Page 1

20-528
PRO-528 1,000-Channel
Handheld
Trunking Scanner
Please read this user’s guide before installing,
setting up and using your new product
www.radioshack.com
Page 2

Contents
Thank you for purchasing your
RadioShack 1000-Channel Handheld
Trunking Scanner from RadioShack.
Your handheld scanner is one of a new
generation of scanners designed to
track Motorola® Type I, Type II, hybrid
analog systems, (such as Smartnet® and
Privacy Plus®) plus M/A-COM EDACS®
and EF Johnson LTR. Those systems are
extensively used in many 800 MHz, 900
MHz, and UHF communication systems.
• scanner
• antenna
• belt clip (2) screws
• user’s guide
• quick start guide
• preprogrammed frequency guide
2
Page 3

Contents
The Basics
your scanner’s features 8
supplying power to your scanner 14
battery cautions 15
connecting the antenna 16
connecting an earphone/ headphone 16
listening safely 17
attaching the belt clip 17
transferring data to or from another
scanner or pc 18
about your scanner 18
understanding banks 19
service banks 19
channel storage banks 20
turning on the scanner and setting
squelch 20
storing known frequencies
into channels 21
Beyond the Basics
copying/moving a frequency 22
searching for and temporarily storing
active frequencies 23
chain search 24
starting chain search 25
storing found frequencies during
chain search 26
programming search ranges 26
direct search 27
service bank search 27
weather search 28
3
Page 4

Contents
search skip memory 28
scanning the stored channels 30
manually selecting a channel 31
special features 32
delay 32
turning channel-storage banks
on and off 33
locking out channels 33
priority 34
using the keylock 35
wired programming 36
cloning your scanner 37
using the display backlight 38
using the auto backlight display 38
search speeds 39
turning the keytone off/on 39
turning the battery save
function off/on 40
skipping data signals 40
receiving nwr-same and weather
alert signals 41
turning on the digital weather
alert feature 42
testing digital weather alert tone
programming a FIPS code 43
programming FIPS 44
Skywarn 45
about Skywarn 45
Signal Stalker I 47
setting the Signal Stalker I options 48
42
4
Page 5

Contents
using Signal Stalker I 51
trunking operation 51
setting the scanner to the
trunking mode 52
simultaneous trunking 52
setting squelch for the trunking
mode 52
programming trunked frequencies 53
searching a trunked bank 56
turning a trunked bank on or off 57
skipping a trunked bank 58
turning the status bit ignore
(s-bit) on or off 58
identifying a trunked frequency 59
selecting the EDACS (Ed) talk
group ID format 60
EDACS (Ed) talk group ID
range search 60
using HOLD to monitor an
active talk group ID 61
locking out talk group IDs 61
unlocking a single talk group ID 62
unlocking all talk group IDs 62
using trunk scanning Scan Delay 63
monitoring talk group IDs 63
using talk group ID lists 64
manually storing talk group IDs
in talk group ID lists 64
Motorola talk groups 65
To enter a Type 2 Talk Group ID: 65
To enter a Type 1 ID: 65
5
Page 6

Contents
EDACS (Ed) talk groups 66
entering EDACS partial talk groups 66
LTR talk groups 67
scanning the talk group ID lists
priority talk group ID scanning 69
scanning type I and hybrid trunked
systems 70
preset fl eet maps table 71
selecting a preset fl eet map 74
programming a fl eet map 74
programming a hybrid system 76
programming the Base and Offset
frequencies 76
turning the Motorola disconnect tone
detect function On/Off 78
68
frequently asked questions 80
My scanner is on but will not
scan, why? 80
Why won’t my scanner work at all? 80
Why doesn’t my keypad work? 81
Why is fl ashing? 81
Why am I getting poor or no
reception? 81
Why does Error appear? 81
Why won’t my scanner track a
trunked system? 81
Why isn’t my scanner acquiring a
data channel? 82
Why is the frequency used for the
data channel missing? 82
6
Page 7

Contents
Why am I missing replies to
conversations? 82
How do I reset my scanner?
FCC notice
84
scanning legally 85
care 86
service and repair 86
specifi cations 87
Hypersearch, Hyperscan, and Adaptaplug
are trademarks used by RadioShack
Corporation.
Motorola, Smartnet, and Privacy Plus are
registered trademarks of Motorla Inc.
EDACS is a registered trademark of
MA-COM Inc.
LTR is a registered trademark of EF
Johnson.
83
7
Page 8
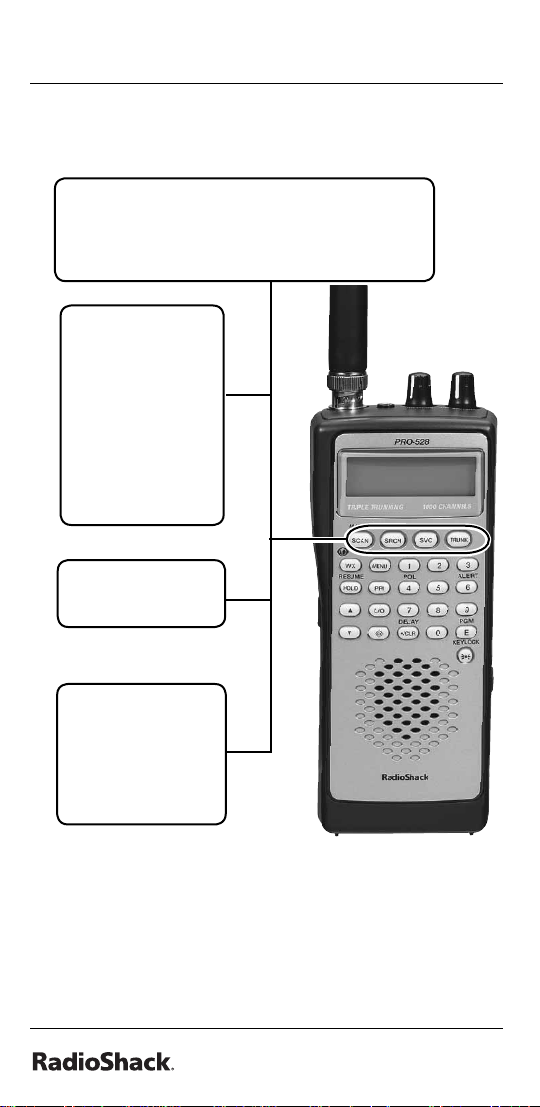
The Basics
your scanner’s features
SCAN/MANUAL — scans the stored channels
and scan lists, or manually enter a channel
or frequency. Manually stores talk group
IDs in scan lists
SRCH (search)
— start a chain
search, search
a specifi ed
frequency
range , or
search another
active ID while
trunking.
SVC — starts a
service.
TRUNK — stores
the trunking ID
code or holds
the trunking ID
while scanning.
8
Page 9
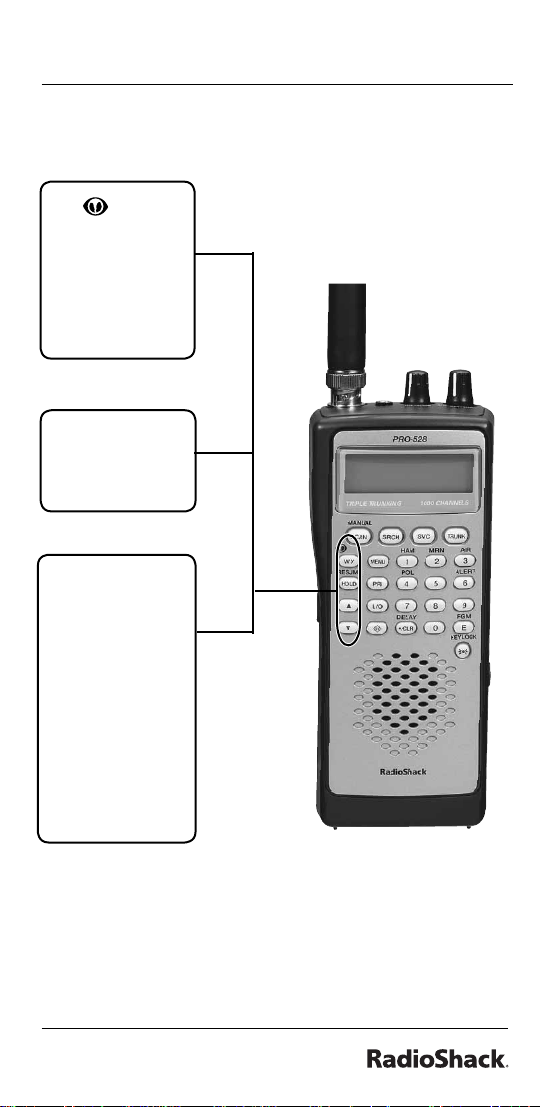
WX/ —
starts weather
search;
activates
Skywarn
function.
HOLD/RESUME
— Stops and
resumes
searching.
ST—Search
and scan up
and down
a selected
frequency
range; selects
options during
programming;
changes the
ID location
number while
trunking.
The Basics
9
Page 10
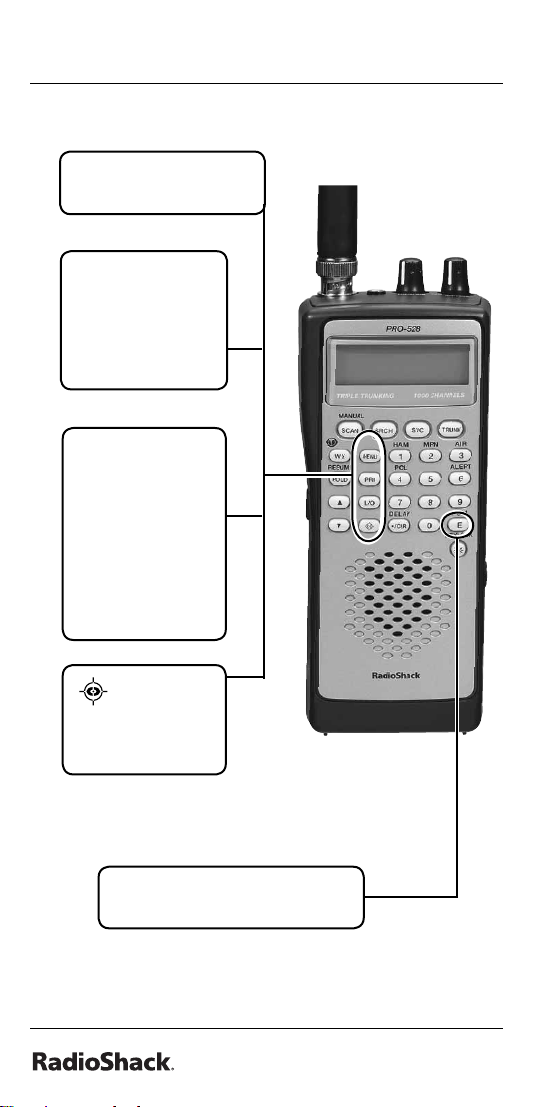
The Basics
MENU — enter the
menu mode.
PRI (Priority)
— sets and
turns the priority
function on or
off.
L/O — lockout
selected
channels or
skip specifi ed
frequencies
during a search;
lock out a
selected ID
while trunking.
— turn
Signal Stalker I
on and off.
E/PGM (Program) — programs
frequencies into channels.
10
Page 11

