Bio-Rad Mini-PROTEAN TGX Precast Gels for 2-D Electrophoresis User Manual

Mini-PROTEAN® Precast Gels
Instruction Manual and Application Guide

Bio-Rad Technical Support
For help and technical advice, please contact the Bio-Rad Technical Support department. In the United States, the Technical Support department is open Monday–Friday, 5:00 am–5:00 pm, Pacific Time.
Phone: 1-800-424-6723
Fax: 1-510-741-5802
Email: LSG_TechServ_US@bio-rad.com (for U.S. and international customers)
Online technical support and worldwide contact information are available at www.consult.bio-rad.com.
Legal Notices
No part of this publication may be reproduced or transmitted in any form or by any means, electronic or mechanical, including photocopy, recording, or any information storage or retrieval system, without permission in writing from Bio-Rad Laboratories.
Bio-Rad reserves the right to modify its products and services at any time. This user guide is subject to change without notice.
Although prepared to ensure accuracy, Bio-Rad assumes no liability for errors, or for any damages resulting from the application or use of this information.
Coomassie is a trademark of BASF Aktiengesellschaft. Ficoll is a trademark of GE Healthcare Group companies. StrepTactin is a trademark of Institut für Bionalytik GmbH. StrepTactin is covered by German patent application P 19641876.3. Bio-Rad Laboratories, Inc. is licensed by Institut für Bioanalytik GmbH to sell these products for research use only. SYBR is a trademark of Invitrogen Corporation. SYPRO is a trademark of Molecular Probes, Inc. Bio-Rad is licensed to sell SYPRO products for research use only, under U.S. Patent 5,616,502. Tween is a trademark of ICI Americas, Inc.
Copyright © 2011 by Bio-Rad Laboratories. All rights reserved.

Contents
Chapter 1: Mini-PROTEAN® Precast Gels . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
. |
1 |
|
1.1 |
Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
|
1 |
1.2 |
Gel Formulations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
|
2 |
1.3 |
Comb Configurations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
. |
2 |
1.4 |
Specifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
. |
2 |
1.5 |
Storage Conditions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
|
3 |
1.6 |
Important Notes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3 |
||
Chapter 2: Setup and Basic Operation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
. |
.4. . . . . . . |
|
2.1 |
Workflow Overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
|
4 |
2.2 |
Required Materials . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
. |
5 |
2.3Setting Up and Running Mini-PROTEAN Gels in the Mini-PROTEAN® Tetra Cell . . . . . . . 5
2.4Removing the Gel . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
Chapter 3: SDS-PAGE . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
. 8 |
|
3.1 |
Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
8 |
3.2 |
Mini-PROTEAN® TGX™ and Mini-PROTEAN® TGX Stain-Free™ Gels . . . . . . . . . . . |
. 8 |
3.3 |
SDS-PAGE Buffers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
10 |
3.4 |
Sample Preparation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
10 |
3.5 |
Running Conditions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
10 |
Chapter 4: Native PAGE . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
. 12. |
|
4.1 |
Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
12 |
4.2 |
Mini-PROTEAN TGX and Mini-PROTEAN TGX Stain-Free Gels . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
12 |
4.3 |
Native PAGE Buffers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
13 |
4.4 |
Sample Preparation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
13 |
4.5 |
Running Conditions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
13 |
Chapter 5: Stain-Free System . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
14. . . . . . . . . . . . |
|
5.1 |
Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
14 |
5.2 |
Stain-Free Workflow . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
15 |
5.3 |
Electrophoresis with Mini-PROTEAN TGX Stain-Free Gels . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
15 |
5.4 |
Stain-Free Detection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
15 |

