Philips SAA1064, SAA1064T Datasheet

INTEGRATED CIRCUITS
DATA SHEET
SAA1064
4-digit LED-driver with I2C-Bus interface
Product specification |
|
February 1991 |
|||||
File under Integrated Circuits, IC01 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|

Philips Semiconductors |
|
|
|
|
Product specification |
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
4-digit LED-driver with I2C-Bus interface |
|
|
|
SAA1064 |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
GENERAL DESCRIPTION |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
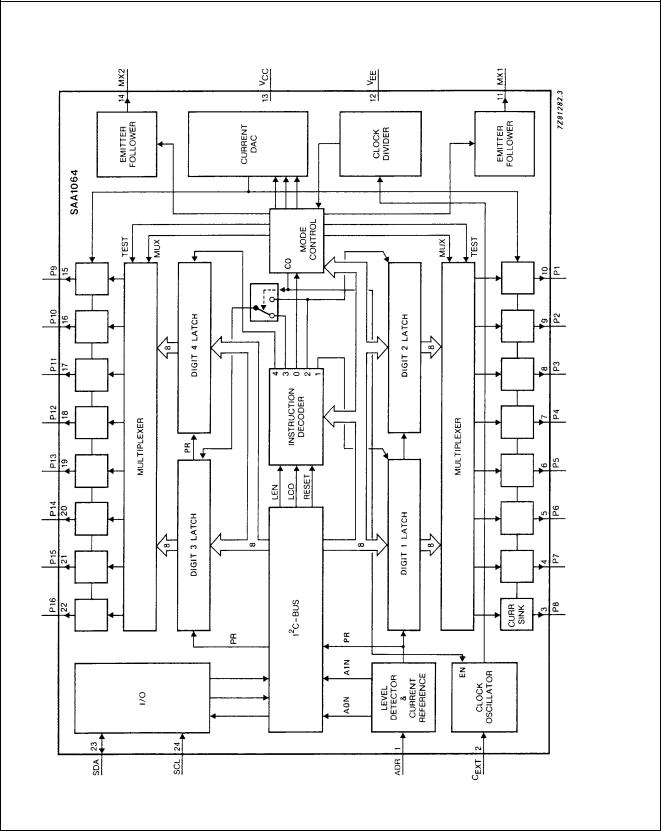
The LED-driver is a bipolar integrated circuit made in an |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
I2L compatible 18 volts process. The circuit is especially |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
designed to drive four 7-segment LED displays with |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
decimal point by means of multiplexing between two pairs |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
of digits. It features an I2C-Bus slave transceiver interface |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
with the possibility to program four different SLAVE |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ADDRESSES, a POWER RESET flag, 16 current sink |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
OUTPUTS, controllable by software up to 21 mA, two |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
multiplex drive outputs for common anode segments, an |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
on-chip multiplex oscillator, control bits to select static, |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
dynamic and blank mode, and one bit for segment test. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
QUICK REFERENCE DATA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
PARAMETER |
CONDITIONS |
SYMBOL |
MIN. |
TYP. |
|
MAX. |
UNIT |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Supply voltage |
VEE = 0 V |
VCC |
4.5 |
5 |
|
15 |
|
V |
Supply current all outputs OFF |
VCC = 5 V |
ICC(1) |
7 |
9.5 |
|
14 |
|
mA |
Total power dissipation |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
24-lead DIL (SOT101B) |
|
Ptot |
− |
− |
|
1000 |
|
mW |
24-lead DIL SO (SOT137A) |
|
Ptot |
− |
− |
|
500 |
|
mW |
Operating ambient |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
temperature range |
|
Tamb |
−40 |
− |
|
+85 |
|
°C |
Note
1. The positive current is defined as the conventional current flow into a device (sink current).
PACKAGE OUTLINE
SAA1064: 24-lead DIL; plastic with internal heat spreader (SOT101B); SOT101-1; 1996 August 30. SAA1064T: 24-lead mini-pack; plastic (SO-24; SOT137A); SOT137-1; 1996 August 30.
February 1991 |
2 |
Philips Semiconductors |
Product specification |
|
|
4-digit LED-driver with I2C-Bus interface |
SAA1064 |
|
|
Fig.1 Block diagram.
February 1991 |
3 |

