HEIDENHAIN iTNC 530 Service Manual

Service Manual
iTNC 530 HSCI
February 2012

1 How to use the iTNC 530 HSCI Service Manual................................................................ 11
1.1 Target group ................................................................................................................... 11
1.2 About this manual...........................................................................................................11
1.3 Other service manuals.................................................................................................... 12
1.4 Other documentation ..................................................................................................... 12
1.5 Support........................................................................................................................... 12
1.6 Service training............................................................................................................... 13
1.7 Meaning of the symbols used in this manual................................................................. 13
1.8 Safety ............................................................................................................................. 13
2 Safety precautions............................................................................................................... 15
2.1 Introduction .................................................................................................................... 15
2.2 Overview ........................................................................................................................ 15
3 Code numbers ...................................................................................................................... 17
3.1 Introduction .................................................................................................................... 17
3.2 Overview ........................................................................................................................ 17
3.3 Input of code numbers ................................................................................................... 18
4 Error messages .................................................................................................................... 21
4.1 Introduction .................................................................................................................... 21
4.2 HELP key........................................................................................................................ 24
4.3 ERR key.......................................................................................................................... 25
4.4 CE key ............................................................................................................................ 26
4.5 List of NC error messages.............................................................................................. 27
5 Errors .................................................................................................................................... 51
5.1 Introduction .................................................................................................................... 51
5.2 Overview of possible errors ........................................................................................... 51
6 Procedures and tips for error diagnosis in the field ......................................................... 55
6.1 Introduction .................................................................................................................... 55
6.2 Power off and on............................................................................................................55
6.3 Sequence for finding serious electrical errors ................................................................ 56
6.4 Sequence for finding errors in the control loop .............................................................. 58
6.5 Error localization by process of interchange ................................................................... 61
6.6 Error localization by process of exclusion....................................................................... 63
6.7 Observing essential values with the integrated oscilloscope......................................... 65
6.8 Finding position differences of direct and indirect encoders......................................... 67
6.9 Error localization by switching from direct to indirect position measurement................ 69
6.10 Notes and tips for the field service............................................................................... 71
7 Creating and reading out service files ............................................................................... 75
7.1 Introduction .................................................................................................................... 75
7.2 Automatic generation of service files............................................................................. 76
7.3 Manual generation of service files.................................................................................. 76
7.4 Generating service files with TNCremoNT..................................................................... 77
7.5 Evaluation of the service files......................................................................................... 78
8 Log......................................................................................................................................... 79
..
8.1 Introduction ..................................................................................................................
8.2 Calling the log................................................................................................................. 80
8.3 Reading out the log with TNCremoNT and filtering by event types............................... 81
8.4 Overview of log entries .................................................................................................. 83
8.5 Log entries at program termination................................................................................ 89
79
February 2012 HEIDENHAIN Service Manual iTNC 530 HSCI

9 DriveDiag .............................................................................................................................. 91
9.1 Introduction .................................................................................................................... 91
9.2 Activation and operation................................................................................................. 91
9.3 Troubleshooting with DriveDiag ..................................................................................... 93
10 Integrated oscilloscope ..................................................................................................... 95
10.1 Introduction .................................................................................................................. 95
10.2 Activation and settings ................................................................................................. 96
10.3 Recording and adjusting the signals........................................................................... 101
10.4 Saving and loading recordings.................................................................................... 106
10.5 For error diagnosis...................................................................................................... 107
10.5.1 Triggering on error marker................................................................................ 107
10.5.2 Circular interpolation test ................................................................................. 109
10.5.3 Finding compensation values ........................................................................... 111
10.5.4 Working with delta triggers .............................................................................. 113
10.5.5 Descriptions in this manual .............................................................................. 114
11 PLC diagnosis................................................................................................................... 115
11.1 Introduction ................................................................................................................ 115
11.2 Error messages .......................................................................................................... 118
11.3 Possible error causes ................................................................................................. 118
11.4 Diagnosis tools in the PLC mode ............................................................................... 119
11.4.1 The ABLE function .......................................................................................... 119
11.4.2 The LOGIC diagram.......................................................................................... 124
11.4.3 The TRACE function ........................................................................................ 127
11.4.4 The WATCH LIST function ............................................................................... 128
11.4.5 The I/O-FORCE LIST......................................................................................... 131
11.5 Non-volatile PLC markers and words ......................................................................... 134
11.6 Overviews .................................................................................................................. 136
11.7 Specifications ............................................................................................................. 144
11.7.1 PLC inputs ........................................................................................................ 144
11.7.2 Analog inputs ................................................................................................... 144
11.7.3 Inputs for Pt 100 thermistors ........................................................................... 144
11.7.4 PLC outputs...................................................................................................... 145
11.7.5 Analog outputs ................................................................................................. 146
11.7.6 Assignment of the inputs and outputs............................................................. 146
12 Bus diagnosis ................................................................................................................... 147
12.1 HSCI bus .................................................................................................................... 147
12.1.1 Introduction ...................................................................................................... 147
12.1.2 Possible error causes ....................................................................................... 147
12.1.3 Calling and operating the HSCI bus diagnosis .................................................. 148
12.1.4 Identification of the PLC operands ................................................................... 149
12.1.5 Read-back outputs ........................................................................................... 150
12.1.6 Master, slaves and clients................................................................................ 152
12.1.7 For error diagnosis............................................................................................ 153
12.2 PROFIBUS................................................................................................................. 162
12.2.1 Introduction ...................................................................................................... 162
12.2.2 Possible error causes ....................................................................................... 162
12.2.3 Calling and operating the PROFIBUS diagnosis ............................................... 163
12.2.4 Identification of the PLC operands ................................................................... 164
12.2.5 Troubleshooting with DriveDiag ....................................................................... 164
12.2.6 Log files ............................................................................................................ 165
HEIDENHAIN Service Manual iTNC 530 HSCI

13 Data media and file management of the iTNC 530 HSCI ............................................. 167
13.1 Introduction ................................................................................................................ 167
13.2 Structure of the data medium .................................................................................... 168
13.3 Possible error causes ................................................................................................. 168
13.4 Test of the data medium ............................................................................................ 169
13.5 Setting the system time............................................................................................. 173
13.6 Settings in the program manager............................................................................... 174
13.7 File management in the TNC partition........................................................................ 175
13.8 File management in the PLC partition ........................................................................ 177
14 Data backup...................................................................................................................... 181
14.1 Introduction ................................................................................................................ 181
14.2 Connection setup ....................................................................................................... 183
14.2.1 Via Ethernet ..................................................................................................... 183
14.2.2 Via RS-232-C/V.24 serial interface .................................................................... 192
14.2.3 Via USB............................................................................................................. 195
14.3 Reading in and out individual files and directories...................................................... 196
14.4 Backup on an external data medium .......................................................................... 202
14.5 Extracting files from the backup file........................................................................... 206
14.6 Restoring data ............................................................................................................ 207
14.7 Cable overview........................................................................................................... 209
14.7.1 Ethernet interface RJ45 connection ................................................................. 209
14.7.2 RS-232-C (V.24)................................................................................................. 210
14.8 Operating modes of the data interfaces..................................................................... 213
14.9 Drive symbols............................................................................................................. 214
15 Reloading the currently used NC software ................................................................... 215
15.1 Introduction ................................................................................................................ 215
15.2 Preparations................................................................................................................ 215
15.3 Procedure ................................................................................................................... 216
16 Loading service packs ..................................................................................................... 219
16.1 Introduction ................................................................................................................ 219
16.2 Preparations................................................................................................................ 220
16.3 Procedure ................................................................................................................... 221
17 Checking the enables on the iTNC 530 HSCI................................................................. 225
17.1 Introduction ................................................................................................................ 225
17.2 Examination................................................................................................................ 228
17.2.1 "Control is ready" output and input (EMERGENCY STOP chain)....................... 228
17.2.2 Axis-specific drive enable via axis groups.........................................................232
17.2.3 Readiness of the inverter system..................................................................... 233
17.2.4 PLC modules, markers and words for drive enabling ...................................... 238
17.3 EMERGENCY STOP test during switch-on ................................................................ 240
18 Power supply.................................................................................................................... 243
18.1 Introduction ................................................................................................................ 243
18.2 Supply voltages in the HSCI system .......................................................................... 243
18.3 PSL 130 low-voltage power supply unit ..................................................................... 246
18.4 PSL 135 low-voltage power supply unit ..................................................................... 250
18.5 Power supply for the MC 62xx computer unit ........................................................... 255
18.6 Buffer battery ............................................................................................................. 257
....................................................................................................... 261
18.7 Information
18.8 Power supply of the CC 61xx feedback control unit .................................................. 262
18.9 Power supply of the UEC 11x feedback control unit.................................................. 267
18.10 Power supply of the MB 620 machine operating panel ........................................... 268
18.11 Power supply of the BF 250 visual display unit........................................................ 269
18.12 Power supply of the TE 6xx keyboard unit ............................................................... 270
18.13 Power supply for the control-is-ready signal............................................................. 271
menu
February 2012 HEIDENHAIN Service Manual iTNC 530 HSCI