Chapter 6: Peptide Analysis . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
. |
16 |
|
6.1 |
Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
. |
16 |
6.2 |
Mini-PROTEAN Tris-Tricine Gels . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
. |
16 |
6.2.1 Gel Composition . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
|
16 |
|
6.2.2 Gel Selection Guide . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
. |
16 |
|
6.3 |
Peptide Analysis Buffers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
|
17 |
6.4 |
Sample Preparation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
. |
17 |
6.5 |
Running Conditions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17 |
||
Chapter 7: Nondenaturing Nucleic Acid PAGE . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
. |
18 |
|
7.1 |
Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
. |
18 |
7.2 |
Mini-PROTEAN TBE Gels . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
. |
18 |
7.2.1 Gel Composition . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
|
18 |
|
7.2.2 Gel Selection Guide . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
. |
18 |
|
7.3 |
Nondenaturing Nucleic Acid PAGE Buffers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
|
19 |
7.4 |
Sample Preparation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
. |
19 |
7.5 |
Running Conditions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19 |
||
Chapter 8: Denaturing Nucleic Acid PAGE . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
. |
20. . . . . |
|
8.1 |
Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
. |
20 |
8.2 |
Mini-PROTEAN TBE-Urea Gels . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
|
20 |
8.2.1 Gel Composition . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
|
20 |
|
8.2.2 Gel Selection Guide . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
. |
20 |
|
8.3 |
Denaturing Nucleic Acid PAGE Buffers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
. |
21 |
8.4 |
Sample Preparation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
. |
21 |
8.5 |
Running Conditions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21 |
||
Chapter 9: 2-D Electrophoresis . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
|
. 22. . . . . . . . |
|
9.1 |
Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
. |
22 |
9.2 |
Equilibration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
. |
22 |
9.3 |
Agarose Overlay . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
|
22 |
9.4 |
Second-Dimension Electrophoresis . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
. |
22 |

Chapter 10: Detection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
. |
23 |
|
10.1 |
SDS-PAGE and Native PAGE Detection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
. |
23 |
10.2 |
Peptide Gel Staining . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
|
24 |
10.3 |
TBE Gel Staining . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
. |
24 |
10.4 |
TBE-Urea Gel Staining . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
. |
24 |
Chapter 11: Blotting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
. .25. . . . . . . . . . . |
||
11.1 |
Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
|
25 |
11.2 |
Transfer . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
. |
25 |
11.2.1 Transfer Buffers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
. |
25 |
|
11.2.2Wet Transfer Using the Mini Trans-Blot® Module . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
11.2.3Transfer Using the Trans-Blot® Turbo™ System . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
11.2.4Semi-Dry Transfer Using the Trans-Blot® SD Cell . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27
11.3 Total Protein Blot Stains . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
. |
28 |
11.4 Immunodetection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
. |
28 |
Chapter 12: Troubleshooting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
. 29. . . . . . . . |
|
Appendix A: Quick Start Guides . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
. |
31 |
SDS-PAGE (Mini-PROTEAN TGX Gels) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 32 |
||
Native PAGE (Mini-PROTEAN TGX Gels) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
|
33 |
Peptide Analysis (Mini-PROTEAN Tris-Tricine Gels) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
|
34 |
Nondenaturing Nucleic Acid PAGE (Mini-PROTEAN TBE Gels) . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
. |
35 |
Denaturing Nucleic Acid PAGE (Mini-PROTEAN TBE-Urea Gels) . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
|
36 |
Appendix B: Buffers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
. |
. 37. . . . . . . . . . |
Appendix C: Related Literature . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
. .40. . . . . . . . . . |
|
Appendix D: Ordering Information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
. |
41 |


1 Mini-PROTEAN®
Precast Gels
1.1 Introduction
Mini-PROTEAN precast gels are 7.2 cm x 8.6 cm gels designed for performing polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (PAGE) with the Mini-PROTEAN family of vertical electrophoresis cells, which includes the Mini-PROTEAN® Tetra and Mini-PROTEAN® 3 Dodeca™ cells and the discontinued Mini-PROTEAN II and Mini-PROTEAN 3 cells. The Mini Trans-Blot®, Trans-Blot® Turbo™, and Trans-Blot® SD blotting cells and precut membrane sandwiches are also available for blotting applications with these gels.
Features of Mini-PROTEAN precast gels include:
n Outlined and numbered well that simplify sample loading and identification n Capacity for up to 15 samples per gel
n Bottom-open cassette design for easy gel handling and blotting setup n Easy-to-open cassette for faster downstream processing
nReference line at the bottom of the cassette indicates where the run should stop (for optimum resolution across the separation range)
n Excellent staining quality and transfer efficiency n No gel foot to remove prior to blotting
nMini-PROTEAN® TGX Stain-Free™ formulations, which enable rapid 5 min gel imaging without staining and destaining
Comb (available in a range of options)
Numbered well outlines
Reference line for monitoring progress of the run
Technical Support: 1-800-4BIORAD • 1-800-424-6723 • www.bio-rad.com |
1 |

