NSC PC97307-IBW-EB, PC97307-IBW-VUL, PC97307-ICE-EB, PC97307-ICE-VUL, PC97307-ICK-VUL Datasheet
PRELIMINARY
March 1998
PC87307/PC97307 Plug and Play Compatible and PC97
Compliant SuperI/O
Highlights
General Description
The PC87307/PC97307 (VUL) are functionally identical parts that offer a single-chip solution to the most commonly used ISA, EISA and MicroChannel® peripherals. This fully Plug and Play (PnP) compatible chip incorporates a Floppy Disk Controller (FDC), a Keyboard and mouse Controller (KBC), a Real-Time Clock (RTC), two fast full function UARTs, Infrared (IR) support, a full IEEE 1284 parallel port, three general purpose chip select signals that can be programmed for game port control, and a separate configuration register set for each module. It also provides support for power management (including a WATCHDOG timer) and standard PC-AT address decoding for on-chip functions.
The Plug and Play (PnP) support in the device conforms to the “Plug and Play ISA Specification” Version 1.0a, May 5, 1994.
The Infrared (IR) interface complies with the IrDA 1.0 SIR and SHARP-IR standards, and supports all four basic protocols for Consumer-IR (TV-Remote) circuitry (RC-5, RC-5 extended, RECS80 and NEC).
Features
■100% compatible with Plug and Play requirements specified in the “Plug and Play ISA Specification”, ISA, EISA, and MicroChannel architectures
■Meets PC97 requirements
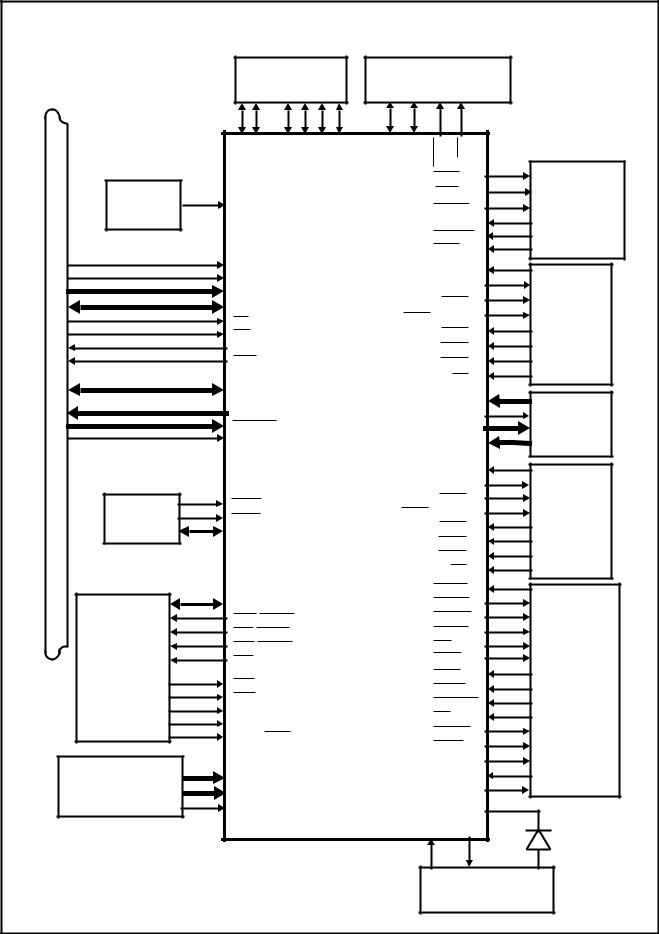
Block Diagram
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
DMA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Serial Infrared |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
|
|
IRQ Channels |
Control |
|
Data |
|
Control Interface Interface Interrupt |
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Plug and Play |
|
Real-Time Clock |
|
|
|
X-Bus |
|
|
|
Two UARTs + IR |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
(RTC and APC) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
(16550 or 16450) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
(PnP) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Floppy Disk |
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(Logical Device 2) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(Logical Devices 5 & 6) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Controller (FDC) |
|
|
|
||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Floppy |
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
with Digital Data |
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Separator (DDS) |
Drive |
||||
μP Address |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(PC8477) |
Interface |
|||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||
Data and |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(Logical Device 3) |
|
|
|
||||
Control |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
Keyboard |
|
Power Management |
|
|
|
|
IEEE1284 |
|
|
Mouse |
|
General Purpose |
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
Controller (KBC) |
|
|
|
Logic |
|
|
|
Parallel Port |
|
|
Controller |
|
|
I/O Registers |
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
(Logical Device 4) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
(Logical Device 0) |
|
(Logical Device 8) |
|
|
(Logical Device 1) |
|
(Logical Device 7) |
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
High Current Driver |
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Data and Ports |
|
|
Control |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Data and |
|
|
I/O Ports |
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||
Control |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Data |
Handshake |
|
|
Control |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||
TRI-STATE® is a registered trademark of National Semiconductor Corporation.
IBM®, MicroChannel®, PC-AT® and PS/2® are registered trademarks of International Business Machines Corporation.
Microsoft® and Windows® are registered trademarks of Microsoft Corporation.
© 1998 National Semiconductor Corporation |
www.national.com |
|
SuperI/O Compliant PC97 and Compatible Play and Plug PC87307/PC97307

Highlights
■A special Plug and Play (PnP) module that includes:
—Flexible IRQs, DMAs and base addresses that meet
the Plug and Play requirements specified by Mi-
crosoft® in their 1995 hardware design guide for Windows® and Plug and Play ISA Revision 1.0A
—Plug and Play ISA mode (with isolation mechanism
– Wait for Key state)
—Motherboard Plug and Play mode
■A Floppy Disk Controller (FDC) that provides:
—A modifiable address that is referenced by a 16-bit programmable register
—Software compatibility with the PC8477, which con-
tains a superset of the floppy disk controller functions in the μDP8473, the NEC μPD765A and the N82077
—13 IRQ channel options
—Four 8-bit DMA channel options
—16-byte FIFO
—Burst and non-burst modes
—A high-performance, internal, digital data separator that does not require any external filter components
—Support for standard 5.25" and 3.5" floppy disk drives
—Automatic media sense support
—Perpendicular recording drive support
—Three-mode Floppy Disk Drive (FDD) support
—Full support for the IBM Tape Drive Register (TDR) implementation of AT and PS/2 drive types
■A Keyboard and mouse Controller (KBC) with:
—A modifiable address that is referenced by a 16-bit programmable register, reported as a fixed address in resource data
—13 IRQ options for the keyboard controller
—13 IRQ options for the mouse controller
—An 8-bit microcontroller
—Software compatibility with the 8042AH and PC87911 microcontrollers
—2 KB of custom-designed program ROM
—256 bytes of RAM for data
—Five programmable dedicated open drain I/O lines for keyboard controller applications
—Asynchronous access to two data registers and one status register during normal operation
—Support for both interrupt and polling
—93 instructions
—An 8-bit timer/counter
—Support for binary and BCD arithmetic
—Operation at 8 MHz,12 MHz or 16 MHz (programmable option)
—Can be customized using the PC87323VUL, which includes a RAM-based KBC, as a development platform for keyboard controller code
■A Real-Time Clock (RTC) that has:
—A modifiable address that is referenced by a 16-bit programmable register
—13 IRQ options, with programmable polarity
—DS1287, MC146818 and PC87911 compatibility
—242 bytes of battery backed up CMOS RAM in two banks
—Selective lock mechanism for the RTC RAM
—Battery backed up century calendar in days, days of the week, months and years, with automatic leapyear adjustment
—Battery backed-up time of day in seconds, minutes and hours that allows a 12 or 24 hour format and adjustments for daylight savings time
—BCD or binary format for time keeping
—Three different maskable interrupt flags:
•Periodic interrupts - At intervals from 122 msec to 500 msec
•Time-of-day alarm - At intervals from once per second to once per day
•Updated Ended Interrupt - Once per second upon completion of update
—Separate battery pin, 2.4 V operation that includes an internal UL protection resistor
—2 μA maximum power consumption during power down
—Double-buffer time registers
■An Advanced Power supply Control (APC) that controls the main power supply to the system, using open-drain output, as follows:
Power turned on when:
—The RTC reaches a pre-determined date and time.
—A high to low transition occurs on the RI input signals of the UARTs.
—A ring pulse or pulse train is detected on the RING input signal.
—A SWITCH input signal indicates a Switch On event Powered turned off when:
—A SWITCH input signal indicates a Switch Off event
—A Fail-safe event occurs (power-save mode detected but the system is hung up).
—Software turns power off.
■Two UARTs that provide:
—Software compatibility with the 16550A and the 16450
—A modifiable address that is referenced by a 16-bit programmable register
—13 IRQ channel options
—Shadow register support for write-only bits
—Four 8-bit DMA options for the UART with Infrared support (UART2)
■An enhanced UART and Infrared (IR) interface on the UART2 that supports:
—UART data rates up to 1.5 Mbaud
—IrDA 1.0 SIR
—ASK-IR option of SHARP-IR
—DASK-IR option of SHARP-IR
—Consumer-IR (TV-Remote) circuitry
—A Plug and Play compatible external transceiver
■A bidirectional parallel port that includes:
—A modifiable address that is referenced by a 16-bit programmable register
www.national.com |
2 |

Highlights
—Software or hardware control
—13 IRQ channel options
—Four 8-bit DMA channel options
—Demand mode DMA support
—An Enhanced Parallel Port (EPP) that is compatible with the new version EPP 1.9, and is IEEE1284 compliant
—An Enhanced Parallel Port (EPP) that also supports version EPP 1.7 of the Xircom specification.
—Support for an Enhanced Parallel Port (EPP) as mode 4 of the Extended Capabilities Port (ECP)
—An Extended Capabilities Port (ECP) that is IEEE 1284 compliant, including level 2
—Selection of internal pull-up or pull-down resistor for Paper End (PE) pin
—Reduction of PCI bus utilization by supporting a demand DMA mode mechanism and a DMA fairness mechanism
—A protection circuit that prevents damage to the parallel port when a printer connected to it powers up or is operated at high voltages
—Output buffers that can sink and source14 mA
■Three general purpose pins for three separate programmable chip select signals, as follows:
—Can be programmed for game port control
—The Chip Select 0 (CS0) signal produces open drain output and is powered by the VCCH
—The Chip Select 1 (CS1) and 2 (CS2) signals have push-pull buffers and are powered by the main VDD
—Decoding of chip select signals depends on the address and the Address Enable (AEN) signals, and can be qualified using the Read (RD) and Write (WR) signals.
■16 single-bit General Purpose I/O ports (GPIO):
—Modifiable addresses that are referenced by a 16-bit programmable register
—Programmable direction for each signal (input or output) with configuration lock
—Programmable drive type for each output pin (opendrain or push-pull) with configuration lock
—Programmable option for internal pull-up resistor on each input pin with configuration lock
—A back-drive protection circuit
■An X-bus data buffer that connects the 8-bit X data bus to the ISA data bus
■Clock source options:
—Source is a 32.768 KHz crystal - an internal frequency multiplier generates all the required internal frequencies.
—Source may be either a 48 MHz or 24 MHz clock input signal.
■Enhanced Power Management (PM), including:
—Special configuration registers for power down
—WATCHDOG timer for power-saving strategies
—Reduced current leakage from pins
—Low-power CMOS technology
—Ability to shut off clocks to all modules
■General features include:
—All accesses to the SuperI/O chip activate a Zero Wait State (ZWS) signal, except for accesses to the Enhanced Parallel Port (EPP) and to configuration registers
—Access to all configuration registers is through an Index and a Data register, which can be relocated within the ISA I/O address space
—160-pin Plastic Quad Flatpack (PQFP) package
3 |
www.national.com |
|
|
|
Highlights |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Basic Configuration |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Keyboard I/O |
|
|
General |
|
||||
|
Interface |
|
Purpose Registers |
|
|||||
|
P17,16,12 P21,20 |
KBCLK |
KBDAT MDAT |
MCLK |
GPIO17-10 |
GPIO27-20 |
CS1,0 |
CS2 |
|
|
WDO |
|
|||||||
|
POR |
Power |
|||||||
Clock |
X1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
ONCTL |
Management |
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
VCCH |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
SWITCH |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
RING |
|
|
|
MR |
|
|
|
|
|
|
SIN1 |
|
|
AEN |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
SOUT1 |
|
||
|
A15-0 |
|
|
|
|
|
EIA |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
RTS1 |
|||
|
D7-0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
DTR1/BOUT1 |
Drivers |
|||
|
RD |
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
CTS1 |
|
||
|
WR |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
IOCHRDY |
|
|
|
|
|
DSR1 |
|
|
|
ZWS |
|
|
|
|
|
DCD1 |
|
|
Bus |
IRQ1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
RI1 |
|
IRQ12-3 |
|
|
|
|
|
IRRX2,1 |
|
||
IRQ15-14 |
|
|
|
|
|
Infrared |
|||
ISA |
DRQ3-0 |
|
|
|
|
|
IRTX |
||
DACK3-0 |
|
|
|
|
|
IRSL2-0 |
Interface |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
TC |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
PC87307/PC97307 |
ID3-0 |
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
SIN2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
SOUT2 |
|
|
|
XDRD |
|
|
|
|
|
RTS2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
DTR2/BOUT2 |
EIA |
|||
X-Bus |
XDCS |
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
CTS2 |
Drivers |
|||
|
XD7-0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
DSR2 |
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
DCD2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
RI2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
RDATA |
|
|
|
PD7-0 |
|
|
|
|
|
WDATA |
|
|
|
SLIN/ASTRB |
|
|
|
|
WGATE |
|
||
|
STB/WRITE |
|
|
|
|
HDSEL |
|
||
Parallel |
AFD/DSTRB |
|
|
|
|
DIR |
|
||
INIT |
|
|
|
|
|
STEP |
|
||
Port |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
TRK0 |
|
||
Connector |
ACK |
|
|
|
|
|
FDC |
||
|
|
|
|
|
INDEX |
||||
|
ERR |
|
|
|
|
|
Connector |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
DSKCHG |
|||
|
SLCT |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
WP |
|
||
|
PE |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
MTR1,0 |
|
||
|
BUSY/WAIT |
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
DR1,0 |
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
DENSEL |
|
|
Configuration |
BADDR1,0 |
|
|
|
|
|
MSEN1,0 |
|
|
Select Logic |
CFG3-0 |
|
|
|
|
|
DRATE0 |
|
|
|
SELCS |
|
|
|
|
|
VBAT |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
X1C |
X2C |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
RTC Crystal |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
and Power |
|
www.national.com |
|
|
4 |
|
|
|
|
|
|

