HP INTEGRATED LIGHTS-OUT 2 (ILO 2) Manual

HP Integrated Lights-Out 2
User Guide
for Firmware 1.35
Part Number 394326-007
July 2007 (Seventh Edition)
© Copyright 2005-2007 Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P.
The information contained herein is subject to change without notice. The only warranties for HP products and services are set forth in the express warranty statements accompanying such products and services. Nothing herein should be construed as constituting an additional warranty. HP shall not be liable for technical or editorial errors or omissions contained herein.
Confidential computer software. Valid license from HP required for possession, use or copying. Consistent with FAR 12.211 and 12.212, Commercial Computer Software, Computer Software Documentation, and Technical Data for Commercial Items are licensed to the U.S. Government under vendor’s standard commercial license.
Microsoft, Windows, Windows NT, and Windows XP are U.S. registered trademarks of Microsoft Corporation. Windows Server 2003 is a U.S. trademark of Microsoft Corporation. Windows Vista is either a registered trademark or trademark of Microsoft Corporation in the United States and/or other countries. AMD is a trademark of Advanced Micro Devices, Inc. .Java is a U.S. trademark of Sun Microsystems, Inc. Intel, Pentium, and Itanium are trademarks or registered trademarks of Intel Corporation or its subsidiaries in the United States and other countries.
Audience assumptions
This document is for the person who installs, administers, and troubleshoots servers and storage systems. HP assumes you are qualified in the servicing of computer equipment and trained in recognizing hazards in products with hazardous energy levels.

Contents
Operational overview ................................................................................................................... |
8 |
Guide overview ........................................................................................................................................ |
8 |
New in this release of iLO 2 ....................................................................................................................... |
8 |
iLO 2 overview ......................................................................................................................................... |
9 |
Typical usage ................................................................................................................................. |
9 |
Differences between iLO 2 and iLO ................................................................................................. |
10 |
HP ProLiant Essentials Rapid Deployment Pack Integration................................................................... |
10 |
Server management through IPMI version 2.0 compliant applications................................................... |
11 |
WS-Management compatibility overview.......................................................................................... |
12 |
iLO 2 browser interface overview .............................................................................................................. |
12 |
Supported browsers and client operating systems .............................................................................. |
13 |
Supported server operating system software...................................................................................... |
13 |
Text-based remote console overview .......................................................................................................... |
14 |
Virtual serial port and remote serial console...................................................................................... |
15 |
iLO 2 setup ................................................................................................................................ |
16 |
Quick setup ............................................................................................................................................ |
16 |
Preparing to setup iLO 2 .......................................................................................................................... |
16 |
Connecting to the network........................................................................................................................ |
18 |
Configuring the IP address........................................................................................................................ |
19 |
Logging into iLO 2 for the first time............................................................................................................ |
19 |
Setting up user accounts........................................................................................................................... |
20 |
Setting up iLO 2 using iLO 2 RBSU .................................................................................................. |
20 |
Setting up iLO 2 using the browser-based option ............................................................................... |
21 |
Activating iLO 2 licensed features using a browser ...................................................................................... |
21 |
Installing iLO 2 device drivers ................................................................................................................... |
21 |
Microsoft device driver support ....................................................................................................... |
22 |
Linux device driver support ............................................................................................................. |
22 |
Novell NetWare device driver support............................................................................................. |
23 |
Configuring iLO 2....................................................................................................................... |
24 |
iLO 2 configuration overview.................................................................................................................... |
24 |
Upgrading iLO 2 firmware ....................................................................................................................... |
24 |
Upgrading iLO 2 using a browser ................................................................................................... |
25 |
Recovering from a failed iLO 2 firmware update ............................................................................... |
26 |
Downgrading the iLO 2 firmware .................................................................................................... |
27 |
Licensing ................................................................................................................................................ |
27 |
User administration.................................................................................................................................. |
29 |
Adding a new user ........................................................................................................................ |
30 |
Viewing or modifying an existing user's settings ................................................................................ |
32 |
Deleting a user.............................................................................................................................. |
32 |
Group administration ..................................................................................................................... |
33 |
Configuring iLO 2 access ......................................................................................................................... |
34 |
Services options ............................................................................................................................ |
34 |
Access options .............................................................................................................................. |
40 |
iLO 2 Remote Console and Remote Serial Console access .................................................................. |
42 |
Security.................................................................................................................................................. |
42 |
Contents |
3 |
General security guidelines............................................................................................................. |
43 |
User accounts and access............................................................................................................... |
45 |
SSH key administration .................................................................................................................. |
46 |
SSL certificate administration........................................................................................................... |
46 |
Two-factor authentication................................................................................................................ |
47 |
Directory settings ........................................................................................................................... |
52 |
Encryption .................................................................................................................................... |
55 |
HP SIM single sign-on (SSO) ........................................................................................................... |
57 |
Remote Console Computer Lock....................................................................................................... |
60 |
Network................................................................................................................................................. |
62 |
Network Settings ........................................................................................................................... |
62 |
DHCP/DNS Settings ...................................................................................................................... |
68 |
SNMP/Insight Manager settings................................................................................................................ |
69 |
Enabling SNMP alerts .................................................................................................................... |
69 |
SNMP generated trap definitions..................................................................................................... |
70 |
Configuring Insight Manager integration .......................................................................................... |
71 |
ProLiant BL p-Class configuration ............................................................................................................... |
72 |
ProLiant BL p-Class user requirements ............................................................................................... |
72 |
Static IP bay configuration .............................................................................................................. |
72 |
HP BladeSystem setup .................................................................................................................... |
75 |
iLO 2 diagnostic port configuration parameters ................................................................................. |
77 |
Using iLO 2 ............................................................................................................................... |
79 |
System status and status summary information ............................................................................................. |
79 |
System Information Summary .......................................................................................................... |
81 |
iLO 2 Log ..................................................................................................................................... |
83 |
IML .............................................................................................................................................. |
83 |
Diagnostics................................................................................................................................... |
84 |
Insight Agents ............................................................................................................................... |
85 |
iLO 2 Remote Console ............................................................................................................................. |
86 |
iLO 2 Remote Console and iLO 2 licensing options............................................................................ |
87 |
Remote Console settings ................................................................................................................. |
88 |
Integrated Remote Console Fullscreen............................................................................................... |
92 |
Integrated Remote Console option ................................................................................................... |
92 |
Shared Remote Console ................................................................................................................. |
96 |
Using Console Capture .................................................................................................................. |
96 |
Acquiring the Remote Console ........................................................................................................ |
97 |
Remote Console ............................................................................................................................ |
98 |
Remote Serial Console ................................................................................................................. |
100 |
Virtual media........................................................................................................................................ |
104 |
Using iLO 2 Virtual Media devices................................................................................................. |
105 |
Virtual folder............................................................................................................................... |
112 |
Power management............................................................................................................................... |
113 |
Server power settings................................................................................................................... |
114 |
