Page 1

Installation & Operation Manual
tekmarNet®2 House Control 402
Introduction
The House Control 402 is designed to operate as part of a
complete hydronic heating system with tekmarNet®2 (tN2)
thermostats. It can provide operation of two outdoor reset
water temperatures such as radiant floor heating on the first
temperature and baseboard or fan coil heating on the second
temperature. In addition the control has Domestic Hot Water
and Setpoint capabilities. It is easy to add more zones, add
schedules or other convenient accessories through the use
of the tekmarNet®4 (tN4) Expansion terminals.
D 402
HVAC Systems
Features
•
Single on-off, two-stage or modulating boiler
•
Boiler outdoor reset temperature
•
Mixing outdoor reset temperature
•
Domestic Hot Water tank operation
•
Setpoint operation
•
Mix with variable speed injection, floating action,
or proportional 0-10 V (dc), proportional 4-20 mA
•
For use with tekmarNet
Four 24 V (ac) powered zone valve outputs
•
Expand to 24 zones per temperature using
•
tekmarNet®4 expansion ports
CSA C US Certified for use in USA and Canada
•
®
2 Thermostats
Replaces: 01/10
09/10
VIEW
Calls
Pumps
Boil Exp Boil System
Menu
Item
House Control 402
Zones
1 2 3 4
Benefi ts
Energy efficiency through Outdoor Temperature
•
Reset with Indoor Feedback
Indoor Feedback minimizes the water temperature
•
(increasing energy savings), and the efficiency of
your mechanical equipment through integrated
tekmarNet® Thermostats
Zone Synchronization reduces equipment cycling
•
Auto Differential - Reduces boiler cycling
•
Compact enclosure for flexible installation
•
Simple zone expansion using Wiring Centers
•
1 of 32 © 2010 D 402 - 09/10
Page 2
Table of Contents
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Installation ...................................................................... 2
Preparation ................................................................ 2
Physical Dimensions ................................................. 3
Installation Location .................................................. 3
Rough-In Wiring ........................................................ 3
Sizing the Transformer .............................................. 4
Control Wiring ........................................................... 4
Sensor Wiring ............................................................ 7
Testing the Sensor Wiring ......................................... 9
Testing the Control Wiring ......................................... 9
Max Heat ..................................................................10
Applic ations .................................................................. 11
User Interface ............................................................... 13
Display......................................................................13
Symbols ...................................................................13
Navigating The Display ............................................14
Access Levels and Thermostat Lock ........................14
Programming and Settings .......................................14
View Menu ...............................................................15
Adjust Menu ........................................................16-18
Monitor Menu ...........................................................19
Toolbox Menu .......................................................... 20
Sequence of Operation ................................................21
tekmarNet
Mix Temperature Reset Operation ...........................21
Boiler Temperature Reset Operation ....................... 22
Domestic Hot Water Tank Operation ....................... 23
Setpoint Operation .................................................. 25
Boiler Operation ...................................................... 25
Domestic Hot Water Heat Source ............................27
Pump Operation .......................................................27
Energy Saving Features .......................................... 28
Trouble shooting ............................................................ 28
Error Messages .................................................. 28-30
Frequently Asked Questions .............................. 30-31
Job Record ...............................................................31
Technical Data ..............................................................32
Limited Warranty and Product Return Procedure ........32
®
System ..................................................21
Getting Started
®
Congratulations on the purchase of your new tekmarNet
This manual covers the complete installation, programming and sequence of operation for this control. You will also find
instruction on testing, commissioning, and troubleshooting the control and system that it operates.
House Control!
Installation
Caution
Improper installation and operation of this control could
result in damage to the equipment and possibly even
personal injury or death. It is your responsibility to ensure
that this control is safely installed according to all applicable
codes and standards. This electronic control is not intended
for use as a primary limit control. Other controls that are
intended and certified as safety limits must be placed into
Radio Frequency Interference
The installer must ensure that this control and its wiring are
isolated and/or shielded from strong sources of electromagnetic
noise. Conversely, this Class B digital apparatus complies
with Part 15 of the FCC Rules and meets all requirements of
the Canadian Interference-Causing Equipment Regulations.
However, if this control does cause harmful interference
to radio or television reception, which is determined by
turning the control off and on, the user is encouraged to try
Preparation
the control circuit. Do not attempt to service the control.
Refer to qualified personnel for servicing. There are no
user serviceable parts. Attempting to do so voids warranty
and could result in damage to the equipment and possibly
even personal injury or death.
to correct the interference by re-orientating or relocating
the receiving antenna, relocating the receiver with respect
to this control, and/or connecting the control to a different
circuit from that to which the receiver is connected.
Cet appareil numérique de la classe B respecte toutes
les exigences du Règlement sur le matériel brouilleur du
Canada.
Tools Required
tekmar or jeweller screwdriver
•
Phillips head screwdriver
•
© 2010 D 402 - 09/10 2 of 32
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Needle-nose Pliers
•
Wire Stripper
•
Page 3
Materials Required
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------
(2) #10 x 1” Wood Screws
•
(3) Wire Nuts
•
18 AWG LVT Solid Wire (Low Voltage Connections)
•
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------
14 AWG Solid Wire (Line Voltage Connections)
•
tekmar 009K (24 V (ac) transformer with 4” x 4” junction box)
•
Cable or Conduit Connectors
•
Power Required
120 V (ac), 1-phase, 15 A service from circuit breaker
• Power disconnect (optional)•
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
panel
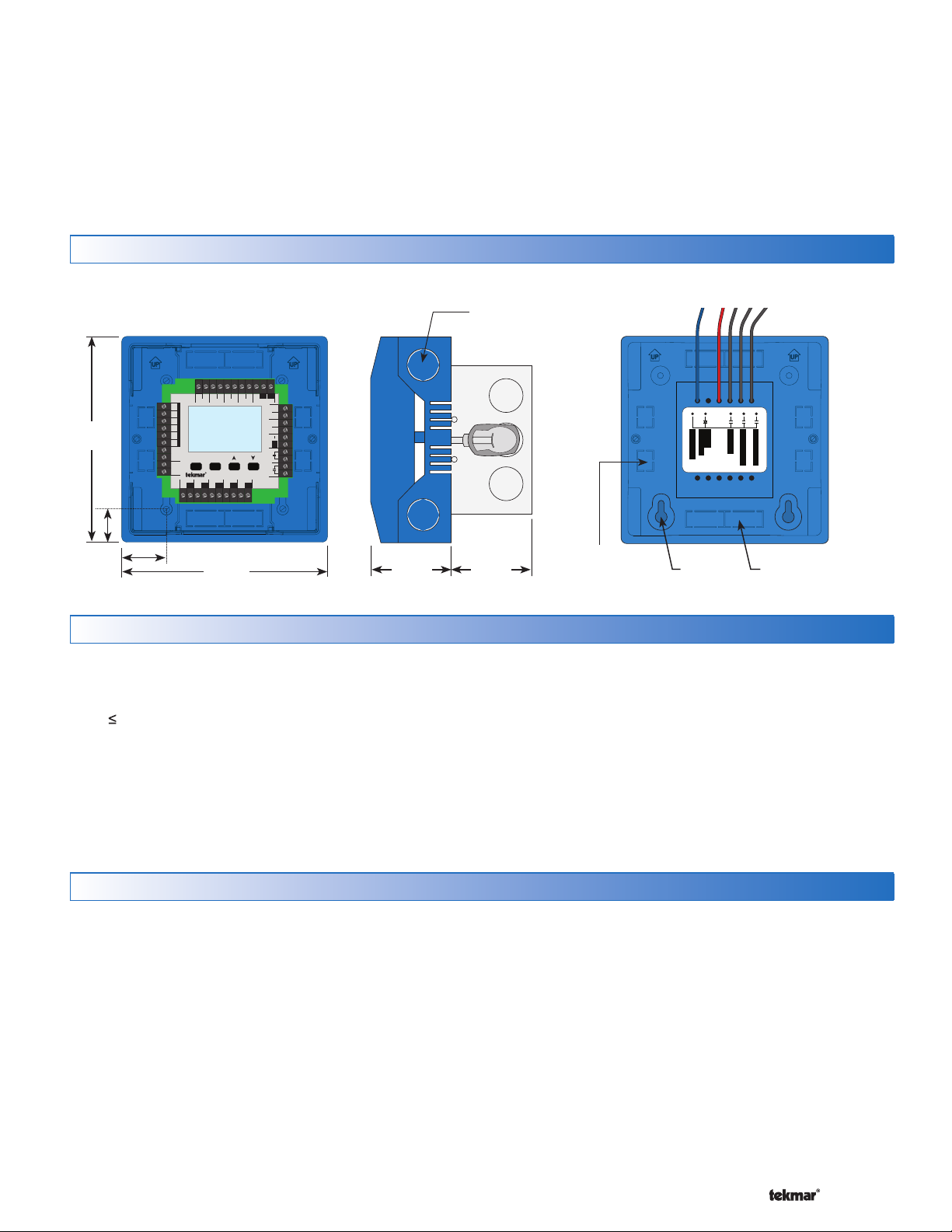
Physical Dimensions
Side ViewCover Off Front View Back View
1/2” Knock-out (x 4)
Contro l designed to mo unt on 4” x 4”
elect rical box (not include d).
Electr ical box shown comes wit h 009K
tN2 C
ClsOpn
Floating Action
Boil Exp. Mix Exp.
tN4 tN4C C
+
Mod dc/mA
Stage 2Stage 1
Input Power
Use at least 167°F
(75°C) conductors
VlvC
RC
2–1/4”
(57 mm)
2–1/4”
(57 mm)
5–1/2”
(140 mm)
7/8”
(22 mm)
CL
Made in Canada
Mix ComBoil Out DHW
Com
Sensors - No Power
Setpoint DHW
Call Call
H8007B
1–1/8”
(30 mm)
tN2 tN2 tN2 tN2 tN2 tN2 tN2
Zone 1
Zone 2 Zone 3 Zone 4
Menu
Item
House Control 402
Zone 3Zone 1 Zone 2 Zone 4
VlvC VlvC VlvC
5–1/2”
(140 mm)
1/2” x 5/8”
(12 mm x 16 mm)
Knock-out (x 4)
Pump Power L
Speed Pump
∅1/ 8”
(3 mm)
Boil System Pump
DHW Pump
Variable
Mix System Pump
7/8” x 1/2” (23 mm x 12 mm)
Knock-out (x 4)
Installation Location
When choosing the location for the control, consider the
•
following:
Keep dry. Avoid potential leakage onto the control.
•
RH 90% to 104°F (40°C).
Non-condensing environment.
Do not expose to operating temperatures beyond 32-
•
104°F (0-40°C)
Provide adequate ventilation.
•
Keep away from equipment, appliances or other
•
sources of electrical interference.
Rough-In Wiring
Line Voltage Wiring
The control operates a number of pumps through wiring
on the back of the control. The control must be mounted
to a 4” x 4” electrical junction box so that these electrical
connections are safely contained.
For ease of service, the circuit breaker or power disconnect
should be located in reasonably close proximity to the
equipment.
All line voltage wire connections are recommended to
be pulled inside a flexible or solid conduit. Always follow
proper wiring practices, building and electrical codes for
your jurisdiction.
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Locate the control near pumps and/or zone valves if
•
possible.
Provide easy access for wiring, viewing and adjusting
•
the control.
Mount approximately 5 ft. (1.5 m) off the finished floor.
•
Install the electrical junction box to a wall using #10
•
x 1” wood screws. Wall anchors are recommended
when mounting to sheet rock wallboard or masonry.
Each cable must be pulled from the equipment to the
electrical junction box. It is recommended to label each
cable for easy identification. All line voltage wires should
be stripped to a length of 1/2” (13 mm).
Pull a three conductor 14 AWG cable for the following
equipment:
Circuit Breaker or Power Disconnect
•
Mix System Pump
•
Boiler System Pump
•
DHW Tank Pump (if applicable)
•
Variable Speed Injection Pump (if applicable)
•
3 of 32 © 2010 D 402 - 09/10
Page 4
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Low Voltage Wiring
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Each cable must be pulled from the equipment to the
control’s plastic enclosure. All low voltage wiring connections
enter the enclosure through conduit knockouts on the
sides, or through the square knockouts on the rear. It is
recommended to label each cable for easy identification.
All low voltage wires are to be stripped to a length of 3/8”
(9 mm) to ensure proper connection to the control.
Pull two conductor 18 AWG LVT cable, up to 500 feet
(150 m) for the following equipment:
tekmarNet®2 Thermostats
•
Zone Valves
•
Mixing Valve Actuator Proportional 0-10 V (dc)
•
Boiler Stage 1 T-T
•
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Sizing the Transformer
The control requires an external transformer. A tekmar
Transformer 009 (or 009K which includes a 4”x 4” electrical
box) can supply up to 40 VA, and includes an in-line fuse
to protect the transformer and control.
In order to correctly size the external transformer, all loads
connected to the control must be taken into account.
When adding up the loads, consider the following:
tekmarNet®2 Thermostats draw approximately 2 VA each.
•
Each zone valve must be sized for peak load. This can
•
be obtained by multiplying the peak current draw (in
Amps) by 24 V (ac).
Boiler Stage 2 T-T (if applicable)
•
Modulating Boiler 0-10 V (dc) or 4-20 mA (if applicable)
•
Outdoor Temperature Sensor
•
Boiler Supply Temperature Sensor
•
Mix Supply Temperature Sensor
•
DHW Tank Temperature Sensor (if applicable)
•
DHW Tank Aquastat (if applicable)
•
Setpoint Devices (if applicable)
•
Pull three conductor 18 AWG LVT cable for the following
equipment:
Mixing Valve Actuator Floating Action
•
tekmarNet®4 Accessories (User Switch, Timer)
•
If using a Floating Action mixing valve, add the VA
•
draw for the actuating motor. A tekmar Actuating Motor
741 draws 1.5 VA during normal operation.
The total power capacity of the power supply should be
larger than the total load of all the devices connected
to the control. This total load must not exceed 100 VA.
Multiple tekmar Transformer 009’s can be wired together
to increase total VA capacity.
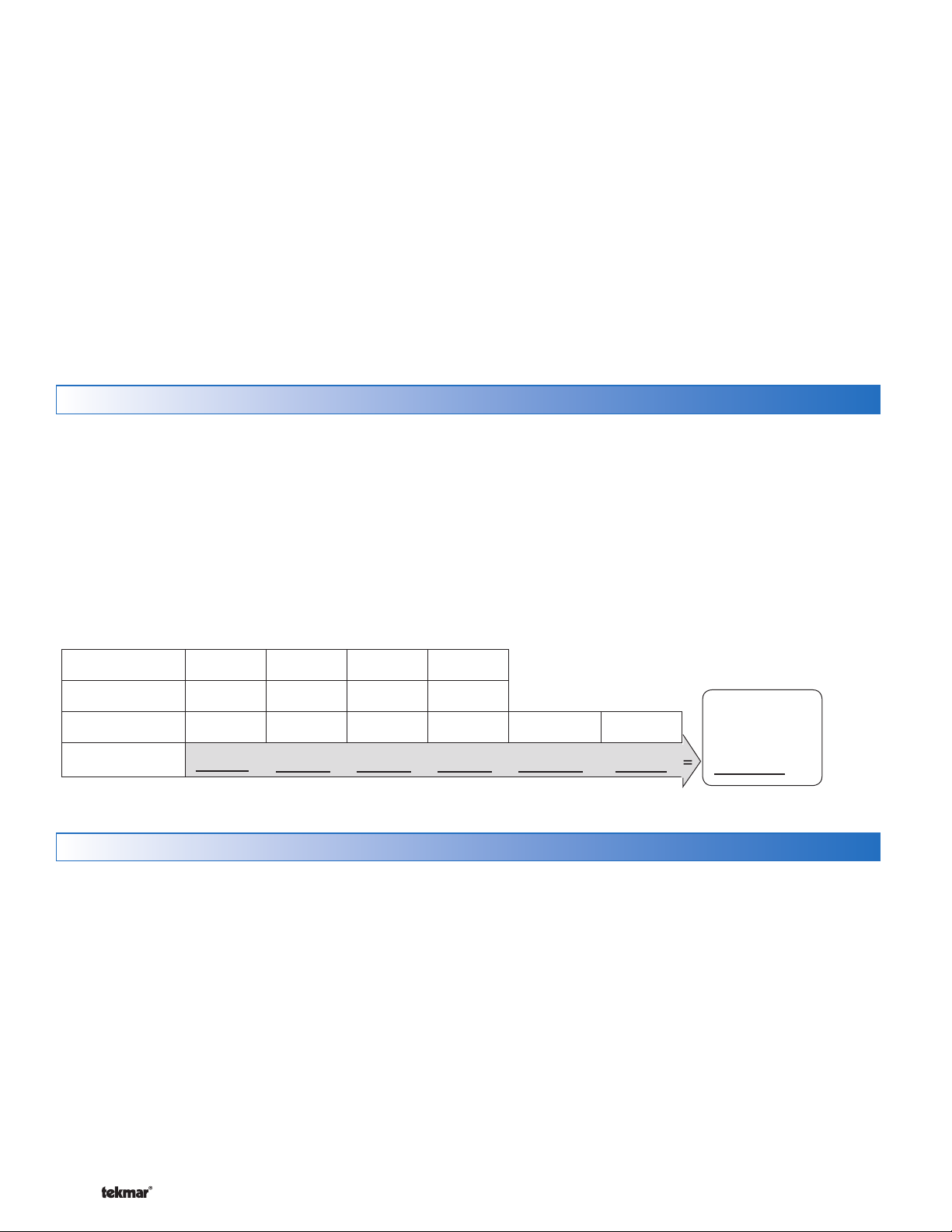
The following chart is provided to simplify transformer
sizing:
Zone
Thermostat Load
Zone Valve Load
Total Zone Load
1234
Floating
Action (VA)
+ +++ +
Control
Load (VA)
Control Wiring
Line Voltage Wiring
CAUTION: TURN ALL POWER OFF BEFORE PERFORMING ANY WIRING.
Ground the Pumps
Connect the pump grounds to the power supply
•
ground as shown in Figure 1. The ground wire must
also be grounded to the electrical box.
Wire the Pump Neutrals
Connect the Neutral (N) wires from each pump and wire
•
to the 115 V (ac) Neutral (N) wire. If the transformer has
been mounted to this electrical box, connect its neutral
wire with this group. This is shown in Figure 2.
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Wire the Pump Power (L)
Connect the 115 V (ac) line voltage (L) wire to the red
•
Pump Power (L) wire on the back of the House Control
and to the 115 V (ac) side of the transformer. Use a
wire nut or approved connector. See Figure 3.
Wire the Pumps
Wire each remaining line voltage pump wire into the
•
push-in wire connector of the corresponding pump
lead on the back of the House Control. This is shown
in Figure 4.
Transformer
must exceed:
2
VA
© 2010 D 402 - 09/10 4 of 32
Page 5
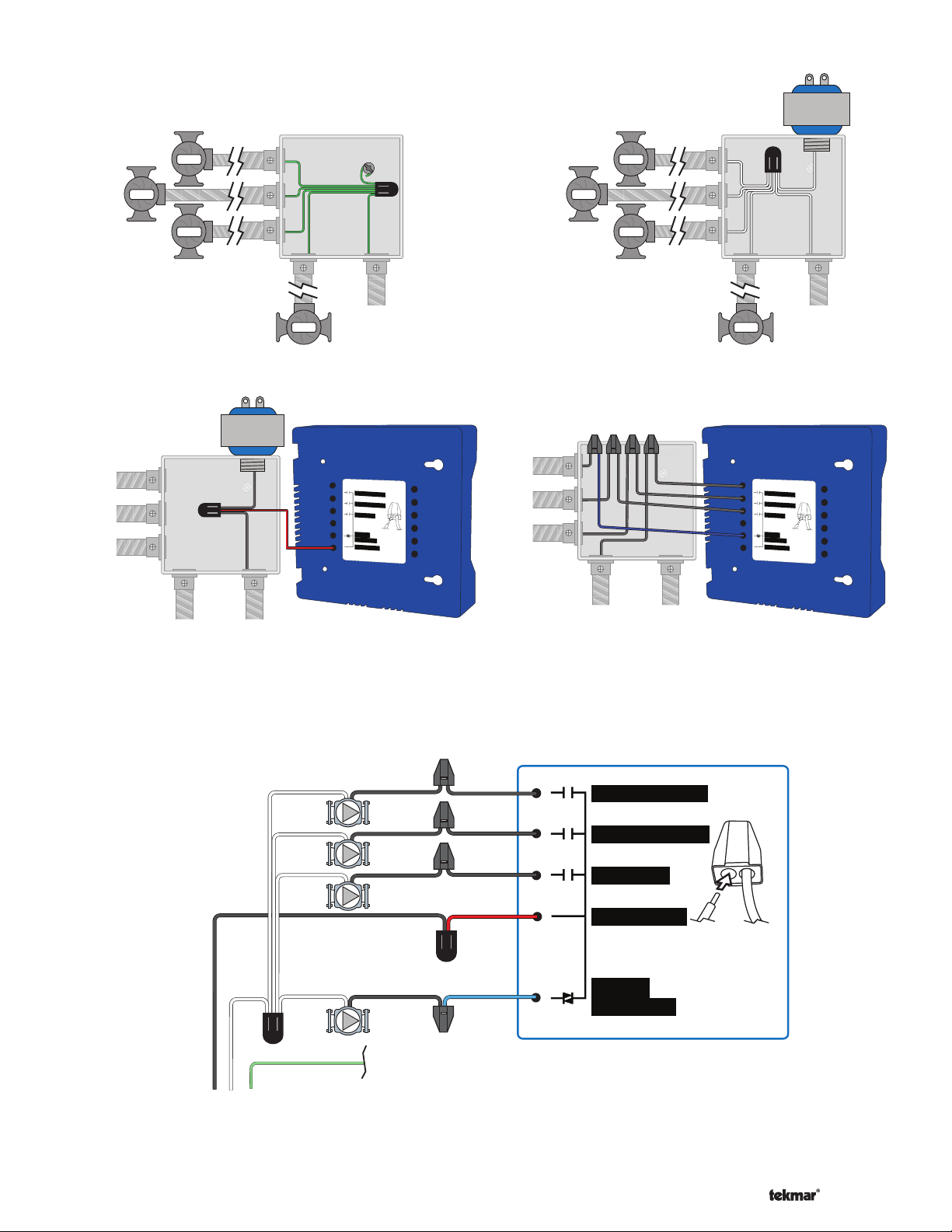
Figure 1 - Connect
-------------------------------------------------------------------
Ground Wires
Variable Speed Pump
Figure 2 - Connect
Neutral Wires
Variable Speed Pump
Pump
Pump
DHW Pump
Pump
Boil System Pump
Figure 3 - Connect
Line Voltage (Hot)
V. S. Pump
DHW Pump
Boil Sys Pump
Mix System
Pump
Mix System
Pump
Power
Source
(L,N)
Pump
Power Source
(L,N)
402
Mix System Pump
Boil System Pump
DHW Pump
Strip wires
Variable
1/2 inch (13 mm).
Speed Pump
Installed wires are
not remov
able.
Pum
p Power L
12-18
AWG
Pump
DHW Pump
Boil System Pump
Figure 4 - Connect
Pump Line (Hot)
V. S. Pump
DHW Pump
Boil Sys Pump
Mix System
Pump
Pump
Pump
Power
Source
(L,N)
Mix System
Pump
Pump
402
Mix System Pump
Boil System Pump
DHW Pump
Variab le
Speed Pump
Pump Power L
Power Source
(L,N)
Strip wires
1/2 inch (13 mm).
Installed wires are
not removable.
12-18 AWG
Rear Line Voltage Wiring Diagram
N
G
L
N
115 V (ac)
-------------------------------------------------------------------
Back of House Control 402
Mix
(black)
Mix System Pump
Boil
(black)
Boil System Pump
DHW
(black)
DHW Pump
(red)
Pump Power L
L
Variable
Speed
to pump grounds
(blue)
Variable
Speed Pump
Strip wires
1/2 inch (13 mm).
Installed wires are
not removable.
12-18 AWG
5 of 32 © 2010 D 402 - 09/10
Page 6
