Page 1

NetAtlas Enterprise 1.00
Element Management System
User’s Guide
Version 1.00
8/2005
Page 2

Page 3

NetAtlas Enterprise 1.00 User’s Guide
Copyright
Copyright © 2005 by ZyXEL Communications Corporation.
The contents of this publication may not be reproduced in any part or as a whole, transcribed,
stored in a retrieval system, translated into any language, or transmitted in any form or by any
means, electronic, mechanical, magnetic, optical, chemical, photocopying, manual, or
otherwise, without the prior written permission of ZyXEL Communications Corporation.
Published by ZyXEL Communications Corporation. All rights reserved.
Disclaimer
ZyXEL does not assume any liability arising out of the application or use of any products, or
software described herein. Neither does it convey any license under its patent rights nor the
patent rights of others. ZyXEL further reserves the right to make changes in any products
described herein without notice. This publication is subject to change without notice.
Trademarks
ZyNOS (ZyXEL Network Operating System) is a registered trademark of ZyXEL
Communications, Inc. Other trademarks mentioned in this publication are used for
identification purposes only and may be properties of their respective owners.
Copyright 2
Page 4

NetAtlas Enterprise 1.00 User’s Guide
Federal Communications
Commission (FCC) Interference
Statement
This device complies with Part 15 of FCC rules. Operation is subject to the following two
conditions:
• This device may not cause harmful interference.
• This device must accept any interference received, including interference that may cause
undesired operations.
This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class B digital
device pursuant to Part 15 of the FCC Rules. These limits are designed to provide reasonable
protection against harmful interference in a commercial environment. This equipment
generates, uses, and can radiate radio frequency energy, and if not installed and used in
accordance with the instructions, may cause harmful interference to radio communications.
If this equipment does cause harmful interference to radio/television reception, which can be
determined by turning the equipment off and on, the user is encouraged to try to correct the
interference by one or more of the following measures:
• Reorient or relocate the receiving antenna.
• Increase the separation between the equipment and the receiver.
• Connect the equipment into an outlet on a circuit different from that to which the receiver
is connected.
• Consult the dealer or an experienced radio/TV technician for help.
Notice 1
Changes or modifications not expressly approved by the party responsible for compliance
could void the user's authority to operate the equipment.
This Class B digital apparatus complies with Canadian ICES-003.
Cet appareil numérique de la classe B est conforme à la norme NMB-003 du Canada.
Certifications
Go to www.zyxel.com
1 Select your product from the drop-down list box on the ZyXEL home page to go to that
product's page.
2 Select the certification you wish to view from this page.
3 Federal Communications Commission (FCC) Interference Statement
Page 5

NetAtlas Enterprise 1.00 User’s Guide
Safety Warnings
For your safety, be sure to read and follow all warning notices and instructions.
• To reduce the risk of fire, use only No. 26 AWG (American Wire Gauge) or larger
telecommunication line cord.
• Do NOT open the device or unit. Opening or removing covers can expose you to
dangerous high voltage points or other risks. ONLY qualified service personnel can
service the device. Please contact your vendor for further information.
• Use ONLY the dedicated power supply for your device. Connect the power cord or
power adaptor to the right supply voltage (110V AC in North America or 230V AC in
Europe).
• Do NOT use the device if the power supply is damaged as it might cause electrocution.
• If the power supply is damaged, remove it from the power outlet.
• Do NOT attempt to repair the power supply. Contact your local vendor to order a new
power supply.
• Place connecting cables carefully so that no one will step on them or stumble over them.
Do NOT allow anything to rest on the power cord and do NOT locate the product where
anyone can walk on the power cord.
• If you wall mount your device, make sure that no electrical, gas or water pipes will be
damaged.
• Do NOT install nor use your device during a thunderstorm. There may be a remote risk of
electric shock from lightning.
• Do NOT expose your device to dampness, dust or corrosive liquids.
• Do NOT use this product near water, for example, in a wet basement or near a swimming
pool.
• Make sure to connect the cables to the correct ports.
• Do NOT obstruct the device ventilation slots, as insufficient airflow may harm your
device.
• Do NOT store things on the device.
• Connect ONLY suitable accessories to the device.
Safety Warnings 4
Page 6

NetAtlas Enterprise 1.00 User’s Guide
ZyXEL Limited Warranty
ZyXEL warrants to the original end user (purchaser) that this product is free from any defects
in materials or workmanship for a period of up to two years from the date of purchase. During
the warranty period, and upon proof of purchase, should the product have indications of failure
due to faulty workmanship and/or materials, ZyXEL will, at its discretion, repair or replace the
defective products or components without charge for either parts or labor, and to whatever
extent it shall deem necessary to restore the product or components to proper operating
condition. Any replacement will consist of a new or re-manufactured functionally equivalent
product of equal value, and will be solely at the discretion of ZyXEL. This warranty shall not
apply if the product is modified, misused, tampered with, damaged by an act of God, or
subjected to abnormal working conditions.
Note
Repair or replacement, as provided under this warranty, is the exclusive remedy of the
purchaser. This warranty is in lieu of all other warranties, express or implied, including any
implied warranty of merchantability or fitness for a particular use or purpose. ZyXEL shall in
no event be held liable for indirect or consequential damages of any kind of character to the
purchaser.
To obtain the services of this warranty, contact ZyXEL's Service Center for your Return
Material Authorization number (RMA). Products must be returned Postage Prepaid. It is
recommended that the unit be insured when shipped. Any returned products without proof of
purchase or those with an out-dated warranty will be repaired or replaced (at the discretion of
ZyXEL) and the customer will be billed for parts and labor. All repaired or replaced products
will be shipped by ZyXEL to the corresponding return address, Postage Paid. This warranty
gives you specific legal rights, and you may also have other rights that vary from country to
country.
5 ZyXEL Limited Warranty
Page 7

NetAtlas Enterprise 1.00 User’s Guide
Customer Support
Please have the following information ready when you contact customer support.
• Product model and serial number.
• Warranty Information.
• Date that you received your device.
• Brief description of the problem and the steps you took to solve it.
METHOD
LOCATION
CORPORATE
HEADQUARTERS
(WORLDWIDE)
CZECH REPUBLIC
DENMARK
FINLAND
FRANCE
GERMANY
NORTH AMERICA
NORWAY
SPAIN
SWEDEN
SUPPORT E-MAIL TELEPHONE
SALES E-MAIL FAX FTP SITE
support@zyxel.com.tw +886-3-578-3942 www.zyxel.com
sales@zyxel.com.tw +886-3-578-2439 ftp.zyxel.com
info@cz.zyxel.com +420 241 091 350 www.zyxel.cz ZyXEL Communications
info@cz.zyxel.com +420 241 091 359
support@zyxel.dk +45 39 55 07 00 www.zyxel.dk Z y X E L C o m m u n i c a t i o n s A / S
sales@zyxel.dk +45 39 55 07 07
support@zyxel.fi +358-9-4780-8411 www.zyxel.fi Z y X EL C o m m un i c a t i on s O y
sales@zyxel.fi +358-9-4780 8448
info@zyxel.fr +33 (0)4 72 52 97 97 www.zyxel.fr Z y XE L Fr a nc e
+33 (0)4 72 52 19 20
support@zyxel.de +49-2405-6909-0 www.zyxel.de ZyXEL Deutschland GmbH.
sales@zyxel.de +49-2405-6909-99
support@zyxel.com +1-800-255-4101
+1-714-632-0882
sales@zyxel.com +1-714-632-0858 ftp.us.zyxel.com
support@zyxel.no +47 22 80 61 80 www.zyxel.no Z y X E L C o m m u n i c a t i o n s A / S
sales@zyxel.no +47 22 80 61 81
support@zyxel.es +34 902 195 420 www.zyxel.es Z y X E L C o m m u ni c a t i o n s
sales@zyxel.es +34 913 005 345
support@zyxel.se +46 31 744 7700 www.zyxel.se Z y X E L C o m m u ni c at io n s A/ S
sales@zyxel.se +46 31 744 7701
A
WEB SITE
www.europe.zyxel.com
ftp.europe.zyxel.com
www.us.zyxel.com ZyXEL Communications Inc.
REGULAR MAIL
ZyXEL Communications Corp.
6 Innovation Road II
Sc ien ce P ar k
Hsinchu 300
Ta iw a n
Czech s.r.o.
Modranská 621
143 01 Praha 4 - Modrany
Ceská Republika
Col um bu sv ej 5
2860 Soeborg
Denmark
Mal mi nk aa ri 10
00700 Helsinki
Finland
1 ru e d e s V er ge r s
Ba t. 1 / C
69760 Limonest
France
Adenauerstr. 20/A2 D-52146
Wuerselen
Germany
1130 N. Miller St.
Anaheim
CA 92806-2001
U.S.A.
Ni ls H ans en s ve i 13
0667 Oslo
Norway
Alejandro Villegas 33
1º, 28043 Madrid
Spain
Sjöporten 4, 41764 Göteborg
Sweden
Customer Support 6
Page 8
NetAtlas Enterprise 1.00 User’s Guide
METHOD
LOCATION
UNITED KINGDOM
SUPPORT E-MAIL TELEPHONE
SALES E-MAIL FAX FTP SITE
support@zyxel.co.uk +44 (0) 1344 303044
08707 555779 (UK
only)
sales@zyxel.co.uk +44 (0) 1344 303034 ftp.zyxel.co.uk
A
WEB SITE
www.zyxel.co.uk ZyXEL Communications UK
a. “+” is the (prefix) number you enter to make an international telephone call.
REGULAR MAIL
Ltd.,11 The Courtyard,
Eastern Road, Bracknell,
Berkshire, RG12 2XB,
United Kingdom (UK)
7 Customer Support
Page 9

NetAtlas Enterprise 1.00 User’s Guide
Table of Contents
Copyright .................................................................................................................. 2
Federal Communications Commission (FCC) Interference Statement ............... 3
Safety Warnings ....................................................................................................... 4
ZyXEL Limited Warranty.......................................................................................... 5
Customer Support.................................................................................................... 6
Table of Contents ..................................................................................................... 8
List of Figures ........................................................................................................ 14
List of Tables .......................................................................................................... 18
Preface .................................................................................................................... 20
Chapter 1
Introducing the EMS ..............................................................................................22
1.1 EMS Overview ...................................................................................................22
1.1.1 SNMPc Network Manager ........................................................................22
1.2 System Requirements ........................................................................................22
1.3 EMS Installation Overview .................................................................................23
1.3.1 Installing the EMS .....................................................................................23
1.4 SNMPc Network Manager ..................................................................................31
1.4.1 Manual SNMPc Startup ............................................................................31
1.4.2 Automatic SNMPc Startup ........................................................................31
1.5 Adding MIBs .......................................................................................................32
1.6 Finding your Switch ............................................................................................34
1.6.1 Device Auto-Discovery .............................................................................34
1.6.2 Add Device(s) Manually ............................................................................35
1.7 Using SNMP .......................................................................................................36
1.8 Configuring MySQL ODBC Driver ......................................................................39
Chapter 2
EMS Main Window.................................................................................................. 44
2.1 Introducing the EMS Main Window ....................................................................44
2.2 Device Icon Colors .............................................................................................45
2.3 System Message Panel Alarm Status ................................................................45
2.4 System Message Panel Port Status ...................................................................46
Table of Contents 8
Page 10

NetAtlas Enterprise 1.00 User’s Guide
2.5 Menu Shortcut Buttons .......................................................................................46
2.6 EMS Main Menu Summary ................................................................................46
2.7 Common EMS Command Buttons .....................................................................48
2.8 View the Switch ..................................................................................................48
2.9 Switch Information ..............................................................................................48
2.10 Configuration Save ...........................................................................................50
Chapter 3
Managing Device Maps in EMS............................................................................. 52
3.1 Submap and Device Mapping ............................................................................52
3.1.1 Adding a Submap or Device .....................................................................52
3.1.2 Edit a Node ...............................................................................................53
3.1.3 Find an Object ..........................................................................................54
3.1.4 Delete a Submap ......................................................................................54
3.1.5 Delete a Device ........................................................................................55
3.2 Exit .....................................................................................................................55
Chapter 4
VLAN Template ....................................................................................................... 56
4.1 VLAN Template Overview ..................................................................................56
4.1.1 Configuring a VLAN Template ..................................................................56
Chapter 5
Status ...................................................................................................................... 60
5.1 Hardware Status .................................................................................................60
5.2 STP Status .........................................................................................................62
5.2.1 Introduction to Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) ..........................................62
5.2.1.1 STP Terminology .............................................................................62
5.2.2 How STP Works .......................................................................................63
5.2.3 STP Port States ........................................................................................64
5.2.4 View STP Status .......................................................................................64
5.3 VLAN Status .......................................................................................................65
5.4 Port Status ..........................................................................................................66
5.5 802.1D ................................................................................................................68
5.5.1 802.1D: MAC Table ...................................................................................68
5.5.2 View the MAC Table .................................................................................68
5.5.3 802.1D: ARP Table ...................................................................................70
5.5.4 How ARP Works .......................................................................................70
5.5.5 View the ARP Table ..................................................................................70
Chapter 6
Fault Menus ............................................................................................................ 72
6.1 Event Log ...........................................................................................................72
9 Table of Contents
Page 11

NetAtlas Enterprise 1.00 User’s Guide
6.2 Loopback Test ....................................................................................................73
Chapter 7
Maintenance ........................................................................................................... 76
7.1 Firmware Upgrade .............................................................................................76
7.1.1 Procedure to Update Firmware .................................................................76
7.2 Device Reset ......................................................................................................77
7.3 Network Element Configuration Backup and Restore ........................................78
7.4 Load Factory Default ..........................................................................................79
7.5 Scheduled Network Element Configuration Backup ..........................................80
7.5.1 Scheduled Network Element Configuration Backup Add ..........................81
7.5.2 Scheduled Network Element Configuration Backup Remove ...................82
Chapter 8
Tools ........................................................................................................................ 84
8.1 Accessing the switch ..........................................................................................84
8.1.1 Telnet ........................................................................................................84
8.1.2 Web Access ..............................................................................................84
8.2 Ping ....................................................................................................................85
Chapter 9
Device Menu Overview .......................................................................................... 86
9.1 Device Menu Summary ......................................................................................86
9.2 Property Configuration .......................................................................................87
9.3 Introducing the EMS Configuration Window ......................................................87
9.3.1 Port List Multiple Port Configuration .........................................................88
9.3.2 Copy to.. Button ........................................................................................89
Chapter 10
System Configuration............................................................................................92
10.1 System Info ......................................................................................................92
10.2 SNMP ...............................................................................................................92
10.2.1 About SNMP ...........................................................................................92
10.2.2 Configuring SNMP ..................................................................................93
10.3 Remote Management .......................................................................................94
10.3.1 Configuring Remote Management ..........................................................94
10.4 Time Setup .......................................................................................................96
10.4.1 Configuring Time Setup ..........................................................................96
Chapter 11
Switch Configuration ............................................................................................. 98
11.1 IGMP Snooping ................................................................................................98
11.2 Switch Setup ....................................................................................................98
Table of Contents 10
Page 12

NetAtlas Enterprise 1.00 User’s Guide
11.3 Priority Queue ................................................................................................100
11.3.1 Strictly Priority .......................................................................................100
11.3.2 Weighted Fair Scheduling .....................................................................101
11.3.3 Configuring Priority Queue ....................................................................101
11.4 STP Configuration ..........................................................................................102
11.5 STP Overview ................................................................................................102
11.5.1 Configuring STP Parameters ................................................................103
11.6 Link Aggregation ............................................................................................104
11.6.1 Introduction to Link Aggregation ...........................................................104
11.6.2 Dynamic Link Aggregation ....................................................................104
11.6.3 Link Aggregation ID ..............................................................................105
11.6.4 Configuring Link Aggregation ................................................................105
11.7 DHCP Relay ...................................................................................................106
11.7.1 Overview ...............................................................................................106
11.7.2 DHCP Relay Agent Information ............................................................106
11.7.3 Configuring DHCP Relay ......................................................................107
11.8 GARP Timer ...................................................................................................108
11.8.1 Configuring GARP Timer ......................................................................108
11.9 RADIUS ..........................................................................................................109
11.9.1 Introduction to Authentication ...............................................................109
11.9.2 Configuring RADIUS .............................................................................109
11.10 MAC Forwarding ..........................................................................................110
11.10.1 Introduction to Static MAC Forward Setup .......................................... 110
11.10.2 Configuring Static MAC Forwarding ....................................................110
11.10.2.1 Adding and Editing Static MAC Forwarding Rules .................... 111
11.11 Filtering ........................................................................................................112
11.11.1 Introduction to Filtering ........................................................................ 112
11.11.2 Configuring Filtering ............................................................................ 112
11.11.2.1 Adding and Editing Static Filtering Rules ...................................113
Chapter 12
VLAN ..................................................................................................................... 116
12.1 Introduction to VLANs ....................................................................................116
12.2 Configuring 802.1Q VLAN ..............................................................................116
12.2.1 Modify an 802.1Q VLAN ....................................................................... 118
12.2.2 Removing a VLAN ................................................................................120
12.3 Introduction to Port-based VLANs ..................................................................120
12.3.1 Configuring Port Based VLAN ..............................................................120
Chapter 13
Ethernet Port Configuration................................................................................ 124
13.1 Port Setup ......................................................................................................124
13.1.1 Configuring Port Setup .........................................................................124
11 Table of Contents
Page 13

