Panasonic KX-TGE212B, KX-TGE233B, KX-TGE232B, KX-TGE210B, KX-TGEA20B User Manual
...
ORDER NO. KM41401789CE F13
KX-TGEA20 |
KX-TGE210 |
(Handset) |
(Base Unit) |
KX-TGE230 |
(Charger Unit) |
|||
(Base Unit) |
|
|
||
Configuration for each model |
|
|
||
Model No |
Base Unit |
Handset |
Charger Unit |
Expandable |
KX-TGE210 |
1 (TGE210) |
1 (TGEA20) |
|
Up to 6 |
KX-TGE212 |
1 (TGE210) |
2 (TGEA20) |
1 |
Up to 6 |
KX-TGE232 |
1 (TGE230) |
2 (TGEA20) |
1 |
Up to 6 |
KX-TGE233 |
1 (TGE230) |
3 (TGEA20) |
2 |
Up to 6 |
KX-TGE234 |
1 (TGE230) |
4 (TGEA20) |
3 |
Up to 6 |
KX-TGEA20* |
|
1 (TGEA20) |
1 |
|
*KX-TGEA20 is also an optional accessory, which contains a handset and a charger.
Telephone Equipment
Model No. KX-TGE210B
KX-TGE212B
KX-TGE232B
KX-TGE233B
KX-TGE234B
KX-TGEA20B
Digital Cordless Phone
Digital Cordless Answering System
B: Black Version
(for U.S.A.)
© Panasonic System Networks Co., Ltd. 2014 Unauthorized copying and distribution is a violation of law.

KX-TGE210/KX-TGE212/KX-TGE232/KX-TGE233/KX-TGE234/TGEA20
 WARNING
WARNING
This service information is designed for experienced repair technicians only and is not designed for use by the general public. It does not contain warnings or cautions to advise non-technical individuals of potential dangers in attempting to service a product. Products powered by electricity should be serviced or repaired only by experienced professional technicians. Any attempt to service or repair the product or products dealt with in this service information by anyone else could result in serious injury or death.
IMPORTANT SAFETY NOTICE
There are special components used in this equipment which are important for safety. These parts are marked by
in the Schematic Diagrams, Circuit Board Diagrams, Exploded Views and Replacement Parts List. It is essential that these critical parts should be replaced with manufacturer’s specified parts to prevent shock, fire or other hazards. Do not modify the original design without permission of manufacturer.
IMPORTANT INFORMATION ABOUT LEAD FREE, (PbF), SOLDERING
If lead free solder was used in the manufacture of this product, the printed circuit boards will be marked PbF. Standard leaded, (Pb), solder can be used as usual on boards without the PbF mark.
When this mark does appear, please read and follow the special instructions described in this manual on the use of PbF and how it might be permissible to use Pb solder during service and repair work.
L When you note the serial number, write down all 11 digits. The serial number may be found on the bottom of the unit. L The illustrations in this Service Manual may vary slightly from the actual product.
2

KX-TGE210/KX-TGE212/KX-TGE232/KX-TGE233/KX-TGE234/TGEA20
TABLE OF CONTENTS
PAGE |
|
|
PAGE |
||
1 Safety Precautions----------------------------------------------- |
5 |
10.1.11. Check Caller ID ------------------------------------- |
|
44 |
|
1.1. For Service Technicians --------------------------------- |
5 |
11 Disassembly and Assembly Instructions--------------- |
|
45 |
|
2 Warning-------------------------------------------------------------- |
5 |
11.1. Disassembly Instructions------------------------------- |
|
45 |
|
2.1. Battery Caution--------------------------------------------- |
5 |
11.1.1. Base Unit ---------------------------------------------- |
|
|
45 |
2.2. About Lead Free Solder (PbF: Pb free)-------------- |
5 |
11.1.2. Handset------------------------------------------------ |
|
|
49 |
2.2.1. Suggested PbF Solder ------------------------------ |
6 |
11.1.3. Charger Unit |
------------------------------------------ |
|
50 |
2.3. Discarding of P. C. Board-------------------------------- |
6 |
11.2. How to Replace the Handset LCD------------------- |
|
51 |
|
3 Specifications ----------------------------------------------------- |
7 |
12 Measurements and Adjustments -------------------------- |
|
52 |
|
4 Technical Descriptions ----------------------------------------- |
8 |
12.1. Equipment Required ------------------------------------ |
|
52 |
|
4.1. US-DECT Description ------------------------------------ |
8 |
12.2. The Setting Method of JIG----------------------------- |
|
52 |
|
4.1.1. TDD Frame Format ---------------------------------- |
8 |
12.2.1. Connections (Base Unit) -------------------------- |
|
52 |
|
4.1.2. TDMA system------------------------------------------ |
8 |
12.2.2. Connections (Handset) ---------------------------- |
|
53 |
|
4.1.3. Signal Flowchart in the Radio Parts-------------- |
9 |
12.2.3. How to install Batch file into P.C. ---------------- |
|
54 |
|
4.2. Block Diagram (Base Unit_Main)--------------------- |
10 |
12.2.4. Commands-------------------------------------------- |
|
|
55 |
4.3. Tel Interface Circuit--------------------------------------- |
11 |
12.3. Adjustment Standard (Base Unit) -------------------- |
|
56 |
|
4.4. Block Diagram (Base Unit_RF Part) ----------------- |
12 |
12.3.1. Bottom View |
------------------------------------------ |
|
56 |
4.5. Circuit Operation (Base Unit) -------------------------- |
13 |
12.4. Adjustment Standard (Handset) ---------------------- |
|
57 |
|
4.5.1. BBIC (Base Band IC: IC501) --------------------- |
13 |
12.4.1. Component View ------------------------------------ |
|
57 |
|
4.5.2. Flash Memory (IC502)------------------------------ |
13 |
12.5. Things to Do after Replacing IC or X'tal ------------ |
58 |
||
4.5.3. Flash Memory (IC601)------------------------------ |
13 |
12.5.1. How to download the data ------------------------ |
|
58 |
|
4.5.4. EEPROM (IC611) ------------------------------------ |
13 |
12.6. Frequency Table------------------------------------------ |
|
59 |
|
4.5.5. Power Supply Circuit/Reset Circuit-------------- |
14 |
13 Miscellaneous---------------------------------------------------- |
|
|
60 |
4.5.6. Telephone Line Interface--------------------------- |
16 |
13.1. How to Replace the LLP (Leadless Leadframe |
|
||
4.5.7. Parallel Connection Detect Circuit/Auto |
|
Package) IC ----------------------------------------------- |
|
|
60 |
Disconnect Circuit ----------------------------------- |
17 |
13.1.1. Preparation-------------------------------------------- |
|
|
60 |
4.5.8. Calling Line Identification (Caller ID)/Call |
|
13.1.2. Caution------------------------------------------------- |
|
|
60 |
Waiting Caller ID ------------------------------------- |
18 |
13.1.3. How to Remove the IC----------------------------- |
|
60 |
|
4.6. Block Diagram (Handset)------------------------------- |
20 |
13.1.4. How to Install the IC -------------------------------- |
|
61 |
|
4.7. Block Diagram (Handset_RF Part)------------------- |
21 |
13.2. How to Replace the Flat Package IC --------------- |
|
62 |
|
4.8. Circuit Operation (Handset)---------------------------- |
22 |
13.2.1. Preparation-------------------------------------------- |
|
|
62 |
4.8.1. Outline -------------------------------------------------- |
22 |
13.2.2. How to Remove the IC----------------------------- |
|
62 |
|
4.8.2. Power Supply Circuit/Reset Circuit-------------- |
22 |
13.2.3. How to Install the IC -------------------------------- |
|
63 |
|
4.8.3. Charge Circuit ---------------------------------------- |
23 |
13.2.4. How to Remove a Solder Bridge ---------------- |
|
63 |
|
4.8.4. Battery Low/Power Down Detector-------------- |
23 |
13.3. Terminal Guide of the ICs, Transistors and |
|
||
4.8.5. Speakerphone ---------------------------------------- |
23 |
Diodes ------------------------------------------------------ |
|
|
64 |
4.9. Behavior of Electric Power Failure ------------------- |
24 |
13.3.1. Base Unit ---------------------------------------------- |
|
|
64 |
4.10. Circuit Operation (Charger Unit) ---------------------- |
24 |
13.3.2. Handset------------------------------------------------ |
|
|
64 |
5 Location of Controls and Components ------------------ |
25 |
14 Schematic Diagram -------------------------------------------- |
|
|
66 |
6 Installation Instructions --------------------------------------- |
25 |
14.1. For Schematic Diagram -------------------------------- |
|
66 |
|
7 Operating Instructions----------------------------------------- |
25 |
14.1.1. Base Unit |
(Schematic Diagram (Base |
|
|
8 Test Mode ---------------------------------------------------------- |
26 |
Unit_Main)) ------------------------------------------- |
|
|
66 |
8.1. Engineering Mode ---------------------------------------- |
26 |
14.1.2. Handset |
(Schematic |
Diagram |
|
8.1.1. Base Unit ---------------------------------------------- |
26 |
(Handset_Main))------------------------------------- |
|
66 |
|
8.1.2. Handset ------------------------------------------------ |
28 |
14.2. Schematic Diagram (Base Unit_Main)-------------- |
67 |
||
9 Service Mode ----------------------------------------------------- |
30 |
14.2.1. KX-TGE210------------------------------------------- |
|
|
67 |
9.1. How to Clear User Setting (Handset Only)--------- |
30 |
14.2.2. KX-TGE230------------------------------------------- |
|
|
69 |
10 Troubleshooting Guide ---------------------------------------- |
31 |
14.3. Schematic Diagram (Base Unit_Operation)------- |
71 |
||
10.1. Troubleshooting Flowchart ----------------------------- |
31 |
14.3.1. KX-TGE230------------------------------------------- |
|
|
71 |
10.1.1. Check Power------------------------------------------ |
32 |
14.4. Schematic Diagram (Handset_Main) --------------- |
|
73 |
|
10.1.2. Check Record ---------------------------------------- |
33 |
15 Printed Circuit Board |
------------------------------------------ |
|
76 |
10.1.3. Check Playback ------------------------------------- |
36 |
15.1. Circuit Board (Base Unit_Main) ---------------------- |
|
76 |
|
10.1.4. Check Battery Charge ------------------------------ |
36 |
15.1.1. Component View ------------------------------------ |
|
76 |
|
10.1.5. Check Link--------------------------------------------- |
37 |
15.1.2. Bottom View |
------------------------------------------ |
|
77 |
10.1.6. Check the RF part ----------------------------------- |
39 |
15.2. Circuit Board (Base Unit_Operation)---------------- |
|
78 |
|
10.1.7. Registering a Handset to the Base Unit-------- |
43 |
15.2.1. KX-TGE230------------------------------------------- |
|
|
78 |
10.1.8. Deregistering a Handset --------------------------- |
43 |
15.3. Circuit Board (Handset_Main) ------------------------ |
|
80 |
|
10.1.9. Check Handset Transmission -------------------- |
44 |
15.3.1. Component View ------------------------------------ |
|
80 |
|
10.1.10. Check Handset Reception------------------------- |
44 |
15.3.2. Bottom View |
------------------------------------------ |
|
81 |
3