Philips Semiconductors |
Product specification |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
4-digit LED-driver with I2C-Bus interface |
SAA1064 |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
PINNING |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
SYMBOL |
PIN |
DESCRIPTION |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ADR |
1 |
I2C-Bus slave address input |
|
|
|
CEXT |
2 |
external control |
|
|
|
P8 to P1 |
3-10 |
segment output |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
MX1 |
11 |
multiplex output |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
VEE |
12 |
ground |
|
|
|
VCC |
13 |
positive supply |
|
|
|
MX2 |
14 |
multiplex output |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
P9 to P16 |
15-22 |
segment output |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
SDA |
23 |
I2C-Bus serial data line |
|
|
|
SCL |
24 |
I2C-Bus serial clock line |
|
|
|
Fig.2 Pinning diagram.
February 1991 |
4 |
Philips Semiconductors |
Product specification |
|
|
4-digit LED-driver with I2C-Bus interface |
SAA1064 |
|
|
FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION |
|
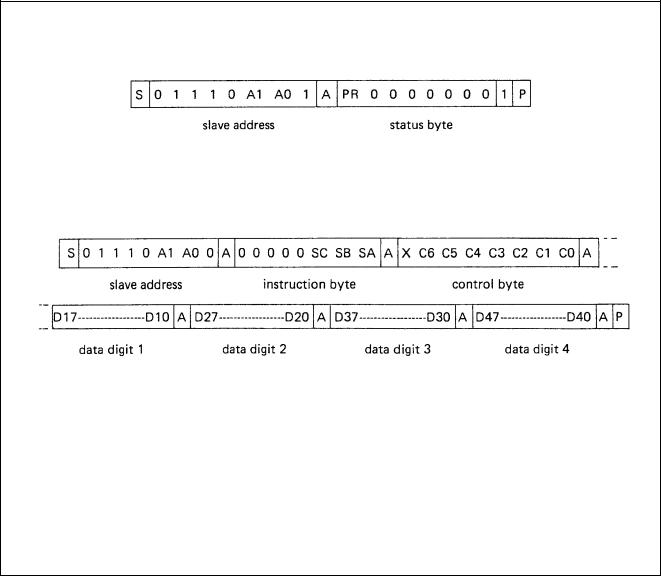
a. READ mode.
b. WRITE mode. |
|
|
S = start condition |
A1, A0 |
= programmable address bits |
P = stop condition |
SC SB SA |
= subaddress bits |
A = acknowledge |
C6 to C0 |
= control bits |
X = don’t care |
PR |
= POWER RESET flag |
Fig.3 |
I2C-Bus format. |
|
Address pin ADR
Four different slave addresses can be chosen by connecting ADR either to VEE, 3/8 VCC, 5/8 VCC or VCC. This results in the corresponding valid addresses HEX 70, 72, 74 and 76 for writing and 71, 73, 75 and 77 for reading. All other addresses cannot be acknowledged by the circuit.
February 1991 |
5 |

Philips Semiconductors |
Product specification |
|
|
4-digit LED-driver with I2C-Bus interface |
SAA1064 |
|
|
Status byte
Only one bit is present in the status byte, the POWER RESET flag. A logic 1 indicates the occurence of a power failure since the last time it was read out. After completion of the READ action this flag will be set to logic 0.
Subaddressing
The bits SC, SB and SA form a pointer and determine to which register the data byte following the instruction byte will be written. All other bytes will then be stored in the registers with consecutive subaddresses. This feature is called Auto-Increment (AI) of the subaddress and enables a quick initialization by the master.
The subaddress pointer will wrap around from 7 to 0. The subaddresses are given as follows:
SC |
SB |
SA |
SUB-ADDRESS |
FUNCTION |
|
|
|
|
|
0 |
0 |
0 |
00 |
control register |
0 |
0 |
1 |
01 |
digit 1 |
0 |
1 |
0 |
02 |
digit 2 |
0 |
1 |
1 |
03 |
digit 3 |
1 |
0 |
0 |
04 |
digit 4 |
1 |
0 |
1 |
05 |
reserved, not used |
1 |
1 |
0 |
06 |
reserved, not used |
1 |
1 |
1 |
07 |
reserved, not used |
|
|
|
|
|
Control bits (see Fig.4)
The control bits C0 to C6 have the following meaning:
C0 = 0 static mode, i.e. continuous display of digits 1 and 2
C0 = 1 dynamic mode, i.e. alternating display of digit 1 + 3 and 2 + 4
C1 = 0/1 digits 1 + 3 are blanked/not blanked
C2 = 0/1 digits 2 + 4 are blanked/not blanked
C3 = 1 all segment outputs are switched-on for segment test(1)
C4 = 1 adds 3 mA to segment output current
C5 = 1 adds 6 mA to segment output current
C6 = 1 adds 12 mA to segment output current
Note
1. At a current determined by C4, C5 and C6.
Data
A segment is switched ON if the corresponding data bit is logic 1. Data bits D17 to D10 correspond with digit 1, D27 to D20 with digit 2, D37 to D30 with digit 3 and D47 to D40 with digit 4.
The MSBs correspond with the outputs P8 and P16, the LSBs with P1 and P9. Digit numbers 1 to 4 are equal to their subaddresses (hex) 1 to 4.
February 1991 |
6 |
 Loading...
Loading...