Page 1

Mac OS X Server
Upgrading and Migrating
For Version 10.5 Leopard
Page 2

Apple Inc.
© 2007 Apple Inc. All rights reserved.
The owner or authorized user of a valid copy of Mac OS
X Server software may reproduce this publication for the
purpose of learning to use such software. No part of this
publication may be reproduced or transmitted for
commercial purposes, such as selling copies of this
publication or for providing paid-for support services.
Every effort has been made to make sure that the
information in this manual is correct. Apple Inc. is not
responsible for printing or clerical errors.
Apple
1 Infinite Loop
Cupertino CA 95014-2084
www.apple.com
The Apple logo is a trademark of Apple Inc., registered
in the U.S. and other countries. Use of the “keyboard”
Apple logo (Option-Shift-K) for commercial purposes
without the prior written consent of Apple may
constitute trademark infringement and unfair
competition in violation of federal and state laws.
Apple, the Apple logo, iChat, Mac, Macintosh,
QuickTime, Xgrid, Xserve, and WebObjects are
trademarks of Apple Inc., registered in the U.S. and other
countries. Finder is a trademark of Apple Inc.
Adobe and PostScript are trademarks of Adobe Systems
Incorporated.
Intel, Intel Core, and Xeon are trademarks of Intel Corp.
in the U.S. and other countries.
TM
and all Java-based trademarks and logos are
Java
trademarks or registered trademarks of Sun
Microsystems, Inc. in the U.S. and other countries.
TM
PowerPC
and the PowerPC logoTM are trademarks of
International Business Machines Corporation, used
under license therefrom.
UNIX is a registered trademark of The Open Group.
Other company and product names mentioned herein
are trademarks of their respective companies. Mention
of third-party products is for informational purposes
only and constitutes neither an endorsement nor a
recommendation. Apple assumes no responsibility with
regard to the performance or use of these products.
019-0937/2007-09-01
Page 3

Contents
1
Preface 5 About This Guide
5
What’s in This Guide
6
Using This Guide
6
Using Onscreen Help
6
Mac OS X Server Administration Guides
8
Viewing PDF Guides on Screen
8
Printing PDF Guides
8
Getting Documentation Updates
9
Getting Additional Information
Chapter 1 11 Before You Begin
11
Servers from Which You Can Upgrade or Migrate
11
12
12
12
12
13
15
Upgrading to v10.5
Migrating from a Pre-10.5 Version Server to v10.5
Migrating from Windows NT
Migrating Users and Groups
Saving and Reusing User and Group Accounts
System Accounts
Applying a New Serial Number
Chapter 2 17 Upgrading Mac OS X Server v10.4
17
Understanding What Can Be Reused
18
Upgrading an Open Directory Master and Its Replicas
18
Step-by-Step Instructions
25
Upgrading Apache Web Server to v2.2 from v1.3
Chapter 3 27 Migrating from Mac OS X Server v10.4
27
Before You Begin
28
Understanding What You Can Migrate
29
Tools You Can Use
30
Step-by-Step Instructions
Chapter 4 47 Upgrading Mac OS X Server v10.3
47
Understanding What Can Be Reused
3
Page 4

48
Upgrading an Open Directory Master and Its Replicas
48
Step-by-Step Instructions
55
Upgrading Apache Web Server to v2.2 from v1.3
Chapter 5 57 Migrating from Mac OS X Server v10.3
57
Before You Begin
58
Understanding What You Can Migrate
59
Tools You Can Use
60
Step-by-Step Instructions
Chapter 6 75 Migrating from Mac OS X Server v10.2
75
Before You Begin
75
Understanding What You Can Migrate
76
Tools You Can Use
77
Step-by-Step Instructions
Chapter 7 89 Migrating to Mac OS X Server from Windows NT
89
Before You Begin
90
Understanding What You Can Migrate
90
91
96
96
96
97
97
97
10 8
111
What Migrated Users Can Do
Planning Your Migration
Tools You Can Use
Tools for Migrating Users, Groups, and Computers
Tools for Migrating the File Service
Tools for Providing Windows Access to Print Service
Step-by-Step Instructions
Migrating Users, Groups, and Computers
Migrating Windows File Service
Providing Windows Access to Print Service
Index 11 5
4
Contents
Page 5

About This Guide
Preface
Use this guide when you want to move to Mac OS X Server
v10.5 from a previous version of the server or to migrate
Windows NT data to Mac OS X Server v10.5.
Upgrading and Migrating
server versions. There are two approaches:
Â
Perform an upgrade installation. This approach leaves all your data and settings in
place and lets you reuse your existing server hardware for Mac OS X Server v10.5. You
can perform an upgrade installation of v10.4 and v10.3 servers.
Â
Manually migrate data and settings. This approach transfers data and settings to a
different computer—one running Mac OS X Server v10.5. You can migrate data and
settings from server versions 10.4, 10.3, and 10.2.
contains instructions for reusing data and settings of previous
What’s in This Guide
This guide includes the following chapters:
Â
Chapter 1, “Before You Begin,” summarizes upgrade and migration options and
requirements.
Â
Chapter 2, “Upgrading Mac OS X Server v10.4,” describes how to upgrade a v10.4.10 or
later server to v10.5.
Â
Chapter 3, “Migrating from Mac OS X Server v10.4,” describes how to migrate data
from a v10.4.10 or later server to a different computer running v10.5.
Â
Chapter 4, “Upgrading Mac OS X Server v10.3,” describes how to upgrade a v10.3.9
server to v10.5.
Â
Chapter 5, “Migrating from Mac OS X Server v10.3,” describes how to migrate data
from a v10.3.9 server to a different computer running v10.5.
Â
Chapter 6, “Migrating from Mac OS X Server v10.2,” describes how to migrate data
from a v10.2.8 server to a different computer running v10.5.
Â
Chapter 7, “Migrating to Mac OS X Server from Windows NT,” describes how to
migrate data from a Windows NT server to a computer running Mac OS X Server
v10.5.
5
Page 6

Using This Guide
Using this guide is easy. Read Chapter 1 to make sure you understand your options.
Then turn to the chapter that addresses your upgrade or migration scenario. You’ll find
step-by-step instructions for preserving and reusing server data by using various tools
and manual techniques.
You’ll also find references to instructions and supplemental information in other guides
in the server suite. The next page tells you about the documents in the suite and where
to find them.
Using Onscreen Help
You can get task instructions onscreen in the Help Viewer application while you’re
managing Leopard Server. You can view help on a server or an administrator computer.
(An administrator computer is a Mac OS X computer with Leopard Server
administration software installed on it.)
To get help for an advanced configuration of Leopard Server:
m
Open Server Admin or Workgroup Manager and then:
Â
Use the Help menu to search for a task you want to perform.
Â
Choose Help > Server Admin Help or Help > Workgroup Manager Help to browse
and search the help topics.
The onscreen help contains instructions taken from
advanced administration guides described in “Mac OS X Server Administration Guides,”
next.
To see the most recent server help topics:
m
Make sure the server or administrator computer is connected to the Internet while
you’re getting help.
Help Viewer automatically retrieves and caches the most recent server help topics from
the Internet. When not connected to the Internet, Help Viewer displays cached help
topics.
Mac OS X Server Administration Guides
Getting Started
configuration of Leopard Server as well as for a standard or workgroup configuration.
An advanced guide,
and more. A suite of additional guides, listed below, covers advanced planning, setup,
and management of individual services. You can get these guides in PDF format from
the Mac OS X Server documentation website:
6 Preface
covers basic installation and initial setup methods for an advanced
Server Administration
About This Guide
Server Administration
, covers advanced planning, installation, setup,
and other
Page 7

www.apple.com/server/documentation
This guide ... tells you how to:
Getting Started
Mac OS X Server Worksheet
Command-Line Administration
File Services Administration
iCal Service Administration
iChat Service Administration
Mac OS X Security Configuration
Mac OS X Server Security
Configuration
Mail Service Administration
Network Services Administration
Open Directory Administration
Podcast Producer Administration
Print Service Administration
QuickTime Streaming and
Broadcasting Administration
Server Administration
System Imaging and Software
Update Administration
Upgrading and Migrating
User Management
Web Technologies Administration
Xgrid Administration and High
Performance Computing
Mac OS X Server Glossary
and
Install Mac OS X Server and set it up for the first time.
Install, set up, and manage Mac OS X Server using UNIX commandline tools and configuration files.
Share selected server volumes or folders among server clients
using the AFP, NFS, FTP, and SMB protocols.
Set up and manage iCal shared calendar service.
Set up and manage iChat instant messaging service.
Make Mac OS X computers (clients) more secure, as required by
enterprise and government customers.
Make Mac OS X Server and the computer it’s installed on more
secure, as required by enterprise and government customers.
Set up and manage IMAP, POP, and SMTP mail services on the
server.
Set up, configure, and administer DHCP, DNS, VPN, NTP, IP firewall,
NAT, and RADIUS services on the server.
Set up and manage directory and authentication services, and
configure clients to access directory services.
Set up and manage Podcast Producer service to record, process,
and distribute podcasts.
Host shared printers and manage their associated queues and print
jobs.
Capture and encode QuickTime content. Set up and manage
QuickTime streaming service to deliver media streams live or on
demand.
Perform advanced installation and setup of server software, and
manage options that apply to multiple services or to the server as a
whole.
Use NetBoot, NetInstall, and Software Update to automate the
management of operating system and other software used by
client computers.
Use data and service settings from an earlier version of Mac OS X
Server or Windows NT.
Create and manage user accounts, groups, and computers. Set up
managed preferences for Mac OS X clients.
Set up and manage web technologies, including web, blog,
webmail, wiki, MySQL, PHP, Ruby on Rails, and WebDAV.
Set up and manage computational clusters of Xserve systems and
Mac computers.
Learn about terms used for server and storage products.
Preface
About This Guide
7
Page 8