18.14 Power supply of the PLB 62xx system module ....................................................... 272
18.15 Supply voltage for PLC outputs................................................................................ 274
18.15.1 Introduction .................................................................................................... 274
18.15.2 Supply voltage for PLC outputs on the UEC 11x ........................................... 275
18.15.3 Supply voltage for PLC outputs on the MB 620 ............................................ 275
18.15.4 Supply voltage for PLC outputs on the PLB 62xx .......................................... 275
18.15.5 Supply voltage for PLC outputs on the PLD-H xx-xx-xx ................................. 276
19 Encoder interface............................................................................................................. 277
19.1 Position encoders...................................................................................................... 277
19.1.1 Introduction ...................................................................................................... 277
19.1.2 Machine parameters......................................................................................... 279
19.1.3 Error messages ................................................................................................ 280
19.1.4 Possible error causes ....................................................................................... 281
19.1.5 Troubleshooting................................................................................................ 281
19.1.6 Possibilities with DriveDiag .............................................................................. 289
19.1.7 Possibilities with the integrated oscilloscope ................................................... 290
19.1.8 Corrective action .............................................................................................. 293
19.1.9 Determining the field angle on linear motors,
torque motors and synchronous spindles ................................................................... 294
19.1.10 Resetting the machine datum ........................................................................ 295
19.1.11 Restoring the spindle orientation.................................................................... 299
19.2 Speed encoders ......................................................................................................... 300
19.2.1 Introduction ...................................................................................................... 300
19.2.2 Machine parameters ........................................................................................ 302
19.2.3 Error messages ................................................................................................ 303
19.2.4 Possible error causes ....................................................................................... 303
19.2.5 Troubleshooting................................................................................................ 304
19.2.6 Possibilities with DriveDiag .............................................................................. 306
19.2.7 Possibilities with the integrated oscilloscope ................................................... 307
19.2.8 Corrective action............................................................................................... 310
19.2.9 Readjusting the trip dog for reference end position ......................................... 311
19.2.10 Resetting the machine datum ........................................................................ 312
19.2.11 Restoring the spindle orientation.................................................................... 312
19.3 Error codes for encoders with EnDat interface
19.4 Further examination of position and speed encoders ................................................ 314
19.5 Position measurement via motor encoder (indirect position measurement).............. 317
19.6 Switching over the position display for servicing ....................................................... 321
20 Reference run ................................................................................................................... 323
20.1 Definition.................................................................................................................... 323
20.2 Traversing the reference marks ................................................................................. 324
20.3 Error messages .......................................................................................................... 324
20.4 Possible error causes ................................................................................................. 324
20.5 Troubleshooting.......................................................................................................... 325
20.6 Corrective action ........................................................................................................ 326
20.7 Deselecting axes referencing..................................................................................... 326
21 Interfaces to the drives.................................................................................................... 327
21.1 Digital PWM interface ................................................................................................ 327
21.1.1 Introduction ...................................................................................................... 327
21.1.2 Machine parameters......................................................................................... 330
21.1.3 Tables for power supply modules, power stages and motors ......................... 332
21.1.4 Reading out power module data ...................................................................... 338
21.1.5 Error messages ................................................................................................ 339
21.1.6 Possible error causes ....................................................................................... 340
21.1.7 Sequence for finding errors in the control loop ................................................ 340
......................................
.................... 313
HEIDENHAIN Service Manual iTNC 530 HSCI

21.1.8 Error finding: Axes swapping............................................................................ 341
21.1.9 Error finding: Swapping power modules
or output stages of the same type .............................................................................. 343
21.1.10 Error finding: Swapping the HEIDENHAIN expansion boards
for the SIMODRIVE 611 system.................................................................................. 347
21.1.11 Corrective action............................................................................................. 348
21.2 Analog speed value interface .................................................................................... 349
21.2.1 Introduction ...................................................................................................... 349
21.2.2 Machine parameters ........................................................................................ 350
21.2.3 Error messages ................................................................................................ 350
21.2.4 Possible error causes........................................................................................ 351
21.2.5 Sequence for finding errors in the control loop ................................................ 351
21.2.6 Checking the analog speed value interface ...................................................... 352
21.2.7 Adjusting the electrical offset (drift adjustment)............................................... 355
21.2.8 Speed adjustment at the servo amplifier (tachometer adjustment) ................. 358
21.2.9 Corrective action...............................................................................................360
22 Visual display unit ........................................................................................................... 361
22.1 Introduction ................................................................................................................ 361
22.2 Possible error causes ................................................................................................. 362
22.3 Troubleshooting.......................................................................................................... 363
22.4 Corrective action.........................................................................................................364
23 Keyboard unit................................................................................................................... 365
23.1 Introduction ................................................................................................................ 365
23.2 Signal paths in the console and to the MC 62xx ........................................................ 367
23.3 Possible error causes ................................................................................................. 369
23.4 Checking the keys ...................................................................................................... 370
23.5 Checking the potentiometers..................................................................................... 376
23.6 Checking the touchpad............................................................................................... 380
23.7 Corrective action.........................................................................................................381
23.8 Key matrix of the keyboard units................................................................................ 382
23.9 Key matrix of the screen soft keys............................................................................. 392
24 Machine operating panel ................................................................................................ 393
24.1 Introduction ................................................................................................................ 393
24.2 Possible error causes ................................................................................................. 395
24.3 Checking the power supply........................................................................................ 396
24.4 Checking the HSCI connection................................................................................... 396
24.5 Checking the keys ...................................................................................................... 397
24.6 Checking the outputs ................................................................................................. 399
24.7 Corrective action.........................................................................................................400
25 Handwheel........................................................................................................................ 401
25.1 Introduction ................................................................................................................ 401
25.2 Error messages .......................................................................................................... 402
25.3 Possible error causes ................................................................................................. 402
25.4 Error diagnosis of HR 520 portable handwheel with display ...................................... 404
25.5 Error diagnosis of HR 410 portable handwheel .......................................................... 409
........................................... 412
25.6 Deselecting and disconnecting the portable handwheel
25.7 Error diagnosis of HR 130 panel-mounted handwheel ............................................... 413
25.8 Corrective action.........................................................................................................414
26 Touch probes.................................................................................................................... 415
26.1 Introduction ................................................................................................................ 415
26.2 Error messages .......................................................................................................... 420
26.3 Possible error causes ................................................................................................. 420
26.4 Error diagnosis on TS touch probes............................................................................ 422
26.5 Error diagnosis on TT touch probes............................................................................ 427
.
February 2012 HEIDENHAIN Service Manual iTNC 530 HSCI

26.6 Error diagnosis on the laser touch probe.................................................................... 431
26.7 Deselecting and disconnecting the touch probe ........................................................ 433
26.8 Corrective action ........................................................................................................ 434
27 Features of HEIDENHAIN components............................................................................ 35
27.1 HEIDENHAIN components in a machine too ............................................................. 435
27.2 Hardware identification .............................................................................................. 436
27.3 Display of important system information ................................................................... 451
28 Connector designations and pin layouts....................................................................... 453
28.1 Important note............................................................................................................ 453
28.2 MC main computer .................................................................................................... 453
28.2.1 Designations and positions of connectors ....................................................... 453
28.2.2Pin layouts ......................................................................................................... 455
28.3 CC controller unit........................................................................................................ 461
28.3.1 Designations and positions of connectors ....................................................... 461
28.3.2 Pin layouts ........................................................................................................ 464
28.4 Controller unit with integrated UEC inverter .............................................................. 473
28.4.1 Designations and positions of connectors........................................................ 473
28.4.2 Pin layouts ........................................................................................................ 474
28.5 PLB basic modules..................................................................................................... 481
28.5.1 Designations and positions of connectors ....................................................... 481
28.5.2 Pin layouts ........................................................................................................ 483
28.6 Digital I/O modules..................................................................................................... 485
28.6.1 Designations and positions of connectors ....................................................... 485
28.6.2 Pin layouts ....................................................................................................... 486
28.7 Analog I/O modules.................................................................................................... 487
28.7.1 Designations and positions of connectors ....................................................... 487
28.7.2 Pin layouts ....................................................................................................... 488
28.8 SPI expansion module................................................................................................ 490
28.8.1 Designations and positions of connectors........................................................ 490
28.8.2 Pin layouts ........................................................................................................ 490
28.9 PSL low-voltage power supply unit............................................................................ 493
28.9.1 Designations and positions of connectors ....................................................... 493
.................................................................................. 494
28.9.2 Pin layouts ...................
28.10 Display unit............................................................................................................... 497
28.10.1 Designations and positions of connectors..................................................... 497
28.10.2 Pin layouts ..................................................................................................... 497
28.11 Keyboard units.......................................................................................................... 498
28.11.1 Designations and positions of connectors...................................................... 498
28.11.2 Pin layouts ...................................................................................................... 499
28.12 Machine operating panel.......................................................................................... 500
28.12.1 Designations and positions of connectors...................................................... 500
28.12.2 Pin layouts ...................................................................................................... 501
28.13 HSCI adapter PLB 6001........................................................................................... 504
28.13.1 Designations and positions of connectors...................................................... 504
28.13.2 Pin layouts ..................................................................................................... 505
28.14 Handwheels ............................................................................................................. 509
28.14.1 HR 4xx or HR 5xx portable handwheel........................................................... 509
28.14.2 HR 130 panel-mounted handwheel................................................................ 510
28.15 Touch probes............................................................................................................ 511
28.16 Encoders .................................................................................................................. 511
28.16.1 Position encoders ........................................................................................... 511
28.16.2 Speed encoders.............................................................................................. 513
28.17 Inverters and motors................................................................................................ 514
28.18 Interface boards for the SIMODRIVE 611D drive system........................................ 514
...
HEIDENHAIN Service Manual iTNC 530 HSCI

