Page 1
FY-91Q
FY-91Q
FY-91Q
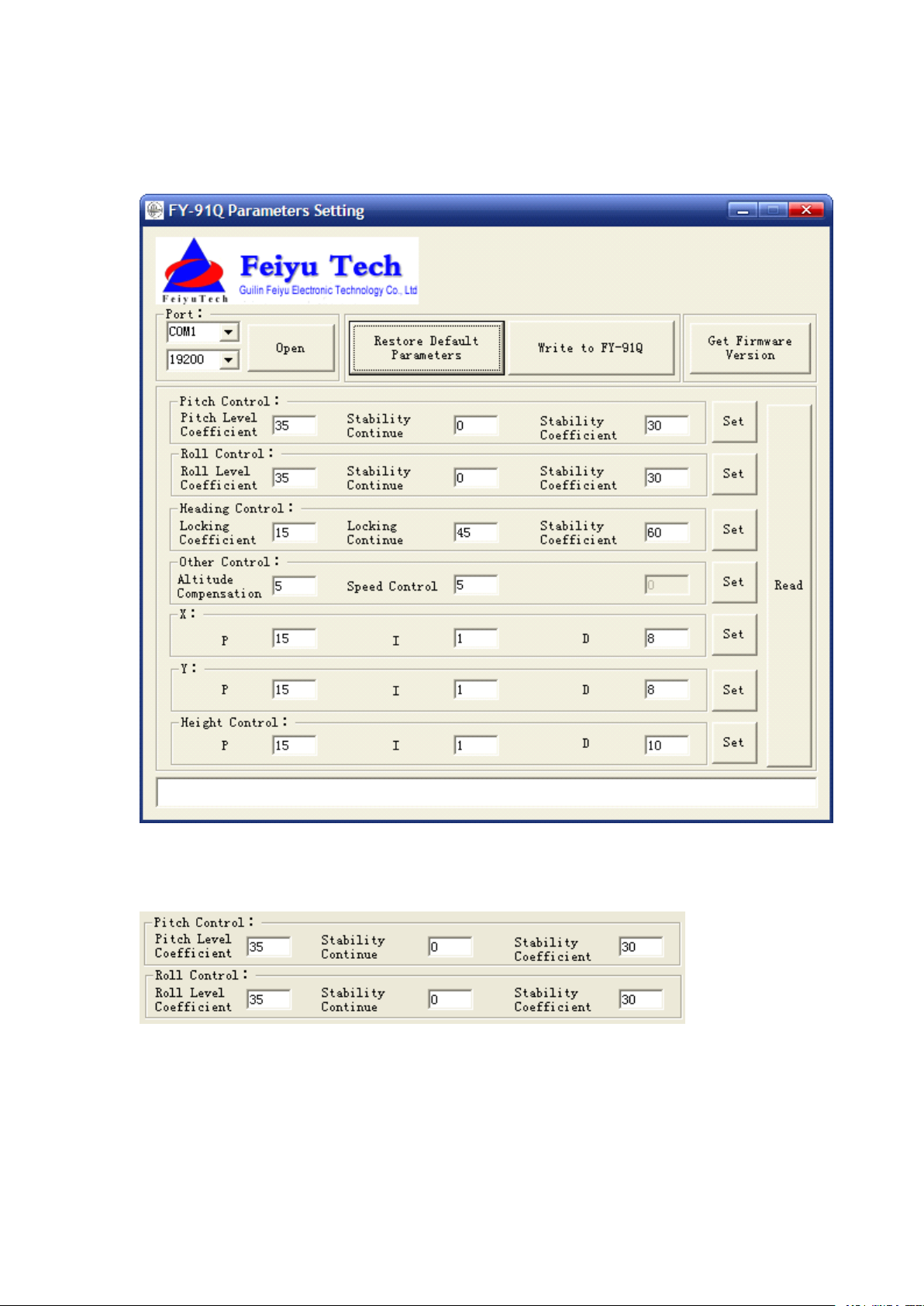
The interface of FY-91Q flight parameter setting:
Parameter
Parameter
Parameter
Setting
Setting
Setting
Pitch
1.1.1.
Pitch
Pitch
Pitch Control and Roll Control changes the strength of flight
stability attitude against pitching and rolling.
(1)
Pitch
(1)
(1)
Pitch
Pitch
Pitch Level Coefficient and Roll Level Coefficient, refer to the
Control
Control
Control
Level
Level
Level
and
Roll
and
and
Coefficient
Coefficient
Coefficient
Control
Roll
Roll
Control
Control
Roll
and Roll
Level
Roll
Level
Level
Coefficient
Coefficient
Coefficient
Page 2

