GE ML2400 User Manual

GE Consumer & Industrial
Multilin
MultiLink ML2400
Ethernet Communications Switch
Instruction Manual
Firmware Revision 3.x
Manual P/N: 1601-0220-AB
Manual Order Code: GEK-113042K
Copyright © 2008 GE Multilin
GE Multilin
215 Anderson Avenue, Markham, Ontario Canada L6E 1B3
Tel: (905) 294-6222 Fax: (905) 201-2098 Internet: http://www.GEmultilin.com
*1601-0220-AB*
|
|
|
T |
E |
|
|
|
|
|
IS |
R |
||||
|
G |
|
|
||||
R |
E |
|
|
|
|
E |
|
|
|
|
|
|
D |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ISO9001:2000 |
|||||||
E |
|
|
|
|
|
IN |
|
G |
|
|
|
|
L |
||
|
|
|
|
I |
|
||
|
|
MULT |
|
|
|||
GE Multilin's Quality Management System is registered to ISO9001:2000
QMI # 005094
UL # A3775
These instructions do not purport to cover all details or variations in equipment nor provide for every possible contingency to be met in connection with installation, operation, or maintenance. Should further information be desired or should particular problems arise which are not covered sufficiently for the purchaser’s purpose, the matter should be referred to the General Electric Company.
To the extent required the products described herein meet applicable ANSI, IEEE, and NEMA standards; but no such assurance is given with respect to local codes and ordinances because they vary greatly.
© 2008 GE Multilin Incorporated. All rights reserved.
GE Multilin Multilink ML2400 instruction manual for revision 3.x. Multilink ML2400 is a registered trademark of GE Multilin Inc.
The contents of this manual are the property of GE Multilin Inc. This documentation is furnished on license and may not be reproduced in whole or in part without the permission of GE Multilin. The content of this manual is for informational use only and is subject to change without notice.
Part numbers contained in this manual are subject to change without notice, and should therefore be verified by GE Multilin before ordering.
Part number: 1601-0220-AB (June 2008)

TOC |
TABLE OF CONTENTS |
Table of Contents
1: INTRODUCTION |
GETTING STARTED ............................................................................................................... |
1-1 |
|
INSPECTING THE PACKAGE AND PRODUCT .......................................................................... |
1-1 |
|
ORDERING ............................................................................................................................. |
1-2 |
|
ORDER CODES ......................................................................................................................... |
1-2 |
|
SPECIFICATIONS ................................................................................................................... |
1-3 |
|
TECHNICAL SPECIFICATIONS .................................................................................................. |
1-3 |
|
ENVIRONMENTAL SPECIFICATIONS ........................................................................................ |
1-5 |
|
TYPE TESTS ............................................................................................................................... |
1-5 |
|
PHYSICAL SPECIFICATIONS ..................................................................................................... |
1-6 |
|
APPROVALS AND WARRANTY ................................................................................................ |
1-6 |
|
FIRMWARE OVERVIEW ........................................................................................................ |
1-8 |
|
COMMAND LINE FIRMWARE .................................................................................................. |
1-8 |
|
ENERVISTA SOFTWARE ........................................................................................................... |
1-8 |
|
BEFORE STARTING ................................................................................................................... |
1-9 |
|
COMMAND LINE INTERFACE FIRMWARE ....................................................................... |
1-10 |
|
CONSOLE CONNECTION ......................................................................................................... |
1-10 |
|
CONSOLE SETUP ...................................................................................................................... |
1-10 |
|
CONSOLE SCREEN ................................................................................................................... |
1-11 |
|
LOGGING IN FOR THE FIRST TIME ......................................................................................... |
1-11 |
|
AUTOMATIC IP ADDRESS CONFIGURATION ......................................................................... |
1-11 |
|
SETTING THE IP PARAMETERS ............................................................................................... |
1-12 |
|
PRIVILEGE LEVELS .................................................................................................................... |
1-14 |
|
USER MANAGEMENT ............................................................................................................... |
1-14 |
|
HELP .......................................................................................................................................... |
1-15 |
|
EXITING ..................................................................................................................................... |
1-17 |
|
ENERVISTA SECURE WEB MANAGEMENT ...................................................................... |
1-18 |
|
LOGGING IN FOR THE FIRST TIME ......................................................................................... |
1-18 |
|
PRIVILEGE LEVELS .................................................................................................................... |
1-19 |
|
USER MANAGEMENT ............................................................................................................... |
1-19 |
|
MODIFYING THE PRIVILEGE LEVEL ........................................................................................ |
1-22 |
|
HELP .......................................................................................................................................... |
1-22 |
|
EXITING ..................................................................................................................................... |
1-23 |
|
ML2400 FIRMWARE UPDATES .......................................................................................... |
1-24 |
|
UPDATING MULTILINK FIRMWARE ........................................................................................ |
1-24 |
|
SELECTING THE PROPER VERSION ........................................................................................ |
1-24 |
|
UPDATING THROUGH THE COMMAND LINE ......................................................................... |
1-24 |
|
UPDATING THROUGH THE ENERVISTA SOFTWARE .............................................................. |
1-25 |
|
|
|
2: PRODUCT |
OVERVIEW .............................................................................................................................. |
2-1 |
DESCRIPTION |
INTRODUCTION TO THE ML2400 ......................................................................................... |
2-1 |
|
DESIGN ASPECTS ..................................................................................................................... |
2-2 |
|
COMMUNICATIONS MODULES ......................................................................................... |
2-3 |
|
FOUR-PORT MODULES ........................................................................................................... |
2-3 |
|
SIX-PORT MODULES ................................................................................................................ |
2-4 |
|
EIGHT-PORT MODULES ........................................................................................................... |
2-4 |
|
GIGABIT (1000 MBPS) MODULES ........................................................................................ |
2-6 |
|
FEATURES AND BENEFITS .................................................................................................. |
2-7 |
|
PACKET PRIORITIZATION, 802.1P QOS ............................................................................... |
2-7 |
|
FRAME BUFFERING AND FLOW CONTROL ........................................................................... |
2-7 |
MULTILINK ML2400 ETHERNET COMMUNICATIONS SWITCH – INSTRUCTION MANUAL |
TOC–I |

TABLE OF CONTENTS
|
MULTILINK SWITCH SOFTWARE ............................................................................................ |
2-7 |
|
REDUNDANT POWER SUPPLY ................................................................................................ |
2-8 |
|
ADDITIONAL FEATURES AND BENEFITS ................................................................................ |
2-8 |
|
APPLICATIONS ...................................................................................................................... |
2-10 |
|
DESCRIPTION ............................................................................................................................ |
2-10 |
|
ML2400 SWITCH FOR A VLAN APPLICATION ................................................................... |
2-10 |
|
NETWORK WITH MULTIPLE SUBNETS ................................................................................... |
2-11 |
|
|
|
3: INSTALLATION |
PREPARATION ....................................................................................................................... |
3-1 |
|
PRECAUTIONS ........................................................................................................................... |
3-1 |
|
LOCATING THE ML2400 ....................................................................................................... |
3-1 |
|
CONNECTING ETHERNET MEDIA ..................................................................................... |
3-3 |
|
DESCRIPTION ............................................................................................................................ |
3-3 |
|
CONNECTING ST-TYPE FIBER OPTICS (TWIST-LOCK) .......................................................... |
3-3 |
|
CONNECTING SC-TYPE FIBER OPTICS (SNAP-IN) ................................................................ |
3-4 |
|
CONNECTING SINGLE-MODE FIBER OPTICS ........................................................................ |
3-4 |
|
CONNECTING RJ45 TWISTED PAIR ...................................................................................... |
3-4 |
|
CONNECTING GIGABIT MEDIA USING GBICS ...................................................................... |
3-5 |
|
MECHANICAL INSTALLATION ............................................................................................ |
3-6 |
|
TABLE-TOP OR SHELF MOUNTING ........................................................................................ |
3-6 |
|
RACK MOUNTING .................................................................................................................... |
3-6 |
|
ELECTRICAL INSTALLATION .............................................................................................. |
3-8 |
|
POWERING THE ML2400 ...................................................................................................... |
3-8 |
|
UL REQUIREMENTS FOR DC-POWERED UNITS .................................................................. |
3-8 |
|
ALARM CONTACTS ................................................................................................................... |
3-9 |
|
DIELECTRIC STRENGTH (HI-POT) TESTING ............................................................................ |
3-10 |
|
CONNECTING A MANAGEMENT CONSOLE TERMINAL TO THE ML2400 ................ |
3-11 |
|
DESCRIPTION ............................................................................................................................ |
3-11 |
|
|
|
4: OPERATION |
FUNCTIONALITY ................................................................................................................... |
4-1 |
|
SWITCHING FUNCTIONALITY .................................................................................................. |
4-1 |
|
FILTERING AND FORWARDING ............................................................................................... |
4-1 |
|
ADDRESS LEARNING ................................................................................................................ |
4-2 |
|
STATUS LEDS .......................................................................................................................... |
4-2 |
|
UP-LINK MANUAL SWITCHES (FOR RJ45 PORT ONLY) ...................................................... |
4-2 |
|
AUTO-NEGOTIATION (FOR FAST ETHERNET COPPER PORTS) ............................................ |
4-2 |
|
FLOW CONTROL (IEEE 802.3X) ........................................................................................... |
4-3 |
|
POWER BUDGET CALCULATIONS WITH FIBER MEDIA ........................................................ |
4-5 |
|
TROUBLESHOOTING ............................................................................................................ |
4-7 |
|
OVERVIEW ................................................................................................................................ |
4-7 |
|
BEFORE CALLING FOR ASSISTANCE ...................................................................................... |
4-7 |
|
WHEN CALLING FOR ASSISTANCE ........................................................................................ |
4-7 |
|
|
|
5: IP ADDRESSING |
IP ADDRESS AND SYSTEM INFORMATION ..................................................................... |
5-1 |
|
OVERVIEW ................................................................................................................................ |
5-1 |
|
IMPORTANCE OF AN IP ADDRESS .................................................................................... |
5-3 |
|
DHCP AND BOOTP ................................................................................................................. |
5-3 |
|
BOOTP DATABASE .................................................................................................................... |
5-3 |
|
CONFIGURING DHCP/BOOTP/MANUAL/AUTO ................................................................ |
5-3 |
|
USING TELNET ......................................................................................................................... |
5-5 |
|
SETTING PARAMETERS ....................................................................................................... |
5-8 |
TOC–II |
MULTILINK ML2400 ETHERNET COMMUNICATIONS SWITCH – INSTRUCTION MANUAL |