Table of Contents
Table of Contents
Highlights ............................................................................................................................. |
1 |
1.0Signal/Pin Connection and Description
1.1 |
CONNECTION DIAGRAM ......................................................................................................... |
14 |
1.2 |
SIGNAL/PIN DESCRIPTIONS ................................................................................................... |
15 |
2.0Configuration
2.1 |
HARDWARE CONFIGURATION ............................................................................................... |
24 |
||
|
2.1.1 |
Wake Up Options ........................................................................................................ |
24 |
|
|
2.1.2 |
The Index and Data Register Pair ............................................................................... |
24 |
|
|
2.1.3 |
The Strap Pins ............................................................................................................. |
25 |
|
2.2 |
SOFTWARE CONFIGURATION ............................................................................................... |
25 |
||
|
2.2.1 |
Accessing the Configuration Registers ........................................................................ |
25 |
|
|
2.2.2 |
Address Decoding ....................................................................................................... |
25 |
|
2.3 |
THE CONFIGURATION REGISTERS ....................................................................................... |
26 |
||
|
2.3.1 |
Standard Plug and Play (PnP) Register Definitions .................................................... |
27 |
|
|
2.3.2 |
Configuration Register Summary ................................................................................ |
30 |
|
2.4 |
CARD CONTROL REGISTERS ................................................................................................ |
34 |
||
|
2.4.1 |
SID Register (In PC87307) .......................................................................................... |
34 |
|
|
2.4.2 |
SID Register (In PC97307) .......................................................................................... |
34 |
|
|
2.4.3 |
SuperI/O Configuration 1 Register, Index 21h ............................................................. |
34 |
|
|
2.4.4 |
SuperI/O Configuration 2 Register, Index 22h ............................................................. |
35 |
|
|
2.4.5 |
Programmable Chip Select Configuration Index Register, Index 23h ......................... |
35 |
|
|
2.4.6 |
Programmable Chip Select Configuration Data Register, Index 24h .......................... |
36 |
|
|
2.4.7 |
SRID Register (In PC97307 only) ................................................................................ |
36 |
|
2.5 |
KBC CONFIGURATION REGISTER (LOGICAL DEVICE 0) .................................................... |
36 |
||
|
2.5.1 |
SuperI/O KBC Configuration Register, Index F0h ....................................................... |
36 |
|
2.6 |
FDC CONFIGURATION REGISTERS (LOGICAL DEVICE 3) .................................................. |
36 |
||
|
2.6.1 |
SuperI/O FDC Configuration Register, Index F0h ....................................................... |
36 |
|
|
2.6.2 |
Drive ID Register, Index F1h ....................................................................................... |
37 |
|
2.7 |
PARALLEL PORT CONFIGURATION REGISTER (LOGICAL DEVICE 4) ............................... |
37 |
||
|
2.7.1 |
SuperI/O Parallel Port Configuration Register, Index F0h ........................................... |
37 |
|
2.8 |
UART2 AND INFRARED CONFIGURATION REGISTER (LOGICAL DEVICE 5) .................... |
38 |
||
|
2.8.1 |
SuperI/O UART2 Configuration Register, Index F0h ................................................... |
38 |
|
2.9 |
UART1 CONFIGURATION REGISTER (LOGICAL DEVICE 6) ................................................ |
38 |
||
|
2.9.1 |
SuperI/O UART1 Configuration Register, Index F0h ................................................... |
38 |
|
2.10 |
PROGRAMMABLE CHIP SELECT CONFIGURATION REGISTERS ...................................... |
39 |
||
|
2.10.1 |
|
39 |
|
|
CS0 |
.....................................................Base Address MSB, Second Level Index 00h |
||
|
2.10.2 |
|
39 |
|
|
CS0 |
.......................................Base Address LSB Register, Second Level Index 01h |
||
|
2.10.3 |
|
39 |
|
|
CS0 |
................................................Configuration Register, Second Level Index 02h |
||
|
2.10.4 |
Reserved, Second Level Index 03h ............................................................................. |
39 |
|
|
2.10.5 |
|
40 |
|
|
CS1 |
......................................Base Address MSB Register, Second Level Index 04h |
||
|
2.10.6 |
|
40 |
|
|
CS1 |
.......................................Base Address LSB Register, Second Level Index 05h |
||
5 |
www.national.com |

Table of Contents
2.10.7 |
CS1 Configuration Register, Second Level Index 06h ................................................ |
40 |
2.10.8 |
Reserved, Second Level Index 07h ............................................................................. |
40 |
2.10.9 |
CS2 Base Address MSB Register, Second Level Index 08h ...................................... |
40 |
2.10.10 |
CS2 Base Address LSB Register, Second Level Index 09h ....................................... |
40 |
2.10.11 |
CS2 Configuration Register, Second Level Index 0Ah ................................................ |
40 |
2.10.12 |
Reserved, Second Level Indexes 0Bh-0Fh ................................................................. |
40 |
2.10.13 |
Not Accessible, Second Level Indexes 10h-FFh ......................................................... |
40 |
2.11 CARD CONTROL REGISTER BITMAPS .................................................................................. |
41 |
|
3.0Keyboard (and Mouse) Controller (KBC) (Logical Devices 0 and 1)
3.1 |
SYSTEM ARCHITECTURE ....................................................................................................... |
43 |
|
3.2 |
FUNCTIONAL OVERVIEW ....................................................................................................... |
44 |
|
3.3 |
DEVICE CONFIGURATION ...................................................................................................... |
44 |
|
|
3.3.1 |
I/O Address Space ...................................................................................................... |
44 |
|
3.3.2 |
Interrupt Request Signals ............................................................................................ |
44 |
|
3.3.3 |
KBC Clock ................................................................................................................... |
45 |
|
3.3.4 Timer or Event Counter ............................................................................................... |
46 |
|
3.4 |
EXTERNAL I/O INTERFACES .................................................................................................. |
46 |
|
|
3.4.1 Keyboard and Mouse Interface ................................................................................... |
46 |
|
|
3.4.2 General Purpose I/O Signals ....................................................................................... |
46 |
|
3.5 |
INTERNAL KBC - PC87307/PC97307 INTERFACE ................................................................. |
47 |
|
|
3.5.1 The KBC DBBOUT Register, Offset 60h, Read Only .................................................. |
47 |
|
|
3.5.2 The KBC DBBIN Register, Offset 60h (F1 Clear) or 64h (F1 Set), Write Only ............ |
47 |
|
|
3.5.3 The KBC STATUS Register, Offset 64h, Read Only ................................................... |
48 |
|
3.6 |
INSTRUCTION TIMING ............................................................................................................. |
48 |
|
4.0Real-Time Clock (RTC) and Advanced Power Control (APC) (Logical Device 2)
4.1 |
RTC OPERATION OVERVIEW ................................................................................................. |
49 |
|||
|
4.1.1 RTC Hardware and Functional Description ................................................................. |
49 |
|||
|
4.1.2 |
Timekeeping ................................................................................................................ |
50 |
||
|
4.1.3 |
Power Supply .............................................................................................................. |
51 |
||
|
4.1.4 |
Interrupt Handling ........................................................................................................ |
52 |
||
4.2 |
THE RTC REGISTERS ............................................................................................................. |
52 |
|||
|
4.2.1 RTC Control Register A (CRA), Index 0Ah .................................................................. |
52 |
|||
|
4.2.2 |
RTC Control Register B (CRB), Index 0Bh ................................................................. |
54 |
||
|
4.2.3 RTC Control Register C (CRC), Index 0Ch ................................................................. |
54 |
|||
|
4.2.4 RTC Control Register D (CRD), Index 0Dh ................................................................. |
55 |
|||
4.3 |
APC OVERVIEW ....................................................................................................................... |
55 |
|||
|
4.3.1 |
User Selectable Parameters ........................................................................................ |
55 |
||
|
4.3.2 |
System Power States .................................................................................................. |
56 |
||
|
4.3.3 System Power Switching Logic ................................................................................... |
56 |
|||
4.4 |
DETAILED FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION ................................................................................ |
58 |
|||
|
|
|
|
||
|
4.4.1 |
The |
ONCTL |
......................................................................................................Signal |
58 |
|
4.4.2 |
Entering Power States ................................................................................................. |
58 |
||
|
4.4.3 System Power-Up and Power-Off Activation Event Description .................................. |
59 |
|||
www.national.com |
6 |

Table of Contents
4.5 |
APC REGISTERS ...................................................................................................................... |
60 |
|
|
4.5.1 APC Control Register 1 (APCR1), Index 40h .............................................................. |
60 |
|
|
4.5.2 APC Control Register 2 (APCR2), Index 41h .............................................................. |
61 |
|
|
4.5.3 APC Status Register (APSR), Index 42h ..................................................................... |
61 |
|
|
4.5.4 RAM Lock Register (RLR), Index 47h ......................................................................... |
62 |
|
4.6 |
RTC AND APC REGISTER BITMAPS ...................................................................................... |
62 |
|
|
4.6.1 |
RTC Register Bitmaps ................................................................................................. |
62 |
|
4.6.2 |
APC Register Bitmaps ................................................................................................. |
63 |
4.7 |
REGISTER BANK TABLES ....................................................................................................... |
64 |
|
5.0The Digital Floppy Disk Controller (FDC) (Logical Device 3)
5.1 |
FDC FUNCTIONS ..................................................................................................................... |
66 |
|
|
5.1.1 |
Microprocessor Interface ............................................................................................. |
66 |
|
5.1.2 |
System Operation Modes ............................................................................................ |
66 |
5.2 |
DATA TRANSFER ..................................................................................................................... |
67 |
|
|
5.2.1 |
Data Rates ................................................................................................................... |
67 |
|
5.2.2 |
The Data Separator ..................................................................................................... |
67 |
|
5.2.3 Perpendicular Recording Mode Support ..................................................................... |
68 |
|
|
5.2.4 |
Data Rate Selection ..................................................................................................... |
68 |
|
5.2.5 |
Write Precompensation ............................................................................................... |
69 |
|
5.2.6 FDC Low-Power Mode Logic ....................................................................................... |
69 |
|
|
5.2.7 |
Reset ........................................................................................................................... |
69 |
5.3 THE REGISTERS OF THE FDC ............................................................................................... |
70 |
||
|
5.3.1 Status Register A (SRA), Offset 00h ........................................................................... |
70 |
|
|
5.3.2 Status Register B (SRB), Offset 01h ........................................................................... |
71 |
|
|
5.3.3 Digital Output Register (DOR), Offset 02h .................................................................. |
71 |
|
|
5.3.4 Tape Drive Register (TDR), Offset 03h ....................................................................... |
73 |
|
|
5.3.5 Main Status Register (MSR), Offset 04h, Read Operations ........................................ |
74 |
|
|
5.3.6 Data Rate Select Register (DSR), Offset 04h, Write Operations ................................ |
75 |
|
|
5.3.7 Data Register (FIFO), Offset 05h ................................................................................ |
76 |
|
|
5.3.8 Digital Input Register (DIR), Offset 07h, Read Operations .......................................... |
77 |
|
|
5.3.9 Configuration Control Register (CCR), Offset 07h, Write Operations ......................... |
78 |
|
5.4 THE PHASES OF FDC COMMANDS ....................................................................................... |
78 |
||
|
5.4.1 |
Command Phase ......................................................................................................... |
78 |
|
5.4.2 |
Execution Phase .......................................................................................................... |
78 |
|
5.4.3 |
Result Phase ............................................................................................................... |
80 |
|
5.4.4 |
Idle Phase .................................................................................................................... |
80 |
|
5.4.5 |
Drive Polling Phase ..................................................................................................... |
80 |
5.5 THE RESULT PHASE STATUS REGISTERS .......................................................................... |
81 |
||
|
5.5.1 Result Phase Status Register 0 (ST0) ......................................................................... |
81 |
|
|
5.5.2 Result Phase Status Register 1 (ST1) ......................................................................... |
81 |
|
|
5.5.3 Result Phase Status Register 2 (ST2) ......................................................................... |
82 |
|
|
5.5.4 Result Phase Status Register 3 (ST3) ......................................................................... |
83 |
|
5.6 |
FDC REGISTER BITMAPS ....................................................................................................... |
84 |
|
|
5.6.1 FDC Standard Register Bitmaps ................................................................................. |
84 |
|
7 |
www.national.com |