29 Exchange of HEIDENHAIN components ........................................................................ 515
29.1 Important information................................................................................................. 515
29.2 Recognizing and accepting hardware updates ........................................................... 523
29.3 Detecting and loading firmware updates.................................................................... 524
29.4 Exchanging the MC 6222 ........................................................................................... 531
29.5 Exchanging the MC 6241 ........................................................................................... 534
29.6 Exchanging the SSDR................................................................................................. 537
29.7 Replacing the HDR ..................................................................................................... 543
29.8 Exchanging the CC ..................................................................................................... 550
29.9 Exchanging the UEC................................................................................................... 551
29.10 Exchanging the buffer battery .................................................................................. 551
29.11 Exchanging other HEIDENHAIN components .......................................................... 552
29.12 Exchanging HEIDENHAIN interface boards in the SIMODRIVE system.................. 553
30 Measuring, testing and inspection equipment............................................................. 559
30.1 Important notes.......................................................................................................... 559
30.2 Test adapter................................................................................................................ 560
30.3 PWM 9 encoder diagnostic kit ................................................................................... 564
30.4 PWT 10/17/18 test unit............................................................................................... 566
30.5 IK 215 adjusting and testing package......................................................................... 568
30.6 PWM 20 encoder diagnostic kit ................................................................................. 569
31 Machine parameters ....................................................................................................... 571
31.1Explanation .................................................................................................................. 571
31.2 The machine parameter editor ................................................................................... 572
31.3 Meaning of the machine parameters ......................................................................... 579
31.4 List of machine parameters........................................................................................ 580
31.4.1 Format: Encoders and machines ......................................................................580
31.4.2 Positioning ........................................................................................................ 585
31.4.3 Operation with velocity feedforward control.................................................... 591
31.4.4 Operation with following error.......................................................................... 592
31.4.5 Integrated speed and current control ............................................................... 593
31.4.6 Spindle.............................................................................................................. 602
31.4.7 Integrated PLC.................................................................................................. 605
31.4.8 Configuration of the data interface ................................................................... 607
31.4.9 3-D touch probe................................................................................................ 609
31.4.10 Tool measurement with TT............................................................................. 611
31.4.11 Tapping ........................................................................................................... 614
31.4.12 Display and operation ..................................................................................... 615
31.4.13 Colors.............................................................................................................. 623
31.4.14 Machining and program run ........................................................................... 625
31.4.15 Hardware ........................................................................................................631
31.4.16 Spindle, second .............................................................................................. 639
1 Annex: Principle of function of the iTNC 530 HSCI control............................................ 641
1.1 Introduction .................................................................................................................. 641
1.2 The control loop............................................................................................................ 641
1.3 The HSCI bus................................................................................................................ 648
February 2012 HEIDENHAIN Service Manual iTNC 530 HSCI

HEIDENHAIN Service Manual iTNC 530 HSCI

1 How to use the iTNC 530 HSCI Service Manual
Note
Note
1.1 Target group
This Service Manual has been written for specialist electricians for service, maintenance and
commissioning.
Specialists who perform work on the electrical system of a machine tool and its components must
have the required technical knowledge and competence.
1.2 About this manual
Objective This Service Manual assists service staff in the field in diagnosing and correcting errors on
machine tools equipped with the HEIDENHAIN control iTNC 530 HSCI.
HSCI This Service Handbook was specifically written for field service of iTNC 530 with HSCI.
The HSCI, the HEIDENHAIN Serial Controller Interface, connects the main computer, controller(s)
and other control components by means of a bus system.
The diagnostic functions of the iTNC 530 HSCI are the same as those of the iTNC 530 plus a special
HSCI bus diagnostics.
For the field service of iTNC 530 without HSCI, refer to the iTNC 530 Service Manual.
Contents This manual includes:
Specific explanations of the HEIDENHAIN Serial Controller Interface (HSCI)
Error messages and types of errors that indicate technical defects
Information on possible error causes
Descriptions for error diagnosis
Application descriptions of the diagnosis tools
Information on corrective action
Data backup instructions
Theoretical explanations of functions and their correlations
The ”List of NC error messages” on page 4 – 27 and the ”Overview of possible errors” on page 5 –
51 contain many references to the descriptions for error diagnosis.
You will find these descriptions in the chapters of this Service Manual sorted by topics.
Commissioning
support?
Validity This manual comprises the servicing possibilities with the control hardware and software
The Service Manual does not provide any commissioning support!
up-to-date at the publishing date of this manual. The servicing possibilities of your equipment may
differ from those described here. The descriptions also provide information on any differences in
servicing that are due to changes in the hardware or software.
This manual is valid for:
Single-processor iTNC 530 with HSCI and NC software 606420 / 421 (without "Functional Safety")
Prerequisites For the instructions for the field service it is assumed that ...
the machine had been working perfectly before the error occurred.
only original spare parts are used!
Basic knowledge of Windows is required for some of the descriptions in this Service Manual that
deal with the use of a service laptop.
February 2012 1 – 11

Update service This Service Manual is updated at irregular intervals.
Note
Note
Attention
You find the current printable version of this SHB iTNC 530 HSCI in HESIS-Web Including Filebase.
If you are not a registered customer with access to this HEIDENHAIN database, you will receive this
Service Manual either on the occasion of a service training course or from your machine tool builder.
Print version If you take part in a service training, you will receive the Service Manual in printed form.
.
1.3 Other service manuals
iTNC 530 Service Manual (for machine tools with iTNC 530 without HSCI)
Service Manual for Inverter Systems and Motors
1.4 Other documentation
For further important information please refer to the following documentation:
Machine documentation by the manufacturer
(circuit diagrams, wiring diagrams, machine operating manual, etc.)
HEIDENHAIN User's Manual for iTNC 530 HSCI
HEIDENHAIN TNCguide on DVD
Mounting instructions by HEIDENHAIN
Brochures of the respective HEIDENHAIN products
PWM 9 User's Manual
PWT Operating Instructions
IK215/PWM 20 Operating Instructions
1.5 Support
You can find up-to-date issues of this and other HEIDENHAIN documents quickly on our website
--> www.heidenhain.de
HEIDENHAIN software tools (e.g. TNCremoNT) feature detailed on-line help.
The machine manufacturer must be contacted first for error diagnosis on your machine tool!
However, support will also be provided by the Service Department of HEIDENHAIN Traunreut or by
the HEIDENHAIN agencies.
You will find telephone numbers as well as e-mail addresses on the back cover of this Service Manual,
or on the HEIDENHAIN website (www.heidenhain.de).
1 – 12 HEIDENHAIN Service Manual iTNC 530 HSCI

1.6 Service training
Note
DANGER
Attention
Note
DANGER
HEIDENHAIN Traunreut offers service training courses in German language. We recommend the
HEIDENHAIN service training courses for iTNC 530 HSCI for technicians who work with this Service
Manual.
Please contact HEIDENHAIN Traunreut or visit our website (www.heidenhain.de).
If required, please inquire at the HEIDENHAIN subsidiary in your country whether service training
courses are offered in your language.
1.7 Meaning of the symbols used in this manual
Failure to comply with this information could result in most serious or fatal injuries, and/or in
substantial material damage.
1.8 Safety
Failure to comply with this information could result in injuries and interruptions of operation,
including material damage.
These boxes contain important and useful information.
It is extremely important that you read the safety precautions in this manual before you start
servicing!
See “Safety precautions” on page 2 – 15.
February 2012 1 – 13