Server power data....................................................................................................................... |
115 |
Processor states ........................................................................................................................... |
116 |
Graceful shutdown ...................................................................................................................... |
117 |
ProLiant BL p-Class Advanced management .............................................................................................. |
117 |
Rack View .................................................................................................................................. |
119 |
iLO 2 control of ProLiant BL p-Class server LEDs ............................................................................... |
123 |
ProLiant BL p-Class alert forwarding ............................................................................................... |
123 |
ProLiant BladeSystem HP Onboard Administrator ...................................................................................... |
123 |
Enclosure bay IP addressing ......................................................................................................... |
124 |
iLO option .................................................................................................................................. |
127 |
|
Contents 4 |
iLO 2 Virtual Fan......................................................................................................................... |
128 |
Web Administration..................................................................................................................... |
128 |
iLO 2 BL c-Class tab..................................................................................................................... |
129 |
BL p-Class and BL c-Class features.................................................................................................. |
129 |
Directory services...................................................................................................................... |
130 |
Overview of directory integration ............................................................................................................ |
130 |
Benefits of directory integration ............................................................................................................... |
130 |
Advantages and disadvantages of schema-free directories and HP schema directory ..................................... |
131 |
Schema-free directory integration .................................................................................................. |
132 |
HP schema directory integration .................................................................................................... |
132 |
Setup for Schema-free directory integration............................................................................................... |
134 |
Active Directory preparation ......................................................................................................... |
134 |
Schema-free browser-based setup .................................................................................................. |
135 |
Schema-free scripted setup............................................................................................................ |
136 |
Schema-free HPLOMIG-based setup ............................................................................................... |
136 |
Schema-free setup options ............................................................................................................ |
136 |
Schema-free nested groups ........................................................................................................... |
137 |
Setting up HP schema directory integration............................................................................................... |
138 |
Features supported by HP schema directory integration .................................................................... |
138 |
Setting up directory services.......................................................................................................... |
138 |
Schema documentation ................................................................................................................ |
139 |
Directory services support ............................................................................................................. |
139 |
Schema required software ............................................................................................................ |
140 |
Schema installer .......................................................................................................................... |
140 |
Management snap-in installer........................................................................................................ |
142 |
Directory services for Active Directory ............................................................................................ |
142 |
Directory services for eDirectory .................................................................................................... |
152 |
User login using directory services ................................................................................................. |
160 |
Directory-enabled remote management ....................................................................................... |
161 |
Introduction to directory-enabled remote management................................................................................ |
161 |
Creating roles to follow organizational structure........................................................................................ |
161 |
Using existing groups................................................................................................................... |
162 |
Using multiple roles...................................................................................................................... |
162 |
How directory login restrictions are enforced ............................................................................................ |
163 |
Restricting roles ........................................................................................................................... |
163 |
User restrictions........................................................................................................................... |
164 |
Creating multiple restrictions and roles ........................................................................................... |
166 |
Using bulk import tools........................................................................................................................... |
167 |
HPQLOMIG directory migration utility......................................................................................... |
168 |
Introduction to HPQLOMIG utility ............................................................................................................ |
168 |
Compatibility ........................................................................................................................................ |
168 |
HP Lights-Out directory package.............................................................................................................. |
168 |
Using HPQLOMIG................................................................................................................................. |
169 |
Finding management processors.................................................................................................... |
169 |
Upgrading firmware on management processors............................................................................. |
171 |
Selecting a directory access method .............................................................................................. |
172 |
Naming management processors .................................................................................................. |
173 |
Configuring directories when HP Extended schema is selected .......................................................... |
174 |
Configuring directories when schema-free integration is selected ....................................................... |
175 |
Setting up management processors for directories............................................................................ |
176 |
HP Systems Insight Manager integration ...................................................................................... |
178 |
|
Contents 5 |
Integrating iLO 2 with HP SIM................................................................................................................. |
178 |
HP SIM functional overview .................................................................................................................... |
178 |
HP SIM identification and association ...................................................................................................... |
179 |
HP SIM status.............................................................................................................................. |
179 |
HP SIM links ............................................................................................................................... |
179 |
HP SIM systems lists ..................................................................................................................... |
180 |
Receiving SNMP alerts in HP SIM............................................................................................................ |
180 |
HP SIM port matching ............................................................................................................................ |
181 |
Reviewing Advanced Pack license information in HP SIM ........................................................................... |
181 |
Troubleshooting iLO 2 ............................................................................................................... |
182 |
iLO 2 POST LED indicators ..................................................................................................................... |
182 |
Event log entries.................................................................................................................................... |
184 |
Hardware and software link-related issues ................................................................................................ |
186 |
JVM support ......................................................................................................................................... |
187 |
Login issues .......................................................................................................................................... |
187 |
Login name and password not accepted......................................................................................... |
188 |
Directory user premature logout..................................................................................................... |
188 |
iLO 2 Management Port not accessible by name ............................................................................. |
188 |
iLO 2 RBSU unavailable after iLO 2 and server reset........................................................................ |
189 |
Inability to access the login page................................................................................................... |
189 |
Inability to access iLO 2 using telnet .............................................................................................. |
189 |
Inability to access virtual media or graphical remote console ............................................................ |
189 |
Inability to connect to iLO 2 after changing network settings ............................................................. |
189 |
Inability to connect to the iLO 2 Diagnostic Port............................................................................... |
189 |
Inability to connect to the iLO 2 processor through the NIC............................................................... |
190 |
Inability to log in to iLO 2 after installing the iLO 2 certificate............................................................ |
190 |
Firewall issues............................................................................................................................. |
191 |
Proxy server issues....................................................................................................................... |
191 |
Two-factor authentication error ...................................................................................................... |
191 |
Troubleshooting alert and trap problems .................................................................................................. |
192 |
Inability to receive HP SIM alarms (SNMP traps) from iLO 2.............................................................. |
192 |
iLO 2 Security Override switch...................................................................................................... |
192 |
Authentication code error message ................................................................................................ |
193 |
Troubleshooting directory problems ......................................................................................................... |
193 |
Domain/name format login issues ................................................................................................. |
193 |
ActiveX controls are enabled and I see a prompt but the domain/name login format does not work....... |
193 |
User contexts do not appear to work.............................................................................................. |
193 |
Troubleshooting Remote Console problems ............................................................................................... |
193 |
Remote Console applet has a red X when running Linux client browser............................................... |
194 |
Inability to navigate the single cursor of the Remote Console to corners of the Remote Console window.. 194 |
|
Remote Console no longer opens on the existing browser session ...................................................... |
194 |
Remote console text window not updating properly.......................................................................... |
