Skil 3410 Instruction Manual

 3410 2610013681 ENG:2610008499 7/20/10 2:14 PM Page 1
3410 2610013681 ENG:2610008499 7/20/10 2:14 PM Page 1
IMPORTANT: |
IMPORTANT : |
IMPORTANTE: |
Read Before Using |
Lire avant usage |
Leer antes de usar |
|
|
|
Operating/Safety Instructions
Consignes de fonctionnement/sécurité
Instrucciones de funcionamiento y seguridad
3410
15
Amp
10” Bla |
de |
mm |
|
Hoja |
Ø |
254 |
mm |
Lame |
Ø 254 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Call Toll Free for |
Pour obtenir des informations et |
Llame gratis para |
|||
Consumer Information |
les adresses de nos centres de |
obtener información |
||||
|
& Service Locations |
|
service après-vente, |
para el consumidor y |
||
|
|
|
appelez ce numéro gratuit |
ubicaciones de servicio |
||
|
|
|
|
|||
|
1-877-SKIL999 (1-877-754-5999) www.skil.com |
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
For English Version |
|
Version française |
Versión en español |
|||
|
See page 2 |
|
Voir page 36 |
Ver la página 70 |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
 3410 2610013681 ENG:2610008499 7/20/10 2:14 PM Page 2
3410 2610013681 ENG:2610008499 7/20/10 2:14 PM Page 2
General Safety Rules
! |
WARNING |
“READ ALL INSTRUCTIONS” Failure to follow the safety rules listed below and other basic safety precautions |
may result in serious personal injury. |
||
|
|
|
Work Area
KEEP CHILDREN AWAY
Do not let visitors contact tool or extension cord. All visitors should be kept away from work area.
KEEP WORK AREAS CLEAN
Cluttered areas and benches invite accidents.
MAKE WORKSHOP CHILD-PROOF
With padlocks, master switches.
AVOID DANGEROUS ENVIRONMENTS
Don’t use power tools in damp or wet locations. Keep work area well-lit. Do not expose power tools to rain. Do not use tool in presence of flammable liquids or gases.
Electrical Safety
•Before plugging in the tool, be certain the outlet voltage supplied is compatible with the voltage marked on the nameplate within 10%. An outlet voltage incompatible with that specified on the nameplate can result in serious hazards and damage to the tool.
•Avoid body contact with grounded surfaces such as pipes, radiators, ranges and refrigerators. There is an increased risk of electric shock if your body is grounded.
•Do not expose power tools to rain or wet conditions.
Water entering a power tool will increase the risk of electric shock.
•Do not abuse the cord. Never use the cord to carry the tools or pull the plug from an outlet. Keep cord away from heat, oil, sharp edges or moving parts. Replace damaged cords immediately. Damaged cords increase the risk of electric shock.
•When operating a power tool outside, use an outdoor extension cord marked “W-A” or “W.” These cords are rated for outdoor use and reduce the risk of electric shock.
Personal Safety
KNOW YOUR POWER TOOL
Read and understand the owner’s manual and labels affixed to the tool. Learn its application and limitations as well as the specific potential hazards peculiar to this tool.
DON’T OVERREACH
Keep proper footing and balance at all times.
STAY ALERT
Watch what you are doing. Use common sense. Do not operate tool when you are tired. Do not operate while under medication or while using alcohol or other drug.
DRESS PROPERLY
Do not wear loose clothing or jewelry. They can be caught in moving parts. Rubber gloves and non-skid footwear are recommended when working outdoors. Wear protective hair covering to contain long hair.
USE SAFETY GOGGLES
Also face or dust mask if cutting operation is dusty, and ear plugs during extended periods of operation.
GUARD AGAINST ELECTRIC SHOCK
Prevent body contact with grounded surfaces. For example: pipes, radiators, ranges, refrigerator enclosures.
DISCONNECT TOOL FROM POWER SOURCE
When not in use, before servicing, when changing blades, bits, cutters, etc.
KEEP GUARDS IN PLACE
In working order, and in proper adjustment and alignment.
REMOVE ADJUSTING KEYS AND WRENCHES
When not in use, before servicing, when changing blades, bits, cutters, etc.
AVOID ACCIDENTAL STARTING
Make sure the switch is in the “OFF” position before plugging in tool.
NEVER STAND ON TOOL OR ITS STAND
Serious injury could occur if the tool is tipped or if the cutting tool is accidentally contacted. Do not store materials on or near the tool such that it is necessary to stand on the tool or its stand to reach them.
CHECK DAMAGED PARTS
Before further use of the tool, a guard or other part that is damaged should be carefully checked to ensure that it will operate properly and perform its intended function. Check for alignment of moving parts, mounting and any other conditions that may affect its operation. A guard or other part that is damaged should be properly replaced.
All repairs, electrical or mechanical, should be attempted only by trained repairmen.
Contact the nearest Skil Factory Service Center, Authorized Service Station or other competent repair service.
! |
WARNING |
Use only Skil replacement parts; any others |
|
may create a hazard. |
|||
|
|
! WARNING Use only accessories that are recommended by the manufacturer for
your model. Accessories that may be suitable for one tool may become hazardous when used on another tool.
“SAVE THESE INSTRUCTIONS”
2.

 3410 2610013681 ENG:2610008499 7/20/10 2:14 PM Page 3
3410 2610013681 ENG:2610008499 7/20/10 2:14 PM Page 3
General Safety Rules
Tool Use
DON’T FORCE TOOL
It will do the job better and safer at the rate for which it was designed.
USE THE RIGHT TOOL
Don’t force small tool or attachment to do the job of a heavyduty tool. Don’t use tool for purpose not intended — for example; don’t use circular saw for cutting tree limbs or logs.
SECURE WORK
Use clamps or a vise to hold work. It’s safer than using your hand and it frees both hands to operate the tool.
DIRECTION OF FEED
Feed work into a blade or cutter against the direction of rotation of the blade or cutter only.
NEVER LEAVE TOOL RUNNING UNATTENDED
Turn power off. Don’t leave tool until it comes to a complete stop.
Additional Safety Rules
Tool Care
DO NOT ALTER OR MISUSE TOOL
These tools are precision built. Any alteration or modification not specified is misuse and may result in dangerous conditions.
AVOID GASEOUS AREAS
Do not operate electric tools in gaseous or explosive atmo - spheres. Motors in these tools normally spark, and may result in a dangerous condition.
MAINTAIN TOOLS WITH CARE
Keep tools sharp and clean for better and safer performance. Follow instructions for lubricating and changing accessories. Inspect tool cords periodically and if damaged, have repaired by authorized service facility. Inspect extension cords periodically and replace if damaged. Keep handles dry, clean and free from oil and grease.
Before connecting the tool to a power source (receptacle, outlet, etc.), be sure voltage supplied is the same as that specified on the nameplate of
the tool. A power source with voltage greater than that specified for the tool can result in serious injury to the user — as well as damage to the tool. If in doubt, DO NOT PLUG IN THE TOOL. Using a power source with voltage less than the nameplate rating is harmful to the motor.
For your own safety, do not operate your ! WARNING table saw until it is completely assembled
and installed according to the instructions … and until you have read and understood the following:
1. General Safety Rules. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2–3 2. Additional Safety Rules . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3–5 3. Connection to a Power Source . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6 4. Extension Cords . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6 5. Getting To Know Your Table Saw . . . . . . . . . . 9–10 6. Assembly. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12–16 7. Adjustments . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17–20 8. Basic Table Saw Operation . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21–33 9. Maintaining Your Table Saw. . . . . . . . . . . . . 33–34
7. STABILITY OF SAW
Your table saw MUST BE BOLTED securely to a stand or workbench. In addition, if there is any tendency for the table saw to tip over or move during certain operations such as cutting long, heavy boards, use an auxiliary support.
8. LOCATION
Use the table saw in a well-lit area and on a level surface, clean and smooth enough to reduce the risk of trips and falls. Use it where neither the operator nor the casual observer is forced to stand in line with the blade.
9. KICKBACK
Kickbacks can cause serious injury: A “KICKBACK” occurs when a part of the workpiece binds between the sawblade and the rip fence or other fixed object. Workpiece binding the blade due to misalignment can also cause kickback. During kickback, workpiece rises from table and is thrown toward the operator. Keep your face and body to one side of the sawblade, out of line with a possible “KICKBACK.”
3.

