Eaton Transmission RTLC-16609E Service Manual

Service Manual
Fuller Heavy Duty Transmissions
TRSM0446
January 2010

For parts or service call us
Pro Gear & Transmission, Inc.
1 (877) 776-4600
(407) 872-1901
parts@eprogear.com
906 W. Gore St.
Orlando, FL 32805
Warnings and Precautions
!
Warnings and Precautions
WARNING
Before starting a vehicle always be seated in the driver’s seat, place the transmission in neutral, set the parking brakes and
disengage the clutch.
Before working on a vehicle place the transmission in neutral, set the parking brakes and block the wheels.
Before towing the vehicle place the transmission in neutral, and lift the rear wheels off the ground, remove the axle shafts,
or disconnect the driveline to avoid damage to the transmission during towing.
The description and specifications contained in this service publication are current at the time of printing.
Eaton Corporation reserves the right to discontinue or modify its models and/or procedures and to change specifications at any
time without notice.
Any reference to brand name in this publication is made as an example of the types of tools and materials recommended for use
and should not be considered an endorsement. Equivalents may be used.
This symbol is used throughout this manual to call attention to procedures where carelessness or failure to follow
specific instructions may result in personal injury and/or component damage.
Departure from the instructions, choice of tools, materials and recommended parts mentioned in this publication may jeopardize
the personal safety of the service technican or vehicle operator.
Warning: Failure to follow indicated procedures creates a high risk of personal injury to the service technician.
Caution: Failure to follow indicated procedures may cause component damage or malfunction.
Note: Additional service information not covered in the service procedures.
Tip: Helpful removal and installation procedures to aid in the service of this unit.
Always use genuine Eaton replacement parts.

Warnings and Precautions
Service Procedure

Table of Contents
General Information
In-Vehicle Service Procedures
Transmission Overhaul
Procedures-Bench Service
Warnings and Precautions .......................................... 0
Transmission Overview ............................................... 0
Purpose and Scope of Manual .................................... 1
Serial Tag Information and Model Nomenclature ........ 5
Lubrication Specifications ........................................... 7
Tool Specifications ...................................................... 9
Transmission Torque Specifications ......................... 13
Preventative Maintenance Check Points .................... 15
Power Flow Diagrams ...............................................18
9 & 13 Speed Shift Patterns ...................................... 32
Air System Overview ................................................. 34
General Troubleshooting Chart ................................. 48
Air System Troubleshooting ...................................... 51
Timing Procedures .................................................... 66
How to Remove Oil Filter Adapter ............................. 68
How to Assemble Oil Filter Adapter ........................... 69
How to Disassemble Roadranger Valve A-5010 ........ 70
How to Assemble Roadranger Valve A-5010 ............. 72
How to Disassemble Roadranger Valve A-4900 ........ 74
How to Assemble Roadranger Valve A-4900 ............. 76
How to Install the Air Lines and Hoses ...................... 78
How to Remove Compression Type Fittings .............. 80
How to Remove the Air Lines and Hoses .................. 81
How to Install Compression Type Fittings ................. 83
How to Remove Push-To-Connect Type Fittings ....... 84
How to Install Push-To-Connect Type Fittings .......... 85
..................... How to Remove Rubber 1/4" Air Hoses 86
How to Remove the Air Filter/Regulator .................... 87
How to Install the Air Filter/Regulator ....................... 88
......................... How to Remove a Roadranger Valve 89
.............................How to Install a Roadranger Valve 90
.........................How to Install Rubber 1/4" Air Hoses 91
................................... How to Remove a Slave Valve 92
.......................................How to Install a Slave Valve 93
How to Remove the Gear Shift Lever/Remote Shift Control
94
How to Install the Gear Shift Lever/Remote Shift Control
95
. How to Adjust the Remote Shift Control (LRC Type) 96
........................Neutral Switch Operation and Testing 98
........................... How to Remove the Neutral Switch 99
............................How to Install the Neutral Switch 100
....................Reverse Switch Operation and Testing 101
....................... How to Remove the Reverse Switch 102
...........................How to Install the Reverse Switch 103
How to Remove the Shift Bar Housing ....................104
How to Install the Shift Bar Housing ........................105
How to Remove the Oil Seal - Mechanical Speedometer
107
How to Install the Oil Seal - Mechanical Speedometer ...
109
How to Remove the Oil Seal - Magnetic Speedometer ...
110
How to Install the Oil Seal - Magnetic Speedometer 113
How to Remove the Output Yoke/Companion Flange and
Nut ...................................................................115
How to Install the Output Yoke/Companion Flange and Nut
117
How to Remove the Auxiliary Section in Chassis .....119
How to Install the Auxiliary Section in Chassis ........121
How to Disassemble the Range Cylinder Assembly .124
How to Assemble the Range Cylinder Assembly ......126
How to Disassemble the Gear Shift Lever ................129
How to Assemble the Gear Shift Lever ....................131
....................How to Remove the Shift Bar Housing 133
....................... How to Install the Shift Bar Housing 135
How to Disassemble the Shift Bar Housing Assembly ...
137
How to Reassemble the Shift Bar Housing Assembly 140
How to Remove the Input Shaft Assembly (without main
case disassembly) ............................................144
How to Install the Input Shaft Assembly (without main
case disassembly) ............................................146
How to Remove the Auxiliary Section with Tapered Bear-
ings ..................................................................148
How to Remove the Auxiliary Countershaft Assemblies
(w/Tapered Bearings) .......................................150
How to Remove the Countershaft Assemblies (w/Ball
Bearings) A Series ............................................153
How to Remove the Splitter Cylinder Assembly .......155
How to Remove the Splitter Gear .............................157
How to Disassemble the Range Cylinder Assembly .158
.... How to Disassemble the Output Shaft Assembly 160
....How to Disassemble the Synchronizer Assembly 163
........ How to Assemble the Synchronizer Assembly 164
How to Assemble the Output Shaft Assembly ..........166
How to Install the Splitter Gear ................................169
How to Assemble the Range Cylinder Assembly ......170
How to Install Splitter Cylinder Assembly ................173
How to Install the Countershaft Assemblies (w/Tapered
Bearings) ..........................................................175
How to Install the Countershaft Assemblies (w/Ball Bear-
ings) A Series ...................................................178
How to Remove the Clutch Housing ........................181
How to Remove the Auxiliary Drive Gear Assembly .183

