Sony STRDE-845, DAV-700, DAV-900, HCDC-700, HCDC-900 Service manual
...
S |
Training Manual |
Multi-Product Hi-Fi Technology and Troubleshooting
Digital Board |
Hi-Fi Output |
Model: STR-DE845 |
Troubleshooting |
Switching Power Supply |
Super Audio CD |
Model: DAV-700/900 |
New Technology |
DAV-S500 |
|
HCD-S500 |
|
HCD-C700/900 |
|
Course: A-124

Table of Contents
1. Introduction ..................................... |
1 |
Purpose ............................................................ |
1 |
Receiver ........................................................... |
1 |
Layout .............................................................. |
1 |
Regulation ....................................................... |
32 |
How to Troubleshoot the Power Supply .......... |
33 |
Testing the Power Supply Unloaded ............... |
35 |
Troubleshooting Shortcuts .............................. |
36 |
2. |
Sound Fields .................................... |
2 |
What is a Sound Field? .................................... |
2 |
|
Sound Field Types............................................ |
2 |
|
Virtual ............................................................... |
3 |
|
Cinema Studio .................................................. |
6 |
|
Semi Cinema Studio......................................... |
6 |
|
Theater ............................................................. |
6 |
|
Music ................................................................ |
6 |
|
Active Speaker Chart ....................................... |
7 |
|
Table 2-1 - Input Software Format .................... |
9 |
|
3. |
Digital Board Inputs ....................... |
10 |
Analog Inputs .................................................. |
10 |
|
Digital Inputs.................................................... |
10 |
|
Software Formats Illustrated ........................... |
12 |
|
4. |
Control Signal Block ...................... |
14 |
Input/Output Select ICs |
|
|
Control Signal Block ........................................ |
14 |
|
Digital Processing ICs |
|
|
Control Signal Block ........................................ |
15 |
|
5. Analog signal Block ....................... |
19 |
|
Circuit Description ........................................... |
21 |
|
6. |
Digital Signal Block ........................ |
23 |
7. |
Mute Signal Block .......................... |
25 |
8. |
Troubleshooting Block .................. |
26 |
9. |
DAV-C700 Switching Type |
|
Power Supply...................................... |
28 |
|
Safety for You and the Circuit .......................... |
28 |
|
Power Supply Operation ................................. |
28 |
|
10. Hi-Fi Output Troubleshooting |
|
Overview ............................................. |
37 |
11. Troubleshooting Driver |
|
Amplifier & Bias Network Circuits .... |
39 |
Protection light will not go off after replacing |
|
Output transistors ............................................ |
39 |
Excessive Current Draw .................................. |
40 |
12. Troubleshooting Audio |
|
Protection Circuits ............................. |
43 |
(+/-) Offset Protection Circuit ........................... |
44 |
Over Current Protection Circuit ....................... |
45 |
13. Super Audio CD ............................ |
46 |
Overview ......................................................... |
46 |
The New Format for the Age of |
|
Digital Pure Audio ............................................ |
46 |
The DSD Format: No Data Decimination |
|
or Interpolation Required ................................. |
48 |
Delta Signal Modulation and A/D Converter .... |
49 |
Disc Features and Watermark Technology ..... |
53 |
Appendix: |
|
Individual IC |
|
Functional Description ....................... |
i |
IC1201 System Control .................................... |
i |
IC1101 Digital Audio I/F Receiver (DIR) ........... |
i |
IC1301 Digital Audio Decoder (DAD) ............... |
i |
IC1401 Audio DSP ........................................... |
i |
IC1503 Audio Codec ........................................ |
i |
IC1403 SRAM (Static RAM) ............................. |
i |

1. Introduction
Introduction
Purpose
The focus of this book is on the digital board operation in the sample receiver (STR-DE845) and covers the following subjects:
•A working understanding of sound fields and what type of movie or music software should be used with each sound field for optimal performance.
•Proper use of the digital board inputs.
•Which speakers receive actual audio while in various sound field modes.
•Simplified circuit diagram and operation of the digital board for troubleshooting.
To properly troubleshoot the Digital board, a good understanding of what sound fields are and how they affect the input is essential. Once a good working knowledge of sound fields is obtained, the receiver can be better set up to process the movie or music software for the best quality audio output. The information in this book will also help the technician determine whether a customer’s problem is a receiver setup or an actual circuit defect.
Receiver
The main receiver used for demonstration throughout this book is the STR-DE845. The STR-V444ES digital board will also be covered, showing the DSP circuit changes as compared to the STR-DE845 only. The overall operation of the digital board in both models is the same.
Layout
Chapter 2 covers the theory and functional description of the various sound fields. Chapter 3 illustrates the proper use of the receiver (digital board) inputs on the rear panel. Chapters 4, 5, 6 and 7 provide the technician with block diagram descriptions of the four main systems found on the digital board. Chapter 8 describes a very practical troubleshooting method for determining a defective component on the digital board. There is also an appendix at the end of the manual that provides a brief description of the function of the main ICs on the digital board.
1
2. Sound Fields
Sound Fields
What is a Sound Field?
Each venue, be it a concert hall, cinema theater or small jazz club, has a characteristic “sound field” made up of direct sounds and reflections from the surfaces of the environment. Some venues sound large and spacious, others sound small and intimate. These characteristics are captured using special microphone pickup systems placed in the actual venue. The microphone pickup system captures the acoustic blue print of the venue, which contains all of the acoustic information about the venue, such as direct sounds, early reflections and reverberations (reverberations occur when the number of reflected sound-waves arriving at the listeners ear becomes very large; ref. Figure 2-1). All the acoustic data about the venue is stored in the computer and then downloaded to the A/V receiver’s microprocessor internal memory. So when you select the concert hall sound field on your A/V receiver, the information stored in the microprocessor’s internal memory is activated and your living room takes on the characteristics of an actual concert hall.
STAGE
Direct
Soundwave |
|
Soundwave |
|
Early |
Reflection |
Sound Field Types
Auto Format Decoding (press AFD button)

 LateSoundwaveReflection
LateSoundwaveReflection
FIGURE 2-1 - Soundwave Reflection Diagram
This mode automatically detects the type of audio signal (Software Format) being input (e.g. Dolby Digital, Dolby Pro-Logic, or Standard 2 Channel Stereo) and performs the proper decoding if necessary. This mode presents the sound as it was recorded/encoded, without adding any sound field effects.
NOTE: This mode can be used as a reference. Set the equalizer to “OFF” while using this mode to hear the source sound exactly as it was recorded. This mode can also be used to determine exactly what type of Software format is encoded on a given disc.
2 Channel (press 2CH button)
Outputs the sound from the front left and right speakers only. Standard two channel (stereo) sources completely bypass the sound field processing. Multi-channel surround formats are down-mixed to two channels.
NOTE: No sound is output from the sub-woofer (LFE) when the 2 Channel mode is selected.
Normal Surround
This mode is designed to be used with a Multi-channel surround audio input (e.g. Dolby Digital/AC-3, DTS or Dolby Prologic) and the normal six-speaker surround system (front left/right, rear left/right, center and LFE) (ref. Figure 2-2). When the playback material is encoded with multi-channel surround audio, it will be heard as it was originally recorded (with no other processing for special effects). For example, a movie will be played back exactly how the producer recorded it during the movie’s production. If Dolby Prologic (2 channel audio) encode material is input, it will be processed to create surround sound effects using the actual six-speaker system.
2

