ATMEL ATmega324P User Manual

Features
• High-performance, Low-power AVR
®
8-bit Microcontroller
• Advanced RISC Architecture
– 131 Powerful Instructions – Most Single-clock Cycle Execution
–32 × 8 General Purpose Working Registers
– Fully Static Operation
– Up to 16 MIPS Throughput at 16 MHz
– On-chip 2-cycle Multiplier
• Nonvolatile Program and Data Memories
– 16/32/64K Bytes of In-System Self-Programmable Flash
Endurance: 10,000 Write/Erase Cycles
– Optional Boot Code Section with Independent Lock Bits
In-System Programming by On-chip Boot Program
True Read-While-Write Operation
– 512B/1K/2K Bytes EEPROM
Endurance: 100,000 Write/Erase Cycles
– 1/2/4K Bytes Internal SRAM
– Programming Lock for Software Security
• JTAG (IEEE std. 1149.1 Compliant) Interface
– Boundary-scan Capabilities According to the JTAG Standard
– Extensive On-chip Debug Support
– Programming of Flash, EEPROM, Fuses, and Lock Bits through the JTAG Interface
• Peripheral Features
– Two 8-bit Timer/Counters with Separate Prescalers and Compare Modes
– One 16-bit Timer/Counter with Separate Prescaler, Compare Mode, and Capture
Mode
– Real Time Counter with Separate Oscillator
– Six PWM Channels
– 8-channel, 10-bit ADC
Differential mode with selectable gain at 1x, 10x or 200x
(1)
– Byte-oriented Two-wire Serial Interface
– Two Programmable Serial USART
– Master/Slave SPI Serial Interface
– Programmable Watchdog Timer with Separate On-chip Oscillator
– On-chip Analog Comparator
– Interrupt and Wake-up on Pin Change
• Special Microcontroller Features
– Power-on Reset and Programmable Brown-out Detection
– Internal Calibrated RC Oscillator
– External and Internal Interrupt Sources
– Six Sleep Modes: Idle, ADC Noise Reduction, Power-save, Power-down, Standby
and Extended Standby
• I/O and Packages
– 32 Programmable I/O Lines
– 44-lead TQFP, and 44-pad QFN/MLF
• Operating Voltages
– 2.7 - 5.5V for ATmega164P/324P/644P
• Speed Grades
– ATmega164P/324P/644P: 0 - 8MHz @ 2.7 - 5.5V, 0 - 16MHz @ 4.5 - 5.5V
• Power Consumption at 8 MHz, 5V, 25°C for ATmega644P
– Active mode: 8 mA
– Idle mode: 2.4 mA
– Power-down Mode: 0.8 µA
8-bit
Microcontroller
with 16/32/64K
Bytes In-System
Programmable
Flash
ATmega164P
ATmega324P
ATmega644P
Automotive
7674E–AVR–02/09
BDTIC www.bdtic.com/ATMEL
2
7674E–AVR–02/09
ATmega164P/324P/644P
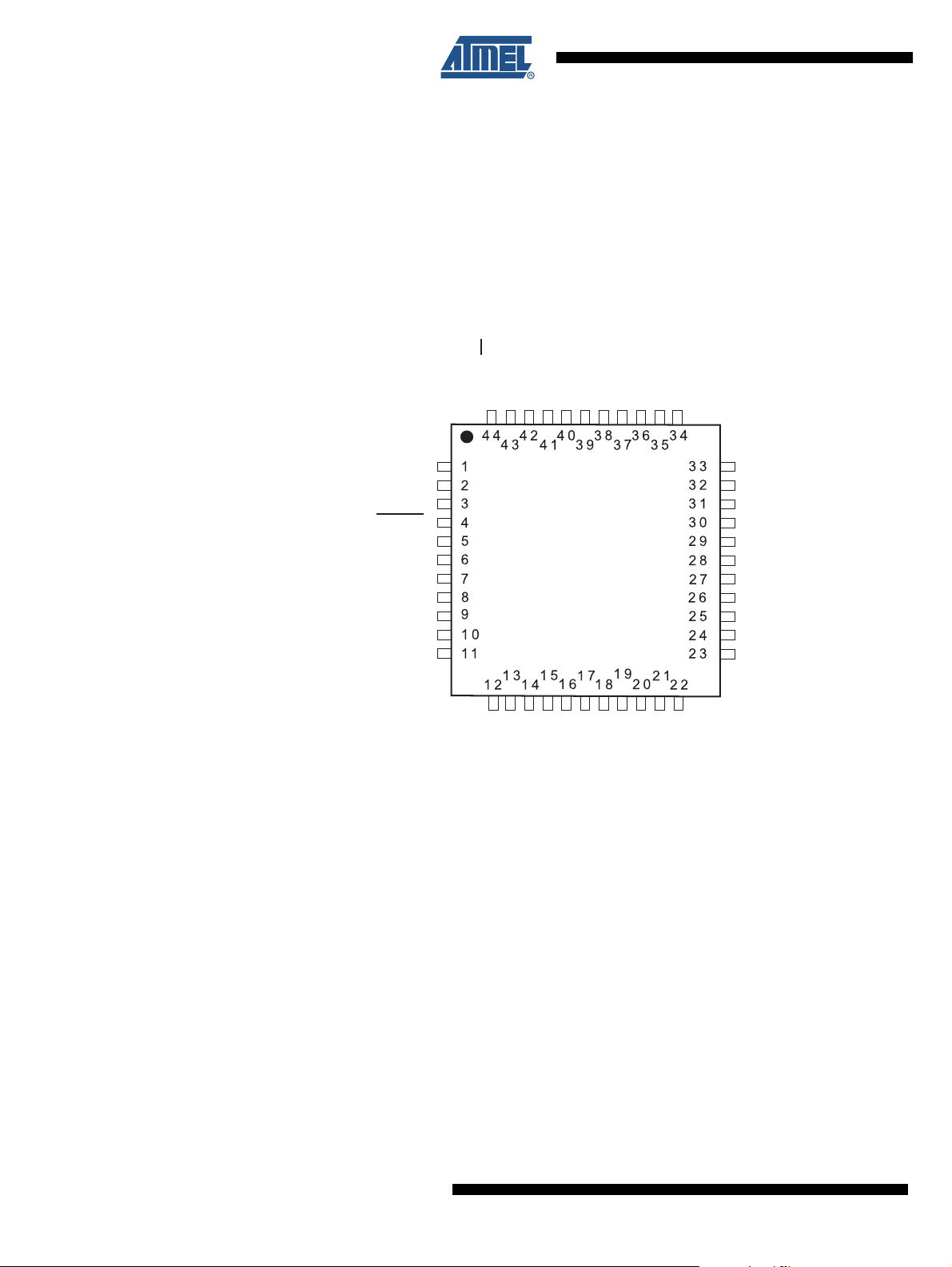
1. Pin Configurations
Figure 1-1. Pinout ATmega164P/324P/644P
Note: The large center pad underneath the QFN/MLF package should be soldered to ground on the
board to ensure good mechanical stability.
PA4 (ADC4/PCINT4)
PA5 (ADC5/PCINT5)
PA6 (ADC6/PCINT6)
PA7 (ADC7/PCINT7)
AREF
GND
AVCC
PC7 (TOSC2/PCINT23)
PC6 (TOSC1/PCINT22)
PC5 (TDI/PCINT21)
PC4 (TDO/PCINT20)
(PCINT13/MOSI) PB5
(PCINT14/MISO) PB6
(PCINT15/SCK) PB7
RESET
VCC
GND
XTAL2
XTAL1
(PCINT24/RXD0) PD0
(PCINT25/TXD0) PD1
(PCINT/RXD1/26/INT0) PD2
(PCINT/TXD1/27/INT1) PD3
(PCINT28/XCK1/OC1B) PD4
(PCINT29/OC1A) PD5
(PCINT30/OC2B/ICP) PD6
(PCINT31/OC2A) PD7
VCC
GND
(PCINT16/SCL) PC0
(PCINT17/SDA) PC1
(PCINT18/TCK) PC2
(PCINT19/TMS) PC3
PB4 (SS/OC0B/PCINT12)
PB3 (AIN1/OC0A/PCINT11)
PB2 (AIN0/INT2/PCINT10)
PB1 (T1/CLKO/PCINT9)
PB0 (XCK0/T0/PCINT8)
GND
VCC
PA0 (ADC0/PCINT0)
PA1 (ADC1/PCINT1)
PA2 (ADC2/PCINT2)
PA3 (ADC3/PCINT3)
TQFP/QF
N
/
M
LF
3
7674E–AVR–02/09
ATmega164P/324P/644P
2. Overview
The ATmega164P/324P/644P is a low-power CMOS 8-bit microcontroller based on the AVR
enhanced RISC architecture. By executing powerful instructions in a single clock cycle, the
ATmega164P/324P/644P achieves throughputs approaching 1 MIPS per MHz allowing the sys-
tem designer to optimize power consumption versus processing speed.
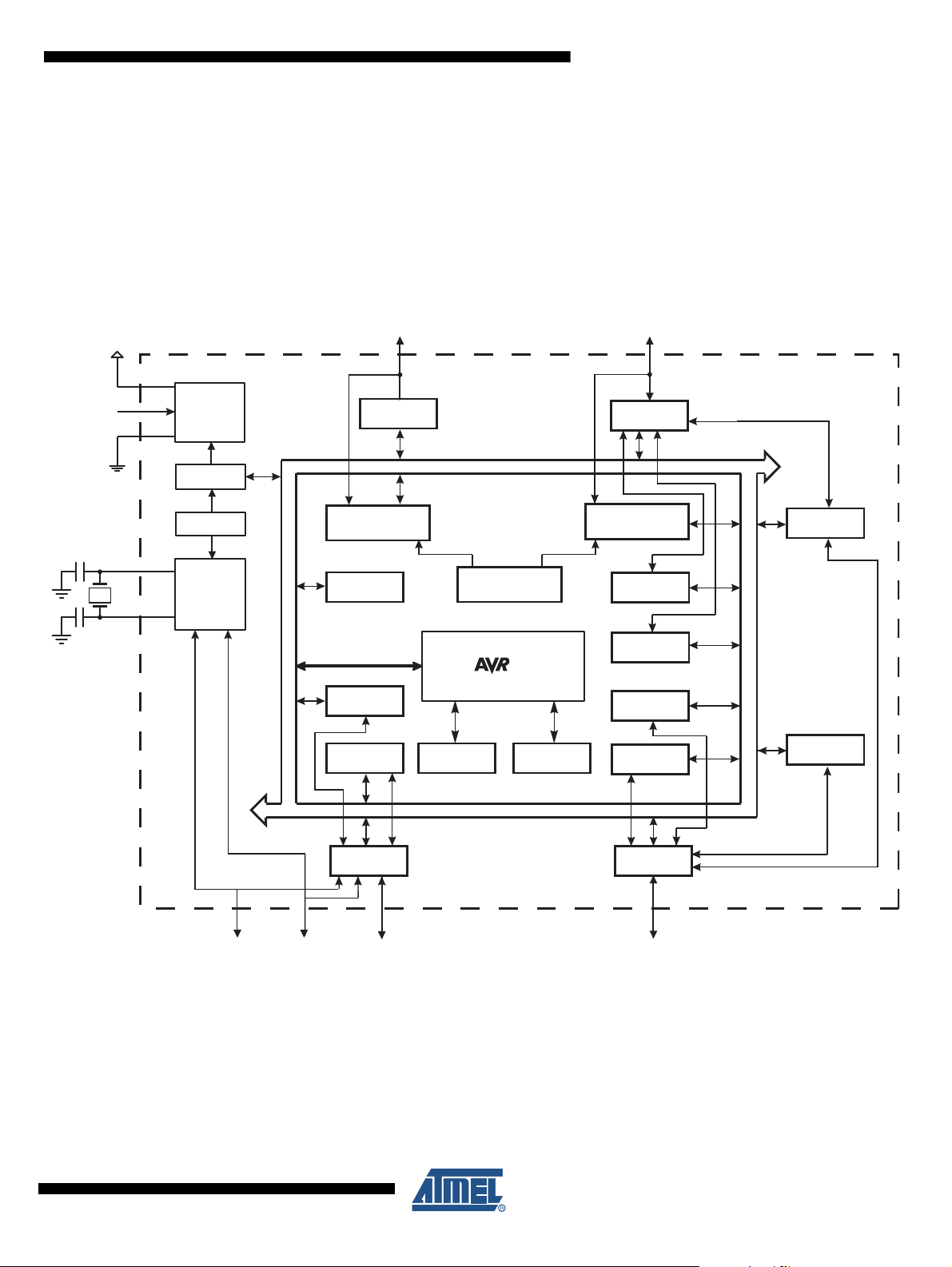
2.1 Block Diagram
Figure 2-1. Block Diagram
The AVR core combines a rich instruction set with 32 general purpose working registers. All the
32 registers are directly connected to the Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU), allowing two independent
registers to be accessed in one single instruction executed in one clock cycle. The resulting
architecture is more code efficient while achieving throughputs up to ten times faster than con-
ventional CISC microcontrollers.
CPU
GND
VCC
RESET
Powe r
Supervision
POR / BOD &
RESET
Watchdog
Oscillator
Watchdog
Timer
Oscillator
Circuits /
Clock
Generation
XTAL1
XTAL2
PORT A (8)
PORT D (8)
PD7..0
PORT C (8)
PC5..0
TWI
SPI
EEPROM
JTAG/OCD
16bit T/C 1
8bit T/C 2
8bit T/C 0
SRAMFLASH
USART 0
Internal
Bandgap reference
Analog
Comparator
A/D
Converter
PA7..0
PORT B (8)
PB7..0
USART 1
TOSC1/PC6TOSC2/PC7
4
7674E–AVR–02/09
ATmega164P/324P/644P
The ATmega164P/324P/644P provides the following features: 16/32/64K bytes of In-System
Programmable Flash with Read-While-Write capabilities, 512B/1K/2K bytes EEPROM, 1/2/4K
bytes SRAM, 32 general purpose I/O lines, 32 general purpose working registers, Real Time
Counter (RTC), three flexible Timer/Counters with compare modes and PWM, 2 USARTs, a byte
oriented 2-wire Serial Interface, a 8-channel, 10-bit ADC with optional differential input stage
with programmable gain, programmable Watchdog Timer with Internal Oscillator, an SPI serial
port, IEEE std. 1149.1 compliant JTAG test interface, also used for accessing the On-chip
Debug system and programming and six software selectable power saving modes. The Idle
mode stops the CPU while allowing the SRAM, Timer/Counters, SPI port, and interrupt system
to continue functioning. The Power-down mode saves the register contents but freezes the
Oscillator, disabling all other chip functions until the next interrupt or Hardware Reset. In
Power-save mode, the asynchronous timer continues to run, allowing the user to maintain a
timer base while the rest of the device is sleeping. The ADC Noise Reduction mode stops the
CPU and all I/O modules except Asynchronous Timer and ADC, to minimize switching noise
during ADC conversions. In Standby mode, the Crystal/Resonator Oscillator is running while the
rest of the device is sleeping. This allows very fast start-up combined with low power consump-
tion. In Extended Standby mode, both the main Oscillator and the Asynchronous Timer continue
to run.
The device is manufactured using Atmel’s high-density nonvolatile memory technology. The
On-chip ISP Flash allows the program memory to be reprogrammed in-system through an SPI
serial interface, by a conventional nonvolatile memory programmer, or by an On-chip Boot pro-
gram running on the AVR core. The boot program can use any interface to download the
application program in the application Flash memory. Software in the Boot Flash section will
continue to run while the Application Flash section is updated, providing true Read-While-Write
operation. By combining an 8-bit RISC CPU with In-System Self-Programmable Flash on a
monolithic chip, the Atmel ATmega164P/324P/644P is a powerful microcontroller that provides a
highly flexible and cost effective solution to many embedded control applications.
The ATmega164P/324P/644P AVR is supported with a full suite of program and system devel-
opment tools including: C compilers, macro assemblers, program debugger/simulators, in-circuit
emulators, and evaluation kits.
2.2 Comparison Between ATmega164P, ATmega324P and ATmega644P
Table 2-1. Differences between ATmega164P and ATmega644P
Device Flash EEPROM RAM
ATmega164P 16 Kbyte 512 Bytes 1 Kbyte
ATmega324P 32 Kbyte 1 Kbyte 2 Kbyte
ATmega644P 64 Kbyte 2 Kbyte 4 Kbyte