1/HAM — select the
HAM band in service
mode.
2/MRN (Marine)
— select the
marine band in
service mode.
3/AIR — select
the air band in
service mode.
4/POL — select
the police band
in service mode.
The Basics
6/ALERT — turns
NWR - SAME
weather alert on
and off.
11
Page 12
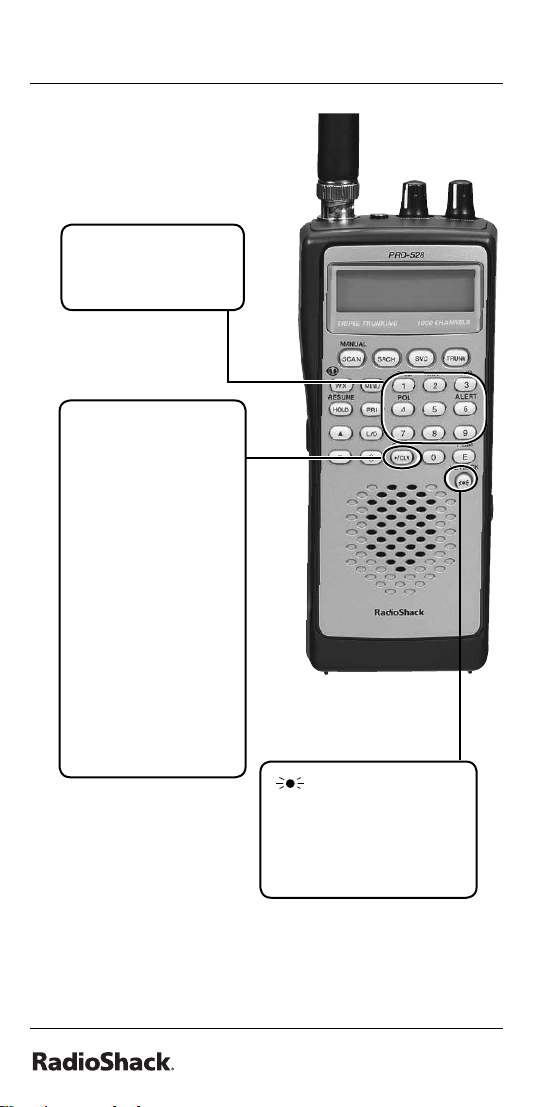
The Basics
0-9 — input
a number or
characters.
•/CLR/DELAY — enter
a decimal point,
space, or programs
delay time for the
selected channel/
search bank, or
enters a hyphen
(in trunking ID
setting). Press CLR
to clear an entry.
Programs a 2second delay for a
selected channel or
service; programs
a 2-second delay
while trunking.
/KEYLOCK — locks
the keypad to prevent
changes; turns the
display and key
backlight on and off.
12
Page 13

PC/IF — connect an
optional PC interface
cable here to use the
scanner with your
computer.
The Basics
POWER DC 9V —
connect an external
power source here
(not included).
VOLUME — turn
the scanner
on or off and
adjust the
volume.
SQUELCH — adjust the
squelch.
— connect
an earphone or
headphone here.
13
Page 14

The Basics
supplying power to your
scanner
You can power your scanner with batteries,
DC adapter, or an AC adapter.
Warning: Only set the ALKALINE e JACK
f NiMH switch to NiMH for use with
nickel metal hydride (NiMH) rechargeable
batteries. Never use non-rechargeable
batteries when the switch is set to NiMH.
1. Set the ALKALINE e JACK f NiMH
switch inside the battery compartment
to the appropriate setting.
• ALKALINE when using alkaline
batteries (not included).
Caution: You must use a Class 2 power
source that supplies 9V DC and delivers at
least 300mA. Its center tip must be set to
positive and its plug must fi t the scanner’s
DC 9V 300mA jack. Using an adapter that
does not meet these specifi cations could
damage the scanner or the adapter.
• NiMH when using rechargeable (NiMH)
AA batteries (not included). The
14
Page 15

The Basics
scanner stops charging automatically
after 14 hours when the DC jack is
connected to power.
battery cautions
• Use only fresh batteries of the required
size and recommended type.
• Always remove old or weak batteries.
Batteries can leak chemicals that
damage electronic circuits.
• Do not mix old and new batteries,
different types of batteries (standard,
alkaline, or rechargeable), or
rechargeable batteries of different
capacities.
• When the battery icon
and the scanner beeps every 15
seconds, replace all four batteries.
• Always dispose of old batteries
promptly and properly. Do not bury or
burn them.
Warning: Do not connect a charging
adapter to the scanner if non-rechargeable
batteries (such as alkaline batteries) are
installed in the scanner and ALKALINE e
JACK f NiMH is set to NiMH, or if you
are unsure of the switch’s position. Nonrechargeable batteries will get hot and can
even explode if you try to recharge them.
fl ashes
15
Page 16

The Basics
• Always connect the AC adapter to the
scanner before you connect it to AC
power. When you fi nish, disconnect
the adapter from AC power before you
disconnect it from the scanner.
connecting the antenna
Attach the supplied
antenna to the
scanner by align
the slots around its
base with the tabs
on the scanner,
then slide into
place.
When using an external antenna, always
use 50-ohm, RG-58, or RG-8, coaxial cable
to connect to it. If the antenna is over 50
feet from the scanner, use RG-8 low-loss
dielectric coaxial cable. If your antenna’s
cable does not have a BNC connector, your
local RadioShack store carries a variety of
BNC adapters.
connecting an earphone/
headphone
For private listening, you can plug
headphones (not included) into the
headphone jack on top of your scanner.
This automatically disconnects the internal
speaker. Note that the sound is “mono” and
not stereo.
16
Page 17

The Basics
listening safely
To protect your hearing, follow these
guidelines when you use an earphone or
headphones.
• Do not listen at extremely high volume
levels. Extended high-volume listening
can lead to permanent hearing loss.
• Set the volume to the lowest setting
before you begin listening. After you
begin listening, adjust the volume to a
comfortable level.
• Once you set the volume, do not
increase it. Over time, your ears adapt
to the volume level, so a volume level
that does not cause discomfort might
still damage your hearing.
If you use an earphone or headphones with
your scanner, be very careful. Do not listen
to a continuous broadcast. Even though
some earphones/headphones let you hear
some outside sounds when listening at
normal volume levels, they still can present
a traffi c hazard.
attaching the belt clip
Use a Phillips-head
screwdriver and the
supplied screws to
attach the clip to the
scanner.
17
Page 18

The Basics
transferring data to or from
another scanner or pc
You can transfer the programmed data to
and from another PRO-528 scanner using a
connecting cable which has 1/8-inch phone
plugs on both ends (not supplied). Connect
the cable between each scanner’s PC/IF
jacks. See “cloning your scanner”. You can
also upload or download the programmed
data to or from a PC using an optional
PC interface cable and software available
through your local RadioShack store. See
“wired programming.”
about your scanner
We use a few simple terms in this manual
to explain the features of the scanner.
Familiarize yourself with these terms and
the scanner’s features, and you can put the
scanner to work for you right away. Simply
determine the type of communications you
want to receive, then set the scanner to
scan those communications.
The scanner scans conventional
frequencies and trunked systems. For more
information about trunked transmissions
(see “trunking operation”).
A frequency, expressed in kHz or MHz,
is the tuning location of a station. To fi nd
active frequencies, you use the search
function.
18
Page 19
The Basics
Besides searching within a selected
frequency range, you can also search your
scanner’s service banks. Service banks are
preset groups of frequencies categorized
by the type of services that use those
frequencies. For example, many amateur
radio frequencies are located in the HAM
service bank.
When you search and fi nd a desired
frequency, you can store it into a
programmable memory location called
a channel. Channels are grouped into
channel-storage banks. The scanner has 10
channel-storage banks. Each bank contains
100-channel sets. So the scanner has
1,000 channels. You can scan the channelstorage banks to see if there is activity on
the frequencies stored there.
Note: You search frequencies
when you want to fi nd your local
Notes
frequencies and scan channels
after you programmed your found
frequencies.
understanding banks
service banks
The scanner is preprogrammed with all the
frequencies allocated to the ham, marine,
aircraft, and police (fi re/emergency)
services. This helps you quickly fi nd active
frequencies instead of doing a chain
search (see “service bank search”).
19
Page 20
The Basics
channel storage banks
To make it easier to identify and select
the channels you want to listen to, all the
channels are divided into 10 banks of 100
channels. Use each channel-storage bank
to group frequencies, such as those for
the police department, fi re department,
ambulance services, or aircraft.
For example, the police department might
use four frequencies in your town while
the fi re department uses an additional
four. You could program the four police
frequencies starting with Channel 1 (the
fi rst channel in bank 1), and program the
fi re department frequencies starting with
Channel 101 (the fi rst channel in bank 2).
turning on the scanner and
setting squelch
Note: Make sure the scanner’s
Notes
antenna is connected before you turn
it on.
1. Turn SQUELCH fully counterclockwise.
2. Turn VOLUME/OFF clockwise until it
clicks and you hear a hissing sound.
3. Turn SQUELCH clockwise until the
hissing stops.
20
Page 21
The Basics
storing known frequencies into
channels
You can locate and store specifi c
frequencies into channels for later use.
Note: To store trunked system
Notes
frequencies, see “programming
trunked frequencies.”
Follow these steps to store frequencies into
channels.
1. Press E/PGM to put the scanner in
programming mode. PGM appears.
2. Use the number keys to enter the
channel number you want to assign to
a frequency.
3. Press SCAN/MANUAL.
4. Use the number keys and •/CLR /
DELAY to enter the frequency, including
the decimal point you want to store.
5. Press E/PGM to store the frequency
into the channel.
Notes:
• If you entered an invalid frequency
in Step 4, Error appears and the
Notes
scanner beeps error tones.
Enter a valid frequency.
21
Page 22

