Honeywell YJ-HF500 User Manual

YJ-HF500
Area-Imaging Scanner
User’s Guide

Disclaimer
Honeywell International Inc. (“HII”) reserves the right to make changes in specifications and other information contained in this document without prior notice, and the reader should in all cases consult HII to determine whether any such changes have been made. The information in this publication does not represent a commitment on the part of HII.
HII shall not be liable for technical or editorial errors or omissions contained herein; nor for incidental or consequential damages resulting from the furnishing, performance, or use of this material. HII disclaims all responsibility for the selection and use of software and/or hardware to achieve intended results.
This document contains proprietary information that is protected by copyright. All rights are reserved. No part of this document may be photocopied, reproduced, or translated into another language without the prior written consent of HII.
Copyright 2016 Honeywell International Inc. All rights reserved.
Web Address: www.honeywellaidc.com
Other product names or marks mentioned in this document may be trademarks or registered trademarks of other companies and are the property of their respective owners.

Table of Contents
Customer Support
Technical Assistance ........................................................................................................... |
vii |
Product Service and Repair ................................................................................................. |
vii |
Limited Warranty .................................................................................................................. |
vii |
Send Feedback .................................................................................................................... |
vii |
Chapter 1 - Getting Started |
|
About This Manual ............................................................................................................... |
1-1 |
Unpacking Your Device ....................................................................................................... |
1-1 |
Connecting the Device......................................................................................................... |
1-1 |
Connecting with USB ..................................................................................................... |
1-1 |
Connecting with RS232 Serial Port................................................................................ |
1-2 |
Reading Techniques ............................................................................................................ |
1-3 |
Menu Bar Code Security Settings........................................................................................ |
1-3 |
Setting Custom Defaults ...................................................................................................... |
1-3 |
Resetting the Custom Defaults ............................................................................................ |
1-4 |
Chapter 2 - Programming the Interface |
|
Introduction .......................................................................................................................... |
2-1 |
Programming the Interface - Plug and Play ......................................................................... |
2-1 |
RS232 Serial Port ................................................................................................................ |
2-1 |
USB IBM SurePos ............................................................................................................... |
2-1 |
USB PC or Macintosh Keyboard.......................................................................................... |
2-2 |
USB HID .............................................................................................................................. |
2-2 |
USB Serial ........................................................................................................................... |
2-2 |
ACK/NAK Mode ............................................................................................................. |
2-2 |
Verifone® Ruby Terminal Default Settings........................................................................... |
2-3 |
Gilbarco® Terminal Default Settings .................................................................................... |
2-3 |
Bioptic Aux Port Configuration ............................................................................................. |
2-3 |
Datalogic™ Magellan© Bioptic Aux Port Configuration........................................................ |
2-3 |
NCR Bioptic Aux Port Configuration .................................................................................... |
2-4 |
Wincor Nixdorf Terminal Default Settings ............................................................................ |
2-4 |
Wincor Nixdorf Beetle™ Terminal Default Settings ............................................................. |
2-4 |
Wincor Nixdorf RS232 Mode A ............................................................................................ |
2-5 |
Keyboard Country Layout .................................................................................................... |
2-5 |
Keyboard Style................................................................................................................... |
2-13 |
Keyboard Conversion ........................................................................................................ |
2-14 |
Control Character Output................................................................................................... |
2-14 |
Keyboard Modifiers ............................................................................................................ |
2-14 |
i