TOC |
TABLE OF CONTENTS |
|
|
SETTING SERIAL PORT PARAMETERS .................................................................................... |
5-8 |
|
SYSTEM PARAMETERS ............................................................................................................. |
5-8 |
|
DATE AND TIME ....................................................................................................................... |
5-9 |
|
NETWORK TIME ....................................................................................................................... |
5-10 |
|
SYSTEM CONFIGURATION .................................................................................................. |
5-13 |
|
SAVING AND LOADING – COMMAND LINE .......................................................................... |
5-13 |
|
CONFIG FILE ............................................................................................................................. |
5-13 |
|
DISPLAYING CONFIGURATION ................................................................................................ |
5-16 |
|
SAVING CONFIGURATION ....................................................................................................... |
5-19 |
|
SCRIPT FILE .............................................................................................................................. |
5-21 |
|
SAVING AND LOADING – ENERVISTA SOFTWARE ............................................................... |
5-22 |
|
HOST NAMES ........................................................................................................................... |
5-24 |
|
ERASING CONFIGURATION ..................................................................................................... |
5-25 |
|
IPV6 .......................................................................................................................................... |
5-29 |
|
INTRODUCTION TO IPV6 ......................................................................................................... |
5-29 |
|
WHAT’S CHANGED IN IPV6? ................................................................................................. |
5-29 |
|
IPV6 ADDRESSING .................................................................................................................. |
5-30 |
|
CONFIGURING IPV6 ................................................................................................................ |
5-31 |
|
LIST OF COMMANDS IN THIS CHAPTER ................................................................................. |
5-32 |
|
|
|
6: ACCESS |
SECURING ACCESS .............................................................................................................. |
6-1 |
CONSIDERATIONS |
DESCRIPTION ............................................................................................................................ |
6-1 |
|
PASSWORDS ............................................................................................................................. |
6-1 |
|
PORT SECURITY FEATURE ....................................................................................................... |
6-2 |
|
CONFIGURING PORT SECURITY THROUGH THE COMMAND LINE INTERFACE .... |
6-3 |
|
COMMANDS .............................................................................................................................. |
6-3 |
|
SECURITY LOGS ....................................................................................................................... |
6-8 |
|
AUTHORIZED MANAGERS ....................................................................................................... |
6-10 |
|
CONFIGURING PORT SECURITY WITH ENERVISTA SOFTWARE ................................ |
6-12 |
|
COMMANDS .............................................................................................................................. |
6-12 |
|
LOGS ......................................................................................................................................... |
6-14 |
|
AUTHORIZED MANAGERS ....................................................................................................... |
6-15 |
|
|
|
7: ACCESS USING RADIUS |
INTRODUCTION TO 802.1X ................................................................................................ |
7-1 |
|
DESCRIPTION ............................................................................................................................ |
7-1 |
|
802.1X PROTOCOL ................................................................................................................. |
7-1 |
|
CONFIGURING 802.1X THROUGH THE COMMAND LINE INTERFACE ..................... |
7-4 |
|
COMMANDS .............................................................................................................................. |
7-4 |
|
EXAMPLE ................................................................................................................................... |
7-6 |
|
CONFIGURING 802.1X WITH ENERVISTA SECURE WEB MANAGEMENT |
|
|
SOFTWARE ............................................................................................. |
7-9 |
|
COMMANDS .............................................................................................................................. |
7-9 |
|
|
|
8: ACCESS USING |
INTRODUCTION TO TACACS+ ........................................................................................... |
8-1 |
TACACS+ |
OVERVIEW ................................................................................................................................ |
8-1 |
|
TACACS+ FLOW .................................................................................................................... |
8-2 |
|
TACACS+ PACKET ................................................................................................................. |
8-2 |
|
CONFIGURING TACACS+ THROUGH THE COMMAND LINE INTERFACE ................ |
8-4 |
|
COMMANDS .............................................................................................................................. |
8-4 |
|
EXAMPLE ................................................................................................................................... |
8-4 |
MULTILINK ML2400 ETHERNET COMMUNICATIONS SWITCH – INSTRUCTION MANUAL |
TOC–III |

TABLE OF CONTENTS
|
CONFIGURING TACACS+ WITH ENERVISTA SECURE WEB MANAGEMENT |
|
|
SOFTWARE ............................................................................................. |
8-6 |
|
|
|
9: PORT MIRRORING AND |
PORT MIRRORING ................................................................................................................ |
9-1 |
SETUP |
DESCRIPTION ............................................................................................................................ |
9-1 |
|
PORT MIRRORING USING THE COMMAND LINE INTERFACE .................................... |
9-2 |
|
COMMANDS .............................................................................................................................. |
9-2 |
|
PORT SETUP ........................................................................................................................... |
9-3 |
|
COMMANDS .............................................................................................................................. |
9-3 |
|
FLOW CONTROL ...................................................................................................................... |
9-5 |
|
BACK PRESSURE ...................................................................................................................... |
9-5 |
|
BROADCAST STORMS .............................................................................................................. |
9-8 |
|
LINK LOSS ALERT .................................................................................................................... |
9-10 |
|
PORT MIRRORING USING ENERVISTA SECURE WEB MANAGEMENT |
|
|
SOFTWARE ............................................................................................. |
9-12 |
|
COMMANDS .............................................................................................................................. |
9-12 |
|
PORT SETUP ............................................................................................................................. |
9-13 |
|
BROADCAST STORMS .............................................................................................................. |
9-15 |
|
|
|
10: VLAN |
VLAN DESCRIPTION ............................................................................................................. |
10-1 |
|
OVERVIEW ................................................................................................................................ |
10-1 |
|
TAG VLAN VS. PORT VLAN .................................................................................................. |
10-3 |
|
CONFIGURING PORT VLANS THROUGH THE COMMAND LINE INTERFACE .......... |
10-4 |
|
DESCRIPTION ............................................................................................................................ |
10-4 |
|
COMMANDS .............................................................................................................................. |
10-4 |
|
EXAMPLE ................................................................................................................................... |
10-5 |
|
CONFIGURING PORT VLANS WITH ENERVISTA SECURE WEB MANAGEMENT |
|
|
SOFTWARE ............................................................................................. |
10-9 |
|
DESCRIPTION ............................................................................................................................ |
10-9 |
|
CONFIGURING TAG VLANS THROUGH THE COMMAND LINE INTERFACE ............. |
10-13 |
|
DESCRIPTION ............................................................................................................................ |
10-13 |
|
COMMANDS .............................................................................................................................. |
10-13 |
|
EXAMPLE ................................................................................................................................... |
10-14 |
|
CONFIGURING TAG VLANS WITH ENERVISTA SECURE WEB MANAGEMENT |
|
|
SOFTWARE ............................................................................................. |
10-20 |
|
DESCRIPTION ............................................................................................................................ |
10-20 |
|
|
|
11: VLAN REGISTRATION |
OVERVIEW .............................................................................................................................. |
11-1 |
OVER GARP |
DESCRIPTION ............................................................................................................................ |
11-1 |
|
GVRP CONCEPTS .................................................................................................................... |
11-1 |
|
GVRP OPERATIONS ................................................................................................................ |
11-2 |
|
CONFIGURING GVRP THROUGH THE COMMAND LINE INTERFACE ........................ |
11-7 |
|
COMMANDS .............................................................................................................................. |
11-7 |
|
GVRP OPERATION NOTES ..................................................................................................... |
11-7 |
|
CONFIGURING GVRP WITH ENERVISTA SECURE WEB MANAGEMENT |
|
|
SOFTWARE ............................................................................................. |
11-9 |
|
EXAMPLE ................................................................................................................................... |
11-9 |
|
|
|
12: SPANNING TREE |
OVERVIEW .............................................................................................................................. |
12-1 |
PROTOCOL (STP) |
DESCRIPTION ............................................................................................................................ |
12-1 |
TOC–IV |
MULTILINK ML2400 ETHERNET COMMUNICATIONS SWITCH – INSTRUCTION MANUAL |