magnitude of leveling correction the flight controller will execute upon
pitching and rolling.
That is, these parameters control the degree (magnitude) of
recovery from when the airframe deviates
position
position
position
and instability.
result in oscillation.
(2)
Stability
(2)
(2)
Stability
Stability
parameter is not allowed in this firmware.
(3)
Pitch
(3)
(3)
Pitch
Pitch
Coefficient, separately control the degree of angular stability rate
convergence in pitching and rolling movements.
prevent movements at the aircraft pitch and roll axis.
.
If the value is too small, this will result in a slow recovery process
If the value is too large, the airframe will recover too quickly and
Continue
Continue
Continue
This parameter is set at zero (0) , meaning adjustment of this
Stability
Stability
Stability
The two parameters, Pitch Stability Coefficient and Roll Stability
It is the degree of control given by the controller which is used to
Coefficient
Coefficient
Coefficient
deviates
deviates
Roll
and Roll
Roll
from
from
from
Stability
Stability
Stability
the
original
the
the
original
original
Coefficient
Coefficient
Coefficient
leveled
leveled
leveled
If the parameter value is too small, the FC will control the
airframe pitching and rolling on its axis too slowly, resulting in poor
stability .
If the value is too high, axial oscillations will occur.
Heading
2.2.2.
Heading
Heading
Locking
(1) Locking
Locking
Locking Coefficient refers to the corrective action taken by the FC
to maintain flight heading hold.
If the value is too small, the heading hold will be too slow
resulting in directional drifting.
If the value is too high, heading hold will be carried out too
quickly resulting in oscillations.
(2)
Locking
(2)
(2)
Locking
Locking
Locking Continue refers to the degree of heading recovery given by
the controller in unit time .
If the value is too small, there will be a constant deviation between
the actual heading angle and the objective heading angle. This results
in difficulty to reach the objective flight heading angle.
Locking
Locking
Locking
Coefficient
Coefficient
Coefficient
Continue
Continue
Continue
Control
Control
Control
Page 3

But if the value is too high, the aircraft can experience oscillations
during flight.
Stability
(3) Stability
Stability
Stability Coefficient controls the degree of angular rate
convergence when the airframe moves vertically (Z axis).
This parameter prevents movement of the aircraft along this Z
axis, especially during changes in aircraft heading.
If the value is too small, the airframe will move in pitch and roll
axis, resulting in aircraft instability.
If the parameter value is too high, oscillation will occur.
Position
3.3.3.
Position
Position
Letter
(1) Letter
Letter
Letter X and Y respectively represent the degree of stability and
leveling control during forward and backward, left and right flight
path.
Coefficient
Coefficient
Coefficient
and
Height
and
and
Height
Height
and
XXX
and
and
YYY
Control
Control
Control
Letter
(2) Letter
Letter
Letter P represents the degree of movement control given by the
controller when there is a deviation between airframe position and
objective hovering position.
If the value is too small, hovering position recovery will be too slow
resulting in instability during a hover procedure.
If the value is too high, oscillations will occur when in the
hovering position.
Letter
(3) Letter
Letter
Letter I represents the degree of control to move in unit time given
by the controller when there is a deviation between airframe position
and objective hovering position.
If the value is too small, there will be a deviation between the
actual airframe position and objective hovering position, making it
more difficult to reach the objective hovering position.
If the value is too large, oscillations will easily occur during
aircraft hovering.
PPP
III
Page 4

Letter
(4) Letter
Letter
Letter D represents the degree of control given by the controller
which is used to prevent moving to the axis(X/Y) when the aircraft is
in flight.
If the value is too small, the heading hold function of the aircraft
will be poor when directional changes are carried out.
If the value is too high, oscillations will occur during flight.
DDD
Other
4.4.4.
Other
Other
Altitude
(1) Altitude
Altitude
Altitude Compensation is the degree of control to compensate power in the
process of positioning movement. That is, the amount of power used to change
airframe position during flight.
Example, when altitude is lost during de s cent, Altitude Compensation is used to
increase power to compensate the lost of propeller lifting force.
Note that if the descent altitude lost rate is too fast resulting in poor stability, you
should increase the value of this parameter.
(2)
Speed
(2)
(2)
Speed
Speed
Speed Control is the degree of input used to control the entry
speed rate to a target position.
T he aircraft will reach the destination with a certain speed when
near the target . The FY91Q will give a Speed Control input for either
deceleration or acceleration.
If the Speed Control value is too small, deceleration or
acceleration may be initiated too slowly resulting in the aircraft
deviating the objective hovering position.
Control
Control
Control
Compensation
Compensation
Compensation
Control
Control
Control
 Loading...
Loading...