Bose Ps1 L1 Schematic
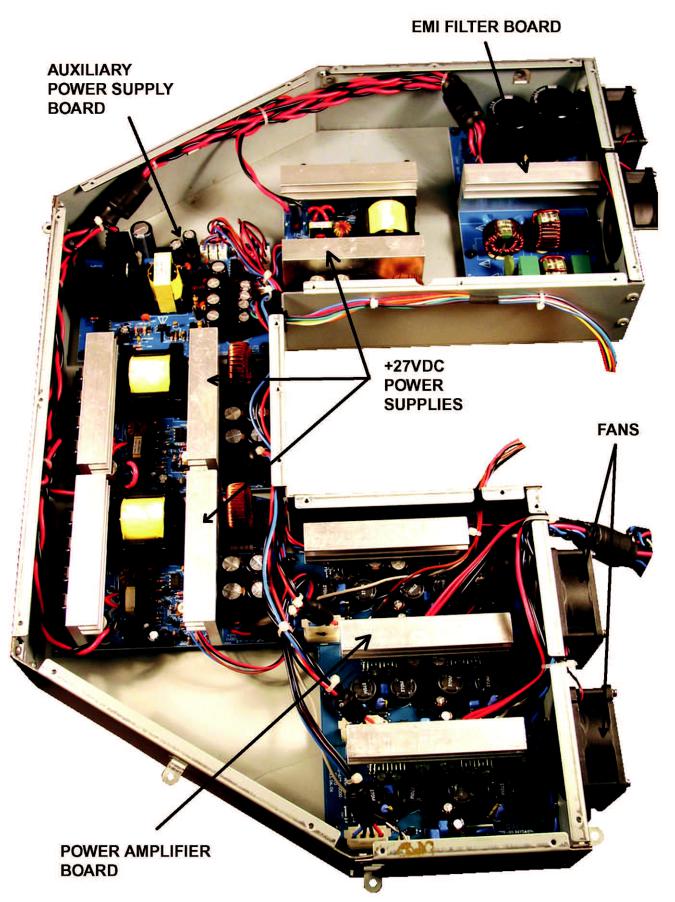
Figure 9. PS1 Power Stand Electronics Module with Top Cover Removed
77

Disassembly Procedures
Power Stand Procedures
Note: Refer to Figure 9 for the following procedures.
1.Lower Housing Removal
1.1Place the power stand on a soft surface so that the line array opening faces down.
1.2Using a Phillips-head screwdriver, remove the 19 screws that secure the lower housing to the upper housing. Lift off the lower housing.
2.Amplifier Housing Removal
2.1Perform procedure 1.
2.2Make a note of the wiring, and disconnect the wiring harnesses and connectors that run to the amplifier housing. The amplifier housing is the large metal box with the four fans.
2.3Using a Phillips-head screwdriver, remove the four screws that secure the power stand base plate to the bottom of the line array cavity. Lift it off of the cavity. Be careful not to damage any wires.
2.4Once all of the wiring is disconnected, use a Phillips-head screwdriver to remove the 16 screws that secure the amplifier housing to the power stand upper housing. Carefully lift the amplifier housing out of the power stand upper housing.
3.Line Array Cavity Removal
3.1Perform procedure 2.
3.2Using a Phillips-head screwdriver, remove the three screws that secure the line array cavity to the upper housing. Lift the line array cavity off of the upper housing. The power stand foot pedal will disengage from the shaft.
78

Disassembly Procedures
4.Amplifier PCB Removal
4.1Perform procedure 2.
4.2Make a note of the wiring and disconnect all of the wiring harnesses that connect the power supply box to the DSP PCB and to the microprocessor PCB.
4.3Using a Phillips-head screwdriver, remove the 24 screws that secure the power supply box top cover in place. Lift off the top cover.
4.4Once you have the top cover off, make a note of the wiring configuration and unplug the wiring harnesses that connect to the amplifier PCB.
4.5Using a Phillips-head screwdriver, remove the 6 screws that secure amplifier PCB in place. Lift the amplifier PCB out of the chassis.
5.Switching DC Power Supply Removal
5.1Perform procedure 2.
5.2Make a note of the wiring and disconnect all of the wiring harnesses that connect the power supply box to the DSP PCB and to the microprocessor PCB.
5.3Using a Phillips-head screwdriver, remove the 24 screws that secure the power supply box top cover in place. Lift off the top cover.
5.4Once you have the top cover off, make a note of the wiring configuration and unplug the wiring harnesses that connect to the switching DC power supply PCB you wish to remove.
5.5Using a Phillips-head screwdriver, remove the 4 screws that secure power supply PCB in place. Lift the power supply PCB out of the chassis.
79

Disassembly Procedures
6.Auxiliary Power Supply Removal
6.1Perform procedure 2.
6.2Make a note of the wiring and disconnect all of the wiring harnesses that connect the power supply box to the DSP PCB and to the microprocessor PCB.
6.3Using a Phillips-head screwdriver, remove the 24 screws that secure the power supply box top cover in place. Lift off the top cover.
6.4Once you have the top cover off, make a note of the wiring configuration and unplug the wiring harnesses that connect to the switching DC power supply PCB you wish to remove.
6.5Using a Phillips-head screwdriver, remove the 4 screws that secure power supply PCB in place. Lift the power supply PCB out of the chassis.
7.EMI Filter PCB Removal
7.1Perform procedure 2.
7.2Make a note of the wiring and disconnect all of the wiring harnesses that connect the power supply box to the DSP PCB and to the microprocessor PCB.
7.3Using a Phillips-head screwdriver, remove the 24 screws that secure the power supply box top cover in place. Lift off the top cover.
7.4Once you have the top cover off, make a note of the wiring configuration and unplug the wiring harnesses that connect to the EMI Filter PCB.
7.5Using a Phillips-head screwdriver, remove the 4 screws that secure the EMI Filter PCB in place. Lift the EMI Filter PCB out of the chassis.
80

Disassembly Procedures
8.Chassis Fan Removal
8.1Perform procedure 2.