5
7674E–AVR–02/09
ATmega164P/324P/644P
2.2.1 Automotive Quality Grade
The ATmega164P/324P/644P have been developed and manufactured according to the most
stringent requirements of the international standard ISO-TS-16949. This data sheet contains
limit values extracted from the results of extensive characterization (Temperature and Voltage).
The quality and reliability of the ATmega164P/324P/644P have been verified during regular
product qualification as per AEC-Q100 grade 1 (–40°C to +125°C).
2.3 Pin Descriptions
2.3.1 VCC
Digital supply voltage.
2.3.2 GND
Ground.
2.3.3 Port A (PA7:PA0)
Port A serves as analog inputs to the Analog-to-digital Converter.
Port A also serves as an 8-bit bi-directional I/O port with internal pull-up resistors (selected for
each bit). The Port A output buffers have symmetrical drive characteristics with both high sink
and source capability. As inputs, Port A pins that are externally pulled low will source current if
the pull-up resistors are activated. The Port A pins are tri-stated when a reset condition becomes
active, even if the clock is not running.
Port A also serves the functions of various special features of the ATmega164P/324P/644P as
listed on page 79.
2.3.4 Port B (PB7:PB0)
Port B is an 8-bit bi-directional I/O port with internal pull-up resistors (selected for each bit). The
Port B output buffers have symmetrical drive characteristics with both high sink and source
capability. As inputs, Port B pins that are externally pulled low will source current if the pull-up
resistors are activated. The Port B pins are tri-stated when a reset condition becomes active,
even if the clock is not running.
Port B also serves the functions of various special features of the ATmega164P/324P/644P as
listed on page 81.
Table 2-2. Temperature Grade Identification for Automotive Products
Temperature
Temperature
Identifier Comments
-40 ; +125 Z Full AutomotiveTemperature Range

6
7674E–AVR–02/09
ATmega164P/324P/644P
2.3.5 Port C (PC7:PC0)
Port C is an 8-bit bi-directional I/O port with internal pull-up resistors (selected for each bit). The
Port C output buffers have symmetrical drive characteristics with both high sink and source
capability. As inputs, Port C pins that are externally pulled low will source current if the pull-up
resistors are activated. The Port C pins are tri-stated when a reset condition becomes active,
even if the clock is not running.
Port C also serves the functions of the JTAG interface, along with special features of the
ATmega164P/324P/644P as listed on page 84.
2.3.6 Port D (PD7:PD0)
Port D is an 8-bit bi-directional I/O port with internal pull-up resistors (selected for each bit). The
Port D output buffers have symmetrical drive characteristics with both high sink and source
capability. As inputs, Port D pins that are externally pulled low will source current if the pull-up
resistors are activated. The Port D pins are tri-stated when a reset condition becomes active,
even if the clock is not running.
Port D also serves the functions of various special features of the ATmega164P/324P/644P as
listed on page 86.
2.3.7
RESET
Reset input. A low level on this pin for longer than the minimum pulse length will generate a
reset, even if the clock is not running. The minimum pulse length is given in “System and Reset
Characteristics” on page 332. Shorter pulses are not guaranteed to generate a reset.
2.3.8 XTAL1
Input to the inverting Oscillator amplifier and input to the internal clock operating circuit.
2.3.9 XTAL2
Output from the inverting Oscillator amplifier.
2.3.10 AVCC
AVCC is the supply voltage pin for Port F and the Analog-to-digital Converter. It should be exter-
nally connected to V
CC
, even if the ADC is not used. If the ADC is used, it should be connected
to V
CC
through a low-pass filter.
2.3.11 AREF
This is the analog reference pin for the Analog-to-digital Converter.

7
7674E–AVR–02/09
ATmega164P/324P/644P
3. Resources
A comprehensive set of development tools, application notes and datasheetsare available for
download on http://www.atmel.com/avr.

8
7674E–AVR–02/09
ATmega164P/324P/644P
4. About Code Examples
This documentation contains simple code examples that briefly show how to use various parts of
the device. Be aware that not all C compiler vendors include bit definitions in the header files
and interrupt handling in C is compiler dependent. Please confirm with the C compiler documen-
tation for more details.
The code examples assume that the part specific header file is included before compilation. For
I/O registers located in extended I/O map, "IN", "OUT", "SBIS", "SBIC", "CBI", and "SBI" instruc-
tions must be replaced with instructions that allow access to extended I/O. Typically "LDS" and
"STS" combined with "SBRS", "SBRC", "SBR", and "CBR".

