Vishay 40CTQ150, 40CTQ150S, 40CTQ150-1 Data Sheet

Bulletin PD-20694 rev. B 07/03
40CTQ150
40CTQ150S 40CTQ150-1
SCHOTTKY RECTIFIER |
40 Amp |
Major Ratings and Characteristics
Characteristics |
40CTQ... |
Units |
|
|
|
|
|
IF(AV) |
Rectangular |
40 |
A |
|
waveform |
|
|
VRRM |
|
150 |
V |
IFSM |
@ tp = 5 µs sine |
1500 |
A |
VF |
@20 Apk, TJ=125°C |
0.71 |
V |
|
(per leg) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
TJ |
|
- 55 to 175 |
°C |
|
|
|
|
Description/ Features
The 40CTQ... center tap Schottky rectifier has been optimized for very low forward voltage drop, with moderate leakage. The proprietary barrier technology allows for reliable operation up to 175° C junction temperature. Typical applications are in switching power supplies, converters, free-wheeling diodes, and reverse battery protection.
 175° C TJ operation
175° C TJ operation
 Center tap TO-220 package
Center tap TO-220 package
 High purity, high temperature epoxy encapsulation for enhanced mechanical strength and moisture resistance
High purity, high temperature epoxy encapsulation for enhanced mechanical strength and moisture resistance
 Very low forward voltage drop
Very low forward voltage drop
 High frequency operation
High frequency operation
 Guard ring for enhanced ruggedness and long term reliability
Guard ring for enhanced ruggedness and long term reliability
Case Styles
40CTQ150
|
Base |
|
|
Common |
|
|
Cathode |
|
|
2 |
|
|
2 |
|
1 |
Common |
3 |
Anode |
Cathode |
Anode |
TO-220AB
40CTQ150S
|
Base |
|
|
Common |
|
|
Cathode |
|
|
2 |
|
|
2 |
|
1 |
Common |
3 |
Anode |
Cathode |
Anode |
D2PAK
40CTQ150-1
|
Base |
|
|
Common |
|
|
Cathode |
|
|
2 |
|
|
2 |
|
1 |
Common |
3 |
Anode |
Cathode |
Anode |
TO-262
www.irf.com |
1 |

40CTQ150, 40CTQ150S, 40CTQ150-1
Bulletin PD-20694 rev. B 07/03
Voltage Ratings
Part number |
Value |
|
VR Max. DC Reverse Voltage (V) |
150 |
|
VRWM Max. Working Peak Reverse Voltage (V) |
||
|
Absolute Maximum Ratings
|
Parameters |
|
40CTQ.. |
Units |
Conditions |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
IF(AV) |
Max. Average Forward |
(Per Leg) |
20 |
A |
50% duty cycle @ TC = 140 °C, rectangular wave form |
||
|
Current * See Fig. 5 |
(Per Device) |
40 |
|
|
|
|
I |
Max. Peak One Cycle Non-Repetitive |
1500 |
|
5µs Sine or 3µs Rect. pulse |
Following any rated |
||
FSM |
|
|
|
A |
|
load condition and with |
|
Surge Current (Per Leg) * See Fig. 7 |
250 |
10msSineor6msRect.pulse |
|||||
|
|
rated VRRM applied |
|||||
EAS |
Non-Repetitive Avalanche Energy |
1.0 |
mJ |
TJ = 25 °C, IAS = 1.5 Amps, L = 0.9 mH |
|||
|
(Per Leg) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
IAR |
Repetitive Avalanche Current |
1.5 |
A |
Current decaying linearly to zero in 1 µsec |
|||
|
(Per Leg) |
|
|
|
Frequency limited by TJ max. VA = 1.5 x VR typical |
||
Electrical Specifications
|
Parameters |
|
40CTQ.. |
Units |
Conditions |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
VFM |
Max. Forward Voltage Drop |
0.93 |
V |
@ 20A |
TJ |
= 25 °C |
|
|
(Per Leg) * See Fig. 1 |
(1) |
1.16 |
V |
@ 40A |
||
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
0.71 |
V |
@ 20A |
TJ |
= 125 °C |
|
|
|
0.85 |
V |
@ 40A |
||
IRM |
Max. Reverse Leakage Current |
50 |
µA |
TJ = 25 °C |
VR |
= rated VR |
|
|
(Per Leg) * See Fig. 2 |
(1) |
15 |
mA |
TJ = 125 °C |
||
|
|
|
|||||
CT |
Max. Junction Capacitance(Per Leg) |
450 |
pF |
VR = 5VDC (test signal range 100Khz to 1Mhz) 25°C |
|||
LS |
Typical Series Inductance |
(Per Leg) |
8.0 |
nH |
Measured lead to lead 5mm from package body |
||
dv/dt |
Max. Voltage Rate of Change |
10000 |
V/ µs |
|
|
|
|
|
(Rated VR) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
(1) Pulse Width < 300µs, Duty Cycle <2% |
|
|
|
|
|
||
Thermal-Mechanical Specifications
|
|
Parameters |
|
|
40CTQ.. |
Units |
Conditions |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
TJ |
Max. Junction Temperature Range |
-55 to 175 |
°C |
|
|
||
|
Tstg |
Max. Storage Temperature Range |
-55 to 175 |
°C |
|
|
||
|
RthJC |
Max.ThermalResistance |
Per Leg |
1.5 |
°C/W |
DC operation |
* See Fig. 4 |
|
|
|
JunctiontoCase |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
RthJC |
Max.ThermalResistance PerPackage |