Table of Contents
5.6.2 |
FDC Result Phase Status Register Bitmaps |
............................................................... 85 |
5.7 THE FDC COMMAND SET ....................................................................................................... |
86 |
|
5.7.1 |
Abbreviations Used in FDC Commands ...................................................................... |
87 |
5.7.2 |
The CONFIGURE Command ...................................................................................... |
88 |
5.7.3 |
The DUMPREG Command ......................................................................................... |
88 |
5.7.4 |
The FORMAT TRACK Command ............................................................................... |
89 |
5.7.5 |
The INVALID Command .............................................................................................. |
92 |
5.7.6 |
The LOCK Command .................................................................................................. |
92 |
5.7.7 |
The MODE Command ................................................................................................. |
92 |
5.7.8 |
The NSC Command .................................................................................................... |
94 |
5.7.9 |
The PERPENDICULAR MODE Command ................................................................. |
94 |
5.7.10 |
The READ DATA Command ....................................................................................... |
96 |
5.7.11 |
The READ DELETED DATA Command ...................................................................... |
98 |
5.7.12 |
The READ ID Command ............................................................................................. |
99 |
5.7.13 |
The READ A TRACK Command ............................................................................... |
100 |
5.7.14 |
The RECALIBRATE Command ................................................................................. |
100 |
5.7.15 |
The RELATIVE SEEK Command .............................................................................. |
101 |
5.7.16The SCAN EQUAL, the SCAN LOW OR EQUAL and the SCAN HIGH OR EQUAL
|
Commands .......................................................................................................... |
101 |
5.7.17 |
The SEEK Command ................................................................................................ |
102 |
5.7.18 The SENSE DRIVE STATUS Command .................................................................. |
103 |
|
5.7.19 The SENSE INTERRUPT Command ........................................................................ |
103 |
|
5.7.20 The SET TRACK Command ...................................................................................... |
104 |
|
5.7.21 |
The SPECIFY Command .......................................................................................... |
105 |
5.7.22 |
The VERIFY Command ............................................................................................. |
106 |
5.7.23 |
The VERSION Command .......................................................................................... |
108 |
5.7.24 The WRITE DATA Command .................................................................................... |
108 |
|
5.7.25 The WRITE DELETED DATA Command .................................................................. |
109 |
|
5.8 EXAMPLE OF A FOUR-DRIVE CIRCUIT USING THE PC87307/PC97307 ........................... |
110 |
|
6.0Parallel Port (Logical Device 4)
6.1 PARALLEL PORT CONFIGURATION .................................................................................... |
111 |
|
6.1.1 Parallel Port Operation Modes .................................................................................. |
111 |
|
6.1.2 |
Configuring Operation Modes .................................................................................... |
111 |
6.1.3 |
Output Pin Protection ................................................................................................ |
111 |
6.2 STANDARD PARALLEL PORT (SPP) MODES ...................................................................... |
111 |
|
6.2.1 Standard Parallel Port (SPP) Modes Register Set .................................................... |
112 |
|
6.2.2 SPP Data Register (DTR), Offset 00h ....................................................................... |
112 |
|
6.2.3 Status Register (STR), Offset 01h ............................................................................. |
113 |
|
6.2.4 SPP Control Register (CTR), Offset 02h ................................................................... |
114 |
|
6.3 ENHANCED PARALLEL PORT (EPP) MODES ...................................................................... |
115 |
|
6.3.1 Enhanced Parallel Port (EPP) Register Set .............................................................. |
115 |
|
6.3.2 SPP or EPP Data Register (DTR), Offset 00h ........................................................... |
115 |
|
6.3.3 SPP or EPP Status Register (STR), Offset 01h ........................................................ |
115 |
|
6.3.4 SPP or EPP Control Register (CTR), Offset 02h ....................................................... |
116 |
|
6.3.5 EPP Address Register (ADDR), Offset 03h ............................................................... |
116 |
|
6.3.6 EPP Data Register 0 (DATA0), Offset 04h ................................................................ |
116 |
|
www.national.com |
8 |

Table of Contents
6.3.7 |
EPP Data Register 1 (DATA1), Offset 05h ................................................................ |
116 |
6.3.8 |
EPP Data Register 2 (DATA2), Offset 06h ................................................................ |
116 |
6.3.9 |
EPP Data Register 3 (DATA3), Offset 07h ................................................................ |
117 |
6.3.10 |
EPP Mode Transfer Operations ................................................................................ |
117 |
6.3.11 |
EPP 1.7 and 1.9 Zero Wait State Data Write and Read Operations ......................... |
118 |
6.4 EXTENDED CAPABILITIES PARALLEL PORT (ECP) ........................................................... |
119 |
|
6.4.1 |
ECP Modes ............................................................................................................... |
119 |
6.4.2 |
Software Operation .................................................................................................... |
119 |
6.4.3 |
Hardware Operation .................................................................................................. |
119 |
6.5 ECP MODE REGISTERS ........................................................................................................ |
120 |
|
6.5.1 |
Accessing the ECP Registers .................................................................................... |
120 |
6.5.2 |
Second Level Offsets ................................................................................................ |
120 |
6.5.3 |
ECP Data Register (DATAR), Bits 7-5 of ECR = 000 or 001, Offset 000h ................ |
121 |
6.5.4 |
ECP Address FIFO (AFIFO) Register, Bits 7-5 of ECR = 011, Offset 000h .............. |
121 |
6.5.5 |
ECP Status Register (DSR), Offset 001h .................................................................. |
121 |
6.5.6 |
ECP Control Register (DCR), Offset 002h ................................................................ |
122 |
6.5.7 |
Parallel Port Data FIFO (CFIFO) Register, Bits 7-5 of ECR = 010, Offset 400h ....... |
122 |
6.5.8 |
ECP Data FIFO (DFIFO) Register, Bits 7-5 of ECR = 011, Offset 400h ................... |
122 |
6.5.9 |
Test FIFO (TFIFO) Register, Bits 7-5 of ECR = 110, Offset 400h ............................. |
123 |
6.5.10 |
Configuration Register A (CNFGA), Bits 7-5 of ECR = 111, Offset 400h .................. |
123 |
6.5.11 |
Configuration Register B (CNFGB), Bits 7-5 of ECR = 111, Offset 401h .................. |
123 |
6.5.12 |
Extended Control Register (ECR), Offset 402h ......................................................... |
124 |
6.5.13 |
ECP Extended Index Register (EIR), Offset 403h ..................................................... |
125 |
6.5.14 |
ECP Extended Data Register (EDR), Offset 404h .................................................... |
126 |
6.5.15 |
ECP Extended Auxiliary Status Register (EAR), Offset 405h ................................... |
126 |
6.5.16 |
Control0, Second Level Offset 00h ............................................................................ |
126 |
6.5.17 |
Control2, Second Level Offset 02h ............................................................................ |
126 |
6.5.18 |
Control4, Second Level Offset 04h ............................................................................ |
127 |
6.5.19 |
PP Confg0, Second Level Offset 05h ........................................................................ |
127 |
6.6 DETAILED ECP MODE DESCRIPTIONS ............................................................................... |
128 |
|
6.6.1 |
Software Controlled Data Transfer (Modes 000 and 001) ......................................... |
128 |
6.6.2 |
Automatic Data Transfer (Modes 010 and 011) ........................................................ |
128 |
6.6.3 |
Automatic Address and Data Transfers (Mode 100) ................................................. |
130 |
6.6.4 |
FIFO Test Access (Mode 110) .................................................................................. |
130 |
6.6.5 |
Configuration Registers Access (Mode 111) ............................................................. |
130 |
6.6.6 |
Interrupt Generation .................................................................................................. |
130 |
6.7 PARALLEL PORT REGISTER BITMAPS ............................................................................... |
131 |
|
6.7.1 |
EPP Modes Parallel Port Register Bitmaps ............................................................... |
131 |
6.7.2 |
ECP Modes Parallel Port Register Bitmaps .............................................................. |
132 |
6.8 PARALLEL PORT PIN/SIGNAL LIST ...................................................................................... |
134 |
|
7.0UART1 and UART2 (with IR) (Logical Devices 5 and 6)
7.1 |
FEATURES .............................................................................................................................. |
135 |
|
7.2 |
FUNCTIONAL MODES OVERVIEW ....................................................................................... |
135 |
|
|
7.2.1 |
UART Modes: 16450 or 16550, and Extended .......................................................... |
135 |
|
7.2.2 |
Sharp-IR, IrDA SIR Infrared Modes ........................................................................... |
135 |
9 |
www.national.com |

Table of Contents
|
7.2.3 |
Consumer IR Mode ................................................................................................... |
135 |
7.3 |
REGISTER BANK OVERVIEW ............................................................................................... |
136 |
|
7.4 |
UART MODES – DETAILED DESCRIPTION .......................................................................... |
136 |
|
|
7.4.1 16450 or 16550 UART Mode ..................................................................................... |
137 |
|
|
7.4.2 |
Extended UART Mode ............................................................................................... |
137 |
7.5 |
SHARP-IR MODE – DETAILED DESCRIPTION ..................................................................... |
138 |
|
7.6 |
SIR MODE – DETAILED DESCRIPTION ................................................................................ |
138 |
|
7.7 |
CONSUMER-IR MODE – DETAILED DESCRIPTION ............................................................ |
138 |
|
|
7.7.1 |
Consumer-IR Transmission ....................................................................................... |
138 |
|
7.7.2 |
Consumer-IR Reception ............................................................................................ |
138 |
7.8 |
FIFO TIME-OUTS .................................................................................................................... |
139 |
|
|
7.8.1 UART, SIR or Sharp-IR Mode Time-Out Conditions ................................................. |
139 |
|
|
7.8.2 Consumer-IR Mode Time-Out Conditions ................................................................. |
139 |
|
|
7.8.3 |
Transmission Deferral ............................................................................................... |
139 |
7.9 |
AUTOMATIC FALLBACK TO A NON-EXTENDED UART MODE .......................................... |
140 |
|
7.10 |
OPTICAL TRANSCEIVER INTERFACE ................................................................................. |
140 |
|
7.11 |
BANK 0 – GLOBAL CONTROL AND STATUS REGISTERS ................................................. |
140 |
|
7.11.1Receiver Data Port (RXD) or the Transmitter Data Port (TXD), Bank 0, Offset 00h . 141
7.11.2 Interrupt Enable Register (IER), Bank 0, Offset 01h ................................................. |
141 |
|
7.11.3 |
Event Identification Register (EIR), Bank 0, Offset 02h ............................................. |
143 |
7.11.4 |
FIFO Control Register (FCR), Bank 0, Offset 02h ..................................................... |
145 |
7.11.5Link Control Register (LCR), Bank 0, Offset 03h, and Bank Selection Register (BSR),
|
All Banks, Offset 03h ........................................................................................... |
145 |
7.11.6 |
Bank Selection Register (BSR), All Banks, Offset 03h .............................................. |
147 |
7.11.7 |
Modem/Mode Control Register (MCR), Bank 0, Offset 04h ...................................... |
147 |
7.11.8 |
Link Status Register (LSR), Bank 0, Offset 05h ........................................................ |
148 |
7.11.9 |
Modem Status Register (MSR), Bank 0, Offset 06h .................................................. |
149 |
7.11.10 |
Scratchpad Register (SPR), Bank 0, Offset 07h ....................................................... |
150 |
7.11.11 |
Auxiliary Status and Control Register (ASCR), Bank 0, Offset 07h ........................... |
150 |
7.11.12 |
Legacy Baud Generator Divisor Ports (LBGD(L) and LBGD(H)), |
|
|
Bank 1, Offsets 00h and 01h ............................................................................... |
151 |
7.11.13 |
Link Control Register (LCR) and Bank Select Register (BSR), Bank 1, Offset 03h .. |
152 |
7.12 BANK 2 – EXTENDED CONTROL AND STATUS REGISTERS ............................................ |
152 |
|
7.12.1 |
Baud Generator Divisor Ports, LSB (BGD(L)) and |
|
|
MSB (BGD(H)),Bank 2, Offsets 00h and 01h ...................................................... |
152 |
7.12.2 |
Extended Control Register 1 (EXCR1), Bank 2, Offset 02h ...................................... |
154 |
7.12.3 |
Link Control Register (LCR) and Bank Select Register (BSR), Bank 2, Offset 03h .. |
155 |
7.12.4 |
Extended Control and Status Register 2 (EXCR2), Bank 2, Offset 04h .................... |
155 |
7.12.5 |
Reserved Register, Bank 2, Offset 05h ..................................................................... |
155 |
7.12.6 |
TX_FIFO Current Level Register (TXFLV), Bank 2, Offset 06h ................................ |
155 |
7.12.7RX_FIFO Current Level Register (RXFLV), IrDA or Consumer-IR Modes,
|
Bank 2, Offset 07h .............................................................................................. |
156 |
7.13 BANK 3 – MODULE REVISION ID AND SHADOW REGISTERS .......................................... |
156 |
|
7.13.1 |
Module Revision ID Register (MRID), Bank 3, Offset 00h ......................................... |
156 |
7.13.2 |
Shadow of Link Control Register (SH_LCR), Bank 3, Offset 01h .............................. |
157 |
www.national.com |
10 |