2. Sound Fields
Note:
Front Left – FLT
Low Frequency Effects - LFE
Center – Cntr
Front Right – FRT
Rear Left – RLT
Rear Right - RRT
Listening Position – LP
L |
|
LFE |
|
C |
|
R |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
LS |
|
RS |
|
|
|
FIGURE 2-2
Virtual
The five different Virtual modes create sets of virtual speakers using the actual existing speaker system which could be a six or three speaker system.
1)V. Multi Dimension: Uses 3D image processing to create four sets of virtual rear speakers surrounding and positioned at an elevation of 30 degrees higher then the listener from a six-speaker system (two actual rear speakers). Depending upon where the actual rear speakers are positioned, the virtual speakers positions will vary (ref. Figures. 2-3, 2-4 and 2-5). The position of the rear speakers (Side, Mid or Rear) must be programmed in the A/V receiver SET-UP menu for this sound field effect to work properly.
NOTE: The virtual speakers are placed at an elevation of 30 degrees higher then the listener to further emulate the theater venue. The surround sound speakers in a theater are always higher then the listeners’ position.
LS
L |
LFE |
C |
R |
L |
LFE |
C |
R |
|
L |
LFE |
C |
R |
1 |
|
|
1 |
1 |
|
|
|
1 |
1 |
|
|
1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
RS |
2 |
|
|
|
2 |
2 |
|
|
2 |
|
|
|
|
3 |
|
|
|
3 |
3 |
|
|
3 |
2 |
|
2 |
|
|
|
|
|
L S |
R S |
4 |
4 |
|
|
4 |
4 |
LS |
R S |
3 |
|
3 |
|
|
|
4 |
4 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
FIGURE 2-4 - Rear Speakers Middle |
FIGURE 2-5 - Rear Speakers Behind |
||
FIGURE 2-3 - Rear Speakers Side
3
2. Sound Fields
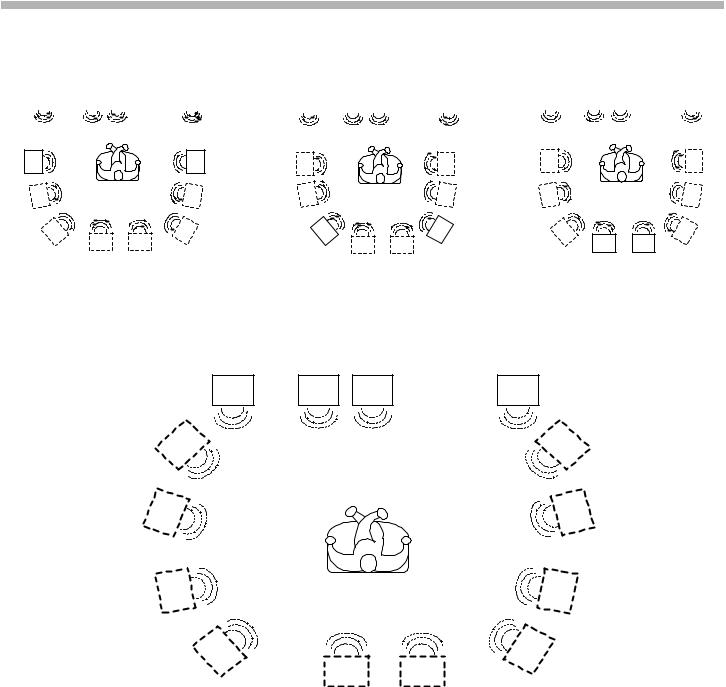
2)V. Multi Rear: Uses 3D image processing to create three sets of virtual speakers from a six-speaker system (two actual rear speakers; ref. Figures. 2-6, 2-7 and 2-8). The position of the rear speakers (Side, Mid or Rear) must be programmed in the A/V receiver SET-UP menu for this sound field effect to work properly. Note: No 30-degree higher effect.
L |
|
LFE |
|
C |
|
R |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
L |
|
LFE |
|
C |
|
R |
|
|
|
|
L |
|
LFE |
|
C |
|
R |
|
|
|
|
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
L S |
|
RS |
1 |
1 |
1 |
1 |
1 |
|
1 |
2 |
2 |
2 |
2 |
2 |
2 |
|
L S |
R S |
3 |
3 |
3 |
3 |
|
3 |
3 |
LS |
RS |
|
|
|
||||
FIGURE 2-6 - Rear Speakers Side |
|
FIGURE 2-7 - Rear Speakers Middle |
FIGURE 2-8 - Rear Speakers Behind |
|||
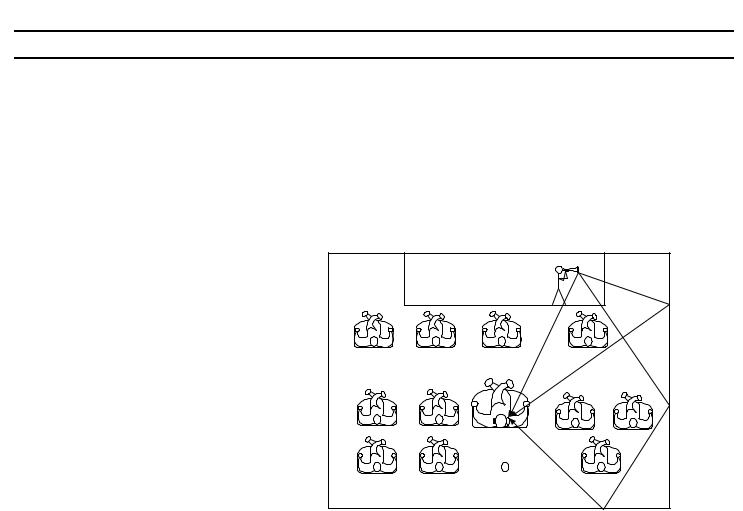
3)V. Semi-M. Dimension: Uses 3D image processing to create five sets of virtual rear/surround speakers surrounding and positioned at an elevation of 30 degrees higher then the listener. This is accomplished using only the front left and right speakers without using actual rear speakers (ref. Figure 2-9).
L |
LFE |
C |
R |
1 |
|
|
1 |
2 |
2 |
3 |
3 |
4 |
4 |
5 |
5 |
FIGURE 2-9
4) Virtual Enhanced A: Uses 3D image processing to create three sets of virtual rear/surround speakers. This is accomplished using only the front left and right speakers without using actual rear speakers (ref. Figure 2-10).
4