KX-TGE210/KX-TGE212/KX-TGE232/KX-TGE233/KX-TGE234/TGEA20 |
|
16 Exploded View and Replacement Parts List ----------- |
82 |
16.1. Cabinet and Electrical Parts (Base Unit) ----------- |
82 |
16.1.1. KX-TGE210 ------------------------------------------- |
82 |
16.1.2. KX-TGE230 ------------------------------------------- |
83 |
16.2. Cabinet and Electrical Parts (Handset)------------- |
84 |
16.3. Cabinet and Electrical Parts (Charger Unit) ------- |
85 |
16.4. Accessories and Packing Materials ----------------- |
86 |
16.4.1. KX-TGE210B ----------------------------------------- |
86 |
16.4.2. KX-TGE212B ----------------------------------------- |
87 |
16.4.3. KX-TGE232B ----------------------------------------- |
88 |
16.4.4. KX-TGE233B ----------------------------------------- |
89 |
16.4.5. KX-TGE234B ----------------------------------------- |
90 |
16.5. Replacement Parts List --------------------------------- |
91 |
16.5.1. Base Unit ---------------------------------------------- |
91 |
16.5.2. Handset ------------------------------------------------ |
94 |
16.5.3. Charger Unit ------------------------------------------ |
95 |
16.5.4. Accessories and Packing Materials------------- |
95 |
16.5.5. Screws ------------------------------------------------- |
96 |
16.5.6. Fixtures and Tools----------------------------------- |
96 |
4

KX-TGE210/KX-TGE212/KX-TGE232/KX-TGE233/KX-TGE234/TGEA20
1 Safety Precautions
1.1.For Service Technicians
•Repair service shall be provided in accordance with repair technology information such as service manual so as to prevent fires, injury or electric shock, which can be caused by improper repair work.
1.When repair services are provided, neither the products nor their parts or members shall be remodeled.
2.If a lead wire assembly is supplied as a repair part, the lead wire assembly shall be replaced.
3.FASTON terminals shall be plugged straight in and unplugged straight out.
•ICs and LSIs are vulnerable to static electricity.
When repairing, the following precautions will help prevent recurring malfunctions.
1.Cover plastic parts boxes with aluminum foil.
2.Ground the soldering irons.
3.Use a conductive mat on worktable.
4.Do not grasp IC or LSI pins with bare fingers.
2 Warning
2.1.Battery Caution
Risk of explosion if battery is replaced by an incorrect type. Dispose of used batteries according to the instructions.
Attention:
A nickel metal hydride battery that is recyclable powers the product you have purchased.
Please call 1-800-8-BATTERY (1-800-822-8837) for information on how to recycle this battery.
2.2.About Lead Free Solder (PbF: Pb free)
Note:
In the information below, Pb, the symbol for lead in the periodic table of elements, will refer to standard solder or solder that contains lead.
We will use PbF solder when discussing the lead free solder used in our manufacturing process which is made from Tin (Sn), Silver (Ag), and Copper (Cu).
This model, and others like it, manufactured using lead free solder will have PbF stamped on the PCB. For service and repair work we suggest using the same type of solder.
Caution
•PbF solder has a melting point that is 50 F ~ 70 F (30 C ~ 40 C) higher than Pb solder. Please use a soldering iron with temperature control and adjust it to 700 F ± 20 F (370 C ± 10 C).
•Exercise care while using higher temperature soldering irons.:
Do not heat the PCB for too long time in order to prevent solder splash or damage to the PCB.
•PbF solder will tend to splash if it is heated much higher than its melting point, approximately 1100 F (600 C).
•When applying PbF solder to double layered boards, please check the component side for excess which may flow onto the opposite side (See the figure below).
Component |
Component |
pin |
|
Remove all of the |
|
excess solder |
|
Solder
(Slice View)
5
KX-TGE210/KX-TGE212/KX-TGE232/KX-TGE233/KX-TGE234/TGEA20
2.2.1.Suggested PbF Solder
There are several types of PbF solder available commercially. While this product is manufactured using Tin, Silver, and Copper (Sn+Ag+Cu), you can also use Tin and Copper (Sn+Cu), or Tin, Zinc, and Bismuth (Sn+Zn+Bi). Please check the manufacturer's specific instructions for the melting points of their products and any precautions for using their product with other materials.
The following lead free (PbF) solder wire sizes are recommended for service of this product: 0.3 mm, 0.6 mm and 1.0 mm.
0.3 mm X 100 g |
0.6 mm X 100 g |
1.0 mm X 100 g |
|
|
|
|
|
|
2.3.Discarding of P. C. Board
When discarding P. C. Board, delete all personal information such as telephone directory and caller list or scrap P. C. Board.
6