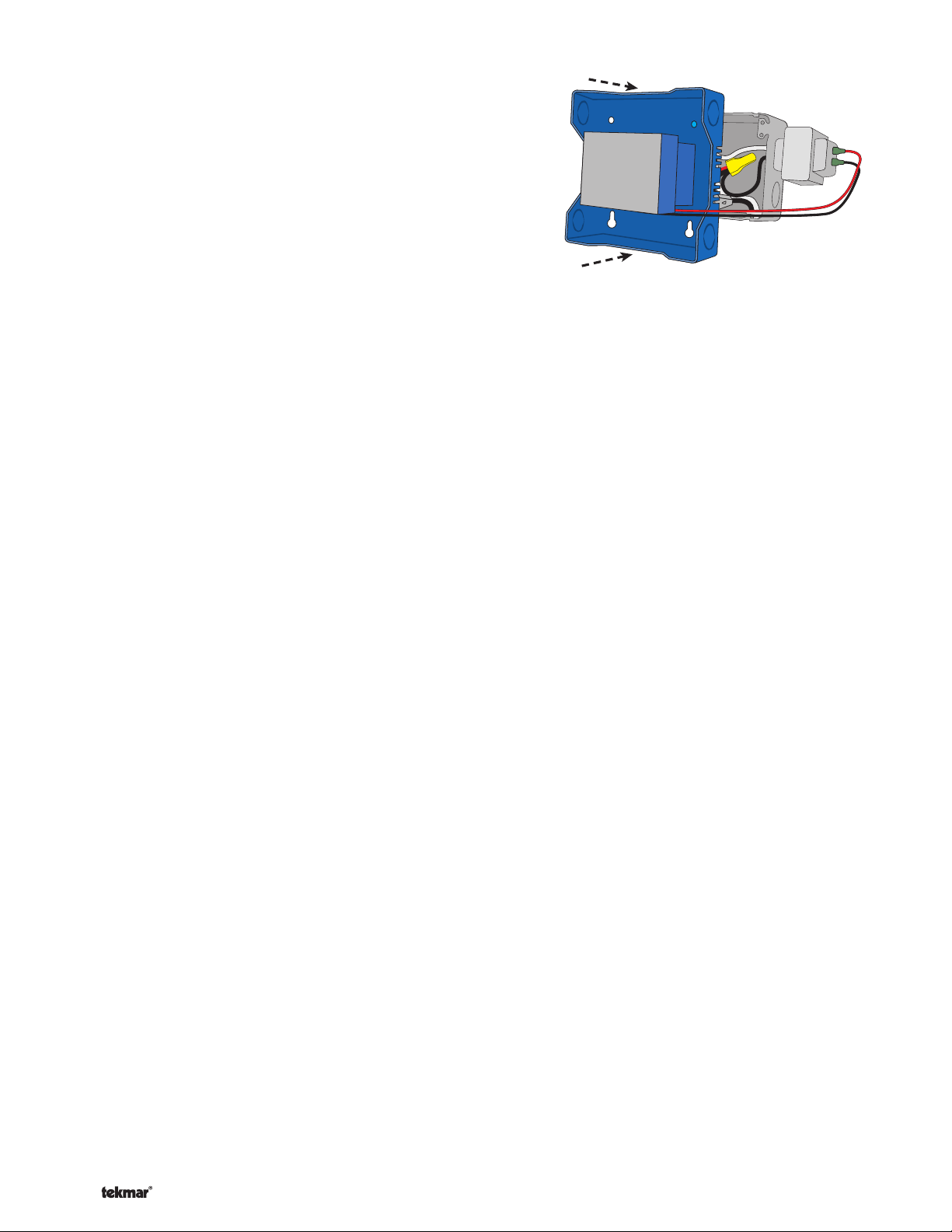
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Install The Enclosure
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Ensure that the pump wires are neatly tucked inside
•
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------
the electrical box.
Using 2 of the 4 holes in the back of the enclosure, se-
•
curely fasten it to the electrical junction box with 2 #10
screws as shown in Figure 5.
Figure 5
Low Voltage Wiring
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------
External Power Supply
It is strongly recommended that a transformer with an in-line
fuse be used in order to protect the transformer from high
currents. The tekmar Transformer 009 includes a fuse.
Connect the 24 V (ac) leads from the transformer to the
•
C and R terminals marked “Input Power” on the 402.
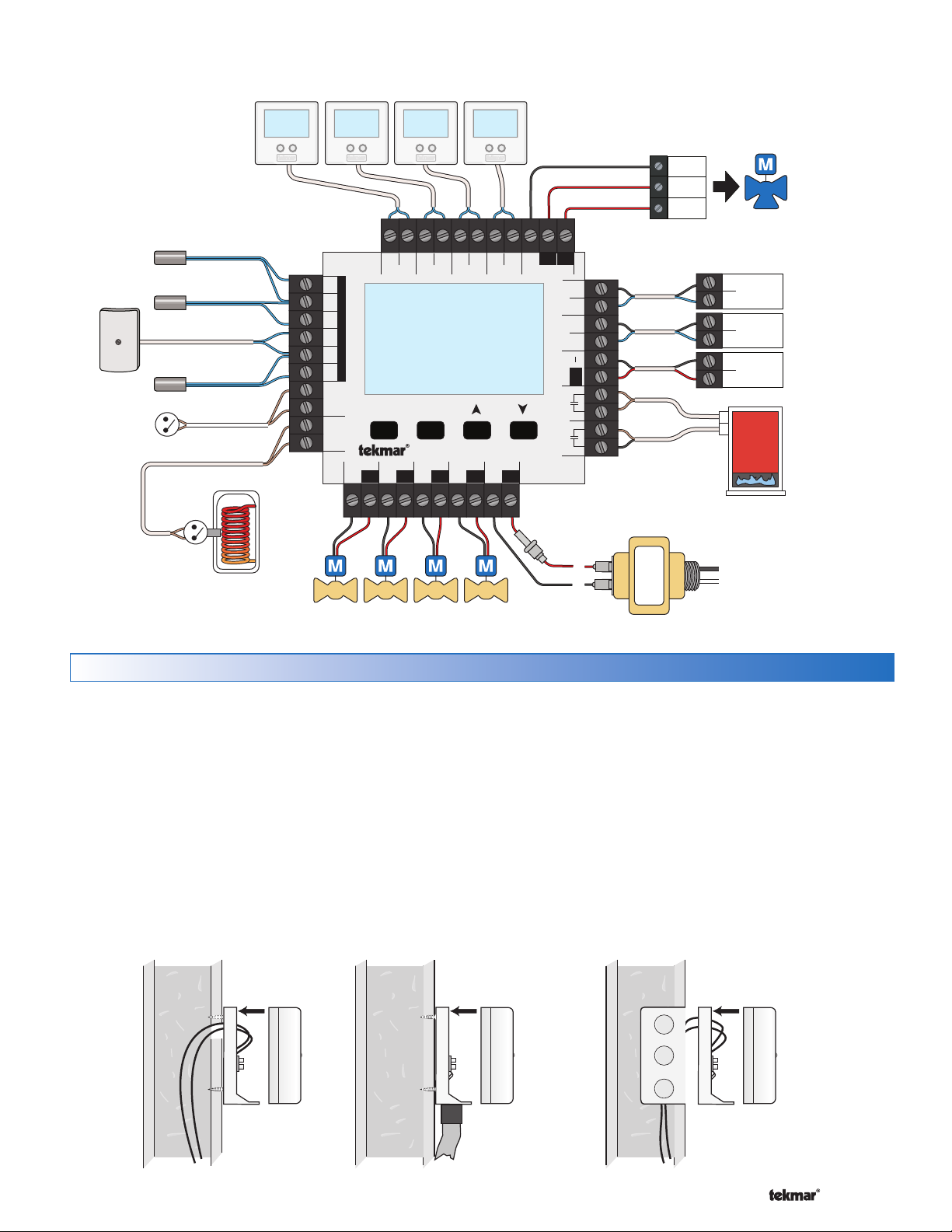
tN2 Thermostats
The 402 is designed to operate with tekmarNet®2 Thermostats.
They provide the heating and cooling control for each zone,
and communicate with any other tekmarNet® device on
the system.
Connect the tN2 terminals from each thermostat to the
•
corresponding tN2 terminals for each zone on the 402.
Zone Valves
Wire the zone valves to the C and Vlv terminals on the
•
402.
End switches on zone valves are not required when
•
using the 402.
tN4 Expansion Terminals
The 402 uses the Expansion tN4 and C terminals to
communicate with additional thermostats, setpoint controls,
and other tekmarNet® devices. There are two sets of tN4
and C terminals on the 402.
Boil Exp.
To add additional boiler water temperature zones (typically
baseboard or fan coil zones) to the system, install a
tekmarNet® Wiring Center.
Connect the tN4 and C Boil Exp. terminals on the 402
•
to the corresponding tN4 and C Expansion terminals
on the external Wiring Center.
Mix Exp.
The 402 has the capacity to expand the number of mixing
zones in the system beyond the four on board zones. To
add additional mix water temperature zones (typically
radiant floor zones) to the system, install a tekmarNet
Wiring Center.
Connect the tN4 and C Mix Exp. terminals on the 402
•
to the corresponding tN4 and C Expansion terminals
on the external Wiring Center.
Domestic Hot Water (DHW) or Setpoint Call
When the control receives a DHW Call or Setpoint Call for
heat it will override Outdoor Reset and Indoor Feedback
and operate the boiler to heat the DHW tank or the Setpoint
equipment.
To create a DHW call, wire a dry contact OR apply 24
•
V (ac) to the DHW call terminals.
To create a Setpoint call, wire a dry contact OR apply
•
24 V (ac) to the Setpoint call terminals.
Wiring the Boiler
The 402 can operate a single modulating boiler, single
on-off, or a single two-stage on-off boiler.
On/Off Boiler
Connect the Boiler Stage 1 terminals on the 402 to the
•
T-T (or R-W) terminals on the boiler.
If required, connect the Boiler Stage 2 terminals on the
•
402 to the second stage T-T (or R-W) terminals on the
boiler.
Modulating Boiler
Wire the Mod (dc/mA) positive (+) and negative (-) ter-
•
minals on the 402 to the input signal terminals on the
boiler. Correct polarity of the wires is important.
In some cases, the modulating boiler also requires
•
contact closure on the T-T terminals to fire the boiler. If
required, connect the Boiler Stage 1 terminals on the
402 to the T-T (or R-W) terminals on the boiler.
Floating Action Terminals
Applications that use a floating action mixing valve actuator
(tekmar type 741) will use the Floating Action Opn, Cls, and
C terminals. This is a powered output (24 V (ac)).
Wire the Opn, Cls, and C terminals on the 402 to the
•
open, close, and C terminals on the floating action
actuator.
Proportional Mixing (0-10 V (dc) or 4-20 mA)
®
Applications that use a proportional mixing valve actuator
will use the Mod (dc/mA) terminals. Proportional mixing can
only be used when a modulating boiler is not installed.
Wire the Mod positive (+) on the 402 to the positive (+)
•
terminal on the actuator.
Wire the Mod negative (-) on the 402 to the negative (-)
•
or common terminal on the actuator.
© 2010 D 402 - 09/10 6 of 32
Page 7
R
C
L
N
Com
Open
Close
Expansion
tN4 Boil
CtN4
Modulating
Boiler
—+
Expansion
tN4 Mix
CtN4
2
1
WC
WC
Menu
House Control 402
Item
+
Mix ComBoil Out DHW
VlvC VlvC VlvC
Zone 3Zone 1 Zone 2 Zone 4
Made in Canada
VlvC
Com
Zone 1
H8007B
Zone 2 Zone 3 Zone 4
tN2 tN2 tN2 tN2 tN2 tN2 tN2 tN2
C
Floating Action
ClsOpn
Sensors - No Power
Call Call
tN4 tN4CC
Mod dc/mA Boil Exp. Mix Exp.
Setpoint DHW
Use at least 167°F
(75°C) conductors
RC
Input Power
Stage 2Stage 1
Front Low Voltage Wiring Diagram
-------------------------------------------------------------------
--------------------------------------------------------------------
tekmarNet
Mix Supply
Sensor 082
Outdoor
Sensor
070
Boiler Supply
Sensor 082
DHW Tank
Sensor 082
Setpoint Call
-------------------------------------------------------------------
®
2 Thermostats
24 V (ac) Floating
Action Actuator
tekmarNet®4
Expansion to
Wiring Centers,
Timers, or
User Switch
One or Two Stage
Boiler T-T
DHW Call
from DHW
Tank Aquastat
(optional)
Zone Valves
Sensor Wiring
Mounting the Outdoor Sensor 070
Note: The temperature sensor (thermistor) is built into the
070 enclosure.
Remove the screw and pull the front cover off the
•
sensor enclosure.
The 070 can either be mounted directly onto a wall or
•
a 2” x 4” electrical box. When the 070 is wall mounted,
the wiring should enter through the back or bottom of
the enclosure. Do not mount the 070 with the conduit
knockout facing upwards as rain could enter the enclosure and damage the sensor.
--------------------------------------------------------------------
24 V (ac) Transformer 009
In order to prevent heat transmitted through the wall
•
from affecting the sensor reading, it may be necessary
to install an insulating barrier behind the enclosure.
The 070 should be mounted on a wall which best rep-
•
resents the heat load on the building (a northern wall
for most buildings and a southern facing wall for buildings with large south facing glass areas). The 070
should not be exposed to heat sources such as ventilation or window openings.
The 070 should be installed at an elevation above
•
the ground that will prevent accidental damage or
tampering.
Sensor with rear
entry wiring
Sensor with bottom
entry wiring
7 of 32 © 2010 D 402 - 09/10
Sensor mounted
onto 2" x 4"
electrical box
Page 8
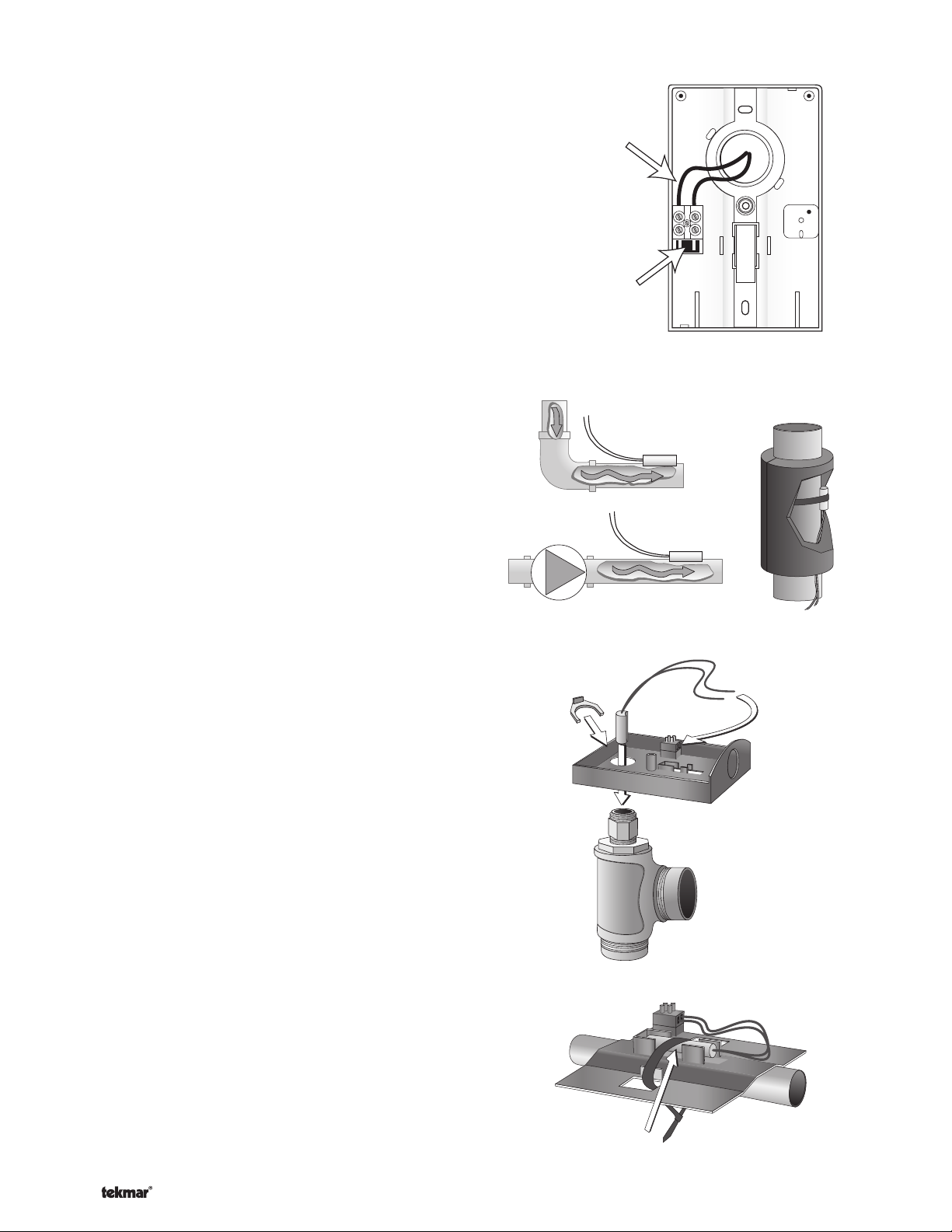
Wiring the Outdoor Sensor 070
-----------------------------------------------------------------------
-------------------------------------------------------------
Connect 18 AWG or similar wire to the two terminals
•
-----------------------------------------------------------------------
provided in the enclosure and run the wires from the
070 to the control. Do not run the wires parallel to telephone or power cables. If the sensor wires are located
in an area with strong sources of electromagnetic interference (EMI), shielded cable or twisted pair should
be used or the wires can be run in a grounded metal
conduit. If using shielded cable, the shield wire should
be connected to the Com or Com Sen terminal on the
control and not to earth ground.
Follow the sensor testing instructions in this brochure
•
and connect the wires to the control.
Replace the front cover of the sensor enclosure.
•
Wires from outdoor
sensor to control
terminals
(Com Sen - Out Sen)
Sensor is built into
the enclosure
Mounting the Boiler and Mix Sensor 082
-------------------------------------------------------------
Note: These sensors are designed to mount on a pipe or
in a temperature immersion well.
The Universal Sensor should be placed downstream of a
pump or after an elbow or similar fitting. This is especially
important if large diameter pipes are used as the thermal
stratification within the pipe can result in erroneous sensor
readings. Proper sensor location requires that the fluid
is thoroughly mixed within the pipe before it reaches the
sensor.
Strapped to Pipe
The Universal Sensor can be strapped directly to the pipe
using the cable tie provided. Insulation should be placed
around the sensor to reduce the effect of air currents on
the sensor measurement.
Immersion Well
If a Universal Sensor is mounted onto 1” (25 mm) diameter
L type copper pipe, there is approximately an 8 second
delay between a sudden change in water temperature and
the time the sensor measures the temperature change.
This delay increases considerably when mild steel (black
iron) pipe is used. In general, it is recommended that
a temperature well be used for steel pipe of diameter
greater than 1-1/4” (32 mm). Temperature wells are also
recommended when large diameter pipes are used and
fluid stratification is present.
Conduit Connection
The Universal Sensor 082 and Universal Sensor Enclosure
080 (sold separately) are specifically designed to mount
onto a 3/8” (10 mm) ID temperature well that is supplied
with an end groove. To install the well, plumb a ‘T’ into the
pipe and fix the well into the ‘T’. The 080 enclosure has
a 7/8” (22 mm) back knockout that must be removed and
fitted over the temperature well. The 082 is then inserted
into the well and the retaining clip supplied with the
enclosure is snapped onto the well end groove. If the well
has a threaded end, the installer must supply a standard
threaded conduit retaining ring. The two wires from the
sensor are connected to the terminal block provided in the
enclosure. The other side of the terminal block is used to
connect wires from the control.
Retaining Clip
Universal
Sensor 082
Universal
Sensor 082
Sensor Well
Bottom of
Enclosure 080
Cable Tie
© 2010 D 402 - 09/10 8 of 32
Page 9
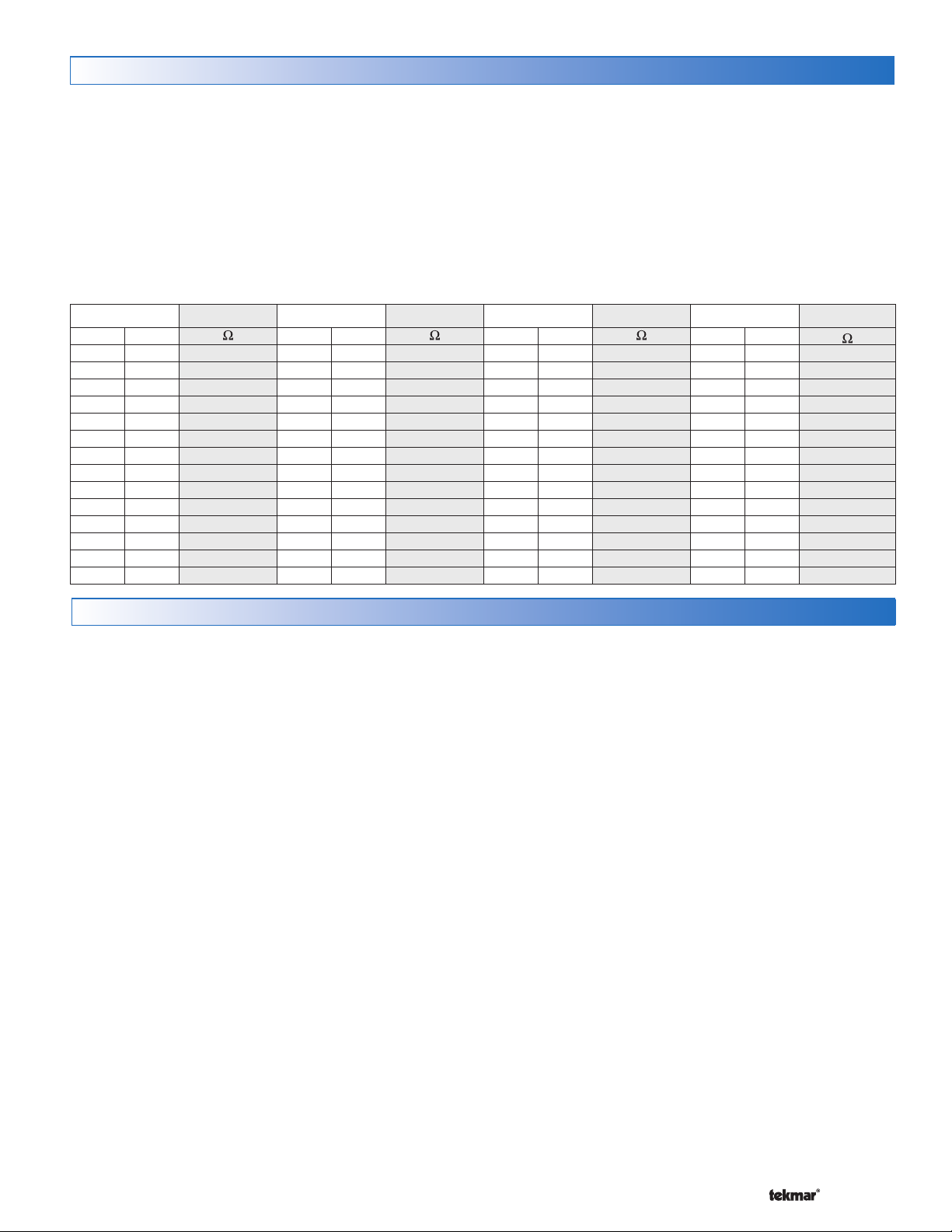
Testing the Sensor Wiring
------------------------------
-----------------------
--------------------------------------
A good quality test meter capable of measuring up to 5,000
kΩ (1 kΩ = 1000 Ω) is required to measure the sensor
resistance. In addition to this, the actual temperature must
be measured with either a good quality digital thermometer,
or if a thermometer is not available, a second sensor can
be placed alongside the one to be tested and the readings
compared.
First measure the temperature using the thermometer and
then measure the resistance of the sensor at the control.
The wires from the sensor must not be connected to the
estimate the temperature measured by the sensor. The
sensor and thermometer readings should be close. If the
test meter reads a very high resistance, there may be a
broken wire, a poor wiring connection or a defective sensor.
If the resistance is very low, the wiring may be shorted,
there may be moisture in the sensor or the sensor may
be defective. To test for a defective sensor, measure the
resistance directly at the sensor location.
Do not apply voltage to a sensor at any time as damage
to the sensor may result.
control while the test is performed. Using the chart below,
TemperatureResistanceTemperatureResistanceTemperatureResistanceTemperatureResistance
°F °C
-50 -46 490,813 20 -7 46,218 90 32 7,334 160 71 1,689
-45 -43 405,710 25 -4 39,913 95 35 6,532 165 74 1,538
-40 -40 336,606 30 -1 34,558 100 38 5,828 170 77 1,403
-35 -37 280,279 35 2 29,996 105 41 5,210 175 79 1,281
-30 -34 234,196 40 4 26,099 110 43 4,665 180 82 1,172
-25 -32 196,358 45 7 22,763 115 46 4,184 185 85 1,073
-20 -29 165,180 50 10 19,900 120 49 3,760 190 88 983
-15 -26 139,402 55 13 17,436 125 52 3,383 195 91 903
-10 -23 118,018 60 16 15,311 130 54 3,050 200 93 829
-5 -21 100,221 65 18 13,474 135 57 2,754 205 96 763
0 -18 85,362 70 21 11,883 140 60 2,490 210 99 703
5-15 72,918 7524 10,501 14563 2,255 215102 648
10 -12 62,465 80 27 9,299 150 66 2,045 220 104 598
15 -9 53,658 85 29 8,250 155 68 1,857 225 107 553
°F °C °F °C °F °C
Testing the Control Wiring
Testing the Power
If the control display does not turn on, check the Input
Power wiring terminals using an electrical multimeter.
The voltage should measure between 21.6 to 26.4 V
(ac). If the voltage is below this range, measure the
line voltage side of the transformer. The voltage should
measure between 103.5 to 126.5 V (ac).
Testing the Thermostats
If the thermostat display turns on, this indicates that
the thermostat is operating correctly and there are no
electrical issues. In the event that the display is off, or
the display is cycling on and off, follow this procedure.
1. Remove the tN2 wires from the thermostat.
2. Use an electrical meter to measure DC voltage between
the tN2 terminals.
If the DC voltage is 0 V (dc) for 20 seconds, then there is
an open or short circuit in the tN2 wires. If the DC voltage
is 0 V (dc) for 10 seconds and then is 23 to 24 V (dc) for 5
seconds, this indicates the wiring is correct.
3. Connect the thermostat to the tN2 wires from a zone
on a House Control, Wiring Center, or Zone Manager.
4. If the thermostat display is off, or is cycling on and off,
move the thermostat to the next available zone on the
House Control, Wiring Center, or Zone Manager.
If the thermostat display remains permanently on, there
may be a fault with the previously tried zone on the House
Control, Wiring Center, or Zone Manager.
------------------------------
-----------------------
If the thermostat display continues to be off, or is cycling
on and off, there may be a fault on the thermostat.
If a fault is suspected, contact your tekmar sales
representative for assistance.
User Test
--------------------------------------
The User Test is found in the Toolbox menu of the control.
Press the Menu button to access the Toolbox Menu. Press
the Item button to locate the User Test.
Start the test sequence by going to the User Test item and
pressing the ‘Up’ arrow button.
Pause the test sequence by pressing the Item button. To
advance to the next step, press the Item button again.
If the test sequence is paused for more than five minutes,
the control exits the entire test routine and returns to normal
operation.
To advance to a particular step, repeatedly press and
release the Item button to display the appropriate device.
User Test Sequence
Step 1
The Mix 1 device ramps up to 100% over 30 seconds
or according to the motor speed setting.
Step 2
The Mix 1 device ramps down to 0% over 30 seconds
or according to the motor speed setting.
Step 3
Step 4
Step 5
Step 6
Step 7
Zone 1 turns on for 10 seconds.
Zone 2 turns on for 10 seconds.
Zone 3 turns on for 10 seconds.
Zone 4 turns on for 10 seconds.
The mix system pump turns on for 10 seconds.
9 of 32 © 2010 D 402 - 09/10
Page 10

