HP HPMX-5001-STR, HPMX-5001-TR1, HPMX-5001-TY1 Datasheet
1.5–2.5 GHz Upconverter/
Downconverter
Technical Data
HPMX-5001
Features
•2.7 V Single Supply Voltage
•Low Power Consumption (60Ê mA in Transmit Mode, 39 mA in Receive Mode Typical)
•2 dBm Typical Transmit Power at 1900 MHz
•Half-Frequency VCO with Frequency Doubler
•32/33 Dual-Modulus Prescaler
•Flexible Chip Biasing, Including Standby Mode
•TQFP-32 Surface Mount Package
•Operation to 2.5 GHz
•Use with Companion HPMX-5002 IF chip
Applications
•DECT, UPCS and ISM Band Handsets and Basestations
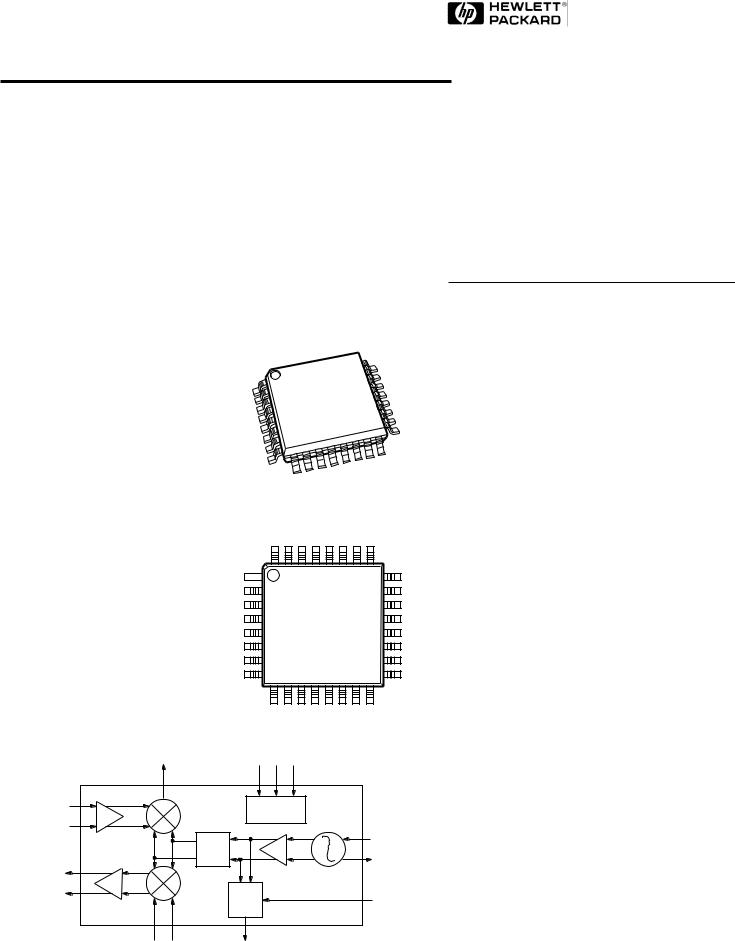
Plastic TQFP-32 Package
H
-5001 HPMX
YYWW
ZZZ XXXX
Pin Configuration
32 |
25 |
||||
1 |
|
|
|
|
24 |
|
|
||||
|
|
|
H |
||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
HPMX-5001 |
||
|
|
|
YYWW |
|
|
|
|
|
XXXX |
ZZZ |
|
8 |
|
|
|
17 |
|
9 |
16 |
||||
Functional Block Diagram
RX IF OUT |
POWER DOWN |
CONTROL |
RX RF IN |
|
|
X2 |
|
EXT. |
|
VCO |
|
|
|
TANK |
TX RF OUT |
|
|
|
32/33 |
RATIO |
|
SELECT |
|
|
|
|
TX IF IN |
PRESCALER |
|
|
OUT |
|
5965-9105E |
|
7-90 |
General Description
The HPMX-5001 Upconverter/ Downconverter provides RF system designers with all of the necessary features to perform an RF-to-IF downconversion for a receive path, as well as an IF-to- RF upconversion for transmit mode.