1 – 14 HEIDENHAIN Service Manual iTNC 530 HSCI
2 Safety precautions
DANGER
DANGER
DANGER
DANGER
DANGER
2.1 Introduction
The safety precautions below are provided to ensure your personal safety and the safety of the
machine tool.
Please read this information carefully before you start servicing the machine!
2.2 Overview
Equipment ground
Ensure that the equipment ground is continuous!
Interruptions in the grounding conductor may cause damage or injury to property or persons.
Zero potential
Fundamental
knowledge
Know-how and
competence
Ensure that the main switch of the control is switched off and that connected devices are not
under power when you engage or disengage any connectors or terminals.
Take precautions against restart!
Use an appropriate voltage test unit to ensure that the unit is not under voltage!
In order to be able to judge the behavior of an NC controlled machine, service engineers need
to have fundamental knowledge of controls, encoders, drives, electronics and mechanics.
Inappropriate use may cause considerable damage to persons or property.
Technicians who work on the electrical system of the machine must have the required know-how
and competence.
Suitable tools
Use suitable tools, e.g. insulated screwdrivers and pincers!
February 2012 2 – 15

Safety
Attention
DANGER
DANGER
DANGER
DANGER
Attention
precautions of
the machine
manufacturer
Regulations for
power installations
and instructions
for safety and
prevention of
accidents
Basic insulation
Note the safety precautions on the machine (e.g. labels, signs) and the safety precautions in the
documentation of the machine manufacturer (e.g. operating instructions).
Observe the national regulations for power installations and the general instructions for safety and
prevention of accidents!
Vertical axes
Changes to
entry values
The interfaces for the PLC inputs/outputs, machine operating panel and PL expansion cards
comply with the basic insulation in accordance with IEC 742 EN 50 178.
Only units that comply with the requirements of IEC 742 EN 50 178 for basic insulation may be
connected, otherwise damage to persons or property may be caused.
The maximum mean dc voltage of the PLC inputs is 31 V.
Always secure vertical axes to prevent them from falling down before you perform tests on these
axes!
Incorrect or non-optimized input values can lead to faulty machine performance and therefore
to serious injury to persons and damage to equipment.
Machine parameters may only be changed by or after consultation with the machine
manufacturer!
Uncontrolled axis and spindle movements must be expected.
Settings that have an effect on the control's feedback loops may only be altered when the
EMERGENCY STOP button of the machine is pressed.
Liability
HEIDENHAIN does not accept any responsibility for indirect or direct damage caused to persons
or property through incorrect use or operation of the machine!
2 – 16 HEIDENHAIN Service Manual iTNC 530 HSCI
3 Code numbers
DANGER
Note
3.1 Introduction
With code numbers …
certain areas of the hard disk
certain file types
certain functions
... can be called.
Code numbers may only be passed on to and be used by trained service technicians.
Keep the code numbers confidential!
Inexpert handling may result in a loss of important data, in faulty machine performance and thus
lead to damage or injury to property or persons.
3.2 Overview
Code number Brief description Description in this
manual
0 Reset the previously entered code numbers --> Soft keys such as MP
EDIT or PLC EDIT are deleted.
123 Edit subset of machine parameters for the machine operator See page 31 – 571
75368 Offset adjustment for analog axes See page 21 – 355
79513 Info menu (U[BATT], U[ACCU], U[VCC], TEMP, T[CPU1]), See page 18 – 261
95148 Call the active machine parameter list See page 31 – 571
531210 Reset non-volatile PLC markers and PLC words in the RAM See page 11 – 134
688379 Integrated oscilloscope See page 10 – 95
807667 Call the PLC area See page 11 – 115
857282 Reset the operating times - - -
LOGBOOK Call and save the internal log of the iTNC See page 8 – 79
NET123 Network settings for the single-processor control See page 14 – 183
SETUP Call for loading service packs and NC software for the single-processor
control
SIK Display of the number of the system identification key and of the enabled
options
VERSION Create the file TNC:\Version.a
System data is saved in this file for diagnostic purposes. The file can be
read out for diagnosis.
In this chapter
See page 16 – 219
See page 29 – 517
- - -
Machine tool builders may define their own MP and PLC code numbers.
In this event the HEIDENHAIN code numbers do not function any longer, or only function to
a limited extent. --> Contact your machine tool builder!
February 2012 3 – 17
3.3 Input of code numbers
Note
Note
Note
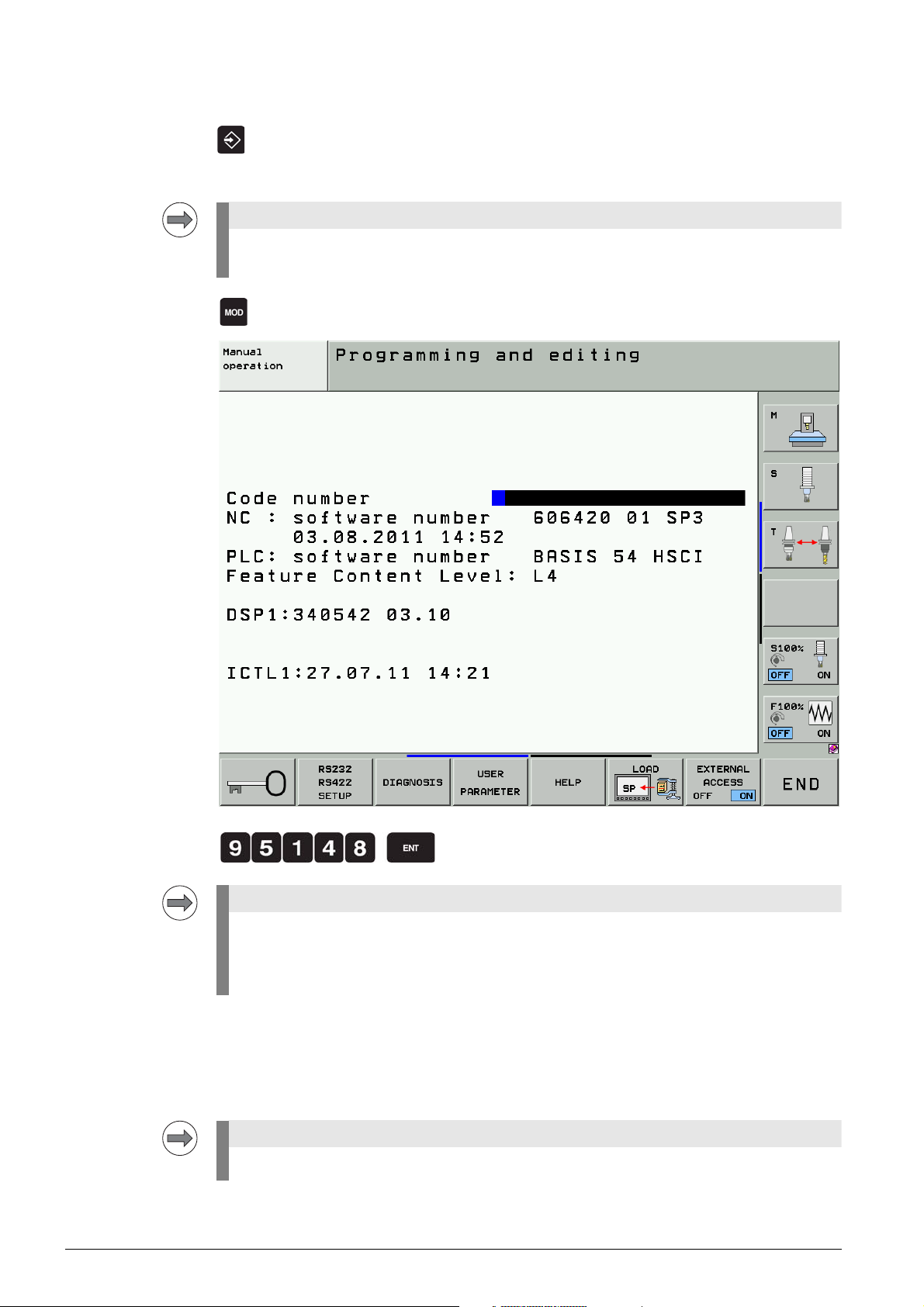
8 If open: Close the program management by pressing the END button.
Pressing the MOD key while the program manager is open calls the screen where you can make
the interface settings.
8 Select the Programming and Editing operating mode.
8 Call the code number window.
8 Enter the code number and press ENT to confirm.
When certain code numbers are entered, new soft keys are displayed, e.g. CONFIG EDIT,
PLC EDIT, OSCI.
With these soft keys you can also change to the corresponding areas without having to enter
the code number again.
When you have finished your work, reset all previously entered code numbers:
8 Enter the code number 0 and press ENT to confirm.
8 Press END to exit the code-number page.
All key codes are reset when the control is restarted.
3 – 18 HEIDENHAIN Service Manual iTNC 530 HSCI