Step 8
----
----------------------
-----------------
------------------------
---------------
-------------
-------------
----------
--------------------------
----------------------
Step 9
Step 10
•
•
•
•
Step 11
Testing the Variable Speed Injection Pump
Activate the User Test sequence and pause at Step 1
by pressing the Item button once the injection pump is
operating at 100%. Using an electrical meter, measure the
voltage between the variable speed pump and a neutral.
The voltage should measure between 103.5 V (ac) and
126.5 V (ac).
Testing the Zone Output
Activate the User Test sequence and pause at Step 3 by
pressing the Item button once Zone 1 turns on. Using an
electrical meter, measure the voltage between the zone
valve and the common (C) terminals. The voltage should
measure between 21.6 V (ac) and 26.4 V (ac). Repeat for
Zones 2, 3, and 4.
Testing the Mix System Pump
Activate the User Test sequence and pause at Step 7 by
pressing the Item button once the mix system pump turns
on. Using an electrical meter, measure the voltage between
the mix system pump and a neutral. The voltage should
measure between 103.5 V (ac) and 126.5 V (ac).
The DHW pump turns on for 10 seconds.
The boiler system pump turns on for 10
seconds.
During the boiler test step, zone relays 1 through 4
turn on, the mix system pump turns on, and the boil
system pump turns on. The mixing device operates
up to 20%. This ensures there is a location for heat
to move when the boiler is turned on.
If the Boil Type is 1 Stage, the boiler stage 1 relay is
closed for 10 seconds and then opened.
If the Boil Type is 2 Stage, the boiler stage 1 relay is
closed for 10 seconds, then the boiler stage 2 relay is
closed for 10 seconds and then both relays are opened.
If Boiler Type is modulating 0 - 10, the boiler stage
1 relay is closed for 10 seconds and the modulating
output operates at 50 % [5 V (dc)].
If Boiler Type is modulating 4 - 20, the boiler stage
1 relay is closed for 10 seconds and the modulating
output operates at 50 % (12 mA).
Control returns to normal operation.
----
----------------------
-----------------
Testing the DHW Pump
Activate the User Test sequence and pause at Step 8 by
pressing the Item button once the DHW pump turns on.
Using an electrical meter, measure the voltage between
the DHW pump and a neutral. The voltage should
measure between 103.5 V (ac) and 126.5 V (ac).
Testing the Boiler System Pump
Activate the User Test sequence and pause at Step 9 by
pressing the Item button once the boiler system pump turns
on. Using an electrical meter, measure the voltage between
the boiler system pump and a neutral. The voltage should
measure between 103.5 V (ac) and 126.5 V (ac).
Testing the Boiler Stage 1 Contact
Activate the User Test sequence and pause at Step 10 by
pressing the Item button once the boiler stage 1 turns on.
Using an electrical meter, measure for continuity over the
boiler stage 1 terminals.
Testing the Boiler Stage 2 Contact
This test applies for 2 stage on-off boilers only.
Activate the User Test sequence and pause at Step 10 by
pressing the Item button once the boiler stage 2 turns on.
Using an electrical meter, measure for continuity over the
boiler stage 2 terminals.
Testing the Boiler Modulating Output
This test applies for modulating boilers only.
Active the User Test sequence and pause at Step 10 by
pressing the Item button once the boiler stage 1 turns on.
Using an electrical meter, measure for either a 5 V (dc) or
12 mA signal. The Boil Type setting selects whether the
signal is V (dc) or mA.
Testing the DHW Call
Remove all wires from the DHW Call terminals. The control
display should show no DHW Call. Reconnect wires. Then
apply either a short circuit or 24 V (ac) over the DHW Call
terminals. The control should now show a DHW Call.
Testing the Setpoint Call
Remove all wires from the Setpoint Call terminals. The
control display should show no Setpoint Call. Reconnect
wires. Then apply either a short circuit or 24 V (ac) over
the Setpoint Call terminals. The control should now show
a Setpoint Call.
------------------------
---------------
-------------
-------------
----------
--------------------------
----------------------
Max Heat
The control has a function called Max Heat. In this mode,
the control turns on and operates the system up to the
maximum set temperatures as long as there is a call for
heat. Use this mode to run the circulators during system
start-up and commissioning, purging air from the piping.
This feature is useful when drying sheet rock and paint in
the building.
To enable Max Heat, enter the Toolbox Menu and find Max
Heat. Use the up arrow to select ‘On’.
When a space heating call is present, the boiler will
•
run to maintain a target of Boil Design + 10°F (+ 6°C).
(One can purge the system using this test and leave
© 2010 D 402 - 09/10 10 of 32
the boiler un-powered. This will prevent heat from entering the system during the purge.)
When a DHW Call or Setpoint Call is present, the
•
boiler will operate at the DHW exchange or Setpoint
temperature settings.
WWSD and DHW Priority is disabled during Max Heat
•
mode.
When Max Heat is on the display will show ‘Max Heat
•
Test ’.
Max Heat will automatically turn off after 24 hours.
•
To Cancel Max Heat, go to Max Heat in the Toolbox menu
and use the down arrow to select ‘Off’.
Page 11

