow the procedures described in Cleaning the Computer Case on page 13.
When cleaning debris from under the keys, review all rules in General cleaning safety precautions on page 13 before following these procedures:
 CAUTION: Use safety glasses equipped with side shields before attempting to clean debris from under the keys.
CAUTION: Use safety glasses equipped with side shields before attempting to clean debris from under the keys.
●Visible debris underneath or between the keys may be removed by vacuuming or shaking.
●Canned, pressurized air may be used to clean debris from under the keys. Caution should be used as too much air pressure can dislodge lubricants applied under the wide keys.
Routine care 13

●If you remove a key, use a specially designed key puller to prevent damage to the keys. This tool is available through many electronic supply outlets.
 CAUTION: Never remove a wide leveled key (like the space bar) from the keyboard. If these keys are improperly removed or installed, the keyboard may not function properly.
CAUTION: Never remove a wide leveled key (like the space bar) from the keyboard. If these keys are improperly removed or installed, the keyboard may not function properly.
●Cleaning under a key may be done with a swab moistened with isopropyl alcohol and squeezed out. Be careful not to wipe away lubricants necessary for proper key functions. Use tweezers to remove any fibers or dirt in confined areas. Allow the parts to air dry before reassembly.
Cleaning the monitor
●Wipe the monitor screen with a clean cloth moistened with water or with a towelette designed for cleaning monitors. Do not use sprays or aerosols directly on the screen; the liquid may seep into the housing and damage a component. Never use solvents or flammable liquids on the monitor.
●To clean the monitor body follow the procedures in Cleaning the Computer Case on page 13.
Cleaning the mouse
Before cleaning the mouse, ensure that the power to the computer is turned off.
●Clean the mouse ball by first removing the retaining plate and the ball from the housing. Pull out any debris from the ball socket and wipe the ball with a clean, dry cloth before reassembly.
●To clean the mouse body, follow the procedures in Cleaning the Computer Case on page 13.
Service considerations
Listed below are some of the considerations that you should keep in mind during the disassembly and assembly of the computer.
Tools and software requirements
To service the computer, you need the following:
●Torx T-15 screwdriver
●Torx T-15 screwdriver
●Flat-bladed screwdriver (may sometimes be used in place of the Torx screwdriver)
●Diagnostics software
Screws
The screws used in the computer are not interchangeable. They may have standard or metric threads and may be of different lengths. If an incorrect screw is used during the reassembly process, it can damage the unit. HP strongly recommends that all screws removed during disassembly be kept with the part that was removed, then returned to their proper locations.
 CAUTION: As each subassembly is removed from the computer, it should be placed away from the work area to prevent damage.
CAUTION: As each subassembly is removed from the computer, it should be placed away from the work area to prevent damage.
Cables and connectors
Apply only the tension required to seat or unseat the cables during insertion or removal from the connector. Handle cables by the connector whenever possible. In all cases, avoid bending or twisting the cables, and
14 Chapter 3 Routine care, SATA drive guidelines, and disassembly preparation

ensure that the cables are routed in such a way that they cannot be caught or snagged by parts being removed or replaced.
 CAUTION: When servicing this computer, ensure that cables are placed in their proper location during the reassembly process. Improper cable placement can damage the computer.
CAUTION: When servicing this computer, ensure that cables are placed in their proper location during the reassembly process. Improper cable placement can damage the computer.
Hard Drives
Handle hard drives as delicate, precision components, avoiding all physical shock and vibration. This applies to failed drives as well as replacement spares.
●If a drive must be mailed, place the drive in a bubble-pack mailer or other suitable protective packaging and label the package “Fragile: Handle With Care.”
●Do not remove hard drives from the shipping package for storage. Keep hard drives in their protective packaging until they are actually mounted in the computer.
●Avoid dropping drives from any height onto any surface.
●If you are inserting or removing a hard drive, turn off the computer. Do not remove a hard drive while the computer is on or in standby mode.
●Before handling a drive, ensure that you are discharged of static electricity. While handling a drive, avoid touching the connector.
●Do not use excessive force when inserting a drive.
●Avoid exposing a hard drive to liquids, temperature extremes, or products that have magnetic fields such as monitors or speakers.
Lithium coin cell battery
The battery that comes with the computer provides power to the real-time clock and has a minimum lifetime of about three years.
See the appropriate removal and replacement chapter for the chassis you are working on in this guide for instructions on the replacement procedures.
 WARNING! This computer contains a lithium battery. There is a risk of fire and chemical burn if the battery is handled improperly. Do not disassemble, crush, puncture, short external contacts, dispose in water or fire, or expose it to temperatures higher than 140ºF (60ºC). Do not attempt to recharge the battery.
WARNING! This computer contains a lithium battery. There is a risk of fire and chemical burn if the battery is handled improperly. Do not disassemble, crush, puncture, short external contacts, dispose in water or fire, or expose it to temperatures higher than 140ºF (60ºC). Do not attempt to recharge the battery.