RS232 Modifiers ................................................................................................................ |
2-16 |
RS232 Baud Rate........................................................................................................ |
2-16 |
RS232 Word Length: Data Bits, Stop Bits, and Parity ................................................. |
2-17 |
RS232 Receiver Time-Out........................................................................................... |
2-18 |
RS232 Handshaking.................................................................................................... |
2-18 |
RS232 Timeout............................................................................................................ |
2-19 |
XON/XOFF .................................................................................................................. |
2-19 |
ACK/NAK ..................................................................................................................... |
2-19 |
Scanner to Bioptic Communication ................................................................................... |
2-20 |
Scanner-Bioptic Packet Mode ..................................................................................... |
2-20 |
Scanner-Bioptic ACK/NAK Mode................................................................................. |
2-20 |
Scanner-Bioptic ACK/NAK Timeout............................................................................. |
2-20 |
Chapter 3 - Input/Output Settings |
|
Power Up Beeper ................................................................................................................ |
3-1 |
Beep on BEL Character....................................................................................................... |
3-1 |
Good Read and Error Indicators.......................................................................................... |
3-1 |
Beeper – Good Read..................................................................................................... |
3-1 |
Beeper Volume – Good Read........................................................................................ |
3-2 |
Beeper Pitch – Good Read............................................................................................ |
3-2 |
Beeper Pitch – Error ...................................................................................................... |
3-2 |
Beeper Duration – Good Read ...................................................................................... |
3-3 |
LED – Good Read ......................................................................................................... |
3-3 |
Number of Beeps – Good Read .................................................................................... |
3-3 |
Number of Beeps – Error............................................................................................... |
3-3 |
Good Read Delay .......................................................................................................... |
3-4 |
User-Specified Good Read Delay.................................................................................. |
3-4 |
Presentation Mode .............................................................................................................. |
3-4 |
LED Illumination............................................................................................................. |
3-4 |
Idle Illumination - Presentation Mode ............................................................................ |
3-5 |
Presentation Sensitivity ................................................................................................. |
3-5 |
Presentation Centering .................................................................................................. |
3-6 |
Poor Quality Codes ............................................................................................................. |
3-7 |
Poor Quality PDF Codes ............................................................................................... |
3-7 |
Mobile Phone Read Mode ................................................................................................... |
3-7 |
Reread Delay....................................................................................................................... |
3-8 |
User-Specified Reread Delay .............................................................................................. |
3-8 |
2D Reread Delay ........................................................................................................... |
3-8 |
Character Activation Mode .................................................................................................. |
3-9 |
Activation Character ...................................................................................................... |
3-9 |
End Character Activation After Good Read ................................................................... |
3-9 |
Character Activation Laser Timeout ............................................................................ |
3-10 |
Character Deactivation Mode ............................................................................................ |
3-10 |
Deactivation Character ................................................................................................ |
3-10 |
Illumination Lights.............................................................................................................. |
3-10 |
Aimer Mode ....................................................................................................................... |
3-11 |
Centering ........................................................................................................................... |
3-11 |
Video Reverse ................................................................................................................... |
3-12 |
ii

Working Orientation........................................................................................................... |
3-13 |
Chapter 4 - Data Editing |
|
Prefix/Suffix Overview ......................................................................................................... |
4-1 |
To Add a Prefix or Suffix:............................................................................................... |
4-1 |
To Clear One or All Prefixes or Suffixes ........................................................................ |
4-2 |
To Add a Carriage Return Suffix to All Symbologies ..................................................... |
4-2 |
Prefix Selections.................................................................................................................. |
4-2 |
Suffix Selections .................................................................................................................. |
4-2 |
Function Code Transmit ...................................................................................................... |
4-3 |
Intercharacter, Interfunction, and Intermessage Delays...................................................... |
4-3 |
Intercharacter Delay ...................................................................................................... |
4-3 |
User Specified Intercharacter Delay .............................................................................. |
4-3 |
Interfunction Delay......................................................................................................... |
4-4 |
Intermessage Delay....................................................................................................... |
4-4 |
Chapter 5 - Data Formatting |
|
Data Format Editor Introduction .......................................................................................... |
5-1 |
Add a Data Format .............................................................................................................. |
5-1 |
Other Programming Selections...................................................................................... |
5-2 |
Terminal ID Table ................................................................................................................ |
5-3 |
Data Format Editor Commands........................................................................................... |
5-3 |
Move Commands........................................................................................................... |
5-4 |
Search Commands ........................................................................................................ |
5-5 |
Miscellaneous Commands............................................................................................. |
5-6 |
Data Formatter .................................................................................................................... |
5-8 |
Primary/Alternate Data Formats .......................................................................................... |
5-9 |
Chapter 6 - Symbologies |
|
All Symbologies ................................................................................................................... |
6-1 |
Message Length Description ............................................................................................... |
6-1 |
Codabar............................................................................................................................... |
6-2 |
Codabar Concatenation................................................................................................. |
6-3 |
Code 39 ............................................................................................................................... |
6-4 |
Code 32 Pharmaceutical (PARAF) ................................................................................ |
6-5 |
Full ASCII....................................................................................................................... |
6-6 |
Code 39 Code Page ...................................................................................................... |
6-6 |
Interleaved 2 of 5................................................................................................................. |
6-7 |
NEC 2 of 5 ........................................................................................................................... |
6-8 |
Code 93 ............................................................................................................................... |
6-9 |
Code 93 Code Page .................................................................................................... |
6-10 |
Straight 2 of 5 Industrial (three-bar start/stop)................................................................... |
6-11 |
Straight 2 of 5 IATA (two-bar start/stop) ............................................................................ |
6-12 |
Matrix 2 of 5....................................................................................................................... |
6-13 |
Code 11 ............................................................................................................................. |
6-14 |
iii

