Deutz 914 Service Manual

Operation Manual |
914 |

Safety guidelines / Accident prevention
●Please read and observe the information given in this Operation Manual. This will enable you to avoid accidents, preserve the manufacturer’s warranty and maintain the engine in peak operating condition.
●This engine has been built exclusively for the application specified in the scope of supply, as described by the equipment manufacturer and is to be used only for the intended purpose. Any use exceeding that scope is considered to be contrary to the intended purpose. The manufacturer will not assume responsibility for any damage resulting therefrom. The risks involved are to be borne solely by the user.
●Use in accordance with the intended purpose also implies compliance with the conditions laid down by the manufacturer for operation, maintenance and servicing. The engine should only be operated by personnel trained in its use and the hazards involved.
●The relevant accident prevention guidelines and other generally accepted safety and industrial hygiene regulations must be observed.
●When the engine is running, there is a risk of injury through:
-turning/hot components
-engines with positive ignition
-ignition systems (high electrical voltage) You must avoid contact at all times!
●Unauthorized engine modifications will invalidate any liability claims against the manufacturer for resultant damage.
Manipulations of the injection and regulating system may also influence the performance of the engine, and its emissions. Adherence to legislation on pollution cannot be guaranteed under such conditions.
●Do not change, convert or adjust the cooling air intake area to the blower.
The manufacturer shall not be held responsible for any damage which results from such work.
●When carrying out maintenance/repair operations on the engine, the use of DEUTZ original parts is prescribed. These are specially designed for your engine and guarantee perfect operation.
Non-compliance results in the expiry of the warranty!
●Maintenance and cleaning of the engine should only be carried out when the engine is switched off and has cooled down.
You must ensure that the electrical systems have been switched off and the ignition key has been removed.
Accident prevention guidelines concerning electrical systems (e.g. VDE-0100/-0101/- 0104/-0105 Electrical protective measures against dangerous touch voltage) are to be observed.
When cleaning with fluids, all electrical components are to be covered impermeably.

Operation Manual
914
0312 0382 en
Engine Serial Number
Technical modifications required to improve our engines are reserved with regard to specification data and other technical information contained in this Operation Manual. No parts of this Manual may be reproduced in any form or by any means without our written approval.
Please enter the engine serial number here. This number should be quoted when inquiring about Customer Service, Repairs or Spare Parts (see Section 2.1).

Foreword
Dear Customer,
Air / liquid-cooled Deutz engines are designed for a large number of applications. Consequently, a wide range of variants is offered to meet the requirements of specific cases.
Your engine is appropriately equipped for the installation concerned, which means that not all of the components described in this Operation Manual are necessarily mounted to your engine.
We have endeavoured to highlight any differences so that you will be able to locate theses differences relevant to your engine.
Please read this Manual before starting your engine, and always observe the operating and maintenance instructions.
We are available to help with any additional inquiries
Sincerely,
DEUTZ AG

