Page 1
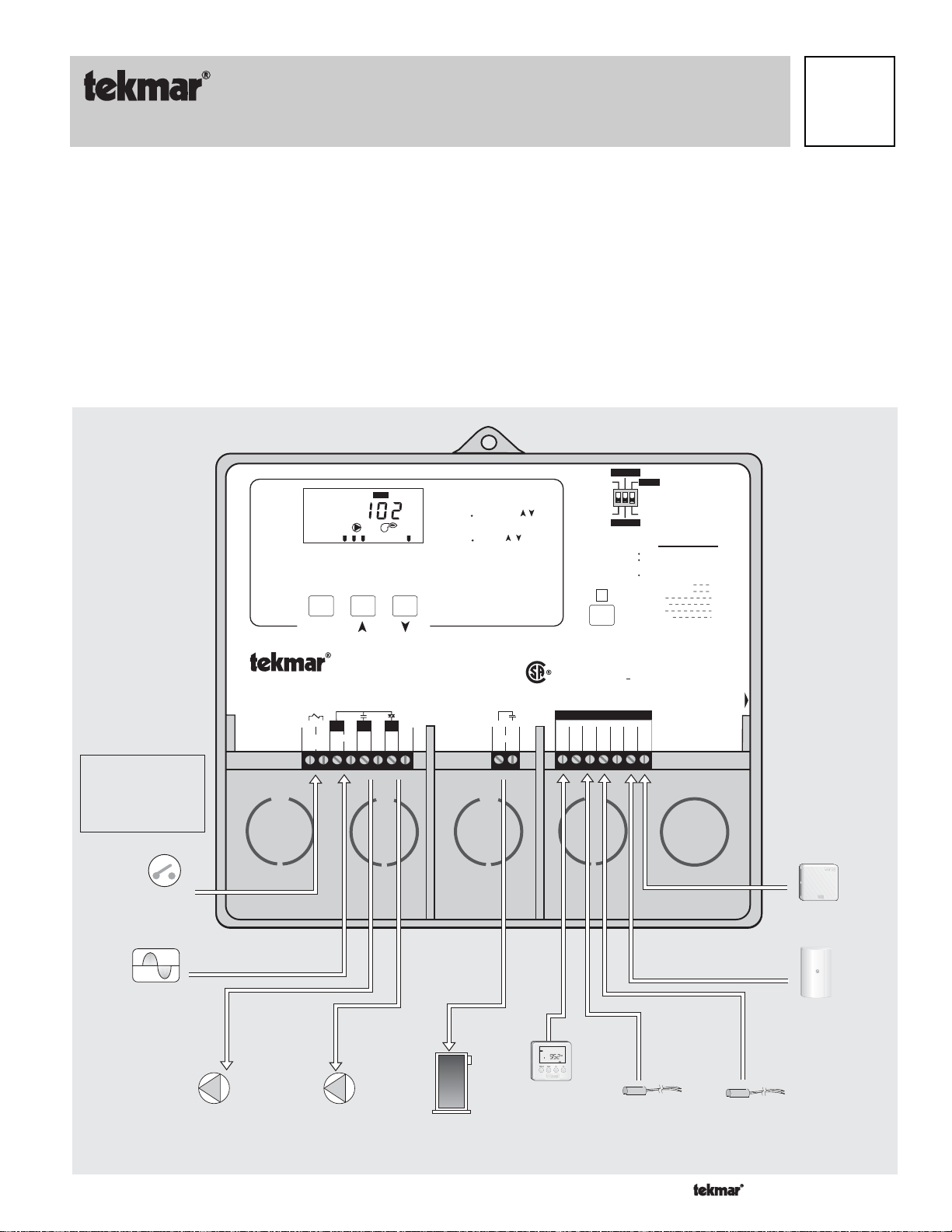
- Data Brochure
D 361
Mixing Control 361
03/09
The Mixing Control 361 is designed to control the supply water temperature to a hydronic system in order to provide outdoor reset or
setpoint operation. The control uses a variable speed injection pump to regulate the supply water temperature, while protecting the
boiler against flue gas condensation. The control has a Liquid Crystal Display (LCD) to view system status and operating information.
Additional functions include:
• Quick Setup for easy installation and programming of control
• User comfort adjustment to increase or decrease building
space temperature
• Advanced settings to fine-tune building requirements
• Boiler Control for improved energy savings
• Optional indoor sensor for room air temperature control
• Test sequence to ensure proper component operation
• Setback input for energy savings
• 120 V (ac) power supply
• CSA C US certified (approved to applicable UL standards)
• Powered mixing system pump output
30% Enable
Note:
Mixing demand must be
powered with 20 to 260
V (ac) before pumps will
operate or the boiler is
able to fire.
MIX
OCC
Terminal
Unit
Item
Mixing Control 361
Variable Speed
2 3 4
1
Power
Mixing
Demand
L
N
VIEW
70 90
503010
% Out
5 6 7 8
Sys
Pmp
N
Pmp
Var
F
°
Mixing
Demand
N
To increase or decrease the
building temperature:
Item
Press the
simultaneously for 1 sec. to
enter the
Use the , buttons to
adjust the
Display defaults back to
menu after 20 sec.
ADJUST
ROOM
910
Boiler
, , buttons
menu
setting
VIEW
C US
11 12 13 14 15 16 17
UnO
Sw
Advanced
Installer
Test
Made in Canada by
tekmar Control Systems Ltd.
tektra 913-01
Power:
Variable Pump:
Relays:
Demand:
Do not apply power
Com
Boil
Return
Boiler Sensor
Supply
10% Enable
Installer Instructions
ROOM
- Set to desired room temp.
OUTDR DSGN
- Set to coldest (design)
outdoor temp.
Terminal Unit Set to
High Mass Radiant
Low Mass Radiant
Fan Coil
Convector
Radiator
Baseboard
Refer to brochure for more information
120V + 10% 50/60 Hz 1650 VA
240V (ac) 2.4 A (FLA) 5 A (LRA), fuse T2.5 A
240V (ac) 10 A 1/3 hp
20 to 260 V (ac) 2 VA
Out
Indr
Signal wiring must be
rated at least 300V.
Mix
Com
1
2
3
4
5
6
Meets Class B:
Canadian ICES
FCC Part 15
Date Code
H1188D
Mixing Demand
120 V (ac) Power
Input
Signal
Input
Supply
Output
Mixing System
Pump
Output
Variable Speed
Driven Pump
Output
Boiler
Input
tekmar Timer
Optional
Input
Universal Sensor
Included
Input
Universal Sensor
Included
Copyright © D 361 - 03/091 of 20
Input
Indoor Sensor
Optional
Input
Outdoor
Included
Sensor
Page 2