Applications
Single Boiler, DHW Tank, Variable Speed Mixing, 4 Mix Zones A402-1
Description: The House Control 402 operates an On/Off boiler with indirect Domestic Hot Water. Mixing is performed with
variable speed injection, which supplies an outdoor reset water temperature to the 4 onboard mix temperature hydronic
zones. Additional zones (boiler or mix) can be added using the tN4 Expansion terminals.
Outdoor
Sensor
(S3)
P2
Mix Sensor (S2)
Boiler Sensor (S1)
S3
P1
tekmarNet
Made in Canada
Mix ComBoil Out DHW
Com
Sensors - No Power
Setpoint DHW
Call Call
Menu
H8007B
VlvC VlvC VlvC
070
402
P3 P4
®
2 Thermostats
tN2 tN2 tN2 tN2 tN2 tN2 tN2 tN2
Zone 1
Zone 2 Zone 3 Zone 4
Item
House Control 402
Zone 3Zone 1 Zone 2 Zone 4
VlvC
Input Power
C
Floating Action
Use at least 167°F
(75°C) conductors
RC
tekmarNet®2 Thermostats
Z1 Z2 Z3 Z4
S2S1
ClsOpn
tN4 tN4CC
+
Mod dc/mA Boil Exp. Mix Exp.
Stage 2Stage 1
CtN4
CtN4
1
tN4 Mix
Expansion
tN4 Boil
Expansion
tekmarNet®4
Expansion to
Wiring Centers,
Timers, or
User Switch
DHW Call
L
115 V (ac)
Boiler T-T
R
C
24 V (ac)
L
N
Transformer 009
Zone Valves (Z1 to Z4)
Back of House Control 402
(black)
(P4)
(P1)
(P2)
Mix
Boil
DHW
(black)
(black)
(red)
L
Variable
Speed
N
G
N
(P3)
to pump grounds
(blue)
Mix System Pump
Boil System Pump
DHW Pump
Pump Power L
Variable
Speed Pump
Strip wires
1/2 inch (13 mm).
Installed wires are
not removable.
12-18 AWG
11 of 32 © 2010 D 402 - 09/10
Page 12