9
7674E–AVR–02/09
ATmega164P/324P/644P
5. AVR CPU Core
5.1 Overview
This section discusses the AVR core architecture in general. The main function of the CPU core
is to ensure correct program execution. The CPU must therefore be able to access memories,
perform calculations, control peripherals, and handle interrupts.
Figure 5-1. Block Diagram of the AVR Architecture
In order to maximize performance and parallelism, the AVR uses a Harvard architecture – with
separate memories and buses for program and data. Instructions in the program memory are
executed with a single level pipelining. While one instruction is being executed, the next instruc-
tion is pre-fetched from the program memory. This concept enables instructions to be executed
in every clock cycle. The program memory is In-System Reprogrammable Flash memory.
Flash
Program
Memory
Instruction
Register
Instruction
Decoder
Program
Counter
Control Lines
32 x 8
General
Purpose
Registrers
ALU
Status
and Control
I/O Lines
EEPROM
Data Bus 8-bit
Data
SRAM
Direct Addressing
Indirect Addressing
Interrupt
Unit
SPI
Unit
Watchdog
Timer
Analog
Comparator
I/O Module 2
I/O Module1
I/O Module n

10
7674E–AVR–02/09
ATmega164P/324P/644P
The fast-access Register File contains 32 x 8-bit general purpose working registers with a single
clock cycle access time. This allows single-cycle Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU) operation. In a typ-
ical ALU operation, two operands are output from the Register File, the operation is executed,
and the result is stored back in the Register File – in one clock cycle.
Six of the 32 registers can be used as three 16-bit indirect address register pointers for Data
Space addressing – enabling efficient address calculations. One of the these address pointers
can also be used as an address pointer for look up tables in Flash program memory. These
added function registers are the 16-bit X-, Y-, and Z-register, described later in this section.
The ALU supports arithmetic and logic operations between registers or between a constant and
a register. Single register operations can also be executed in the ALU. After an arithmetic opera-
tion, the Status Register is updated to reflect information about the result of the operation.
Program flow is provided by conditional and unconditional jump and call instructions, able to
directly address the whole address space. Most AVR instructions have a single 16-bit word for-
mat. Every program memory address contains a 16- or 32-bit instruction.
Program Flash memory space is divided in two sections, the Boot Program section and the
Application Program section. Both sections have dedicated Lock bits for write and read/write
protection. The SPM instruction that writes into the Application Flash memory section must
reside in the Boot Program section.
During interrupts and subroutine calls, the return address Program Counter (PC) is stored on the
Stack. The Stack is effectively allocated in the general data SRAM, and consequently the Stack
size is only limited by the total SRAM size and the usage of the SRAM. All user programs must
initialize the SP in the Reset routine (before subroutines or interrupts are executed). The Stack
Pointer (SP) is read/write accessible in the I/O space. The data SRAM can easily be accessed
through the five different addressing modes supported in the AVR architecture.
The memory spaces in the AVR architecture are all linear and regular memory maps.
A flexible interrupt module has its control registers in the I/O space with an additional Global
Interrupt Enable bit in the Status Register. All interrupts have a separate Interrupt Vector in the
Interrupt Vector table. The interrupts have priority in accordance with their Interrupt Vector posi-
tion. The lower the Interrupt Vector address, the higher the priority.
The I/O memory space contains 64 addresses for CPU peripheral functions as Control Regis-
ters, SPI, and other I/O functions. The I/O Memory can be accessed directly, or as the Data
Space locations following those of the Register File, 0x20 - 0x5F. In addition, the
ATmega164P/324P/644P has Extended I/O space from 0x60 - 0xFF in SRAM where only the
ST/STS/STD and LD/LDS/LDD instructions can be used.
5.2 ALU – Arithmetic Logic Unit
The high-performance AVR ALU operates in direct connection with all the 32 general purpose
working registers. Within a single clock cycle, arithmetic operations between general purpose
registers or between a register and an immediate are executed. The ALU operations are divided
into three main categories – arithmetic, logical, and bit-functions. Some implementations of the
architecture also provide a powerful multiplier supporting both signed/unsigned multiplication
and fractional format. See the “Instruction Set” section for a detailed description.