2. Sound Fields
L |
|
LFE |
|
C |
|
R |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1 |
1 |
2 |
2 |
3 |
3 |
FIGURE 2-10
5)Virtual Enhanced B: Uses 3D image processing to create one set of virtual rear speakers. This is accomplished using only the front left and right speakers without using actual rear speakers (ref. Figure 2-11).
L |
|
LFE |
|
C |
|
R |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
1 |
|||||||
|
||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
FIGURE 2-11
5
2. Sound Fields
Cinema Studio
This mode is designed to be used with a Multi-channel surround audio input (e.g. Dolby Digital/AC-3, DTS or Dolby Prologic) and the normal six-speaker surround system (front left/right, rear left/right, center and subwoofer). Cinema Studio is similar to Normal Surround except now the acoustical characteristics of a Sony Pictures Entertainment cinema production studio are present. The 3D image processing of the V. Multi Dimension (a virtual speaker mode which will be discussed shortly) is added to the normal surround sound audio to produce the cinema studio atmosphere. There are three Cinema Studio sound fields:
1)Cinema Studio EX. A: Reproduces the sound characteristics of the Sony pictures Entertainment “Cary Grant Theater” cinema production studio. This sound field can be used when viewing almost any type of movie.
2)Cinema Studio EX. B: Reproduces the sound characteristics of the Sony pictures Entertainment “Kim Novak Theater” cinema production studio. This sound field is ideal for viewing science fiction or action movies with lots of sound effects.
3)Cinema Studio EX. C: Reproduces the sound characteristics of the Sony pictures Entertainment scoring stage. This sound field is ideal for viewing musicals or classic films where music is featured in the soundtrack.
Note: The Cary Grant and Kim Novak Studios are actual Sony Pictures Entertainment Movie Production Studios where a movie is shot and produced. Each has its own unique acoustical characteristics, which in these cases even have particular characteristics for certain types of movies (e.g. The Kim Novak Studio is particularly good for Science Fiction movies). The Sony Entertainment Scoring Stage is an actual studio used for recording the music portion of the movie. Once again, this studio has especially good characteristics for recording movie sound tracks. This makes this mode particularly good for playing back certain movies where the sound track is a major part of the movie (e.g. a musical movie).
Note: These sound fields use the 3D sound imaging of V. Multi Dimension. Reference figures 2-3, 2-4 and 2-5 for the three possible virtual speaker system positioning, which depends on the positioning of the two actual rear speakers.
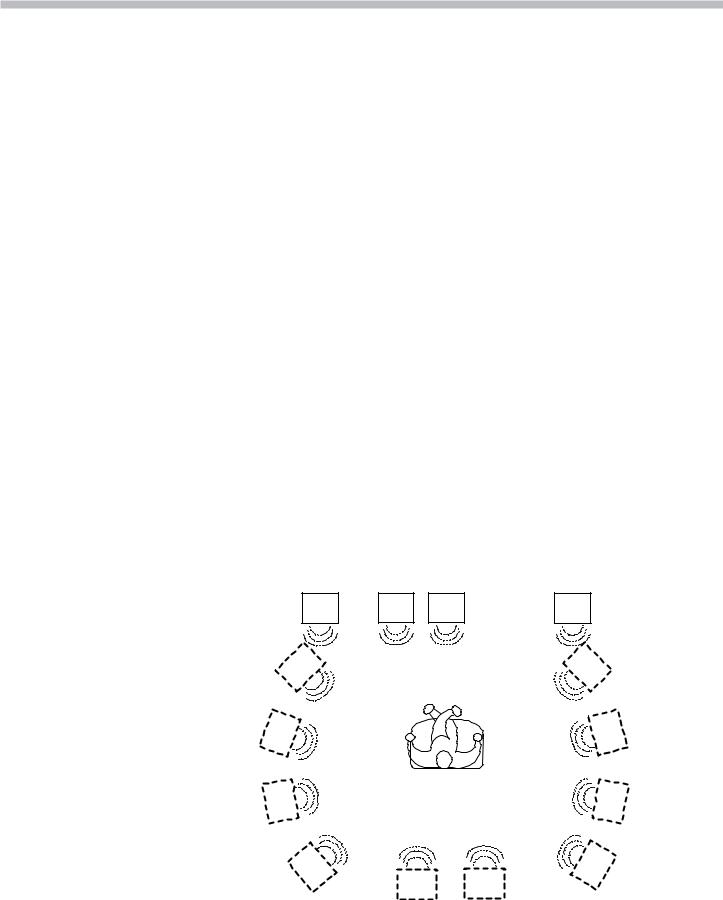
Semi Cinema Studio
These three sound fields (Semi Cinema Studio EX. A, Semi Cinema Studio EX. B and Semi Cinema Studio EX. C) are identical to the above Cinema Studio mode except now the Sony Picture Entertainment cinema production studio sound characteristics are reproduced using only front left, right and center speakers. All other speakers are virtual (ref. Figure 2-12).
L |
LFE |
C |
R |
1 |
|
|
1 |
2 |
2 |
3 |
3 |
4 |
4 |
5 5
FIGURE 2-12 - Listener, Actual and Virtual Speaker Setup
6

2. Sound Fields
Theater
There are four theater sound fields:
1)Night theater: Retains theater-like sound characteristics while listening at a low volume level, ideal for late night movie viewing.
2)Mono Movie: Creates theater-like sound characteristics from movies with mono soundtracks.
3)Stereo Movie: Creates theater-like sound characteristics from movies with stereo soundtracks.
4)Headphone theater: Retains theater-like sound characteristics while listening through a pair of headphones.
NOTE: Mono Movie and Stereo Movie modes do not convert input signals to Mono or Stereo signals. They are strictly used for optimal playback of analog 2ch movie soundtracks.
Music
Nine different sound fields reproduce the acoustical characteristics of nine different venues. Each one of these sound fields is designed for a 2-channel stereo input (e.g. from a CD, DAT, TV Broadcast, etc.). Some of these sound fields are designed to perform better with certain types of music (e.g. Jazz Club with Jazz, Rock music with Live House and so on). These sound fields are listed below:
Small Hall |
Church |
Large Hall |
Live House |
Opera House |
Arena |
Jazz Club |
Stadium |
Disco Club |
|
Video Games
Game: This sound field is designed to be used with video game software and a stereo input. This mode will produce dynamic audio while playing video games.
Active Speaker Chart
With so many sound fields and software formats, it can be very difficult to know which speakers are active (actual audio applied to them by the receiver) for the software while in a particular sound field mode. Chart 2-1 on the following page shows Sound Fields on its vertical axis and Software Formats on the top horizontal axis. It indicates which speakers are active with the chosen Sound Field and Software Format. This chart also indicates when Virtual Speakers are present. To get the same results as this chart at any location, the following conditions must be met:
Conditions
1)The input device (e.g. DVD, CD etc.) must be set up properly to output the desired Software Format (e.g. AC-3, DTS etc.).
2)The proper input on the receiver must be used to receive the desired Software format.
a.Optical and Coax Inputs: Dolby Digital (AC-3), DTS, Dolby Prologic, Dolby Surround and PCM
b.Analog Inputs: Dolby Prologic, Dolby Surround, Stereo and Mono
c.5.1 Channel Input: This input bypasses all surround sound processing of the receiver. Note:
This is a good input to use to test if all the speakers in the system are receiving audio. The input device must have a 5.1 Channel output.
7

