Avaya 4550T-PWR+, 4850GTS, 4826GTS, 4850GTS-PWR+, 4826GTS-PWR+ Fundamentals
...
Fundamentals
Avaya Ethernet Routing Switch 4000
Series
NN47205-102, 05.01
December 2011
5.6
©
2011 Avaya Inc.
All Rights Reserved.
Notice
While reasonable efforts have been made to ensure that the
information in this document is complete and accurate at the time of
printing, Avaya assumes no liability for any errors. Avaya reserves the
right to make changes and corrections to the information in this
document without the obligation to notify any person or organization of
such changes.
Documentation disclaimer
“Documentation” means information published by Avaya in varying
mediums which may include product information, operating instructions
and performance specifications that Avaya generally makes available
to users of its products. Documentation does not include marketing
materials. Avaya shall not be responsible for any modifications,
additions, or deletions to the original published version of
documentation unless such modifications, additions, or deletions were
performed by Avaya. End User agrees to indemnify and hold harmless
Avaya, Avaya's agents, servants and employees against all claims,
lawsuits, demands and judgments arising out of, or in connection with,
subsequent modifications, additions or deletions to this documentation,
to the extent made by End User.
Link disclaimer
Avaya is not responsible for the contents or reliability of any linked Web
sites referenced within this site or documentation provided by Avaya.
Avaya is not responsible for the accuracy of any information, statement
or content provided on these sites and does not necessarily endorse
the products, services, or information described or offered within them.
Avaya does not guarantee that these links will work all the time and has
no control over the availability of the linked pages.
Warranty
Avaya provides a limited warranty on its Hardware and Software
(“Product(s)”). Refer to your sales agreement to establish the terms of
the limited warranty. In addition, Avaya’s standard warranty language,
as well as information regarding support for this Product while under
warranty is available to Avaya customers and other parties through the
Avaya Support Web site:
you acquired the Product(s) from an authorized Avaya reseller outside
of the United States and Canada, the warranty is provided to you by
said Avaya reseller and not by Avaya.
Licenses
THE SOFTWARE LICENSE TERMS AVAILABLE ON THE AVAYA
WEBSITE,
APPLICABLE TO ANYONE WHO DOWNLOADS, USES AND/OR
INSTALLS AVAYA SOFTWARE, PURCHASED FROM AVAYA INC.,
ANY AVAYA AFFILIATE, OR AN AUTHORIZED AVAYA RESELLER
(AS APPLICABLE) UNDER A COMMERCIAL AGREEMENT WITH
AVAYA OR AN AUTHORIZED AVAYA RESELLER. UNLESS
OTHERWISE AGREED TO BY AVAYA IN WRITING, AVAYA DOES
NOT EXTEND THIS LICENSE IF THE SOFTWARE WAS OBTAINED
FROM ANYONE OTHER THAN A V A Y A, AN A V A Y A AFFILIA TE OR AN
AVAYA AUTHORIZED RESELLER; AVAYA RESERVES THE RIGHT
TO TAKE LEGAL ACTION AGAINST YOU AND ANYONE ELSE
USING OR SELLING THE SOFTWARE WITHOUT A LICENSE. BY
INSTALLING, DOWNLOADING OR USING THE SOFTWARE, OR
AUTHORIZING OTHERS TO DO SO, YOU, ON BEHALF OF
YOURSELF AND THE ENTITY FOR WHOM YOU ARE INSTALLING,
DOWNLOADING OR USING THE SOFTWARE (HEREINAFTER
REFERRED TO INTERCHANGEABL Y AS “YOU” AND “END USER”),
AGREE TO THESE TERMS AND CONDITIONS AND CREATE A
BINDING CONTRACT BETWEEN YOU AND AVAYA INC. OR THE
APPLICABLE AVAYA AFFILIATE (“AVAYA”).
HTTP://SUPPORT.AVAYA.COM/LICENSEINFO/ ARE
http://support.avaya.com. Please note that if
Copyright
Except where expressly stated otherwise, no use should be made of
materials on this site, the Documentation, Software, or Hardware
provided by Avaya. All content on this site, the documentation and the
Product provided by Avaya including the selection, arrangement and
design of the content is owned either by Avaya or its licensors and is
protected by copyright and other intellectual property laws including the
sui generis rights relating to the protection of databases. You may not
modify, copy, reproduce, republish, upload, post, transmit or distribute
in any way any content, in whole or in part, including any code and
software unless expressly authorized by Avaya. Unauthorized
reproduction, transmission, dissemination, storage, and or use without
the express written consent of Avaya can be a criminal, as well as a
civil offense under the applicable law.
Third-party components
Certain software programs or portions thereof included in the Product
may contain software distributed under third party agreements (“Third
Party Components”), which may contain terms that expand or limit
rights to use certain portions of the Product (“Third Party Terms”).
Information regarding distributed Linux OS source code (for those
Products that have distributed the Linux OS source code), and
identifying the copyright holders of the Third Party Components and the
Third Party Terms that apply to them is available on the A vaya Support
Web site:
Trademarks
The trademarks, logos and service marks (“Marks”) displayed in this
site, the Documentation and Product(s) provided by Avaya are the
registered or unregistered Marks of Avaya, its affiliates, or other third
parties. Users are not permitted to use such Marks without prior written
consent from Avaya or such third party which may own the Mark.
Nothing contained in this site, the Documentation and Product(s)
should be construed as granting, by implication, estoppel, or otherwise,
any license or right in and to the Marks without the express written
permission of Avaya or the applicable third party.
Avaya is a registered trademark of Avaya Inc.
All non-Avaya trademarks are the property of their respective owners,
and “Linux” is a registered trademark of Linus Torvalds.
Downloading Documentation
For the most current versions of Documentation, see the Avaya
Support Web site:
Contact Avaya Support
Avaya provides a telephone number for you to use to report problems
or to ask questions about your Product. The support telephone number
is 1-800-242-2121 in the United States. For additional support
telephone numbers, see the Avaya W eb site:
http://support.avaya.com/Copyright.
http://support.avaya.com.
http://support.avaya.com.
2 Fundamentals December 2011
Comments? infodev@avaya.com