Viewing PDF Guides on Screen
While reading the PDF version of a guide onscreen:
Â
Show bookmarks to see the guide’s outline, and click a bookmark to jump to the
corresponding section.
Â
Search for a word or phrase to see a list of places where it appears in the document.
Click a listed place to see the page where it occurs.
Â
Click a cross-reference to jump to the referenced section. Click a web link to visit the
website in your browser.
Printing PDF Guides
If you want to print a guide, you can take these steps to save paper and ink:
Â
Save ink or toner by not printing the cover page.
 Save color ink on a color printer by looking in the panes of the Print dialog for an
option to print in grays or black and white.
 Reduce the bulk of the printed document and save paper by printing more than one
page per sheet of paper. In the Print dialog, change Scale to 115% (155% for Getting
Started). Then choose Layout from the untitled pop-up menu. If your printer supports
two-sided (duplex) printing, select one of the Two-Sided options. Otherwise, choose
2 from the Pages per Sheet pop-up menu, and optionally choose Single Hairline from
the Border menu. (If you’re using Mac OS X v10.4 or earlier, the Scale setting is in the
Page Setup dialog and the Layout settings are in the Print dialog.)
You may want to enlarge the printed pages even if you don’t print double sided,
because the PDF page size is smaller than standard printer paper. In the Print dialog or
Page Setup dialog, try changing Scale to 115% (155% for Getting Started, which has CDsize pages).
Getting Documentation Updates
Periodically, Apple posts revised help pages and new editions of guides. Some revised
help pages update the latest editions of the guides.
 To view new onscreen help topics for a server application, make sure your server or
administrator computer is connected to the Internet and click “Latest help topics” or
“Staying current” in the main help page for the application.
 To download the latest guides in PDF format, go to the Mac OS X Server
documentation website:
www.apple.com/server/documentation
8 Preface
About This Guide
Page 9

Getting Additional Information
For more information, consult these resources:
 Read Me documents—important updates and special information. Look for them on
the server discs.
 Mac OS X Server website (www.apple.com/server/macosx)—gateway to extensive
product and technology information.
 Mac OS X Server Support website (www.apple.com/support/macosxserver)—access to
hundreds of articles from Apple’s support organization.
 Apple Training website (www.apple.com/training)—instructor-led and self-paced
courses for honing your server administration skills.
 Apple Discussions website (discussions.apple.com)—a way to share questions,
knowledge, and advice with other administrators.
 Apple Mailing Lists website (www.lists.apple.com)—subscribe to mailing lists so you
can communicate with other administrators using email.
Preface About This Guide 9
Page 10

10 Preface About This Guide
Page 11

1 Before You Begin
1
Take a few moments to become familiar with upgrade and
migration options and requirements.
If you’re using Mac OS X Server v10.3 or v10.4, you may not need to migrate server data
to a different computer. You might be able to upgrade your server, a process that
installs and sets up Mac OS X Server v10.5 on your existing server computer while
preserving data and service settings.
Servers from Which You Can Upgrade or Migrate
You can reuse server data and settings with Mac OS X Server v10.5 by:
 Upgrading server v10.4.10 or later or v10.3.9
 Migrating from versions 10.4.10 or later, 10.3.9, or 10.2.8
 Migrating from Windows NT
Upgrading to v10.5
You can upgrade your v10.4.10 or later or v10.3.9 server to v10.5 or later if:
 You don’t need to reformat the current computer’s hard disk.
 Your server hardware has:
 An Intel or PowerPC G5 or G4 (1 GHz or faster) processor
 At least 1 gigabyte (GB) of random access memory (RAM)
 At least 20 gigabytes (GB) of disk space available
When you upgrade a server, you perform an upgrade installation from the server
installation disc on your server computer. Data and settings are preserved for you, and
manual adjustments are minimal.
Note: Mac OS X Server v10.5 does not support Macintosh Manager.
11
Page 12

Migrating from a Pre-10.5 Version Server to v10.5
Even if your existing server meets the minimum requirements for upgrading, you may
want to migrate instead of upgrade. For example, you may be updating computers and
decide that you want to reestablish your server environment on newer computers.
Migrations from Mac OS X Server versions 10.4.10 or later, 10.3.9, and 10.2.8 are
supported. When you migrate, you install and perform initial setup of Mac OS X Server
v10.5 on a computer, restore files onto the v10.5 computer from the pre-v10.5
computer, and make manual adjustments as required.
Note: Migrating Macintosh Manager data is not supported.
You’ll need to migrate, not upgrade, to Mac OS X Server v10.5 if:
 Your v10.2.8, v10.3.9, or v10.4.10 or later server’s hard disk needs reformatting.
 Your v10.2.8, v10.3.9, or v10.4.10 or later server doesn’t have:
 An Intel or PowerPC G5 or G4 (1 GHz or faster) processor
 At least 1 GB of RAM
 At least 20 GB of disk space available
 You want to move data and settings you’ve been using on a v10.2.8, v10.3.9, or
v10.4.10 or later server to different server hardware.
 The server version you’ve been using is earlier than v10.2.8.
Migrating from Windows NT
Mac OS X Server can provide a variety of services to users of Microsoft Windows 95, 98,
ME (Millennium Edition), XP, Vista, NT 4, and 2000 computers. By providing these
services, Mac OS X Server can replace Windows NT servers in small workgroups.
Chapter 7, “Migrating to Mac OS X Server from Windows NT,” explains how to import
users, groups, and computers from a Microsoft Windows NT server to a Mac OS X
Server primary domain controller (PDC). This chapter also explains how to migrate
home directories, share points, and server configuration information.
Migrating Users and Groups
All versions of Mac OS X Server you can migrate from are supported by tools that help
you move user and group accounts from an existing server to a v10.5 server.
Saving and Reusing User and Group Accounts
To save user and group accounts to be imported later, back up the Open Directory
master database or export the user and group accounts using Workgroup Manager. To
restore user and group accounts, restore the Open Directory master database or use
Workgroup Manager or the dsimport tool.
Each migration chapter provides instructions for using these tools.
12 Chapter 1 Before You Begin
Page 13

System Accounts
When you install Mac OS X Server, several user and group accounts are created in the
local directory. These accounts are sometimes called system accounts because they’re
used by the server system software. For a description of how predefined accounts are
used, see User Management.
You can’t change the names or IDs of system accounts, so when you migrate users and
groups, don’t try to. However, you can add users during migration to two system
groups—admin and wheel:
 The wheel and admin groups allows members to use the su (substitute user)
command in the Terminal application to log in on a remote computer as the root
user. (Members should know the root password to use the su command.)
Use ssh to log in, enter su, then supply the root password when prompted.
 The admin group gives members the right to administer Mac OS X Server. Admin
users can use server management applications and install software that requires
administrator privileges. By default, members of the admin group can gain root
privilege using the sudo command.
Here are the predefined user accounts:
Name Short name UID
Unprivileged User nobody -2
System Administrator root 0
System Services daemon 1
Printing Services lp 26
Postfix User postfix 27
VPN MPPE Key vpn_nnnnnnnnnnnn 57
World Wide Web Server www 70
Apple Events User eppc 71
MySQL Server mysql 74
sshd Privilege separation sshd 75
QuickTime Streaming Server qtss 76
Cyrus IMAP User cyrus 77
Mailman User mailman 78
Application Server appserver 79
Clamav User clamav 82
Amavisd User amavisd 83
Jabber User jabber 84
Xgrid Controller xgridcontroller 85
Xgrid Agent xgridagent 86
Chapter 1 Before You Begin 13
Page 14

Name Short name UID
Application Owner appowner 87
WindowServer windowserver 88
Unknown User unknown 99
Here are the predefined groups:
Short name Group ID
nobody -2
nogroup -1
wheel 0
daemon 1
kmem 2
sys 3
tty 4
operator 5
mail 6
bin 7
staff 20
lp 26
postfix 27
postdrop 28
utmp 45
uucp 66
dialer 68
network 69
www 70
mysql 74
sshd 75
qtss 76
mailman 78
appserverusr 79
admin 80
appserveradm 81
clamav 82
amavisd 83
jabber 84
xgridcontroller 85
14 Chapter 1 Before You Begin
Page 15

Short name Group ID
xgridagent 86
appowner 87
windowserver 88
accessibility 90
unknown 99
Applying a New Serial Number
When upgrading to Mac OS X Server v10.5 from v10.4, you must configure your system
to use a v10.5 serial number.
Chapter 1 Before You Begin 15
Page 16