 3410 2610013681 ENG:2610008499 7/20/10 2:14 PM Page 4
3410 2610013681 ENG:2610008499 7/20/10 2:14 PM Page 4
Additional Safety Rules
KICKBACKS AND POSSIBLE INJURY
CAN USUALLY BE AVOIDED BY:
a.Maintaining the rip fence parallel to the sawblade.
b.Keeping the sawblade sharp. Replacing or sharpening anti-kickback pawls when points become dull.
c.Keeping sawblade guard, spreader and anti-kickback pawls in place and operating properly. The spreader must be in alignment with the sawblade and the pawls must stop a kickback once it has started. Check their action before ripping.
d.NOT ripping workpiece that is twisted or warped or does not have a straight edge to guide along the rip fence.
e.NOT releasing work until you have pushed it all the way past the sawblade.
f.Using a Push Stick for ripping widths of 2" to 6" and an auxiliary fence and Push Block for ripping widths narrower than 2" (See “Basic Saw Operation, Using the Rip Fence” section, pages 27–28).
g.NOT confining the cut-off piece when ripping or crosscutting.
h.When ripping, apply the feed force to the section of the workpiece between the sawblade and the rip fence. Use Push Stick or Push Block when appropriate (see item f. above).
10. PROTECTION: Eyes, hands, face, ears and body.
! |
WARNING |
TO AVOID BEING PULLED INTO |
|
THE SPINNING TOOL, |
|||
|
|
||
DO NOT WEAR: Loose-Fitting Gloves |
|||
|
|
Loose Clothing |
|
|
|
Necktie, Jewelry |
|
DO: |
TIE BACK LONG HAIR |
||
|
ROLL LONG SLEEVES ABOVE ELBOWS |
||
a.If any part of your saw is missing, malfunctioning, has been damaged or broken … such as the motor switch, or other operating control, a safety device or the power cord … cease operating immediately until the particular part is properly repaired or replaced.
b.Wear safety goggles and a face shield if operation is dusty. Wear ear plugs or muffs during extended periods of operation. Small loose pieces of wood or other objects that contact the rear of the revolving blade can be thrown back at the operator at excessive speed. This can usually be avoided by keeping the guard and spreader in place for all “THRU-SAWING” operations (sawing entirely through the work) AND by removing all loose pieces from the table with a long stick of wood IMMEDIATELY after they are cut off.
c.Use extra caution when the guard assembly is removed for resawing, dadoing, rabbeting or molding — replace the guard as soon as that operation is completed.
d.NEVER turn the saw “ON” before clearing the table of all tools, wood scraps, etc., except the workpiece and related feed or support devices for the operation planned.
e. NEVER place your face or body in line with the cutting tool.
•NEVER place your fingers and hands in the path of the sawblade or other cutting tool.
•NEVER reach in back of the cutting tool with either hand to hold down or support the workpiece, remove wood scraps, or for any other reason. Avoid awkward operations and hand positions where sudden slip could cause fingers or hand to move into a sawblade or other cutting tool.
•DO NOT perform any operation “FREEHAND” — always use either the rip fence or the miter gauge to position and guide the work.
•NEVER use the rip fence when crosscutting or the miter gauge when ripping. DO NOT use the rip fence as a length stop.
•NEVER hold onto or touch the “free end” of the workpiece or a “free piece” that is cut off, while power is “ON” and/or the sawblade is rotating.
•Shut “OFF” the saw and disconnect the power cord when removing the table insert, changing the cutting tool, removing or replacing the blade guard, or making adjustments.
•Provide adequate support to the rear and sides of the saw table for wider or long workpieces.
•Plastic and composition (like hardboard) materials may be cut on your saw. However, since these are usually quite hard and slippery, the anti-kickback pawls may not stop a kickback. Therefore, be especially attentive to following proper setup and cutting procedures for ripping. Do not stand, or permit anyone else to stand, in line with a potential kickback.
f.If you stall or jam the sawblade in the workpiece, turn saw “OFF”, remove the workpiece from the sawblade, and check to see if the sawblade is parallel to the table slots or grooves and if the spreader is in proper alignment with the sawblade. If ripping at the time, check to see if rip fence is parallel with the sawblade. Readjust as indicated.
g.NEVER gang crosscut — lining up more than one workpiece in front of the blade (stacked vertically, or horizontally outward on the table) and then pushing through sawblade. The blade could pick up one or more pieces and cause a binding or loss of control and possible injury.
h.DO NOT remove small pieces of cut-off material that may become trapped inside the blade guard while the saw is running. This could endanger your hands or cause a kickback. Turn saw “OFF” and wait until blade stops.
4.
 3410 2610013681 ENG:2610008499 7/20/10 2:14 PM Page 5
3410 2610013681 ENG:2610008499 7/20/10 2:14 PM Page 5
Additional Safety Rules
11. KNOW YOUR CUTTING TOOLS
Dull, gummy or improperly sharpened or set cutting tools can cause material to stick, jam, stall the saw, or kickback at the operator. Minimize potential injury by proper cutting tool and machine maintenance. NEVER ATTEMPT TO FREE A STALLED SAWBLADE WITHOUT FIRST TURNING THE SAW OFF.
a.NEVER use grinding wheels, abrasive cut-off wheels, friction wheels (metal slitting blades) wire wheels or buffing wheels.
b.USE ONLY RECOMMENDED ACCESSORIES.
c.Crosscutting operations are more conveniently worked and with greater safety if an auxiliary wood facing is attached to the miter gauge (see page 24).
d. Make sure the top of the cutting tool rotates toward you when standing in normal operating position. Also make sure the cutting tool, arbor collars and arbor nut are installed prop - erly. Keep the cutting tool as low as possible for the operation being performed. Keep all guards in place whenever possible.
• Do not use any blade or other cutting tool marked for an operating speed less than 5000 R.P.M. Never use a cutting tool larger in diameter than the diameter for which the saw was designed. For greatest safety and efficiency when ripping, use the maximum diameter blade for which the saw is designed, since under these conditions the spreader is nearest the blade.
e.Make sure the table insert is flush or slightly below the table surface on all sides except for rear side. NEVER operate the saw unless the proper insert is installed.
f.Do not perform plunge cut operation.
NOTE AND FOLLOW SAFETY INSTRUCTIONS THAT APPEAR
ON THE FRONT OF YOUR TABLE SAW.
12. THINK SAFETY
SAFETY IS A COMBINATION OF OPERATOR COMMON SENSE AND ALERTNESS AT ALL TIMES WHEN THE TABLE SAW IS BEING USED.
Do not allow familiarity (gained from fre- ! WARNING quent use of your table saw) to become
commonplace. Always remember that a careless fraction of a second is sufficient to inflict severe injury.
The operation of any power tool can result in foreign objects being
thrown into the eyes, which can result in severe eye damage. Always wear safety goggles that comply with ANSI Z87.1 (shown on package) before
commencing power tool operation.
Some dust created by power sanding, ! WARNING sawing, grinding, drilling, and other
construction activities contains chemicals known to cause cancer, birth defects or other reproductive harm. Some examples of these chemicals are:
•Lead from lead-based paints,
•Crystalline silica from bricks and cement and other masonry products, and
•Arsenic and chromium from chemically treated lumber.
Your risk from these exposures varies, depending on how often you do this type of work. To reduce your exposure to these chemicals: work in a well-ventilated area, and work with approved safety equipment, such as those dust masks that are specially designed to filter out microscopic particles.
5.

 3410 2610013681 ENG:2610008499 7/20/10 2:14 PM Page 6
3410 2610013681 ENG:2610008499 7/20/10 2:14 PM Page 6
Connection to a Power Source
This machine must be grounded while in use to protect the operator from electric shock.
Plug power cord into a 110-120V properly grounded type outlet protected by a 15-amp dual element time delay fuse or circuit breaker.
Not all outlets are properly grounded. If you are not sure that your outlet, as pictured on this page, is properly grounded, have it checked by a qualified electrician.
! |
DANGER |
To avoid electric shock, do not touch the |
|
metal prongs on the plug when installing or |
|||
|
|||
|
|
||
removing the plug to or from the outlet. |
|||
|
|
Failure to properly ground this power tool |
|
! |
DANGER |
||
can cause electrocution or serious shock, |
|||
|
|||
|
|
||
particularly when used near metal plumbing or other metal objects. If shocked, your reaction could cause your hands to hit the tool.
If power cord is worn, cut or damaged in ! DANGER any way, have it replaced immediately to
avoid shock or fire hazard.
Your unit is for use on 120 volts; it has a plug that looks like the one shown on this page.
This power tool is equipped with a 3-conductor cord and  grounding type plug, approved by Underwriters Laboratories and the Canadian Standards Association. The ground conductor has a green jacket and is attached to the tool housing at one end and to the ground prong in the
grounding type plug, approved by Underwriters Laboratories and the Canadian Standards Association. The ground conductor has a green jacket and is attached to the tool housing at one end and to the ground prong in the  attachment plug at the other end.
attachment plug at the other end.
If the outlet you are planning to use for this power tool is of the two-prong type, DO NOT REMOVE OR ALTER THE GROUNDING PRONG IN ANY MANNER. Have a qualified electrician replace the TWO-prong outlet with a properly grounded THREE-prong outlet.
Improper connection of the equipment-grounding conductor can result in a risk of electric shock. The conductor with insulation having an outer surface that is green with or without yellow stripes is the equipment conductor. If repair or replacement of the electric cord or plug is necessary, do not connect the equipment-grounding conductor to a live terminal.
Check with a qualified electrician or service personnel if the grounding instructions are not completely understood, or if in doubt as to whether the tool is properly grounded.
Extension Cords
! WARNING Replace damaged cords immediately. Use of damaged cords can shock, burn or
electrocute.
Always use proper extension cord. If an extension cord is necessary, a cord with adequate size conductors should be used to prevent
excessive voltage drop, loss of power or overheating. The table shows the correct size to use, depending on cord length and nameplate amperage rating of tool. If in doubt, use the next heavier gauge. Always use U.L. and CSA listed extension cords.
Always use proper extension cord. The use of any extension cord will cause some loss of power. To keep this to a minimum and to prevent overheating and motor burn-out, use the table to determine the minimum wire size (A.W.G.) extension cord. Use only 3-wire extension cords which have 3-prong grounding type plugs and 3-pole receptacles which accept the tool’s plug. Make sure your extension cord is in good condition.
RECOMMENDED SIZES OF EXTENSION CORDS 120 VOLT ALTERNATING CURRENT TOOLS
Tool’s |
Cord Size in A.W.G. |
Wire Sizes in mm2 |
|||||||
Ampere |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Cord Length in Feet |
Cord Length in Meters |
||||||||
Rating |
|||||||||
25 |
50 |
100 |
150 |
15 |
30 |
60 |
120 |
||
|
|||||||||
3-6 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
18 |
16 |
16 |
14 |
.75 |
.75 |
1.5 |
2.5 |
||
6-8 |
18 |
16 |
14 |
12 |
.75 |
1.0 |
2.5 |
4.0 |
|
8-10 |
18 |
16 |
14 |
12 |
.75 |
1.0 |
2.5 |
4.0 |
|
10-12 |
16 |
16 |
14 |
12 |
1.0 |
2.5 |
4.0 |
— |
|
12-16 |
14 |
12 |
— |
— |
— |
— |
— |
— |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
NOTE: The smaller the gauge number, the heavier the cord.
“SAVE THESE INSTRUCTIONS”
6.

 3410 2610013681 ENG:2610008499 7/20/10 2:14 PM Page 7
3410 2610013681 ENG:2610008499 7/20/10 2:14 PM Page 7
Table of Contents
|
Page |
General Safety Rules..................................................... |
2–3 |
Additional Safety Rules.................................................. |
3–5 |
Connection to a Power Source & Extension Cords ........... |
6 |
Table of Contents............................................................... |
7 |
Glossary of Terms.............................................................. |
8 |
Tools Needed for Assembly .......................................... |
8 |
Getting To Know Your Table Saw................................ |
9–10 |
Power Switch ................................................................ |
9 |
Table ............................................................................. |
9 |
Base .............................................................................. |
9 |
Blade Bevel Lock Handle .............................................. |
9 |
Table Extension ............................................................ |
9 |
Table Extension Lock Lever.......................................... |
9 |
Elevation Wheel ............................................................ |
9 |
Blade Bevel Scale ......................................................... |
9 |
Rip Fence Scale............................................................ |
9 |
Miter Gauge .................................................................. |
9 |
Rip Fence Storage ........................................................ |
9 |
Miter Gauge Storage..................................................... |
9 |
Blade Storage & Wrench............................................... |
9 |
Cord Wrap..................................................................... |
9 |
Rip Fence...................................................................... |
9 |
Smart Guard System................................................... |
10 |
Smart Guard System Storage ..................................... |
10 |
Table Insert ................................................................. |
10 |
Push Stick ................................................................... |
10 |
Stand........................................................................... |
10 |
Unpacking and Checking Contents.................................. |
11 |
Table of Loose Parts ................................................... |
11 |
Assembly ................................................................... |
12–16 |
Assembling the Stand ................................................. |
12 |
Mounting Saw to Stand ............................................... |
12 |
Attaching the Smart Guard System....................... |
13–14 |
Changing the Blade..................................................... |
15 |
Attaching Rip Fence.................................................... |
16 |
|
Page |
Mounting the Table Saw .................................................. |
16 |
Adjustments ............................................................... |
17–20 |
Adjusting 0° and 45° Positive Stops............................ |
17 |
Adjusting Blade Parallel to the Miter Gauge Slots |
......18 |
Aligning Rip Fence ...................................................... |
19 |
Rip Fence Pointer Adjustment .................................... |
19 |
Riving Knife Alignment ................................................ |
20 |
Basic Table Saw Operation ....................................... |
21–33 |
Safety Power Switch ................................................... |
21 |
Smart Guard System................................................... |
21 |
Blade Bevel Control .................................................... |
22 |
Extending Table Extension ......................................... |
22 |
Work Helpers .............................................................. |
23 |
Push Stick and Push Block ......................................... |
23 |
Auxiliary Fence............................................................ |
23 |
Making a Featherboard ............................................... |
23 |
Using the Miter Gauge ................................................ |
24 |
Crosscutting ................................................................ |
25 |
Repetitive Cutting........................................................ |
26 |
Miter Cutting................................................................ |
26 |
Bevel Crosscutting ...................................................... |
27 |
Compound Miter Cutting ............................................. |
27 |
Using the Rip Fence.............................................. |
27–28 |
Ripping ........................................................................ |
29 |
Non Thru-Sawing ........................................................ |
30 |
Rabbeting.................................................................... |
30 |
Dado Cutting ......................................................... |
31–32 |
Special Cutting Techniques ........................................ |
33 |
Cutting Metals and Masonry ....................................... |
33 |
Maintaining Your Table Saw ...................................... |
33–34 |
Maintenance.......................................................... |
33–34 |
Lubrication................................................................... |
34 |
Troubleshooting ............................................................... |
35 |
7.