Single Boiler, 2 Boiler Zones, DHW, 3 Way Mix, 4 Mix Zones A402-2
Description: The House Control 402 operates a modulating boiler with indirect Domestic Hot Water. Mixing is performed with
a three-way floating action mixing valve, which supplies a reset water temperature to four mix temperature hydronic zones.
Two boiler water temperature zones shown are operated by a Wiring Center through the tN4 Boil Expansion terminals.
Outdoor
Sensor
(S3)
P2
S1
Mix Sensor (S2)
Boiler Sensor (S1)
DHW Sensor (S4)
S4
P1
tekmarNet
Made in Canada
Mix ComBoil Out DHW
Com
Sensors - No Power
Setpoint DHW
Call Call
H8007B
S3
313
®
2 Thermostats
tN2 tN2 tN2 tN2 tN2 tN2 tN2 tN2
Zone 1
Zone 2 Zone 3 Zone 4
Menu
Item
House Control 402
Zone 3Zone 1 Zone 2 Zone 4
VlvC VlvC VlvC
070
VlvC
Input Power
402
C
Floating Action
Use at least 167°F
(75°C) conductors
RC
P3
ClsOpn
tN4 tN4CC
+
Mod dc/mA Boil Exp. Mix Exp.
Stage 2Stage 1
tekmarNet®2 ThermostatstekmarNet®2 Thermostats
Z1 Z2 Z3 Z4
S2
Com
Open
Close
1
CtN4
tN4 Mix
Expansion
CtN4
tN4 Boil
Expansion
—+
Modulating
Boiler
tekmarNet
Expansion to
313
Wiring Centers,
Timers, or
User Switch
®
4
Zone Valves (Z1 to Z4)
Back of House Control 402
(black)
(P3)
(P1)
(P2)
Mix
Boil
DHW
(black)
(black)
(red)
L
(blue)
to pump grounds
G
L
N
115 V (ac)
© 2010 D 402 - 09/10 12 of 32
Mix System Pump
Boil System Pump
DHW Pump
Pump Power L
Variable
Speed Pump
R
C
Strip wires
1/2 inch (13 mm).
Installed wires are
not removable.
12-18 AWG
24 V (ac)
L
N
Transformer 009
Page 13

User Interface
Display
Menu Field
Displays the
current menu
Status Fields
Displays the current
status of the control’s
inputs, outputs and
operation. Most symbols
in the status field are
only visible when the
VIEW Menu is selected
Symbols
VIEW
ADJUST
MONITOR
MAXMIN
Calls
Boil Exp
Mix Exp
DHW Setp
Pumps WWSD Saving
Boil System
Mix System Zones
DHW Var 1 2 3 4
1 2
min
sec
PM
hr
AM
Cls
Opn
Mix
Item Field
Displays the name
of the selected item
Number Field
Displays the
current value of
the selected item
Calls
Pumps
Zones
1 2 3 4
Saving
WWSD
CALLS
Displays any call for heat the control is
receiving.
PUMPS
Displays any pump currently operating.
ZONES
Displays if an on-board zone is operating.
WARNING
Displays if an error exists on the system.
ENERGY SAVING INDICATOR
Displays when the system is saving energy.
See the Energy Saving Features section.
WWSD
Displays when the system is in Warm
Weather Shut Down.
°F°C
minhr
sec%
Cls
Opn
MAXMIN
°F, °C, %, HOURS, MINUTES, SECOND
Units of measurement for current number.
UNOCCUPIED
Indicates that a User Switch or Timer has
put the system into UnOccupied.
BOILER
Indicates that the boiler should be
heating.
DEVICE OUTPUT SCALE
Displays output of the mixing valve or
injection pump.
CLOSE / OPEN
Displays whether the mixing valve motor
is opening or closing.
MIN / MAX
Displays when an operating temperature
reaches a minimum or maximum value.
13 of 32 © 2010 D 402 - 09/10
Page 14

Navigating The Display
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
The 402 uses a simple user interface to accomplish a
variety of functions. The four buttons beneath the display
Menu Button
The menus display in the Menu Field at the top left side of
the LCD. Four menus are available: View, Adjust, Monitor
and Toolbox (identified by the wrench symbol).
The View menu allows the user to view the current
•
status of various system parameters.
The Adjust menu allows the installer to adjust settings
•
to ensure control operation matches requirements of
the mechanical system.
Item Button
Each menu contains a list of Items that can be viewed and,
in some cases, adjusted. Press the item button to scroll
through the list in each Menu.
Up and Down Buttons
The Up and Down buttons are primarily used for adjusting
settings.
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
are used to change the menu, sort through Items, and
adjust each setting as required.
The Monitor menu keeps track of run times and
•
other important data that is collected during system
operation.
The Toolbox menu is a source of system information
•
and includes useful tools for commissioning and testing the system.
To view the next available item, press and release the
•
Item button.
To view the previous item, hold down the Item button,
•
and press and release the Up button.
To adjust a setting:
Select the appropriate menu using the Menu button.
•
Select the item using the Item button.
•
Use the Up or Down button to make the adjustment.
•
Default Item
When navigating menus, the display reverts back to the
default item (View Menu) after 60 seconds of button
inactivity.
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Access Levels and Thermostat Lock
The 402 is shipped pre-programmed with common settings.
The 402 has an ‘Installer’ access level that allows full access
to all settings and a ‘User’ access level that restricts the
number of settings to only the Warm Weather Shut Down
and the temperature units. The 402 defaults to the ‘User’
access level after 12 hours of operation.
All thermostats are locked while the 402 is in the ‘User’
access level. Certain settings on the thermostat will be
unavailable while the thermostat is locked.
Programming and Settings
The 402 settings can be found in the ‘Adjust’ menu. When
changing the items value, the setting is saved to the control’s
memory once the Item button is pressed to advance to the
next item, or after 60 seconds, the control times out and
reverts back to the ‘View’ menu.
To set the default item in the View menu, display the
•
item for more than five seconds.
To change to the ‘Installer’ access level and Unlock the
thermostats:
In the Toolbox menu, locate Access
•
Adjust the access level to ‘Installer’ by pressing the
•
up or down button. This prevents unwanted setting
changes to the control.
All settings are stored in permanent memory and will be
kept correctly during any loss of power.
© 2010 D 402 - 09/10 14 of 32
Page 15

View Menu (1 of 1)
Item Field Range Description
VIEW
Calls
Pumps
Zones
VIEW
Calls
Pumps
Zones
The View menu items display the current operating temperatures and status information
of the system.
OUTDOOR SECTION B, C
-76 to 149°F
(-60.0 to 65.0°C)
Current outdoor air temperature as measured by the outdoor sensor. The
outdoor air temperature is shared to all thermostats in the tekmarNet®
system.
-22 to 266°F
(-30.0 to 130.0°C)
MIX SUPPLY
Current mix supply water temperature as measured by the mix supply
sensor. The control operates the mixing device so that the mix supply
SECTION B
is equal to the mix target temperature.
VIEW MENU
VIEW
VIEW
VIEW
VIEW
Calls
Calls
Calls
Calls
Pumps
Pumps
Pumps
Pumps
Zones
Zones
Zones
Zones
– – –, 35 to 180°F
(1.5 to 82.0°C)
-22 to 266°F
(-30.0 to 130.0°C)
– – –, 35 to 200°F
(1.5 to 93.0°C)
0-100%
-22 to 266°F
(-30.0 to 130.0°C)
MIX TARGET SECTION B
The temperature the control is currently trying to maintain at the mix
supply sensor. The mix target is calculated based on the outdoor
design and mix design settings. “– – –” is displayed when no heat is
required for mix zones.
BOILER SUPPLY SECTION C
Current boiler supply water temperature as measured by the boiler
sensor. The control operates the boiler so that the boiler supply is
within the boiler differential of the boiler target. ‘MIN’ is shown when
the control is providing boiler minimum protection to the boiler.
BOILER TARGET SECTION C
The boiler target is the temperature the control is currently trying to
maintain at the boiler supply sensor. The boiler target is calculated based
on the outdoor design, boiler design, and boiler minimum settings. “– – –”
is displayed when no heat is required for boiler zones. ‘MIN’ is shown
when the control is providing boiler minimum protection to the boiler.
BOILER MODULATION SECTION F
Current percent modulation of the boiler’s burner. The boiler modulation
increases when the boiler supply is less than the boiler target. The
boiler modulation decreases when the boiler supply is greater than the
boiler target.
Note: This item is only available when the Boil Type setting is set to
0-10 or 4-20.
DHW TANK SECTION D
Current Domestic Hot Water tank temperature as measured by the optional
DHW sensor. If the DHW tank temperature falls 6°F (3.0°C) below the
DHW Occ setting, a DHW call is created and the tank is heated.
Note: This item is only available when a DHW sensor is installed and
DHW Mode is set to 1 to 4.
DHW SUPPLY SECTION D
-22 to 266°F
(-30.0 to 130.0°C)
Current supply water temperature to the indirect DHW tank heat
exchanger as measured by the DHW sensor.
Note: This item is only available when a DHW sensor is installed and
DHW Mode is set to 5.
SYSTEM IN AWAY SECTION I
--
The heating system is in the Away scene. The DHW tank will not be
heated. Setpoint calls are still responded to.
Use the User Switch to change scene out of Away.
After the last item, the control returns to the first item in the menu.
15 of 32 © 2010 D 402 - 09/10
Page 16

Adjust Menu (1 of 3)
The Adjust menu items are the programmable settings used to operate
the mechanical equipment.
Item Field Range
ADJUST
ADJUST
(21.0 to 82.0°C)
Default = 120°F
ADJUST
-60 to 45°F
(-51.0 to 7.0°C)
Default = 10°F
(-12.0°C)
70 to 180°F
(49.0°C)
4-20 mA,
0-10 V (dc)
FLOT,
VAR
Default = VAR
Access
Installer
Installer
Installer
Description Set to
OUTDOOR DESIGN SECTION B, C
Typically set to the temperature of the coldest day
of the year. The outdoor air temperature used in the
boiler and mixing heating curves that determine the
boiler target and the mix target temperatures.
MIX DESIGN
SECTION B
The supply water temperature required for the mix
zones to heat the building on the typical coldest day
of the year. Recommendations:
High mass radiant floor = 120°F (50°C)
Low mass radiant floor = 140°F (60°C)
Fancoil or air handling unit = 190°F (90°C)
Copper fin-tube convector = 180°F (80°C)
Radiators = 160°F (70°C)
Low profile baseboard = 150°F (65°C)
MIX TYPE SECTION B
Select the type of mixing device.
VAR = Variable speed injection pump
FLOT = Floating action motor for mixing valves
0-10 = 0 -10 V (dc) analog signal for mixing valves
4-20 = 4-20 mA analog signal for mixing valves
Note: 0-10 and 4-20 are only available when Boiler
Type = 1 Stage or 2 Stage.
ADJUST MENU
ADJUST
30 to 230 seconds
sec
Default = 105 seconds
Installer
MIX MOTOR
The time that the mix actuating motor requires to
operate from fully closed to fully open.
tekmar actuating motors = 105 sec.
Refer to actuating motor for correct setting.
Note: This item is only available when the Mix Type
is set to FLOT (floating action motor), 0-10, or 4-20.
BOILER TYPE
EMS2,
EMS1,
4-20
0-10,
2STG,
1STG
Default = 1STG
Installer
The type of boiler connected to the control.
1STG = single one-stage on-off boiler
2STG = single two-stage on-off boiler
0-10 = 0-10 V (dc) modulating boiler
4-20 = 4-20 mA modulating boiler
EMS1 = tekmar boiler staging controls
EMS2 = Viessmann modulating boilers with
OpenTherm
Note: Only 1STG and 2STG are available when the
Mix Type is set to 0-10 V (dc) or 4-20 mA.
Continued on next page.
© 2010 D 402 - 09/10 16 of 32
SECTION B
SECTION F
Page 17

Adjust Menu (2 of 3)
Item Field Range
VIEW
(21.0 to 93.5°C)
OFF, 80 to 180°F
(26.5 to 82.0°C)
70 to 200°F
Default = 180
(82.0°C)
Default = 140
(60.0°C)
°F
°F
Access
Installer
Installer
Description Set to
BOILER DESIGN SECTION C
The supply water temperature required for the boiler
zones to heat the building on the typical coldest day
of the year. Recommendations:
High mass radiant floor = 120°F (50°C)
Low mass radiant floor = 140°F (60°C)
Fancoil or air handling unit = 190°F (90°C)
Copper fin-tube convector = 180°F (80°C)
Radiators = 160°F (70°C)
Low profile baseboard = 150°F (65°C)
BOILER MINIMUM SECTION B, C
The minimum allowed boiler target temperature and
temperature at which the mixing device begins to
provide boiler protection against cold return water
temperatures. The mixing valve or variable speed
injection pump operate at low percent output when
the boiler supply temperature drops below this
setting.
Recommendations:
Condensing gas or electric boiler = OFF
Non-condensing gas and oil boilers = 140°F (60°C)
Note: If Boiler Type is 0-10 V (dc), 4-20 mA, EMS1
or EMS2, this setting is defaulted to Off. The mixing
device does not provide boiler protection when Boiler
Type is set to EMS1 or EMS2.
ADJUST MENU
ADJUST
ADJUST
ADJUST
ADJUST
10 to 230 seconds
sec
Default = 30
seconds
0 to 50%
Default = 0%
0 to 3:00 minutes
sec
Default = 10
seconds
Off or On
Default = Off
Installer
Installer
Installer
Installer
BOILER MOTOR SECTION F
The time required for the modulating actuating motor
to fully open the gas valve or ramp the burner fan
from off to full speed on a modulating boiler. Set to
30 seconds unless otherwise recommended by the
boiler manufacturer.
Note: This item is only available when the Boiler
Type is 0-10 V (dc) or 4-20 mA.
MINIMUM MODULATION SECTION F
The minimum percent modulation of the boiler
burner.
Note: This item is only available when the Boiler
Type is 0-10 V (dc) or 4-20 mA.
MODULATION DELAY SECTION F
Delay time between the burner firing and the boiler
releasing to modulation.
Note: This item is only available when the Boiler
Type is 0-10 V (dc) or 4-20 mA.
FLUSHING SECTION G
Set to On when a domestic hot water tank is used
to heat the building. When On, the control ensures
that each zone is operated at least once daily to
prevent stagnation.
Continued on next page.
17 of 32 © 2010 D 402 - 09/10
Page 18

Adjust Menu (3 of 3)
Item Field Range
ADJUST
(4.5 to 38.0°C)
ADJUST
(4.5 to 38.0°C)
Off, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5
(38.0 to 93.5°C)
40 to 100°F
Default = 70
°F
(21.0°C)
40 to 100°F
Default = 60
°F
(15.5°C)
Default = 2
100 to 200°F
Default = 180
(82°C)
°F
Access
Installer
User
Installer
Installer
Installer
Description Set to
WWSD OCCUPIED
SECTION I
The system’s Warm Weather Shut Down temperature
during Occupied periods or when a schedule is not
used.
WWSD UNOCCUPIED
SECTION I
The system’s Warm Weather Shut Down temperature
during Unoccupied periods.
Note: Item is only available when a schedule or User
Switch is present on the system.
DHW MODE SECTION D
Selects the DHW mode of operation. The
mode determines the zone and boiler system
pumps operation whenever the DHW pump is in
operation.
DHW EXCHANGE SECTION D
Selects the minimum boiler target to the DHW heat
exchanger.
Note: Item is only available in DHW Modes 1 through 4
when a DHW sensor is not connected. It is available in
DHW Mode 5 when a DHW sensor is connected.
ADJUST MENU
ADJUST
ADJUST
ADJUST
70 to 180°F
(21.0 to 82.0°C)
Default = 125
°F
(51.5°C)
Off or On
Default = On
60 to 200°F
(15.5 to 93.5°C)
Default = 180
°F
(82.0°C)
°F or °C
Default =
°F
Installer
Installer
Installer
Installer
User
DHW OCCUPIED SECTION D
Selects the temperature of the indirect DHW tank.
Note: Item is only available when an optional DHW
sensor is installed except in DHW Mode 5.
DHW UNOCCUPIED SECTION I
Selects whether or not the indirect DHW tank should
be heated to during Unoccupied time periods.
Note: Item is only available when Schedule #1
is available or a User Switch is present on the
system.
SETPOINT SECTION E
The minimum boiler target temperature when a
Setpoint Call is present.
UNITS
Selects units for temperature display.
After the last item, the control returns to the first item in the menu.
© 2010 D 402 - 09/10 18 of 32
Page 19