16 Chapter 1 Before You Begin
Page 17

2 Upgrading Mac OS X Server v10.4
2
Use the instructions in this chapter to upgrade a v10.4.10 or
later server to v10.5.
You can upgrade computers with Mac OS X Server v10.4.10 or later that don’t require
hard disk reformatting and that have:
 An Intel or PowerPC G5 or G4 (867 MHz or faster) processor
 At least 1 GB of RAM
 At least 20 GB of disk space available
Understanding What Can Be Reused
When you upgrade from Mac OS X Server v10.4.10 or later, virtually all existing data and
settings remain available for use, but note the following:
 NetBoot images created using Mac OS X Server versions 10.3 and 10.4 can be reused.
NetBoot images created using earlier versions cannot be used.
 When upgrading to Mac OS X Server v10.5, the launch daemons (/System/Library/
LaunchDaemons) are replaced by the Mac OS X Server v10.5 version of these
daemons.
 Upgrading to v10.5 removes the QTSS Publisher application but leaves the files used
by the application. These files should continue to work on v10.5, but you must move
them to the appropriate locations. For more information about moving them, see
“QTSS Publisher Files and Folders” on page 45.
 PHP: Hypertext Preprocessor (PHP) 4 will reach its end of life on December 31, 2007
and critical security fixes will not be made after August 8, 2008, as announced at
www.php.net. If you upgrade to Mac OS X Server v10.5 and retain PHP 4.4.x and
Apache 1.3, plan on switching to PHP 5.x and Apache 2.2 before August 8, 2008 to
maintain a secure PHP.
Note: Macintosh Manager is not supported in Mac OS X Server v10.5.
17
Page 18
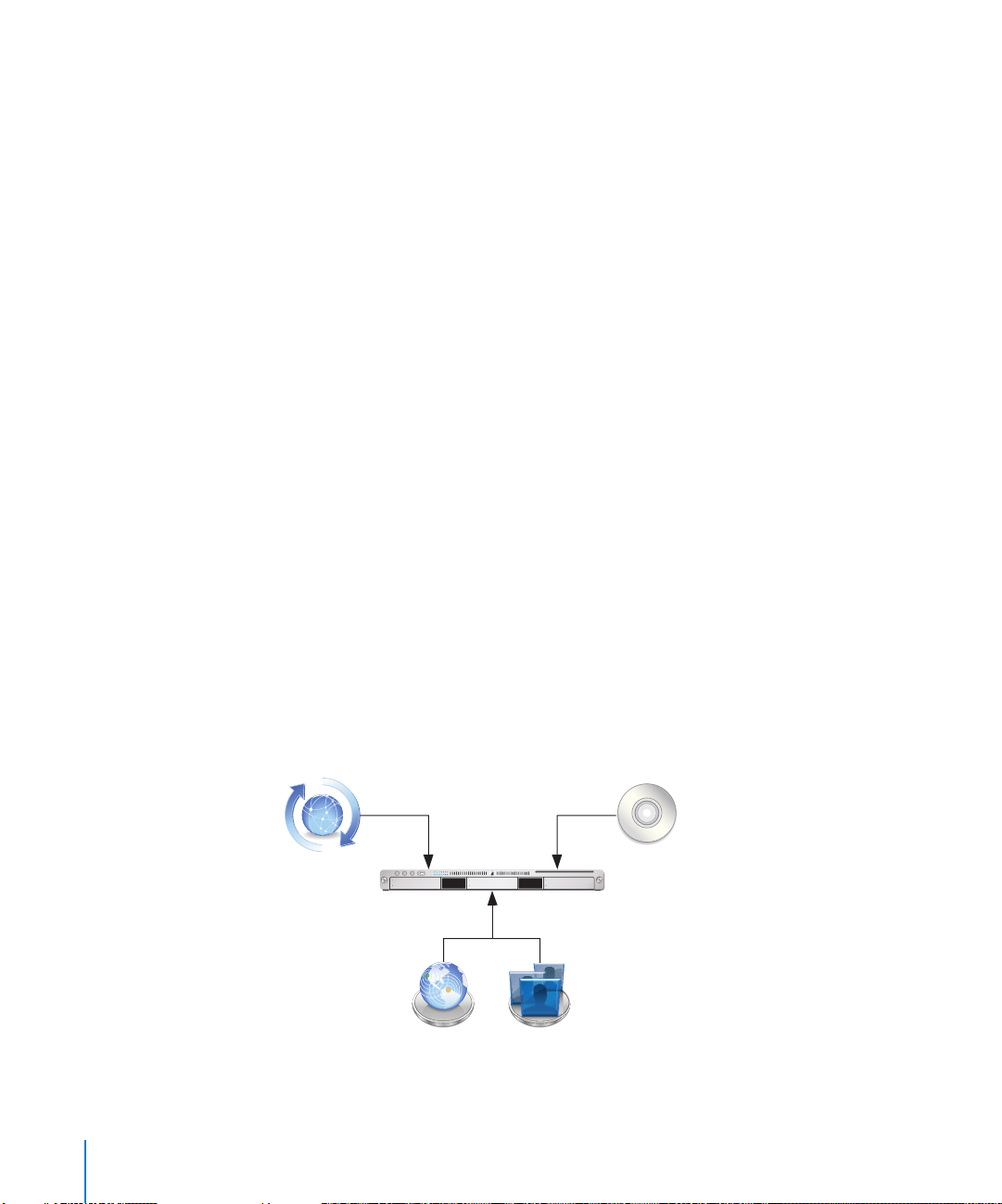
.
Upgrading an Open Directory Master and Its Replicas
When the server you want to upgrade is an Open Directory master or replica, upgrade
the master and then upgrade the replicas.
To upgrade the master and its replicas:
1 Upgrade the master to v10.5 using the instructions in “Step-by-Step Instructions” on
page 18.
While you’re upgrading the master, client computers can’t connect to it for Open
Directory services.
Clients may experience a delay while automatically finding an Open Directory replica
server. In addition, you can eliminate this delay by changing the DHCP service to use
the address of an Open Directory replica server if the server provides clients with an
LDAP server address.
When the master upgrade is complete, you can change the DHCP service to use the
address of the master. For instructions on configuring LDAP settings in DHCP service,
see Network Services Administration.
2 Upgrade each replica server to v10.5.
3 Using Server Admin, connect to each replica server and reconnect the replicas with the
master.
For information about resetting passwords in the master, see “Directory Services” on
page 23.
Step-by-Step Instructions
To upgrade a v10.4.10 or later server to v10.5, follow the instructions in this section.
1 Update your
server to v10.4.10.
3 Make adjustments as needed
after initial server setup.
2 Perform an
upgrade to v10.5
18 Chapter 2 Upgrading Mac OS X Server v10.4
Page 19

Step 1: Update your server to v10.4.10 or later
If necessary, use Software Update to update your server to v10.4.10 or later.
Step 2: Save all service settings
Use serveradmin or Server Admin to export all service settings for reference. Also, use
System Profiler to generate a full profile of your system. Store the exported service
settings and your server’s profile on a removable drive or another system.
Important: Before upgrading you should also create a full, bootable, tested-by-booting
clone of your server as a backup in case you need it in the future.
Step 3: Save Print service settings
Use the serveradmin settings print command to save the print service settings
before you start the upgrade.
serveradmin settings print >
exported_print_settings
Also, record the names and IDs of the CUPS queues for later use.
Step 4: Perform an upgrade to v10.5
You can use the v10.5 installation disc to perform the upgrade locally on your server
computer if it has a display, keyboard, and optical drive attached.
After the upgrade is complete, the computer restarts and Server Assistant leads you
through initial server setup. Your existing settings are displayed, and you can change
them if you like.
To upgrade to v10.5 and perform initial server setup locally:
1 Make sure that DHCP or DNS servers your server depends on are running.
2 Turn on the computer and insert the installation disc into the optical drive.
3 Restart the server while holding down the C key on the keyboard.
The computer boots from the installation disc. You can release the C key when you see
the Apple logo.
For information about restarting a headless Xserve system, see the user’s guide that
came with the system.
4 When the Installer opens, follow the onscreen instructions to proceed through each
pane, then click Continue.
Note: In the Select a Destination pane, be sure to select the disk or partition on which
v10.4.10 or later is installed.
During installation, progress information is displayed.
After installation is complete, the computer restarts and Server Assistant opens so you
can perform initial server setup.
Chapter 2 Upgrading Mac OS X Server v10.4 19
Page 20