Code 128 ........................................................................................................................... |
6-15 |
ISBT 128 Concatenation.............................................................................................. |
6-15 |
Code 128 Code Page .................................................................................................. |
6-16 |
GS1-128 ............................................................................................................................ |
6-17 |
UPC-A ............................................................................................................................... |
6-17 |
UPC-A/EAN-13 with Extended Coupon Code ................................................................... |
6-19 |
Coupon GS1 DataBar Output............................................................................................ |
6-20 |
UPC-E0 ............................................................................................................................. |
6-20 |
UPC-E1 ............................................................................................................................. |
6-22 |
EAN/JAN-13 ...................................................................................................................... |
6-23 |
Convert UPC-A to EAN-13 .......................................................................................... |
6-23 |
ISBN Translate ............................................................................................................ |
6-25 |
EAN/JAN-8 ........................................................................................................................ |
6-25 |
MSI .................................................................................................................................... |
6-27 |
GS1 DataBar Omnidirectional ........................................................................................... |
6-29 |
GS1 DataBar Limited......................................................................................................... |
6-29 |
GS1 DataBar Expanded .................................................................................................... |
6-30 |
Codablock A ...................................................................................................................... |
6-30 |
Codablock F ...................................................................................................................... |
6-31 |
PDF417 ............................................................................................................................. |
6-32 |
MacroPDF417 ................................................................................................................... |
6-32 |
MicroPDF417..................................................................................................................... |
6-33 |
GS1 Composite Codes...................................................................................................... |
6-33 |
UPC/EAN Version........................................................................................................ |
6-34 |
GS1 Emulation .................................................................................................................. |
6-34 |
TCIF Linked Code 39 (TLC39) .......................................................................................... |
6-35 |
QR Code............................................................................................................................ |
6-35 |
QR Code Page ............................................................................................................ |
6-36 |
Data Matrix ........................................................................................................................ |
6-37 |
Data Matrix Code Page ............................................................................................... |
6-37 |
MaxiCode .......................................................................................................................... |
6-38 |
Aztec Code ........................................................................................................................ |
6-39 |
Aztec Code Page......................................................................................................... |
6-39 |
Chinese Sensible (Han Xin) Code..................................................................................... |
6-40 |
Postal Codes - 2D ............................................................................................................. |
6-41 |
Single 2D Postal Codes:.............................................................................................. |
6-41 |
Combination 2D Postal Codes:.................................................................................... |
6-42 |
Postal Codes - Linear ........................................................................................................ |
6-45 |
China Post (Hong Kong 2 of 5).................................................................................... |
6-45 |
Korea Post ................................................................................................................... |
6-46 |
Chapter 7 - Utilities |
|
To Add a Test Code I.D. Prefix to All Symbologies ............................................................. |
7-1 |
Show Decoder Revision ...................................................................................................... |
7-1 |
Show Scan Driver Revision ................................................................................................. |
7-1 |
Show Software Revision...................................................................................................... |
7-1 |
Show Data Format............................................................................................................... |
7-1 |
Test Menu............................................................................................................................ |
7-2 |
iv

