Page 1
Overview
The LB1863M and LB1869 (LB1669M) are 2-phase
unipolar brushless motor drivers that are provided in a
miniature flat package that contributes to end product
miniaturization and supports automatic mounting. These
products support the implementation of motor drive lock
protection and automatic recovery circuits, and alarm
specifications with a minimal number of external
components.
Features and Functions
• Hall elements can be connected directly to the IC itself.
• 1.5-A output current output transistors built in
• Rotation detection function that provides a low-level
output during motor drive and a high-level output when
the motor is stopped
• Motor lock protection and automatic recovery functions
built in
• Thermal shutdown circuit
• Switching noise can be reduced with an external ceramic
capacitor.
Classification
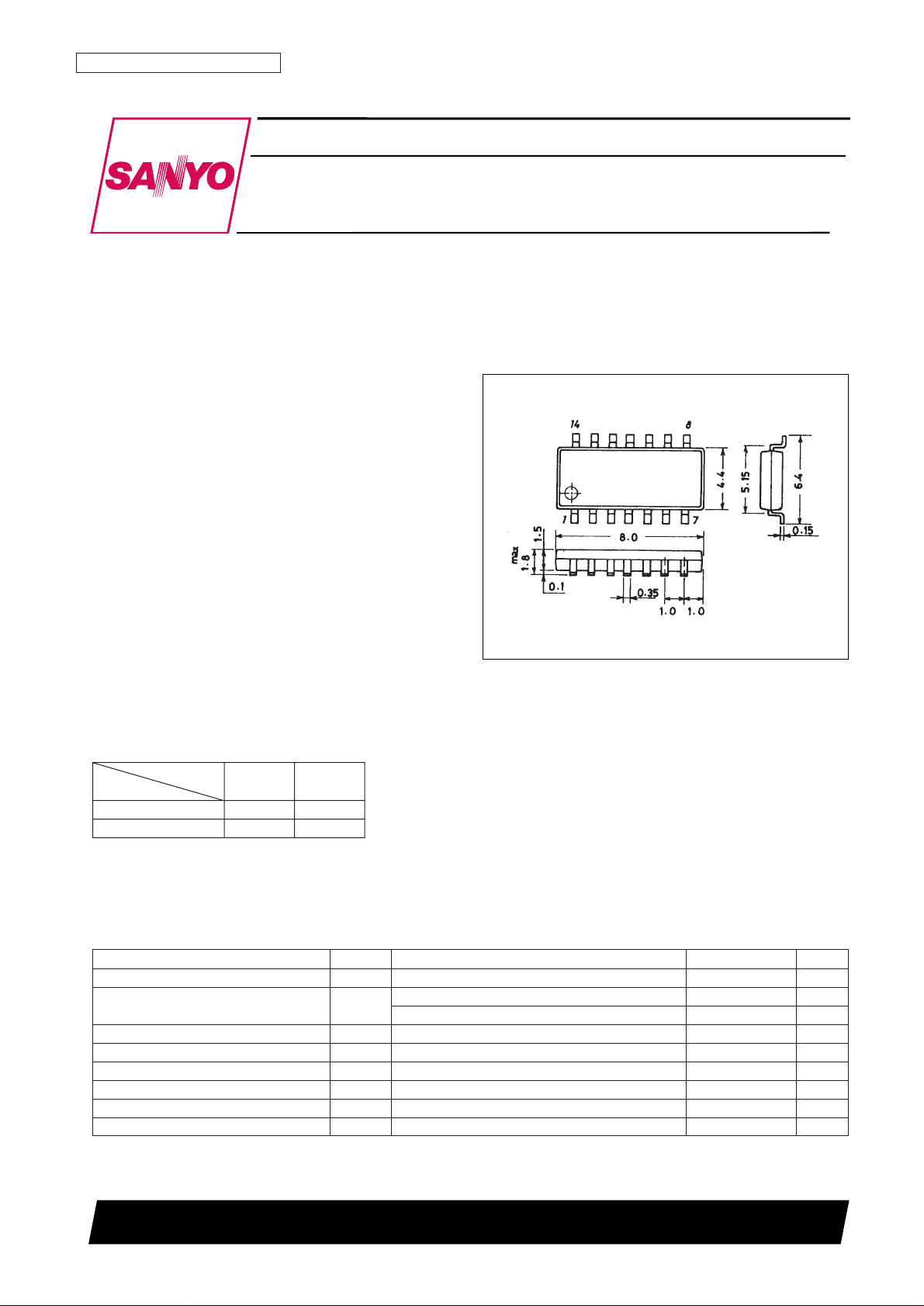
Package Dimensions
unit: mm
3111-MFP14S
Monolithic Digital IC
Ordering number : N4943
13097HA (OT) No. 4943-1/5
SANYO: MFP14S
[LB1863M, 1869M]
SANYO Electric Co.,Ltd. Semiconductor Bussiness Headquarters
TOKYO OFFICE Tokyo Bldg., 1-10, 1 Chome, Ueno, Taito-ku, TOKYO, 110 JAPAN
Two-Phase Unipolar Brushless Motor Driver
Automatic Recovery Type Circuit in a Miniature Flat Package
LB1863M, 1869M
Package
MFP-10S MFP-14S
System voltage
12 V LB1669M LB1869M*
24 V LB1863M*
Note: * The LB1869M and LB1863M are pin compatible
so that the same printed circuit board can be
used for both 12 V and 24 V products.