NetAtlas Enterprise 1.00 User’s Guide
13.2 Port VLAN ......................................................................................................126
13.2.1 Configuring Port VLAN .........................................................................126
13.3 Port Link Aggregation .....................................................................................127
13.3.1 Configuring Port Link Aggregation ........................................................128
13.4 Port STP .........................................................................................................128
13.4.1 Configuring Port STP ............................................................................128
13.5 Bandwidth Control ..........................................................................................129
13.5.1 Configuring Bandwidth Control .............................................................129
13.6 Broadcast Storm Control ................................................................................130
13.6.1 Configuring Broadcast Storm Control ...................................................130
13.7 Queue Method ...............................................................................................131
13.7.1 Configuring Queue Method ...................................................................131
13.8 Port 802.1x .....................................................................................................132
13.8.1 Configuring Port 802.1x ........................................................................132
13.9 Port Security ...................................................................................................133
13.9.1 About Port Security ...............................................................................133
13.9.2 Configuring Port Security ......................................................................133
13.10 Port Mirroring ...............................................................................................134
13.10.1 Configuring Port Mirroring ...................................................................135
13.11 VLAN Stacking .............................................................................................135
13.11.1 Introduction to VLAN Stacking ............................................................135
13.11.2 Configuring VLAN Stacking .................................................................136
Chapter 14
Routing Configuration ......................................................................................... 138
14.1 Static Route ....................................................................................................138
14.1.1 Configuring Static Routing ....................................................................138
14.1.2 Add or Modify a Static Route ................................................................139
14.2 Switch Manager .............................................................................................140
14.2.1 Access Log ...........................................................................................141
14.2.2 Database Backup and Restore .............................................................143
14.2.3 Database Scheduled Backup Configuration .........................................143
14.2.4 Database Log Storage Configuration ....................................................144
Chapter 15
Performance .........................................................................................................148
15.1 Interface .........................................................................................................148
15.1.1 View Interface Performance .................................................................148
15.2 Table Menu Bar Icons ....................................................................................150
15.2.1 Editing a Table Entry .............................................................................150
15.2.2 Expand Dialog Box ...............................................................................152
15.3 Graph Menu Bar Icons ...................................................................................153
15.3.1 Graph Styles .........................................................................................154
Table of Contents 12
Page 14

NetAtlas Enterprise 1.00 User’s Guide
15.3.2 Chart Format Display Variable ..............................................................154
15.3.3 Graph Labels ........................................................................................155
Chapter 16
Troubleshooting ...................................................................................................158
16.1 General Installation Problems ........................................................................158
16.2 EMS Installation Problems .............................................................................158
16.3 Uninstalling the EMS ......................................................................................158
16.4 Problems Finding a Device ............................................................................159
16.5 Problems Accessing the EMS ........................................................................160
Appendix A
SNMPc Network Manager.................................................................................... 162
Starting the SNMPc Network Manager .................................................................. 162
Manual Startup................................................................................................. 162
Automatic Startup ............................................................................................ 162
SNMPc Main Window ...................................................................................... 163
Selection Tool .................................................................................................. 164
Event Log Tool ................................................................................................. 164
View Window Area........................................................................................... 165
• Main and Edit Button Bar Icons .....................................................................165
Appendix B
Alarm Types and Causes ................................................................................... 168
Alarm Types and Causes Table ............................................................................. 168
Index...................................................................................................................... 170
13 Table of Contents
Page 15

NetAtlas Enterprise 1.00 User’s Guide
List of Figures
Figure 1 Installing MySQL: Welcome .................................................................................. 23
Figure 2 Installing MySQL: Information ............................................................................... 24
Figure 3 Installing MySQL: Choose Destination Location ................................................... 24
Figure 4 Installing MySQL: Setup Type ............................................................................... 25
Figure 5 Installing MySQL: Setup Complete ....................................................................... 25
Figure 6 Installing EMS: Welcome ...................................................................................... 26
Figure 7 Installing EMS: License Agreement ...................................................................... 26
Figure 8 Installing EMS: Customer Information ................................................................. 27
Figure 9 Installing EMS: Choose Destination Location ...................................................... 27
Figure 10 Installing EMS: Specify MySQL Directory ........................................................... 28
Figure 11 Installing EMS: Start Copying Files ..................................................................... 28
Figure 12 Installing EMS: MySQL ODBC: Welcome ........................................................... 29
Figure 13 Installing EMS: MySQL ODBC: License Agreement ........................................... 29
Figure 14 Installing EMS: MySQL ODBC: Start Installing ................................................... 30
Figure 15 Installing EMS: MySQL ODBC: Finish ................................................................ 30
Figure 16 Installing EMS: Finish ......................................................................................... 31
Figure 17 SNMPc Task Setup ............................................................................................ 32
Figure 18 Config: MIB Database ......................................................................................... 32
Figure 19 Compile Mibs (First Screen) ............................................................................... 33
Figure 20 Add Mib Files ...................................................................................................... 33
Figure 21 Compile Mibs (Second Screen) .......................................................................... 33
Figure 22 Compile Mibs ...................................................................................................... 34
Figure 23 Config, Discovery Agents .................................................................................... 34
Figure 24 Discovery Agents Screen .................................................................................... 35
Figure 25 Insert, MAP Object, Device ................................................................................. 35
Figure 26 Map Object Properties: Generall ......................................................................... 36
Figure 27 Map Object Properties ........................................................................................ 37
Figure 28 Network Manager Shortcuts ............................................................................... 38
Figure 29 Startup MySQL .................................................................................................... 39
Figure 30 Data Sources (ODBC) ........................................................................................ 40
Figure 31 ODBC Data Source Administrator ...................................................................... 40
Figure 32 MySQL: Connection Setup ................................................................................. 41
Figure 33 Switch Device List Icon ....................................................................................... 41
Figure 34 Switch Manager .................................................................................................. 41
Figure 35 Switch Graphic Display ....................................................................................... 42
Figure 36 EMS Main Screen Overview ............................................................................... 44
Figure 37 EMS Main Screen Shortcut Bar ......................................................................... 46
Figure 38 Switch View ........................................................................................................ 48
List of Figures 14
Page 16

NetAtlas Enterprise 1.00 User’s Guide
Figure 39 Configuration: Switch System Configuration ....................................................... 49
Figure 40 Configuration: Save ............................................................................................ 50
Figure 41 Submaps and Device Mapping ........................................................................... 52
Figure 42 Map: Add Submap/Device .................................................................................. 53
Figure 43 Map: Edit Node .................................................................................................. 54
Figure 44 Map: Find Object ................................................................................................. 54
Figure 45 Map: Delete Warning .......................................................................................... 55
Figure 46 Template: VLAN .................................................................................................. 57
Figure 47 Status: Hardware Status ..................................................................................... 61
Figure 48 Status: STP Status .............................................................................................. 64
Figure 49 Status: VLAN Status ............................................................................................ 66
Figure 50 Status: Port Status .............................................................................................. 67
Figure 51 MAC Table Flowchart .......................................................................................... 68
Figure 52 Status: 802.1d: MAC Table ................................................................................. 69
Figure 53 Status: 802.1d: ARP Table .................................................................................. 71
Figure 54 Fault: Event Log .................................................................................................. 72
Figure 55 Fault: Loopback Test .......................................................................................... 74
Figure 56 Maintenance: Firmware Upgrade ........................................................................ 77
Figure 57 Maintenance: Device Reset ................................................................................ 78
Figure 58 Maintenance: Configuration Backup/Restore ..................................................... 79
Figure 59 Maintenance: Load factory Defaults ................................................................... 80
Figure 60 Maintenance: Scheduled NE Config Backup ...................................................... 81
Figure 61 Maintenance: Scheduled NE Config Backup Add ............................................... 82
Figure 62 Telnet .................................................................................................................. 84
Figure 63 Web Access ........................................................................................................ 85
Figure 64 Ping ..................................................................................................................... 85
Figure 65 Device Panel List Menus .................................................................................... 86
Figure 66 Configuration Window Panels ............................................................................. 88
Figure 67 Applied Results ................................................................................................... 89
Figure 68 Copy Port Screen ................................................................................................ 90
Figure 69 Copy Successful ................................................................................................. 91
Figure 70 SNMP Management Model ................................................................................. 92
Figure 71 Configuration: System Configuration: SNMP Conf. ............................................ 94
Figure 72 Configuration: System Configuration: Remote Management .............................. 95
Figure 73 Configuration: System Configuration: Time Setup .............................................. 97
Figure 74 Configuration: Switch Configuration: Switch Setup ............................................. 99
Figure 75 Configuration: Switch Configuration: Priority Queue ........................................... 101
Figure 76 Configuration: Switch Configuration: STP Conf. ................................................. 103
Figure 77 Configuration: Switch Configuration: Link Aggregation ...................................... 105
Figure 78 Configuration: Switch Configuring: DHCP Relay ............................................... 107
Figure 79 Configuration: Switch Configuration: Garp Timer ................................................ 108
Figure 80 Configuration: Switch Configuration: RADIUS .................................................... 109
Figure 81 Configuration: Switch Configuration: MAC Forwarding ....................................... 111
15 List of Figures
Page 17

NetAtlas Enterprise 1.00 User’s Guide
Figure 82 Configuration: Switch Configuration: MAC Forwarding: Add .............................. 112
Figure 83 Configuration: Switch Configuration: Filtering ..................................................... 113
Figure 84 Configuration: Switch Configuration: Filtering: Add ............................................ 114
Figure 85 Selecting a VLAN Type ....................................................................................... 117
Figure 86 Configuration: VLAN Configuration: 802.1Q ....................................................... 117
Figure 87 Configuration: VLAN Configuration: 802.1Q: Modify .......................................... 119
Figure 88 Configuration: VLAN Configuration: Port Based ................................................. 121
Figure 89 Configuration: Ethernet Port Configuration: Port Setup ...................................... 125
Figure 90 Configuration: Ethernet Port Configuration: Port VLAN ...................................... 127
Figure 91 Configuration: Ethernet Port Configuration: Port Link Aggregation .................... 128
Figure 92 Configuration: Ethernet Port Configuration: Port STP ........................................ 129
Figure 93 Configuration: Ethernet Port Configuration: Bandwidth Ctrl. ............................... 130
Figure 94 Configuration: Ethernet Port Configuration: Broadcast Storm Ctrl. ..................... 131
Figure 95 Configuration: Ethernet Port Configuration: Queue Method ............................... 132
Figure 96 Configuration: Ethernet Port Configuration: Port 802.1x ..................................... 133
Figure 97 Configuration: Ethernet Port Configuration: Port Security .................................. 134
Figure 98 Configuration: Ethernet Port Configuration: Port Mirroring ................................. 135
Figure 99 Configuration: Ethernet Port Configuration: VLAN Stacking ............................... 136
Figure 100 Configuration: Routing Configuration ................................................................ 138
Figure 101 Configuration: Routing Configuration: Add or Modify ........................................ 139
Figure 102 Switch Manager Menus .................................................................................... 141
Figure 103 Switch Manager: Admin: Access Log ............................................................... 142
Figure 104 Switch Manager: Database Management: Backup/Restore ............................. 143
Figure 105 Switch Manager: Database Management: Scheduled Backup ......................... 144
Figure 106 Switch Manager: Database Management: Log Storage ................................... 145
Figure 107 Performance: Interface ..................................................................................... 149
Figure 108 Table Menu Bar Icons ....................................................................................... 150
Figure 109 Edit Table Entry ................................................................................................. 151
Figure 110 Expand Field ..................................................................................................... 153
Figure 111 Graph Menu Bar ................................................................................................ 154
Figure 112 Cell Properties Select ........................................................................................ 154
Figure 113 Chart Color Codes and Line Styles ................................................................... 155
Figure 114 Graph Variables ................................................................................................. 155
Figure 115 EMS: Remove ................................................................................................... 159
Figure 116 Automatic Startup ............................................................................................. 163
Figure 117 SNMPc Main Windows ...................................................................................... 163
Figure 118 SNMPc Main Button Bar Icons .......................................................................... 166
Figure 119 SNMPc Edit Button Bar Icons ........................................................................... 166
List of Figures 16
Page 18

NetAtlas Enterprise 1.00 User’s Guide
17 List of Figures
Page 19

NetAtlas Enterprise 1.00 User’s Guide
List of Tables
Table 1 System Requirements ........................................................................................... 22
Table 2 Map Object Properties: General ............................................................................ 36
Table 3 Required Map Object Properties ........................................................................... 37
Table 4 EMS Main Screen Overview .................................................................................. 45
Table 5 Device Icon Colors ................................................................................................ 45
Table 6 System Message Panel Alarm Status ................................................................... 45
Table 7 EMS Menu Summary ............................................................................................ 46
Table 8 EMS Navigation Panel Sub-link Descriptions ........................................................ 47
Table 9 Common EMS Command Buttons ........................................................................ 48
Table 10 Configuration: Switch System Configuration ....................................................... 49
Table 11 Map: Add Submap/Device ................................................................................... 53
Table 12 Template: VLAN ................................................................................................... 57
Table 13 Status: Hardware Status ...................................................................................... 61
Table 14 STP Path Costs ................................................................................................... 63
Table 15 STP Port States ................................................................................................... 64
Table 16 Status: STP Status ............................................................................................... 64
Table 17 Status: VLAN Status ............................................................................................ 66
Table 18 Status: Port Status ............................................................................................... 67
Table 19 Status: 802.1d: MAC Table .................................................................................. 69
Table 20 Status: 802.1d: ARP Table ................................................................................... 71
Table 21 Fault: Event Log .................................................................................................. 72
Table 22 Maintenance: Configuration Backup/Restore ...................................................... 79
Table 23 Maintenance: Scheduled NE Config Backup ....................................................... 81
Table 24 Device Menu Summary ....................................................................................... 86
Table 25 Configuration Window Panels ............................................................................. 88
Table 26 Copy Port Screen ................................................................................................ 90
Table 27 SNMP Commands ............................................................................................... 93
Table 28 Configuration: System Configuration: SNMP Conf. ............................................. 94
Table 29 Configuration: System Configuration: Remote Management .............................. 95
Table 30 Configuration: System Configuration: Time Setup ............................................... 97
Table 31 Configuration: Switch Configuration: Switch Setup ............................................. 99
Table 32 Configuration: Switch Configuration: Priority Queue ........................................... 102
Table 33 Configuration: Switch Configuration: STP Conf. .................................................. 103
Table 34 Aggregation ID Local Switch ............................................................................... 105
Table 35 Aggregation ID Peer Switch ................................................................................ 105
Table 36 Configuration: Switch Configuration: Link Aggregation ....................................... 106
Table 37 Configuration: Switch Configuring: DHCP Relay ................................................. 107
Table 38 Configuration: Switch Configuration: Garp Timer ................................................ 108
List of Tables 18
Page 20