EZConfig-Scanning Introduction.......................................................................................... |
7-2 |
Installing EZConfig-Scanning from the Web.................................................................. |
7-2 |
Resetting the Factory Defaults ............................................................................................ |
7-3 |
Chapter 8 - Serial Programming Commands |
|
Conventions......................................................................................................................... |
8-1 |
Menu Command Syntax ...................................................................................................... |
8-1 |
Query Commands ............................................................................................................... |
8-1 |
Responses..................................................................................................................... |
8-2 |
Resetting the Custom Defaults............................................................................................ |
8-3 |
Menu Commands ................................................................................................................ |
8-3 |
Chapter 9 - Product Specifications |
|
YJ-HF500 Scanner Product Specifications ......................................................................... |
9-1 |
Standard Cable Pinouts....................................................................................................... |
9-2 |
Serial Output.................................................................................................................. |
9-2 |
USB ............................................................................................................................... |
9-2 |
Chapter 10 - Maintenance and Troubleshooting |
|
Repairs .............................................................................................................................. |
10-1 |
Maintenance ...................................................................................................................... |
10-1 |
Cleaning the Device..................................................................................................... |
10-1 |
Inspecting Cords and Connectors ............................................................................... |
10-1 |
Replacing Cable in the Scanner ........................................................................................ |
10-1 |
Troubleshooting the Scanner ............................................................................................ |
10-1 |
Appendix A - Reference Charts |
|
Symbology Charts ............................................................................................................... |
A-1 |
Linear Symbologies ....................................................................................................... |
A-1 |
2D Symbologies............................................................................................................. |
A-2 |
Postal Symbologies ....................................................................................................... |
A-2 |
ASCII Conversion Chart (Code Page 1252)........................................................................ |
A-3 |
Lower ASCII Reference Table............................................................................................. |
A-4 |
ISO 2022/ISO 646 Character Replacements ...................................................................... |
A-7 |
Unicode Key Maps .............................................................................................................. |
A-9 |
Sample Symbols
Programming Chart
v

vi

Customer Support
Technical Assistance
To search our knowledge base for a solution or to log in to the Technical Support portal and report a problem, go to www.hsmcontactsupport.com.
For our latest contact information, see www.honeywellaidc.com/locations.
Product Service and Repair
Honeywell International Inc. provides service for all of its products through service centers throughout the world. To find your service center, go to www.honeywellaidc.com and select Support. Contact your service enter to obtain a Return Material Authorization number (RMA #) before you return the product.
To obtain warranty or non-warranty service, return your product to Honeywell (postage paid) with a copy of the dated purchase record.
Limited Warranty
For warranty information, go to www.honeywellaidc.com and click Resources>Warranty.
Send Feedback
Your feedback is crucial to the continual improvement of our documentation. To provide feedback about this manual, contact the Honeywell Technical Communications department at ACSHSMTechnicalCommunications@honeywell.com.
vii

viii
1
Getting Started
About This Manual
This User’s Guide provides installation and programming instructions for the Honeywell HF500 corded area-imaging scanners. Product specifications, dimensions, warranty, and customer support information are also included.
Honeywell bar code scanners are factory programmed for the most common terminal and communications settings. If you need to change these settings, programming is accomplished by scanning the bar codes in this guide.
An asterisk (*) next to an option indicates the default setting.
Unpacking Your Device
After you open the shipping carton containing the product, take the following steps:
•Check for damage during shipment. Report damage immediately to the carrier who delivered the carton.
•Make sure the items in the carton match your order.
•Save the shipping container for later storage or shipping.
Connecting the Device
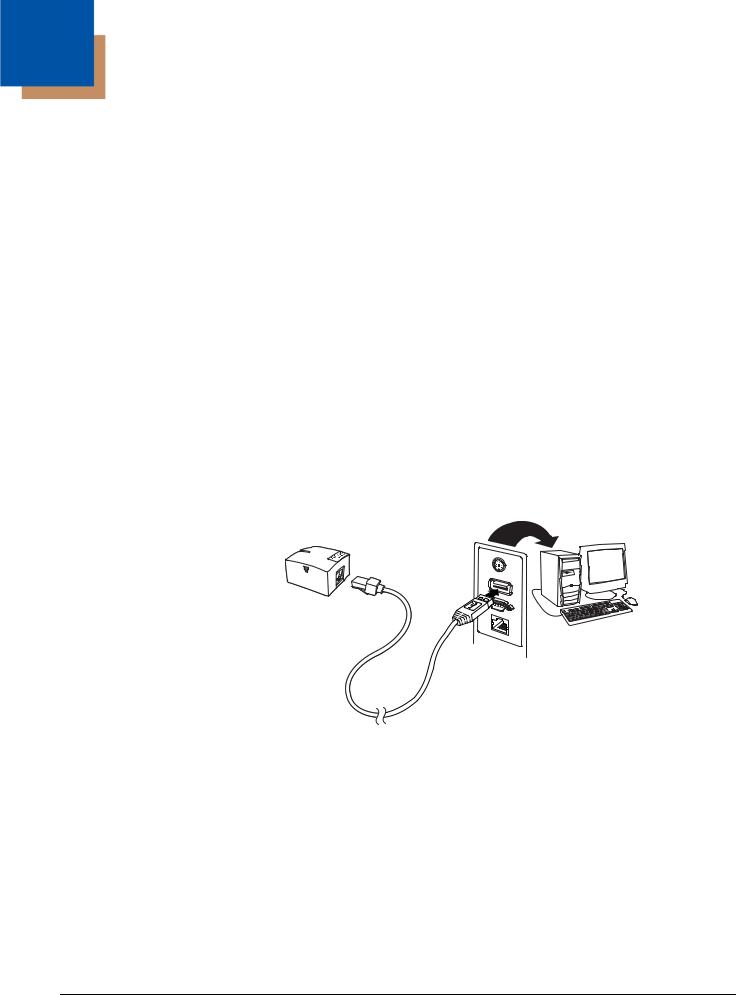
Connecting with USB
A scanner can be connected to the USB port of a computer.
1. Connect the appropriate interface cable to the device first, then to the computer.
YJ-HF500 USB
Connection:
Note: The power supply must be ordered separately, if needed.
2.The scanner beeps.
3.Verify the scanner operation by scanning a bar code from the Sample Symbols in the back of this manual. The unit defaults to a USB PC Keyboard. Refer to page 2-2 for other USB terminal settings.
1 - 1