8.2Using a Phillips-head screwdriver, remove the 24 screws that secure the power supply box top cover in place. Lift off the top cover.
8.3Using a Phillips-head screwdriver, remove the 4 screws that secure the fan to the chassis.
8.4Follow the wire harness for the fan you are removing to the auxiliary power supply PCB and unplug it. Lift the fan out of the chassis.
Re-assembly note: When installing the new fan, be sure to match the orientation of the fan next to it so that it will move air in the proper direction when in use.
9.Microprocessor PCB Removal
9.1Perform procedure 1.
9.2Make a note of the wiring configuration and unplug the six wire harnesses from the connectors on the board.
9.3Lift the microprocessor PCB off of the connectors that engage it on the bottom of the board and the pins that connect to the preset switches.
Re-assembly note: When re-installing this PCB, be sure that all of the pins from the preset switches are straight and properly engage the connectors on the bottom of the microprocessor PCB.
81

Disassembly Procedures
10.DSP PCB Removal
10.1Perform procedure 1.
10.2Make a note of the wiring configuration and unplug the six wire harnesses from the connectors on the board.
10.3Using a pair of needle-nose pliers, compress the bottoms of the plastic standoff posts used to attach the DSP PCB to the Input/Output PCB. Lift the DSP PCB off of the I/O PCB.
11.Input/Output PCB Removal
11.1Perform procedures 9 and 10.
11.2On the front panel of the power stand, remove the four knobs for the mic trim and level controls.
11.3Using a nut driver, remove the nine nuts and washers for the 1/4 inch phono jacks.
11.4Using a Phillips-head screwdriver, remove the 16 screws that secure the XLR, Data in/out and Neutrik connectors to the front panel.
11.5Lift the I/O PCB off of the input panel.
82

Disassembly Procedures
Line Array Procedures
Note: The line arrays are divided into a lower line array, which plugs directly into the power stand, and an upper line array, which uses a bayonet arrangement to align the upper array to the lower array for connection. All electrical connections are automatically made when the arrays are mounted into the power stand and the upper array is mounted to the lower array.
Note: Refer to Figure 7 for the following procedures.
1.Grille Removal
1.1Using a Phillips-head screwdriver, remove the six screws that secure the end cap to the line array enclosure. Lift off the end cap. Unplug the molex connector from the speaker harness.
1.2Grasp the edge of the grille and gently lift it away from the enclosure.
2.Nameplate Removal
2.1Perform procedure 1.
2.2On the back of the grille, unbend the legs of the logo. Lift off the nameplate.
3.Driver Removal
3.1Perform procedure 1.
3.2Using a Phillips-head screwdriver, remove the four screws that secure the driver to the enclosure.
3.3Lift the driver out of the enclosure. Note the wiring configuration and cut the wires as close to the driver terminals as possible.
4.Upper Line Array Top End Cap Removal
4.1Using a Phillips-head screwdriver, remove the seven screws that secure the end cap to the line array enclosure. Lift off the end cap.
Re-assembly note: Make sure that the end cap gasket is properly aligned to achieve an airtight seal.
5. Upper Line Array Bottom End Cap
Removal
5.1 Using a Phillips-head screwdriver, remove the seven screws that secure the end cap to the line array enclosure. Lift the end cap away from the enclosure. Unplug the molex connector from the speaker harness.
Re-assembly note: Make sure that the end cap gasket is properly aligned to achieve an airtight seal.
6.Lower Line Array Top End Cap Removal
6.1Using a Phillips-head screwdriver, remove the six screws that secure the end cap to the line array enclosure. Lift off the end cap. Unplug the molex connector from the speaker harness.
Re-assembly note: Make sure that the end cap gasket is properly aligned to achieve an airtight seal.
7. Lower Line Array Bottom End Cap
Removal
7.1 Using a Phillips-head screwdriver, remove the seven screws that secure the end cap to the line array enclosure. Lift the end cap away from the enclosure. Unplug the molex connector from the speaker harness.
Re-assembly note: Make sure that the end cap gasket is properly aligned to achieve an airtight seal.
83

Disassembly Procedures
8.Front Cap Removal
8.1Using a Phillips-head screwdriver, remove the four screws that secure the front cap to the bottom front of the line array enclosure. Lift the end cap away from the enclosure.
Bass Module Procedures
Note: Refer to Figure 8 for the following procedures.
1.Grille Removal
1.1Using an allen wrench, remove
the four screws that secure the grille to the upper and lower speaker end caps.
1.2Lift off the grille.
2.Nameplate Removal
2.1Perform procedure 1.
2.2On the back of the grille, remove the retaining nut and spring from the post of the nameplate. Lift the nameplate off of the grille.
3.Driver Removal
3.1Perform procedure 1.
3.2Using a Phillips-head screwdriver, remove the four screws that secure the driver to the bass module enclosure.
3.3Lift the driver out of the enclosure. Note the wiring configuration and cut the wires as close to the driver terminals as possible.
Re-assembly notes:
-When soldering the speaker harness wires to the new driver, be sure to observe polarity of the driver harness wires.
-Be sure to properly align the gasket behind the new driver to ensure an airtight fit.
4.Input Panel Removal
4.1Using a Phillips-head screwdriver, remove the four screws that secure the input panel to the bass module enclosure.
4.2Lift the input panel away from the bass module enclosure.
4.3Make a note of the wiring configuration and un-solder the speaker harness wires from the input panel.