Contents
Chapter 1: New in this release...........................................................................................
Features....................................................................................................................................................
Cisco CLI Phase 1............................................................................................................................
Disable MAC Learning.....................................................................................................................
Equal Cost Multi Path (ECMP).........................................................................................................
Internet Group Management Protocol (IGMP) Querier....................................................................
Internet Group Management Protocol (IGMP) version 3 Snooping and Proxy................................
IP Phone automatic PoE changes....................................................................................................
Layer 3 Brouter Port.........................................................................................................................
Many to Many Port Mirroring............................................................................................................
MLT/DMLT/LAG Dynamic VLAN changes........................................................................................
Network Time Protocol (NTP)...........................................................................................................
Ping Source Address........................................................................................................................
Secure File Transfer Protocol (SFTP)..............................................................................................
SFP Plus..........................................................................................................................................
Show Flash command......................................................................................................................
SSH Client........................................................................................................................................
SSH RSA Authentication..................................................................................................................
Stack Health Monitoring and Recovery............................................................................................
Static FDB MAC Entry......................................................................................................................
Terminal Mode Permanent Setting...................................................................................................
VLAN Scaling...................................................................................................................................
Voice VLAN Integration....................................................................................................................
Other changes...........................................................................................................................................
New Avaya Ethernet Routing Switch 4000 Series models...............................................................
Avaya Identity Engines Ignition Server.............................................................................................
Diagnostic Auto Unit Replacement (DAUR).....................................................................................
Enterprise Device Manager enhancements.....................................................................................
Chapter 2: Feature licensing fundamentals.....................................................................
Feature licenses........................................................................................................................................
License generation....................................................................................................................................
Generating a license file............................................................................................................................
Installing a license file...............................................................................................................................
Displaying licenses....................................................................................................................................
Deleting a license......................................................................................................................................
License transfer.........................................................................................................................................
Special cases with software licensing..............................................................................................
Chapter 3: User interface fundamentals...........................................................................
ACLI concepts...........................................................................................................................................
ACLI command modes.....................................................................................................................
ACLI access procedures..................................................................................................................
ACLI help..................................................................................................................................................
Enterprise Device Manager concepts.......................................................................................................
Supported Web browsers.................................................................................................................
5
5
5
5
5
6
6
6
6
6
7
7
7
7
7
8
8
8
8
9
9
9
9
9
10
10
11
11
13
13
14
14
16
16
17
17
18
19
19
19
21
22
24
25
Fundamentals December 2011 3

Memory requirements......................................................................................................................
Online help.......................................................................................................................................
Interface components.......................................................................................................................
Enterprise Device Manager procedures...................................................................................................
Configuring EDM through ACLI........................................................................................................
Starting EDM....................................................................................................................................
Using shortcut menus.......................................................................................................................
Opening folders and tabs.................................................................................................................
Using dialog boxes...........................................................................................................................
Editing objects..................................................................................................................................
Graphing statistics............................................................................................................................
Getting EDM online help files for embedded EDM...........................................................................
Chapter 4: Configuration files fundamentals...................................................................
ACLI configuration files.............................................................................................................................
Configuration file management procedures.....................................................................................
Enterprise Device Manager configuration files.........................................................................................
ASCII and binary configuration file procedures................................................................................
Chapter 5: Supported standards and Request for comments........................................
Standards..................................................................................................................................................
RFCs.........................................................................................................................................................
Chapter 6: ACLI quick reference.......................................................................................
Connect to the switch................................................................................................................................
Start ACLI from the main menu.................................................................................................................
ACLI command modes..............................................................................................................................
Use the factory default configuration........................................................................................................
Configure the management IP address....................................................................................................
Configure Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP)......................................................................
Configure Network Time Protocol (NTP)...................................................................................................
Configure VLANs and tagged uplinks.......................................................................................................
Configure Internet Group Management Protocol (IGMP).........................................................................
Configure a port........................................................................................................................................
Configure passwords................................................................................................................................
Configure Secure Shell (SSH)..................................................................................................................
Configure Telnet........................................................................................................................................
Configure Simple Network Time Protocol (SNTP)....................................................................................
Configure log settings...............................................................................................................................
Configure Secure Socket Layer (SSL)......................................................................................................
Configure access control...........................................................................................................................
Check a configuration...............................................................................................................................
ACLI commands listed by mode...............................................................................................................
25
25
26
36
37
38
39
40
42
44
51
51
55
55
55
60
61
69
69
69
73
73
73
74
74
74
75
75
76
77
79
80
81
81
81
82
82
83
83
84
4 Fundamentals December 2011

Chapter 1: New in this release
The following sections detail what is new in Avaya Ethernet Routing Switch 4000 Series Fundamentals
(NN47205-102) for release 5.6.
Features
For information about changes for this release that apply to features, see the following
sections.
Cisco CLI Phase 1
In Release 5.6 selected ACLI commands for ARP, Spanning Tree, and VLAN have been
modified to use Cisco CLI syntax. While the interface software remains backwards compatible,
and ASCII configuration files you created prior to Release 5.6 will function normally, from
Release 5.6 and up the new Cisco CLI command syntax will be used for the commands for
ARP, Spanning Tree, and VLAN.
Disable MAC Learning
Y ou can use Disable MAC Learning on a port when you want to control the Layer 2 Forwarding
Database (FDB) entries to prevent MAC tables from filling unnecessarily . Y ou use Disable MAC
Learning in combination with Static MAC FDB Entry.
Equal Cost Multi Path (ECMP)
Routers use Equal Cost Multi Path to load balance traffic on equal cost paths to the same
destination prefix and to assure faster convergence to other active paths in case of network
failure.
Fundamentals December 2011 5

New in this release
Internet Group Management Protocol (IGMP) Querier
When you configure IGMP Querier the system sends IGMP general queries to designated
sources when the switch or VLANs operate in Layer 2 mode. IGMP Querier sends IGMP
general queries to all ports, Multi-Link Trunks (ML T), Distributed Multi-Link Trunks (DML T), and
Link Aggregation Groups (LAG) on the configured VLAN.
Internet Group Management Protocol (IGMP) version 3 Snooping and Proxy
From Release 5.6 and up the switch supports full IGMPv3 Snooping and Proxy. IGMPv3
Snooping provides the ability to pack multiple group members in a single report message to
reduce the amount ot network traffic. When you enable IGMPv3 Snooping, you can use IGMP
proxy to receive and consolidate multiple reports for the same multicast group.
IP Phone automatic PoE changes
PoE settings and IP Phone discovery have been enhanced to allow the provision of PoE priority
levels and power limits when the system discovers an IP Phone.
Layer 3 Brouter Port
From Release 5.6 and up, the switch supports the configuration of brouter ports. A brouter port
is a single-port VLAN that can route IP packets as well as bridge all non-routable traffic. An
advantage of this feature is that it eliminates interruptions caused by Spanning Tree Protocol
recalculations in routed traffic.
Many to Many Port Mirroring
You can use Many to Many Port Mirroring to monitor more than one traffic pattern because
you can use multiple instances of port mirroring simultaneously. In a network that supports a
variety of complex scenarious, when you can monitor multiple traffic patterns you can, for
example, set up one port mirror to allow duplication of VoIP traf fic for call recording processes
and use another instance for intrusion detection while additional instances remain available
for other activities or network troubleshooting.
6 Fundamentals December 2011
Comments? infodev@avaya.com