 3410 2610013681 ENG:2610008499 7/20/10 2:14 PM Page 8
3410 2610013681 ENG:2610008499 7/20/10 2:14 PM Page 8
Glossary of Terms
WORKPIECE
The item on which the cutting operation is being performed. The surfaces of a workpiece are commonly referred to as faces, ends and edges.
ANTI-KICKBACK PAWLS
Device which, when properly maintained, is designed to stop the workpiece from being kicked back at the operator during operation.
ARBOR
The shaft on which a cutting tool is mounted.
BEVEL
Blade angle relative to the table surface.
CROSSCUT
A cutting or shaping operation made across the width of the workpiece cutting the workpiece to length.
DADO
A non-through cut which produces a square sided notch or trough in the workpiece.
FEATHERBOARD
A device which can help guide workpieces during rip type operation by keeping workpiece in contact with the rip fence. It also helps prevent kickback.
FREEHAND
Performing a cut without a fence, miter gauge, fixture, hold down or other proper device to keep the workpiece from twisting during the cut.
GUM
A sticky, sap-based residue from wood products. After it has hardened, it is referred to as “RESIN.”
HEEL
Misalignment of the blade which causes the trailing or outfeed side of the blade to contact the cut surface of the workpiece. Heel can cause kickback, binding, excessive force,
burning of the workpiece or splintering. In general, heel creates a poor quality cut and can be a safety hazard.
KERF
The space in the workpiece where the material was removed by the blade.
KICKBACK
An uncontrolled grabbing and throwing of the workpiece back toward the front of the saw during a rip-type operation.
LEADING END
The end of the workpiece which, during a rip-type operation, is pushed into the cutting tool first.
MOLDING
A non-through cut which produces a special shape in the workpiece used for joining or decoration.
NON THRU-SAWING
Any cutting operation where the blade does not extend through the workpiece (e.g. Dado, Rabbet).
PUSH STICK
A device used to feed the workpiece through the saw during narrow ripping-type operation and helps keep the operator’s hands well away from the blade. Use the Push Stick for rip widths less than 6" and more than 2".
PUSH BLOCK
A device used for ripping-type operations too narrow to allow use of a Push Stick. Use a Push Block for rip widths less than 2".
RABBET
A notch in the edge of a workpiece. Also called an edge dado.
RIPPING
A cutting operation along the length of the workpiece cutting the workpiece to width.
REVOLUTIONS PER MINUTE (R.P.M.)
The number of turns completed by a spinning object in one minute.
Tools Needed for Assembly
COMBINATION SQUARE MUST BE TRUE
|
|
|
STRAIGHT EDGE OF BOARD 3/4" |
|
|
|
THICK. THIS EDGE MUST BE |
FLAT SCREWDRIVER |
PHILLIPS SCREWDRIVER |
DRAW LIGHT LINE ON |
PERFECTLY STRAIGHT. |
|
|
BOARD ALONG THIS EDGE. |
|
|
1/2 or 13 mm WRENCH |
SHOULD BE NO GAP OR OVERLAP |
COMBINATION SQUARE |
OR ADJUSTABLE WRENCH |
HERE WHEN SQUARE IS FLIPPED |
|
|
OVER IN DOTTED POSITION. |
8.

3410 2610013681 ENG:2610008499 7/20/10 2:14 PM Page 9
Getting To Know Your Table Saw
1. POWER SWITCH
Switch incorporates hole for use with padlock to prevent accidental starting.
2. TABLE
Provides large working surface to support workpiece.
3. BASE
Supports table saw. Holes are provided in base to bolt the saw to a workbench or stand.
4.BLADE BEVEL LOCK HANDLE
Locks the blade to desired bevel angle.
5.TABLE EXTENSION
Provides a larger work surface for wider workpieces.
6. TABLE EXTENSION LOCK LEVER
Allows you to lock the table extension at desired distances. Also prevents use of table saw with unlocked extension.
7. ELEVATION WHEEL
Elevates or lowers the blade. Also used to tilt the blade 0° to 45°.
8. BLADE BEVEL SCALE
Shows the degree the blade is tilted.
9. RIP FENCE SCALE
Shows the distance from the blade to rip fence through a convenient viewing and magnifying window. Upper portion of scale can be used up to 18". Lower portion of scale is used for cuts beyond 18".
10. MITER GAUGE
Head can be locked in desired position for crosscutting or mitering by tightening the lock knob. ALWAYS SECURELY LOCK IT WHEN IN USE.
11. RIP FENCE STORAGE
Conveniently stores rip fence when not in use.
12. MITER GAUGE STORAGE
Conveniently stores miter gauge when not in use.
13. BLADE STORAGE & WRENCH
Allows you to store 10" blades and arbor wrench.
14. CORD WRAP
Allows you to easily secure the cord so it’s out of the way when transporting or storing.
15. RIP FENCE
Exclusive Self-Aligning rip fence can be easily moved or locked in place by simply raising or lowering lock handle.
FIG. 1 |
16 |
|
|
18 |
5 |
||
10 |
|||
2 |
|
|
17 






14 













 12
12 
1
4
15 |
Amp |
||
|
|||
Blade |
|
||
10” |
Ø 254mm |
||
Hoja |
|
254mm |
|
Lame Ø |
|
|
|
8
7
FIG. 2
13
11
15  9
9
6
3
 20
20
19
9.

3410 2610013681 ENG:2610008499 7/20/10 2:14 PM Page 10
Getting To Know Your Table Saw
16. SMART GUARD SYSTEM
Consists of three key elements: Adjustable (3 position) Riving Knife, Anti-Kickback Device and Barrier Guard Device. All of these are part of a modular system that requires no tools to assemble or unassemble. This Guard System must always be in place and working properly for all thru-sawing cuts.
17. SMART GUARD SYSTEM STORAGE
When not in use, the Main Barrier Guard and Anti-Kickback Device can be stored under the right side table extension.
18. TABLE INSERT
Removable for removing or installing blade or other cutting tools.
19. PUSH STICK
Allows you to rip smaller pieces of stock with a greater level of safety.
20. STAND
Allows table saw to be raised during use.
General Specifications
Voltage Rating............................................................... |
120 V, 60 Hz |
Amperage Rating ......................................................................... |
15A |
No Load Speed............................................................. |
No 5,000/min |
Sawing Capacity ............................................... |
3.5" (8.89 cm) at 90° |
|
2.5" (6.35 cm) at 45° |
|
13/16" (2.06 cm) with dado |
Table Size........................................................................... |
19 x 32.5" |
FIG. 1 |
|
16 |
|
18 |
|
2 |
|
17 







14 















 12
12 
1
4
FIG. 2
10 5 15
9
15 |
Amp |
|
||
|
6 |
|||
Blade |
|
|||
10” |
Ø 254mm |
|||
Hoja |
|
254mm |
||
Lame Ø |
|
|
|
|
3
8
 20
20
7
13
11 |
19 |
10.

 3410 2610013681 ENG:2610008499 7/20/10 2:14 PM Page 11
3410 2610013681 ENG:2610008499 7/20/10 2:14 PM Page 11
Unpacking and Checking
Contents
To avoid injury from unexpected starting or ! WARNING electrical shock during unpacking and setting up,
do not plug the power cord into a source of power. This cord must remain unplugged whenever you are working on the table saw.
Model 3410 Table Saw is shipped complete in one carton.
Separate all parts from packing materials and check each one with the illustration and the list of Loose Parts to make certain all items are accounted for before discarding any packing material (Fig. 3).
! |
WARNING |
If any parts are missing, do not attempt to |
|
assemble the table saw, plug in the power cord or |
|||
|
|
turn the switch on until the missing parts are obtained and are installed correctly.
Table of Loose Parts
ITEM |
DESCRIPTION |
QTY. |
1 |
Table Saw Assembly |
1 |
2 |
Rip Fence |
1 |
3 |
Table Insert |
1 |
4 |
Barrier Guard Assembly |
1 |
5 |
Anti-Kickback Device |
1 |
6 |
Miter Gauge |
1 |
7 |
Push Stick |
1 |
8 |
Outfeed Assembly |
1 |
|
TABLE SAW STAND |
|
9 |
Leg (A) |
4 |
10 |
Front - Top Rail (20-1/4" Long) (B) |
2 |
11 |
Front - Bottom Rail (24-1/4" Long) (C) |
2 |
12 |
Side - Top Rail (17-3/4" Long) (D) |
2 |
13 |
Side - Bottom Rail (21-3/4" Long) (E) |
2 |
14 |
Carriage Bolt (5/16" - 18 x 5/8") |
24 |
15 |
Hex Nut (5/16" - 18) |
24 |
16 |
Leg Pad |
4 |
|
PARTS FOR TABLE SAW MOUNTING |
|
17 |
Hex Bolt (5/16" - 18 x 1-3/4") |
4 |
18 |
Flat Washer (5/16") |
4 |
19 |
Hex Nut (5/16" - 18) |
4 |
NOTE: Remove styrofoam block (for shipping purpose only) located between the table and motor (Fig. 4). You may cause damage to the blade elevation system if trying to raise blade if styrofoam is not removed.
Assembly Time
The expected time to assemble and properly adjust this saw is two hours.
FIG. 3 |
4 |
5 |
2 |
|
|
7 |
|
8 |
6 |
3 |
15 |
Amp |
||
|
|||
Blade |
|
||
10” |
Ø 254mm |
||
Hoja |
|
254mm |
|
Lame Ø |
|
|
|
1
|
12 |
10 |
|
11 |
13 |
|
|
|
16 |
|
17 |
9 |
18 |
|
|
|
19 |
14 |
15 |
FIG. 4
11.

 3410 2610013681 ENG:2610008499 7/20/10 2:14 PM Page 12
3410 2610013681 ENG:2610008499 7/20/10 2:14 PM Page 12
Assembly
Assembling the Leg Stand
After completing adjustments, securely tighten all fasteners. An unstable stand may shift in use
and cause serious personal injury.
! WARNING |
The stamped rails may have sharp edges. Be |
|
careful in handling the rails to prevent being cut. |
NOTE: Use the screws 1 and lock nuts 2 supplied in the hardware kit to attach the pieces of the leg stand together (Fig. 6). Do not tighten the hardware completely until the leg stand is completely assembled.
The following letters are stamped on pieces for identification:
A - Legs (qty. 4).
B - Front and rear top plates (qty. 2).
C - Front and rear support plates (qty. 2). D - Side top plates (qty. 2).
E - Side support plates (qty. 2).
1.Attach the side top plates D to the legs A.
2.Attach the side support plates E to the legs A.
3.Place the front and rear top plates B over the side top plates D and attach to the legs A.
4.Attach the front and rear support plates C to the legs A.
5.Tap the four rubber feet 3 onto the bottom of the legs A.
Mounting the Table Saw
to the Leg Stand
NOTE: Mount the table saw to the leg stand using the hardware supplied in the hardware kit.
1.Place the table saw onto the assembled leg stand so that the four (4) mounting holes in the base of the saw are over the four (4) mounting holes in the front and rear top plates (Fig. 7).
2.Secure the table saw to the leg stand using four (4) bolts 4, washers 5, and lock nuts 6.
IMPORTANT! When mounting the table saw to the leg stand, DO NOT overtighten the mounting hardware.
Before operating table saw, securely fasten table saw to stand and entire unit must be
placed on solid, level surface.
! |
WARNING |
Do not stand on table saw stand or use as |
|
|
ladder or scaffolding. |
|
|
Do not use table saw if stand tips, slides, or |
! |
WARNING |
|
|
|
moves in any way. |
FIG. 5
|
|
A |
1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
B |
D |
|
|
|
|
|
A |
C 2 |
E |
|
|
|
|
|
|
D |
|
1 |
|
2 |
B |
|
|
E |
C |
|
|
|
3
A

 3
3
FIG. 7
15 |
Amp |
||
|
|||
10” Blade |
mm |
||
Hoj |
a Ø 254 |
|
|
|
254mm |
||
Lame Ø |
|
|
|
FIG. 6
A
3
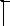

 4
4
5
6
12.