How To Use The Data Brochure
This brochure is organized into four main sections. They are: 1)
Troubleshooting
Sequence of Operation
of the
that apply to your installation. For quick installation and setup of the control, refer to the
followed by the
The
Control Settings
displayed by the control. The control functions of each adjustable item are described in the
Sequence of Operation
. The
, as this contains important information on the overall operation of the control. Then read the sub-sections
Quick Setup
section.
section (starting at
section has three sub-sections. We recommend reading
DIP Switch Settings
Sequence of Operation
) of this brochure, describes the various items that are adjusted and
, 2)
Installation
Table of Contents
User Interface .............................................. pg 2
Description of Display Elements ............... pg 3
Sequence of Operation ...............................pg 4
Section A: General Operation .........
Section B: Mixing .............................
Section C: Boiler Operation
Installation ................................................. pg 10
DIP Switch Settings................................... pg 14
............. pg 8
pg 4
pg 5
Quick Setup .............................................. pg 14
Control Settings ....................................... pg 15
View Menu
Adjust Menu
Testing and Troubleshooting .................. pg 17
Error Messages
Technical Data .......................................... pg 20
Limited Warranty ...................................... pg 20
Installation
section,
Sequence of Operation
...................................... pg 15
................................... pg 16
............................. pg 19
Control Settings
, 3)
Section A: General Operation
DIP Switch Settings
.
, and 4)
section,
Reference Material: Essay E 003 “Characterized Heating Curve and Reset Ratio”
Essay E 021 “Mixing Methods and Sizing of Variable Speed Injection Pumps”
User Interface
The 361 uses a Liquid Crystal Display (LCD) as the method of supplying information. You use the LCD in order to set up and monitor
the operation of your system. The 361 has three push buttons (
your control, record your settings in the ADJUST menu table which is found in the second half of this brochure.
Item
The abbreviated name of the selected item will be displayed in the item field of the
display. To view the next available item, press and release the
have reached the last available item, pressing and releasing the
the display to the first item.
Adjust
To make an adjustment to a setting in the control, press and hold simultaneously for 1
second, all three buttons. The display will then show the word ADJUST in the top right
corner. Then select the desired item using the
button to make the adjustment.
To exit the ADJUST menu, either select the ESC item and press the
seconds.
When the
Item
button is pressed and held in the VIEW menu, the display scrolls through all the adjust items in both access levels.
Item
Item
, ,) for selecting, viewing, and adjusting settings. As you program
Item
button. Once you
Item
button will return
button. Finally, use the
or button, or leave the adjustment buttons alone for 20
and / or
Item
Item
Additional information can be gained by observing the status field and pointers of the LCD. The status field will indicate which of the
control’s outputs are currently active. Most symbols in the status field are only visible when the VIEW menu is selected.
Copyright © D 361 - 03/09 2 of 20
Page 3
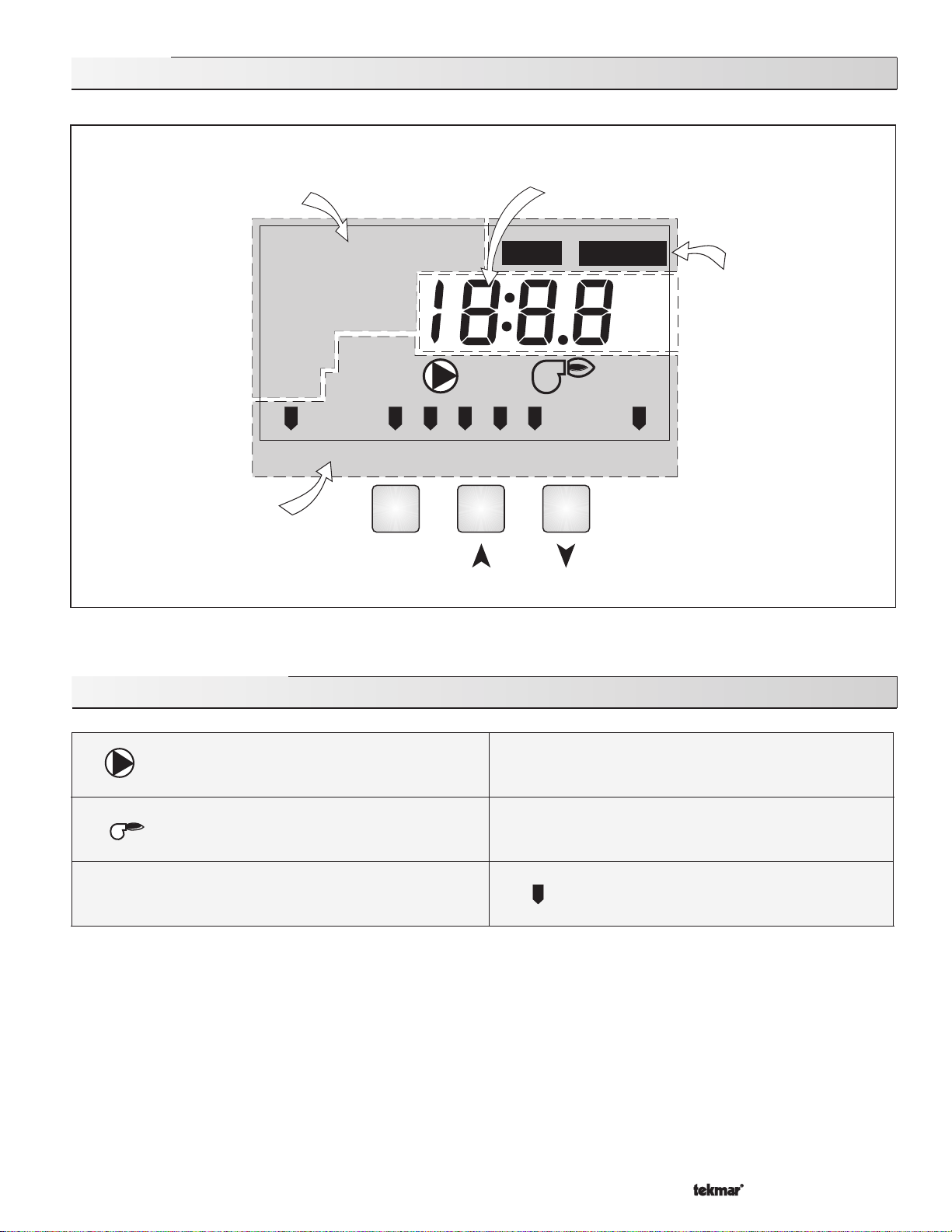
Display
Item Field
Displays an abbreviated
name of the selected item
OUTDR
BOIL
MIX
ROOM WWSD
INDR
Terminal
Unit
Status Field
Displays the current
status of the control’s
inputs, outputs and
operation
DSGN
TARGET
MAXMIN
UNOCC
Item
DIFF
3010 7050
% Out
Number Field
Displays the current value of
the selected item
VIEW
90
ADJUST
Demand
°
F
°
C
Mixing
Menu Field
Displays the
current menu
Buttons
Selects Menus, Items and
adjusts settings
{
Symbol Description
Pump
Displays when the mixing system pump is in
operation.
Burner
Displays when the boiler relay is turned on.
OCC
Occupied Schedule
Displays when the control is in occupied (Day)
mode.
UNOCC
°
F, °C
Unoccupied Schedule
Displays when the control is in unoccupied
(Night) mode.
°F, °C
Displays the unit of measure that all of the
temperatures are to be displayed in the control.
Pointer
Displays the control operation as indicated by
the text.
Copyright © D 361 - 03/093 of 20
Page 4
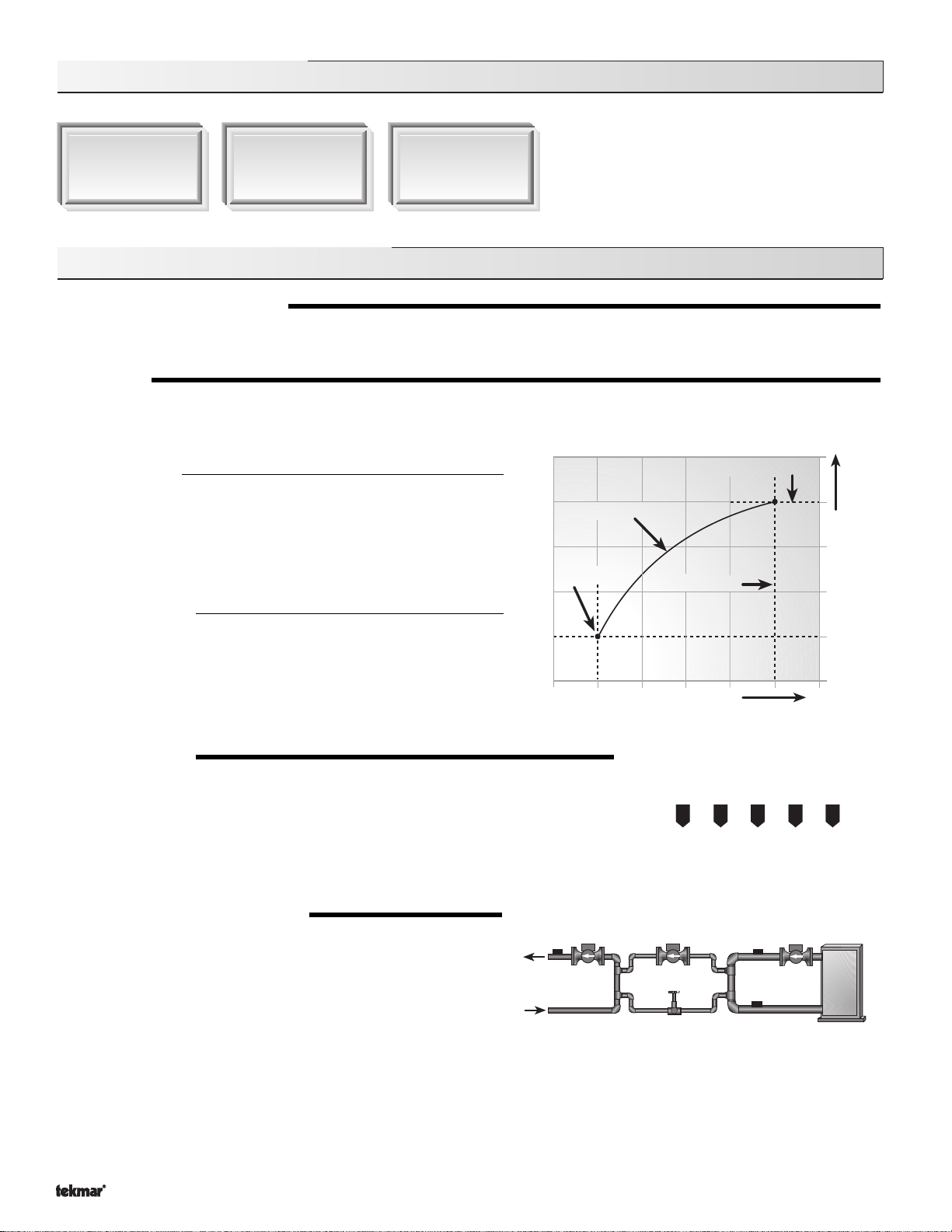
Sequence of Operation
% Out
Current output of variable
speed injection pump
3010 7050 90
Mixing
sensor
Boiler return
sensor
Boiler supply
sensor
or
Section A
General Operation
Page 4-5
Section B
Mixing
Page 5-8
Section C
Boiler Operation
Page 8-9
Section A —General Operation
POWERING UP THE CONTROL
When the Mixing Control 361 is powered up, the control displays the control type number in the LCD for 2 seconds. Next, the software
version is displayed for 2 seconds. Finally, the control enters into the normal operating mode.
OPERATION
The 361 uses a variable speed injection pump to control the supply water temperature to a hydronic system. The supply water
temperature is based on either the current outdoor temperature, or a fixed setpoint.
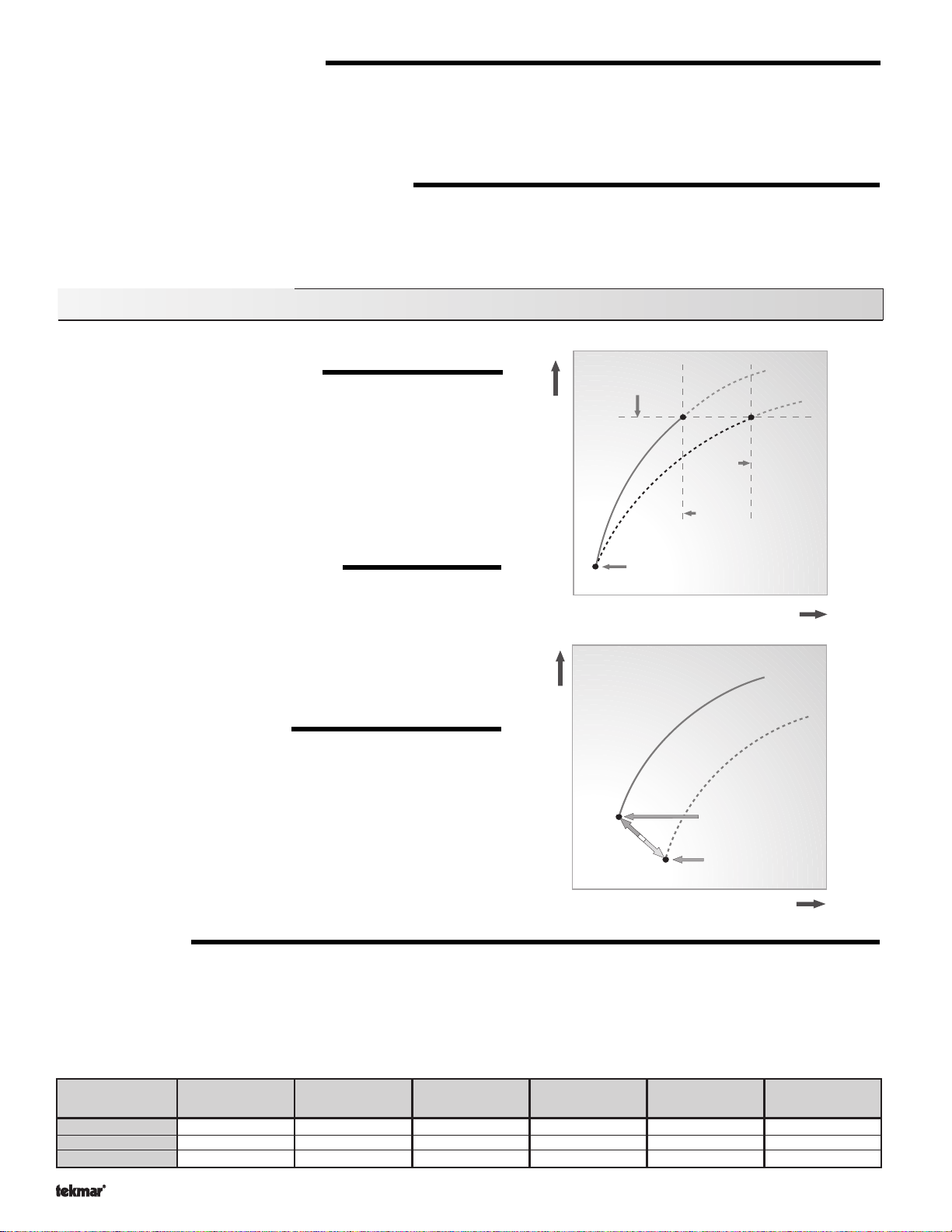
Outdoor Reset
When the outdoor design (OUTDR DSGN) setting is not set to OFF, the
361 calculates a mixing supply temperature based on the outdoor air
temperature. The 361 uses a
optionally indoor temperature feedback from an indoor sensor in this
calculation.
Characterized Heating Curve
and
Terminal Unit
Indoor Design
Design Supply
Outdoor Design
Setpoint Control
When the outdoor design (OUTDR DSGN) setting is set to OFF, the
361 supplies a fixed mixing supply temperature equal to the MIX
TARGET setting. An outdoor sensor is not required during this mode
of operation.
VARIABLE SPEED
A standard wet rotor circulator is connected to the 361 on the
and 8). The 361 increases or decreases the power output to the circulator when there is a
mixing demand. The circulator speed varies to maintain the correct mixed supply water
temperature at the mix sensor. For correct sizing and piping of the variable speed driven
circulator, refer to essay E 021. A visual indication of the current variable speed output is
displayed in the LCD in the form of a horizontal bar graph.
BOILER PROTECTION (BOIL MIN)
The 361 is capable of providing boiler protection from cold mixing system
return water temperatures. If the boiler sensor temperature is cooler than
the BOIL MIN setting while the boiler is firing, the 361 reduces the output
to the variable speed injection pump. This limits the amount of cool return
water to the boiler, and allows the boiler temperature to recover. This
feature can only be used if a boiler sensor is installed.
Var Pmp
and N terminals (7
Decreasing Outdoor Temperature
Increasing Water Temperature
Copyright © D 361 - 03/09 4 of 20
Page 5
EXERCISING
The 361 has a built-in exercising function. If a pump has not been operated at least once every 3 days, the control turns on the output
for 10 seconds. This minimizes the possibility of a pump seizing during a long period of inactivity. While the control is exercising, the
Test
LED flashes.
Note:
The exercising function does not work if power to the control or pumps is disconnected.
SETBACK (UNOCCUPIED)
To provide greater energy savings, the 361 has a setback capability. With setback, the
supply water temperature in the system is reduced when the building is unoccupied. By
reducing the supply water temperature, air temperature in the space may be reduced even
when thermostat(s) are not turned down. Any time the
terminals are shorted together, the control operates in the unoccupied (Night) mode. When
in the unoccupied (Night) mode, the UNOCC segment is displayed in the LCD. The 361
adjusts the supply water temperature based on the UNOCC settings made in the control.
This feature has no effect when the control is used as a setpoint control.
FACTORY DEFAULTS
The control comes preset with several factory defaults. These defaults are based on the terminal unit selection (see section B2). To
fine-tune building requirements, these defaults may be changed. If a factory default value for a terminal unit is changed, the terminal
unit number will flash when selected in the ADJUST menu.
To reload the factory defaults listed in section B2, power down the control and wait for 10 seconds. Power up the control while
simultaneously holding the
flashing.
12
11
UnO
Com
Sw
UnO Sw
(11) and the
Com
(12)
Timer Switch
Item
and buttons. The terminal unit number should now be displayed constantly in the LCD rather than
Section B: Mixing
Section B1
General
Section B2
Installer
Section B3
Advanced
Section B1: General
MIXING DEMAND
A mixing demand is required in order for the 361 to provide heat. A mixing demand is
generated by applying a voltage between 24 and 240 V (ac) across the
terminals (1 and 2). Once voltage is applied, the
LCD. If the 361 is not in WWSD, the 361 closes the
a MIX TARGET supply temperature based on the outdoor air temperature and settings. If
required, the 361 operates the boiler in order to provide heat to the variable speed injection pump.
SYSTEM PUMP OPERATION (
The system pump contact (
pump segment is displayed in the LCD. After the mixing demand has been satisfied, the 361 continues to operate the system pump for
20 seconds. This allows some residual heat to be purged out to the heating system. During WWSD, the system pump is operated based
on the exercise function.
INDOOR SENSOR
An indoor sensor may be used in order to provide indoor temperature feedback. The indoor sensor is connected to the
terminals (15 and 17). In addition, power must be applied to the
DEMAND section. With the indoor sensor connected, the 361 is able to sense the actual room temperature. Indoor temperature
feedback fine-tunes the supply water temperature in the mixing system to maintain room temperature. To adjust the room temperature,
use the ROOM OCC or ROOM UNOCC setting in the ADJUST menu at the control.
If a multiple zone system is used with an indoor sensor, proper placement of the indoor sensor is essential. The indoor sensor should
be located in an area which best represents the average air temperature of the zones.
1
Mixing
Demand
Sys Pmp
Sys Pmp
Mixing Demand
Mixing Demand
Sys Pmp
)
, terminal 5) closes whenever there is a mixing demand and the 361 is not in WWSD. The system
pointer is displayed in the
contact. The 361 calculates
24 to 240 V (ac)
Com
and
Mixing Demand
terminals (1 and 2) as described in the MIXING
2
Indr
Copyright © D 361 - 03/095 of 20
Page 6
CHARACTERIZED HEATING CURVE
When used as a mixing reset control, the 361 varies the supply water temperature based on the outdoor air temperature. The control
takes into account the type of terminal unit that the system is using. Since different types of terminal units transfer heat to a space
using different proportions of radiation, convection and conduction, the supply water temperature must be controlled differently. Once
the control is told what type of terminal unit is used, the control varies the supply water temperature according to the type of terminal
unit. This improves the control of the air temperature in the building.
MIXING TARGET TEMPERATURE (MIX TARGET)
When used as a mixing reset control, the MIX TARGET temperature is calculated from the
Characterized Heating Curve
settings,
outdoor air temperature and optionally, indoor air temperature. When used as a setpoint control, the installer sets the MIX TARGET
temperature. The control displays the temperature that it is currently trying to maintain as the mixing supply temperature. If the control
does not have a mixing demand, “- - -” is displayed as the MIX TARGET.
Section B2: Installer
OUTDOOR DESIGN (OUTDR DSGN)
The OUTDR DSGN is the outdoor air temperature that is the typical
coldest temperature of the year where the building is located. This temperature is used when doing heat loss calculations for the building. If a
cold outdoor design temperature is selected, the mixing supply temperature rises gradually as the outdoor temperature drops. If a warm
outdoor design temperature is selected, the mixing supply temperature
rises rapidly as the outdoor temperature drops.
SETPOINT OPERATION (MIX TARGET)
For setpoint operation, set the OUTDR DSGN to OFF. The MIX TARGET becomes the setpoint supply temperature that the control is to
maintain. The MIX TARGET temperature is set by the installer in the
ADJUST menu. An outdoor sensor is not required during this mode of
operation.
ROOM OCC & UNOCC (ROOM)
The ROOM is the desired room temperature for the mixing zones, and
it provides a parallel shift of the
temperature desired by the occupants is often different from the design
indoor temperature (MIX INDR). If the room temperature is not correct,
adjusting the ROOM setting increases or decreases the amount of heat
available to the building. A ROOM setting is available for both the occupied (Day) and unoccupied (Night) modes.
Characterized Heating Curve
MIX DSGN
cold
OUTDR
DSGN
warm
Increasing Water Temperature
Decreasing Outdoor Temperature
. The room
Increasing Water Temperature
MIX INDR
A
u
t
c
m
e
T
l
a
N
ROOM
MIX INDR
.
p
n
g
i
s
e
D
l
a
m
r
o
Decreasing Outdoor Temperature
TERMINAL UNITS
When using a
shape of the
E 003). The 361 provides for selection between six different terminal unit types: two types of radiant floor heat, fancoil, fin-tube
convector, radiator and baseboard. When a terminal unit is selected, the control automatically loads the design supply temperature
(MIX DSGN), maximum supply temperature (MIX MAX) and minimum supply temperature (MIX MIN). The factory defaults are listed
below. To change defaults, refer to section B3. If a default has been changed, refer to section A to reload the factory defaults.
Terminal Unit
MIX DSGN
MIX MAX
MIX MIN
Copyright © D 361 - 03/09 6 of 20
Characterized Heating Curve
Characterized Heating Curve
High Mass Radiant
Low Mass Radiant
(1)
120°F (49°C)
140°F (60°C)
140°F (60°C)
160°F (71°C)
OFF
, the control requires the selection of a terminal unit. The terminal unit determines the
according to how the terminal unit delivers heat into the building space (refer to Essay
(2)
OFF
Fancoil
(3)
190°F (88°C)
210°F (99°C)
100°F (38°C)
Fin-tube Convector
(4)
180°F (82°C)
200°F (93°C)
OFF
Radiator
(5)
160°F (71°C)
180°F (82°C)
OFF
Baseboard
(6)
150°F (66°C)
170°F (77°C)
OFF
Page 7

