Mindray PM-7000 Service Manual
PM-7000
Patient Monitor
Service Manual

Service Manual
Copyright
Statement
SHENZHEN MINDRAY BIO-MEDICAL ELECTRONICS CO., LTD. (hereinafter called Mindray) owns all rights to this unpublished work and intends to maintain this work as confidential. Mindray may also seek to maintain this work as an unpublished copyright. This publication is to be used solely for the purposes of reference, operation, maintenance, or repair of Mindray equipment. No part of this can be disseminated for other purposes.
In the event of inadvertent or deliberate publication, Mindray intends to enforce its rights to this work under copyright laws as a published work. Those having access to this work may not copy, use, or disclose the information in this work unless expressly authorized by Mindray to do so.
All information contained in this publication is believed to be correct. Mindray shall not be liable for errors contained herein nor for incidental or consequential damages in connection with the furnishing, performance, or use of this material. This publication may refer to information and protected by copyrights or patents and does not convey any license under the patent rights of Mindray, nor the rights of others. Mindray does not assume any liability arising out of any infringements of patents or other rights of third parties.
Content of this manual is subject to changes without prior notice.
PROPERTY OF SHENZHEN MINDRAY BIO-MEDICAL ELECTRONICS CO., LTD. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED
Responsibility on the manufacturer party
Mindray is responsible for safety, reliability and performance of this equipment only in the condition that:
•all installation, expansion, change, modification and repair of this equipment are conducted by Mindray qualified personnel;
•applied electrical appliance is in compliance with relevant National Standards;
•the monitor is operated under strict observance of this manual.
Warning 
For continued safe use of this equipment, it is necessary that the listed instructions are followed. However, instructions listed in this manual in no way supersede established medical practices concerning patient care.
zDo not rely only on audible alarm system to monitor patient. When monitoring
I

Service Manual
adjusting the volume to very low or completely muting the sound may result in the disaster to the patient. The most reliable way of monitoring the patient is at the same time of using monitoring equipment correctly, manual monitoring should be carried out.
zThis multi-parameter patient monitor is intended for use only by medical professionals in health care institutions.
zTo avoid electrical shock, you shall not open any cover by yourself. Service must be carried out by qualified personnel.
zUse of this device may affect ultrasonic imaging system in the presence of the interfering signal on the screen of ultrasonic imaging system. Keep the distance between the monitor and the ultrasonic imaging system as far as possible.
zIt is dangerous to expose electrical contact or applicant coupler to normal saline, other liquid or conductive adhesive. Electrical contact and coupler such as cable connector, power supply and parameter module socket-inlet and frame must be kept clean and dry. Once being polluted by liquid, they must be thoroughly dried. If to further remove the pollution, please contact your biomedical department or Mindray.
It is important for the hospital or organization that employs this equipment to carry out a reasonable maintenance schedule. Neglect of this may result in machine breakdown or injury of human health.
II

Service Manual
Warranty
THIS WARRANTY IS EXCLUSIVE AND IS IN LIEU OF ALL OTHER WARRANTIES, EXPRESSED OR IMPLIED, INCLUDING WARRANTIES OF MERCHANT ABILITY OR FITNESS FOR ANY PARTICULAR PURPOSE.
Exemptions
Mindray's obligation or liability under this warranty does not include any transportation or other charges or liability for direct, indirect or consequential damages or delay resulting from the improper use or application of the product or the substitution upon it of parts or accessories not approved by Mindray or repaired by anyone other than a Mindray authorized representative.
This warranty shall not extend to any instrument which has been subjected to misuse, negligence or accident; any instrument from which Mindray's original serial number tag or product identification markings have been altered or removed, or any product of any other manufacturer.
Safety, Reliability and Performance
Mindray is not responsible for the effects on safety, reliability and performance of the PM-7000 Patient Monitor if:
■assembly operations, extensions, re-adjusts, modifications or repairs are carried out by persons other than those authorized by Mindray.
■the PM-7000 is not used in accordance with the instructions for use, or the electrical installation of the relevant room does not comply with NFPA 70: National Electric Code or NFPA 99: Standard for Health Care Facilities (Outside the United States, the relevant room must comply with all electrical installation regulations mandated by the local and regional bodies of government).
III