TOC |
TABLE OF CONTENTS |
|
|
FEATURES AND OPERATION ................................................................................................... |
12-1 |
|
CONFIGURING STP .............................................................................................................. |
12-3 |
|
|
|
13: RAPID SPANNING |
OVERVIEW .............................................................................................................................. |
13-1 |
TREE PROTOCOL |
DESCRIPTION ............................................................................................................................ |
13-1 |
|
RSTP CONCEPTS ..................................................................................................................... |
13-1 |
|
TRANSITION FROM STP TO RSTP ......................................................................................... |
13-2 |
|
CONFIGURING RSTP THROUGH THE COMMAND LINE INTERFACE ......................... |
13-4 |
|
NORMAL RSTP ........................................................................................................................ |
13-4 |
|
SMART RSTP (RING-ONLY MODE) THROUGH THE COMMAND LINE INTERFACE ........... |
13-14 |
|
CONFIGURING STP/RSTP WITH ENERVISTA SECURE WEB MANAGEMENT |
|
|
SOFTWARE ............................................................................................. |
13-16 |
|
NORMAL RSTP ........................................................................................................................ |
13-16 |
|
SMART RSTP (RING-ONLY MODE) WITH ENERVISTA SECURE WEB MANAGEMENT |
|
|
SOFTWARE ........................................................................................... |
13-20 |
|
|
|
14: QUALITY OF SERVICE |
QOS OVERVIEW .................................................................................................................... |
14-1 |
|
DESCRIPTION ............................................................................................................................ |
14-1 |
|
QOS CONCEPTS ....................................................................................................................... |
14-1 |
|
DIFFSERV AND QOS ............................................................................................................... |
14-2 |
|
IP PRECEDENCE ....................................................................................................................... |
14-2 |
|
CONFIGURING QOS THROUGH THE COMMAND LINE INTERFACE .......................... |
14-4 |
|
COMMANDS .............................................................................................................................. |
14-4 |
|
EXAMPLE ................................................................................................................................... |
14-6 |
|
CONFIGURING QOS WITH ENERVISTA SECURE WEB MANAGEMENT |
|
|
SOFTWARE ............................................................................................. |
14-9 |
|
DESCRIPTION ............................................................................................................................ |
14-9 |
|
|
|
15: IGMP |
OVERVIEW .............................................................................................................................. |
15-1 |
|
DESCRIPTION ............................................................................................................................ |
15-1 |
|
IGMP CONCEPTS .................................................................................................................... |
15-1 |
|
IP MULTICAST FILTERS ........................................................................................................... |
15-4 |
|
RESERVED ADDRESSES EXCLUDED FROM IP MULTICAST (IGMP) FILTERING ................. |
15-5 |
|
IGMP SUPPORT ....................................................................................................................... |
15-5 |
|
CONFIGURING IGMP THROUGH THE COMMAND LINE INTERFACE ........................ |
15-6 |
|
COMMANDS .............................................................................................................................. |
15-6 |
|
EXAMPLE ................................................................................................................................... |
15-8 |
|
CONFIGURING IGMP WITH ENERVISTA SECURE WEB MANAGEMENT |
|
|
SOFTWARE ............................................................................................. |
15-11 |
|
EXAMPLE ................................................................................................................................... |
15-11 |
|
|
|
16: SNMP |
OVERVIEW .............................................................................................................................. |
16-1 |
|
DESCRIPTION ............................................................................................................................ |
16-1 |
|
SNMP CONCEPTS ................................................................................................................... |
16-1 |
|
CONFIGURING SNMP THROUGH THE COMMAND LINE INTERFACE ....................... |
16-4 |
|
COMMANDS .............................................................................................................................. |
16-4 |
|
EXAMPLE ................................................................................................................................... |
16-5 |
|
CONFIGURING SNMP WITH ENERVISTA SECURE WEB MANAGEMENT |
|
|
SOFTWARE ............................................................................................. |
16-10 |
|
EXAMPLE ................................................................................................................................... |
16-10 |
MULTILINK ML2400 ETHERNET COMMUNICATIONS SWITCH – INSTRUCTION MANUAL |
TOC–V |

TABLE OF CONTENTS
|
CONFIGURING RMON ......................................................................................................... |
16-13 |
|
DESCRIPTION ............................................................................................................................ |
16-13 |
|
COMMANDS .............................................................................................................................. |
16-13 |
|
|
|
17: MISCELLANEOUS |
ALARM RELAYS ..................................................................................................................... |
17-1 |
COMMANDS |
DESCRIPTION ............................................................................................................................ |
17-1 |
|
CONFIGURING ALARM RELAYS THROUGH THE COMMAND LINE INTERFACE .................. |
17-2 |
|
CONFIGURING ALARM RELAYS WITH ENERVISTA SECURE WEB MANAGEMENT |
|
|
SOFTWARE ........................................................................................... |
17-5 |
|
E-MAIL ..................................................................................................................................... |
17-6 |
|
DESCRIPTION ............................................................................................................................ |
17-6 |
|
COMMANDS .............................................................................................................................. |
17-6 |
|
EXAMPLE ................................................................................................................................... |
17-8 |
|
STATISTICS ............................................................................................................................. |
17-9 |
|
VIEWING PORT STATISTICS WITH ENERVISTA SECURE WEB MANAGEMENT |
|
|
SOFTWARE ........................................................................................... |
17-9 |
|
SERIAL CONNECTIVITY ........................................................................................................ |
17-11 |
|
DESCRIPTION ............................................................................................................................ |
17-11 |
|
HISTORY .................................................................................................................................. |
17-12 |
|
COMMANDS .............................................................................................................................. |
17-12 |
|
PING ........................................................................................................................................ |
17-13 |
|
PING THROUGH THE COMMAND LINE INTERFACE .............................................................. |
17-13 |
|
PING THROUGH ENERVISTA SECURE WEB MANAGEMENT SOFTWARE ........................... |
17-13 |
|
PROMPT .................................................................................................................................. |
17-14 |
|
CHANGING THE COMMAND LINE PROMPT .......................................................................... |
17-14 |
|
SYSTEM EVENTS .................................................................................................................... |
17-15 |
|
DESCRIPTION ............................................................................................................................ |
17-15 |
|
COMMAND LINE INTERFACE EXAMPLE ................................................................................. |
17-15 |
|
ENERVISTA EXAMPLE .............................................................................................................. |
17-16 |
|
COMMAND REFERENCE ...................................................................................................... |
17-18 |
|
MAIN COMMANDS ................................................................................................................... |
17-18 |
|
CONFIGURATION COMMANDS ................................................................................................ |
17-20 |
|
|
|
18: MODBUS PROTOCOL |
MODBUS CONFIGURATION ............................................................................................... |
18-1 |
|
OVERVIEW ................................................................................................................................ |
18-1 |
|
COMMAND LINE INTERFACE SETTINGS ................................................................................. |
18-1 |
|
ENERVISTA SETTINGS .............................................................................................................. |
18-2 |
|
MEMORY MAPPING .............................................................................................................. |
18-3 |
|
MODBUS MEMORY MAP ......................................................................................................... |
18-3 |
|
FORMAT CODES ....................................................................................................................... |
18-36 |
|
|
|
19: APPENDIX |
REVISION HISTORY .............................................................................................................. |
19-1 |
|
CHANGE NOTES ....................................................................................................................... |
19-1 |
|
CHANGES TO THE MANUAL .................................................................................................... |
19-2 |
|
WARRANTY ............................................................................................................................ |
19-5 |
|
GE MULTILIN WARRANTY STATEMENT ................................................................................ |
19-5 |
TOC–VI |
MULTILINK ML2400 ETHERNET COMMUNICATIONS SWITCH – INSTRUCTION MANUAL |

GE Consumer & Industrial
Multilin
Multilink ML2400
Ethernet Communications Switch
Chapter 1: Introduction
1.1Getting Started
1.1.1 Inspecting the Package and Product
Examine the shipping container for obvious damage prior to installing this product; notify the carrier of any damage that you believe occurred during shipment or delivery. Inspect the contents of this package for any signs of damage and ensure that the items listed below are included.
This package should contain:
•MultiLink ML2400 Ethernet Switch, base unit (configured with user-selected port module options installed)
•Set of metal “ears” for 19-inch rack mounting
•Installation and user guide (this manual)
Remove the items from the shipping container. Be sure to keep the shipping container should you need to re-ship the unit at a later date. To validate the product warranty, please complete and return the enclosed product registration card to GE Multilin as soon as possible.
In the event there are items missing or damaged, contact the party from whom you purchased the product. If the unit needs to be returned, please use the original shipping container if possible. Refer to Troubleshooting on page 4–7, for specific return procedures.
MULTILINK ML2400 ETHERNET COMMUNICATIONS SWITCH – INSTRUCTION MANUAL |
1–1 |