11
7674E–AVR–02/09
ATmega164P/324P/644P
5.3 Status Register
The Status Register contains information about the result of the most recently executed arithme-
tic instruction. This information can be used for altering program flow in order to perform
conditional operations. Note that the Status Register is updated after all ALU operations, as
specified in the Instruction Set Reference. This will in many cases remove the need for using the
dedicated compare instructions, resulting in faster and more compact code.
The Status Register is not automatically stored when entering an interrupt routine and restored
when returning from an interrupt. This must be handled by software.
5.3.1 SREG – Status Register
The AVR Status Register – SREG – is defined as:
• Bit 7 – I: Global Interrupt Enable
The Global Interrupt Enable bit must be set for the interrupts to be enabled. The individual inter-
rupt enable control is then performed in separate control registers. If the Global Interrupt Enable
Register is cleared, none of the interrupts are enabled independent of the individual interrupt
enable settings. The I-bit is cleared by hardware after an interrupt has occurred, and is set by
the RETI instruction to enable subsequent interrupts. The I-bit can also be set and cleared by
the application with the SEI and CLI instructions, as described in the instruction set reference.
• Bit 6 – T: Bit Copy Storage
The Bit Copy instructions BLD (Bit LoaD) and BST (Bit STore) use the T-bit as source or desti-
nation for the operated bit. A bit from a register in the Register File can be copied into T by the
BST instruction, and a bit in T can be copied into a bit in a register in the Register File by the
BLD instruction.
• Bit 5 – H: Half Carry Flag
The Half Carry Flag H indicates a Half Carry in some arithmetic operations. Half Carry Is useful
in BCD arithmetic. See the “Instruction Set Description” for detailed information.
• Bit 4 – S: Sign Bit, S = N
⊕ V
The S-bit is always an exclusive or between the Negative Flag N and the Two’s Complement
Overflow Flag V. See the “Instruction Set Description” for detailed information.
• Bit 3 – V: Two’s Complement Overflow Flag
The Two’s Complement Overflow Flag V supports two’s complement arithmetics. See the
“Instruction Set Description” for detailed information.
• Bit 2 – N: Negative Flag
The Negative Flag N indicates a negative result in an arithmetic or logic operation. See the
“Instruction Set Description” for detailed information.
• Bit 1 – Z: Zero Flag
Bit 76543210
0x3F (0x5F) ITHSVNZCSREG
Read/Write R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W
Initial Value00000000
12
7674E–AVR–02/09
ATmega164P/324P/644P
The Zero Flag Z indicates a zero result in an arithmetic or logic operation. See the “Instruction
Set Description” for detailed information.
• Bit 0 – C: Carry Flag
The Carry Flag C indicates a carry in an arithmetic or logic operation. See the “Instruction Set
Description” for detailed information.
5.4 General Purpose Register File
The Register File is optimized for the AVR Enhanced RISC instruction set. In order to achieve
the required performance and flexibility, the following input/output schemes are supported by the
Register File:
• One 8-bit output operand and one 8-bit result input
• Two 8-bit output operands and one 8-bit result input
• Two 8-bit output operands and one 16-bit result input
• One 16-bit output operand and one 16-bit result input
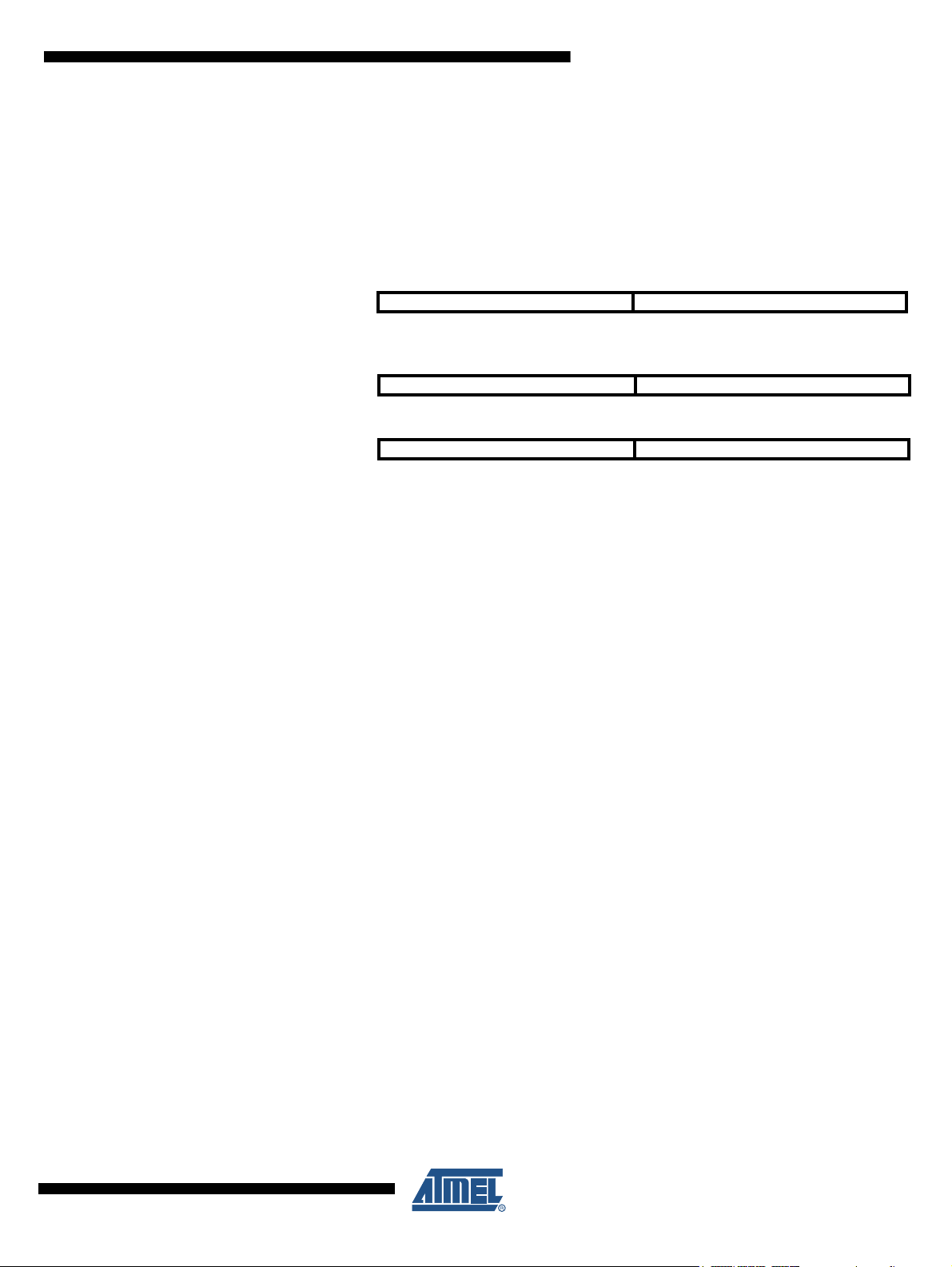
Figure 5-2 shows the structure of the 32 general purpose working registers in the CPU.
Figure 5-2. AVR CPU General Purpose Working Registers
Most of the instructions operating on the Register File have direct access to all registers, and
most of them are single cycle instructions.
As shown in Figure 5-2, each register is also assigned a data memory address, mapping them
directly into the first 32 locations of the user Data Space. Although not being physically imple-
mented as SRAM locations, this memory organization provides great flexibility in access of the
registers, as the X-, Y- and Z-pointer registers can be set to index any register in the file.
70Addr.
R0 0x00
R1 0x01
R2 0x02
…
R13 0x0D
General R14 0x0E
Purpose R15 0x0F
Working R16 0x10
Registers R17 0x11
…
R26 0x1A X-register Low Byte
R27 0x1B X-register High Byte
R28 0x1C Y-register Low Byte
R29 0x1D Y-register High Byte
R30 0x1E Z-register Low Byte
R31 0x1F Z-register High Byte
13
7674E–AVR–02/09
ATmega164P/324P/644P
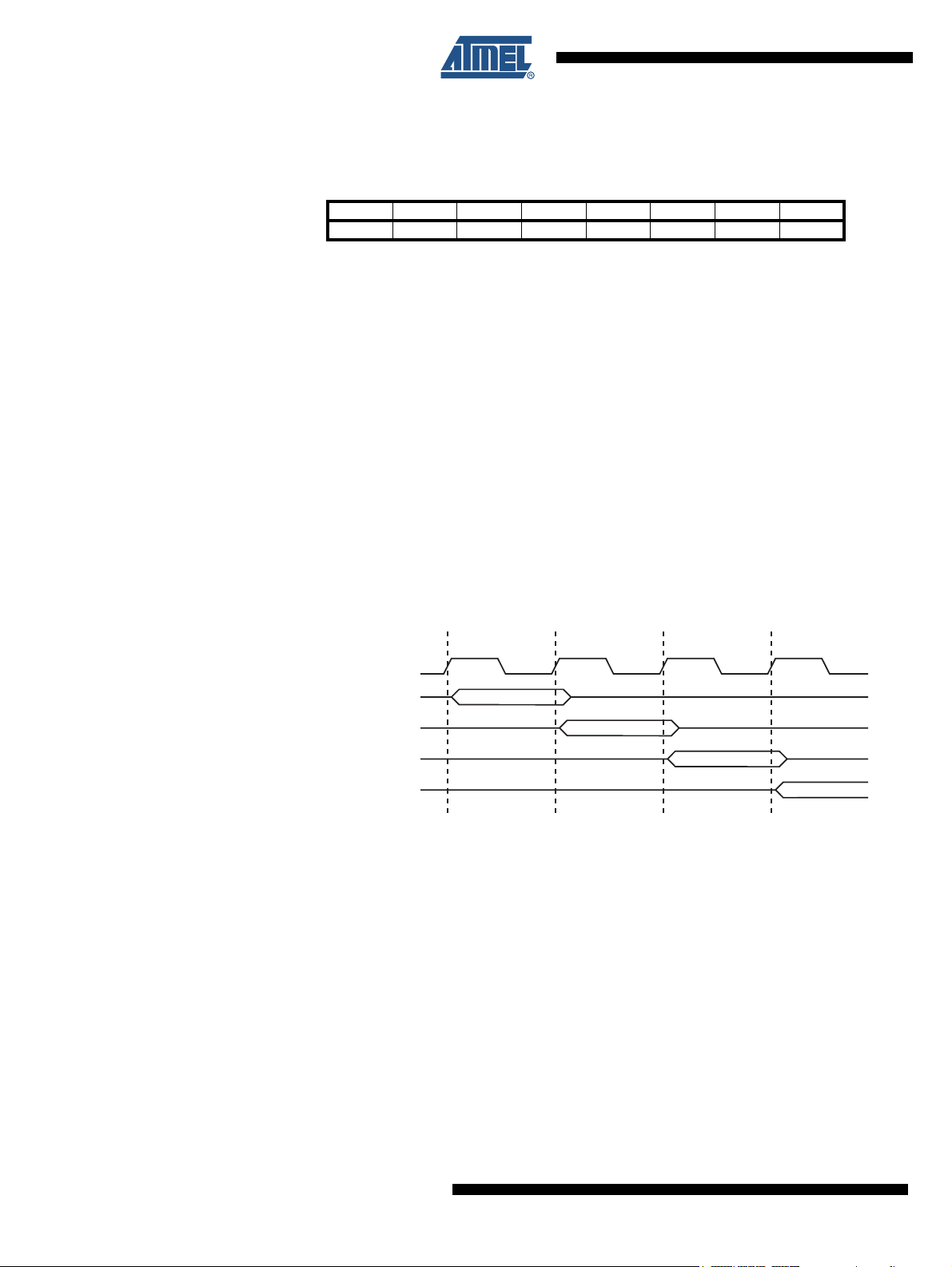
5.4.1 The X-register, Y-register, and Z-register
The registers R26..R31 have some added functions to their general purpose usage. These reg-
isters are 16-bit address pointers for indirect addressing of the data space. The three indirect
address registers X, Y, and Z are defined as described in Figure 5-3.
Figure 5-3. The X-, Y-, and Z-registers
In the different addressing modes these address registers have functions as fixed displacement,
automatic increment, and automatic decrement (see the instruction set reference for details).
5.5 Stack Pointer
The Stack is mainly used for storing temporary data, for storing local variables and for storing
return addresses after interrupts and subroutine calls. The Stack Pointer Register always points
to the top of the Stack. Note that the Stack is implemented as growing from higher memory loca-
tions to lower memory locations. This implies that a Stack PUSH command decreases the Stack
Pointer.
The Stack Pointer points to the data SRAM Stack area where the Subroutine and Interrupt
Stacks are located. This Stack space in the data SRAM must be defined by the program before
any subroutine calls are executed or interrupts are enabled. The Stack Pointer must be set to
point above 0x0100. The initial value of the stack pointer is the last address of the internal
SRAM. The Stack Pointer is decremented by one when data is pushed onto the Stack with the
PUSH instruction, and it is decremented by three when the return address is pushed onto the
Stack with subroutine call or interrupt. The Stack Pointer is incremented by one when data is
popped from the Stack with the POP instruction, and it is incremented by three when data is
popped from the Stack with return from subroutine RET or return from interrupt RETI.
The AVR Stack Pointer is implemented as two 8-bit registers in the I/O space. The number of
bits actually used is implementation dependent. Note that the data space in some implementa-
tions of the AVR architecture is so small that only SPL is needed. In this case, the SPH Register
will not be present.
15 XH XL 0
X-register 707 0
R27 (0x1B) R26 (0x1A)
15 YH YL 0
Y-register 707 0
R29 (0x1D) R28 (0x1C)
15 ZH ZL 0
Z-register 70 7 0
R31 (0x1F) R30 (0x1E)
14
7674E–AVR–02/09
ATmega164P/324P/644P
5.5.1 SPH and SPL – Stack Pointer High and Stack pointer Low
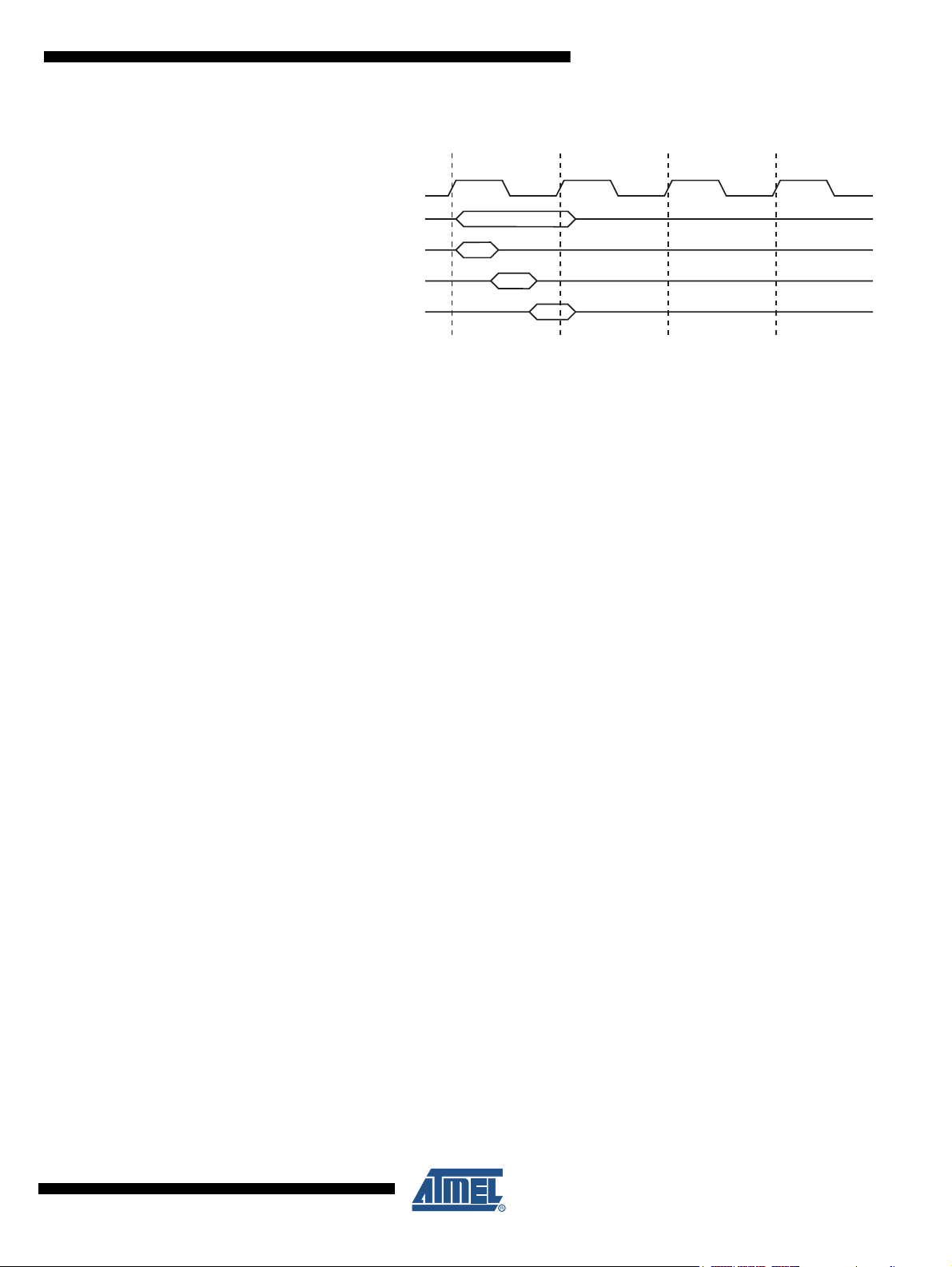
5.6 Instruction Execution Timing
This section describes the general access timing concepts for instruction execution. The AVR
CPU is driven by the CPU clock clk
CPU
, directly generated from the selected clock source for the
chip. No internal clock division is used.
Figure 5-4 on page 14 shows the parallel instruction fetches and instruction executions enabled
by the Harvard architecture and the fast-access Register File concept. This is the basic pipelin-
ing concept to obtain up to 1 MIPS per MHz with the corresponding unique results for functions
per cost, functions per clocks, and functions per power-unit.
Figure 5-4. The Parallel Instruction Fetches and Instruction Executions
Figure 5-5 shows the internal timing concept for the Register File. In a single clock cycle an ALU
operation using two register operands is executed, and the result is stored back to the destina-
tion register.
Bit 151413121110 9 8
0x3E (0x5E) – – – SP12 SP11 SP10 SP9 SP8 SPH
0x3D (0x5D) SP7 SP6 SP5 SP4 SP3 SP2 SP1 SP0 SPL
76543210
Read/Write R R R R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W
R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W
Initial Value 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0
11111111
clk
1st Instruction Fetch
1st Instruction Execute
2nd Instruction Fetch
2nd Instruction Execute
3rd Instruction Fetch
3rd Instruction Execute
4th Instruction Fetch
T1 T2 T3 T4
CPU
15
7674E–AVR–02/09
ATmega164P/324P/644P
Figure 5-5. Single Cycle ALU Operation
5.7 Reset and Interrupt Handling
The AVR provides several different interrupt sources. These interrupts and the separate Reset
Vector each have a separate program vector in the program memory space. All interrupts are
assigned individual enable bits which must be written logic one together with the Global Interrupt
Enable bit in the Status Register in order to enable the interrupt. Depending on the Program
Counter value, interrupts may be automatically disabled when Boot Lock bits BLB02 or BLB12
are programmed. This feature improves software security. See the section “Memory Program-
ming” on page 296 for details.
The lowest addresses in the program memory space are by default defined as the Reset and
Interrupt Vectors. The complete list of vectors is shown in “Interrupts” on page 60. The list also
determines the priority levels of the different interrupts. The lower the address the higher is the
priority level. RESET has the highest priority, and next is INT0 – the External Interrupt Request
0. The Interrupt Vectors can be moved to the start of the Boot Flash section by setting the IVSEL
bit in the MCU Control Register (MCUCR). Refer to “Interrupts” on page 60 for more information.
The Reset Vector can also be moved to the start of the Boot Flash section by programming the
BOOTRST Fuse, see “Memory Programming” on page 296.
When an interrupt occurs, the Global Interrupt Enable I-bit is cleared and all interrupts are dis-
abled. The user software can write logic one to the I-bit to enable nested interrupts. All enabled
interrupts can then interrupt the current interrupt routine. The I-bit is automatically set when a
Return from Interrupt instruction – RETI – is executed.
There are basically two types of interrupts. The first type is triggered by an event that sets the
Interrupt Flag. For these interrupts, the Program Counter is vectored to the actual Interrupt Vec-
tor in order to execute the interrupt handling routine, and hardware clears the corresponding
Interrupt Flag. Interrupt Flags can also be cleared by writing a logic one to the flag bit position(s)
to be cleared. If an interrupt condition occurs while the corresponding interrupt enable bit is
cleared, the Interrupt Flag will be set and remembered until the interrupt is enabled, or the flag is
cleared by software. Similarly, if one or more interrupt conditions occur while the Global Interrupt
Enable bit is cleared, the corresponding Interrupt Flag(s) will be set and remembered until the
Global Interrupt Enable bit is set, and will then be executed by order of priority.
The second type of interrupts will trigger as long as the interrupt condition is present. These
interrupts do not necessarily have Interrupt Flags. If the interrupt condition disappears before the
interrupt is enabled, the interrupt will not be triggered.
Total Execution Time
Register Operands Fetch
ALU Operation Execute
Result Write Back
T1 T2 T3 T4
clk
CPU