High Mass Radiant (1)
This type of a hydronic radiant floor is embedded in either a thick concrete or gypsum
pour. This heating system has a large thermal mass and is slow acting.
Default values: MIX DSGN = 120°F (49°C), MIX MAX = 140°F (60°C), MIX MIN = OFF
Low Mass Radiant (2)
This type of radiant heating system is either attached to the bottom of a wood sub-floor,
suspended in the joist space, or sandwiched between the sub-floor and the surface.
This type of radiant system has a relatively low thermal mass and responds faster than
a high mass system.
Default values: MIX DSGN = 140°F (60°C), MIX MAX = 160°F (71°C), MIX MIN = OFF
Fancoil (3)
A fancoil terminal unit or air handling unit (AHU) consists of a hydronic heating coil and
either a fan or blower. Air is forced across the coil at a constant velocity by the fan or
blower, and is then delivered into the building space.
Default values: MIX DSGN = 190°F (88°C), MIX MAX = 210°F (99°C),
MIX MIN = 100°F (38°C)
Fin–tube Convector (4)
A convector terminal unit is made up of a heating element with fins on it. This type of
terminal unit relies on the natural convection of air across the heating element to deliver
heated air into the space. The amount of natural convection to the space is dependant
on the supply water temperature to the heating element and the room air temperature.
Default values: MIX DSGN = 180°F (82°C), MIX MAX = 200°F (93°C), MIX MIN = OFF
Radiator (5)
A radiator terminal unit has a large heated surface that is exposed to the room. A radiator provides heat to the room through radiant heat transfer and natural convection.
Default values: MIX DSGN = 160°F (71°C), MIX MAX = 180°F (82°C), MIX MIN = OFF
Baseboard (6)
A baseboard terminal unit is similar to a radiator, but has a low profile and is installed at
the base of the wall. The proportion of heat transferred by radiation from a baseboard is
greater than that from a fin-tube convector.
Default values: MIX DSGN = 150°F (66°C), MIX MAX = 170°F (77°C), MIX MIN = OFF
Section B3: Advanced
MIXING INDOOR (MIX INDR)
The MIX INDR is the room temperature used in the original heat loss calculations for the building. This setting establishes the
beginning of the
Characterized Heating Curve
MIXING DESIGN (MIX DSGN)
The MIX DSGN temperature is the supply water temperature required to heat the mixing zones when the outdoor air is as cold as the
OUTDR DSGN temperature.
MIXING MAXIMUM (MIX MAX)
The MIX MAX sets the highest water temperature that the control is allowed to calculate as the MIX TARGET temperature. If the
control does target the MIX MAX setting, and the MIX temperature is near the MIX MAX, the MAX segment will be displayed in the
LCD while either the MIX TARGET temperature or the MIX temperature is being viewed.
for the mixing zones.
Copyright © D 361 - 03/097 of 20
Page 8