84
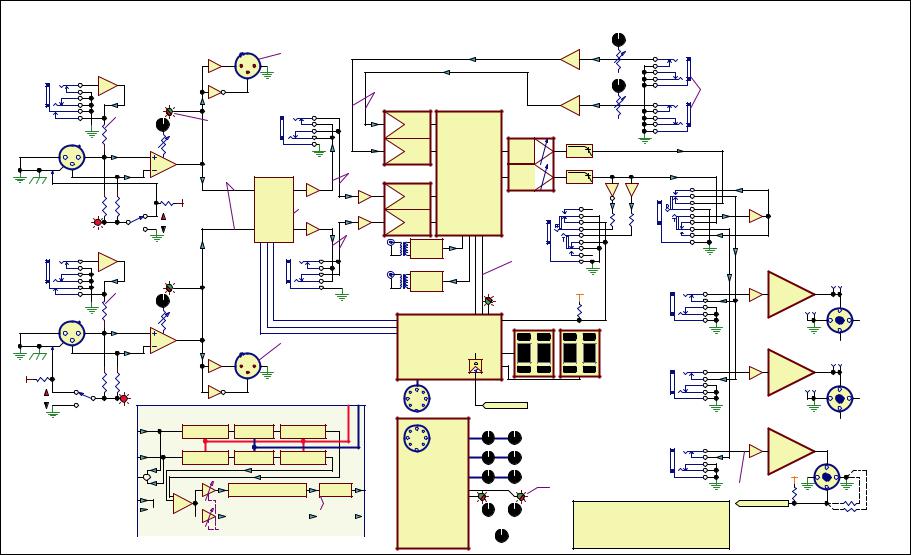
Figure 10. PS1 Power Stand Block Diagram
|
|
|
|
|
BLOCK DIAGRAM - Signal Processing + Routing |
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
Max. Level = +18dBV [input buffer clips] |
|
Ch1 Line Out |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Level |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
+20dB |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
Nom. Level = -1dBV |
|
|
|
|
Nom.: +6dBV (Balanced) |
|
|
|
|
|
20K 15A |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||
Min. Level = -46dBV for full output |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Clip@+24dBV |
|
" |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
(Ch1 Vol+Master @ Max) |
|
|
+1 |
2 |
|
1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Ch 3 IN |
|
|
|
|
|
|||
Input-LINE |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
+2.6dB @ 12:00 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
+1 |
-12 to +30 dB |
|
|
3 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Level |
|
|
Max. Level = +40dBV+ |
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Nom. -10dBV |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Nom. Level = -13dBV (pot @ ctr) |
|
|
|
|||||||||
|
|
|
-1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
+20dB |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||
|
|
|
|
+1dB @ ctr |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Clip@+6dBV |
|
|
|
20K 15A |
|
Min. Level = -30dBV for full output |
|
|
|
|||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||
|
|
|
Line (1/4") input |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
CS5361 |
ADS21065L |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
Sig/OL |
|
|
|
|
Ch1 Insert |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Ch 4 IN |
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
-20dB |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
Red=Clip=+6dBV |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
Trim |
|
|
|
|
|
|
A/D |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
+8 to +50 dB |
Green=Signal= -30dBV |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
CS4392 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
Ch1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
+21dB @ ctr |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
-1.5dB |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
Mic (XLR) input |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
Ring = Send |
|
|
|
A/D |
|
|
|
D/A |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
1 |
2 |
|
|
|
5K 10C |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
LPF |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
Tip = Return |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
INA163 |
Nom.: 0dBV |
TCA9459F |
|
|
Nom. -10dBV |
|
DSP |
|
|
|
-1.5dB |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
3 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
CS5361 |
|
D/A |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||
|
|
|
|
Clip@+18dBV |
|
|
|
|
Clip@+6dBV |
|
|
LPF |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
Input-MIC |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2-Ch. |
+1 |
|
|
0dB |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
-1 |
+1 |
1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
+1 |
A/D |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2 |
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Bass Send 1 |
|
|
|
3 |
|
|
|
|
|
||||
Max. Level = +10dBV |
|
|
|
|
+24 |
|
|
|
Digital Max. Gain = 0dB |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
8 |
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||
Nom. Level = -21dBV(Trim ctr) |
|
|
|
|
+24v |
|
|
|
|
|
Nom. Gain = -10dB (12:00) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
2 |
|
|
|
4 |
0dB |
|
|
|
|
|||
Min. Level = -66dBV for full output |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Volume |
Min. Gain = -40dB |
0dB |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
+1 |
|
|
|
|
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
A/D |
|
|
|
|
|
3 |
|
|
|
7 |
|
|
|
|
||||||||||
(Trim, Ch1 Vol+Master @ Max) |
|
|
|
|
Off |
|
|
|
Control |
+1 |
|
+1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
8 |
|
|
|
6 |
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
PHANTOM |
|
|
|
|
Nom. -10dBV |
|
|
|
|
|
|
4 |
|
|
|
5 |
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
0dB |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Clip@+6dBV |
|
|
|
|
|
|
7 |
|
|
|
9 |
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
SPDIF |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
Input-LINE |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Ch2 Insert |
Data In |
|
|
|
|
|
6 |
|
|
All-Amps |
Hi/Full Range |
|
|
|
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Rcvr |
|
Master Vol Ctrl |
|
5 |
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
|
|
+1 |
-12 to +30 dB |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(SPDIF) |
CS8416 |
|
|
9 |
|
|
Input |
|
|
Amp1 |
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
+1dB @ ctr |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
LineSource Top |
||||
|
|
|
Line (1/4") input |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Data-Out |
SPDIF |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Bass |
|
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Xmiter |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0dB |
Power |
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
-20dB |
Sig/OL |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(SPDIF) |
|
Power / Protect / Diagnostic |
+5 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Ring = Send |
CS8406 |
|
|
|
|
|
+1 |
|
|
|
|||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
Trim |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Amp In 1 |
|
Amp |
|
|
1+ |
||||||
|
|
|
+8 to +50 dB |
|
|
|
|
Tip = Return |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
Ch2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
S3PC8475 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
|
|
+21dB @ ctr |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Bass Slave Sense |
|
|
|
|
|
|
+29dB |
|
1- |
2- |
|||
|
|
Mic (XLR) input |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
1 |
2 |
|
|
|
5K 10C |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
µC |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Amp2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Ch2 Line Out |
Nom.: +6dBV (Balanced) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2+ |
|||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