MLT/DMLT/LAG Dynamic VLAN changes
Enhancements have been made to Link Aggregation Groups (LAG) that provide consistent
operation of Multi-Link Trunk (MLT), Distributed Multi-Link Trunk (DMLT), and LAGs so that
you can make VLAN changes on trunks without disabling the trunk first.
Network Time Protocol (NTP)
The switch supports both Simple Network Time Protocol (SNTP) and Network Time Protocol
(NTP) for time synchronization. You can configure SNTP and/or NTP with both primary and
secondary server for SNTP and up to 10 servers for NTP, IPv4 and IPv6 for SNTP and only
IPv4 for NTP.
Ping Source Address
Features
For more flexible testing and network setup diagnostics, Ping has been enhanced so that you
can specify the IPv4 source address of the outgoing ICMP request. The source address must
be one of the active Layer 3 interfaces and you cannot specify the VRRP virtual address as
the source address for Ping.
Secure File Transfer Protocol (SFTP)
For secure (SSH) software images Secure File Transfer supports download of Agent and
diagnostic files and ASCII configuration file download and upload. SFTP allows secure transfer
of a binary configuration file between a switch or stack and an SFTP server that uses SFTP
with SSH version 2. Enabled by default, and available through ACLI and EDM, SFTP interacts
with SSH Client.
SFP Plus
Release 5.6 introduces four Avaya ERS 4800 Series models that support Small Form factor
Pluggable Plus (SFP+) devices. SFP+ supports 10 Gbps connectivity.
The following SFP+ devices are supported:
SFP+ order code Description
AA1403011–E6 1–Port 10 Gigabit-LR SFP+ (LC) Single
mode up to 10 km
Fundamentals December 2011 7
New in this release
SFP+ order code Description
AA1403013–E6 1–Port 10 Gigabit-ER SFP+ (LC) Single
AA1403015–E6 1–Port 10 Gigabit-SR SFP+ (LC) Multi-mode
AA1403017–E6 1–Port 10 Gigabit-LRM SFP+ (LC) Multi-
AA1403018–E6 SFP+ direct attach cable 10 m
AA1403019–E6 SFP+ direct attach cable 3 m
AA1403020–E6 SFP+ direct attach cable 5 m
Show Flash command
You can use the show flash command to display FLASH capacity and current usage
information about FLASH allocation and files, if present, to provide information about dual
images and backup configurations. You can display the actual file sizes and space allocated
to them.
mode up to 40 km
fibre up to 300 m
mode fibre up to 220 m
SSH Client
Present only on switches with SSH images, and available only through ACLI, SSH Client uses
SSH version 2. It is a secure shell protocol you can use to connect to an SSH Server device
in the network that accepts remote connections.
SSH RSA Authentication
SSH RSA Authentication provides increased security for Secure Shell (SSH) login. With this
feature, the switch supports RSA public-private key encryption that uses a digital certificate.
SSH RSA Authentication is supported when you select the RSA certificate option for a Secure
Shell connection from a client PC to the switch.
Stack Health Monitoring and Recovery
You can use Stack Health Monitoring and Recovery for more robust switch discovery and to
obtain additional reports about stack communication failure. You can also use the recovery
function to detect logical or software problems in a switch or stack.
8 Fundamentals December 2011
Comments? infodev@avaya.com

Static FDB MAC Entry
You can use Static FDB MAC Entry to configure a static MAC address entry in the Layer 2
Forwarding Database (FDB). A static address does not age out and is saved in the
configuration file. You use Static FDB MAC Entry in conjunction with Disable MAC Learning.
Terminal Mode Permanent Setting
When you use Terminal Mode Permanent Setting, the system saves terminal settings across
login sessions. Retaining the terminal settings makes it easier to use scripts to configure or
poll the switch.
VLAN Scaling
The switch supports up to 1,024 concurrent VLANs with VIDs in a range from 1 to 4094. VLAN
scaling is an enhancement that enables actions on multiple VLANs simultaneously for faster
configuration of a high number of VLANs. If you add multiple VLANs to a single port you must
set VLAN configuration control to flexible.
Other changes
Voice VLAN Integration
Voice VLAN is enhanced to provide centralized creation and management of V oice VLAN using
VLAN-specific commands. The enhancement also includes the option to configure a statically
allocated port that you can permanently assign to the Voice VLAN, where that port will still
persist after a system boot. Another advantage of a statically allocated port is that it does not
have to participate in the ADAC or 802.1AB discovery processes, when this behavior is desired.
With Voice VLAN Integration, the switch creates static V oice VLANs and Layer 3 configurations
can be applied as per standard operational procedures. Voice VLAN integration is specifically
useful when Layer 3 configurations are needed for ADAC Voice VLAN.
Other changes
See the following sections for information about changes that do not apply to new features.
Fundamentals December 2011 9

New in this release
New Avaya Ethernet Routing Switch 4000 Series models
Release 5.6 introduces the following six new hardware models to the A vaya Ethernet Routing
Switch 4000 Series:
• Avaya Ethernet Routing Switch 4550T-PWR+
• Avaya Ethernet Routing Switch 4526T-PWR+
• Avaya Ethernet Routing Switch 4850GTS
• Avaya Ethernet Routing Switch 4850GTS-PWR+
• Avaya Ethernet Routing Switch 4826GTS
• Avaya Ethernet Routing Switch 4826GTS-PWR+
The new 4500 and 4800 PWR+ models support PoE+, according to the IEEE 802.3at standard,
and can deliver power up to 32W, as opposed to 16W for the 4500 PWR legacy units.
Release 5.6 also introduces one new removable power supply for the A vaya Ethernet Routing
Switch 4000 Series — the ERS4x00 PoE+ PSU, a stackable 1000W AC Power over Ethernet
plus power supply unit.
The PoE+ models include a 1000w power supply that enables full support for 48 ports when
all ports are operating at class 3 802.3af PoE.
On the new PoE+ hardware variants, the switch CPU speed is 533 MHz, and the FLASH is
larger to allow for large images, backup images, and configurations.
The standard ADS console port (DTE) on all new products is an RJ-45 Female Connector: (8
pin RJ45).
Avaya Identity Engines Ignition Server
Avaya Identity Engines Ignition Server (Ignition Server) is an 802.1X-capable RADIUS
authentication server and T ACACS+ server that grants or denies users access to your network
based on your policies. When you use Ignition Server you can create a single set of policies
that control access for all user connection methods: over a wired Ethernet jack, wireless, or
VPN.
Ignition Server also authenticates devices and you can configure an 802.1X authentication
bypass for older devices on your network that cannot perform an 802.1X authentication.
10 Fundamentals December 2011
Comments? infodev@avaya.com
Diagnostic Auto Unit Replacement (DAUR)
The DAUR feature is disabled in Release 5.6. You can download a diagnostic image through
the download ACLI command.
Enterprise Device Manager enhancements
Release 5.6 includes the following Enterprise Device Manager (EDM) user interface
enhancements:
• a Save Config button was added to the Navigation tree toolbar to allow you to quickly and
easily save a configuration
• a search function, called Auto Complete Search, appears just beneath the Navigation tree
toolbar. You can use the entry field in this search function to help you find navigation tree
folders quickly. For example, you can enter only IP in the search window and the
navigation tree changes to reveal only items related to the text “IP”.
Other changes
Fundamentals December 2011 11