MIXING MINIMUM (MIX MIN)
The MIX MIN is the lowest temperature that the control is allowed to use
as a MIX TARGET temperature. During mild conditions, if the 361 calculates a MIX TARGET temperature that is below the MIX MIN setting,
the MIX TARGET temperature is adjusted to match the MIX MIN setting. During this condition, the MIN segment will be displayed in the
LCD when either the MIX TARGET or MIX temperature is being viewed.
If an indoor sensor is used, and the 361 is operating at the MIX MIN
temperature, the system pump is cycled using Pulse Width Modulation
(PWM) with a 15 minute cycle length. By cycling the system pump and
controlling the flow of supply water, the control provides an average
supply water temperature to the system. This average temperature is
equal to the original MIX TARGET. This minimizes overheating of the
zone while the control is operating at the MIX MIN temperature.
WARM WEATHER SHUT DOWN (WWSD) OCC & UNOCC
When the outdoor air temperature rises above the WWSD setting, the
361 turns on the WWSD segment in the display. When the control is in
Warm Weather Shut Down, the
Mixing Demand
pointer is displayed, if
there is a demand. However, the control does not operate the heating
system to satisfy this demand. If the control is in setpoint mode, the
WWSD feature is not functional.
Section C: Boiler Operation
210°F
-20
(-29)
(99°C)
190
(88)
170
(77)
150
(66)
130
(54)
110
(43)
90
(32)
70
(21)
50
(10)
Supply Water Temperature
MIX MAX
Mixing Characterized
MIX DSGN
Heating Curve
MIX MIN
OUTDR DSGN
WWSD OCC
MIX INDR
80°F
(27°C)
60
(16)
Outdoor Air Temperature
WWSD UNOCC
ROOM OCC
ROOM UNOCC
40
(5)
(-7)
20
0
(-18)
Section C1
General Operation
Section C2
Boiler Sensor
Placement
Section C1: General Operation
BOILER OPERATION
When the 361 determines that boiler operation is required, the
closed, the burner segment in the LCD is displayed.
BOILER MINIMUM (BOIL MIN)
Most boilers require a minimum water temperature in order to prevent flue gas condensation. The BOIL MIN adjustment is set to the
boiler manufacturer’s minimum recommended operating temperature. Only when the boiler temperature is measured by a boiler
sensor can the 361 provide boiler protection. In this case, when the boiler is firing and the boiler temperature is below the BOIL MIN
setting, the 361 turns on the MIN segment and reduces the heating load on the boiler by limiting the output of the variable speed
injection pump. If the installed boiler is designed for low temperature operation, set the BOIL MIN adjustment to OFF.
BOILER PROTECTION
Refer to section A for a description of boiler protection.
Boiler
contact terminals (9 and 10) close. While the
Boiler
contact is
Copyright © D 361 - 03/09 8 of 20
Page 9