Additional
information
As long as the machine parameter list is in the editor, no further code number can be entered.
I.e., first close the MP editor if you want to enter a new code number
Figure: As long as the text Machine parameter programming is displayed in the header, no further
code numbers are accepted (exception: NET123).
After you have entered the code number for the machine parameters the PLC tree can be seen
in the program management.
Only files with the extension .MP are displayed.
After entering the PLC code number, all files in the PLC tree can be seen and loaded in the editor.
However, to edit machine parameters you must press the MP EDIT soft key first.
Figure: The soft key MP EDIT must be pressed (or the code number 95148 entered) before you
are entitled to edit machine parameters.
February 2012 3 – 19

3 – 20 HEIDENHAIN Service Manual iTNC 530 HSCI
4 Error messages
Note
4.1 Introduction
The iTNC 530 features a comprehensive integral monitoring system for the prevention of input
or operation errors, as well as for identification and diagnosis of technical defects on the control
and the connected devices. The monitoring system is an integral component of the iTNC hardware
and software and is active as long as the control is switched on. The presence of a technical fault
or an operation error is made known through a plain-language message.
Moreover, the machine manufacturer can define specific PLC error messages.
Type of
error message
PLC error messages
Machine-specific error messages
Are defined by the machine manufacturer (e.g., coolant pump defective, protective door
open)
The machine manufacturer defines how the control reacts to a PLC error message (NC Stop,
EMERGENCY STOP, etc.)
The machine manufacturer defines whether the control can still be operated or has to be rebooted
after a PLC error message.
If you have any questions, please contact your machine manufacturer.
NC error messages
Are part of the HEIDENHAIN NC software.
Can be subdivided into error messages that result from operation, programming and machine
applications and those that indicate a technical defect (devices, electronic and mechanical
components, etc.)
HEIDENHAIN defines how the control reacts to an NC error message (NC Stop, EMERGENCY
STOP, etc.)
HEIDENHAIN defines whether the control can still be operated or has to be rebooted after
an NC error message.
If you have any questions, please contact your machine manufacturer and/or HEIDENHAIN.
Is the displayed error message an NC or PLC error message?
Call the ERR window or the log to answer this question:
Display PLC error message NC error message
ERR window
In the Group column.
Call --> See ”ERR key” on page 4 – 25.
Log
In lines that start with the entry ERR.
Call --> See ”Log” on page 8 – 79.
No error numbers are assigned to NC error messages that begin with N-1.
Operating-system error messages
Often contain the note CHILD PROCESS ERROR.
The control cannot be operated any more and has to be rebooted.
If you have any questions, please contact your machine manufacturer and/or HEIDENHAIN.
PLC GENERAL
or
OPERATION
or
PROGRAMMING
P
(number and text of
error message)
N
(number and text of
error message)
February 2012 4 – 21

Display of
error message
All error messages that can be acknowledged with the CE key are …
displayed in the screen header (at the top of the screen), usually in red color
as a plain-language message.
Figure: Error message in the header
The machine manufacturer can display additional information on PLC error messages in the small
PLC window (above the soft-key row).
Figure: Additional information in the small PLC window
Error messages that require a restart of the control ...
are displayed in the middle of the screen in a gray window
as a plain-language message.
Figure: Gray error window
4 – 22 HEIDENHAIN Service Manual iTNC 530 HSCI

