HP LaserJet 1022nw User Manual

HP LaserJet 1022nw
Wireless Printer User Guide

HP LaserJet 1022nw Wireless Printer
User Guide
Copyright information
© 2005 Copyright Hewlett-Packard
Development Company, L.P.
Reproduction, adaptation or translation without prior written permission is prohibited, except as allowed under the copyright laws.
The information contained in this document is subject to change without notice.
The only warranties for HP products and services are set forth in the express warranty statements accompanying such products and services. Nothing herein should be construed as constituting an additional warranty. HP shall not be liable for technical or editorial errors or omissions contained herein.
Part number: Q5914-90904
Edition 1, 02/2005
Trademark credits
Microsoft® and Windows® are U.S. registered trademarks of Microsoft Corporation.
Energy Star® and the Energy Star logo® are U.S. registered marks of the United States Environmental Protection Agency.
Table of contents
1 Networking basics |
|
Manual contents and sources for support and information ...................................................... |
2 |
WWW links for drivers, software, and support ................................................................... |
2 |
Where to look for more information ................................................................................... |
2 |
Wireless networking basics ...................................................................................................... |
3 |
Channels and communication modes ............................................................................... |
3 |
Security .............................................................................................................................. |
4 |
Wireless profiles ................................................................................................................ |
6 |
2 Support information for installing to a wireless network |
|
Chapter overview ..................................................................................................................... |
8 |
Printer Wireless light ................................................................................................................ |
9 |
Configuration page ................................................................................................................. |
10 |
Printing a configuration page ........................................................................................... |
10 |
General and wireless network settings ............................................................................ |
10 |
Embedded Web server .......................................................................................................... |
13 |
To open the embedded Web server ................................................................................ |
13 |
Information tab ................................................................................................................. |
14 |
Settings tab ...................................................................................................................... |
14 |
Networking tab ................................................................................................................. |
14 |
Other links ....................................................................................................................... |
14 |
Switching from wired to wireless ............................................................................................ |
15 |
Resetting the printer to the factory default settings ................................................................ |
16 |
Resetting the factory defaults .......................................................................................... |
16 |
3 Problem solving |
|
Solving problems that occur during installation ...................................................................... |
18 |
Computer is unable to discover a device ......................................................................... |
18 |
Personal software firewall is blocking communication ..................................................... |
18 |
Device is unable to connect to the network after removing cable (infrastructure |
|
only) .............................................................................................................................. |
18 |
System Requirements Error: No TCP/IP error displays .................................................. |
18 |
Printer not found screen appears during installation ..................................................... |
19 |
Unable to determine or verify network name during installation ...................................... |
19 |
Verification fails at end of installation .............................................................................. |
20 |
Setup failed ...................................................................................................................... |
21 |
Installation software does not install correctly ................................................................. |
23 |
Solving infrastructure mode problems ................................................................................... |
24 |
The printer cannot find the WLAN ................................................................................... |
24 |
Printer cannot find your computer ................................................................................... |
24 |
Computer is unable to discover device ............................................................................ |
24 |
ENWW |
Table of contents iii |
Solving ad-hoc mode problems ............................................................................................. |
25 |
Printer cannot find your computer ................................................................................... |
25 |
Solving general wireless networking problems ...................................................................... |
26 |
Check the Wireless light .................................................................................................. |
26 |
Printer has the wrong wireless network settings ............................................................. |
27 |
To change the printer’s network settings: ........................................................................ |
27 |
Computer's wireless card is set to the wrong wireless profile ......................................... |
28 |
Radio signal is weak ........................................................................................................ |
28 |
Wireless access point (WAP) filters MAC addresses ...................................................... |
28 |
Appendix A Regulatory information |
|
USA Federal Communications Commission (FCC) compliance ............................................ |
29 |
Declaration of Conformity ...................................................................................................... |
30 |
Regulatory statements ........................................................................................................... |
31 |
Laser safety statement .................................................................................................... |
31 |
Canadian regulations ....................................................................................................... |
31 |
European Union regulatory notice ................................................................................... |
31 |
Laser statement for Finland ............................................................................................. |
32 |
Environmental product stewardship program ........................................................................ |
34 |
Protecting the environment .............................................................................................. |
34 |
Ozone production ............................................................................................................ |
34 |
Power consumption ......................................................................................................... |
34 |
Toner consumption .......................................................................................................... |
34 |
Paper use ........................................................................................................................ |
34 |
Plastics ............................................................................................................................ |
34 |
HP LaserJet printing supplies .......................................................................................... |
35 |
HP printing supplies returns and recycling program information ..................................... |
35 |
Paper ............................................................................................................................... |
36 |
Material restrictions ......................................................................................................... |
36 |
For more information ....................................................................................................... |
36 |
Material safety data sheet ...................................................................................................... |
37 |
OpenSSL License .................................................................................................................. |
38 |
Original SSLeay License ........................................................................................................ |
39 |
Glossary |
|
Index |
|
iv |
ENWW |