Mini-PROTEAN Precast Gels
1.2 Gel Formulations
Mini-PROTEAN precast gels are composed of polyacrylamide with a bisacrylamide crosslinker, and they are available in a range of formulations (Table 1.1) and in a selection of single percentages and gradients.
Table 1.1. Mini-PROTEAN precast gel formulations.
Application |
Gel Formulation |
Sample Buffer |
Running Buffer |
|
|
|
|
SDS-PAGE |
Mini-PROTEAN TGX™ |
Laemmli |
Tris/glycine/SDS |
|
Mini-PROTEAN TGX Stain-Free |
|
|
Native PAGE |
Mini-PROTEAN TGX |
Native |
Tris/glycine |
|
Mini-PROTEAN TGX Stain-Free |
|
|
Peptide analysis |
Mini-PROTEAN Tris-Tricine |
Tricine |
Tris/Tricine/SDS |
dsDNA separation |
Mini-PROTEAN TBE |
Nucleic acid |
Tris/boric acid/EDTA (TBE) |
ssDNA and RNA |
Mini-PROTEAN TBE-urea |
TBE-urea |
TBE |
separation |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1.3 Comb Configurations
Comb Type |
Well Volume |
10-well |
50 μl |
10-well |
30 μl |
12-well |
20 μl |
15-well |
15 μl |
8 + 1 well* |
30 μl |
IPG/prep |
7 cm ReadyStrip™ IPG strip (450 μl) |
1.4 Specifications
Gel material |
Polyacrylamide |
Gel dimensions |
7.2 x 8.6 cm |
Gel thickness |
1.0 mm |
Resolving gel height |
6.2 cm (5.6 cm for 50 μl well) |
Cassette dimensions |
8.5 x 10 cm |
Cassette material |
Styrene copolymer |
Comb material |
Polycarbonate |
Running buffer |
750 ml for 1–2 gels, 1,000 ml for 3–4 gels (Mini-PROTEAN Tetra cell) |
|
325 ml for 1–2 gels (Mini-PROTEAN II or Mini-PROTEAN 3 cell) |
* Multichannel pipet compatible.
2 Technical Support: 1-800-4BIORAD • 1-800-424-6723 • www.bio-rad.com

Instruction Manual and Application Guide
1.5 Storage Conditions
Table 1.2. Storage conditions for Mini-PROTEAN precast gels. Store gels flat. Shelf life is from date of manufacture; expiration dates are printed on the packaging.
Storage |
|
|
Temperature |
Gel Formulation |
Shelf Life |
|
|
|
2–8°C |
Mini-PROTEAN TGX |
12 months |
|
Mini-PROTEAN TGX Stain-Free |
12 months |
|
Mini-PROTEAN Tris-Tricine |
12 weeks |
|
Mini-PROTEAN TBE |
12 weeks |
|
Mini-PROTEAN TBE-urea |
8 weeks |
|
|
|
1.6 Important Notes
Use each Mini-PROTEAN precast gel as soon as possible after removing it from the storage pouch.
Improper storage of Mini-PROTEAN precast gels can produce artifacts. Store gels flat and at 2–8°C. Avoid freezing or prolonged storage above 8°C. If your gels have been stored improperly, discard them.
Do not run more than one gel type in the same apparatus at the same time. Different gel percentages and formulations have different conductivities and different run times.
With the Mini-PROTEAN Tetra cell: n When running 1–2 gels:
Use the electrode assembly (with banana plugs), not the companion running module (without banana plugs)
Do not place the companion running module in the tank. Doing so generates excessive heat and degrades the quality of the electrophoretic separation
n When running 3–4 gels, use both the electrode assembly and companion running module n When using voltages >200 V, fill the outer buffer chamber to the 4 gel (800 ml) mark
Technical Support: 1-800-4BIORAD • 1-800-424-6723 • www.bio-rad.com |
3 |