Reaction of
control and
machine
Display only
A message (info, warning, error) is only displayed.
The machine does not react; programs are not stopped.
The error message can be acknowledged anytime.
Feed stop
The feed-rate enable is reset. The "F" symbol for the feed rate is highlighted.
The axes are braked at the nominal value characteristic.
I.e., the contour of the workpiece is usually not damaged.
Once the error message has been acknowledged, the machine continues to operate at the set feed
rate.
NC Stop
The running NC program is stopped. The control-in-operation symbol (STIB) flashes.
The axes are braked at the nominal value characteristic.
I.e., the contour of the workpiece is usually not damaged.
After the error message has been acknowledged, the NC program can be restarted at the position
where it was interrupted (NC START key).
Program cancelation
The running NC program is canceled (internal stop).
The axes are braked at the nominal value characteristic.
I.e., the contour of the workpiece is usually not damaged.
After the error message has been acknowledged, the NC program needs to be restarted
(GOTO 0, NC START).
Automatic
generation of
service files
EMERGENCY STOP
An EMERGENCY STOP is triggered at the machine.
Axes and spindles decelerate at the current limit; the machine must be brought to a standstill as
quickly as possible.
The contour of the workpiece is not taken into account and may be damaged.
After the error message was acknowledged, the machine must be switched on completely.
Now, the PLC program can be restarted (GOTO 0, NC START).
RESET
An EMERGENCY STOP is triggered at the machine.
Axes and spindles decelerate at the current limit; the machine must be brought to a standstill as
quickly as possible.
The contour of the workpiece is not taken into account and may be damaged.
The error message cannot be acknowledged. The control must be shut down and restarted.
Now, the PLC program can be restarted (GOTO 0, NC START).
In the event of serious NC software errors or especially defined PLC error messages, service files are
generated automatically.
See ”Creating and reading out service files” on page 7 – 75.
February 2012 4 – 23
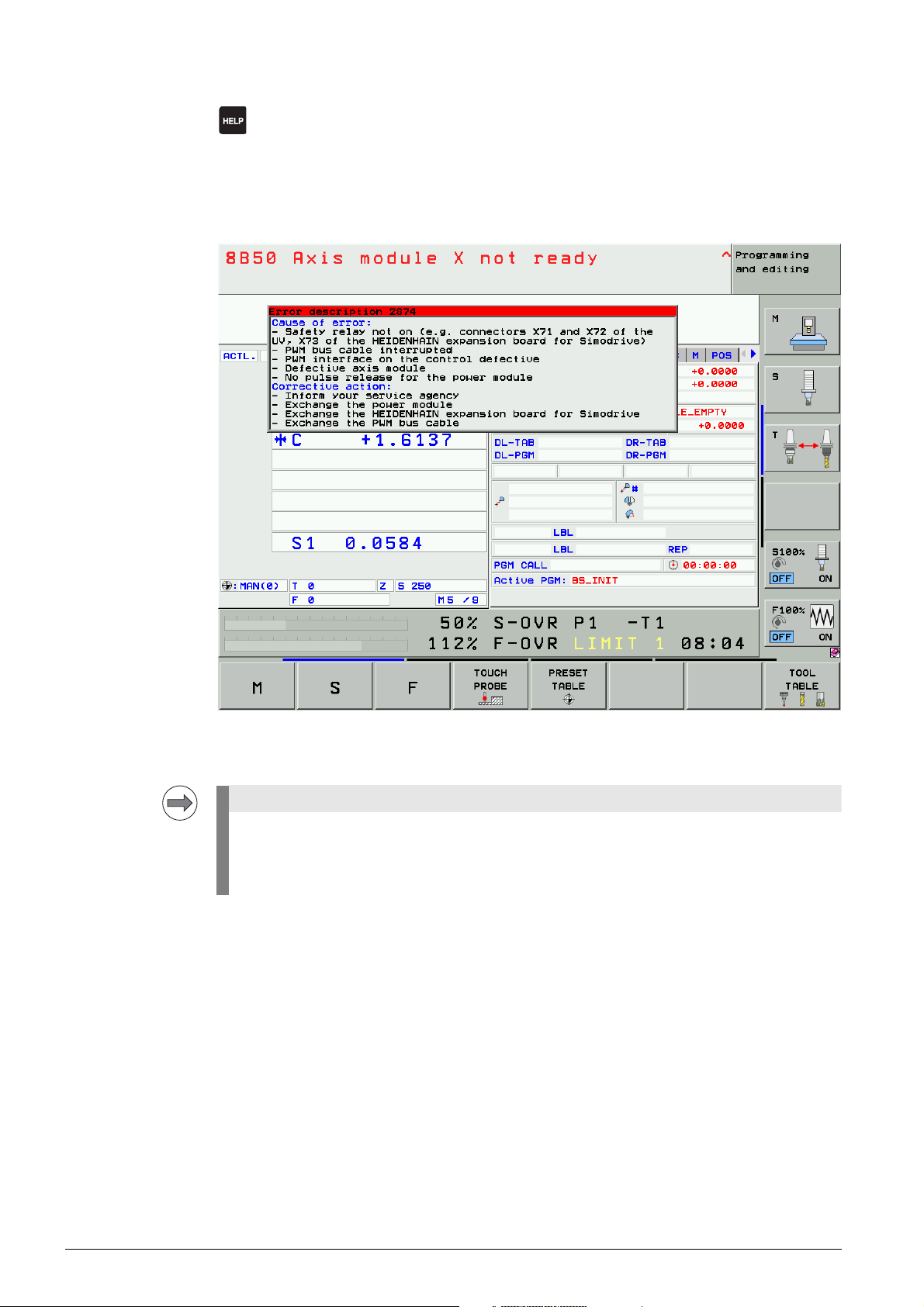
4.2 HELP key
Note
8 Display help texts for error messages
(If you press this key again, the window will close.)
When the service technician presses the HELP key, a window is shown that describes the cause
of the error and possibilities of corrective action in addition to the displayed error message.
The machine manufacturer may also have implemented this function for PLC error messages.
Figure: HELP window
HELP texts cannot be displayed for error messages in gray windows.
The control must be rebooted.
For information on these errors refer to the list of NC error messages.
--> See ”List of NC error messages” on page 4 – 27.
4 – 24 HEIDENHAIN Service Manual iTNC 530 HSCI
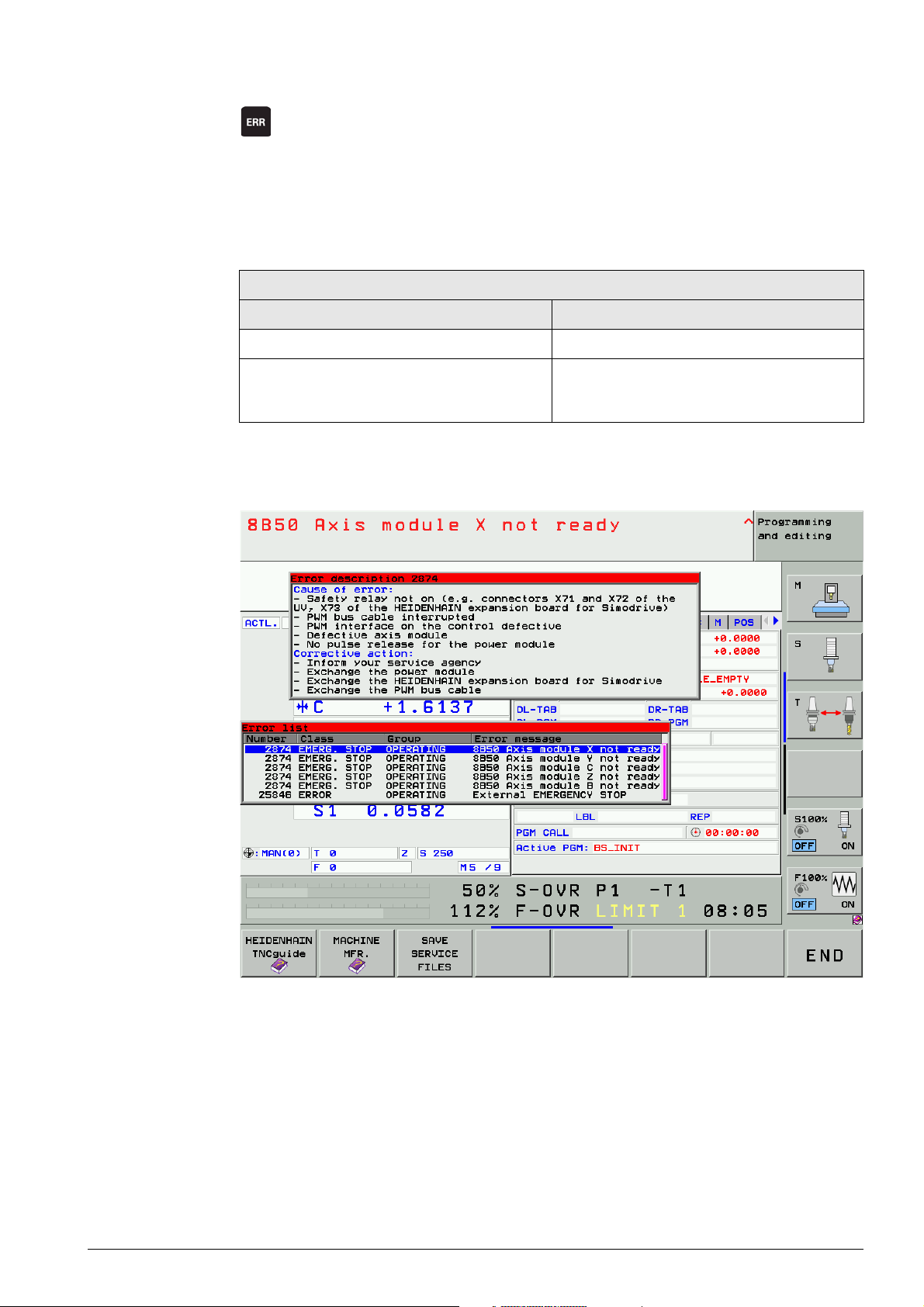
4.3 ERR key
8 Display all pending error messages in a list.
(When you press this key again, the window will close.)
If there is an AND symbol (red caret) in the header in addition to the error message, there is more than
one error message pending.
The ERR key (ERROR) is located directly above the HELP key. When this key is pressed all NC and
PLC error messages pending at the control are displayed in their own window.
List of error messages
In the ERR window In the log
By priority In chronological order
Errors with a higher priority are higher up in
the list.
The log is written from top to bottom, i.e. older
errors are at the top, more recent errors at the
bottom.
In addition to the error list, the help window can be called with the HELP key.
The contents of the Help window refers to the error message highlighted in the ERR window.
Figure: ERR window with open HELP window
February 2012 4 – 25
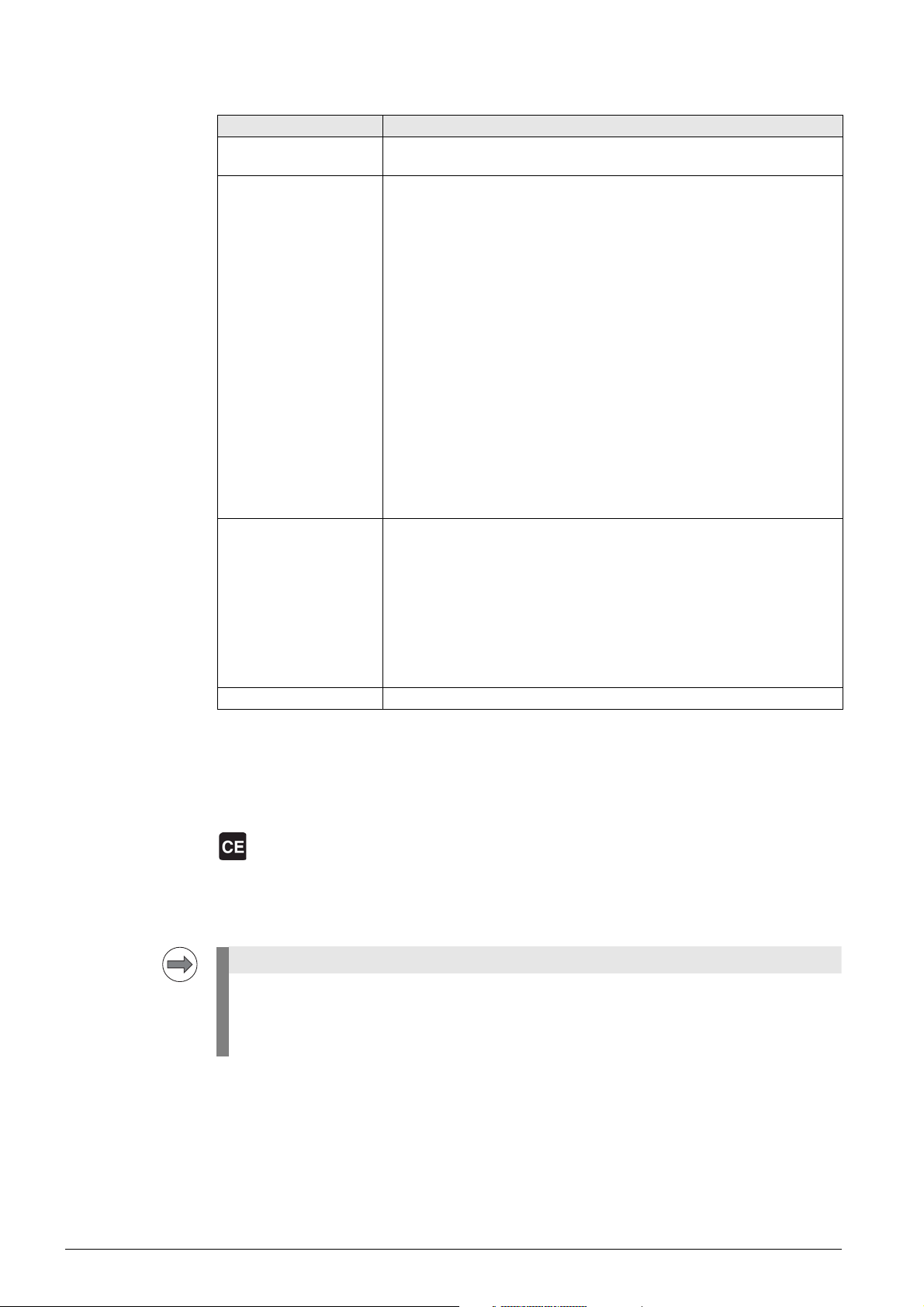
The columns in the ERR window have the following meanings:
Note
Column in ERR window Description
Number Error number defined by HEIDENHAIN or the machine manufacturer
(-1: No error number defined)
Class Error class; defines the reaction of the control:
ERROR
Group error
The error reaction depends on the status or current operating mode
of the control.
FEED HOLD
The feed-rate enable is deleted.
PGM HOLD
The program run is interrupted (the control-in-operation symbol blinks)
PGM ABORT
The program run is interrupted (INTERNAL STOP.)
EMERG. STOP
An emergency stop is triggered.
RESET
The iTNC executes a system restart.
WARNING
Warning message, program run resumes
INFO
Information message, program run resumes
Group Error source; shows the cause of the error:
GENERAL
General error
OPERATING
Error during machining and machine traverse
PROGRAMMING
Error in programming and editing
PLC
PLC error message of the machine manufacturer
Error message Displayed error text
4.4 CE key
The individual error messages can be selected with the cursor; the open Help window shows the
associated text.
8 Clear error message (Clear Error)
Acknowledge displayed error messages by pressing the CE key.
If the error cause is still existing, the error message will be displayed again. --> Correct the error!
Messages reporting particularly severe errors cannot be confirmed with the CE key.
The control must be restarted.--> Press the END key.
If this does not work --> Switch off the power switch of the machine and wait for several seconds
before switching it on again.
4 – 26 HEIDENHAIN Service Manual iTNC 530 HSCI
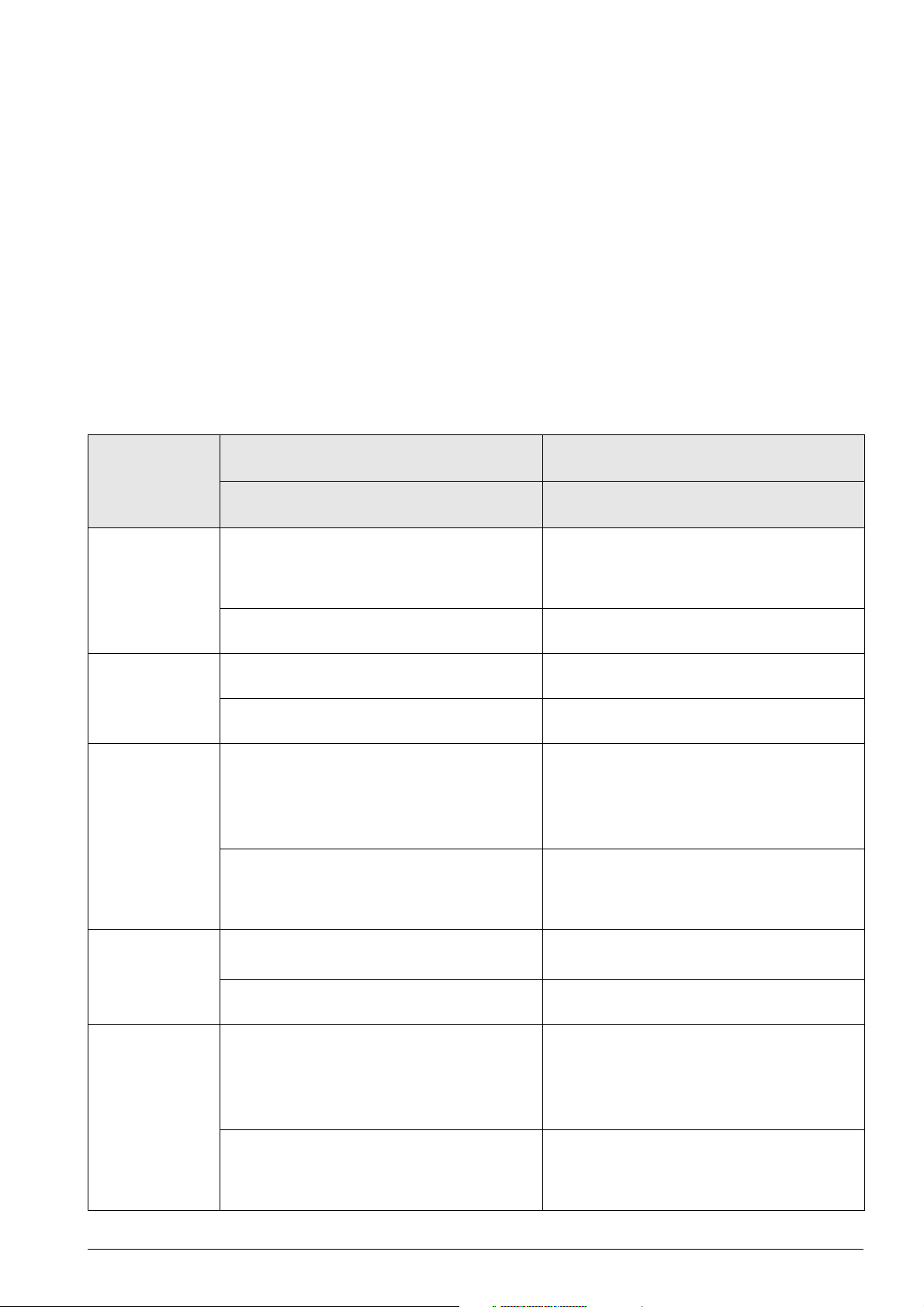
4.5 List of NC error messages
Complete list You can find the complete list of all NC error messages (including operator errors) on the TNCguide
DVD in several languages and sorted by error numbers.
This TNCguide information is also available on our website -->
www.heidenhain.de/....
This list is the official list of NC error messages. It contains all error messages of HEIDENHAIN controls
that operate with the HeROS operating system.
It consists primarily of error messages related to operation and handling as well as technical error