Section C2: Boiler Sensor Placement
BOILER SENSOR ON THE SUPPLY (
Boiler Sensor
DIP switch
= Supply
)
The boiler sensor can be located on the boiler supply if the 361 is the only control that is
operating the boiler. When in the supply mode, the 361 determines the required operating
temperature of the boiler using
Boiler Load Reset
. With
Boiler Load Reset
, the 361 operates
the boiler at the lowest possible supply temperature that is sufficient to satisfy the
requirements of the variable speed injection pump. If this mode of operation is selected,
the boiler pump should either operate continuously, or be operated in parallel with the
system pump contact (
Note:
The boiler pump should not be operated by the boiler’s aquastat, as this may lead to
Sys Pmp
).
improper cycling of the boiler because of inconsistent flow past the boiler supply sensor.
BOILER DIFFERENTIAL (BOIL DIFF)
An on / off heat source such as a boiler must be operated with a
differential in order to prevent short cycling. When the boiler supply
temperature drops below the bottom rail of the differential, the 361 closes
the
Boiler
contact to fire the boiler. When the boiler supply temperature
rises above the top rail of the differential, the 361 opens the
Boiler
contact
to turn off the boiler. With the 361, either a fixed or automatic differential
setting is selected. If automatic differential (Ad) is selected, the 361
automatically adjusts the boiler differential under the current load conditions to avoid short cycling.
BOILER SENSOR ON THE RETURN (
Boiler Sensor
DIP switch
The boiler sensor should be located on the boiler return if the 361 is one of many controls
that can call for boiler operation. When in the return mode, the 361 provides a boiler
enable as described in the BOILER ENABLE section. The 361 no longer tries to control
the boiler supply water temperature directly, but allows the boiler to operate at its operating
aquastat setting when required. If this mode of operation is selected, the boiler pump
should either operate continuously, or be operated in parallel with the system pump contact
(
Sys Pmp
Note
).
: The boiler pump should not be operated by the boiler’s aquastat, as this may lead to
improper cycling of the boiler because of inconsistent flow past the boiler sensor.
165°F(74°C)
160°F (71°C)
155°F (68°C)
Supply Water Temperature
= Return
Boiler supply
sensor
Differential = 10°F (5°C)
B
o
i
l
e
n
o
r
e
l
i
o
B
)
r
o
f
f
Time
Boiler return
sensor
n
o
r
le
i
o
B
B
o
i
l
e
r
o
f
f
NO BOILER SENSOR
The 361 is capable of operating without a boiler sensor if desired. Without a boiler sensor,
the 361 provides a boiler enable as described in the BOILER ENABLE section, but is
unable to provide boiler protection. This type of application is typical if the 361 is drawing
No boiler
sensor
heat from a heat source that already incorporates some form of boiler protection.
BOILER ENABLE (
30% Enable / 10% Enable
)
The 361 has a DIP switch that allows for the selection between a 30% boiler enable and a 10% boiler enable. This switch is only
functional when the
In the 30% position, the 361 closes the
Boiler Sensor
DIP switch is set to
Boiler
contact when the variable speed output exceeds 30%. The
Return
.
Boiler
contact remains
closed until the variable speed output reduces below 15%. This setting would normally be chosen for low mass boilers (copper fintube, etc.), or systems with low thermal mass in the loop between the boiler and the variable speed injection pump.
In the 10% position, the 361 closes the
contact when the variable speed output exceeds 10%. The
Boiler
contact remains
Boiler
closed until the variable speed output reduces below 5%. This setting is normally chosen for high mass boilers (cast iron, steel firetube, etc.), or systems with large thermal mass in the loop between the boiler and the variable speed injection pump.
Boiler
In order to prevent short cycling, the
contact has a minimum on time, and a minimum off time.
Copyright © D 361 - 03/099 of 20
Page 10

Installation
CAUTION
Improper installation and operation of this control could result in damage to the equipment and possibly even personal injury. It is
your responsibility to ensure that this control is safely installed according to all applicable codes and standards. This electronic
control is not intended for use as a primary limit control. Other controls that are intended and certified as safety limits must be placed
into the control circuit.
STEP ONE
Check the contents of this package. If any of the contents listed are missing or damaged, please contact your wholesaler or tekmar
sales representative for assistance.
Type 361 includes: One Mixing Control 361, One Outdoor Sensor 070, Two Universal Sensors 082, Data Brochures D 361,
Note
STEP TWO
Remove the control from its base by pressing down on the release clip in the wiring chamber and sliding the control away from it. The
base is then mounted in accordance with the instructions in the Data Brochure D 001.
STEP THREE
All electrical wiring terminates in the control base wiring chamber. The base has standard 7/8” (22 mm) knockouts which accept
common wiring hardware and conduit fittings. Before removing the knockouts, check the wiring diagram and select those sections of
the chamber with common voltages. Do not allow the wiring to cross between sections, as the wires will interfere with safety dividers
which should be installed at a later time.
Power must not be applied to any of the wires during the rough-in wiring stage.
• Install the Outdoor Sensor 070, Boiler Sensor 082, and Mixing Sensor 082 according to the instructions in the Data Brochure D 070,
• If an Indoor Sensor 076 or 077 is used, install the indoor sensor according to the instructions in the Data Brochure D 074, and run
: Carefully read the details of the
and run the wiring back to the control.
the wiring back to the control.
GETTING READY
D 070, D 001, Application Brochure A 361, Essay E 021.
Sequence of Operation
MOUNTING THE BASE
ROUGH-IN WIRING
to ensure that you have chosen the proper control for your application.
• Run wire from other system components (pump, boiler, etc.) to the control.
• Run wires from the 120 V (ac) power to the control. Use a clean power source to ensure proper operation. Multi-strand 16 AWG
wire is recommended for all 120 V (ac) wiring due to its superior flexibility and ease of installation into the terminals.
STEP FOUR
The installer should test to confirm that no voltage is present at any of the wires. Push the control into the base and slide it down until
it snaps firmly into place.
Powered Input Connections
ELECTRICAL CONNECTIONS TO THE CONTROL
120 V (ac) Power
Connect the 120 V (ac) power supply to the
4). This connection provides power to the microprocessor and display of the control.
As well, this connection provides power to the
Pmp
terminal (7) from the
Power L
terminal (3).
Power L
Sys Pmp
and
Power N
terminal (5) and to the
terminals (3 and
Var
120 V (ac)
4
3
Power
L
N
1
Mixing
Demand
Mixing Demand
To generate a mixing demand, a voltage between 24 V (ac) and 240 V (ac) must be
applied across the
Mixing Demand
terminals (1 and 2).
24 to 240 V (ac)
2
Copyright © D 361 - 03/09 10 of 20
Page 11

Output Connections
System Pump Contact (
The
Sys Pmp
Sys Pmp
output terminal (5) on the 361 is a powered output.
)
When the relay in the 361 closes, 120 V (ac) is provided to the
Pmp
terminal (5) from the
Power L
terminal (3). To operate the
system pump, connect one side of the system pump circuit to terminal (5), and the second side of the pump circuit to the neutral (N)
terminal (6).
Variable Speed Injection Pump (
Var Pmp
)
The 361 can vary the speed of a permanent capacitor, impedance
protected, or equivalent pump motor that has a locked rotor current
of less than 2.4 A. Most small wet rotor circulators are suitable as
described in Essay E 021. The 361 has an internal overload protection fuse which is rated at 2.5 A 250 V (ac). Contact your tekmar
sales representative for details on the repair procedures if this fuse
is blown.
The
Var Pmp
supplied to the
terminal (7) on the 361 is a powered output. Power is
Var Pmp
terminal (7) from the
Power L
terminal (3).
To operate the variable speed injection pump, connect one side of
the pump circuit to
Var Pmp
terminal (7), and the second side of the
pump circuit to the neutral (N) terminal (8).
Sys
4
3
Power
N
L
L
120V (ac)
4
3
Power
Sys
L
Pmp
N
L
N
120V (ac)
7
Var
Pmp
N
5
6
N
System
pump
8
N
Variable speed
injection pump
Boiler Contact
The
Boiler
terminals (9 and 10) are an isolated output in the 361.
There is no power available on these terminals from the control.
These terminals are to be used as a switch to either make or break
the boiler circuit. When the 361 requires the boiler to fire, it closes
the contact between terminals 9 and 10.
Sensor and Unpowered Input Connections
Do not apply power to these terminals as this will damage the
control.
Outdoor Sensor
Connect the two wires from the Outdoor Sensor 070 to the
and
Out
terminals (15 and 16). The outdoor sensor is used by the
361 to measure the outdoor air temperature.
Boiler Sensor
Connect the two wires from the Boiler Sensor 082 to the
Boil
terminals (12 and 13). The boiler sensor is used by the 361 to
measure the boiler temperature.
Com
Com
and
12
Com
13
Boil
10
9
Boiler
T
T
T
T
15
16
Com
Out
Boiler supply
sensor
or
Mixing Sensor
Connect the two wires from the Mixing Sensor 082 to the
Mix
terminals (12 and 14). The mixing sensor is used by the 361 to
measure the mixed supply water temperature after the variable
speed injection pump. Normally the sensor is attached to the pipe
downstream of the system pump.
Com
and
Com
Boiler return
sensor
13
14
12
Boil
Mix
Mixing
sensor
System
pump
Copyright © D 361 - 03/0911 of 20
Page 12