Parameter Symbol Conditions Ratings Unit
Maximum input current I
CC
max t ≤ 20 ms 200 mA
Output voltage V
OUT
LB1863M –0.3 to +85 V
LB1869M –0.3 to +60 V
Output current I
OUT
1.5 A
RD influx current I
RD
10 mA
RD voltage V
RD
30 V
Allowable power dissipation Pd max
When mounted (on a 20 × 15 × 1.5-mm3glass-epoxy printed circuit board)
800 mW
Operating temperature Topr –30 to +80 °C
Storage temperature Tstg –55 to +150 °C
Specifications
Absolute Maximum Ratings at Ta = 25°C
Page 2

No. 4943-2/5
LB1863M, 1869M
Parameter Symbol Conditions Ratings Unit
Input current range I
CC
6.0 to 50 mA
Common-mode input voltage range V
ICM
0 to VIN–1.5 V
Allowable Operating Ranges at Ta = 25°C
Parameter Symbol Conditions
Ratings
Unit
min typ max
Output voltage 1 V
OR
LB1863M 80 V
LB1869M 60 V
Output voltage 2 V
O(SUS)
LB1863M : IO= 0.1 A 65 V
LB1869M : I
O
= 0.1 A 40 V
Output saturation voltage
V
O
(sat)1 IO= 0.5 A 0.95 1.2 V
V
O
(sat)2 IO= 1.0 A 1.15 1.5 V
Input voltage V
INICC
= 7.0 mA 6.4 6.7 7.0 V
Amplifier input offset voltage V
OFF
–7 0 7.0 mA
Amplifier input bias current I
BA
–250 nA
RD output saturation voltage V
RD
(sat) IRD= 5 mA 0.1 0.3 V
Capacitor discharge current
I
C
1 2.1 3 3.9 µA
I
C
2 0.31 0.44 0.59 µA
Comparator input threshold voltage
V
TH
1 0.77 0.8V
IN
0.83 V
V
TH
2 0.42 0.45V
IN
0.48 V
Electrical Characteristics at Ta = 25°C, ICC= 10 mA
Pin Assignment
Page 3

Equivalent Circuit, Block Diagram, and Sample Application
Sample Application Circuit
No. 4943-3/5
LB1863M, 1869M
Page 4

Sample Application Circuit Output Waveforms
No. 4943-4/5
LB1863M, 1869M
Truth Table
Design Documentation (See the application circuit diagram.)
1. Power-supply voltage (VINpin)
Since these miniature flat package products supply power to the Hall amplifier block and the control block from an
internal parallel regulator, they operate with good stability with respect to kickback currents from the motor and
variations in the power-supply voltage. They also provide an adequate ability to withstand surges. The resistor R1
between the VCCand VINpins should be set up so that a current in the range ICC= 6 to 50 mA flows into the VINpin
in the fan motor power-supply voltage range.
VINhas a typical value of 6.7 volts when ICCis 7 mA. The current flowing into VINcan be calculated with the
following formula.
VCC– V
IN
ICC= ————— ......................(1)
R1
• Abnormal voltage considerations
The maximum allowable current for the VINpin is 200 mA. Therefore, the IC design allows it to withstand voltages
up to the plus side abnormal voltage Vsurge give by formula (2).