NetAtlas Enterprise 1.00 User’s Guide
Table 39 Configuration: Switch Configuration: RADIUS ..................................................... 109
Table 40 Configuration: Switch Configuration: MAC Forwarding ....................................... 111
Table 41 Configuration: Switch Configuration: MAC Forwarding: Add ............................... 112
Table 42 Configuration: Switch Configuration: Filtering ..................................................... 113
Table 43 Configuration: Switch Configuration: Filtering: Add ............................................. 114
Table 44 Configuration: VLAN Configuration: 802.1Q ........................................................ 117
Table 45 Configuration: VLAN Configuration: 802.1Q: Modify ........................................... 119
Table 46 VLAN Port Type Descriptions .............................................................................. 120
Table 47 Configuration: VLAN Configuration: Port Based .................................................. 121
Table 48 Configuration: Ethernet Port Configuration: Port Setup ....................................... 125
Table 49 Configuration: Ethernet Port Configuration: Port VLAN ....................................... 127
Table 50 Configuration: Ethernet Port Configuring: Port Link Aggregation ........................ 128
Table 51 Configuration: Ethernet Port Configuration: Port STP ......................................... 129
Table 52 Configuration: Ethernet Port Configuration: Bandwidth Ctrl. ............................... 130
Table 53 Configuration: Ethernet Port Configuration: Broadcast Storm Ctrl. ..................... 131
Table 54 Configuration: Ethernet Port Configuration: Queue Method ................................ 132
Table 55 Configuration: Ethernet Port Configuration: Port 802.1x ..................................... 133
Table 56 Configuration: Ethernet Port Configuration: Port Security ................................... 134
Table 57 Configuration: Ethernet Port Configuration: Port Mirroring .................................. 135
Table 58 Configuration: Ethernet Port Configuration: VLAN Stacking ................................ 136
Table 59 Configuration: Routing Configuration .................................................................. 139
Table 60 Configuration: Routing Configuration: Add or Modify .......................................... 140
Table 61 Switch Manager Menus Overview ....................................................................... 141
Table 62 Switch Manager: Admin: Access Log .................................................................. 142
Table 63 Switch Manager: Database Management: Backup/Restore ................................ 143
Table 64 Switch Manager: Database Management: Scheduled Backup ........................... 144
Table 65 Switch Manager: Database Management: Log Storage ...................................... 145
Table 66 Performance: Interface ........................................................................................ 149
Table 67 Edit Table Entry ................................................................................................... 151
Table 68 Variable Types ..................................................................................................... 153
Table 69 Edit Table Entry ................................................................................................... 154
Table 70 Edit Style Dialog Box ........................................................................................... 155
Table 71 Graph Variables ................................................................................................... 155
Table 72 General Installation Problems ............................................................................. 158
Table 73 EMS Installation Problems .................................................................................. 158
Table 74 Problems Accessing the EMS ............................................................................. 159
Table 75 Problems Accessing the EMS ............................................................................. 160
Table 76 SNMPc Main Window .......................................................................................... 164
Table 77 Selection Tool ...................................................................................................... 164
Table 78 Alarm Types and Causes .................................................................................... 168
19 List of Tables
Page 21

NetAtlas Enterprise 1.00 User’s Guide
Preface
Congratulations on your purchase of the NetAtlas Enterprise 1.00 Element Management
System (EMS) for the ES-3124 Series.
Note: Register your product online to receive e-mail notices of firmware upgrades and
information at
North American products.
About This User's Guide
This manual is designed to guide you through the configuration of your EMS for its
applications.
Syntax Conventions
• “Enter” means for you to type one or more characters. “Select” or “Choose” means for
you to use one predefined choices.
• The SMT menu titles and labels are in Bold Times New Roman font. Predefined field
choices are in Bold Arial font. Command and arrow keys are enclosed in square
brackets. [ENTER] means the Enter, or carriage return key; [ESC] means the Escape key
and [SPACE BAR] means the Space Bar.
• Mouse action sequences are denoted using a comma. For example, “click the Apple icon,
Control Panels and then Modem” means first click the Apple icon, then point your
mouse pointer to Control Panels and then click Modem.
• For brevity’s sake, we will use “e.g.,” as a shorthand for “for instance”, and “i.e.,” for
“that is” or “in other words” throughout this manual.
• The Element Management System for ES-3124 Series may be referred to as the EMS in
this User’s guide.
• The switches being managed by the EMS may be referred to as the switch in this User’s
Guide.
www.zyxel.com for global products, or at www.us.zyxel.com for
Related Documentation
• Supporting Disk
Refer to the included CD for support documents.
• ES-3124 User’s Guide or the ES-3124PWR User’s Guide
Refer to the ES User’s Guide for directions on installation, connections, maintenance,
hardware troubleshooting and safety warnings.
• ZyXEL Glossary and Web Site
Please refer to www.zyxel.com for an online glossary of networking terms and additional
support documentation.
Preface 20
Page 22

