Linksys SPA901, SPA941, SPA921, SPA962, SPA922 Manual
...
Linksys 900 Series IP Phone Administrator Guide
Document Version 3.0
Corporate Headquarters
Linksys
121 Theory Drive
Irvine, CA 92617 USA
http://www.linksys.com Tel: 949 823-1200
800 546-5797 Fax: 949 823-1100
Linksys 900 Series IP Phone Administrator Guide
Copyright ©2007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.Specifications are subject to change without notice. Linksys is a registered trademark or trademark of Cisco Systems, Inc. and/or its affiliates in the U.S. and certain other countries. Other brands and product names are trademarks or registered trademarks of their respective holders.
Compliance and Safety Information
This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class B digital device in accordance with the specifications in part 15 of the FCC rules. This product bears the CE Marking indicating compliance with the 89/336/EEC directive. Standards to which conformity is Declared: EN 61000-4-2:1995, EN 61000-4-3:1997, EN 61000-4-4:1995, EN 61000-4-5:1995, EN 61000-4-6:1996, EN 61000-4-8:1994, EN 61000-4-11:1994, EN 61000-3-2:2001, EN 61000-3-3:1995 & EN 55022:1998
Class B Modifications to this product not authorized by Linksys could void FCC approval, thereby terminating end user authority to use this product. For indoor use only. Read installation instructions before connecting to a power source. The electric plug and socket must be accessible at all times as this is the main method to disconnect power from the device.
Shock Hazard: Do not operate near water or similar fluid. Do not work with this device during periods of lightning activity. Do not touch wires at the end of cables or within sockets.
One Year Limited Hardware Warranty
Linksys provides a one (1) year limited hardware warranty. Linksys warrants to customer that this product conforms to its published specifications and will be free from defects in material and workmanship at the time of delivery and for a period of one year thereafter. Without limiting the foregoing, this warranty does not cover any defect resulting from (i) any design or specification supplied by an entity other than Linksys, (ii) non-observance of technical operating parameters (e.g., exceeding limiting values), or (iii) misuse, abuse, abnormal conditions or alteration by anyone other than Linksys. Replacement, Repair, Refund: After the receipt of an RMA (Return Materials Authorization) request, Linksys will attempt to refund, repair or replace this device. To receive an RMA number for this device, contact the party from whom it.