Beyond the Basics
• If you entered a frequency in
Step 4, which already exists on
another channel, the scanner beeps
an error tone and displays that
channel. Press •/CLR /DELAY to
clear the display, or press E/PGM
to store the frequency in both
channels.
• The scanner automatically rounds
the entered number to the nearest
valid frequency. For example, if you
enter 151.473 (MHz), your scanner
accepts it as 151.475.
• After a transmission, the scanner
automatically pauses for 2 seconds
on this channel before proceeding
to the next active transmission.
Press •/CLR /DELAY to turn the
delay function off or on. See
“delay”). The scanner stores this
setting in the channel.
6. To program the next channel in
sequence, press S or T and repeat
Steps 4 and 5.
copying/moving a frequency
If you want to copy/move a frequency to a
channel, follow the steps below:
1. Manually select the channel which
contains the frequency you want to
copy or move.
22
Page 23

Beyond the Basics
2. Press E/PGM.
3. Press and hold E/PGM during program
mode. Scanner displays the copy/move
menu.
4. Press S or T to select the copy/move
function, then press E/PGM to decide
on copy or move.
5. Select the bank where you want to
copy or move the frequency. The
smallest empty channel number and
“000.0000” fl ashes on and off over the
frequency you want to store.
6. Press S or T to move to the channel
where you wish to store the frequency.
7. Press E/PGM to enter the frequency,
and return to the program mode. To
cancel the copy or move, press •/CLR
/DELAY. If there is no empty channel,
the scanner automatically selects the
fi rst channel of the bank.
searching for and temporarily
storing active frequencies
If you do not have a reference to
frequencies in your area, use a chain,
direct, or service search (except weather
search) to fi nd a transmission.
23
Page 24
Beyond the Basics
Notes:
• While doing a chain, direct, or
service bank search, press • /CLR /
DELAY if you want to turn the delay
on or off (see “delay”).
• While doing a chain, direct, or
Notes
service bank search, press MENU if
you want the scanner to skip data
signals (such as fax or modem
signals) and search only for audio
(voice) signals to enter the menu
mode and turn Data Skip Option to
off (see “skipping data signals”).
chain search
This feature lets you search through preset
frequency ranges. You can also preset a
range. There are three modes within this
feature: chain search mode, chain search
hold mode, and program band select
mode.
The preset frequency ranges are:
Bank No. Frequency
(MHz)
1 29.0000
– 49.9950
2 50.0000
– 54.0000
3 137.0000
– 147.9950
Step (kHz)
5
5
5
24
Page 25
Beyond the Basics
4 216.0000
– 224.9950
5 400.0000
– 419.99375
6 420.0000
– 449.99375
7 450.0000
– 469.99375
8 470.0000
– 512.0000
9 806.0000
– 956.0000
10 1240.0000
– 1300.0000
5
6.25
6.25
6.25
6.25
12.5
12.5
starting chain search
1. Press SRCH. SRCH appears.
2. Press 0 – 9 to enable or disable the
search bank number being searched.
Note: At least one bank needs to be
Notes
entered. If you disable all the banks,
the error tone beeps.
3. Press T to search down or S to search
up.
4. When the scanner stops on a
transmission, quickly press HOLD/
RESUME to stop searching to listen to
the transmission. HOLD appears.
25
Page 26

Beyond the Basics
5. To release the hold and continue
searching, press HOLD/RESUME.
Note: To step through the
Notes
frequencies while HOLD appears,
press T or S.
storing found frequencies
during chain search
You can store frequencies you fi nd in chain
search mode or chain search hold mode.
1. Press E/PGM when you fi nd a
frequency. The bank numbers fl ash.
2. Press the bank number you want to
store the frequency. The smallest empty
channel number and “000.0000” fl ashes
on and off over the frequency you want
to store.
3. Press S or T to move to the channel
where you wish to store the frequency.
4. Press E/PGM to enter the frequency.
programming search ranges
You can defi ne the search range during a
chain search in each search bank.
1. Press and hold E/PGM in chain search
or chain search hold mode. The lowest
and the highest frequencies of Bank 1
appear alternately.
26
Page 27

Beyond the Basics
2. Press the bank number you want to
change the range. The lower frequency
range appears.
3. Using the number keys, enter the lower
limit frequency, and then press E/PGM.
4. Press S or T to change the frequency
to an upper limit frequency.
5. Using the number keys, enter the upper
limit frequency, and then press E/PGM.
6. When you fi nish programming
frequency ranges, press SRCH.
direct search
You can search up or down from the
currently displayed frequency using direct
search. SRCH appears during searching.
Press and hold SRCH when the frequency
you want to start from appears. Or, enter
the frequency you want to start from using
the number keys in search hold mode, then
press S or T.
Note: If you enter an invalid
Notes
frequency, the scanner displays Error.
Press •/CLR /DELAY.
service bank search
You can search for ham, marine, aircraft,
or police (fi re/emergency) transmissions
without knowing the specifi c frequencies
used in your area. The scanner is
27
Page 28
Beyond the Basics
preprogrammed with all the frequencies
allocated to these services. To use this
feature, press SVC. The current service
symbol appears and the scanner starts
searching. To select a different service
bank, press 1/HAM, 2/MRN, 3/AIR or
4/POL.
The newly selected service symbol
appears. Press S or T to search.
Note: Because there are many
different frequencies allocated to
Notes
fi re and police departments, it can
take several minutes to search all the
service frequencies.
weather search
You can also search for weather
transmissions. To start weather search:
1. Press WX/
change the search direction by using S
or T.
2. If you want to stop the search, press
HOLD/RESUME. HOLD appears.
. WX appears. You can
search skip memory
You can skip up to 200 specifi ed
frequencies during a chain, direct and
service search and Signal Stalker I. This lets
you avoid unwanted frequencies or those
already stored in a channel.
28
Page 29

Beyond the Basics
Note: You cannot skip frequencies
during WX service search.
To skip a frequency, press L/O when the
scanner stops on the frequency during a
chain, direct and service search and Signal
Stalker I. The scanner stores the frequency
in memory and automatically resumes the
search.
To clear a single frequency from skip
memory so the scanner stops on it during a
chain, direct and service search and Signal
Stalker I:
1. Press HOLD/RESUME to stop the
search.
2. Press S or T to select the frequency.
L/O appears.
3. Press L/O. L/O disappears.
To clear all the skip frequencies at once
while searching, press HOLD/RESUME,
then hold down L/O until the scanner
beeps twice.
Notes:
• If you selected all frequencies to be
skipped within the search range,
Notes
the scanner beeps 3 times and
does not search.
• If you select more than 200
frequencies to skip, each new
frequency replaces a frequency
29
Page 30

Beyond the Basics
previously stored, beginning with
the fi rst stored frequency.
• Press S or T to select a skipped
frequency while HOLD appears.
L/O appears when you select a
skipped frequency.
scanning the stored channels
To begin scanning channels, press SCAN/
MANUAL. The scanner scans through
all non-locked channels in the activated
banks. (See “locking out channels”
and “turning channel-storage banks on
and off”). When the scanner fi nds a
transmission, it stops on it. When the
transmission ends, the scanner resumes
scanning.
Notes:
• If you have not stored frequencies
into any channels, the scanner
does not scan.
Notes
• If the scanner picks up
unwanted partial, or very weak
transmissions, turn SQUELCH
clockwise to decrease the
scanner’s sensitivity to these
signals.
30
Page 31

Beyond the Basics
• To listen to a weak or distant
station, turn SQUELCH
counterclockwise.
• To ensure proper scanning, adjust
SQUELCH until the audio mutes
• To scan in the trunk scanning
mode, see “trunking operation.”
manually selecting a channel
You can continuously monitor a single
channel without scanning. This is useful
if you hear an emergency broadcast on
a channel and do not want to miss any
details —even though there might be
periods of silence — or if you want to
monitor a specifi c channel.
Press SCAN/MANUAL to stop scanning,
enter the channel number, and then press
SCAN/MANUAL. The selected channel
appears.
Or, during scanning, if the radio stops at a
channel you want to listen to, press HOLD/
RESUME. Press HOLD/RESUME to resume
automatic scanning.
31
Page 32

Beyond the Basics
special features
delay
Sometimes a user might pause before
replying to a transmission. To avoid
missing a reply on a specifi c channel, the
scanner automatically programs a 2-second
delay into any channel or frequency. You
can monitor the channel frequency for an
additional 2 seconds after the transmission
stops before resuming scanning or
searching.
Depending on the scanner operation,
follow one of these steps to turn off or on a
delay.
• To turn off the 2-second delay, press
•/CLR /DELAY while the scanner is
monitoring a channel, scanning, or
searching. DLY disappears.
• To turn on the 2-second delay to a
channel again, select the channel and
press •/CLR /DELAY. DLYappears.
• To turn on the 2-second delay to search
again, press •/CLR /DELAY while the
scanner is searching.
DLY appears and the scanner automatically
adds a 2-second delay to every frequency it
stops on in that band.
Signal Stalker I also has a delay feature. It’s
delay time is 10 seconds.
32
Page 33