New in this release
12 Fundamentals December 2011
Comments? infodev@avaya.com

Chapter 2: Feature licensing fundamentals
About this task
This section provides information to help understand, install, and manage feature licensing. Review this
section before using licensed features or before making changes to the license configuration.
Important:
If you reset a standalone device to the default configuration, you erase the license file.
Feature licenses
This section describes the types of licenses and lists the features that require a license.
Software releases prior to Release 5.4 require no licenses. Switches and licenses are
purchased separately. The Avaya Ethernet Routing Switch 4000 series supports trial and
advanced license types.
To use the following features you must obtain the appropriate license:
• Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) (beginning with Release 5.4)
• Virtual Router Redundancy Protocol (VRRP) (beginning with Release 5.5)
• Equal Cost Multi Path (ECMP) (beginning with Release 5.6)
A trial license can be obtained to try out advanced license features for 30 days. Trial licenses
are obtained from Avaya and installed using the ACLI. After the trial period has expired the
licensed feature is disabled.
To minimize network and device impacts, the following events occur before the expiration of a
trial license:
• A system trap is sent five days before license expiration.
• A system trap is sent one day before license expiration.
• A system trap is sent at license expiration.
To fully enable advanced license features, a license kit must be purchased, a license file
generated, and the file installed on the switch. Each license kit contains a license certificate
and a License Authorization Code (LAC) for a specific number or level of licenses. The license
certificate contains the following instructions for license file generation:
• deposit LACs into an online license bank
• find and use the switch MAC address for license file generation
Fundamentals December 2011 13
Feature licensing fundamentals
• license file generation
• installation of the license file on the switch
License generation
After purchasing a license kit, a license file must be generated on the licensing portal. This
licensing portal acts as a license bank to store all license entitlements and licenses.
The license certificate found in the license kit contains a License Authorization Code (LAC).
This LAC is submitted to the license portal, which deposits license entitlements into a license
bank. This license entitlement is combined with the switch MAC address to generate a license
file. Because license files are generated based on a switch MAC address, the license file must
contain the authorized MAC addresses of the switches where it will be installed.
A license can contain multiple MAC addresses and MAC addresses can be added to the
license file at a later time. A single license file can support more than one MAC address. The
number of MAC addresses supported is dependent on the type of license. To support licensed
features in a stack, use the MAC address of the Base Unit.
The following table provides information on the license kits available for the Avaya Ethernet
Routing Switch 4000:
Part Number
AL4516001 ERS4500 Adv License 1
AL4516002 ERS4500 Adv License 10
Generating a license file
About this task
This section contains the procedure for license file generation. Ensure the following
prerequisites are met before generating a license:
• Purchase a license kit
• Ensure a properly configured TFTP server is reachable from the switch or stack on, which
the license file will be installed.
• Obtain the switch base MAC addresses for the switches that use licensed features.
License Type Number of Switches / MAC
Addresses Supported
• Ensure the default web browser does not automatically decompress the files.
14 Fundamentals December 2011
Comments? infodev@avaya.com

Generating a license file
License file names must conform to the following limitations:
• 63 character maximum
• Lower case characters only
• No spaces or special characters permitted with the exception of the underscore ( _ )
• A three character file extension is required. This file extension can be any three
characters.
To generate a license file for multiple MAC addresses, the addresses must be specified in a
text file that conforms to the following rules:
• ASCII text file
• one MAC address per line
• no additional characters, spaces, or special characters besides those used in the MAC
addresses
• MAC addresses in hexadecimal, capitalized format with each pair of characters separated
by colons
• must contain correct MAC addresses
• the number of MAC addresses specified must not exceed the maximum for the license
type
Procedure
1. Use a web browser to access the licensing portal.
2. Enter contact information in the required boxes.
3. Create a new license bank or access one already created.
4. Select an e-mail notification option.
5. Enter the LAC specified on the license certificate.
6. Click Submit.
7. Wait for notification from the system.
8. Click Go to License Bank to Download License.
9. Select the appropriate LAC on the License Bank screen.
10. Click Generate License.
11. Specify a single MAC address or multiple MAC addresses by submitting a text file
12. Specify the license file name.
13. Click Generate License File.
Generated license files are sent based the e-mail notification options.
that conforms to the preceding limitations.
Fundamentals December 2011 15

Feature licensing fundamentals
Installing a license file
About this task
This procedure is used to install a license file. If the switch is reset to default, the license file
must be reinstalled and the switch reset to reenable licensed features. Resetting a switch to
default removes the license file from its storage area in NVRAM.
Store the license file on a TFTP server accessible by the switch or stack before starting the
installation procedure. For switches equipped with a USB port, you can also use a USB mass
storage device to copy the license file to the switch.
Procedure
1. At the Privileged Executive command prompt, enter the command copy [tftp|
usb] license <tftp_ip_address> filename <license_file_name>.
2. Restart the switch.
Result
License installation example using USB
1. Insert a USB mass storage device into a USB port on the front of the switch.
2. To copy a license from a USB mass storage device, use the following command:
copy usb license 4500_adv.lic
The switch generates the message: License successfully downloaded
Note:
You must reboot the system to activate the license.
Displaying licenses
About this task
Display an installed license file using the command show license {<1-10> | all}
[verbose]. Specify an individual license with the designated number or use the all keyword
to display all installed licenses.
16 Fundamentals December 2011
Comments? infodev@avaya.com

Deleting a license
About this task
Delete an installed license file using the command clear license { <1-10> | all} in
Privileged Exec mode. Specify an individual license with the designated number or use the all
keyword to delete all installed licenses.
License transfer
About this task
The Avaya Ethernet Routing Switch 4000 implements Licensing Auto Unit Replacement. If a
base unit fails, the other units in the stack will transfer a virtual key to the new base unit to
eliminate the need for transfer of a license to the new base unit. Even with this functionality in
place, there are still several situations where it becomes necessary to transfer the license from
one device to another. These conditions are as follows:
Deleting a license
• replacement of failed non base unit
• incorrect MAC address entered during license file generation
• the system displays an error message indicating the limit of MAC swaps for the license
has been exceeded
Use the following procedure to transfer a license.
Procedure
1. Use a web browser to access the licensing portal.
2. Click License Bank.
3. Enter the appropriate user name and password.
4. Select the License Authorization Code (LAC) entry associated with the license
type.
5. Click View Details.
6. Select the transaction that contains the appropriate license file name.
7. Click Replace Switch.
8. In Step 1: Enter Replacement MAC Address, enter the new MAC address.
9. In Step 2: Select the MAC Address to Replace, select the entry for the MAC
address to be replaced.
10. Click Replace Switch MAC.
Fundamentals December 2011 17