195 |
Remote Console turns gray or black ............................................................................................... |
195 |
Remote Serial Console troubleshooting........................................................................................... |
195 |
Troubleshooting Integrated Remote Console problems ................................................................................ |
195 |
Internet Explorer 7 and a flickering remote console screen ................................................................ |
195 |
Configuring Apache to accept exported capture buffers ................................................................... |
196 |
No console replay while server is powered down............................................................................ |
197 |
Skipping information during boot and fault buffer playback .............................................................. |
197 |
Out of Memory error starting Integrated Remote Console.................................................................. |
197 |
Session leader does not receive connection request when IRC is in replay mode.................................. |
197 |
Keyboard LED does not display correctly ........................................................................................ |
197 |
Inactive IRC ................................................................................................................................ |
198 |
Contents 6 |
|
IRC Failed to connect to server error message ................................................................................. |
198 |
IRC toolbar icons do not update .................................................................................................... |
198 |
GNOME interface does not lock ................................................................................................... |
199 |
Repeating keys on the Remote Console .......................................................................................... |
199 |
Remote Console playback does not work when the host server is powered down................................. |
199 |
Troubleshooting SSH and Telnet problems ................................................................................................ |
199 |
Initial PuTTY input slow................................................................................................................. |
199 |
PuTTY client unresponsive with Shared Network Port ........................................................................ |
199 |
SSH text support from a Remote Console session ............................................................................. |
200 |
Troubleshooting terminal services problems............................................................................................... |
200 |
Terminal Services button is not working .......................................................................................... |
200 |
Terminal Services proxy stops responding....................................................................................... |
200 |
Troubleshooting video and monitor problems ............................................................................................ |
200 |
General guidelines ...................................................................................................................... |
200 |
Telnet displays incorrectly in DOS® ............................................................................................... |
200 |
Video applications not displaying in the Remote Console.................................................................. |
201 |
User interface is not displaying correctly......................................................................................... |
201 |
Troubleshooting Virtual Media problems .................................................................................................. |
201 |
Virtual drive listing....................................................................................................................... |
201 |
Virtual Media applet has a red X and will not display ...................................................................... |
201 |
Virtual Floppy media applet is unresponsive.................................................................................... |
201 |
Troubleshooting miscellaneous problems .................................................................................................. |
202 |
Cookie sharing between browser instances and iLO 2 ..................................................................... |
202 |
Inability to access ActiveX downloads ............................................................................................ |
203 |
Inability to get SNMP information from HP SIM ............................................................................... |
203 |
Incorrect time or date of the entries in the event log.......................................................................... |
204 |
Inability to upgrade iLO 2 firmware ............................................................................................... |
204 |
iLO 2 does not respond to SSL requests .......................................................................................... |
204 |
Testing SSL ................................................................................................................................. |
205 |
Resetting iLO 2............................................................................................................................ |
205 |
Server name still present after ERASE utility is executed .................................................................... |
205 |
Troubleshooting a remote host....................................................................................................... |
206 |
Directory services schema .......................................................................................................... |
207 |
HP Management Core LDAP OID classes and attributes.............................................................................. |
207 |
Core classes ............................................................................................................................... |
207 |
Core attributes ............................................................................................................................ |
207 |
Core class definitions ................................................................................................................... |
207 |
Core attribute definitions .............................................................................................................. |
208 |
Lights-Out Management specific LDAP OID classes and attributes ................................................................ |
211 |
Lights-Out Management classes ..................................................................................................... |
211 |
Lights-Out Management attributes .................................................................................................. |
211 |
Lights-Out Management class definitions......................................................................................... |
211 |
Lights-Out Management attribute definitions .................................................................................... |
212 |
Technical support...................................................................................................................... |
214 |
Software technical support and update service.......................................................................................... |
214 |
HP contact information........................................................................................................................... |
214 |
Before you contact HP............................................................................................................................ |
215 |
Acronyms and abbreviations...................................................................................................... |
216 |
Index....................................................................................................................................... |
223 |
Contents 7

Operational overview
In this section |
|
Guide overview ....................................................................................................................................... |
8 |
New in this release of iLO 2...................................................................................................................... |
8 |
iLO 2 overview ........................................................................................................................................ |
9 |
iLO 2 browser interface overview............................................................................................................. |
12 |
Text-based remote console overview......................................................................................................... |
14 |
Guide overview
HP iLO 2 provides multiple ways to configure, update, and operate servers remotely. The HP Integrated Lights-Out 2 User Guide describes these features and how to use them with the browser-based interface and RBSU. Some features are licensed features and may only be accessed after purchasing an optional license. See the section, "Licensing (on page 27)" for more information.
The HP Integrated Lights-Out Management Processor Scripting and Command Line Resource Guide describes the syntax and tools available to use iLO 2 through a command-line or scripted interface.
This guide includes information about iLO 2 firmware version 1.11, 1.2x, and 1.30.
New in this release of iLO 2
iLO 2 version 1.30 added support for:
•WS-Management ("WS-Management compatibility overview" on page 12)
•Virtual media folder mapping ("Virtual folder" on page 112)
•Remote console screen capture and replay ("Using Console Capture" on page 96)
•Shared remote console (on page 96)
•HP SIM single sign-on ("HP SIM single sign-on (SSO)" on page 57)
•AES encryption (on page 55) for browser, XML, and SSH
•Infinite iLO 2 timeout setting ("Access options" on page 40)
•Automatic operating system locking when a remote console session terminates ("Remote Console Computer Lock" on page 60)
•Remote Microsoft® Windows® Kernel Debugging ("Using a remote Windows Kernel Debugger" on page 103)
•Schema-free nested groups (on page 137)
•Version 1.30 improved support for:
o Integrated Remote Console for international keyboards ("Hot keys and international keyboards" on page 91)
o Authentication logging with iLO 2 records client hostname ("iLO 2 Log" on page 83)
Operational overview 8
o Default-schema directory support to navigate nested directory groups
o Virtual serial port performance ("Remote Serial Console" on page 100)
iLO 2 overview
Four versions of iLO 2 are available:
•iLO 2 Standard—Enables as standard features essential remote control and management capabilities on next-generation HP ProLiant ML/DL servers. With iLO 2 Standard, you can remotely perform basic system administration tasks. You can also access system management information at any time. These remote control capabilities reduce the need for onsite support.
•iLO 2 Advanced—Provides comprehensive Lights-Out remote management capabilities for ProLiant servers. iLO 2 Advanced also gives you the freedom to enable full remote control of your ProLiant servers. You can perform the same tasks remotely that you can at the terminal, regardless of server or operating system conditions. iLO 2 Advanced is also suitable for routine administration, giving you a single tool for any situation. iLO 2 features comprehensive data encryption, enterprise-class user authentication and the ability to isolate iLO 2 traffic on separate networks.
•iLO 2 Standard Blade Edition—Provides all of the remote control capabilities typically offered as standard features on ProLiant servers, plus the new high-performance, Virtual KVM remote console and browser-based virtual media that is essential to administering HP BladeSystem servers. In addition, you can access system management information such as hardware health, event logs, and configuration anytime to troubleshoot and maintain blades.
•iLO 2 Select—Provides Standard Blade Edition enabled servers an easy upgrade to full Lights-Out functionality. It also provides a cost-effective upgrade to advanced Lights-Out functionality on ProLiant 300 and 500 Series servers that are managed using iLO 2 Standard text-based remote consoles, typically found in Linux environments.
For information about the features available in each version iLO 2, see "Licensing (on page 27)."
Typical usage
iLO 2 can remotely perform most functions that otherwise require a visit to servers at the data center, computer room, or remote location. The following are just a few examples of using iLO 2 features.
•iLO 2 Remote Console and virtual power enables you to view a stalled remote server with blue screen conditions and restart the server without onsite assistance.
•iLO 2 Remote Console enables you to change BIOS settings when necessary.
•iLO 2 Virtual KVM technology provides a high-performance remote console that enables you to remotely administer operating systems and applications in everyday situations.
•iLO 2 virtual CD/DVD-ROM or floppy enables you to install an operating system or flash system firmware over the network from images on your workstations or on centralized web servers.
•iLO 2 Virtual Folder enables you to update operating system drivers or copy system files without physical media or creating a disk image.
•iLO 2 scripting enables you to use virtual power and virtual media in other scripting tools to automate deployment and provisioning.
Operational overview 9
These examples are just a few ways iLO 2 is used to manage HP ProLiant servers from your office, home, or travel location. As you begin using iLO 2 and defining your specific infrastructure requirements refer to this guide for additional ways to simplify your remote server management needs.
Differences between iLO 2 and iLO
The iLO 2 product is based on the iLO product and shares many common features. However, to use iLO 2 to access a pre-operating system, text-based remote console, you must use the remote serial console. For more information, see the section, "Text-based remote console overview (on page 14)."