Monitor Menu (1 of 1)
The Monitor menu items provide information about the system’s operation and performance.
To clear any item back to default, press and hold the Up and Down buttons while viewing
that item.
MONITOR
MONITOR
MONITOR
MONITOR
Item Field
Pumps
DHW
Range
Description
OUTDOOR HIGH
-76 to 149°F
(-60.0 to 65.0°C)
Records the highest outdoor temperature since the item was
last cleared. Press and hold the Up and Down buttons while
viewing to reset.
OUTDOOR LOW
-76 to 149°F
(-60.0 to 65.0°C)
Records the lowest outdoor temperature since the item was
last cleared. Press and hold the Up and Down buttons while
viewing to reset.
RUN TIME (BOILER)
hr
0 to 9999 Hours
Default = 0 hr
The total ‘on’ time of the boiler relay since the item was last
cleared. Press and hold the Up and Down buttons while
viewing to reset.
RUN TIME (DHW PUMP)
hr
0 to 9999 Hours
Default = 0 hr
The total running time of the DHW Pump since this item was
last cleared. Press and hold the Up and Down buttons while
viewing to reset.
MONITOR
MONITOR MENU
MONITOR
MONITOR
Pumps
Boil System
Pumps
Mix System
Saving
hr
0 to 9999 Hours
Default = 0 hr
hr
0 to 9999 Hours
Default = 0 hr
hr
0 to 9999 Hours
Default = 0 hr
RUN TIME (BOIL SYSTEM PUMP)
The total running time of the Boil System Pump since this item
was last cleared. Press and hold the Up and Down buttons
while viewing to reset.
RUN TIME (MIX SYSTEM PUMP)
The total running time of the Mix System Pump since this item
was last cleared. Press and hold the Up and Down buttons
while viewing to reset.
RUN TIME ($AVING)
Maintains a record of the total length of time the $aving icon
has been active. Press and hold the Up and Down buttons
while viewing to reset.
BOILER ENERGY USE
MONITOR
hr
0 to 9999 Hours
Default = 0 hr
Multiply this value by the BTU rating (input BTU/hr) of the boiler
to get an approximate energy consumption (in BTU’s) for the
boiler. Press and hold the Up and Down buttons while viewing
to reset. Not available when Boiler Type is EMS1 or EMS2.
After the last item, the control returns to the first item in the menu.
19 of 32 © 2010 D 402 - 09/10
Page 20

Toolbox Menu (1 of 1)
The Toolbox Menu is a location for system information and
Test functions. If any errors are present on the system, they
will be located at the beginning of this menu.
Item Field
Range
On or Off
Default = Off
On or Off
Default = Off
402
J12 06B
INST (Installer)
or USER
Default = INST
Description
USER TEST TESTING
Begins the test routine which tests the main control’s functions.
See the Testing the Control section for more details. Use the
up button to turn the User Test On.
MAX HEAT TESTING
When selected, control operates the system up to maximum set
temperatures. Will operate up to 24 hours, or can be manually
turned Off. See Max Heat in the Testing the Control section
for more details.
TYPE AND SOFTWARE VERSION
Displays the type number of the product, followed by the current
software version beneath.
ACCESS LEVEL
Selects the Access Level of the control, which determines the
Menu items available. USER provides the most limited level of
access and shows the fewest possible items.
When set to USER, all thermostats are locked and the number
of thermostat settings available are reduced.
OFF, SEL
Default = Off
FACTORY DEFAULTS
Loads the factory default settings. Hold the Up and Down
buttons for 1 second until SEL is shown.
TOOLBOX MENU
MIX DEVICES
0 to 24 devices
0 to 24 devices
See Troubleshooting
Guide
After the last item, the control returns to the first item in the menu.
© 2010 D 402 - 09/10 20 of 32
Displays the number of devices on the Mix bus (Water
Temperature). This is made up of thermostats connected to
the House Control, and to the Mix Expansion terminals.
BOIL DEVICES
Displays the number of devices on the Boil Expansion bus
(Water Temperature). This is made up of thermostats connected
to the Boil Expansion terminals on the House Control.
HISTORY - 1 THROUGH 5
Displays a history of any past errors that have occurred on the
system. Will clear after 30 days, or press Up and Down buttons
for 1 second to manually clear. The last 5 history items will
display if present.
Page 21

Sequence of Operation
-----------------------------------------------------------------------
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
tekmarNet® System
tekmarNet® is a family of products that use communication
to operate the HVAC system in a comfortable and efficient
manner. The House Control is the central component in
a tekmarNet® system and requires tekmarNet®2 (tN2)
Thermostats to be directly connected to the control.
The tekmarNet®4 (tN4) Expansion terminals can link the
House Control with other tekmarNet® components:
Mix Temperature Reset Operation
Mix Call or Mix Expansion Call
When an onboard tN2 Thermostat calls for heat, the House
Control registers a Mix call for hydronic heating.
When a device connected to the tN4 Mix Expansion
terminals calls for heat, the House Control registers a Mix
Expansion Call for hydronic heating on the mix loop.
Mix Target
When there are no Mix or Mix Expansion calls, the mix
target in the View menu on the display will show ‘– – –’ to
indicate there is no requirement for mixing operation.
Once a Mix Call or Mix Expansion Call is present, a mix
target is determined by the control using the mixing heating
curve (mix design and outdoor design settings) together
with indoor temperature feedback from the thermostats.
The heating curve operates based on the principle that
a buildings heat loss increases with colder outdoor
temperatures. The calculated Mix Target will be shown in
the View menu on the display.
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
-----------------------------------------------------------------------
Section A
Wiring Centers 313, 314, 315, 316 - Add additional zones
•
tN2 and tN4 Thermostats - Add thermostats
•
tN4 Timer 033 - Adds 4 programmable schedules
•
tN4 User Switch 479 - Provides a system override for
•
vacations and holidays
tN4 Setpoint Control 161 - Control hot tubs, pools and
•
more
Section B
Calls
Mix
Mix Heating Curve
(Outdoor Design,
Mix Design)
Calls
Mix Exp
Mix Maximum
The control has a fixed mix maximum temperature of +10°F
(+5.5°C) higher than the Mix Design setting. When this
occurs, the “MAX” segment will display when viewing the
mix target or mix supply temperature in the view menu.
Mix Supply
Once a Mix Target water temperature has been calculated,
the House Control measures the temperature at the mix
supply sensor location and then operates the mixing device
to maintain the mix supply temperature. The heat source will
also be turned on and operated so that the mixing device
is able to maintain the mix target temperature.
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
(70°F Outdoor,
70°F Mix Supply)
Increasing Water Temperatures
Decreasing Outdoor Temperatures
Boiler Minimum Protection
If the boiler supply water temperature is cooler than the
boiler minimum setting, the control reduces the output of the
mixing device. This limits the amount of cool return water
to the boiler and allows the boiler return water temperature
to recover. Once the boiler supply temperature exceeds
the boiler minimum setting, the mixing device will return
to normal operation.
Note: The mixing device does not provide boiler minimum
protections when the Boiler Type setting is EMS1 or EMS2.
21 of 32 © 2010 D 402 - 09/10
Page 22

Mixing Device Type
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
The House Control can operate a mixing device such as
a mixing valve or variable speed injection pump based
upon one of four output signals. The device output bar
graph on the display indicates the approximate position
of the mixing device.
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Variable Speed Injection Pump
A standard wet rotor circulator can be connected to the
Variable Speed Pump output on the back of the control.
The control varies the circulator speed to maintain the
correct mixed supply water temperature at the mix supply
sensor. For correct sizing and piping of the variable speed
injection circulator, refer to essay E 021. Note: Pumps
manufactured with an internal variable speed controller
are not compatible with the House Control.
Floating Action 24 V (ac)
A 24 V (ac) floating action actuator motor and mixing valve
can be connected to the Floating Action outputs on the
front of the House Control. The control pulses the actuator
motor open or closed to maintain the correct supply water
temperature at the mix supply sensor when there is a
requirement for mixing.
Modulating 0-10 V (dc)
*Only available if a one or two stage on-off boiler is
used.
A modulating 0-10 V (dc) actuating motor can be used to
operate the mixing valve. The control uses the Mod dc/mA
output to provide an analog 0-10 V (dc) signal to the actuator
in order to maintain the correct mix supply temperature.
Modulating 4-20 mA
*Only available if a one or two stage on-off boiler is
used.
A modulating 4-20 mA actuating motor can be used to
operate the mixing valve. The control uses the Mod dc/mA
output to provide an analog 4-20 mA signal to the actuator
in order to maintain the correct mix supply temperature.
Mixing Device Exercising
The control operates the mixing device from 0 to 100% output
every 3 days to help prevent corrosion and / or precipitate
build up on the mixing valve or pump that could lead to
seizure of the mixing device. The control ensures that no
heat is supplied to the zones during exercising.
Boiler Temperature Reset Operation
Boiler Expansion Call
When a device connected to the tN4 Boil Expansion
terminals calls for heat, the House Control registers a Boil
Expansion call for hydronic heating on the boiler loop.
Boiler Target
When there are no Boiler Expansion or Mix calls, the boiler
target in the View menu on the display will show ‘– – –’ to
indicate there is no requirement for boiler operation.
Once a Boiler Expansion Call is present, a boiler target
is determined by the control using the boiler heating
curve (boiler minimum, boiler design and outdoor design
settings) together with indoor temperature feedback from
the thermostats. The heating curve operates based on the
principle that a buildings heat loss increases with colder
outdoor temperatures. The calculated Boiler Target will be
shown in the View menu on the display.
When a Mix or Mix Expansion Call is present, the control
calculates a boiler target that is higher than the mix target
using Boiler Load Reset.
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Section C
Calls
Boil Exp
Boiler Heating Curve
(Outdoor Design,
Boiler Design)
(70°F Outdoor,
Boiler Minimum)
Increasing Water Temperatures
Decreasing Outdoor Temperatures
Boiler Minimum
The House Control protects non-condensing boilers from
sustained flue gas condensation and thermal shock through
the Boiler Minimum setting. The boiler minimum is the
lowest temperature that the control is allowed to use as a
boiler target temperature. If the boiler is operating at the
boiler minimum temperature, the “MIN” segment is turned
on in the display when viewing either the boiler supply
temperature or the boiler target temperature.
© 2010 D 402 - 09/10 22 of 32
Boiler Maximum
The control has a fixed boiler maximum temperature of +
10°F (+5.5°C) higher than the Boiler Design setting for the
Boiler Heating Curve. When this occurs, the “MAX” segment
will display when viewing the boiler target or boiler supply
temperature in the view menu. The control will operate
the boiler so that the boiler supply temperature will never
exceed 210°F (99.0°C).
Page 23

Domestic Hot Water Tank Operation
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Section D
DHW Call
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
A DHW Call is required in order for the control to provide
heat to a DHW tank. Once the control registers a DHW Call,
it will display the “DHW” icon under Calls in the display.
This can be done in three ways:
DHW Tank Aquastat
If a DHW aquastat (mechanical switch) is used to
•
apply a DHW Call, the tank is heated to the aquastat temperature setting. A dry contact or 24 V (ac)
signal is applied across the DHW Call terminals on the
House Control.
DHW Tank Sensor
A DHW tank sensor provides superior temperature
•
control of the tank compared to an aquastat. The
House Control automatically detects whether a DHW
sensor is installed. The upper limit of the DHW temperature is set by the DHW setting. The DHW tank differential is fixed to 6°F (3°C).
DHW - Boiler Target
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------
When a DHW Call is present, a boiler target is
determined.
When using a DHW Tank Aquastat, the boiler target is
•
set to the DHW Exchange setting.
When using a DHW Tank Sensor, the boiler target is
•
set to the DHW Occupied setting plus 40°F (22°C).
Calls
DHW
tekmarNet® Setpoint Control with Sensor
A DHW Call is provided through the tekmarNet®
•
system. This can be done through the Boil Expansion
tN4 terminals with a tekmarNet® setpoint device such
as a Setpoint Control 161.
®
•
When using a tekmarNet
target is set to the devices Exchange Supply setting.
If there are multiple devices calling for heat, the boiler target
is set to the highest temperature requirement.
Setpoint Control, the boiler
DHW Mode
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
The control has five different settings available for DHW
Mode that affect pump operation. The required DHW
Mode setting will depend on the piping arrangement of the
DHW tank and whether or not priority for the DHW tank
is necessary. DHW Priority stops or limits the delivery of
heat to the building heating system while the DHW tank
calls for heat. This allows for quick DHW tank temperature
recovery.
DHW MODE 1 - DHW in Parallel no Priority
When a DHW Call is present, the DHW pump is activated.
The boiler system pump does not turn on, but may operate
based on either a Boiler, Mixing, or Setpoint Call.
It is assumed that the DHW pump will provide adequate
flow through the heat exchanger and the boiler.
DHW MODE 2 - DHW in Parallel with Priority
When a DHW Call is present, the DHW pump is activated.
The boiler system pump and all boiler temperature zones
are shut off through tekmarNet® communication to achieve
DHW priority.
It is assumed that the DHW pump will provide adequate
flow through the heat exchanger and the boiler.
DHW Mode = 1
DHW
Zone
Pump
Valve
ON Or
ON
OFF
Boiler System
Pump
ON Or OFF
DHW Mode = 2
DHW
Zone
Pump
Valve
ON
Boiler System
Pump
OFF
OFF
23 of 32 © 2010 D 402 - 09/10
Page 24