Service Manual
Return Policy
Return Procedure
In the event that it becomes necessary to return a unit to Mindray, the following procedure should be followed:
1.Obtain return authorization. Contact the Mindray Service Department and obtain a Customer Service Authorization (Mindray) number. The Mindray number must appear on the outside of the shipping container. Return shipments will not be accepted if the Mindray number is not clearly visible. Please provide the model number, serial number, and a brief description of the reason for return.
2.Freight policy. The customer is responsible for freight charges when equipment is shipped to Mindray for service (this includes customs charges).
Company Contact
Manufacture: Shenzhen Mindray Bio-Medical Electronics Co., Ltd.
Address: Mindray Building, Keji 12th Road South, Hi-tech Industrial
Park, Nanshan, Shenzhen 518057, P.R.China
Phone: +86 755 26582479 26582888
Fax: +86 755 26582934 26582500
IV

Service Manual
Safety Precautions
1. Meaning of Signal Words
In this manual, the signal words DANGER, WARNING, and CAUTION are used
regarding safety and other important instructions. The signal words and their meanings are defined as follows. Please understand their meanings clearly before reading this manual.
Signal word |
Meaning |
|
|
|
|
DANGER |
Indicates an imminently hazardous situation which, if not |
|
avoided, will result in death or serious injury. |
||
|
||
|
|
|
WARNING |
Indicates a potentially hazardous situation which, if not avoided, |
|
could result in death or serious injury. |
||
|
||
|
|
|
CAUTION |
Indicates a potentially hazardous situation which, if not avoided, |
|
may result in minor or moderate injury. |
||
|
||
|
|
2.Meaning of Safety Symbols
Symbol |
Description |
Type-BF applied part
"Attention" (Refer to the operation manual.)
Safety Precautions
Please observe the following precautions to ensure the safety of service engineers as well as operators when using this system.
 DANGER: Do not use flammable gases such as anesthetics, or flammable
DANGER: Do not use flammable gases such as anesthetics, or flammable
liquids such as ethanol, near this product, because there is danger of explosion.
 WARNING: Do not connect this system to outlets with the same circuit
WARNING: Do not connect this system to outlets with the same circuit
breakers and fuses that control current to devices such as life-support systems. If this system malfunctions and generates an over current, or when there is an instantaneous
V

Service Manual
current at power ON, the circuit breakers and fuses of the building’s supply circuit may be tripped.
CAUTION: |
1. Malfunctions due to radio waves |
(1)Use of radio-wave-emitting devices in the proximity of this kind of medical electronic system may interfere with its operation. Do not bring or use devices which generate radio waves, such as cellular telephones, transceivers, and radio controlled toys, in the room where the system is installed.
(2)If a user brings a device which generates radio waves near the system, they must be instructed to immediately turn OFF the device. This is necessary to ensure the proper operation of the system.
2. Do not allow fluids such as water to contact the system or peripheral devices. Electric shock may result.
VI

Service Manual
Symbols
Equipotential |
grounding |
CE mark 93/42/EEC a |
terminal |
|
directive of the European |
|
|
Economic Community |
Be Careful |
|
Protective earth ground |
Direct current and alternating |
Direct current (DC) |
|
current (DC&AC) |
|
|
|
|
|
Alternating current (AC) |
Battery indicator |
|
ESD sensitivity |
|
Power ON/OFF |
Network connector |
High voltage |
Indicates that the instrument is IEC-60601-1 Type CF equipment. The unit displaying this symbol contains an F-Type isolated (floating) patient applied part providing a high degree of protection against shock, and is suitable for use during defibrillation.
VII