Connecting with RS232 Serial Port
1.Turn off power to the terminal/computer.
2.Connect the appropriate interface cable to the device.
Note: For the scanner to work properly, you must have the correct cable for your type of terminal/computer.
YJ-HF500
RS232 Serial Port Connection:
Note: The power supply must be ordered separately, if needed.
3.Plug the serial connector into the serial port on your computer. Tighten the two screws to secure the connector to the port.
4.Once the scanner has been fully connected, power up the computer.
This interface programs 115,200 baud, 8 data bits, no parity, and 1 stop bit.
1 - 2

Reading Techniques
The scanner has a view finder that projects a bright red aiming beam that corresponds to the scanner’s horizontal field of view. The aiming beam should be centered over the bar code, but it can be positioned in any direction for a good read.
Linear bar code |
2D Matrix symbol |
|||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
The aiming beam or pattern is smaller when the scanner is closer to the code and larger when it is farther from the code. Symbologies with smaller bars or elements (mil size) should be read closer to the unit. Symbologies with larger bars or elements (mil size) should be read farther from the unit. To read single or multiple symbols (on a page or on an object), hold the scanner at an appropriate distance from the target and center the aiming beam or pattern on the symbol. If the code being scanned is highly reflective (e.g., laminated), it may be necessary to tilt the code up 15° to 18° to prevent unwanted reflection.
Menu Bar Code Security Settings
Honeywell scanners are programmed by scanning menu bar codes or by sending serial commands to the scanner. If you want to restrict the ability to scan menu codes, you can use the Menu Bar Code Security settings. Please contact the nearest technical support office (see Technical Assistance on page -vii) for further information.
Setting Custom Defaults
You have the ability to create a set of menu commands as your own, custom defaults. To do so, scan the Set Custom Defaults bar code below before scanning the menu commands for your custom defaults. If a menu command requires scanning numeric codes from the back cover, then a Save code, that entire sequence will be saved to your custom defaults. When you have entered all the commands you want to save for your custom defaults, scan the Save Custom Defaults bar code.
Set Custom Defaults
Save Custom Defaults
1 - 3

You may have a series of custom settings and want to correct a single setting. To do so, just scan the new setting to overwrite the old one. For example, if you had previously saved the setting for Beeper Volume at Low to your custom defaults, and decide you want the beeper volume set to High, just scan the Set Custom Defaults bar code, then scan the Beeper Volume High menu code, and then Save Custom Defaults. The rest of the custom defaults will remain, but the beeper volume setting will be updated.
Resetting the Custom Defaults
If you want the custom default settings restored to your scanner, scan the Activate Custom Defaults bar code below. This is the recommended default bar code for most users. It resets the scanner to the custom default settings. If there are no custom defaults, it will reset the scanner to the factory default settings. Any settings that have not been specified through the custom defaults will be defaulted to the factory default settings.
Activate Custom Defaults
1 - 4