Index
1General
2Engine Description
2.1Model
2.1.1Rating Plate
2.1.2Position of the Rating Plate
2.1.3Engine Serial Number
2.1.4Cylinder numbering
2.1.5Direct injection
2.2Engine Illustrations
2.2.1Operation side BF3L 914
2.2.2Air outlet side BF3L 914
2.2.3Operation side F4L 914
2.2.4Air outlet side F4L 914
2.2.5Operation side BF6L 914 Intercooler over air-intake line
2.2.6Air outlet side BF6L 914 C Intercooler over air-intake line
2.2.7Operation side BF6L 914 C Intercooler over flywheel
2.2.8Air outlet side BF6L 914
Intercooler over flywheel
2.3Lube Oil Circuit Schematic
2.3.1Lube Oil Circuit Schematic
2.4Fuel System Plan
2.4.1Fuel System
2.5Engine cooling
2.5.1Amount of cool air regulated by exhaust thermostat
2.5.2Amount of cool air regulated by exhaust thermostat and solenoid valve
3Engine Operation
3.1Commissioning
3.1.1Pour in Engine Oil
3.1.2Filling Oil BathAir Filter with Engine Oil
3.1.3Pour in Fuel
3.1.4Bleed
3.1.5Other Preparations
3.1.6Additional maintenance work
3.1.7Change-over switch for oil heater
3.2Starting
3.2.1Starting
3.3Monitoring Operation
3.3.1Engine Oil Pressure
3.3.2Engine temperature
3.3.3Cooling fan drive
3.4Shutting off
3.4.1Mechanical shut-off
3.4.2Electrical shut-off
3.5Operating Conditions
3.5.1Winter Operation
3.5.2High Ambient Temperature, High Altitude
4Operating Media
4.1Lube Oil
4.1.1Quality
4.1.2Viscosity
4.2Fuel
4.2.1Quality
4.2.2Winter Fuel
5Routine Maintenance
5.1Maintenance Plan
5.2Maintenance Diagram
5.3Maintenance Work Completed
6Service and Maintenance
6.1Lube oil system
6.1.1Oil change intervals
6.1.2Check Oil Level / Change Engine Oil
6.1.3Replace Oil Filter
6.1.4Change bypass-oil filter use
6.2Fuel System
6.2.1Replace fuel filter
6.2.2Precleaning fuel/clean fuel filter
6.3Cooling system
6.3.1Cleaning Intervals
6.4Combustion Air Filter
6.4.1Cleaning Intervals
6.4.2Emptying Cyclone Type Precleaner
6.4.3Clean Oil Bath Air Filter
6.4.4Dry Type Air Cleaner
6.5Belt Drives
6.5.1Check V-belts
6.5.2Change fan belt
6.5.3Tension alternator belts
6.5.4Change alternator belts
6.5.5Check warning system
6.5.6Tension/change air compressor belts
6.5.7Air compressor model with dual belts
6.6Adjustments
6.6.1Check valve clearance
(adjust if necessary)
6.7Accessories
6.7.1Battery
6.7.2Rotary Current Alternator
6.7.3Transportation Shackles
6.8Engine cleaning
6.8.1Engine cleaning
6.9Additional Maintenance Work
6.9.1Check fastenings
6.9.2Check functioning of glow plugs
7Faults, Causes and Remedies
7.1Fault Table
8Engine Preservation
8.1Preservation
8.1.1Preserve engine
8.1.2Remove engine preservation
9Technical Specification
9.1Engine Specifications and Settings
9.2Screw Tightening Torques
9.3Tools
10 Service

General
DEUTZ Diesel Engines |
Care and Maintenance |
Service |
|
1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
are the product of many years of research and development. The resulting know-how, coupled with stringent quality standards, guarantee their long service life, high reliability and low fuel consumption.
It goes without saying that DEUTZ Diesel Engines meet the highest standards for environmental protection.
Sound care and maintenance practices will ensure that the engine continues to meet the requirements placed on it. Recommended service intervals must be observed and service and maintenance work carried out conscientiously.
Special care should be taken under abnormally demanding operating conditions.
Please contact one of our authorized service representatives in the event of breakdowns or for spare parts inquiries. Our trained specialists will carry out repairs quickly and professionally, using only genuine spare parts.
Original parts from DEUTZ AG are always produced in accordance with state-of-the-art technology. Please turn to the end of this manual for further service information.
Beware of Running Engine |
Safety |
Shut the engine down before carrying out maintenance or repair work. Ensure that the engine cannot be accidentally started. Risk of accidents.
When the work is complete, be sure to refit any panels and guards that may have been removed. Never fill the fuel tank while the engine is running. Observe industrial safety regulations when running the engine in an enclosed space or underground.
This symbol is used for all safety warnings. Please follow them ! carefully. The attention of operating personnel should be drawn to these safety instructions. General safety
and accident prevention regulations laid down by law must also be observed.
Asbestos
California
Proposition 65 Warning
Diesel engine exhaust and some of its constituents are known to the State of California to cause cancer, birth defects, and other reproductive harm.
DEUTZ original parts are asbestosfree.

1

Engine Description
2
2.1Model
2.2Engine Illustrations
2.3Lube Oil Circuit Schematic
2.4Fuel System Plan
2.5Engine cooling
© 2001

Engine Description |
2.1 Model |
2 |
2.1.1 Rating Plate |
|
© 34 570 0
The model A, the engine serial number B and the performance data are stamped on the rating plate.
The model and engine serial number must be given when ordering parts.
2.1.2 Position of the Rating |
2.1.3 Engine Serial Number |
Plate |
|
© 34 571 |
0 |
The rating plate C is attached to the crankcase. Depending on the model, a second rating plate may be affixed to the air duct hood.
© 34 572 |
0 |
The engine serial number is stamped on the crankcase (arrow) as well as the rating plate.
© 2001

2.1 Model |
Engine Description |
2.1.4 Cylinder numbering
© 34 599 0 |
Cylinders are numbered consecutively, beginning at the flywheel.
2.1.5 |
Direct injection |
2 |
|
B/FL 914 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
© 35 215 0 |
Engines with direct injection are used if high output is required.
© 2001