How to Disassemble the Upper Reverse Idler Gear Assem-
bly .................................................................... 185
How to Remove the Upper and Lower Countershaft Bear-
ings .................................................................. 187
How to Remove the Mainshaft Assembly ................ 189
.........How to Remove the Countershaft Assemblies 190
How to Disassemble the Countershaft Assemblies . 192
How to Remove the Input Shaft and Main Drive Gear 194
How to Prepare the Main Case for Assembly .......... 197
......... How to Disassemble the Mainshaft Assembly 198
How to Assemble the Mainshaft Assembly with Selective
(Adjustable) Thickness
Tolerance Washers .......................................... 200
How to Assemble the Mainshaft Assembly with Non-Se-
lective (Non-Adjustable) Tolerance Washers .... 206
How to Assemble the Countershaft Assemblies ...... 209
How to Assemble the Lower Reverse Idler Gear Assembly
211
.................. How to Install Countershaft Assemblies 214
How to Install the Lower Countershaft Bearings ..... 215
How to Install .the Input Shaft and Main Drive Gear 217
....................How to Install the Mainshaft Assembly 219
How to Install the ...... Upper Countershaft Bearings 221
How to Assemble the Upper Reverse Idler Gear Assembly
224
How to Install the Auxiliary Drive Gear Assembly .... 227
How to Install the Clutch Housing ...........................229
How to Disassemble the Integral Oil Pump without Auxil-
iary Oil Tube .....................................................230
How to Assemble the Integral Oil Pump without Auxiliary
Oil Tube ........................................................... 233
.....................How to Remove the Integral Oil Pump 236
How to Install the Integral Oil Pump ....................... 238
How to Disassemble the Integral Oil Pump with Auxiliary
Oil Tube ........................................................... 240
How to Assemble the Integral Oil Pump with Auxiliary Oil
Tube ................................................................. 244
How to Install the Auxiliary Section with Tapered Bearings
248
Shim Procedure without a Shim Tool for Tapered Bear-
ings .................................................................. 250
Table of Contents

Table of Contents

Transmission Overview
Shift Bar Housing:
Shift Bar Housing:
Levers/Housings
Levers/Housings
& Isolators
& Isolators
Introduction
Air System:
Roadranger® Valve
Auxiliary Section:
Range Cylinder
Shift Bar Housing:
Shift Bar Housing:
Shiftbar Housing Assembly
Shiftbar Housing Assembly
Front Section:
Clutch Housing / Case Assembly
Front Section:
Input Shaft / Drive Gear
106004-8-94 15 spd trans
Front Section:
Reverse Idler
Front Section:
Countershafts
Auxiliary Section:
Auxiliary Countershaft
Auxiliary Section:
Auxiliary Housing
Air System:
Slave Valve
Air System:
Air Filter/Regulator
Auxiliary Section:
Auxiliary Drive Gear
Front Section:
Mainshaft
Auxiliary Section:
Reduction Cylinder

Introduction

Introduction
Purpose and Scope of Manual
This manual is designed to provide information necessary to service and repair the Fuller® transmissions listed on the front.
How to use this Manual
The service procedures have been divided into two sections: In-Vehicle Service Procedures and Transmission Overhaul Procedures—Bench Service. In-Vehicle Service Procedures contain procedures that can be performed while the transmission is still
installed in the vehicle. Transmission Overhaul Procedures contain procedures that are performed after the transmission has been
removed from the vehicle.
The procedure sections are laid out with a general heading at the top outside edge of each page followed by more specific headings
and the procedures. To find the information you need in these sections, first go to the section that contains the procedure you
need. Then look at the heading at the top and outside edge of each page until you find the one that contains the procedure you need.
Transmission Overhaul Procedures follow the general steps for complete disassembly and then assembly of the transmission.
Note: In some instances the transmission appearance may be different from the illustrations, but the procedure is the same.
Disassemble Precautions
It is assumed in the detailed assembly instructions that the lubricant has been drained from the transmission, the necessary linkage and vehicle air lines disconnected and the transmission has been removed from vehicle chassis. Removal of the gear shift
lever housing assembly (or remote control assembly) is included in the detailed instructions (How to Remove the Gear Shift Lever). This assembly MUST be detached from the shift bar housing before the transmission can be removed.
General Information
Follow closely each procedure in the detailed instructions, make use of the text, illustrations, and photographs provided.
Assemblies
• When disassembling the various assemblies, such as the mainshaft, countershafts, and shift bar housing, lay all parts
on a clean bench in the same sequence as removed. This procedure will simplify assembly and reduce the possibility of
losing parts.
Bearings
• Carefully wash and lubricate all usable bearings as removed and protectively wrap until ready for use. Remove bearings
planned to be reused with pullers designed for this purpose.
Cleanliness
• Provide a clean place to work. It is important that no dirt or foreign material enters the unit during repairs. Dirt is an
abrasive and can damage bearings. It is always a good practice to clean the outside of the unit before starting the planned
disassembly.
Input Shaft
• The input shaft can be removed from the transmission without removing the countershafts, mainshaft, or main drive
gear. Special procedures are required and provided in this manual.
1

Introduction
Snap Rings
• Remove snap rings with pliers designed for this purpose. Snap rings removed in this manner can be reused, if they are
not sprung or loose.
When Using Tools to Move Parts
• Always apply force to shafts, housings, etc., with restraint. Movement of some parts is restricted. Never apply force to
driven parts after they stop solidly. The use of soft hammers, soft bars, and mauls for all disassembly work is recom-
mended.
Inspection Precautions
Before assembling the transmission, check each part carefully for abnormal or excessive wear and damage to determine reuse or
replacement. When replacement is necessary, use only genuine Fuller
extended life from your unit.
Since the cost of a new part is generally a small fraction of the total cost of downtime and labor, avoid reusing a questionable part
which could lead to additional repairs and expense soon after assembly. To aid in determining the reuse or replacement of any
transmission part, consideration should also be given to the unit's history, mileage, application, etc.
Recommended inspection procedures are provided in the following checklist.
Bearings
• Wash all bearings in clean solvent. Check balls, rollers, and raceways for pitting, discoloration, and spalled areas. Re-
place bearings that are pitted, discolored, spalled, or damaged during disassembly.
• Lubricate bearings that are not pitted, discolored, or spalled and check for axial and radial clearances.
• Replace bearings with excessive clearances.
• Check bearing fit. Bearing inner races should be tight to shaft; outer races slightly tight to slightly loose in case bore. If
the bearing spins freely in the bore the case should be replaced.
Bearing Covers
• Check covers for wear from thrust of adjacent bearing. Replace covers damaged from thrust of bearing outer race.
• Check cover bores for wear. Replace those worn or oversized.
Clutch Release Parts
®
Transmission parts to assure continued performance and
• Check clutch release parts. Replace yokes worn at cam surfaces and bearing carrier worn at contact pads.
• Check pedal shafts. Replace those worn at bushing surfaces.
Gears
• Check gear teeth for frosting and pitting. Frosting of gear teeth faces presents no threat of transmission failure. Often
in continued operation of the unit, frosted gears "heal" and do not progress to the pitting stage. In most cases, gears
with light to moderate pitted teeth have considerable gear life remaining and can be reused, but gears in the advanced
stage of pitting should be replaced.
• Check for gears with clutching teeth abnormally worn, tapered, or reduced in length from clashing during shifting. Re-
place gears found in any of these conditions.
• Check axial clearance of gears.
2