Table of Contents
7.13.3 Shadow of FIFO Control Register (SH_FCR), Bank 3, Offset 02h ............................ |
157 |
7.13.4 Link Control Register (LCR) and Bank Select Register (BSR), Bank 3, Offset 03h .. |
157 |
7.14 BANK 4 – IR MODE SETUP REGISTER ................................................................................ |
157 |
7.14.1 Reserved Registers, Bank 4, Offsets 00h and 01h ................................................... |
157 |
7.14.2 Infrared Control Register 1 (IRCR1), Bank 4, Offset 02h .......................................... |
157 |
7.14.3 Link Control Register (LCR) and Bank Select Register (BSR), Bank 4, Offset 03h .. |
158 |
7.14.4 Reserved Registers, Bank 4, Offsets 04h -07h ......................................................... |
158 |
7.15 BANK 5 – INFRARED CONTROL REGISTERS ..................................................................... |
158 |
7.15.1 Reserved Registers, Bank 5, Offsets 00h -02h ......................................................... |
158 |
7.15.2 (LCR/BSR) Register, Bank 5, Offset 03h .................................................................. |
158 |
7.15.3 Infrared Control Register 2 (IRCR2), Bank 5, Offset 04h .......................................... |
158 |
7.15.4 Reserved Registers, Bank 5, Offsets 05h -07h ......................................................... |
158 |
7.16 BANK 6 – INFRARED PHYSICAL LAYER CONFIGURATION REGISTERS ......................... |
159 |
7.16.1 Infrared Control Register 3 (IRCR3), Bank 6, Offset 00h .......................................... |
159 |
7.16.2 Reserved Register, Bank 6, Offset 01h ..................................................................... |
159 |
7.16.3 SIR Pulse Width Register (SIR_PW), Bank 6, Offset 02h ......................................... |
159 |
7.16.4 Link Control Register (LCR) and Bank Select Register (BSR), Bank 6, Offset 03h .. |
159 |
7.16.5 Reserved Registers, Bank 6, Offsets 04h-07h .......................................................... |
159 |
7.17BANK 7 – CONSUMER-IR AND OPTICAL TRANSCEIVER CONFIGURATION REGISTERS 159
7.17.1 Infrared Receiver Demodulator Control Register (IRRXDC), Bank 7, Offset 0 ......... |
160 |
7.17.2 Infrared Transmitter Modulator Control Register (IRTXMC), Bank 7, Offset 01h ...... |
160 |
7.17.3 Consumer-IR Configuration Register (RCCFG), Bank 7, Offset 02h ........................ |
163 |
7.17.4 Link Control/Bank Select Registers (LCR/BSR), Bank 7, Offset 03h ........................ |
163 |
7.17.5 Infrared Interface Configuration Register 1 (IRCFG1), Bank 7, Offset 04h ............... |
163 |
7.17.6 Reserved Register, Bank 7, Offset 05h ..................................................................... |
164 |
7.17.7 Infrared Interface Configuration 3 Register (IRCFG3), Bank 7, Offset 06h ............... |
164 |
7.17.8 Infrared Interface Configuration Register 4 (IRCFG4), Bank 7, Offset 07h ............... |
164 |
7.18 UART2 REGISTER WITH FAST IR REGISTER BITMAPS .................................................... |
165 |
8.0General Purpose Input and Output (GPIO) Ports (Logical Device 7) and Chip Select Output Signals
8.1 |
GENERAL PURPOSE INPUT AND OUTPUT (GPIO) PORTS ............................................... |
170 |
8.2 |
PROGRAMMABLE CHIP SELECT OUTPUT SIGNALS ......................................................... |
171 |
9.0Power Management (Logical Device 8)
9.1 POWER MANAGEMENT OPTIONS ....................................................................................... |
172 |
|
9.1.1 |
Configuration Options ................................................................................................ |
172 |
9.1.2 |
The WATCHDOG Feature ......................................................................................... |
172 |
9.2 THE POWER MANAGEMENT REGISTERS .......................................................................... |
172 |
|
9.2.1 Power Management Index Register, Base Address + 00h ........................................ |
172 |
|
9.2.2 Power Management Data Register, Base Address + 01h ......................................... |
173 |
|
9.2.3 Function Enable Register 1 (FER1), Index 00h ......................................................... |
173 |
|
9.2.4 Function Enable Register 2 (FER2), Index 01h ......................................................... |
173 |
|
9.2.5 Power Management Control 1 Register (PMC1), Index 02h ..................................... |
174 |
|
9.2.6 Power Management Control 2 Register (PMC2), Index 03h ..................................... |
174 |
|
11 |
www.national.com |
Table of Contents
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
9.2.7 |
Power Management Control 3 Register (PMC3), Index 04h ..................................... |
175 |
|
|
|
|
9.2.8 |
Watchdog Time-Out (WDTO) Register, Index 05h .................................................... |
175 |
|
|
|
|
9.2.9 |
WATCHDOG Configuration Register (WDCF), Index 06h ........................................ |
175 |
|
|
|
|
9.2.10 |
WATCHDOG Status Register (WDST), Index 07h .................................................... |
176 |
|
|
|
9.3 |
POWER MANAGEMENT REGISTER BITMAPS .................................................................... |
177 |
|
|
|
10.0 |
X-Bus Data Buffer |
|
|
||
|
|
10.1 |
FUNCTIONAL OVERVIEW ..................................................................................................... |
179 |
|
|
|
|
10.2 |
MAPPING ................................................................................................................................ |
179 |
|
|
|
11.0 |
The Internal Clock |
|
|
||
|
|
11.1 |
THE CLOCK SOURCE ............................................................................................................ |
180 |
|
|
|
|
11.2 |
THE INTERNAL ON-CHIP CLOCK MULTIPLIER ................................................................... |
180 |
|
|
|
|
11.3 |
SPECIFICATIONS ................................................................................................................... |
180 |
|
|
|
12.0 |
Interrupt and DMA Mapping |
|
|
||
|
|
12.1 |
IRQ MAPPING ......................................................................................................................... |
181 |
|
|
|
|
12.2 |
DMA MAPPING ....................................................................................................................... |
181 |
|
|
|
13.0 |
Device Description |
|
|
||
|
|
13.1 |
GENERAL DC ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS ............................................................... |
182 |
|
|
|
|
|
13.1.1 |
Recommended Operating Conditions ....................................................................... |
182 |
|
|
|
|
13.1.2 |
Absolute Maximum Ratings ....................................................................................... |
182 |
|
|
|
|
13.1.3 |
Capacitance ............................................................................................................... |
182 |
|
|
|
|
13.1.4 |
Power Consumption Under Recommended Operating Conditions ........................... |
183 |
|
|
|
13.2 |
DC CHARACTERISTICS OF PINS, BY GROUP .................................................................... |
183 |
|
|
|
|
|
13.2.1 |
Group 1 ...................................................................................................................... |
183 |
|
|
|
|
13.2.2 |
Group 2 ...................................................................................................................... |
184 |
|
|
|
|
13.2.3 |
Group 3 ...................................................................................................................... |
184 |
|
|
|
|
13.2.4 |
Group 4 ...................................................................................................................... |
184 |
|
|
|
|
13.2.5 |
Group 5 ...................................................................................................................... |
185 |
|
|
|
|
13.2.6 |
Group 6 ...................................................................................................................... |
185 |
|
|
|
|
13.2.7 |
Group 7 ...................................................................................................................... |
185 |
|
|
|
|
13.2.8 |
Group 8 ...................................................................................................................... |
186 |
|
|
|
|
13.2.9 |
Group 9 ...................................................................................................................... |
186 |
|
|
|
|
13.2.10 |
Group 10 .................................................................................................................... |
187 |
|
|
|
|
13.2.11 |
Group 11 .................................................................................................................... |
187 |
|
|
|
|
13.2.12 |
Group 12 .................................................................................................................... |
188 |
|
|
|
|
13.2.13 |
Group 13 .................................................................................................................... |
188 |
|
|
|
|
13.2.14 |
Group 14 .................................................................................................................... |
189 |
|
|
|
|
13.2.15 |
Group 15 .................................................................................................................... |
189 |
|
|
|
|
13.2.16 |
Group 16 .................................................................................................................... |
189 |
|
|
|
|
13.2.17 |
Group 17 .................................................................................................................... |
190 |
|
|
|
|
13.2.18 |
Group 18 .................................................................................................................... |
190 |
|
|
|
|
13.2.19 |
Group 19 .................................................................................................................... |
190 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
www.national.com |
12 |

Table of Contents
13.2.20 |
Group 20 .................................................................................................................... |
190 |
13.2.21 |
Group 21 .................................................................................................................... |
190 |
13.2.22 |
Group 22 .................................................................................................................... |
191 |
13.2.23 |
Group 23 .................................................................................................................... |
191 |
13.3 AC ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS .................................................................................. |
191 |
|
13.3.1 |
AC Test Conditions TA = 0 °C to 70 °C, VDD = 5.0 V ±10% ...................................... |
191 |
13.3.2 |
Clock Timing .............................................................................................................. |
192 |
13.3.3 |
Microprocessor Interface Timing ............................................................................... |
193 |
13.3.4 |
Baud Output Timing ................................................................................................... |
195 |
13.3.5 |
Transmitter Timing ..................................................................................................... |
196 |
13.3.6 |
Receiver Timing ......................................................................................................... |
197 |
13.3.7 |
UART, Sharp-IR and Consumer-IR Timing ............................................................... |
199 |
13.3.8 |
SIR Timing ................................................................................................................. |
200 |
13.3.9 |
IRSLn Write Timing ................................................................................................... |
200 |
13.3.10 |
Modem Control Timing .............................................................................................. |
201 |
13.3.11 |
DMA Timing ............................................................................................................... |
202 |
13.3.12 |
Reset Timing ............................................................................................................. |
204 |
13.3.13 |
Write Data Timing ...................................................................................................... |
204 |
13.3.14 |
Drive Control Timing .................................................................................................. |
205 |
13.3.15 |
Read Data Timing ...................................................................................................... |
205 |
13.3.16 |
Parallel Port Timing ................................................................................................... |
206 |
13.3.17 |
Enhanced Parallel Port 1.7 Timing ............................................................................ |
207 |
13.3.18 |
Enhanced Parallel Port 1.9 Timing ............................................................................ |
208 |
13.3.19 |
Extended Capabilities Port (ECP) Timing .................................................................. |
209 |
13.3.20 |
GPIO Write Timing .................................................................................................... |
210 |
13.3.21 |
RTC Timing ............................................................................................................... |
210 |
13.3.22 |
APC Timing ............................................................................................................... |
211 |
13.3.23 |
Chip Select Timing .................................................................................................... |
212 |
13 |
www.national.com |

Signal/Pin Connection and Description
1.0 Signal/Pin Connection and Description |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
1.1 |
CONNECTION DIAGRAM |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
SS |
AFD/DSTRB |
SLIN/ASTRB INIT ERR |
PE |
SLCT ACK STB/WRITE |
BUSY/WAIT |
P21 P20 |
P17 P16 P12 MDAT MCLK KBDAT |
SS |
DD |
TRK0 RDATA DENSEL WGATE HDSEL STEP |
DIR |
WDATA DR1 |
DR0 |
MTR1 |
MTR0 |
DRATE0 |
MSEN1 |
MSEN0 |
IRTX |
|
|
|
|
V |
KBCLK V |
V DSKCHG WP INDEX |
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
|
120 |
|
115 |
|
110 |
105 |
100 |
95 |
|
90 |
|
|
|
85 |
|
|
|
81 |
|
|||
|
VDD |
121 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
80 |
IRRX1 |
|
PD0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
IRRX2/IRSL0/ID0 |
|
PD1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
IRSL1/XD7/ID1 |
|
PD2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
IRSL2/XD6/SELCS/GPIO21 |
|
PD3 |
125 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
GPIO27/XD5 |
|
PD4 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
75 |
GPIO26/XD4 |
|
PD5 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
GPIO25/XD3 |
|
PD6 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
GPIO24/XD2 |
|
PD7 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
CS2/XD1 |
|
VSS |
130 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
70 |
CS1/XD0 |
|
CTS1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
XDRD/ID3 |
|
|
DCD1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
RING/XDCS |
|
DSR1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
CS0/CSOUT-NSC-Test |
DTR1/BADDR0/BOUT1 |
135 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ONCTL |
|
|
RI1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
65 |
SWITCH |
|
|
RTS1/BADDR1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
VCCH |
|
|
SIN1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
VBAT |
|
SOUT1/CFG0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
X2C |
|
VSS |
140 |
|
|
|
|
|
PC87307/PC97307 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
X1C |
|||||
|
VDD |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
VDD |
|||||||
|
CTS2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
60 |
VSS |
||||||
|
DCD2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
DACK3 |
|
DSR2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
DACK2 |
DTR2/CFG1/BOUT2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
DACK1 |
|
|
RI2 |
145 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
DACK0 |
|
RTS2/CFG2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
55 |
DRQ3 |
|
SIN2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
DRQ2 |
|
SOUT2/CFG3 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
DRQ1 |
|
GPIO10 |
150 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
DRQ0 |
|
GPIO11 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
50 |
MR |
|
|
GPIO12 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
X1 |
|
|
GPIO13 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
IRQ15 |
|
GPIO14 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
IRQ14 |
|
GPIO15 |
155 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
IRQ12 |
|
GPIO16 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
45 |
IRQ11 |
|
|
GPIO17/WDO |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
IRQ10 |
|
|
GPIO20/IRSL1/ID1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
IRQ9 |
GPIO21/IRSL2/IRSL0/ID2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
IRQ8 |
|
|
GPIO22/POR |
160 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
41 |
IRQ7 |
|
GPIO23/RING |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
IRQ6 |
||
|
|
1 |
|
5 |
|
|
10 |
|
15 |
20 |
|
25 |
30 |
|
|
|
35 |
|
|
|
|
40 |
|
|
|
DD |
SS |
|
|
|
|
SS |
|
|
DD |
SS |
AEN |
ZWS |
IOCHRDY RD |
|
|
IRQ1 |
IRQ3 |
IRQ4 |
IRQ5 |
SS |
|
|
|
V |
V |
D0 D1 D2 |
D3 |
D4 D5 D6 |
D7 |
V A0 |
A1 A2 A3 A4 A5 A6 A7 A8 A9 A10 A11 V |
V A12 A13 A14 A15 |
WR |
TC |
V |
|
|||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
PlasticQuad Flatpack (PQFP), EIAJ |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Order Number PC87307VUL/PC97307VUL |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
See NS Package Number VUL160A |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
www.national.com |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
14 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||

Signal/Pin Connection and Description
1.2SIGNAL/PIN DESCRIPTIONS
Table 1-1 lists the signals of the part in alphabetical order and shows the pin(s) associated with each. Table 1-2 on page 23 lists the X-Bus Data Buffer (XDB) signals that are multiplexed and Table 1-3 on page 23 lists the pins that have strap functions during reset.
The Module column indicates the functional module that is associated with these pins. In this column, the System label indicates internal functions that are common to more than one module.
The I/O and Group # column describes whether the pin is an input, output, or bidirectional pin (marked as Input, Output or I/O, respectively). This column also specifies the DC characteristics group to which this pin belongs. See Section 13.2 on page 183 for details.
Refer to the glossary for an explanation of abbreviations and terms used in this table, and throughout this document. Use the Table of Contents to find more information about each register.
TABLE 1-1. Signal/Pin Description Table
|
Signal/Pin |
Pin |
Module |
I/O and |
|
|
Function |
|||||||||||
|
Name |
Number |
Group # |
|
|
|||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
|
A15-0 |
29-26, |
ISA-Bus |
Input |
ISA-Bus Address –A15-0 are used for address decoding on any |
|||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
23-12 |
|
Group 1 |
access except DMA accesses, on the condition that the AEN signal |
||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
is low. See Address Decoding in Section 2.2.2 on page 25. |
||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
113 |
Parallel Port |
Input |
Acknowledge –This input signal is pulsed low by the printer to |
||||||||||
|
ACK |
|
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Group 3 |
indicate that it has received data from the parallel port. It is pulled up |
||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
by an internal nominal 25 KΩ pull-up resistor. |
||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
119 |
Parallel Port |
I/O |
Automatic Feed –When this signal is low the printer should |
||||||||||
|
AFD |
|
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Group 13 |
automatically feed a line after printing each line. This pin is in TRI- |
||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
STATE after a 0 is loaded into the corresponding control register bit. |
||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
An external 4.7 KΩ pull-up resistor should be attached to this pin. |
||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
For Input mode see bit 5 in “Control0, Second Level Offset 00h” on |
||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
page 126. |
||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
This signal is multiplexed with |
DSTRB. |
See Table 6-12 on page 134 |
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
for more information. |
||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||
AEN |
30 |
ISA-Bus |
Input |
DMA Address Enable –This input signal disables function selection |
||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Group 1 |
via A15-0 when it is high. Access during DMA transfer is not affected |
||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
by this signal. |
||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
118 |
Parallel Port |
Output |
Address Strobe (EPP) –This signal is used in EPP mode as an |
||||||||||
|
ASTRB |
|
||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Group 1 |
address strobe. It is active low. |
||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
This signal is multiplexed with |
SLIN. |
|
See Table 6-12 on page 134 for |
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
more information. |
||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||
BADDR1,0 |
136, 134 |
Configuration |
Input |
Base Address Strap Pins 0 and 1 –These pins determine the base |
||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Group 5 |
addresses of the Index and Data registers, the value of the Plug and |
||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Play ISA Serial Identifier and the configuration state immediately after |
||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
reset. These pins are pulled down by internal 30 KΩ resistors. |
||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
External 10 KΩ pull-up resistors to VDD should be employed. |
||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
BADDR1 is multiplexed with |
RTS1. |
|
BADDR0 is multiplexed with |
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
DTR1 and BOUT1. See Table 2-2 on page 25 and Section 2.1 on |
||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
page 24. |
||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||
BOUT2,1 |
144, 134 |
UART1, |
Output |
Baud Output –This multi-function pin provides the associated serial |
||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
UART2 |
Group 17 |
channel Baud Rate generator output signal if test mode is selected, |
||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
i.e., bit 7 of the EXCR1 register is set. (See Section “Bit 7 - Baud |
||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Generator Test (BTEST)” on page 155.) |
||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
After Master Reset this pin provides the SOUT function. |
||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
BOUT2 is multiplexed with |
DTR2 |
and CFG1. BOUT1 is multiplexed |
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
with DTR1 and BADDR0. |
||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||
BUSY |
111 |
Parallel Port |
Input |
Busy –This pin is set high by the printer when it cannot accept |
||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Group 2 |
another character. It is internally connected to a nominal 25 KΩ pull- |
||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
down resistor. |
||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
This signal is multiplexed with |
WAIT. |
See Table 6-12 on page 134 for |
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
more information. |
||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
15 |
www.national.com |