Engine Description |
2.2 Engine Illustrations |
2 |
2.2.1 |
Operation side |
|
|
BF3L 914 |
|
|
|
|
1 |
Cooling fan |
|
|
2 |
V-Belts (fan) |
|
|
3 |
Optional attachment of hydraulic pumps |
|
|
4 |
V-belt washer |
|
|
5 |
Tension roller |
|
|
6 |
Oil pan |
|
|
7 |
Oil drain screw |
|
|
8 |
Oil filler neck |
|
|
9 |
Oil dipstick |
|
|
10 Fuel change filter |
|
|
|
11 |
Solenoid (shut-off magnet) |
|
|
12 |
Lube oil filter |
|
|
13 Full-stop depending on charge air pressure |
|
|
|
14 Air duct hood |
|
|
|
15 Cylinder head cover |
|
2001 |
|
|
|
© |
|
© 34 575 0 |
|
|
|
|
|

2.2 Engine Illustrations |
Engine Description |
2.2.2 |
Exhaust side |
|
BF3L 914 |
|
© 34 576 0 |
2
16Air-intake line
17Shielding plate
18Flywheel
19Oil drain screw
20Starter
21Exhaust turbocharger manifold
© 2001

Engine Description |
2.2 Engine Illustrations |
2 |
2.2.3 |
Operation side |
|
|
F4L 914 |
|
|
|
|
1 |
Cooling fan |
|
|
2 |
V-Belts (fan) |
|
|
3 |
Optional attachment of hydraulic pumps |
|
|
4 |
V-belt washer |
|
|
5 |
Tension roller |
|
|
6 |
Oil filler neck |
|
|
7 |
Fuel pump |
|
|
8 |
Fuel change filter |
|
|
9 |
Injection pump |
|
|
10 |
Oil dipstick |
|
|
11 |
Shut-off magnet |
|
|
12 SAE housing |
|
|
|
13 |
Lube oil filter |
|
|
14 Air duct hood |
|
|
|
15 Cylinder head cove |
|
2001 |
|
|
|
© |
|
© 34 597 0 |
|
|
|
|
|

2.2 Engine Illustrations |
Engine Description |
2.2.4 |
Exhaust side |
|
F4L 914 |
|
© 34 576 0 |
2
16Date plate
17Flywheel
18Oil drain screw
19Starter
20Oil pan
21Air-intake manifold
22Crankcase ventilation
© 2001

2.2 Engine Illustrations |
Engine Description |
2 |
2.2.5 |
Operation side |
|
BF6L 914 C- intercooler over air-intake line |
|
|
|
|
2001 |
|
© |
© 34 577 0 |
|
1 Cooling fan
2 V-Belts (fan)
3 V-belt pulley on crankshaft
4 Tension roller
5 Oil filler neck
6 Oil drain screw
7 Fuel pump with fuel precleaning
8 Fuel filter cartridge
9 Injection pump
10 Shut-off lifting magnet
11Oil dipstick
12LDA
13Lube oil filter cartridge
14Engine oil cooler
15Air duct hood
16Cylinder head cover

2.2 Engine Illustrations |
Engine Description |
2.2.6 Exhaust side |
|
2 |
|
BF6L 914 C- intercooler over air-intake line |
|||
|
|||
|
|
|
|
© 34 578 |
0 |
17Intercooler
18Air-intake line
19Exhaust manifold line
20Date plate
21Flywheel
22Starter
23Oil drain screw
24Turbocharger
25Air-intake manifold to exhaust turbocharger
26Alternator
© 2001

Engine Description |
2.2 Engine Illustrations |
2 |
2.2.7 |
Operation side |
|
|
BF6L 914 C- intercooler over flywheel |
|
|
|
|
1 |
Cooling fan |
|
|
2 |
V-Belts (fan) |
|
|
3 |
V-belt pulley on crankshaft |
|
|
4 |
Tension roller |
|
|
5 |
Oil filler neck |
|
|
6 |
Oil drain screw |
|
|
7 |
Fuel pump with fuel precleaning |
|
|
8 |
Fuel filter cartridge |
|
|
9 |
Injection pump |
|
|
10 |
Shut-off lifting magnet |
|
|
11 |
Oil dipstick |
|
|
12 |
LDA |
|
|
13 |
Lube oil filter cartridge |
|
|
14 |
Engine oil cooler |
|
|
15 |
Air duct hood |
|
|
16 |
Cylinder head cover |
2001 |
|
|
|
© |
|
© 35 579 0 |
|
|
|
|