 3410 2610013681 ENG:2610008499 7/20/10 2:14 PM Page 13
3410 2610013681 ENG:2610008499 7/20/10 2:14 PM Page 13
Attaching the Smart Guard
System
FIG. 8
To prevent personal injury, always disconnect plug from power source before attaching or
removing the Smart Guard System.
POSITIONING THE RIVING KNIFE
1.Remove table insert using finger hole.
2.Raise the blade as high as it will go and set it perpendicular to table (0° on bevel scale) (Fig. 8).
3.Rotate the riving knife release lever 1 clockwise, so that it points upward (Fig. 8).
4. Pull riving knife 2 towards release lever to disengage it from the pins 3.
5.Slide the riving knife 2 up to its highest position, so that it is directly over the center of the blade (Fig. 9).
6.Align holes in riving knife with pins 3 and lock the release lever 1 by rotating it counterclockwise. Push/pull riving knife to verify that it is locked in place (Fig. 9).
7.Replace table insert (Fig. 10).
FIG. 9
2
1
2
3
1
13.

 3410 2610013681 ENG:2610008499 7/20/10 2:14 PM Page 14
3410 2610013681 ENG:2610008499 7/20/10 2:14 PM Page 14
ATTACHING THE GUARD ASSEMBLY
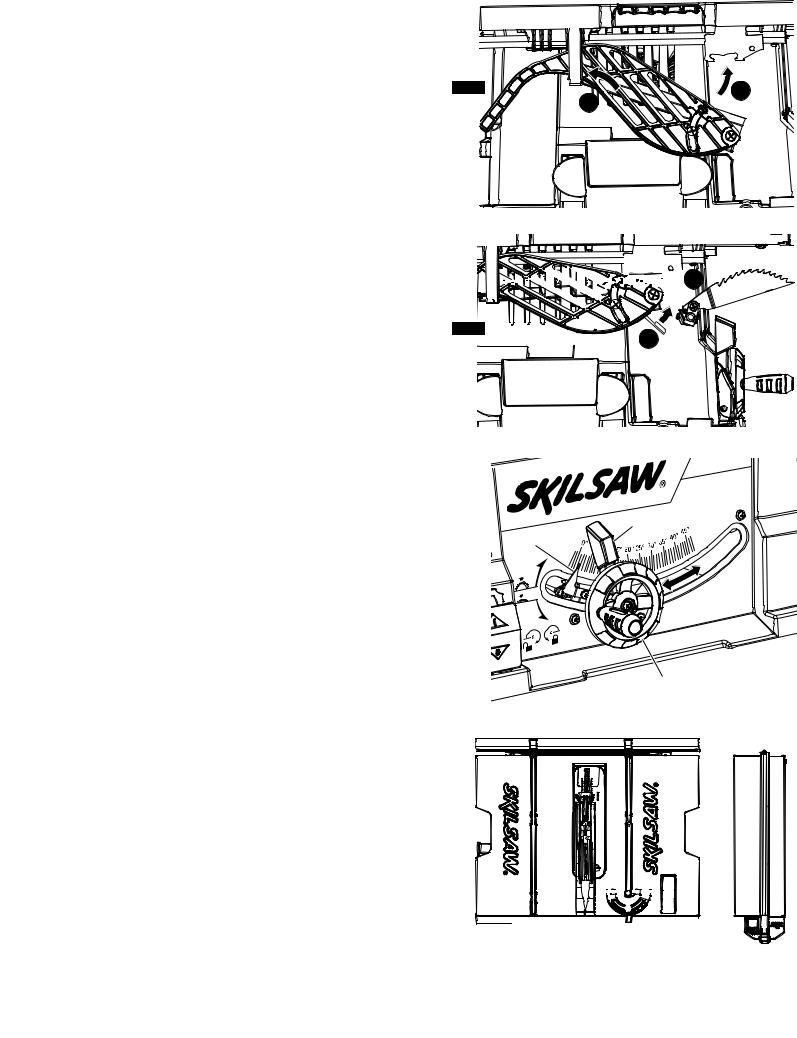
8.With one hand, hold the front of the barrier guard assembly 4 by the metal “fork.” With the other hand, hold the guard release lever 5 up (Fig. 10).
FIG. 10
9.Lower the rear of guard assembly and slip the cross bar 6 into the rear notch 7 on top of the riving knife 2 (Fig. 10).
10.Lower the front of the guard assembly 4 until the metal “fork” is parallel with the table (Fig. 11).
11.Press down on the guard release lever 5 until you feel and hear it snap into the locking position. Check that the guard assembly is securely connected (Fig. 11).
ATTACHING THE ANTI-KICKBACK DEVICE
12. Attach the Anti-Kickback Device 7 into the flat recessed area 8 of the riving knife 2 (Fig. 12).
13. Squeeze the compression pads 9 while nesting the device into the flat area (Fig. 12).
14. Release the compression pads such that the Anti-Kickback
Device locks onto the riving knife immediately behind the
FIG. 11
guard assembly. Check that the attachment pin is securely connected into locking hole. Carefully raise and lower the pawls 10 – when letting go, the spring-loaded pawls must come down and contact the table insert (Fig. 12).
Hint: Position the Anti-Kickback Device behind the flat recessed area and slide it towards the front until it drops into the recessed area – then release the compression pins.
Note: The two attachments are independant of each other, so the Anti-Kickback Device can be attached before the Guard Assembly.
ATTACHING THE OUTFEED ASSEMBLY
FIG. 12
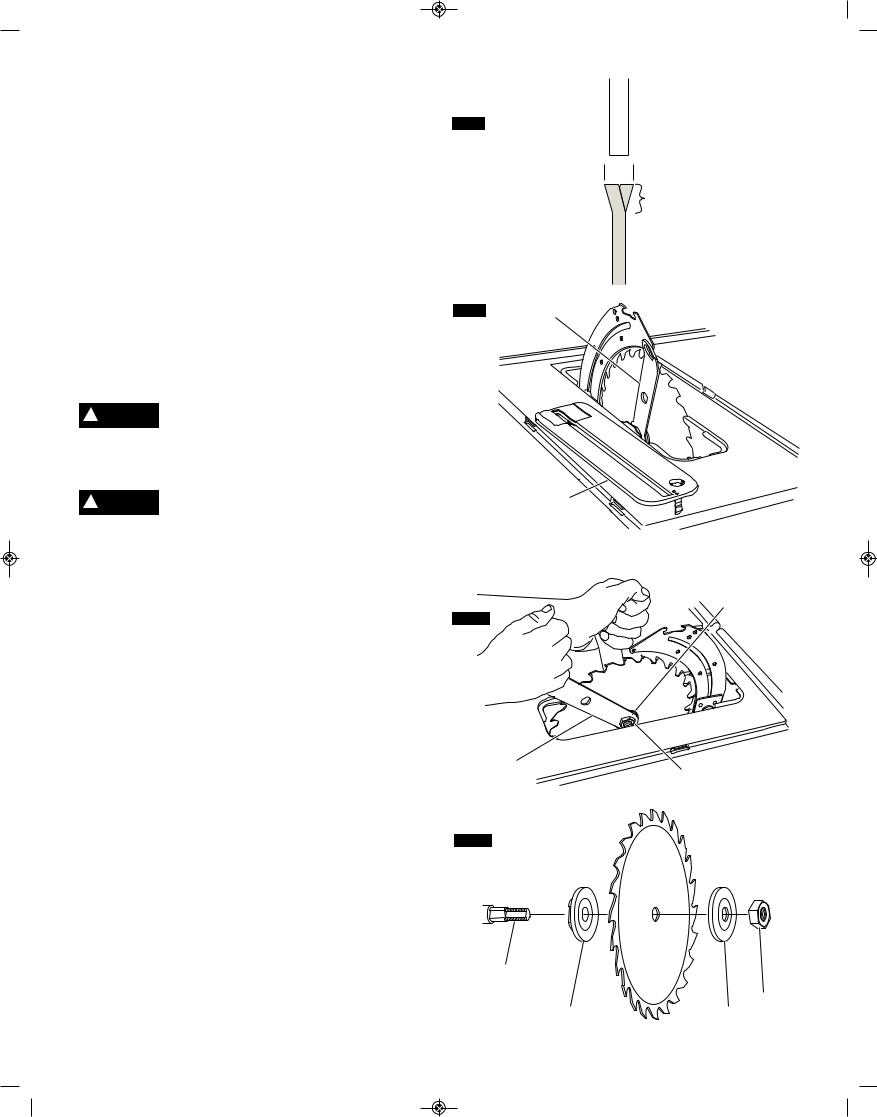
1.Attach the steel outfeed support 1 using the screws and washers 2 (Fig. 13).
2.Tighten the screws using a Phillips screwdriver.
FIG. 13
 2 1
2 1
4
5
7
6
 2
2
4 |
5 |
7 9
9
10
 8
8
 2
2
14.
 3410 2610013681 ENG:2610008499 7/20/10 2:14 PM Page 15
3410 2610013681 ENG:2610008499 7/20/10 2:14 PM Page 15
Changing the Blade
! |
WARNING |
To prevent personal injury, always discon- |
|
nect plug from power source before chang- |
|||
|
|
ing blades.
Using the Correct Blade
IMPORTANT: The saw blade provided on this tool has a carbide-tipped kerf width of .128" and a plate (body) thickness that is .086" thick. When looking for a replacement blade, select one with dimensions close to the original blade. This information may not be printed on the blade’s packaging. If not, check the manufacturer’s catalog or website. Skil offers an extensive line of Premium-Quality Professional Saw Blades that match the requirements for this tool. You must select a blade with a kerf width of .092" or more and a plate (body) thickness .088" or less (Fig. 14).
! |
WARNING |
To reduce the risk of injury, do not use extra |
|
thin kerf saw blades. The kerf of the blade |
|||
|
|
must be wider than .092". Extra thin kerf saw blades (less than
.092") may cause the workpiece to bind against the riving knife during cutting. It is recommended that the kerf of the replacement blade used on this saw be .092" or more.
To reduce the risk of injury, do not use saw blades made with a thick body plate. If the replacement saw blade’s plate thickness is greater than .088",
the riving knife would not properly serve as an aid to reduce kickback. The replacement blade’s plate thickness must be less than .088".
To reduce the risk of injury, do not use blade “dampeners,” “stabilizers” or “stiffening collars” on both sides of a replacement blade. These are
metal plates positioned against the sides of the blade to reduce deflection that may occur when using thin saw blades. Use of these devices on both sides will prevent the blade from being properly aligned with the riving knife, which may bind the workpiece during cutting. One “stabilizer” plate may be placed only against the outside of a thin replacement blade. These plates are not required with the supplied Skil blade.
Changing the Blade
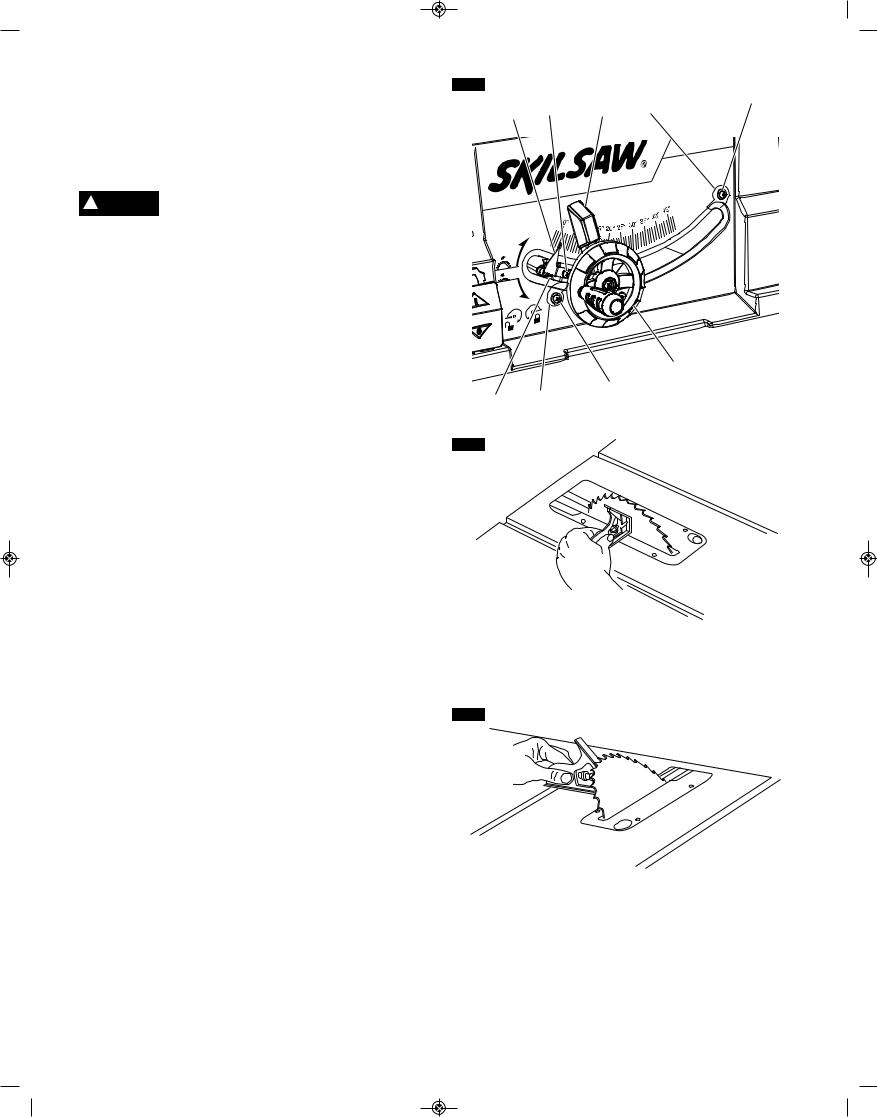
1.Turn elevation wheel clockwise until the blade is up as high as it will go, remove table insert 1 using finger hole (Fig. 15).
2.Insert the wrench 2 next to the blade onto the arbor shaft (Fig. 15). Slowly rotate the blade by hand until the wrench fully engages on the two flats on the arbor shaft. While holding the first wrench, loosen the arbor nut 3 counterclockwise using the other arbor wrench 4 (Fig. 16). Set wrench aside and continue to loosen arbor nut 3 by hand and remove arbor nut 3 and outer washer 5. Blade may now be removed or installed by sliding on or off arbor shaft 6.
3.Assemble inner washer 7 and new blade as shown in figure 17, making certain the TEETH OF THE BLADE ARE POINTING DOWN AT THE FRONT OF THE TABLE.
NOTE: The printing on different saw blades are not always on the same side.
4.Assemble outer washer 5, arbor nut 3 as shown in figure 17. While holding arbor shaft with wrench 2 securely tighten arbor nut 3 clockwise with the wrench 4 (Fig. 16).
5.Position table insert in pocket of table so tab on table insert is in slots in pocket of table and push down and secure in place.
.090" 
FIG. 14
MUST BE .092" OR MORE 
DOIT ÊTRE DE 0,092 po OU PLUS DEBE SER 0.092 PULGADAS O MÁS
MUST BE LESS THAN .088" 
DOIT ÊTRE DE MOINS DE 0,088 po DEBE SER MENOS DE 0.088 PULGADAS
FIG. 15 |
2 |
|
1
FIG. 16
4
FIG. 17
6
7
 RIVING KNIFE
RIVING KNIFE
COUTEAU DIVISEUR
CUCHILLA SEPARADORA
KERF WIDTH
 LARGEUR DE VOIE
LARGEUR DE VOIE
ANCHURA DE LA SECCIÓN DE CORT
BLADE TEETH
DENTS DE LA SCIE
DIENTES DE LA HOJA
 BLADE BODY PLATE
BLADE BODY PLATE
PLAQUE DU CORPS DE LA LAME PLACA DEL CUERPO DE LA HOJA
5
3
3
5
15.