INTRODUCTION |
CHAPTER 1: INTRODUCTION |
1.2Ordering
1.2.1 Order Codes
The following table illustrates the order codes for the MultiLink ML2400 Ethernet Switch.
The fiber optic LC ports are limited to a total of 12.
Table 1–1: ML2400 Order Code
ML2400 |
* |
* |
* |
* |
* |
* |
* |
|
|
|
|
Module |
|
|
|
A |
B |
C |
D |
| |
|
|
|
Base ML2400 |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
|
MultiLink ML2400 Ethernet Switch |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Port mounting |
F |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
|
Front-mounted ports |
|
|
B |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
|
Rear-mounted ports |
|
Power supply |
|
AC |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
|
100 to 240 V AC power supply |
|
|
|
HI |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
|
88 to 300 V DC / 85 to 865 V AC |
|
|
|
LO |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
|
36 to 70 V DC |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Redundant power |
|
|
XX |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
|
No redundant power supply |
|
supply |
|
|
HI |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
|
88 to 300 V DC / 85 to 865 V AC power supply |
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
|
|
|
LO |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
|
36 to 70 V DC power supply |
|
Modules |
|
|
|
A1 |
A1 |
A1 |
A1 |
| |
|
4 |
× 10 Mb - ST mm fiber |
|
|
|
|
A2 |
A2 |
A2 |
A2 |
| |
|
4 |
× 100 Mb - ST mm fiber |
|
|
|
|
A3 |
A3 |
A3 |
A3 |
| |
|
4 |
× 100 Mb - SC mm fiber |
|
|
|
|
A4 |
A4 |
A4 |
A4 |
| |
|
8 |
× 10/100 Mb RJ45 copper |
|
|
|
|
A5 |
A5 |
A5 |
A5 |
| |
|
2 |
× 10 Mb - ST mm fiber + 4 × 10/100 Mb RJ45 copper |
|
|
|
|
A6 |
A6 |
A6 |
A6 |
| |
|
2 |
× 100 Mb - ST mm fiber + 4 × 10/100 Mb RJ45 copper |
|
|
|
|
A7 |
A7 |
A7 |
A7 |
| |
|
2 |
× 100 Mb - SC mm fiber + 4 × 10/100 Mb RJ45 copper |
|
|
|
|
A8 |
A8 |
A8 |
A8 |
| |
|
2 |
× 100 Mb - SC sm fiber 20 km + 4 × 10/100 Mb RJ45 copper |
|
|
|
|
AA |
AA |
AA |
AA |
| |
|
4 |
× 100 Mb - LC mm fiber + 4 × 10/100 Mb - RJ45 copper |
|
|
|
|
AB |
AB |
AB |
AB |
| |
|
8 |
× 100 Mb - LC mm fiber |
|
|
|
|
AC |
AC |
AC |
AC |
| |
|
4 |
× 100 Mb - LC sm fiber + 4 × 10/100 Mb - RJ45 copper |
|
|
|
|
AD |
AD |
AD |
AD |
| |
|
8 |
× 100 Mb - LC sm fiber |
|
|
|
|
AE |
AE |
AE |
AE |
| |
|
2 |
× 100 Mb - LC sm fiber + 6 × 10/100 Mb - RJ45 copper |
|
|
|
|
AF |
AF |
AF |
AF |
| |
|
2 |
× 10 Mb - ST mm fiber + 2 × 100 Mb - ST mm fiber |
|
|
|
|
AH |
AH |
AH |
AH |
| |
|
8 x 100 Mb - MTRJ mm fiber |
|
|
|
|
|
AJ |
AJ |
AJ |
AJ |
| |
|
4 x 100 Mb - MTRJ mm fiber + 4 x 10/100 Mb - RJ45 copper |
|
|
|
|
|
AK |
AK |
AK |
AK |
| |
|
2 x 100 Mb - MTRJ mm fiber + 6 x 10/100 Mb - RJ45 copper |
|
|
|
|
|
G3 |
G3 |
G3 |
G3 |
| |
|
1 |
× 1000 Mb - SC mm fiber 2 km + 2 x 100 Mb - SC mm fiber |
|
|
|
|
G4 |
G4 |
G4 |
G4 |
| |
|
1 |
× 1000 Mb - SC mm fiber 2 km + 4 × 10/100 Mb - RJ45 copper |
|
|
|
|
G5 |
G5 |
G5 |
G5 |
| |
|
2 |
× 1000 Mb - SC mm fiber 2 km |
|
|
|
|
G6 |
G6 |
G6 |
G6 |
| |
|
1 |
× 1000 Mb - RJ45 copper |
|
|
|
|
G7 |
G7 |
G7 |
G7 |
| |
|
1 |
× 1000 Mb - SC mm fiber 2 km |
|
|
|
|
G8 |
G8 |
G8 |
G8 |
| |
|
1 |
× 1000 Mb - SC sm fiber 10 km |
|
|
|
|
GC |
GC |
GC |
GC |
| |
|
1 |
× 1000 Mb - RJ45 copper + 2 × 100 Mb - SC mm fiber |
|
|
|
|
GD |
GD |
GD |
GD |
| |
|
1 |
× 1000 Mb - RJ45 copper + 4 × 10/100 Mb - RJ45 copper |
|
|
|
|
GE |
GE |
GE |
GE |
| |
|
2 |
× 1000 Mb - RJ45 copper |
|
|
|
|
GF |
GF |
GF |
GF |
| |
|
1 |
× 1000 Mb - SC sm fiber 10 km + 2 × 100 Mb - SC mm fiber |
|
|
|
|
GH |
GH |
GH |
GH |
| |
|
1 |
× 1000 Mb - SC sm fiber 10 km + 4 × 10/100 Mb - RJ45 copper |
|
|
|
|
GJ |
GJ |
GJ |
GJ |
| |
|
2 |
× 1000 Mb - SC sm fiber 10 km |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
X |
|
Standard Environment |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
H |
|
Harsh Chemical Environment Option |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1–2 |
MULTILINK ML2400 ETHERNET COMMUNICATIONS SWITCH – INSTRUCTION MANUAL |

