Motorola TDA1085C Datasheet
Order this document by TDA1085C/D
Universal Motor
Speed Controller
The TDA1085C is a phase angle triac controller having all the necessary functions for universal motor speed control in washing machines. It operates in closed loop configuration and provides two ramp possibilities.
•On±Chip Frequency to Voltage Converter
•On±Chip Ramps Generator
•Soft±Start
•Load Current Limitation
•Tachogenerator Circuit Sensing
•Direct Supply from AC Line
•Security Functions Peformed by Monitor
TDA1085C
UNIVERSAL MOTOR
SPEED CONTROLLER
SEMICONDUCTOR
TECHNICAL DATA
|
16 |
16 |
1 |
|
|
1 |
D SUFFIX |
PLASTIC PACKAGE |
PLASTIC PACKAGE |
CASE 648 |
CASE 751B |
|
(SO±16) |
ORDERING INFORMATION
|
Operating |
|
|
Device |
Temperature Range |
Package |
|
|
|
|
|
TDA1085CD |
TJ = ± 10° to +120°C |
SO±16 |
|
|
|
||
TDA1085C |
Plastic DIP |
||
|
|||
|
|
|
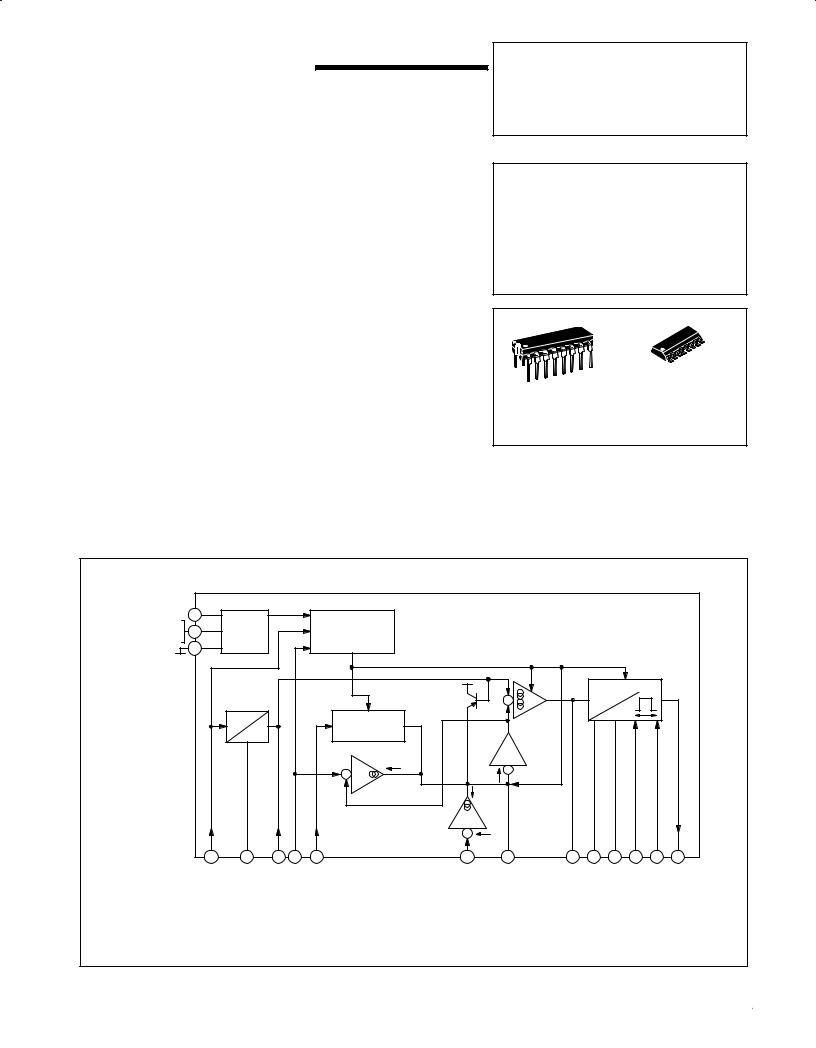
Figure 1. Representative Block Diagram and Pin Connections
+ VCC
Shunt Regulator
Ballast Resistor
9 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
10 |
Voltage |
|
|
Monitoring |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Reg |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
8 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Reset |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Speed |
|
|
|
|
± |
|
Trigger Pulse |
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
Gen. |
|
|
|
|||
|
Detector |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
Ramp |
|
+ |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Control |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Generator |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Amp. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0.7 V |
= |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Current |
±VCC |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Limiter |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
12 |
11 |
4 |
5 |
6 |
3 |
7 |
16 |
14 |
15 |
2 |
1 |
13 |
Digital Speed Sense |
F/VC Pump Capacitor |
Actual Speed |
Set Speed |
Ramp Current Gen. Control |
Motor Current Limit |
Ramp Gen. Timing |
Closed Loop Stability |
Sawtooth Capacitor |
Sawtooth Set Current |
Voltage Synchronization |
Current Synchronization |
Trigger Pulse Output |
Motorola, Inc. 1995

TDA1085C
MAXIMUM RATINGS (TA = 25°C, voltages are referenced to Pin 8, ground) |
|
||
Rating |
Symbol |
Value |
Unit |
|
|
|
|
Power Supply, when externally regulated, VPin 9 |
VCC |
15 |
V |
Maximum Voltage per listed pin |
VPin |
+ 5.0 |
V |
Pin 3 |
|
|
|
Pin 4±5±6±7±13±14±16 |
|
0 to + VCC |
|
Pin 10 |
|
0 to + 17 |
|
|
|
|
|
Maximum Current per listed pin |
IPin |
± 3.0 to + 3.0 |
mA |
Pin 1 and 2 |
|
|
|
Pin 3 |
|
± 1.0 to + 0 |
|
Pin 9 (VCC) |
|
15 |
|
Pin 10 shunt regulator |
|
35 |
|
Pin 12 |
|
± 1.0 to + 1.0 |
|
Pin 13 |
|
± 200 |
|
|
|
|
|
Maximum Power Dissipation |
PD |
1.0 |
W |
Thermal Resistance, Junction±to±Air |
RθJA |
65 |
°C/W |
Operating Junction Temperature |
TJ |
± 10 to + 120 |
°C |