Indoor Sensor
If an indoor sensor is used, connect the two wires from the sensor
to the
Com
and
Indr
terminals (15 and 17). The indoor sensor is
used by the 361 to measure the room air temperature.
Unoccupied Switch
If an external timer (tekmar Timer 032) or switch is used, connect the two wires from
the external switch to the
terminals are shorted together, the control registers an unoccupied signal.
UnO Sw
and
Com
terminals (11 and 12). When these two
15
Com
Timer Switch
Out
16
17
Indr
12
11
UnO
Com
Sw
STEP FIVE
Each terminal block
TESTING THE WIRING
must be unplugged
from its header on the control before power is applied for testing. To remove a terminal block,
pull it straight down from the control.
The following tests are to be performed using standard testing practices and procedures, and should only be carried out by properly
trained and experienced persons.
A good quality electrical test meter, capable of reading from at least 0 - 300 V (ac) and at least 0 - 2,000,000 Ohms, is essential to
properly test the wiring and sensors.
14
13
Test The Sensors
In order to test the sensors, the actual temperature at each sensor
location must be measured. A good quality digital thermometer with a
surface temperature probe is recommended for ease of use and ac-
Ω
Ω
V
12
Com
Boil
Mix
curacy. Where a digital thermometer is not available, a spare sensor
can be strapped alongside the one to be tested and the readings
compared. Test the sensors according to the instructions in the Data
Brochure D 070.
4
Test The Power Supply
Make sure exposed wires and bare terminals are not in contact with
other wires or grounded surfaces. Turn on the power and measure
the voltage between the
Power L
and
Power N
terminals (3 and 4)
V
Ω
V
3
Power
L
N
108 to 132 V (ac)
using an AC voltmeter. The reading should be between 108 and
132 V (ac).
Test The Powered Inputs
Mixing Demand
Measure the voltage between the
2). When the mixing demand device calls for heat, you should
measure between 20 and 260 V (ac) at the terminals. When the
mixing demand device is off, you should measure less than 5 V (ac).
Copyright © D 361 - 03/09 12 of 20
Mixing Demand
terminals (1 and
2
1
Mixing
V
Ω
V
Demand
20 to 260 V (ac)
Page 13

Test The Outputs
System Pump (Sys Pmp)
If a system pump is connected to the
Sys Pmp
terminal (5), make
3
Power
L
6
5
4
Sys
N
N
Pmp
sure that power to the terminal block is off, and install a jumper
between the
a second jumper between
power is applied to the
Power L
and the
Power N
Power L
Sys Pmp
terminals (3 and 5). Install
and N terminals (4 and 6). When
and
Power N
terminals (3 and 4),
the system pump should start. If the pump does not turn on, check
the wiring between the terminal block and pump, and refer to any
installation or troubleshooting information supplied with the pump.
If the pump operates properly, disconnect the power and remove
the jumpers.
Variable Speed Injection Pump (
If a variable speed injection pump is connected to the
install a jumper between the
Var Pmp
Power L
and the
)
Var Pmp
Var Pmp
terminals (3 and 7). Install a second jumper between
L
N
120V (ac)
terminal (7), make sure that power to the terminal block is off, and
System
pump
Power N
and
terminals (4 and 8). When the variable speed pump circuit is powered up, the variable speed pump should operate at full speed.
If the pump does not operate, check the wiring between the terminal block and the pump, and refer to any installation or
troubleshooting information supplied with the pump. If the pump operates properly, disconnect the power and remove the jumpers.
Boiler
If the boiler circuit is connected to the
between the terminals. When the boiler circuit is powered up, the boiler should fire. If the boiler does not turn on, refer to any
installation or troubleshooting information supplied with the boiler. (The boiler may have a flow switch that prevents firing until the
boiler loop pump is running). If the boiler operates properly, disconnect the power and remove the jumper.
Boiler
terminals (9 and 10), make sure power to the boiler circuit is off, and install a jumper
N
Connecting The Control
Make sure all power to the devices and terminal blocks is off, and remove any
remaining jumpers from the terminals.
Reconnect the terminal blocks to the control by carefully aligning them with their respective headers on the control, and then pushing the terminal blocks into the headers.
The terminal blocks should snap firmly into place.
Install the supplied safety dividers between the unpowered sensor inputs and the powered 120 V (ac) or 24 V (ac) wiring chambers.
Apply power to the control. The operation of the control on power up is described in the
Sequence of Operation
section of this brochure.
11
UnO
Sw
12
Com
13
Boil
14
Mix
Copyright © D 361 - 03/0913 of 20
Page 14

DIP Switch Settings
The DIP Switch settings on the control are very important and should be
set to the appropriate settings prior to making any adjustments to the
control through the user interface. The DIP switch settings change the
items that are available to be viewed and / or adjusted in the user
interface.
Advanced
Installer
30% Enable
Return
Boiler Sensor
Supply
10% Enable
ADVANCED / INSTALLER
The
Advanced / Installer
DIP switch is used to select which items are available to be viewed and / or adjusted in the user interface.
30% ENABLE / 10% ENABLE
The position of the
normal conditions. This switch is only operational if the
30% Enable / 10 % Enable
DIP switch determines at which pump output the control will close the
Boiler Sensor
DIP switch is set to
Return
. Refer to section C2.
Boiler
contact under
BOILER SENSOR (RETURN / SUPPLY)
The
Boiler Sensor
of the boiler loop, the DIP switch must be set to
DIP switch selects the installation location for the boiler sensor. When the boiler sensor is installed on the supply side
Supply
. The boiler aquastat should be set at least 20°F (11°C) higher than the required
design boiler water temperature. The boiler is controlled as described in section C.
For systems where the 361 provides a heat demand to an external boiler control, the boiler sensor should be installed on the return side
of the boiler loop. When the boiler sensor is installed on the return side of the boiler loop, the DIP switch must be set to
Return
. The 361
only enables the boiler when the output of the variable speed injection pump exceeds the boiler enable DIP switch setting. The
contact is controlled as described in section C. The boiler’s operating temperature is controlled by its aquastat, or an external boiler reset
control.
Quick Setup
Boiler
The quick setup can be used for both outdoor reset and setpoint operation. To enter the installer programming mode, set the
Installer
DIP switch to
Installer
.
Advanced /
OUTDOOR RESET
Access the ADJUST menu by pressing and holding simultaneously for 1 second, all three buttons. The display will now show the word
ADJUST in the top right corner.
The ROOM OCC adjustment is the first item displayed. Use the or button to set the ROOM temperature.
°
F
The ROOM OCC setting is set to the desired room air temperature during the occupied (Day) mode.
Note
: To increase or decrease space temperature during the occupied (Day) mode, only adjust the ROOM
OCC setting.
Press and release the
°
F
set the desired temperature. The ROOM UNOCC setting is set to the desired room air temperature during
Item
button to advance to the ROOM UNOCC adjustment. Use the or button to
the unoccupied (Night) mode.
Note:
To increase or decrease space temperature during the unoccupied (Night) mode, only adjust the
ROOM UNOCC setting.
°
F
Press and release the
Item
button to advance to the OUTDR DSGN adjustment. Use the or button to
set the outdoor design temperature. The OUTDR DSGN setting is set to the typical coldest temperature of
the year.
Press and release the
button to advance to the
Terminal Unit
adjustment. Use the or button to select
Item
the desired terminal unit. The terminal unit number corresponds to the type of terminal that is being used.
The table below lists the terminal units and their default values.
ROOM
ROOM
OUTDR
Terminal Unit
UN
OCC
OCC
DSGN
ADJUST
ADJUST
ADJUST
ADJUST
Terminal Unit
MIX DSGN
MIX MAX
MIX MIN
Copyright © D 361 - 03/09 14 of 20
High Mass Radiant
(1)
120°F (49°C)
140°F (60°C)
OFF
Low Mass Radiant
(2)
140°F (60°C)
160°F (71°C)
OFF
Fancoil
(3)
190°F (88°C)
210°F (99°C)
100°F (38°C)
Fin-tube Convector
(4)
180°F (82°C)
200°F (93°C)
OFF
Radiator
(5)
160°F (71°C)
180°F (82°C)
OFF
Baseboard
(6)
150°F (66°C)
170°F (77°C)
OFF
Page 15