2. Sound Fields
3)Speaker wires must be connected correctly, e.g. the Positive (+) on the receiver terminal connected to the Positive terminal on the speaker. Same for the Negative (-) terminal.
4)The speaker impedance switch on the receiver should match the impedance of the speakers connected.
Note: If only output “A” is used, the impedance switch should be set to match the speaker impedance (e.g. 4 or 8 ohms). Caution!!! - If the “A” and “B” output are used simultaneously, the impedance of each speaker must not be less then 8 ohms and the impedance switch must be set for 4 ohms. This is because the speakers are placed in parallel when in this configuration so the impedance of the speakers is cut in half.
Notes for Chart:
1)The box around the speaker letter indicates that this is an actual physical speaker (not virtual) and audio is applied to the speaker.
2)There are notes under pictures to indicate if virtual speakers are being created.
NOTE: The actual rear surround sound speakers will be inactive in the following sound field modes:
•Semi-Cinema Studio EX. A, B, and C
•V. Semi-M Dimension
•Virtual Enhanced A and B
•2 Channel
8

2. Sound Fields
T A B LE 2 -1 - IN P U T S O F T W A R E F O R M A T
¾ |
D olby D igital (A C -3) |
D olby P rologic |
|
P C M |
¾ |
S tereo |
|
|||||||||||||||||
¾ |
5 .1 C hanel S urround |
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
¾ |
D T S |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
¾ |
M ono |
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
S ound F ield |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
L |
|
|
C |
|
R |
|
LF E |
|
L C |
|
R |
|
L |
R |
L |
R |
||||||
A .F .D .
N orm al S urround
C inem a S tudio
E x . A , B , C
S em i-C inem a S tudio E x . A , B , C
N ight T heater
|
|
LS |
|
|
|
|
R S |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
S |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
L |
|
|
C |
|
|
R |
|
|
LF E |
|
|
|
|
L |
|
C |
|
|
|
R |
|
|
|
L |
C |
|
R |
|
|
|
L |
|
|
C |
|
|
|
R |
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
LS |
|
|
|
|
R S |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
S |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
S |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
S |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
L |
|
|
C |
|
|
R |
|
|
LF E |
|
|
|
|
L |
|
C |
|
|
|
R |
|
|
|
L |
C |
|
R |
|
|
|
L |
|
|
C |
|
|
|
R |
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
LS |
|
|
|
|
R S |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
S |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
S |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
S |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
virtual |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
W ith |
|
additional |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
|
speak er |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
L |
|
|
C |
|
R |
|
|
LF E |
|
|
|
|
L |
C |
|
|
|
R |
|
|
|
L |
C |
|
R |
|
|
|
L |
|
C |
|
|
|
R |
|
||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
A ll other speak ers |
|
A ll other speak ers |
A ll other speak ers |
A ll other speak ers |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
virtual |
|
|
|
|
|
|
virtual |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
virtual |
|
|
|
|
|
|
virtual |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
L |
|
|
C |
|
|
R |
|
|
LF E |
|
|
|
|
L |
|
C |
|
|
|
|
R |
|
|
|
L |
|
C |
|
|
R |
|
|
|
L |
|
|
C |
|
|
|
R |
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
LS |
|
|
|
|
R S |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
S |
|
(reverb) |
|
|
|
|
S |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
S |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
M ono M ovie |
|
L |
|
C |
|
R |
|
|
LF E |
|
L |
|
C |
|
R |
|
|
|
|
|
L |
|
C |
|
R |
|
|
|
|
|
L |
|
|
|
|
|
R |
|
||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
LS |
|
|
|
|
R S |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
S |
(reverb) |
|
|
|
|
|
S |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
S |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
S tereo M ovie |
|
L |
|
C |
|
R |
|
|
LF E |
|
L |
|
C |
|
R |
|
|
|
L |
|
C |
|
R |
|
|
|
|
|
L |
|
|
|
|
|
R |
|
||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
LS |
|
|
|
|
R S |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
S |
(reverb) |
|
|
|
|
|
S |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
S |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
V . M ulti |
|
L |
|
C |
|
R |
|
LF E |
|
L |
|
C |
|
R |
|
|
|
L |
|
C |
|
R |
|
|
|
|
L |
|
|
C |
|
|
R |
|
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
D im ension |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
LS |
|
|
|
|
R S |
|
|
|
|
|
|
S |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
S |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
S |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
W ith additional |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
|
|
|
virtual speak ers |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
V . M ulti R ear |
|
L |
|
C |
|
R |
|
|
LF E |
|
L |
|
C |
|
R |
|
|
|
L |
|
C |
|
R |
|
|
|
|
L |
|
C |
|
R |
|
|
||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
LS |
|
|
|
|
R S |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
S |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
S |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
S |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
W ith additional |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
|
|
|
virtual speak ers |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||
V . S em i - M |
|
L |
|
C |
|
R |
|
|
LF E |
|
L |
|
C |
|
R |
|
|
|
L |
|
|
C |
|
|
R |
|
|
|
L |
|
C |
|
|
R |
|
|
||||||||||||||
D im ension |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
A ll other speak ers |
A ll other s peak ers |
A ll other speak ers |
A ll other speak ers |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
virtual |
|
|
|
|
|
|
virtual |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
virtual |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
virtual |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||
V irtual E nhanced |
|
L |
|
C |
|
R |
|
|
LF E |
|
L |
|
C |
|
R |
|
|
|
L |
|
|
C |
|
|
R |
|
|
|
L |
|
C |
|
|
R |
|
|
||||||||||||||
A , B |
|
A ll other speak ers |
A ll other speakers |
A ll other speak ers |
A ll other speak ers |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
virtual |
|
|
|
|
|
|
virtual |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
virtual |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
virtual |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
2 C hannel |
|
|
L |
|
|
|
|
R |
|
|
L |
|
|
|
R |
|
|
|
L |
|
|
|
|
|
R |
|
|
|
L |
|
|
|
|
|
R |
|
|
|||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
S m all H all Large H all
O pera H ouse Jazz C lub
D isco C lub C hurch Live H ouse A rena
S tadium G am e
L |
|
C |
|
R |
|
LF E |
|
L |
|
C |
|
R |
|
L |
|
|
|
R |
|
L |
|
R |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
LS |
|
|
|
R S |
|
|
|
|
|
S |
|
|
|
|
|
S |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
T his table show s w hich speak ers are active during a particular sound and softw are form at input.
9