INA163 |
|
|
|
|
Clip@+24dBV |
|
" |
|
|
|
|
|
0 1 |
|
0 1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
3 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
PresetCh1/2 Remote |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
LineSource Bottom |
|||||||
Input-MIC |
|
|
|
|
2 |
3 |
1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0dB |
||||||||||
|
|
|
+1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Power |
|
|
1+ |
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
+1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Amp |
|
|
|
|
+24 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Ch1 |
|
Ch2 |
Amp In 2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
+24v |
|
|
|
|
|
-1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
PRESET |
|
|
|
|
|
+29dB |
|
1- |
2- |
||||
Off |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
DSP Processing Block Diag |
|
|
|
|
|
8/4 ohm Sense |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
|
PHANTOM |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Amp3 |
|
|
2+ |
|||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Ch1 |
Ch2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
Ch1 In |
|
NoiseGate |
|
User EQ |
Preset EQ |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
High |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Bass |
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0dB |
Power |
|
Clip @ +30dBV |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
Ch2 In |
|
NoiseGate |
|
User EQ |
Preset EQ |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Mid |
|
|
|
|
|
|
+1 |
Amp |
|
1+ |
(250W 4ohms) |
|||
|
|
|
L |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Amp In 3 |
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
S-DATA Out |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Remote |
|
|
Low |
Clip= -4dBV into A/D |
|
|
|
|
+29dB +5 |
1- |
|
2- |
||||
|
|
(to SPDIF) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
+1dBV (1.1V) for |
|
|
|
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
Sys. EQ+X-Over, Hi |
Limiter |
|
|
|
|
Signal= -40dBV into A/D |
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
R |
|
|
Hi Out |
|
|
|
|
|
Persistence = 100msec |
|
|
250W@4 Ohms |
|
2+ |
|
|||||||||||
|
|
|
Ch 3 In |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Knee=+1.5dBV |
|
|
|
Sig/OL |
Sig/OL |
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
8/4 ohm Sense |
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
Ch 4 In |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Level |
BASS SPEAKER SENSING: |
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Sys. EQ+X-Over, Lo |
|
Limiter |
|
|
Bass Out |
|
|
|
|
R=Open: Amp1&2 Wider-Band EQ |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
R=10K: |
40-150Hz X-Over on Bass, >150Hz-Hi |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Master Vol. Range: -80 to +22dB (+10 @ 12:00) |
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Master |
R=5K: |
X-Over on Bass Ch, -6dB Hi Range |
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
R<5K: |
Debug Mode: All outs flat, Limiter Off |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Rev: U
85

Test Procedures
PS1 Power Stand Tests
Equipment Required
•dB Meter
•Digital Multi-meter
•Audio Signal Generator
•Distortion Meter
•3 - 4 Ohm, 250 Watt Load Resistors
•Test cables, see Appendix
Overall PS1 System Tests
Notes:
1.Do not connect the R1 remote control for the following tests, unless specified. Powering up the PS1 power stand without the remote has the same effect as setting all of the controls on the remote to the midpoint.
2.On the front panel of the PS1, set the Channel 1 and Channel 2 Preset Select switches to 00. Short out the 2+ and 2- connections on the Amp 3 out connector using the test cable described in section 1 of the appendix of this manual. This will put the PS1 into debug mode for the following tests. In this mode the crossover, the compressor and the EQ are disabled. The DSP will pass a flat response. The level controls and the clip indicators still operate in this mode.
3.Refer to Figure 10, PS1 Block Diagram, for the following procedures.
1.Channel 1 and 2 Mic Input Gain Tests
1.1Place a 1/4” mono shorting plug into the Amp 2 IN and Amp 3 IN jacks on the right hand side of the input/output panel. This will disable the channel 2 and 3 amplifiers while testing the channel 1 amplifier.
1.2On the left hand side of the input/output panel, set the channel 1 Mic Trim control to the 6 setting. Ensure that the Phantom Power push button is not pushed in.
1.3Using a balanced XLR male input cable, apply a 1 kHz, -30dBV signal to the channel 1 input.
1.4Reference a dB meter to the input level. Measure the gain output at the Amp 1 OUT jack. It should be +48.5 dB + 3 dB.
1.5Move the shorting plug from the Amp 2 IN jack to the Amp 1 IN jack and repeat steps 1.1 to 1.4 for the channel 2 Mic input.
2.Channel 1 and 2 Mic Input Frequency Reponse and Distortion Tests
2.1Place a 1/4” mono shorting plug into the Amp 2 IN and Amp 3 IN jacks on the right hand side of the input/output panel. This will disable the channel 2 and 3 amplifiers while testing the channel 1 amplifier.
2.2On the left hand side of the input/output panel, set the channel 1 Mic Trim control to the 6 setting. Ensure that the Phantom Power push button is not pushed in.
2.3Using a balanced XLR male input cable, apply a 1 kHz, -30 dBV signal to the channel 1 input.
2.4Use an 80kHz low-pass filter on your measuring equipment. Reference a dB meter to the input level. Measure the frequency response at the Amp 1 OUT jack. It should be 0 dB + 3 dB from 30 Hz to 15 kHz.
2.5Measure the Total Harmonic Distortion (THD) level at the Amp 1 OUT jack.
It should be 0.25% max at 1 kHz and 1.5% max at 15 kHz.
2.6Move the shorting plug from the Amp 2 IN jack to the Amp 1 IN jack and repeat steps 2.1 to 2.5 for the channel 2 Mic input.
86

Test Procedures
3.Channel 1 and 2 Mic Input Signal to Noise Ratio (Dynamic Range) Tests
3.1Place a 1/4” mono shorting plug into the Amp 2 IN and Amp 3 IN jacks on the right hand side of the input/output panel. This will disable the channel 2 and 3 amplifiers while testing the channel 1 amplifier.
3.2On the left hand side of the input/output panel, set the channel 1 Mic Trim control to the 6 setting. Ensure that the Phantom Power push button is not pushed in.
3.3Using a balanced XLR male input cable, apply a 1 kHz, -30 dBV signal to the channel 1 input.
3.4Reference a dB meter to the output level at the Amp 1 OUT jack. Remove the input signal and measure the A-Weighted output level. It should be -80 dB minimum.