Storage Temperature Range |
Tstg |
± 55 to + 150 |
°C |
ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS (TA = 25°C)
|
Characteristic |
Symbol |
Min |
Typ |
Max |
Unit |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
VOLTAGE REGULATOR |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Internally Regulated Voltage (VPin 9) |
VCC |
15 |
15.3 |
15.6 |
V |
|
(IPin 7 = 0, IPin 9 + IPin 10 = 15 mA, IPin 13 = 0) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
VCC Temperature Factor |
TF |
Ð |
± 100 |
Ð |
ppm/°C |
|
Current Consumption (IPin 9) |
ICC |
Ð |
4.5 |
6.0 |
mA |
|
(V9 = 15 V, V12 = V8 = 0, I1 = I2 = 100 μA, |
|
|
|
|
|
|
all other pins not connected) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
VCC Monitoring |
Enable Level |
VCC EN |
Ð |
VCC ± 0.4 |
Ð |
V |
VCC Monitoring |
Disable Level |
VCC DIS |
Ð |
VCC ± 1.0 |
Ð |
|
RAMP GENERATOR |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Reference Speed Input Voltage Range |
VPin 5 |
0.08 |
Ð |
13.5 |
V |
|
Reference Input Bias Current |
± IPin 5 |
0 |
0.8 |
1.0 |
μA |
|
Ramp Selection Input Bias Current |
± IPin 6 |
0 |
Ð |
1.0 |
μA |
|
Distribution Starting Level Range |
VDS |
0 |
Ð |
2.0 |
V |
|
Distribution Final Level |
VDF/VDS |
2.0 |
2.09 |
2.2 |
|
|
VPin 6 = 0.75 V |
|
|
|
|
|
|
High Acceleration Charging Current |
± IPin 7 |
1.0 |
Ð |
1.7 |
mA |
|
VPin 7 = 0 V |
|
|
|
|||
VPin 7 = 10 V |
|
|
1.0 |
1.2 |
1.4 |
|
Distribution Charging Current |
± IPin 7 |
4.0 |
5.0 |
6.0 |
μA |
|
VPin 7 = 2.0 V |
|
|
|
|
|
|
2 |
MOTOROLA ANALOG IC DEVICE DATA |

TDA1085C
ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS (continued)
|
|
|
|
Characteristic |
Symbol |
Min |
Typ |
Max |
Unit |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
CURRENT LIMITER |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
Limiter Current Gain Ð I Pin 7/IPin 3 |
Cg |
130 |
180 |
250 |
|
||||||
(IPin3 = ± 300 μA) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
Detection Threshold Voltage |
|
VPin 3 TH |
50 |
65 |
80 |
mV |
|||||
IPin 3 = ± 10 μA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
FREQUENCY TO VOLTAGE CONVERTER |
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
Input Signal ªLow Voltageº |
|
V12 L |
±100 |
Ð |
Ð |
mV |
|||||
Input Signal ªHigh Voltageº |
|
V12 H |
+100 |
Ð |
Ð |
mV |
|||||
Monitoring Reset Voltage |
|
|
V12 R |
5.0 |
Ð |
Ð |
V |
||||
Negative Clamping Voltage |
|
± V12 CL |
Ð |
0.6 |
Ð |
V |
|||||
IPin 12 = ± 200 μA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
Input Bias Current |
|
|
|
± IPin12 |
Ð |
25 |
Ð |
μA |
|||
Internal Current Source Gain |
|
G.0 |
9.5 |
Ð |
11 |
|
|||||
G + |
IPin 4 |
, V |
Pin 4 |
+ V |
Pin 11 |
+ 0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
IPin 11 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Gain Linearity versus Voltage on Pin 4 |
G/G8.6 |
|
|
|
|
||||||
(G8.6 = Gain for VPin 4 = 8.6 V) |
|
1.04 |
1.05 |
1.06 |
|
||||||
V4 = 0 V |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
V4 = 4.3 V |