Signal/Pin Connection and Description
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Signal/Pin |
Pin |
Module |
I/O and |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Function |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
Name |
Number |
Group # |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
CFG3-0 |
148, 146, |
Configuration |
Input |
|
Configuration Strap Pins 3-0 –These pins determine the default |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
144, 138 |
|
Group 5 |
|
configuration upon power up. These pins are pulled down by internal |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
30 KΩ resistors. External 10 KΩ pull-up resistors to VDD should be |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
employed. |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
CFG3 is multiplexed with SOUT2. CFG2 is multiplexed with |
RTS2. |
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
CFG1 is multiplexed with DTR2 and BOUT2. |
|
CFG0 is multiplexed |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
with SOUT1. See Table 2-2 on page 25 and Section 2.1 on page 24 |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
for more information. |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
68 |
General |
Output |
|
Programmable Chip Select – |
|
|
|
|
|
and |
|
|
are |
|
||||||||||||||
|
|
CS0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
CS0, |
CS1 |
CS2 |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Purpose |
Group 21 |
|
programmable chip select and/or latch enable and/or output enable |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
signals that have many uses, for example, as game ports or for I/O |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
CS2,1 |
|
|
|
|
|
72, 71 |
General |
I/O |
|
port expansion. |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Purpose |
Group 9 |
|
The decoded address and the assertion conditions are configured via |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
the chip configuration registers. See Section 2.3 on page 26. |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
is an open-drain pin that is in TRI-STATE unless VDD is applied. |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
CS0 |
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
CS2 |
|
|
is multiplexed with XD1, |
CS1 |
is multiplexed with XD0, and |
CS0 |
|
|
||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
is multiplexed with CSOUT-NSC-Test. |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
- |
|
68 |
NSC use |
Output |
Chip Select Read Output, NSC-Test –National Semiconductor test |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
CSOUT |
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
NSC-Test |
|
|
Group 21 |
output. This is an open-drain output signal. |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
This signal is multiplexed with |
CS0. |
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
141, 131 |
UART1, |
Input |
|
UART1 and UART2 Clear to Send –When low, these signals indicate |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
CTS2,1 |
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
UART2 |
Group 1 |
|
that the modem or other data transfer device is ready to exchange data. |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
The |
CTS |
|
signal is a modem status input signal whose condition the |
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
CPU can test by reading bit 4 (CTS) of the Modem Status Register |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(MSR) for the appropriate serial channel. Bit 4 is the complement of the |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
CTS signal. Bit 0 (DCTS) of MSR indicates whether the CTS input signal |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
has changed state since the previous reading of MSR. CTS has no |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
effect on the transmitter. |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Whenever the DCTS bit of the MSR is set, an interrupt is generated |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
if modem status interrupts are enabled. |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
D7-0 |
10-3 |
ISA-Bus |
I/O |
|
ISA-Bus Data –Bidirectional data lines to the microprocessor. D0 is |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Group 8 |
|
the LSB and D7 is the MSB. These signals have 24 mA (sink) |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
buffered outputs. |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
59-56 |
ISA-Bus |
Input |
|
DMA Acknowledge 0,1,2 and 3 –These active low input signals |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
DACK3-0 |
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Group 1 |
|
acknowledge a request for DMA services and enable the IOWR and |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
IORD input signals during a DMA transfer. These DMA signals can |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
be mapped to the following logical devices: FDC, UART1, UART2 or |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
parallel port. |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
142, 132 |
UART1, |
Input |
|
UART1 and UART2 Data Carrier Detected –When low, this signal |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
DCD2,1 |
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
UART2 |
Group 1 |
|
indicates that the modem or other data transfer device has detected |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
the data carrier. |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
The |
DCD |
signal is a modem status input signal whose condition the |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
CPU can test by reading bit 7 (DCD) of the Modem Status Register |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(MSR) for the appropriate serial channel. Bit 7 is the complement of |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
the DCD signal. |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Bit 3 (DDCD) of the MSR indicates whether the |
DCD |
input signal has |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
changed state since the previous reading of MSR. Whenever the |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
DDCD bit of the MSR is set, an interrupt is generated if modem |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
status interrupts are enabled. |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
DENSEL |
94 |
FDC |
Output |
Density Select (FDC) –Indicates that a high FDC density data rate |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Group 16 |
(500 Kbps or 1 Mbps) or a low density data rate (250 or 300 Kbps) |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
is selected. |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
DENSELs polarity is controlled by bit 5 of the SuperI/O FDC |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Configuration register as described in Section 2.6.1 on page 36. |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
www.national.com |
16 |

Signal/Pin Connection and Description
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Signal/Pin |
Pin |
Module |
I/O and |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Function |
|
|||||||||||
|
|
Name |
Number |
Group # |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
90 |
FDC |
Output |
Direction (FDC) –This output signal determines the direction of the |
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|
DIR |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Group 16 |
Floppy Disk Drive (FDD) head movement (active = step in, inactive = |
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
step out) during a seek operation. During reads or writes, DIR is |
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
inactive. |
|
||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
88, 87 |
FDC |
Output |
Drive Select 0 and 1 (FDC) –These active low output signals are |
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|
DR1,0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Group 16 |
the decoded drive select output signals. DR0 and DR1 are controlled |
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
by Digital Output Register (DOR) bits 0 and 1. They are encoded with |
|
||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
information to control four FDDs when bit 7 of the SuperI/O FDC |
|
||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Configuration register is 1, as described in Section 2.6.1 on page 36. |
|
||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
See |
MTR0,1 |
for more information. |
|
||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||
|
DRATE0 |
84 |
FDC |
Output |
Data Rate 0 (FDC) –This output signal reflects the value of bit 0 of |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Group 20 |
the Configuration Control Register (CCR) or the Data Rate Select |
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Register (DSR), whichever was written to last. Output from the pin is |
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
totem-pole buffered (6 mA sink, 6 mA source). |
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||
|
DRQ3-0 |
55-52 |
ISA-Bus |
Output |
DMA Request 0, 1, 2 and 3 –These active high output signals |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Group 18 |
inform the DMA controller that a data transfer is needed. These DMA |
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
signals can be mapped to the following logical devices: Floppy Disk |
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Controller (FDC), UART1, UART2 or parallel port. |
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
99 |
FDC |
Input |
|
Disk Change (FDC) –This input signal indicates whether or not the |
|
||||||||||||||
|
|
DSKCHG |
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Group 1 |
|
drive door has been opened. The state of this pin is available from |
|
||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
the Digital Input Register (DIR). This pin can also be configured as |
|
||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
the RGATE data separator diagnostic input signal via the MODE |
|
||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
command. See the MODE command in Section 5.7.7 starting on |
|
||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
page 92. |
|
||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
143, 133 |
UART1, |
Input |
|
Data Set Ready –When low, this signal indicates that the data |
|
||||||||||||||
|
|
DSR2,1 |
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
UART2 |
Group 1 |
|
transfer device, e.g., modem, is ready to establish a communications |
|
||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
link. |
|
||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
The |
DSR |
signal is a modem status input signal whose condition the |
|
||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
CPU can test by reading bit 5 (DSR) of the Modem Status Register |
|
||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(MSR) for the appropriate channel. Bit 5 is the complement of the |
|
||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
DSR signal. Bit 1 (DDSR) of the MSR indicates whether the DSR |
|
||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
input signal has changed state since the previous reading of the |
|
||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
MSR. |
|
||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Whenever the DDSR bit of the MSR is set, an interrupt is generated |
|
||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
if modem status interrupts are enabled. |
|
||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
119 |
Parallel Port |
Output |
Data Strobe (EPP) –This signal is used in EPP mode as a data |
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|
DSTRB |
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Group 23 |
strobe. It is active low. |
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
DSTRB |
is multiplexed with |
AFD. |
See Table 6-12 on page 134 for |
|
|||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
more information. |
|
||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
144, 134 |
UART1, |
Output |
|
Data Terminal Ready –When low, this output signal indicates to the |
|
||||||||||||||
|
|
DTR2,1 |
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
UART2 |
Group 17 |
|
modem or other data transfer device that the UART1 or UART2 is |
|
||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ready to establish a communications link. |
|
||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
The |
DTR |
signal can be set active low by programming bit 0 (DTR) of |
|
||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
the Modem Control Register (MCR) to high (1). |
|
||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
A Master Reset (MR) deactivates this signal high, and loopback |
|
||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
operation holds this signal inactive. |
|
||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
is multiplexed |
|
||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
DTR2 |
is multiplexed with CFG1 and BOUT2. |
DTR1 |
|
||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
with BADDR0 and BOUT1. |
|
||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
116 |
Parallel Port |
Input |
|
Error –This input signal is set active low by the printer when it has |
|
||||||||||||||
|
|
ERR |
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Group 3 |
|
detected an error. This pin is internally connected to a nominal 25 KΩ |
|
||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
pull-up resistor. |
|
||||||||||||||
|
GPIO17-10 |
156-149 |
General |
I/O |
General Purpose I/O Signals 17-10 –General purpose I/O signals |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Purpose |
Group 10 |
of I/O Port 1. |
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
GPIO17 is multiplexed with |
WDO. |
|
|
|||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
17 |
www.national.com |

Signal/Pin Connection and Description
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Signal/Pin |
Pin |
Module |
I/O and |
|
Function |
|
|||||||
|
|
Name |
Number |
Group # |
|
|
|||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
|
GPIO20 |
157 |
General |
I/O |
General Purpose I/O Signals 27-20 –General purpose I/O port 2 |
|
|||||||||
|
GPIO21 |
77, 158 |
Purpose |
Group 10 |
signals. |
|
|||||||||
|
GPIO22 |
159 |
|
|
GPIO27-24 are multiplexed with XD5-2, respectively. |
|
|||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
GPIO23 |
160 |
|
|
GPIO23 is multiplexed with |
RING. |
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
GPIO27-24 |
76-73 |
|
|
GPIO22 is multiplexed with |
POR. |
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
GPIO21 is multiplexed on pin 158 with IRSL2, IRSL0 and on pin 77 |
|
|||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
with IRSL2, SELCS and XD6. See “SuperI/O Configuration 2 |
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Register, Index 22h” on page 35. |
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
GPIO20 is multiplexed with IRSL1. |
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
92 |
FDC |
Output |
Head Select –This output signal determines which side of the FDD |
|
|||||
|
|
HDSEL |
|
|
|||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Group 16 |
is accessed. Active low selects side 1, inactive selects side 0. |
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
|
ID0 |
79 |
UART2 |
Input |
Identification – These ID signals identify the infrared transceiver for |
|
|||||||||
|
ID1 |
78 or 157 |
|
Group 1 |
Plug and Play support. These pins are read after reset. |
|
|||||||||
|
ID2 |
158 |
|
|
ID0 is multiplexed on pin 79 with IRRX2 and IRSL0. |
|
|||||||||
|
|
|
ID1 is multiplexed on pin 78 with IRSL1 and XD7, or on pin 157 with |
|
|||||||||||
|
ID3 |
70 |
|
|
|
||||||||||
|
|
|
GPIO20 and IRSL1. |
|
|||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ID2 is multiplexed on pin 158 with GPIO21, IRSL2 and IRSL0. |
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ID3 is multiplexed on pin 70 with |
XDRD. |
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
See Table 1-2 on page 23 for more information. |
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
97 |
FDC |
Input |
Index –This input signal indicates the beginning of an FDD track. |
|
|||||
|
|
INDEX |
|
|
|||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Group 1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
117 |
Parallel Port |
I/O |
Initialize –When this signal is active low, it causes the printer to be |
|
|||||
|
|
INIT |
|
|
|||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Group 13 |
initialized. This signal is in TRI-STATE after a 1 is loaded into the |
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
corresponding control register bit. |
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
An external 4.7 KΩ pull-up resistor should be employed. |
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
|
IOCHRDY |
32 |
ISA-Bus |
Output |
I/O Channel Ready –This is the I/O channel ready open drain |
|
|||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Group 22 |
output signal. When IOCHRDY is driven low, the EPP extends the |
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
host cycle. |
|
|||||
|
IRQ1 |
36 |
ISA-Bus |
I/O |
Interrupt Requests 1, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 14 and 15 –IRQ |
|
|||||||||
|
IRQ5-3 |
39-37 |
|
Group 15 |
polarity and push-pull or open-drain output selection is software |
|
|||||||||
|
IRQ12-6 |
47-41 |
|
|
configurable by the logical device mapped to the IRQ line. |
|
|||||||||
|
|
|
Keyboard Controller (KBC) or Mouse interrupts can be configured by |
|
|||||||||||
|
IRQ15,14 |
49,48 |
|
|
|
||||||||||
|
|
|
the Interrupt Request Type Select 0 register (index 71h) as either |
|
|||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
edge or level. |
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
The parallel port interrupt is either edge or level, according to the |
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
operation mode (default edge, configured by the SuperI/O Parallel |
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Port Configuration register at index F0h). |
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
|
IRRX2,1 |
79, 80 |
UART2 |
Input |
Infrared Reception 1 and 2 –Infrared serial input data. |
|
|||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(SIR) |
Group 1 |
IRRX2 is multiplexed with IRSL0 and ID0. See Table 1-2 on page 23 |
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
for more information. |
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
|
IRSL0 |
79 or 158 |
|
|
Infrared Control Signals 0, 1 and 2 –These signals control the |
|
|||||||||
|
IRSL1 |
78 or 157 |
|
Output |
Infrared analog front end. The pins on which these signals are driven |
|
|||||||||
|
|
is determined by the SuperI/O Configuration 2 register (index 22h). |
|
||||||||||||
|
IRSL2 |
77 or 158 |
|
|
|
||||||||||
|
|
|
See Section 2.4.4 on page 35. IRSL0 or ID0/IRRX2 on pin 79 is |
|
|||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
79, 78, 77 |
UART2 |
Group 17 |
determined by UART2 bit 5 of the IRCFG4 register (See page 165). |
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
IRSL0 is multiplexed on pin 79 with IRRX2 and ID0, or on pin 158 |
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
158, 157 |
(SIR) |
Group 10 |
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
with GPIO21, IRSL2 and ID2. |
|
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
IRSL1 is multiplexed on pin 78 with XD7 and ID1, or on pin 157 with |
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
GPIO20 and ID1. |
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
IRSL2 is multiplexed on pin 77 with XD6, SELCS and GPIO21, or on |
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
pin 158 with GPIO21, IRSL0 and ID2. |
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
www.national.com |
18 |