3.5Move the shorting plug from the Amp 2 IN jack to the Amp 1 IN jack and repeat steps 3.1 to 3.4 for the channel 2 Mic input.
4.Channel 1 and 2 Mic Input Phantom Power Test
4.1Plug an XLR connector into the channel 1 Mic input. Do not connect any cables to the channel 1 or channel 2 Mic inputs. Power on the unit.
4.2Press the channel 1 phantom power switch. Verify that the LED lights. Using a DMM, measure the DC voltage level across pins 1 and 2 of the XLR connector. Verify that the DC level is +24Vdc + 1Vdc relative to pin 1.
4.3Measure the DC voltage level across pins 1 and 3 of the XLR connector. Verify that the DC level is +24Vdc + 1Vdc relative to pin 1.
4.4Repeat steps 4.1 to 4.3 for channel 2.
5.Channel 1 and 2 Line Input Gain Tests
5.1Place a 1/4” mono shorting plug into the Amp 2 IN and Amp 3 IN jacks on the right hand side of the input/output panel. This will disable the channel 2 and 3 amplifiers while testing the channel 1 amplifier.
5.2On the left hand side of the input/output panel, set the channel 1 Mic Trim control to the 6 setting. Ensure that the Phantom Power push button is not pushed in.
5.3Using an unbalanced 1/4” phono jack input cable, apply a 1 kHz, -10 dBV signal to the channel 1 input.
5.4Reference a dB meter to the input level. Measure the gain output at the Amp 1 OUT jack. It should be +28.5 dB + 4 dB.
5.5On the signal generator, turn the input level all the way down. Verify that the channel 1 Signal/OL LED is off. Increase the signal generator level. Verify that the LED lights green. Increase the signal level again and verify that the LED lights red.
Note: You may have to increase the Mic Trim level on the PS1 channel 1 input as well to get the LED to light red.
5.5Move the shorting plug from the Amp 2 IN jack to the Amp 1 IN jack and repeat steps 5.1 to 5.5 for the channel 2 Line input.
6.Channel 1 and 2 Line Input Frequency Reponse and Distortion Tests
6.1Place a 1/4” mono shorting plug into the Amp 2 IN and Amp 3 IN jacks on the right hand side of the input/output panel. This will disable the channel 2 and 3 amplifiers while testing the channel 1 amplifier.
6.2On the left hand side of the input/output panel, set the channel 1 Mic Trim control to the 6 setting. Ensure that the Phantom Power push button is not pushed in.
87
Test Procedures
6.3Using an unbalanced 1/4” phono jack input cable, apply a 1 kHz, -10 dBV signal to the channel 1 input.
6.4Use an 80 kHz low-pass filter on your measuring equipment. Reference a dB meter to the input level. Measure the frequency response at the Amp 1 OUT jack. It should be 0 dB + 3 dB from 30 Hz to 15 kHz.
6.5Measure the Total Harmonic Distortion (THD) level at the Amp 1 OUT jack. It should be 0.25% max at 1 kHz and 1.5% max at 15 kHz.
6.6Move the shorting plug from the Amp 2 IN jack to the Amp 1 IN jack and repeat steps 6.1 to 6.5 for the channel 2 Line input.
7.Channel 1 and 2 Line Input Signal to Noise Ratio (Dynamic Range) Tests
7.1Place a 1/4” mono shorting plug into the Amp 2 IN and Amp 3 IN jacks on the right hand side of the input/output panel. This will disable the channel 2 and 3 amplifiers while testing the channel 1 amplifier.
7.2On the left hand side of the input/output panel, set the channel 1 Mic Trim control to the 6 setting. Ensure that the Phantom Power push button is not pushed in.
7.3Using an unbalanced 1/4” phono jack input cable, apply a 1 kHz, -10 dBV signal to the channel 1 input.
7.4Reference a dB meter to the output level at the Amp 1 OUT jack. Remove the input signal and measure the A-Weighted output level. It should be -80 dB minimum.
7.5Move the shorting plug from the Amp 2 IN jack to the Amp 1 IN jack and repeat steps 7.1 to 7.4 for the channel 2 Line input.
8.Channel 3 and 4 Line Input Gain Tests
8.1Place a 1/4” mono shorting plug into the Amp 1 IN and Amp 2 IN jacks on the right hand side of the input/output panel. This will disable the channel 1 and 2 amplifiers while testing the channel 3 amplifier.
8.2On the left hand side of the input/output panel, set the channel 3 Level control to the 6 setting.
8.3Using an unbalanced 1/4” phono jack input cable, apply a 1 kHz, -20 dBV signal to the channel 1 input.
8.4Reference a dB meter to the input level. Measure the gain output at the Bass/Amp 3 OUT jack. It should be +40.1 dB + 3 dB.
8.5Repeat steps 8.1 to 8.4 for the channel 4 Line input.
9.Channel 3 and 4 Line Input Frequency Reponse and Distortion Tests
9.1Place a 1/4” mono shorting plug into the Amp 1 IN and Amp 2 IN jacks on the right hand side of the input/output panel. This will disable the channel 1 and 2 amplifiers while testing the channel 3 amplifier.
9.2On the left hand side of the input/output panel, set the channel 4 Mic Trim control to the 6 setting.
9.3Using an unbalanced 1/4” phono jack input cable, apply a 1 kHz, -20 dBV signal to the channel 1 input.
9.4Use an 80 kHz low-pass filter on your measuring equipment. Reference a dB meter to the input level. Measure the frequency response at the Amp 1 OUT jack. It should be 0 dB + 3 dB from 30 Hz to 15 kHz.
9.5Measure the Total Harmonic Distortion (THD) level at the Amp 1 OUT jack. It should be 0.25% max at 1 kHz and 1.5% max at 15 kHz.
88

Test Procedures
9.6Repeat steps 9.1 to 9.5 for the channel 4 Line input.
10.Channel 3 and 4 Line Input Signal to Noise Ratio (Dynamic Range) Tests
10.1Place a 1/4” mono shorting plug into the Amp 1 IN and Amp 2 IN jacks on the right hand side of the input/output panel.