Networking basics
This chapter provides information on the following topics:
●Manual contents and sources for support and information
●Wireless networking basics
ENWW |
1 |

Manual contents and sources for support and information
NOTE |
Only the HP LaserJet 1022nw printer contains wireless capability. |
This manual is a supplementary document to the HP LaserJet 1022 Series Printer User Guide and to the HP LaserJet 1022nw Wireless Getting Started Guide. Both of these documents are included with the printer. This manual provides the following information about installing and connecting the printer to a wireless network:
●The Networking basics chapter contains overview information about wireless networking and the wireless features of the HP LaserJet 1022nw printer.
●The Support information for installing to a wireless network chapter contains support information that will be useful if you are installing the printer to a wireless network, or if you wish to change printer or network settings after you have installed the printer. You can find procedures for installing to a wireless network in the HP LaserJet 1022nw Printer Wireless Start Guide packaged with the printer.
●The Problem solving chapter contains troubleshooting information.
In addition, this manual contains an appendix of regulatory information, a glossary of wireless terms, and an index.
WWW links for drivers, software, and support
If you need to contact HP for service or support, use the following link: http://www.hp.com/ support/lj1022/.
Where to look for more information
●CD user guide: Detailed information on using and troubleshooting the printer. Available on the CD-ROM that came with the printer.
●Online Help: Information on printer options that are available from within printer drivers. To view a Help file, access the online Help through the printer driver.
HTML (online) user guide: Detailed information on using and troubleshooting the printer. Available at http://www.hp.com/support/lj1022. Once connected, select Manuals.
2 Chapter 1 Networking basics |
ENWW |
Wireless networking basics
|
The HP LaserJet 1022nw printer has an internal HP wireless print server that supports both |
|
wired and wireless connectivity. However, the printer does not support simultaneous wired |
|
and wireless connections. To connect to a wireless network, the printer uses wireless |
|
protocol IEEE 802.11b/g that communicates data through radio transmission. After installing |
|
the printer to a wireless network, cables are not required to communicate with the computers |
|
or devices that are part of the network. |
|
The printer is compatible with 802.11b/g-compliant devices. |
NOTE |
|
|
A wireless local area network (WLAN) is a collection of two or more computers, printers, and |
|
other devices linked by radio waves. A WLAN uses high-frequency airwaves (radio) to |
|
communicate information from one point to another. |
|
To connect a computer or device to a wireless network, the computer or device must have a |
|
wireless network adapter. The HP LaserJet 1022nw printer uses an internal networking |
|
component that contains a wireless network adapter and radio. No cabling is necessary |
|
between networked devices that use wireless technology, although it is possible to use a |
|
cable to configure your printer for a wireless network. This is the recommended installation |
|
method. |
|
Common wireless network adapters include the following: |
|
● USB adapter: An external device that connects to a USB port on the computer (typically |
|
has a PCMCIA card attached to one end). |
|
● Notebook adapter: A PCMCIA card that plugs directly into one of the PCMCIA slots on |
|
your laptop or other portable computer. |
|
● Desktop computer adapter: A dedicated ISA or PCI card, or a PCMCIA card with a |
|
special adapter, that plugs into your desktop computer. |
|
● AirPort adapter: A wireless card that plugs directly into the AirPort slot on your |
|
Macintosh laptop or desktop computer. AirPort adapters eliminate the need for cable |
|
connections to the computer. |
|
The following sections contain overview information about wireless channels and |
|
communication modes, networking profiles, and network security. |
Channels and communication modes
The band of radio signals used for IEEE 802.11b/g wireless networking is segmented into specific frequencies, or channels. For IEEE 802.11b/g wireless networks, 14 channels are available. But each country/region specifies the channels that are authorized for use. For example, in North America, only channels 1 through 11 are allowed. In Japan, channels 1 through 14 can be used. In Europe, except for France, channels 1 through 13 are allowed. Because existing standards change frequently, you should check with your local regulatory agencies for authorized channel use. In most countries/regions channels 10 and 11 may be used without restriction.
Channel selection depends on the communication mode of the network. The communication mode defines how devices, such as computers and printers, communicate on a wireless network. There are two primary types of wireless communication modes: infrastructure and ad-hoc.
ENWW |
Wireless networking basics 3 |
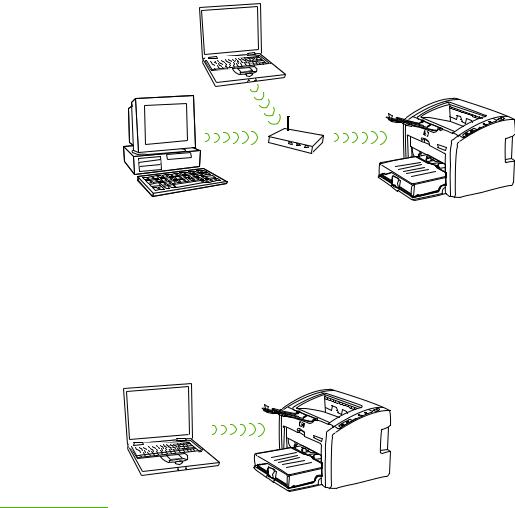
Infrastructure mode (preferred)
In infrastructure mode, the printer communicates with network computers through a wireless access point (WAP) or a base station. The access point acts as a central hub or gateway connecting wireless and, optionally, wired devices. (Most access points have an integrated Ethernet controller to connect to an existing wired-Ethernet network.) If your printer connects through a wireless residential gateway that provides access point functions, choose infrastructure mode.
Ad-hoc mode
In ad-hoc mode, which is sometimes called peer-to-peer mode, the printer communicates with your computer directly, rather than through an access point or base station. Each device on an ad-hoc network must have a wireless network adapter. The adapter enables each device to communicate with the other devices on the network. Ad-hoc mode is usually limited to simple, small wireless networks because performance degrades significantly after connecting too many network devices. This option is most often used if you are connecting only two network devices that are not sharing an Internet connection.
NOTE |
For maximum performance, HP recommends connecting the printer to a network that |
|
communicates using the infrastructure mode. |
Security
As with other networks, security for wireless networks focuses on access control and privacy. Traditional wireless network security includes the use of Service Set Identifiers (SSIDs), open or shared-key authentication, static Wired Equivalent Privacy (WEP) keys, and optional Media Access Control (MAC) authentication. This combination offers a basic level of access control and privacy.
4 Chapter 1 Networking basics |
ENWW |