 3410 2610013681 ENG:2610008499 7/20/10 2:14 PM Page 16
3410 2610013681 ENG:2610008499 7/20/10 2:14 PM Page 16
|
Assembly |
FIG. 18 |
|
4 |
|
Attaching Rip Fence |
|
|
1 |
1. |
Raise rip fence handle 1, so holding clamp 2 is out far enough |
|
|
|
2 |
2 |
|
||
|
to fit on the table 3 (Fig. 18). |
3 |
||
2. |
Position the rip fence 4 over table 3 holding up the front |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
end, first engage holding clamp 2 with rear rail. |
|
|
|
3. Lower front end onto front rail 5.
15 |
Amp |
||
|
|||
10” |
Blade |
|
|
|
Ø 254mm |
||
Hoja |
Ø 25 |
4mm |
|
Lame |
|
||
|
|
||
3
1
5
Mounting the |
|
FIG. 19 |
|
Table Saw |
|
If table saw is to be used in a permanent location, it should be fastened securely to a firm supporting surface such as a stand or workbench, using the four mounting holes 6 (Fig. 19).
1. If mounting to a workbench, the base should be bolted securely using 5/16" hex bolts (not included) through mounting holes 6.
Hint: If workbench is 3/4" thick, bolts will have to be at least 3-1/2" long - if workbench is 1-1/2" thick, bolts should be at least 4-1/2" long.
2. Locate and mark where the saw is to be mounted, relative to holes in the base of the tool.
3.Drill four (4) 3/8" diameter holes through workbench.
4.Place table saw on workbench aligning holes in base with holes drilled in workbench.
5.Insert four (4) 5/16" diameter bolts through holes in base and supporting surface; then secure with (4) 5/16" flat washers and (4) 5/16" hex nuts.
15 |
Amp |
|
|
||
10” Blade |
|
|
Hoja |
Ø 254mm |
|
Lame |
Ø |
|
5/16 Hex Bolt
Washer & Hex
Nut - X 4
16.
 3410 2610013681 ENG:2610008499 7/20/10 2:14 PM Page 17
3410 2610013681 ENG:2610008499 7/20/10 2:14 PM Page 17
Adjustments FIG. 20
3
Adjusting 0° and 45° Positive Stops
Your saw is equipped with positive stops for fast and accurate positioning of the saw blade at 90° and 45° to the table.
To prevent personal injury, always disconnect ! WARNING plug from power source when making
adjustments.
1.Turn elevation wheel 2 clockwise and raise blade to maximum 
height (Fig. 20).
Adjusting 0° Positive Stop:
2. Loosen the blade tilt lock handle 1 and push the elevation wheel 2 to the left as far as possible and tighten the blade tilt lock handle 1 (Fig. 20).
3. Place a combination square on the table with one end of square against the blade as shown (Fig. 21), and check to see
if the blade is 90° to the table. If the blade is not 90° to the
table, loosen the blade tilt lock handle 1, loosen 90° 7 adjustment screw 4, loosen 90° bevel stop cam 5 and push
the elevation wheel until the blade is 90° to the table.
FIG. 21
4.Tighten blade tilt lock handle 1, rotate the bevel stop cam 5 until it touches the bevel stop housing 7, then tighten 90° adjustment screw 3.
5.Loosen adjustment screw 6 and adjust pointer 3 to indicate 0° on the bevel scale.
Adjusting 45° Positive Stop:
6.Loosen the blade tilt lock handle 1 and push the elevation wheel 2 to the right as far as possible and tighten the blade tilt lock handle 1.
7.Place a combination square on the table with one end of square against the blade as shown (Fig. 22), and check to see if the blade is 45° to the table. If the blade is not 45° to the table, loosen the blade tilt lock handle 1, loosen 45° adjustment screw 8, loosen 45° bevel stop cam 9 and push the elevation wheel until the blade is 45° to the table.
FIG. 22
8. Tighten blade tilt lock handle 1, rotate the 45° bevel stop cam 9 until it touches the bevel stop housing 7, then tighten 45° adjustment screw 8.
8
6 1 9
15 |
||||
10” |
Blade |
|||
|
Ø 254mm |
|||
Hoja |
||||
|
Ø 254mm |
|||
Lame |
||||
|
||||
2
4
5
17.

 3410 2610013681 ENG:2610008499 7/20/10 2:14 PM Page 18
3410 2610013681 ENG:2610008499 7/20/10 2:14 PM Page 18
Adjusting Blade Parallel to the Miter Gauge Slots
The blade was adjusted parallel to the miter gauge slots at the factory. In order to ensure accurate cuts and help prevent kickback, this adjustment should be rechecked. If adjustment is necessary, follow the steps below.
To prevent personal injury, always discon - nect the plug from power source before mak-
ing any adjustments.
1.Turn elevation wheel and raise blade as high as it will go.
2.Select a point on the body of the saw blade that is set to the left when viewing blade from the front of saw, and mark with a pencil (Fig. 23).
3.Place the base of a combination square against the edge of the miter gauge slot, and extend the sliding rule of square so it just touches the marked point on the body of the saw blade at the rear of the table.
4.Rotate blade and check the same marked point of the saw blade at the front of the table (Fig. 23).
5.If the front and back measurements, shown in Figure 23, are not identical, loosen the four alignment bolts 2, located on the underside of the table at the front and rear of the saw (Fig. 24 & 25). Carefully move the saw blade until the blade is parallel to the miter gauge slot, and securely tighten all four bolts.
FIG. 23
FIG. 24
2
UNDER FRONT OF TABLE
FIG. 25 |
UNDER REAR OF TABLE |
|
2
18.