16
7674E–AVR–02/09
ATmega164P/324P/644P
When the AVR exits from an interrupt, it will always return to the main program and execute one
more instruction before any pending interrupt is served.
Note that the Status Register is not automatically stored when entering an interrupt routine, nor
restored when returning from an interrupt routine. This must be handled by software.
When using the CLI instruction to disable interrupts, the interrupts will be immediately disabled.
No interrupt will be executed after the CLI instruction, even if it occurs simultaneously with the
CLI instruction. The following example shows how this can be used to avoid interrupts during the
timed EEPROM write sequence..
When using the SEI instruction to enable interrupts, the instruction following SEI will be exe-
cuted before any pending interrupts, as shown in this example.
Assembly Code Example
in r16, SREG ; store SREG value
cli ; disable interrupts during timed sequence
sbi EECR, EEMPE ; start EEPROM write
sbi EECR, EEPE
out SREG, r16 ; restore SREG value (I-bit)
C Code Example
char cSREG;
cSREG = SREG; /* store SREG value */
/* disable interrupts during timed sequence */
__disable_interrupt();
EECR |= (1<<EEMPE); /* start EEPROM write */
EECR |= (1<<EEPE);
SREG = cSREG; /* restore SREG value (I-bit) */
Assembly Code Example
sei ; set Global Interrupt Enable
sleep; enter sleep, waiting for interrupt
; note: will enter sleep before any pending
; interrupt(s)
C Code Example
__enable_interrupt(); /* set Global Interrupt Enable */
__sleep(); /* enter sleep, waiting for interrupt */
/* note: will enter sleep before any pending interrupt(s) */

17
7674E–AVR–02/09
ATmega164P/324P/644P
5.7.1 Interrupt Response Time
The interrupt execution response for all the enabled AVR interrupts is five clock cycles minimum.
After five clock cycles the program vector address for the actual interrupt handling routine is exe-
cuted. During these five clock cycle period, the Program Counter is pushed onto the Stack. The
vector is normally a jump to the interrupt routine, and this jump takes three clock cycles. If an
interrupt occurs during execution of a multi-cycle instruction, this instruction is completed before
the interrupt is served. If an interrupt occurs when the MCU is in sleep mode, the interrupt exe-
cution response time is increased by five clock cycles. This increase comes in addition to the
start-up time from the selected sleep mode.
A return from an interrupt handling routine takes five clock cycles. During these five clock cycles,
the Program Counter (three bytes) is popped back from the Stack, the Stack Pointer is incre-
mented by three, and the I-bit in SREG is set.

18
7674E–AVR–02/09
ATmega164P/324P/644P
6. AVR Memories
6.1 Overview
This section describes the different memories in the ATmega164P/324P/644P. The AVR archi-
tecture has two main memory spaces, the Data Memory and the Program Memory space. In
addition, the ATmega164P/324P/644P features an EEPROM Memory for data storage. All three
memory spaces are linear and regular.
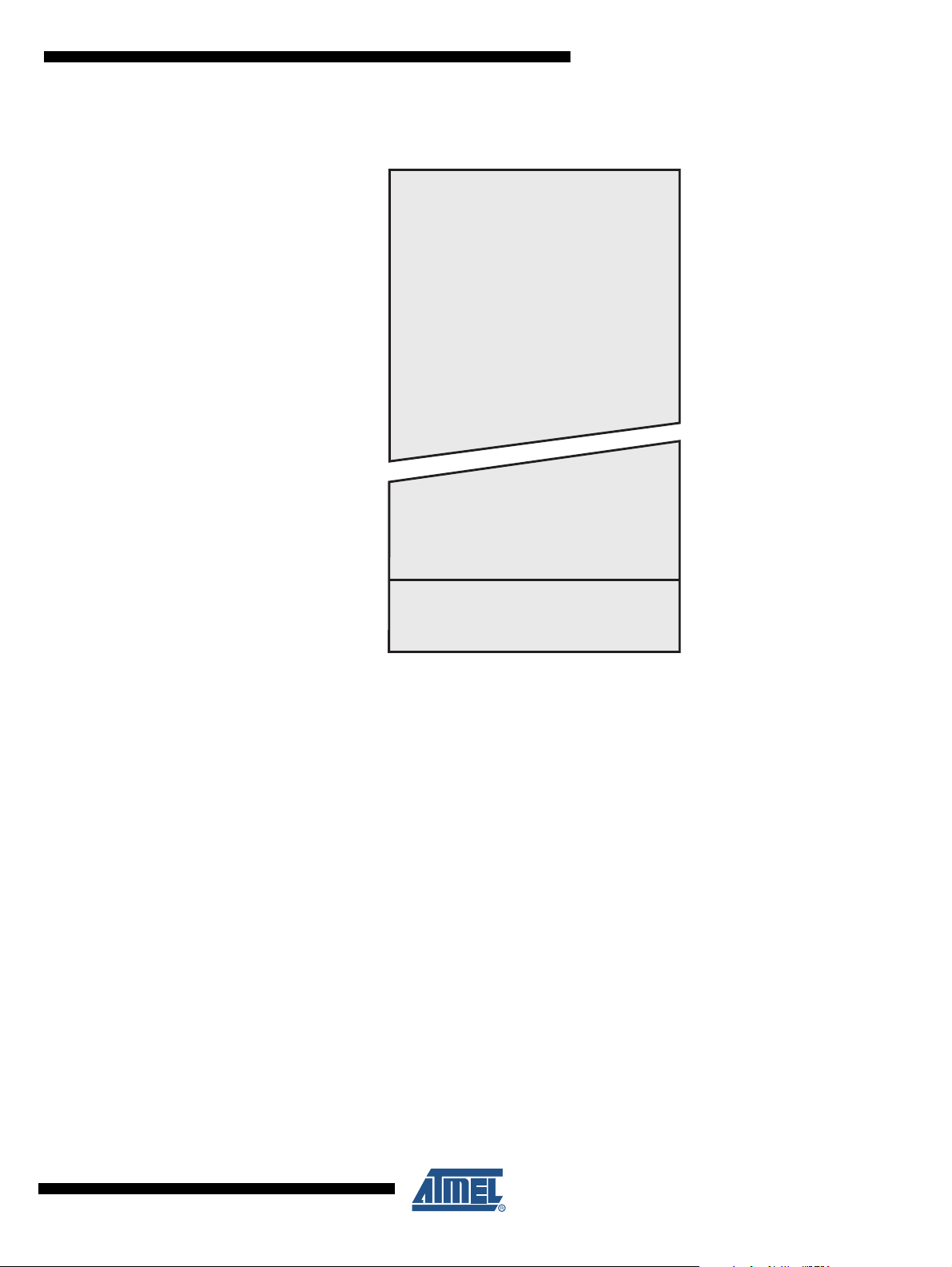
6.2 In-System Reprogrammable Flash Program Memory
The ATmega164P/324P/644P contains 16/32/64K bytes On-chip In-System Reprogrammable
Flash memory for program storage. Since all AVR instructions are 16 or 32 bits wide, the Flash
is organized as 32/64 x 16. For software security, the Flash Program memory space is divided
into two sections, Boot Program section and Application Program section.
The Flash memory has an endurance of at least 10,000 write/erase cycles. The
ATmega164P/324P/644P Program Counter (PC) is 15/16 bits wide, thus addressing the 32/64K
program memory locations. The operation of Boot Program section and associated Boot Lock
bits for software protection are described in detail in “Memory Programming” on page 296.
“Memory Programming” on page 296 contains a detailed description on Flash data serial down-
loading using the SPI pins or the JTAG interface.
Constant tables can be allocated within the entire program memory address space (see the LPM
– Load Program Memory instruction description.
Timing diagrams for instruction fetch and execution are presented in “Instruction Execution Tim-
ing” on page 14.
19
7674E–AVR–02/09
ATmega164P/324P/644P
Figure 6-1. Program Memory Map
6.3 SRAM Data Memory
Figure 6-2 shows how the ATmega164P/324P/644P SRAM Memory is organized.
The ATmega164P/324P/644P is a complex microcontroller with more peripheral units than can
be supported within the 64 location reserved in the Opcode for the IN and OUT instructions. For
the Extended I/O space from $060 - $FF in SRAM, only the ST/STS/STD and LD/LDS/LDD
instructions can be used.
The first 4,352 Data Memory locations address both the Register File, the I/O Memory,
Extended I/O Memory, and the internal data SRAM. The first 32 locations address the Register
file, the next 64 location the standard I/O Memory, then 160 locations of Extended I/O memory
and the next 4,096 locations address the internal data SRAM.
The five different addressing modes for the data memory cover: Direct, Indirect with Displace-
ment, Indirect, Indirect with Pre-decrement, and Indirect with Post-increment. In the Register file,
registers R26 to R31 feature the indirect addressing pointer registers.
The direct addressing reaches the entire data space.
The Indirect with Displacement mode reaches 63 address locations from the base address given
by the Y- or Z-register.
When using register indirect addressing modes with automatic pre-decrement and post-incre-
ment, the address registers X, Y, and Z are decremented or incremented.
Application Flash Section
Boot Flash Section
Program Memory
0x1FFF
0x0000
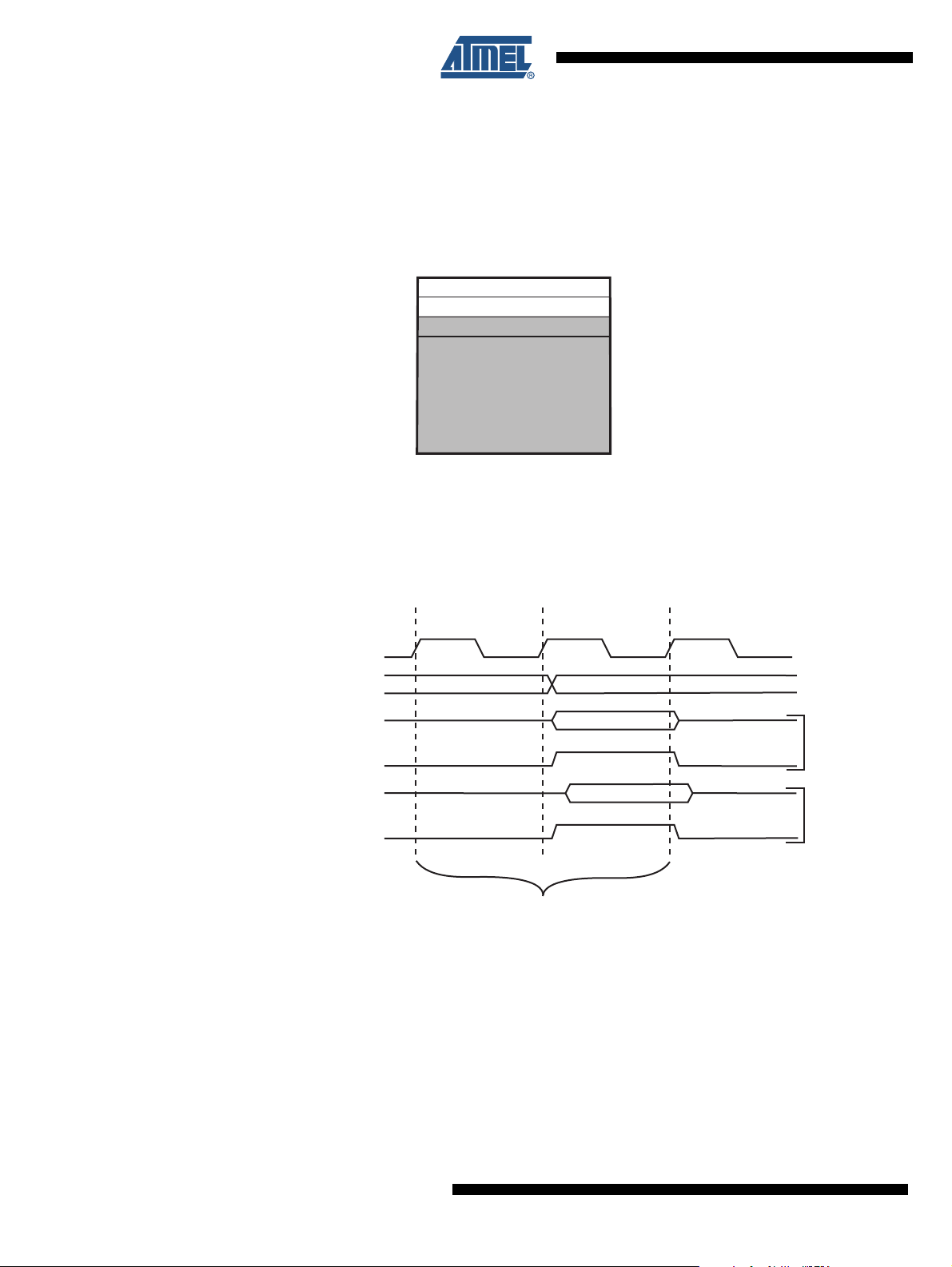
20
7674E–AVR–02/09
ATmega164P/324P/644P
The 32 general purpose working registers, 64 I/O registers, 160 Extended I/O Registers and the
1024/2048/4096 bytes of internal data SRAM in the ATmega164P/324P/644P are all accessible
through all these addressing modes. The Register File is described in “General Purpose Regis-
ter File” on page 12.
Figure 6-2. Data Memory Map
6.3.1 Data Memory Access Times
This section describes the general access timing concepts for internal memory access. The
internal data SRAM access is performed in two clk
CPU
cycles as described in Figure 6-3.
Figure 6-3. On-chip Data SRAM Access Cycles
32 Registers
64 I/O Registers
Internal SRAM
(1024/2048/4096 x 8)
$0000 - $001F
$0020 - $005F
$10FF
$0060 - $00FF
Data Memory
160 Ext I/O Reg.
$0100
clk
WR
RD
Data
Data
Address
Address valid
T1 T2 T3
Compute Address
Read
Write
CPU
Memory Access Instruction
Next Instruction