C O N T E N T S
|
|
|
Preface xi |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Document Audience |
xi |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
Linksys 900 Series IP Telephones |
xi |
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
How This Document is Organized |
xii |
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
Document Conventions |
xii |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
Related Documentation |
xiii |
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
Technical Support |
xiii |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Introducing Linksys 900 Series IP Phones |
|
|
|
|
||||||
C H A P T E R |
1 |
1-1 |
|
|
|
|||||||
|
|
|
Overview |
1-1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
SPA900 Series Features |
1-2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
SPA901 Features |
1-4 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
SPA92x, SPA94x, and SPA962 Features |
1-4 |
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
Ensuring Voice Quality |
1-4 |
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
Feature Descriptions |
1-6 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
SIP Proxy Redundancy |
1-6 |
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
Supported Codecs |
1-6 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
Other Features |
1-7 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
Technology Background |
1-10 |
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
Session Initiation Protocol |
1-10 |
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
Using 900 Series Phones with a Firewall or Router 1-11 |
|||||||||
|
|
|
Network Address Translation 1-11 |
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
NAT Overview |
1-12 |
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
NAT Types |
1-12 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
Simple Traversal of UDP Through NAT 1-13 |
|||||||||
|
|
|
SIP-NAT Interoperation |
1-13 |
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
Where to Go From Here |
1-14 |
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
Getting Started |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
C H A P T E R |
2 |
2-1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
Linksys 900 Series IP Phones |
2-1 |
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
Caring for Your Hardware |
2-2 |
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
SPA901 |
2-2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Linksys 900 Series IP Phone Administrator Guide |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
Document Version 3.0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
iii |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Contents |
|
|
|
|
Front Panel and Side of Phone 2-2 |
||
|
|
Back Panel |
2-3 |
|
|
|
SPA92x, SPA94x, and SPA962 Hardware Features 2-3 |
||
|
|
SPA921 |
2-4 |
|
|
|
Front Panel |
2-4 |
|
|
|
Back Panel |
2-5 |
|
|
|
SPA922 |
2-5 |
|
|
|
SPA941 |
2-5 |
|
|
|
Front Panel |
2-6 |
|
|
|
Back Panel |
2-6 |
|
|
|
SPA942 |
2-7 |
|
|
|
SPA962 |
2-7 |
|
|
|
Front Panel |
2-8 |
|
|
|
Back Panel |
2-8 |
|
Establishing Connectivity |
2-8 |
|
|
|
Bandwidth Requirements |
2-8 |
|
||
Installing the SPA900 Series IP Phone 2-9 |
||||
Assembling the Phone and Connecting to the Network 2-9 |
||||
Attaching the Desk Stand |
2-10 |
|
||
Mounting the Phone to the Wall |
2-10 |
|||
Turning on the Phone |
2-11 |
|
|
|
Using the Administration Web Server |
2-11 |
|||
Connecting to the Administration Web Server 2-11 |
||||
Administrator Account Privileges |
2-12 |
|||
Web Interface URLs 2-13 |
|
|
|
|
Upgrade URL |
2-13 |
|
|
|
Resync URL |
2-13 |
|
|
|
Reboot URL |
2-14 |
|
|
|
Provisioning 2-14 |
|
|
|
|
Provisioning Capabilities 2-14 |
||||
Configuration Profile |
2-14 |
|
||
Using the Interactive Voice Response Interface 2-15 |
||||
Using the IVR Menu |
2-15 |
|
|
|
IVR Options |
2-16 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Entering a Password through the IVR |
2-18 |
|
|
|
Managing Linksys 900 Series IP Phones |
|
|
|||
C H A P T E R 3 |
|
3-1 |
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
Using the LCD Display 3-1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
LCD Display Controls 3-1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Linksys 900 Series IP Phone Administrator Guide |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
iv |
|
|
|
|
Document Version 3.0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Contents |
|
|
|
Using Soft Keys |
3-3 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
Entering and Saving Settings |
3-4 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
Localization 3-5 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Changing the Display Background (SPA962) |
3-7 |
|
|
|
|
|||||||
|
Call Appearances and Extensions |
3-8 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
Line Key LEDs |
3-9 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Using Call Features |
3-10 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
Selecting the Audio I/O Device and Line |
3-11 |
|
|
|
|
|||||||
|
Making Calls |
3-11 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Answering and Ending Calls |
3-12 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
Hold and Resume |
3-12 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
Call Waiting 3-12 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
Speed Dialing |
3-13 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
Three-Way Conferencing |
|
3-13 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
Attended Call Transfer |
3-13 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
Blind Call Transfer |
3-14 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
Call Back |
3-14 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Message Waiting Indication (MWI) |
3-14 |
|
|
|
|
|||||||
|
Accessing Voicemail |
3-15 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
Muting Calls |
3-15 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Shared Call Appearances |
3-15 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
Personal Directory |
3-15 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
Caller and Called Name Matching |
3-16 |
|
|
|
|
|||||||
|
Dialing Assistance |
3-16 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
Supplementary Services |
3-16 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
Call Logs |
3-17 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Audio Volume Adjustment |
3-18 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
Managing Ring Tones |
3-19 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
Configuring a Dial Plan |
3-20 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
Dial Plan Digit Sequences |
3-20 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
Dial Plan Rules |
3-21 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
Digit Sequence Syntax |
3-21 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
Element Repetition |
3-21 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
Sub-sequence Substitution |
3-21 |
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
Intersequence Tones |
3-22 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
Number Barring |
3-22 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
Interdigit Timer Master Override |
|
3-22 |
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
Local Timer Overrides |
3-22 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
Pause |
3-22 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Linksys 900 Series IP Phone Administrator Guide |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
Document Version 3.0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
v |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Contents |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Dial Plan Examples |
3-23 |
|
|
|||
|
|
|
Dial Plan Timers |
3-23 |
|
|
|||
|
|
|
Interdigit Long Timer |
3-24 |
|
||||
|
|
|
Interdigit Short Timer |
3-24 |
|
||||
|
|
|
Dial Plans |
3-24 |
|
|
|||
|
|
|
System Administration |
3-24 |
|
|
|||
|
|
|
Reboot and Restart |
3-25 |
|
|
|||
|
|
|
Factory Reset |
|
3-25 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Password Protection |
3-25 |
|
||||
|
|
|
Managing the Time/Date |
3-25 |
|
||||
|
|
|
Daylight Saving Time |
3-25 |
|
||||
|
|
|
Using Star Codes to Activate/Deactivate Services |
3-26 |
|||||
|
|
|
Disabling Services |
3-28 |
|
|
|||
|
|
|
Error and Log Reporting |
3-29 |
|
||||
|
|
|
Troubleshooting FAQ |
3-29 |
|
|
|||
|
|
LCD Command Reference Guide |
|
|
|||||
|
C H A P T E R 4 |
4-1 |
|
||||||
|
|
|
1 Directory |
4-2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Entering Names and Numbers into the Directory |
4-2 |
|||||
|
|
|
Entering Directory Names, Numbers and Ring Default 4-2 |
||||||
|
|
|
2 Speed Dial |
4-3 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
3 Call History |
4-3 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Redial List |
4-3 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Answered Calls |
4-4 |
|
|
|||
|
|
|
Missed Calls |
4-4 |
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
4 Ring Tone |
4-4 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
5 Preferences |
4-4 |
|
|
|
|
|
5.1 |
Block Caller ID |
4-5 |
|
5.2 |
Block Anonymous Call |
4-5 |
|
5.3 |
Do Not Disturb |
4-5 |
|
5.4 |
Secure Call 4-5 |
|
|
5.5 |
Dial Assistance |
4-6 |
|
5.6 |
Preferred Audio Device |
4-6 |
|
6 |
Call Forward |
4-6 |
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
6.1 CFWD All Number |
4-6 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
6.2 CFWD Busy Number |
4-6 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
6.3 CFWD No Ans Number 4-7 |
|||
|
|
|
|
6.4 CFWD No Ans Delay |
4-7 |
|
|
7 |
Time/Date |
4-7 |
|
|
|||
|
|
|
Linksys 900 Series IP Phone Administrator Guide |
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
vi |
|
|
|
|
Document Version 3.0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Contents |
|
|
|
|
8 Voice Mail |
4-7 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
9 Network |
4-8 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
9.1 DCHP |
|
4-8 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
9.2 Current IP Address |
4-8 |
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
9.3 Host Name |
4-9 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
9.4 Domain |
4-9 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
9.5 Current NetMask |
|
4-9 |
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
9.6 Current Gateway |
|
4-9 |
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
9.7 Enable Web Server |
4-9 |
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
9.8 Non DHCP IP Address 4-10 |
|
|||||||||||
|
|
|
9.9 Non DHCP Subnet Mask |
4-10 |
|
|
|
|
|||||||
|
|
|
9.10 Non DHCP Default Route |
4-10 |
|
|
|
|
|||||||
|
|
|
9.11 Non DHCP DNS 1 |
4-10 |
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
9.12 Non DHCP DNS 2 |
4-10 |
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
9.13 Non DHCP NTP Server 1 |
4-10 |
|
|
|
|
|||||||
|
|
|
9.14 Non DHCP NTP Server 2 |
4-11 |
|
|
|
|
|||||||
|
|
10 |
Product Info |
4-11 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
10.1 Product Name |
4-11 |
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
10.2 Serial Number |
4-11 |
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
10.3 Software Version |
4-11 |
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
10.4 Hardware Version |
4-12 |
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
10.5 MAC Address |
4-12 |
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
10.6 Client Cert |
4-12 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
11 |
Status |
4-12 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Phone |
4-12 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
Ext 1/2/3/4 |
4-13 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
Line 1, 2,3,4 |
|
4-13 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
12 |
Reboot |
4-13 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
13 |
Restart |
4-13 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
14 |
Factory Reset |
|
4-13 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
15 |
Set Password |
|
4-14 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
16 |
Set LCD Contrast |
4-14 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
17 |
CallPark Status |
|
4-14 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
18 |
Language (SPA922, 942, and 962) |
4-14 |
|
|
|
|
|||||||
|
SPA900 Series Phone Field Reference |
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
C H A P T E R 5 |
4-1 |
|
|
|
|
||||||||||
|
|
Info Tab 4-2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
System Information |
4-2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Linksys 900 Series IP Phone Administrator Guide |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
Document Version 3.0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
vii |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Contents |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
Product Information |
4-2 |
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
Phone Status 4-3 |
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
Ext 1/2/3/4/5/6 Status |
4-4 |
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
Line 1/2/3/4/5/6 Status |
4-4 |
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
Downloaded Ring Tone |
4-5 |
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
System Tab |
4-6 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
System Configuration |
4-6 |
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
Internet Connection Type |
4-6 |
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
Static IP Settings |
4-7 |
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
PPPoE Settings |
4-7 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Optional Network Configuration |
4-7 |
|
||||
|
|
|
|
VLAN Settings |
4-8 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
SIP Tab 4-9 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
SIP Parameters |
4-9 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
SIP Timer Values (sec) |
|
4-11 |
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
Response Status Code Handling |
4-12 |
|
||||
|
|
|
|
RTP Parameters |
4-13 |
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
SDP Payload Types |
4-14 |
|
|
|||
4-17 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
NAT Support Parameters |
4-17 |
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
Linksys Key System Parameters |
4-18 |
|
||||
|
|
|
|
Regional Tab |
4-19 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Call Progress Tones |
4-19 |
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
Distinctive Ring Patterns |
4-21 |
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
Control Timer Values (sec) 4-22 |
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
Vertical Service Activation Codes |
4-22 |
|
||||
|
|
|
|
Outbound Call Codec Selection Codes 4-27 |
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
Miscellaneous |
4-29 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Phone Tab |
4-33 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
General |
4-33 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Line Key 1/2/3/4/5/6 |
4-33 |
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
Miscellaneous Line Key Settings |
4-34 |
|
||||
|
|
|
|
Line Key LED Pattern |
4-34 |
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
Supplementary Services |
4-35 |
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
Ring Tone 4-36 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Auto Input Gain (dB) |
4-37 |
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
Background Picture (SPA 962) 4-37 |
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
Ext 1/2/3/4/5/6 Tab |
4-38 |
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
General |
4-38 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Linksys 900 Series IP Phone Administrator Guide |
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
viii |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Document Version 3.0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||