Designed to meet the unique needs of portable applications, the HPMX-5001 combines the qualities of flexible chip biasing, low power consumption, and true 2.7 V minimum supply voltage operation to provide superior performance and battery life. By incorporating the active elements of the VCO on-chip, as well as a 32/33 dual-modulus prescaler, overall system component count and costs are decreased. The 32-TQFP package insures that this high level of integration occupies a small amount of printed circuit board space.
The HPMX-5001 can be used in either dual-conversion systems (with the HPMX-5002 IF Demodulator/Modulator) or single-conversion systems. The HPMX-5001 is manufactured
using Hewlett-Packard’s HP-25 |
|
Silicon Bipolar Process with |
|
25Ê GHz f and 30 GHz f . |
|
T |
Max |

HPMX-5001 Absolute Maximum Ratings[1]
Parameter |
Min. |
Max. |
|
|
|
VCC Supply Voltage |
-0.2V |
8 V |
Voltage at Any Pin[4] |
-0.2V |
V + 0.2 V |
|
|
CC |
Power Dissipation[2,3] |
|
600mW |
RF Input Power |
|
15 dBm |
|
|
|
Junction Temperature |
|
+150°C |
Storage Temperature |
-55°C |
+125°C |
Thermal Resistance[2]:
θjc = 100°C/W
Notes:
1.Operation of this device in excess of any of these parameters may cause permanent damage.
2.TCASE = 25°C.
3.Derate at 10 mW/°C for TCASE > 90°C.
4.Except CMOS logic inputs – see Summary Characterization Information table.
HPMX-5001 Guaranteed Electrical Specifications
Unless otherwise noted, all parameters are guaranteed under the following conditions: VCC = 3.0 V. Test results are based upon use of networks shown in test board schematic diagram (see Figure 28). Typical values are for VCC = 3.0 V, TA = 25°C.
Symbol |
Parameters and Test Conditions |
Units |
Min. |
Typ. |
Max. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
GC |
Receive Conversion Gain[1] |
|
dB |
12 |
14 |
|
Pout |
Transmitter Power Output |
Input[2] |
|
|
|
|
|
|
2:1 output VSWR |
dBm |
0 |
2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ICC |
Device Supply Current |
Transmit Mode |
mA |
|
64 |
80 |
|
|
Receive Mode |
mA |
|
43 |
54 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Synth Mode |
mA |
|
15 |
19 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Standby Mode (with DIVMC Set High) |
μA |
|
1 |
50 |
|
V |
DIV Single-Ended Swing[3] |
|
V |
0.7 |
1 |
|
DIV |
|
|
PP |
|
|
|
Notes:
1.50 Ω RF source, 100 MHz < IF < 300 MHz, 1.89 GHz RF. There is a 750 Ω resistor on chip between RXIF and RXIFB (pins 3 and 4). A matching network from 750 Ω to 50 Ω is used for this measurement. Insertion loss of the matching network is included in the net
conversion gain figure. See Figure 28.
2.Signal injected into P3 in Figure 28 is -12.5 dBm.
3.DIV output AC coupled into a 2 kΩ || 10 pF load. See test board schematic diagram, Figure 28.
7-91
HPMX-5001 Summary Characterization Information
Typical values measured on test board shown in Figure 28 at VCC = 3.0 V, TA = 25°C, RXIF = 110.592 MHz, TXRF = 1.89 GHz, unless otherwise noted.