Introduction
Gear Shift Lever Housing Assembly
• Check spring tension on shift lever. Replace tension spring if lever moves too freely.
• If housing is disassembled, check gear shift lever bottom end and shift finger assembly for wear. Replace both gears if
excessively worn.
Gray Iron Parts
• Check all gray iron parts for cracks and breaks. Replace parts found to be damaged.
Oil Return Threads and Seals
• Check oil return threads on the input shaft. If return action of threads has been destroyed, replace the input shaft.
• Check oil seal in rear bearing cover. If sealing action of lip has been destroyed, replace seal.
O-Rings
• Check all o-rings for cracks or distortion. Replace if worn.
Reverse Idler Gear Assemblies
• Check for excessive wear from action of roller bearings.
Shift Bar Housing Assembly
• Check for wear on shift yokes and block at pads and lever slot. Replace excessively worn parts.
• Check yokes for correct alignment. Replace sprung yokes.
• Check lockscrew in yoke and blocks. Tighten and rewire those found loose.
General Information
• If housing has been disassembled, check neutral notches of shift bars for wear from interlock balls.
Sliding Clutches
• Check all shift yokes and yoke slots in sliding clutches for extreme wear or discoloration from heat.
• Check engaging teeth of sliding clutches for partial engagement pattern.
Splines
• Check splines on all shafts for abnormal wear. If sliding clutch gears, companion flange, or clutch hub has wear marks
in the spline sides, replace the specific shaft effected.
Synchronizer Assembly
• Check synchronizer for burrs, uneven and excessive wear at contact surface, and metal particles.
• Check blocker pins for excessive wear or looseness.
• Check synchronizer contact surfaces on the synchronizer cups for wear.
Washers
• Check surfaces of all washers. Washers scored or reduced in thickness should be replaced.
3

Introduction
Assembly Precautions
Make sure that case interiors and housings are clean. It is important that dirt and other foreign materials are kept out of the transmission during assembly. Dirt is an abrasive and can damage polished surfaces of bearings and washers. Use certain precautions, as listed below, during assembly.
Axial Clearances
• Maintain original axial clearances of 0.006-0.015 in. for mainshaft gears.
Bearings
• Use a flange-end bearing driver for bearing installation. These special drivers apply equal force to both bearing races,
preventing damage to balls/rollers and races while maintaining correct bearing alignment with bore and shaft. Avoid us-
ing a tubular or sleeve-type driver, whenever possible, as force is applied to only one of the bearing races.
Capscrews
• To prevent oil leakage and loosening, use Fuller
Gaskets
• Use new gaskets throughout the transmission as it is being rebuilt. Make sure all gaskets are installed. An omission of
any gasket can result in oil leakage or misalignment of bearing covers.
®
sealant #71205 on all capscrews.
Initial Lubrication
• Coat all limit washers and shaft splines with Lubricant during assembly to prevent scoring and galling of such parts.
O-Rings
• Lubricate all o-rings with silicon lubricant.
Universal Joint Companion Flange or Yoke
• Pull the companion flange or yoke tightly into place with the output shaft nut, using 450-500 lb-ft (610.12-677.91 N•m)
of torque. Make sure the speedometer drive gear or a replacement spacer of the same width has been installed. Failure
to pull the companion flange or yoke tightly into place can result in damage to the mainshaft rear bearing.
IMPORTANT
See the appropriate Illustrated Parts Lists (specified by model series) to ensure that proper parts are used during assembly of the
transmission.
4

Model Designations and Specifications
Serial Tag Information and Model Nomenclature
Transmission model designation and other transmission identification information are stamped on the transmission tag. To identify the transmission model designation and serial number, locate the tag on the transmission and then locate the numbers as
shown.
When calling for service assistance or parts, have the model and serial numbers handy.
T
R
Roadranger
Twin Countershaft
Low-Inertia
C= Convertible
F= Forward Opening Shift Housing
C
or
F
1 6 6 0 9
This (x) 100 = Nominal Torque Capacity
E
Service Procedure
Ratio Set
Forward Speeds
6= Multi-Mesh Gearing
7= Helical Auxiliary Gearing and
Multi-Mesh Front Section Gearing
9= Improved Seal System
L
Do not remove or destroy the transmission identification tag.
The model number gives basic information about the transmission. Use this number when calling for service assistance or replacement parts.
Serial Number
The serial number is the sequential identification number of the transmission. Before calling for service assistance, write the number down. It may be needed.
Bill of Material or Customer Number
This number may be located below the model and serial numbers. It is a reference number used by Eaton®.
5
Model Designations and Specifications
Model Options
Torque Rating
The torque rating of the transmission specified in the model number is the input torque capacity inLb•ft. Various torque ratings
are available. For more information, call your Eaton Fuller regional sales and service office at 1-800-826-HELP (4357).
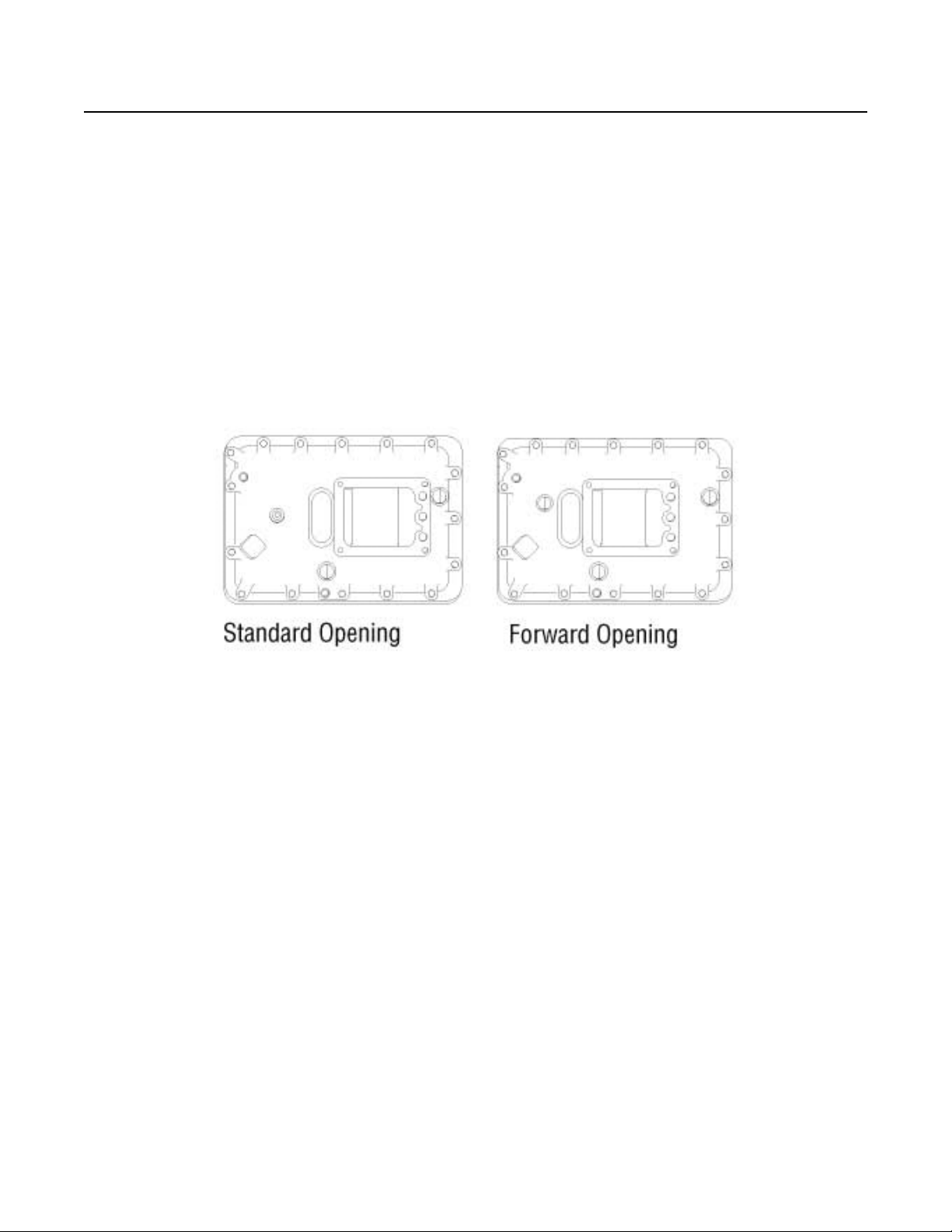
Shift Bar Housings
Two types of shift bar housings are available for this transmission. Both are described and shown below.
Standard
The standard shift bar housing has a gear shift lever opening that is located toward the rear of the transmission.
Forward
The forward shift bar housing has a gear shift lever opening located three inches closer to the transmission front than the standard
opening. This forward design allows greater flexibility in mounting the transmission and is indicated by an "F" in the model number
.
Power Take Off (PTO) Usage
PTOs can be mounted in the following way:
6 or 8 Bolt: The 6 or 8 bolt openings are standard with the transmission. The PTO is mounted to the opening and driven
from the PTO gear on the front countershaft.
Thru-Shaft: The thru-shaft PTO mounts on the rear of the transmission. It requires a special auxiliary housing and main
case countershaft with internal splines.
Lubrication Pumps
Internal: An internal lubrication pump is located in the lower front of the transmission and is driven off the upper coun-
tershaft. Transmissions rated
PTO Driven: A PTO driven pump is externally mounted on the 6 or 8 bolt PTO openings and driven off the PTO gear.
6