Contents
Share Line Appearance |
4-38 |
|||
NAT Settings |
4-39 |
|
|
|
Network Settings 4-39 |
|
|||
SIP Settings |
4-40 |
|
|
|
Call Feature Settings |
4-42 |
|||
Proxy and Registration |
|
4-43 |
||
Subscriber Information |
|
4-44 |
||
Audio Configuration |
4-46 |
|||
Dial Plan 4-47 |
|
|
||
User |
4-49 |
|
|
|
Call Forward |
4-49 |
|
|
|
Speed Dial |
4-50 |
|
|
|
Supplementary Services |
4-50 |
|||
Audio Volume |
4-51 |
|
|
|
Phone GUI Menu Color Settings (SPA962) 4-51
A P P E N D I X |
A |
Acronyms |
|
|
Glossary |
A P P E N D I X |
B |
|
|
|
|
I N D E X |
|
|
|
|
Linksys 900 Series IP Phone Administrator Guide |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
Document Version 3.0 |
|
|
ix |
|
|
|
|
|

Contents
|
Linksys 900 Series IP Phone Administrator Guide |
x |
Document Version 3.0 |

Preface
This guide describes administration and use of the Linksys SPA900 Series IP phones. It contains the following sections:
•Document Audience, page xi
•Linksys 900 Series IP Telephones, page xi
•How This Document is Organized, page xii
•Document Conventions, page xii
•Related Documentation, page xiii
•Technical Support, page xiii
Document Audience
This document is written for the following audience:
•Service providers offering services using LVS products
•VARs and resellers who need LVS configuration references
•System administrators or anyone who performs LVS installation and administration
Note This guide does not provide the configuration information required by specific service providers. Please consult with the service provider for specific service parameters.
Linksys 900 Series IP Telephones
The following summarizes the ports and features provided by the Linksys 900 Series IP phones described in this document.
•SPA901—One line, small, affordable, no display.
•SPA921—One-line business phone.
•SPA922—One-line business phone with Power over Ethernet (PoE) support and an extra Ethernet port for connecting another device to the LAN.
|
|
Linksys 900 Series IP Phone Administrator Guide |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
Document Version 3.0 |
|
|
xi |
|
|
|
|
|

Preface
How This Document is Organized
•SPA941—Default two lines, upgradeable to four lines.
•SPA942—Default is two lines, upgradeable to four lines. Power over Ethernet (PoE) support and an extra Ethernet port for connecting another device to the LAN.
•SPA962—Six lines, hi-res color display. Power over Ethernet (PoE) support and an extra Ethernet port for connecting another device to the LAN.
Note PoE units (SPA922, SPA942, and SPA962) do not come with an external power adapter. The PA100 power supply must be ordered separately if you are not using a PoE switch.
How This Document is Organized
This document is divided into the following chapters and appendices.
Chapter |
Contents |
|
|
Chapter 1, “Introducing |
This chapter introduces the Linksys 900 Series IP phones. |
Linksys 900 Series IP Phones” |
|
|
|
Chapter 2, “Getting Started” |
This chapter describes how to use the different administration and |
|
configuration tools provided for managing a Linksys 900 Series IP |
|
phone. |
|
|
Chapter 3, “Managing Linksys |
This chapter describes how to configure and monitor a Linksys 900 |
900 Series IP Phones” |
Series IP phone. |
|
|
Chapter 5, “SPA900 Series |
This chapter lists the function and usage for each field or parameter |
Phone Field Reference” |
on the Linksys 900 Series IP phone administration web server |
|
pages. |
|
|
Appendix A, “Acronyms” |
This appendix provides the expansion of acronyms used in this |
|
document. |
|
|
Appendix B, “Glossary” |
This appendix defines the terms used in this document. |
|
|
Document Conventions
The following are the typographic conventions used in this document.
Typographic Element |
Meaning |
|
|
Boldface |
Indicates an option on a menu or a literal value to be entered in a field. |
|
|
<parameter> |
Angle brackets (<>) are used to identify parameters that appear on the |
|
configuration pages of the 900 Series phone administration web server. The |
|
index at the end of this document contains an alphabetical listing of each |
|
parameter, hyperlinked to the appropriate table in Chapter 5, “SPA900 |
|
Series Phone Field Reference” |
|
|
Italic |
Indicates a variable that should be replaced with a literal value. |
|
|
Monospaced Font |
Indicates code samples or system output. |
|
|
|
Linksys 900 Series IP Phone Administrator Guide |
xii |
Document Version 3.0 |

Preface
Related Documentation
Related Documentation
The following documentation provides additional information about features and functionality of Linksys 900 Series IP phones:
•AA Quick Guide
•IVR Quick Guide
•SPA Provisioning Guide
The following documentation describes how to use other Linksys Voice System products:
•SPA9000 Administrator Guide
•LVS CTI Integration Guide
•LVS Integration with ITSP Hosted Voicemail Guide
•SPA900 Series IP Phones Administrator Guide
•Linksys Voice over IP Product Guide: SIP CPE for Massive Scale Deployment
•SPA 2.0 Analog Telephone Adapter Administrator Guide
Technical Support
If you are an end user of LVS products and need technical support, contact the reseller or Internet telephony service provider (ITSP) that supplied the equipment.
Technical support contact information for authorized Linksys Voice System partners is as follows:
•LVS Phone Support (requires an authorized partner PIN) 888 333-0244 Hours: 4am-6pm PST, 7 days a week
•E-mail support voipsupport@linksys.com
|
|
Linksys 900 Series IP Phone Administrator Guide |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
Document Version 3.0 |
|
|
xiii |
|
|
|
|
|

Preface
Technical Support
|
Linksys 900 Series IP Phone Administrator Guide |
xiv |
Document Version 3.0 |