Signal/Pin Connection and Description
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Signal/Pin |
Pin |
Module |
I/O and |
Function |
|
||
|
|
Name |
Number |
Group # |
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
IRTX |
81 |
UART2 |
Output |
Infrared Transmit –Infrared serial output data. |
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
(SIR) |
Group 19 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
KBCLK |
102 |
KBC |
I/O |
Keyboard Clock –This I/O pin transfers the keyboard clock between |
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Group 11 |
the SuperI/O chip and the external keyboard using the PS/2 protocol. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
This pin is connected internally to the internal TO signal of the KBC. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
KBDAT |
103 |
KBC |
I/O |
Keyboard Data –This I/O pin transfers the keyboard data between |
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Group 11 |
the SuperI/O chip and the external keyboard using the PS/2 protocol. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
This pin is connected internally to KBC’s P10. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
MCLK |
104 |
KBC |
I/O |
Mouse Clock –This I/O pin transfers the mouse clock between the |
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Group 11 |
SuperI/O chip and the external keyboard using the PS/2 protocol. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
This pin is connected internally to KBC’s T1. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
MDAT |
105 |
KBC |
I/O |
Mouse Data –This I/O pin transfers the mouse data between the |
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Group 11 |
SuperI/O chip and the external keyboard using the PS/2 protocol. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
This pin is connected internally to KBC’s P11. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
MR |
51 |
ISA-Bus |
Input |
Master Reset –An active high MR input signal resets the controller |
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Group 1 |
to the idle state, and resets all disk interface output signals to their |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
inactive states. MR also clears the DOR, DSR and CCR registers, |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
and resets the MODE command, CONFIGURE command, and LOCK |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
command parameters to their default values. MR does not affect the |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
SPECIFY command parameters. MR sets the configuration registers |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
to their selected default values. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
MSEN1,0 |
83, 82 |
FDC |
Input |
Media Sense –These input pins are used for media sensing when |
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Group 4 |
bit 6 of the SuperI/O FDC Configuration register (at index F0h) is 1. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
See Section 2.6.1 on page 36. Each pin has a 40 KΩ internal pull-up |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
resistor. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
86, 85 |
FDC |
Output |
Motor Select 1,0 –These motor enable lines for drives 0 and 1 are |
|
|
|
MTR1,0 |
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Group 16 |
controlled by bits D7-4 of the Digital Output Register (DOR). They are |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
output signals that are active when they are low. They are encoded with |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
information to control four FDDs when bit 7 of the SuperI/O FDC |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Configuration register is set, as described in Section 2.6.1 on page 36. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
See DR1,0. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
67 |
APC |
Output |
On/Off Control for the RTC’s Advanced Power Control (APC) – |
|
|
|
ONCTL |
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Group 23 |
This signal indicates to the main power supply that power should be |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
turned on. ONCTL is an open-drain output signal that is powered by |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
VCCH. |
|
|
P17,16 |
108, 107 |
KBC |
I/O |
I/O Port –KBC quasi-bidirectional port for general purpose input and |
|
|||
|
P12 |
106 |
|
Group 12 |
output. |
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
P21,20 |
110, 109 |
KBC |
I/O |
I/O Port –KBC open-drain signals for general purpose input and |
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Group 12 |
output. These signals are controlled by KBC firmware. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
PD7-0 |
129-122 |
Parallel Port |
I/O |
Parallel Port Data –These bidirectional signals transfer data to and |
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Group 14 |
from the peripheral data bus and the appropriate parallel port data |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
register. These signals have a high current drive capability. See |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
“GENERAL DC ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS” on page 182. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
PE |
115 |
Parallel Port |
Input |
Paper End –This input signal is set high by the printer when it is out |
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Group 2 |
of paper. This pin has an internal nominal 25 KΩ pull-up or pull-down |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
resistor that is selected by bit 2 of the PP Confg0 register (second |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
level offset 05h) of the parallel port. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
19 |
www.national.com |

Signal/Pin Connection and Description
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Signal/Pin |
Pin |
Module |
I/O and |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Function |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
Name |
Number |
Group # |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
159 |
APC |
Output |
Power Off Request –This signal becomes active when an APC |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
POR |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Group 21 |
Switch Off event occurs, regardless of the fail-safe delay. Selection of |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
edge or level for POR is via the APCR1 register of the APC. |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Selection of an output buffer is via GPIO22 output buffer control bits |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(in the Port 2 Output Type and Port 2 Pull-up Control registers |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
described in Table 8-1 on page 170). See Section 4.3 on page 55. |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
This signal is multiplexed with GPIO22. |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
33 |
ISA-Bus |
Input |
|
I/O Read –An active low |
|
input signal indicates that the |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
RD |
|
|
|
|
|
|
RD |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Group 1 |
|
microprocessor has read data. |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
95 |
FDC |
Input |
|
|
Read Data –This input signal holds raw serial data read from the |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
RDATA |
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Group 1 |
|
|
Floppy Disk Drive (FDD). |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
145, 135 |
UART1, APC |
Input |
|
Ring Indicators (Modem) –When low, this signal indicates that a |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
RI2,1 |
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Group 7 |
|
telephone ring signal has been received by the modem. |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
The CPU can test the status of the |
RI |
|
|
modem status input signal by |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
reading bit 6 (RI) of the Modem Status Register (MSR) for the |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
appropriate serial channel. Bit 6 is the complement of the |
RI |
signal. |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Bit 2 (TERI) of the MSR indicates whether the RI input signal has |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
changed from low to high since the previous reading of the MSR. |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
When the TERI bit of the MSR is set, an interrupt is generated if |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
modem status interrupts are enabled. |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
When enabled, a high to low transition on |
RI1 |
or |
RI2 |
activates the |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ONCTL pin. The |
RI1 |
and RI2 pins each have an schmitt-trigger input |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
buffer. |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
69 or 160 |
APC |
Input |
|
Ring Indicator (APC) –Detection of an active low |
|
|
pulse or |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
RING |
|
|
RING |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Group 7 |
|
pulse train activates the ONCTL signal. The APC’s APCR2 register |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
determines which pin the RING signal uses. The pins have a schmitt- |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
trigger input buffer. |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
is multiplexed on pin 69 with |
|
|
|
and on pin 160 with |
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
RING |
|
XDCS |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
GPIO23. |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
146, 136 |
UART1, |
Output |
|
|
Request to Send –When low, these output signals indicate to the |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
RTS2,1 |
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
UART2 |
Group 17 |
|
|
modem or other data transfer device that the corresponding UART1 |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
or UART2 is ready to exchange data. |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
The |
RTS |
signal can be set active low by programming bit 1 (RTS) of |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
the Modem Control Register (MCR) to a high level. A Master Reset |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(MR) sets |
RTS |
to inactive high. Loopback operation holds it inactive. |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
is multiplexed with BADDR1. |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
RTS2 |
is multiplexed with CFG2. |
RTS1 |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
SELCS |
77 |
Configuration |
Input |
|
Select CSOUT –During reset, this signal is sampled into bit 1 of the |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Group 4 |
|
SuperI/O Configuration 1 register (index 21h). |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
A 40 KΩ internal pull-up resistor (or a 10 KΩ external pull-down |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
resistor for National Semiconductor testing) controls this pin during |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
reset. Do not pull this signal low during reset. |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
This signal is multiplexed with GPIO21, IRSL2 and XD6. |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
SIN2,1 |
147, 137 |
UART1, |
Input |
|
Serial Input –This input signal receives composite serial data from |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
UART2 |
Group 1 |
|
the communications link (peripheral device, modem or other data |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
transfer device.) |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
SLCT |
114 |
Parallel Port |
Input |
|
Select –This input signal is set active high by the printer when the |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Group 2 |
|
printer is selected. This pin is internally connected to a nominal |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
25 KΩ pull-down resistor. |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
118 |
Parallel Port |
I/O |
Select Input –When this signal is active low it selects the printer. |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
SLIN |
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Group 13 |
This signal is in TRI-STATE after a 0 is loaded into the corresponding |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
control register bit. |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
An external 4.7 KΩ pull-up resistor should be used. |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
This signal is multiplexed with |
ASTRB. |
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
www.national.com |
20 |

Signal/Pin Connection and Description
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Signal/Pin |
Pin |
Module |
I/O and |
Function |
|
|||||||||||
|
|
Name |
Number |
Group # |
|
|||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||
|
SOUT2,1 |
148, 138 |
UART1, |
Output |
Serial Output –This output signal sends composite serial data to the |
|
||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
UART2 |
Group 17 |
communications link (peripheral device, modem or other data transfer |
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
device). |
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
The SOUT2,1 signals are set active high after a Master Reset (MR). |
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
SOUT2 is multiplexed with CFG3. SOUT1 is multiplexed with CFG0. |
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
112 |
Parallel Port |
I/O |
Data Strobe –This output signal indicates to the printer that valid |
|
||||
|
|
STB |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Group 13 |
data is available at the printer port. |
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
This signal is in TRI-STATE after a 0 is loaded into the corresponding |
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
control register bit. |
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
An external 4.7 KΩ pull-up resistor should be employed. |
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
This signal is multiplexed wiTH |
WRITE. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
91 |
FDC |
Output |
Step –This output signal issues pulses to the disk drive at a software |
|
||||
|
|
STEP |
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Group 16 |
programmable rate to move the head during a seek operation. |
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
66 |
APC |
Input |
Switch On/Off –Indicates a request to the APC to switch the power |
|
||||
|
|
SWITCH |
|
|
||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Group 7 |
on or off. When VDD does not exist, a high to low transition on this |
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
signal indicates a Switch On request. When VDD exists, a high to low |
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
transition on this pin indicates a Switch Off request. |
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
The pin has an internal pull-up of 1 MΩ (nominal), a schmitt-trigger |
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
input buffer and debounce protection of at least 16 msec. |
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
|
|
TC |
35 |
ISA-Bus |
Input |
DMA Terminal Count –The DMA controller issues TC to indicate |
|
|||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Group 1 |
the termination of a DMA transfer. TC is accepted only when a |
DACK |
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
signal is active. |
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
TC is active high in PC-AT mode, and active low in PS/2 mode. |
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
96 |
FDC |
Input |
Track 0 –This input signal indicates to the controller that the head of |
|
||||
|
|
TRK0 |
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Group 1 |
the selected floppy disk drive is at track 0. |
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||
|
VBAT |
64 |
RTC and |
Input |
Battery Power Supply –Power signal from the battery to the Real- |
|
||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
APC |
|
Time Clock (RTC) or for Advanced Power Control (APC) when VCCH |
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
is less than VBAT (by at least 0.5 V). VBAT includes a UL protection |
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
resistor. |
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||
|
VCCH |
65 |
RTC and |
Input |
VCC Help Power Supply –This signal provides power to the RTC or |
|
||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
APC |
|
APC when VCCH is higher than VBAT (by at least 0.5 V). |
|
||||
|
VDD |
1, 24, 61, |
Power |
Input |
Main 5 V Power Supply –This signal is the 5 V supply voltage for |
|
||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
100, 121, |
Supply |
|
the digital circuitry. |
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
140 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||
|
VSS |
2, 11, 25, |
Power |
Output |
Ground –This signal provides the ground for the digital circuitry. |
|
||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
40, 60, |
Supply |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
101, 120, |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
130, 139 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
111 |
Parallel Port |
Input |
Wait –In EPP mode, the parallel port device uses this signal to |
|
||||
|
|
WAIT |
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Group 2 |
extend its access cycle. WAIT is active low. It is internally connected |
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
to a nominal 25 KΩ pull-down resistor. |
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
This signal is multiplexed with BUSY. See Table 6-12 on page 134 for |
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
more information. |
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
89 |
FDC |
Output |
Write Data (FDC) –This output signal holds the write |
|
||||
|
|
WDATA |
|
|
||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Group 16 |
precompensated serial data that is written to the selected floppy disk |
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
drive. Precompensation is software selectable. |
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
156 |
Power |
Output |
WATCHDOG Out –This output pin becomes low when a |
|
||||
|
|
WDO |
|
|
||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Management |
Group 10 |
WATCHDOG time-out occurs. See “The WATCHDOG Feature” on |
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
page 172. This pin is configured by bit 6 of the SuperI/O |
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Configuration Register 2. |
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
This signal is multiplexed with GPIO17. |
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
21 |
www.national.com |