2 Setup and Basic
Operation
2.1 Workflow Overview
Prepare Buffers
Prepare sample and running buffers
Prepare Gels and
Assemble Electrophoresis Cell
Prepare and Load Samples
Dilute in sample buffer
Perform Electrophoresis
SDS-PAGE (Chapter 3)
Native PAGE (Chapter 4)
Peptide Analysis (Chapter 6)
Nondenaturing Nucleic Acid PAGE (Chapter 7)
Denaturing Nucleic Acid PAGE (Chapter 8)
2-D Electrophoresis (Chapter 9)
Analyze the Separation
(Chapter 10)
Blot the Gels (Optional)
(Chapter 11)
4 Technical Support: 1-800-4BIORAD • 1-800-424-6723 • www.bio-rad.com
Instruction Manual and Application Guide
2.2 Required Materials
n Mini-PROTEAN® precast gels
nMini-PROTEAN® Tetra cell (or Mini-PROTEAN® 3 Dodeca™, Mini-PROTEAN II or Mini-PROTEAN 3 cell)
nPowerPac™ Basic or PowerPac HC power supply (or equivalent); PowerPac HV or PowerPac Universal required for high-voltage applications (>300 V)
n Sample buffer
nRunning buffer (750 ml for 1–2 gels; 1,000 ml for 3–4 gels or when running at voltages >200 V)
nOpening lever (catalog #456-0000)
2.3Setting Up and Running Mini-PROTEAN Gels in the Mini-PROTEAN Tetra Cell
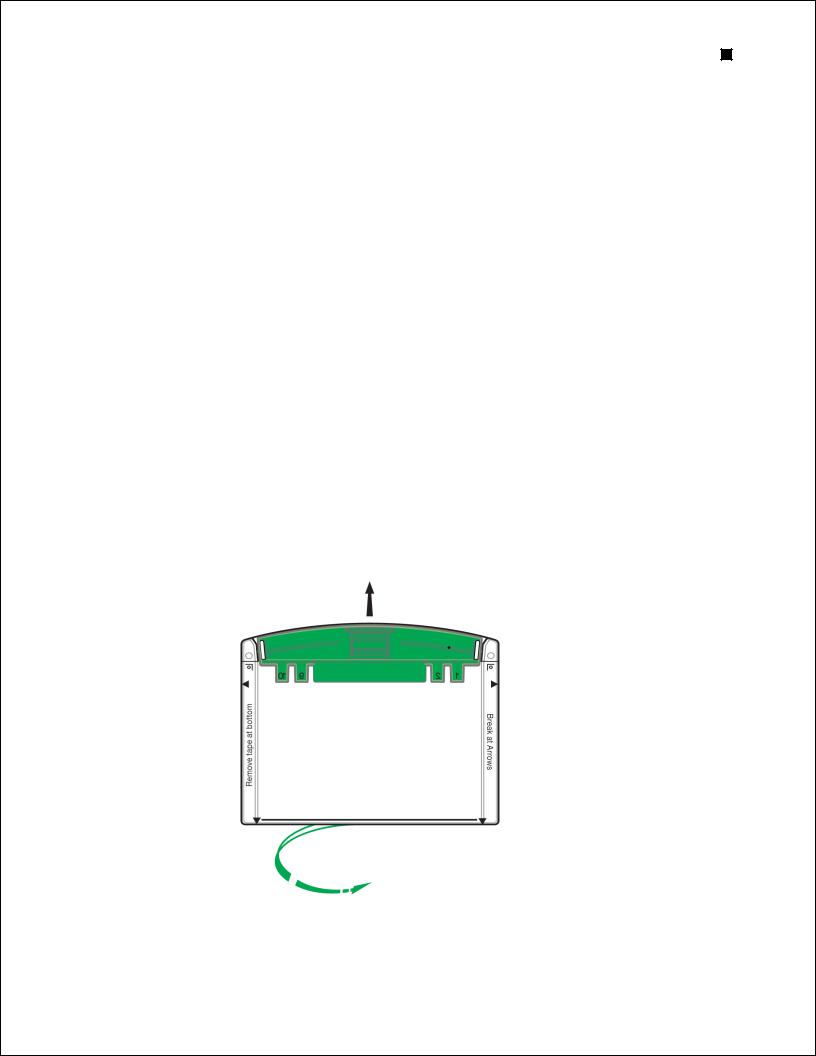
1.Remove the gels from the storage pouch and prepare them for assembly:
a.Remove the comb: Position thumb on the indentation (middle of comb) and remove the comb by pulling upward in one smooth motion.
b.Remove the tape: Pull gently to remove the green tape from the bottom of the cassette. If necessary, use the opening key or comb to help remove the tape at the corners.
c.Rinse the wells: Use a syringe, wash bottle, or disposable transfer pipet to rinse the wells with
Remove the comb
Remove the tape
Technical Support: 1-800-4BIORAD • 1-800-424-6723 • www.bio-rad.com |
5 |