DHW MODE 3 - DHW in Primary / Secondary no
--------------------------
------------------------------
Priority
When a DHW Call is present, the DHW pump and the boiler
system pump is operated. Boiler temperature zones can
turn on if required.
DHW MODE 4 - DHW in Primary / Secondary with
Priority
When a DHW Call is present, the DHW pump and the
boiler system pump is operated. All boiler temperature
zones are shut off through tekmarNet® communication to
achieve DHW priority.
DHW Mode = 3
DHW
Pump
ON
Boiler System
Pump
ON
Zone
Valve
ON Or
OFF
DHW Mode 5 - DHW in Near Boiler Piping with
Priority
DHW Mode 5 requires that a DHW sensor be located on
the boiler outlet pipe and a DHW call from an aquastat
inside the DHW tank. The aquastat operates the DHW
tank temperature while the DHW sensor is used to control
the boiler temperature delivered to the DHW indirect heat
exchanger.
When a DHW Call is present, the DHW pump is activated.
The boiler system pump and all boiler temperature zones
are shut off through tekmarNet® communication to achieve
DHW priority.
It is assumed that the DHW pump will provide adequate
flow through the heat exchanger and the boiler.
DHW Priority Override
--------------------------
To prevent the building from cooling off too much or the
possibility of a potential freeze up during DHW priority,
the control limits the amount of time for DHW priority
during cold weather. During warm weather the DHW
priority is 120 minutes. During cold weather the DHW
priority is 15 minutes. Once the allowed time for priority
has elapsed, the control overrides the DHW priority and
resumes space heating for 15 minutes. It will then revert
back to DHW Priority and repeat.
DHW Mode = 4
Zone
DHW
Pump
ON
Boiler System
Pump
ON
Valve
OFF
DHW Mode = 5
DHW
Pump
DHW
Sensor
ON
Boiler
Pump
OFF
Boiler
Sensor
Boiler System
DHW Priority Override Time
Zone
Valve
OFF
Pump
OFF
DHW Post Purge
------------------------------
After the DHW Call is removed, the control performs a purge
on the boiler. The control shuts off the boiler and continues
to operate the DHW pump and the Boiler System pump if
applicable. This purges the residual heat from the boiler
into the DHW tank. The control continues this purge for a
maximum of two minutes. The control also stops the purge
if the boiler supply temperature drops below the current
boiler target temperature.
© 2010 D 402 - 09/10 24 of 32
Increasing Time
Decreasing Outdoor Air Temperature
Page 25

Setpoint Operation
--------------------------------
-------
-----------------------------
----------------------
----------------------
--------------------------------
Section E
A Setpoint Call is required in order for the control to provide
heat to a setpoint load, such as a spa, pool, or snowmelt
load. This can be done in two ways:
Contact Closure
A dry contact or 24 V (ac) signal is applied across the
Setpoint Call terminals on the 402.
tekmarNet® Setpoint Control with Sensor
A Setpoint Call is provided through the tekmarNet®
system. This can be done through the tN4 Expansion
terminals with a setpoint device such as a Setpoint
Control 161.
Once the control registers a Setpoint Call, it will display
the “Setp” icon under Calls in the display.
Note: Setpoint operation has a fixed priority of on.
Setpoint Operation
The control can operate to satisfy the requirements of a
setpoint load in addition to a space heating load and a
DHW load. A setpoint load overrides the current outdoor
reset temperature and WWSD setting in order to provide
heat to the setpoint load.
Setpoint
--------------------------------
-------
-----------------------------
Setpoint Priority
Setpoint
Pump
ON
Boiler System Pump
If Mix demand = On
Otherwise = Off
Zone
Valve
OFF
When the control receives a Setpoint Call:
All Boil zones are turned off.
•
The Mix device is ramped down to a minimum level.
•
The boiler will operate to maintain the Setpoint tem-
•
perature as set in the Adjust menu, or as set on the
tekmarNet
®
Setpoint control if one is being used.
Calls
Setp
It is assumed that the Setpoint pump will provide adequate
flow through the heat exchanger and the boiler.
Setpoint calls will also be responded to when the system
is in Away, which can be set using a 479 User Switch.
Setpoint Priority Override
To prevent the building from cooling off too much or
the possibility of a potential freeze up during setpoint
priority, the control attempts to limit the amount of time
for setpoint priority.
As the outdoor air temperature becomes colder, the length
of time the control provides setpoint priority is reduced.
Once the allowed time for priority has elapsed, the control
will check the space heating target.
If there is a space heating target, the boiler operates at
•
that target for 15 minutes.
If after 15 minutes there is still a Setpoint Call, the con-
•
trol will reduce mixing outputs, shut off all boiler heating zones and target the Setpoint temperature.
Note: It is possible to disable Setpoint Priority by using
•
a tekmarNet® Setpoint control and turning the priority
to Off in the Setpoint control.
----------------------
Boiler Operation
The 402 is able to operate a single 1-stage or 2-stage onoff boiler or a single modulating boiler as a heat source.
For proper operation of the boiler, the 402 must be the only
control that determines when the boiler is to fire.
*Important note: The operating control in the boiler, also
known as an aquastat, remains in the burner circuit and acts
as a secondary upper limit on the boiler temperature. The
boiler operator temperature setting can be adjusted above
210°F, which is the fixed Boiler Maximum on the 402.
Boiler Target Temperature
The boiler target temperature is the temperature which
the control is trying to operate the boiler at. There are
four items that determine the boiler target temperature:
Mix Call
•
Boil Exp Call
•
DHW Call
•
Setpoint Call
•
If the control receives more than one call for heat at the
same time, it will operate the boiler at the highest of the
four calls.
----------------------
Section F
The control displays the temperature that it is currently
trying to maintain as the boiler supply temperature in the
View menu. If the control does not presently have a call for
heat, it does not show a boiler target temperature. Instead,
‘– – –’ is displayed on the LCD.
Boiler Minimum
When operating non-condensing boilers, it is important
to prevent cool water from returning to the boiler. Cold
return temperatures create flue gas condensation, which
if left too long, can severely damage the boiler.
The 402 protects the boiler through the Boiler Minimum
setting. The boiler minimum is the lowest temperature that
the control is allowed to use as a boiler target temperature.
If the boiler is operating at the boiler minimum temperature,
the “MIN” segment is turned on in the display when viewing
either the boiler supply temperature or the boiler target
temperature.
25 of 32 © 2010 D 402 - 09/10
--------------------------------
Page 26

Boiler Maximum
--------------------------------
-------------------------------------
-------------------------------
-------------------
--------------------------------
The 402 will operate the boiler so that the boiler
supply temperature will never exceed 210°F (99.0°C).
The highest allowed boiler target is the boiler design
temperature + 10°F (5.5°C).
Boiler Type
-------------------------------------
The 402 can operate either of the following types of
boilers:
One single-stage on-off boiler
•
One two-stage on-off boiler
•
Modulating boiler using a 0-10 V (dc) signal
•
Modulating boiler using a 4-20 mA signal
•
tekmar EMS signal (for use with multiple boiler
•
stagers)
EMS signal for Viessmann modulating boilers
•
On-Off Operation
-------------------------------
The 402 operates a single hot-water on-off boiler to
maintain the boiler target within a differential. The boiler
target is the average temperature and the boiler supply
temperature can fluctuate by 1/2 of the differential above
and below of the boiler target.
Modulation Boiler Operation
-------------------
The 402 can operate a single hot-water modulating
boiler using the Mod dc/mA output and the Boiler Stage
contact. Not all boilers require the use of the Boiler
Stage contact.
The control operates the boiler by first switching the boiler
stage contact to allow the modulating boiler to go through
the ignition sequence (the boiler stage contact may not
be required on all modulating boilers). A 0-10 V (dc) or 420 mA analog signal is then used to modulate the boiler
firing rate starting from 50% (5 V (dc) or 12 mA signal) for
30 seconds.
After the 30 second delay has elapsed, the control will
then allow the boiler to modulate down to the minimum
modulation setting and hold it there for the Modulation Delay
time setting. The Modulation Delay setting is determined
by the boiler manufacturer. It is the amount of time that
the burner must operate before the internal boiler control
allows an external signal to operate the burner.
After the Modulation Delay has elapsed, the control uses
PID logic to change the boiler firing rate signal in order
to satisfy the boiler target temperature. When the firing
rate signal is reduced down to the Minimum Modulating
setting and the boiler supply temperature exceeds the
boiler target by 1/2 of the differential, the control will shut
off the burner.
Minimum Modulation
The Minimum Modulation is the lowest signal the control
can send to modulate the boiler. This operates the boiler
at low fire.
•
Refer to the boiler manufacturer’s literature to determine the minimum output voltage V (dc) or current
(mA) that the boiler will successfully operate at.
For 0-10 V (dc):
Minimum Modulation =
Boiler’s Minimum Input Signal x 100%
10 V (dc)
For 4-20 mA:
Minimum Modulation =
Boiler’s Minimum Input Signal - 4mA x 100%
16 mA
Example:
A boiler requires a 1.8 V (dc) signal to fire the boiler at
low fire. The boiler can be modulated to 10 V (dc) where
it reaches high fire.
Minimum Modulation = 1.8 V x 100% = 18%
10 V
10 V (dc)
Control
Range
Boiler
Range
18%
0 Vdc
1.8 V (dc)
tekmar EMS Signal Operation
The 402 can provide a 0-10 V (dc) signal proportional to
the boiler target which is compatible with tekmar Boiler
Staging controls that accept an EMS input.
•
To use the tekmar EMS signal operation, the Boil Type
setting in the Adjust menu must be set to EMS1.
Viessmann EMS Signal
The 402 has a special 0-10 V (dc) signal proportional to
the boiler target that is designed to be compatible with
Viessmann Open Therm 0-10 V (dc) inputs.
To use the Viessmann EMS signal operation, the Boil
•
Type setting in the Adjust menu must be set to EMS2.
The signal is 0 V (dc) when the boiler is off. The voltage
is 2.2 V (dc) to provide a boiler target of 81°F (27°C),
up to maximum of 10 V (dc) to provide a boiler target of
176°F (80°C).
© 2010 D 402 - 09/10 26 of 32
Page 27

Auto Differential
--------------------------------
------------------------------
----------------------------
-------------------------------------
-----------------
------------------------------
Both on-off and modulating boilers are operated with
a differential. In some cases, a modulating boiler must
be operated with a differential while operating at low
fire because this indicates the load is smaller than
the minimum modulation of the boiler. For modulating
boilers, the differential no longer applies once operating
the boiler above low fire.
The differential operates by closing the boiler contact
when the boiler supply water temperature is 1/2 of the
differential below the boiler target temperature. As the
supply temperature reaches 1/2 of the differential above
the boiler target temperature, the boiler is shut off.
Boiler On
--------------------------------
Boiler Off
+1/2 Dif ferential
Boiler Target
- 1/2 Differential
In order to decrease temperature swings and increase boiler
efficiency, the Auto Differential feature automatically adjusts
the operating differential of the boiler based on the heating
load. As the load increases, the differential will decrease
to minimize temperature swings. As the load decreases,
the differential will increase to prevent short cycling. This
can significantly improve operating efficiency and prevent
equipment failures through excessive cycling.
Off
Differential
Time
On
Heating Load
Domestic Hot Water Heat Source
The 402 can use a high-efficiency water heater as a source
of heat for space heating zones in addition to providing
domestic hot water. This is an open-loop system in which
potable water is circulated through the zones. When the
flushing feature is set to on, the mixing valve is moved to the
fully open position, all four zone valves are opened, and the
mix system pump is turned on for 5 minutes each day. This
prevents stagnation of the water in the heating system.
Pump Operation
Mix System Pump
The mix system pump operates whenever all the
following conditions are met:
A Mix Call is present.
•
The thermostat calling for heat has the Heat 1 pump
•
setting set to On.
The heating system is not in Warm Weather Shut Down.
•
Boiler System Pump
The boiler system pump operates whenever all the
following conditions are met:
A Mix or a Boiler Call is present.
•
The thermostat calling for heat has the Heat 1 pump
•
setting set to On.
There is no DHW priority.
•
The heating system is not in Warm Weather Shut Down.
•
DHW Pump
The DHW pump operates whenever all the following
conditions are met:
A DHW Call is present.
•
The heating system is not in DHW priority override.
•
DHW post purge.
•
-------------------------------------
------------------------------
----------------------------
Section G
070
402
Section H
Variable Speed Injection Pump
The variable speed pump operates whenever the
following conditions are met:
A Mix Call is present.
•
The heating system is not in Warm Weather Shut
•
Down.
Note: The variable speed pump operates at minimum
speed whenever the boiler supply temperature falls below
the boiler minimum setting and whenever there is a DHW
Call and DHW priority has been selected.
Pump Exercising
The control operates each pump every three days for 10
seconds to help prevent corrosion and / or precipitate build
up on the pump components that can lead to pump seizure.
The control ensures that no heat is supplied to the zones
during exercising.
------------------------------
-----------------
27 of 32 © 2010 D 402 - 09/10
Page 28

----------------------------
--------------------------
-----------------------
------------
Energy Saving Features
-------------------------
------------------------------
Section I
The “$aving” icon is displayed when energy is being saved.
The following features reduce energy consumption.
Network Schedules
Adding a schedule to a tekmarNet® system is both easy
and valuable. A Timer 033 provides scheduling with up to
4 events per day for every tekmarNet® Thermostat. Turning
down the room temperatures when they are unoccupied
reduces boiler on-time and energy consumption which
helps save money and the environment.
One-Touch Economy
A User Switch 479 allows for one-touch overrides of the
system. For example, if leaving the building for vacation,
simply press the “Away” button and all the thermostats
will immediately operate at a lower temperature, instead
of having to walk around the building lowering the heating
temperature setting and raising the cooling temperature
setting on each thermostat.
DHW Tank During Away
In addition to the One-Touch setback, a User Switch 479
also allows the user to press the ‘Away’ button and tell the
House Control 402 to ignore DHW Calls, preventing the
DHW tank from unnecessarily heating up when no one is
living in the building.
Warm Weather Shut Down (WWSD)
During warmer weather, heating of the rooms is typically no
longer required. To prevent energy waste from unnecessary
boiler operation, the control goes into Warm Weather Shut
Down (WWSD) when the outdoor temperature rises above
the WWSD temperature set in the Adjust menu.
----------------------------
--------------------------
-----------------------
------------
Further Savings!
Use a Timer 033 with programmable schedule #1 to
gain the WWSD Unoccupied setting. This provides an
additional WWSD temperature that can be set even lower
for Unoccupied and Sleep time periods.
This setting will appear after WWSD in the Adjust
•
menu if a Timer 033 or User Switch is present on the
system.
Zone Synchronization
Another feature of the House Control is Zone Synchronization.
In typical zoned systems, the thermostats operate on a standalone basis. This means that a zone turns on and off as
required without any regard for other zones. The net effect
is random operation of the zones causing short cycling of
the heat source. tekmarNet® thermostats communicate to
ensure that their cycles are synchronized. Energy is saved
by ensuring zones requiring heat operate on the same cycle,
therefore reducing short cycling of the boiler.
Zone Post Purge
When the last zone is nearly satisfied for heating, the boiler is
shut off and the zone continues to operate together with the
boiler system pump and / or mix system pump. This purges
the residual heat from the boiler into this zone. The control
continues this purge for a maximum of two minutes. The
control will stop the purge if the boiler supply temperature
drops below the boiler minimum setting.
-------------------------
------------------------------
Troubleshooting
It is recommended to complete all wiring to ensure trouble free operation. Should an error occur, simply follow these steps:
1. Find: If the House Control or tekmarNet® Thermostat flashes on the screen, it is indicating a problem on the system.
2. Identify: Use the Menu button to locate the Toolbox Menu. The Error code should appear as the first item.
3. Solve: Using the lookup chart below, match the Error code to the one on the control. Use the Description in the chart
to solve the problem.
Error Messages (1 of 3)
Error Message Description
ADJUST ERROR
The control failed to read the Adjust menu settings, and reloaded the factory default settings.
Operation stops until all the Adjust menu settings are checked.
Note: To clear the error, the access level must be set to Installer and each setting in the Adjust
menu must be checked.
OUTDOOR SENSOR SHORT CIRCUIT
Due to a short circuit, the control failed to read the outdoor sensor. As a result, the control
assumes an outdoor temperature of 32°F (0°C) and continues operation. Locate and repair
the problem as described in the “Test the Sensor Wiring” section.
© 2010 D 402 - 09/10 28 of 32
Page 29