CHAPTER 1: INTRODUCTION INTRODUCTION
1.3 |
Specifications |
|
|
1.3.1 Technical Specifications |
|
|
PERFORMANCE |
|
|
Ethernet (10 Mb).............................................. |
14880 pps |
|
Fast Ethernet (100 Mb):................................ |
148,800 pps |
|
Gigabit Ethernet (1000 Mb): ...................... |
1488000 pps |
|
Switching processing: .................................. |
Store and forward with IEEE 802.3x full-duplex flow - |
|
|
control, non-blocking |
|
Data rate:........................................................... |
10 Mbps, 100 Mbps and 1000 Mbps |
|
Address table capacity:............................... |
4K node, self-learning with address aging |
|
Packet buffer size:.......................................... |
240 KB for 10/100; 120 KB for 1000 Mb |
|
Latency: .............................................................. |
5 μs + packet time (100 to 100Mbps) |
|
|
15 μs + packet time (10 to 10 Mbps and 10 to 100 Mbps) |
|
RO mode recovery time (typical):............ |
≤5 ms/hop |
|
NETWORK STANDARDS AND COMPLIANCE |
|
|
Ethernet V1.0/V2.0 IEEE 802.3: ................ |
10Base-T |
|
IEEE 802.3u:....................................................... |
100Base-TX, 100Base-FX |
|
IEEE 802.3z: ....................................................... |
1000Base-X Ethernet (auto-negotiation) |
|
IEEE 802.3ab:.................................................... |
1000Base-X Ethernet |
|
IEEE 802.1p:....................................................... |
Priority protocol |
|
IEEE 802.1d:....................................................... |
Spanning tree protocol |
|
IEEE 802.1q:....................................................... |
VLAN tagging |
|
IEEE 802.3x: ....................................................... |
Flow control |
|
MAXIMUM 10 MBPS ETHERNET SEGMENT LENGTHS |
|
|
Unshielded twisted pair: ............................. |
100 m (328 ft.) |
|
Shielded twisted pair:................................... |
150 m (492 ft.) |
|
10Base-FL multi-mode fiber optic: ....... |
2 km (6562 ft.) |
|
10Base-FL single-mode fiber optic: ..... |
10 km (32810 ft.) |
|
MAXIMUM STANDARD FAST ETHERNET SEGMENT LENGTHS |
|
|
10Base-T (CAT 3, 4, 5 UTP): ........................ |
100 m (328 ft.) |
|
100Base-TX (CAT 5 UTP): ............................. |
100 m (328 ft.) |
|
Shielded twisted pair:................................... |
150 m (492 ft.) |
|
100Base-FX, half-duplex, multi-mode: 412 m (1350 ft.) |
|
|
100Base-FX, full-duplex, multi-mode: .2.0 km (6562 ft.) |
|
|
100Base-FX, half-duplex, single-mode: 412 m (1350 ft.) |
|
|
100Base-FX, full-duplex, long reach: ... |
40.0 km (122K ft.) |
MAXIMUM STANDARD GIGABIT ETHERNET SEGMENT LENGTHS
1000Base-T (CAT5e or higher is recommended): 100 m (328 ft.) 1000Base-SX, full-duplex, multi-mode (62.5 μm cable): 220 m 1000Base-SX, full-duplex, multi-mode (50 μm cable): 550 m
FIBER MULTI-MODE CONNECTORS
Fiber port, ST (twist-lock): .......................... |
fiber multi-mode, 10 Mb 10Base-FL |
Fiber port, SC-type (snap-in): ................... |
fiber multi-mode, 100Base-FX |
Fiber port, ST-type (twist-lock): ............... |
fiber multi-mode, 100Base-FX |
Fiber port, 1000Base-FX:............................ |
GBIC modules |
MULTILINK ML2400 ETHERNET COMMUNICATIONS SWITCH – INSTRUCTION MANUAL |
1–3 |
INTRODUCTION CHAPTER 1: INTRODUCTION
FIBER SINGLE-MODE CONNECTORS
Fiber port, SC-type:........................................ |
Fiber optic single-mode, 100Base-FX |
Fiber port, 1000Base-FX:............................ |
GBIC modules |
LEDS |
|
LK:.......................................................................... |
steady ON when media link is operational |
ACT: ....................................................................... |
ON with receiver port activity |
FDX/HDX:............................................................ |
ON = full-duplex mode |
|
OFF = half-duplex mode |
100/10: ................................................................ |
ON = 100 Mbps; OFF = 10 Mbps |
ALARM RELAY CONTACTS
One NC indicating internal power, one NC firmware controllable
Maximum Voltage:......................................... |
up to 250 V AC, 220 V DC |
Maximum Switching Power:...................... |
60 W, 125 VA |
Maximum Carrying Current:...................... |
2 A @ 30 V DC |
|
0.2 A @ 220 V DC |
MANAGEMENT CONSOLE |
|
Connector:......................................................... |
DB-9 for RS-232 “null-modem” cable (sometimes called |
|
an X-modem cable) |
POWER SUPPLY |
|
Input voltage: ................................................... |
LOW RANGE (LO Power Supply) |
|
Nominal DC Voltage: 48 V DC |
|
Min/Max DC Voltage: 36/60 V DC |
................................................................................ |
HIGH RANGE (HI and AC Power Supply) |
|
Nominal DC Voltage: 110 to 250 V DC |
|
Min/Max DC Voltage: 88/300 V DC |
|
Nominal AC Voltage: 100 to 240 V AC |
|
Min/Max AC Voltage: 85/265 V AC |
Input current (fiber): ...................................... |
LO: 1.59 A maximum |
|
HI: 1.8 A maximum for AC voltage |
|
0.9 A maximum for DC voltage |
|
AC: 1.8 A maximum |
Standard terminal block: ........................... |
“–”, “+”, internally floating |
Ground: ............................................................... |
Terminal for filter ground wire, external connection to the |
|
ML2400 chassis |
Power consumption:..................................... |
55 watts typical; 60 watts maximum for a fully loaded |
|
fiber model; 35 watts maximum for a fully-loaded RJ45 |
|
model |
Internal Fuse:.......................................... |
HI: Ceramic, axial SLO BLO, 3 A /350 V AC |
|
Manufacturer: Conquer |
|
Part Number: SCD-A 003 |
|
LO: Ceramic, axial SLO BLO, 5 A /350 V AC |
|
Manufacturer: Conquer |
|
Part Number: SCD-A 005 |
PER-PORT JUMPERS AND SWITCHES
The copper daughter board has on internal switch for selecting MDI-MDIX crossover on port # 1. Other port-specific user settings (such as FDX or HDX, copper 10/100 speed) can be fixed using firmware commands.
1–4 |
MULTILINK ML2400 ETHERNET COMMUNICATIONS SWITCH – INSTRUCTION MANUAL |
CHAPTER 1: INTRODUCTION INTRODUCTION
1.3.2 |
Environmental Specifications |
|
|
|
|
|
OPERATING ENVIRONMENT |
|
|
||
|
Ambient temperature: ................................. |
|
–40 to 185°F (–40 to 85°C) for IEC 60068-2-1, IEC 60068- |
||
|
|
|
|
2-2 for 16 hours |
|
|
|
|
|
Nominal ≤ 50°C |
|
|
Storage temperature:................................... |
|
–60 to 210°F (–50 to 100°C) |
||
|
Ambient relative humidity: ........................ |
5% to 95% (non-condensing) |
|||
|
Altitude:............................................................... |
|
2000 m |
|
|
1.3.3 |
Type Tests |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Standard Name |
Standard Number:Date code |
Severity levels Tested |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Electrostatic Discharge: Air |
EN/IEC61000-4-2:1995 |
8Kv contact,15Kv Air (Level 4) |
|
|
|
and Direct |
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Electrostatic Discharge: Air |
IEEE C37.90.3:2001 |
8Kvcontact,15Kv air |
|
|
|
and Direct |
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Electrical Fast Transient/ |
|
|
(+/-4KV @2.5Khz for Common and Transverse |
|
|
EN/IEC61000-4-4:2004 |
modes) & 2KV 5Khz Common and transverse |
||
|
|
Burst Immunity |
|||
|
|
|
|
(Level 3 & 4) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Electrical Fast Transient/ |
IEEE C37.90.1:2002 |
Class 4 (+/-4KV for Common and Transverse |
|
|
|
Burst Immunity |
modes) |
||
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Power Transients )high |
NEMA TS2 2.1.6.1:2003 |
300V,2500W |
|
|
|
repetition |
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Power Transients (low |
NEMA TS2 :2003 |
|
600V, 1 ohm impedance |
|
|
repetition high energy) |
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Transients I/O terminals |
NEMA TS2 2.1.7.1 :2003 |
300V,1000ohms impedance |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Surge Immunity |
IEC61000-4-5:2005 |
Class 4 (2KV Line to Earth and 1KV Line to Line) |
|
|
|
Installation Class 3, Level 2 & 3 |
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Non Destructive transient |
NEMA TS2:2003 |
|
1000V,1 ohm X 3 |
|
|
Immunity |
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Ring Wave Surge ,IEC |
|
|
|
|
|
Damped Oscillatory Burst |
EN/IEC61000-4-12 :2006 |
Ring wave: (1KV Common), 0.5KV (diff) (Level 2) |
|
|
|
1Mhz |
|
|
|
|
|
SWC Damped Oscillatory |
IEEEC37.90.1:2002 |
Common and transverse to 2.5KV, No Transverse |
|
|
|
for Data Comms and Signal cct |
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Voltage Dip; 2. Voltage |
EN/IEC 61000-4-11 :2004 |
0%(5000msec),40%(6 cycles), 70%(10msec) of |
|
|
|
Interruption; |
test voltage |
||
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Ripple on DC power I/P port |
IEC 61000-4-17 |
|
10% of rated voltage (Level 3) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
RF Immunity 80-1000MHz |
EN/IEC 61000-4-3 :1998 |
10V/m (Level 3) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
RF Immunity 80-1000MHz |
IEEE C37.90.2:2004 |
35V/m (20V/m + modulation) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Conducted RF Immunity |
IEC61000-4-6:1996 |
10Vrms (Level 3) |
|
|
|
150Khz -80 MHz |
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Conducted RF Immunity 0- |
EN/IEC 61000-4-16:1998 |
15Hz-150 Khz 1-10V (Level 3) |
|
|
|
150Khz |
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Power Frequency Magnetic |
EN/IEC 61000-4-8:1993,2001 |
continuous 100/200A/m (Level 5 - continuous) |
|
|
|
Field Immunity |
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Damped magnetic Immunity |
IEC61000-4-10 |
|
10A/m (Level 3) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Voltage dips and Interrupts |
IEC61000-4-29 |
|
All test levels and durations - Passes to Criteria B |
|
|
for DC power ports |
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Conducted & Radiated |
CISPR22 / EN 55022 |
Class A |
|
|
|
Emissions |
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Conducted & Radiated |
FCC Part 15 Subpart B |
Class A |
|
|
|
Emissions |
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
MULTILINK ML2400 ETHERNET COMMUNICATIONS SWITCH – INSTRUCTION MANUAL |
1–5 |
INTRODUCTION |
|
|
|
CHAPTER 1: INTRODUCTION |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Standard Name |
Standard Number:Date code |
Severity levels Tested |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
A-rated control power inputs |
IEEE 1613:2003 |
Test operation @85% to110% or rated - as per |
|
|
5.1 and 5.3 |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
AC voltage ranges |
IEC60870-2-1 |
+ / - 10% (AC1) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
DC voltage ranges |
IEC60870-2-1 |
+ / - 15% (DC2) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ENVIRONMENTAL TESTS |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Relative Humidity Cyclic |
EN/IEC 60068-2-30:2005 |
6-day 93% @ 55deg C |
|
|
(Variant 2) |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Cold Temperature |
EN/IEC 60068-2-1: 1993/1990 |
16 hours -40 deg start up (Ad) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Dry Heat Temperature |
EN/IEC 60068-2-2:1994,1974 |
16 hours at rated upper limit, hot start up (Bd) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Humidity: -34 to 74C, 10-95% |
NEMA TS2 |
Humidity: -34 to 74C, 10-95% |
|
|
Defined in 2.1.5 |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
MECHANICAL TESTS |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Sinusoidal Vibration |
EN/IEC 60255-21-1 :1996,1988, |
10-150hz Response/Endurance @1G (Class 1) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Shock; 2. Bump; |
EN/IEC 60255-21-2:1996,1988 |
Class 2 for shock(30g) and Bump (20g) (Class 2) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Shock |
NEMA TS2 |
10g, x,,y,z (As per 2.2.9) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Vibration 5-30Hz 0.015" research+ 1hr(0.5g) dwell |
|
|
Vibration Endurance |
NEMA TS2 |
on resonant freq |
|
|
|
|
(As per 2.2.8) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Vibration |
MIL-STD -167-1 (variable amplitudes 4- |
5-30Hz,0.5g plus resonance frequency dwell |
|
|
50Hz) |
(Type 1 Environmental vibration) |
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
FUNCTIONAL TESTS |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Operating Voltage |
NEMA TS2 -89-135VAC |
Test @max nominal rating (As per 2.1.2) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Operational frequency |
NEMA TS2 -57-63Hz |
60Hz +/- 3Hz (As per 2.1.3) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
SAFETY TESTS |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
IT -Safety |
EN60950-1:2006 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
UL IT -Safety |
UL60950-1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
cUL IT -Safety |
C22.2 No. 60950-1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Dielectric |
IEEE 1613:2003 |
2000V (2000VAC & 500VAC) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Impulse |
IEEE 1613:2003 |
5000V |
|
|
|
|
|
1.3.4 |
Physical Specifications |
|
|
|
|
MOUNTING |
|
|
|
|
Vertical: ............................................................... |
suitable for stand-alone or rack mounting |
||
|
PACKAGING |
|
|
|
|
Enclosure: .......................................................... |
rugged high-strength sheet metal |
||
|
Dimensions:....................................................... |
1.70 in. × 17.0 in. × 9.2 in. (H × W × D) |
||
|
|
|
4.32 cm × 43.2 cm × 22.9 cm (H × W × D) |
|
1.3.5 |
Approvals and Warranty |
|
|
|
|
APPROVALS |
|
|
|
|
FCC: ....................................................................... |
Emissions meet FCC part 15 class A |
||
|
NEBS:.................................................................... |
level 3 |
|
|
|
ETSI:....................................................................... |
certified for carrier central offices |
||
|
IEEE: ...................................................................... |
IEEE P1613 environmental standard for electric power |
||
|
|
|
substations |
|
1–6 |
MULTILINK ML2400 ETHERNET COMMUNICATIONS SWITCH – INSTRUCTION MANUAL |
CHAPTER 1: INTRODUCTION INTRODUCTION
IEC:......................................................................... |
IEC61850 EMC and operating conditions class C for |
|
power susbstations |
CE:.......................................................................... |
EN 50082-1, EN 55022:1998, EN 60950 3rd Edition |
UL:.......................................................................... |
UL listed/recognized (file E156407), UL 60950-1 1st |
|
edition |
CSA:....................................................................... |
Certified per C22.1 No. 60950-1 1st edition |
WARRANTY
24 months from date of shipment Manufactured in USA
GE Multilin reserves the right to change specifications, performance, characteristics, and/or model offerings without notice.
MULTILINK ML2400 ETHERNET COMMUNICATIONS SWITCH – INSTRUCTION MANUAL |
1–7 |