3. Digital Board Inputs
Digital Board Inputs
Analog Inputs
2 Channel Stereo Inputs
There are nine analog inputs on the digital board. They are as follows:
-Tuner
-Phono
-CD
-MD/Tape
-TV/SAT
-DVD/LD
-Video 1, 2, 3
These inputs enter the digital board as analog audio and supply one of the following audio formats: Mono, Stereo or Dolby Prologic. They go through a switching IC and then onto the Audio CODEC to be digitized. The digital data stream is applied first to the Audio Decoder and then to the Audio DSP, which processes and applies the effects of the chosen sound field.
5.1 Channel Input
The 5.1 Channel Input is a full surround sound analog audio input that bypasses the sound field processing of the digital board in the receiver. All the surround sound processing required to produce the 5.1 Channel Input is performed by the device connected to this input, such as a DVD player with a 5.1 Channel Output. The 5.1 Channel Input is applied directly to the output selector IC1502. IC1502’s outputs are connected directly to the amplifier system. The 5.1 Channel Input actual consists of six signals: Front Left, Front Right, Rear Left, Rear Right, Center and Subwoofer. The Subwoofer is the “1” in the 5.1 designation.
Digital Inputs
There are two types of digital inputs - the Optical input and the Coaxial input. The only difference between these two inputs is the medium used to transfer the signal between devices. The Optical input utilizes Fiber Optic cable to transmit data as light pulses down a glass fiber center conductor. Because light pulses are used, the Fiber Optic cable is virtually immune to any external electrical interference, making it the preferred digital signal source. The Coaxial Input uses Coaxial cable similar to that found in Cable TV connections. It consists of a copper center conductor, a foam insulator and an outer braided wire shield. The Coaxial cable has good external noise immunity characteristics, but cannot compare to the Fiber Optic cable. Also, the bandwidth characteristic of the Fiber Optic cable is much greater. Both of these input types are digital, using the same data protocol (S/P DIF format). There are three Optical inputs, one Optical Output and one Coaxial input on this receiver.
Optical: |
Coaxial: |
DVD/LD input |
DVD/LD |
TV/SAT input |
|
DAT/MD input |
|
MD/DAT output |
|
10
3. Digital Board Inputs
Table 3-1 – Digital Input Sampling Frequency Compatibility
Input |
Sampling Frequency |
|
|
Optical DVD/LD |
96KHz, 48KHz, 44.1KHz, 32KHz |
|
|
Optical TV/SAT |
48KHz, 44.1Khz, 32KHz |
|
|
Optical DAT/MD |
48KHz, 44.1Khz, 32KHz |
|
|
Coaxial DVD/LD |
96KHz, 48KHz, 44.1KHz, 32KHz |
|
|
NOTE: If a signal with a sampling rate of 96kHZ is applied to the MD/DAT or TV/SAT inputs, intermittent audio at the receiver outputs may occur.
These digital inputs are sent through the complete surround sound processing circuitry of the digital board to produce the 5.1 Channel Output signals. This processing and signal flow will be discussed in detail in the next chapter.
ANALOG |
|
|
DIGITAL INPUTS |
|
|
|
|
|
SOFTWARE |
|
|
||||
INPUTS |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
DEVICES |
FORMATS |
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
MD/DAT |
DOLBY DIGITAL |
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
TV/SAT |
AC-3 (5.1) |
|
|
||
DEVICES |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
DTS (5.1) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
DOLBY PROLOGIC |
|
|||
DVD |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
PCM 48kHz, 41.1kHz, |
|
|||
MULTI-CHANNEL DECODE |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
32kHz |
|
|
|
||||
NOTE: THE DEVICE MUST BE CAPABLE OF |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
PROCESSING AC-3,OR DTS SOFTWARE AND |
|
|
|
|
|
|
SOFTWARE |
|
|||||||
OUTPUT 5.1 CHANNEL SIGNALS |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
DEVICES FORMATS |
|
||||||
|
|
|
REAR |
|
|
|
|
|
|
DVD/LD |
DOLBY DIGITAL |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
DVD/LD |
AC-3 (5.1) |
|
||||
|
|
FRONT |
CENTER |
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
(COAX) |
DTS (5.1) |
|
|||||||
|
|
|
L |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
R |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
DOLBY PROLOGIC |
||
|
|
|
|
SUB |
|
|
|
|
|
|
PCM 96kHz, 48kHz, |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
WOOF |
|
|
|
|
|
41.1kHz, 32kHz |
|
|||
DIPOLE |
ANTENNA |
|
|
|
|
|
OPTICAL |
|
|
COAX |
|
|
SPEAKERS |
||
|
|
L |
|
|
|
MD/DAT |
TV/ |
|
DVD/LD |
|
|
+ |
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
MD/DAT |
IN |
|
|
|
B |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
SAT |
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
FRONT |
REAR |
CENT. |
|
OUT |
|
|
IN |
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
IN |
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
AM |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
R |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
SUB |
|
|
|
DVD/LD IN |
|
|
|
R |
|
|
|
|
|
5.1 CH INPUT |
|
|
|
DIGITAL |
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
WOOF. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
WIRE |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
- |
|
COAXIAL |
|
|
CTR S |
|
CTR S |
|
|
CTR S |
CTR S |
|
|
|
|
||
ANTENNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
IN |
S-VIDEO |
STAT.INS-VIDEO S-VIDEO |
OUT |
OUT |
S-VIDEO S-VIDEO |
|
IMPED |
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
OUT |
|
IN |
IN |
|
|
OUT |
IN |
|
||
|
FM |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
VIDEO |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
75Ω |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
STR- |
SIGNAL |
|
OUT |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
VIDEO |
VIDEO |
VIDEO OUTVIDEO IN VIDEO VIDEO IN |
CONTROL AII |
||||||||
|
GND |
|
MONITOR |
|
|||||||||||
DE845 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
IN |
IN |
|
|
OUT |
|
|
|
L |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(REAR |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
VIEW) |
R |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
IN |
IN |
OUT |
IN |
OUT |
IN |
A |
IN |
A IN |
AUDIO OUT A IN |
AUDIO OUT IN |
2ND AUDIO |
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
OUT |
|
ANALOG
INPUTS
PHONO CD |
MD/DAT |
TAPE |
DVD/LD |
VCR |
VCR |
DEVICES |
|
|
TV/SAT |
|
|
SOFT |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
DOLBY SURROUND DOLBY |
PROLOGIC STEREO |
MONO |
WARE |
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
FORMATS |
FIGURE 3-1 - STR-DE845 ANALOG & DIDITAL INPUTS |
13CA124 1380 10/15/01 |
|||||
11