Lubrication
Lubrication Specifications
IMPORTANT
Transmission filters should be changed during regular lube intervals. Inspection of the transmission filter should be conducted during preventive maintenance checks for damage or corrosion. Replace as necessary.
Note: For a list of Eaton
Note: The use of lubricants not meeting these requirements will affect warranty coverage.
Note: Additives and friction modifiers must not be introduced. Never mix engine oils and gear oils in the same transmission.
®
Approved Synthetic Lubricants, see TCMT0021 or call 1-800-826-HELP (4357).
Buy from a reputable dealer
For a complete list of approved and reputable dealers, write to: Eaton Corporation, Worldwide Marketing Services, P.O. Box 4013,
Kalamazoo, MI 49003,
Transmission Operating Angles
If the transmission operating angle is more than 12 degrees, improper lubrication will occur. The operating angle is the transmission mounting angle in the chassis plus the percent of upgrade (expressed in degrees). For operating angles over 12 degrees, the
transmission must be equipped with an oil pump or cooler kit to insure proper lubrication.
Operating Temperatures with Oil Coolers
The transmission must not be operated consistently at temperatures above 250°F. Operation at temperatures above 250°F [121°C]
causes loaded gear tooth temperatures to exceed 350°F [177°C] which will ultimately destroy the heat treatment of the gears. If
the elevated temperature is associated with an unusual operating condition that will reoccur, a cooler should be added, or the capacity of the existing cooling system increased.
The following conditions in any combination can cause operating temperatures of over 250° F [121°C]:
General Information
• Operating consistently at slow speed.
• High ambient temperatures.
• Restricted air flow around transmission.
• Use of engine retarder.
• High horsepower operation.
Note: Transmission coolers must be used to reduce the operating temperatures when the above conditions are encountered.
7

Lubrication
Oil Cooler Chart
Table 4
TRANSMISSION OIL COOLERS ARE:
Recommended
• With engines of 350 H.P. and above.
Required
• With engines 399 H.P. and above and GCW’s over 90,000 lbs.
• With engines 399 H.P. and above and 1400 lb-ft (1898.15 N•m) or greater torque.
• With engines 1500 lb-ft (2033.73 N•m) and above
18-speed AutoShift transmissions require use of an Eaton® supplied oil-to-water cooler or approved equivalent.
• With engines 450 H.P. and above.
8

Recommended Tools
Tool Specifications
Some repair procedures pictured in this manual show the use of specialized tools. Their actual use is recommended as they make
transmission repair easier, faster, and prevent costly damage to critical parts.
For the most part, ordinary mechanic's tools such as socket wrenches, screwdrivers, etc., and other standard shop items such as
a press, mauls and soft bars are the only tools needed to successfully disassemble and reassemble any Fuller
The following tables list and describe the typical tools required to properly service this model transmission above and beyond the
necessary basic wrenches, sockets, screwdrivers, and prybars.
®
transmission.
General Tools
The following tools are available from several tool manufacturers such as Snap-On, Mac, Craftsman, OTC, and many others.
Table 5 General Tools
TOOL PURPOSE
0-100 lb-ft 1/2" drive Torque Wrench General torquing of fasteners (Typically 15-80 lb-ft [20.34-108.47
N•m])
0-600 lb-ft 3/4" or 1" drive Torque Wrench Torquing of output nut to 500 lb-ft (677.91 N•m)
0-50 lb-in 3/8" drive Torque Wrench General torquing of fasteners
0-30 lb-in 1/4" drive Torque Wrench Torquing of capscrews to 7 lb-in (0.79 N•m) during auxiliary coun-
tershaft bearing endplay setting procedure
General Information
70 MM or 2 2/4" Socket - Standard Depth To remove the output yoke nut
Large Brass Drift Used to protect shafts and bearings during removal
Large Dead Blow Hammer or Maul To provide force for shaft and bearing removal
Snap Ring Pliers - Large Standard External To remove the snap rings at the auxiliary drive gear, input shaft
bearing, and countershaft bearings
Feeler Gauges To set mainshaft washer endplay and auxiliary tapered bearing
endplay
Rolling Head (Crow's Foot) Prybar To remove the auxiliary drive gear bearing
(2) Air Pressure Gauges 0-100 PSI (0-1034 kPa) To troubleshoot and verify correct operation of air system
Universal Bushing Driver To remove and install clutch housing bushings. Bushing OD =
1.125 in., ID = 1.000 in.
9
Recommended Tools
The following special tools are designed for this Fuller® transmission. The addresses and phone numbers of the tool suppliers are
listed after the table. This list is provided as a convenience to our customers. These tools are manufactured by independent companies with no relationship to Eaton. Eaton does not warrant the fit or function of the listed tools. To obtain the tools, contact the
tool supplier directly.
Table 6 Special Tools
REFERENCE
NUMBER
T1 Output Yoke Puller May be required to remove a
T2 Auxiliary Section
T3 Auxiliary Counter-
T4 Shift Lever Spring
T5 Slide Hammer To remove the output seal
TOOL PURPOSE G & W TOOL NO. GREAT LAKES
rusted output yoke.
To support, or hang, the aux-
Hanger
shaft Support and
Shim Tool
Installation Tool
(Tension Spring
Driver)
iliary section in the horizontal position.
To hold the auxiliary countershafts in position while installing the auxiliary section
in the horizontal position.
Also to simplify the checking
and setting of the auxiliary
countershaft bearing endplay.
To install the shift tower tension spring.
and reverse idler shafts. Requires 1/2"-13 threads. (Optional, idler shaft can be
driven out from front.)
OTC
TOOL NO.
SP-450 7075
G-40 T-125 5061
G-250 T-311 5062
G-116 T-170
G-70 T-150 1155 Slide
TOOL NO.
Hammer / 8007
1/2" -13 Adapter
T6 Bearing Puller To remove front section
countershaft bearings.
T7 Bearing Driver To install front section coun-
tershaft bearings (3.97" OD,
1.78" ID).
T8 Bearing Driver To install the front counter-
shaft rear bearings (3.5" OD,
1.6" ID).
T9 Countershaft Sup-
port Tools (2)
T10 Input Bearing Driver To install input bearing on
T11 Bearing Puller To remove the auxiliary
10
To support and locate the
front section countershafts
during bearing removal and
installation.
input shaft.
countershaft tapered bearings.
G-10 or G-15 T-1 and T-2
for 9-Series
G200 Kit T-101 Kit
G200 Kit T-101 Kit
G-50 / G-51 / G-58 T-145S 7109
G-35 T-120 5066 (2" shaft)
4332/4232 1123 / 927
7070A Kit