2.2 Engine Illustrations |
Engine Description |
2.2.8 Exhaust side |
|
2 |
|
BF6L 914 - intercooler over flywheel |
|||
|
|||
|
|
|
|
© 34 580 |
0 |
17Intercooler
18Flywheel
19Starter
20Oil drain screw
21Alternator
22Exhaust connection supports
23Exhaust manifold line
24Air-intake manifold to exhaust turbocharger
© 2001

Engine Description |
2.3 Lube Oil Circuit Schematic |
22.3.1 Lube Oil Circuit Schematic FL 914
|
24 |
|
|
2001 |
© 34 581 |
0 |
|
© |
|||
|
|
1 Oil pan
2 Intake manifold
3 Oil pump
4 Oil pressure regulating valve
5 Pressure oil line
6 Short-circuit line or alternative
7 Ribbed tube coil or alternative
8 Block oil cooler
9 Lube oil filter
10 Safety valve
11Main oil channel
12Crankshaft bearing
13Con-rod bearing
14Camshaft bearing
15Tappet
16Pushrod (hollow, for oil intake to lubricate rocker arm)
17Rocker arm bearings
18Rocker arm lubrication
19Pushrod protective tube
20Throttle bore (to lubricate cogwheels)
21Spray nozzle for piston cooling
22Connection for oil pressure gauge
23Oil pressure gauge
24Injection pump connected to lube oil circuit schematic
25Connection option for oil heater **
**here the filter carrier must be exchanged. Please contact DEUTZ Service when changing-over.

2.3 Lube Oil Circuit Schematic |
Engine Description |
2.3.2 Lube Oil Circuit Schematic |
|
2 |
|
BFL 914 |
|||
|
|||
|
|
|
|
© 35 583 |
0 |
1 Oil pan
2 Intake line
3 Oil pump
4 Oil pressure regulating valve
5 Pressure oil line
6 Connection line to oil cooler
7 Block oil cooler
8 Lube oil filter
9 Safety valve
10Main oil channel
11Crankshaft bearing
12Con-rod bearing
13Camshaft bearing
14Tappet (with impulse lubrication of rocker arm)
15Pushrod (hollow, for oil intake to lubricate rocker arm)
16Rocker arm bearings
17Rocker arm lubrication
18Pushrod protective tube (oil return from the cylinder head to crankcase)
19Throttle bore (to lubricate cogwheels)
20Spray nozzle for piston cooling
21Oil line to lubricate turbocharger
22Oil return line from exhaust turbocharger to crankcase
23Oil pressure gauge
24Bypass lube oil fine filter
25Connection option for oil heater **
26Injection pump connected to lube oil circuit schematic
**here the filter carrier must be exchanged. Please contact DEUTZ Service when changing-over.
© 2001
Engine Description |
2.4 Fuel System Schematic |
2 |
2.4.1 |
Fuel System |
|
|
|
|
|
2001 |
|
© 35 582 |
0 |
© |
|
||
|
|
|
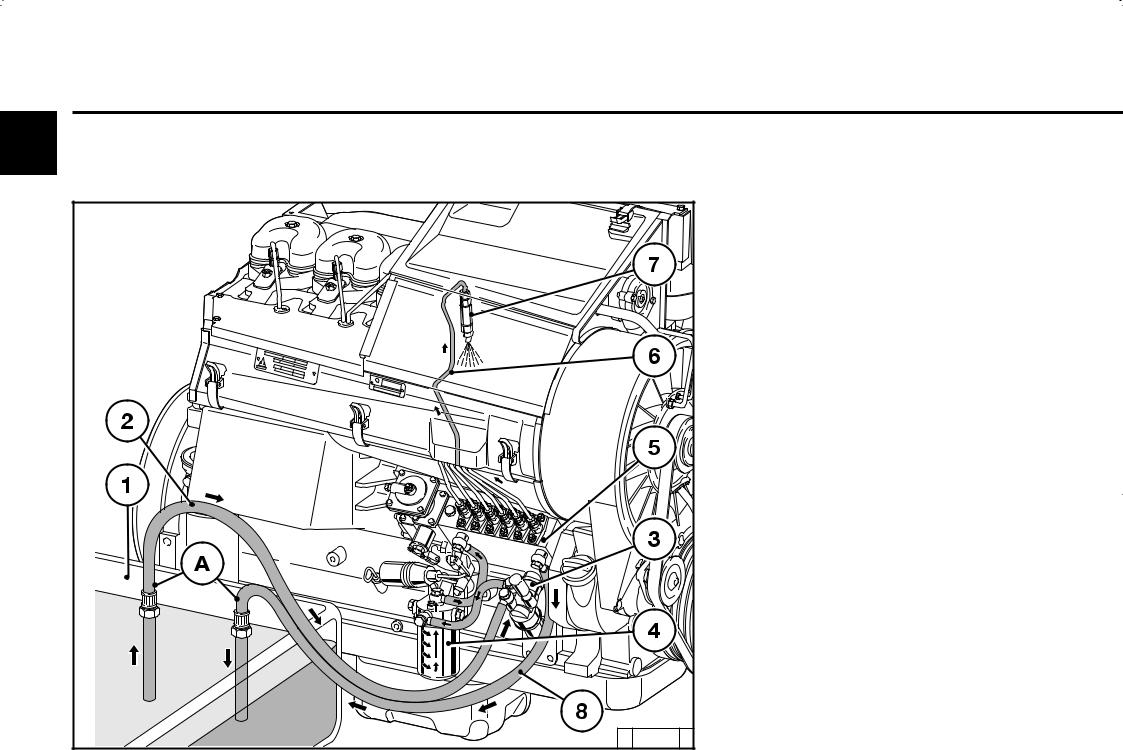
1 Fuel tank
2 Fuel line from tank to fuel pump
3 Fuel pump
4 Fuel change filter
5 Injection pump
6 Injection line
7 Injection valve
8 Fuel overflow pipe
ADistance: must be routed as far away from each other as possible