5 Move through the Assistant’s panes, following the onscreen instructions.
Your existing settings are displayed in the panes, but you can change them if you like.
Enter a unique server software serial number for each server you upgrade. You’ll find
the number printed on the materials provided with the server software package. If you
have a site license, a registered owner name and organization must be entered exactly
as specified by your Apple representative.
After all setup data has been entered, Server Assistant displays a summary of the data.
6 Review the setup data, optionally click Go Back to change it.
7 To initiate setup of the server, click Apply.
8 When server setup is complete, click Restart Now.
Note: You may need to manually start Mail service after upgrading the server.
To upgrade to v10.5 and perform initial server setup remotely:
1 Make sure that DHCP or DNS servers your server depends on are running.
2 Start the computer from the installation disc.
The procedure you use depends on whether the target server has an optical drive that
can read your installation disc. If you have an installation DVD, the optical drive must
be able to read DVD discs.
If the target server has a keyboard and an optical drive that can read your installation
disc, insert the installation disc into the optical drive, then hold down the C key on the
keyboard while restarting the computer.
If the target server is an Xserve system with a built-in optical drive that can read your
installation disc, start the server using the installation disc by following the instructions
in Xserve User’s Guide for starting from a system disc.
If the target server lacks a built-in optical drive that can read your installation disc, you
can start it in target disk mode and insert the installation disc into the optical drive on
your administrator computer. You can also use an external FireWire optical drive.
If the target server is an Xserve system, you can move its drive module to another
Xserve system that has an optical drive capable of reading your installation disc.
Instructions for using target disk mode and external optical drives are in the Quick Start
guide, Getting Started guide, or user’s guide that came with your Xserve system or
Macintosh computer.
3 On an administrator computer, navigate to /Applications/Server/ and open Server
Assistant (you don’t need to be an administrator on the local computer to use Server
Assistant), then select “Install software on a remote server.”
20 Chapter 2 Upgrading Mac OS X Server v10.4
Page 21

4 Identify the server you want to upgrade.
If it’s on the local subnet, select it in the list.
Otherwise, click “Server at IP Address” and enter an IP address in IPv4 format
(000.000.000.000).
5 When prompted for a password, enter the old administrator password.
6 Proceed by following the onscreen instructions.
7 When the Volumes pane appears, select a target disk or volume (partition) and click
Continue.
During installation, progress information is displayed.
After installation is complete, the computer restarts, and then Server Assistant opens
and displays a Welcome pane.
8 To initiate server setup, select “Set up a remote server” and click Continue.
9 In the Destination pane, put a check in the Apply column for the server you’re
upgrading, then enter its preset password in the Password field and click Continue to
connect to the server.
If you don’t see the server in the list, click Add to add it or Refresh to determine
whether it’s available.
10 Move through the Assistant’s panes, following the onscreen instructions.
Your existing settings are displayed in the panes, but you can change them if you like.
You must enter a unique server software serial number for each server you upgrade.
You’ll find the number printed on the materials provided with the server software
package. If you have a site license, enter the registered owner name and organization
exactly as specified by your Apple representative.
After all setup data has been entered, Server Assistant displays a summary of the data.
11 Review the setup data, optionally clicking Go Back to change it.
12 To initiate setup of the server, click Apply.
13 When server setup is complete, click Restart Now.
Note: You may need to manually start Mail service after upgrading the server.
Step 5: Make adjustments as needed after initial server setup
Now you can use Workgroup Manager, Server Admin, Terminal, and other applications
to refine your server’s settings and take advantage of new v10.5 features.
For an explanation of new and changed features, see the administration guide for
individual services. Following are a few suggestions of particular interest.
Chapter 2 Upgrading Mac OS X Server v10.4 21
Page 22

Print Service Settings
To restore Print service settings, you must first recreate the original CUPS queues before
importing the saved settings.
For printers connected directly to the server via USB, the queues are created by CUPS
when the printers are plugged in and turned on. However, for network printers, you
must add the printers using either Server Admin > Print (for LPR or AppleTalk printers)
or System Preferences > Print & Fax (for all printer types).
Important: When recreating a CUPS queue, make sure you give it the same name as
the one it had before the upgrading process. If the name is not the same, Server Admin
won’t import the settings correctly.
Important: When creating the print queues using the Print & Fax pane of System
Preferences, specify Generic Postscript (Generic PPD) for any queue that enforces
quotas because there are known issues with third-party printer drivers and CUPS
quotas. For more information about this issue, see the Knowledge Base article at
http://docs.info.apple.com/article.html?artnum=303538.
After creating the print queues, import the saved settings:
serveradmin settings
exported_print_settings
WebObjects
Restore httpd.conf to the previous version (httpd.conf.AppleSaved), or include the
following line in the new httpd.conf file:
Include /System/Library/WebObjects/Adaptors/Apache/apache.conf
If you didn’t install JavaTM 1.4.2 on your v10.4.10 or later server, you must manually
update WebObjects application projects to use the version of the Java Virtual Machine
(JVM) included with v10.5.
To update a WebObjects project:
1 Open the project in Xcode.
2 In the Expert View for the main target’s settings, change the property value for
JAVA_VM to java.
Note: JavaMonitor and WebObjects Task Daemon (wotaskd) services are now managed
by launchd and can be accessed through Server Admin. If the server you’re upgrading
has the startup item /System/Library/StartupItems/WebObjects, you can ignore it. It’s
disabled by default and isn’t necessary for autostarting WebObjects services with
Mac OS X Server v10.5. For more information, see Web Technologies Administration and
WebObjects Deployment.
22 Chapter 2 Upgrading Mac OS X Server v10.4
Page 23

Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) Certificates
Use Server Admin to import existing SSL certificates you want to continue to use for
iChat, Open Directory, Mail, or Web services.
To import an SSL certificate:
1 Open Server Admin.
2 Select the upgraded server in the list of computers and services.
3 Click Certificates.
4 Import the certificates you want to use.
You can also create a self-signed certificate and generate a Certificate Signing Request
(CSR) to obtain an SSL certificate from a certificate authority and then install the
certificate.
5 Click Save.
6 Activate the certificates per service.
For more information about importing, creating, and activating self-signed certificates,
see iChat Service Administration, Mail Service Administration, Open Directory
Administration, and Web Technologies Administration.
Groups
If you want groups to use new v10.5 features such as nesting and stricter membership
checking, upgrade group records using Workgroup Manager.
To upgrade a group record:
1 Open Workgroup Manager.
2 Open the directory that contains the groups of interest.
3 Select one or more groups and click “Upgrade legacy group.”
4 Click Save.
Directory Services
After upgrading, you may want to convert a shared NetInfo directory to LDAP. For
information about the advantages of using LDAP and how to use Server Admin to
conduct the conversion, see Open Directory Administration.
If you want to enable Kerberos for an Open Directory master that it’s not enabled for,
use the following command, which maintains existing passwords and adds them to a
new KDC:
slapconfig -kerberize
Chapter 2 Upgrading Mac OS X Server v10.4 23
Page 24

If you have user accounts with crypt passwords and you don’t Kerberize them using the
above command, you can use Workgroup Manager to upgrade to Open Directory
passwords.
To use Workgroup Manager, open the application and access the directory where the
user account resides. Authenticate as domain administrator, then select a user with a
crypt password. Click Advanced, choose Open Directory from the User Password Type
pop-up menu, click Basic, specify a new password, and click Save.
For more information about slapconfig, see its man page.
LDAP ACLs
Due to a change in format, you must manually move the LDAP access control lists
(ACLs) after the upgrade is finished. During the upgrade process, the container or
record for accesscontrols and ACL information is made available as Read-Only.
Add custom ACLs to the new olcAccess attribute (in olcBDBConfig). You must also use
set directive instead of the group directive.
the
LDAP Schemas
If you update the slapd.conf file when adding schema files, run the slaptest
command. This command identifies the change for the new schema addition and
makes it persistent in the database.
To run the slaptest command:
1 Back up the slapd.d directory (in /etc/openldap).
2 Run the following command to specify an alternative slapd.conf file:
slaptest -f
<path_to_slapd.conf>
-F
<path_to_slapd.d>
3 Compare the old slapd.d directory with the new directory to determine which changes
need to be made.
4 Restart slapd.
DNS
When you select DNS in Server Admin for the first time after an upgrade, Server Admin
prompts you whether to upgrade.
If you click Don’t Upgrade, Server Admin leaves the DNS configuration files as they
were before the v10.5 upgrade. DNS still runs, but you can’t make DNS configuration
changes using Server Admin. If you need to make changes, you must edit the DNS
configuration files.
If you click Upgrade, Server Admin upgrades the configuration files to the v10.5 format.
After that, you can use Server Admin to make DNS configuration changes.
24 Chapter 2 Upgrading Mac OS X Server v10.4
Page 25

NetBoot Images
You can reuse NetBoot images created using versions 10.3 and 10.4 following the
upgrade.
To manage Netboot images, you use System Image Utility, which replaces Network
Image Utility during the upgrade.
The Open Directory Upgrade Log
Information about upgrading the Open Directory LDAP server is stored in
/Library/Logs/slapconfig.log.
Web Service
If you’ve modified /etc/httpd/workers.properties, reapply your changes to the version
of the file that’s installed with Mac OS X Server v10.5.
Upgrading Apache Web Server to v2.2 from v1.3
When you upgrade from Mac OS X Server v10.4.10 or later to Mac OS X Server v10.5, the
upgrade process keeps Web service configured to run Apache v1.3.
To switch to Apache v2.2 after upgrading to Mac OS X Server v10.5, use Web service’s
Apache upgrade option in Server Admin.
To upgrade to Apache v2.2:
1 Open Server Admin.
2 From the list of computers and services, select Web.
3 Click Overview and then click Upgrade Apache Version.
4 Click 2.2.
5 Click Continue.
6 After Upgrading succeeds, click Close.
7 In the Overview pane, verify that the Apache version is 2.2.
Important: Apache 2.2 runs as a 64-bit process on appropriate hardware, but Apache
1.3 is 32-bit only.
WARNING: There are possible side-effects when running of the Apache 1-to-Apache 2
conversion script, particularly for security-related settings, which will impact the
security of your upgrade.
For more information about upgrading to Apache 2.2, see Network Services
Administration.
Chapter 2 Upgrading Mac OS X Server v10.4 25
Page 26