3Specifications
█Standard:
DECT 6.0 (Digital Enhanced Cordless
Telecommunications 6.0)
█ Number of channels:
60 Duplex Channels (DECT 6.0)
█Frequency range:
1.92GHz to 1.93 GHz (DECT 6.0)
█Duplex procedure:
TDMA (Time Division Multiple Access)
█ Channel spacing:
1.728MHz (DECT 6.0)
KX-TGE210/KX-TGE212/KX-TGE232/KX-TGE233/KX-TGE234/TGEA20
█ Bit rate:
1.152Mbit/s (DECT 6.0)
█ Modulation:
GFSK (Gaussian Frequency Shift Keying)
█RF transmission power:
115 mW (max/DECT6.0)
█Voice coding:
ADPCM 32 kbit/s (DECT 6.0)
|
|
Base Unit |
|
|
Handset |
Charger |
||
Power source |
AC Adaptor |
Rechargeable Ni-MH battery |
AC Adaptor |
|||||
|
|
(PNLV226Z, 120 V AC, 60 Hz) |
AAA (R03) size (1.2 V 400 mAh) |
(PNLV233AZ, 120 V AC, 60 Hz) |
||||
Receiving Method |
Super Heterodyne |
Super Heterodyne |
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
||||||
Oscillation Method |
PLL synthesizer |
PLL synthesizer |
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
||||||
Detecting Method |
Quadrature Discriminator |
Quadrature Discriminator |
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
||||||
Tolerance of OSC Frequency |
10.368 MHz ±41 Hz |
13.824 MHz ±100 Hz |
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
||||||
Modulation Method |
Frequency Modulation |
Frequency Modulation |
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
||||||
ID Code |
40 bit |
40 bit |
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
||||||
Ringer Equivalence No. (REN) |
0.1B |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
Tone (DTMF)/Pulse |
|
|
|
|||||
Dialing Mode |
Tone (DTMF)/Pulse |
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
||||||
Redial |
Up to 48 digits |
Up to 48 digits |
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
||||||
Speed Dialer |
Up to 24 digits (Phonebook) |
Up to 24 digits (Phonebook) |
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
||||||
Power Consumption |
Base Unit*1 |
8 days at Standby, |
Standby: Approx 0.1 W |
|||||
|
|
Standby: Approx. 1.0 W |
||||||
|
|
Maximum: Approx. 4.3 W |
10 hours at Talk |
Maximum: Approx 1.8 W |
||||
|
|
Base Unit*2 |
8 days at Standby, |
Standby: Approx 0.1 W |
||||
|
|
Standby: Approx. 1.0 W |
||||||
|
|
Maximum: Approx. 4.3 W |
10 hours at TalkApprox. 130 |
Maximum: Approx 1.8 W |
||||
Operating Conditions |
0 °C - 40 °C (32 °F – 104 °F) |
0 °C - 40 °C (32 °F – 104 °F) |
0 °C - 40 °C (32 °F – 104 °F) |
|||||
|
|
20 % – 80 % relative air humidity |
20 % – 80 % relative air humidity |
20 % – 80 % relative air humidity |
||||
|
|
(dry) |
(dry) |
(dry) |
||||
Dimensions (W x D x H) |
Approx. 197 mm x 88 mm x 83 mm |
Approx. 54 mm x 31 mm x 171 mm |
Approx. 72 mm x 72 mm x 38 mm |
|||||
Mass (Weight) |
Approx. 270 g |
Approx. 130 g |
Approx. 90 g |
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
*1 |
KX-TGE210 series |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
*2 |
KX-TGE230 series |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Note:
Design and specifications are subject to change without notice.
Note for Service:
•Operation range: Up to 300 m outdoors, Up to 50 m indoors, depending on the condition.
•Analog telephone connection: Telephone Line
•Optional headset: KX-TCA60, KX-TCA93, KX-TCA400, KX-TCA430
•Optional Range extender: KX-TGA405
•Optional Key detector: KX-TGA20
•T-adaptor: KX-J66
7
KX-TGE210/KX-TGE212/KX-TGE232/KX-TGE233/KX-TGE234/TGEA20
4 Technical Descriptions
4.1.US-DECT Description
The frequency range of 1.92 GHz-1.93 GHz is used. Transmitting and receiving carrier between base unit and handset is same frequency. Refer to Frequency Table (P.59).
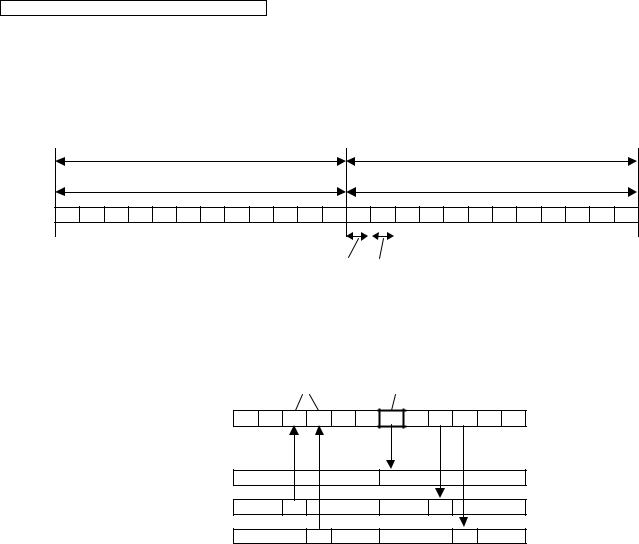
4.1.1. |
TDD Frame Format |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
5 ms |
|
|
|
|
|
5 ms |
|
|
|
|
Up Link ( Handset -> Base Unit ) |
|
|
Down Link ( Base Unit -> Handset ) |
|||||||
|
RX1 |
RX2 |
RX3 |
RX4 |
RX5 |
RX6 |
TX1 |
TX2 |
TX3 |
TX4 |
TX5 |
TX6 |
|
|
DATA rate : 1.152 Mbps |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
417 μs (available) |
417 μs (blind) |
|
|
|
|
||
4.1.2. |
TDMA system |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
This system is the cycles of 10 ms, and has 6 duplex paths, but maximum duplex communication path is 5 because of dummy bearer use.
In 1 slot 417 s, the 10 ms of voice data is transmitted.
• 2 - Handsets Link
|
Traffic Bearer |
Dummy bearer |
Base unit |
RX1 RX2 RX3 RX4 RX5 RX6 TX1 TX2 TX3 TX4 TX5 TX6 |
|
Handset 1 |
|
|
(Stand by) |
TX |
RX |
Handset 2 |
||
(Link) |
TX |
RX |
Handset 3 |
||
(Link) |
|
|
Traffic Bearer
A link is established between base unit and handset.
The state where duplex communication is performed.
Handset doesn't make up duplex in no free RF channels because of interference. (*1)
Dummy Bearer
Base unit sends Dummy-data to the all stand-by state handsets.
Handsets receive that data for synchronization and monitoring request from the base unit.
Base unit doesn't send Dummy bearer in no free RF channels because of interference. (*1)
Note:
(*1) It is a feature under FCC 15 regulation and for interference avoidance. In the case of checking RF parts, it is better in least interference condition.
8