Error Messages (2 of 3)
Error Message Description
OUTDOOR SENSOR OPEN CIRCUIT
Due to an open circuit (disconnected or broken wire), the control failed to read the outdoor
sensor. As a result, the control assumes an outdoor temperature of 32°F (0.0°C) and
continues operation. Locate and repair the problem as described in the “Test the Sensor
Wiring” section.
MIX SENSOR SHORT CIRCUIT
Due to a short circuit, the control failed to read the Mix supply sensor. As a result, the control
operates the mixing device at a fixed output as long as there is a call for heat. Locate and
repair the problem as described in the “Test the Sensor Wiring” section.
MIX SENSOR OPEN CIRCUIT
Due to an open circuit (disconnected or broken wire), the control failed to read the Mix supply
sensor. The control operates the mixing device at a fixed output as long as there is a call for
heat. Locate and repair the problem as described in the “Test the Sensor Wiring” section.
BOILER SENSOR SHORT CIRCUIT
Due to a short circuit, the control failed to read the boiler sensor. When there is a call for heat,
the control no longer controls the boiler. Instead, the control provides a boiler enable and the
boiler operates on its aquastat/limit until the sensor is repaired. The control will not operate
the boiler contact if the Boil Minimum setting is set to Off. Locate and repair the problem as
described in the “Test the Sensor Wiring” section.
BOILER SENSOR OPEN CIRCUIT
Due to an open circuit, the control failed to read the boiler sensor. The control no longer
controls the boiler. Instead, the control provides a boiler enable and the boiler operates on its
aquastat/limit until the sensor is repaired. The control will not operate the boiler contact if the
Boil Minimum setting is set to Off. Locate and repair the problem as described in the “Test
the Sensor Wiring” section.
DOMESTIC HOT WATER SENSOR SHORT CIRCUIT
Due to a short circuit, the control failed to read the DHW sensor. As a result, the control no
longer heats the DHW tank. Locate and repair the problem as described in the “Test the
Sensor Wiring” section. DHW tank heating will resume once the sensor problem is corrected.
The error message self clears once the error condition is corrected.
DOMESTIC HOT WATER SENSOR OPEN CIRCUIT
Due to an open circuit, the control failed to read the DHW sensor. As a result, the control
no longer heats the DHW tank. Locate and repair the problem as described in the “Test the
Sensor Wiring” section. DHW tank heating will resume once the sensor problem is corrected.
The error message self clears once the error condition is corrected.
DOMESTIC HOT WATER CALL ERROR
A DHW sensor and a DHW call have been applied at the same time. The DHW tank will not
be heated until the DHW call signal is removed. The error message self clears once the error
condition is corrected.
BOILER DEVICE LOST (b:01 TO b:24)
Each tekmarNet® device (thermostat, setpoint control, timer) has an address. The device with
this address on the boiler water temperature is no longer reporting back to the 402.
The device can be located by either the address, or by going to each device in the building,
checking that the LCD is on, and the tekmarNet® communication symbol is on. Trace the wires
from the control to the lost device looking for loose or damaged wires.
Note: If you deliberately remove a tekmarNet
®
device, hold the Up and Down buttons to clear
this error.
29 of 32 © 2010 D 402 - 09/10
Page 30

Error Messages (3 of 3)
Error Message Description
MIX DEVICE LOST (1:01 TO 1:24)
Each tekmarNet® device (thermostat, setpoint control, timer) has an address. The device with
this address on the mix water temperature is no longer reporting back to the 402.
The device can be located by either the address, or by going to each device in the building,
checking that the LCD is on, and the tekmarNet® communication symbol is on. Trace the wires
from the control to the lost device looking for loose or damaged wires.
Note: If you deliberately remove a tekmarNet® device, hold the Up and Down buttons to clear
this error.
MASTER DEVICE ERROR
More than one master has been detected on the tekmarNet®4 expansion terminals. The 402
is a “Master Device” and no other tekmarNet® reset controls can be added to the tekmarNet®4
expansion terminals. If one has been added, remove it from the system.
DEVICE ERROR AT ADDRESS b:01 to b:24
Each tekmarNet® device (thermostat, setpoint control, timer) has an address. One of the
devices on the boiler water temperature has an error. If there is a record of the device
address together with the room name, go to that device to correct the error. Otherwise, go
to each device in the building, checking for the flashing Warning symbol. Once the error on
the device is corrected, the error message will clear.
DEVICE ERROR AT ADDRESS 1:01 to 1:24
Each tekmarNet® device (thermostat, setpoint control, timer) has an address. One of the
devices on the mix water temperature has an error. If there is a record of the device address
together with the room name, go to that device to correct the error. Otherwise, go to each
device in the building, checking for the flashing Warning symbol. Once the error on the device
is corrected, the error message will clear.
MIX MODULE ERROR
A Mixing Module has been connected to the Mix Exp. tN4 terminals. The 402 controls mixing
devices through outputs on the control and cannot operate tekmarNet® mixing expansion
modules. Remove the device and connect the mixing actuator or pump directly to the appropriate
output terminals on the 402.
Frequently Asked Questions (1 of 2)
Symptom Look For...
Fuse holder
LCD display is off
Power to control
DHW Call on LCD If a DHW call is present, the control is aware that the DHW tank requires heat.
DHW tank reading Ensure the DHW tank temperature is accurate and replace if necessary.
Burner symbol on
No DHW tank
heating
LCD
DHW pump symbol
on LCD
Corrective Action
Control power supply has a 24 V (ac) fuse which if blown, requires
replacement.
Use electrical meter to measure 24 V (ac) voltage on input power R and C
terminals.
If the burner symbol is on the LCD, there is a problem with the boiler. Ensure
the boiler aquastat manual limit is reset to the on position.
If the DHW pump symbol is on, check to ensure the DHW pump is in operation
by checking for pump vibration or voltage on the pump wiring terminals.
DHW pump in
operation
© 2010 D 402 - 09/10 30 of 32
If DHW pump and boiler are operating, the system may require the boiler system
pump to operate to heat the DHW tank. Ensure the DHW Mode setting is set
correctly.
Page 31

Frequently Asked Questions (2 of 2)
Symptom Look For...
Burner symbol on
LCD
WWSD symbol on
LCD
No central
heating
Boiler short
cycling
Single zone over
heating
Mix or Boil Calls on
LCD
DHW Call on LCD During DHW tank heating, the central heating may not be heated.
System in AWAY
“MIN” shown
together with boiler
target or boiler
supply on LCD
Burner symbol
cycling on and off
LCD shows zone on
LCD shows zone off
Corrective Action
If the burner symbol is on the LCD, there is a problem with the boiler. Ensure
the boiler aquastat manual limit is reset to the on position.
Warm Weather Shut Down (WWSD) is an energy saving feature that prevents
central heating during the summer. Ensure the outdoor temperature reading
is accurate and replace outdoor sensor if necessary. WWSD setting can be
increased if heating is required.
If there are no Mix or Boil Calls, there are no thermostats calling for heat.
During AWAY, the thermostats operate at a lower temperature. Locate a ‘User
Switch’ and set to Normal to resume heating.
Boiler is operating below the boiler minimum setting and the mixing valve is
closed or the mix injection pump is operating at low speed. The mixing device
will operate normally once the boiler warms up.
Mixing using variable speed injection pumps requires the balancing valve to
be set correctly. Lack of head pressure can lead the injection pump speed to
ramp up and down.
Thermostats have a differential of +/- 1.5°F of the temperature setting. Due to
the display rounding numbers up, heating can appear on when the temperature
is 2°F above the setting. This is normal operation.
Ensure zone valve terminals measure 0 V (ac). Measuring 0 V (ac) indicates
mechanical zone valve may have failed in open position. Measuring 24 V (ac)
indicates control relay may have failed.
Single zone under
heating
LCD shows zone on
LCD shows zone off Check for calls
Ensure zone valve terminals measure 24 V (ac). Measuring 24 V (ac) indicates
mechanical zone valve may have failed in closed position. Measuring 0 V (ac)
indicates control relay may have failed.
Job Record
Item Setting
OUTDOOR DESIGN
MIX DESIGN
MIX TYPE
MIX MOTOR
BOILER TYPE
BOILER DESIGN
BOILER MINIMUM
BOILER MOTOR
MINIMUM MODULATION
Item Setting
FLUSHING
WWSD OCCUPIED
WWSD UNOCCUPIED
DHW MODE
DHW EXCHANGE
DHW OCCUPIED
DHW UNOCCUPIED
SETPOINT
UNITS
MODULATION DELAY
31 of 32 © 2010 D 402 - 09/10
Page 32

Technical Data
tN2 House Control 402 Boiler, DHW & Setpoint, Mixing, Four Zone Valves
Literature D402, Q402, SB057
Control Microprocessor control. This is not a safety (limit) control.
Packaged weight 1.4 lbs (640 g)
Dimensions 5.5” H x 5.5” W x 2.25” D (140 x 140 x 57 mm)
Enclosure NEMA 1 rated, blue PC+ABS plastic
Approvals
Ambient conditions Indoor use only, 32 to 104°F (0 to 40°C), RH 90% Non-condensing
Power supply 24 V (ac) ±10% 60 Hz, 100 VA max, Class 2
Control load 2 VA
Zone valve / floating action load 89 VA, 24 V (ac), 3.7 A for zones 1 to 4 plus fl oating action output
Boiler stage 1, 2 relays 24 V (ac) 5 A
Boiler system pump relay 115 V (ac) 5 A, 1/6 hp
Mix system pump relay 115 V (ac) 5 A, 1/6 hp
DHW pump relay 115 V (ac) 5 A, 1/6 hp
Variable speed pump relay
Pump power 115 V (ac) 12 A max
Setpoint and DHW calls Short, 0 - 32 V (ac)
Boil/Mix modulating output 0 - 10 V (dc) 500 Ω min load impedance, 4 - 20 mA 1 kΩ max load impedance
Sensors NTC thermistor, 10k @ 77°F (25°C ± 0.2°C) ß=3892
- Included Outdoor Sensor 070 and 2 of Universal Sensors 082
Warranty Limited 3 Year
CSA C US, meets class B: ICES & FCC Part 15
115 V (ac) 2.4 A
Limited Warranty and Product Return Procedure
Limited Warranty The liability of tekmar under this warranty is lim-
ited. The Purchaser, by taking receipt of any tekmar product (“Product”), acknowledges the terms of the Limited Warranty in effect at
the time of such Product sale and acknowledges that it has read
and understands same.
The tekmar Limited Warranty to the Purchaser on the Products sold
hereunder is a manufacturer’s pass-through warranty which the
Purchaser is authorized to pass through to its customers. Under
the Limited Warranty, each tekmar Product is warranted against
defects in workmanship and materials if the Product is installed and
used in compliance with tekmar’s instructions, ordinary wear and
tear excepted. The pass-through warranty period is for a period of
twenty-four (24) months from the production date if the Product is
not installed during that period, or twelve (12) months from the documented date of installation if installed within twenty-four (24) months
from the production date.
The liability of tekmar under the Limited Warranty shall be limited to, at
tekmar’s sole discretion: the cost of parts and labor provided by tekmar
to repair defects in materials and/or workmanship of the defective product; or to the exchange of the defective product for a warranty replacement product; or to the granting of credit limited to the original cost of the
defective product, and such repair, exchange or credit shall be the sole
remedy available from tekmar, and, without limiting the foregoing in any
way, tekmar is not responsible, in contract, tort or strict product liability, for any other losses, costs, expenses, inconveniences, or damages,
whether direct, indirect, special, secondary, incidental or consequential,
arising from ownership or use of the product, or from defects in workmanship or materials, including any liability for fundamental breach of
contract.
The pass-through Limited Warranty applies only to those defective Products returned to tekmar during the warranty period. This Limited Warranty does not cover the cost of the parts or labor to remove or transport
the defective Product, or to reinstall the repaired or replacement Product,
all such costs and expenses being subject to Purchaser’s agreement and
warranty with its customers.
Any representations or warranties about the Products made by Purchaser
to its customers which are different from or in excess of the tekmar Limited Warranty are the Purchaser’s sole responsibility and obligation. Purchaser shall indemnify and hold tekmar harmless from and against any
and all claims, liabilities and damages of any kind or nature which arise
out of or are related to any such representations or warranties by Purchaser to its customers.
The pass-through Limited Warranty does not apply if the returned Product has been damaged by negligence by persons other than tekmar,
accident, fire, Act of God, abuse or misuse; or has been damaged by
modifications, alterations or attachments made subsequent to purchase
which have not been authorized by tekmar; or if the Product was not
installed in compliance with tekmar’s instructions and/or the local codes
and ordinances; or if due to defective installation of the Product; or if the
Product was not used in compliance with tekmar’s instructions.
THIS WARRANTY IS IN LIEU OF ALL OTHER WARRANTIES, EXPRESS
OR IMPLIED, WHICH THE GOVERNING LAW ALLOWS PARTIES TO
CONTRACTUALLY EXCLUDE, INCLUDING, WITHOUT LIMITATION,
IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS FOR
A PARTICULAR PURPOSE, DURABILITY OR DESCRIPTION OF THE
PRODUCT, ITS NON-INFRINGEMENT OF ANY RELEVANT PATENTS
OR TRADEMARKS, AND ITS COMPLIANCE WITH OR NON-VIOLATION OF ANY APPLICABLE ENVIRONMENTAL, HEALTH OR SAFETY
LEGISLATION; THE TERM OF ANY OTHER WARRANTY NOT HEREBY
CONTRACTUALLY EXCLUDED IS LIMITED SUCH THAT IT SHALL NOT
EX TEND BEYOND TWEN TY-FO UR (24) M ONTH S FR OM T HE PROD UCTION DATE, TO THE EXTENT THAT SUCH LIMITATION IS ALLOWED BY
THE GOVERNING LAW.
Product Warranty Return Procedure All Products that are believed to
have defects in workmanship or materials must be returned, together
with a written description of the defect, to the tekmar Representative
assigned to the territory in which such Product is located. If tekmar
receives an inquiry from someone other than a tekmar Representative,
including an inquiry from Purchaser (if not a tekmar Representative) or
Purchaser’s customers, regarding a potential warranty claim, tekmar’s
sole obligation shall be to provide the address and other contact information regarding the appropriate Representative.
tekmar Control Systems Ltd., Canada, tekmar Control Systems, Inc., U.S.A.
Vernon, B.C. Canada V1B 3K4, 250-545-7749, Fax. 250-545-0650 Web Site: www.tekmarcontrols.com
Product design, software and literature are Copyright © 2010 by:
tekmar Control Systems Ltd. and tekmar Control Systems, Inc.
32 of 32
Head Offi ce: 5100 Silver Star Road,
All specifications are subject to change without notice.
Printed in Canada. D 402 - 09/10.
 Loading...
Loading...