This will disable the channel 1 and 2 amplifiers while testing the channel 3 amplifier.
10.2On the left hand side of the input/ output panel, set the channel 3 Level control to the 6 setting.
10.3Using an unbalanced 1/4” phono jack input cable, apply a 1 kHz, -10 dBV signal to the channel 1 input.
10.4Reference a dB meter to the output level at the Bass/Amp 3 OUT jack. Remove the input signal and measure the A- Weighted output level. It should be -80 dB minimum.
10.5Repeat steps 10.1 to 10.4 for the channel 4 Line input.
11.Channel 1 and 2 Remote Control, Preset Switch and Insert Function Tests
11.1Connect the PS1 power stand to a known good L1 line array. Set the channel 1 preset switch to 00. Connect the remote control to the unit using the remote control MIDI cable supplied with the PS1.
11.2Connect an analog audio source to the Channel 1 line input 1/4 inch jack. This source can be a CD player with a music disc.
11.3Adjust the trim level so that the LED is lit mostly green. The audio should sound normal.
11.4With the audio playing, change the channel 1 preset to 97 and back to 00. The channel should mute gracefully when the preset switch is operated. The audio should fade back in again about a second after the switch has stopped operating.
Note: Preset 97 is a 1 kHz band pass (telephone-type sound). Preset 00 should sound normal.
11.5Operate all channel 1 controls on the remote (high, mid, low, volume and master volume). All tone controls should have a clearly audible effect and operate smoothly. Channel volume may display a little “zipper” noise, which is normal.
Note: Channel volume all the way down does not mute the channel, but the output level should be very low. There is a small, but noticeable time delay between operating the control and the audible effect. This is normal. The master volume control should operate smoothly without any artifacts.
11.6Insert a 1/4 inch phono jack all the way into the channel 1 Insert jack. The audio should sound normal.
11.7Insert a 1/4 inch phono jack into the channel 3 Line IN jack and operate the volume control on the power stand. The audio should sound normal.
11.8Repeat steps 11.1 to 11.7 for the channel 2 input.
12.Channel 1 Send, Line Output and Digital Output Tests
Note: For these tests you will need an external device that can accept both 1/4 inch and XLR inputs. A small mixer, such as a Mackie or Behringer with headphones connected works well for this. The master volume control on the PS1’s remote control should be set all the way down to mute all sound coming from the unit under test.
89

Test Procedures
12.1Connect the PS1 power stand to a known good L1 line array. Set the channel 1 preset switch to 00. Connect the remote control to the unit using the remote control MIDI cable supplied with the PS1.
12.2Connect an analog audio source to the Channel 1 Line IN 1/4 inch jack. This source can be a CD player with a music disc.
12.3Adjust the trim level so that the LED is lit mostly green. The audio should sound normal.
12.4Insert a 1/4 inch plug halfway into the channel 1 Insert jack. The audio should sound normal.
12.5Connect the PS1 channel 1 XLR Line OUT jack to the XLR input of the mixer. The audio should sound normal.
Note: The PS1 puts out a “professional” +4dBu level. You may have to turn the the input trim control on the mixer all the way down to prevent overloading the signal and distorting it.
12.6Connect the Data Out jack of the PS1 to a device that accepts a 48 kHz S/PDIF data stream. The audio should sound normal.
13.Power Amplifier Tests
13.1Connect the PS1 power stand to a known good L1 line array. Set the channel 1 preset switch to 00. Connect the remote control to the unit using the remote control MIDI cable supplied with the PS1.
13.2Connect an analog audio source to the Amp 1 IN 1/4 inch phono jack. This source can be a CD player with a music disc.
13.3Verify that the audio comes from the upper section of the L1 line array. The audio should sound clean and undistorted.
13.4Connect the audio source to the Amp 2 IN 1/4 inch phono jack. Verify that the audio comes from the lower section of the L1 line array. The audio should sound clean and undistorted.
13.5Connect a B1 bass module to the PS1 power stand at the Bass/Amp 3 OUT jack. Connect the audio source to the Amp 3 IN 1/4 inch phono jack. Sound should come from the bass module only and be clean and undistorted.
13.6Connect the audio source to the All Amps IN 1/4 inch phono jack. Sound should come from both of the L1 line array sections and the bass module simultaneously. The audio should be clear and undistorted.
14.High SPL System Sweep Test
CAUTION: This test will be extremely loud. Hearing protection is advised.
14.1Connect a R1 remote control to the PS1 power stand under test. Set the channel 1 controls to mid-level. Set the master volume control on the remote to the 1 o’clock position. Set the channel 1 Mic Trim control on the PS1 to 6. Connect a L1 line array to the PS1. Connect a B1 bass module to the PS1.
14.2Connect a signal generator to the channel 1 input on the PS1. Adjust the signal generator and/or trim control so that the Signal/OL LED is just below red.
14.3Sweep the input frequency from 40 Hz to 14 kHz. Listen for any unusual noises and excessive distortion or drop-outs.
15.Bass Module Auto-EQ Test
15.1Connect a L1 line array to the PS1 power stand. Connect an R1 remote control to the power stand. Connect a B1 bass module to the Bass/Amp 3 OUT jack on the power stand. Connect an audio source to the channel 1 and 2 inputs of the power stand.
90
Test Procedures
15.2Set the channel 1 and 2 level controls to identical settings so that both LEDs are mainly green.
15.3While the audio is playing, disconnect the B1 bass module from the power stand. The system should mute and un-mute and audio should resume. The audio should sound normal, but not punchy (no deep bass).
15.4Plug a dummy 1/4 inch phono jack into the Bass Line Out jack. The system should mute and un-mute again, but the audio should sound thinner than before.
15.5Remove the dummy plug. The system should mute and un-mute and the audio should sound normal again.
15.6Re-connect the B1 bass module to the power stand. The audio should mute and unmute again and sound normal.