Beyond the Basics
turning channel-storage banks
on and off
You can turn each channel-storage bank
on and off. When you turn off a bank, the
scanner does not scan any of the 100
channels in that bank.
While scanning, press the number key
that corresponds to the bank you want
to turn on or off. Numbers appear at the
top of the display, showing the currently
selected banks. The scanner scans all
the channels within the displayed banks
that are not locked out (see “locking out
channels”). The bank number fl ashes when
the scanner scans a channel that belongs
to the bank.
Notes:
• You can manually select any
channel within a bank, even if that
Notes
bank is turned off.
• One bank must always be active. If
you try to turn off all banks, bank 1
remains.
locking out channels
You can increase the scanning speed
by locking out channels that have a
continuous transmission, such as a
weather channel. To lock out a channel,
33
Page 34

Beyond the Basics
manually select the channel, then press
L/O. L/O appears.
Note: You can still manually select
Notes
locked-out channels.
To remove the lockout from a channel,
manually select the channel, then press
L/O. L/O disappears.
To unlock all channels in the banks that are
turned on, press HOLD/RESUME to stop
scanning, then hold down L/O until the
scanner beeps twice.
priority
The priority feature lets you scan through
the channels and still not miss important or
interesting calls on specifi c channels. You
can program one stored channel in each
bank as a priority channel. If the priority
feature is turned on, as the scanner scans
the bank, it checks that bank’s priority
channel for activity every 2 seconds.
The scanner automatically designates each
bank’s fi rst channel as its priority channel.
Follow these steps to select a different
channel in a bank as the priority channel.
1. Press E/PGM.
2. Enter the channel number you want
to select as the priority channel, then
press PRI.
selected channel number.
P appears to the right of the
34
Page 35

Beyond the Basics
3. Repeat Steps 1 and 2 for the channel
in each bank you want to program as a
priority channel.
To review all priority channels (in
ascending order only), repeatedly press
PRI to see the numbers of the priority
channels.
To turn on the priority feature, press PRI
during scanning. PRI appears.
Then the scanner checks the designated
priority channel every 2 seconds in each
bank. The bank number appears at the top
of the display.
To turn off the priority feature, press PRI.
PRI disappears.
Note: If you have locked out all
priority channels, “CH Loc Out”
appears when you activate the
Notes
priority feature. To unlock any
desired priority channels, see
“locking out channels.”
using the keylock
To protect the scanner from accidental
program changes, turn on the keylock
feature. When the scanner is locked, the
only controls that operate are SCAN/
MANUAL, HOLD/RESUME and /
KEYLOCK.
To turn on the keylock, hold down
/KEYLOCK until appears.
35
Page 36

Beyond the Basics
To turn it off, hold down /KEYLOCK
until disappears.
Note: Using keylock does not prevent
Notes
the scanner from scanning channels.
wired programming
You can transfer programming data to your
scanner using your PC and an optional
interface cable (available at your local
RadioShack store) and software (available
at your local RadioShack or
www.radioshack.com).
Note: If the scanner receives no
data from the PC for more than 20
Notes
seconds, T-Err appears and wired
programming stops.
1. Make sure your scanner is turned off.
2. Connect the interface cable to your
computer and then connect the other
end of the cable to PC/IF on the side of
the scanner.
3. Install the software to your computer
and run the program.
4. To set up the program, click on Tools,
select Confi guration, and select PRO-
528 (if necessary).
5. Turn the scanner on. The scanner
automatically goes into the wired
programming mode. PGM and WirEd
36
Page 37

Beyond the Basics
appear. Then send the data from the
PC. Data frame numbers being received
appear.
6. When the scanner has successfully
received all data, End appears. If
the scanner received an error while
receiving data, End, d-Err, and its frame
number appear. If the scanner received
a communication error while receiving
data, C-Err indicates the packet
number where the error occurred. If
the scanner received a checksum error
while receiving data, S-Err indicates
the packet number where the error
occurred. If the scanner received a
length fi eld error while receiving data,
L-Err indicates the packet number
where the error occurred.
cloning your scanner
You can clone all the frequencies, trunking
talk groups, and fl eet maps programmed in
your PRO-528 to another PRO-528 or PRO433 using an optional interface cable and
software.
1. Make sure the scanners are turned
off and then plug the cable into each
scanner’s PC/IF jack.
2. While you press and hold E/PGM on
both scanners, turn on both scanners.
37
Page 38

Beyond the Basics
3. Determine the scanner which has
the frequency data that you want to
transfer and set it to be the FirSt unit.
4. Set the other unit to be the CLONE unit.
5. Press E/PGM on the First Unit and
then CLONE unit. The First Unit checks
whether the CLONE unit is connected
correctly. When a First Unit receives the
response from the CLONE unit, the data
transfer starts. During data transfer,
SND and REC fl ash.
6. When the data transfer is completed,
done appears. If the data transfer is not
successful, Error appears.
7. After the clone operation is complete,
remove the cable, turn both unit off and
then on again.
using the display backlight
To turn on the display light for easy viewing
at night, press .The display lights for 15
seconds. To turn off the light sooner, press
again.
using the auto backlight
display
You can set the scanner so the auto
backlight turns on for about 5 seconds
when the scanner receives signals.
38
Page 39

Beyond the Basics
If you press a key (except ) within 5
seconds, the display remains lighted for
more than 15 seconds.
To turn auto backlight display on or off:
1. Press MENU.
2. Repeatedly press S or T to select
AutoLit, then press E/PGM.
3. Repeatedly press S or T to select ON
or OFF, then press E/PGM.
4. Press MENU to exit the menu mode.
search speeds
Note: Hypersearch applies only to the
Notes
5 kHz step bands (29–54 MHz, 137–
174 MHz, and 216–224.9950 MHz).
The scanner has two search speeds.
Normal Search (90 steps/second )
Hypersearch (270 steps/second)
turning the keytone off/on
Each time you press any of the scanner’s
keys, the scanner sounds a tone. To turn
the scanner’s key tone off or on:
1. Press MENU.
2. Repeatedly press S or T to display
bEEP, then press E/PGM.
3. Repeatedly press S or T to select OFF
or ON, then press E/PGM.
39
Page 40

Beyond the Basics
4. Press MENU to exit the menu mode.
turning the battery save
function off/on
When the scanner is set to receive
(monitor) a manually selected channel, and
it is not actively scanning, using the battery
save feature conserves energy.
To turn the battery save function off or
back on:
1. Press MENU.
2. Repeatedly press S or T to display b-
SAVE, then press E/PGM.
3. Repeatedly press S or T to select OFF
or ON, then press E/PGM.
4. Press MENU to exit the menu mode.
When the battery save feature is active,
the scanner repeatedly turns off the
internal power for 1 second, then turns
it back on for about 1/2 second to
check for a transmission.
skipping data signals
To prevent the scanner from stopping on
channels that consist of nonmodulated
or data signals (such as fax or modem
transmissions) during a search or scan,
turn on the data skip feature. When the
radio receives a data signal and data skip is
selected, the signal is ignored.
40
Page 41

Beyond the Basics
To turn on the data skip feature;
1. Turn off the priority feature if it is on
(see “priority”).
2. Press MENU.
3. Repeatedly press S or T to display
dAtA-S, then press E/PGM.
4. Repeatedly press S or T to select OFF
or ON, then press E/PGM.
5. Press MENU to exit the menu mode.
Note: This feature does not apply
to the air band and weather search
Notes
mode as data signals are not
generally found in these services.
receiving nwr-same and
weather alert signals
In 1994, the National Oceanic and
Aerospace Administration (NOAA) began
broadcasting alerts that include digitally
encoded data. Specifi c Area Message
Encoding (SAME) includes information
which identifi es the severity of the alert.
While this scanner does not encode
specifi c geographical data, it does detect
SAME signals and decode the alert level.
The scanner displays this data as codes
corresponding to the levels of severity (L1,
L2, and L3).
41
Page 42

Beyond the Basics
turning on the digital weather alert
feature
1. Press WX/ and start weather search.
See “weather search.”
2. Press 6/ALERT. ALERT appears. This
mutes the audio until the scanner
receives a SAME-coded signal. When
the scanner receives a SAME-coded
signal, ALERT fl ashes and an associated
“L” code (which indicates the severity
of the alert) and SAME-coded signal
appears alternately. The scanner
remains on the weather channel and
the audio turns on so you can hear the
weather broadcast.
The scanner displays one of the following
codes to indicate the alert level .
L1: Warning
L2: Watch
L3: Advisory
WXA: Weather Alert (1050 Hz)
testing digital weather alert
tone
To hear and test the tones for the three alert
levels, press WX/ to select the weather
service, then hold down ALERT for about 1
second. The tones sound in the order L3,
42
Page 43

Beyond the Basics
L2, then L1, and TEST fl ashes. Each alert
code appears as its tone sounds. Press any
key to end the test sequence.
programming a FIPS code
To specify a county, SAME uses a standard
established by the US Census bureau,
called FIPS.
The format of a FIPS code is:
PSSCCC, where...
P = area subdivision (0=entire area)
SS = State code (00=all states)
CCC = County code (000=all counties)
For example, the FIPS code for Tarrant
County, Texas is:
048439 (48=Texas; 439=Tarrant County).
Some counties are further subdivided,
in which cases, the fi rst digit will be 0 for
all subdivisions in the county and each
subdivision will be labeled 1-9.
To program your scanner to alert you when
the weather service issues an alert, you
must set the scanner to the alert mode,
and then leave the scanner monitoring the
weather service. You cannot scan weahter
channels and monitor for weather alerts at
the same time.
43
Page 44