21
7674E–AVR–02/09
ATmega164P/324P/644P
6.4 EEPROM Data Memory
The ATmega164P/324P/644P contains 512B/1K/2K bytes of data EEPROM memory. It is orga-
nized as a separate data space, in which single bytes can be read and written. The EEPROM
has an endurance of at least 100,000 write/erase cycles. The access between the EEPROM and
the CPU is described in the following, specifying the EEPROM Address Registers, the EEPROM
Data Register, and the EEPROM Control Register.
For a detailed description of SPI, JTAG and Parallel data downloading to the EEPROM, see
page 311, page 315, and page 300 respectively.
6.4.1 EEPROM Read/Write Access
The EEPROM Access Registers are accessible in the I/O space. See “Register Description” on
page 23 for details.
The write access time for the EEPROM is given in Table 6-2 on page 25. A self-timing function,
however, lets the user software detect when the next byte can be written. If the user code con-
tains instructions that write the EEPROM, some precautions must be taken. In heavily filtered
power supplies, V
CC
is likely to rise or fall slowly on power-up/down. This causes the device for
some period of time to run at a voltage lower than specified as minimum for the clock frequency
used. See “Preventing EEPROM Corruption” on page 21. for details on how to avoid problems in
these situations.
In order to prevent unintentional EEPROM writes, a specific write procedure must be followed.
Refer to the description of the EEPROM Control Register for details on this.
When the EEPROM is read, the CPU is halted for four clock cycles before the next instruction is
executed. When the EEPROM is written, the CPU is halted for two clock cycles before the next
instruction is executed.
6.4.2 Preventing EEPROM Corruption
During periods of low V
CC,
the EEPROM data can be corrupted because the supply voltage is
too low for the CPU and the EEPROM to operate properly. These issues are the same as for
board level systems using EEPROM, and the same design solutions should be applied.
An EEPROM data corruption can be caused by two situations when the voltage is too low. First,
a regular write sequence to the EEPROM requires a minimum voltage to operate correctly. Sec-
ondly, the CPU itself can execute instructions incorrectly, if the supply voltage is too low.
EEPROM data corruption can easily be avoided by following this design recommendation:
Keep the AVR RESET active (low) during periods of insufficient power supply voltage. This can
be done by enabling the internal Brown-out Detector (BOD). If the detection level of the internal
BOD does not match the needed detection level, an external low V
CC
reset Protection circuit can
be used. If a reset occurs while a write operation is in progress, the write operation will be com-
pleted provided that the power supply voltage is sufficient.

22
7674E–AVR–02/09
ATmega164P/324P/644P
6.5 I/O Memory
The I/O space definition of the ATmega164P/324P/644P is shown in “Register Summary” on
page 356.
All ATmega164P/324P/644P I/Os and peripherals are placed in the I/O space. All I/O locations
may be accessed by the LD/LDS/LDD and ST/STS/STD instructions, transferring data between
the 32 general purpose working registers and the I/O space. I/O Registers within the address
range 0x00 - 0x1F are directly bit-accessible using the SBI and CBI instructions. In these regis-
ters, the value of single bits can be checked by using the SBIS and SBIC instructions. Refer to
the instruction set section for more details. When using the I/O specific commands IN and OUT,
the I/O addresses 0x00 - 0x3F must be used. When addressing I/O Registers as data space
using LD and ST instructions, 0x20 must be added to these addresses. The
ATmega164P/324P/644P is a complex microcontroller with more peripheral units than can be
supported within the 64 location reserved in Opcode for the IN and OUT instructions. For the
Extended I/O space from 0x60 - 0xFF in SRAM, only the ST/STS/STD and LD/LDS/LDD instruc-
tions can be used.
For compatibility with future devices, reserved bits should be written to zero if accessed.
Reserved I/O memory addresses should never be written.
Some of the Status Flags are cleared by writing a logical one to them. Note that, unlike most
other AVRs, the CBI and SBI instructions will only operate on the specified bit, and can therefore
be used on registers containing such Status Flags. The CBI and SBI instructions work with reg-
isters 0x00 to 0x1F only.
The I/O and peripherals control registers are explained in later sections.
The ATmega164P/324P/644P contains three General Purpose I/O Registers, see “Register
Description” on page 23. These registers can be used for storing any information, and they are
particularly useful for storing global variables and Status Flags. General Purpose I/O Registers
within the address range 0x00 - 0x1F are directly bit-accessible using the SBI, CBI, SBIS, and
SBIC instructions.