Mini-PROTEAN Precast Gels
running buffer. Straighten the sides of the wells, if necessary.
2.Set the electrode assembly to the open position on a clean, flat surface (A).
3.Place the gel cassettes into the electrode assembly. Two cassettes are required to create a functioning assembly; when using 1 or 3 gels, use the buffer dam (included with the cell) to complete the assembly.
a.Place the first cassette with the short plate facing inward and so the gel rests at a 30° angle away from the center of the electrode assembly. Make sure the electrode assembly remains balanced and does not tip over.
b.Place the second gel or buffer dam on the other side of the electrode assembly, again by resting the gel on the supports. The gels rest at 30° angles, one on either side of the electrode assembly, tilting away from the center of the frame (B).
4.Gently push both gels toward each other, making sure that they rest firmly and squarely against the green gasket that is built into the electrode assembly. Align the short plates to ensure the edge sits just below the notch at the top of the green gasket (C).
5.While gently squeezing the gel cassettes
(or cassette and buffer dam) against the green gaskets (maintaining constant pressure and with both gels in place), slide the green arms of the clamping frame one at a time over the gels, locking them into place (D,E).
6.The wing clamps of the electrode assembly lift each gel cassette up against the notch in the green gasket, forming a seal. Check again that
Clamping frame
Gasket
Notch
Gel cassette
Short plate
Long plate
Gel support
D
A
B
C
E
6Technical Support: 1-800-4BIORAD • 1-800-424-6723 • www.bio-rad.com

|
|
Instruction Manual and Application Guide |
F |
the short plates sit just below the notch at the top of |
|
|
the green gasket (C). |
|
|
If running more than 2 gels, repeat steps 2–6 with the |
|
|
companion running module. |
|
|
7. Place the electrophoresis module into the tank (F) and |
|
|
fill the buffer chambers with 1x running buffer: |
|
|
n |
200 ml in the inner buffer chamber |
|
n |
550 ml (1–2 gels) or 800 ml (3–4 gels, or |
|
|
>200 V) in the outer buffer chamber |
8.Wash the sample wells with running buffer (if this was not done earlier).
9.Load samples and run the gels using the running
conditions appropriate to your application. Stop the run when the dye front reaches the reference line imprinted on the bottoms of the cassettes.
2.4 Removing the Gel
1.After electrophoresis is complete, turn off the power supply and disconnect the electrical leads.
2.Remove the lid from the tank and remove the gels from the cell. Pour off and discard the running buffer.
3.To open the cassette, align the arrow on the opening lever with the arrows marked on the cassette and insert the lever between the cassette plates at indicated locations. Apply downward pressure to break each seal. Do not twist the lever.
4.Pull the two plates apart from the top of the cassette, and gently remove the gel.
Technical Support: 1-800-4BIORAD • 1-800-424-6723 • www.bio-rad.com |
7 |