KX-TGE210/KX-TGE212/KX-TGE232/KX-TGE233/KX-TGE234/TGEA20
4.1.3.Signal Flowchart in the Radio Parts
Reception Base unit:
A voice signal from TEL line is encoded to digital data and converted into a 1.9GHz modulated radio signal by BBIC(IC501). The RF signal, after which is amplified in BBIC, is fed to selected antenna.
Handset:
As for a handset RF, RF signal is received in one antenna.
BBIC down-converts to 864 kHz IF signal from RX signal and demodulates it to digital data "RXDATA". BBIC (IC1) converts RXDATA into a voice signal and outputs it to speaker.
Transmission
Handset:
A voice signal from microphone is encoded to digital data and converted into a 1.9GHz modulated radio signal by BBIC(IC1). The RF signal, after which is amplified in BBIC, is fed to an antenna.
Base unit:
As for a base unit RF, RF signal is received in two antennas.
BBIC (IC501) compares RF signal levels and selects the antenna to be used. Then BBIC down-converts to 864 kHz IF signal from RX signal in the selected antenna, and demodulates it to digital data "RXDATA".
BBIC (IC501) converts RXDATA into a voice signal and outputs it to TEL line.
9
10
LED |
|
|
|
|
|
Q141 |
|
TEL_JACK |
|
|
|
Crystal |
|
Q161 |
TR_RLY |
D101 |
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
3 |
2 |
TIP |
|
|
|
|
|
10.368MHz |
|
SIDE_TONE |
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
CIRCUIT |
4 |
1 |
RING |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
LSRp |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
MICh |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
P3_6 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
CKM/STM |
IC501 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
CIDINn |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
BBIC |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
CIDINp |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
+1.8V |
+3.0V |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
QSPI |
IC502 |
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
ANT1 |
|
|
Flash(Program) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
AVD/VDD |
|
|
Q301 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
RF_Block |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
DC_JACK |
|
|
|
VRF |
|
|
|
|
IC302 |
|
|
|
|
VBAT |
|
|
|
|
DC5.5V+ |
||
VDDPA |
RFVDD |
/VPA |
|
|
|
REGULATOR |
|
|
|
|
PDN_DET |
|
|
|
|
|
GND |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
CHARGE_DET |
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
Power Down |
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
DET |
|
|
|
IC611 |
|
|
Q701 |
|
|
CHARGE |
|
|
|
|
|
CHARGE |
|
|
+ |
||
|
|
EEPROM |
|
|
DETECT |
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
IC601 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
- |
|
|
KEY |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Flash |
|
|
|
|
Power supply |
|
||
|
|
PAD |
|
|
|
|
|||
|
(Voice prompt) |
|
|
|
at AC failure |
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
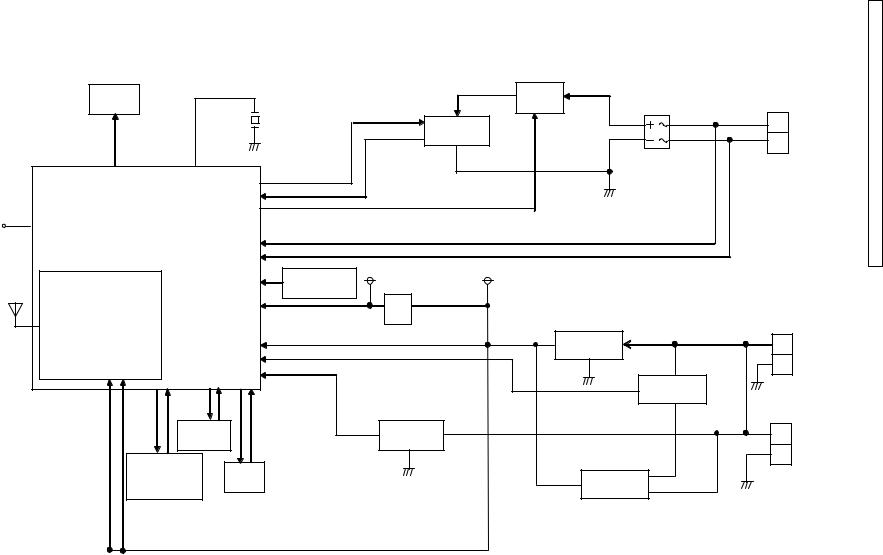
TGE234/TGEA20-TGE233/KX-TGE232/KX-TGE212/KX-TGE210/KX-KX Main)_Unit (Base Diagram Block .2.4
KX-TGE210/212/232/233/234 BLOCK DIAGRAM (Base Unit_Main)

4.3.Tel Interface Circuit
|
TIP |
RING |
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
 P101
P101
SA101
C101 |
2 |
1 |
D101 |
C102 |
|
|
3 |
4 |
R141
Q141 |
R142 |
|
TX AMP SIDE TONE |
RX AMP |
KX-TGE210/KX-TGE212/KX-TGE232/KX-TGE233/KX-TGE234/TGEA20
C103 |
C105 |
C104 |
C106 |
R101 |
R103 |
R102 |
R104 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
CALLER ID |
DETECT |
|
|
|
|
|
|||
BELL DETECT |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
|
|
|
REGULATOR |
|
|||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
CONTROL |
CIRCUIT |
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
11

KX-TGE210/KX-TGE212/KX-TGE232/KX-TGE233/KX-TGE234/TGEA20
4.4.Block Diagram (Base Unit_RF Part)
|
|
10.368 |
MHz |
|
TXDATA |
RXDATA |
|
RF Part) |
IC501 RF block |
PLL |
3856-3843MHz |
/3859-3845MHz |
Modulator |
Control |
Logic |
Mixer Demodulator |
KX-TGE210/212/232/233/234 BLOCK DIAGRAM (Base Unit |
|
|
RF TXp |
RF TXn |
|
|
RF RXp |
RF RXn |
|
ANT1
12

KX-TGE210/KX-TGE212/KX-TGE232/KX-TGE233/KX-TGE234/TGEA20
4.5.Circuit Operation (Base Unit)
General Description:
(BBIC, Flash Memory, EERROM) is a digital speech/signal processing system that implements all the functions of speech compression, record and playback, and memory management required in a digital telephone answering machine.
The BBIC system is fully controlled by a host processor. The host processor provides activation and control of all that functions as follows.
TDD & TDMA |
ADPCM |
Digital |
|
TEL |
|
with FHSS |
|
|
|||
|
Speech |
Analog |
|||
Processor |
ADPCM |
Line |
|||
Processor |
Front |
||||
|
Interface |
||||
RF part |
|
|
End |
||
|
|
|
|||
Host CPU |
|
& |
|
||
Caller ID |
|
|
|||
|
|
Multi- |
|
||
|
|
Modem |
|
||
|
BBIC (IC501) |
|
plexer |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
Digital TAM System |
|
SP |
||
EEPROM |
|
Keys/ LEDs |
|
Flash Memory |
|
Flash Memory IC601 |
IC611 |
|
/ Charge |
|
(Program) |
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
IC502 |
|
|
4.5.1.BBIC (Base Band IC: IC501)
•Voice Message Recording/Play back
The BBIC system uses a proprietary speech compression technique to record and store voice message in Flash Memory. An error correction algorithm is used to enable playback of these messages from the Flash Memory.
•DTMF Generator
When the DTMF data from the handset is received, the DTMF signal is output.
•Synthesized Voice (Pre-recorded message)
The BBIC implements synthesized Voice, utilizing the built in speech detector and a Flash Memory, which stored the vocabulary.
•Caller ID demodulation
The BBIC implements monitor and demodulate the FSK/DTMF signals that provide CID information from the Central Office.
•Digital Switching
The voice signal from telephone line is transmitted to the handset or the voice signal from the handset is transmitted to the Telephone line, etc. They are determined by the signal path route operation of voice signal.
•Block Interface Circuit
RF part, LED, Key scan, Speaker, Telephone line.
4.5.2.Flash Memory (IC502)
Main program data is stored.
4.5.3.Flash Memory (IC601)
Following information data is stored.
•Voice signal
ex: Pre-recorded Greeting message, Incoming message
4.5.4.EEPROM (IC611)
Following information data is stored.
•Settings
ex: message numbers, ID code, Flash Time, Tone/Pulse
13