26 Chapter 2 Upgrading Mac OS X Server v10.4
Page 27

3 Migrating from Mac OS X Server
v10.4
3
Use the instructions in this chapter when you need to
migrate data from a v10.4.10 or later server to a different
computer running v10.5.
You can migrate data from Mac OS X Server v10.4.10 or later computers that can’t or
won’t be upgraded to v10.5 or later. Such computers may:
 Require hard disk reformatting or replacement with a newer computer.
 Be using server hardware that doesn’t have:
 An Intel or PowerPC G5 or G4 (867 MHz or faster) processor
 At least 1 GB of RAM
 At least 20 GB of available disk space
Before You Begin
Before using the instructions in this chapter, perform initial setup of the v10.5 server
that you’ll migrate data to. For instructions, see Getting Started.
If necessary, upgrade the server whose data you’ll migrate so it’s running v10.4.10
or later.
When the server is an Open Directory master or replica, set up the v10.5 master and
then set up the v10.5 replicas.
27
Page 28

To reestablish the master and its replicas:
1 Set up the v10.5 master.
While you’re setting up the master, client computers can’t connect to the v10.4.10 or
later master for Open Directory services.
In addition, clients may experience a delay while automatically finding the nearest
Open Directory replica server. You can eliminate this delay by changing the DHCP
service to use the address of an Open Directory replica server if it provides clients with
an LDAP server address.
When the v10.5 master is ready, you can change the DHCP service to use the address of
the master.
For instructions on configuring LDAP settings in DHCP service, see Network Services
Administration.
2 Change the v10.4.10 or later replica’s role to standalone, then set up the v10.5 server to
be a replica of the v10.5 master.
For instructions about changing a server’s Open Directory role to standalone and
replica, see Open Directory Administration.
For information about resetting passwords in the master, see Step 6 on page 37.
Understanding What You Can Migrate
The information in “Step-by-Step Instructions” on page 30 describes how to reuse the
following v10.4 data with v10.5:
 Web configuration data
 Web content
 MySQL data
 Mail database
 WebMail data
 FTP configuration files
 LDAP server settings
 NetBoot images
 WebObjects applications and frameworks
 Tomcat data
 JBoss applications
 AFP settings
 SMB Settings
 IP firewall configuration
 DNS settings
 DHCP settings
28 Chapter 3 Migrating from Mac OS X Server v10.4
Page 29

 NAT settings
 Print settings
 VPN settings
 User data, including home directories
 QuickTime Streaming Server files and folders
 QTSS Publisher files and folders
 User and group accounts
 iChat server settings
Use serveradmin or Server Admin to export all service settings for reference. Store the
exported service settings on a removable drive or another system.
Note: One way to save service settings in Server Admin is to select the service from the
list of computers and services on the left, click Settings, and drag the button on the
bottom-right to the Desktop. Dragging this button creates a file on the Desktop
containing the service settings.
In v10.5,
watchdog has been replaced by launchd. To reenable automatic hardware
restart, use the Energy Saver pane of System Preferences. To migrate settings for
services you added to /etc/watchdog.conf, create a launchd plist file and install it into
/System/Library/LaunchDaemons/. For more information about launchd, see its man
page.
Tools You Can Use
Several tools are available:
 You can use Workgroup Manager to export v10.4 user and group accounts to a
delimited file and then import them into a v10.5 server. You can also import users
and groups using the command-line dsimport tool.
 Workgroup Manager’s import facility and the dsimport tool also let you import other
kinds of data, such as computers and computer lists.
 Use the 59_webconfigmigrator tool to migrate Web service settings.
 Use the 50_ipfwconfigmigrator to export Firewall service settings.
 Use the 58_jabbermigrator.pl to migrate iChat service settings.
Instructions in the following sections explain when and how to use these utilities.
Chapter 3 Migrating from Mac OS X Server v10.4 29
Page 30
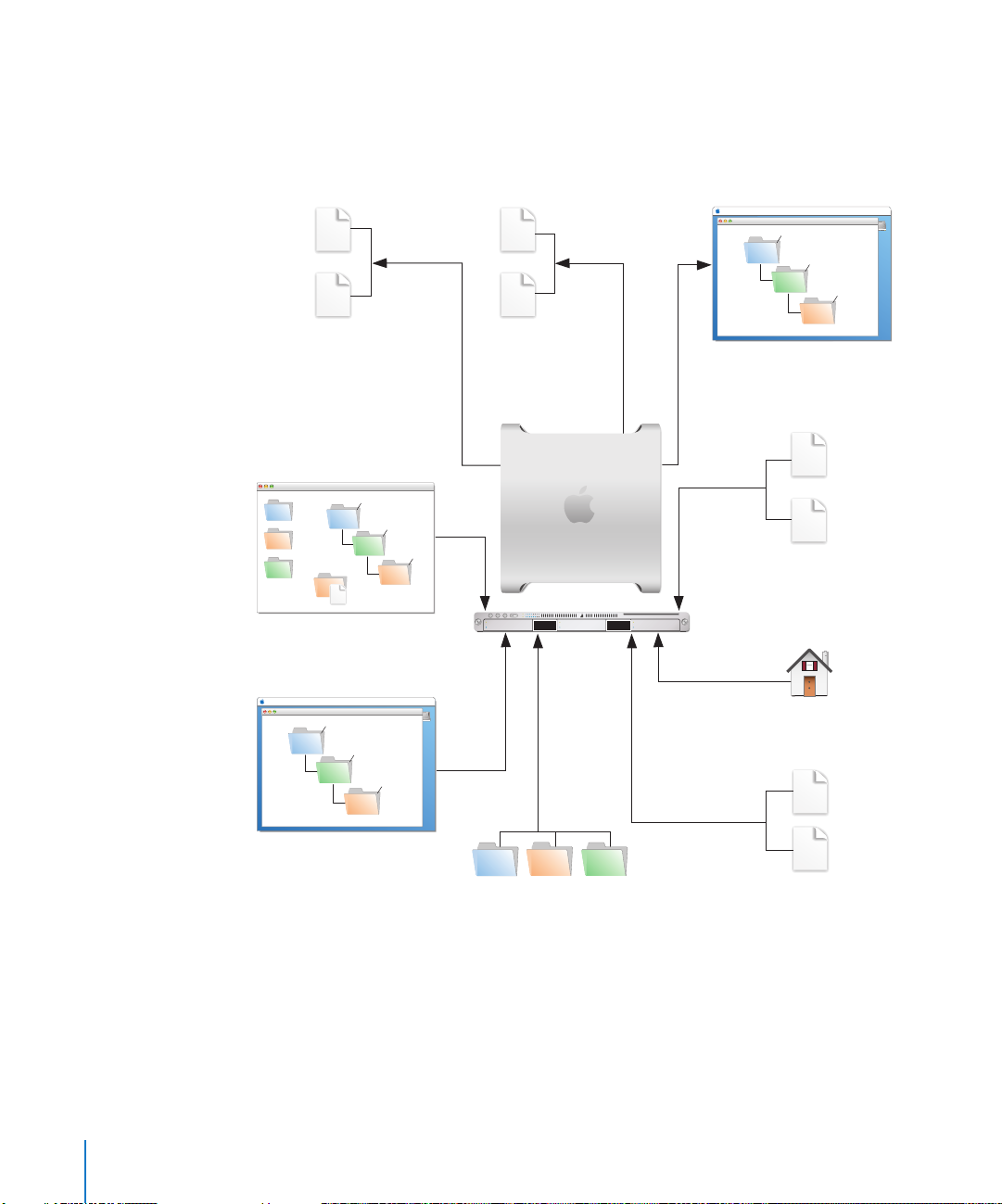
Step-by-Step Instructions
To move data from a Mac OS X Server v10.4.10 or later computer to a computer with
Mac OS X Server v10.5 installed, follow the instructions in this section.
1 Export user and
group information.
user
group
2017
Workgroup Manager
9 Test the new server.
Shared Folders
Read & Write
Engineering
Read & Write
Designs
Documents
.XML
8 Set up share points
and privileges.
Shared Folders
Read & Write
Engineering
Read & Write
Designs
Read Only
Documents
2 Create archive files of data
and user export files.
userdata.tar
database.tar
Read Only
3 Note current share
points and privileges.
Shared Folders
Read & Write
Engineering
Read & Write
Designs
Read Only
Documents
4 Copy archive files
to new server.
userdata.tar
database.tar
5 Set up home
directory
infrastructure.
6 Import user
and other data.
user
Workgroup
Manager or
dsimport tool
group
2017
7 Relocate data files
on new server.
30 Chapter 3 Migrating from Mac OS X Server v10.4
Page 31