Service Manual
Contents
Chapter 1 About the Product ..................................................................................................... |
1 |
|
1.1 |
Introduction...................................................................................................................... |
1 |
1.2 |
Application ....................................................................................................................... |
1 |
1.2.1 |
General ...................................................................................................................... |
1 |
1.3 |
Environment .................................................................................................................... |
3 |
1.3.1 |
Temperature............................................................................................................. |
3 |
1.3.2 |
Humidity ................................................................................................................... |
3 |
1.3.3 |
Electrical specification .............................................................................................. |
3 |
Chapter 2 Principles.................................................................................................................... |
4 |
|
2.1 |
General ............................................................................................................................ |
4 |
2.1.1 |
Parameter Measurement............................................................................................ |
5 |
2.1.2 |
Main Control Part...................................................................................................... |
5 |
2.1.3 |
Man-Machine Interface............................................................................................. |
5 |
2.1.4 |
Power Supply ............................................................................................................ |
5 |
2.1.5 |
Other Auxiliary Functions......................................................................................... |
5 |
2.2 |
Hardware Description ....................................................................................................... |
6 |
2.2.1 |
Main Board ............................................................................................................... |
7 |
2.2.2 |
ECG/RESP/TEMP Module ....................................................................................... |
9 |
2.2.3 |
CO/IBP Module....................................................................................................... |
11 |
2.2.4 |
SpO2 Module........................................................................................................... |
12 |
2.2.5 |
NIBP Module .......................................................................................................... |
13 |
2.2.6 |
Recorder Module..................................................................................................... |
14 |
2.2.7 |
Button Panel............................................................................................................ |
15 |
2.2.8 |
Power PCB.............................................................................................................. |
16 |
2.3 |
Software Description....................................................................................................... |
17 |
2.3.1 |
General .................................................................................................................... |
17 |
2.3.2 |
System Task............................................................................................................. |
18 |
2.3.3 System Function............................................................................................................. |
19 |
|
2.4 |
System Parameter............................................................................................................ |
20 |
2.4.1 |
General .................................................................................................................... |
20 |
2.4.2 |
ECG/RESP .............................................................................................................. |
20 |
2.4.3 |
NIBP........................................................................................................................ |
21 |
2.4.4 |
SpO2 ........................................................................................................................ |
22 |
2.4.5 |
TEMP...................................................................................................................... |
22 |
2.4.6 |
IBP .......................................................................................................................... |
22 |
2.4.7 |
CO ........................................................................................................................... |
23 |
2.4.8 |
CO2.......................................................................................................................... |
23 |
2.4.9 |
AG........................................................................................................................... |
23 |
I

Service Manual
Chapter 3 |
Product Specifications................................................................................................. |
25 |
|
3.1 |
Safety Classifications............................................................................................................ |
25 |
|
3.2 |
Environmental Specifications ............................................................................................... |
26 |
|
3.3 |
Power Source Specifications................................................................................................. |
27 |
|
3.4 |
Hardware Specifications ....................................................................................................... |
28 |
|
3.5 Wireless network................................................................................................................... |
29 |
||
3.6 |
Data Storage.......................................................................................................................... |
30 |
|
3.7 |
|
Signal Output Specifications........................................................................................... |
31 |
3.8 |
|
ECG Specifications ......................................................................................................... |
32 |
3.9 |
RESP Specifications.............................................................................................................. |
34 |
|
3.10 SpO2 Specifications............................................................................................................. |
35 |
||
1.1.1. Mindray SpO2 Module .................................................................................................. |
35 |
||
1.1.2. Masimo SpO2 Specifications......................................................................................... |
35 |
||
1.1.3. Nellcor SpO2 Specifications.......................................................................................... |
36 |
||
3.11 |
IBP Specifications........................................................................................................... |
37 |
|
3.12 TEMP Specifications........................................................................................................... |
38 |
||
3.13 IBP Specifications............................................................................................................... |
39 |
||
3.14 CO Specifications ............................................................................................................... |
40 |
||
3.15 CO2 Specifications .............................................................................................................. |
41 |
||
1.1.4. Mindray CO2 Specifications ......................................................................................... |
41 |
||
1.1.5. Oridion CO2 Specifications........................................................................................... |
42 |
||
1.1.6. Welch Allyn CO2 Specifications ................................................................................... |
43 |
||
3.16 AG Specifications ............................................................................................................... |
44 |
||
Chapter 4 Disassembling/Assembling & Troubleshooting ............................................................. |
47 |
||
4.1 |
|
PM-7000 Disassembling/Assembling ............................................................................. |
47 |
4.1.2 PM-7000 Support Assembly .......................................................................................... |
48 |
||
4.1.3 Front Bezel Assembly .................................................................................................... |
50 |
||
4.1.4 Rear Housing Assembly................................................................................................. |
51 |
||
4.1.5 Microstream CO2 Assembly........................................................................................... |
52 |
||
4.2 |
|
Troubleshooting ............................................................................................................ |
53 |
4.2.1 Black Screen, Startup Failure ................................................................................... |
53 |
||
4.2.2 White Screen & Other Abnormal Screen ................................................................ |
54 |
||
4.2.3 Encoder Faults............................................................................................................ |
54 |
||
4.2.4 No Audio Alarm ........................................................................................................... |
54 |
||
4.2.5 Printing Failure............................................................................................................ |
54 |
||
4.2.6 Abnormal Paper Drive................................................................................................ |
54 |
||
Chapter 5 Test and Material List ............................................................................................. |
55 |
||
5.1 |
|
Test Procedure.............................................................................................................. |
55 |
5.1.1 Connection and Checking ......................................................................................... |
55 |
||
5.1.2 Functions of Buttons .................................................................................................. |
55 |
||
5.1.3 ECG/RESP .................................................................................................................. |
55 |
||
5.1.4 Temperature ................................................................................................................ |
56 |
||
II