NOTE
NOTE
More advanced levels of security (such as Wi-Fi protected access [WPA] and Pre-shared key) are available through the printer’s embedded Web server. For introductory information about the embedded Web server, see Embedded Web server. For detailed information about using the features, see the embedded Web server online help.
It is highly recommended that you implement a wireless security scheme (either WEP or WPA) prior to setup. In addition, use an antivirus program to protect against computer viruses, and follow basic security rules such as setting strong passwords and not opening unknown attachments. Other network components, including firewalls, intrusion-detection systems, and segmented networks, should also be considered as part of your network design.
Authentication and encryption are two different approaches to network security. Authentication verifies the identity of a user or device before granting access to the network, making it more difficult for unauthorized users to access network resources. Encryption encodes the data being sent across the network, making the data unintelligible to unauthorized users. Both of these security methods are common on wireless networks.
Authentication
The HP installation software supports Open System authentication. More advanced forms of authentication are available through the embedded Web server.
A network with Open System authentication does not screen network users based on their identities and usually involves supplying the correct SSID. Such a network might use Wired Equivalent Privacy (WEP) encryption to provide a first level of security, or Wi-Fi protected access (WPA) to provide security by encrypting data sent over radio waves from one wireless device to another wireless device. The HP LaserJet 1022nw wireless printer allows for either WEP or WPA.
Shared key and server-based authentication protocols are implemented through the embedded Web server. For introductory information about the embedded Web server, see Embedded Web server. For detailed information about using the features, see the embedded Web server online help.
Network name (SSID)
Wireless devices are configured with the name of the network to which they will connect. The network name is also called the SSID and identifies the ESS (Extended Service Set) that is normally associated with larger infrastructure networks.
The SSID should not be considered a security feature because it can be easily identified. However, as a network administration or management feature, it does provide basic network access control.
Encryption
To reduce your network exposure to eavesdropping, establish a wireless security key for your network. The printer installation software supports the WEP security scheme, which hinders unauthorized users from accessing data transmitted over the radio waves. It is based on the use of a single WEP key, in which case each computer or device is configured with the same key to communicate on that network.
ENWW |
Wireless networking basics 5 |