3 SDS-PAGE
3.1 Introduction
Mini-PROTEAN® TGX™ (Tris-Glycine eXtended shelf life) gels provide a versatile system for separating proteins by either molecular weight (SDS-PAGE) or mass-to-charge ratio (native PAGE). (See Chapter 4 for native PAGE applications and protocols.) This versatility is possible because the gels are made without SDS; this allows the sample buffer and running buffer to determine the separation mechanism.
SDS-PAGE relies on a discontinuous buffer system. Two ions differing in electrophoretic mobility (glycinate and chloride) form a moving boundary when voltage is applied. Proteins have an intermediate mobility that causes them to concentrate, or stack, into a narrow zone at the beginning of electrophoresis. As that zone moves through the gel, the sieving effect of the polyacrylamide gel matrix causes proteins of different molecular weighs to move at different rates. This stacking effect is responsible for the high resolving power of SDS-PAGE: the sample is loaded in a relatively broad zone, and the moving boundary concentrates the proteins into sharp bands prior to separation.
Protein samples for SDS-PAGE are prepared using SDS and a thiol reducing agent, usually β-mercaptoethanol or dithiothreitol (DTT). SDS forms complexes with proteins, giving them a rodlike shape and similar mass-to-charge ratio. The reducing agent disrupts disulfide bonds between and within proteins, allowing complete denaturation and dissociation. Heat treatment in the presence of SDS and reducing agent effectively eliminates the effects of native charge and higher order structure on electrophoretic mobility, so the migration distance depends primarily on molecular weight.
Molecular weight is estimated by plotting the logarithm of protein molecular weight vs. the relative mobility (Rf) of the protein (Rf = distance migrated by the protein/distance migrated by the dye front) or by using the point-to-point semilog interpolation method in Quantity One® or Image Lab™ software. Refer to bulletins 3133, 3144, and 10014472 for more information.
3.2 Mini-PROTEAN TGX and
Mini-PROTEAN® TGX Stain-Free™ Gels
Mini-PROTEAN TGX gels are Laemmli-like gels that have a proprietary modification that extends shelf life to 12 months and enhances separation characteristics relative to conventional gel types. They are run using standard Laemmli sample buffer and Tris/glycine/SDS running buffer, and they generate protein migration patterns that are similar to those observed with standard Laemmli Tris-HCl gels.
Two types of TGX formulations are available:
n Mini-PROTEAN TGX — Laemmli-like, extended shelf life gels
nMini-PROTEAN TGX Stain-Free — Laemmli-like, extended shelf life gels with trihalo compounds that allow rapid fluorescent detection of proteins with the stain-free system, eliminating staining and destaining steps for faster results (see Chapter 5 for more details)
8 Technical Support: 1-800-4BIORAD • 1-800-424-6723 • www.bio-rad.com