Beyond the Basics
To limit weather alerts to a specifi c area,
you must also program in the FIPS code(s)
for the area(s) you want to receive alerts.
The scanner can be set to either alert
for all areas, or only the areas you have
programmed.
programming FIPS
1. During weather scan hold mode, press
E/PGM. The scanner sends itself into
FIPS programming mode. If the scanner
is set to alert for all FIPS, ALLFIPS
appears on the display. If the scanner
is set to alert only the area you have
programmed, F1 appears.
2. Press S or T to change the displayed
FIPS code from F1 to F15. If a FIPS code
is not programmed, ------- appears.
3. Use the keypad to enter the FIPS code.
Press •/CLR /DELAY to cancel an
inputted FIPS code.
4. Press E/PGM to store the FIPS code.
Press 0 then E/PGM to clear a FIPS
code. ------ appears. If an invalid value
has been inputted, the FIPS code is
cleared.
5. To set the scanner so it alerts you when
you receive any FIPS code, press S or
T to move ALLFIPS. Then press E/
PGM. Then go to WX hold mode.
44
Page 45

Beyond the Basics
6. To set to alert only for the area you
have programmed, press S or T to
move F1 to F15, then press E/PGM.
Then go to WX hold.
Skywarn
The Skywarn function lets you jump
directly to the last channel in memory
(Channel 1000) from any mode by press
and holding WX/ . The scanner goes
into scan hold mode and starts receiving
transmissions in the last channel. Before
using this feature, enter the local Skywarn
frequency for your area into Channel 1000.
If no frequency is programmed in the last
channel, No Prog appears and the scanner
sounds an error tone.
about Skywarn
Skywarn is an organized group of trained
weather observers. A Skywarn group
exists in virtually every US county with a
signifi cant population. During inclement
weather, reports made by Skywarn
observers include information about:
• Pea-sized and larger hail
• Wind and wind gusts of 40 MPH and
greater
• Heavy rainfall
45
Page 46

Beyond the Basics
• Lightning (cloud-to-cloud and
especially cloud-to-ground)
• Wall clouds seen in severe
thunderstorms (which spawn
tornadoes)
• Severe lowering of a wall cloud
• Turbulence in a wall cloud
• Funnel clouds
• Tornadoes
• High water areas
• Downed power lines
• Other emergency conditions that affect
life or property
Listen to NOAA for weather alerts and
warnings, watch box notices, and weatherforecasts. Listen to Skywarn to hear trained
observers in your vicinity call in offi cial
reports to a net control station which
relays those reports to NOAA and other
emergency agencies.
Note: If you tune to a Skywarn
frequency when the Skywarn net is
not active, you may hear nothing,
Notes
or you may hear amateur radio
operators talking on a local repeater
system.
46
Page 47

Beyond the Basics
Signal Stalker I
Your scanner’ s Signal Stalker I feature
lets you set the scanner so it detects and
then displays the frequency of a nearby
strong radio transmission. You can set the
scanner so Signal Stalker I works “in the
background” while you are scanning other
frequencies; turn off normal scanning while
Signal Stalker I works; or turn off Signal
Stalker I and use the scanner normally. You
can set the scanner so it alerts you when
Signal Stalker I fi nds a frequency. You can
also set the frequency band where you
want the scanner to look for transmissions.
You can also turn on the pager screening
feature so the scanner ignores common
pager frequencies.
Note: Signal Stalker I works well for
locating the source of strong local
transmissions, such as mobile and
handheld two way radios in areas
with no other strong transmission
sources. You can screen unwanted
transmissions by pressing L/O to
Notes
lock them out. See “search skip
memory” for more information. It
might not correctly display frequency
information for transmitters using a
highly directive antenna (such as an
amateur radio beam antenna), if there
are many transmitters operating
at the same time in the same area,
47
Page 48

Beyond the Basics
or if the transmitter is a broadcast
television station.
setting the Signal Stalker I options
1. Press MENU.
2. Repeatedly press S or T to select
SIG-St., then press E/PGM. One of
the following Signal Stalker I options
appears:
• S-S.bnd: Lets you select the Signal
Stalker I band.
• S-S.ALt: Lets you select the Signal
Stalker I alert settings.
• S-S.Lit: Lets you select the Signal
Stalker I back light settings.
• S-S.PS: Lets you select the pager
screen settings.
• S-S.OnlY: Lets you select the Signal
Stalker I mode settings.
• S-S.Int: Lets you select the Signal
Stalker I voice interrupt settings.
While the Signal Stalker I is on and the
scanner is receiving an audio signal
(voice) in normal scanning, the scanner
checks the Signal Stalker I every 2
seconds and the audio signal breaks
at that moment. If you do not want the
48
Page 49

Beyond the Basics
break, set this function to OFF. The
scanner does not check signals while
receiving an audio signal. The scanner
resumes checking signals when the
audio signal ends. If you want to keep
the Signal Stalker I active despite the
interruption, set this function to ON.
• S-S.LOG: Lets you select the Signal
Stalker I logging setting.
When the scanner fi nds a strong
signal, it automatically saves the
signal to one of 10 log channels. If the
scanner fi nds a new frequency after
the 10 log channels are fully stored
with frequencies, the oldest memory
is deleted and the new frequency is
stored in that channel. You can scan
the log channels along with the normal
1000 channels.
• The 10 log channels are located after
Channel 1000 and you can manually
access them by selecting channals
as Channel 1001, Channel 1002, ...
Channel 1010. “-1-”, “-2-”, ... “-10-”
appear as channel numbers.
You cannot program frequencies in the
log channels.
You can lock out the log channels like
normal channels.
49
Page 50

Beyond the Basics
Set S-S.LOG to ON to scan the log
channels along with the normal
channels. If you do not want to scan
the channels, set it to OFF.
The scanner stores signals found by
the Signal Stalker I even the S-S.LOG
function is OFF.
The frequencies in the log channels
are deleted when the scanner is
turned off.
3. Repeatedly press S or T to select the
option you want, then press E/PGM.
• S-S.bnd: If you selected S-S.bnd, one
of the following band names appears:
29-54 : VHF Low Band
108-137: AIR Band
137-225: VHF High Band
400-512: UHF Band
806-956: 800MHz Band
Repeatedly press S or T to select
the band you want to set, then press
E/PGM.
4. Repeatedly press S or T to select ON
or OFF, then press E/PGM.
50
Page 51

Beyond the Basics
5. When you select the option, press •/
CLR /DELAY to exit the option mode.
6. Press MENU to exit the menu mode.
using Signal Stalker I
Note: Turn off the data skip feature if
Notes
it is on.
To turn on Signal Stalker I, turn SQUELCH
fully clockwise, then press
in WX search, program search range,
or program mode. appears. Every
2 seconds, the scanner searches for
frequencies in the range you specifi ed in
“Setting the Signal Stalker I Options.”
When the scanner fi nds a frequency, it
sounds the alert you specifi ed in “Setting
the Signal Stalker I Options”, and Found
fl ashes. Press any key to confi rm the
displayed frequency. Press HOLD/RESUME
to resume scanning.
except
To turn on Signal Stalker I and turn off
normal scanning, turn S-S.OnlY of Signal
Stalker I options to on.
“setting the Signal Stalker I options.”
To turn off Signal Stalker I and turn on
normal scanning, press
disappears.
fl ashes. See
and
trunking operation
The scanner tracks transmissions that use
the Motorola Type I, Type II, hybrid, and
EDACS and LTR analog trunking systems.
51
Page 52

Beyond the Basics
setting the scanner to the
trunking mode
simultaneous trunking
The scanner allows you to track up to 10
systems at a time. You can trunk scan or
search and scan conventional frequencies
at the same time. You can also program
conventional frequencies in the same bank
as trunking systems.
After the scanner is fi nished checking
activity in the trunked system, it scans
other conventional frequencies in the
bank. (Only trunking frequencies are
programmed in trunk mode.)
If a system is inactive for 1 second and
there are no conventional channels in the
bank, the scanner starts scanning the next
selected trunk bank. If you turned DELAY
on, the scanner starts scanning the next
trunk bank after about 2 seconds.
To scan both trunking and conventional
banks, select the banks you wish to be
active with trunking off, then press TRUNK.
The scanner begins scanning. To return
to conventional scanning, press TRUNK
again.
setting squelch for the trunking mode
For trunked reception, a good squelch
setting is in the center of the range with
the white marker pointing to the rear of
52
Page 53

Beyond the Basics
the scanner. If it is set too high, it could
prevent your scanner from locking on the
control channel reliably. If it is set too low,
it will slightly delay fi nding the control
channel. The best setting is the same as
for conventional reception and is critical
for monitoring trunked systems.
programming trunked
frequencies
Follow these steps to select, program, and
store trunked frequencies.
1. Press E/PGM in conventional mode to
set the scanner in programming mode.
Then, press TRUNK. Your scanner
beeps a tone. Then TRUNK and all of
the bank numbers fl ash.
2. Press the number key (1-9 and 0) of
the desired target storage bank. Select
one of the trunk systems by repeatedly
pressing S or T to select a trunking
system type, then press E/PGM.
Note: You can select from the
following six systems:
Notes
You See Trunk
System
E2 – 800 Motorola
Type II,
800 MHz
frequencies
53
Page 54

Beyond the Basics
E2 – 900 Motorola
E2 – Hi Motorola
E2 – UHF Motorola
E1 Motorola
Ed EDACS Wide
Ed – SCt EDACS Scat
Lt LTR
Type II,
900 MHz
frequencies
Type II,
VHF(136174 MHz)
frequencies
Type II,
UHF (400512 MHz)
frequencies
Type I, and
Hybrid
Band: 9600
baund
3. Prog F appears, then press E/PGM. The
scanner automatically selects the fi rst
channel in the selected bank.
4. Use the number keys to enter a valid
frequency within the trunk system,
then press E/PGM. The bank number,
the channel number, and E (EDACS),
M (Motorola), or L (LTR) appears
54
Page 55