Feature licensing fundamentals
If you exceed the MAC replacement threshold, a message appears confirming that
the MAC swap is unsuccessful. Select a different LAC entry and try again. If no
other LAC entries appear in the list, contact technical support.
11. After the system displays MAC swap successful, click Return to License Bank
Details.
12. Select the transaction that contains the license file name with the new MAC
address.
13. Click Download.
Special cases with software licensing
About this task
The following sections describe situations when software licensing can be lost or fail.
Downgrade of switch software followed by upgrade of switch software
On a standalone switch, if you downgrade from R5.4 or later software to R5.3 or earlier
software, and then upgrade back to R5.4 or later software, the software license is lost.
In a stack, if you downgrade from R5.4 or later software to R5.3 or earlier software, and then
upgrade back to R5.4 or later software, the license is retained. The system sets the operational
license to Advanced software and the installed license displays as none. Because R5.3 is
unaware of software licensing, the license can be lost in the rare event that memory is reused.
If this happens, you must reinstall the software license after upgrade.
Base unit failure in a stack of 2 units
It is not recommended to operate a stack of two switches with a software license based only
on the base unit (BU) MAC address. If the base unit fails, after you reboot the former non-base
unit (NBU), now a standalone switch, the switch is unlicensed.
To prevent the loss of the software license, Avaya recommends that you install a software
license that contains the NBU MAC address.
Base unit failure in a stack of more than 2 units
It is not recommended to install a license file when the system is operating in temporary base
unit (TBU) mode.
In a stack, if you create a license file based on the MAC address of the base unit (BU), then
designate another unit in the stack as the BU, when you download the license file the system
generates error messages and the license process fails.
18 Fundamentals December 2011
Comments? infodev@avaya.com
Chapter 3: User interface fundamentals
This chapter provides basic information to help you understand the interfaces you can use to configure
and manage an Avaya Ethernet Routing Switch. Available features depend on switch model and
configuration.
ACLI concepts
Avaya Command Line Interface (ACLI) is a text-based interface that you can use for switch
configuration and management. A common command line interface (CLI), ACLI follows the
industry standard used for device management across Avaya products.
The command modes within ACLI are listed in order of increasing privileges and each mode
is based on user logon permission level. User logon permission is determined by logon
password as supplied by your system administrator.
Y ou can access ACLI directly through a console connection, remotely through a dial-up modem
connection, or in-band through a Telnet session.
Y ou can use ACLI interactively or use configure network to load and execute ACLI scripts,
manually loading the script in the console menu or automatically loading the script at startup.
For more information about the command, see
using ACLI on page 58.
The following topics describe ACLI command modes, provide procedures to access ACLI, and
describe ACLI help.
• ACLI command modes
• ACLI access procedures
• ACLI help
ACLI command modes
This section describes the use and purpose of ACLI command modes.
ACLI provides the following command modes:
• User EXEC
• Privileged EXEC
Downloading a configuration file automatically
Fundamentals December 2011 19

User interface fundamentals
• Global Configuration
• Interface Configuration
• Router Configuration
Command mode access is determined by access permission levels and password
protection.
If no password is set, you can enter ACLI in User EXEC mode and use enable to move to
the next level, Privileged EXEC mode.
However, if you have read-only access, you cannot progress beyond User EXEC mode, the
default command mode.
If you have read-write access you can progress from the default mode through all of the
available command modes.
User EXEC mode is the default ACLI command mode and the initial access mode. Also known
as exec mode, it is the most restrictive ACLI mode and has few commands available; for
example, ping and logoff. User EXEC commands are available from the other modes.
Privileged EXEC mode is an unrestricted command mode that can display all switch settings,
and, if you are logged on with write access, you can access all configuration modes and
commands that affect switch operation from this mode. In Privileged EXEC mode, also known
as privExec mode, you can perform basic switch level management tasks such as downloading
software images, setting passwords, and starting the switch. Privileged EXEC commands are
also available in Global and Interface configuration modes.
Global Configuration mode, also known as config mode, provides commands used to set and
display general switch configurations such as IP address, Simple Network Management
Protocol (SNMP) parameters, Telnet access, and Virtual Local Area Networks (VLAN).
From the Global Configuration mode, access the Router Configuration Mode by entering one
of the following commands:
router rip
•
router ospf
•
router vrrp
•
Interface Configuration mode, also known as config-if mode, provides commands used to
configure parameters for each port or VLAN such as speed, duplex mode, and rate limiting.
With sufficient permission, you can use the rules in the following table to move between the
command modes.
Command mode and
sample prompt
User EXEC 4548GT-PWR> No entrance command,
Entrance commands Exit commands
exit
default mode
or
logout
20 Fundamentals December 2011
Comments? infodev@avaya.com
ACLI concepts
Command mode and
sample prompt
Privileged EXEC 4548GTPWR#
Global Configuration
4548GT-PWR(config)#
Interface Configuration
4548GT-PWR(config-if)#
Entrance commands Exit commands
enable exit
or
logout
From Privileged EXEC
mode, enter
configure
To return to Privileged EXEC
mode, enter
end
or
exit
To exit ACLI completely,
enter
logout
From Global Configuration
mode: To configure a port
enter
interface
fastethernet <port
number>
To configure a VLAN enter:
interface vlan
<vlan number>
To return to Global
Configuration mode, enter:
exit
To return to Privileged EXEC
mode, enter:
end
To exit ACLI completely,
enter:
logout
Router Configuration
ERS4000(config-router)#
ACLI access procedures
About this task
Perform the procedures in this section to access ACLI.
Prerequisites
• Connect to the switch with a console cable, connected directly to the console port, or use
Telnet.
• To connect to the switch remotely, through Telnet, ensure that you enable remote access
and that the switch IP address is valid.
From Global Configuration
mode, to configure OSPF,
enter:
router ospf
To configure RIP, enter:
router rip
To configure VRRP, enter:
router vrrp
To return to Global
Configuration mode, enter:
exit
To return to Privileged EXEC
mode, enter:
end
To exit ACLI completely,
enter:
logout
Fundamentals December 2011 21