2.5 Engine cooling |
Engine Description |
2.5.1 Amount of cool air regulated by exhaust thermostat |
|
|
2 |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1 |
Pressure oil line from engine to exhaust |
||
|
|||||
|
|
|
thermostat |
||
2 |
Air line to exhaust thermostat |
||||
3 |
Exhaust manifold line |
||||
4 |
Exhaust thermostat |
||||
5 |
Control line to hydraulic coupling |
||||
6 |
Hydraulic coupling |
||||
7 |
Cooling fan |
||||
8 |
Cooling fan drive |
||||
9 |
Oil return line to crankcase |
||||
10 |
Ventilation line |
||||
11 |
Adjusting screw with special seal ring |
||||
© 26 120 1
© 2001

Engine Description |
2.5 Engine cooling |
22.5.2 Amount of cool air regulated by exhaust thermostat and solenoid valve
1 Pressure oil line from engine to exhaust thermostat
2 Air line to exhaust thermostat
3 Exhaust manifold line
4 Exhaust thermostat
5 Control line to hydraulic coupling
6 Hydraulic coupling
7 Cooling fan
8 Cooling fan drive
9 Oil return line to crankcase
10 Ventilation line
11 Adjusting screw with special seal ring
12 Solenoid valve
© 2001
© 26 121 2

Engine Operation
3
3.1Commissioning
3.2Starting
3.3Monitoring Operation
3.4Shutting off
3.5Operating Conditions
© 2001

Engine Operation |
3.1 Commissioning |
33.1.1 Pour in Engine Oil
© 35 201 |
0 |
As a rule, engines are delivered without oil. Pour lube oil into the oil filler neck (arrow). For oil grade and viscosity, see 4.1.
3.1.2Oil Bath Air Filter with Engine Oil
© 24 980 2
Fill oil cup 1 of the oil bath air cleaner with oil up to the arrow.
For oil grade and viscosity, see 4.1.
3.1.3 Pour in Fuel
© 26 398 0
Use only commercial-grade diesel fuel. For fuel grade, see 4.2. Use summer or wintergrade fuel, depending on the ambient temperature.
© 2001
Do not fill the precleaner dust collector (if fitted) with oil.
Never fill the tank while the engine is running.
Ensure cleanliness! Do not spill fuel!

3.1 Commissioning |
Engine Operation |
3.1.4 |
Bleed |
3 |
|
Model: |
|
|
|
|
|
“Motorpal” model |
|
|
© 35 212 |
0 |
●Position collecting tank below the injection pump.
●Unscrew ventilation valve 1 with screwdriver.
●Move hand hump 2 in the direction of the arrow until bubble-free fuel escapes from the ventilation valve 1.
●Tighten ventilation valve 1, still pumping.
●Remove collecting tank and dispose of the fuel in an environmentally-friendly manner.
© 2001
 Loading...
Loading...