Honeywell Zoning System Design INSTRUCTIONS

Zoning System Design Manual
Zoning Made Effortless
70-2321-03

Zoning System Design Manual
Introduction
The Concept of Zoning
The basic principle of forced air zoning is to allow one HVAC system to be controlled by multiple thermostats, heating and cooling a building in zones rather than as a whole. This makes homes and businesses more comfortable. When combined with setback thermostats, zone setback is possible, resulting in significant energy savings. Forced air zoning makes a common HVAC system more efficient by concentrating the unit’s capacity where and when you need it instead of pouring air throughout the building regardless of the temperature in the individual rooms.
According to a 2006 American Home Comfort Study, 67% of US homeowners are uncomfortable in their homes at certain times of the year. Zoning solves this problem.
To accomplish this we utilize:
Zoning Panel—Receives requests from thermostats and coordinates the HVAC system and damper positions. Thermostats—Requests conditioned air only in zones where required.
Duct Dampers—Directs air to rooms (zones) only when called for by a room thermostat. A By-Pass Damper—Efficiently controls excess supply air as dampers open and close.
Discharge Air Temperature Sensor (DATS)—Avoids freeze-up and tripping on high limit by sensing the supply duct temperature. The zone panel cycles off the equipment when DATS limits are exceeded. The equipment is turned back on automatically.
Fig. 1 depicts typical home temperatures compared to those of a home with Honeywell zoning.
TYPICAL HOME |
|
IDEAL HOME - WITH HONEYWELL ZONING |
||
SECOND FLOOR |
|
ZONE 1 |
THERMOSTAT SETPOINT: |
|
(SLEEPING AREA) |
|
(SLEEPING AREA) |
72°F/22°C |
|
ROOM TEMPERATURE |
|
ROOM TEMPERATURE |
|
|
76-80°F |
|
72°F |
|
|
25-27°C |
|
22°C |
|
|
FIRST FLOOR |
|
ZONE 2 |
|
|
(LIVING AREA) |
THERMOSTAT |
(LIVING AREA) |
THERMOSTAT SETPOINT: |
|
ROOM TEMPERATURE |
ROOM TEMPERATURE |
|||
SETPOINT: |
72°F/22°C |
|||
72°F |
72°F |
|||
72°F/22°C |
|
|||
22°C |
22°C |
|
||
|
|
|||
|
|
|
M28112 |
|
Fig. 1. Typical home (no zoning) compared to ideal home with Honeywell zoning.
Need Help?
For assistance with this product please visit http://yourhome.honeywell.com or call Honeywell Zoning Hotline toll-free at 1-800-828-8367
70-2321—03

Zoning System Design Manual
Introduction
Fig. 2 depicts a typical residential layout with three zones. Zoning provides two key benefits:
•Customer Comfort: heating and cooling where you want it, when you want it.
•Energy Savings: heat and cool only zones that are occupied.
In the following pages you will learn how to apply the principles of forced air zoning in new and existing projects, creating a more comfortable indoor environment.
FAMILY |
|
|
|
|
LIVING |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ENTRY |
|
|
|
BEDROOM |
|
|
|
BEDROOM |
|||||||||||||||||||||
ROOM |
|
|
|
|
ROOM |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1 |
2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
KITCHEN |
DINING |
MASTER |
|
ROOM |
SUITE |
|
BATH |
BATH |
ZONE THERMOSTAT |
HVAC EQUIPMENT |
M28051 |
ROUND ZONE DAMPER |
|
|
DIFFUSER |
Fig. 2. Typical residential layout with multiple zones on one HVAC system. |
|
70-2321—03
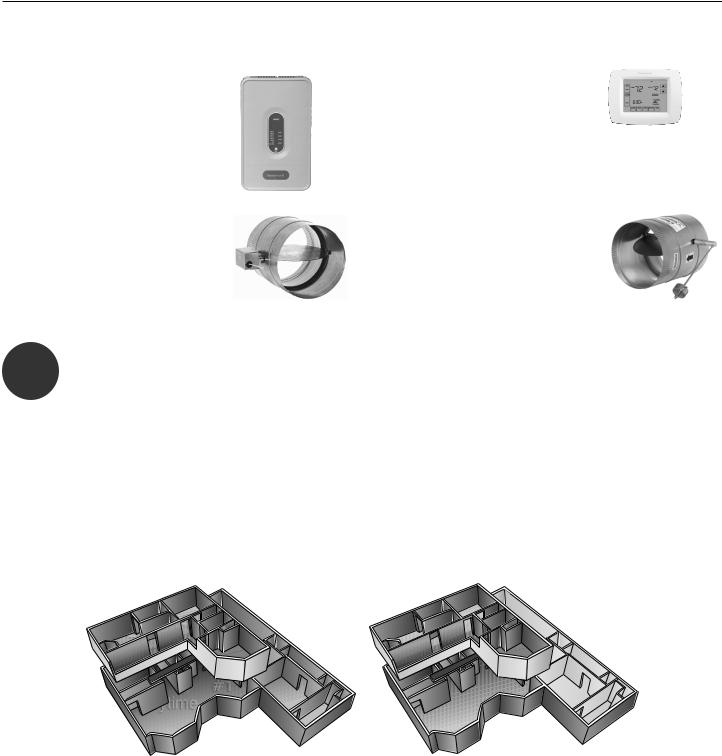
Zoning System Design Manual
Plan The Zones
In planning a zone system, here's what you need:
Panel
•To Operate Dampers and Equipment
•Transformer to power panel
Dampers
• Round/Rectangular
Thermostats
•Programmable or Non Programmable
Bypass and Discharge Air
Temperature Sensor:
•To Prevent Static Pressure Buildup
•DATS protects Equipment
Divide the Home Into Zones
1There are a number of ways to divide a house into zones: by floor, in groups of rooms adjacent to each other, rooms grouped by compass orientation—here is a typical setup:
Zone 1: areas primarily used at night (bedrooms)
Zone 2: areas primarily used during the day (living room, kitchen)
Zone 3: a third space that would benefit from its own HVAC control, such as a master bedroom suite, a basement, living space above a garage, a home office, etc.
A good rule of thumb is to make no zone smaller than about 25% of total system capacity, measured in cubic feet/minute (CFM).
Zone 2: Nighti -timei |
Zone 2: Nighti -timei |
|
|
|
|
Zone 3: |
|
Zone 1: Daytimei |
Zone 1: Daytimei |
Home |
|
officei |
|||
|
|
M28111
Fig. 3. Typical residential layout with multiple zones on one HVAC system.
70-2321—03 |
|
 Loading...
Loading...