Vsurge = VIN+ R1 × 200 mA......(2)
2. Hall input pin voltages (IN–and IN+pins)
The Hall element output voltages to the Hall element input pins must be in the range 0 to (VIN–1.5 V). The gain from
the Hall input pins to the output pin is over 100 dB. The Hall input amplifier offset voltage is ±7 mV. This means that
the Hall element output must be set up taking this ±7 mV offset into account.
3. Output transistors (OUT1 and OUT2 pins)
Output current: IO= 1.5 A maximum
Output saturation voltage: VOsat = 1.15V/1.0 A (typical)
Applications should adopt one of the following three output protection techniques.
➀ If a capacitor is inserted between OUT and ground, use a capacitor with a value up to C = 10 µF, and design that
value so that the kickback and reverse voltages do not exceed VOR.
➁ If a Zener diode is added, determine a value for the Zener voltage that is lower than V
O(SUS)
. If radio-frequency
noise is a problem, insert a capacitor between B1 and B2.
➂ If a capacitor is inserted between OUT and B1, set the capacitor value so that the kickback voltage is lower than
V
O(SUS)
. If oscillation occurs, insert a resistor in series with the capacitor.
IN
+
IN
–
C OUT1 OUT2 RD
H L L H L L
L H L L H L
H L H H H H
L H H H H H
Page 5

No. 4943-5/5
LB1863M, 1869M
4. Output protection function (C pin)
This pin connects the capacitor that forms the automatic recovery circuit. If rotation stops due to, for example, a
motor overload, the pin voltage rises and the output stops. The system automatically recovers from stopped to drive
mode when the load is set to an appropriate level. The lock detection time can be set by changing the value of the
capacitor.
For a 1-µF capacitor:Lock detection time About 2 seconds
Lock protection time (output on) About 1 second
(output off) About 6 seconds
This catalog provides information as of January, 1997. Specifications and information herein are subject to
change without notice.
■ No products described or contained herein are intended for use in surgical implants, life-support systems, aerospace
equipment, nuclear power control systems, vehicles, disaster/crime-prevention equipment and the like, the failure of
which may directly or indirectly cause injury, death or property loss.
■ Anyone purchasing any products described or contained herein for an above-mentioned use shall:
➀
Accept full responsibility and indemnify and defend SANYO ELECTRIC CO., LTD., its affiliates, subsidiaries and
distributors and all their officers and employees, jointly and severally, against any and all claims and litigation and all
damages, cost and expenses associated with such use:
➁
Not impose any responsibility for any fault or negligence which may be cited in any such claim or litigation on
SANYO ELECTRIC CO., LTD., its affiliates, subsidiaries and distributors or any of their officers and employees
jointly or severally.
■ Information (including circuit diagrams and circuit parameters) herein is for example only; it is not guaranteed for
volume production. SANYO believes information herein is accurate and reliable, but no guarantees are made or implied
regarding its use or any infringements of intellectual property rights or other rights of third parties.
➀While the blades are turning, the capacitor is charged with a current of about 3 µA (typical), and C is discharged by
pulses that correspond to the motor speed.
➁When the blades lock, the capacitor is no longer discharged, and the voltage across the capacitor increases. The
output is turned off when that voltage reaches 0.8 × VIN.
➂When the output is turned off, the capacitor is discharged at a current of about 0.44 µA (typical). When the
capacitor voltage falls under VTH2, if the lock state is not yet cleared the capacitor continues discharging until
VTH1. (Note that the output is turned on at this time.) These operations, i.e. items ➁ and ➂, are repeated with a
ton:toff ratio of about 1:6 to protect the motor.
④If the lock state has been cleared when the capacitor voltage reaches VTH2, motor rotation is started by turning the
output on.
5. Rotation detection signal (RD pin)
This is an open collector output, and outputs a low level in drive mode and a high level when the motor is stopped.
6. Radio-frequency noise reduction function (B1 and B2 pins)
These are base pins for Darlington pair outputs. Add capacitors of about 0.01 to 0.1 µF if radio-frequency noise is a
problem.
7. Thermal shutdown function
Turns off the output in response to coil shorting or IC overheating.
Automatic recovery circuit pin C voltage
 Loading...
Loading...