 3410 2610013681 ENG:2610008499 7/20/10 2:14 PM Page 19
3410 2610013681 ENG:2610008499 7/20/10 2:14 PM Page 19
Aligning Rip Fence
To prevent personal injury, always disconnect ! WARNING plug from power source before making any
adjustments. The rip fence must be parallel with the SAWBLADE in order to prevent KICKBACK when ripping.
Your table saw is equipped with a Self-Aligning, Quick-Set rip fence. Once the adjustments below have been made, the rip fence will self align when the fence is locked into position.
NOTE: The blade must be parallel with the miter gauge slots (see page 18) and be perpendicular to table before proceeding with rip fence alignment.
! |
WARNING |
To prevent personal injury, always make sure |
|
the rip fence is locked before making rip cuts. |
|||
|
|
1.Lift both guard barriers 2 to their up locked position.
2.Raise lock handle 1 and slide fence 3 until it is alongside the sawblade, by lifting right side pawl 4 above fence (Fig. 26).
The fence should touch the blade teeth at the front and rear of the blade. If fence does not touch the teeth at front and rear of blade continue with the following the steps:
3.Loosen the two screws 5 on the top front section of the rip fence using the included 5mm hex wrench.
4.Move fence 3 until it touches the teeth and is parallel to the blade.
5.Hold fence in place and lower lock handle, check to make sure the fence stayed parallel to the blade then tighten screws (Fig. 26).
6.Clamp rip fence to check if it holds securely at front and rear. If rear is not clamped securely, unclamp fence and turn rear clamp adjustment screw 6 clockwise for increased clamping. Try clamping the fence to verify if it self aligns and clamps tightly at the front and rear. Overtightening of the rear clamp adjustment screw 6 will cause the rip fence to be non-self aligning (Fig. 26). Overtightening may cause friction or “chatter” when fence is moved side to side.
Rip Fence Pointer Adjustment
The distance of the rip fence body from the blade when ripping on the right side of the blade is determined by lining the pointer 7 with the desired dimension on the scale 8 (Fig. 27).
To set the rip fence pointer:
1.Lift both guard barriers 2 to their up locked position (Fig. 26).
2.Raise lock handle 1 and slide fence 3 until it is alongside the sawblade, by lifting right side pawl 4 above fence (Fig. 26).
3.Loosen pointer adjustment screw 9, adjust pointer 7 to “0” mark on lower scale 8, then re-tighten screw 9 (Fig. 27).
FIG. 26
2
4
5
6 |
1 |
3
FIG. 27
7
0
0
8 9
19.

 3410 2610013681 ENG:2610008499 7/20/10 2:14 PM Page 20
3410 2610013681 ENG:2610008499 7/20/10 2:14 PM Page 20
Riving Knife Alignment
IMPORTANT: The Riving Knife 1 must always be in line with the Saw Blade 2. The Riving Knife 1 is thinner than the width of the Kerf 4 by approximately three thicknesses of paper 5 on each side (Fig. 28). Note: The Kerf is the width of the cut made by the teeth on the saw blade.
To prevent personal injury, always disconnect plug from power source before making any adjustments
and when attaching or removing the Smart Guard System.
Checking Riving Knife Alignment
NOTE: The Riving Knife has been properly aligned at the factory - Check the alignment before making any adjustments.
1.Raise the Saw Blade to maximum height and set the bevel angle to 0°.
2.Remove the Barrier Guard Assembly and Anti-Kickback Device (see manual).
3.Place the Rip Fence 3 on the right side and slide it until it touches the tips of the Saw Blade 2 - Lock fence.
4.Check the alignment:
A.From the top, look down over the Fence and check that the Riving Knife is in line (front to back) with the blade and parallel with the fence.
B.Slide the fence away from the blade. Look over the front of the blade and check that the Riving Knife is in line with the blade.
C.If steps A or B show misalignment, proceed to “Adjusting Riving Knife.”
Adjusting Riving Knife
1.Raise the Saw Blade 2 to maximum height and set the bevel angle to 0°.
2.Remove the Barrier Guard Assembly and Anti-Kickback Device (see manual).
3.Remove the Table Insert.
4.Place the Rip Fence 3 on the right side and slide it until it touches the tips of the Saw Blade 2 - Lock fence.
5.Loosen Hex Nut 6 with 10mm open end wrench (Fig. 29). Slightly loosen Clamping Screws 8 (1/4-1/2 turns) using a 5mm Allen wrench. Loosen Set Screw 7 using a flat screwdriver (Fig. 29).
6.Make two folds in a small piece of paper (6" x 6") forming three layers (Fig. 28). Paper 5 is used as a “Spacing Gauge.”
NOTE: The spacing instructions above are based on using a standard kerf blade (.128" kerf on the Skil blade included). If a smaller kerf blade is used, adjust the paper spacer. For instance, if the kerf of the replacement blade is near .100", use 1 thickness of paper as a spacer; if the kerf is near .110", use 2 thicknesses.
7.Insert folded paper 5 between Riving Knife 1 and Fence 3.
A.Hold Riving Knife and paper firmly against Fence (Fig. 29 & 30).
B.Lightly tighten the clamp screws 8.
C.Remove the paper - slide fence away from blade.
D.Slowly turn the Set Screw 7 while watching the Riving Knife tilt until it is in line with the blade.
E.Recheck squareness of riving knife to table by sliding fence against blade. Readjust if necessary.
8.After completing adjustments:
A.Lightly tighten hex nut 6 (hold set screw position with screwdriver while tightening nut).
B.Fully tighten Clamp Screws 8 with Allen wrench. Then fully tighten the hex nut.
NOTE: Check that the riving knife stays in line with blade when the blade is tilted at any angle. Replace the Barrier Guard Assembly and Anti-Kickback Device before making cuts.
FIG. 28
1 5
5
WORK
BOIS
MADERA
4
5
2
LOOKING DOWN ON SAW
VUE DE DESSUS
VISTA HACIA ABAJO SOBRE LA SIERRA
FIG. 29 |
5 |
|
|
1 |
|
|
|
|
8
7
6
8
3
2
5
FIG. 30
3 |
1 |
3
8
20.

 3410 2610013681 ENG:2610008499 7/20/10 2:14 PM Page 21
3410 2610013681 ENG:2610008499 7/20/10 2:14 PM Page 21
Basic Table Saw Operation
Safety Power Switch
NOTE: This table saw has a safety feature that helps prevent accidental starting.
To turn saw on: lift switch lever by pinching side walls and pulling up. This action starts the saw (Fig. 31).
To turn off power: push switch lever down to its original position (Fig. 32).
To prevent unauthorized use, the switch can accommodate a padlock with a long, 3/16" or 1/4" diameter shackle (not provided with table saw) (Fig. 32).
Smart Guard System
The Skil Smart Guard has been designed for modularity, enabling the use of multiple combinations of the three main components – Main barrier guards, Anti-kickback device and riving knife. Additionally, the riving knife can be quickly adjusted to three positions (high, middle and stored), depending on the application requirement.
Component Parts (figure 33):
∂ Riving Knife
The Riving Knife is the central element of the Skil Smart Guard blade guarding system, serving as the attachment point for both the Main Barrier Guard and the Anti-Kickback Device. In the event that the Main Barrier Guard and AntiKickback Device are removed, the Riving Knife maintains its functionality as material splitter, and is adjustable to three positions. Because of this adjustability, the Riving Knife can be appropriately positioned for all cutting applications.
Note: The highest position of the Riving Knife is used for all “thru-cutting.” The middle position of the Riving Knife is for “non thru-cutting” with a 10" blade. The lowest position of the Riving Knife is used for dado cutting (up to 8" dado blade can be used with this saw). When the Riving Knife is at its lowest position and mounted to a workbench, do not lower the dado blade to more than slightly below the table saw top. Otherwise, there may be interference of the Riving Knife to the workbench.
∑ Main Barrier Guard
The main guard is comprised of a pair of plastic barriers attached to the metal upper barrier guard. The side barriers (one to the left and one to the right of the blade) operate independently of one another, maintaining maximum blade coverage during cutting operations. The main guard incorporates a quick-connect attachment point and can be attached or removed from the blade guarding system independent of the Anti-Kickback Device and Riving Knife.
Note: To best secure the main guard for transport, adjust the blade to its lowest position. This keeps the guard tight to the table surface and prevents damage related to the guard swinging during transport.
∏ Anti-Kickback Device
In the event of kickback, the Anti-Kickback Device, (also known as dogs, or pawls) is intended to help prevent the board from being thrown in the direction of the user. The sharp teeth of the pawls are intended to “catch” the material in the event of kickback.
FIG. 31
 ON
ON
FIG. 32
 OFF
OFF
FIG. 33
2
3
1
21.
3410 2610013681 ENG:2610008499 7/20/10 2:14 PM Page 22
Attachment/Removal
(see pages 13–14 for detailed instructions)
The three primary components of the Smart Guard blade guarding system are designed for rapid attachment, adjustment and/or removal without the need for additional tools.
The Main Barrier Guard component can be quickly attached and detached through the use of a quick release lever. The guard is attached by seating the crossbar into the top of the Riving Knife and engaging the locking lever. Following this process in reverse, the guard can be easily removed for special operations such as dados or rabbets.
The Anti-Kickback Device can be easily attached by aligning the attachment pin with the hole in the rear of the riving knife. It can be easily removed by depressing the compression pads on either side of the Anti-Kickback Device and lifting it away.
The Riving Knife can be easily adjusted to one of three heights by removing the table insert, raising the blade to its full height and releasing the riving knife release lever at the base of the Riving Knife. The Riving Knife should be locked in its highest position for use with the Main Barrier Guard and Anti-Kickback Device. It can be adjusted to its middle position for non-through cuts and for use as a material splitter without the Main Barrier Guard and Anti-Kickback Device.
In the event that the Riving Knife cannot be used for a specific cut, it can be adjusted to its lowest position, thus placing it 1" above the surface of the table (while the blade is at its full height).
System Storage
When not in use, the Main Barrier Guard and Anti-Kickback Device can be stored under the right side table extension.
Use of all the components of the Smart Guard ! WARNING System, including Main Barrier Guard, Anti-
Kickback Device, and Riving Knife is highly recommended to provide protection against accidents and injury.
1.Slide the Main Barrier Guard assembly (upside down) up and back into the U-bracket at the rear right side of the saw (Fig. 34).
2.Pivot the rear of the guard up and into the front mounting bracket.
3.Lock the Main Barrier Guard assembly into place in the same manner as you would attach it to the Riving Knife (Fig. 35).
4.Attach the Anti-Kickback Device to the hanging bracket in the same manner that it attaches to the Riving Knife.
Blade Bevel Control
Loosen blade bevel lock handle 1 counterclockwise (Fig. 36), slide the elevation wheel 2 until pointer 3 is at desired angle and tighten blade tilt lock handle 1 clockwise.
Extending Table Extension
To extend the table, raise the table extension lock handle 4 (Fig. 36) and slide table extension 5 to desired width (Fig. 37). To secure table setting, lower the lock handle 4.
FIG. 34 |
2 |
|
1 |









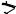
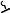


 3
3
FIG. 35 








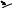
 4
4
15 |
||||
10” |
Blade |
|||
|
Ø 254mm |
|||
Hoja |
||||
|
Ø 254mm |
|||
Lame |
||||
|
||||
1
FIG. 36 |
3 |
|
2
FIG. 37
5
4
22.