|
|
|
|
|
1.015 |
1.025 |
1.035 |
|
||
V4 = 12 V |
|
|
|
|
|
0.965 |
0.975 |
0.985 |
|
||
Gain Temperature Effect (VPin 4 = 0) |
TF |
Ð |
350 |
Ð |
ppm/°C |
||||||
Output Leakage Current (IPin 11 = 0) |
± IPin 4 |
0 |
Ð |
100 |
nA |
||||||
CONTROL AMPLIFIER |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
Actual Speed Input Voltage Range |
VPin 4 |
0 |
Ð |
13.5 |
V |
||||||
Input Offset Voltage VPin 5 ± VPin 4 |
Voff |
0 |
Ð |
50 |
mV |
||||||
(IPin 16 = 0, VPin 16 = 3.0 and 8.0 V) |
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
Amplifier Transconductance |
|
T |
270 |
340 |
400 |
μA/V |
|||||
(IPin 16/ (V5 ± V4) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
(IPin 16 = + and ± 50 μA, VPin 16 = 3.0 V) |
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
Output Current Swing Capability |
|
IPin 16 |
± 200 |
± 100 |
± 50 |
μA |
|||||
Source |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
Sink |
|
|
|
|
|
50 |
100 |
200 |
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
Output Saturation Voltage |
|
|
V16 sat |
Ð |
Ð |
0.8 |
V |
||||
TRIGGER PULSE GENERATOR |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
Synchronization Level Currents |
|
|
|
|
|
μA |
|||||
Voltage Line Sensing |
|
|
IPin 2 |
Ð |
± 50 |
± 100 |
|
||||
Triac Sensing |
|
|
|
|
IPin 1 |
Ð |
± 50 |
± 100 |
|
||
Trigger Pulse Duration (CPin 14 = 47 nF, RPin 15 = 270 kΩ) |
Tp |
Ð |
55 |
Ð |
μs |
||||||
Trigger Pulse Repetition Period, conditions as a.m. |
TR |
Ð |
220 |
Ð |
μs |
||||||
Output Pulse Current VPin 13 = VCC ± 4.0 V |
± IPin 13 |
180 |
192 |
Ð |
mA |
||||||
Output Leakage Current VPin 13 = ± 3.0 V |
I13 L |
Ð |
Ð |
30 |
μA |
||||||
Full Angle Conduction Input Voltage |
V14 |
Ð |
11.7 |
Ð |
V |
||||||
Saw Tooth ªHighº Level Voltage |
|
V14 H |
12 |
Ð |
12.7 |
V |
|||||
Saw Tooth Discharge Current, IPin15 = 100 μA |
IPin 14 |
95 |
Ð |
105 |
μA |
||||||
MOTOROLA ANALOG IC DEVICE DATA |
3 |
|

TDA1085C
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
The TDA 1085C triggers a triac accordingly to the speed regulation requirements. Motor speed is digitally sensed by a tachogenerator and then converted into an analog voltage.
The speed set is externally fixed and is applied to the internal linear regulation input after having been submitted to programmable acceleration ramps. The overall result consists in a full motor speed
range with two acceleration ramps which allow efficient washing machine control (Distribute function).
Additionally, the TDA 1085C protects the whole system against AC line stop or variations, overcurrent in the motor and tachogenerator failure.
INPUT/OUTPUT FUNCTIONS (Refer to Figures 1 and 8)
Voltage Regulator ± (Pins 9 and 10) This is a parallel type regulator able to sink a large amount of current and offering good characteristics. Current flow is provided from AC line by external dropping resistors R1, R2, and rectifier: This half wave current is used to feed a smoothering capacitor, the voltage of which is checked by the IC.