Symbol |
|
Parameters and Test Conditions |
Units |
Typical |
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
VIH |
|
CMOS Input High Voltage (Can Be Pulled |
V |
³ VCC-0.8 |
|||
|
|
up as High as V + 7 V)[1] |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
CC |
|
|
|
|
|
VIL |
|
CMOS Input Low Voltage |
V |
£ VCC-1.9 |
|
||
IIH |
|
CMOS Input High Current |
mA |
<10 |
|
|
|
IIL |
|
CMOS Input Low Current |
mA |
>-300 |
|
|
|
ts |
|
DIVMC Setup Time[2,8] |
ns |
4 |
|
|
|
th |
|
DIVMC Hold Time[2,8] |
ns |
0 |
|
|
|
tpd |
|
DIV Propagation Delay[2,8] |
ns |
<7 |
|
|
|
|
|
Mode Switching Time[3] |
ms |
<1 |
|
|
|
Receive Mode |
|
|
|
1.89GHz |
|
2.45GHz |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Gc |
|
Receive Conversion Gain[9] |
dB |
14 |
|
13.5 |
|
NF |
|
Noise Figure[4] |
dB |
10 |
|
10 |
|
IIP3 |
|
Input Third Order Intercept Point |
dBm |
-8 |
|
-9 |
|
IP1dB |
|
Input 1 dB Gain Compression Point |
dBm |
-18 |
|
-18 |
|
|
|
LO Leakage (2 x fVCO) at IF Port |
dBm |
-57 |
|
— |
|
VSWRin |
|
Input VSWR[5] |
|
1.3:1 |
|
1.3:1 |
|
Transmit Mode[6] |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
PIM3 |
|
Power Output Level for >35 dB IM3 Suppression[10] |
dBm |
— |
|
-5 |
|
OP1dB |
|
Output 1 dB Gain Compression Point |
dBm |
0 |
|
0 |
|
VSWRout |
|
Output VSWR |
|
1.8:1 |
|
1.8:1 |
|
|
|
LO Suppression (2 x fVCO) |
dBc |
25 |
|
30 |
|
F3dBIF |
|
IF 3 dB Bandwidth |
MHz |
500 |
|
500 |
|
|
|
Transmitter C/N @ 2 x fVCO + 4 MHz[11] |
dBc/Hz |
+137 |
|
+134 |
|
Synth Mode |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1LO Frequency Range[7] |
MHz |
750-1200 |
|
|
|
Notes:
1.All CMOS logic inputs are internally pulled up to logic high level.
2.See Figure 2 for detailed timing diagram.
3.Between any two different biasing modes. This switching time does not include PLL lock-up time.
4.Single sideband noise figure.
5.In modes other than receive, the VSWR may be as high as 10:1.
6.Single-ended 50 Ω RF load, 300 Ω series IF terminations (600 Ω differential), 100 MHz < IF < 300 MHz, 1.89 GHz RF.
7.The LO is followed by a frequency doubler which raises the LO range to 1500-2400 MHz.
8.DIV output AC coupled into a 2 kΩ || 10 pF load. See test diagram, Figure 28.
9.50 Ω RF source, 110 MHz < IF < 300 MHz, 1.89 GHz or 2.45 GHz RF. There is a 750 Ω resistor on chip between RXIF and RXIFB (pins 3 and 4). A matching network from 750 Ω to 50ÊΩ is used for this measurement. Insertion loss of the matching network is
included in the net conversion gain figure.
10.PIM3 is the maximum SSB output power for at least 35 dB IM3 spur suppression.
11.Measured at saturated output power for 1.89 GHz. Measured at -5 dBm SSB output power for 2.45Ê GHz.