Signal/Pin Connection and Description
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Signal/Pin |
Pin |
Module |
I/O and |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Function |
|
|||||||||||
|
|
Name |
Number |
Group # |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
93 |
FDC |
Output |
|
Write Gate (FDC) –This output signal enables the write circuitry of |
|
|||||||||
|
|
WGATE |
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Group 16 |
|
the selected disk drive. WGATE is designed to prevent glitches |
|
|||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
during power up and power down. This prevents writing to the disk |
|
|||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
when power is cycled. |
|
|||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
98 |
FDC |
Input |
|
Write Protected –This input signal indicates that the disk in the |
|
|||||||||
|
|
WP |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Group 1 |
|
selected drive is write protected. |
|
|||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
34 |
ISA-Bus |
Input |
|
I/O Write – |
|
|
is an active low input signal that indicates a write |
|
||||||
|
|
WR |
|
|
|
|
|
WR |
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Group 1 |
|
operation from the microprocessor to the controller. |
|
|||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
112 |
Parallel Port |
Output |
Write Strobe –In EPP mode, this active low signal is a write strobe. |
|
||||||||||
|
|
WRITE |
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
See Table 6-12 on page 134 for |
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Group 23 |
This signal is multiplexed with |
STB. |
|
|
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
more information. |
|
|||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||
|
X1 |
50 |
Clock |
Input |
|
Clock In –A TTL or CMOS compatible 24 MHz or 48 MHz clock. |
|
|||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Group 6 |
|
See Chapter 11. |
|
|||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||
|
X1C |
62 |
RTC |
Input |
|
Crystal 1 Slow –Input signal to the internal Real-Time Clock (RTC) |
|
|||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
crystal oscillator amplifier. |
|
|||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||
|
X2C |
63 |
RTC |
Output |
|
Crystal 2 Slow –Output signal from the internal Real-Time Clock |
|
|||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(RTC) crystal oscillator amplifier. |
|
|||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||
|
XD7,6, |
78, 77 |
X-Bus |
I/O |
|
X-Bus Data –These bidirectional signals hold the data in the X Data |
|
|||||||||||||||||
|
XD1,0 |
72, 71 |
|
Group 9 |
|
Buffer (XDB). |
|
|||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
XD7 is multiplexed with IRSL1 and ID1. |
|
|||||||||
|
XD5-2 |
76-73 |
X-Bus |
I/O |
|
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
|
XD6 is multiplexed with IRSL2, SELCS and GPIO21. |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Group 10 |
|
XD5-2 are multiplexed with GPIO27-24, respectively. |
|
|||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
XD1,0 are multiplexed with CS2,1 respectively. |
|
|||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
See Table 1-2 on page 23. |
|
|||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
69 |
X-Bus |
Input |
|
X-Bus Data Buffer (XDB) Chip Select –This signal enables and |
|
|||||||||
|
|
XDCS |
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Group 7 |
|
disables the bidirectional XD7-0 data buffer signals. |
|
|||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
This signal is multiplexed with |
RING. |
See Table 1-2 on page 23. |
|
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
70 |
X-Bus |
Input |
|
X-Bus Data Buffer (XDB) Read Command –This signal controls |
|
|||||||||
|
|
XDRD |
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Group 1 |
|
the direction of the bidirectional XD7-0 data buffer signals. |
|
|||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
This signal is multiplexed with ID3. See Table 1-2 on page 23. |
|
|||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
31 |
ISA-Bus |
Output |
Zero Wait State –When this open-drain output signal is activated |
|
||||||||||
|
|
ZWS |
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Group 22 |
(driven low), it indicates that the access time can be shortened, i.e., |
|
||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
zero wait states. |
|
||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ZWS |
is never activated (driven low) on access to SuperI/O chip |
|
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
configuration registers (including during the Isolation state) or on |
|
|||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
access to the parallel port in SPP or EPP 1.9 mode. |
|
|||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ZWS |
is always activated (driven low) on access to the parallel port in |
|
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ECP mode. |
|
|||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Assertion of |
ZWS |
on access to a parallel port in EPP 1.7 mode is |
|
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
controlled by bit 3 of the Control2 register (at second level offset 02h) |
|
|||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
of the parallel port (accessed by the Index and Data registers at |
|
|||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
base+403h and base+404h). See page 127. |
|
|||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Bit 0 of the SuperI/O Configuration 1 register (at index 21h) controls |
|
|||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
assertion of ZWS on access to any other addresses of the part. See |
|
|||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
page 35. |
|
|||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
www.national.com |
22 |

Signal/Pin Connection and Description
In Table 1-2, unselected (XDB or alternate function) input signals are internally blocked high.
TABLE 1-2. Multiplexed X-Bus Data Buffer (XDB) Pins
|
X-Bus Data Buffer (XDB) |
|
Alternate Function |
|
|||||||||
Pin |
Bit 4 of SuperI/O Configuration |
I/O |
Bit 4 of SuperI/O Configuration 1 |
I/O |
|||||||||
|
Register 1 = 1 |
|
Register = 0 |
|
|||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
69 |
|
|
|
|
Input |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Input |
|
XDCS |
|
|
|
RING |
|
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
70 |
|
|
|
|
Input |
|
|
|
ID3 |
Input |
|||
|
XDRD |
|
|
|
|
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
71 |
|
XD0 |
I/O |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Output |
||
|
|
|
|
CS1 |
|
|
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
72 |
|
XD1 |
I/O |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Output |
||
|
|
|
CS2 |
|
|||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
73 |
|
XD2 |
I/O |
GPIO24 |
I/O |
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
73 |
|
XD3 |
I/O |
GPIO25 |
I/O |
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
75 |
|
XD4 |
I/O |
GPIO26 |
I/O |
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
76 |
|
XD5 |
I/O |
GPIO27 |
I/O |
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
77 |
XD6/SELCS |
I/O |
IRSL2/SELCS/GPIO21 |
I/O |
|||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
78 |
|
XD7 |
I/O |
IRSL1/ID1 |
I/O |
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
TABLE 1-3. Pins with a Strap Function During Reset
Strap Pins |
Pin |
|
|
|
|
|
Symbols |
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
BADDR1,0 |
134 |
|
|
|
|
|
DTR1/BADDR0/BOUT1 |
|||
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
136 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
RTS1/BADDR1 |
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
CFG3-0 |
138 |
|
|
|
SOUT1/CFG0 |
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
144 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
DTR2/CFG1/BOUT2 |
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
146 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
RTS2/CFG2 |
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
148 |
|
|
|
SOUT2/CFG3 |
|||||
|
|
|
||||||||
SELCS |
77 |
IRSL2/XD6/SELCS/GPIO21 |
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
23 |
www.national.com |

Configuration
2.0Configuration
The part is partially configured by hardware, during reset. The configuration can also be changed by software, by changing the values of the configuration registers.
The configuration registers are accessed using an Index register and a Data register. During reset, hardware strapping options define the addresses of the configuration registers. See Section 2.1.2.
After the Index and Data register pair have determined the addresses of the configuration registers, the addresses of the Index and Data registers can be changed within the ISA I/O address space, and a 16-bit programmable register controls references to their addresses and to the addresses of the other registers.
This chapter describes the hardware and software configuration processes. For each, it describes configuration of the Index and Data register pair first. See Sections 2.1 and 2.2.
Section 2.3 starting on page 26 presents an overview of the configuration registers of the part and describes each in detail.
2.1HARDWARE CONFIGURATION
The part supports two Plug and Play (PnP) configuration modes that determine the status of register addresses upon wake up from a hardware reset, Full PnP ISA mode and PnP Motherboard mode.
2.1.1Wake Up Options
During reset, strapping options on the BADDR0 and BADDR1 pins determine one of the following modes.
•Full Plug and Play ISA mode – System wakes up in Wait for Key state.
Index and Data register addresses are as defined by Microsoft and Intel in the “Plug and Play ISA Specification, Version 1.0a, May 5, 1994.”
•Plug and Play Motherboard mode – system wakes up in Config state.
The BIOS configures the part. Index and Data register addresses are different from the addresses of the PnP Index and Data registers. Configuration registers can be accessed as if the serial isolation procedure had already been done, and the part is selected.
The BIOS may switch the addresses of the Index and Data registers to the PnP ISA addresses of the Index and Data registers, by using software to modify the base address bits of the SuperI/O Configuration 2 register (at Index 22h). See Section 2.4.4
2.1.2The Index and Data Register Pair
During reset, a hardware strapping option on the BADDR0 and BADDR1 pins defines an address for the Index and Data Register pair. This prevents contention between the registers for I/O address space.
Table 2-1 shows the base addresses for the Index and Data registers that hardware sets for each combination of values of the Base Address strap pins (BADDR0 and BADDR1). You can access and change the content of the configuration registers at any time, as long as the base addresses of the Index and Data registers are defined.
When BADDR1 is low (0), the PnP protocol defines the addresses of the Index and Data register, and the system wakes up from reset in the Wait for Key state.
When BADDR1 is high (1), the addresses of the Index and Data register are according to Table 2-1, and the system wakes up from reset in the Config state.
This configures the part with default values, automatically, without software intervention. After reset, use software as described in Section 2.2 to modify the selected base address of the Index and Data register pair, and the defaults for configuration registers.
The Plug and Play soft reset has no effect on the logical devices, except for the effect of the Activate registers (index 30h) in each logical device.
The part can wake up with the FDC, the KBC and the RTC either active (enabled) or inactive (disabled). The clock multiplier, if configured via CFG3,2 strap pins, wakes up enabled. The other logical devices wake up inactive (disabled).
TABLE 2-1. Base Addresses
BADDR1 |
BADDR0 |
|
Address |
Configuration Type |
|
|
|
|
|||
Index Register |
|
Data Register |
|||
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0 |
x |
0279h |
|
Write: 0A79h |
Full PnP ISA Mode |
Write Only |
|
Read: RD_DATA Port |
Wake up in Wait for Key state |
||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
1 |
0 |
015Ch Read/Write |
|
015Dh Read/Write |
PnP Motherboard Mode |
|
Wake up in Config state |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1 |
1 |
002Eh Read/Write |
|
002Fh Read/Write |
PnP Motherboard Mode |
|
Wake up in Config state |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
www.national.com |
24 |

Configuration
2.1.3The Strap Pins
TABLE 2-2. Strap Pins
Pin |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Reset Configuration |
Affected |
|||
|
|
|
|
||||||||||
|
|
|
|
||||||||||
CFG0 |
0 |
- FDC, KBC and RTC wake up inactive. |
Bit 0 of Activate registers (index |
||||||||||
|
1 |
- FDC, KBC and RTC wake up active. |
30h) of logical devices 0,2 and 3. |
||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||
|
|
|
|||||||||||
CFG1 |
0 - No X-Bus Data Buffer. (See XDB pins multiplexing in Table 1-2.) |
Bit 4 of SuperI/O Configuration 1 |
|||||||||||
|
1 |
- X-Bus Data Buffer (XDB) enabled. |
register (index 21h). |
||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
||||||||||
CFG3,2 |
00 |
- Clock source is 24 MHz fed via X1 pin. |
Bits 2-0 of PMC2 register of Power |
||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Management (logical device 8) |
|
01 |
- Reserved for CSOUT-NSC-Test fed via X1 pin. |
|||||||||||
|
CFG2 affects bits 0 and 2. |
||||||||||||
|
10 |
- Clock source is 48 MHz fed via X1 pin. |
|||||||||||
|
CFG3 affects bit 1. |
||||||||||||
|
11 - Clock source is 32.768 KHz with on-chip clock multiplier. |
||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
||||||||||
BADDR1,0 |
00 |
- Full PnP ISA, Wake in Wait For Key state. Index PnP ISA. |
Bits 1 and 0 of SuperI/O |
||||||||||
|
01 |
- Full PnP ISA, Wake in Wait For Key state. Index PnP ISA. |
Configuration 2 register (index 22h) |
||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||
|
10 |
- PnP Motherboard, Wake in Config state. Index 015Ch. |
|
||||||||||
|
11 - PnP Motherboard, Wake in Config state. Index 002Eh. |
|
|||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
SELCS |
0 |
- |
|
|
-NSC-test on |
|
|
pin. |
Bit 1 of SuperI/O Configuration 1 |
||||
CSOUT |
CS0 |
||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
register (index 21h). |
|
1 |
- CS0 on CS0 pin. |
|||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2.2SOFTWARE CONFIGURATION
2.2.1Accessing the Configuration Registers
Only two system I/O addresses are required to access any of the configuration registers. The Index and Data register pair is used to access registers for all read and write operations.
In a write operation, the target configuration register is identified, based on a value that is loaded into the Index register. Then, the data to be written into the configuration register is transferred via the Data register.
Similarly, for a read operation, first the source configuration register is identified, based on a value that is loaded into the Index register. Then, the data to be read is transferred via the Data register.
Reading the Index register returns the last value loaded into the Index register. Reading the Data register returns the data in the configuration register pointed to by the Index register.
If, during reset, the Base Address 1 (BADDR1) signal is low (0), the Index and Data registers are not accessible immediately after reset. As a result, all configuration registers of the part are also not accessible at this time. To access these registers, apply the PnP ISA protocol.
If during reset, the Base Address 1 (BADDR1) signal is high (1), all configuration registers are accessible immediately after reset.
It is up to the configuration software to guarantee no conflicts between the registers of the active (enabled) logical devices, between IRQ signals and between DMA channels. If conflicts of this type occur, the results are unpredictable.
To maintain compatibility with other SuperI/O‘s, the value of reserved bits may not be altered. Use read-modify-write.
2.2.2Address Decoding
In full Plug and Play mode, the addresses of the Index and Data registers that access the configuration registers are decoded using pins A11-0, according to the ISA Plug and Play specification.
In Plug and Play Motherboard mode, the addresses of the Index and Data registers that access the configuration registers are decoded using pins A15-1. Pin A0 distinguishes between these two registers.
KBC and mouse register addresses are decoded using pins A1,0 and A15-3. Pin A2 distinguishes between the device registers.
RTC/APC and Power Management (PM) register addresses are decoded using pins A15-1. PM has only five registers and only responds to accesses to those registers.
FDC, UART, and GPIO register addresses are decoded using pins A15-3.
Parallel Port (PP) modes determine which pins are used for register addresses. In SPP mode, 14 pins are used to decode Parallel Port (PP) base addresses. In ECP and EPP modes, 13 address pins are used. Table 2-3 shows which address pins are used in each mode.
TABLE 2-3. Address Pins Used for Parallel Port
|
Pins Used to |
Pins Used to |
|
PP Mode |
Decode Base |
||
Distinguish Registers |
|||
|
Address |
||
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
SPP |
A15-2 |
A1,0 |
|
|
|
|
|
ECP |
A9-2 and A15-11 |
A1,0 and A10 |
|
|
|
|
|
EPP |
A15-3 |
A2-0 |
|
|
|
|
25 |
www.national.com |
Configuration
TABLE 2-4. Parallel Port Address Range Allocation
|
SuperI/O Parallel Port |
|
||||
Parallel Port Mode |
Configuration Register Bits |
Decoded Range a |
||||
|
7 |
6 |
5 |
4 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
SPP |
0 |
0 |
x |
x |
Three registers, from base to base + 02h |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
EPP (Non ECP Mode 4) |
0 |
1 |
x |
x |
Eight registers, from base to base + 07h |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ECP, No Mode 4, |
1 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
Six registers, from base to base + 02h and |
|
No Internal Configuration |
from base + 400h to base + 402h |
|||||
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ECP with Mode 4, |
1 |
1 |
1 |
0 |
11 registers, from base to base + 07h and |
|
No Internal Configuration |
from base + 400h to base + 402h |
|||||
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ECP with Mode 4, |
1 |
0 |
0 |
1 |
16 registers, from base to base + 07h and |
|
|
or |
|
|
|||
Configuration within Parallel Port |
|
|
|
from base + 400h to base + 407h |
||
1 |
1 |
1 |
1 |
|||
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
a. The SuperI/O processor does not decode the Parallel Port outside this range.
2.3THE CONFIGURATION REGISTERS
The configuration registers control the setup of the part. Their major functions are to:
•Identify the chip
•Enable major functions (such as, the Keyboard Controller (KBC) for the keyboard and the mouse, the RealTime Clock (RTC), including Advanced Power Control (APC), the Floppy Disc Controller (FDC), UARTs, parallel and general purpose ports, power management and pin functionality)
•Define the I/O addresses of these functions
•Define the status of these functions upon reset
Section 2.3.2 summarizes information for each register of each function. In addition, the following non-standard, or card control registers are described in detail in Section 2.4, starting on page 34.
•Card Control Registers
—SuperI/O Configuration 1 Register (SIOC1)
—SuperI/O Configuration 2 Register (SIOC2)
—Programmable Chip Select Configuration Index Register
—Programmable Chip Select Configuration Data Register
•KBC Configuration Register (Logical Device 0)
—SuperI/O KBC Configuration Register
•FDC Configuration Registers (Logical Device 3)
—SuperI/O FDC Configuration Register
—Drive ID Register
•Parallel Port Configuration Register (Logical Device 4)
—SuperI/O Parallel Port Configuration Register
•UART2 and Infrared Configuration Register (Logical Device 5)
—SuperI/O UART2 Configuration Register
•UART1 Configuration Register (Logical Device 6)
—SuperI/O UART1 Configuration Register
•Programmable Chip Select Configuration Registers
—CS0 Base Address MSB Register
—CS0 Base Address LSB Register
—CS0 Configuration Register
—CS1 Base Address MSB Register
—CS1 Base Address LSB Register
—CS1 Configuration Register
—CS2 Base Address MSB Register
—CS2 Base Address LSB Register
—CS2 Configuration Register
www.national.com |
26 |