Step 1: Export users and groups
Use Workgroup Manager to export user and group accounts from a NetInfo or LDAPv3
directory into a character-delimited file that you can import into a directory for use
with Mac OS X Server v10.5.
To export users and groups:
1 In Workgroup Manager, click Accounts, then click the globe icon below the toolbar and
choose the directory that you want to export accounts from.
2 Click the lock to authenticate as domain administrator (typically diradmin).
3 Click the Users button to export users or click the Groups button to export groups.
4 Export user or group accounts as follows:
 To export all accounts, select all of them.
 To export one account, select it.
 To export multiple accounts, select them while holding down the Command or Shift
key.
5 Choose Server > Export.
6 Specify a name to assign to the export file and the location where you want it created.
7 Click Export.
When you export users using Workgroup Manager, password information isn’t
exported. If you want to set passwords, you can modify the export file before you
import it or you can individually set passwords after importing using the passwd
command or Workgroup Manager. For more information about setting passwords after
importing users, see User Management.
Step 2: Create archives of the following files
Save all data files that you want to reuse with Mac OS X Server v10.5. In Step 4 you’ll
move the files described below, as well as the export file created in Step 1, to the v10.5
computer.
For large amounts of data, you may want to create one or more tar archives or use
/usr/bin/mkdmg to create disk image files. You can transfer disk images and tar files
using AFP or FTP.
Note: You can also use scp -r for secure copying of files and rsync for remote file
copying. The rsync command is particularly useful where you have a large amount of
data that can be migrated before cutting over, and then updated in a small downtime
window.
Chapter 3 Migrating from Mac OS X Server v10.4 31
Page 32

To create a tar archive, use the tar command in the Terminal application. The
command’s -c flag creates an archive file in tar format. Use the -f flag to specify the
archive file name. Use the
-v (verbose) flag to view progress information as the
command executes:
tar -cvf /MyHFSVolume/Stuff.tar /MyHFSVolume/My\ Stuff
The escape character (\ in the example above) indicates a space in the name. You can
also use quotation marks to handle embedded spaces:
tar -cvf /MyHFSVolume/Stuff.tar "/MyHFSVolume/My Stuff"
Web Configuration Data
Save the following files and directories:
 /etc/httpd/httpd.conf
 /etc/httpd/httpd_macosxserver.conf
 /etc/httpd/httpd_mailman.conf
 /etc/httpd/httpd_squirrelmail.conf
 /etc/httpd/magic
 /etc/httpd/mime.types
 /etc/httpd/mime_macosxserver.types
 /etc/httpd/ssl.crt
 /etc/httpd/ssl.key
 /etc/httpd/tomcat.conf
 /etc/webperfcache/webperfcache.conf
 /Library/WebServer/
Web Content
Copy web content you want to reuse from:
 /Library/WebServer/Documents/
 /Library/WebServer/CGI-Executables/
 Any other location where it resides
MySQL Data
Mac OS X Server v10.4.10 or later inlcludes MySQL v4.1.22. Mac OS X Server v10.5 installs
MySQL v5.0.45.
To migrate MySQL databases from one computer to another, you can use the
mysqldump command to back up your data. This command has several forms
depending on the scope of data to be backed up: individual tables, single databases,
or the entire set of databases on the server.
To back up individual tables, enter:
mysqldump
32 Chapter 3 Migrating from Mac OS X Server v10.4
database tb1 [tb2 tb3
...] >
backup-file
.sql
Page 33

where
and
database
tb3
represent table names.
is the name of the database containing the listed tables and
tb1, tb2
,
To back up one or more databases, enter:
mysqldump --databases
db1 [db2 db3
...] >
backup-file
.sql
To back up all database on the system, enter:
mysqldump --all-databases >
backup-file
.sql
Additional instructions for database backup and restore can be found in the MySQL
documentation at www.mysql.org.
To back up tables or databases that require root access (for example, grant tables or
other restricted data), run mysqldump with the --user=root and -p options:
mysqldump --user=root -p --all-datagases >
backup-file
.sql
The -p option causes mysqldump to prompt for the MySQL root password before
proceeding.
Mail Database
If you want to reuse the Mail service database and store, stop Mail service if it’s running
and save the mail files. When Mail service is not running, you can copy all Mail service
directories.
By default:
 The mail database resides in /var/imap/.
 The mail store resides in /var/spool/imap/. You can back up individual mail storage
folders or the entire mail store.
The ditto command-line tool is useful for backing up mail files. For more information
about ditto, see its man page.
Also, save a copy of the file /usr/bin/cyrus/bin/ctl_mboxlist so you can move it to the
v10.5 server in Step 4 on page 36. You need this file to migrate the mail database
successfully in Step 7 on page 39.
Webmail Data
If you’ve been using SquirrelMail that was installed when you installed v10.4 and you
want to continue using it after migration, make copies of the address books and
preferences stored in /var/db/squirrelmail/data/.
Chapter 3 Migrating from Mac OS X Server v10.4 33
Page 34

FTP Configuration Files
To migrate your FTP settings, save these configuration files:
In this directory Save these files
/Library/FTPServer/Configuration/ ftpaccess
ftpconversions
ftphosts
ftpgroups
ftpusers
/Library/FTPServer/Messages/ banner.txt
welcome.txt
limit.txt
LDAP Server
Back up the LDAP server configuration information.
To back up the Open Directory database, which includes LDAP server configuration:
1 In Server Admin, select Open Directory from the list of computers and services.
2 Click Archive.
3 In the “Archive in” field, browse for the archive path.
4 Click the Archive button.
5 In the Archive Name field, enter the name of the file where the information will be
stored.
6 In the Password field, enter the password for the archive.
7 Click OK.
AFP
Save /Library/Preferences/com.apple.AppleFileServer.plist.
SMB
Save /Library/Preferences/SystemConfiguration/com.apple.smb.server.plist.
NetBoot Images
You can migrate NetBoot images created using Mac OS X Server v10.4.
Save the <name>.nbi folder for each image you want to migrate, noting the path to
the folder if you want to recreate it in v10.5.
Also save the NetBoot settings. In Server Admin, select NetBoot from the list of
computers and services on the left, click Settings, and drag the button on the bottomright to the Desktop. Dragging this button creates a file on the Desktop containing the
NetBoot service settings. Save this file.
34 Chapter 3 Migrating from Mac OS X Server v10.4
Page 35

WebObjects Applications and Frameworks
Save WebObjects applications and frameworks located in:
 /Library/WebObjects/
 /System/Library/WebObjects/
Tomcat Data
Save any Tomcat servlets you want to reuse. They’re in /Library/Tomcat/webapps/.
If you’ve installed Axis independent of the version supplied with your server, save any
Simple Object Access Protocol (SOAP) services.
JBoss Applications
Save JBoss applications located in /Library/JBoss/3.2/deploy/.
IP Firewall
In the Terminal application, run this command:
sudo /System/Library/ServerSetup/MigrationExtras/50_ipfwconfigmigrator
Then, save the contents of /etc/ipfilter.
NAT
Save the contents of /etc/nat/natd.plist.
Print
Use the serveradmin settings print command to save print settings before you start
the migration process.
serveradmin settings print >
exported_print_settings
Also, record the names and IDs of the CUPS queues for later use.
VPN
Copy:
 /Library/Preferences/SystemConfiguration/com.apple.RemoteAccessServers.plist
 /Library/Keychains/System.keychain
 /etc/racoon/psk.text
If L2TP is set up and psk.text stores the IPsec shared secret, the shared secret may
also be stored in com.apple.RemoteAccessServers.plist or System.keychain.
DNS
Save the file /etc/named.conf and the directory /var/named/ and all its contents.
Chapter 3 Migrating from Mac OS X Server v10.4 35
Page 36

DHCP
In Server Admin, select DHCP from the list of computers and services on the left, click
Settings, and drag the button on the bottom-right to the Desktop.
Dragging this button creates a file on the Desktop containing the DHCP service
settings.
Save this file.
User Data
Save any user data files or folders you want to reuse, especially home directory folders.
QuickTime Streaming Server Files and Folders
Save files and folders in /Library/QuickTimeStreaming/.
QTSS Publisher Files and Folders
Save the following:
 The files and folders in /Library/Application Support/Apple/QTSS Publisher/
 The files and folders in each QTSS Publisher user’s path:
/Users/<publisher_user>/Library/Application Support/Apple/QTSS Publisher
iChat Server
Save the following folders:
 /var/jabber/spool
 /etc/jabber
Step 3: Note current share points and privileges
If your v10.4 server has share points and privileges you want to recreate on the v10.5
server, make a note of them. Record which share points are for home directories.
Step 4: Copy archive files to the new server
Transfer the files you saved in Steps 1 and 2 to the v10.5 server.
To transfer tar files or disk images using FTP:
1 Use Server Admin on the new server to start FTP service.
2 Set up sharing for a folder where you’ll place files you transfer from the v10.4 computer.
3 From the v10.4 server, use FTP service to copy the tar files or disk images to the v10.5
computer.
4 On the v10.5 server, double-click a tar file to extract its contents or double-click a disk
image to mount it.
36 Chapter 3 Migrating from Mac OS X Server v10.4
Page 37