The following highlights the differences between iLO 2 and iLO:
Feature |
iLO 2 |
iLO |
|
|
|
Standard features |
|
|
|
|
|
Text console |
Pre-OS |
Pre-OS and OS |
|
|
|
Remote Serial Console (virtual serial |
Pre-OS and OS |
Pre-OS and OS |
port) |
|
|
|
|
|
Advanced features |
|
|
|
|
|
Text console |
Pre-OS and OS |
Pre-OS and OS |
|
|
|
Remote console |
Yes (Virtual KVM ) |
Yes |
|
|
|
Integrated Remote Console |
Yes |
No |
|
|
|
Support for Microsoft® JVM |
Yes |
No |
|
|
|
Remote Console Acquire button |
Yes |
Yes |
|
|
|
Terminal Services integration |
Yes |
Yes |
|
|
|
HP schema directory integration |
Yes |
Yes |
|
|
|
Schema-free directory integration |
Yes |
Yes |
|
|
|
Two-factor authentication |
Yes |
Yes |
|
|
|
Power Regulator reporting |
Yes |
Yes |
|
|
|
Virtual Floppy and CD/DVD-ROM |
Yes |
Yes |
|
|
|
USB key virtual media |
Yes |
Yes |
|
|
|
Virtual folder |
Yes |
No |
|
|
|
HP ProLiant Essentials Rapid Deployment Pack Integration
HP ProLiant Essentials Rapid Deployment Pack integrates with iLO 2 to allow the management of remote servers and the performance of remote console operations regardless of the state of the operating system or hardware.
The Deployment Server provides the ability to use the power management features of iLO 2 to power on, power off, or cycle power on the target server. Each time a server connects to the Deployment Server, the Deployment Server polls the target server to see if a LOM management device is installed. If installed, the server gathers information including the DNS name, IP address, and first user name. Security is maintained by requiring the user to enter the correct password for that user name.
Operational overview 10
For more information about the ProLiant Essentials Rapid Deployment Pack, refer to the documentation that ships on the ProLiant Essentials Rapid Deployment Pack CD or the HP website (http://www.hp.com/servers/rdp).
Server management through IPMI version 2.0 compliant applications
Server management through the IPMI is a standardized method for controlling and monitoring the server. iLO 2 provides server management based on the IPMI version 2.0 specification.
The IPMI specification defines a standardized interface for platform management. The IPMI specification defines the following types of platform management:
•Monitoring of system information, such as fans, temperatures, and power supplies
•Recovery capabilities, such as system resets and power on/off operations
•Logging capabilities, for abnormal events such as over temperature readings or fan failures
•Inventory capabilities, such as identifying failed hardware components
IPMI communications are dependent on the BMC and the SMS. The BMC manages the interface between the SMS and the platform management hardware. iLO 2 emulates the BMC functionality and the SMS functionality can be provided by various industry-standard tools. For additional information, see the IPMI specification on the Intel® website (http://www.intel.com/design/servers/ipmi/tools.htm).
iLO 2 provides the KCS interface, or open interface, for SMS communications. The KCS interface provides a set of I/O mapped communications registers. The default system base address for the I/O mapped SMS Interface is 0xCA2 and is byte aligned at this system address.
The KCS interface is accessible to SMS software that is running on the local system. Examples of compatible SMS software applications are as follows:
•IPMI version 2.0 Command Test Tool is a low-level MS-DOS command line tool that enables hexformatted IPMI commands to be sent to an IPMI BMC that implements the KCS interface. You can locate this tool on the Intel® website (http://www.intel.com/design/servers/ipmi/tools.htm).
•IPMItool is a utility for managing and configuring devices that support the IPMI version 1.5 and version 2.0 specifications and can be used in a Linux environment. You can locate this tool on the IPMItool website (http://ipmitool.sourceforge.net/index.html).
IPMI functionality provided by iLO 2
When emulating a BMC for the IPMI interface, iLO 2 supports all mandatory commands listed in the IPMI version 2.0 specification. See the IPMI version 2.0 specification for a listing of these commands. Also, the SMS should use the methods described in the specification for determining which IPMI features are enabled or disabled in the BMC (for example, using the Get Device ID command).
If the server operating system is running and the health driver is enabled, any IPMI traffic through the KCS interface can affect the performance of the health driver and overall health performance of the system. Do not issue any IPMI commands through the KCS interface that could have a detrimental affect on the monitoring performed by the health driver. These commands include any commands that sets or changes IPMI parameters, such as Set Watchdog Timer and Set BMC Global Enabled. Any IPMI command that simply returns data is safe to use, such as Get Device ID and Get Sensor Reading.
Operational overview 11
WS-Management compatibility overview
The iLO 2 firmware implementation of WS-Management is in accordance with the specification, DTMF
Web Services for Management 1.0.0a. Authentication
•iLO 2 uses basic authentication over SSL, compliant with profile: wsman:secprofile/https/basic
•Authenticated users are authorized to execute WS-Management commands in accordance with designated privileges in their local or directory accounts.
•To enable basic authentication on Microsoft® Windows Vista™, at the command prompt, enter gpedit.msc to launch the Group Policy Object Editor. Select Computer Configuration> Administrative Templates> Windows Components> Windows Remote Management (WinRM)> WinRM Client. Set Allow Basic authentication to Enabled.
Compatibility
•WS-Management in iLO 2 are compatible with the Windows Vista™ WinRM utility, Microsoft® Operations Manager 3, and the Management Pack provided by HP.
•The full set of WS-Management commands is available on iLO 2 servers that support embedded system health. A greatly reduced subset of these commands is available on servers without embedded systems health support.
Commands are available for remote invocation of the following devices:
•Server power
•UID
Status
The WS-Management in iLO 2 returns status information for fans, temperatures, power supplies, and VRMs.
iLO 2 browser interface overview
The iLO 2 browser interface groups similar tasks for easy navigation and workflow. These tasks are organized under high-level tabs across the top of the iLO 2 interface. These tabs are always visible and include System Status, Remote Console, Virtual Media, Power Management, and Administration.
Each high-level iLO 2 tab has a menu on the left side of the interface with various options. This menu changes every time you select a different high-level tab, displaying the options available from that tab. Each menu option displays a page title, which is a description of the information or settings available on that page. This page title might not reflect the name displayed on the menu option.
Assistance for all iLO 2 pages is available from iLO 2 Help. Links on each iLO 2 page provide summary information about the features of iLO 2 and helpful information to optimize its operation. To access pagespecific help, click the question mark (?) on the right side of the browser window.
Typical user tasks are found under the System Status, Remote Console, Virtual Media, and Power Management tabs of the iLO 2 interface. These tasks are described in the "Using iLO 2 (on page 79)" section.
The Administration tab is typically used by an advanced or administrative user who must manage users, configure global and network settings as well as configure or enable the more advanced functions of iLO
Operational overview 12
2. These tasks are discussed in the sections, "iLO 2 setup (on page 16)" and "Configuring iLO 2 (on page 24)".
Subject-specific areas of iLO 2 functionality and integration are detailed in:
•Directory services (on page 130)
•Directory-enabled remote management (on page 161)
•HPQLOMIG directory migration utility (on page 168)
•HP Systems Insight Manager integration (on page 178)
•Troubleshooting iLO 2 (on page 182)
•Directory services schema (on page 207)
Supported browsers and client operating systems
•Microsoft® Internet Explorer 7
o This browser is supported on Microsoft® Windows® products.
o HP supports Microsoft® JVM and SUN Java™ 1.4.2_13. To download the recommended JVM for your system configuration, refer to the HP website (http://www.hp.com/servers/manage/jvm).
•Microsoft® Internet Explorer 6 with Service Pack 1 or later
o This browser is supported on Microsoft® Windows® products.
o HP supports Microsoft® JVM and SUN Java™ 1.4.2_13. To download the recommended JVM for your system configuration, refer to the HP website (http://www.hp.com/servers/manage/jvm).
•Firefox 2.0
o This browser is supported on Red Hat Enterprise Linux Desktop 4 and Novell Linux Desktop 9.
o HP supports Microsoft® JVM and SUN Java™ 1.4.2_13. To download the recommended JVM for your system configuration, refer to the HP website (http://www.hp.com/servers/manage/jvm).
Certain browsers and operating system combinations might not work correctly, depending on the implementation of the required browser technologies.