KX-TGE210/KX-TGE212/KX-TGE232/KX-TGE233/KX-TGE234/TGEA20
4.5.5.Power Supply Circuit/Reset Circuit
The power supply voltage from AC adaptor is converted to VBAT (3.0V) in IC302. And +3.0V for peripherals and analog part is insulated from VBAT by Doubler of BBIC.
Circuit Operation:
+5.5V |
+3.0V |
VDD3 |
VDD4 |
|
|
|
|
+5.5V |
|
|
IC302 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
IC501 |
|
|
IC611 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
+3.0V |
|
|
+3.0V_CP |
||||||||
|
|
3.0V |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
EEPROM |
||||||
AC Adaptor |
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
REGULATOR |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
VDD1 |
BBIC |
VDD5 |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
+1.8V |
|
+3.0V_CP2 |
|
IC601 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
TAM FLASH |
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Q301 |
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
IC502
QSPI FLASH
RF Part
LEDs
VBAT
VDD1 (1.8 V)
Reset (RSTN) (IC501_77pin)
Startmonitor (IC501 57pin)
(CKM/STM)
BBIC chip initialize
14
KX-TGE210/KX-TGE212/KX-TGE232/KX-TGE233/KX-TGE234/TGEA20
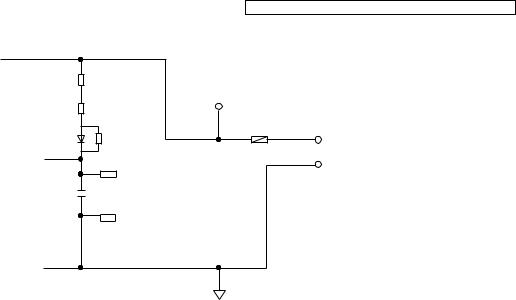
4.5.5.1.Charge Circuit
The voltage from the AC adaptor is supplied to the charge circuits.
R371 |
|
|
R372 |
+5.5V |
|
|
|
|
62 A |
F301 |
DCP |
3 |
R373 |
|
D K |
|
|
|
|
|
|
CHARGE+ |
DCM |
|
|
|
C351 |
|
|
|
CHARGE- |
|
15
KX-TGE210/KX-TGE212/KX-TGE232/KX-TGE233/KX-TGE234/TGEA20
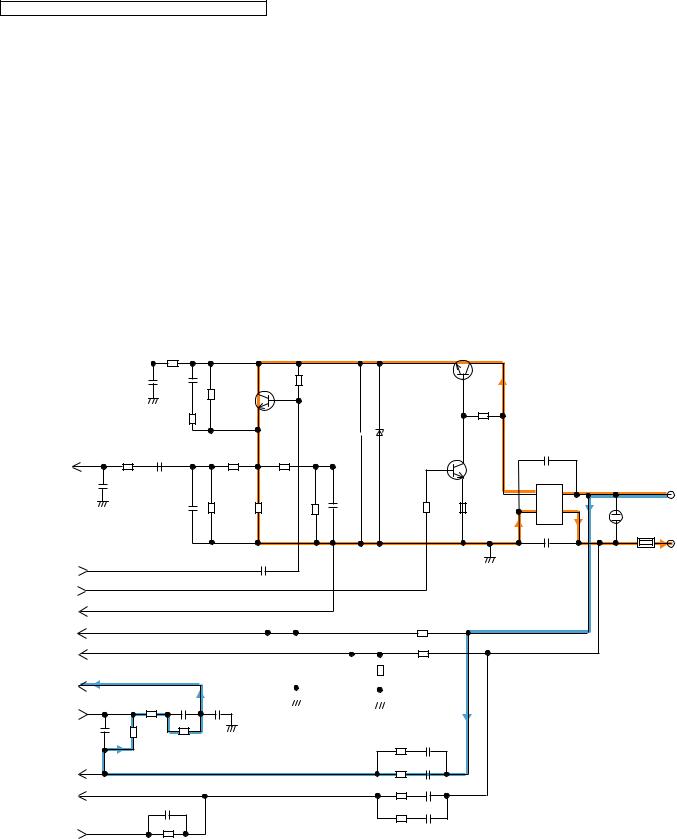
4.5.6.Telephone Line Interface
Telephone Line Interface Circuit:
Function
•Bell signal detection
•ON/OFF hook and pulse dial circuit
•Side tone circuit
Bell (RINGING) signal detection and OFF HOOK circuit:
In the idle mode, Q141 is open to cut the DC loop current and decrease the ring load. When ring voltage appears at the Tip (T) and Ring (R) leads (When the telephone rings), the AC ring voltage is transferred as follows:
L1T C105 R103 R110 R11 1 R112 BBIC pin18(RINGING)
When the CPU (BBIC) detects a ring signal, Q141 turns on, thus providing an off-hook condition (active DC current flow through the circuit). Following signal flow is the DC current flow.
T D101 Q141 Q161 R163 D101 P101 R
ON HOOK Circuit:
Q141 is open, Q141 is connected as to cut the DC loop current and to cut the voice signal. The unit is consequently in an onhook condition.
Pulse Dial Circuit:
Pin 19 of BBIC turns Q141 ON/OFF to make the pulse dialing.
Side Tone Circuit:
Basically this circuit prevents the TX signal from feeding back to RX signal. As for this unit, TX signal feed back from Q161 is canceled by the canceller circuit of BBIC.
|
|
|
R160 |
|
|
|
|
|
C161 |
+ |
C167 |
R165 |
|
|
R162 |
|
|
C |
Q161 |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
R168 |
|
E |
B |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
RX |
R178 |
C173 |
R164 |
|
R151 |
|
|
Pin25 of IC501 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
C174 |
|
C171 |
R166 |
R163 |
|
R152 |
|
|
|
|
||||
TX
Pin27 of IC501
HOOK
Pin19 of IC501
PARADET
Pin17 of IC501
ADC1
Pin33 of IC501
ADC0
Pin32 of IC501
RINGING
Pin18 of IC501
CIDOUT
Pin24 of IC501
|
R111 |
C111 |
C113 |
C110 |
R110 |
R112 |
|
|
|
|
C184
C115 |
|
|
R117 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
C |
Q141 |
E |
|
|
B |
R141
C142 |
|
K |
D142 |
|
|
|
|||
|
A |
|
||
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
Q142 |
|
C101 |
|
|
|
|
|
C |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
B |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
OFF Hook |
|
|
|
|
E |
D101 |
|
||
|
|
|
|
+ |
|
|
L1T |
C152 |
R145 |
R142 |
3 |
~ |
2 |
SA101 |
|
4 |
_ |
~ |
1 |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
L1R |
|
|
|
|
C102 |
|
|
P101 |
R115
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
C116 |
|
|
R118 |
|
|
|
R116 |
|||
|
|
|
|
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
R101 C103
CIDINn |
BELL signal detection |
R103 |
C105 |
Pin23 of IC501 |
|
|
|
CIDINp |
|
R102 |
C104 |
Pin21 of IC501 |
C109 |
|
|
|
R104 |
C106 |
|
|
|
||
LSRn |
|
|
|
Pin28 of IC501 |
R109 |
|
|
|
|
|
16