Service Manual
5.1.5 NIBP............................................................................................................................... |
56 |
|
5.1.6 SpO2 ............................................................................................................................... |
56 |
|
5.1.7 IBP ................................................................................................................................. |
56 |
|
5.1.8 CO .................................................................................................................................. |
57 |
|
5.1.9 CO2................................................................................................................................. |
57 |
|
5.1.10 Recorder....................................................................................................................... |
58 |
|
5.1.12 Power Supply ............................................................................................................... |
58 |
|
5.1.13 Clock ............................................................................................................................ |
58 |
|
5.1.14 System Test .................................................................................................................. |
58 |
|
5.2 |
NIBP Calibration............................................................................................................. |
59 |
5.3 |
IBP CALIBRATE.............................................................................................................. |
59 |
5.4 CO2 CHECK....................................................................................................................... |
62 |
|
5.5 AG CALIBRATE ................................................................................................................. |
64 |
|
5.5.1 AG Check..................................................................................................................... |
64 |
|
5.5.2 AG CALIBRATE .......................................................................................................... |
65 |
|
5.6 |
Bill of Materials for PM-7000 Main Unit ....................................................................... |
66 |
Chapter 6 Maintenance and Cleaning ............................................................................................. |
67 |
|
6.1 Maintenance.......................................................................................................................... |
67 |
|
6.1.1Checking Before Using................................................................................................... |
67 |
|
6.1.2 Regular Checking........................................................................................................... |
67 |
|
6.2 |
Cleaning .......................................................................................................................... |
67 |
6.3 |
Cleaning Reagent ............................................................................................................ |
67 |
6.4 |
Sterilization ..................................................................................................................... |
68 |
6.5 |
Disinfection..................................................................................................................... |
68 |
III

Chapter 1 About the Product
Chapter 1 About the Product
1.1Introduction
The PM-7000 Patient Monitor (hereinafter called PM-7000 for short), a portable and accessible patient monitor, is supplied by rechargeable batteries or external AC/DC power, which applies to adults, pediatric and neonates. You can select different configurations as required. Besides, the PM-7000 can be connected with the central monitoring system whereby a monitoring network will be formed. Parameters that the PM-7000 can monitor include: ECG, RESP, SpO2, NIBP, 2-channel TEMP, 2-channel IBP, CO, CO2 and AG. It, integrating the functions of parameter measurement, waveform monitoring, freezing and recording, is a compact and lightweight patient monitor. Its color TFT LCD is able to show patient parameters and 7 waveforms clearly. The compact control panel and knob control, and the easy-to-use menu system enable you to freeze, record, or perform other operations conveniently.
The PM-7000 measures patient’s ECG, NIBP, SpO2, TEMP, RESP, IBP, CO and CO2 physiological signals through the ECG electrode, SpO2 sensor, cuff, temperature sensor and pressure transducer. During the measurement, the patient monitor does not get energy or any substance from the human body, and does not release any substance to the human body. However, it releases sine wave signals to the patient when measuring the respiration rate. The patient monitor converts the measured physiological signals to the digital signals, waveforms and values, and then displays them on the screen. You can control the patient monitor through the control panel. For example, you can set different alarm limits for different patients. Thus, when the patient monitor detects any physiological parameter exceeding the preset alarm limit, it will enable the audio and visual alarm.
1.2 Application
1.2.1General
In the treatment processes, it is necessary to monitor important physiological information of patients. Therefore, the patient monitor has been playing an outstanding role among medical devices. The development of technology does not only help medical staff get the important physiological information, but also simplifies the procedures and makes it more effective. For patients in hospital, the basic and important physiological information is required, including ECG, SpO2, RESP, IBP, CO, CO2, TEMP, etc. In recent years, the development of science and technology helping measure and get important physiological information of patients has made the patient monitor more comprehensive in performance and better in quality. Today, multi-parameter patient monitors are widely used.
1.2.2Usage
Parameters that the PM-7000 include: ECG, RESP, SpO2, NIBP, TEMP, IBP, CO AG and CO2. PM-7000 converts these physiological signals to digital signals, processes them and displays them on the screen. You can set the alarm limit as required. When the monitored parameter
1