When VCC is reached, the excess of current is derived by another dropping resistor R10 and by Pin 10. These three resistors must be determined in order:
•To let 1.0 mA flow through Pin 10 when AC line is minimum and VCC consumption is maximum (fast ramps and pulses present).
•To let V10 reach 3.0 V when AC line provides maximum current and VCC consumption is minimum (no ramps and no pulses).
•All along the main line cycle, the Pin 10 dynamic range must not be exceeded unless loss of regulation.
An AC line supply failure would cause shut down.
The double capacitive filter built with R1 and R2 gives an efficient VCC smoothing and helps to remove noise from set speeds.
Speed Sensing ± (Pins 4, 11, 12) The IC is compatible with an external analog speed sensing: its output must be applied to Pin 4, and Pin 12 connected to Pin 8.
In most of the applications it is more convenient to use a digital speed sensing with an unexpensive tachogenerator which doesn′t need any tuning. During every positive cycle at Pin 12, the capacitor CPin 11 is charged to almost VCC and during this time, Pin 4 delivers a current which is 10 times the one charging CPin 11. The current source gain is called G and is tightly specified, but nevertheless requires an adjustment on RPin 4. The current into this resistor is proportional to CPin 11 and to the motor speed; being filtered by a capacitor, VPin 4 becomes smothered and represents the ªtrue actual motor speedº.
To maintain linearity into the high speed range, it is important to verify that CPin 11 is fully charged: the internal source on Pin 11 has 100 KW impedance. Nevertheless CPin 11 has to be as high as possible as it has a large influence on FV/C temperature factor. A 470 KW resistor between Pins 11 and 9 reduces leakage currents and temperature factor as well, down to neglectable effects.
Pin 12 also has a monitoring function: when its voltage is above 5.0 V, the trigger pulses are inhibited and the IC is reset. It also senses the tachogenerator continuity, and in case of any circuit aperture, it inhibits pulse, avoiding the motor to run out of control. In the TDA 1085C, Pin 12 is negatively clamped by an internal diode which removes the necessity of the external one used in the former circuit.
Ramp Generator ± (Pins 5, 6, 7) The true Set Speed value taken in consideration by the regulation is the output of the ramp generator (Pin 7). With a given value of speed set input (Pin 5), the ramp generator charges an external capacitor CPin 7 up to the moment VPin 5 (set speed) equals VPin 4 (true speed), see Figure 2. The IC has an internal charging current source of 1.2mA and delivers it from 0 to 12 V at Pin 7. It is the high acceleration ramp (5.0 s typical) which allows rapid motor speed changes without excessive strains on the mechanics. In addition, the TDA 1085C offers the possibility to break this high acceleration with the introduction of a low acceleration ramp (called Distribution) by reducing the Pin 7 source current down to
5.0 mA under Pin 6 full control, as shown by following conditions:
•Presence of high acceleration ramp VPin 5 > VPin 4
•Distribution occurs in the VPin 4 range (true motor speed) defined by VPin 6 x VPin 4 x 2.0 VPin 6
For two fixed values of VPin 5 and VPin 6, the motor speed will have high acceleration, excluding the time for VPin 4 to go from VPin 6 to two times this value, high acceleration again, up to the moment the motor has reached the set speed value, at which it will stay, see Figure 3.
Should a reset happen (whatever the cause would be), the above mentioned successive ramps will be fully reprocessed from 0 to the maximum speed. If VPin 6 = 0, only the high acceleration ramp occurs.
To get a real zero speed position, Pin 5 has been designed in such a way that its voltage from 0 to 80 mV is interpreted as a true zero. As a consequence, when changing the speed set position, the designer must be sure that any transient zero would not occur: if any, the entire circuit will be reset.
As the voltages applied by Pins 5 and 6 are derived from the internal voltage regulator supply and Pin 4 voltage is also derived from the same source, motor speed (which is determined by the ratios between above mentioned voltages) is totally independent from VCC variations and temperature factor.
Control Amplifier ± (Pin 16) It amplifies the difference between true speed (Pin 4) and set speed (Pin 5), through the ramp generator. Its output available at Pin 16 is a double sense current source with a maximum capability of ± 100 mA and a specified transconductance (340 mA/V typical). Pin 16 drives directly the trigger pulse generator, and must be loaded by an electrical network which compensates the mechanical characteristics of the motor and its load, in order to provide stability in any condition and shortest transient response; see Figure 4.
This network must be adjusted experimentally.
In case of a periodic torque variations, Pin 16 directly provides the phase angle oscillations.
4 |
MOTOROLA ANALOG IC DEVICE DATA |
 Loading...
Loading...