0.75 |
°C/W |
DC operation |
|
||
|
|
JunctiontoCase |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
RthCS |
TypicalThermalResistance, |
|
|
0.5 |
°C/W |
Mounting surface , smooth and greased |
|
|
|
CasetoHeatsink |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
wt |
Approximate Weight |
|
|
2 (0.07) |
g (oz.) |
|
|
|
T |
Mounting Torque |
|
Min. |
6 (5) |
Kg-cm |
Non-lubricated threads |
|
|
|
|
Max. |
12 (10) |
(Ibf-in) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
www.irf.com |
|
|
|
|
|
|
40CTQ150, 40CTQ150S, 40CTQ150-1 |
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Bulletin |
PD-20694 |
rev. B |
07/03 |
|
100 |
|
|
|
|
1000 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
<![if ! IE]> <![endif]>(mA) |
100 |
|
Tj = 175˚C |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
150˚C |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
<![if ! IE]> <![endif]>R |
10 |
|
125˚C |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
<![if ! IE]> <![endif]>I |
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
<![if ! IE]> <![endif]>- |
|
|
100˚C |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
<![if ! IE]> <![endif]>Current |
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
1 |
|
|
75˚C |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| <![if ! IE]> <![endif]>(A) |
|
|
|
|
<![if ! IE]> <![endif]>Reverse |
0.1 |
|
|
50˚C |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
25˚C |
|||
| <![if ! IE]> <![endif]>F |
|
|
|
|
0.01 |
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
| <![if ! IE]> <![endif]>I |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
| <![if ! IE]> <![endif]>- |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| <![if ! IE]> <![endif]>Current |
|
|
|
Tj = 175˚C |
0.001 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0 |
20 40 |
60 80 100 120 140 160 |
|||||
| <![if ! IE]> <![endif]>Forward |
10 |
|
|
Tj = 125˚C |
|
Reverse Voltage - VR (V) |
|
|||
|
|
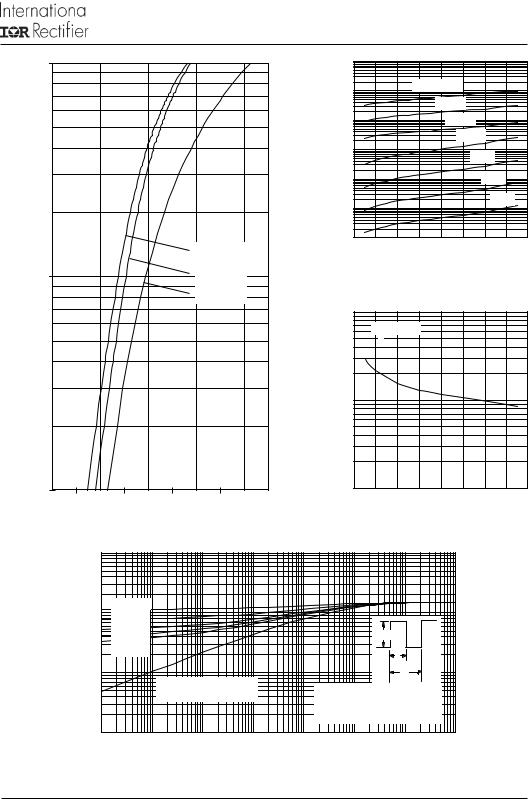
Fig. 2 - Typical Values of Reverse Current |
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|||||||
|
|
|
Tj = |
25˚C |
|
Vs. Reverse Voltage |
|
|||
| <![if ! IE]> <![endif]>Instantaneous |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
1000 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
<![if ! IE]> <![endif]>(pF) |
|
TJ = 25˚C |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
<![if ! IE]> <![endif]>T |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
<![if ! IE]> <![endif]>- C |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
<![if ! IE]> <![endif]>Junction Capacitance |
100 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1 |
|
|
|
|
10 |
|
|
|
160 |
|
0 |
0.4 |
0.8 |
1.2 |
1.6 |
0 |
40 |
80 |
120 |
|
Forward Voltage Drop - VFM (V) |
Reverse Voltage - VR (V) |
Fig. 1 - Maximum Forward Voltage Drop Characteristics |
Fig. 3 - Typical Junction Capacitance |
|
Vs. Reverse Voltage |
|
10 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| <![if ! IE]> <![endif]>(°C/W) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| <![if ! IE]> <![endif]>thJC |
1 |
D = 0.75 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
D = 0.50 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
| <![if ! IE]> <![endif]>Z |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
D = 0.33 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
| <![if ! IE]> <![endif]>Impedance |
|
|
|
|
PDM |
|
|||
|
D = 0.25 |
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
D = 0.20 |
|
|
|
|
t1 |
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
0.1 |
|
|
Single Pulse |
|
|
|
t 2 |
|
|
| <![if ! IE]> <![endif]>Thermal |
|
|
|
|
|
Notes: |
|
|
|
|
|
(Thermal Resistance) |
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
1. Duty factor D = |
t1/ t 2 |
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
2. Peak Tj = Pdmx ZthJC + Tc |
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
0.01 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0.00001 |
0.0001 |
0.001 |
0.01 |
0.1 |
1 |
10 |
100 |
|
t1, Rectangular Pulse Duration (Seconds)
Fig. 4 - Max. Thermal Impedance Z thJC Characteristics
www.irf.com |
3 |
 Loading...
Loading...