3. Digital Board Inputs
Figure 3-1 illustrates the typical devices connected to the various receiver inputs and what software formats are compatible with each input.
NOTE: The audio from the Tuner antenna section is also an input to the digital board. It is processed the same as any of the other analog inputs in order to apply the desired sound field effects. The input signals to the tuner are off the air (FM and AM) signals. There is also an analog Video 3 Input on the front panel of the receiver that can accommodate another VCR.
Software Formats Illustrated
Dolby Surround Prologic
|
Left |
|
|
|
|
Dolby |
|||
Four |
Right |
|||
Surround |
||||
Channel |
Center |
|
||
ProLogic |
||||
Signals |
||||
Surround |
Encoder |
|||
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Note: From a live performance or recording
|
Software Medium |
|
|
S |
|
|
y |
Laser Disk |
|
|
L |
LT |
y |
DVD Disk |
|
|
|
LT |
Dolby |
|
|||
|
y |
CD |
Surround |
|
|
RT |
y |
VHS Tape |
|
C |
|
RT |
ProLogic |
||||
|
y |
Cassette Tape |
Decoder |
|
|
|
y |
Cable |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
y |
Satellite TV |
|
|
R |
|
y |
Regular Tv |
|
|
S |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
DOLBY SURROUND PROLOGIC |
|
|||
FIGURE 3-2
Figure 3-2 illustrates the encoding and decoding of a Dolby Surround Prologic format. Note that this format can be encoded on the software medium (DVD disk, VHS tape etc.) in a digital data stream or analog signal. The original four channels are encoded into two channels (Left Total and Right Total). At the decoder, the twochannel signal is decoded back to the original four channel surround signals (Left, Right, Center and Surround). Also note that the surround signal in the Prologic format in fed to both rear speakers, so both speakers receive equal signals. There is a slight delay in time as compared to the front speakers.
Dolby Digital (AC-3), and DTS
|
Left |
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
Center |
|
|
|
|
Right |
|
Dolby |
|
|
Left |
|||
5.1 |
Digital |
|||
Surround |
||||
Channel |
or |
|||
Right |
||||
Signals |
DTS |
|||
Surround |
||||
|
Encoder |
|||
|
Low |
|||
|
|
|||
|
Freq. |
|
||
|
Effect |
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Note: From a live performance or recording
|
|
|
|
|
|
RS |
Digital |
Software Medium |
Digital |
Dolby |
L |
|
|
y |
Laser Disk |
|
||||
Data |
Data |
Digital |
|
|
||
Stream |
y |
DVD |
Stream |
or |
C |
|
|
y |
Cable |
|
DTS |
|
|
|
y |
Satellite TV |
|
LFE |
|
|
|
|
Decoder |
|
|||
|
y |
Regular TV |
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
R |
LS |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
DOLBY DIGITAL & DTS
FIGURE 3-3
12

3. Digital Board Inputs
Figure 3-3 illustrates the encoding and decoding Dolby Digital and DTS 5.1 channel formats. These formats are encoded into a digital data stream only, such as a DVD disc, Satellite signal, etc. (no analog encoding). There are actually six channels in the 5.1 channel format (Left, Right, Center, Subwoofer or LFE, Left surround and Right surround). Note that the rear speakers are now fed totally separate surround signals that provide a superior separation between the speakers when sounds are traveling around the system. Also added to this format is the Low Frequency Effects (LFE) or Subwoofer signal.
5.1 Channel format compatibility
|
|
|
|
|
|
L |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
C |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Decoder "A" |
R |
5.1 Channel |
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
LS |
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
Signals |
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
RS |
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
LFE |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
L |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
LT |
|
|
Dolby |
Four Channel |
|
Dolby Digital |
|
|
|
|
Decoder "B" |
|
|
C |
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Prologic |
R |
Dolby Surround |
||
or |
|
|
|
|
RT |
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Decoder |
S |
signals |
||
DTS 5.1 Channel |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Data Stream |
|
|
|
|
|
L |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Two Channel |
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
Decoder "C" |
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
R |
Stereo Signals |
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Decoder "D" |
|
Mono Signal |
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
FIGURE 3-4 - 5.1 Channel Downmixing
Figure 3-4 illustrates that the 5.1 Channel format is compatible with all of the other formats. The 5.1 channel signal as shown can be DOWN-MIXED into any other format depending on the decoding applied. This is similar to the Prologic format, which is compatible with stereo and mono system due to the way it is encoded.
New Development in Digital Surround Technology
Dolby Digital Surround EX (6.1)
L |
|
LFE |
|
C |
|
R |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
LS |
R S |
CS
FIGURE 3-5
Dolby Digital; EX (6.1)
A center screen channel (or speaker) is necessary to ensure the precise localization of the front sounds for the viewers. Dolby Digital Surround EX brings similar benefits to the surround sound field (side or rear speakers). With Dolby Digital Surround EX, a center surround channel is reproduced. This speaker driven by the center surround channel is positioned at the back/center of the listening room. Left and right surround sound is still reproduced by the side speakers (Ref. Fig. 3-5). This means that sounds can now be positioned behind the audience, opening the door to exciting new effects such as true 360-degree pans. The center surround channel also makes front-to-back and back-to-front transitions more realistic. Dolby Digital Surround EX is fully compatible with the current 5.1 Channel digital formats, and will play back normally on current 5.1 systems. Dolby Digital Surround EX basically adds a center surround channel to 5.1 digital formats.
13