C H A P T E R 1
Introducing Linksys 900 Series IP Phones
This guide describes the administration and use of Linksys analog telephone adapters (ATAs). This chapter introduces the functionality of the Linksys 900 Series IP phones and includes the following sections:
•Overview, page 1-2
•Feature Descriptions, page 1-8
•Technology Background, page 1-12
•Where to Go From Here, page 1-16
Overview
Table 1-1 summarizes the ports and features provided by the Linksys 900 Series IP phones described in this document.
Table 1-1 Linksys SPA900 Series IP Phones
|
|
Ethernet |
|
|
|
(LAN) |
|
Product Name |
RJ-45 |
Voice Lines |
Additional Features/Notes |
|
|
|
|
SPA901 |
One (1) |
One (1) |
Small, affordable, no display |
|
|
|
|
SPA921 |
One (1) |
One (1) |
One-line business phone |
|
|
|
|
SPA922 |
Two (2) |
One (1) |
Power over Ethernet (PoE) support |
|
|
|
|
SPA941 |
One (1) |
Four (4) |
Default is 2-lines active, upgradeable |
|
|
|
|
SPA942 |
Two (2) |
Four (4) |
Default is 2-lines active, upgradeable. Power |
|
|
|
over Ethernet (PoE) support |
|
|
|
|
SPA962 |
Two (2) |
Six (6) |
Six lines, hi-res color display |
|
|
|
|
Note PoE units (SPA922, SPA942, and SPA962) do not come with an external power adapter. The PA100 power supply must be ordered separately if you are not using a PoE switch.
|
|
Linksys 900 Series IP Phone Administrator Guide |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
Document Version 3.0 |
|
|
1-1 |
|
|
|
|
|

Chapter 1 Introducing Linksys 900 Series IP Phones
SPA900 Series Features
Figure 1-1 illustrates how the IP phones are connected in a VoIP network, including the SPA3102, which acts as a SIP-PSTN gateway. As shown, the RTP400 and WRTP54G provide QoS-enabled IP routers in addition to two ports for connecting analog telephone devices.
Figure 1-1 Linksys SPA900 Series IP Phones in a VoIP Network
PSTN
Up to 4 FXO lines Local voicemail
SPA400
SIP-PSTN gateway
Switch
ISP Internet
SPA901, 921, 922, 941, 942, 962 |
ITSP |
SPA9000
IP PBX
FXS1
FXS2
Fax/Analog
Phones
SPA900 Series Features
The following telephony features are provided by the different models of the SPA900 Series IP phones:
•Shared Line Appearance **
–SPA901: Two Call Appearances Accessed Via Flash Key or Hook-Flash
–SPA921 and SPA922: Two call appearances
–SPA941 and SPA942: Four call appearances
–SPA962: Six call appearances
•Line Status Indicators
•Call Hold
•Music on Hold **
•Call Waiting
•Outbound Caller ID Blocking
•Call Transfer - Attended and Blind
|
Linksys 900 Series IP Phone Administrator Guide |
1-2 |
Document Version 3.0 |

Chapter 1 Introducing Linksys 900 Series IP Phones
SPA900 Series Features
•Call Conferencing
•Call Pick Up - Selective and Group **
•Call Park and UnPark **
•Call Swap
•Call Back on Busy
•Call Blocking - Anonymous and Selective
•Call Forwarding - Unconditional, No Answer, On Busy
•Hot Line and Warm Line Automatic Calling
•Call Logs (60 entries each): Made, Answered, and Missed Calls
•Do Not Disturb (callers hear line busy tone)
•URI (IP) Dialing Support (Vanity Numbers)
•Date and Time with Intelligent Daylight Savings Support
•Call Duration and Start Time Stored in Call Logs
•Ten-User Downloadable Ring Tones - Ring Tone Generator Free from www.linksys.com
•Speed Dialing
•Automatic Redial
•Configurable Dial/Numbering Plan Support - per Line
•Intercom **
•Group Paging **
•DNS SRV and Multiple A Records for Proxy Lookup and Proxy Redundancy
•Syslog, Debug, Report Generation, and Event Logging
•Secure Call Encrypted Voice Communication Support
•Built-in Web Server for Administration and Configuration with Multiple Security Levels
•Automated Provisioning, Multiple Methods. Up to 256-Bit Encryption: (HTTP, HTTPS, TFTP)
•Optionally Require Admin Password to Reset Unit to Factory Defaults
•NAT Traversal
•Set Preferred CODEC, Per Call, All Calls
•Call Return - Redial Last Caller
•Configurable Dial/Numbering Plan Support
•Support Linksys Voice System Automatic Configuration
** Feature requires support by SIP server
SPA901 Features
The SPA901 provides the following features that are not needed with the SPA900 Series IP phones that provide an LCD display:
• Built-in Interactive Voice Response (IVR) system to check status and change configuration
|
|
Linksys 900 Series IP Phone Administrator Guide |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
Document Version 3.0 |
|
|
1-3 |
|
|
|
|
|
||

Chapter 1 Introducing Linksys 900 Series IP Phones
SPA900 Series Features
•Ringer and Handset Volume Controls
•Handset Input Gain Adjustment
SPA92x, SPA94x, and SPA962 Features
The SPA921, SPA922, SPA941, SPA942, and SPA962 provide an LCD display and additional features that are not provided with the SPA901, including the following:
•Line Status Indicators: Active Line, Name, and Number
•Menu-Driven User Interface
•Digits Dialed with Number Auto-Completion
•Caller ID Name and Number and Outbound Caller ID Blocking
•On-Hook Dialing
•Redial from Call Logs
•Personal Directory with Auto-dial (100 entries)
•On Hook Default Audio Configuration (Speakerphone and Headset)
•Called Number with Directory Name Matching
•Call Number using Name - Directory Matching or via Caller ID
•Subsequent Incoming Calls with Calling Name and Number
•Name and Identity (Text) Displayed at Start Up
•Distinctive Ringing Based on Calling and Called Number
Ensuring Voice Quality
Voice quality perceived by the subscribers of the IP Telephony service should be indistinguishable from that of the PSTN. Voice quality can be measured with such methods as Perceptual Speech Quality Measurement (PSQM), with a scale of 1–5, in which lower is better; and Mean Opinion Score (MOS), with a scale of 1–5, in which higher is better.
Table 1-2 displays speech quality metrics associated with various audio compression algorithms.
Table 1-2 Speech Quality Metrics
Algorithm |
Bandwidth |
Complexity |
MOS Score |
|
|
|
|
G.711 |
64 kbps |
Very low |
4.5 |
|
|
|
|
G.726 |
16, 24, 32, 40 kbps |
Low |
4.1 (32 kbps) |
|
|
|
|
G.729a |
8 kbps |
Low–medium |
4 |
|
|
|
|
G.729 |
8 kbps |
Medium |
4 |
|
|
|
|
G.723.1 |
6.3, 5.3 kbps |
High |
3.8 |
|
|
|
|
|
Linksys 900 Series IP Phone Administrator Guide |
1-4 |
Document Version 3.0 |