Supported server operating system software
iLO 2 is an independent microprocessor running an embedded operating system. The architecture ensures that the majority of iLO 2 functionality is available, regardless of the host operating system.
For graceful host operating system shutdown, HP SIM integration requires health drivers and Management Agents or remote console access.
iLO 2 provides two interface drivers:
•iLO 2 Advanced Server Management Controller Driver (health driver)—Provides system management support, including monitoring of server components, event logging, and support for the Management Agents.
•iLO 2 Management Interface Driver—Enables system software and SNMP Insight Agents to communicate with iLO 2.
Operational overview 13
These drivers and agents are available for the following network operating systems:
•Microsoft®
o Windows® 2000 Server
o Windows® 2000 Advanced Server o Windows Server™ 2003
o Windows Server™ 2003, Web Edition
o Windows® Small Business Server 2003 (ML300 series) o Windows Vista™
•Red Hat
o Red Hat Enterprise Linux 3 (x86)
o Red Hat Enterprise Linux 3 (AMD64/EM64T) o Red Hat Enterprise Linux 4 (x86)
o Red Hat Enterprise Linux 4 (AMD64/EM64T) o Red Hat Enterprise Linux 5 (x86)
o Red Hat Enterprise Linux 5 (AMD64/EM64T)
•SUSE
o SUSE LINUX Enterprise Server 9 (x86)
o SUSE LINUX Enterprise Server (AMD64/EM64T) o SUSE LINUX Enterprise Server 10
Text-based remote console overview
iLO and its predecessors support a true text-based remote console. Video information is obtained from the server and the contents of the video memory are sent to the management processor, compressed, encrypted, and forwarded to the management client application. iLO uses a screen-frame buffer, which detects changes in text information, encrypts the changes, and sends the characters (including screen positioning information) to text-based client applications. This method provides compatibility with standard text-based clients, good performance, and simplicity. However, you cannot display non-ASCII or graphical information, and screen positioning information (displayed characters) might be sent out of order.
New video technology (known as Virtual KVM on HP ProLiant servers) used in the iLO 2 high-performance remote console does not provide a true text-based console. iLO 2 uses the video adapter DVO port to access video memory directly. This method significantly increases iLO 2 performance. However, the digital video stream does not contain useful text data. Data obtained from the DVO port represents graphical data (non-character-based), and is not comprehensible ASCII or text data. This video data cannot be rendered by a text-based client application such as telnet or SSH.
The iLO 2 text-based remote console remains available on iLO 2 until the operating system POST is complete. iLO 2 firmware continues to use the virtualized serial-port functionality of the management processor. The virtual serial port capability is available in iLO and iLO 2. However, on the iLO 2 firmware, the virtual serial port was renamed Remote Serial Console. iLO 2 uses the Remote Serial Console to access a pre-operating system, text-based remote console. The iLO 2 Remote Serial Console applet appears as a text-based console, but the information is rendered using graphical video data.
Operational overview 14
iLO 2 displays this information through the remote console applet while in the server pre-operating system state, enabling a non-licensed iLO 2 to observe and interact with the server during POST activities. A nonlicensed iLO 2 cannot use remote console access after the server completes POST and begins to load the operating system. The iLO 2 Advanced License enables access to the remote console at all times. For more information, see the section, "Licensing (on page 27)."
Virtual serial port and remote serial console
The management processor contains serial-port hardware that can replace the physical serial port on the server's motherboard. Using an electronic switch, the iLO 2 firmware disconnects the server's physical serial port and commands its own serial-port hardware to connect. The iLO 2 serial-port hardware establishes a connection between the server and the management processor network. The firmware encapsulates the characters sent by the server to the serial port into network packets and sends the network packets to the remote serial console applet or application (the application may be a telnet or SSH client). Characters sent by the remote applet or application are encapsulated into network packets and sent to the iLO 2 firmware, which then extracts the characters and feeds them to the server. The iLO 2 remote serial console provides a bi-directional serial communication path between the remote user and the server.
Using the iLO 2 remote serial console, the remote user is able to perform operations such as interacting with the server POST sequence and operating system boot sequence; establishing a login session with the operating system, interacting with the operating system; and executing and interacting with applications on the server operating system. Users of the Microsoft® Windows Server™ 2003 operating system have the ability to execute the EMS subsystem through the remote serial console. EMS is useful for debugging operating system boot and problems at the operating system kernel level.
Operational overview 15

iLO 2 setup
In this section |
|
Quick setup ........................................................................................................................................... |
16 |
Preparing to setup iLO 2 ......................................................................................................................... |
16 |
Connecting to the network....................................................................................................................... |
18 |
Configuring the IP address ...................................................................................................................... |
19 |
Logging into iLO 2 for the first time........................................................................................................... |
19 |
Setting up user accounts.......................................................................................................................... |
20 |
Activating iLO 2 licensed features using a browser..................................................................................... |
21 |
Installing iLO 2 device drivers.................................................................................................................. |
21 |
Quick setup
To quickly setup iLO 2 using the default settings for iLO 2 Standard and iLO Advanced features, follow the steps below:
1.Prepare—Decide how you want to handle networking and security ("Preparing to setup iLO 2" on page 16)
2.Connect iLO 2 to the network ("Connecting to the network" on page 18).
3.If you are not using dynamic IP addressing, use the iLO 2 RBSU to configure a static IP address ("Configuring the IP address" on page 19).
4.Log into iLO 2 from a supported browser or command line using the default user name, password, and DNS name provided on the iLO 2 Network Settings tag attached to the server ("Logging into iLO 2 for the first time" on page 19).
5.Change the default user name and password on the administrator account to your predefined selections
6.If you are using the local accounts feature, set up your user accounts ("Setting up user accounts" on page 20).
7.Activate iLO 2 advanced features ("Activating iLO 2 licensed features using a browser" on page 21).
8.Install the iLO 2 device drivers ("Installing iLO 2 device drivers" on page 21).
Preparing to setup iLO 2
Before setting up your iLO 2 management processors, you must decide how to handle networking and security. The following questions can help you configure iLO 2 for your needs:
1.How should iLO 2 connect to the network? For a graphical representation and explanation of the available connections, see the section, "Connect to the network ("Connecting to the network" on page 18)."
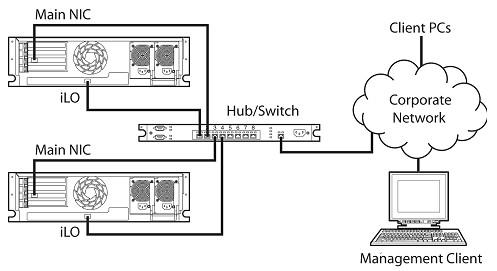
Typically iLO 2 is connected to the network using either:
iLO 2 setup 16
oA corporate network where both the NIC and the iLO 2 port are connected to the corporate network. This connection enables access to iLO 2 from anywhere on the network and reduces the amount of networking hardware and infrastructure required to support iLO 2. However, on a corporate network, network traffic can hinder iLO 2 performance.
oA dedicated management network with the iLO 2 port on a separate network. A separate network improves performance and security because you can physically control which workstations are connected to the network. A separate network also provides redundant access to the server when a hardware failure occurs on the corporate network. In this configuration, iLO 2 cannot be accessed directly from the corporate network.
2.How will iLO 2 acquire an IP address?
To access iLO 2 after connecting it to the network, the management processor must acquire an IP address and subnet mask using either a dynamic or static process:
oDynamic IP address is set by default. iLO 2 obtains the IP address and subnet mask from DNS/DHCP servers. This method is the simplest.
oStatic IP address is used to configure a static IP address if DNS/DHCP servers are not available on the network. A static IP address can be configured in iLO 2 using the RBSU.