ADJUST
°
F
ADJUST
Press and release the
Item
button to advance to the units adjustment. Use the or button to set the scale
to °F or °C.
Item
To exit the ADJUST menu, press and release the
button to advance to the ESC item. Then either press
the or button, or leave the buttons alone for 20 seconds.
SETPOINT CONTROL
Access the ADJUST menu by pressing and holding simultaneously for 1 second, the
the word ADJUST in the top right corner.
OUTDR
DSGN
ADJUST
Press and release the
Item
button to advance to the OUTDR DSGN adjustment. Press and hold the button
until OFF is displayed.
ADJUST
°
F
Press and release the
Item
button to advance to the MIX TARGET adjustment. Use the or button to select
MIX
TARGET
the desired temperature. The MIX TARGET setting is set to the desired setpoint supply temperature.
ADJUST
°
F
Press and release the
Item
button to advance to the units adjustment. Use the or button to set the scale
to °F or °C.
ADJUST
To exit the ADJUST menu, press and release the
Item
the or button, or leave the buttons alone for 20 seconds.
View Menu (1 of 1)
Item
, and buttons. The display will now show
button to advance to the ESC item. Then either press
Display Description Range
Advanced
Installer
Section
OUTDR
ROOM
MIX
MIX
BOIL
OCC
OCC
OCC
TARGET
OCC
OCC
VIEW
VIEW
VIEW
VIEW
VIEW
°
F
°
F
B1
°
F
B3
°
F
B1
B2
B3
°
F
Current outdoor air temperature as measured by the outdoor
sensor. This is also the default display for the control.
(OUTDR DSGN ≠ OFF)
Current room air temperature as measured by the indoor sensor.
(Indoor sensor is present)
Current mixed supply water temperature as measured by the
mixing sensor.
Target mixed supply is the temperature the control is currently
trying to maintain at the mixing sensor.
Current boiler temperature as measured by the boiler sensor.
(Boiler sensor is present)
-67 to 149°F
(-55 to 65°C)
23 to 113°F
(-5 to 45°C)
14 to 266°F
(-10 to 130°C)
---, 14 to 266°F
(---, -10 to 130°C)
14 to 266°F
(-10 to 130°C)
Copyright © D 361 - 03/0915 of 20
Page 16

Adjust Menu (1 of 2)
Display Description Range
Advanced
Installer
Section
ADJUST
°
ROOM
ROOM
MIX
OUTDR
Terminal Unit
OCC
UN
OCC
TARGET
DSGN
F
ADJUST
°
F
ADJUST
°
F
ADJUST
°
F
ADJUST
B2
B2
B2
B2
B2
The desired room air temperature during an
occupied (Day) period.
(OUTDR DSGN
≠ OFF)
The desired room air temperature during an
unoccupied (Night) period.
(OUTDR DSGN
≠ OFF)
Mixing setpoint temperature.
(OUTDR DSGN = OFF)
The design outdoor air temperature used in the
heat loss calculation for the heating system. For
setpoint operation, set the OUTDR DSGN to OFF.
The type of terminal units that are being used in the
heating system.
(OUTDR DSGN ≠ OFF)
1 (High Mass Radiant), 2 (Low Mass
Radiant), 3 (Fancoil),
4 (Fin-tube Convector), 5 (Radiator),
6 (Baseboard)
Actual
Setting
35 to 100°F
(2 to 38°C)
35 to 100°F
(2 to 38°C)
60 to 200°F
(16 to 93°C)
-60 to 32°F, OFF
(-51 to 0°C, OFF)
MIX
INDR
MIX
MIX
MIX
BOIL
BOIL
MIN
MIN
DSGN
MAX
DIFF
ADJUST
°
F
ADJUST
°
F
ADJUST
°
F
ADJUST
ADJUST
°
F
ADJUST
B3
B3
B3
B3
C1
C2
The design indoor air temperature used in the heat
loss calculation for the heating system.
(OUTDR DSGN ≠ OFF)
The design supply water temperature used in the
heat loss calculation for the heating system.
(OUTDR DSGN ≠ OFF)
The maximum supply temperature for the mixing
system.
(OUTDR DSGN ≠ OFF)
The minimum supply temperature for the mixing
system.
(OUTDR DSGN ≠ OFF)
The minimum temperature allowed for the boiler
target temperature.
(Boiler sensor is present)
The differential that the control is to use when it is
operating the boiler.
(
Boiler Sensor
DIP switch =
Supply
AND Boiler
sensor is present)
35 to 100°F
(2 to 38°C)
70°F to 220°F
(21 to 104°C)
80 to 210°F
(27 to 99°C)
OFF, 35 to 150°F
(OFF, 2 to 65°C)
OFF, 80 to 180°F
(OFF, 27 to 82°C)
Ad, 2 to 42°F
(Ad, -17 to 6°C)
Copyright © D 361 - 03/09 16 of 20
Page 17

Adjust Menu (2 of 2)
Test
not testing
testing
testing paused
off
red
red
Display Description Range
Advanced
Installer
Section
ADJUST
°
WWSD
OCC
WWSD
UN
OCC
F
ADJUST
°
F
ADJUST
°
F
ADJUST
B3
B3
The system’s warm weather shut down during the
occupied (Day) period.
The system’s warm weather shut down during the
unoccupied (Night) period.
The units of measure that all of the temperatures
are to be displayed in the control.
35 to 100°F, OFF
(2 to 38°C, OFF)
35 to 100°F, OFF
(2 to 38°C, OFF)
°F, °C
This item exits the ADJUST menu by pressing
either the or button.
Testing the Control
Actual
Setting
The Mixing Control 361 has a built-in test routine which is used to test the
main control functions. The 361 continually monitors the sensors, and
displays an error message whenever a fault is found. See the following
pages for a list of the 361’s error messages and possible causes. When
the
Test
button is pressed, the test light is turned on. The individual
outputs and relays are tested in the following test sequence.
TEST SEQUENCE
Each step in the test sequence lasts 10 seconds.
Test
During the test routine, the test sequence may be paused by pressing the
be paused in a step. If the
test routine. If the test sequence is paused, the
Test
button is not pressed again for 5 minutes while the test sequence is paused, the control exits the entire
Test
button can be pressed again to advance to the next step. This can also be used
button. Only if there is a mixing demand can the control
to rapidly advance through the test sequence. To reach the desired step, repeatedly press and release the
appropriate device and segment in the display turn on.
Step 1
Step 2
Step 3
Step 4
- The injection pump operates at 100% for 10 seconds. After 10 seconds, the injection pump is shut off.
- The system pump (
- The
Boiler
contact is turned on for 10 seconds. After 10 seconds, the
Sys Pmp
) is turned on for 10 seconds.
Boiler
and
Sys Pmp
contacts are shut off.
- After the test sequence is completed, the control resumes its normal operation.
Test
button until the
Copyright © D 361 - 03/0917 of 20
Page 18

Troubleshooting
When troubleshooting any heating system, it is always a good idea to establish a set routine to follow. By following a consistent routine,
many hours of potential headaches can be avoided. Below is an example of a sequence that can be used when diagnosing or
troubleshooting problems in a hydronic heating system.
Establish the problem. Get as much information from the customer as possible about the problem. Is there
Establish the
Problem
too much heat, not enough heat, or no heat? Is the problem only in one particular zone or area of the building,
or does the problem affect the entire system? Is this a consistent problem or only intermittent? How long
has the problem existed for? This information is critical in correctly diagnosing the problem.
Understand the
Sequence of
Operation
Use the Test
Routine
Sketch the
Piping in the
System
Document the
Control
Isolate the
Problem
Understand the sequence of operation of the system. If a particular zone is not receiving enough heat, which
pumps or valves in the system must operate in order to deliver heat to the affected zone? If the zone is
receiving too much heat, which pumps, valves, or check valves must operate in order to stop the delivery
of heat?
Press the
Testing section. Pause the control as necessary to ensure that the correct device is operating as it should.
Sketch the piping of the system. This is a relatively simple step that tends to be overlooked, however, it can
often save hours of time in troubleshooting a system. Note flow directions in the system paying close
attention to the location of pumps, check valves, pressure bypass valves, and mixing valves. Ensure correct
flow direction on all pumps. This is also a very useful step if additional assistance is required.
Document the control for future reference. Before making any adjustments to the control, note down all of
the items that the control is currently displaying. This includes items such as error messages, current
temperatures and settings, and which devices should be operating as indicated by the LCD. This
information is an essential step if additional assistance is required to diagnose the problem.
Isolate the problem between the control and the system. Now that the sequence of operation is known
and the system is sketched, is the control operating the proper pumps and valves at the correct times? Is
the control receiving the correct signals from the system as to when it should be operating? Are the proper
items selected in the menus of the control for the device that is to be operated?
Test
button on the control and follow the control through the test sequence as described in the
Test the Contacts
Voltages &
Sensors
Copyright © D 361 - 03/09 18 of 20
Test the contacts, voltages and sensors. Using a multimeter, ensure that the control is receiving adequate
voltage to the power terminals and the demand terminals as noted in the technical data. Use the multimeter
to determine if the internal contacts on the control are opening and closing correctly. Follow the instructions
in the Testing the Wiring section to simulate closed contacts on the terminal blocks as required. Test the
sensors and their wiring as described in the sensor Data Brochures.
Page 19