Beyond the Basics
depending upon the trunk system
selected.
Notes:
• If you enter an invalid frequency
(outside the selected range),
the scanner beeps, the channel
number fl ashes and Error appears.
If this happens, press •/CLR /
DELAY to clear the frequency, then
repeat the entry.
Notes
• For EDACS (Ed) and LTR systems,
you must enter the frequencies
in logical channel number (LCN)
order.
• If you try to enter a duplicate
frequency in a bank, the scanner
beeps and the channel which was
previously stored appears
5. Press S or T to select the next
channel in the bank and repeat Step 4
to enter frequencies in that bank.
6. Repeatedly press •/CLR /DELAY to
return back to Step 2. Repeat Steps 2
and 5 until all frequencies have been
entered.
7. Press SRCH to begin searching for
the trunk’s data channel and scan
conventional frequencies at the same
55
Page 56

Beyond the Basics
time. As the scanner looks through
the frequencies, you see them on the
display. When the scanner fi nds the
controlling data channel, the scanner
begins trunking.
searching a trunked bank
Once the data channel is acquired, the
scanner begins a trunk search.
With the search function, you will be able
to fi nd all the active talk groups within the
trunked system.
Press SCAN/MANUAL. You can switch to
the trunk scan mode from the trunk search
mode. See “scanning the talk group ID
lists”.
While scanning conventional frequencies,
follow the steps below to switch to the
trunk mode after the scanner fi nds the data
channel.
1. Press TRUNK. The scanner begins
scanning both trunking and
conventional banks.
2. Hold down TRUNK for about 1 second.
The scanner switches to the trunk scan
mode.
3. Hold down TRUNK for about 1 second
again. The scanner switches to the
trunk search mode.
56
Page 57

Beyond the Basics
Hint: While searching, you may not
know exactly to whom the talk group
IDs are assigned until you listen
awhile. To locate talk group ID lists
for your local police, fi re, and other
agencies, refer to frequency guides
available at your local RadioShack
store or on internet sites such as
www.trunkscanner.com. You can also
determine the type of agency you are
listening to after a short while, be it
a police, fi re, or emergency medical
2-way radio user. Once you have
identifi ed the type of service, note
the associated talk group ID of that
unit for future programming. See
“identifying a trunked frequency”.
Determining the service associated
with a talk group ID might take
awhile, but discovering the ID owner
of each signal is half the fun of trunk
scanning!
turning a trunked bank on or
off
1. Press and hold SCAN/MANUAL during
trunk scanning. The selected trunked
banks appear.
2. Press the bank number (0–9), to turn
the desired bank on or off.
57
Page 58

Beyond the Basics
skipping a trunked bank
You can scan conventional frequencies
programmed in the same bank by holding
down S for about 1 second. If there is no
conventional frequency, the scanner scans
the next bank.
turning the status bit ignore
(s-bit) on or off
You can set how your scanner works
with status bits (also called S-Bits), letting
you control how the scanner interprets
and displays talk group IDs. The last four
bits of a Motorola Type II talk group ID (a
binary 16-bit code) are the status bits. In
some systems, status bits identify special
situations (such as an emergency status).
Your scanner is preset to assume that the
status bits in a talk group ID are set to 0
and ignores them. For example, when
the scanner receives the talk group ID
010111001110 0011, it reads the ID as
010111001110 0000 and converts the fi rst
12 bits of the ID to 23776 (the talk group
ID). However, since the status bit value is 3
(0011 converted to decimal equals 3), the
ID is actually 23779.
If you are scanning a Motorola Type I
system and do not have a fl eet map for that
system, you might have to turn off status
bit ignore in order to determine the proper
fl eet map.
58
Page 59

Beyond the Basics
Important: If you are scanning any
system other than a Motorola Type
I system, be sure status bit ignore
is set to ON or you will miss some
transmissions.
Follow these steps to turn status bit ignore
on or off.
1. Set the scanner to conventional
programming mode and then press
TRUNK.
2. Select the bank.
3. Repeatedly press S or T to select
Motorola Type, then press E/PGM.
4. Repeatedly press S or T to select S-
bit, then press E/PGM.
5. Repeatedly press S or T to select ON
or OFF, then press E/PGM.
identifying a trunked frequency
While ID scanning (looking for IDs within
a trunked system) or performing an ID
search, press T to see the current trunked
frequency. (The frequency fl ashes twice.)
Then hold down T until a confi rmation
tone sounds and the ID and the frequency
alternately appear.
To return to normal operation, press T.
59
Page 60

Beyond the Basics
selecting the EDACS (Ed) talk
group ID format
Your scanner can also enter or display
EDACS (Ed) talk groups in decimal format
(0-2047).
1. Select the trunking programming mode
and the bank you want to change.
2. Press S or T to select EDACS (Ed),
then press E/PGM.
3. Press S or T to select AFS, then press
E/PGM.
4. Press S or T to select AFS ON or AFS
OFF, then press E/PGM. You can use
this feature to translate decimal talk
group lists to the much more powerful
AFS format. It is very easy to use. Be
sure to become familiar with AFS partial
entry, and your scanning will become
far more fl exible and effi cient.
EDACS (Ed) talk group ID range
search
When your scanner searches EDACS (Ed)
talk group IDs, the scanner can search
within a range you set for agency or fl eet
listings. For example, if you want to search
within the 01 agency, while in hold mode
press 0, 1, •/CLR /DELAY then SRCH. Or
if you want to search within the 01 agency
and 01 fl eet, while trunking press 0, 1, •/
60
Page 61

Beyond the Basics
CLR /DELAY, 0, 1, then SRCH.
To stop the ID range search, press S while
the talk group is deactivated.
using HOLD to monitor an
active talk group ID
Follow these steps to stop scanning and
searching and keep the scanner tuned to a
desired ID.
1. Press HOLD/RESUME. HOLD appears
and the scanner stays on the current ID.
2. If you want to listen to (and hold) a
different ID, use the number keys to
enter that ID.
3. Press T. HOLD fl ashes, then the
scanner monitors the ID.
4. Press HOLD/RESUME to resume
scanning or searching for a data
channel.
locking out talk group IDs
Many municipal and commercial services
use trunk systems to transmit signals from
such devices as water meter transmitters,
door alarms, and traffi c signals. Some
signals are encrypted, as well, and most
are not voice signals. Since all these are
assigned IDs just like other users, you
may want to lock out reception of these ID
61
Page 62

Beyond the Basics
signals. You can lock out up to 100 IDs at
one time.
Note: If you lock out an ID while
searching, it is also locked out of the
Notes
scan list(s). See “using talk group ID
lists.”
To lock out an ID, press L/O when the ID
appears. The ID is locked out, and the next
active ID appears.
unlocking a single talk group ID
You can check all IDs already locked out.
1. Select the trunking programming mode
and the bank you want to review.
2. When the selected trunked system is
displayed, press E/PGM.
3. Use S or T to choose Id Lout, and
press E/PGM.
4. Press L/O, the ID is unlocked and the
next locked ID displays.
5. If you unlocked all locked IDs, the
scanner displays Non.
unlocking all talk group IDs
Hold down L/O while searching until you
hear two short beeps. You can check all
locked out IDs. Hold down L/O while
you are reviewing all locked out IDs. The
scanner beeps twice. All locked out IDs in a
62
Page 63

Beyond the Basics
bank are unlocked. Press SRCH to resume
the search.
using trunk scanning Scan
Delay
Sometimes a user might pause before
replying to a transmission. You can set the
scanner to hold on an ID for 2 seconds
to wait for a reply. That way, the scanner
continues to monitor the ID for 2 seconds
after the transmission stops before
resuming scanning.
Press •/CLR /DELAY to turn trunk
scanning scan delay on or off. DLY
appears when the scan delay is set to on.
Note: If you consistently miss
responses even with scan delay
turned on, change the default
Notes
system type or the fl eet map being
used. See “scanning type I and
hybrid trunked systems”.
monitoring talk group IDs
You can use your scanner’s display to
monitor the frequencies/talk group IDs of
a trunked system for activity, to determine
which talk group IDs are the most active.
To set the scanner to monitor IDs, hold
down SRCH until you hear two short
beeps, and SRCH fl ashes. All active group
63
Page 64

Beyond the Basics
IDs appear in quick succession. To stop
monitoring IDs, press S.
Note: When you monitor IDs, any
Notes
IDs you have locked out also appear.
using talk group ID lists
When you program trunked frequencies
into a bank (see “programming trunked
frequencies”), your scanner sets up ten
scan lists for that one bank in which you
can store your favorite IDs. Each list can
contain up to 10 IDs, for a total of 100 IDs
for each trunk scanning bank. If you use
all the banks as trunking banks, you can
store 1000 IDs.
Talk group ID lists help you organize
trunking system users into categories.
For example, you might use List 1 for
police IDs, List 2 for fi re department IDs,
List 3 for emergency medical service IDs,
and so on. Once you store all the IDs in a
list, you can scan them just as you scan
conventional channels. You can program
IDs into talk group ID lists manually,
during a search, or automatically.
manually storing talk group
IDs in talk group ID lists
1. Select the trunking programming
mode and the bank you want to
change.
64
Page 65

Beyond the Basics
2. Use S or T to choose trunk system,
then press E/PGM.
3. Use S or T and choose Prog id, then
press E/PGM.
4. Press S or T to select the scan list
location.
5. Enter the talk group IDs for each trunk
system.
Motorola talk groups
To enter a Type 2 Talk Group ID:
1. Enter the ID you want to store by using
the keypad.
2. Press E/PGM.
To enter a Type 1 ID:
For a Type I ID, enter the block number,
fl eet number and subfl eet number to form
the talk group ID number.
1. Enter the ID you want to store by using
the keypad (ID = Block number + Fleet
number + •/CLR/DELAY + Subfl eet
number).
2. Press E/PGM.
65
Page 66