If using a static IP, you must have an IP address before starting iLO 2 setup.
3.What access security is required and what user accounts and privileges are needed?
iLO 2 provides several options to control user access. You must select one of the following methods to prevent unauthorized access to corporate IT assets:
oLocal accounts with up to 12 user names and passwords can be stored on iLO 2. This is ideal for small environments such as labs and smalland medium-sized businesses.
oDirectory services use the corporate directory (Microsoft® Active Directory or Novell eDirectory) to manage iLO 2 user access. This is ideal for environments with a large number of frequently changing users. If you plan to use Directory services leave at least one local account enabled for alternate access.
For more information about iLO 2 access security see the section, "Security (on page 42)."
4.How do you want to configure iLO 2?
iLO 2 supports various interfaces for configuration and operation. This guide discusses the following interfaces:
oiLO 2 RBSU ("Setting up iLO 2 using iLO 2 RBSU" on page 20) can be used when the system environment does not use DHCP, DNS, or WINS.
oBrowser-based setup ("Setting up iLO 2 using the browser-based option" on page 21) can be used when you can connect to iLO 2 on the network using a browser. This method can also reconfigure a previously configured iLO 2.
oSMASH CLP can be used when a command line is accessible through telnet, SSH, or physical serial port. See the HP Integrated Lights-Out Management Processor Scripting and Command Line Resource Guide.
The iLO 2 default settings enable you to use most features with no additional configuration. However, the extensive configuration flexibility of iLO 2 enables customization for multiple enterprise environments. See the section, "Configuring iLO 2 (on page 24)" for all available options.
For advanced setup of multiple iLO 2 management processors using scripting commands, the following methods are available. Scripts are text files written in an XML-based scripting language called RIBCL. You can use RIBCL scripts to configure iLO 2 on the network, during initial deployment, or from an already
iLO 2 setup 17
deployed host. Each method is described in the HP Integrated Lights-Out Management Processor Scripting and Command Line Resource Guide.
•CPQLOCFG is a Microsoft® Windows® utility that sends RIBCL scripts to iLO 2 over the network.
•HPONCFG is a local online scripted-setup utility that runs on the host and passes RIBCL scripts to the local iLO 2. There are Windows® and Linux versions of this utility, which require the HP iLO 2 Management Interface Driver.
•Perl is a scripting language that can be used from Linux clients to send RIBCL scripts to iLO 2 over the network.
Connecting to the network
Typically iLO 2 is connected to the network in one of two ways. iLO 2 can be connected through a:
•Corporate network where both ports are connected to the corporate network. In this configuration, the server has two network ports (one server NIC, and one iLO 2 NIC) connected to a corporate network.
iLO 2 setup 18
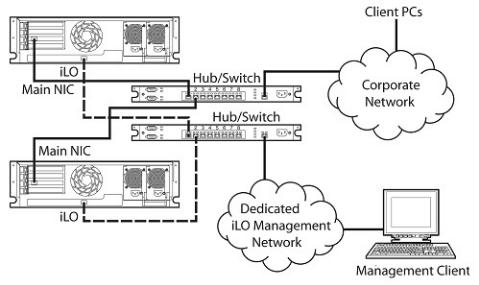
•Dedicated management network where the iLO 2 port is on a separate network.
Configuring the IP address
This step is necessary only if you are using a static IP address. When using dynamic IP addressing, your DHCP server will automatically assign an IP address for iLO 2. HP recommends using DNS or DHCP with iLO 2 to simplify installation
To configure a static IP address, use the iLO 2 RBSU with the following procedure to disable DNS and DHCP and configure the IP address and the subnet mask:
1.Restart or power up the server.
2.Press the F8 key when prompted during POST. The iLO 2 RBSU runs.
3.Select Network>DNS/DHCP, press the Enter key, and then select DHCP Enable. Press the spacebar to turn off DHCP. Be sure that DHCP Enable is set to Off, and save the changes.
4.Select Network>NIC>TCP/IP, press the Enter key, and enter the appropriate information in the IP Address, Subnet Mask, and Gateway IP Address fields.
5.Save the changes.
6.Exit iLO 2 RBSU. The changes take effect when you exit iLO 2 RBSU.
Logging into iLO 2 for the first time
iLO 2 is configured with a default user name, password, and DNS name. Default user information is located on the iLO 2 Network Settings tag attached to the server containing the iLO 2 management processor. Use these values to access iLO 2 remotely from a network client using a standard Web browser.
For security reasons, HP recommends changing the default settings after logging in to iLO 2 for the first time.
The default values are:
iLO 2 setup 19

•User name—Administrator
•Password—A random, eight-character, alphanumeric string
•DNS Name—ILOXXXXXXXXXXXX, where the Xs represent the serial number of the server
NOTE: User names and passwords are case sensitive.
If you enter an incorrect user name and password or a log in attempt fails, iLO 2 imposes a security delay. For more information on login security, refer to "Login security (on page 45)."
Setting up user accounts
iLO 2 comes preconfigured with default factory settings, including a default user account and password. For security reasons, HP recommends changing the default settings after logging in to iLO 2 for the first time. These changes can be made using any of the iLO 2 user interfaces. RBSU and browser procedures are explained in this user guide. Other options including the SMASH CLP and scripting methods are described in the "HP Integrated Lights-Out Management Processor Scripting and Command Line Resource Guide".
If iLO 2 is connected to a network running DNS or DHCP, you can use it immediately without changing any settings.
Setting up iLO 2 using iLO 2 RBSU
HP recommends iLO 2 RBSU to initially set up iLO 2 and configure iLO 2 network parameters for environments that do not use DHCP and DNS or WINS. RBSU provides the basic tools to configure iLO 2 network settings and user accounts to get iLO 2 on the network.
You can use RBSU to configure network parameters, directory settings, global settings, and user accounts. iLO 2 RBSU is not intended for continued administration. RBSU is available every time the server is booted and can be run remotely using the iLO 2 Remote Console.
iLO 2 RBSU can be disabled in the Global Settings preferences. Disabling iLO 2 RBSU prevents reconfiguration from the host unless the iLO 2 Security Override Switch is set.
To run iLO 2 RBSU to set up local accounts:
1.Restart or power up the server.
2.Press the F8 key when prompted during POST. The iLO 2 RBSU runs.
3.If prompted, enter a valid iLO 2 user ID and password with the appropriate iLO 2 privileges (Administer User Accounts>Configure iLO 2 Settings). Default account information is located on the iLO 2 Default Network Settings tag attached to the server containing the iLO 2 management processor. If iLO 2 has not been configured to present a login challenge to the RBSU, no prompt will appear.
4.Make and save any necessary changes to the iLO 2 configuration.
5.Exit iLO 2 RBSU.
iLO 2 setup 20
Setting up iLO 2 using the browser-based option
Use the browser-based setup method if you can connect to iLO 2 on the network using a browser. You can also use this method to reconfigure a previously configured iLO 2.
Access iLO 2 from a remote network client using a supported browser, and provide the default DNS name, user name, and password. Default DNS name and account information is located on the iLO 2 Network Settings tag attached to the server containing the iLO 2 management processor.
When you successfully log onto iLO 2, you can change the default values of the local user accounts by selecting User Administration under the iLO 2 Administration tab.
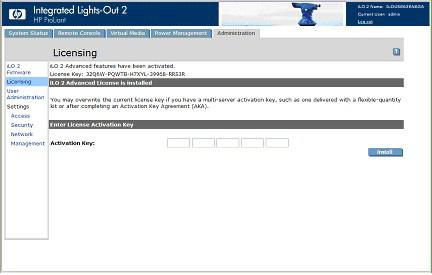
Activating iLO 2 licensed features using a browser
The Licensing page enables you to view the current license status and enter a key to activate iLO 2 license features. The iLO 2 version and current license information is displayed in this section. If a license is installed (including an evaluation license), the license number is displayed. See "Licensing (on page 27)" for more information about iLO 2 license options.