Error Messages
OUTDR
OUTDR
MIX
MIX
VIEW
VIEW
VIEW
VIEW
VIEW
The control was unable to read a piece of information from its EEPROM. This error can be caused by a
noisy power source. The control will load the factory defaults and stop operation until all the settings are
verified.
The control is no longer able to read the outdoor sensor due to a short circuit. In this case the control
assumes an outdoor temperature of 32°F (0°C) and continues operation. Locate and repair the problem as
described in the Data Brochure D 070. To clear the error message from the control after the sensor has
been repaired, press the
Item
button.
The control is no longer able to read the outdoor sensor due to an open circuit. In this case the control
assumes an outdoor temperature of 32°F (0°C) and continues operation. Locate and repair the problem as
described in the Data Brochure D 070. To clear the error message from the control after the sensor has
been repaired, press the
Item
button.
The control is no longer able to read the mixing supply sensor due to a short circuit. In this case the control
will operate the variable speed injection pump at a fixed output as long as there is a mixing demand. Locate
and repair the problem as described in the Data Brochure D 070. To clear the error message from the
control after the sensor has been repaired, press the
Item
button.
The control is no longer able to read the mixing supply sensor due to a short circuit. In this case the control
will operate the variable speed injection pump at a fixed output as long as there is a mixing demand. Locate
and repair the problem as described in the Data Brochure D 070. To clear the error message from the
control after the sensor has been repaired, press the
Item
button.
BOIL
BOIL
ROOM
ROOM
VIEW
VIEW
VIEW
VIEW
The control is no longer able to read the boiler sensor due to a short circuit. If the BOIL MIN adjustment is
higher than 100°F (38°C), the control operates the
Boiler
contact as a boiler enable (see section C). The
boiler temperature is then limited by the operating aquastat. If the BOIL MIN adjustment is lower than 100°F
(38°C), the control does not operate the
Boiler
contact. Locate and repair the problem as described in the
Data Brochure D 070. To clear the error message from the control after the sensor has been repaired, press
the
Item
button.
The control is no longer able to read the boiler sensor due to an open circuit. If the BOIL MIN adjustment is
higher than 100°F (38°C), the control operates the
Boiler
contact as a boiler enable (see section C). The
boiler temperature is then limited by the operating aquastat. If the BOIL MIN adjustment is lower than 100°F
(38°C), the control does not operate the
Boiler
contact. Locate and repair the problem as described in the
Data Brochure D 070. If the boiler sensor is deliberately removed, the control must be powered down, and
then powered back up. To clear the error message from the control after the sensor has been repaired,
press the
Item
button.
The control is no longer able to read the indoor sensor due to a short circuit. The control will continue to
operate as if there was nothing connected to the indoor sensor input. Locate and repair the problem as
described in the Data Brochure D 074. To clear the error message from the control after the sensor has
been repaired, press the
Item
button.
The control is no longer able to read the indoor sensor due to an open circuit. The control will continue to
operate as if there was nothing connected to the indoor sensor input. Locate and repair the problem as
described in the Data Brochure D 074. If the indoor sensor is deliberately removed, the control must be
powered down, and then powered back up. To clear the error message from the control after the sensor has
been repaired, press the
Item
button.
Copyright © D 361 - 03/0919 of 20
Page 20

Technical Data
Mixing Control 361
Variable Speed
Literature — D 361, A 361’s, D 001, D 070, E 021.
Control — Microprocessor PID control; This is not a safety (limit) control.
Packaged weight — 3.0 lb. (1380 g), Enclosure A, blue PVC plastic
Dimensions — 6-5/8” H x 7-9/16” W x 2-13/16” D (170 x 193 x 72 mm)
Approvals —
Ambient conditions — Indoor use only, 32 to 102°F (0 to 39°C), < 90% RH nonPower supply — 120 V ±10%, 50/60 Hz, 1650 VA
Variable Pump — 240 V (ac) 2.4 A (FLA) 5 A (LRA), fuse T2.5 A
Relays — 240 V (ac) 10 A 1/3 hp
Demand — 20 to 260 V (ac) 2 VA
Sensors included — NTC thermistor, 10 kΩ @ 77°F (25°C ±0.2°C) ß=3892
Optional devices — tekmar type #: 032, 076, 077.
CSA C US, CSA 22.2 No 24 and UL 873, meets class B: ICES & FCC Part 15.
condensing.
(ac)
Outdoor Sensor 070 and 2 of Universal Sensor 082.
MIX
OCC
Terminal
Unit
Item
Mixing Control 361
Variable Speed
2 3 4
1
Power
Mixing
Demand
L
503010
% Out
Sys
N
Pmp
VIEW
7090
5 6 7 8
Var
N
Pmp
F
°
Mixing
Demand
N
To increase or decrease the
building temperature:
Item
• Press the
,, buttons
simultaneously for 1 sec. to
ADJUST
menu
enter the
• Use the , buttons to
ROOM
adjust the
setting
VIEW
Display defaults back to
menu after 20 sec.
C US
11 12 13 14 15 16 17
910
UnO
Boiler
Sw
30% Enable
Advanced
Installer
10% Enable
Tes t
Made in Canada by
tekmar Control Systems Ltd.
tektra 913-01
Power:
120 V +10% 50/60 Hz 1650 VA
Variable Pump:
240 V (ac) 2.4 A (FLA) 5 A (LRA), fuse T2.5 A
Relays:
240 V (ac) 10 A 1/3 hp
Demand:
20 to 260 V (ac) 2 VA
Do not apply power
Com
Boil
Mix
Com
Out
Return
Boiler Sensor
Supply
Installer Instructions
ROOM
- Set to desired room temp.
OUTDR DSGN
- Set to coldest (design)
outdoor temp.
Terminal Unit Set to
High Mass Radiant
1
Low Mass Radiant
2
Fan Coil
3
Convector
4
Radiator
5
Baseboard
Indr
Signal wiring must be
rated at least 300V.
6
Meets Class B:
Canadian ICES
FCC Part 15
Refer to brochure for more information
H1188D
The installer must ensure that this control and its wiring are isolated and/or shielded from strong sources of electromagnetic noise.
Conversely, this Class B digital apparatus complies with Part 15 of the FCC Rules and meets all requirements of the Canadian
Interference-Causing Equipment Regulations. However, if this control does cause harmful interference to radio or television reception,
which is determined by turning the control off and on, the user is encouraged to try to correct the interference by reorienting or relocating
the receiving antenna, relocating the receiver with respect to this control, and/or connecting the control to a different circuit from that
to which the receiver is connected.
Cet appareil numérique de la classe B respecte toutes les exigences du Règlement sur le matériel brouilleur du Canada.
Date Code
Caution The nonmetallic enclosure does not provide grounding between conduit connections. Use grounding type bushings and jumper
wires.
Attention Un boîtier nonmétallique n’assure pas la continuité électrique des conduits. Utiliser des manchons ou des fils de accord
spécialement conçus pour la mise á la terre.
Limited Warranty and Product Return Procedure
Limited Warranty The liability of tekmar Control Systems Ltd. and tekmar
Control Systems, Inc. (“tekmar”) under this warranty is limited. The purchaser,
by taking receipt of the tekmar product (“product”), acknowledges receipt of
the terms of the warranty and acknowledges that it has read and
understands same.
tekmar warrants each tekmar product against defects in workmanship and materials, if the product is installed and used in compliance with tekmar's instructions. The
warranty period is for a period of twenty-four (24) months from the production date
if the product is not installed during that period, or twelve (12) months from the
documented date of installation if installed within twenty-four (24) months from the
production date.
The liability of tekmar under this warranty shall be limited to, at tekmar's sole discretion: the cost of parts and labor provided by tekmar to repair defects in materials
and/or workmanship of the defective product; or to the exchange of the defective
product for a replacement product; or to the granting of credit limited to the original
cost of the defective product, and such repair, exchange or credit shall be the sole
remedy available from tekmar, and, without limiting the foregoing in any way,
tekmar is not responsible, in contract, tort or strict product liability, for any
other losses, costs, expenses, inconveniences, or damages, whether direct, indirect, special, secondary, incidental or consequential, arising from ownership or use
of the product, or from defects in workmanship or materials, including any liability
for fundamental breach of contract.
This warranty applies only to those products returned to tekmar during the
warranty period. This warranty does not cover the cost of the parts or labor
to remove or transport the defective product, or to reinstall the repaired or
replacement product. Returned products that are not defective are not covered by this warranty.
This warranty does not apply if the product has been damaged by negligence
by persons other than tekmar, accident, fire, Act of God, abuse or misuse; or
has been damaged by modifications, alterations or attachments made subsequent to purchase which have not been authorized by tekmar; or if the
product was not installed in compliance with tekmar’s instructions and the
local codes and ordinances; or if due to defective installation of the product;
or if the product was not used in compliance with tekmar’s instructions.
This warranty is in lieu of all other warranties, express or implied, which the
Governing Law (being the law of British Columbia) allows parties to contractually exclude, including, without limitation, warranties of merchantability,
fitness for a particular purpose, durability or description of the product, its
non-infringement of any relevant patents or trademarks, and its compliance
with or non-violation of any applicable environmental, health or safety legislation; the term of any other warranty not hereby contractually excluded is
limited such that it shall not extend beyond twenty-four (24) months from the
production date, to the extent that such limitation is allowed by the Governing Law.
Product Return Procedure Products that are believed to have defects in work-
manship or materials must be returned, together with a written description of the
defect, to the tekmar representative for that territory. If the address of the representative is not known, please request it from tekmar at the telephone number
listed below
.
tekmar Control Systems Ltd., Canada
Control Systems
tekmar Control Systems, Inc., U.S.A.
Head Office: 5100 Silver Star Road
Vernon, B.C. Canada V1B 3K4
Tel. (250) 545-7749 Fax. (250) 545-0650
Web Site: www.tekmarcontrols.com
Product design, software and literature are Copyright © 2009 by:
tekmar Control Systems Ltd. and tekmar Control Systems, Inc.
20 of 20
All specifications are subject to change without notice.
Printed in Canada. D 361 - 03/09.
 Loading...
Loading...