Recommended Tools
Table 6 Special Tools (Continued)
REFERENCE
NUMBER
T12 Bearing Driver To install the auxiliary coun-
T13 Output Seal Remov-
T14 Auxiliary Section
T15 Mainshaft Hook To assist in lifting of main-
T16 Input Bearing Puller To remove input bearing. G-38 T-3 7070A Kit
T17 Bearing Race Puller To remove the auxiliary
T18 Bearing Race In-
TOOL PURPOSE G & W TOOL NO. GREAT LAKES
TOOL NO.
G-200 Kit T-105 Kit
tershaft tapered bearings.
To remove the output seal in
al Tool
Removal Adapter
Plate
staller
chassis. Can use slide hammer.
To attach transmission jack
to auxiliary section for auxiliary section removal in chassis.
shaft from front section.
countershaft tapered bearing
outer races.
To install the auxiliary countershaft tapered bearing outer races.
G-115 49611 (Used
G-225 T-165
OTC
TOOL NO.
Use 27315
hook with 1155
slide hammer
with OTC transmission jack P/
N 5019.)
7136 puller attached to 1155
slide hammer
27524/27530
discs used with
27488 handle
and 10020
screw.
General Information
* Tool ID numbers are referenced in the service procedures.
Special Tools
Table 7 Shop Equipment
20 Ton capacity press To press countershaft gears from countershaft.
Specialty Tool Manufacturers
Below are the addresses and phone numbers of the companies that make tools specifically for Eaton®Fuller® transmissions:
G and W Tool Company
1105 E. Louisville, Broken Arrow, OK 74012-5724, Phone: 800-247-5882, or 918-258-6881
Great Lakes Tool
8530 M-89, Richland, MI 49083, Phone: 800-877-9618, or 269-629-9628
O.T.C. 655 Eisenhower Dr., Owatonna, MN 55060-117, Phone: 800-533-6127, or 507-455-7000
The specialized tools can be obtained from a tool supplier or made from tool prints as required by the individual user. Detailed
®
Fuller
Transmission Tool Prints are available upon request by writing to:
Eaton Corporation, Truck Components Operations Technical Service, P.O. Box 4013, Kalamazoo, Michigan 49003
11
Recommended Tools
Eaton Aftermarket Parts
The following tools are available through Eaton Aftermarket Parts. To obtain any of the tools listed, contact your local Eaton parts
distributor.
Table 8
TOOL PURPOSE EATON® PART NUMBER
5/32” Air Line Release Tool To remove 5/32” air lines from push-to-
connect fittings.
Air Line Cutting Tool To cut plastic air lines smoothly and
squarely.
Output Seal Driver To install output seal. For 7 series: Eaton P/N 5564501 driver.
Output Seal Slinger Driver To install output seal slinger. For 7 series: Eaton P/N 71223.
P/N 4301157 included in kit K-2394
P/N 4301158 included in kit K-2394.
For 9 series: Use Eaton® P/N 5564509
adapter with 5564501 driver. Both parts
included in complete Eaton® seal kit P/
N TCMT0912.
For 9 series: Eaton P/N 4303829.
12

Torque Specifications
Transmission Torque Specifications
Correct torque application is extremely important to assure long transmission life and dependable performance. Over-tightening
or under-tightening can result in a loose installation and in many instances, eventually cause damage to transmission gears,
shafts, and/or bearings. Use a torque wrench whenever possible to attain recommended Lbs•ft. ratings. Do not torque capscrews
dry.
FRONT SECTION: ALL MODELS
Service Procedure
Cut 7190 K-11/87
13
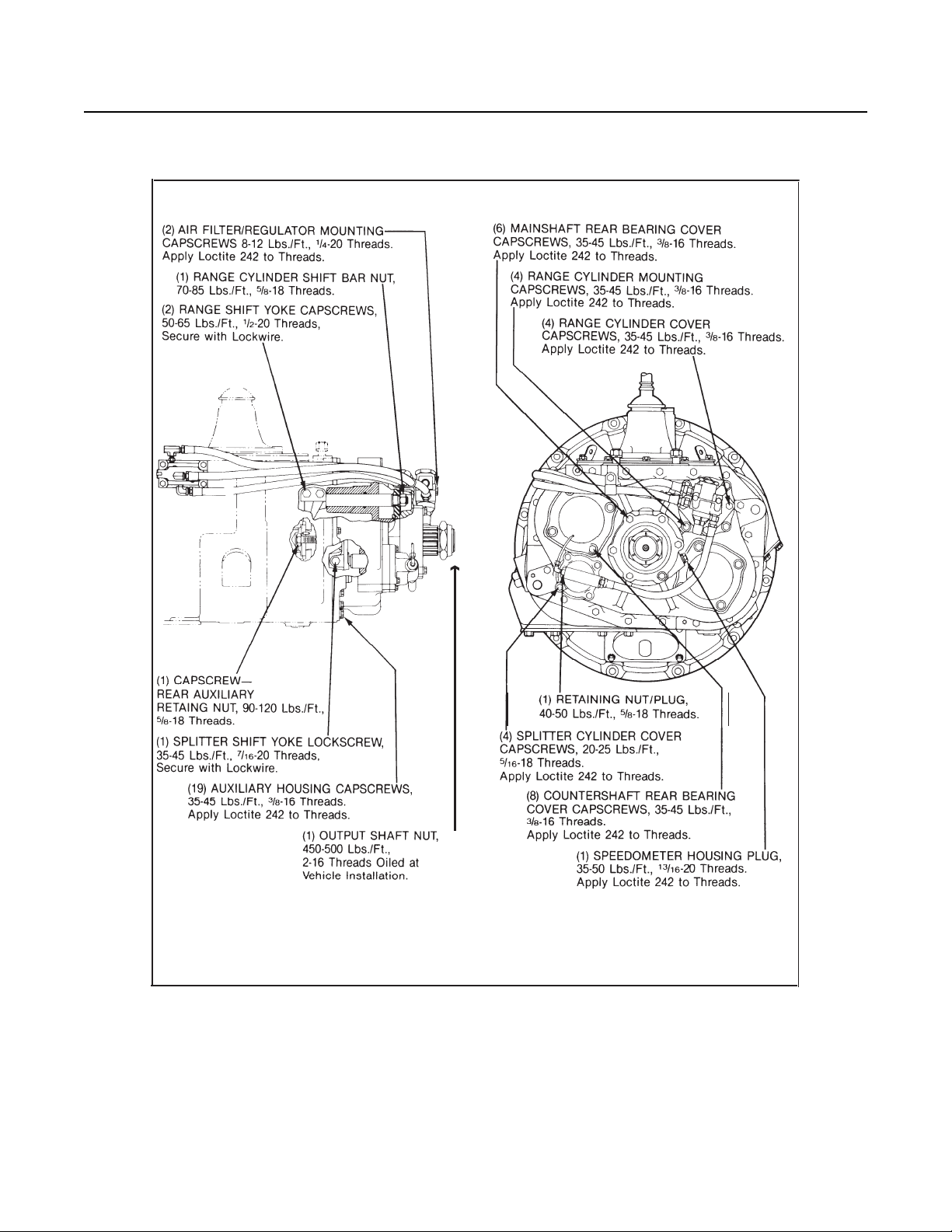
Torque Specifications
Auxiliary Sections
AUXILIARY SECTIONS
14
Cut 7191 Q-11/87