23
7674E–AVR–02/09
ATmega164P/324P/644P
6.6 Register Description
6.6.1 EEARH and EEARL – The EEPROM Address Register
• Bits 15:12 – Res: Reserved Bits
These bits are reserved bits in the ATmega164P/324P/644P and will always read as zero.
• Bits 11:0 – EEAR8:0: EEPROM Address
The EEPROM Address Registers – EEARH and EEARL specify the EEPROM address in the 4K
bytes EEPROM space. The EEPROM data bytes are addressed linearly between 0 and 4096.
The initial value of EEAR is undefined. A proper value must be written before the EEPROM may
be accessed.
6.6.2 EEDR – The EEPROM Data Register
• Bits 7:0 – EEDR7:0: EEPROM Data
For the EEPROM write operation, the EEDR Register contains the data to be written to the
EEPROM in the address given by the EEAR Register. For the EEPROM read operation, the
EEDR contains the data read out from the EEPROM at the address given by EEAR.
6.6.3 EECR – The EEPROM Control Register
• Bits 7:6 – Res: Reserved Bits
These bits are reserved bits in the ATmega164P/324P/644P and will always read as zero.
• Bits 5:4 – EEPM1 and EEPM0: EEPROM Programming Mode Bits
The EEPROM Programming mode bit setting defines which programming action that will be trig-
gered when writing EEPE. It is possible to program data in one atomic operation (erase the old
value and program the new value) or to split the Erase and Write operations in two different
operations. The Programming times for the different modes are shown in Table 6-1 on page 24.
Bit 15141312 11 10 9 8
0x22 (0x42) – – – – EEAR11 EEAR10 EEAR9 EEAR8 EEARH
0x21 (0x41) EEAR7 EEAR6 EEAR5 EEAR4 EEAR3 EEAR2 EEAR1 EEAR0 EEARL
76543 2 10
Read/Write R R R R R/W R/W R/W R/W
R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W
Initial Value 0 0 0 0 X X X X
XXXX X X XX
Bit 76543210
0x20 (0x40) MSB LSB EEDR
Read/Write R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W
Initial Value00000000
Bit 76543 2 10
0x1F (0x3F) – – EEPM1 EEPM0 EERIE EEMPE EEPE EERE EECR
Read/Write R R R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W
Initial Value 0 0 X X 0 0 X 0
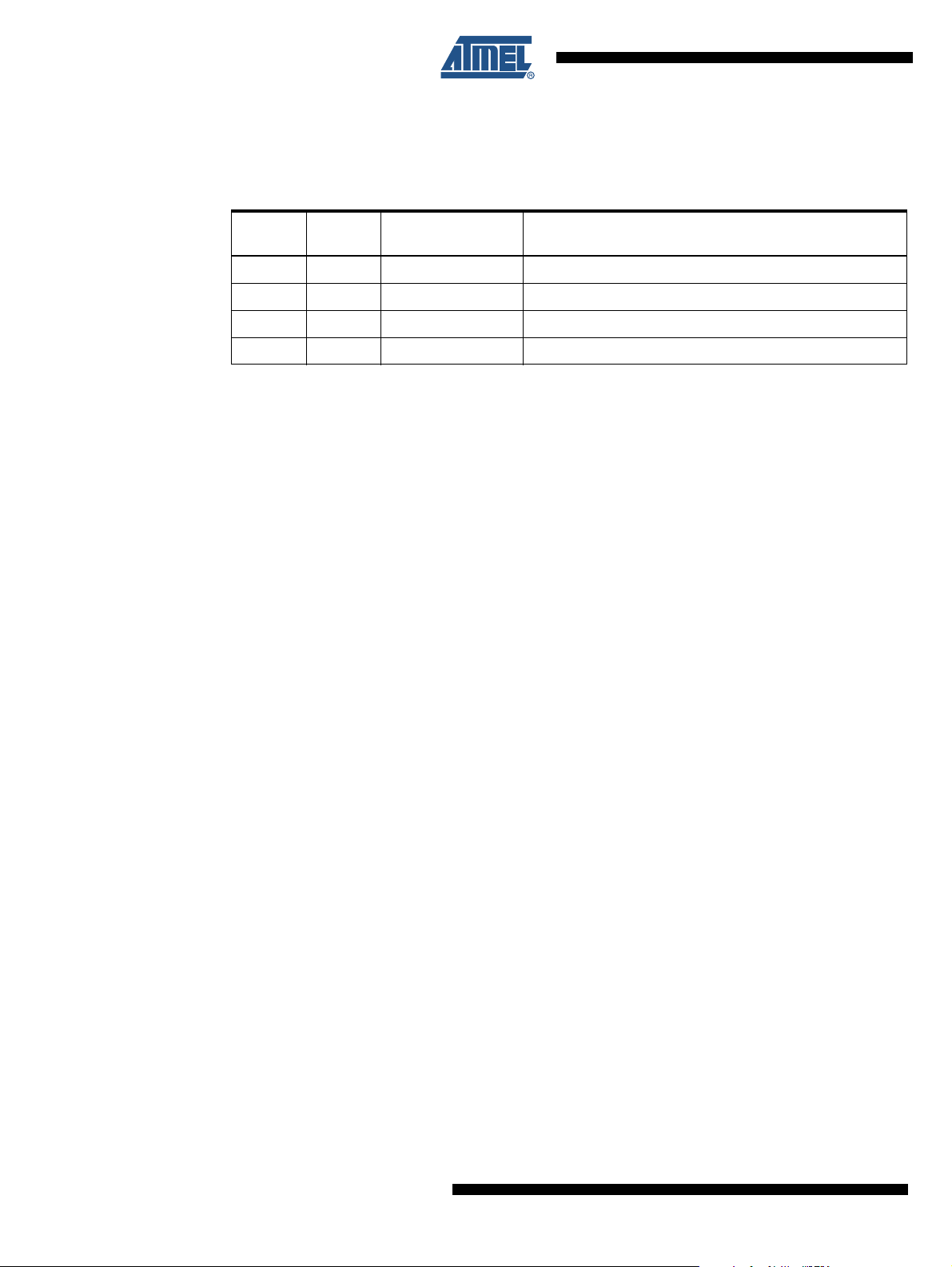
24
7674E–AVR–02/09
ATmega164P/324P/644P
While EEPE is set, any write to EEPMn will be ignored. During reset, the EEPMn bits will be
reset to 0b00 unless the EEPROM is busy programming.
• Bit 3 – EERIE: EEPROM Ready Interrupt Enable
Writing EERIE to one enables the EEPROM Ready Interrupt if the I bit in SREG is set. Writing
EERIE to zero disables the interrupt. The EEPROM Ready interrupt generates a constant inter-
rupt when EEPE is cleared.
• Bit 2 – EEMPE: EEPROM Master Programming Enable
The EEMPE bit determines whether setting EEPE to one causes the EEPROM to be written.
When EEMPE is set, setting EEPE within four clock cycles will write data to the EEPROM at the
selected address If EEMPE is zero, setting EEPE will have no effect. When EEMPE has been
written to one by software, hardware clears the bit to zero after four clock cycles. See the
description of the EEPE bit for an EEPROM write procedure.
• Bit 1 – EEPE: EEPROM Programming Enable
The EEPROM Write Enable Signal EEPE is the write strobe to the EEPROM. When address
and data are correctly set up, the EEPE bit must be written to one to write the value into the
EEPROM. The EEMPE bit must be written to one before a logical one is written to EEPE, other-
wise no EEPROM write takes place. The following procedure should be followed when writing
the EEPROM (the order of steps 3 and 4 is not essential):
1. Wait until EEPE becomes zero.
2. Wait until SELFPRGEN in SPMCSR becomes zero.
3. Write new EEPROM address to EEAR (optional).
4. Write new EEPROM data to EEDR (optional).
5. Write a logical one to the EEMPE bit while writing a zero to EEPE in EECR.
6. Within four clock cycles after setting EEMPE, write a logical one to EEPE.
The EEPROM can not be programmed during a CPU write to the Flash memory. The software
must check that the Flash programming is completed before initiating a new EEPROM write.
Step 2 is only relevant if the software contains a Boot Loader allowing the CPU to program the
Flash. If the Flash is never being updated by the CPU, step 2 can be omitted. See “Memory Pro-
gramming” on page 296 for details about Boot programming.
Caution: An interrupt between step 5 and step 6 will make the write cycle fail, since the
EEPROM Master Write Enable will time-out. If an interrupt routine accessing the EEPROM is
interrupting another EEPROM access, the EEAR or EEDR Register will be modified, causing the
interrupted EEPROM access to fail. It is recommended to have the Global Interrupt Flag cleared
during all the steps to avoid these problems.
Table 6-1. EEPROM Mode Bits
EEPM1 EEPM0
Programming
Time Operation
0 0 3.4 ms Erase and Write in one operation (Atomic Operation)
0 1 1.8 ms Erase Only
1 0 1.8 ms Write Only
1 1 – Reserved for future use
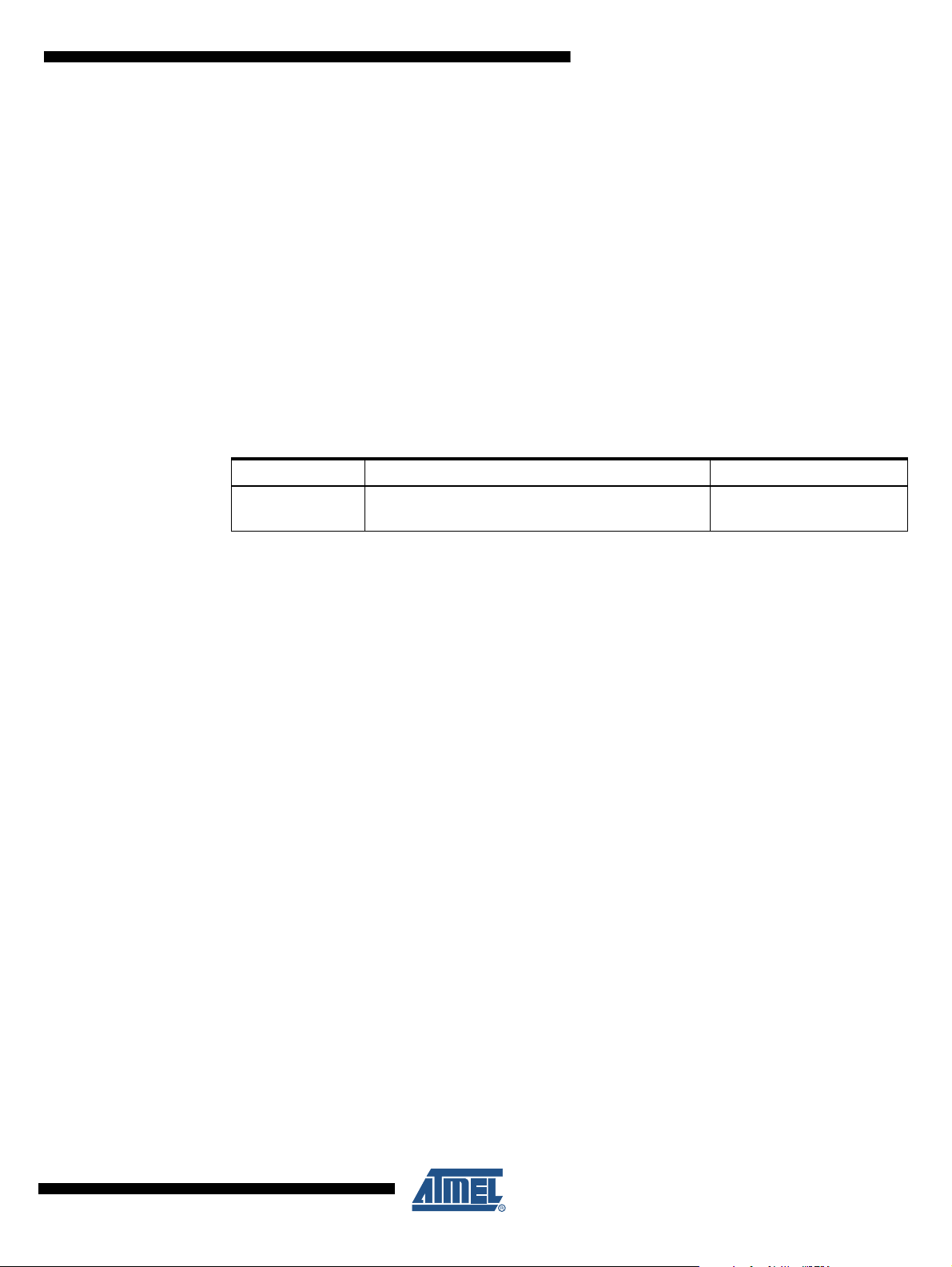
25
7674E–AVR–02/09
ATmega164P/324P/644P
When the write access time has elapsed, the EEPE bit is cleared by hardware. The user soft-
ware can poll this bit and wait for a zero before writing the next byte. When EEPE has been set,
the CPU is halted for two cycles before the next instruction is executed.
• Bit 0 – EERE: EEPROM Read Enable
The EEPROM Read Enable Signal EERE is the read strobe to the EEPROM. When the correct
address is set up in the EEAR Register, the EERE bit must be written to a logic one to trigger the
EEPROM read. The EEPROM read access takes one instruction, and the requested data is
available immediately. When the EEPROM is read, the CPU is halted for four cycles before the
next instruction is executed.
The user should poll the EEPE bit before starting the read operation. If a write operation is in
progress, it is neither possible to read the EEPROM, nor to change the EEAR Register.
The calibrated Oscillator is used to time the EEPROM accesses. Table 6-2 on page 25 lists the
typical programming time for EEPROM access from the CPU.
Table 6-2. EEPROM Programming Time
Symbol Number of Calibrated RC Oscillator Cycles Typ Programming Time
EEPROM write
(from CPU)
26,368 3.3 ms