NetAtlas Enterprise 1.00 User’s Guide
User Guide Feedback
Help us help you. E-mail all User Guide-related comments, questions or suggestions for
improvement to techwriters@zyxel.com.tw or send regular mail to The Technical Writing
Team, ZyXEL Communications Corp., 6 Innovation Road II, Science-Based Industrial Park,
Hsinchu, 300, Taiwan. Thank you.
21 Preface
Page 23
1.1 EMS Overview
The Element Management System (EMS) retrieves management information from switches
using SNMP protocol.
An EMS is composed of Network Elements (NE) that represent resources in a Network
Management System (NMS). The network elements can represent a physical piece of
equipment on the network, the components of a device on the network, or parts of the network
itself. The EMS is designed to manage the ES-3124 Series switches in the NMS. The ES-3124
Series covers the ES-3124 and the ES-3124PWR.
NetAtlas Enterprise 1.00 User’s Guide
CHAPTER 1
Introducing the EMS
1.1.1 SNMPc Network Manager
SNMPc is network management software produced by Castle Rock.
You must have SNMPc properly installed before you can use the EMS; please refer to the
appendices in this User’s Guide; go to the Castle Rock web site at www.castlerock.com or see
your SNMPc user's guide.
1.2 System Requirements
These are the system requirements for the Windows version of the EMS.
Table 1 System Requirements
HARDWARE SOFTWARE
CPU: Intel Pentium IV, 1.6 GHz or above Operating System: Windows 2000 (with service
Memory (RAM): 1 GB or more Database Program: MySQL 4.0.18 with ODBC
Hard Disk free space: 20 GB Castle Rock’s SNMPc 7.0 (Enterprise or
Screen Resolution: 1024x768 pixels Ethernet Adaptor: 10/100 Mbps
pack 1), Windows XP or Windows 2003 Server.
3.51.05 or later versions.
Please see www.mysql.com for details on MySQL.
Workgroup edition)
Chapter 1 Introducing the EMS 22
Page 24
NetAtlas Enterprise 1.00 User’s Guide
1.3 EMS Installation Overview
The following steps give an overview of what you need to do to install the EMS:
1 Install SNMPc
2 Install MySQL
3 Install the EMS software. Install the MySQL driver during the EMS installation.
4 Add custom MIB files in SNMPc
5 Locate device(s) that you want the EMS to manage
6 Configure the MySQL ODBC driver to connect to MySQL database.
1.3.1 Installing the EMS
Follow the steps below to install the EMS server on a computer.
1 Install SNMPc if it is not already installed. See the appendices for futher information.
2 Install MySQL. If it is already installed skip to step 11.
Note: You must install MySQL and the EMS on the same computer.
3 Find and unzip the mysql-4.0.18-win file on your CD.
4 Find and double-click the setup.exe file.
5 A Welcome screen displays. Click Next to continue.
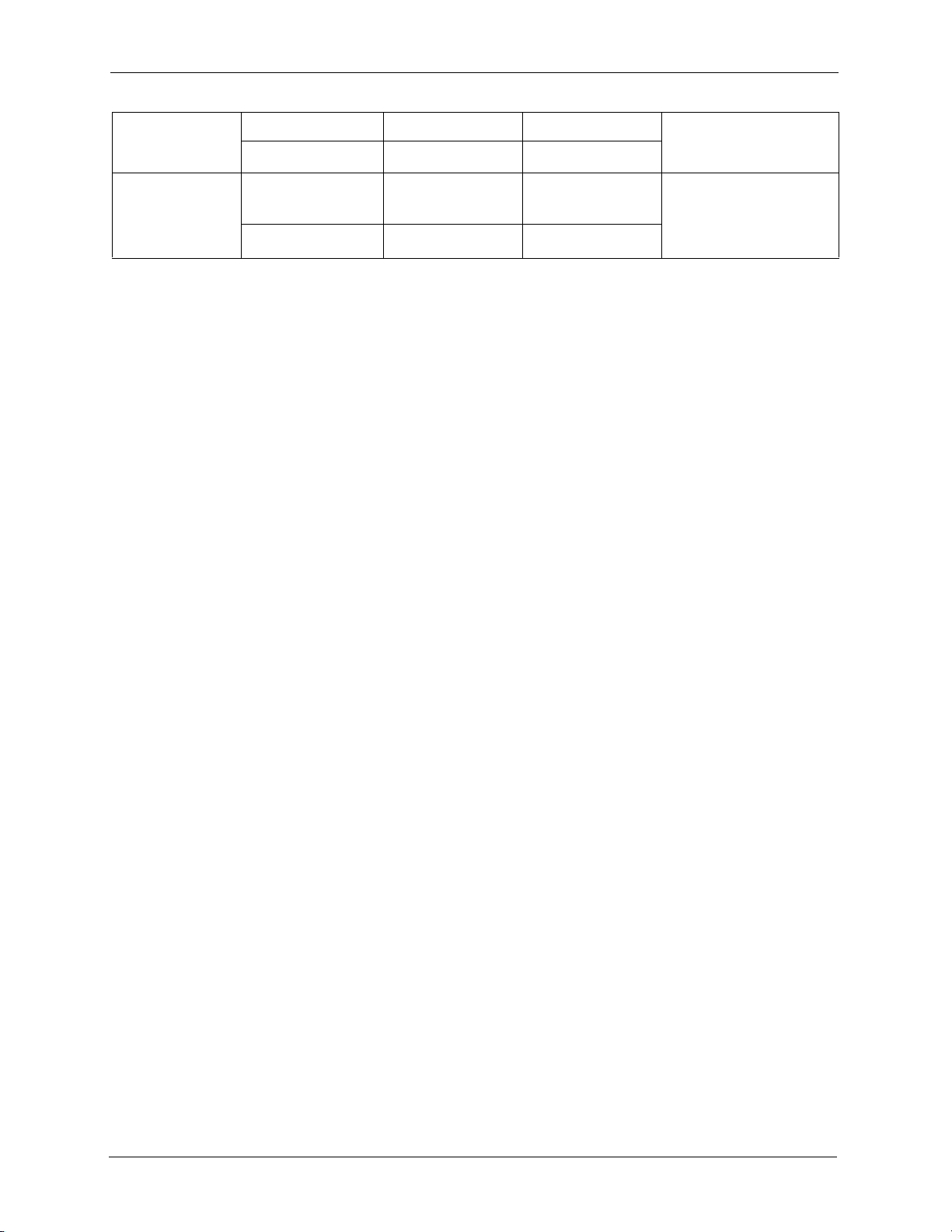
Figure 1 Installing MySQL: Welcome
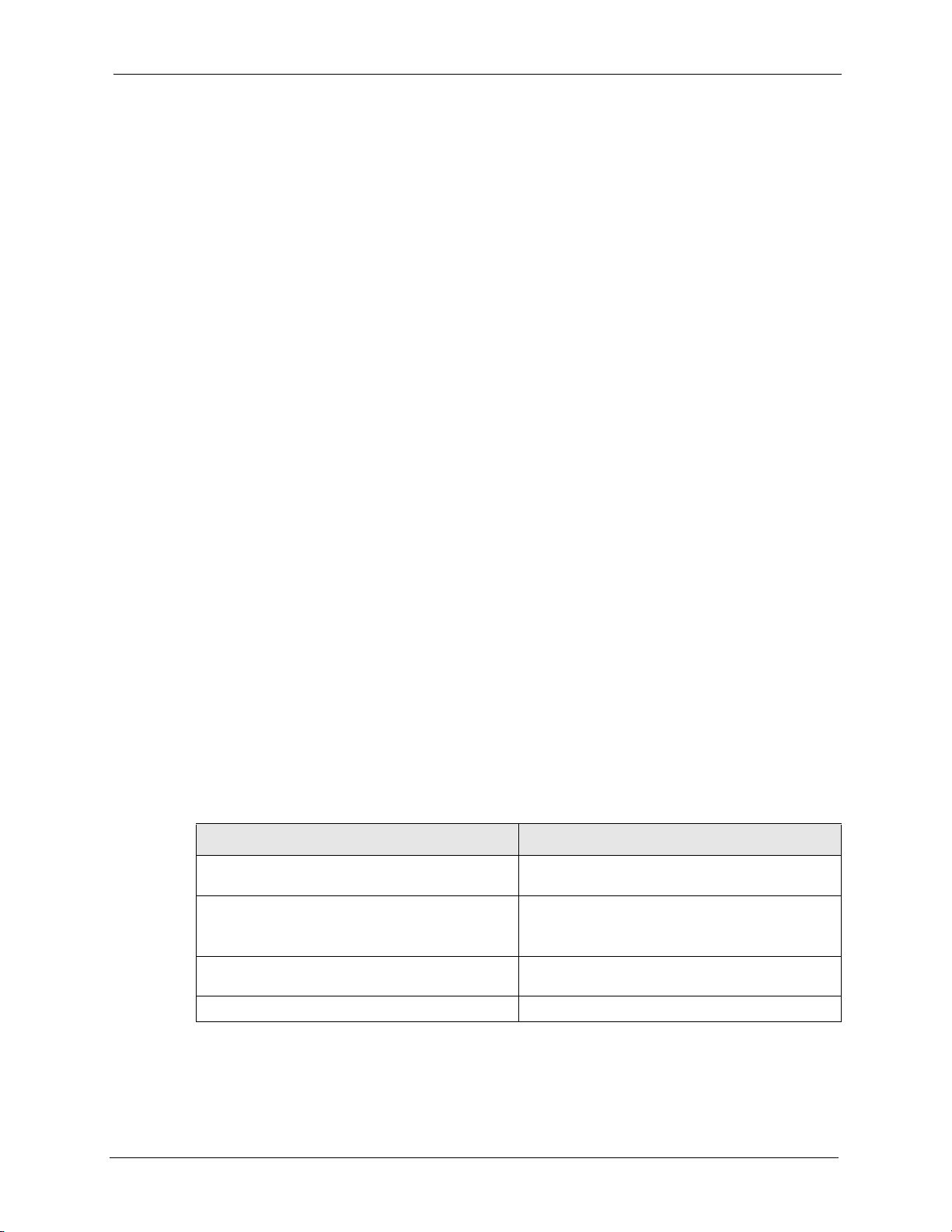
6 An Information screen displays. Click Next to continue.
23 Chapter 1 Introducing the EMS
Page 25
NetAtlas Enterprise 1.00 User’s Guide
Figure 2 Installing MySQL: Information
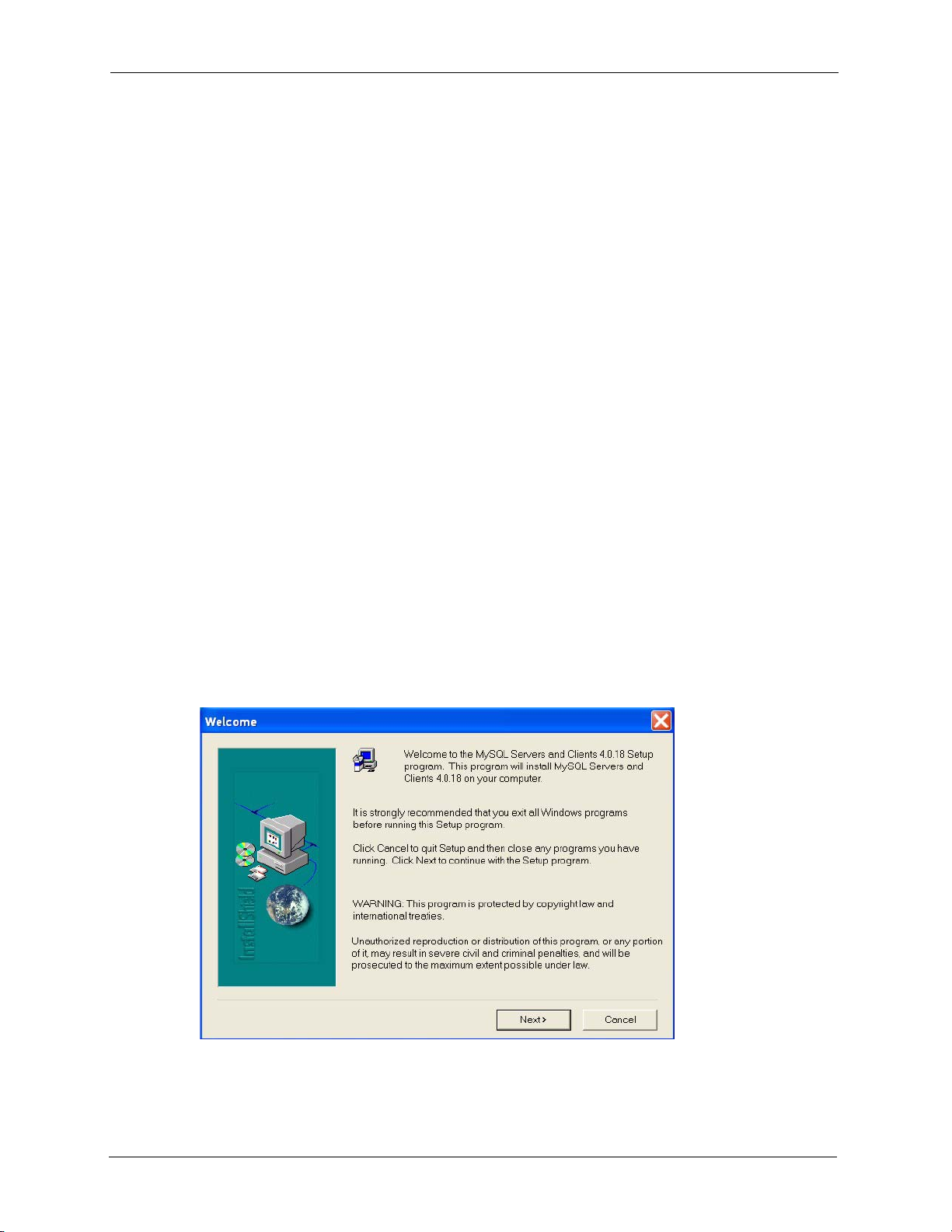
7 Click Browse if you want to install MySQL to a destination folder other than the
destination shown.
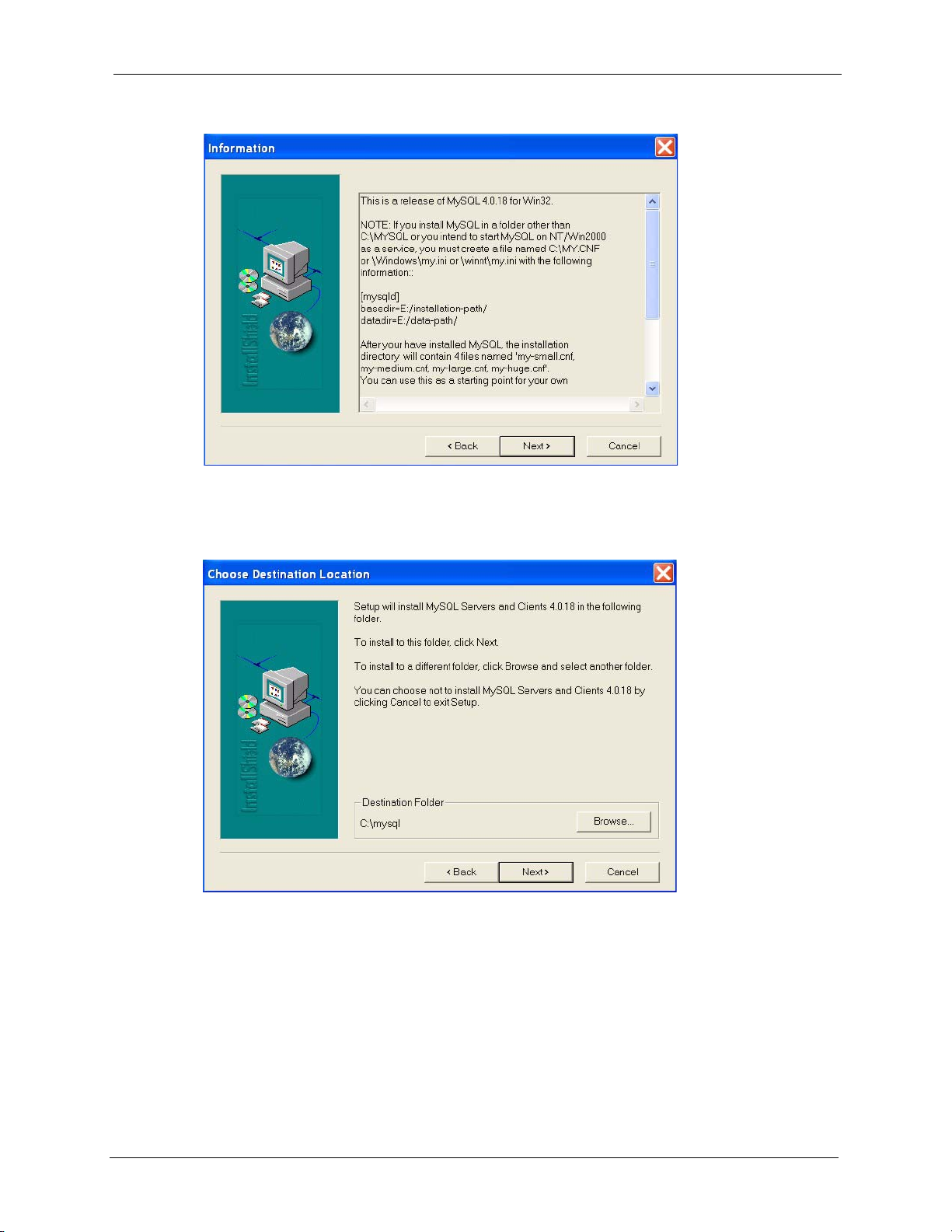
Figure 3 Installing MySQL: Choose Destination Location
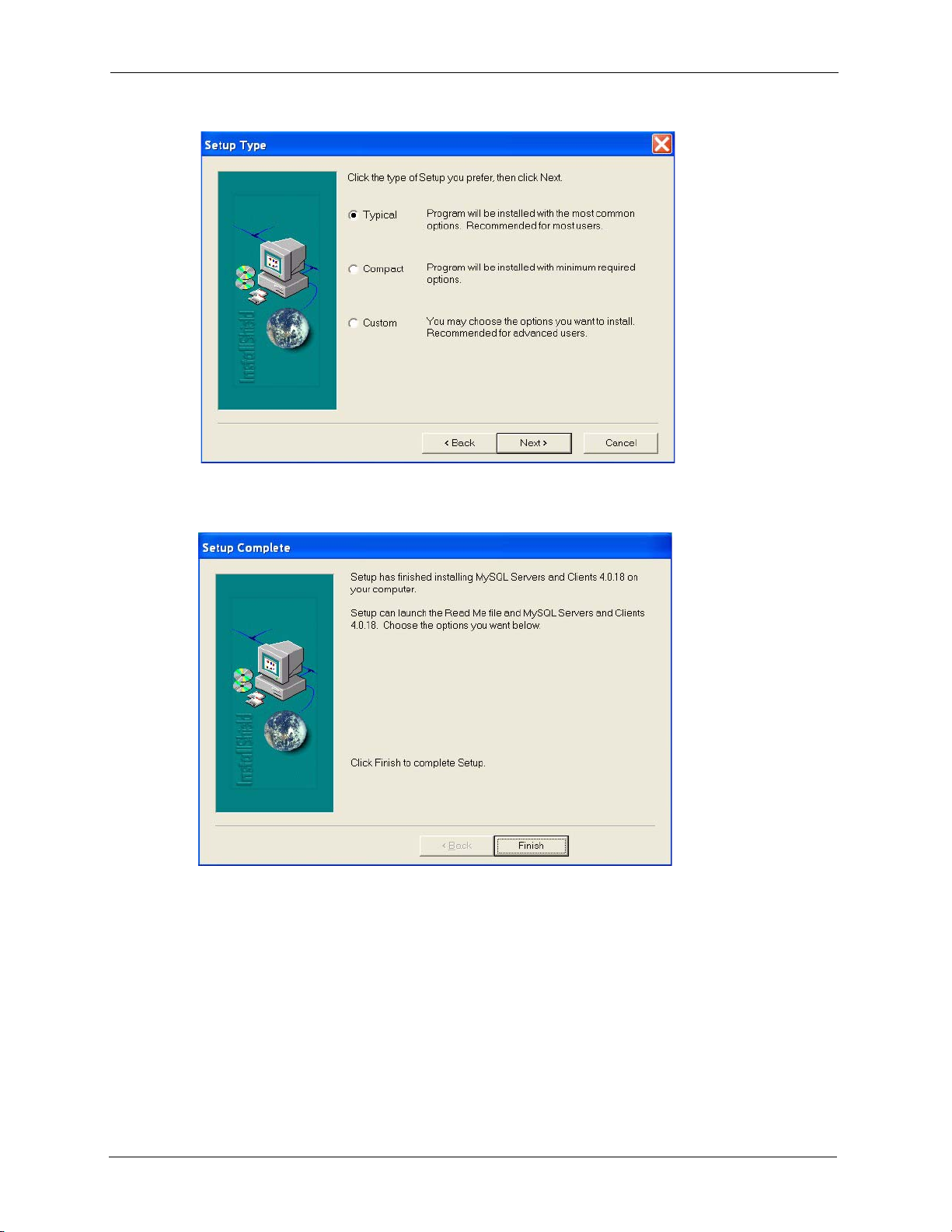
8 You must select a setup type to install MySQL. Select Typi cal and click Next to
continue.
Chapter 1 Introducing the EMS 24
Page 26
NetAtlas Enterprise 1.00 User’s Guide
Figure 4 Installing MySQL: Setup Type
9 Click Finish to complete the MySQL installation.
Figure 5 Installing MySQL: Setup Complete
10 You must restart Windows to activate MySQL.
11 Find and double-click NetAtlasEnterprise_S100.exe on your EMS CD.
12 A Welcome screen displays. Click Next to continue.
25 Chapter 1 Introducing the EMS
Page 27
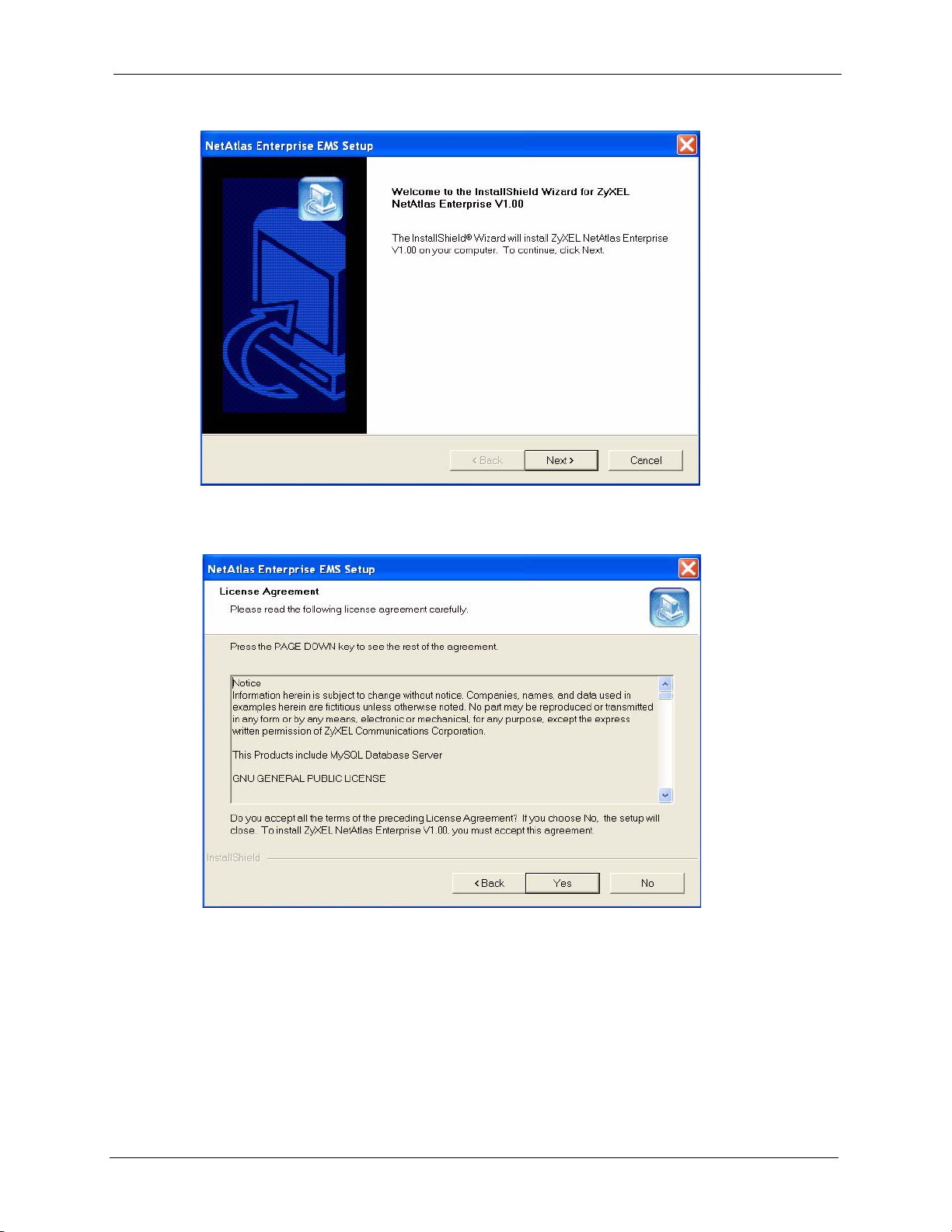
NetAtlas Enterprise 1.00 User’s Guide
Figure 6 Installing EMS: Welcome
13 Read the license agreement. Click Ye s to accept the agreement.
Figure 7 Installing EMS: License Agreement
14 Type your name, company name and product serial number in the following screen.
Click Next to continue.
Chapter 1 Introducing the EMS 26
Page 28
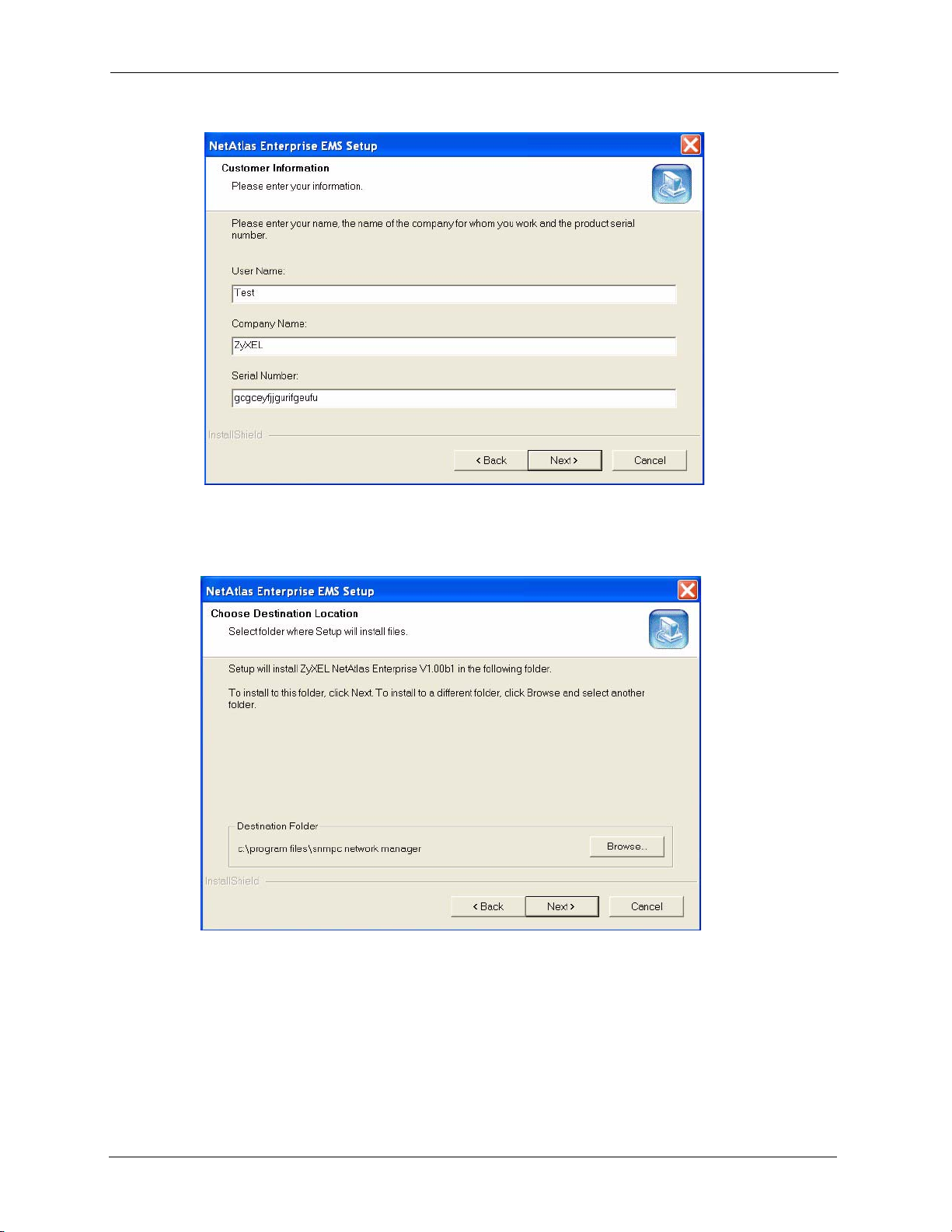
NetAtlas Enterprise 1.00 User’s Guide
Figure 8 Installing EMS: Customer Information
15 You must select the same directory where you installed SNMPc. Click Browse if it’s
different from the destination folder shown.
Figure 9 Installing EMS: Choose Destination Location
16 You must select the directory where you installed MySQL. Click Browse if you did not
install MySQL database in the default folder shown. Click Next.
27 Chapter 1 Introducing the EMS
Page 29
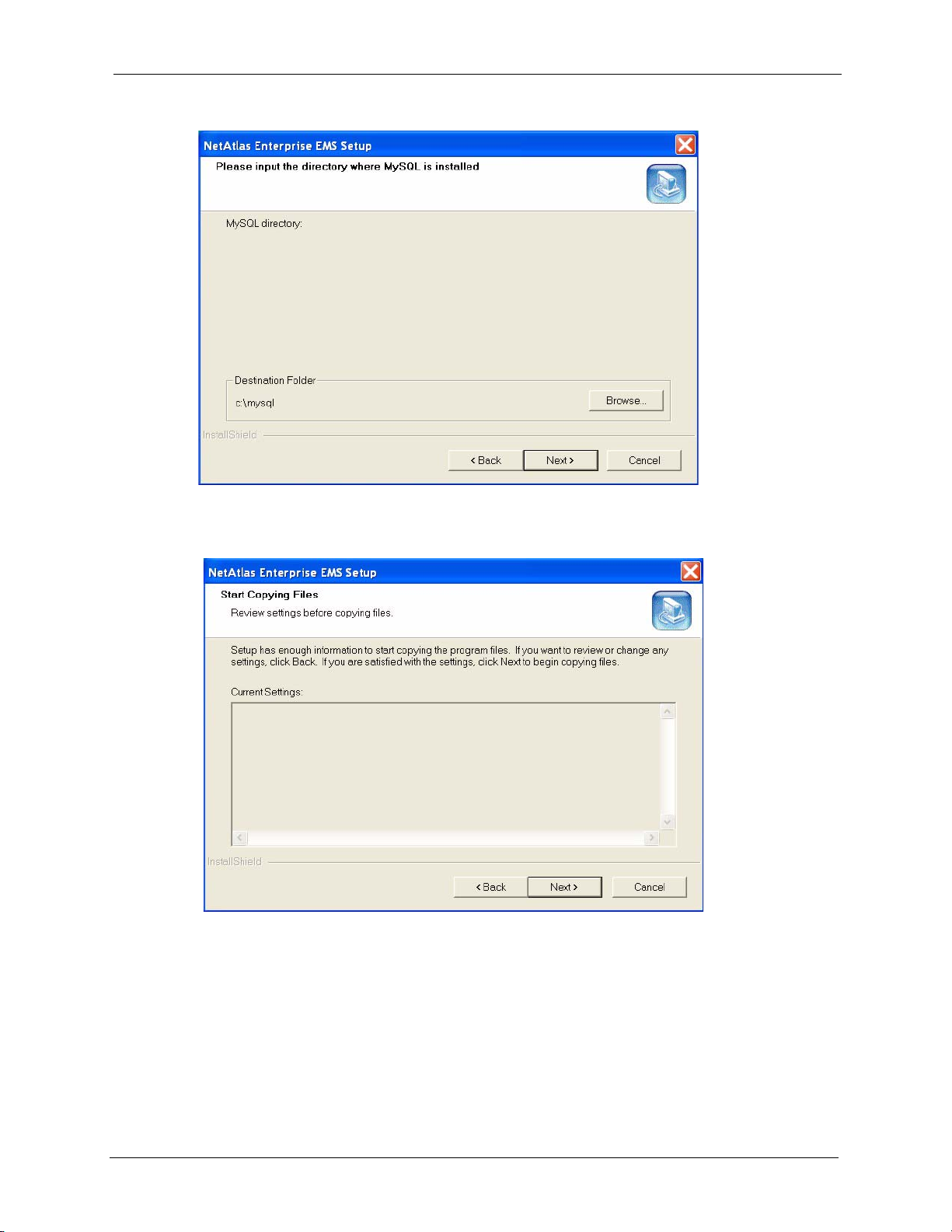
NetAtlas Enterprise 1.00 User’s Guide
Figure 10 Installing EMS: Specify MySQL Directory
17 In the next screen, click Next to begin the installation and start copying files.
Figure 11 Installing EMS: Start Copying Files
18 When a Welcome screen displays. Click Next to install the MySQL ODBC driver.
Chapter 1 Introducing the EMS 28
Page 30
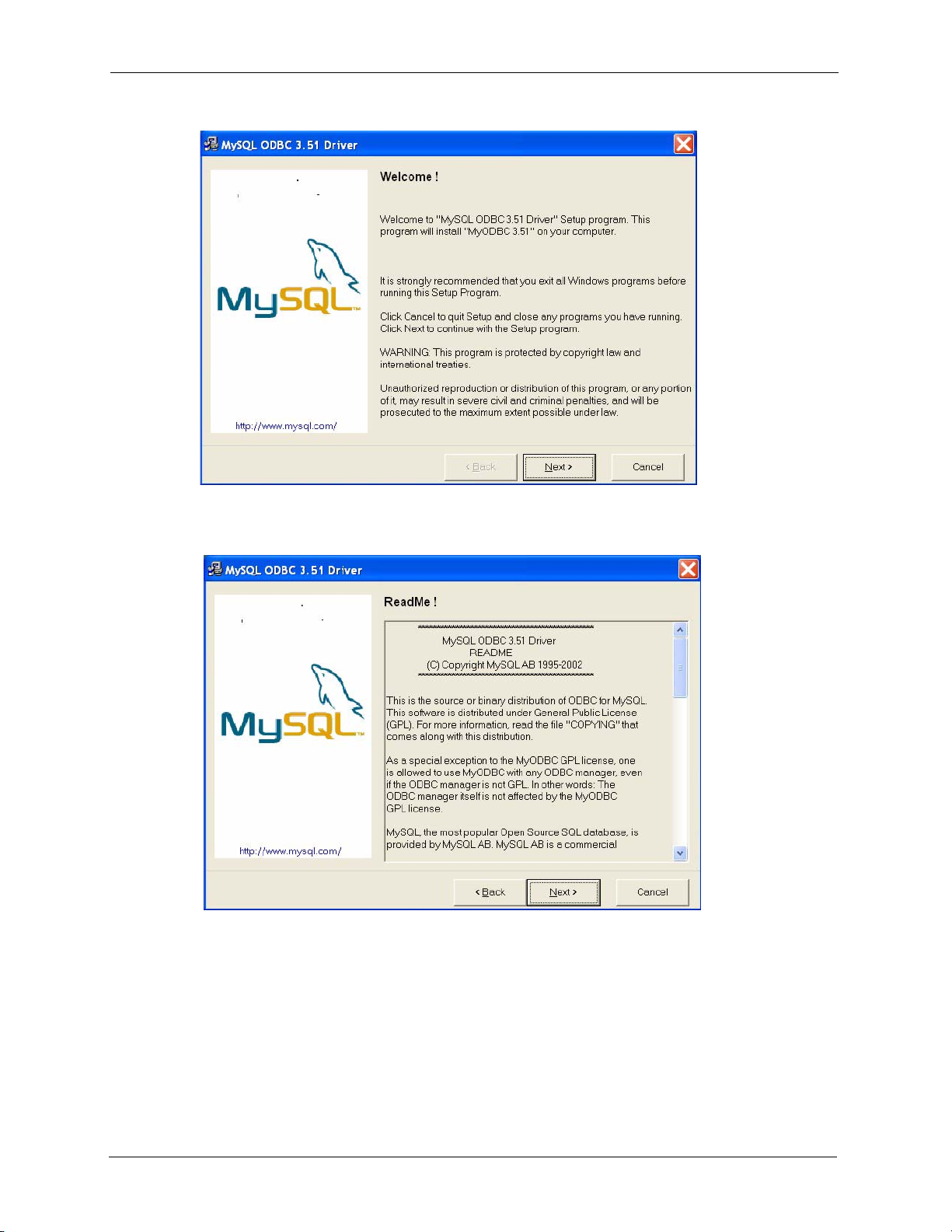
NetAtlas Enterprise 1.00 User’s Guide
Figure 12 Installing EMS: MySQL ODBC: Welcome
19 Read the license agreement. Click Next to accept the agreement.
Figure 13 Installing EMS: MySQL ODBC: License Agreement
20 Click Next again to begin the MySQL ODBC driver installation.
29 Chapter 1 Introducing the EMS
Page 31