Beyond the Basics
EDACS (Ed) talk groups
To enter a full EDACS ID:
1. Enter the Agency number.
2. Press •/CLR/DELAY to enter the dash.
3. Enter the fl eet number and subfl eet
number.
4. Press E/PGM.
entering EDACS partial talk
groups
You can enter partial group numbers in an
EDACS talk group. By entering only the
desired portion of a group, you can select
either 128, 8, or 1 talk group. For example,
you might program every talk group in a
police department by pressing just four
keys.
Note: You cannot use partial talk
groups in decimal mode. (See
Notes
“selecting the EDACS talk group ID
format”).
You can program a specifi c talk group
such as 01-011 into the scan list memory.
In AFS mode, you can program the talk
groups for an entire agency by pressing
corresponding keys.
66
Page 67

Beyond the Basics
For example:
You Press To Scan
01 . E all 01 groups
01 . 01 E all 01 talk groups
within the 01
agency
To enter a Partial EDACS ID:
1. Enter the agency number you want to
store. Press •/CLR /DELAY to enter
the dash.
2. Press E/PGM. Or you can program all
the talk group numbers for one fl eet of
an agency.
3. Enter the agency number.
4. Press •/CLR /DELAY to enter the
dash.
5. Enter the fl eet number.
6. Press E/PGM. Remember the AFS
format allows you to enter full or
partial EDACS IDs for powerful
fl exibility in all modes. The scanner
defaults to AFS talk group displays for
EDACS only.
LTR talk groups
Users on an LTR system are assigned to
specifi c talk groups, which are identifi ed
67
Page 68

Beyond the Basics
by the radio as a six-digit number. The
number is in the form AHHUUU, where:
A = Area code (0 to 1)
H = Home repeater (01 through 20)
U = User ID (000 through 254)
To enter an LTR ID:
1. Enter the area code.
2. Enter the home repeater number.
3. Enter the ID you want to store.
4. Press E/PGM.
Note: To clear a stored ID while
Notes
entering an ID, press 0 and E/PGM
successively, then start over.
scanning the talk group ID lists
Press SCAN/MANUAL to begin scanning
the lists you have stored.
Note: If one or more of the IDs you
stored are incorrect, Error fl ashes
Notes
twice and the scanner beeps several
times, then the scan list numbers
appear at the top of the display. To
correct the entry, delete at least one
of the incorrect IDs.
To remove a scan list from active scanning,
use the number keys to enter the scan list’s
68
Page 69

Beyond the Basics
number. The scan list number turns off,
and the IDs in that list are not scanned.
Note: One of the ten scan lists must
Notes
always be active. You cannot remove
all of them.
To restore a scan list to active scanning,
use the number keys to enter the number
of the list again.
priority talk group ID scanning
You can assign a priority to a favorite ID so
during scanning the scanner checks that ID
more frequently than the others in the list.
Each of the ten memory locations reserved
for storing lists (see “using talk group ID
lists”) can have only one priority ID, and the
ID assigned that priority in List 1 has the
highest priority of all.
To assign a priority to an ID, press and hold
PRI. P appears.
To turn priority ID scanning on or off,
repeatedly press PRI during ID scanning or
manual operation.
PRI appears when priority scanning is
turned on.
Note: Priority ID scanning does not
Notes
operate when priority IDs are locked
out. See “locking out talk group IDs”.
69
Page 70

Beyond the Basics
scanning type I and hybrid
trunked systems
Your scanner is preset to scan Type II
system IDs. When you scan trunked
frequencies, each Type II user ID you see
appears as an even number without a dash
(example 2160). Your scanner can also
scan Type I trunked systems. Each Type I ID
appears as a three- or four-digit number,
followed by a hyphen, followed by a oneor two-digit number (example 200-14).
If you notice a mix of odd- and even-user
IDs (examples 6477, 2160, 6481, 6144, and
1167), then you are probably monitoring
either a Type I or hybrid (a combination of
Type I and Type II user IDs) system with the
S-Bit function turned off (see “turning the
status bit ignore (S-Bit) on or off”).
Subfl eet information is included with the
frequency list for a Type I system. To enter
the provided map, see “programming a
fl eet map”.
Note: To locate suitable fl eet map
Notes
information, review the contents of
website www.trunkscanner.com.
If you do not already know the size codes
used, you will have to guess. Since you do
not have to fi gure out all the blocks at one
time, this is not as hard as it might seem.
70
Page 71

Beyond the Basics
Select a size code for a block, then press
SRCH and listen to the conversations. If
you are receiving most of the replies, then
you have probably selected the right size
code and can program the next block of
the map. There are 16 preset fl eet maps
to choose from, and it is best to start with
these when setting up a Type I or hybrid
trunk scanning bank.
If none of the following preset fl eet
maps allow you to follow complete
conversations, then you probably need
to program your own fl eet map (see
“Programming a Fleet Map”).
preset fl eet maps table
E1P1
Block
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
Size
Code
S11
S11
S11
S11
S11
S11
S11
S11
E1P2
Block
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
Size
Code
S4
S4
S4
S4
S4
S4
S4
S4
71
E1P3
Bock
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
Size
Code
S4
S4
S4
S4
S4
S4
(S12)
(S12)
Page 72

Beyond the Basics
E1P4
Block
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
E1P7
Block
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
Size
Code
S12
(S12)
S4
S4
S4
S4
S4
S4
Size
Code
S10
S10
S11
S4
S4
S4
S4
S4
E1P5
Block
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
E1P8
Block
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
Size
Code
S4
S4
S12
(S12)
S4
S4
S4
S4
Size
Code
S1
S1
S2
S2
S3
S3
S4
S4
E1P6
Block
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
E1P9
Block
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
Size
Code
S3
S10
S4
S4
S12
(S12)
S12
(S12)
Size
Code
S4
S4
SO
SO
SO
SO
SO
SO
E1P10
Block
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
Size
Code
S0
S0
S0
S0
S0
S0
S4
S4
E1P11
Block
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
72
Size
Code
S4
S0
S0
S0
S0
S0
S0
S0
E1P12
Block
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
Size
Code
S0
S0
S0
S0
S0
S0
S0
S4
Page 73

Beyond the Basics
E1P13
Block
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
E1P16
Block
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
Size
Code
S3
S3
S11
S4
S4
S0
S0
S0
Size
Code
S3
S10
S10
S11
S0
S0
S12
(S12)
E1P14
Block
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
Size
Code
S4
S3
S10
S4
S4
S4
S12
(S12)
E1P15
Block
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
Size
Code
S4
S4
S4
S11
S11
S0
S12
(S12
73
Page 74

Beyond the Basics
selecting a preset fl eet map
1. Set the scanner for conventional
scanning and press E/PGM, then
press TRUNK to select the trunking
programming mode and the bank you
want to change.
2. Repeatedly press S or T to select
TYPE 1 SYSTEM (E1), then press E/
PGM.
3. Repeatedly press S or T to select
FLEEt, then press E/PGM.
4. Repeatedly press S or T to select the
name of the desired map (example
E1P7). The preprogrammed fl eet map
appears.
5. Press E/PGM. FLEEt displays.
Note: When the scanner searches
for transmissions, Type I fl eet and
Notes
subfl eet IDs such as 100-12, 100-9,
000-12, or 400-8 display.
If you are still unable to listen to a complete
conversation, then try another preset map.
programming a fl eet map
1. Select the trunking programming mode
and the bank you want to change.
2. Repeatedly press S or T to select Type
1 System (E1), then press E/PGM.
74
Page 75

Beyond the Basics
3. Repeatedly press S or T to select
FLEEt, then press E/PGM. A
preprogrammed fl eet map appears.
4. Repeatedly press S or T until USr
appears. Then press E/PGM.
5. Repeatedly press S or T to select
the size code for the fi rst block, then
press E/PGM. The next available block
appears.
6. Repeat Step 5 until you have selected a
size code for each desired block.
7. Press SRCH. The scanner exits the
trunking programming mode, tunes the
data channel, then searches using the
map you programmed.
Note: If you select size code S-12, S13, or S-14, these restrictions apply:
• S-12 can only be assigned to Blocks
0, 2, 4, or 6
Notes
• S-13 can only be assigned to Blocks
0 and 4
• S-14 can only be assigned to Block
0
Since these size codes require multiple
blocks, you will be prompted for the next
available block when you program a fl eet
map. For example, if you assign Block 0
as S-12, the scanner prompts you for b2,
the next block available, instead of b1. If
75
Page 76

Beyond the Basics
you assign Block 0 as S-14, you would not
see another prompt because S-14 uses all
available blocks.
programming a hybrid system
A hybrid system is simply a Type I system
with some of its blocks designated as Type
II blocks.
To program a hybrid system, follow the
steps listed in “Programming a Fleet Map.”
However, if you want a block to be Type
II, instead of pressing S or T to select
the size block (Step 5), enter size code S-0
instead.
programming the Base and
Offset frequencies
To properly track Motorola VHF and UHF
trunked systems, you must program the
applicable base and offset frequencies for
each system. For a list of these frequencies
and other scanner information, go to
www.trunkscanner.com and other similar
frequency resources.
1. Select the trunking programming mode.
2. Press the number key of the bank
where you want to store the base
frequency.
76
Page 77

Beyond the Basics
3. Repeatedly press S or T to select
Motorola Type UHF, or VHF system, then
press E/PGM.
4. Repeatedly press S or T to select
bASE, then press E/PGM.
5. Press the confi guration Block Number
(1-3) .
6. Press the number keys to enter a new
base frequency, then press E/PGM.
7. Press S. The display changes to the
spacing frequency entering mode.
8. Enter the frequency using the number
keys according to the following guide,
then press E/PGM.
• For Motorola Type II VHF (E2-VHF Hi
band), use 5kHz steps between 5 kHz
– 100 kHz.
• For Motorola Type II UHF (E2-UHF
band), use 12.5kHz steps between 12.5
kHz – 100 kHz.
9. Press S. The display changes to the
offset channel entering mode.
10. Enter an offset channel using the
number keys, then press E/PGM.
Note: You can only input a frequency
Notes
between 380 – 759.
77
Page 78