 NOTE: Batteries, battery packs, and accumulators should not be disposed of together with the general household waste. In order to forward them to recycling or proper disposal, please use the public collection system or return them to HP, their authorized partners, or their agents.
NOTE: Batteries, battery packs, and accumulators should not be disposed of together with the general household waste. In order to forward them to recycling or proper disposal, please use the public collection system or return them to HP, their authorized partners, or their agents.
Service considerations |
15 |

SATA hard drives
Serial ATA Hard Drive Characteristics
Number of pins/conductors in data cable |
7/7 |
|
|
Number of pins in power cable |
15 |
|
|
Maximum data cable length |
39.37 in (100 cm) |
|
|
Data interface voltage differential |
400-700 mV |
|
|
Drive voltages |
3.3 V, 5 V, 12 V |
|
|
Jumpers for configuring drive |
N/A |
|
|
Data transfer rate |
6.0 Gb/s |
|
|
SATA hard drive cables
SATA data cable
Always use an HP approved SATA 6.0 Gb/s cable as it is fully backwards compatible with the SATA 1.5 Gb/s drives.
Current HP desktop products ship with SATA 6.0 Gb/s hard drives.
SATA data cables are susceptible to damage if overflexed. Never crease a SATA data cable and never bend it tighter than a 30 mm (1.18 in) radius.
The SATA data cable is a thin, 7-pin cable designed to transmit data for only a single drive.
SMART ATA drives
The Self Monitoring Analysis and Recording Technology (SMART) ATA drives for the HP Personal Computers have built-in drive failure prediction that warns the user or network administrator of an impending failure or crash of the hard drive. The SMART drive tracks fault prediction and failure indication parameters such as reallocated sector count, spin retry count, and calibration retry count. If the drive determines that a failure is imminent, it generates a fault alert.
Cable management
Always follow good cable management practices when working inside the computer.
●Keep cables away from major heat sources like the heat sink.
●Keep cables clear of sliding or moveable parts to prevent them from being cut or crimped when the parts are moved.
●When folding a flat ribbon cable, never fold to a sharp crease. Sharp creases may damage the wires.
●Do not bend any cable sharply. A sharp bend can break the internal wires.
●Never bend a SATA data cable tighter than a 30 mm (1.18 in) radius.
●Never crease a SATA data cable.
16 Chapter 3 Routine care, SATA drive guidelines, and disassembly preparation
4 Removal and replacement procedures
Adherence to the procedures and precautions described in this chapter is essential for proper service. After completing all necessary removal and replacement procedures, run the Diagnostics utility to verify that all components operate properly.
 NOTE: Not all features listed in this guide are available on all computers.
NOTE: Not all features listed in this guide are available on all computers.

 NOTE: HP continually improves and changes product parts. For complete and current information on supported parts for your computer, go to http://partsurfer.hp.com, select your country or region, and then follow the on-screen instructions.
NOTE: HP continually improves and changes product parts. For complete and current information on supported parts for your computer, go to http://partsurfer.hp.com, select your country or region, and then follow the on-screen instructions.
Preparation for disassembly
See Routine care, SATA drive guidelines, and disassembly preparation on page 10 for initial safety procedures.
1.Remove/disengage any security devices that prohibit opening the computer.
2.Remove all removable media, such as a USB flash drive, from the computer.
3.Turn off the computer properly through the operating system, then turn off any external devices.
 CAUTION: Turn off the computer before disconnecting any cables.
CAUTION: Turn off the computer before disconnecting any cables.
Regardless of the power-on state, voltage is always present on the system board as long as the system is plugged into an active AC outlet. In some systems the cooling fan is on even when the computer is in the “Standby,” or “Suspend” modes. The power cord should always be disconnected before servicing a unit.
4.Disconnect the power cord from the power outlet and disconnect any external devices.
5.If the computer is on a stand, remove the computer from the stand.
 WARNING! Beware of sharp edges inside the chassis.
WARNING! Beware of sharp edges inside the chassis.
Preparation for disassembly 17

Access panel
1.Prepare the computer for disassembly (Preparation for disassembly on page 17).
2.Remove the rubber plugs from the two holes closest to the front of the computer (1).
3.Remove the screws from the two holes closest to the front of the computer (2).
4.Turn the computer over.
5.Loosen the screw on the rear of the computer (1) then slide the panel forward and lift if off the computer (2).
To install the access panel, reverse the removal procedure.
18 Chapter 4 Removal and replacement procedures