Preventive Maintenance
Preventative Maintenance Check Points
Everyday there are countless vehicles operating over the highways with transmissions in such a neglected mechanical condition,
they can be referred to as failures looking for a place to break down. They lack a proper and organized preventive maintenance
program.
Preventive maintenance is a general term which applies to all procedures necessary to have maximum life and satisfactory service
at the lowest possible cost, short of removing and repairing the unit.
A number of conditions contrary to good preventive maintenance can generally be pointed to when inspecting a failed transmission. Taking a few minutes every so many hours or miles to do a few simple checks could help avoid eventual breakdown or
reduce the repair cost. If the transmission is not cared for, it will breakdown.
Service Procedure
Note: Transmission appearance may differ, however the procedure is the same.
15

Preventive Maintenance
1. Air System and Connections
• Check for leaks, worn air lines, loose connections and capscrews.
2. Clutch Housing Mounting
• Check all capscrews of clutch housing flange for looseness.
3. Clutch Release Bearing (Not Shown)
• Remove hand hole cover and check radial and axial clearance in release bearing.
• Check relative position of thrust surface of release bearing with thrust sleeve on push-type clutches.
4. Clutch Pedal Shaft and Bores
• Pry upward on shafts to check wear.
• If excessive movement is found, remove clutch release mechanism and check bushings on bores and wear on
shafts. See OEM literature.
5. Lubricant
• Change at specified service intervals.
• Use only the types and grades as recommended. See “Recommended Lubrication Chart” (see Table 2).
6. Filler and Drain Plugs
• Remove filler plugs and check level of lubricant at specified intervals. Tighten fill and drain plugs securely.
7. Capscrews and Gaskets
• For applicable models, check all capscrews, especially those on PTO covers and rear bearing covers for looseness
which would cause oil leakage.
• Check PTO opening and rear bearing covers for oil leakage due to faulty gasket.
8. Gear Shift Lever
• Check for looseness and free play in housing. If lever is loose in housing, proceed with Check No. 9.
9. Gear Shift Lever Housing Assembly
• If present, remove air lines at air valve or slave valve. Remove the gear shift lever housing assembly from the transmission.
• Check the tension spring and washer for set and wear.
• Check the gear shift lever spade pin and slot for wear.
• Check bottom end of gear shift lever for wear and check slot of yokes and blocks in shift bar housing for wear at
contact points with shift lever.
Checks With Drive Line Dropped
10. Universal Joint Companion Flange or Yoke Nut
• Check for tightness. Tighten to recommended torque.
11. Output Shaft (Not Shown)
• Pry upward against output shaft to check radial clearance in mainshaft rear bearing.
16
Preventive Maintenance
Checks With Universal Joint Companion Flange or Yoke Removed
Note: If necessary, use solvent and shop rag to clean sealing surface of companion flange or yoke. Do not use crocus cloth, emery
paper, or other abrasive materials that will mar surface finish.
12. Splines on Output Shaft (Not Shown)
• Check for wear from movement and chucking action of the universal joint companion flange or yoke.
13. Mainshaft Rear Bearing Cover (Not Shown)
• Check oil seal for wear.
Oil Leak Inspection Process
Inspect for Oil Leak
Determine if it is a Weep or a Leak
Weep: Stained, damp, no drips, light oil film,
dirt adhered to the contaminated area.
Gasket Rear Seal Leak