Chapter 1 About the Product
exceeds the preset alarm limit, the patient monitor will start the alarm function. In addition, you can control the patient monitor through the control panel. Usually, patient monitors are seen in some clinical areas in hospital, such as ICU, CCU, intensive care units for heart disease patients, operating rooms, emergency departments and observation wards. They can also be used in clinics. The PM-7000 should be run under the control of clinical staff.
PM-7000 has the following functions:
ECG |
Heart Rate (HR) |
|
2-channel ECG waveform |
|
Arrhythmia analysis and S-T analysis (optional) |
RESP |
Respiration Rate (RR) |
|
Respiration waveform |
SpO2 |
Pulse Oxygen Saturation(SpO2), Pulse Rate (PR) |
|
SpO2 Plethysmogram |
NIBP |
Systolic pressure (NS), diastolic pressure (ND), mean pressure |
|
(NM) |
TEMP |
T1, T2, TD |
IBP |
CH1: SYS, DIA |
|
CH2: SYS, DIA |
|
IBP waveform |
CO |
Temperature of blood (TB) |
|
Cardiac Output (CO) |
CO2
AG
End-tidal carbon dioxide (EtCO2)
Inspired minimum CO2 (InsCO2)
Airway Respiration Rate (AwRR)
Inhaled and exhaled CO2 (FiCO2, EtCO2) Inhaled and exhaled N2O (FiN2O, EtN2O) Inhaled and exhaled O2 (FiO2, EtO2)
Inhaled and exhaled anesthetic agent (FiAA, EtAA, where AA refers to any of the following anesthetic agents.)
HAL (Halothane)
ISO (Isoflurane)
ENF (Enflurane)
2

Chapter 1 About the Product
SEV (Sevoflurane)
DES (desflurane)
Airway Respiration Rate (rpm: Respiration Per Minute): AwRR
Minimum Alveolar Concentration (MAC)
4 AG waveforms (CO2, N2O, O2, AA)
The PM-7000 provides the functions of audio/visual alarm, trend graphic storage and output, NIBP measurement, alarm event identification, large font screen, defibrillator synchronization, oxyCRG recall, drug calculation, etc.
1.3 Environment
1.3.1 |
Temperature |
|
|
Work mode |
0 ~40 |
||
MINDRAY CO2 module |
+5 ~ +35 |
||
Welch Allyn mainstream CO2 module |
+10 |
~ +35 |
|
Microstream CO2 module |
+5 |
~ +35 |
|
Artema AION AG module |
+10 ~ +35 |
||
Transportation & Storage |
-20 ~ 60 |
||
1.3.2 |
Humidity |
|
|
Work mode |
15% – 95 % (non-condensing) |
||
Transportation & Storage |
10% |
– 95 % (non-condensing) |
|
Atmospheric pressure |
70.0kPa – 106.0kPa |
||
1.3.3Electrical specification
AC power supply: 100 to 240 V AC, 50/60 Hz, Maximum input power: 140VA DC power supply: 12 V (nominal), 10 to 16 V, Power: 80W
2.3 Ah 12V lead-acid rechargeable battery
Working time of fully-charged batteries in normal status: 75 minutes (1 battery).
From the first low-battery alarm, the batteries can supply power to the patient monitor for 5 ~ 15 minutes.
Maximum charging time: about 8h
4.4Ah 11.1V lithium battery
Working time of fully-charged batteries in normal status: 150 minutes (1 battery).
From the first low-battery alarm, the batteries can supply power to the patient monitor for 5 ~ 15 minutes.
Maximum charging time: about 8h
3