User interface fundamentals
• Use a terminal or PC, with a terminal emulator, as the ACLI command station.
• If you use a console cable and console port, ensure that the terminal emulation program
conforms to settings listed in the following table.
Property Value
Baud Rate 9600 bps
Data Bits 8
Stop Bits 1
Parity None
Flow Control None
Terminal Protocol VT100 and VT100/ANSI
Opening an ACLI session
Procedure
ACLI help
This section describes help available in ACLI.
ACLI help is available at all levels.
Command list
To obtain a list of all commands available from a prompt, enter a question mark (?).
Command options
1. Connect to the switch.
2. Enter the password, if applicable.
3. At the ACLI Banner Screen, enter CTRL+Y.
4. To access ACLI, from the main menu, press c or scroll to Command Line
Interface.
5. Press Enter.
To obtain a list of all options for a command, at the prompt enter a portion of a command
followed by a space and a question mark (?).
22 Fundamentals December 2011
Comments? infodev@avaya.com
ACLI help
Command names
To obtain a correct command name, at the prompt enter a portion of the command name, and
then press the Tab key. The system displays the first unambiguous match for your selection.
For example, enter down + Tab and the system displays download.
Command modes
To obtain a list of ACLI command modes available, enter help modes.
Commands organized by mode
To obtain a list of ACLI commands, organized by command mode, enter help commands. A
short explanation of each command is included.
Keystroke shortcuts
To make using ACLI easier, use the keystroke shortcuts in the following table.
Key combination Function
Ctrl+A Start of line
Ctrl+B Back 1 character
Ctrl+C Abort command
Ctrl+D Delete the character indicated by the cursor
Ctrl+E End of line
Ctrl+F Forward 1 character
Ctrl+H Delete character left of cursor (Backspace key)
Tab Command or parameter completion
Ctrl+K and Ctrl+R Redisplay line
Ctrl+N or Down arrow Next history command
Ctrl+P or Up arrow Previous history command
Ctrl+T Transpose characters
Ctrl+U Delete entire line
Ctrl+W Delete word to left of cursor
Ctrl+X Delete all characters to left of cursor
Ctrl+z Exit Global Configuration mode to Privileged EXEC mode
? Context sensitive help
Esc+C and Exc+U Capitalize character at cursor
Esc+l Change character at cursor to lower case
Esc+B Move back 1 word
Fundamentals December 2011 23
User interface fundamentals
Key combination Function
Esc+D Delete 1 word to the right
Esc+F Move 1 word forward
Enterprise Device Manager concepts
This section provides information to start and use Enterprise Device Manager (EDM) to
monitor, manage, and configure Avaya Ethernet Routing Switch 4000 Series switches.
If you want to manage the switch from a centralized location, using Configuration and
Orchestration Manager (COM) 2.0 and higher, Avaya offers optional, product-specific EDM
plug-ins for COM that include other features such as centralized syslog, trap viewer,
troubleshooting and diagnostic tools. For more information, or to purchase plug-ins, go to
www.avaya.com.
The following table compares EDM functions in the embedded version to COM plug-in
version.
Table 1: EDM functions: embedded version compared to COM plug-in version
EDM functions Embedded
version
100% device configuration: device view, devicespecific configuration
Stackable Device Web User Interface features Yes No
Centralized off-box multi-user element
management:
• user and device credential manager
• user preference
• SSO-based user access control
• user-based Device Access Control (read only and
read-write)
• authentication through third party (RADIUS,
Microsoft AD, Sun AM)
Centralized EM plug-in management
(downloadable install and uninstall, upgrade, patch,
and inventory view
Yes Yes
No Yes
No Yes
Plug-in version
User activity log and audit trail No Yes
24 Fundamentals December 2011
Comments? infodev@avaya.com

Enterprise Device Manager concepts
EDM functions Embedded
Device performance monitoring and polling Limited High
Device-specific single device wizards and template No Yes
Centralized syslog and trap viewer No Yes
Troubleshooting and diagnostic tools (ping,
CLI*Manager, path-trace)
EDM is an embedded application that you can use for single device element management and
configuration through a standard Web browser. Because EDM is embedded into Ethernet
Routing Switch software, and the switch operates as a Web server, you do not require
additional client software.
Supported Web browsers
The following is a list of Internet Web browsers supported by EDM:
• Microsoft Internet Explorer versions 7.0 and 8.0
Plug-in version
version
performance and
low latency
No Yes
• Mozilla Firefox version 3.x
Memory requirements
If you install Configuration and Orchestration Manager on a PC to manage your switch, the
PC must have at least 500 MB of free disk space.
There are no memory requirements to use EDM through a Web browser.
Online help
Online help is context-sensitive and appears in a separate window in the Web browser.
To obtain help for the current topic, click the help button on the toolbar in the work area.
If you are using EDM through a Web browser, you need to download the help file to a TFTP
server or a USB mass storage device and configure the EDM Help file path. For procedures,
go to Getting EDM online help files for embedded EDM on page 51.
Fundamentals December 2011 25

User interface fundamentals
Interface components
This section describes Enterprise Device Manager interface components.
The Enterprise Device Manager window includes the following parts:
• Navigation tree toolbar
• Switch Summary View
• Device Physical View
• EDM window
• Navigation tree
• Menu bar
• Tool bar
• Work area
Switch summary view
The EDM initial view displays a switch summary view in the work area.
The Switch Summary tab displays basic switch information. This information-only display
derives from the configuration tab Edit > Chassis > Chassis.
Following is a list of the fields on the Switch Summary tab:
• hardware model
• hardware version
• firmware version
• software version
• system up time
• system object identifier
• system contact
• system name
• system location
A Stack Information panel appears at the bottom of the switch summary view work area that
provides a description of your switch or the units in your switch stack.
26 Fundamentals December 2011
Comments? infodev@avaya.com