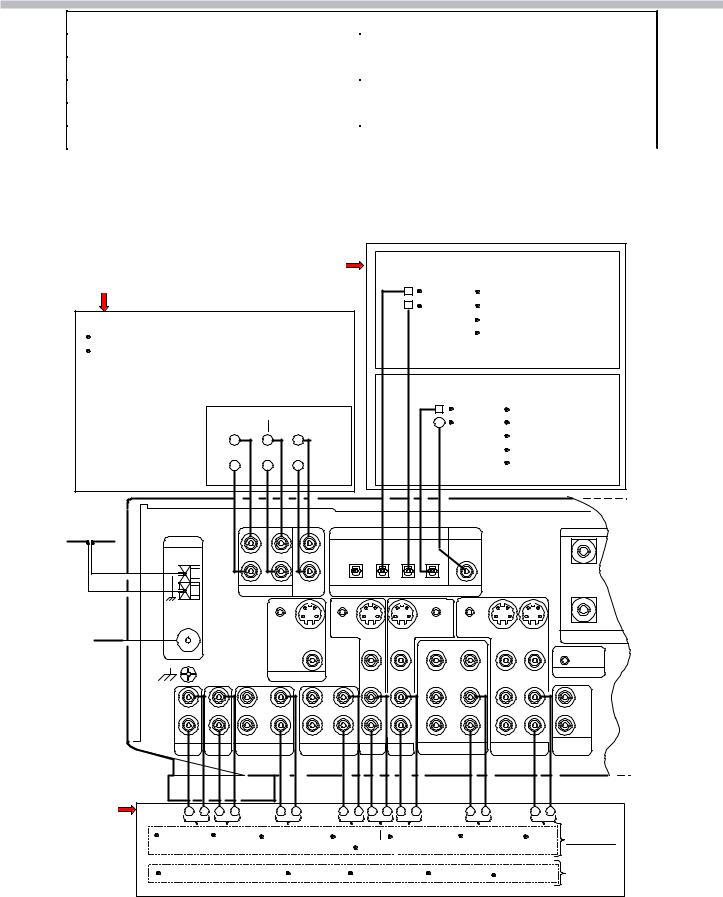
4. Control Signal Block
Control Signal Block
Input/Output Select ICs Control Signal Block
|
DIGITAL BOARD |
|
|
|
MAIN BOARD |
|
|
|
AU SW BOARD |
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
ANALOG INPUTS |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
REAR PANEL |
|
|
|
|
|
L |
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
7 |
TO |
JACKS |
|
|
|
|
12 |
TO IC304/ |
|
|
|||
|
|
IC1005 |
|
IC1101/ |
|
|
|
IC303 |
|
17 |
R |
PINS 3 & 5 |
|
|
|||
|
|
|
PIN 3 |
TO |
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
|
|
DIGITAL |
|
ANALOG |
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
|
|
|
|
IC304/ |
2 CH. MODE |
|
|
|
|
||||||||
|
|
INPUT |
|
|
|
|
INPUT |
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
L |
R |
PINS 3 |
|
FROM IC304 |
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
DIGITAL |
SELECT |
|
SELECT |
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
|
12 |
17 |
& 5 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
|
INPUTS |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
FROM |
2 |
14 |
|
|
|
15 |
14 |
16 |
|
|
|
IC1502 |
|
|||
|
IC1001 |
A |
B |
ANALOG |
|
|
|
|
EXTERNAL |
|
|
||||||
|
|
IC301 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
OUTPUT |
|
||||||
OPTICAL IC1002 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
5.1 CH. |
|
|
|||||
|
IC1003 |
|
|
INPUTS |
ANALOG |
|
|
|
|
|
|
SELECT |
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
J307 |
|
|
|||||||
|
|
|
|
REAR |
INPUT |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
COAXIAL |
|
|
|
PANEL |
|
|
|
|
|
|
5.1 CH. |
|
|
|
|
||
J1001 |
|
|
SELECT |
|
|
|
|
|
15 |
14 |
16 |
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
JACKS |
|
|
|
|
|
CLK |
|
|
INPUT |
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
SDI |
CLK |
CE |
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
FROM |
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2 |
1 |
3 |
CNP11 |
|
|
|
|
|
R1006 |
15 |
14 |
16 |
SDI |
|
|
|
|
IC1503 |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
CE |
|
|
|
CNP301 |
||||||
|
|
R1007 |
|
|
SDI |
|
CE |
|
|
|
|
|
19 |
AC |
18 |
||
TABLE 4-1
IC1005 CONTROL LINES
PIN No. |
A |
B |
|
2 |
14 |
||
|
|||
(COAX) DVD/LD |
1 |
0 |
|
|
|
|
|
(OPTICAL)TV/SAT |
0 |
1 |
|
|
|
|
|
(OPTICAL)DAT/MD |
1 |
1 |
|
|
|
|
|
(OPTICAL) DVD/LD |
0 |
0 |
|
|
|
|
CLK |
3 |
5 |
4 |
CNS306 |
|
|
CNS5 19 |
17 |
18 |
FIGURE 4-1 |
|
R1282 |
|
R1281 |
|
|
DIGITAL BOARD |
|
|
|
|
INPUT/OUTPUT |
|||
108 |
107 |
47 |
48 |
46 |
SELECTOR ICs |
|
CONTROL BLOCK |
||||||
A |
B |
SDI |
CLK |
CE |
||
|
||||||
|
|
IC1201 |
|
|
|
SYSTEM CONTROL
93 92
|
|
|
X1201 |
DIGITAL BOARD |
1A124 1365 11/20/01 |
|
|
|
16MHz |
||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Circuit description
NOTE: Reference Figure 4-1 for the following circuit description:
Data, Clock and Chip Enable Lines
All control signals are supplied by IC1201 (System Control). IC1201/Pins 108 and 107 control the digital input selection of IC1005 (pins 2 and 14). These control lines are a simple two-bit input. Table 4-1 shows the two-bit code for the corresponding input. The resistors on the output of IC1201 (R1282 and R1281) and on the input of IC1005 (R1006 and R1007) are easy probe points to confirm the bit pairs in the table.
The control lines for IC301, IC303 (analog input select ICs) and IC1502 (output select IC) are at IC1201/pins 46 (CE), 47 (Data) and 48 (CLK). These control signals are somewhat difficult to view due the fact that they are only present while switching between inputs via the front panel buttons of the receiver. However, the main concern here is that there is communications between ICs and that the actual inputs do change. Waveforms 4-1, 4-2 and 4-3 illustrate how the waveforms will appear on the oscilloscope while switching between inputs (e.g. Video 1, Video2, DVD/LD etc). Once again, these are not exact waveforms. Confirmation of data communications between ICs and data amplitude (5Vpp) are the important factors. All three pins (IC1201/46, 47 and 48) are at a low state (0V) while waiting for a button to be pressed (standby state).
14