15.7Connect a second B1 bass module to the first one. The audio should mute and unmute. The audio will sound very similar to having only one bass module attached. Disconnect the second bass module. The system should mute and un-mute and the audio should sound normal again.
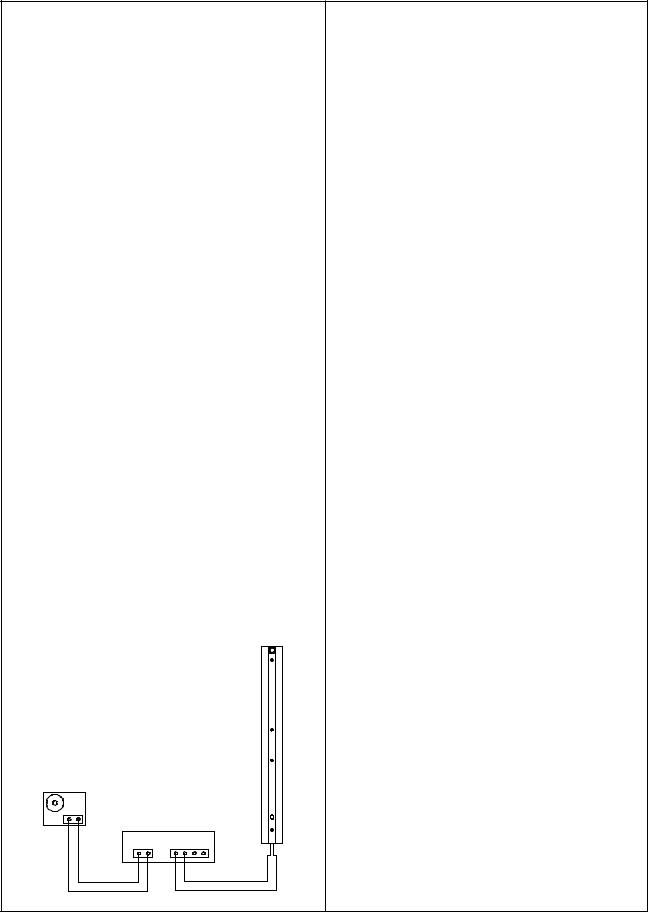
L1 Line Array Tests
Set up the unit under test as shown below.
Upper or Lower
L1 Line Array
Audio Signal
Generator
Power Amplifier
INPUT |
OUTPUT |
Upper or Lower L1
Line Array Test Cable
1.Air Leak Test
1.1Apply a 100 Hz, 10 Vrms sine wave to the unit under test.
1.2Listen carefully for air leaks from around the end cap, the transducers and the grille. Air leaks will be heard as a hissing or sputtering sound. All repairs must be hidden.
Test duration should be 5 seconds minimum.
2.Transducer Rub and Tick Test
2.1Remove the transducer you wish to test using the disassembly procedures in this manual. Do not unplug the wires at the transducer assembly terminals.
2.2Connect a signal generator directly to the terminals of the transducer assembly under test.
2.3Apply a 20 Hz, 5 Vrms signal to the transducer assembly.
2.4Listen carefully for any extraneous noises such as rubbing, scraping or ticking.
Note: To distinguish between normal suspension noise and rubs or ticks, displace the cone slightly with your fingers. If the noise stays the same, it is normal suspension noise and the driver is good. Suspension noise will not be heard with program material.
3.Transducer Phase Test
3.1Apply a DC voltage of 10V, positive applied to the positive tab of the dual banana jack on the line array test cable and negative applied to negative (gnd) tab.
3.2All of the driver cones should move outward when the DC voltage is applied.
3.3Rewire any incorrectly connected transducers.
91
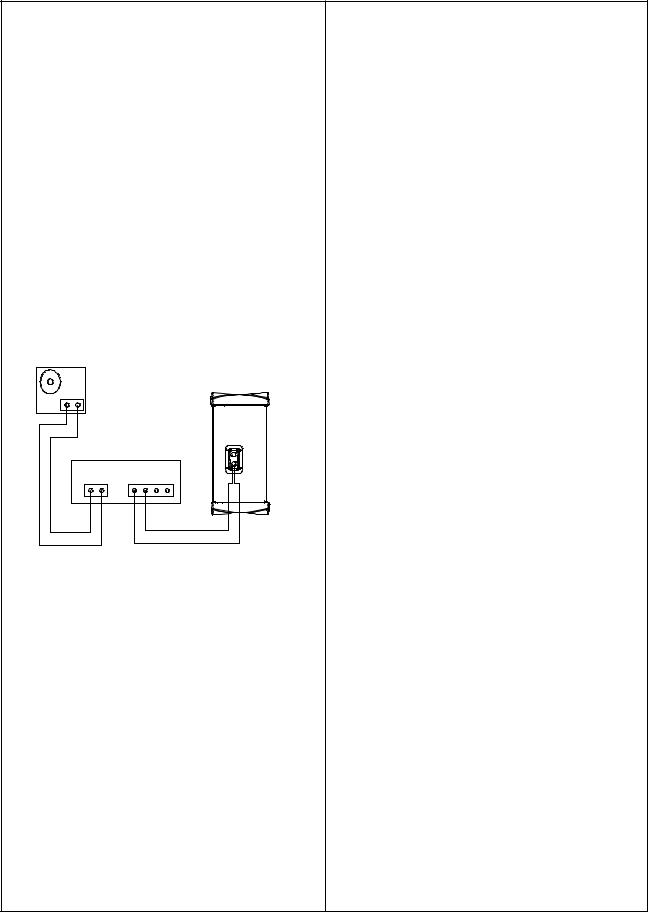
Test Procedures
4.L1 Line Array Sweep Test
4.1Set up the upper or lower line array section as shown in the figure on the previous page.
4.2Apply a 100 Hz, 10 Vrms sine wave to the input.
4.3While listening to the output of the system, sweep the input frequency slowly from 100 Hz to 15 kHz.
4.4Listen carefully for any extraneous noises such as buzzing and ticking.
B1 Bass Module Tests
Set up the unit under test as shown below.