NetAtlas Enterprise 1.00 User’s Guide
Figure 14 Installing EMS: MySQL ODBC: Start Installing
21 Click Finish to complete the MySQL ODBC installation.
Figure 15 Installing EMS: MySQL ODBC: Finish
22 In the final screen of the EMS wizard, click Finish to complete the EMS installation.
Chapter 1 Introducing the EMS 30
Page 32

NetAtlas Enterprise 1.00 User’s Guide
Figure 16 Installing EMS: Finish
1.4 SNMPc Network Manager
Start the SNMPc Network Manager manually or have it start automatically each time you turn
on your computer.
1.4.1 Manual SNMPc Startup
Manually starting SNMPc depends on your operating system. In Windows 2000, click Start,
Programs, SNMPc Network Manager, Startup System to start the SNMPc Network
Manager.
1.4.2 Automatic SNMPc Startup
To start SNMPc automatically each time you turn on your computer, first click Config,
System Startup.
Then, select Auto Startup and finally click OK. Conversely, clear this checkbox if you do not
wish SNMPc to automatically start each time you turn on your computer.
31 Chapter 1 Introducing the EMS
Page 33

Figure 17 SNMPc Task Setup
1.5 Adding MIBs
NetAtlas Enterprise 1.00 User’s Guide
The Management Information Base (MIB) is designed for holding management information
on systems such as the MSC that the standard MIB does not include.
1 From the SNMPc Network Manager main screen, click Config, MIB Database.
Figure 18 Config: MIB Database
2 Click Add in the Compile Mibs screen.
Chapter 1 Introducing the EMS 32
Page 34

NetAtlas Enterprise 1.00 User’s Guide
Figure 19 Compile Mibs (First Screen)
3 Scroll down the Add Mibs dialog box and select the MIB: rfc2674.mib (P-BRIDGE-
MIB). Click OK.
Figure 20 Add Mib Files
4 Click Compile in the Compile Mibs screen.
Figure 21 Compile Mibs (Second Screen)
5 Click Ye s when asked to confirm, then click OK.
33 Chapter 1 Introducing the EMS
Page 35

NetAtlas Enterprise 1.00 User’s Guide
Figure 22 Compile Mibs
6 Repeat Steps 2 to 5 for the following;
• rfc2925.mib (DISMAN-PING-MIB)
• rfc3291.mib (INET-ADRESS-MIB)
• rfc3621.mib (POWER-ETHERNET-MIB)
•zyxel.mib
• zyxel-es3124.mib
• zyxel-es3124pwr.mib.
Note: You must add and compile the MIBs separately in the order specified.
7 Finally click Done in the Compile Mibs screen.
1.6 Finding your Switch
The SNMPc Network Manager can find new devices automatically using auto-discovery
(enabled by default) or you will have to add device(s) manually.
1.6.1 Device Auto-Discovery
1 To enable auto-discovery and then find your device, click Config, Discovery/Polling.
Figure 23 Config, Discovery Agents
2 Select the Enable Discovery check box and click OK.
Chapter 1 Introducing the EMS 34
Page 36

NetAtlas Enterprise 1.00 User’s Guide
Figure 24 Discovery Agents Screen
3 Find your device in the Device List panel. Double-click the device icon to access the
EMS.
1.6.2 Add Device(s) Manually
If you have disabled auto-discovery, follow the steps below to add your device(s) manually.
1 Click Insert, MAP Object, Device.
Figure 25 Insert, MAP Object, Device
2 Fill in the MAP Object Properties screen and then click OK.
35 Chapter 1 Introducing the EMS
Page 37

Figure 26 Map Object Properties: Generall
NetAtlas Enterprise 1.00 User’s Guide
Table 2 Map Object Properties: General
FIELD DESCRIPTION
Label Type a device name for identification purposes. If you do not configure this field,
Type This field shows what type of device it is, for example a hub, workstation, router
Address Type the IP address of the switch.
Icon You may change the default icon by clicking >> and then choosing a different
Group This is the group number associated with this type of device. This field is
Descr Type a description of your device in this (optional) field.
1.7 Using SNMP
Check that you are using SNMPv2c. If you are not using SNMPv2c, you must uninstall any
previous versions and install SNMPv2c. Refer to RFC 1901 for more information on SNMP
Version 2c (SNMPv2c). Follow this procedure to use SNMPv2c.
1 Right-click the Device icon and select Properties.
the default label is “New Object”.
etc. This field displays Device for the switch.
icon.
optional.
2 Click the Access tab.
Chapter 1 Introducing the EMS 36
Page 38

NetAtlas Enterprise 1.00 User’s Guide
Figure 27 Map Object Properties
3 Follow the instructions in the table below to set the specified fields in the Map Object
Properties screen.
Table 3 Required Map Object Properties
FIELD VAL UE
Read Access Mode “SNMPV2c”
Read/Write Access Mode “SNMPV2c”
Read Community field For initial configuration, “public” is the default for most devices.
After initial configuration, you assign this field.
Read/Write Community field For initial configuration, “public” is the default for most devices.
After initial configuration, you assign this field.
Note: For security purposes, we strongly recommend you change the Read
Community and Read Read/Write Community defaults.
Write down this information in a secure place so you will not forget it later!
4 Click OK.
After the device has been found, the icon and label appear in the network manager view
window.
5 Right-click on the device icon to view a set of SMNPc network manager shortcuts. Click
Properties to verify the information you entered in the previous step.
37 Chapter 1 Introducing the EMS
Page 39

NetAtlas Enterprise 1.00 User’s Guide
Figure 28 Network Manager Shortcuts
6 Make sure the MySQL database is running. You must restart windows after you install
MySQL. MySQL should start automatically when you restart Windows. If it does not,
click start, Programs, Startup and then click WinMySQLadmin.
Chapter 1 Introducing the EMS 38
Page 40

NetAtlas Enterprise 1.00 User’s Guide
Figure 29 Startup MySQL
1.8 Configuring MySQL ODBC Driver
The MySQL driver should already be installed from the EMS installation. You must configure
the MySQL ODBC driver for the EMS to connect to the MySQL database successfully.
Follow the steps below to configure the ODBC driver in Windows XP. Steps may be similar
for Windows NT4.0.
Click Start, Settings and Control Panel to open the Control Panel screen. Double-click
Administrative Tools.
1 Click start, Settings, Control Panel, Administrative Tools and click Data Sources
(ODBC).
39 Chapter 1 Introducing the EMS
Page 41

Figure 30 Data Sources (ODBC)
NetAtlas Enterprise 1.00 User’s Guide
2 Click the User DSN tab and select the switch MySQL driver from the User Data
Sources list.
3 Click Configure.
Figure 31 ODBC Data Source Administrator
4 The MySQL ODBC DSN Configuration screen displays as shown next. Specify your
MySQL database settings and click OK.
Chapter 1 Introducing the EMS 40
Page 42

NetAtlas Enterprise 1.00 User’s Guide
Figure 32 MySQL: Connection Setup
5 Double-click the switch icon to view the Switch Manager.
Figure 33 Switch Device List Icon
6 Double-click the Switch Manager icon.
Figure 34 Switch Manager
41 Chapter 1 Introducing the EMS
Page 43

NetAtlas Enterprise 1.00 User’s Guide
Note: For information on the Window, Admin and Help options in the Switch
Manager screen, see
Section 14.2 on page 140.
The EMS polls for all the available switch cards. Select a device icon to display a graphic of
the switch in the Device Panel. You can only display one switch in the Device Panel at one
time.
Figure 35 Switch Graphic Display
Chapter 1 Introducing the EMS 42
Page 44

NetAtlas Enterprise 1.00 User’s Guide
43 Chapter 1 Introducing the EMS
Page 45

CHAPTER 2
EMS Main Window
This chapter describes the EMS main window.
2.1 Introducing the EMS Main Window
After you have logged into the EMS, double-click the switch device icon in the Device List
Panel to display the EMS main screen (shown next). The EMS retrieves device information
from the switch (using SNMP protocol).
Figure 36 EMS Main Screen Overview
NetAtlas Enterprise 1.00 User’s Guide
Device List Panel
Menu Shortcut Bar
Device Panel
System Message Panel
Chapter 2 EMS Main Window 44
Page 46

NetAtlas Enterprise 1.00 User’s Guide
The following table describes the elements in the EMS screen.
Table 4 EMS Main Screen Overview
ELEMENT FUNCTION
Menu Shortcut Bar Use these buttons to execute common commands quickly. Hold the cursor
over an icon to see a tool tip.
Device Panel This is a graphical device display. Double-click on a switch to display the
EMS GUI management window for the switch.
Device List Panel View devices in a tree structure. The colors of the device icons indicate the
real-time status of the represented devices.
System Message Panel View the alarm status and port status of the selected switch.
2.2 Device Icon Colors
The colors of the device icons (in the Device List Panel) indicate the real-time status of the
represented devices. The following table describes the colors used.
Table 5 Device Icon Colors
COLOR DESCRIPTION
Green The device is working and is responding to polling.
Red There is no response from the device or the device is not turned on.
2.3 System Message Panel Alarm Status
The colors of the alarm icons (in the System Message Panel) indicate the real-time status of
the the current selected device. The following table describes the alarm states used.
Table 6 System Message Panel Alarm Status
PANEL ALARMS ALARM OFF ALARM ON
ALARM The device fan, temperature
or voltage alarm is off.
FAN The device fans are
functioning properly
j
j
The fan, temperature and
voltage alarms are all on. A
serious hardware problem
exists.
One or more of the device
fans has a problem.
TEMP Temperatures at all sensor
points in the switch are within
the threshold temperature
range.
VOL The power supply at all
sensor points in the switch is
within the tolerance range.
The temperature at a sensor
point in the switch has risen
above or below the threshold
temperature range.
The power supply at a sensor
point in the switch has fallen
out of tolerance range.
45 Chapter 2 EMS Main Window
Page 47