4. Control Signal Block
Data and Control Line Waveforms for IC1301 and IC502
Oscilloscope Settings: |
|
|
5v/div. |
|
|
100us/div. |
PIN No.46 |
|
DC coupling |
CE |
|
(R1202) |
||
Trigger rising edge |
||
|
PIN No.48
CLK 5Vp-p (R1204)
5Vp-p
WAVEFORM 4-1
PIN No.47
DATA 5Vp-p (R1203)
WAVEFORM 4-2 |
WAVEFORM 4-3 |
Digital Processing ICs Control Signal Block |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
|
|
|
13 |
12.282MHz |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
MCLK |
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
SDI |
|
IC1101 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
BCLK |
|
|
|
||
36 |
14 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
DIGITAL |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
CLK 38 |
15 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
LRCLK |
|
|
|
|
|
||||
CE |
37 |
AUDIO |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
DATA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
I/F |
|
|
IC1404 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
|
22 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
RECEIVER |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
WE |
|
IC1402 |
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
IC1401 |
|
74 |
17 |
SRAM |
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
48 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
AUDIO |
|
70 |
OE |
|
41 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
RST |
|
|
|
|
|
PDI |
16 |
DSP |
|
97 |
|
|
6 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
LR |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
X3501 |
|
|
|
|
25 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
12.282 |
|
CLK |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
12.282 |
|
|
|
|
|
100 |
X1401 10MHz |
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
MHz |
MHz |
|
8 |
82 |
83 |
15 |
14 |
26 |
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
IC1301 |
|
RST |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
CLK |
69 |
|
|
HAD |
CE |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
DOLBY |
|
|
IC1202 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
SDI |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
68 |
|
DIGITAL |
|
|
|
|
|
|
5 |
4 |
39 |
|
|||||
|
|
|
CE |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
|
|
|
66 |
|
AUDIO |
|
|
|
|
|
|
IC1503AUDIOCODEC |
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
DECODER |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
43 |
|
42 |
41 |
17 |
11 |
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
RST |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
|
R1288 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
CDTI |
CLK |
CE |
RST |
96 |
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
62 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
KHz |
|
|
|
|
|
R1270 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
R1245 R1285 |
|
||||||
R1289 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
R1263 |
R1252 |
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
|
R1286 |
|
R1275 |
|
|
|
|
R1242 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
R1265 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
112 |
110 |
111 |
100 |
1 |
2 |
3 |
5 |
17 |
24 |
25 |
16 |
26 |
30 |
29 |
28 |
32 |
35 |
SDO CLK |
CE RSTCLK |
SDO |
CE RST |
PDO |
HAO |
CE RST |
CDTO |
CLK |
CE RST |
96 |
|||||||
|
|
|
|
IC1201 SYSTEM CONTROL |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
KHz |
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
93 |
92 |
|
|
90 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
X1201 |
RST FROM Q108 |
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
16MHz |
DISPLAY BOARD |
|
|||
|
|
FIGURE 4-2 - DIGITAL BOARD PROCESSING IC's CONTROL BLOCK |
2A124 1367 11/20/01 |
||||||||||||||
15

4. Control Signal Block
Circuit Description
Data, Clock, and Chip Enable Lines
The control lines for IC1401 (IC1201/parallel data lines 17 to 24, pin 25 (address line) and pin 16 (CE)) and IC1503 (IC1201/pins 30 (data), 29 (CLK) and 28 (CE)) are only present during input switching. The waveforms on the control lines are the same as those shown in Waveforms 4-1, 4-2 and 4-3, except standby voltage state is high (5V dc).
The waveforms on the control lines for IC1101 (IC1201/pins 112 (data), 110 (CLK), and 111 (CE)), and IC1301 (IC1201/pins 1 (CLK), 2 (data), and 3 (CE)) are always present as digital data is present at one of the digital input jacks (optical or coax). Waveforms 4-4 and 4-5 illustrate what is displayed on the oscilloscope. When the Input mode is set to Analog input, all three control lines on IC1101 are inactive and the chip select line on IC1301 is inactive (the other two lines on IC1301 are active with data, but the chip is not enabled).
The following waveforms can be viewed on the oscilloscope continuously when digital data is present at the digital inputs and that digital input is selected.
Oscilloscope Settings:
5V/div. |
Data and Control Line Waveforms for IC1101 |
100us/div or 50us/div |
|
Trigger rising edge |
|
DATA |
|
DATA |
|
|
|
CLK |
|
CLK |
|
|
|
CE |
|
CE |
|
|
|
|
WAVEFORM 4-4 |
WAVEFORM 4-5 |
|
|
Master, Bit and Left/Right Channel Clock lines
All the control lines discussed so far are used either for input/output switching or to set up an IC for a particular function (e.g. Dolby Digital decoding). The Clock lines that will be looked at now are used for data manipulation. The Clock lines MCLK (Master Clock), BCLK (Bit Clock) and LRCLK (Left Right channel Clock) are all developed by IC1101 using X3501 (12.282MHz). The MCLK is applied only to IC1503 (CODEC), while BCLK and LRCLK are applied to IC1301 and IC1503. These Clock lines are used to synchronize the system to the incoming audio data stream so that appropriate decoding and coding can be performed. The following waveforms are always present and can be viewed easily with the oscilloscope. Waveform 4-7 is an expanded view of Waveform 4-6. The frequency for each clock signal is as follows:
MCLK —— 12.282MHz BCLK —— 3MHz LRCLK — 48KHz
Oscilloscope Settings:
5V/div.
2us and 200ns/div
Trigger rising edge
MCLK
BCLK
LRCK
MCLK
BCLK
LRCK
WAVEFORM 4-6 |
WAVEFORM 4-7 |
16

4. Control Signal Block
Reset lines and Crystals
The main Reset line is applied to IC1201/pin 90. During normal operation, this line is High (5V dc).
The other Resets are output to IC1101/ pin 48 (normal high 5V), IC1301/pin 62 (normal high 5V), IC1503/pin 17 (normal high 5V) and IC1401/pin 26. This output is Low (0V), but it passes through inverter IC1202 and a High (5V) is applied to IC1401. The crystal frequencies and amplitudes are shown in Table 4-2 below:
Table 4-2 – Crystal Frequencies and Amplitudes
IC Ref. Number |
Crystal Ref. |
Frequency |
Amplitude |
|
Number |
|
|
|
|
|
|
IC1101 & 1301 |
X3501 |
12.282MHz |
4Vpp |
|
|
|
|
IC1401 |
X1401 |
10MHz |
3Vpp |
|
|
|
|
IC1201 |
X1201 |
16Mhz |
4Vpp |
|
|
|
|
SRAM Control Lines
|
D0 - D3 |
7 |
- 10 |
53 |
|
|
D4 - D7 |
13 |
- 16 |
|
|
|
| |
IC1401 |
|||
|
D8 - D11 |
20 |
- 32 |
||
|
D12 - D15 |
35 |
- 38 |
69 |
AUDIO |
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
DSP |
IC1402 |
A0 - A4 |
5 |
- 1 |
53 |
|
SRAM |
|
||||
A5 - A7 |
44 |
- 42 |
|
||
|
A8 - A11 |
27 |
- 24 |
| |
|
|
69 |
|
|||
|
A12 - A15 |
21 - 18 |
|
||
|
|
|
|||
WE 17 74 XWE
74 XWE
OE 41 70 XOE
70 XOE
FIGURE 4-3 - SRAM BLOCK |
9/26/01 |
There are 16 Data, 16 Address and two control lines (WE and OE) for the SRAM IC1402.. The SRAM is mainly used for the processing of the Cinema and Hall sound fields where reverberation (Delay) is required to produce the appropriate characteristics of a particular venue. The SRAM IC1402 is not used in any of the Virtual Speaker Modes. All processing is performed by internal RAM in IC1401, so no data is present on either the Data, WE or OE lines. Waveforms 4-8, 4-9 and 4-10 show the activity on the Data lines. WE and OE lines are in three different modes: AFD, 2CH and Mode (sound field selection mode). The main point of interest of these three
17
 Loading...
Loading...