NOTE
NOTE
Up to four WEP keys might be used on a wireless network for transmission of data. For example, if you have three computers and an access point, each might be assigned a distinct key for transmitting data. However, the remaining keys must also be entered on each device so they can communicate with each other. The installation software for the
HP LaserJet 1022nw printer provides the option to type one WEP key. If you want to use more than one WEP key, those keys must be entered into the printer’s embedded Web server prior to installing the software. For introductory information about the embedded Web server, see Embedded Web server. For detailed information about using the features, see the embedded Web server online help.
Media access control address authentication
Some WLAN vendors support authentication based on the physical address, or MAC address, of the client Network Interface Card (NIC). In this scenario, an access point allows association by a client only if that client’s MAC address matches an address in an authentication table used by the access point. This is not configurable through the printer.
Wireless profiles
A wireless profile is a set of network settings unique to a given wireless network. Many wireless devices have configuration utilities that allow the device to have wireless profiles for several wireless networks. In order to use the printer, the printer's wireless settings must match the computer's network settings for that wireless network.
For example, a person uses the same wireless-enabled laptop at work and at home. Each network has a unique set of wireless settings. The person creates the following wireless profiles on the laptop:
●at_work: Contains the network settings for the office wireless network
●at_home: Contains the network settings for the home wireless network
When the laptop is being used at work, the person must set the wireless profile to at_work in order to connect to the office network. Conversely, the laptop must be set to the at_home wireless profile when the person is at home and wants to connect the laptop to the home network.
The HP LaserJet 1022nw printer cannot be connected to a wired and wireless network at the same time.
6 Chapter 1 Networking basics |
ENWW |

Support information for installing to a wireless network
This chapter provides information on the following topics:
●Chapter overview
●Printer Wireless light
●Configuration page
●Embedded Web server
●Switching from wired to wireless
●Resetting the printer to the factory default settings
ENWW |
7 |

Chapter overview
NOTE
NOTE
This chapter contains information that will be useful if you are installing the printer to a wireless network, or if you are changing printer or network settings after you have installed the printer. Specifically, this chapter contains a description of the printer Wireless light and the configuration page, and an overview of the embedded Web server (EWS). In addition, this chapter contains procedures for resetting the printer network setting and for switching between wireless and wired communications.
The procedure you follow for installing the printer to a wireless network depends on whether the network communicates through an infrastructure mode or through an ad-hoc mode. You can find procedures for installing the printer to a wireless network in the HP LaserJet 1022nw printer Wireless Getting Started Guide that was packaged with the printer. For more information about infrastructure and ad-hoc networks, see Wireless networking basics.
For maximum efficiency, HP recommends the printer be connected to a network that uses the infrastructure communication mode.
The printer cannot be connected to a wired and wireless network at the same time.
8 |
Chapter 2 Support information for installing to a wireless network |
ENWW |

Printer Wireless light
The HP LaserJet 1022nw printer has an internal networking component that provides wireless connectivity. To view the status of the wireless communications, the printer contains a Wireless light.
●If the light is on, the printer is connected to a wireless network.
●If the light flashes, the printer is scanning for a wireless network.
●If the light is off, wireless networking is disabled.
ENWW |
Printer Wireless light 9 |
Configuration page
|
The printer includes an internal component that provides networking capability for both wired |
||
|
and wireless connectivity. This section contains a procedure for printing a configuration |
||
|
page, as well as a description of the general network and wireless network fields that display |
||
|
on the page. |
|
|
|
Printing a configuration page |
||
|
When the printer is in the Ready state, press and hold the GO button until the Ready light |
||
|
starts blinking. |
|
|
|
General and wireless network settings |
||
|
All of the settings on the configuration page should match the settings of the network with |
||
NOTE |
|||
|
which you are trying to connect. If any values are different, you might not be able to connect |
||
|
to the network. |
|
|
|
The following sections describe the various fields on the configuration page. |
||
|
General network settings |
||
|
Field |
Description |
|
|
Hardware Address |
The Media Access Control (MAC) address that uniquely identifies |
|
|
|
the printer. This is a unique 12-digit identification number assigned |
|
|
|
to networking hardware for identification, like a digital fingerprint. No |
|
|
|
two pieces of hardware have the same MAC address. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
NOTE |
|
|
|
Some ISPs require that you register the MAC address of the |
|
|
|
Network Card or LAN Adapter that was connected to your cable or |
|
|
|
DSL modem during installation. |
|
|
Firmware Version |
The internal networking component and device firmware revision |
|
|
|
code separated by a hyphen. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
NOTE |
|
|
|
You might be asked to provide the firmware revision code if you call |
|
|
|
for support. |
|
|
Host Name |
The TCP/IP name assigned by the install software to the device. By |
|
|
|
default, these are the letters NPI followed by the last six digits of the |
|
MAC address. You can also configure the device name through the embedded Web server.
10 |
Chapter 2 Support information for installing to a wireless network |
ENWW |