If an alarm turns on, click the Port Status tab in the System Message Panel or proceed to
Section 5.1 on page 60 for hardware troubleshooting.
2.4 System Message Panel Port Status
Proceed to Section 5.4 on page 66 for information on the details displayed in this screen.
2.5 Menu Shortcut Buttons
The following is a brief overview of the menu shortcut buttons.
Figure 37 EMS Main Screen Shortcut Bar
NetAtlas Enterprise 1.00 User’s Guide
2.6 EMS Main Menu Summary
This is a summary of the EMS menus in the main screen.
Table 7 EMS Menu Summary
MAP TEMPLATE STATUS PERFORMANCE FAULT MAINTENANCE TOO L
Add
Submap/
Device
Edit Node STP Status Loopback Test Device Reset Web
Search
Node
Delete Port Status Load Factory Default
Refresh 802.1d Scheduled NE
Exit
VLAN
Te mp l at e
Hardware Status Interface Event Log Firmware Upgrade Te ln e t
Access
VLAN Status NE (Network
Element)
Configuration
Backup and Restore
Config Backup
Ping
Chapter 2 EMS Main Window 46
Page 48

NetAtlas Enterprise 1.00 User’s Guide
The following table summarizes these sub-links in the navigation panel.
Table 8 EMS Navigation Panel Sub-link Descriptions
DESCRIPTION LABEL
MAP Screens
Add Submap/Device This link takes you to a screen where you can add a device or a submap
Edit Node This link takes you to a screen where you can edit device properties.
Search Node This link takes you to a screen where you can search for a device or a
Delete Click this link to delete a submap folder or devices within a folder.
Refresh Click this link to update the screen with the most recently saved settings.
Te mp l at e
VLAN Template This link takes you to a screen where you can pre-configure a template of
Status Screens
Hardware Status This link takes you to a screen where you can view the hardware status of
STP Status This link takes you to a screen where you can view the software status of a
VLAN Status This link takes you to a screen where you can view the VLAN status of a
Port Status This link takes you to a screen where you can view the port status of a
802.1d This link takes you to a screen where you can view the MAC addresses
Performance
Interface This link takes you to a screen where you can configure interface
Fault Screens
Event Log This link takes you to a screen where you can configure an alarm filter.
Loopback Test This link takes you to a screen where you can perform a loopback test.
Maintenance
Firmware Upgrade This link takes you to a screen where you can perform a device firmware
Device Reset This link takes you to a screen where you can reset a device.
NE (Network Element)
Configuration Backup
and Restore
Load Factory Default This link takes you to a screen where you can load the factory default
Scheduled NE Config
Backup
Tool Screens
folder to the EMS Device List Panel.
submap folder.
settings for upload to multiple devices.
a device.
device.
device.
device.
(and types) of devices attached to what ports and VLAN IDs or view the
MAC addresses – IP address resolution table.
performance graphs and tables.
upgrade.
This link takes you to a screen where you can backup or restore
configuration files.
settings.
This link takes you to a screen where you can schedule when you want to
backup a device configuration file.
47 Chapter 2 EMS Main Window
Page 49

Table 8 EMS Navigation Panel Sub-link Descriptions (continued)
DESCRIPTION LABEL
Te ln e t This link takes you to a screen where you can access a device Telnet
service.
Web Access This link takes you to a screen where you can access a device Web
configurator.
Ping This link takes you to a screen where you can ping a device directly
through the EMS.
2.7 Common EMS Command Buttons
NetAtlas Enterprise 1.00 User’s Guide
The following table shows common command buttons found on most EMS screens.
Table 9 Common EMS Command Buttons
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Apply Click Apply to save the changes back to the switch.
OK Click OK to save your changes and close the screen.
Cancel Click Cancel to discard all changes and close the screen.
Close Click Close to close the screen.
2.8 View the Switch
To display a selected switch, double-click the apporopriate switch in the Device List Panel or
on the switch icon in the Device Panel. You can only display one switch in the device Panel
window at a time. Refer to the appropriate chapters or sections for the descriptions of each
menu screen.
Figure 38 Switch View
2.9 Switch Information
Follow the steps to display information on a switch.
1 Right-click on the switch icon in the Device List Panel.
2 Click Configuration, System and then System Info. The switch information window
displays as shown next.
Chapter 2 EMS Main Window 48
Page 50

NetAtlas Enterprise 1.00 User’s Guide
3 Choose a switch from the list located on the left-hand side of the screen.
Figure 39 Configuration: Switch System Configuration
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 10 Configuration: Switch System Configuration
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Device Name This field displays the selected switch name.
Device IP This field displays the selected switch IP address.
Name Enter a descriptive name for identification purposes. If you want to change the
name, enter up to 32 printable characters; spaces are not allowed.
Contact Enter the name (up to 32 characters) of the person in charge of the selected
Location Enter the geographic location (up to 32 characters) of the selected switch.
Serial No. This field displays the serial number of the selected switch.
HW Version This field displays the hardware version of the selected switch.
OS FW Version This field displays the firmware version of the selected switch.
Ethernet Address This field displays the switch Ethernet MAC address in six hexadecimal
49 Chapter 2 EMS Main Window
switch.
character pair format.
Page 51

Table 10 Configuration: Switch System Configuration (continued)
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Apply Click Apply to save the changes back to the switch.
Close Click Close to close the screen.
2.10 Configuration Save
You can save the current configuration of the switch(es).
Note: Do not turn off the switch during the updating process, as it may corrupt the
firmware and make your switch unusable.
1 To save the current switch configuration, right-click on the switch icon in the Device List
Panel.
2 Click Configuration Save.
3 Choose a switch from the list located in the screen.
NetAtlas Enterprise 1.00 User’s Guide
4 Click Apply to save the current configuration.
5 All settings configured on the EMS will be saved to the selected switch.
Figure 40 Configuration: Save
Chapter 2 EMS Main Window 50
Page 52

NetAtlas Enterprise 1.00 User’s Guide
51 Chapter 2 EMS Main Window
Page 53

Managing Device Maps in EMS
This chapter describes the Map menus you use to add, edit or delete device mappings in the
EMS.
3.1 Submap and Device Mapping
The EMS mapping displays logical hierarchy for the switch in the EMS. When you first start
the EMS, the default Root Map and an icon for your switch device are created in the Device
List Panel automatically. Both devices and submaps (or folders) can be added below the
rootmap. Devices can also be added to submap folders.
In the following figure the “TestSubmap” folder and the “Switch-2319” are both mapped to
the “Rootmap” folder. The “TestSubmap” is a submap folder that contains a mapped device
“TestSubmapDevice”.
NetAtlas Enterprise 1.00 User’s Guide
CHAPTER 3
Figure 41 Submaps and Device Mapping
Note: You cannot create, edit or delete the Root Map.
3.1.1 Adding a Submap or Device
To add a new submap or a new device, select the Root Map or a submap icon in the Device
List Panel. Click Map and Add Submap/Device to display the following screen.
Chapter 3 Managing Device Maps in EMS 52
Page 54

NetAtlas Enterprise 1.00 User’s Guide
Figure 42 Map: Add Submap/Device
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 11 Map: Add Submap/Device
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Properties Select the Submap or Device radio button to add a new submap or device
icon to the Device List Panel.
If you select Submap, only the Name and Description fields display ; all other
fields appear as read-only.
Name Enter a descriptive name (up to 32 characters) for this node for identification
IP Address Enter the IP address of the device.
Password Enter a password (up to 32 characters). This password is used by the EMS
Description Enter a description (up to 32 characters) about the device.
Get Community Enter the get community, which is the password for the incoming Get- and
Set Community Enter the set community, which is the password for incoming Set- requests
Trap Community Enter the trap community, which is the password sent with each trap to the
OK Click OK to save the changes and close the screen.
Cancel Click Cancel to discard the changes and close the screen.
purposes.
administrator for device firmware upload.
GetNext- requests from the management station.
from the management station.
SNMP manager.
3.1.2 Edit a Node
Select a submap icon in the Device List Panel and then click Map and Edit Node.
53 Chapter 3 Managing Device Maps in EMS
Page 55

Figure 43 Map: Edit Node
NetAtlas Enterprise 1.00 User’s Guide
Refer to Table 11 on page 53 for the field descriptions.
3.1.3 Find an Object
To find or locate a device (or node), click Map and then Find Object.
Figure 44 Map: Find Object
Enter a descriptive text (for example, the node name) in the Find field and click OK to start
the search.
3.1.4 Delete a Submap
To delete a submap, select the submap icon in the Device List Panel and click Map and then
Delete.
Chapter 3 Managing Device Maps in EMS 54
Page 56

NetAtlas Enterprise 1.00 User’s Guide
Figure 45 Map: Delete Warning
Note: If you delete a submap, all devices under a submap will be removed.
3.1.5 Delete a Device
To remove a device from the Device List Panel, select the device icon and click Map and then
Delete.
3.2 Exit
Click Map and then Exit to close the EMS screen.
55 Chapter 3 Managing Device Maps in EMS
Page 57

This chapter describes how to configure a VLAN template.
4.1 VLAN Template Overview
A template is a pre-configured set of configuration settings. Templates allow you to configure
device VLANs efficiently. The template can then be uploaded to one or more devices thus
removing the need to configure the VLAN settings for each device. See the VLAN
Configuration chapter for more information on the template upload.
4.1.1 Configuring a VLAN Template
NetAtlas Enterprise 1.00 User’s Guide
CHAPTER 4
VLAN Template
Click Templa te and then click VLAN to display the screen as shown.
Chapter 4 VLAN Template 56
Page 58

NetAtlas Enterprise 1.00 User’s Guide
Figure 46 Template: VLAN
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 12 Template: VLAN
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Device Type Select a device type from the drop-down list box to view the device’s VLAN
configuration.
VLAN Identity
VLAN ID Enter a unique number to identify the VLAN.
VLAN Name Enter a descriptive name for identification purposes.
Egress Ports A port that is in the egress list in a VLAN. Only select this if the subscriber's DSL
modem or router supports 802.1Q VLAN.
Select the ports which you want to be egress ports from the list provided.
Forbidden Ports A port that is blocked from joining a VLAN group. No frames are transmitted
through this port.
A forbidden port cannot be an egress or untagged port.
Select the ports which you want to be forbidden ports from the list provided.
Untag A port that does not tag all outgoing frames transmitted.
An egress port can be untagged.
Select the ports which you want to be untagged ports from the list provided.
New Click New to create a new VLAN. You must enter a VLAN ID and a VLAN Name
to create a new VLAN. The new VLAN and name is displayed in the left-hand
column in this screen.
57 Chapter 4 VLAN Template
Page 59

NetAtlas Enterprise 1.00 User’s Guide
Table 12 Template: VLAN (continued)
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Delete Click on a VLAN in the left-hand column of this screen and then click the Delete
button to remove it from the VLAN template.
Modify Click on a VLAN in the left-hand column of this screen. Change the VLAN Name
or change the configuration of the egress, forbidden and untagged ports. Click
the Modify button to save the changes to the switch.
If you want to change the VLAN ID of a VLAN configuration, you can only delete
the VLAN configuration or create a new VLAN configuration using a different
VLAN ID.
Port List Click on a port in the Egress Ports list to add the selected port to the port list. If
Close Click Close to close the screen.
a port is not selected from any of the three port lists, then it is a normal tagged
port.
This fields displays all available ports that are participating in a VLAN. A tagged
port is marked T while an untagged port is marked U.
Chapter 4 58
Page 60

NetAtlas Enterprise 1.00 User’s Guide
59 Chapter 4
Page 61

This chapter covers the hardware status, STP status, VLAN status, port status and 802.1d
status screens.
5.1 Hardware Status
Follow the steps below to view fan speeds, voltage levels and temperatures of a switch.
1 To view the hardware status of a switch, click Status and then Hardware Status.
2 Choose a switch from the list located on the left-hand side of the screen as shown next.
It may take a few seconds to update the screen.
NetAtlas Enterprise 1.00 User’s Guide
CHAPTER 5
Status
Chapter 5 Status 60
Page 62

NetAtlas Enterprise 1.00 User’s Guide
Figure 47 Status: Hardware Status
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 13 Status: Hardware Status
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Fan RPM A properly functioning fan is an essential component (along with a sufficiently
ventilated, cool operating environment) in order for the device to stay within the
temperature threshold. Each fan has a sensor that is capable of detecting and
reporting if the fan speed falls below the threshold shown.
Index This field displays the fan number.
Current This field displays this fan’s current speed in Revolutions Per Minute (RPM).
Max This field displays this fan’s maximum speed recorded in Revolutions Per Minute
(RPM).
Min This field displays this fan’s minimum speed recorded in Revolutions Per Minute
(RPM). "<41" is displayed for speeds too small to measure (under 2000 RPM).
Threshold This field displays the minimum speed at which a normal fan should work.
Status NORMAL indicates that this fan is functioning above the minimum speed. ERROR
indicates that this fan is functioning below the minimum speed.
Voltage (V) The power supply for each voltage has a sensor that is capable of detecting and
reporting if the voltage falls out of the tolerance range.
Index This field displays the first voltage sensor number.
Current This is the current voltage reading in volts.
Max This field displays the maximum voltage recorded at this sensor in volts.
61 Chapter 5 Status
Page 63

NetAtlas Enterprise 1.00 User’s Guide
Table 13 Status: Hardware Status (continued)
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Min This field displays the minimum voltage recorded at this sensor in volts.
Threshold This field displays the minimum voltage percentage at which the switch should work.
Status NORMAL indicates that the voltage is within an acceptable operating range at this
Temperature The switch has temperature sensors that are capable of detecting and reporting if the
Celsius Select this option to display the temperature in degrees Centigrade.
Fahrenheit Select this option to display the temperature in degrees Fahrenheit.
Index This field displays the temperature sensor number.
Current Value This shows the current temperature at this sensor.
Max This field displays the maximum temperature recorded at this sensor.
Min This field displays the minimum temperature recorded at this sensor.
Threshold This field displays the upper temperature limit at this sensor.
Status This field displays NORMAL for temperatures below the threshold and ERROR for
Polling The text box displays how often (in seconds) this screen refreshes. You may change
Close Click Close to close the screen.
point; otherwise ERROR is displayed. ABSENT indicates that there is no power
reading at a sensor(s).
temperature rises above the threshold. You may choose the temperature unit
(Centigrade or Fahrenheit).
those above.
the refresh interval by typing a new number in the text box and then clicking Apply
button.
5.2 STP Status
5.2.1 Introduction to Spanning Tree Protocol (STP)
STP detects and breaks network loops and provides backup links between switches, bridges or
routers. It allows a switch to interact with other STP-compliant switches in your network to
ensure that only one route exists between any two stations on the network.
5.2.1.1 STP Terminology
The root bridge is the base of the spanning tree; it is the bridge with the lowest identifier value
(MAC address).
Chapter 5 Status 62
Page 64

NetAtlas Enterprise 1.00 User’s Guide
Path cost is the cost of transmitting a frame onto a LAN through that port. It is assigned
according to the speed of the link to which a port is attached. The slower the media, the higher
the cost - see the next table.
Table 14 STP Path Costs
LINK SPEED RECOMMENDED VALUE RECOMMENDED RANGE ALLOWED RANGE
4Mbps 250 100 to 1000 1 to 65535
10Mbps 100 50 to 600 1 to 65535
16Mbps 62 40 to 400 1 to 65535
100Mbps 19 10 to 60 1 to 65535
1Gbps 4 3 to 10 1 to 65535
10Gbps 2 1 to 5 1to 65535
On each bridge, the root port is the port through which this bridge communicates with the root.
It is the port on this switch with the lowest path cost to the root (the root path cost). If there is
no root port, then this switch has been accepted as the root bridge of the spanning tree
network.
For each LAN segment, a designated bridge is selected. This bridge has the lowest cost to the
root among the bridges connected to the LAN.
5.2.2 How STP Works
After a bridge determines the lowest cost-spanning tree with STP, it enables the root port and
the ports that are the designated ports for connected LANs, and disables all other ports that
participate in STP. Network packets are therefore only forwarded between enabled ports,
eliminating any possible network loops.
STP-aware switches exchange Bridge Protocol Data Units (BPDUs) periodically. When the
bridged LAN topology changes, a new spanning tree is constructed.
Once a stable network topology has been established, all bridges listen for Hello BPDUs
(Bridge Protocol Data Units) transmitted from the root bridge. If a bridge does not get a Hello
BPDU after a predefined interval (Max Age), the bridge assumes that the link to the root
bridge is down. This bridge then initiates negotiations with other bridges to reconfigure the
network to re-establish a valid network topology.
63 Chapter 5 Status
Page 65