KX-TGE210/KX-TGE212/KX-TGE232/KX-TGE233/KX-TGE234/TGEA20
4.5.7.Parallel Connection Detect Circuit/Auto Disconnect Circuit
Function:
In order to disable call waiting and stutter tone functions when using telephones connected in parallel, it is necessary to have a circuit that judges whether a telephone connected in parallel is in use or not. This circuit determines whether the telephone connected in parallel is on hook or off hook by detecting changes in the T/R voltage.
Circuit Operation:
Parallel connection detection when on hook:
When on hook, the voltage is monitored at pin 32 of IC501. There is no parallel connection if the voltage is 0.54 V or higher, while a parallel connection is deemed to exist if the voltage is lower.
Parallel connection detection when off hook:
When off hook, the voltage is monitored at pin 17 of IC501; the presence/absence of a parallel connection is determined by detecting the voltage changes.
If the Auto disconnect function is ON and statuses are Hold, receiving ICM, OGM transmitting, BBIC disconnects the line after detecting parallel connection is off hook.
|
|
|
R160 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Q141 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
C161 |
+ |
C167 |
|
|
R162 |
|
|
|
C |
|
E |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
B |
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
R165 |
Q161 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
C |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
B |
|
|
|
|
R141 |
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
R168 |
|
E |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
C142 |
K |
D142 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
A |
|
|
|
C101 |
|
|
|
|||
RX |
R178 |
C173 |
R164 |
R151 |
|
|
|
|
Q142 |
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
C |
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
Pin25 of IC501 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
B |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
C174 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
E |
|
D101 |
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
L1T |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
+ |
|
|
||
|
|
C171 |
R166 |
R163 |
R152 |
C152 |
|
R145 |
R142 |
|
3 |
~ |
2 |
SA101 |
||
|
|
|
|
|
4 |
_ |
~ |
1 |
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
L1R |
TX |
|
|
|
|
C184 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
C102 |
|
|
P101 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Pin27 of IC501 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
HOOK |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Pin19 of IC501 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
PARADET |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Pin17 of IC501 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
R115 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
ADC1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Pin33 of IC501 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ADC0 |
C115 |
R117 |
C116 |
R118 |
|
|
Pin32 of IC501 |
R116 |
|||||
|
|
|
|
17

KX-TGE210/KX-TGE212/KX-TGE232/KX-TGE233/KX-TGE234/TGEA20
4.5.8.Calling Line Identification (Caller ID)/Call Waiting Caller ID
Function: Caller ID
The caller ID is a chargeable ID which the user of a telephone circuit obtains by entering a contract with the telephone company to utilize a caller ID service. For this reason, the operation of this circuit assumes that a caller ID service contract has been entered for the circuit being used. The data for the caller ID from the telephone exchange is sent during the interval between the first and second rings of the bell signal. The data from the telephone exchange is a modem signal which is modulated in an FSK (Frequency Shift Keying) * format. Data "1" is a 1200 Hz sine wave, and data "0" is a 2200 Hz sine wave. There are two types of the message format which can be received: i.e. the single message format and plural message format. The plural message format allows to transmit the name and data code information in addition to the time and telephone number data.
*: Also the telephone exchange service provides other formats.
 Single message format
Single message format
1st Ring |
Silent interval 4 sec |
2nd Ring |
|
2 sec |
2 sec |
||
0.5 s |
575 ms |
min 0.5 s |
|
|
DATA |
|
|
STD Ring / 20 Hz |
|
|
|
Tip-Ring |
|
0.1 Vrms |
|
70 Vrms
A |
DATA in |
1200 Hz |
2200 Hz |
=DATA "1" |
=DATA "0 " |
B DATA out
1 bit=833 µs
month |
|
day |
|
hour |
|
minute |
|
number |
04 |
|
15 |
|
16 |
|
35 |
|
2013487000 |
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
 Plural message format
Plural message format
1st Ring 0.5 s |
718 ms |
2 sec |
2nd Ring |
|
|
|
DATA |
DATA CODE NAME |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
month |
|
day |
|
hour |
|
minute |
|
number |
||
201 |
John Smith |
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
04 |
|
16 |
|
16 |
|
35 |
|
2013487000 |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
18

KX-TGE210/KX-TGE212/KX-TGE232/KX-TGE233/KX-TGE234/TGEA20
Call Waiting Caller ID
Calling Identity Delivery on Call Waiting (CIDCW) is a CLASS service that allows a customer, while off-hook on an existing call, to receive information about a calling party on a waited call. The transmission of the calling information takes place almost immediately after the customer is alerted to the new call so he/she can use this information to decide whether to take the new call.
Function:
The telephone exchange transmits or receives CAS and ACK signals through each voice RX/TX route. Then FSK data and MARK data pass the following route.
Telephone Line P101 C105, C104 R103, R104 RA101 IC501(23, 21).
If the unit deems that a telephone connected in parallel is in use, ACK is not returned even if CAS is received, and the information for the second and subsequent callers is not displayed on the portable handset display.
Call Waiting Format
CAS: CPE Alerting Signal
Dual Tone of 2130 Hz, 2750 Hz -15 dBm (900 ohm load)
Signal Flow |
CAS |
|
|
|
|||
Telephone Exchange |
Cordless phone |
|
|
|
|
||
80  5 ms
5 ms
Signal Flow |
ACK |
||
Cordless phone |
Telephone Exchange |
||
|
|||
|
|||
Continuance Signal |
|
|
of 1200 Hz (Data "1") |
"FSK" |
|
|
|
|
|
MARK |
DATA |
|
|
|
0~500 ms 58~75 ms |
about 300 ms |
|
|
|
(be changed by |
|
|
Information Volume) |
ACK: Acknowledged Signal DTMF
"D"
0~100 ms 60  5 ms
5 ms
CIDOUT
Pin 24
CIDINn
Pin 23
IC501
CIDINp
Pin 21
LSRn
Pin 28
C110 |
R110 |
C109 |
R109 |
R101 |
C103 |
|
R103 |
C105 |
L1T |
R102 |
C104 |
SA101 |
L1R |
||
R104 |
C106 |
P101 |
19
KX-TGE210/KX-TGE212/KX-TGE232/KX-TGE233/KX-TGE234/TGEA20
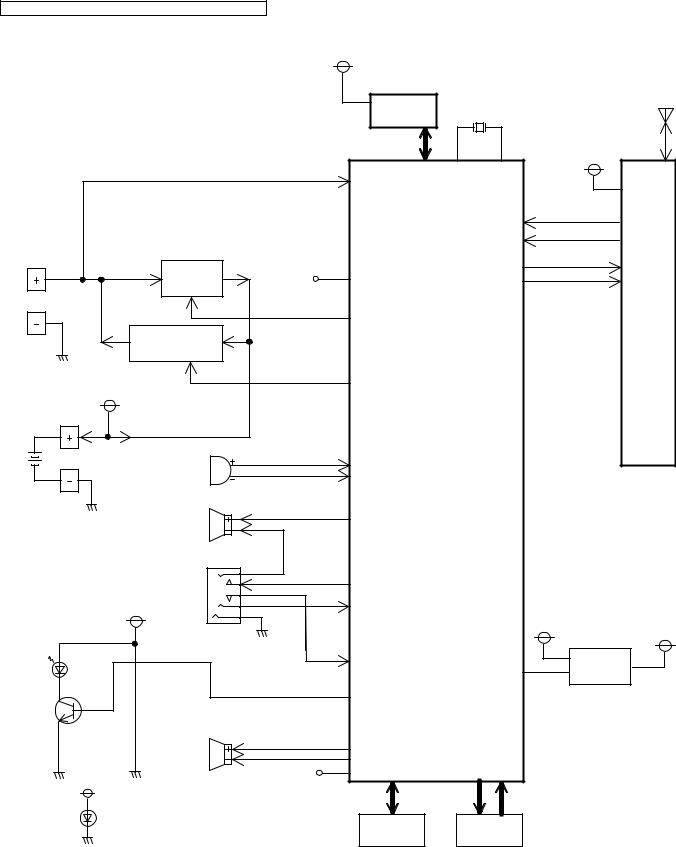
4.6.Block Diagram (Handset)
|
|
3V |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
IC3 |
X1 |
|
ANT1 |
||
|
|
EEPROM |
|
||||
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
13.824 MHz |
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
DATACLK, |
|
|
VBAT |
|
|
|
CHG_DET |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
WP, |
|
RXp |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
RXn |
|
|
CHARGE |
RSTN |
RESET |
|
|
TXp |
|
|
|
|
TXn |
|
RF part |
|||
CONTROL |
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
CHARGE |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
CHG_CTL |
|
|
|
|
|
POWER SUPPLY |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
CONTROL |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
VBAT |
|
BATTERY_ON |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
MIC |
|
|
IC1 |
|
|
|
|
BATTERY |
|
MIP |
BBIC |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
MIN |
|
|
|
|
|
Receiver |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
HSSPOUTP |
|
|
|
|
|
Headset Jack |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
LOUT |
|
|
|
|
|
3V |
|
HSMIP |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
4.0V |
|
CN4 |
|
|
|
|
|
IC4 |
VBAT |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
LED |
|
HEADSET_DET |
|
|
CHARGE |
|
|
(KEY) |
|
|
CP_OFF |
|
|||
|
|
|
|
PUMP |
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Q6 |
|
KEY_LED |
|
A~EKEYSTOROBE |
|
|
|
|
|
|
1~5KEYIN |
|
|
||
Monitor SP |
CKM/STM |
CKM//STM |
|
|
|
||
|
|
SPOUTP |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
SPOUTN |
|
|
|
|
|
4V |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
LED |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(LCD) |
|
LCD |
|
KEYS |
|
|
|
KX-TGEA20 BLOCK DIAGRAM (Handset)
20
KX-TGE210/KX-TGE212/KX-TGE232/KX-TGE233/KX-TGE234/TGEA20
4.7.Block Diagram (Handset_RF Part)
TXp
TXn
ANT
RXp
RXn
KX-TGEA20 BLOCK DIAGRAM (Handset_RF Part)
21