2
Programming the Interface
Introduction
This chapter describes how to program your system for the desired interface.
Programming the Interface - Plug and Play
Plug and Play bar codes provide instant scanner set up for commonly used interfaces.
Note: After you scan one of the codes, power cycle the host terminal to have the interface in effect.
RS232 Serial Port
The RS232 Interface bar code is used when connecting to the serial port of a PC or terminal. The following RS232 Interface bar code also programs a carriage return (CR) and a line feed (LF) suffix, baud rate, and data format as indicated below.
Option |
Setting |
Baud Rate |
115,200 bps |
Data Format |
8 data bits, no parity bit, 1 stop bit |
RS232 Interface
USB IBM SurePos
Scan one of the following “Plug and Play” codes to program the scanner for an IBM SurePos (USB handheld scanner) or IBM SurePos (USB tabletop scanner) interface.
Note: After scanning one of these codes, you must power cycle the cash register.
USB IBM SurePos
(USB Handheld Scanner)
Interface
USB IBM SurePos
(USB Tabletop Scanner)
Interface
Each bar code above also programs the following suffixes for each symbology:
Symbology |
Suffix |
Symbology |
Suffix |
|
|
EAN 8 |
0C |
Code 39 |
00 |
0A |
0B |
EAN 13 |
16 |
Interleaved 2 of 5 |
00 |
0D 0B |
|
UPC A |
0D |
Code 128 |
00 |
18 |
0B |
UPC E |
0A |
Code 39 |
00 |
0A |
0B |
2 - 1

USB PC or Macintosh Keyboard
Scan one of the following codes to program the scanner for USB PC Keyboard or USB Macintosh Keyboard. Scanning these
codes also adds a CR and LF.
USB Keyboard (PC)
USB Keyboard (Mac)
USB Japanese Keyboard (PC)
USB HID
Scan the following code to program the scanner for USB HID bar code scanners.
USB HID Bar Code Scanner
USB Serial
Scan the following code to program the scanner to emulate a regular RS232-based COM Port. If you are using a Microsoft® Windows® PC, you will need to download a driver from the Honeywell website (www.honeywellaidc.com). The driver will use the next available COM Port number. Apple® Macintosh computers recognize the scanner as a USB CDC class device and automatically uses a class driver.
USB Serial
Note: No extra configuration (e.g., baud rate) is necessary.
ACK/NAK Mode
ACK/NAK Mode On
* ACK/NAK Mode Off
2 - 2

Verifone® Ruby Terminal Default Settings
Scan the following Plug and Play code to program the scanner for a Verifone Ruby terminal. This bar code sets the baud rate to 1200 bps and the data format to 8 data bits, mark parity bit, 1 stop bit. It also adds a line feed (LF) suffix and programs the following prefixes for each symbology:
Symbology |
Prefix |
UPC-A |
A |
UPC-E |
A |
EAN-8 |
FF |
EAN-13 |
F |
Verifone Ruby Settings
Gilbarco® Terminal Default Settings
Scan the following Plug and Play code to program the scanner for a Gilbarco terminal. This bar code sets the baud rate to 2400 bps and the data format to 7 data bits, even parity, 2 stop bits. It also adds a carriage return (CR) suffix and programs the following prefixes for each symbology:
Symbology |
Prefix |
UPC-A |
A |
UPC-E |
E0 |
EAN-8 |
FF |
EAN-13 |
F |
Gilbarco Settings
Bioptic Aux Port Configuration
Scan the following Plug and Play code to program the scanner for a Honeywell bioptic scanner auxiliary port configuration. This bar code sets the baud rate to 38400 bps and the data format to 8 data bits, no parity, 1 stop bit.
Honeywell Bioptic Settings
Datalogic™ Magellan© Bioptic Aux Port Configuration
Scan the following Plug and Play code to program the scanner for a Datalogic Magellan bioptic scanner auxiliary port configuration. This bar code sets the baud rate to 9600 bps and the data format to 8 data bits, no parity, 1 stop bit.
Datalogic Magellan Bioptic Settings
2 - 3