5.2.3 STP Port States
STP assigns five port states (see next table) to eliminate packet looping. A bridge port is not
allowed to go directly from blocking state to forwarding state so as to eliminate transient
loops.
Table 15 STP Port States
PORT STATE DESCRIPTION
Disabled STP is disabled (default).
Blocking Only configuration and management BPDUs are received and processed.
Listening All BPDUs are received and processed.
Learning All BPDUs are received and processed. Information frames are submitted
Forwarding All BPDUs are received and processed. All information frames are
5.2.4 View STP Status
NetAtlas Enterprise 1.00 User’s Guide
to the learning process but not forwarded.
received and forwarded.
Follow the steps below to view the STP status of a switch.
1 Click Status and then STP Status.
2 Choose a switch from the list located on the left-hand side of the screen.
Figure 48 Status: STP Status
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 16 Status: STP Status
LABEL DESCRIPTION
STP This field displays Running if STP is activated; otherwise, it displays Unknown.
Bridge Root refers to the base of the spanning tree (the root bridge).
Bridge ID This is the unique identifier for this bridge, consisting of bridge priority plus MAC
Chapter 5 Status 64
address.
Page 66

NetAtlas Enterprise 1.00 User’s Guide
Table 16 Status: STP Status (continued)
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Hello Time
(second)
Max Age (second) This is the maximum time (in seconds) a switch can wait without receiving a
Forwarding Delay
(second)
Cost to Bridge This is the path cost from the root port on this switch to the root switch.
Port ID This is the priority and number of the port on the switch through which this switch
Topology Changed
Times
Time Since Last
Change
Polling The text box displays how often (in seconds) this screen refreshes. You may
Close Click Close to close the screen.
5.3 VLAN Status
This is the time interval (in seconds) at which the root device transmits a
configuration message. The root bridge determines Hello Time, Max Age and
Forwarding Delay
configuration message before attempting to reconfigure.
This is the time (in seconds) the root switch will wait before changing states (that
is, listening to learning to forwarding).
must communicate with the root of the spanning tree.
This is the number of times the spanning tree has been reconfigured.
This is the time since the spanning tree was last reconfigured.
change the refresh interval by typing a new number in the text box and then
clicking the Apply button.
Follow the steps below to view the VLAN status of a switch.
1 Click Status and then VLAN Status.
2 Choose a switch from the list located on the left-hand side of the screen.
65 Chapter 5 Status
Page 67

Figure 49 Status: VLAN Status
NetAtlas Enterprise 1.00 User’s Guide
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 17 Status: VLAN Status
LABEL DESCRIPTION
VLAN ID This field displays the identification number of the VLAN.
Name This field displays a unique number for identification purposes.
Elapsed Time This field displays the time since the VLAN was created.
Status This field displays Active if the VLAN is active and will remain so after the
Port List This table displays all available ports that are participating in a VLAN. A
Polling The text box displays how often (in seconds) this screen refreshes. You may
Close Click Close to close the screen.
5.4 Port Status
next reset of the device. This field displays GVRP if the VLAN is active and
will remain so until removed by GVRP. This field is other if the VLAN is active,
but is not permanent or created by GVRP.
tagged port is marked T while an untagged port is marked U.
change the refresh interval by typing a new number in the text box and then
clicking the Apply button.
Follow the steps below to view the port status of a switch.
1 Click Status and then Port Status to display the following screen.
Chapter 5 Status 66
Page 68

NetAtlas Enterprise 1.00 User’s Guide
2 To view the port status of a switch choose a switch from the list located on the left-hand
side of the screen.
Figure 50 Status: Port Status
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 18 Status: Port Status
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Port This identifies the Ethernet port.
Link Speed This field displays the speed (either 10M for 10Mbps, 100M for 100Mbps or 1000M
Stat e This field displays the STP state of the port. See the Spanning Tree Protocol
PD This field displays the power device (PD) module status on the switch. If Not
TxPkts This field shows the number of transmitted frames on this port.
RxPkts This field shows the number of received frames on this port.
Errors This field shows the number of received errors on this port.
Polling The text box displays how often (in seconds) this screen refreshes. You may
Close Click Close to close the screen.
for 1000Mbps) and the duplex (F for full duplex or H for half). It also shows the cable
type (Copper or Fiber) for the combo ports.
chapter for details on STP port states.
Supported is displayed, the switch does not have a PD.
This field displays On if the switch has a PD and it is in use.
This field displays Of if the switch has a PD, but it is not in use.
change the refresh interval by typing a new number in the text box and then clicking
the Apply button.
67 Chapter 5 Status
Page 69

5.5 802.1D
Use the following screens to view a table of MAC address entries or to view a table of IP
address mappings.
5.5.1 802.1D: MAC Table
The MAC table shows how frames are forwarded or filtered across the switch’s ports. It shows
what device MAC address, belonging to what VLAN group (if any) is forwarded to which
port(s) and whether the MAC address is dynamic (learned by the switch) or static (manually
entered in Static MAC Forwarding).
The switch uses the Filtering Database to determine how to forward frames. See the following
figure.
1 The switch examines a received frame and learns the port on which this source MAC
address came.
2 The switch checks to see if the frame's destination MAC address matches a source MAC
address already learned in the Filtering Database.
NetAtlas Enterprise 1.00 User’s Guide
If the switch has already learned the port for this MAC address, then it forwards the frame
to that port.
If the switch has not already learned the port for this MAC address, then the frame is
flooded to all ports. Too much port flooding leads to network congestion.
If the switch has already learned the port for this MAC address, but the destination port is
the same as the port it came in on, then it filters the frame.
Figure 51 MAC Table Flowchart
5.5.2 View the MAC Table
Follow the steps below to view the MAC table.
Chapter 5 Status 68
Page 70

NetAtlas Enterprise 1.00 User’s Guide
1 Click Status and then 802.1d.
2 To view the MAC table of a switch choose a switch from the list located on the left-hand
side of the screen and click the MAC Table tab.
Figure 52 Status: 802.1d: MAC Table
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 19 Status: 802.1d: MAC Table
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Sort by Click one of the following buttons to display and arrange the data according to that
button type. The information is then displayed in the summary table below.
MAC Click this button to display and arrange the data according to MAC address.
VID Click this button to display and arrange the data according to VLAN group.
Port Click this button to display and arrange the data according to port number.
Index This is the incoming frame index number.
Name This field displays a descriptive name for this static MAC address forwarding rule.
MAC Address This is the MAC address of the device from which this incoming frame came.
VID This is the VLAN group to which this frame belongs.
Port This is the port from which the above MAC address was learned.
Type This shows whether the MAC address is dynamic (learned by the switch) or static
(manually entered in Static MAC Forwarding).
Polling The text box displays how often (in seconds) this screen refreshes. You may
change the refresh interval by typing a new number in the text box and then
clicking the Apply button.
Close Click Close to close the screen.
69 Chapter 5 Status
Page 71

5.5.3 802.1D: ARP Table
Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) is a protocol for mapping an Internet Protocol address (IP
address) to a physical machine address, also known as a Media Access Control or MAC
address, on the local area network.
An IP (version 4) address is 32 bits long. In an Ethernet LAN, MAC addresses are 48 bits
long. The ARP Table maintains an association between each MAC address and its
corresponding IP address.
5.5.4 How ARP Works
When an incoming packet destined for a host device on a local area network arrives at the
switch, the switch's ARP program looks in the ARP Table and, if it finds the address, sends it
to the device.
If no entry is found for the IP address, ARP broadcasts the request to all the devices on the
LAN. The switch fills in its own MAC and IP address in the sender address fields, and puts the
known IP address of the target in the target IP address field. In addition, the switch puts all
ones in the target MAC field (FF.FF.FF.FF.FF.FF is the Ethernet broadcast address). The
replying device (which is either the IP address of the device being sought or the router that
knows the way) replaces the broadcast address with the target's MAC address, swaps the
sender and target pairs, and unicasts the answer directly back to the requesting machine. ARP
updates the ARP Table for future reference and then sends the packet to the MAC address that
replied.
NetAtlas Enterprise 1.00 User’s Guide
The ARP table can hold up to 16K entries.
5.5.5 View the ARP Table
Follow the steps below to view the ARP table.
1 Click Status and then 802.1d.
2 To view the ARP table of a switch choose a switch from the list located on the left-hand
side of the screen and click the ARP Table tab.
Chapter 5 Status 70
Page 72

NetAtlas Enterprise 1.00 User’s Guide
Figure 53 Status: 802.1d: ARP Table
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 20 Status: 802.1d: ARP Table
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Index This is the ARP table entry number.
IP Address This is the learned IP address of a device connected to a switch port with
MAC Address This is the MAC address of the device with corresponding IP address above.
Type This shows whether the MAC address is dynamic (learned by the switch) or
Polling The text box displays how often (in seconds) this screen refreshes. You may
Close Click Close to close the screen.
corresponding MAC address below.
static (manually entered in Static MAC Forwarding).
change the refresh interval by typing a new number in the text box and then
clicking the Apply button.
71 Chapter 5 Status
Page 73

This chapter describes the event logs and how to perform loopback tests.
6.1 Event Log
To display system event logs click Fault and then Event Log to view the following screen.
Figure 54 Fault: Event Log
NetAtlas Enterprise 1.00 User’s Guide
CHAPTER 6
Fault Menus
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 21 Fault: Event Log
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Alarm Filter
Port To display event logs of a port, select the port from the drop-down list box.
Chapter 6 Fault Menus 72
Page 74

NetAtlas Enterprise 1.00 User’s Guide
Table 21 Fault: Event Log (continued)
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Alarm Type Select the type of logs from the drop-down list box. Choices are All,
Severity Select the severity level of the logs you want to display from the drop-down
Sorted by Select Log Time to sort event logs by the time at which they were generated
Date / To Specify the time range to display the event logs.
Apply Click Apply to display event logs generated within the specified time period.
Alarm
Index This field displays the index number of the event logs.
Acknowledge This field displays whether a log has been acknowledged so that EMS users
Type This field displays the type of the event log.
Severity This field displays the severity of the event log.
Device Name This field displays the name of the device on which the event log was
Port This field displays the port number on which the event log was generated.
Date Time This field displays the date and time on which the event log was generated.
Description This field displays some information about the event log.
Acknowledge Click this button to acknowledge any selected log messages.
Delete Click Delete to remove a log.
Close Click Close to close this screen.
Communication, QualityOfService, ProcessingError, Equipment and
Environmental.
Select All for system event logs generated by all alarm types.
Select Communication for transmission and signal logs.
Select QualityOfService for performance logs.
Select Processing Error for software and configuration problem logs.
Select Equipment for hardware-related logs.
Select Environmental for environmental logs.
See the appendix for a more detailed list of possible alarm causes.
list box. The choices and associated colors are as follows:
• Critical - Red
• Major - Orange
• Minor - Yellow
• Warning - Blue
• Normal - Green
or select Device Name to sort event logs by the device from which they were
generated.
will know when a log has been dealt with by an administrator.
generated.
6.2 Loopback Test
Follow the steps below to perform an internal loopback test.
1 Click Fault and then Loopback Test.
73 Chapter 6 Fault Menus
Page 75

NetAtlas Enterprise 1.00 User’s Guide
2 Choose a switch from the list located on the left-hand side of the screen.
3 Choose a port from the list located on the right-hand side of the screen.
4 Click Apply to start the loopback test.
Figure 55 Fault: Loopback Test
Chapter 6 Fault Menus 74
Page 76

NetAtlas Enterprise 1.00 User’s Guide
75 Chapter 6 Fault Menus
Page 77

This chapter tells you how to backup and restore your configuration file as well as upload new
firmware and configuration files.
7.1 Firmware Upgrade
You must be logged in with system administrator rights to use this function.
Note: Do not turn off the switch during the updating process, as it may corrupt the
firmware and make the selected switch unusable.
7.1.1 Procedure to Update Firmware
NetAtlas Enterprise 1.00 User’s Guide
CHAPTER 7
Maintenance
You can perform firmware upgrade on all switches of the same type simultaneously on
the EMS. To update firmware, first download the latest firmware, then unzip and store it
on your computer. You can use this EMS FTP client to connect to a selected switch.
Note: Do not turn off the switch during the updating process, as it may corrupt the
firmware and make your switch unusable.
1 Click Maintenance and then Firmware Upgrade.
2 Type the path and file name of the firmware file you wish to upload to the switch in the
FW Image text box or click Browse to locate it. After you have specified the file, click
Apply.
Chapter 7 Maintenance 76
Page 78

NetAtlas Enterprise 1.00 User’s Guide
Figure 56 Maintenance: Firmware Upgrade
The switch(es) automatically restarts when the firmware upload is complete.
7.2 Device Reset
Reboot System allows you to restart a switch without physically turning the power off. Select
a device from the list and click Apply.
Click Apply again and then wait for the switch to restart. This takes up to two minutes. This
does not affect the switch’s configuration.
77 Chapter 7 Maintenance
Page 79

NetAtlas Enterprise 1.00 User’s Guide
Figure 57 Maintenance: Device Reset
7.3 Network Element Configuration Backup and Restore
A Network Element is a piece of telecommunications equipment that provides support or
services to the user.
Follow the steps below to backup or restore a switch configuration file.
1 Click Maintenance and then NE (Network Element) Configuration Backup and
Restore.
2 Select a switch from the drop-down list box.
3 Type the path and file name of the file you wish to restore to the switch or backup to your
computer in the Directory / File Name text box or click Browse to locate it.
4 Select the Save configuration before backup? text box to save the most recent switch
configuration if you want to backup to your computer.
5 Click either the Backup or Restore radio button.
6 Click Apply.
7 If you chose Restore, the switch automatically restarts when the configuration file upload
is complete.
8 Click Close to close this screen.
Chapter 7 Maintenance 78
Page 80

NetAtlas Enterprise 1.00 User’s Guide
Figure 58 Maintenance: Configuration Backup/Restore
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 22 Maintenance: Configuration Backup/Restore
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Directory/File Name Type the path and file name of the configuration file you wish to restore
to the switch or backup to your computer in the Directory / File Name
text box or click Browse to locate it.
Save running-config to
configuration
Backup Click the Backup radio button to transfer the configuration file from your
Restore Click the Restore radio button to transfer the configuration file from your
Apply Click Apply to backup or restore the switch(es) configuration file.
Close Click Close to close this screen.
Select the Save running-config to configuration text box to save the
most recently updated configuration to a file specified in the Directory/
File Name field.
switch to a computer.
computer to a switch.
7.4 Load Factory Default
Follow the steps below to reset a switch configuration to the factory defaults.
1 Click Maintenance and then Load Factory Default.
2 Select a switch from the list of devices shown.
3 Click Apply to clear all configuration information and return the switch to the factory
defaults.
This takes up to two minutes. If you want to access the switch web configurator again,
you may need to change the IP address of your computer to be in the same subnet as that
of the default switch IP address.
4 Click Close to close this screen.
79 Chapter 7 Maintenance
Page 81

Figure 59 Maintenance: Load factory Defaults
NetAtlas Enterprise 1.00 User’s Guide
7.5 Scheduled Network Element Configuration Backup
Perform configuration backups according to a schedule. Set the frequency, time and date of
the backup and the location where you want to backup the configuration file.
Chapter 7 Maintenance 80
Page 82

NetAtlas Enterprise 1.00 User’s Guide
Figure 60 Maintenance: Scheduled NE Config Backup
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 23 Maintenance: Scheduled NE Config Backup
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Backup Schedule
Frequency Scheduled backups can be performed on a Daily, Weekly or Monthly basis.
Select a radio button to schedule configuration backups starting at the date
and time specifed below. The default setting is No Backup.
Starting date Specify the starting date to begin a configuration file backup for the selected
device(s). Select a date from the drop-down list box.
Starting time Specify the starting time to begin a configuration file backup for the selected
device(s). Select a time from the selection box or enter a time (hh:mm:ss AM/
PM format).
Backup Directory Type the path and file name of the configuration file you wish to backup to
your computer in the Backup Directory text box or click Browse to locate it.
User info for Windows
Account This read-only field displays the Windows login account user.
Password Enter a password in this field for the administrator Account above.
Add Click the Add button to add a switch to the list of devices in the backup
schedule.
Remove Click the Remove button to remove a switch from the list of devices in the
Apply Click Apply to save changes to the EMS.
Close Click Close to close this screen.
backup schedule.
7.5.1 Scheduled Network Element Configuration Backup Add
Follow the steps below to add a device to the list of devices in the Scheduled NE
Configuration Backup screen.
81 Chapter 7 Maintenance
Page 83