This information includes the following:
• Unit number (for stacks) — also lists which unit is the base unit in a stack Switch type
• Description
• Running software version
Device Physical View
When you access EDM, the first panel in the work area displays a switch summary view. The
tab behind the summary view is a real-time physical view of the front panel of a device or stack
called the Device Physical View.
Objects in the Device Physical View are
• a stand-alone switch, called a unit
• a switch stack, called a chassis
• a port
From the Device Physical View you can
Enterprise Device Manager concepts
• determine the hardware operating status
• select a switch or a port to perform management tasks on specific objects or view fault,
configuration, and performance information for specific objects
To select an object, click the object. The system outlines the object in yellow, indicating that
the object selected.
The conventions on the device view are similar to the actual switch appearance except that
LEDs in Device Physical View do not blink. The LEDs and the ports are color-coded to reflect
hardware status. Green indicates the port is up and running; red indicates that the port is
disabled.
From the menu bar you can click the Device Physical View tab to open the Device Physical
View any time during a session.
Fundamentals December 2011 27
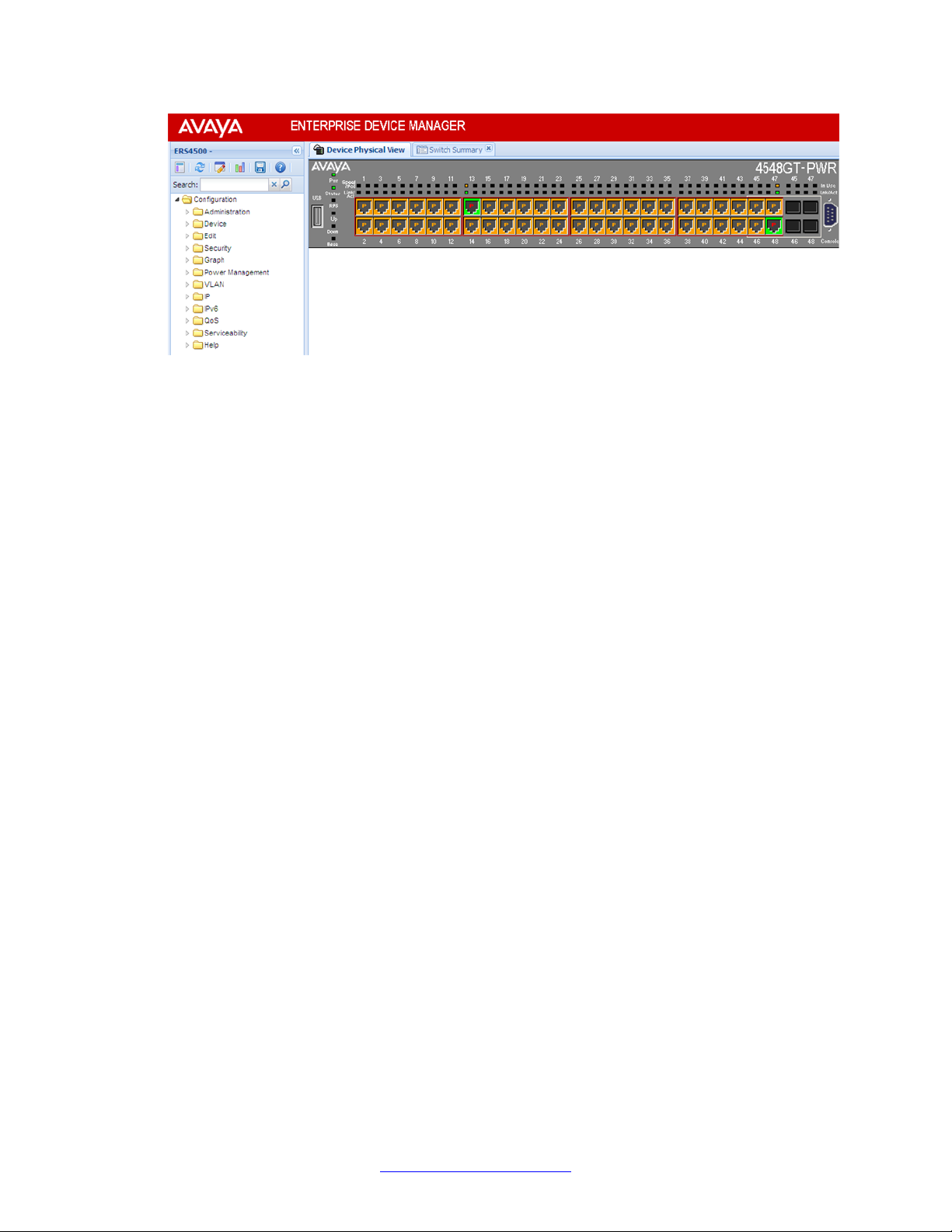
User interface fundamentals
Figure 1: Device Physical View
EDM window
The EDM window contains the following parts:
1. navigation tree—the navigation pane on the left side of the window that displays
available command folders in a tree format
2. navigation tree toolbar—the area displays buttons for common functions
3. menu bar—the area at the top of the window that displays primary and secondary
tabs that you accessed during the session; the tabs remain available until you close
them
4. toolbar—the area just below the menu bar that provides quick access to the most
common operational commands such as Apply, Refresh, and Help
5. work area—the main area on the right side of the window that displays the dialog
boxes where you view or configure switch parameters
6. Auto Complete Search — the area between the navigation tree toolbar and the
navigation tree where you can type a partial or complete search string to find menus.
When you type the search string, the navigation tree changes to display only the
entries associated with your search. T o return to the full navigation tree display , click
the x beside the Auto Complete Search dialog box.
28 Fundamentals December 2011
Comments? infodev@avaya.com
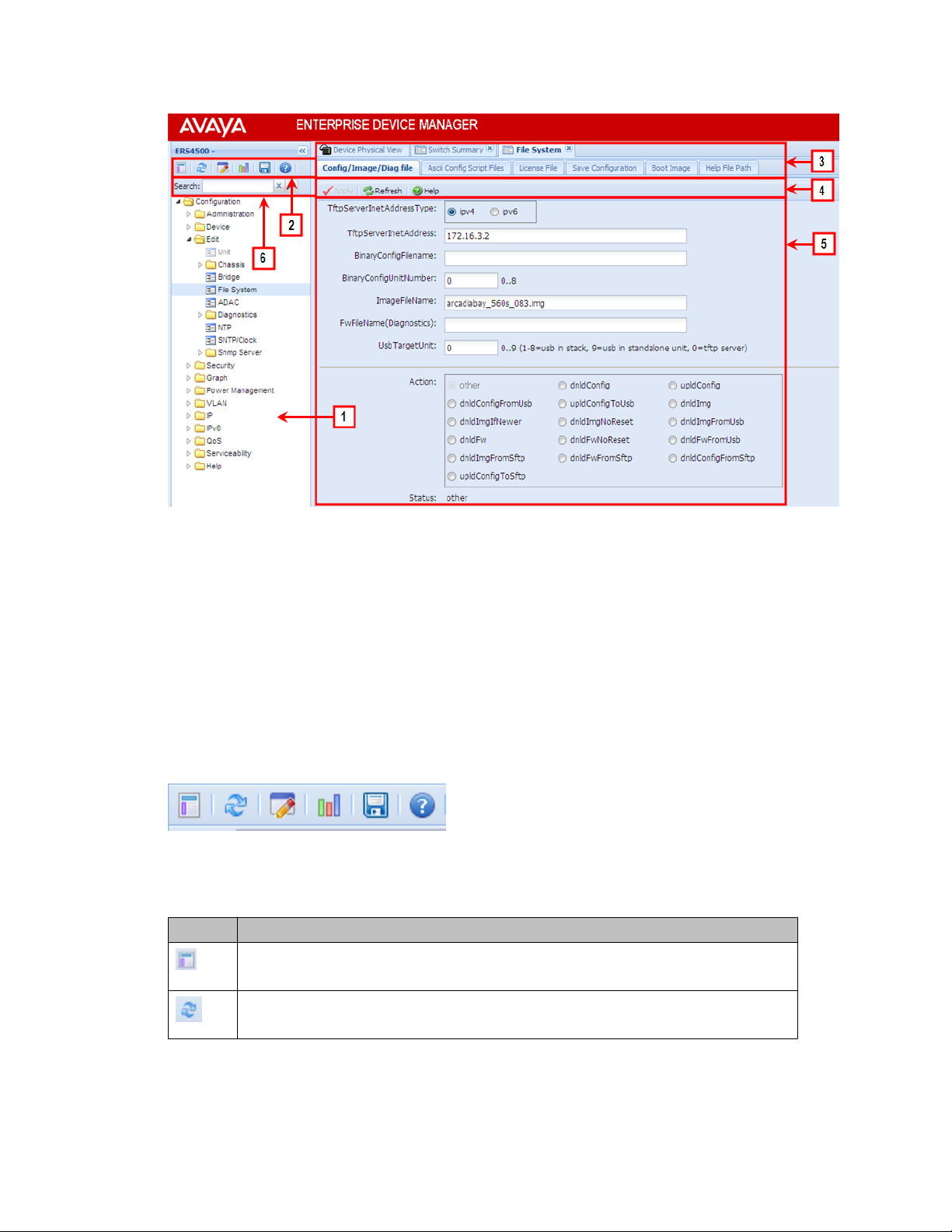
Enterprise Device Manager concepts
Figure 2: EDM window
Navigation tree
The navigation tree displays available command topics as folders in a tree.
To open a folder or sub-folder, you can click the arrowhead to the left of the folder or double-
click the folder to display the available commands tabs.