 3410 2610013681 ENG:2610008499 7/20/10 2:14 PM Page 23
3410 2610013681 ENG:2610008499 7/20/10 2:14 PM Page 23
Work Helpers
Before cutting any wood on your saw, study all of the “Basic Saw Operations.”
Notice that in order to make some of the cuts, it is necessary to use certain devices, “Work Helpers”, like the Push Stick, the Push Block and the Auxiliary Fence, which you can make yourself.
After you have made a few practice cuts, make these “helpers” before starting any projects. Make the “Push Stick” first.
Push Stick and Push Block
Make the Push Stick 1 using a piece of 1" x 2" as shown (Fig. 38).
Make the Push Block 2 using pieces of 3/8" plywood 3 and 3/4" hardwood 4 (Fig. 39). For proper use of push block (see page 29).
The small piece of wood, 3/8" x 3/8" x 2-1/2", should be GLUED to the plywood… DO NOT USE NAILS. This is to prevent dulling the sawblade in the event you mistakenly cut into the Push Block.
Position the handle in the center of the plywood and fasten together with glue and woodscrews.
Use a push stick whenever the fence is 2" or more from the blade. Use a push block when the operation is too narrow to allow the use of a push stick. For proper use, see page 29.
Both a push stick or block should be used in the place of the user’s hand to guide the material only between the fence and blade.
When using a push stick or push block, the trailing end of the board must be square. A push stick or block against an uneven end could slip off or push the work away from the fence.
Auxiliary Fence
Make one using pieces of 3/8" plywood 3 and 3/4" hardwood 4. Fasten together with glue and woodscrews (Fig. 40).
NOTE: Since the Push Block 2 is used with the Auxiliary Fence 5, the 4-3/4" dimensions must be held identical on both the pieces.
Making a Featherboard
Figure 41 illustrates dimensions for making a typical featherboard. It should be made from a straight piece of wood that is free of knots or cracks.
Kerf 5 should be about 1/4" apart (Fig. 41).
FIG. 38 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
3/4 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1-1/2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
WORKPIECE |
15 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
45° NOTCH |
||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||
1/4 |
|
|
|
|
|
1/4 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
END |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||
1/4 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ENCOCHE À |
|||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
EXTRÉMITÉ |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
CONTACT AVEC |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
45° |
|||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
L’OUVRAGE |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
MUESCA DE |
||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
EXTREMO DE |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
45° |
||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
LA PIEZA DE |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
TRABAJO |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||
FIG. 39 |
4-3/4 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
12 |
|
4 |
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
5 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2 |
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
3/8 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
12 |
|
|
2-1/2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
2-1/2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
5-1/8 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
THESE EDGES MUST BE PARALLEL |
|
|
3/8 |
|
|
|
|
3/8 |
3 |
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
CES BORDS DOIVENT ÊTRE PARALLÈLES |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||
ESTOS BORDES DEBEN SER PARALELOS |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
|
FIG. 40 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
3 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
4 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
5 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2-1/4 |
||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
4-3/4 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
THIS FACE AND THIS EDGE |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
21-1/2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
MUST BE PARALLEL |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
5-1/2 |
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
CETTE FACE ET CE BORD DOIVENT |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
ÊTRE PARALLÈLES |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
|
ESTA CARA Y ESTE BORDE DEBEN |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
ER PARALELOS |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||
8
FIG. 41
25 |
5 |
|
5
4-1/2
3/4
NOTE: All dimensions in inches.
REMARQUE : Toutes les dimensions sont en pouces.
NOTA: Todas las dimensiones están en pulgadas.
23.
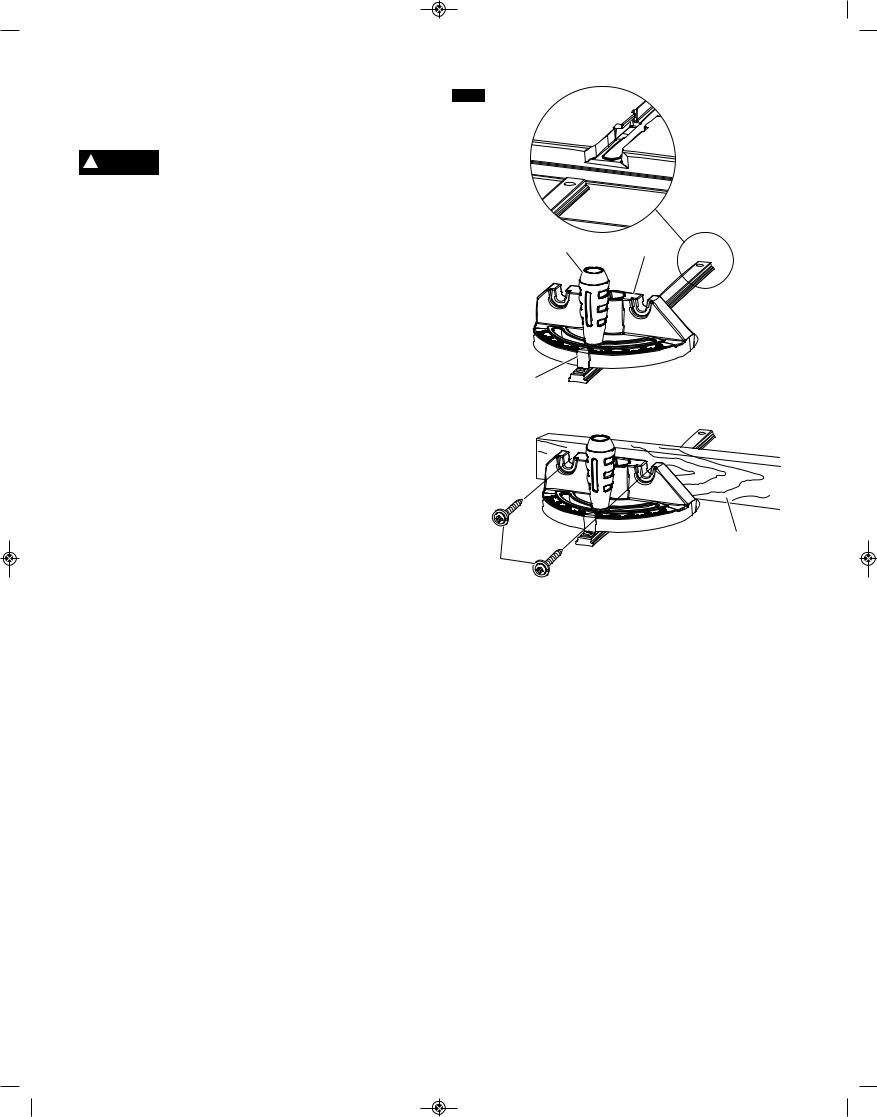
 3410 2610013681 ENG:2610008499 7/20/10 2:14 PM Page 24
3410 2610013681 ENG:2610008499 7/20/10 2:14 PM Page 24
Using the Miter Gauge
CROSSCUTTING, MITER CUTTING, BEVEL CUTTING, COMPOUND MITER CUTTING and when RABBETING across the end of a narrow workpiece, the MITER GAUGE is used.
For your own safety, always observe the following safety precautions in addition to the safety
instructions on pages 2–6.
Never make these cuts freehand (without using the miter gauge or other auxiliary devices) because the blade could bind in the cut and cause a KICKBACK or cause your fingers or hand to slip into the blade.
Always lock the miter gauge securely when in use.
Remove rip fence from table during any operations which utilize the miter gauge.
When cross cutting and the blade set at 90° to the table, the miter gauge can be used in either slot on the table. When cross cutting and the blade is tilted, use slot on right side of table where the blade is tilted away from your hands and miter gauge.
To adjust the miter angle:
Loosen lock knob 1 and set the miter gauge body 2 so the pointer 3 is at desired angle, then tighten lock knob 1 (Fig. 42).
Miter Gauge Auxiliary Facing
Select a suitable piece of smooth straight wood, drill two holes through it and attach it with screws and washers 5 (Fig. 42).
Example:
A.Drill 1/4" dia. holes through miter gauge.
B.Drill 5/32" dia. holes through (board 3/4" thick, 3" high, and desired length).
C.Attach with two No. 12 round head wood screws 1-1/2" long with washers, 5, not included (Fig. 42).
Be sure screws never protrude above outside surface of facing.
Be sure facing does not interfere with the proper operation of the saw blade guard.
NOTE: When bevel crosscutting, attach facing so that it extends to the right of the miter gauge and use the miter gauge in the groove to the right of the blade.
FIG. 42
1 2
3
4
5
24.

 3410 2610013681 ENG:2610008499 7/20/10 2:14 PM Page 25
3410 2610013681 ENG:2610008499 7/20/10 2:14 PM Page 25
Crosscutting
CROSSCUTTING is known as cutting wood across the grain, at 90°, or square with both the edge and the flat side of the wood.
This is done with the miter gauge set at 90° (Fig. 43). |
|
Make sure blade guard is installed for all “thru-sawing” operations |
|
(when sawblade cuts entirely through the thickness of the |
|
workpiece). Replace guard IMMEDIATELY after completion of |
|
dadoing, molding or rabbeting cuts. |
|
Have blade extend approximately 1/8" above top of workpiece. |
|
Additional blade exposure would increase the hazard potential. |
FIG. 43 |
Do not stand directly in front of the blade in case of a |
|
THROWBACK (small cut-off piece caught by the back of the blade |
|
and thrown toward the operator). Stand to either side of the blade. |
|
Keep your hands clear of the blade and out of the path of the |
|
blade. |
|
If blade stalls or stops while cutting, TURN SWITCH OFF before |
|
attempting to free the blade. |
|
Do not reach over or behind the blade to pull the workpiece |
|
through the cut … to support long or heavy workpieces … to |
|
remove cut-off pieces of material or FOR ANY OTHER REASON. |
|
Do not pick up small pieces of cut-off material from the table. |
|
REMOVE them by pushing them OFF the table with a long stick. |
|
Otherwise they could be thrown back at you by the rear of the |
|
blade. |
|
Do not remove small pieces of cut-off material that are close to or |
|
may become TRAPPED inside the blade guard while the saw is |
|
RUNNING. THIS COULD ENDANGER YOUR HANDS or cause a |
|
KICKBACK. Turn the saw OFF. After the blade has stopped |
|
turning, lift the guard and remove the piece. |
|
If workpiece is warped, place the CONCAVE side DOWN. This will |
|
help prevent it from rocking while it is being cut. |
|
The graduations on the miter gauge provide accuracy for average |
|
woodworking. In some cases where extreme accuracy is required, |
|
when making angle cuts, for example, make a trial cut and then |
|
recheck it with an accurate square or protractor. |
|
If necessary, the miter gauge head can be swiveled slightly to |
|
compensate for any inaccuracy. |
|
TIP: The space between the miter gauge bar and the groove in the |
|
table is held to a minimum during manufacturing. For maximum |
|
accuracy when using the miter gauge, always “favor” one side of |
|
the groove in the table. In other words, don’t move the miter gauge |
|
from side to side while cutting but keep one side of the bar riding |
|
against one side of the groove. |
|
TIP: Glue a piece of sandpaper to the face of the miter gauge |
|
head. This will help prevent the workpiece from “creeping” while it |
|
is being cut. |
|
The miter gauge may be used in either of the grooves in the table. |
|
Make sure it is locked. |
|
When using the miter gauge in the LEFT hand groove, hold the |
|
workpiece firmly against gauge head with your left hand, and |
|
grip the lock knob with your right hand. |
|
When using the RIGHT hand groove, hold the workpiece with |
|
your right hand and the lock knob with your left hand. |
|
25.