Audio Signal
Generator
B1 Bass Module
Power Amplifier
INPUT OUTPUT
B1 Bass Module
Test Cable
1.Air Leak Test
1.1Apply a 100 Hz, 20 Vrms sine wave to the unit under test.
1.2Listen carefully for air leaks from around the end cap, the transducers and the grille. Air leaks will be heard as a hissing or sputtering sound. All repairs must be hidden.
Test duration should be 5 seconds minimum.
2.Transducer Rub and Tick Test
2.1Remove the transducer you wish to test using the disassembly procedures in this manual. Do not unplug the wires at the transducer assembly terminals.
2.2Connect a signal generator directly to the terminals of the transducer assembly under test.
2.3Apply a 10 Hz, 10 Vrms signal to the transducer assembly.
2.4Listen carefully for any extraneous noises such as rubbing, scraping or ticking.
Note: To distinguish between normal suspension noise and rubs or ticks, displace the cone slightly with your fingers. If the noise stays the same, it is normal suspension noise and the driver is good. Suspension noise will not be heard with program material.
3.Transducer Phase Test
3.1Apply a DC voltage of 20V, positive applied to the positive tab of the dual banana jack on the bass module test cable and negative applied to negative (gnd) tab.
3.2Notice carefully that all driver cones should move outward when the DC voltage is applied.
3.3Rewire any incorrectly connected transducers.
4.System Sweep Test
4.1Set up the system as shown in the figure at left.
4.2Apply a 10 Hz, 20 Vrms sine wave to the input.
4.3While listening to the output of the system, sweep the input frequency slowly from 10 Hz to 400 Hz.
4.4Listen carefully for any extraneous noises such as buzzing and ticking.
92

|
|
|
1 |
|
|
|
|
|
2 |
|
|
|
|
|
3 |
|
|
|
|
4 |
|
D |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
D |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
TH601 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
SCK2R515 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
! |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
C607 |
|
(TO AUX PS AND +/-27V PS) |
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2200uF 200V |
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1 |
2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
V+ |
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
! |
|
C603 |
|
|
|
! |
C605 |
|
! |
|
R603 |
|
(CN603,605,607,609) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1n5 |
DB601 |
|
100K 1/2W |
|
||||||
|
|
|
! |
|
|
! |
|
1n5 |
|
|
! |
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
! |
|
|
MB354S |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
! |
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
! |
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
C |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
C |
|
|
|
VDR601 |
|
R601 |
|
|
|
|
! |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
14D271K |
|
220K 3W |
! |
|
|
|
|
L603 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
L602 |
|
|
|
! |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
! |
3.8mH |
|
|
|
3.8mH |
|
C606 |
|
! |
|
! |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(16A) |
|
C604 |
|
|
(16A) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
! |
1n5 |
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1n5 |
1 |
2 |
|
L604 |
|
|
R604 |
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
C601 |
|
|
|
C602 |
|
|
|
|
1mH |
|
|
100K 1/2W |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(16A) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
1uF 300V |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
! |
|
1uF 300V |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ACGND |
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
TH602 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
C608 |
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
SCK2R515 |
|
|
|
|
ACGND |
(CN604,606,608,610) |
93 |
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2200uF 200V |
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
EGND |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(TO AUX PS AND +/-27V PS) |
||||
|
CN602 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
L |
E |
N |
|
( Earth GND) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
DT-4-3P |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
! |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
B |
F601 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
B |
15A 125VAC |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
! |
|
! |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
L601 |
70uH 6Ts |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
SW601 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
20A 125V |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
! |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
CN601 |
L |
E |
N |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
IEC |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
! |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
A |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
PS1 Power Stand |
A |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
FCC Filter PCB, Rev. F |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
120V Version 1.0 Systems |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
P/N: 275436 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Sheet 1 of 1 |
|
|
|
|
1 |
|
|
|
|
|
2 |
|
|
|
|
|
3 |
|
|
|
|
4 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
2 |
|
|
|
|
|
3 |
|
|
|
4 |
|
D |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
D |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
TH601 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
SCK0512 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
! |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
C607 |
(TO AUX PS AND +/-27V PS) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1 |
2 |
|
|
|
|
2200uF 200V |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
V+ |
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
C605 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
C603 |
|
|
|
! |
|
! |
R603 |
(CN603,605,607,609) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
! |
|
|
|
|
1nF |
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
DB601 |
|
|
||||||
C |
|
! |
|
|
! |
|
1nF |
|
|
! |
|
|
|
100K 1/2W |
C |
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
! |
|
|
|
GL3506 |
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
! |
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
! |
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
VDR601 |
|
R601 |
|
|
|
|
! |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
220K 3W |
! |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
14D471K |
|
L602 |
|
|
! |
|
L603 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
! |
3.8mH |
|
|
|
3.8mH |
|
C606 |
|
! |
! |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
C604 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
(16A) |
|
|
|
(16A) |
! |
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1nF |
|
|
1nF |
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1 |
2 |
|
L604 |
|
R604 |
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
C601 |
|
|
|
C602 |
|
|
|
|
1mH |
|
100K 1/2W |
94 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(16A) |
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
1uF 300V |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ACGND |
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
! |
|
1uF 300V |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
TH602 |
|
|
|
|
|
C608 |
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ACGND |
(CN604,606,608,610) |
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
SCK0512 |
|
|
|
|
|
2200uF 200V |
|
||
CN602 |
|
|
|
|
EGND |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(TO AUX PS AND +/-27V PS) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
( Earth GND) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
DT-4-3P |
L |
E |
N |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
! |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
B |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
B |
F601 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
10A 250VAC |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
! |
|
! |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
L601 |
|
70uH,6Ts |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
SW601 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
15A 250V |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
! |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
CN601 |
L |
E |
N |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
IEC |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
! |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
A |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
PS1 Power Stand |
A |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
FCC Filter PCB, Rev. F |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
120V Version 1.1 Systems |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
P/N: 283370 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Sheet 1 of 1 |
|
1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
2 |
|
|
|
|
|
3 |
|
|
|
4 |
|
 Loading...
Loading...