To close a folder, click the arrowhead once.
To access a command tab, click the selection in the navigation tree.
Navigation tree toolbar
You can use the toolbar above the navigation tree to perform common functions more easily.
Figure 3: Toolbar
The following is a description of the toolbar button functions:
Button Description
Switch Summary — you can use the Switch Summary toolbar button to open
or reopen the switch summary tab.
Refresh Status — in addition to the existing refresh methods you can use the
Refresh Status toolbar button to refresh the device status
Fundamentals December 2011 29
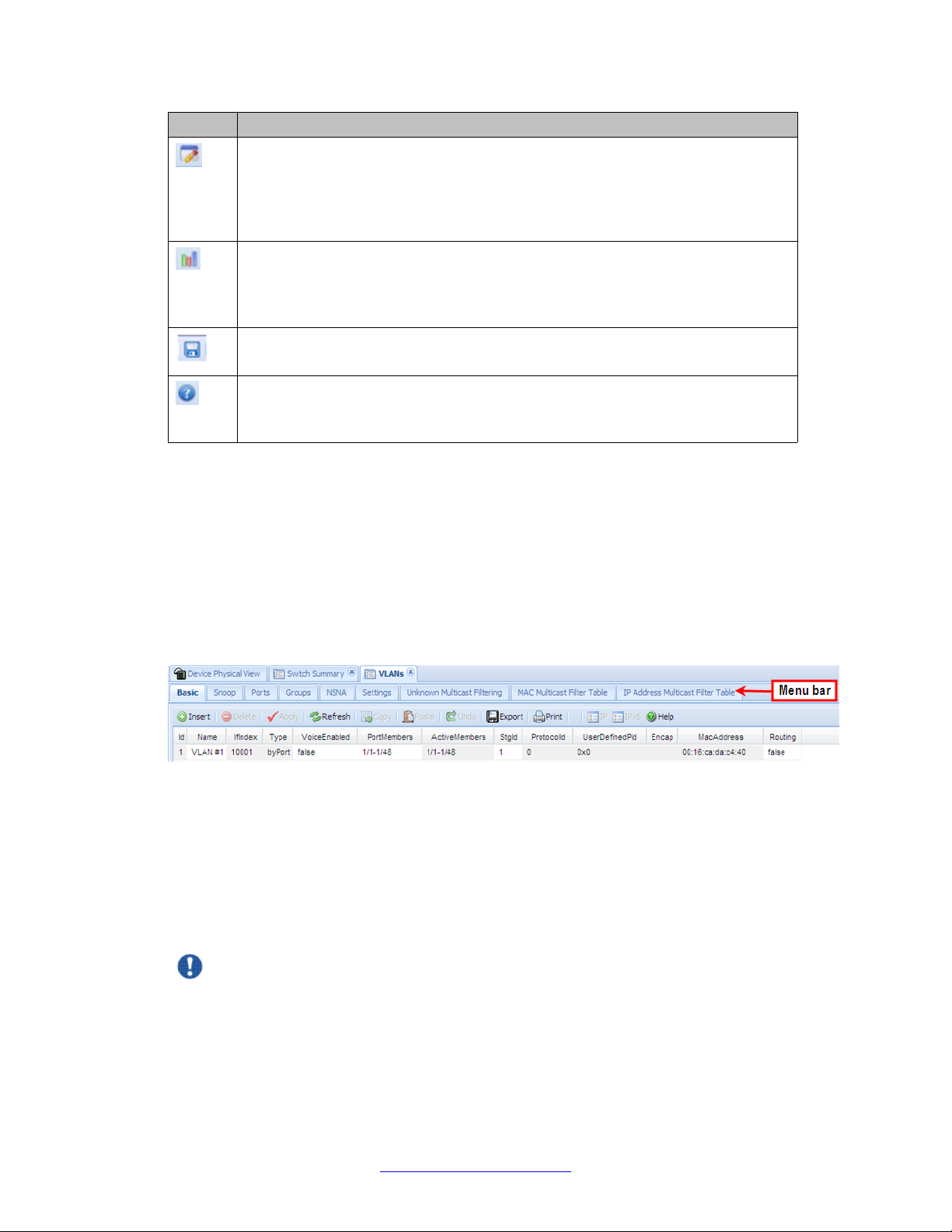
User interface fundamentals
Button Description
Edit Selected — in addition to the existing edit methods, and depending on which
object you select on the Device Physical View , you can use this toolbar button to
open Edit > Chassis, Edit > Unit, or Edit > Ports tabs. If you do not select an
object from the Device Physical View and you click the Edit Select toolbar button,
the Edit > Chassis tab opens.
Graph Selected — depending on which object you select on the Device Physical
View , you can use this toolbar button to open Graph > Chassis or Graph > Port
tabs. If you do not make a selection on the Device Physical View , or if you select
Unit, the Graph > Chassis tab opens.
Save Config — you can use the Save Config toolbar button to save the
configuration to flash memory.
Help Setup Guide — this button connects you to the help setup guide for
embedded EDM and it replaces the link that appeared on the top right of work
panes.
Menu bar
The menu bar appears above the work area and consists of two rows of tabs.
The top row displays tabs that were accessed from the navigation tree during the active
session. The tabs in this row, called primary tabs, are docked and available to reopen on
demand. The docked tabs appear in the sequence that you accessed them.
When you click a primary tab from the menu bar, the associated secondary tabs appear in the
second row and the default dialog box appears in the work area. Click any secondary tab to
display its associated dialog box.
Figure 4: Menu bar
If you want to open a dialog without displacing the current open dialog, you can go to the tab
on the menu bar and undock the tab by using your mouse to drag and drop it into the work
area. You can drag the dialog box to any location on the screen and you can toggle between
the open dialog boxes to compare information and make changes. When you no longer need
the undocked tab, you can use the three buttons on the upper right side of the tab to temporarily
shrink it, re-dock it, or close it.
Important:
When you undock a tab to make changes, and then return to another open tab, in order to
see the effects of the changes you must click the Refresh button on the tool bar.
30 Fundamentals December 2011
Comments? infodev@avaya.com
 Loading...
Loading...