Chapter 2 Principles
Chapter 2 Principles
2.1General
The intended use of the PM-7000 is to monitor a fixed set of parameters including ECG, RESP, SpO2, NIBP, TEMP, IBP, CO and CO2 (IBP, CO and CO2 are optional). It consists of the following functional parts:
Parameter measurement; Main control part; Man-machine interface; Power supply;
Other auxiliary functions;
These functional units are respectively detailed below.
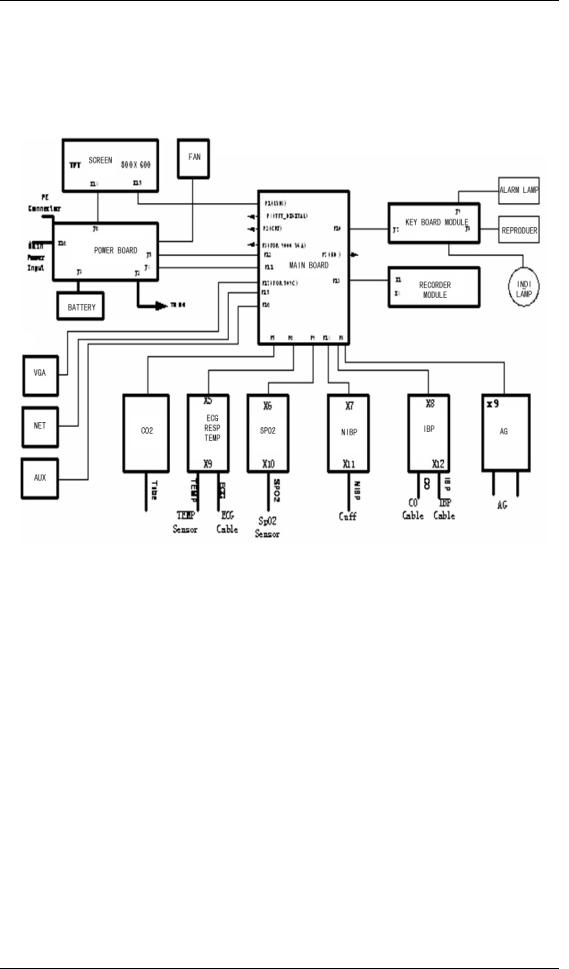
Figure 2-1 Structure of the PM-7000
4

Chapter 2 Principles
2.1.1Parameter Measurement
The parameter measurement and monitoring are the core functions of the patient monitor. The parameter measurement part of the PM-7000 consists of the measurement probe, parameter input socket assembly, NIBP assembly and the main control board.
This part converts the physiological signals to electric signals, processes the those signals and conducts the calculation by the preset program or command delivered from the main control board, and then sends the values, waveforms and alarm information (which will be displayed by using the man-machine interface) to the main control board.
2.1.2Main Control Part
In the PM-7000, the main control part refers to the main control part of the main control board. It drives the man-machine interface, manages the parameter measurement and provides users with other special functions, such as storage, recall of waveforms and data. (See Figure 2-1)
2.1.3Man-Machine Interface
The man-machine interface of the PM-7000 includes the TFT display, recorder, speaker, indicator, buttons and control knob.
The TFT display is the main output interface. It, with the high resolution, provides users with abundant real-time and history data and waveforms as well as various information and alarm information.
The recorder is a subsidiary of the display, which is used for the user to print data.
The speaker provides the auditory alarm function.
The indicator provides additional information about the power supply, batteries, alarms and so on.
The buttons and control knob are the input interface, which are used for the user to input the information and commands to the patient monitor.
2.1.4Power Supply
The power supply part is an important part of the patient monitor. It includes the main power PCB, backlight board, batteries and fan.
The main power PCB converts the external AC current respectively to the 5V DC and 12V DC current, which are supplied for the whole system. For the TFT display, there is a special requirement on the power supply, so a backlight board is used. The batteries supply power for the system for a short time when there is no external AC current. The fan is used for the heat sink of the system.
2.1.5Other Auxiliary Functions
The PM-7000 also provides the network upgrade function for the service engineers to upgrade the system software without disassembling the enclosure.
5
Chapter 2 Principles
2.2Hardware Description
The structure of the PM-7000 is shown in the following figure.
Figure 2-2 Functional structure of the PM-7000
6