messages.
Filtered list The list below contains the most important error messages that indicate a technical defect in
numerical and in alphabetical order.
A reference is made, if there are additional descriptions in this Service Manual.
Error message Possible cause of error Measures for error diagnosis and/or
corrective action
8040 Heat sink
temp. in UV 1xx
8041 Excessive Iz
in UV 1xx
8043 No inverterready signal
8060 Leakage
current in UV 1xx
too high
Additional information and descriptions
in the manual
Heat-sink temperature of UV 1xx power supply
unit too high
If the heat-sink temperature continues to
increase, the unit will be switched off.
DC-link current of UV 1xx power supply unit
too high
Readiness signal of the inverter (supply unit) is
inactive after the feedback control starts.
Master contactor has opened.
Error in PLC program
Inverter defective
Insulation problem (e.g. defective motor). Check the motor.
Additional information and descriptions
in the manual
Stop the machine and let it cool down.
Continue working with lower power
(reduce the feed rate).
See Service Manual Inverter Systems and
Motors.
Continue working with lower power
(reduce the feed rate).
See Service Manual Inverter Systems and
Motors.
Try restarting the inverter.
Check the wiring (master contactor).
Check the PLC program.
Exchange the inverter (supply unit).
See ”Readiness of the inverter system” on
page 17 – 233.
See Service Manual Inverter Systems and
Motors.
Check the wiring.
See Service Manual Inverter Systems and
Motors.
8061 No inverterready signal
February 2012 4 – 27
Readiness signal of the inverter (supply unit) is
inactive after the feedback control starts.
Master contactor has opened.
Error in PLC program
Inverter defective
Try restarting the inverter.
Check the wiring (master contactor).
Check the PLC program.
Exchange the inverter (supply unit).
See ”Readiness of the inverter system” on
page 17 – 233.
See Service Manual Inverter Systems and
Motors.
Error message Possible cause of error Measures for error diagnosis and/or
corrective action
8080 Uz UV 1xx
too high
8092 Pos. contr.
cyc. time error
8130 Motor brake
defective <axis>
8140 Error <axis>
field orientation
Additional information and descriptions
in the manual
DC-link voltage of the power supply unit
too high.
MC is outputting erroneous cycle time for
CC position controller.
A hardware error has occurred.
Motor brake defective. Traverse the axis to a safe position before
Field orientation impossible for mechanical
reasons.
Incorrect relation between electrical field and
mechanical motor motion.
Incorrect motor encoder signal.
Incorrect motor connection.
Mechanical brakes not released.
Additional information and descriptions
in the manual
Check the machine parameter (braking the
spindle).
Check the braking resistor.
Replace the power supply unit.
See Service Manual Inverter Systems and
Motors.
Check machine parameter 7600.x.
Exchange drive control board.
power-off.
Check controls for motor brakes.
Exchange the motor.
See Service Manual Inverter Systems and
Motors.
Check the machine parameters for number of
signal periods and distance for the number of
signal periods.
Check the machine parameter for the linear
distance of one motor revolution.
For linear motors: Check column STR of the
motor table.
Check the speed encoder connection.
Check the motor connection.
Release brakes during orientation.
8300 Motor brake
defective <axis>
8310 No current in
brake test <axis>
8610 I2T value is
too high <axis>
See ”Speed encoders” on page 19 – 300. See ”Sequence for finding errors in the control
loop” on page 6 – 58.
See ”Speed encoders” on page 19 – 300.
See Service Manual Inverter Systems and
Motors.
Motor brake defective. Traverse the axis to a safe position before
power-off.
Check controls for motor brakes.
Exchange the motor.
See Service Manual Inverter Systems and
Motors.
Motor connected incorrectly
Inverter connected incorrectly
Inverter defective
Motor defective
Excessive load over the time of the drive. Reduce the load or the duration.
Check
Check the inverter.
Check the motor.
See Service Manual Inverter Systems and
Check the motor table, power module table,
Check whether the motor and power module
the wiring of motor and inverter.
Motors.
and machine parameters.
are designed for the load.
See Service Manual Inverter Systems and
Motors.
4 – 28 HEIDENHAIN Service Manual iTNC 530 HSCI
Error message Possible cause of error Measures for error diagnosis and/or
corrective action
8620 Load is too
high <axis>
8640 I2T value of
motor is too high
<axis>
8650 I2T value of
motor is too high
<axis>
Additional information and descriptions
in the manual
Drive has maximum current and cannot
accelerate.
Excessive load (torque, power) on the drive.
The load of the motor is too high over the
duration.
The load of the power module is too high over
the duration.
Additional information and descriptions
in the manual
Reduce the load on the drive.
Check the motor table, power module table,
and machine parameters.
Check whether the motor and power module
are designed for the load.
See ”Sequence for finding errors in the control
loop” on page 6 – 58.
See Service Manual Inverter Systems and
Motors.
Reduce the load or the duration.
Check the motor table and machine
parameters.
Check whether the motor is designed for the
load.
See Service Manual Inverter Systems and
Motors.
Reduce the load or the duration.
Check the motor table and machine
parameters.
Check whether the power module is designed
for the load.
8800 Signal LTRDY inactive
<axis>
8810 Signal LTRDY inactive
<axis>
8820 Field angle
unknown <axis>
8830 EnDat: No
field angle <axis>
Inverter switch-off during closed-loop control of
a vertical axis (cause = vertical axis).
Inverter switch-off during closed-loop control of
a vertical axis (cause = vertical axis).
Field angle of the motor on the reference point
of the speed encoder has not yet been
ascertained.
Field angle of the motor with unaligned speed
encoder with EnDat interface has not yet been
ascertained.