7-92
Table 1 - HPMX-5001 Pin Description
No. |
Mnemonic |
I/O Type |
Description |
|
|
|
|
1 |
TXCTRL |
CMOS I/P |
Controls biasing of transmit mixer, amplifiers, and doubler |
|
|
|
|
3 |
RXIFB |
Analog O/P |
Inverted single-ended downconverted receiver output, |
|
|
|
normally tied to VCC (internal 750 Ω resistor connects to RXIF) |
4 |
RXIF |
Analog O/P |
Single-ended downconverted receiver output, drives SAW |
|
|
|
filter (internal 750 Ω resistor connects to RXIFB) |
5 |
TXIF |
Analog I/P |
Transmit non-inverting IF input |
|
|
|
|
6 |
TXIFB |
Analog I/P |
Transmit inverting IF input |
|
|
|
|
7 |
LNAREF |
Analog DC I/P |
Reference input for receive input amplifier |
|
|
|
|
8 |
RXRF |
Analog I/P |
Receive RF input |
|
|
|
|
10 |
TXRXVCC |
DC Supply |
Supply voltage for transmit path, receive front-end and mixer |
|
|
|
|
11,15 |
TXRXGND |
Ground |
Ground for transmit path, receive front-end and mixer |
|
|
|
|
12 |
TXRFB |
Analog O/P |
Inverting output of transmit path (see test diagram for |
|
|
|
matching network) |
|
|
|
|
14 |
TXRF |
Analog O/P |
Non-inverting output of transmit path (see test diagram for |
|
|
|
matching network) |
|
|
|
|
16 |
DBLVCC |
DC Supply |
Supply voltage for LO frequency doubler |
|
|
|
|
17 |
DBLGND |
Ground |
Ground for LO frequency doubler |
|
|
|
|
20 |
VCOTNKS |
Analog I/P |
Sense line from external tank circuit to on-chip VCO amplifier |
|
|
|
|
21 |
VCOTNKF |
Analog O/P |
Force line from on-chip VCO amplifier to external tank circuit |
|
|
|
|
22 |
VCOVCC |
DC Supply |
Supply voltage for on-chip VCO amplifier |
|
|
|
|
23 |
VCOGND |
Ground |
Ground for on-chip VCO amplifier |
|
|
|
|
26 |
DIVVCC |
DC Supply |
Supply voltage for 32/33 dual-modulus prescaler |
|
|
|
|
27 |
DIVGND |
Ground |
Ground for 32/33 dual-modulus prescaler |
|
|
|
|
28 |
DIV |
Analog O/P |
Output from 32/33 dual-modulus prescaler |
|
|
|
|
30 |
DIVMC |
CMOS I/P |
Modulus control signal for 32/33 dual-modulus prescaler |
|
|
|
|
31 |
LOCTRL |
CMOS I/P |
Controls biasing for VCO and 32/33 dual modulus prescaler |
|
|
|
|
32 |
RXCTRL |
CMOS I/P |
Controls biasing for receive mixer, amplifiers, and doubler |
|
|
|
|
2,9,13, |
VSUB |
Ground |
Substrate bias voltage |
18,19,24, |
|
|
|
25,29 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Table 2 - HPMX-5001 Mode Control
(CMOS Logic Levels - all pins internally pulled up to high level)
Mode |
TXCTRL |
RXCTRL |
LOCTRL |
|
|
|
|
Transmit |
0 |
1 |
0 |
|
|
|
|
Receive |
1 |
0 |
0 |
|
|
|
|
Synth |
1 |
1 |
0 |
|
|
|
|
Standby |
1 |
1 |
1 |
|
|
|
|
7-93

31 |
32 |
1 |
2 |
16 |
17 |
18 |
19 |
32 |
33 |
1 |
2 |
VCO |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
DIV |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
DIVMC |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
DIVIDE BY 33 (DIVMC = 0) |
|
|
|
|
|
||
31 |
33 |
1 |
2 |
16 |
17 |
18 |
19 |
32 |
1 |
2 |
3 |
VCO |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
DIV |
|
tpd |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
DIVMC |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ts |
th |
DIVIDE BY 32 (DIVMC = 1) |
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
Figure 2. HPMX-5001 Prescaler Timing Diagram.
FRONT-END RF FILTER
|
CERAMIC |
TX IF INPUT |
|
|
|
||
|
TX |
|
|
TX PA |
FILTER |
|
|
|
|
||
T/R |
|
X2 |
|
RX LNA |
|
32/33 |
|
CERAMIC |
HPMX-5001 |
||
|
|||
|
IMAGE |
||
|
|
||
|
FILTER |
|
|
|
|
RX IF FILTER |
|
|
|
RX IF OUTPUT |
LO1 REFERENCE OSCILLATOR
TANK 
˜ 30 MHz
SYNTHESIZER
Figure 3. HPMX-5001 Block Diagram/Typical Application.
7-94
 Loading...
Loading...