KX-TGE210/KX-TGE212/KX-TGE232/KX-TGE233/KX-TGE234/TGEA20
4.8.Circuit Operation (Handset)
4.8.1.Outline
Handset consists of the following ICs as shown in Block Diagram (Handset) (P.20).
•DECT BBIC (Base Band IC): IC1
-All data signals (forming/analyzing ACK or CMD signal)
-All interfaces (ex: Key, Detector Circuit, Charge, EEPROM, LCD)
•EEPROM: IC3
-Setting data is stored. (e.g. ID, user setting)
4.8.2.Power Supply Circuit/Reset Circuit
Circuit Operation:
When powering on the Handset, the voltage is as follows;
BATTERY(2.2 V ~ 2.6 V: BATT+) F1 BBC1 (IC1) 10 pin
The Reset signal generates IC1 (54 pin) and 1.8 V.
VBAT
VDDC (1.2 V) |
|
|
Reset (RSTN) |
|
|
(IC1_54 pin) |
|
|
Start monitor |
|
|
(IC1 57pin) |
|
|
(CKM/STM) |
|
|
|
BBIC chip initialize |
|
VBAT |
|
|
|
3.0V |
|
|
3.0V |
|
BATTERY |
EEPROM |
|
2CELL |
||
|
||
GND |
|
|
VDDC (1.2V) |
|
|
|
DOUBLER OUT (Charge Pump) |
|
|
For all peripherals |
|
|
3.0V |
|
BBIC |
LCD |
VBAT
4.0V
External Charge Pump
Circuit or IC
3.0V
4.0 output
KEY LED
LCD BACKLIT LED
GND
22

KX-TGE210/KX-TGE212/KX-TGE232/KX-TGE233/KX-TGE234/TGEA20
4.8.3.Charge Circuit
Circuit Operation:
When charging the handset on the Base Unit, the charge current is as follows;
DCP(5.5V) F301 R371 R372 D362 CHARGE+(Base) CHARGE+(Handset) R8 Q3 F1 BATTERY+...
Battery...
BATTERYR45 GND CHARGE-(Handset) CHARGE-(Base) GND DC-(GND) In this way, the BBIC on Handset detects the fact that the battery is charged.
The charge current is controlled by switching Q9 of Handset. Refer to Fig.101 in Power Supply Circuit/Reset Circuit (P.14).
|
Q2 |
|
C27 |
|
R2 |
R8 |
R9 |
|
|
CHG + |
|
|
|
Q3 |
|
|
BATT + |
R4 47K |
Q4 |
BATTERY |
|
|
2CELL |
|
R6 |
|
|
10K |
BATT - |
CHG - |
Q9 |
R45 |
|
|
|
GND |
|
GND |
|
|
GND |
CHG CTRL (32) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
BBIC |
R7 |
CHG DET (34) |
IC1 |
100K |
|
|
4.8.4.Battery Low/Power Down Detector
Circuit Operation:
“Battery Low” and “Power Down” are detected by BBIC which check the voltage from battery. The detected voltage is as follows;
•Battery Low
Battery voltage: V(Batt)  2.35 V ± 50 mV
2.35 V ± 50 mV
The BBIC detects this level and " " starts flashing.
" starts flashing.
•Power Down
Battery voltage: V(Batt)  2.1 V ± 50 mV The BBIC detects this level and power down.
2.1 V ± 50 mV The BBIC detects this level and power down.
4.8.5.Speakerphone
The hands-free loudspeaker at SP+ and SPis used to generate the ring alarm.
23

KX-TGE210/KX-TGE212/KX-TGE232/KX-TGE233/KX-TGE234/TGEA20
4.9.Behavior of Electric Power Failure
In case that the power from AC adaptor is lost and lose radio waves, BBIC (IC1) turns Q11 ON since handset presumes that base unit's power is falied.
Base unit detects that power voltage of AC adaptor +5.5V is OFF, then turns Q351 ON.
It's possible to use the units during the power failure, supplying power to VBAT of base unit from battery of handset through Q10, CHG terminal and Q351.
|
|
Handset |
|
Base Unit |
|
|
|
|
CHG+ |
Q351 |
VBAT |
BATT+ |
|
Power Supply |
|
||
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
at AC failure |
|
|
+5.5V |
|
|
(Q10,Q11,Q12) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
BATT_ |
|
|
CHG- |
|
R351 |
|
|
|
|
Power Down |
|
|
R45 |
3 |
|
|
|
|
|
DET |
|
||
|
BBIC |
|
|
||
|
|
|
(Q352,Q353,Q354) |
|
|
|
|
IC1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
R352 |
|
|
|
|
PDN_DET |
|
|
|
|
|
(pin101-IC501) |
|
4.10. Circuit Operation (Charger Unit)
Charge control is executed at handset side so that the operation when using charger is also controlled by handset. Refer to Circuit Operation (Handset) (P.22)
 TP1
TP1
J1
 TP2
TP2
AC Adaptor
The route for this is as follows: DC+pin of J1(+) CHARGE+pad Handset CHARGE-pad DC-pin of J1(-)
24

KX-TGE210/KX-TGE212/KX-TGE232/KX-TGE233/KX-TGE234/TGEA20
5 Location of Controls and Components
Refer to the Operating Instructions.
Note:
You can download and refer to the Operating Instructions (Instruction book) on TSN Server.
6 Installation Instructions
Refer to the Operating Instructions.
Note:
You can download and refer to the Operating Instructions (Instruction book) on TSN Server.
7 Operating Instructions
Refer to the Operating Instructions.
Note:
You can download and refer to the Operating Instructions (Instruction book) on TSN Server.
25

KX-TGE210/KX-TGE212/KX-TGE232/KX-TGE233/KX-TGE234/TGEA20
8 Test Mode
8.1.Engineering Mode
8.1.1.Base Unit
Important:
Make sure the address on LCD is correct when entering new data. Otherwise, you may ruin the unit.
Make sure the link between Base and Handset before that. Then in case using not original Handset, you need to deregister Handset.
Note: Refer to Registering a Handset to a Base Unit in the Operating Instructions.