Chapter 1 Introducing Linksys 900 Series IP Phones
SPA900 Series Features
Note SPA900 Series IP phones support all the above voice coding algorithms.
The following factors contribute to voice quality:
•Audio compression algorithm—Speech signals are sampled, quantized, and compressed before they are packetized and transmitted to the other end. For IP Telephony, speech signals are usually sampled at 8000 samples per second with 12–16 bits per sample. The compression algorithm plays a large role in determining the voice quality of the reconstructed speech signal at the other end. SPA900 Series IP phones support the most popular audio compression algorithms for IP Telephony: G.711 a-law and µ-law, G.726, G.729a, and G.723.1.
The encoder and decoder pair in a compression algorithm is known as a codec. The compression ratio of a codec is expressed in terms of the bit rate of the compressed speech. The lower the bit rate, the smaller the bandwidth required to transmit the audio packets. Although voice quality is usually lower with a lower bit rate, it is usually higher as the complexity of the codec gets higher at the same bit rate.
•Silence suppression—SPA900 Series IP phones apply silence suppression so that silence packets are not sent to the other end to conserve more transmission bandwidth. Instead, a noise level measurement can be sent periodically during silence suppressed intervals so that the other end can generate artificial comfort noise that mimics the noise at the other end (using a CNG or comfort noise generator).
•Packet loss—Audio packets are transported by UDP, which does not guarantee the delivery of the packets. Packets may be lost or contain errors that can lead to audio sample drop-outs and distortions and lower the perceived voice quality. SPA900 Series IP phones apply an error concealment algorithm to alleviate the effect of packet loss.
•Network jitter—The IP network can induce varying delay of received packets. The RTP receiver in SPA900 Series IP phones keeps a reserve of samples to absorb the network jitter, instead of playing out all the samples as soon as they arrive. This reserve is known as a jitter buffer. The bigger the jitter buffer, the more jitter it can absorb, but this also introduces bigger delay. Therefore, the jitter buffer size should be kept to a relatively small size whenever possible. If jitter buffer size is too small, many late packets may be considered as lost and thus lowers the voice quality. SPA900 Series IP phones dynamically adjust the size of the jitter buffer according to the network conditions that exist during a call.
•Echo—Impedance mismatch between the telephone and the IP Telephony gateway phone port can lead to near-end echo. SPA900 Series IP phones have a near-end echo canceller with at least 8 ms tail length to compensate for impedance match. SPA900 Series IP phones implement an echo suppressor with comfort noise generator (CNG) so that any residual echo is not noticeable.
•Hardware noise—Certain levels of noise can be coupled into the conversational audio signals because of the hardware design. The source can be ambient noise or 60 Hz noise from the power adaptor. The SPA900 Series hardware design minimizes noise coupling.
•End-to-end delay—End-to-end delay does not affect voice quality directly but is an important factor in determining whether subscribers can interact normally in a conversation taking place over an IP network. A reasonable delay figure should be about 50–100 ms. End-to-end delay larger than
300 ms is unacceptable to most callers. SPA900 Series IP phones support end-to-end delays well within acceptable thresholds.
|
|
Linksys 900 Series IP Phone Administrator Guide |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
Document Version 3.0 |
|
|
1-5 |
|
|
|
|
|
||

Chapter 1 Introducing Linksys 900 Series IP Phones
Feature Descriptions
Feature Descriptions
SPA900 Series IP phones are full featured, fully programmable IP phones that can be custom provisioned within a wide range of configuration parameters. This chapter contains a high-level overview of features to provide a basic understanding of the feature breadth and capabilities of SPA900 Series IP phones.
•SIP Proxy Redundancy, page 1-8
•Supported Codecs, page 1-8
•Other Features, page 1-9
SIP Proxy Redundancy
In typical commercial IP Telephony deployments, all calls are established through a SIP proxy server. An average SIP proxy server may handle tens of thousands of subscribers. It is important that a backup server be available so that an active server can be temporarily switched out for maintenance. SPA900 Series IP phones support the use of backup SIP proxy servers so that service disruption should be nearly eliminated.
A simple way to support proxy redundancy is to configure a static list of SIP proxy servers in the SPA900 Series IP phone configuration profile, where the list is arranged in order of priority. The SPA900 Series IP phone attempts to contact the highest priority proxy server whenever possible.
The dynamic nature of SIP message routing makes the use of a static list of proxy servers inadequate in some scenarios. In deployments where user agents are served by different domains, for instance, it would not be feasible to configure one static list of proxy servers per covered domain into every SPA900 Series IP phone. One solution to this situation is through the use of DNS SRV records. SPA900 Series IP phones can be instructed to contact a SIP proxy server in a domain named in SIP messages. The SPA900 Series IP phone consults the DNS server to get a list of hosts in the given domain that provides SIP services. If an entry exists, the DNS server returns an SRV record that contains a list of SIP proxy servers for the domain, with their host names, priority, listening ports, and so on. The SPA900 Series IP phone tries to contact the list of hosts in the order of their stated priority.
If the SPA900 Series IP phone is currently using a lower priority proxy server, it periodically probes the higher priority proxy to see whether it is back on line, and attempts to switch back to the higher priority proxy whenever possible.
Supported Codecs
Negotiation of the optimal voice codec sometimes depends on the ability of SPA900 Series IP phone to “match” a codec name with the far-end device/gateway codec name. SPA900 Series IP phones allow the network administrator to individually name the various codecs that are supported such that the correct codec successfully negotiates with the far-end equipment.
|
Linksys 900 Series IP Phone Administrator Guide |
1-6 |
Document Version 3.0 |

Chapter 1 Introducing Linksys 900 Series IP Phones
Feature Descriptions
The administrator can select the low-bit-rate codec used for each line. G.711a and G.711u are always enabled. Table 1-3 describes the codecs supported by the Linksys SPA900 Series IP phones.
Table 1-3 Codecs Supported by Linksys SPA900 Series IP Phones
Codec (Voice Compression |
|
Algorithm) |
Description |
|
|
G.711 (A-law and mµ-law) |
This very low complexity codec supports uncompressed 64 |
|
kbps digitized voice transmission at one through ten 5 ms |
|
voice frames per packet. This codec provides the highest |
|
voice quality and uses the most bandwidth of any of the |
|
available codecs. |
|
|
G.726 |
This low complexity codec supports compressed 16, 24, 32, |
|
and 40 kbps digitized voice transmission at one through ten |
|
10 ms voice frames per packet. This codec provides high |
|
voice quality. |
|
|
G.729A |
The ITU G.729 voice coding algorithm is used to compress |
|
digitized speech. Linksys supports G.729. G.729A is a |
|
reduced complexity version of G.729. It requires about half |
|
the processing power to code G.729. The G.729 and G.729A |
|
bit streams are compatible and interoperable, but not |
|
identical. |
|
|
G.723.1 |
SPA900 Series IP phones support the use of ITU G.723.1 |
|
audio codec at 6.4 kbps. Up to two channels of G.723.1 can be |
|
used simultaneously. For example, Line 1 and Line 2 can be |
|
using G.723.1 simultaneously, or Line 1 or Line 2 can initiate |
|
a three-way conference with both call legs using G.723.1. |
|
|
When no static payload value is assigned per RFC 1890, SPA900 Series IP phones can support dynamic payloads for G.726.
|
|
Linksys 900 Series IP Phone Administrator Guide |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
Document Version 3.0 |
|
|
1-7 |
|
|
|
|
|
||