1. Clean suspected oil weep
area with a clean dry cloth
or mild soluble degreaser.
2. Ensure lube is to proper
level.
3. Notify the customer that it
is only a weep and it is not
considered to be detrimental
to the life of the transmission.
4. Repair is complete.
1. Do not repair: Rear seal is
designed to allow min
seepage (refer to Roadranger
TCSM-0912 Seal Maintance
Guide).
2. Ensure lube is to proper
level.
imal
Leak: Extremely wet or dripping of oil in the
contaminated area.
Step 1
Step 2
Step 3
1. Determine the origin of the leak path.
2. If origin of leak is obvious skip to Step 3.
3. If the origin of the oil leak is not obvious then
use either of the two following steps to determine
the oil leak:
Note: Do not use a high pressure spray washer to
clean the ar
force contamination into the area of concern and
temporarily disrupt the leak path.
i. Clean area with a clean dry cloth or mild
soluble degreaser and fill the transmission to
the proper lube level.
OR
ii. Clean the area as noted above and insert tracer
dye into the tr
transmission to proper lube level.
Operate vehicle to normal transmission operating
temperature and inspect the area for oil leak(s)
visually or if tracer dye was introduced use an UVL
(Ultraviolet Light) to detect the tracer dye’s point
of origin.
Note: When i
make sure the assumed leak area is not being
contaminated by a source either forward or above
the identified area such as the engine, shift tower,
shift bar housing, top mounted oil cooler, etc...
Once the origin of the leak is identified, repair the
oil leak using proper repair proced
designated model service manual.
ea. Use of a high pressure spray may
ansmission lube and fill
nspecting for the origin of the leak(s)
ures from the
Service Procedure
Step 4
After the repair is completed, verify the leak is
repaired and operate the vehicle to normal
transmission operating temperature.
Inspect repaired area to ensure oil leak has been
eliminated. If the leak(s) still occurs, repeat steps
or contact the Roadranger Call Cen
1-800-826-4357.
ter at
17
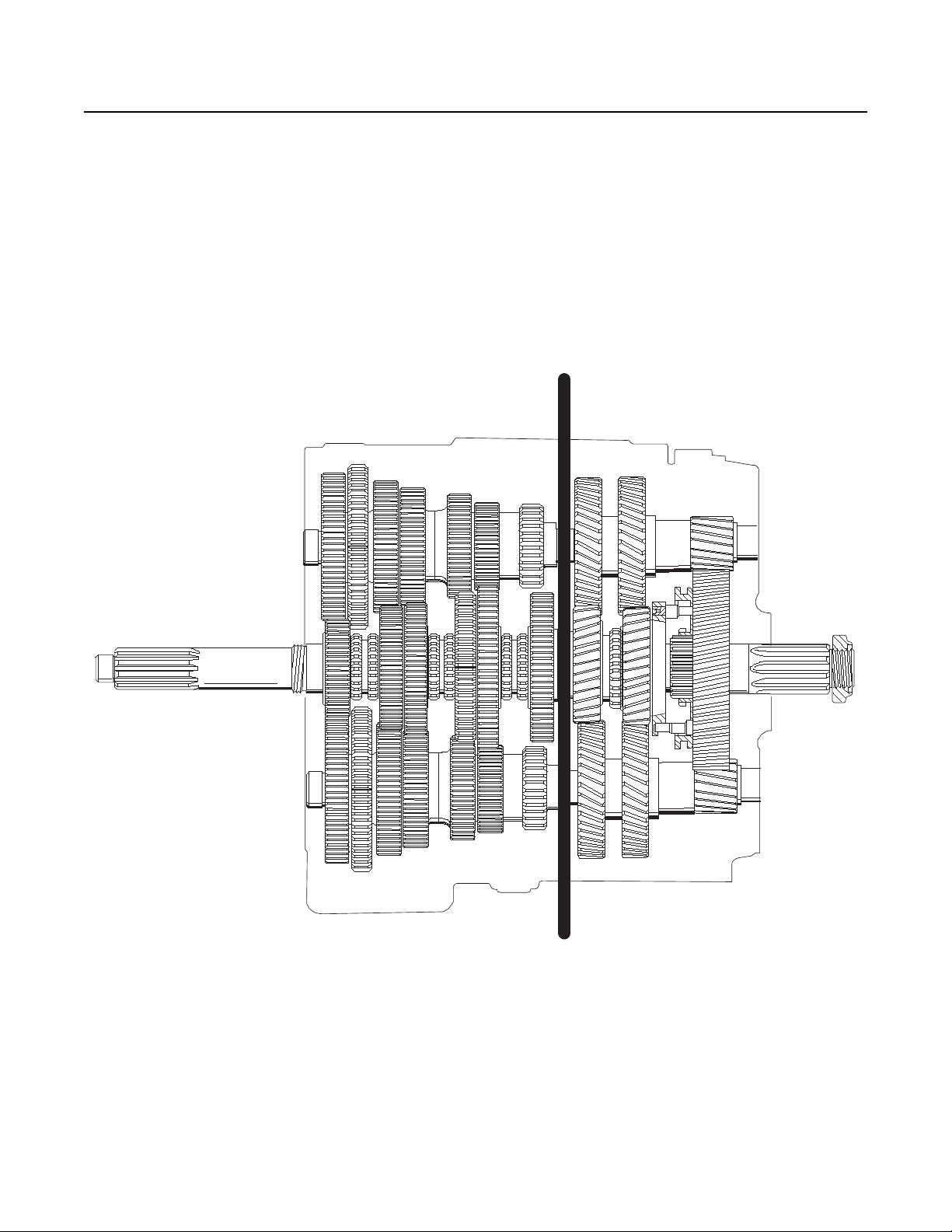
Power Flow
Power Flow Diagrams
An understanding of the engine's power flow through a transmission in each particular gear will assist the technician in troubleshooting and servicing a transmission.
The Eaton®Fuller®Roadranger transmission can be thought of as two separate "transmissions" combined into one unit. The first
"transmission" or front section contains six gear sets which are shifted with the gear shift lever. The second "transmission" called
the auxiliary section, contains three gear sets and is shifted with air pressure.
Note: This transmission is referred to as a constant mesh type transmission. When in operation, all gears are turning even though
only some of them are transferring power.
12
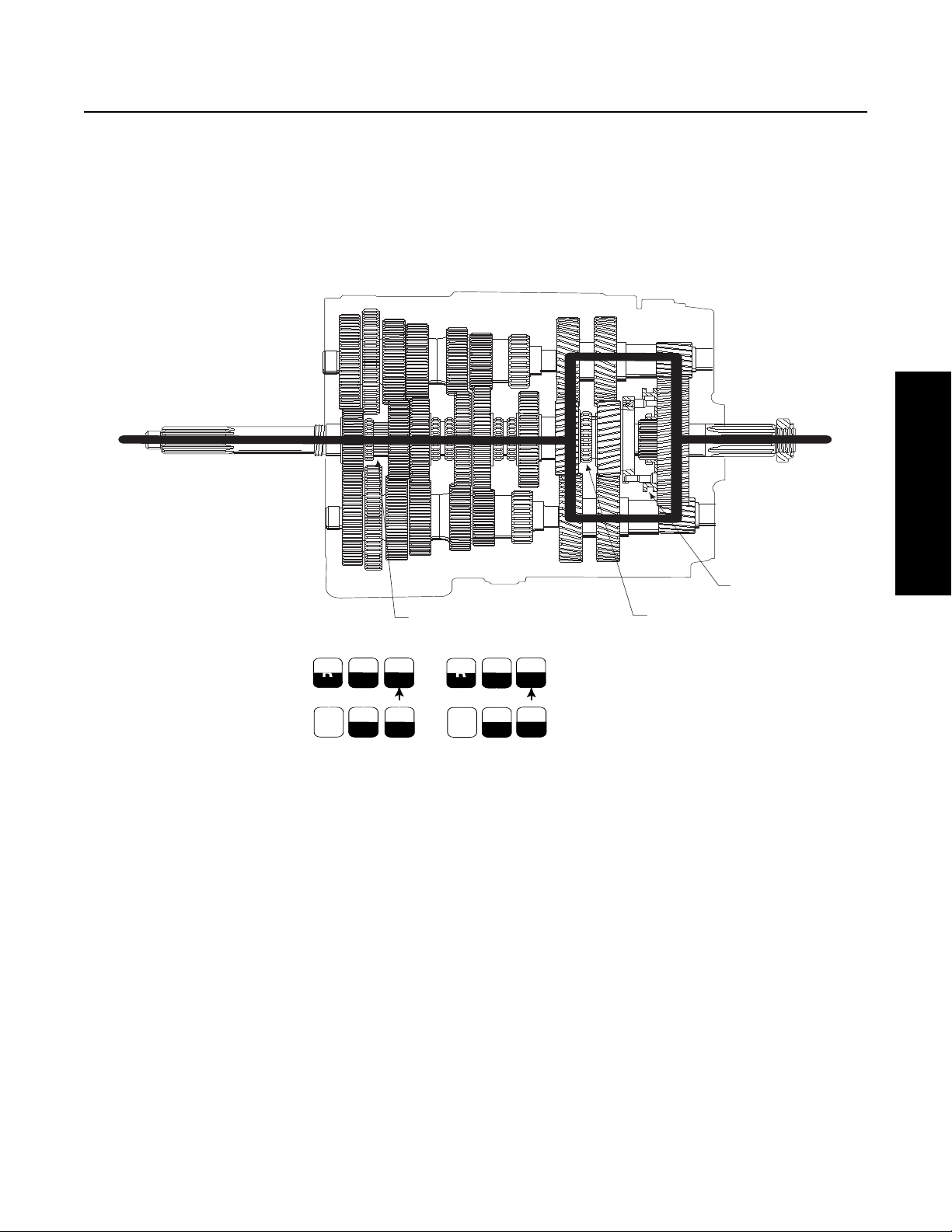
Cross Sectional View
1. Front Section
2. Front Section
18
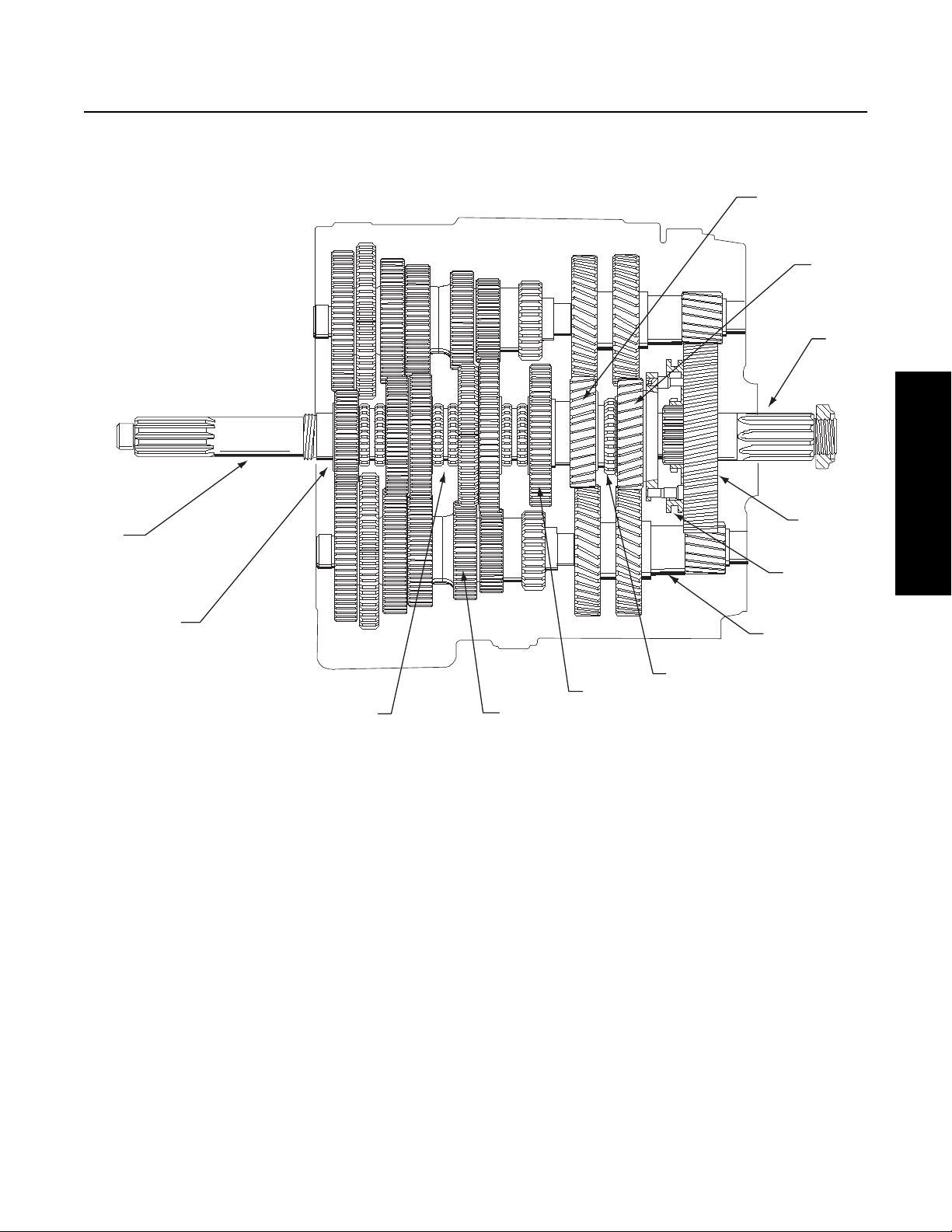
Power Flow
The transmission components in the figure below shows the transmission with the main components called out. Note that the
transmission is in the neutral position because the sliding clutches are all in their center positions and not engaged in any gears.
12
11
10
Service Procedure
1
2
34
Transmission Components
1. Input Shaft
2. Main Drive Gear
3. Sliding Clutch
4. Countershaft
5. Mainshaft Gear
6. Auxiliary Splitter Clutch (slides on front section mainshaft)
9
8
7
6
5
7. Auxiliary Countershaft
8. Range Sliding Clutch
9. Auxiliary Mainshaft Reduction Gear
10. Output Shaft (Auxiliary Mainshaft)
11. Splitter Gear
12. Auxiliary Drive Gear
19