NetAtlas Enterprise 1.00 User’s Guide
1 Click the Add button in the Scheduled NE Config Backup screen.
2 Click the OK button.
Figure 61 Maintenance: Scheduled NE Config Backup Add
7.5.2 Scheduled Network Element Configuration Backup Remove
To remove a device from the Scheduled NE Configuration Backup screen, click the
Remove button in the Scheduled NE Config Backup screen.
Chapter 7 Maintenance 82
Page 84

NetAtlas Enterprise 1.00 User’s Guide
83 Chapter 7 Maintenance
Page 85

This chapter shows you how to access a switch via Telnet or web configurator directly through
the EMS. You may need to do this to test the switch network connection for example.
8.1 Accessing the switch
Access the switch remotely via Telnet or web browser.
Note: When you access a switch via Telnet or the web configurator, you CANNOT
make any changes to that switch using the EMS.
8.1.1 Telnet
NetAtlas Enterprise 1.00 User’s Guide
CHAPTER 8
Tools
Telnet is the login and terminal emulation protocol common on the Internet and in UNIX
environments. It operates over TCP/IP networks. Its primary function is to allow users to log
into remote host systems.
The administrator uses Telnet from a computer on a remote network to access the switch. You
can use remote Telnet access as shown next.
1 Select a switch from the list of devices shown in the Device List Panel.
2 Click Tool and then Telnet to open a console session for Telnet access to the switch.
3 Type the switch User name and Password to access the switch command line prompt.
Figure 62 Telnet
4 Refer to the switch User’s Guide for information on the commands used in this screen.
8.1.2 Web Access
Configure the switch using the web configurator as shown.
1 Select a switch from the list of devices shown in the Device List Panel.
Chapter 8 Tools 84
Page 86

NetAtlas Enterprise 1.00 User’s Guide
2 Click Tool and then Web Access to open the switch web configurator password screen.
From here you can log in directly to the switch.
3 Type the switch User name and Password to access the web configurator.
Figure 63 Web Access
4 Refer to the switch User’s Guide for information on the web configurator main screen.
8.2 Ping
Ping the host to see if the links and TCP/IP protocol on both your computer and the switch is
working. Follow the steps below:
Note: The device IP address varies according to whether the switch connection to the
Figure 64 Ping
1 Select a switch from the list of devices shown in the Device List Panel.
2 Click Tool and then Ping to have the switch ping the IP address of the selected device.
EMS computer uses an in-band or an out-of-band IP address.
85 Chapter 8 Tools
Page 87

Device Menu Overview
This chapter introduces the device configuration menus.
9.1 Device Menu Summary
To select a device configuration menu, right-click on a device in the Device List Panel.
Figure 65 Device Panel List Menus
NetAtlas Enterprise 1.00 User’s Guide
CHAPTER 9
The following table shows the menus, sub menus and menu tab names.
Table 24 Device Menu Summary
MENU SUBMENU SUBMENU TABS
Property Edit Device
Configuration System Configuration System Info
SNMP Conf.
Remote Mgmt.
Time Setup
Switch Configuration Switch Setup
Priority Queue
STP Conf.
Link Aggregation
DHCP Relay
GARP Timer
RADIUS
MAC Forwarding
Chapter 9 Device Menu Overview 86
Page 88

NetAtlas Enterprise 1.00 User’s Guide
Table 24 Device Menu Summary
MENU SUBMENU SUBMENU TABS
VLAN Configuration
Ethernet Port
Configuration
Routing Configuration Static Route
Configuration Save Configuration
Filtering
Port Setup
Port VLAN
Port Link Aggregation
Port STP
Bandwidth Ctrl.
Broadcast Storm Ctrl.
Queue Method
Port 802.1x
Port Security
Port Mirroring
VLAN Stacking
9.2 Property Configuration
See Section 3.1.2 on page 53 for information on the Edit Device screen.
9.3 Introducing the EMS Configuration Window
The following example screen displays the main features used to configure EMS managed
devices. See the individual screen selections for details on switch feature configuration.
87 Chapter 9 Device Menu Overview
Page 89

NetAtlas Enterprise 1.00 User’s Guide
Figure 66
Configuration Window Panels
Device Panel
Port List
Panel
Switch Configurator
Panel
The following table describes the elements in this screen.
Table 25 Configuration Window Panels
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Device Panel This panel displays all active devices currently managed by the EMS.
Port List Panel This field displays a list of switch ports. This list displays in the Ethernet
Port Configuration screens only.
To make configuration changes to each port or ports select a port number
or multiple port numbers (by pressing the [CTRL] key and clicking at the
same time) in the Port List Panel.
Copy to.. Click the Copy to.. button to copy the configuration from the switch that
you are currently configuring to one or more switches. Port configurations
can also be copied to other device ports in the Ethernet Port
Configuration screens.
Switch Configurator Use this panel to make configuration changes to a device based on a port
or multiple ports selected in the Port List Panel.
If the screen does not have a Port List Panel, then use this panel to make
configuration changes to a device selected in the Device Panel.
Apply Click Apply to save configuration changes to the switch.
Close Click Close to close a configuration screen. If you close a screen without
first clicking Apply, configuration changes will not be saved.
9.3.1 Port List Multiple Port Configuration
Configure more than one port at the same time by pressing the [CTRL] key and clicking at the
same time in the Port List Panel. Click Apply when you are satisfied with the configuration
changes.
The following example screen displays.
Chapter 9 Device Menu Overview 88
Page 90

NetAtlas Enterprise 1.00 User’s Guide
Figure 67 Applied Results
3 Click Done to close the screen.
9.3.2 Copy to.. Button
The Copy to.. button allows you to copy the configuration from the switch you are currently
configuring to one or more switches.
1 In the Device Panel list, select a device that you want configure.
2 Select a tab in the Switch Configurator Panel.
3 Select a port or multiple ports (by pressing the [CTRL] key and clicking at the same time)
from the Port List Panel.
4 Make your configuration changes in the Switch Configurator Panel and click the Apply
button.
5 Click the Copy to.. button.
6 The following example screen displays.
89 Chapter 9 Device Menu Overview
Page 91

NetAtlas Enterprise 1.00 User’s Guide
Figure 68
Device List
Panel
Copy Port Screen
Port List
Panel
Copy Port
List Panel
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 26 Copy Port Screen
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Device List Select a device to which you want to copy from the switch you are currently
configuring.
Port List Panel Select one port or multiple ports (by pressing the [CTRL] key and clicking at
the same time) from the Port List Panel .
Add Click Add to display the port(s) to which you want to copy from the switch
Remove Click Remove to move a selected port(s) from the Copy Port List Panel list
Copy Port List Panel This panel displays the device port(s) to which you want to copy from the
OK Click OK to copy the configuration from ycurrent switch to the device port(s)
Cancel Click Cancel to return to the previous screen.
you are currently configuring.
to the Port List Panel.
switch you are currently configuring.
displayed in the Copy Port List Panel panel.
7 Click OK to display the following screen.
Chapter 9 Device Menu Overview 90
Page 92

NetAtlas Enterprise 1.00 User’s Guide
Figure 69 Copy Successful
8 Click Done to close the screen.
91 Chapter 9 Device Menu Overview
Page 93

This chapter shows you how to view general system information, configure SNMP, remote
management and time setup.
10.1 System Info
See Section 2.9 on page 48 for information about the switch.
10.2 SNMP
This explains explains SNMP configuration.
NetAtlas Enterprise 1.00 User’s Guide
CHAPTER 10
System Configuration
10.2.1 About SNMP
Simple Network Management Protocol is a protocol used for exchanging management
information between network switches. SNMP is a member of TCP/IP protocol suite. A
manager station can manage and monitor the switch through the network via SNMP version
2c. The next figure illustrates an SNMP management operation. SNMP is only available if
TCP/IP is configured.
Figure 70 SNMP Management Model
An SNMP managed network consists of two main components: agents and a manager.
Chapter 10 System Configuration 92
Page 94

NetAtlas Enterprise 1.00 User’s Guide
An agent is a management software module that resides in a managed switch (the ES-3124).
An agent translates the local management information from the managed switch into a form
compatible with SNMP. The manager is the console through which network administrators
perform network management functions. It executes applications that control and monitor
managed devices.
The managed devices contain object variables/managed objects that define each piece of
information to be collected about a switch. Examples of variables include such as number of
packets received, node port status etc. A Management Information Base (MIB) is a collection
of managed objects. SNMP allows a manager and agents to communicate for the purpose of
accessing these objects.
SNMP itself is a simple request/response protocol based on the manager/agent model. The
manager issues a request and the agent returns responses using the following protocol
operations:
Table 27 SNMP Commands
COMMAND DESCRIPTION
Get Allows the manager to retrieve an object variable from the agent.
GetNext Allows the manager to retrieve the next object variable from a table or list
Set Allows the manager to set values for object variables within an agent.
Trap Used by the agent to inform the manager of some events.
within an agent. In SNMP, when a manager wants to retrieve all elements of
a table from an agent, it initiates a Get operation, followed by a series of
GetNext operations.
See the switch User’s Guide for a list of supported Traps.
10.2.2 Configuring SNMP
Follow the steps below to configure SNMP.
1 In the Device Panel list, select a device and then right-click.
2 Click Configuration, System Configuration and then the SNMP Conf. tab.
93 Chapter 10 System Configuration
Page 95

NetAtlas Enterprise 1.00 User’s Guide
Figure 71 Configuration: System Configuration: SNMP Conf.
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 28 Configuration: System Configuration: SNMP Conf.
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Get Community Enter the get community, which is the password for the incoming Get- and
GetNext- requests from the management station.
Set Community Enter the set community, which is the password for incoming Set- requests
from the management station.
Trap Community Enter the trap community, which is the password sent with each trap to the
Apply Click Apply to save your changes back to the switch.
Trap Destination Enter the IP addresses of up to four stations to send your SNMP traps to.
Apply Click Apply to save the trap destination changes back to the switch.
SNMP manager.
10.3 Remote Management
Remote management allows you to determine which services/protocols can access which
device interface (if any) from which computers. You can customize the service port and the
secured client IP address to enhance security and flexibility.
10.3.1 Configuring Remote Management
Follow the steps below to configure remote management.
1 In the Device Panel list, select a device and then right-click.
2 Click Configuration, System Configuration and then the Remote Mgnt. tab.
Chapter 10 System Configuration 94
Page 96

NetAtlas Enterprise 1.00 User’s Guide
Figure 72 Configuration: System Configuration: Remote Management
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 29 Configuration: System Configuration: Remote Management
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Services This panel displays the services that you may use to remotely manage the
switch. Select the check box(es) to allow remote management using the
service(s).
Port Enter the number of the server port to use with the corresponding service.
Apply Click Apply to save the changes back to the switch.
Secured Clients Select the check box(es) to enable the client set.
Star t To allow a range of computers to use Telnet, FTP, HTTP, ICMP, SSH or
HTTPS services, enter the first IP address in the range here.The default
value for a start and end address is 0.0.0.0, which means you don’t care
which host is trying to use a service (Telnet, FTP, HTTP, SNMP, ICMP, SSH
or HTTPS).If you enter an IP address in this field, the switch will check if the
client IP address matches the value here when a (Telnet, FTP, HTTP,
SNMP, ICMP, SSH or HTTPS) session is up. If it does not match, the
session is disconnected immediately.
End To allow a range of computers to use Telnet, FTP, Web, SNMP or ICMP
services, enter the End IP address in the range here. To allow a single
computer to use Telnet, FTP, HTTP, SNMP, ICMP, SSH or HTTPS
services, enter the same IP address here as in the Start field.
95 Chapter 10 System Configuration
Page 97

NetAtlas Enterprise 1.00 User’s Guide
Table 29 Configuration: System Configuration: Remote Management (continued)
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Telnet, FTP, HTTP,
ICMP, SNMP, ICMP,
SSH, HTTPS
Apply Click Apply to save the changes back to the switch.
Select the checkbox to allow the trusted computer(s) in the IP address range
specified above to use this service to manage the switch.
10.4 Time Setup
The EMS keeps track of the time and date. There is also a software mechanism to set the time
manually or get the current time and date from an external server when you log in to the EMS.
Use the Time Setup screen to update the time and date settings of the EMS. The real time is
then displayed in the system messages.
10.4.1 Configuring Time Setup
Follow the steps below to configure your system time.
1 In the Device Panel list, select a device and then right-click.
2 Click Configuration, System Configuration and then the Time Setup tab.
Chapter 10 System Configuration 96
Page 98

NetAtlas Enterprise 1.00 User’s Guide
Figure 73 Configuration: System Configuration: Time Setup
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 30 Configuration: System Configuration: Time Setup
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Use Time Server When Select the time service protocol that your time server sends when you start
Time Server IP Address Enter the IP address or domain name of your time server. Check with your
Current Time This field displays an updated time only when you reenter this menu.
New Time (hh:mm:ss) Enter the new time in hour, minute and second format.
Current Date This field displays an updated date only when you re-enter this menu.
New Date (yyyy:mm:dd) Enter the new date in year, month and day format.
Time Zone Select the time difference between your time zone and Universal Time
Apply Click Apply to save the changes.
the EMS. Not all time servers support all protocols, so you may have to
check with your ISP/network administrator or use trial and error to find a
protocol that works. The main differences between them are the format.
Daytime (RFC 867) format is day/month/year/time zone of the server.
Time (RFC-868) format displays a 4-byte integer giving the total number of
seconds since 1970/1/1 at 0:0:0.
NTP (RFC-1305) is similar to Time (RFC-868).
None is the default; enter the time manually.
ISP/network administrator if you are unsure of this information.
Coordinate (UTC) formerly known as Greenwich Mean Time (GMT).
97 Chapter 10 System Configuration
Page 99

This chapter shows how to configure priority queuing, STP, link aggregation, DHCP relay,
GARP timer and RADIUS.
11.1 IGMP Snooping
IGMP (Internet Group Multicast Protocol) is a session-layer protocol used to establish
membership in a multicast group - it is not used to carry user data. Refer to RFC 1112 and
RFC 2236 for information on IGMP versions 1 and 2 respectively.
A layer-2 switch can passively snoop on IGMP Query, Report and Leave (IGMP version 2)
packets transferred between IP multicast routers/switches and IP multicast hosts to learn the IP
multicast group membership. It checks IGMP packets passing through it, picks out the group
registration information, and configures multicasting accordingly.
NetAtlas Enterprise 1.00 User’s Guide
CHAPTER 11
Switch Configuration
Without IGMP snooping, multicast traffic is treated in the same manner as broadcast traffic,
that is, it is forwarded to all ports. With IGMP snooping, group multicast traffic is only
forwarded to ports that are members of that group. IGMP Snooping generates no additional
network traffic, allowing you to significantly reduce multicast traffic passing through your
switch.
11.2 Switch Setup
Use the switch setup screen to set a VLAN type, a queuing method and enable or disable
features in the Active Control panel.
1 In the Device Panel list, select a device and then right-click.
2 Click Configuration, Switch Configuration and then the Switch Setup tab.
The VLAN setup screens change depending on whether you choose 802.1Q or Port Based in
the VLAN Type field in this screen. Refer to
Section 13.2 on page 126 for more information.
Chapter 11 Switch Configuration 98
Page 100

NetAtlas Enterprise 1.00 User’s Guide
Figure 74 Configuration: Switch Configuration: Switch Setup
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 31 Configuration: Switch Configuration: Switch Setup
LABEL DESCRIPTION
VLAN Type Choose 802.1Q or Port Based from the drop-down list box. The VLAN
Setup screen changes depending on whether you choose 802.1Q VLAN
Type or Port Based VLAN Type in this screen. See
126 and the VLAN chapter for more information on VLANs.
Queuing Method Select Strictly Priority or Weighted Fair Scheduling from the drop-down
list box.
Strictly Priority services queues based on priority only. When the highest
priority queue empties, traffic on the next highest-priority queue begins.
Q7 has the highest priority and Q0 the lowest.
Weighted Fair Scheduling is used to guarantee each queue’s minimum
bandwidth based on their bandwidth portion (weight). Queues with larger
weights get more guaranteed bandwidth than queues with smaller
weights.
MAC Address Learning MAC address learning reduces outgoing traffic broadcasts. For MAC
address learning to occur on a port, the port must be active.
Enter a time from 10 to 3000 seconds. This is how long all dynamically
learned MAC addresses remain in the MAC address table before they age
out (and must be relearned).
Active Control
STP Configuration Select the check box to activate STP.
Link Aggregation Select the check box to activate link aggregation.
Section 13.2 on page
99 Chapter 11 Switch Configuration
 Loading...
Loading...