INTRODUCTION |
CHAPTER 1: INTRODUCTION |
1.4Firmware Overview
1.4.1 Command Line Firmware
Commands typed by the user will be shown in the following color and font.
command
The MultiLink Switch Software prompt will be shown in bold and fixed-width text, with a # or > character at the end. The default prompt is indicated as follows:
ML2400#
The following hold for syntax rules:
•Syntax rules are italicized
•The command part is in bold
•Optional entries are shown in [square brackets]
•Parameter values within are shown in <pointed brackets>
•Optional parameter values are shown again in [square brackets]
Thus, the syntax
command [parameter1=<value1>[,paramter2=<value2>]] parameter3=<value3|value4>
indicates the following:
•parameters 1 and 2 are optional
•parameter 2 can be used optionally only if parameter 1 is specified
•parameter 3 is mandatory.
Whenever the word PC is used, it implies a UNIX, Linux, Windows, or any other operating system based workstation, computer, personal computer, laptop, notebook or any other computing device. Most of the manual uses Windows XP based examples. While effort has been made to indicate other operating system interactions, it is best to use a Windows-XP based machine when in doubt.
The documentation reflects features of MultiLink Switch Software version 1.7.x or later. If your switch is not at the current version, GE Multilin recommends upgrade to version 1.7.x or later. Please refer to the GE Multilin website for information on upgrading the MultiLink Switch Software.
1.4.2EnerVista Software
Icons common to the EnerVista MultiLink Secure Web Management (SWM) firmware for edit, delete, save and refresh are:
• Edit - edit the values
Edit - edit the values
• Delete - delete the current row or the value(s)
Delete - delete the current row or the value(s)
• Save - save configuration changes
Save - save configuration changes
• Refresh - repaint the screen
Refresh - repaint the screen
1–8 |
MULTILINK ML2400 ETHERNET COMMUNICATIONS SWITCH – INSTRUCTION MANUAL |
CHAPTER 1: INTRODUCTION |
INTRODUCTION |
1.4.3Before Starting
This section explains how to setup the GE MultiLink family of switches using the console port on the switch. Some of the functionality includes setting up the IP address of the switch, securing the switch with a user name and password, setting up VLANs and more.
Before you start, it is recommended to acquire the hardware listed below and be ready with the items listed.
For initial configuration through the serial/console port:
1.A female-female null modem cable.
2.A serial port. If your PC does not have a serial port, you may want to invest in a USB-to-serial converter or USB-to-serial cable.
3.Terminal emulation firmware such as HyperTerminal or other equivalent firmware. Ensure the firmware supports Xmodem protocol, as you may need this in the future to update the MultiLink Switch Software.
4.Enough disk space to store and retrieve the configuration files as well as copy firmware files. We recommend at least 15 MB of disk space for this purpose.
5.For access security - decide on a manager level account name and password
6.IP address, netmask, default gateway for the switch being configured.
As a default, the switch has no IP (Internet Protocol) address and subnet mask. For first time use, the IP address has to be assigned. This can only be done by using the console interface provided.
The same procedure can also be used for other configuration changes or updates (for example, changing the IP address, VLAN assignments and more). Once the IP address is assigned and a PC is networked to the switch, the switch's command line interface (CLI) can be accessed via telnet. To manage the switch through in-band (networked) access (e.g. telnet, or web browser Interface), you should configure the switch with an IP address and subnet mask compatible with your network. Also, change the manager password to control access privileges from the console.
Many other features such as optimizing the switch's performance, traffic engineering and traffic prioritizing, VLAN configuration, and improving network security can be configured through the switch's console interface as well as in-band (networked) access, once the IP address is setup. Besides the IP address, setting up the SNMP parameters allows configuration and monitoring through an SNMP network management station running a network management program.
MULTILINK ML2400 ETHERNET COMMUNICATIONS SWITCH – INSTRUCTION MANUAL |
1–9 |