Field |
Description |
IP Address |
The printer's Internet Protocol (IP) address. This address uniquely |
|
identifies the device on the network. |
|
IP addresses are assigned dynamically through DHCP or AutoIP. |
|
You can also set up a static IP address, though this is not |
|
recommended. |
|
Manually assigning an invalid IP address during install will cause |
|
your network components to not see the device. |
Config by |
The protocol used to assign the IP address to the device: |
|
● AutoIP: the installation software determines the configuration |
|
parameters. |
|
● DHCP: the configuration parameters are supplied by a dynamic |
|
host configuration protocol (DHCP) server on the network. On |
|
small networks, this could be a router. |
|
● Manual: the configuration parameters are set manually, such |
|
as a static IP address. |
|
● BOOTP: Bootstrap Protocol (BOOTP) is an Internet protocol |
|
that enables a device to discover its own IP address, the IP |
|
address of a BOOTP server on the network, and a file to be |
|
loaded into memory to boot the machine. This enables the |
|
device to boot without requiring a hard or floppy disk drive. |
mDNS Name |
Multicast Domain Name Server Service Name. The name used by |
|
Apple Rendezvous to identify the printer, which consists of the |
|
device name and the MAC address. |
|
Apple Rendezvous is used with local and ad-hoc networks that do |
|
not use central DNS servers. To perform name services, |
|
Rendezvous uses a DNS alternative called mDNS. |
|
With mDNS, your computer can find and use any printer connected |
|
to your local area network. It can also work with any other Ethernet- |
|
enabled device that appears on the network. |
Link Status |
The protocol for transmitting data over a network: |
|
● 802.11b and 802.11g: for wireless network |
|
● 10T-Full: for wired network |
|
● 10T-Half: for wired network |
|
● 100TX-Full: for wired network |
|
● 100TX-Half: for wired network |
ENWW |
Configuration page 11 |

Wireless network settings
Field |
Description |
Wireless Status |
Status of the wireless network: |
|
● Disabled: the wireless 802.11b/g network is disabled when the |
|
wired 802.3 network is active. This is the default setting. |
|
● Enabled |
Communication |
An IEEE 802.11 networking framework in which devices or stations |
Mode |
communicate with each other: |
|
● Infrastructure: the printer communicates with other network |
|
devices through a wireless access point, such as a wireless |
|
router or base station. |
|
● Ad-hoc: the printer communicates directly with each device on |
|
the network. No wireless access point is used. This is also |
|
called a peer-to-peer network. On Macintosh networks, ad-hoc |
|
mode is called computer-to-computer mode. |
Network Name |
Service Set Identifier. A unique identifier (up to 32 characters) that |
(SSID) |
differentiates one wireless local area network (WLAN) from another. |
|
The SSID is also referred to as the Network Name—the name of |
|
the network to which the printer is connected. |
Data transmission and receipt information
Field |
Description |
Total Packets |
The number of packets received by the printer without error since it |
Received |
has been turned on. The counter clears after the printer is turned off. |
Bad Packets |
The number of packets received with errors since the printer has |
Received |
been turned on. The counter clears after the printer is turned off. |
Total Packets |
The number of packets transmitted by the printer without error since |
Transmitted |
it has been turned on. The counter clears after the printer is turned |
|
off. |
|
When a message is transmitted over a packet-switching network, it |
|
is broken up into packets. Each packet contains the destination |
|
address as well as the data. |
12 |
Chapter 2 Support information for installing to a wireless network |
ENWW |
 Loading...
Loading...