26
7674E–AVR–02/09
ATmega164P/324P/644P
The following code examples show one assembly and one C function for writing to the
EEPROM. The examples assume that interrupts are controlled (e.g. by disabling interrupts glob-
ally) so that no interrupts will occur during execution of these functions. The examples also
assume that no Flash Boot Loader is present in the software. If such code is present, the
EEPROM write function must also wait for any ongoing SPM command to finish.
Note: 1. See “About Code Examples” on page 8.
Assembly Code Example
()
EEPROM_write:
; Wait for completion of previous write
sbic EECR,EEPE
rjmp EEPROM_write
; Set up address (r18:r17) in address register
out EEARH, r18
out EEARL, r17
; Write data (r16) to Data Register
out EEDR,r16
; Write logical one to EEMPE
sbi EECR,EEMPE
; Start eeprom write by setting EEPE
sbi EECR,EEPE
ret
C Code Example
(1)
void EEPROM_write(unsigned int uiAddress, unsigned char ucData)
{
/* Wait for completion of previous write */
while(EECR & (1<<EEPE))
;
/* Set up address and Data Registers */
EEAR = uiAddress;
EEDR = ucData;
/* Write logical one to EEMPE */
EECR |= (1<<EEMPE);
/* Start eeprom write by setting EEPE */
EECR |= (1<<EEPE);
}

27
7674E–AVR–02/09
ATmega164P/324P/644P
The next code examples show assembly and C functions for reading the EEPROM. The exam-
ples assume that interrupts are controlled so that no interrupts will occur during execution of
these functions.
Note: 1. See “About Code Examples” on page 8.
Assembly Code Example
(1)
EEPROM_read:
; Wait for completion of previous write
sbic EECR,EEPE
rjmp EEPROM_read
; Set up address (r18:r17) in address register
out EEARH, r18
out EEARL, r17
; Start eeprom read by writing EERE
sbi EECR,EERE
; Read data from Data Register
in r16,EEDR
ret
C Code Example
(1)
unsigned char EEPROM_read(unsigned int uiAddress)
{
/* Wait for completion of previous write */
while(EECR & (1<<EEPE))
;
/* Set up address register */
EEAR = uiAddress;
/* Start eeprom read by writing EERE */
EECR |= (1<<EERE);
/* Return data from Data Register */
return EEDR;
}
28
7674E–AVR–02/09
ATmega164P/324P/644P
6.6.4 GPIOR2 – General Purpose I/O Register 2
6.6.5 GPIOR1 – General Purpose I/O Register 1
6.6.6 GPIOR0 – General Purpose I/O Register 0
Note: 1. SRWn1 = SRW11 (upper sector) or SRW01 (lower sector), SRWn0 = SRW10 (upper sector) or
SRW00 (lower sector). The ALE pulse in period T4 is only present if the next instruction
accesses the RAM (internal or external).
Bit 76543210
0x2B (0x4B) MSB LSB GPIOR2
Read/Write R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W
Initial Value00000000
Bit 76543210
0x2A (0x4A) MSB LSB GPIOR1
Read/Write R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W
Initial Value00000000
Bit 76543210
0x1E (0x3E) MSB LSB GPIOR0
Read/Write R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W
Initial Value00000000
29
7674E–AVR–02/09
ATmega164P/324P/644P
7. System Clock and Clock Options
7.1 Clock Systems and their Distribution
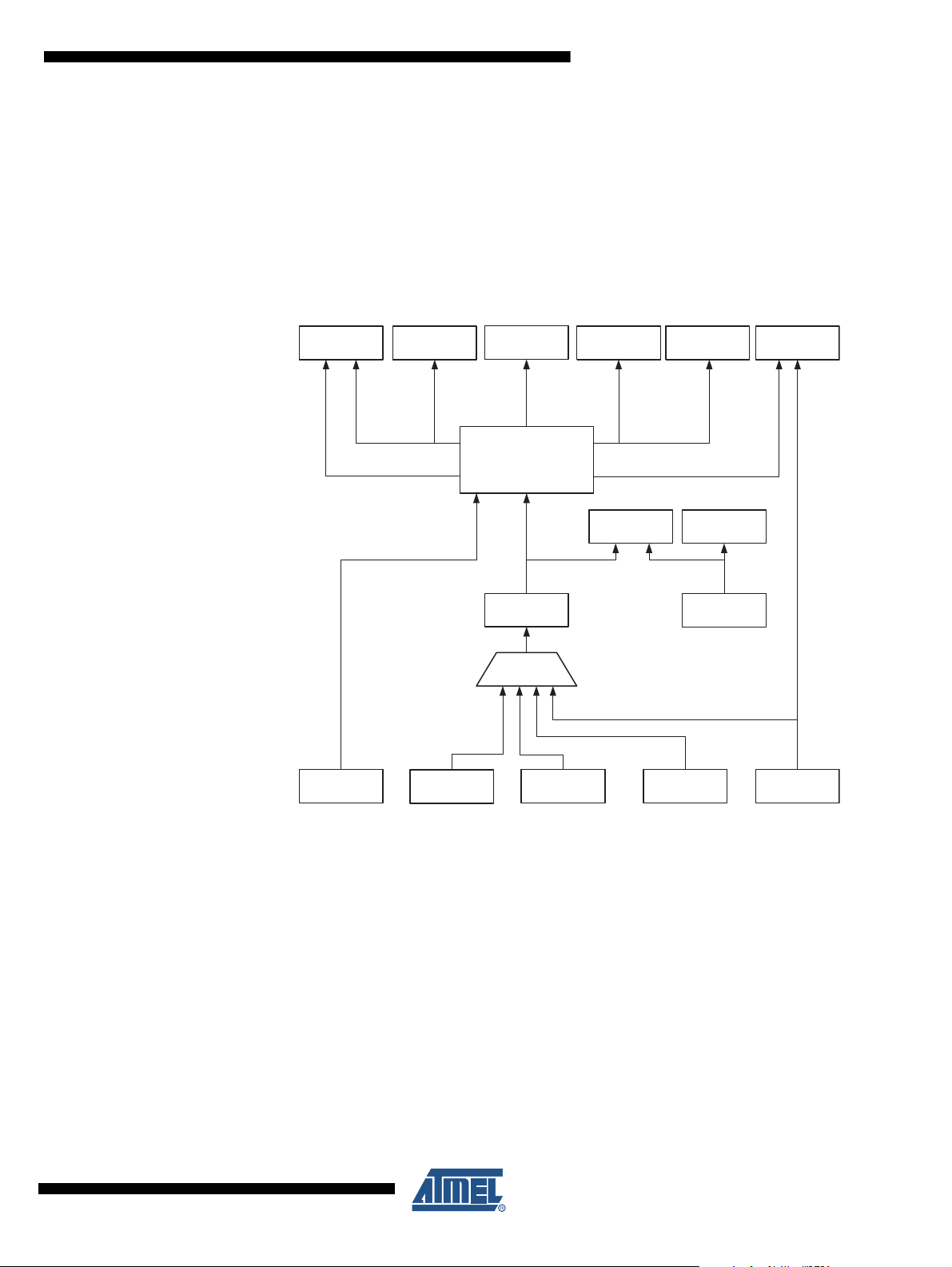
Figure 7-1 presents the principal clock systems in the AVR and their distribution. All of the clocks
need not be active at a given time. In order to reduce power consumption, the clocks to modules
not being used can be halted by using different sleep modes, as described in “Power Manage-
ment and Sleep Modes” on page 41. The clock systems are detailed below.
Figure 7-1. Clock Distribution
7.1.1 CPU Clock – clk
CPU
The CPU clock is routed to parts of the system concerned with operation of the AVR core.
Examples of such modules are the General Purpose Register File, the Status Register and the
data memory holding the Stack Pointer. Halting the CPU clock inhibits the core from performing
general operations and calculations.
7.1.2 I/O Clock – clk
I/O
The I/O clock is used by the majority of the I/O modules, like Timer/Counters, SPI, and USART.
The I/O clock is also used by the External Interrupt module, but note that some external inter-
rupts are detected by asynchronous logic, allowing such interrupts to be detected even if the I/O
clock is halted. Also note that start condition detection in the USI module is carried out asynchro-
nously when clk
I/O
is halted, TWI address recognition in all sleep modes.
General I/O
Modules
Asynchronous
Timer/Counter
CPU Core RAM
clk
I/O
clk
ASY
AVR Clock
Control Unit
clk
CPU
Flash and
EEPROM
clk
FLASH
Source clock
Watchdog Timer
Watchdog
Oscillator
Reset Logic
Clock
Multiplexer
Watchdog clock
Calibrated RC
Oscillator
Timer/Counter
Oscillator
Crystal
Oscillator
Low-frequency
Crystal Oscillator
External Clock
ADC
clk
ADC
System Clock
Prescaler

30
7674E–AVR–02/09
ATmega164P/324P/644P
7.1.3 Flash Clock – clk
FLASH
The Flash clock controls operation of the Flash interface. The Flash clock is usually active simul-
taneously with the CPU clock.
7.1.4 Asynchronous Timer Clock – clk
ASY
The Asynchronous Timer clock allows the Asynchronous Timer/Counter to be clocked directly
from an external clock or an external 32 kHz clock crystal. The dedicated clock domain allows
using this Timer/Counter as a real-time counter even when the device is in sleep mode.
7.1.5 ADC Clock – clk
ADC
The ADC is provided with a dedicated clock domain. This allows halting the CPU and I/O clocks
in order to reduce noise generated by digital circuitry. This gives more accurate ADC conversion
results.
7.2 Clock Sources
The device has the following clock source options, selectable by Flash Fuse bits as shown
below. The clock from the selected source is input to the AVR clock generator, and routed to the
appropriate modules.
Note: 1. For all fuses “1” means unprogrammed while “0” means programmed.
7.2.1 Default Clock Source
The device is shipped with internal RC oscillator at 8.0MHz and with the fuse CKDIV8 pro-
grammed, resulting in 1.0MHz system clock. The startup time is set to maximum and time-out
period enabled. (CKSEL = "0010", SUT = "10", CKDIV8 = "0"). The default setting ensures that
all users can make their desired clock source setting using any available programming interface.
Table 7-1. Device Clocking Options Select
(1)
Device Clocking Option CKSEL3..0
Low Power Crystal Oscillator 1111 - 1000
Full Swing Crystal Oscillator 0111 - 0110
Low Frequency Crystal Oscillator 0101 - 0100
Internal 128 kHz RC Oscillator 0011
Calibrated Internal RC Oscillator 0010
External Clock 0000
Reserved 0001
 Loading...
Loading...