INTRODUCTION |
CHAPTER 1: INTRODUCTION |
1.5Command Line Interface Firmware
1.5.1 Console Connection
The connection to the console is accessed through the DB-9 RS232 connector on the switch marked as the console port. This command line interface (or CLI) provides access to the switch commands. It can be accessed by attaching a VT100 compatible terminal or a PC running terminal emulation firmware to the console port.
USB-to-serial adapters are also available for computers that do not native serial ports but have access to USB ports.
The interface through the console or the console management interface (or CMI) enables you to reconfigure the switch and to monitor switch status and performance.
Once the switch is configured with an IP address, the command line interface (or CLI) is also accessible using telnet as well as the serial port. Access to the switch can be either through the console interface or remotely over the network. Simultaneous access (that is, through the console port as well as through the network) to the MultiLink switch is not permitted.
The Command Line Interface (CLI) enables local or remote unit installation and maintenance. The MultiLink family of switches provides a set of system commands which allow effective monitoring, configuration and debugging of the devices on the network.
1.5.2Console Setup
Connect the console port on the switch to the serial port on the computer using the serial cable listed above. The settings for the HyperTerminal firmware emulating a VT100 are shown below. Make sure the serial parameters are set as shown (or bps = 38400, data bits = 8, parity = none, stop bits = 1, flow control = none).
FIGURE 1–1: Serial Settings in HyperTerminal
1–10 |
MULTILINK ML2400 ETHERNET COMMUNICATIONS SWITCH – INSTRUCTION MANUAL |
CHAPTER 1: INTRODUCTION |
INTRODUCTION |
1.5.3Console Screen
Once the console cable is connected to the PC and the firmware configured, ML2400 legal disclaimers and other text scrolls by on the screen.
The line interface prompt appears displaying the switch model number (e.g. ML2400>)
The switch has three modes of operation: operator (least privilege), manager, and configuration. The prompts for the switches change as the switch changes modes from operator to manager to configuration. The prompts are shown below with a brief description.
•ML2400>
Operator Level - for running operations queries
•ML2400#
Manager Level - for setting and reviewing commands
•ML2400##
Configuration Level - for changing the switch parameter values
For additional information on default users, user levels and more, refer to User
Management on page 1–14.
1.5.4Logging In for the First Time
For the first time, use the default user name and passwords assigned by GE. They are:
•Username: manager Password: manager
•Username: operator Password: operator
We recommend you login as manager for the first time to set up the IP address as well as change user passwords or create new users.
1.5.5Automatic IP Address Configuration
The ML2400 is operational immediately after it is powered up. The advanced management and configuration capabilities of the ML2400 allows you to easily configure, manage, and secure your devices and network.
Before starting, ensure you have the following items:
•RJ45 Ethernet cable
•PC with an Ethernet port
•Microsoft Internet Explorer 6.0 or higher
•Macromedia Flash Player 5.0 or higher (available from http:// www.macromedia.com/shockwave/download/ download.cgi?P1_Prod_Version=ShockwaveFlash)
Ensure both firmware components are installed before proceeding.
The ML2400 can search the network for commonly used services that can issue an IP address. If the switch is connected to a network, the ML2400 uses the following process to find an IP address.
MULTILINK ML2400 ETHERNET COMMUNICATIONS SWITCH – INSTRUCTION MANUAL |
1–11 |

INTRODUCTION |
CHAPTER 1: INTRODUCTION |
If the ML2400 is not connected to a network, then proceed to Step 3 below. or use the default IP address.
Step 1:
The ML2400 will scan the network for a DHCP server. If the server responds, the ML2400 will acquire and set the assigned IP address. To manage the switch, determine the assigned IP address and enter as follows in Internet Explorer:
https://<assigned_IP_address>
Ensure that https is entered, not http, and that there is connectivity (that is, you can ping the switch).
Step 2:
If there is no response from a DCHP server, the ML2400 will query for a BOOTP server. If the server responds, the ML2400 will acquire and set the assigned IP address. To manage the switch, determine the assigned IP address and enter as follows in Internet Explorer:
https://<assigned_IP_address>
Ensure that https is entered, not http, and that there is connectivity (that is, you can ping the switch).
Step 3:
If there is no response from either a DCHP or BOOTP server, or if the switch is not connected to a network, the switch will assign itself an IP address. The ML2400 will check to see if IP address 192.168.1.2, with a network mask of 255.255.255.0, is free. If so, it will assume these values. If this IP address is assigned to another device, the ML2400 will repeat steps 1 through 3 to find a DCHP or BOOTP server or wait for the 192.168.1.2 address to become free.
Once connected, the browser will display a login prompt. The default login is:
•Username: manager Password: manager
1.5.6Setting the IP Parameters
To setup the switch, the IP address and other relevant TCP/IP parameters have to be specified.
The IP address on the MultiLink switch is set to 192.168.1.2 from the factory. The switch is fully operational as a Layer 2 switch as a default. Setting a default IP address can potentially cause duplicate IP address problem if multiple switches are powered on and installed on the network. To manage the switch, an IP address has to be programmed.
Before starting, please ensure that the IP address assigned to the switch is known or contact your system/network administrator to get the IP address information. Follow the steps listed below to configure the switch.
ZEnsure the power is off.
ZFollow the steps described above for connecting the console cable and setting the console firmware.
ZPower on the switch.
1–12 |
MULTILINK ML2400 ETHERNET COMMUNICATIONS SWITCH – INSTRUCTION MANUAL |