Hard drive
Description
Hard drives:
500 GB, 7200 rpm hard drive, 2.5-inch
Solid-state drives:
256 GB, self-encrypting (SED), OPAL 2.0
128 GB
Grommet, hard drive
 NOTE: Before you remove the old hard drive, be sure to back up the data from the old hard drive so that you can transfer the data to the new hard drive.
NOTE: Before you remove the old hard drive, be sure to back up the data from the old hard drive so that you can transfer the data to the new hard drive.
1.Prepare the computer for disassembly (Preparation for disassembly on page 17).
2.Remove the access panel Access panel on page 18.
3.Push down the release lever next to the rear of the hard drive (1). Hold the release lever down and slide the drive back until it stops, then lift the drive up and out of the bay (2).
Hard drive 19
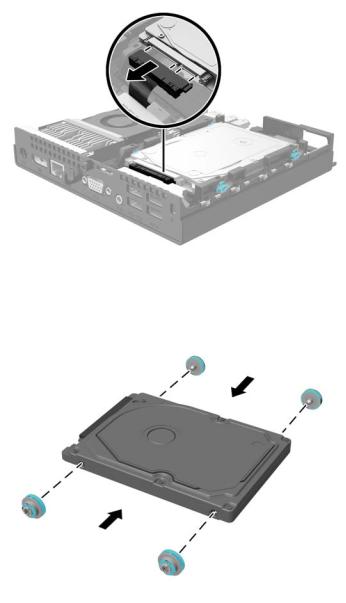
4.Unplug the combined power and data cable from the hard drive.
5.Transfer the silver and blue isolation mounting guide screws from the old hard drive to the new hard drive.
Reverse this procedure to replace the hard drive.
20 Chapter 4 Removal and replacement procedures
Memory
Description
8-GB, PC3-12800, SODIMM
4-GB, PC3-12800, SODIMM
2-GB, PC3-12800, SODIMM
The computer comes with double data rate 3 synchronous dynamic random access memory (DDR3-SDRAM) small outline dual inline memory modules (SODIMMs).
SODIMMs
The memory sockets on the system board can be populated with up to two industry-standard SODIMMs. These memory sockets are populated with at least one preinstalled SODIMM. To achieve the maximum memory support, you can populate the system board with up to 16 GB of memory.
DDR3L-SDRAM SODIMMs
For proper system operation, the SODIMMs must be:
●industry-standard 204-pin
●unbuffered non-ECC PC3-12800 DDR3L-1333 MHz-compliant
●1.35 volt DDR3L-SDRAM SODIMMs The DDR3L-SDRAM SODIMMs must also:
●support CAS latency 11 DDR3L 1333 MHz (11-11-11 timing)
●contain the mandatory Joint Electronic Device Engineering Council (JEDEC) specification In addition, the computer supports:
●512-Mbit, 1-Gbit, and 2-Gbit non-ECC memory technologies
●single-sided and double-sided SODIMMS
●SODIMMs constructed with x8 and x16 devices; SODIMMs constructed with x4 SDRAM are not supported
 NOTE: The system will not operate properly if you install unsupported SODIMMs.
NOTE: The system will not operate properly if you install unsupported SODIMMs.
Memory 21
Populating SODIMM sockets
There are two SODIMM sockets on the system board, with one socket per channel. The sockets are labeled DIMM1 and DIMM2. The DIMM1 socket operates in memory channel B. The DIMM2 socket operates in memory channel A.
Item |
Description |
System Board Label |
Socket Color |
|
|
|
|
1 |
SODIMM1 socket, Channel B |
DIMM1 |
Black |
|
|
|
|
2 |
SODIMM2 socket, Channel A |
DIMM2 |
Black |
|
|
|
|
The system will automatically operate in single channel mode, dual channel mode, or flex mode, depending on how the SODIMMs are installed.
●The system will operate in single channel mode if the SODIMM sockets are populated in one channel only.
●The system will operate in a higher-performing dual channel mode if the memory capacity of the SODIMM in Channel A is equal to the memory capacity of the SODIMM in Channel B.
●The system will operate in flex mode if the memory capacity of the SODIMM in Channel A is not equal to the memory capacity of the SODIMM in Channel B. In flex mode, the channel populated with the least amount of memory describes the total amount of memory assigned to dual channel and the remainder is assigned to single channel. If one channel will have more memory than the other, the larger amount should be assigned to channel A.
●In any mode, the maximum operational speed is determined by the slowest SODIMM in the system.
22 Chapter 4 Removal and replacement procedures
 Loading...
Loading...