Chapter 1 Introducing Linksys 900 Series IP Phones
Feature Descriptions
Other Features
Table 1-4 summarizes the features provided by SPA900 Series IP Phones.
Table 1-4 Linksys ATA Features
Feature |
Description |
|
|
Music On Hold |
On a connected call, SPA900 Series IP phones may place the remote |
|
party on call. If the remote party indicates that they can still receive |
|
audio while the call is holding, the MOH server sends streaming |
|
audio. |
|
|
Secure Calls |
A user (if enabled by service provider or administrator) has the option |
|
to make an outbound call secure in the sense that the audio packets in |
|
both directions are encrypted. |
|
|
Adjustable Audio |
This feature allows the user to set the number of audio frames |
Frames Per Packet |
contained in one RTP packet. Packets can be adjusted to contain from |
|
1–10 audio frames. Increasing the number of packets decreases the |
|
bandwidth utilized, but it also increases delay and may affect voice |
|
quality. |
|
|
DTMF |
In-Band and Out-of-Band (RFC 2833) (SIP INFO *) SPA900 Series |
|
IP phones may relay DTMF digits as out-of-band events to preserve |
|
the fidelity of the digits. This can enhance the reliability of DTMF |
|
transmission required by many IVR applications such as dial-up |
|
banking and airline information. |
|
|
Call Progress Tone |
SPA900 Series IP phones have configurable call progress tones. |
Generation |
Parameters for each type of tone may include number of frequency |
|
components, frequency and amplitude of each component, and |
|
cadence information. |
|
|
Call Progress Tone |
This feature allows the user to hear the call progress tones (such as |
Pass Through |
ringing) that are generated from the far-end network. |
|
|
Jitter |
SPA900 Series IP phones can buffer incoming voice packets to |
Buffer—Dynamic |
minimize out-of-order packet arrival. This process is known as jitter |
(Adaptive) |
buffering. The jitter buffer size proactively adjusts or adapts in size, |
|
depending on changing network conditions. |
|
SPA900 Series IP phones have a Network Jitter Level control setting |
|
for each line of service. The jitter level decides how aggressively |
|
SPA900 Series IP phones try to shrink the jitter buffer over time to |
|
achieve a lower overall delay. If the jitter level is higher, it shrinks |
|
more gradually. If jitter level is lower, it shrinks more quickly. |
|
|
|
Linksys 900 Series IP Phone Administrator Guide |
1-8 |
Document Version 3.0 |

Chapter 1 Introducing Linksys 900 Series IP Phones
|
|
Feature Descriptions |
|
|
|
Table 1-4 Linksys ATA Features (continued) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Feature |
Description |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Voice Activity |
Voice Activity Detection (VAD) with Silence Suppression is a means |
|
|
|
Detection with |
of increasing the number of calls supported by the network by |
|
|
|
Silence Suppression |
reducing the required bidirectional bandwidth for a single call. VAD |
|
|
|
and Comfort Noise |
uses a very sophisticated algorithm to distinguish between speech and |
|
|
|
Generation |
non-speech signals. Based on the current and past statistics, the VAD |
|
|
|
|
algorithm decides whether or not speech is present. If the VAD |
|
|
|
|
algorithm decides speech is not present, the silence suppression and |
|
|
|
|
comfort noise generation is activated. This is accomplished by |
|
|
|
|
removing and not transmitting the natural silence that occurs in |
|
|
|
|
normal two-way connection. The IP bandwidth is used only when |
|
|
|
|
someone is speaking. During the silent periods of a telephone call, |
|
|
|
|
additional bandwidth is available for other voice calls or data traffic |
|
|
|
|
because the silence packets are not being transmitted across the |
|
|
|
|
network. Comfort Noise Generation provides artificially-generated |
|
|
|
|
background white noise (sounds), designed to reassure callers that |
|
|
|
|
their calls are still connected during silent periods. If Comfort Noise |
|
|
|
|
Generation is not used, the caller may think the call has been |
|
|
|
|
disconnected because of the “dead silence” periods created by the |
|
|
|
|
VAD and Silence Suppression feature. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Configurable Dial |
SPA900 Series IP phones have three configurable interdigit timers: |
|
|
|
Plan with Interdigit |
• Initial timeout (T)—Handset off hook; no digit pressed yet. |
|
|
|
Timers |
|
|
|
|
• Long timeout (L)—One or more digits pressed, more digits needed to |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
reach a valid number (as per the dial plan). |
|
|
|
|
• Short timeout (S)—Current dialed number is valid, but more digits |
|
|
|
|
would also lead to a valid number. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Report Generation |
SPA900 Series IP phones report a variety of status and error reports |
|
|
|
and Event Logging |
to assist service providers in diagnosing problems and evaluating the |
|
|
|
|
performance of their services. The information can be queried by an |
|
|
|
|
authorized agent, using HTTP with digested authentication, for |
|
|
|
|
instance. The information may be organized as an XML page or |
|
|
|
|
HTML page. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Syslog and Debug |
SPA900 Series IP phones support detailed logging of all activities for |
|
|
|
Server Records |
further debugging. The debug information may be sent to a |
|
|
|
|
configured Syslog server. SPA900 Series IP phones provide |
|
|
|
|
configuration settings that determine the type of activity/events that |
|
|
|
|
should be logged, as for instance, a debug level setting. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Dynamic Payload |
When no static payload value is assigned per RFC 1890, SPA900 |
|
|
|
|
Series IP phones can support dynamic payloads for G.726. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Call Statistics and |
The statistics collected by SPA900 Series IP phones during normal |
|
|
|
Reporting |
operation statistics are available in the Info tab. Line status is reported |
|
|
|
|
for each line (1 and 2). Each line maintains up to 2 calls: Call 1 and 2. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Linksys 900 Series IP Phone Administrator Guide |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
Document Version 3.0 |
|
|
1-9 |
|
|
|
|
|
||
Chapter 1 Introducing Linksys 900 Series IP Phones
Technology Background
Technology Background
This section provides background information about the technology and protocols used by the ATA. It includes the following topics:
•Session Initiation Protocol, page 1-12
•Using 900 Series Phones with a Firewall or Router, page 1-12
•Using 900 Series Phones with a Firewall or Router, page 1-12
Session Initiation Protocol
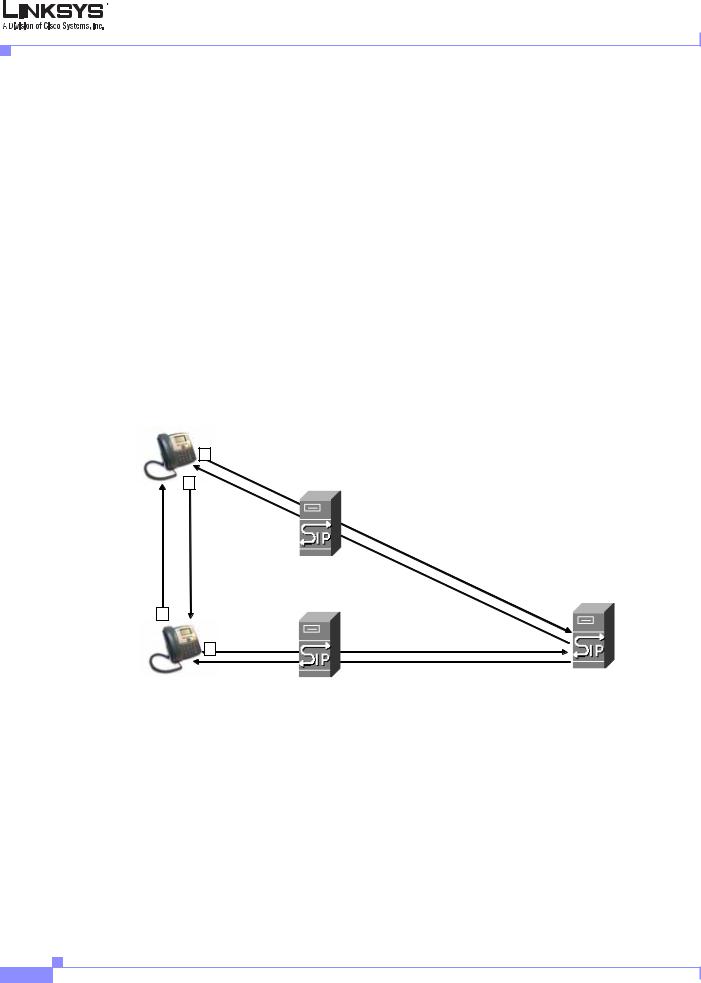
Linksys 900 Series IP phones are implemented using open standards, such as Session Initiation Protocol (SIP), allowing interoperation with all ITSPs supporting SIP. Figure 1-2 illustrates a SIP request for connection to another subscriber in the network. The requestor is called the user agent server (UAS), while the recipient is called the user agent client (UAC).
Figure 1-2 SIP Requests and Responses
SIP UA
2
4
SIP Proxy
RTP
SIP Proxy
3
SIP Proxy
1
SIP UA
In a SIP VoIP network, when the SIP proxy receives a request from a UAS for a connection and it does not know the location of the UAC, it forwards the message to another SIP proxy in the network. Once the UAC is located and the response is routed back to the UAS, a direct peer-to-peer session is established between the two UAs. The actual voice traffic is transmitted between UAs over dynamically assigned ports using the Real-time Protocol (RTP).
Using 900 Series Phones with a Firewall or Router
When using a 900 Series phone behind a firewall or router, make sure that the following ports are not blocked:
|
Linksys 900 Series IP Phone Administrator Guide |
1-10 |
Document Version 3.0 |