 3410 2610013681 ENG:2610008499 7/20/10 2:14 PM Page 26
3410 2610013681 ENG:2610008499 7/20/10 2:14 PM Page 26
Repetitive Cutting
REPETITIVE CUTTING is known as cutting a quantity of pieces the same length without having to mark each piece (Fig. 44).
When making repetitive cuts from a long workpiece, make sure it is supported.
Never use the rip fence as a length stop because the cutoff piece could bind between the fence and
the blade causing a kickback.
1.When making repetitive cuts, clamp a block of wood 3" long to the table at desired length to act as a length stop.
When clamping the block, make sure that the end of the block is well in front of the sawblade. Be
sure it is clamped securely.
2.Slide the workpiece along the miter gauge until it touches the block … hold it securely.
3.Make the cut … pull the workpiece back … push the cut-off piece off the table with a long Push Stick … DO NOT ATTEMPT TO PICK IT UP AS THIS COULD ENDANGER YOUR HANDS.
Miter Cutting
MITER CUTTING is known as cutting wood at an angle other than 90° with the edge of the wood. Follow the same procedure as you would for crosscutting (Fig. 45).
Adjust the miter gauge to the desired angle, and lock it.
The miter gauge may be used in either of the grooves in the table.
When using the miter gauge in the LEFT hand groove, hold the workpiece firmly against the miter gauge head with your left hand, and grip the lock knob with your right hand.
When using the RIGHT hand groove, hold the workpiece with your right hand and the lock knob with your left hand.
FIG. 44
FIG. 45
26.

 3410 2610013681 ENG:2610008499 7/20/10 2:14 PM Page 27
3410 2610013681 ENG:2610008499 7/20/10 2:14 PM Page 27
Bevel Crosscutting |
FIG. 46 |
|
BEVEL CROSSCUTTING is the same as crosscutting except that the wood is also cut at a bevel angle (Fig. 46) … other than 90° with the flat side of the wood.
Adjust the blade to the desired angle.
Use the Miter Gauge in the groove to the RIGHT of the blade where the blade is tilted away from your hands and miter gauge.
Compound Miter Cutting
COMPOUND MITER CUTTING is a combination of miter cutting and bevel crosscutting. The cut is made at an angle other than 90° to both the edge and the flat side of the wood (Fig. 46).
Adjust the miter gauge and the blade to the desired angle and make sure miter gauge is locked.
Only use the miter gauge in the groove to the RIGHT of the blade where the blade is tilted away from your hands and miter gauge.
Using the Rip Fence
RIPPING, BEVEL RIPPING, RESAWING AND RABBETING are performed using the RIP FENCE together with the AUXILIARY FENCE / WORK SUPPORT, PUSH STICK OR PUSH BLOCK.
For your own safety, always observe the following safety precautions in addition to the safety
instructions on pages 2–6.
1.Never make these cuts FREEHAND (without using the rip fence or auxiliary devices when required) because the blade could bind in the cut and cause a KICKBACK.
2.Always lock the rip fence securely when in use.
3.Remove miter gauge from table during any operations which utilize the rip fence.
4.Make sure blade guard is installed for all thru-sawing type cuts. Replace the guard IMMEDIATELY following completion of resawing, rabbeting, dadoing or molding operations.
Frequently check the action of the ANTIKICKBACK PAWLS by passing the workpiece alongside of the spreader while saw is OFF.
Pull the workpiece TOWARD you. If the PAWLS do not DIG into the workpiece and HOLD it … the pawls must be REPLACED or SHARPENED (see “Maintenance” on page 33).
5.Have blade extend approximately 1/8" above top of workpiece. Additional blade exposure would increase the hazard potential.
6.Do not stand directly in front of the blade in case of a KICKBACK. Stand to either side of the blade.
7.Keep your hands clear of the blade and out of the path of the blade.
8.If the blade stalls or stops while cutting, TURN SWITCH OFF before attempting to free the blade.
9.Do not reach over or behind the blade to pull the workpiece through the cut … to support long or heavy workpieces … to remove small cut-off pieces of material or FOR ANY OTHER REASON.
27.

 3410 2610013681 ENG:2610008499 7/20/10 2:14 PM Page 28
3410 2610013681 ENG:2610008499 7/20/10 2:14 PM Page 28
10.Do not pick up small pieces of cut-off material from the table. REMOVE them by pushing them OFF the table with a long stick. Otherwise they could be thrown back at you by the rear of the blade.
11.Do not remove small pieces of cut-off material that may become TRAPPED inside the blade guard while the saw is RUNNING. THIS COULD ENDANGER YOUR HANDS or cause a KICKBACK. Turn the saw OFF and disconnect power source. After the blade has stopped turning, lift the guard and remove the piece.
12.If workpiece is warped, place the CONCAVE side DOWN. This will prevent it from rocking while it is being ripped.
RIP FENCE AUXILIARY FACING
When using dado or molding head accessories, an auxiliary facing board should be used. This will help prevent damage to the aluminum fence. The facing should be made of 3/4" thick wood – Figure 47 shows dimensional plans to make a facing board to fit this saw.
Parts Required:
3/4" thick wood board (solid or plywood) cut to size
Two (2) 1/4" x 20 x 1-3/4" long hex. head machine screws
Two (2) 1/4" Washers
Two (2) 1/4" x 20 machine nuts
The facing is made to the same height (2") as the fence and can work with the blade guard system in place when moving the fence to contact the blade. The taller facing design (4-1/4") is optional and can be used for clamping on other accessories. Cut the board to the size shown, drill through 9/32" holes, then counter-sink each hole (down 3/8") using a 3/4" drill bit.
Assembly:
1.Install each machine screw 1 through the holes 2 in the rear fence housing.
2.Place facing board 3 over screws.
3.Place washers over screw threads.
4.Thread and tighten the nuts onto the screws.
FIG. 47 |
2 |
|
1 |
|
|
||
3 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
6-1/8˝ |
|
|
4-1/4 |
19- |
|
1˝ |
2˝ |
6- |
|
||
|
|
||
3/8˝ |
|
|
|
|
5/8˝ |
|
|
|
3/4˝ |
|
|
WASHER 3/8˝
NUT
3/4˝ |
9/32˝ |
1/4˝X 20 X 1-3/4˝ LONG |
DIA. |
HOLE. |
STANDARD HEX HEAD. |
TALLER AUXILIARY FACING
28.

 3410 2610013681 ENG:2610008499 7/20/10 2:14 PM Page 29
3410 2610013681 ENG:2610008499 7/20/10 2:14 PM Page 29
Ripping
RIPPING is known as cutting a piece of wood with the grain, or lengthwise. This is done using the rip fence. Position the fence to the desired WIDTH OF RIP and lock in place. Before starting to rip, be sure:
A.Rip Fence is parallel to sawblade.
B.Riving knife is properly aligned with sawblade.
C.Antikickback pawls are functioning properly.
When ripping LONG BOARDS or LARGE PANELS, always use a work support (Fig. 48).
BEVEL RIPPING
When bevel ripping material 6" or narrower, use fence on the right side of the blade ONLY. This will provide more space between the fence and the sawblade for use of a Push Stick. If the fence is mounted to the left, the sawblade guard may interfere with proper use of a Push Stick.
When “WIDTH OF RIP” is 6" and WIDER use your RIGHT hand to feed the workpiece, use LEFT hand ONLY to guide the workpiece … do not FEED the workpiece with the left hand (Fig. 48).
When “WIDTH OF RIP” is 2" to 6" wide USE THE PUSH STICK 1 to feed the work (Fig. 49).
When WIDTH OF RIP is NARROWER than 2" the Push Stick CANNOT be used because the guard will interfere … USE the AUXILIARY FENCE, and PUSH BLOCK.
Attach auxiliary fence 2 to rip fence with two “C” clamps (Fig. 50).
Feed the workpiece by hand until the end is approx. 1" from the front edge of the table. Continue to feed using the PUSH BLOCK 3 on top of auxiliary fence UNTIL THE CUT IS COMPLETE (Fig. 51).
FIG. 50
FIG. 48
2 |
-6” |
|
FIG. 51
FIG. 49
29.

 3410 2610013681 ENG:2610008499 7/20/10 2:14 PM Page 30
3410 2610013681 ENG:2610008499 7/20/10 2:14 PM Page 30
Non Thru-Sawing
Add 8" high flat facing board to the fence, the full length of the fence (Fig. 52).
Use featherboards for all “Non Thru-Sawing” operations (when sawblade guard must be removed). Featherboards 1 are used to keep the work in contact with the fence and table as shown, and to stop kickbacks.
Before starting the operation, switch saw “OFF,” and remove blade guard and anti-kickback pawls. Set riving knife to middle position and set cutter below table surface.
Mount featherboards 1 to fence and table as shown, so that leading edges of featherboards will support workpiece until cut is complete, and the workpiece has been pushed completely past the cutter (sawblade, dado head, molding head, etc.) with a Push Stick 2, as in ripping.
A.Install featherboards so they exert pressure on the workpiece; BE POSITIVE THEY ARE SECURELY ATTACHED.
B.Make sure by trial that the featherboards will stop a kickback if one should occur.
Featherboards are not employed during non thru-sawing operations when using the miter gauge.
REPLACE THE SMART GUARD SYSTEM AS SOON AS THE NON THRU-SAWING OPERATION IS COMPLETE.
Rabbeting
RABBETING is known as cutting out a section of the corner of a piece of material, across an end or along an edge (Fig. 53).
Making a RABBET requires cuts which do not go all the way through the material. Therefore the Smart Guard System must be removed.
1.Before starting the operation, switch saw “OFF,” and remove blade guard and anti-kickback pawls. Set riving knife to middle position and set cutter below table surface.
2.For rabbeting along an edge (long way of workpiece) as shown, add facing to rip fence approximately as high as the workpiece is wide. Adjust rip fence and blade to required dimensions; then make first cut with board flat on table, follow setup (Fig. 52). Make second cut with workpiece on edge. Follow all precautions, safety instructions and operation instructions as for ripping or rip-type operations, including featherboards and Push Stick, etc.
3.For rabbeting across an end, for workpiece 10-1/2" and narrower make the rabbet cut with the board flat on the table. Using the miter gauge fitted with a facing, follow the same procedures and instructions for crosscutting making successive cuts across the width of the workpiece to obtain the desired width of cut. DO NOT use the rip fence for rabbeting across the end.
4.INSTALL SMART GUARD SYSTEM IMMEDIATELY UPON COMPLETION OF RABBETING OPERATION.
Rabbet cuts can also be made in one pass of the workpiece over the cutter using the dado head or molding head.
FIG. 52
1
|
|
|
|
|
FIRST CUT |
|||
|
|
|
PREMIÈRE COUPE |
|||||
|
FIG. 53 |
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
PRIMER CORTE |
|||
|
RABBET |
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|||||
FEUILLURE |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
REBAJO |
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
SECOND CUT
DEUXIÈME COUPE
SEGUNDO CORTE
RABBETING ALONG
THE EDGE
RÉALISATION D’UNE
FEUILLURE LE LONG D’UN
BORD
REBAJO A LO LARGO
DEL BORDE
1
 2
2
RABBETING ACROSS
THE END
RÉALISATION D’UNE FEUILLURE EN TRAVERS D’UNE EXTRÉMITÉ
REBAJO TRANSVERSAL
AL EXTREMO
30.
 Loading...
Loading...