1.Log into iLO 2 through a supported browser.
2.Click Administration>Licensing to display the iLO 2 license activation screen.
3.Enter the license key. Press the Tab key or click inside a field to move between fields. The Activation Key field advances automatically as you enter data. Click Licensing to clear the fields and reload the page.
4.Click Install. The EULA confirmation appears. The EULA details are available on the HP website (http://www.hp.com/servers/lights-out) and with the license kit.
5.Click OK.
The advanced features of iLO 2 are now enabled.
Installing iLO 2 device drivers
The iLO 2 Management Interface Driver enables system software such as SNMP Insight Agents and the Terminal Services Pass-Through service to communicate with iLO 2.
iLO 2 setup 21
The device drivers required to support iLO 2 are part of the PSP located on the SmartStart CD, Management CD, or on the HP website (http://www.hp.com/servers/lights-out).
All the support drivers for your server and iLO 2 can be downloaded from the HP website (http://www.hp.com/servers/lights-out).
To download the drivers:
1.Click the iLO 2 graphic.
2.Select Software and Drivers.
Microsoft device driver support
The device drivers that support the iLO 2 are part of the PSP that is located on the HP website (http://www.hp.com/support) or on the SmartStart CD. Before you install the Windows® drivers, obtain the Windows® documentation and the latest Windows® Service Pack.
iLO 2 prerequisite files:
•CPQCIDRV.SYS provides the iLO 2 Management Interface Driver support.
•CPQASM2.SYS, SYSMGMT.SYS, and SYSDOWN.SYS provide the iLO 2 Advanced Server Management Controller Driver support.
PSP for Microsoft® Windows® products includes an installer that analyzes system requirements and installs all drivers. The PSP is available on the HP website (http://www.hp.com/support) or on the SmartStart CD.
To install the drivers in the PSP:
1.Download the PSP from the HP website (http://www.hp.com/support).
2.Run the SETUP.EXE file included in the download, and follow the installation instructions.
For additional information about the PSP installation, read the text file included in the PSP download.
Linux device driver support
You can download the LSP files containing the iLO 2 driver, the foundation agents, and health agents from the HP website (http://www.hp.com/support). The instructions on how to install or update the iLO 2 driver are available on the website. The HP Management Agents for Linux are:
•ASM package (hpasm) which combines the health driver, IML viewer, foundation agents, health agent, and standard equipment agent into one package.
•RSM package (hprsm) which combines the RIB driver, rack daemon, RIB agent, and rack agent into one package.
To load the health and iLO 2 driver packages, use the following commands:
rpm –ivh hpasm-d.vv.v-pp.Linux_version.i386.rpm
rpm –ivh hprsm-d.vv.v-pp.Linux_version.i386.rpm
where d is the Linux distribution and version and vv.v-pp are version numbers.
For additional information, refer to the Software and Drivers website (http://www.hp.com/support). To remove the health and iLO 2 drivers, use the following commands:
rpm –e hpasm
iLO 2 setup 22
rpm –e hprsm
For additional information, refer to the Software and Drivers website (http://www.hp.com/support).
Novell NetWare device driver support
The device drivers required to support iLO 2 are part of the PSP that is located on the SmartStart CD and the HP website (http://www.hp.com/support). The PSP for Novell NetWare includes an installer that analyzes system requirements and installs all drivers.
iLO 2 requires the following files:
•The CPQHLTH.NLM file provides the Health Driver for Novell NetWare.
•The CPQCI.NLM file provides iLO 2 Management Interface Driver support.
When updating iLO 2 drivers, be sure iLO 2 is running the latest version of iLO 2 firmware. You can obtain the latest version as a Smart Component from the HP website (http://www.hp.com/servers/lightsout).
To install the drivers download the PSP from the HP website (http://www.hp.com/support) to a NetWare server. After downloading the PSP, follow the Novell NetWare component installation instructions to complete the installation. For additional information about the PSP installation, read the text file included in the PSP download.
When using Novell NetWare 6.X, use the ATI ES1000 video driver that is provided by the operating system for best results.
iLO 2 setup 23

Configuring iLO 2
In this section |
|
iLO 2 configuration overview................................................................................................................... |
24 |
Upgrading iLO 2 firmware ...................................................................................................................... |
24 |
Licensing ............................................................................................................................................... |
27 |
User administration................................................................................................................................. |
29 |
Configuring iLO 2 access........................................................................................................................ |
34 |
Security................................................................................................................................................. |
42 |
Network................................................................................................................................................ |
62 |
SNMP/Insight Manager settings .............................................................................................................. |
69 |
ProLiant BL p-Class configuration .............................................................................................................. |
72 |
iLO 2 configuration overview
Typically, an advanced or administrative user who must manage users and configure global and network settings configures iLO 2. You can configure iLO 2 using the iLO 2 browser-based GUI or scripting tools such as CPQLOCFG and HPONCFG (described in the HP Integrated Lights-Out Management Processor Scripting and Command Line Resource Guide.)
The iLO 2 Administration tab enables you to configure and manage user settings, SNMP alerting (through integration with HP SIM), security settings, licensing, certificate administration, directory settings, and network environment settings. The Administration tab includes the following menu options:
•iLO 2 Firmware ("Upgrading iLO 2 firmware" on page 24)
•Licensing (on page 27)
•User Administration (on page 29)
•Settings
o Access ("Configuring iLO 2 access" on page 34) o Security (on page 42)
o Network (on page 62)
o Management ("SNMP/Insight Manager settings" on page 69)
Upgrading iLO 2 firmware
Firmware upgrades enhance the functionality of iLO 2. You can find the latest firmware on the HP website (http://www.hp.com/servers/lights-out). Select your iLO 2 product and then select Software & Drivers. After the software and drivers page appears, select your iLO 2 product and operating system, and then click Locate Software. You can also locate your iLO 2 software by selecting the Operating System and Category options.
You must have the Configure iLO 2 privilege (configure local device settings) to update the firmware unless you set then the security override switch ("iLO 2 Security Override Switch administration" on page
Configuring iLO 2 24
44). If the security override switch is set, any iLO 2 user can update the firmware. You must run firmware updates from an Administrator or root context on the host operating system.
To update the iLO 2 choose one of the following methods:
•Online firmware update—Download the appropriate operating system component and run it from the Administrator or root context of the operating system. The online firmware update software runs on the host operating system and updates the iLO 2 firmware without requiring you to log in to iLO 2.
•Offline firmware update for SmartStart maintenance—Download the iLO 2 firmware image file you plan to install and see the section, "Upgrading iLO 2 using a browser (on page 25)."
•Firmware Maintenance CD-ROM—Download the component to create a bootable CD that contains many firmware updates for ProLiant servers and options.
•Scripting with CPQLOCFG—Download the CPQLOCFG component to get the network-based scripting utility, CPQLOCFG. CPQLOCFG enables you to use RIBCL scripts that perform firmware updates, iLO 2 configuration, and iLO 2 operations in bulk, securely over the network. Linux users should consider reviewing the HP Lights-Out XML PERL Scripting Samples for Linux.
•Scripting with HPONCFG—Download the HPONCFG component to get the host-based scripting utility, HPONCFG. This utility enables you to use RIBCL scripts that perform firmware updates, LightsOut processor configuration and operations in bulk, from Administrator or root account access on supported host operating systems.