Chapter 1 Introducing Linksys 900 Series IP Phones
Technology Background
•SIP ports—By default, UDP port 5060 and 5061
•RTP ports—16384 to 16482
If security is not a concern in your environment, you can consider disabling SPI, if this function exists on your firewall.
Network Address Translation
This section describes issues that arise when using the LVS system on a network behind a network address translation (NAT) device. It includes the following topics:
•NAT Overview, page 1-13
•NAT Types, page 1-14
•Simple Traversal of UDP Through NAT, page 1-14
•SIP-NAT Interoperation, page 1-15
NAT Overview
Network Address Translation (NAT) allows multiple devices to share the same public, routable, IP address for establishing connections over the Internet. NAT is typically performed by a router that forwards packets between the Internet and the internal, private network.
The association between a private address and port and a public address and port is called a NAT mapping. This mapping is maintained for a short period of time, that varies from a few seconds to several minutes. The expiration time is extended whenever the mapping is used to send a packet from the source device.
The ITSP may support NAT mapping using a Session Border Controller (see Figure 1-3).
Figure 1-3 NAT Support with Session Border Controller Provided by ITSP
Private IP address |
External IP address |
192.168.1.1 |
assigned by ISP |
192.168.1.101 192.168.1.102
NAT Device |
|
ISP |
Internet |
DHCP |
|
server |
|
SPA9000
SIP Proxy |
|
ITSP |
|
|
|
|
|
||
Session Border |
||||
192.168.1.100 |
||||
Controller |
||||
|
||||
|
|
Linksys 900 Series IP Phone Administrator Guide |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
Document Version 3.0 |
|
|
1-11 |
|
|
|
|
|
||

Chapter 1 Introducing Linksys 900 Series IP Phones
Technology Background
This is the preferred option because it eliminates the need for managing NAT on the 900 Series phone. If this is not available, you need to discuss with the ITSP how to use the NAT Support Parameters provided by the 900 Series phone, such as <Outbound Proxy> and <STUN Server Enable>.
A typical application of a NAT is to allow all the devices in a subscriber home network to access the Internet through a router with a single public IP address assigned by an ISP. The IP header of the packets sent from the private network to the public network is substituted by NAT with the public IP address and a port assigned by the router. The receiver of the packets on the public network sees the packets as coming from the external address instead of the private address of the device.
NAT Types
The ways that NAT is implemented can be divided into the following categories:
•Full cone NAT—Also known as one-to-one NAT. All requests from the same internal IP address and port are mapped to the same external IP address and port. An external host can send a packet to the internal host, by sending a packet to the mapped external address
•Restricted cone NAT—All requests from the same internal IP address and port are mapped to the same external IP address and port. Unlike a full cone NAT, an external host can send a packet to the internal host only if the internal host had previously sent a packet to it.
•Port restricted cone NAT/symmetric NAT—Port restricted cone NAT or symmetric NAT is like a restricted cone NAT, but the restriction includes port numbers. Specifically, an external host can send a packet to a particular port on the internal host only if the internal host had previously sent a packet from that port to the external host.
With symmetric NAT, all requests from the same internal IP address and port to a specific destination IP address and port are mapped to a unique external source IP address and port. If the same internal host sends a packet with the same source address and port to a different destination, a different mapping is used. Only an external host that receives a packet can send a UDP packet back to the internal host.
Simple Traversal of UDP Through NAT
Simple Traversal of UDP through NATs (STUN) is a protocol defined by RFC 3489, that allows a client behind a NAT device to find out its public address, the type of NAT it is behind, and the port associated on the Internet connection with a particular local port. This information is used to set up UDP communication between two hosts that are both behind NAT routers. Open source STUN software can be obtained at the following website:
http://www.voip-info.org/wiki-Open+Source+VOIP+Software
STUN does not work with a symmetric NAT router. To determine the type of NAT your router uses, complete the following steps:
Step 1 Enable debugging on the 900 Series phone:
1.Make sure you do not have firewall running on your PC that could block the syslog port (by default this is 514).
|
Linksys 900 Series IP Phone Administrator Guide |
1-12 |
Document Version 3.0 |