Chapter 2 Principles
The PM-7000 PCB connection is shown in the following figure.
Figure 2-3 PCB connection
Basic functions and working principles of modules are described in the following sections.
2.2.1Main Board
2.2.1.1General
The main board is the heart of the patient monitor. It implements a series of tasks, including the system control, system scheduling, system management, data processing, file management, display processing, printing management, data storage, system diagnosis and alarm.
7

Chapter 2 Principles
2.2.1.2 Principle diagram
Figure 2-4 Working principle of the main board
2.2.1.3 Principle
The main board is connected with external ports, including the power input port, multi-way serial port, TFT display interface, analog VGA interface, network port and analog output port. Besides, on the main board is also a BDM interface reserved for the software debugging and software downloading.
CPU System
CPU is the core part of the main board. It, connected with other peripheral modules through the bus and I/O cable, implements the data communication, data processing, logical control and other functions.
RTC
RTC provides the calendar information (such as second, minute, hour, day, month and year). CPU can read and modify the calendar information from RTC.
Ethernet Controller
Ethernet Controller supports the IEEE802.3/IEEE802.3u LAN standard, and supports two data transmission rate: 10Mbps and 100Mbps. CPU exchanges data with the Ethernet through the Ethernet Controller.
Analog Output
The D/A converter converts the digital ECG/IBP signals sent from CPU to the analog signals, which are provided for the external after low-pass filtered by the filter and amplified by the amplifier.
FPGA and VRAM
VRAM stores the displayed data. CPU stores the displayed data to VRAM through FPGA. FPGA gets data from VRAM, processes them, and then sends them to the relevant graphic display device.
8

Chapter 2 Principles
In addition, FPGA also extends multiple serial ports, which communicate with peripheral modules. FPGA transfers the received data to CPU through the bus; CPU delivers data to FPGA through the bus, and then the FPGA transfers those data to the peripheral modules.
Watchdog
When powered on, watchdog provides reset signals for CPU, FPGA and Ethernet Controller.
The patient monitor provides the watchdog timer output and voltage detection functions.
2.2.2ECG/RESP/TEMP Module
2.2.2.1 General
This module provides the function of measuring three parameters: electrocardiograph (ECG), respiration (RESP) and temperature (TEMP).
2.2.2.2 Principle diagram
Figure 2-5 Working principle of the ECG/RESP/TEMP module
2.2.2.3 Principle
This module collects the ECG, RESP and TEMP signals through the transducer, processes the signals, and sends the data to the main board through the serial port.
ECG Signal Input Circuit
The input protection and filtering circuits receive the ECG signal from the transducer, and filter the high-frequency interference signal to protect the circuit against the damage by defibrillator high-voltage and ESD.
The right-leg drive circuit gets the 50/60Hz power common-mode signal from the lead cable, and sends the negative feedback signal to the human body to reject the common-mode interference signal on the lead cable, which helps the detection of the ECG signal.
The lead-off detecting circuit checks whether the ECG lead is off, and sends the information to CPU.
ECG Signal Process Circuit
The difference amplifying circuit conducts the primary amplification of the ECG signal and
9

Chapter 2 Principles
rejects the common-mode interference signal.
The low-pas filtering circuit filters the high-frequency interference signal beyond the frequency band of the ECG signal.
The PACE signal refers to the ECG pace signal. It has significant interference to the ECG signal detection. The PACE rejection circuit can rejects the PACE signal, which helps the ECG signal detection.
The main amplifying/filtering circuit conducts the secondary amplification of the ECG signal, filters the signal, and then sends the ECG signal to the A/D conversion part.
Pace Detect
This part detects the PACE signal from the ECG signal and sends it to CPU.
Temperature Detect Circuit
This circuit receives the signal from the temperature transducer, amplifies and filters it, and then sends it to the A/D conversion part.
Carrier Generate Circuit
The RESP measurement is based on the impedance method. While a man is breathing, the action of the breast leads to changes of the thoracic impedance, which modulates the amplitude of the high-frequency carrier signal. Finally, the modulated signal is sent to the measurement circuit. The purpose of this module is generating the high-frequency carrier.
RESP Signal Input Circuit
This circuit couples the RESP signal to the detecting circuit.
RESP Signal Process Circuit
The pre-amplifying circuit conducts the primary amplification of the RESP signal and filters it. The detecting circuit detects the RESP wave that has been modulated on the actuating signal. The level shifting circuit removes the DC component from the RESP signal.
The main amplifying/filtering circuit conducts the secondary amplification of the RESP signal, filters the signal, and then sends it to the A/D conversion part.
A/D
The A/D conversion part converts the analog signal to the digital signal, and sends the signal to CPU for further processing.
CPU System
Implementing the logical control of all parameter parts and A/D conversion parts;
Implementing the data processing for all parameters;
Implementing the communication with the main board.
Power & Signal isolate Circuit
Isolating the external circuits to ensure the safety of human body;
Supplying power for all circuits;
Implementing the isolation communication between the CPU System and the main board.
10