Step 5: Set up the home directory infrastructure
Set up the destination for home directories you want to restore.
The home directory location identified in imported user accounts must match the
physical location of the restored home directories, including the share point location.
For details on how to perform the steps in the following procedure, see User
Management.
To prepare the server to store home directories:
1 Create the folder you want to serve as the home directory share point, if required.
You can use the predefined /Users folder, if you like.
2 Open Server Admin on the server where you want home directories to reside.
3 Click File Sharing to set up a share point for home directories.
If user accounts will reside in a shared Open Directory directory, create a dynamically
automounted AFP or NFS share point for the home directories. Make sure the share
point is published in the directory where the user accounts that depend on it will
reside.
4 In Workgroup Manager on the computer where you’ll import users, click Accounts, then
open the directory where you’ll import users.
If you restore home directories in locations that won’t exactly match the locations
identified in exported user records, you can define a preset that identifies the restore
location. If you identify the preset when you import users, the new location will replace
the existing location in user records.
You can also use the preset to specify other default settings you want imported users
to inherit, such as password settings, mail settings, and so forth.
Step 6: Import users and groups and other data
If you’re migrating users and groups from an Open Directory master, use the
instructions in “LDAP Server Settings” on page 41. If you’re migrating local node users
and groups, use Workgroup Manager or the dsimport tool.
For more information about importing by using Workgroup Manager, see User
Management.
For more information about passwords of users originally created with Mac OS X Server
v10.1.5 or earlier, see Open Directory Administration.
For more information about
dsimport and a description of Workgroup Manager export
format, see Command-Line Administration.
Chapter 3 Migrating from Mac OS X Server v10.4 37
Page 38

To import users and groups using Workgroup Manager:
1 Place the export files you created in Step 1 in a location accessible from your server.
You can modify user accounts in an export file if you want to set passwords before
importing users. For instructions, see User Management.
Additionally, you can set up the preset you defined in Step 5 above so that user
passwords are validated using Open Directory authentication, and you can set up the
password validation options so users must change their passwords the next time they
log in.
For information about using Kerberos passwords, see the last step in this sequence.
2 In Workgroup Manager, click the Accounts button.
3 Click the globe icon in the toolbar to open the directory where you want to import
accounts.
4 Click the lock to authenticate as domain administrator.
5 Choose Server > Import, select the import file, and specify import options.
If you’re using a preset, make sure you specify the preset.
6 Click Import.
7 If you want groups to use new v10.5 features, upgrade groups using Workgroup
Manager.
In Workgroup Manager, open the directory containing the groups, select one or more
of the groups, click “Upgrade legacy group,” and click Save.
8 To create home directories for imported users, use one of the following options.
Create home directories one at a time by selecting a user account in Workgroup
Manager, clicking Home, then clicking Create Home Now.
Create all home directories by using the -a argument of the createhomedir command.
For details, see Command-Line Administration or the man page for createhomedir.
A home directory associated with an AFP share point is created the first time a user
logs in, if it doesn’t exist already.
9 If you want to enable Kerberos for an Open Directory master that it’s not enabled for,
use the following command, which maintains existing passwords and adds them to a
new KDC.
slapconfig -kerberize
If you have user accounts with crypt passwords and you don’t Kerberize them using the
above command, you can use Workgroup Manager to upgrade to Open Directory
passwords.
38 Chapter 3 Migrating from Mac OS X Server v10.4
Page 39

To use Workgroup Manager, open the application and access the directory where the
user account resides. Authenticate as the Open Directory administrator (typically
diradmin), then select a user with a crypt password. Click Advanced, choose Open
Directory from the User Password Type pop-up menu, click Basic, specify a new
password, and click Save.
For more information about slapconfig, see its man page.
Step 7: Relocate the following saved data files
Place the files you saved from your v10.4 server in their final locations.
Web Configuration Data
To migrate the web configuration:
1 Open Server Admin.
2 Under the v10.5 server in the list of computers and services, click Web.
3 Click Stop Web if Web service is running.
4 Delete the following files:
 /etc/httpd/sites
 /etc/httpd/ssl.crt
 /etc/httpd/ssl.key
5 Copy the saved v10.4 files and directory onto the v10.5 server.
6 In the Terminal application, enter the following command:
sudo cd /etc/httpd
7 As the root user, open the httpd.conf file for editing.
8 In the httpd.conf file:
 Replace var/run/proxy with /var/run/proxy-1.3.
 Replace /var/run/httpd.pid with /var/run/http-1.3.pid.
9 Save your changes.
10 To migrate the web settings, in Terminal, run the following command:
sudo /System/Library/ServerSetup/translateApache.rb
11 If you’ve modified /etc/httpd/workers.properties, reapply all your changes to the
version of the file that’s installed with server v10.5.
The v10.5 workers.properties file has a new entry for Blog service.
12 In Server Admin, start Web service.
Chapter 3 Migrating from Mac OS X Server v10.4 39
Page 40

Web Content
Copy saved web content to the following locations and anywhere else you have placed
web content on the server:
 /Library/WebServer/Documents/
 /Library/WebServer/CGI-Executables/
MySQL Data
Before importing backed up MySQL data, make sure that the MySQL service is active.
You can activate the MySQL service using Server Admin or the serveradmin command.
To activate the MySQL service using the serveradmin command, enter:
serveradmin start mysql
To import database backups enter:
mysql <
backup-file
.sql
To import data into databases that require privileged access, run mysql with the --
user=root
mysql --user=root -p <
and -p options:
backup-file
.sql
The -p option causes mysql to prompt for the MySQL root password before proceeding.
Additional instructions for MySQL database backup and restoration can be found in the
MySQL documentation at www.mysql.org.
Mail Database
To migrate the mail database:
1 Make sure that v10.5 Mail service isn’t running.
Open Server Admin, then click Mail. If the Mail circle on the left side is not grayed out,
click Stop Mail at the lower left.
2 Restore the saved mail database and mail store.
By default the mail database resides in /var/imap/ and the mail store in /var/spool/
imap/.
3 Make sure the mail directories and their contents are owned by the _cyrus user and
mail group.
4 Rename the saved ctl_mboxlist file to ctl_mboxlist.old and then move it to /usr/bin/
cyrus/bin/.
If ctl_mboxlist.old is not present, the upgradedb script will fail in step 8 below.
5 In Server Admin, select Mail from the list of computers and services.
6 Click Settings, click Advanced, and click Database to indicate where you restored the
database and mail store.
7 Click Save.
40 Chapter 3 Migrating from Mac OS X Server v10.4
Page 41

8 Run the mail database upgradedb script:
sudo -u cyrusimap /System/Library/ServerSetup/MigrationExtras/
61_migrate_cyrus_db
9 Run the following command to insure that the index files for all mail accounts are in
good working order:
sudo /usr/bin/cyrus/bin/reconstruct –i
10 In Server Admin, start Mail service by clicking Mail, then click Start Mail.
Webmail Data
Place saved address books and preferences in /var/db/squirrelmail/data/.
FTP Configuration Files
Copy saved FTP configuration files to:
 /Library/FTPServer/Configuration/
 /Library/FTPServer/Messages/
LDAP Server Settings
Restore the LDAP server configuration information.
To restore the Open Directory database, which includes LDAP server configuration:
1 In Server Admin, select Open Directory from the list of computers and services:
2 Click Archive.
3 In the “Archive from” field, browse for the archive.
4 Click the Restore button.
5 In the Password field, enter the password for the archive.
6 Click OK.
AFP Configuration
To migrate the AFP configuration, restore /Library/Preferences/
com.apple.AppleFileServer.plist.
SMB Configuration
To migrate the AFP configuration, restore /Library/Preferences/SystemConfiguration/
com.apple.smb.server.plist.
NetBoot Images
Copy the <name>.nbi folder for each image you want to migrate, optionally placing it
into the location where it previously resided.
Also, restore the NetBoot settings file.
Chapter 3 Migrating from Mac OS X Server v10.4 41
Page 42

To restore the NetBoot settings:
1 Open Server Admin and select NetBoot from the list of computers and services.
2 Choose Server > Import > Service Settings to import the NetBoot settings from the file
you exported earlier (see “NetBoot Images” on page 34).
3 Review the NetBoot settings to make sure they were imported correctly.
WebObjects Applications and Frameworks
To migrate WebObjects:
1 Copy saved applications to /Library/WebObjects/Applications/.
2 Copy saved frameworks to /Library/Frameworks/.
3 Add the following line to the new httpd.conf file:
Include /System/Library/WebObjects/Adaptors/Apache/apache.conf
Note: JavaMonitor and WebObjects Task Daemon (wotaskd) services are now managed
by launchd and can be accessed through Server Admin. If the server you’re upgrading
has the startup item /System/Library/StartupItems/WebObjects, you can ignore it. It’s
disabled by default and isn’t necessary for autostarting WebObjects services with
Mac OS X Server v10.5. For more information, see Web Technologies Administration and
WebObjects Deployment.
4 (Optional) If you didn’t have Java 1.4.2 installed on your v10.4.10 or later server, manually
update WebObjects application projects by opening each project in Xcode; then, in the
Expert View for the main target’s settings, change the property value for JAVA_VM to
java.
These projects must be manually updated to use the version of the Java Virtual
Machine (JVM) included with Mac OS X Server v10.5.
Important: Mac OS X Server v10.5 includes WebObjects 5.4, which requires Java 1.5 to
be installed.
Tomcat Data
Restore Tomcat servlets to /Library/Tomcat/webapps/.
Place SOAP services you want to migrate in /Library/Tomcat/webapps/axis/. Mac OS X
Server v10.5 includes a version of Axis that may be newer or older than the version
you’ve been using.
JBoss Applications
JBoss does not come with Mac OS X Server v10.5. Before you can restore your JBoss
applications, install JBoss on your server.
For more information about installing and migrating JBoss applications, see the JBoss
documentation.
42 Chapter 3 Migrating from Mac OS X Server v10.4
Page 43