Configuration
2.3.1Standard Plug and Play (PnP) Register Definitions
Tables 2-5 through 2-10 describe the standard Plug and Play registers. For more detailed information on these registers, refer the “Plug and Play ISA Specification, Version 1.0a, May 5, 1994.”.
|
|
TABLE 2-5. PnP Standard Control Registers |
|
|
|
Index |
Name |
Definition |
|
|
|
|
|
|
00h |
Set RD_DATA Port |
Writing to this location modifies the address of the port used for reading from the |
|
|
Plug and Play ISA cards. Data bits 7-0 are loaded into I/O read port address bits |
|
|
9-2. |
|
|
Reads from this register are ignored. Bits1 and 0 are fixed at the value 11. |
|
|
|
01h |
Serial Isolation |
Reading this register causes a Plug and Play card in the Isolation state to compare |
|
|
one bit of the ID of the board. This register is read only. |
|
|
|
02h |
Config Control |
This register is write-only. The values are not sticky, that is, hardware automatically |
|
|
clears the bits and there is no need for software to do so. |
|
|
Bit 0 - Reset |
|
|
Writing this bit resets all logical devices and restores the contents of |
|
|
configuration registers to their power-up (default) values. |
|
|
In addition, all the logical devices of the card enter their default state and the |
|
|
CSN is preserved. |
|
|
Bit 1 - Return to the Wait for Key state. |
|
|
Writing this bit puts all cards in the Wait for Key state, with all CSNs preserved |
|
|
and logical devices not affected. |
|
|
Bit 2 - Reset CSN to 0. |
|
|
Writing this bit causes every card to reset its CSN to zero. |
|
|
|
03h |
Wake[CSN] |
A write to this port causes all cards that have a CSN that matches the write data in |
|
|
bits 7-0 to go from the Sleep state to either the Isolation state, if the write data for |
|
|
this command is zero, or the Config state, if the write data is not zero. It also resets |
|
|
the pointer to the byte-serial device. |
|
|
This register is write-only. |
|
|
|
04h |
Resource Data |
This address holds the next byte of resource information. The Status register must |
|
|
be polled until bit 0 of this register is set to 1 before this register can be read. |
|
|
This register is read-only. |
|
|
|
005 |
Status |
When bit 0 of this register is set to 1, the next data byte is available for reading |
|
|
from the Resource Data register. |
|
|
This register is read-only. |
|
|
|
06h |
Card Select |
Writing to this port assigns a CSN to a card. The CSN is a value uniquely assigned |
|
Number (CSN) |
to each ISA card after the serial identification process so that each card may be |
|
|
individually selected during a Wake[CSN] command. |
|
|
This register is read/write. |
|
|
|
07h |
Logical Device |
This register selects the current logical device. All reads and writes of memory, I/O, |
|
Number |
interrupt and DMA configuration information access the registers of the logical |
|
|
device written here. In addition, the I/O Range Check and Activate commands |
|
|
operate only on the selected logical device. |
|
|
|
20h - 2Fh |
Card Level, |
Vendor defined registers. |
|
Vendor Defined |
|
|
|
|
27 |
www.national.com |

Configuration
|
|
TABLE 2-6. PnP Logical Device Control Registers |
||
|
|
|
|
|
Index |
Name |
|
|
Definition |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0030h |
Activate |
|
For each logical device there is one Activate register that controls whether or not the |
|
|
|
|
logical device is active on the ISA bus. |
|
|
|
|
This is a read/write register. |
|
|
|
|
Before a logical device is activated, I/O Range Check must be disabled. |
|
|
|
|
Bit 0 - Logical Device Activation Control |
|
|
|
|
0 |
- Do not activate the logical device. |
|
|
|
1 |
- Activate the logical device. |
|
|
|
Bits 7-1 - Reserved |
|
|
|
|
These bits are reserved and return 0 on reads. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
0031h |
I/O Range Check |
|
This register is used to perform a conflict check on the I/O port range programmed |
|
|
|
|
for use by a logical device. |
|
|
|
|
This register is read/write. |
|
|
|
|
Bit 0 - I/O Range Check control |
|
|
|
|
0 |
- The logical device drives 00AAh. |
|
|
|
1 |
- The logical device responds to I/O reads of the logical device's assigned I/O |
|
|
|
|
range with a 0055h when I/O Range Check is enabled. |
|
|
|
Bit 1 - Enable I/O Range Check |
|
|
|
|
0 |
- I/O Range Check is disabled. |
|
|
|
1 - I/O Range Check is enabled. (I/O Range Check is valid only when the logical |
|
|
|
|
|
device is inactive). |
|
|
|
Bits 7-2 - Reserved |
|
|
|
|
These bits are reserved and return 0 on reads. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
TABLE 2-7. PnP I/O Space Configuration Registers |
|
|
|
Index |
Name |
Definition |
|
|
|
|
|
|
60h |
I/O Port Base |
Read/write value indicating the selected I/O lower limit address bits 15-8 for I/O |
|
Address Bits (15-8) |
descriptor 0. |
|
Descriptor 0 |
|
|
|
|
61h |
I/O Port Base |
Read/write value indicating the selected I/O lower limit address bits 7-0 for I/O |
|
Address Bits (7-0) |
descriptor 0. |
|
Descriptor 0 |
|
|
|
|
62h |
I/O Port Base |
Read/write value indicating the selected I/O lower limit address bits 15-8 for I/O |
|
Address Bits (15-8) |
descriptor 1. |
|
Descriptor 1 |
|
|
|
|
63h |
I/O Port Base |
Read/write value indicating the selected I/O lower limit address bits 7-0 for I/O |
|
Address Bits (7-0) |
descriptor 1. |
|
Descriptor 1 |
|
|
|
|
www.national.com |
28 |

Configuration
|
|
TABLE 2-8. PnP Interrupt Configuration Registers |
|
|
|
Index |
Name |
Definition |
|
|
|
|
|
|
70h |
Interrupt Request |
Read/write value indicating selected interrupt level. |
|
Level Select 0 |
Bits3-0 select the interrupt level used for interrupt 0. A value of 1 selects IRQL 1, a value |
|
|
|
|
|
of 15 selects IRQL 15. IRQL 0 is not a valid interrupt selection and (represents no |
|
|
interrupt selection. |
|
|
|
71h |
Interrupt Request |
Read/write value that indicates the type and level of the interrupt request level selected in |
|
Type Select 0 |
the previous register. |
|
|
If a card supports only one type of interrupt, this register may be read-only. |
|
|
Bit 0 - Type of the interrupt request selected in the previous register. |
|
|
0 - Edge |
|
|
1 - Level |
|
|
Bit1 - Level of the interrupt request selected in the previous register. (see also “IRQ |
|
|
Mapping” on page 181). |
|
|
0 - Low polarity (implies open-drain output with strong pull-up for a short time, followed |
|
|
by weak pull-up). |
|
|
1 - High polarity (implies push-pull output). |
|
|
|
|
|
TABLE 2-9. PnP DMA Configuration Registers |
|
|
|
Index |
Name |
Definition |
|
|
|
|
|
|
74h |
DMA Channel |
Read/write value indicating selected DMA channel for DMA 0. |
|
Select 0 |
Bits 2-0 select the DMA channel for DMA 0. A value of 0 selects DMA channel 0; a |
|
|
|
|
|
value of 7 selects DMA channel 7. |
|
|
Selecting DMA channel 4, the cascade channel, indicates that no DMA channel is |
|
|
active. |
|
|
|
75h |
DMA Channel |
Read/write value indicating selected DMA channel for DMA 1 |
|
Select 1 |
Bits 2-0 select the DMA channel for DMA 1. A value of 0 selects DMA channel 0; a |
|
|
|
|
|
value of 7 selects DMA channel 7. |
|
|
Selecting DMA channel 4, the cascade channel, indicates that no DMA channel is |
|
|
active. |
|
|
|
TABLE 2-10. PnP Logical Device Configuration Registers
Index |
Name |
Definition |
|
|
|
|
|
|
F0h-FEh |
Logical Device |
Vendor defined. |
|
Configuration |
|
|
Vendor Defined |
|
|
|
|
29 |
www.national.com |

Configuration
2.3.2Configuration Register Summary
The tables in this section specify the Index, type (read/write), reset value and configuration register or action that controls each register associated with each function. When the reset value is not fixed, the table indicates what controls the value or points to another section that provides this information.
Soft Reset is related to a Reset executed by utilizing the Reset Bit (Bit 0) of the Config Control Register. (See Table 2-5 on page 27.)
TABLE 2-11. Card Configuration Registers
Index |
Type |
Hard Reset |
Soft Reset |
Configuration Register or Action |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
00h |
W |
00h |
PnP ISA |
Set RD_DATA Port. |
|
|
|
|
|
01h |
R |
|
|
Serial Isolation. |
|
|
|
|
|
02h |
W |
PnP ISA |
PnP ISA |
Configuration Control. |
|
|
|
|
|
03h |
W |
00h |
PnP ISA |
Wake[CSN]. |
|
|
|
|
|
04h |
R |
|
|
Resource Data. |
|
|
|
|
|
05h |
R |
|
|
Status. |
|
|
|
|
|
06h |
R/W |
00h |
PnP ISA |
Card Select Number (CSN). |
|
|
|
|
|
07h |
R/W |
00h |
PnP ISA |
Logical Device Number. |
|
|
|
|
|
20h |
R |
See section 2.4.1 and 2.4.2 on page 34. |
SID Register. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
21h |
R/W |
See Section 2.4.3 on page 34. |
No Effect |
SuperI/O Configuration 1 Register. |
|
|
|
|
|
22h |
R/W |
See Section 2.4.4 on page 35. |
No Effect |
SuperI/O Configuration 2 Register. |
|
|
|
|
|
23h |
R/W |
See Section 2.4.5 on page 35. |
No Effect |
Programmable Chip Select Configuration Index Register. |
|
|
|
|
|
24h |
R/W |
See Section 2.4.6 on page 36. |
No Effect |
Programmable Chip Select Configuration Data Register. |
|
|
|
|
|
27h |
R |
See Section 2.4.7 on page 36. |
SRID Register (in pc97307 only). |
|
|
|
|
|
|
TABLE 2-12. KBC Configuration Registers for Keyboard - Logical Device 0
Index |
R/W |
Hard Reset |
Soft Reset |
Configuration Register or Action |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
30h |
R/W |
00h or 01h |
00h or 01h |
Activate. |
|
|
See CFG0, Section 2.1.3. |
See CFG0,Section |
See also FER1 of power management device |
|
|
|
2.1.3. |
(logical device 8). |
|
|
|
|
|
31h |
R/W |
00h |
00h |
I/O Range Check. |
|
|
|
|
|
60h |
R/W |
00h |
00h |
Data Base Address MSB Register. |
|
|
|
|
|
61h |
R/W |
60h |
60h |
Data Base Address LSB Register. |
|
|
|
|
Bit 2 (for A2) is read only, 0. |
|
|
|
|
|
62h |
R/W |
00h |
00h |
Command Base Address MSB Register. |
|
|
|
|
|
63h |
R/W |
64 |
64h |
Command Base Address LSB. |
|
|
|
|
Bit 2 (for A2) is read only,1. |
|
|
|
|
|
70h |
R/W |
01h |
01h |
KBC Interrupt (KBC IRQ1 pin) Select. |
|
|
|
|
|
71h |
RW |
02h |
02h |
KBC Interrupt Type. |
|
|
|
|
Bits 1,0 are read/write; other bits, read only. |
|
|
|
|
|
74h |
R |
04h |
04h |
Report no DMA assignment. |
|
|
|
|
|
75h |
R |
04h |
04h |
Report no DMA assignment. |
|
|
|
|
|
F0h |
R/W |
See Section 2.5.1 on page 36. |
No Effect |
SuperI/O KBC Configuration Register. |
|
|
|
|
|
www.national.com |
30 |
 Loading...
Loading...