Beyond the Basics
11. Press •/CLR /DELAY. The scanner
returns to the previous screen.
Repeat steps 5 through 10 to program
additional confi gurations.
turning the Motorola
disconnect tone detect function
On/Off
When the Motorola disconnect tone
detect function is disabled, the scanner
looks for squelch before returning to the
control channel instead of waiting for the
disconnect tone. Only in rare instances
will you need to adjust the default settings.
The condition to return to control channels
depends on whether the signal is present
or not.
1. Select the trunking programming mode
and the bank you want to change.
2. Press S or T to select Motorola Type 2
or Motorola Type 1, then press E/PGM.
3. Press S or T to select Eot, then press
E/PGM.
4. Press S or T to select Eot ON or Eot
OFF, then press E/PGM.
78
Page 79

Notes
Beyond the Basics
Note: If you set the squelch so you
hear a hissing sound, the scanner
will remain on the voice channel,
even when a disconnect tone is
transmitted or there is no signal at
all.
79
Page 80

Beyond the Basics
frequently asked
questions
These suggestions might help you locate
the problem.
My scanner is on but will not
scan, why?
• SQUELCH is not adjusted correctly;
adjust SQUELCH.
• Only one channel or no channels are
stored.
• Store frequencies into more than one
channel.
Why won’t my scanner work at
all?
• Check the batteries or make sure the
AC adapter or DC adapter is connected
properly.
• Recharge the rechargeable batteries or
replace the non-rechargeable batteries.
• The AC adapter or DC adapter is not
connected.
• Be sure the adapter’s barrel plug is
fully plugged into the 9V 300 mA jack.
80
Page 81

Beyond the Basics
Why doesn’t my keypad work?
The keylock function is activated. To turn
off the keylock, press / KEYLOCK until
disappears.
Why is fl ashing?
Recharge the rechargeable batteries or
replace the alkaline batteries.
Why am I getting poor or no
reception?
Batteries are weak or completely
discharged.
Check the batteries or make sure the
AC adapter or DC adapter is connected
properly.
Make sure an antenna is connected to the
scanner.
Why does Error appear?
Programming error: re-enter the frequency
correctly, including the decimal point.
Why won’t my scanner track a
trunked system?
The transmission might not use a system
that can be tracked by your scanner.
Scan another transmission.
The data frequency is missing: see
81
Page 82

Beyond the Basics
“programming trunked frequencies.”
The system you are trying to track is a Type
I system, and the scanner is set to scan
Type II systems. Set the scanner to receive
Type I trunked frequencies. See “scanning
type I and hybrid trunked systems”.
Scanner is set to receive Type I trunked
frequencies, but does not scan them. The
fl eet map you have selected or entered
might be incorrect.
Check the fl eet map and correct it if
necessary (see “scanning type I and hybrid
trunked systems” and “programming a
fl eet map”).
Why isn’t my scanner acquiring
a data channel?
SQUELCH is not correctly adjusted for
trunk scanning. Adjust squelch for trunk
scanning. See “setting squelch for the
trunking mode”.
Why is the frequency used for
the data channel missing?
Press SRCH to search for the data channel
(see “programming trunked frequencies”).
Why am I missing replies to
conversations?
The system you are trying to track is a Type
I system, and the scanner is set to scan
82
Page 83

Beyond the Basics
Type II systems. Set the scanner to receive
Type I trunked frequencies. See “scanning
type I and hybrid trunked systems”.
The selected fl eet map is incorrect. Try
another preset fl eet map or program your
own fl eet map (see “scanning type I and
hybrid trunked systems”).
Enter all of the trunk’s frequencies: see
“programming trunked frequencies”.
How do I reset my scanner?
If the scanner’s display locks up or stops
operating properly, you might need to reset
the scanner.
Caution: This procedure clears all the
information you have stored in the scanner.
Before you reset the scanner, try turning
it off and on to see if it begins working
properly. Reset the scanner only when you
are sure it is not working properly.
1. Turn off the scanner.
2. While holding down 2, 9 and HOLD/
RESUME, turn on the scanner. CLEAr
fl ashes for about 5 seconds as the
scanner clears its memory.
Note: Do not turn off the scanner
again until CLEAr stops fl ashing.
Notes
Otherwise, the scanner might not
clear its memory properly.
83
Page 84

Beyond the Basics
Follow these steps to restore the 150
preprogrammed frequencies stored in the
private bank.
1. Make sure your scanner is turned off.
2. Press 3 and E/PGM simultaneously
while turning on the scanner. After
several seconds, the scanner restores
the frequencies.
FCC notice
Your scanner might cause radio or TV
interference even when it is operating
properly. To determine whether your
scanner is causing the interference, turn off
your scanner. If the interference goes away,
your scanner is causing it. Try the following
methods to eliminate the interference:
• move your scanner away from the
receiver
• connect your scanner to an outlet that
is on a different electrical circuit from the
receiver
• contact your local RadioShack store for
help
Note: Mobile use of this scanner is
Notes
unlawful or requires a permit in some
areas. Check the laws in your area.
84
Page 85

Beyond the Basics
scanning legally
Your scanner covers frequencies used by
many different groups including police
and fi re departments, ambulance services,
government agencies, private companies,
amateur radio services, military operations,
pager services, and wireline (telephone
and telegraph) service providers. It is legal
to listen to almost every transmission your
scanner can receive. However, there are
some transmissions you should never
intentionally listen to. These include:
• telephone conversations (cellular,
cordless, or other private means of
telephone signal transmission)
• pager transmissions
• any scrambled or encrypted
transmissions
According to the Electronic
Communications Privacy Act (ECPA), as
amended, you are subject to fi nes and
possible imprisonment for intentionally
listening to, using, or divulging the
contents of such a transmission unless
you have the consent of a party to the
communication (unless such activity is
otherwise illegal).
This scanner is designed to prevent
reception of illegal transmissions, in
compliance with the law which requires
that scanners be manufactured in such a
way as to not be easily modifi able to pick
85
Page 86

Beyond the Basics
up those transmissions. Do not open your
scanner’s case to make any modifi cations
that could allow it to pick up transmissions
that it is not legal to listen to. Doing so
could subject you to legal penalties.
We encourage responsible, legal scanner
use.
care
Keep the scanner dry; if it gets wet, wipe it
dry immediately. Use and store the scanner
only in normal temperature environments.
Handle the scanner carefully; do not
drop it. Keep the scanner away from dust
and dirt, and wipe it with a damp cloth
occasionally to keep it looking new.
service and repair
If your scanner is not performing as it
should, take it to your local RadioShack
store for assistance. To locate your
nearest RadioShack, use the store locator
feature on RadioShack’s website (www.
radioshack.com), or call 1-800-The Shack
(800-843-7422) and follow the menu
options. Modifying or tampering with the
scanner’s internal components can cause
a malfunction and might invalidate its
warranty and void your FCC authorization
to operate it.
86
Page 87

Beyond the Basics
specifi cations
Frequency Coverage:
29–54 MHz (in 5 kHz steps)
108–136.9875 MHz (in 12.5 kHz steps)
137–174 MHz (in 5 kHz steps)
216–224.995 MHz (in 5 kHz steps)
400–512 MHz (in 6.25 kHz steps)
806.0000–823.9875 MHz (in 12.5 kHz steps)
849.0125–868.9875 MHz (in 12.5 kHz steps)
894.0125–956.0000 MHz (in 12.5 kHz steps)
1240.0000–1300.0000 MHz (in 12.5 kHz
steps)
Number of Banks ..................................... 10
Sensitivity (AM/FM):
FM .................. 20 dB S/N at 3 kHz deviation
29–54 MHz.......................................... 0.4 μV
137–174 MHz ......................................0.5 μV
216–225 MHz ......................................0.5 μV
400–512 MHz ......................................0.6 μV
806–956 MHz ......................................0.7 μV
1240–1300 MHz ..................................1.0 μV
AM ................20 dB S/N at 60% modulation
108–136.9875 MHz .............................1.5 μV
IF Rejection (at 162.4 MHz) ...............100 dB
Channels .............................................. 1000
87
Page 88

Beyond the Basics
Operating Temperature:
Normal ................–4° to 140°F (–20° to 60°C)
Signal Stalker I ...14° to 140°F (–10° to 60°C)
Scan Speed ................ 90 Channels/Second
Search Speed:
Normal ............................. 90 Steps/Second
Hypersearch ....................270 Steps/Second
Priority Sampling ........................ 2 Seconds
Delay Time .................................. 2 Seconds
IF Frequencies 380.7 MHz, 10.85 MHz, 450
kHz
Antenna Impedance .............................. 50Ω
Audio Output .................270 mW maximum
Built-in Speaker .......1&7/16 Inches (36 mm)
8Ω Dynamic Type
Power:
4 AA Alkaline Batteries (6.0 VDC),
or 4 AA Rechargeable Ni-MH Batteries (4.8
VDC) or Optional AC Adapter
Current Drain:
Squelched ..........................................80 mA
Full Output ........................................160 mA
Dimensions (HWD) ..... 6 x 2.6 x 1.75 inches
(153 x 66 x 44 mm)
Weight (without antenna, batteries, belt
clip) 8.4 oz (238 g)
88
Page 89

Beyond the Basics
Specifi cations are typical; individual units
might vary. Specifi cations and depictions
are subject to change and improvement
without notice.
89
Page 90

Beyond the Basics
90
Page 91

Beyond the Basics
91
Page 92

This product is warranted by RadioShack against manufacturing
defects in material and workmanship under normal use for one (1) year
from the date of purchase from RadioShack company-owned stores
and authorized RadioShack franchisees and dealers. For complete
warranty details and exclusions, check with your local RadioShack
store.
RadioShack Customer Relations
300 RadioShack Circle, Fort Worth, TX 76102
04/04
20-528
Printed in China
UBZZ01344ZZ(0)
06A06
©2006. RadioShack Corporation.
All rights reserved. RadioShack and
RadioShack.com are trademarks used by
RadioShack Corporation.
 Loading...
Loading...