Power Flow
Front Section Power Flow
Note: The heavy lines in the figure below outline the power flow description. For help in understanding the transmission compo-
nents, refer to the figure “Transmission Components” on the previous page.
1. Power (torque) from the vehicle's engine is transferred to the transmission's input shaft.
2. The input shaft rotates the main drive gear through internal splines in the hub of the gear.
3. The main drive gear meshes with both countershaft driven gears and the torque is split between both countershafts.
4. Because the countershaft gears are in constant mesh with the mainshaft gears, all the front section gearing rotates. However, only the engaged or selected mainshaft gear will have torque. External clutching teeth on the sliding clutch will
engage internal clutching teeth on the selected mainshaft gear. Torque will now be provided from both opposing countershaft gears, into the engaged mainshaft gear, and through the sliding clutch to the front section mainshaft.
5. The rear of the front section mainshaft is splined into the auxiliary splitter clutch and torque is now delivered to the auxiliary splitter clutch.
Front Section Power Flow
1. Sliding Clutch forward
2. Sliding Clutch forward
3. Sliding Clutch rearward
20
R
LO
RTO
153
Neutral
264
3
1
RTX
7
8
R
Neutral
LO
8
154
7
263
2
Power Flow
Front Section Power Flow - Direct Gear
In direct gear, the front sliding clutch is moved forward and engages into the back of the main drive gear. Torque will flow from
the input shaft to the main drive gear, main drive gear to sliding clutch, sliding clutch straight into the front section mainshaft
which delivers the torque to the auxiliary splitter clutch. See figure below.
Note: All countershaft and mainshaft gears will rotate, but the gears will not be loaded.
Service Procedure
Front Section Power Flow - Direct Gear
1. Sliding Clutch forward
2. Sliding Clutch forward
3. Sliding Clutch rearward
R
LO
RTO
153
Neutral
264
3
1
7
8
R
LO
RT
1
7
5
3
1
6
8
4
2
2
21
 Loading...
Loading...