 {OFF}
{OFF}
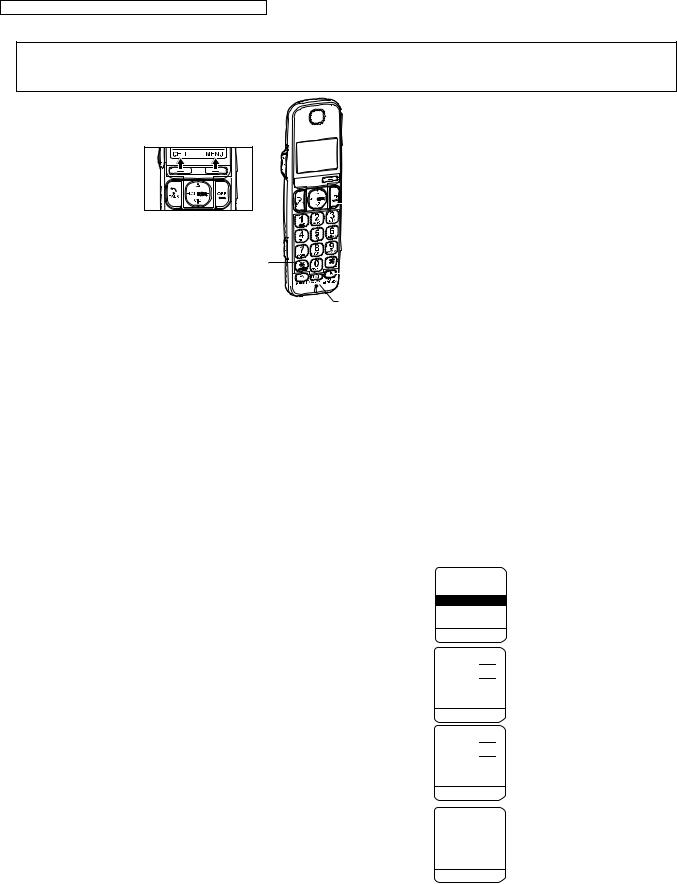
Dial keypad |
{FLASH}
H/S key operation {CALL WAIT}
This pictured model is KX-TGE230.
H/S LCD
1). Press {MENU}.
2). Select "Settings" using {^}or {V} then press {SELECT} or {>}.
Select "Set tel line" using {^}or{V} then press {SELECT} or {>}.
3). Enter "7", "2", "6", "2", "7", "6", "6", "4".
Note: 7262 7664 = PANA SONI
(see letters printed on dial keys)
4). Select "Write EEP" using {^}or{V} then press {SELECT} or {>}.
5). Enter " ", " ", " ", " " (Address). (*1)
6). Enter " ", " " (New Data). (*1)
Service Mode
Read EEP
Write EEP
BACK SELECT
Set Addr.:




 Default Data
Default Data
CLEAR OK
26

KX-TGE210/KX-TGE212/KX-TGE232/KX-TGE233/KX-TGE234/TGEA20
7). Press {OK} , a long confirmation beep will be heard.
8). Press to return to standby mode.
After that, turn the base unit power off and then power on.
Note: * "Set tel line" isn't displayed in Cell line only mode.
To return to normal mode, execute the following procedure:
1{MENU} i{#}{1}{5}{7}
2{V}/{^}: Select "off "i{SELECT}
3{OFF}
Frequently Used Items (Base Unit)
ex.)
Set Addr.:




 New Data
New Data
CLEAR OK
Set Addr.:
_ _ _ _ _ _
BACK
|
|
|
|
|
|
Items |
Address |
Default Data |
New Data |
Remarks |
|
C-ID (FSK) sensitivity |
06 0B |
00 |
01 (6dB UP) |
02 (12dB UP) |
When hex changes from"00" to "01" or "02" |
|
|
|
|
|
gain increases by 6dB or 12dB. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Frequency |
00 07 / 00 08 |
70/02 |
- |
- |
Use these items in a READ-ONLY mode to |
|
|
|
|
|
confirm the contents. Careless rewriting may |
ID |
00 02 ~ 00 06 |
Given value |
- |
- |
|
|
|
|
|
|
cause serious damage to the computer system. |
Note:
(*1) When you enter the address or New Data, please refer to the table below.
|
Desired Number (hex) |
|
Input Keys |
|
|
|
|
||
|
0 |
|
0 |
|
|
1 |
|
1 |
|
|
. |
|
. |
|
|
. |
|
. |
|
|
. |
|
. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
9 |
|
9 |
|
Desired Number (hex) |
Input Keys |
A |
[Flash] + 0 |
B |
[Flash] + 1 |
C |
[Flash] + 2 |
D |
[Flash] + 3 |
E |
[Flash] + 4 |
F |
[Flash] + 5 |
27
KX-TGE210/KX-TGE212/KX-TGE232/KX-TGE233/KX-TGE234/TGEA20
8.1.2.Handset
Important:
Make sure the address on LCD is correct when entering new data. Otherwise, you may ruin the unit.

 {OFF}
{OFF}
Dial keypad |
H/S key operation |
{FLASH} |
H/S LCD |
{CALL WAIT} |
||
|
||
1). Press {MENU}. |
|
|
2). Select "Settings" using {^}or{V} then press {SELECT} or {>}.
3). Enter "7", "2", "6", "2", "7", "6", "6", "4".
Note: 7262 7664 = PANA SONI
(see letters printed on dial keys)
4). Select "Write EEP" using{^} or{V} then press {SELECT} or {>}.
5). Enter " ", " ", " ", " " (Address). (*1)
6). Enter " ", " " (New Data). (*1)
7). Press {OK} , a long confirmation beep
will be heard.
8). Press {OFF} to return to standby mode.
Service Mode
Read EEP
Write EEP
BACK SELECT
Set Addr.:



 Default Data
Default Data
CLEAR OK
Set Addr.:




 New Data
New Data
CLEAR OK
Set Addr.:
_ _ _ _ _ _
BACK
After that, remove and reinsert the batteries. Press the Power button for about 1 second if the power is not turned on.
28
KX-TGE210/KX-TGE212/KX-TGE232/KX-TGE233/KX-TGE234/TGEA20
Frequently Used Items (Handset) ex.)
Items |
Address |
Default Data |
New Data |
Possible Adjusted |
Possible Adjusted |
Remarks |
|
|
|
|
Value MAX (hex) |
Value MIN (hex) |
|
Battery Low |
00 12/00 13 |
00 / 00 |
- |
- |
- |
(*2) |
Frequency |
00 07 / 00 08 |
00 / 01 |
- |
- |
- |
|
ID |
00 02 ~ 00 06 |
Given value |
- |
- |
- |
|
Note:
(*1) When you enter the address or New Data, please refer to the table below.
|
Desired Number (hex.) |
|
Input Keys |
|
|
|
|
||
|
0 |
|
0 |
|
|
1 |
|
1 |
|
|
. |
|
. |
|
|
. |
|
. |
|
|
. |
|
. |
|
|
9 |
|
9 |
|
Desired Number (hex.) |
Input Keys |
A |
[Flash] + 0 |
B |
[Flash] + 1 |
C |
[Flash] + 2 |
D |
[Flash] + 3 |
E |
[Flash] + 4 |
F |
[Flash] + 5 |
(*2) Use these items in a READ-ONLY mode to confirm the contents. Careless rewriting may cause serious damage to the handset.
29
 Loading...
Loading...