•HP Directories Support for Management Processors—-Download the HP Directories Support for Management Processors executable file to get the directory support components. One of the components, HPLOMIG, can be used to discover iLO, iLO 2, RILOE, and RILOE II processors, and update their firmware. You do not have to use directory integration to take advantage of this functionality.
Upgrading iLO 2 using a browser
You can complete the firmware upgrade from any network client using a supported browser. You must have the Update iLO 2 Firmware privilege to upgrade the iLO 2 firmware. The most recent firmware for iLO 2 is available on the HP website (http://www.hp.com/servers/lights-out).
To upgrade the iLO 2 firmware using a supported browser:
1.Log in to iLO 2 using an account that has the Configure iLO 2 Settings privilege.
Configuring iLO 2 25
2.Click Administration>Upgrade iLO 2 Firmware. The Upgrade iLO 2 Firmware page appears.
3.Enter the file name in the New firmware image field or browse for the file.
4.Click Send firmware image. The firmware upgrade takes a few minutes. A progress bar displays the progress of the firmware upgrade.
Do not interrupt an Upgrade iLO 2 Firmware session. The iLO 2 system automatically resets after a successful firmware upgrade. The iLO 2 system reset does not affect the host operating system and server.
If the firmware upgrade is interrupted or fails, attempt the upgrade again immediately. Do not reset the iLO 2 system before reattempting a firmware upgrade.
Recovering from a failed iLO 2 firmware update
To recover from a failed firmware update using the HP Drive Key Boot Utility:
1.Copy the iLO 2 offline flash component to your USB drive key.
2.Verify that the iLO 2 security override switch is set to disabled.
3.Boot the USB drive key drive containing the iLO 2 flash component.
To download the HP Drive Key Boot Utility and for information on how to create a boot USB key, see the HP website (http://h18023.www1.hp.com/support/files/server/us/download/23839.html).
4.After the first screen displays, switch to text console by pressing the Ctrl+Alt+F1 keys.
5.Switch to the directory where the flash component is stored by entering cd /mnt/usb/components/ at the # prompt.
6.Remove the loaded HP Lights-Out driver by entering /etc/init.d/hprsm stop.
7.Run the component using the --direct option. For example:
./CP00xxxx.scexe –-direct
8.Enter y at the Continue (y/N)? prompt.
9.After programming is successfully completed, set the security override switch to enabled and reboot the server.
Configuring iLO 2 26

Downgrading the iLO 2 firmware
If you downgrade the iLO 2 firmware, you must remove the iLO 2 1.30 Remote Console ActiveX applet 1.3.0.19 from your Internet Explorer client browser. To remove the applet:
1.Open Internet Explorer.
2.Select Tools>Internet Options>Settings>View objects.
3.To remove 1.30.19, right-click iLO2 Remote console 1.3.0.18.
Licensing
HP iLO Advanced Pack and HP iLO Select Pack software support both iLO and iLO 2 and activate optional iLO 2 features that are not bundled with an unlicensed system. For additional information, see the HP website (http://h18004.www1.hp.com/products/servers/proliantessentials/valuepack/licensing.html).
Effective July 9, 2007, you can purchase iLO Advanced Packs and iLO Select Packs individually or as part of an Insight Control software suite.
If you purchase the iLO Advanced Pack or the iLO Select Pack with any Insight Control software suite or iLO Power Management Pack, HP provides Technical Support and Update Services. See the "Software technical support and update service (on page 214)" section for more information.
If you purchase the iLO Advanced Pack or the iLO Select Pack as a one-time activation of licensed features, you must purchase future functional upgrades. See the "Software technical support and update service (on page 214)" section for more information.
One iLO Advanced or iLO Select license is required for each server on which the product is installed and used. Licenses are nontransferable. Full details are contained in the EULA.
HP will continue to provide maintenance releases with fixes as well as iLO Standard, and iLO Standard Blade Edition feature enhancements at no extra charge.
A 60-day evaluation license key is available for download from the HP website (http://h10018.www1.hp.com/wwsolutions/ilo/iloeval.html). The evaluation license activates and enables access to iLO 2 Advanced features. You can only install one evaluation license per iLO 2. When the evaluation period expires, the iLO 2 features deactivate. To install a license, see the section, "Activating iLO 2 licensed features using a browser (on page 21)."
The following versions of iLO 2 are available:
NOTE: The features annotated with an asterisk (*) are not supported on all systems.
•iLO 2 Standard (unlicensed:)
o Virtual Power and Reset control
o Remote serial console through POST only o Event logs
o UID light*
o DMTF SMASH CLP o RIBCL/XML scripting o Browser access
Configuring iLO 2 27
o SSH access
oShared network port*
oSerial access*
oRemote Console Computer Lock
•iLO 2 Standard Blade Edition (unlicensed blade server):
oVirtual power and reset control
oRemote Console and IRC
oEvent logs
oUID light*
oDMTF SMASH CLP
oRIBCL/XML scripting
oBrowser access
oSSH access
oShared network port*
oSerial access*
oApplet-based virtual media
oTerminal Services integration
•iLO 2 Select:
oDirectory integration
oPower Regulator for ProLiant
oScripted virtual media
oApplet-based virtual media
oTwo-factor authentication
oConsole replay
oShared Remote Console
oHP SIM SSO
•iLO 2 Advanced:
oDirectory integration
o Power Regulator for ProLiant o Scripted virtual media
o Applet-based virtual media o Two-factor authentication o Remote Console and IRC
o Terminal Services integration o Console replay
o Shared Remote Console o HP SIM SSO
In addition to the standard iLO 2 single-server licenses, two other licensing options are available:
Configuring iLO 2 28
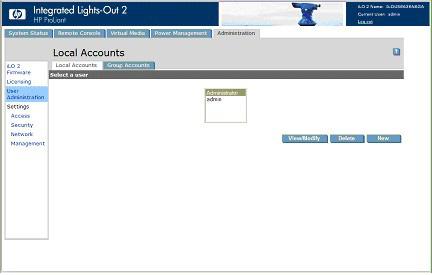
•The Flexible Quantity License Kit allows you to purchase a single software package, one copy of the documentation, and a single license key to activate the exact number of licenses requested.
•The Activation Key Agreement allows a volume purchase of ProLiant Essentials and Insight Control software over time, typically in conjunction with new ProLiant servers that are acquired on a regular basis.
User administration
iLO 2 enables you to manage user accounts stored locally in the secure iLO 2 memory and directory group accounts. Use MMC or ConsoleOne to manage directory user accounts.
iLO 2 supports up to 12 users with customizable access rights, login names, and advanced password encryption. Privileges control individual user settings. Users can have privileges customized to their individual access requirements. To support more than 12 users, you must have the Advanced Pack, which enables integration with an unlimited number of directory-based user accounts.
You must have the Administer User Accounts privilege to view iLO 2 users, add new users, and modify or delete existing users. If you do not have this privilege, you can view and modify only your account.
To access local accounts, click Administration>User Administration>Local Accounts.
Configuring iLO 2 29

iLO 2 Directory Accounts enables you to view iLO 2 groups and modify the settings for those groups. You must have the Administer Directory Groups privilege. To access Directory Accounts, click
Administration>User Administration>Group Accounts.
Adding a new user
IMPORTANT: Only users with the Administer User Accounts privilege can manage other users on iLO 2.
You can assign a different access privilege to each user. Each user can have a unique set of privileges designed for the tasks that the user must perform. You can grant or deny access to critical functions such as remote access, user management, virtual power, and other features.
To add a new user to iLO 2:
1.Log in to iLO 2 using an account that has the Administer User Accounts privilege.
2.Click Administration.
3.Select User Administration>Local Accounts.
Configuring iLO 2 30
 Loading...
Loading...