NCR Bioptic Aux Port Configuration
Scan the following Plug and Play code to program the scanner for an NCR bioptic scanner auxiliary port configuration. The following prefixes are programmed for each symbology:
Symbology |
Prefix |
Symbology |
Prefix |
UPC-A |
A |
Interleaved 2 of 5 |
b |
UPC-E |
E0 |
Code 128 |
f |
|
|
GS1 DataBar |
r |
|
|
Omnidirectional |
|
EAN-8 |
FF |
GS1 DataBar |
r |
|
|
Expanded |
|
EAN-13 |
F |
Codabar |
N |
Code 39 |
a |
Code 32 |
a |
|
|
Pharmaceutical |
|
|
|
(PARAF) |
|
NCR Bioptic Settings
Wincor Nixdorf Terminal Default Settings
Scan the following Plug and Play code to program the scanner for a Wincor Nixdorf terminal. This bar code sets the baud rate to 9600 bps and the data format to 8 data bits, no parity, 1 stop bit.
Wincor Nixdorf Terminal Settings
Wincor Nixdorf Beetle™ Terminal Default Settings
Scan the following Plug and Play code to program the scanner for a Wincor Nixdorf Beetle terminal. This bar code sets the baud rate to 115200 bps and the data format to 8 data bits, no parity, 1 stop bit. The following prefixes are programmed for each symbology:
Symbology |
Prefix |
Symbology |
Prefix |
|
|
|
|
Aztec Code |
V |
Interleaved 2 of 5 |
I |
Codabar |
N |
MaxiCode |
T |
Code 93 |
L |
MicroPDF417 |
S |
Code 128 |
K |
PDF417 |
Q |
Data Matrix |
R |
QR Code |
U |
EAN-8 |
B |
Straight 2 of 5 IATA |
H |
EAN-13 |
A |
UPC-A |
A0 |
GS1 DataBar |
E |
UPC-E |
C |
GS1-128 |
P |
All other bar codes |
M |
Wincor Nixdorf Beetle Settings
2 - 4

Wincor Nixdorf RS232 Mode A
Scan the following Plug and Play code to program the scanner for a Wincor Nixdorf RS232 Mode A terminal. This bar code sets the baud rate to 9600 bps and the data format to 8 data bits, odd parity, 1 stop bit. The following prefixes are programmed for each symbology:
Symbology |
Prefix |
Symbology |
Prefix |
Code 128 |
K |
EAN-13 |
A |
Code 93 |
L |
GS1-128 |
K |
Codabar |
N |
Interleaved 2 of 5 |
I |
UPC-A |
A0 |
Plessey |
O |
UPC-E |
C |
Straight 2 of 5 IATA |
H |
EAN-8 |
B |
GS1 DataBar |
E |
All other bar codes |
M |
|
|
Wincor Nixdorf RS232 Mode A
Settings
Keyboard Country Layout
If your interface is USB Keyboard, your keyboard layout default is a US keyboard. To change this layout, refer to the chart below for your keyboard country. Scan the appropriate bar code below to change the layout.
By default, national character replacements are used for the following characters: #$@[\]^‘{|}~ See ISO 2022/ISO 646 Character Replacements on page A-7 to view the character replacements for each country.
Keyboard Countries
* United States
Albania
Azeri (Cyrillic)
Azeri (Latin)
Belarus
2 - 5

Keyboard Countries (Continued)
Belgium
Bosnia
Brazil
Brazil (MS)
Bulgaria (Cyrillic)
Bulgaria (Latin)
Canada (French legacy)
Canada (French)
Canada (Multilingual)
Croatia
Czech
2 - 6

Keyboard Countries (Continued)
Czech (Programmers)
Czech (QWERTY)
Czech (QWERTZ)
Denmark
Dutch (Netherlands)
Estonia
Faroese
Finland
France
Gaelic
Germany
2 - 7

Keyboard Countries (Continued)
Greek
Greek (220 Latin)
Greek (220)
Greek (319 Latin)
Greek (319)
Greek (Latin)
Greek (MS)
Greek (Polytonic)
Hebrew
Hungarian (101 key)
Hungary
2 - 8

Keyboard Countries (Continued)
Iceland
Irish
Italian (142)
Italy
Japan ASCII
Kazakh
Kyrgyz (Cyrillic)
Latin America
Latvia
Latvia (QWERTY)
Lithuania
2 - 9

Keyboard Countries (Continued)
Lithuania (IBM)
Macedonia
Malta
Mongolian (Cyrillic)
Norway
Poland
Polish (214)
Polish (Programmers)
Portugal
Romania
Russia
2 - 10