Chapter 1 Introducing Linksys 900 Series IP Phones
Technology Background
2.On the administration web server, System tab, set <Debug Server> to the IP address and port number of your syslog server.
Note that this address and port number has to be reachable from the SPA900 Series IP phone.
3.Set <Debug level> to 3, but do not change the value of the <syslog server> parameter.
4.To capture SIP signaling messages, under the Line tab, set <SIP Debug Option> to Full. The output is named syslog.514.log.
Step 2 To determine the type of NAT your router is using set <STUN Test Enable> to yes.
Step 3 View the syslog messages to determine if your network uses symmetric NAT.
SIP-NAT Interoperation
In the case of SIP, the addresses where messages/data should be sent to a 900 Series phone system are embedded in the SIP messages sent by the device. If the 900 Series phone system is sitting behind a NAT device, the private IP address assigned to it is not usable for communications with the SIP entities outside the private network.
Note If the ITSP offers an outbound NAT-Aware proxy, this discovers the public IP address from the remote endpoint and eliminates the need to modify the SIP message from the UAC.
The 900 Series phone system must substitute the private IP address information with the proper external IP address/port in the mapping chosen by the underlying NAT to communicate with a particular public peer address/port. For this, the 900 Series phone system must perform the following tasks:
•Discover the NAT mappings used to communicate with the peer.
This can be done with the help of an external device, such as a STUN server. A STUN server responds to a special NAT-Mapping-Discovery request by sending back a message to the source IP address/port of the request, where the message contains the source IP address/port of the original request. The 900 Series phone system can send this request when it first attempts to communicate with a SIP entity over the Internet. It then stores the mapping discovery results returned by the server.
•Communicate the NAT mapping information to the external SIP entities.
If the entity is a SIP Registrar, the information should be carried in the Contact header that overwrites the private address/port information. If the entity is another SIP UA when establishing a call, the information should be carried in the Contact header as well as in the SDP embedded in SIP message bodies. The VIA header in outbound SIP requests might also need to be substituted with the public address if the UAS relies on it to route back responses.
•Extend the discovered NAT mappings by sending keep-alive packets.
Because the mapping is alive only for a short period, the 900 Series phone system continues to send periodic keep-alive packets through the mapping to extend its validity as necessary.
|
|
Linksys 900 Series IP Phone Administrator Guide |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
Document Version 3.0 |
|
|
1-13 |
|
|
|
|
|
||

|
|
|
|
Chapter 1 Introducing Linksys 900 Series IP Phones |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Where to Go From Here |
|
|
|
Where to Go From Here |
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
To do this ... |
Refer to |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Use the different administration and |
Chapter 2, “Getting Started” |
|
|
|
|
configuration tools provided for managing |
|
|
|
|
|
Linksys 900 Series IP phone. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Configure and monitor a Linksys 900 Series |
Chapter 3, “Managing Linksys 900 Series IP |
|
|
|
|
IP phone. |
Phones” |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Refer to the function and usage for each field |
Chapter 5, “SPA900 Series Phone Field |
|
|
|
|
or parameter on the Linksys 900 Series IP |
Reference” |
|
|
|
|
phone administration web server pages. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Find the expansion of an acronym used in this |
Appendix A, “Acronyms” |
|
|
|
|
document. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Find the definition of a term used in this |
Appendix B, “Glossary” |
|
|
|
|
document. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
The following documentation provides additional documentation for Linksys SPA900 Series IP phones:
•IVR Quick Guide
•SPA Provisioning Guide
The following documentation describes how to use other Linksys Voice System products:
•SPA9000 Administrator Guide
•LVS CTI Integration Guide
•LVS Integration with ITSP Hosted Voicemail Guide
•Linksys Voice over IP Product Guide: SIP CPE for Massive Scale Deployment
•SPA 2.0 Analog Telephone Adapter Administrator Guide
|
Linksys 900 Series IP Phone Administrator Guide |
1-14 |
Document Version 3.0 |

C H A P T E R 2
Getting Started
This chapter describes the tools and utilities available for administering Linksys SPA900 Series phones. It includes the following sections:
•Linksys 900 Series IP Phones, page 2-1
•Establishing Connectivity, page 2-9
•Using the Administration Web Server, page 2-11
•Web Interface URLs, page 2-13
•Provisioning, page 2-14
•Using the Interactive Voice Response Interface, page 2-16
Note If the SPA900 Series IP phone is supplied or sponsored by an Internet telephone service provider (ITSP), certain network and service settings may be preconfigured. Depending on the configuration policy, access by an end user to specific configuration settings may be restricted or blocked.
Linksys 900 Series IP Phones
The Linksys SPA900 Series provides fully-featured VoIP phones that integrate with the Linksys SPA9000 to provide connectivity to other local stations, and through an ITSP to IP phones over the Internet, In addition, the optional SPA400 integrates with the SPA9000 and provides connectivity between SPA900 IP phones and the PSTN. This section summarizes the ports and hardware features provided by each device. It includes the following topics:
•Caring for Your Hardware, page 2-2
•SPA901, page 2-2
•SPA92x, SPA94x, and SPA962 Hardware Features, page 2-3
•SPA92x, SPA94x, and SPA962 Hardware Features, page 2-3
•SPA922, page 2-5
•SPA941, page 2-5
•SPA942, page 2-7
•SPA962, page 2-7
|
|
Linksys 900 Series IP Phone Administrator Guide |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
Document Version 3.0 |
|
|
2-1 |
|
|
|
|
|

Chapter 2 Getting Started
Linksys 900 Series IP Phones
Caring for Your Hardware
The Linksys 900 Series IP phones are electronic devices that should not be exposed to excessive heat, sun, cold or water. To clean the equipment, use a slightly moistened paper or cloth towel. Do not spray or pour cleaning solution directly onto the hardware unit.
SPA901
The SPA901 provides an entry-level IP phone that can be wall mounted (see Figure 2-1). The following are the hardware features provided by the SPA901:
•Voice Mail Message Waiting Indicator Light
•Redial Button
•Dedicated Flash Button
•Volume Control Button Cycles Through Volume Levels. Controls Ringer and Handset Volume.
•Standard 12-Button Dialing Pad
•High Quality Handset and Cradle
•Ethernet LAN – 10BaseT RJ-45
•5-volt DC Universal (100-240 Volt) Switching Power Adaptor
Figure 2-1 SPA901
The following tables describe the status indicators and controls on the front of the device and the ports on the back panel of the device.
|
Linksys 900 Series IP Phone Administrator Guide |
2-2 |
Document Version 3.0 |
 Loading...
Loading...