Instruction Manual and Application Guide
Both gel types gels are available in polyacrylamide single percentages and gradients. Use the protein migration charts and tables to select the gel type that optimizes resolution of your sample:
nUse single-percentage gels to separate bands of similar molecular weight. Optimum separation occurs in the lower half of the gel, so use a percentage in which the protein migrates to the lower half of the gel
nUse gradient gels to separate samples containing a broad range of molecular weights. Gradient gels allow resolution of both highand low-molecular weight bands on the same gel. Larger pore sizes at the top of the gel permit resolution of larger molecules, smaller pore sizes toward the bottom of the gel restrict excessive separation of small molecules
Gel Composition |
|
|
|
Crosslinker |
2.6% C |
|
|
Stacking gel |
4% T, 2.6% C |
|
|
Shelf life |
~12 months at 2–8°C; expiration date is printed on package |
||
Gel Percentage |
Optimum Separation |
Gel Percentage |
Optimum Separation |
|
Range |
|
Range |
7.5% |
40–200 kD |
4–15% |
20–250 kD |
10% |
30–150 kD |
4–20% |
10–200 kD |
12% |
20–120 kD |
Any kD™ |
10–100 kD |
|
Precision Plus Protein™ Unstained |
|
|
|
Broad Range Unstained |
|
||||
7.5% |
10% |
12% |
4–15% |
4–20% Any kD™ |
7.5% |
10% |
12% |
4–15% |
4–20% Any kD™ |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
250 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
200 |
||
250 |
|
|
250 |
|
250 |
|
|
|
|
250 |
|
|
|
200 |
|
200 |
|
200 |
|
200 |
|
|
|
|
|
150 |
|
150 |
250 |
|
|
150 |
|
200 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
116 |
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
150 |
|
100 |
|
|
150 |
|
100 |
|
|
|
|
116 |
|
|
|
|
97.4 |
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
100 |
|
|
150 |
|
100 |
75 |
|
|
116 |
|
97.4 |
|
|
116 |
|
66 |
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
97.4 |
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
100 |
|
|
|
75 |
|
100 |
|
|
|
50 |
116 |
|
|
116 |
97.4 |
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
75 |
|
75 |
|
|
|
|
66 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
97.4 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
|
|
50 |
75 |
|
|
37 |
|
66 |
|
|
97.4 |
|
66 |
45 |
|||||||||
|
|
|
|
50 |
|
|
|
|
|
66 |
|
|
|||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
45 |
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
37 |
|
50 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
45 |
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
75 |
|
|
50 |
|
37 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
31 |
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
25 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
45 |
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
25 |
37 |
|
|
20 |
66 |
45 |
|
31 |
31 |
|
|
||||||||
|
|
37 |
25 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
31 |
|
|
21.5 |
||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
50 |
|
|
|
20 |
|
|
20 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
25 |
|
|
15 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
21.5 |
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
25 |
|
|
20 |
|
|
45 |
|
31 |
|
|
|
21.5 |
|
14.4 |
14.4 |
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
15 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
37 |
|
|
|
|
15 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
21.5 |
|
|
|
|
|||
|
20 |
|
|
15 |
|
10 |
|
10 |
|
|
21.5 |
|
14.4 |
|
14.4 |
6.5 |
|
6.5 |
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
31 |
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
10 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
6.5 |
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Migration charts for protein standards on Mini-PROTEAN TGX and Mini-PROTEAN TGX Stain-Free gels.
Technical Support: 1-800-4BIORAD • 1-800-424-6723 • www.bio-rad.com |
9 |
Mini-PROTEAN Precast Gels
3.3 SDS-PAGE Buffers
See Appendix B for buffer formulations. Do not adjust pH.
Running buffer (1x) 25 mM Tris, 192 mM glycine, 0.1% SDS
Dilute 100 ml 10x stock (catalog #161-0732) with 900 ml deionized water (diH2O).
Sample buffer (2x) 62.5 mM Tris-HCl, pH 6.8, 2% SDS, 25% (v/v) glycerol, 0.01% bromophenol blue, 5% β-mercaptoethanol or 100 mM DTT (added fresh)
Use Laemmli sample buffer (catalog #161-0737) and add β-mercaptoethanol or DTT before use.
Sample buffer (4x) 250 mM Tris-HCl, pH 6.8, 4% LDS, 40% (w/v) glycerol, 0.02% bromophenol blue, 15% beta-mercaptoethanol or 200 mM DTT (added fresh)
Use 4x Laemmli sample buffer (catalog #161-0747) and add β-mercaptoethanol or DTT before use.
3.4 Sample Preparation
1.Determine the appropriate concentration of sample to load (depends on the load volume and the detection method used; see Chapter 10 for approximate stain sensitivities).
2.Dilute the sample with sample buffer with added reducing agent.
2x: dilute 1 part sample with 1 part sample buffer. 4x: dilute 3 parts sample with 1 part sample buffer. For nonreducing conditions, omit the reducing agent.
3. Heat the diluted sample at 90–95°C for 5 min or at 70°C for 10 min.
3.5 Running Conditions
Run conditions and times are approximate. Run times represent the time required for the dye front to reach the line at the bottom of the cassette. Conditions may vary depending on water and buffer conductivity, which vary from one lab setting to the next. Multiply current by the number of gels run.
Table 3.1. Standard running conditions for SDS-PAGE in the Mini-PROTEAN Tetra cell.
Gel |
Optimum Range |
Run Conditions |
Run Time |
|
|
|
|
|
|
7.5% |
40 |
–200 kD |
|
|
10% |
30 |
–150 kD |
300 V constant: |
|
12% |
20 |
–120 kD |
Starting current (per gel): 55–75 mA |
15–20 min |
4–15% |
20 |
–250 kD |
Final current (per gel): 45–70 mA |
(Fill outer buffer volume |
4–20% |
10–200 kD |
|
to the 4-gel mark) |
|
Any kD |
10–100 kD |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
10 Technical Support: 1-800-4BIORAD • 1-800-424-6723 • www.bio-rad.com
 Loading...
Loading...