The transferred EnDat serial number does not
match the one saved.
EnDat encoder or encoder cable is
nected
Con
defective.
See Service Manual Inverter Systems and
Motors.
Check the PLC program.
Check the wiring of the inverter.
See Service Manual Inverter Systems and
Motors.
Check the PLC program.
Check the wiring of the inverter.
See Service Manual Inverter Systems and
Motors.
Run a field orientation.
Check the motor table (column SYS).
See ”Speed encoders” on page 19 – 300.
Run a field orientation.
Check the motor table (column SYS).
See ”Speed encoders” on page 19 – 300.
8860 Input
frequency from
speed encoder
<axis>
February 2012 4 – 29
Noise on speed encoder signals Check the encoder signals.
Check the shielding.
See ”Further examination of position and
speed encoders” on page 19 – 314.
Error message Possible cause of error Measures for error diagnosis and/or
corrective action
8870 Input
frequency from
position encoder
<axis>
88C0 Max.
nominal motor
speed %s
exceeded
8A00 No inverter
enabling %.2s
Additional information and descriptions
in the manual
Noise on position encoder signals Check the encoder signals.
Axis: Maximum feed rate is greater than the
maximum motor speed (N-MAX) multiplied by
MP1054.
Spindle: Maximum spindle speed is greater
than the maximum motor speed (N-MAX)
multiplied by the gear transmission ratio.
The relationship between the line count of the
position encoder and that of the motor encoder
is faulty.
The N-MAX entry in the motor table is faulty.
Incorrect entry in MP2200
EcoDyn: The selected feed rate exceeds the
max. permissible voltage.
Power-on of the drive not possible due to
missing enabling of the inverter via –SH1.
Additional information and descriptions
in the manual
Check the shielding.
See ”Further examination of position and
speed encoders” on page 19 – 314.
Check the N-MAX entry in the motor table.
Check MP1010 and MP1054.
Check the machine parameters for spindle
speed.
Check the STR column in the motor table and
MP3142.
Check MP2200.x.
Check the wiring.
See ”Readiness of the inverter system” on
page 17 – 233.
See Service Manual Inverter Systems and
Motors.
8A10 AC fail %.2s Power-on of the drive not possible, because an
8A20 Powerfail
%.2s
8A40 Enabling of
axis group %.2s
8A50 Inverter not
ready %.2s
AC-fail signal (power supply) is active.
Power-on of the drive not possible, because a
powerfail signal (power supply) is active.
Power-on of the drive not possible due to
missing drive enabling for axis groups (X150/
X151).
Po
wer-on of the drive not possible, because an
inverter is not ready (RDY signal).
Test the power supply.
Check the wiring of the power supply.
See Service Manual Inverter Systems and
Motors.
Test the power supply.
Check the wiring of the power supply.
See Service Manual Inverter Systems and
Motors.
Check the connector on X150/X151 for correct
fit.
Check the wiring of X150/X151.
Check MP2040.x.
See ”Axis-specific drive enable via axis groups”
on page 17 – 232.
Check the Ready LED of the inverter.
Check the wiring of the inverter.
On interface PCBs for Siemens inverters, the
second axis is not enabled.
See ”Readiness of the inverter system” on
page 17 – 233.
See Service Manual Inverter Systems and
Motors.
8AF0 Encoder
<axis> defective
4 – 30 HEIDENHAIN Service Manual iTNC 530 HSCI
Contamination of the position encoder
Encoder cabling defective
Motor control board defective
See ”Position encoders” on page 19 – 277. See ”Position encoders” on page 19 – 277.
Exchange the position encoder.
Check the encoder cable.
Exchange the motor drive-control board.
Error message Possible cause of error Measures for error diagnosis and/or
corrective action
8B00 <axis>
motor encoder
defective
8B00 Zn track
%.2s error
8B10 Wrong
traverse direction
<axis>
8B20 Error <axis>
field orientation
Additional information and descriptions
in the manual
No encoder signal available
Interruption in motor encoder cable
Signal amplitude of motor encoder is missing or
too small.
See ”Speed encoders” on page 19 – 300. See ”Speed encoders” on page 19 – 300.
Contamination of the motor encoder (Zn track)
Motor encoder cable defective.
Motor control board defective
See ”Speed encoders” on page 19 – 300. See ”Speed encoders” on page 19 – 300.
DIR entry in motor table is incorrect.
Incorrect motor power connection.
Field orientation impossible for mechanical
reasons.
Incorrect relation between electrical field and
mechanical motor motion.
Incorrect motor encoder signal.
Incorrect motor connection.
Mechanical brakes not released.
Additional information and descriptions
in the manual
Check connection of motor encoder.
Check the motor encoder.
Check the amplitude of the encoder signal.
Exchange the motor.
Check the motor table entry.
Exchange the motor drive-control board.
Check the DIR entry in the motor table.
Check the motor power connection.
See Service Manual Inverter Systems and
Motors.
Check the machine parameters for number of
signal periods and distance for the number of
signal periods.
Check the machine parameter for the linear
distance of one motor revolution.
For linear motors: Check column STR of the
motor table.
Check the speed encoder connection.
Check the motor connection.
Release brakes during orientation.
8B30 Motor
temperature %.2s
too high
See ”Speed encoders” on page 19 – 300. See ”Sequence for finding errors in the control
Measured motor temperature is too high
No temperature sensor
tor encoder cable is defective (wire broken)
Mo
Entry in motor table
Incorrect or defective temperature sensor was
installed.
See ”Speed encoders” on page 19 – 300.
See Service Manual Inverter Systems and
Motors.
is incorrect.
loop” on page 6 – 58.
See ”Speed encoders” on page 19 – 300.
See Service Manual Inverter Systems and
Motors.
Let the motor cool down.
Check the motor table entry.
Check the entry in the motor table.
Measure the temperature sensor (576 [ohms]
at 20 [°C], 1000 [ohms] at 100 [°C]).
See ”Speed encoders” on page 19 – 300.
See Service Manual Inverter Systems and
Motors.
February 2012 4 – 31
 Loading...
Loading...