Keyboard Countries (Continued)
Russian (MS)
Russian (Typewriter)
SCS
Serbia (Cyrillic)
Serbia (Latin)
Slovakia
Slovakia (QWERTY)
Slovakia (QWERTZ)
Slovenia
Spain
Spanish variation
2 - 11

Keyboard Countries (Continued)
Sweden
Switzerland (French)
Switzerland (German)
Tatar
Turkey F
Turkey Q
Ukrainian
United Kingdom
United States (Dvorak)
United States (Dvorak left)
United Stated (Dvorak right)
2 - 12

Keyboard Countries (Continued)
United States (International)
Uzbek (Cyrillic)
Keyboard Style
This programs keyboard styles, such as Caps Lock and Shift Lock. If you have used Keyboard Conversion settings, they will override any of the following Keyboard Style settings. Default = Regular.
Regular is used when you normally have the Caps Lock key off.
* Regular
Caps Lock is used when you normally have the Caps Lock key on.
Caps Lock
Shift Lock is used when you normally have the Shift Lock key on (not common to U.S. keyboards).
Shift Lock
Automatic Caps Lock is used if you change the Caps Lock key on and off. The software tracks and reflects if you have Caps Lock on or off . This selection can only be used with systems that have an LED that notes the Caps Lock status (AT keyboards).
Automatic Caps Lock
Autocaps via NumLock bar code should be scanned in countries (e.g., Germany, France) where the Caps Lock key cannot be used to toggle Caps Lock. The NumLock option works similarly to the regular Autocaps, but uses the NumLock key to retrieve the current state of the Caps Lock.
Autocaps via NumLock
2 - 13

Emulate External Keyboard should be scanned if you do not have an external keyboard (IBM AT or equivalent).
Emulate External Keyboard
Note: After scanning the Emulate External Keyboard bar code, you must power cycle your computer.
Keyboard Conversion
Alphabetic keyboard characters can be forced to be all upper case or all lowercase. So if you have the following bar code: “abc569GK,” you can make the output “ABC569GK” by scanning Convert All Characters to Upper Case, or to “abc569gk” by scanning Convert All Characters to Lower Case.
These settings override Keyboard Style selections.
Default = Keyboard Conversion Off.
* Keyboard Conversion Off
Convert All Characters
to Upper Case
Convert All Characters
to Lower Case
Control Character Output
This selection sends a text string instead of a control character. For example, when the control character for a carriage return is expected, the output would display [CR] instead of the ASCII code of 0D. Refer to ASCII Conversion Chart (Code Page
1252) on page A-3. Only codes 00 through 1F are converted (the first column of the chart). Default = Off.
Note: Control + ASCII Mode overrides this mode.
Control Character Output On
* Control Character Output Off
Keyboard Modifiers
This modifies special keyboard features, such as CTRL+ ASCII codes and Turbo Mode.
2 - 14

Control + ASCII Mode On: The scanner sends key combinations for ASCII control characters for values 00-1F. Windows is the preferred mode. All keyboard country codes are supported. DOS mode is a legacy mode, and it does not support all keyboard country codes. New users should use the Windows mode. Refer to Keyboard Function Relationships, page 7-1 for CTRL+ ASCII Values.
Windows Mode Prefix/Suffix Off: The scanner sends key combinations for ASCII control characters for values 00-1F, but it does not translate any prefix or suffix information.
Default = Control + ASCII Mode Off.
Windows Mode Control + X
Mode On
* Control + X Mode Off
DOS Mode Control + X Mode On
Windows Mode Prefix/Suffix Off
Turbo Mode: The scanner sends characters to a terminal faster. If the terminal drops characters, do not use Turbo Mode.
Default = Off.
Turbo Mode On
* Turbo Mode Off
Numeric Keypad Mode: Sends numeric characters as if entered from a numeric keypad. Default = Off.
Numeric Keypad Mode On
* Numeric Keypad Mode Off
2 - 15

Automatic Direct Connect Mode: This selection can be used if you have an IBM AT style terminal and the system is dropping
characters. Default = Off.
Automatic Direct Connect Mode
On
* Automatic Direct Connect
Mode Off
RS232 Modifiers
RS232 Baud Rate
Baud Rate sends the data from the scanner to the terminal at the specified rate. The host terminal must be set for the same baud rate as the scanner. Default = 9600.
300
600
1200
2400
4800
* 9600
19200
2 - 16
 Loading...
Loading...