CHAPTER 1: INTRODUCTION |
INTRODUCTION |
ZOnce the login prompt appears, login as manager using default password (manager).
ZConfigure the IP address, network mask and default gateway as per the IP addressing scheme for your network.
ZSet the manager password (this step is recommended; refer to the following section).
ZSave the settings (without saving, the changes made will be lost).
ZPower off the switch (or a firmware reboot as discussed below).
ZPower on the switch - login with the new login name and password.
ZFrom the PC (or from the switch) ping the IP address specified for the switch to ensure connectivity.
ZFrom the switch ping the default gateway specified (ensure you are connected to the network to check for connectivity) to ensure network connectivity.
Syntax:
ipconfig [ip=<ip-address>] [mask=<subnet-mask>] [dgw=<gateway>]
An example is shown below.
ML2400# ipconfig ip=3.94.247.41 mask=255.255.252.0 dgw=3.94.247.41
ML2400# save
This manual assumes the reader is familiar with IP addressing schemes as well as how net mask is used and how default gateways and routers are used in a network.
Reboot gives an opportunity to save the configuration prior to shutdown. For a reboot, simply type in the command reboot. Note that even though the passwords are not changed, they can be changed later.
ML2400# reboot
Proceed on rebooting the switch? ['Y' or 'N'] Y
Do you wish to save current configuration? ['Y' or 'N'] Y
ML2400#
The ML2400 forces an answer by prompting with a “Y” or a “N” to prevent accidental keystroke errors and loss of work.
The parameters can be viewed at any time by using the show command. The show command will be covered in more detail later in various sections throughout the document.
The example below illustrates the basic setup parameters. You can use show setup or show sysconfig commands to view setup parameters.
ML2400# show setup
Version: ML2400 build 1.6.1 Apr 29 2005 11:10:13
MAC Address: 00:20:06:27:0a:e0
IP Address: 3.94.247.41
Subnet Mask: 255.255.252.0
Gateway Address: 3.94.244.1
CLI Mode: Manager
System Name: ML2400
MULTILINK ML2400 ETHERNET COMMUNICATIONS SWITCH – INSTRUCTION MANUAL |
1–13 |
INTRODUCTION |
CHAPTER 1: INTRODUCTION |
System Description: 25 Port Modular Ethernet Switch
System Contact: multilin.tech@ge.com
System Location: Markham, Ontario
System ObjectId: 1.3.6.1.4.1.13248.12.7
ML2400# show sysconfig
System Name: ML2400
System Contact: multilin.tech@ge.com
System Location: Markham, Ontario
Boot Mode: manual
Inactivity Timeout(min): 120
Address Age Interval(min): 300
Inbound Telnet Enabled: Yes
Web Agent Enabled: Yes
Time Zone: GMT-05hours:00minutes
Day Light Time Rule: Canada
System UpTime: 0 Days 0 Hours 45 Mins 55 Secs
ML2400#
Some of the parameters in the MultiLink family of switches are shown above. The list of parameters below indicates some of the key parameters on the switch and the recommendations for changing them (or optionally keeping them the same).
1.5.7Privilege Levels
Two privilege levels are available - manager and operator. Operator is at privilege level 1 and the manager is at privilege level 2 (the privilege increases with the levels). For example, to set up a user for basic monitoring capabilities use lower number or operator level privilege (level 1).
The Manager level provides all operator level privileges plus the ability to perform systemlevel actions and configuration commands. To select this level, enter the enable <username> command at the Operator level prompt and enter the Manager password, when prompted.
enable <user-name>
For example, switching from an operator-level to manager-level, using the enable command is shown below.
ML2400> enable manager
Password: *******
ML2400#
Note the prompt changes with the new privilege level.
Operator privileges allow views of the current configurations but do not allow changes to the configuration. A “>” character delimits the operator-level prompt.
Manager privileges allow configuration changes. The changes can be done at the manager prompt or for global configuration as well as specific configuration. A “#” character delimits any manager prompt.
1.5.8User Management
A maximum of five users can be added per switch. Users can be added, deleted or changed from a manager level account. There can be more than one manager account, subject to the maximum number of users on the switch being restricted to five.
1–14 |
MULTILINK ML2400 ETHERNET COMMUNICATIONS SWITCH – INSTRUCTION MANUAL |
CHAPTER 1: INTRODUCTION |
INTRODUCTION |
To add a user, use the add command as shown below. The user name has to be a unique name. The password is recommended to be at least 8 characters long with a mix of upper case, lower case, numbers and special characters.
add user=<name> level=<number>
The following example adds a user “peter” with manager-level privilege:
ML2400# user
ML2400(user)## add user=peter level=2
Enter User Password:******
Confirm New Password:******
ML2400(user)##
To delete a user, use the delete command as shown below. delete user=<name>
The following example deletes the user “peter”:
ML2400(user)## delete user=peter
Confirm User Deletion(Y/N): Y
User successfully deleted
ML2400(user)##
The syntax to modify a password is shown below: passwd user=<name>
The following example changes the password for user “peter”.
ML2400(user)## passwd user=peter
Enter New Password:******
Confirm New Password :******
Password has been modified successfully
ML2400(user)##
The syntax to modify the privilege level for a specific user is shown below: chlevel user=<name> level=<number>
The following example modifies the privilege level of user “peter” to Operator privileges.
ML2400(user)## chlevel user=peter level=1
Access Permission Modified
ML2400(user)##
The syntax to set the access privileges for telnet and Web services is shown below: useraccess user=<name> service=<telnet|web> <enable|disable>
The following example sets the access privileges for telnet and Web services.
ML2400(user)## useraccess user=peter service=telnet disable
Telnet Access Disabled.
1.5.9Help
Typing the help command lists the commands you can execute at the current privilege level. For example, typing help at the Operator level shows the following:
ML2400> help
MULTILINK ML2400 ETHERNET COMMUNICATIONS SWITCH – INSTRUCTION MANUAL |
1–15 |
INTRODUCTION |
CHAPTER 1: INTRODUCTION |
logout |
ping |
set |
terminal |
telnet |
walkmib |
Contextless Commands:
!? clear
enable |
exit |
help |
show |
whoami |
|
alarm |
|
|
ML2400>
Help for any command that is available at the current context level can be viewed by typing help followed by enough of the command string to identify the command. The following syntax applies:
help <command string>
For example, to list the help for the set time command
ML2400# help set time
set time |
: Sets the device Time |
Usage
set time hour=<0-23> min=<0-59> sec=<0-59> [zone=GMT[+/-]hh:mm]
ML2400#
The options for a specific command can be displayed by typing the command and pressing enter. The following syntax applies:
command <Enter>
For example, the options for the show command are:
ML2400# show <Enter>
Usage
show active-stp show active-snmp show active-vlan show address-table show age
show alarm show arp
show auth <config|ports> show backpressure
show bootmode --more--
Other ways to display help, specifically, with reference to a command or a set of commands, use the TAB key. The following syntax applies:
<TAB>
<Command string> <TAB>
<First character of the command> <TAB>
For example, following the syntax listed above, the <TAB> key will list the available commands in the particular privilege level:
ML2400> <TAB>
?
alarm clear enable exit help logout
1–16 |
MULTILINK ML2400 ETHERNET COMMUNICATIONS SWITCH – INSTRUCTION MANUAL |
CHAPTER 1: INTRODUCTION |
INTRODUCTION |
ping set show telnet
terminal walkmib whoami
ML2400>
The following example lists commands starting with a specific string:
ML2400> s <TAB>
set show
ML2400>
In the following example, the <TAB> key completes the command:
ML2400> se<TAB>
password timeout vlan
ML2400> set
1.5.10 Exiting
To exit from the CLI interface and terminate the console session use the logout command. This command prompts to ensure that the logout was not mistakenly typed. The following syntax applies:
logout
The following example illustrates logging out from a session:
ML2400> logout
Logging out from the current session [’Y’ or ’N’] Y
Connection to the host lost
MULTILINK ML2400 ETHERNET COMMUNICATIONS SWITCH – INSTRUCTION MANUAL |
1–17 |
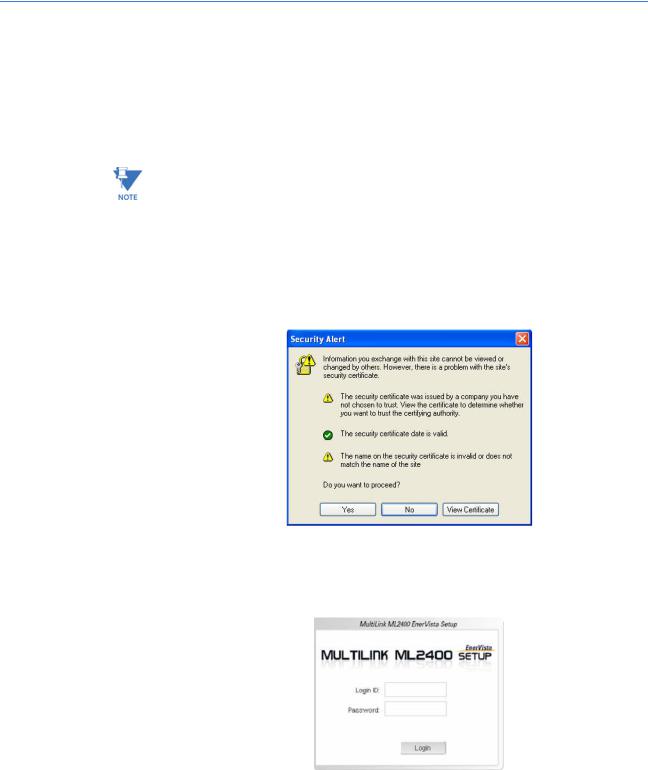
INTRODUCTION |
CHAPTER 1: INTRODUCTION |
1.6EnerVista Secure Web Management
1.6.1Logging in for the First Time
Enter the following URL in the web browser to login to the EnerVista Secure Web
Management software.
https://<IP Address assigned to the switch>
Make sure you use HTTPS (secure HTTP) and not HTTP in the URL.
In the example shown in the previous section, the URL is:
https://3.94.247.41
If your site uses name services, you can use a name instead of the IP address. Please make sure that the name is resolved to the IP address assigned to the switch.
The secure site will issue the certificate check shown below.
FIGURE 1–2: Security certificate
Once you click Yes on the security certificate, the browser will prompt you to login.
FIGURE 1–3: Login screen
For the first time,
Z Login with the name manager and password manager.
1–18 |
MULTILINK ML2400 ETHERNET COMMUNICATIONS SWITCH – INSTRUCTION MANUAL |

CHAPTER 1: INTRODUCTION |
INTRODUCTION |
Z Click on Login.
After a successful login, the welcome screen is shown. Note the different information provided on the screen and different areas. The menus are used to configure settings on the switch. Users can click on a specific port to open the port configuration view.
FIGURE 1–4: Welcome screen
1.6.2Privilege Levels
•Operator privilege users: operator privileges allow views of the current configurations but do not allow changes to the configuration.
•Manager privilege users: manager privileges allow configuration changes. The changes can be done at the manager prompt or for global configuration as well as specific configuration.
1.6.3User Management
A maximum of five users can be added per switch. Users can be added, deleted or changed from a manager level account. There can be more than one manager account, subject to the maximum number of users on the switch being restricted to five.
ZSelect the Administration > User Mgmt > User Accounts menu item.
ZTo add a user, use the add button.
The username must be a unique name. The password is recommended to be at least 8 characters long with a mix of upper case, lower case, numbers and special characters.
MULTILINK ML2400 ETHERNET COMMUNICATIONS SWITCH – INSTRUCTION MANUAL |
1–19 |
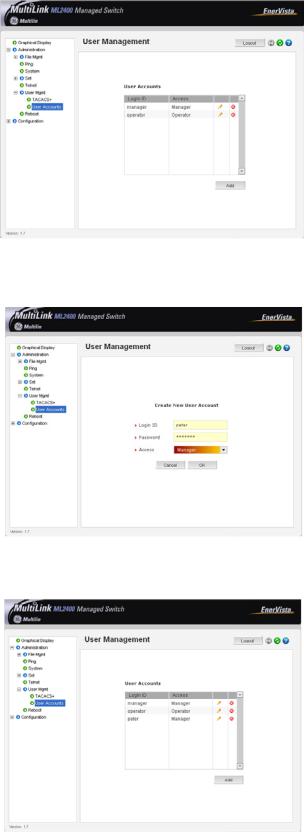
INTRODUCTION |
CHAPTER 1: INTRODUCTION |
In the following example below, the user peter was added with manager privilege after clicking the add button.
After successfully adding a user, the added user is displayed in the list of users as shown below.
1–20 |
MULTILINK ML2400 ETHERNET COMMUNICATIONS SWITCH – INSTRUCTION MANUAL |

CHAPTER 1: INTRODUCTION |
INTRODUCTION |
Z To delete a user, click on the delete icon ( )as shown below.
)as shown below.
The firmware will prompt to verify the delete command.
ZTo modify the password, view the users as described above and click on the edit icon ( ).
).
MULTILINK ML2400 ETHERNET COMMUNICATIONS SWITCH – INSTRUCTION MANUAL |
1–21 |
INTRODUCTION |
CHAPTER 1: INTRODUCTION |
After clicking on the edit icon, the screen opens up for modifying the password.
In this example, the user ID peter was selected for modification. The password for peter will be modified after the new password is entered.
1.6.4Modifying the Privilege Level
Privilege levels cannot be changed from the EnerVista Secure Web Management (SWM) firmware. This can only be done through the CLI interface, or alternately, by deleting the user and adding the same user with the proper privilege level.
1.6.5Help
Help for the EnerVista Secure Web Management software can be obtained by clicking on the Help icon as shown below.
1–22 |
MULTILINK ML2400 ETHERNET COMMUNICATIONS SWITCH – INSTRUCTION MANUAL |
 Loading...
Loading...