Chapter 2 Principles
2.2.3CO/IBP Module
2.2.3.1 General
This module provides the function of measuring two parameters: Cardiac Output (CO) and Invasive Blood Pressure (IBP).
2.2.3.2 Principle diagram
Figure 2-6 Working principle of the CO/IBP module
2.2.3.3 Principle
This module collects the CO/IBP signal through the transducers, processes it and sends it to the main board throgh the serial port.
CO Signal Process Network
The CO parameter is measured with the thermal dilution method. The transducer sends two signals (TI: Temperature of Injectate; TB: Temperature of Blood) to the CO Signal Process Network. After that, the signals are amplified and low-pass filtered, and then sent to the CPU System for processing.
IBP Signal Process Network
The IBP signal is the differential signal. After the common-mode filtering, the difference signal is amplified by the difference amplifying circuit which changes the dual-end signal to the single-end signal. After the low-pass filtering, the IBP signal is sent to the CPU System for processing.
CPU System
Converting the analog signal obtained by the circuit to the digital signal;
Implementing the logical control of all parameter parts;
Implementing the data processing for the two parameters;
Implementing the communication with the main board.
Power & Signal isolate Circuit
Isolating the external circuits to ensure the safety of human body;
Supplying power for all circuits;
Implementing the isolation communication between the CPU System and the main board.
11

Chapter 2 Principles
2.2.4SpO2 Module
2.2.4.1 General
This module provides the function of measuring the Pulse Oxygen Saturation (SPO2).
2.2.4.2 Principle diagram
Figure2-7 Working principle of the SpO2 module
2.2.4.3 Principle
The SpO2 measurement principle
1.Collecting the light signal of the red light and infrared transmitting through the finger or toe which is pulsing;
2.Processing the collected signal to get the measured result.
The drive circuit of the LED and the gain of the amplifying circuit should be controlled according to the different perfusions and transmittances of the tested object.
Led Drive Circuit
This circuit supplies the LED with the drive current, which can be regulated.
SPO2 Signal Process Network
The pre-amplifying circuit converts the photoelectric signal to the voltage signal and conducts the primary amplification.
The gain adjusting and amplifying circuit conducts the secondary signal amplification and adjusts the gain.
The biasing circuit adjusts the dynamic range of the signal, and sends it to the A/D conversion part.
A/D
The A/D conversion part converts the analog signal to the digital signal, and then sends it to CPU for further processing.
D/A
The D/A conversion part converts the digital signal received from CPU to the analog signal, and provides the control signal for the Led Drive Circuit and SPO2 Signal Process Network.
12

Chapter 2 Principles
CPU System
Implementing the logical control of all the circuits;
Implementing the data processing for the SpO2 parameter;
Implementing the communication with the main board.
Power & Signal isolate Circuit
Isolating the external circuits to ensure the safety of human body;
Supplying power for all circuits;
Implementing the isolation communication between the CPU System and the main board.
2.2.5NIBP Module
2.2.5.1 General
This module provides the function of measuring the Non-Invasive Blood Pressure (NIBP) parameter.
2.2.5.2 Principle diagram
Figure 2-8 Working principle of the NIBP module
2.2.5.3 Principle
The NIBP is measured based on the pulse vibration principle. Inflate the cuff which is on the forearm till the cuff pressure blocks the arterial blood, and then deflate the cuff according to a specified algorithm. While the cuff pressure is decreasing, the arterial blood has pulses, which are sensed by the pressure transducer in the cuff. Consequently, the pressure transducer, connected with the windpipe of the cuff, generates a pulsation signal, which is then processed by the NIBP module to get the NIBP value.
13
 Loading...
Loading...