IP Firewall Configuration
To migrate the IP firewall configuration, restore the /etc/ipfilter folder.
Open Server Admin and click Firewall to inspect the settings and make sure they are
correct.
NAT
Restore the contents of /etc/nat/natd.plist.
You can restore the v10.5 default settings for NAT (stored in
/etc/natd/natd.plist.default) at any time by deleting the active configuration file (/etc/
nat/natd.plist). The next time NAT is accessed using Server Admin, the default
configuration file is used to recreate the active configuration file.
Note: In v10.5, the default setting of unregistered_only in /etc/nat/natd.plist.default is
true.
Print Service Settings
To restore Print service settings, you must first recreate the original CUPS queues before
importing the saved settings.
In the case of printers connected directly to the server via USB, the queues are created
by CUPS when the printers are plugged in and turned on. However, for network
printers, you must add the printers using Server Admin > Print (for LPR or AppleTalk
printers) or System Preferences > Print & Fax (for all printer types).
Important: When recreating a CUPS queue, make sure you give it the same name as
the one it had on the older system. If the name is not the same, Server Admin won’t
import the settings correctly.
Important: When creating the print queues using the Print & Fax pane of System
Preferences, specify Generic Postscript (Generic PPD) for any queue that enforces
quotas because there are known issues with third-party printer drivers and CUPS
quotas. For more information about this issue, see the Knowledge Base article at
http://docs.info.apple.com/article.html?artnum=303538.
After creating the print queues, import the saved settings:
serveradmin settings
Chapter 3 Migrating from Mac OS X Server v10.4 43
exported_print_settings
Page 44

VPN
Restore the following:
 /Library/Preferences/SystemConfiguration/com.apple.RemoteAccessServers.plist.
 /Library/Keychains/System.keychain
 /etc/racoon/psk.text
If L2TP is set up and psk.text stores the IPsec shared secret, the shared secret may
also be stored in com.apple.RemoteAccessServers.plist or System.keychain.
Migrate the VPN MPPE Key user by using the vpnaddkeyagentuser command-line tool.
For more information about this command, see its man page.
DNS Configuration
To migrate the DNS configuration:
1 Restore the file /etc/named.conf and the directory /var/named/ and all its contents.
2 In Server Admin, select DNS from the list of computers and services.
A dialog box appears prompting you whether to upgrade:
 If you click Don’t Upgrade, Server Admin leaves the DNS configuration files as they
were before the v10.5 migration. DNS will still run, but you can’t make DNS
configuration changes using Server Admin. To make changes, you must directly edit
the DNS configuration files.
 If you click Upgrade, Server Admin upgrades the configuration files to the v10.5
format. After that, you can use Server Admin to make DNS configuration changes.
DHCP Settings
To migrate the DHCP configuration:
1 Open Server Admin and select DHCP from the list of computers and services.
2 Choose Server > Import > Service Settings to import DHCP settings from the file you
exported earlier (see “DHCP” on page 36).
3 Inspect the Subnets and Static Maps panes of the DHCP service to make sure the
subnet and static binding settings have been imported correctly.
User Data
Restore saved user data files.
Place home directories in locations that match the locations in the imported user
records. If necessary, you can use Workgroup Manager to edit user accounts so the
locations in the account and on disk are the same.
QuickTime Streaming Server Files and Folders
Follow instructions in QuickTime Streaming and Broadcasting Administration to reuse
files and folders saved from /Library/QuickTimeStreaming/.
44 Chapter 3 Migrating from Mac OS X Server v10.4
Page 45

QTSS Publisher Files and Folders
QTSS Publisher has been removed from Mac OS X Server v10.5. However, files created
using the QTSS Publisher on v10.4 should continue to work on v10.5.
Restore QTSS Publisher files and folders on Mac OS X Server v10.5.
QTSS Publisher Media and MP3 files should be stored in:
 /Library/Application Support/Apple/ QTSS Publisher/Libraries/
 /Users/<publisher_user>/Library/Application Support/Apple/QTSS Publisher/
Libraries/
To migrate QTSS Publisher media and MP3 playlists to QTSS Web Admin:
1 Move all folders in /Library/Application Support/Apple/QTSS Publisher/Playlists/ to
/Library/QuickTimeStreaming/Playlists.
For example, you would move:
/Library/Application Support/Apple/QTSS Publisher/Playlists/my_playlist/
to
/Library/QuickTimeStreaming/Playlists/my_playlist/
2 Verify that the owner of folders and files in /Library/QuickTimeStreaming/Playlists is
qtss.
3 For media playlists, verify that the folder /Library/Application Support/Apple/QTSS
Publisher/Libraries/Media/ contains the media files listed in the .playlist files.
4 For MP3 playlists, verify that the folder /Library/Application Support/Apple/QTSS
Publisher/Libraries/MP3/ contains the media files listed in the .playlist files.
5 For every playlist, update its .config file so that paths point to the new playlist folder in
/Library/QuickTimeStreaming/Playlists.
This includes the paths defined in the pid_file, playlist_file, and sdp_file (media playlists
only) preferences.
6 Enable QTSS web-based administration using Server Admin.
7 Open Web Admin using Safari (http://<hostname>:1220) and log in.
8 Click Playlists.
You can now start manage QTSS Publisher playlists using QTSS Web Admin.
For information about using Web Admin, see the QuickTime Streaming Server Darwin
Streaming Server Administrator’s Guide available at developer.apple.com/opensource/
server/streaming.
Chapter 3 Migrating from Mac OS X Server v10.4 45
Page 46

iChat Server
To migrate iChat server settings:
1 Restore the following folders:
 /var/jabber/spool
 /etc/jabber
2 Run the following script with root privileges:
sudo execute "/System/Library/ServerSetup/MigrationExtras/
58_jabbermigrator.pl
The 58_jabbermigrator.pl script invokes three other scripts to migrate the iChat
server settings. If needed, you can run these scripts individually to customize the
migration. The scripts are documented and contain helpful information.
Step 8: Set up share points and privileges
Recreate the share points and privileges as required.
To create a share point and set privileges:
1 Open Server Admin and click File Sharing.
2 Click Volumes and select the volume or folder you want to share.
3 Click Share.
4 Click Permissions to set up access privileges.
5 Click Save.
New share points are shared using AFP, SMB, and FTP, but not NFS. To export a share
point using NFS, use the Protocol pane. For more information about setting up share
points, see File Services Administration.
Step 9: Test the new server
To test the new server:
1 Open Workgroup Manager and inspect user and group accounts.
2 Open Server Admin and inspect settings for services whose configuration data you
migrated.
46 Chapter 3 Migrating from Mac OS X Server v10.4
Page 47

4 Upgrading Mac OS X Server v10.3
4
Use the instructions in this chapter to upgrade a v10.3.9
server to v10.5.
You can upgrade computers with Mac OS X Server v10.3.9 that don’t require hard disk
reformatting and that have:
 An Intel or PowerPC G5 or G4 (867 MHz or faster) processor
 At least 1 GB of RAM
 At least 20 GB of disk space available
Understanding What Can Be Reused
When you upgrade from Mac OS X Server v10.3.9, virtually all existing data and settings
remain available for use, but note the following:
 NetBoot images created using v10.3 can be reused.
 In v10.5, watchdog has been replaced by launchd. To re-enable automatic hardware
restart, use the Energy Saver pane of System Preferences. To migrate settings for
services you added to /etc/watchdog.conf, create a launchd plist file and install it into
/System/Library/LaunchDaemons/. For more information, see the man page for
launchd.conf.
 In v10.5, hwmond has been replaced by launchd.
 Upgrading to v10.5 removes the QTSS Publisher application but leaves the files used
by the application. These files should continue to work on v10.5, but you must move
them to the appropriate locations. For more information about how to do that, see
“QTSS Publisher Files and Folders” on page 45.
Note: Macintosh Manager is not supported in Mac OS X Server v10.5.
47
Page 48

.
Upgrading an Open Directory Master and Its Replicas
When the server you want to upgrade is an Open Directory master or replica, upgrade
the master and then upgrade the replicas.
To upgrade the master and its replicas:
1 Upgrade the master to v10.5 following the instructions in “Step-by-Step Instructions”
on page 48.
While you’re upgrading the master, client computers can’t connect to it for Open
Directory services.
In addition, clients may experience a delay when finding the nearest Open Directory
replica server. You can eliminate this delay by changing the DHCP service to use the
address of an Open Directory replica server if the server provides clients with an LDAP
server address.
When the master upgrade is complete, you can change the DHCP service to use the
address of the master.
For instructions on configuring LDAP settings in DHCP service, see Network Services
Administration.
2 Upgrade each replica server to v10.5.
3 Using Server Admin, connect to each replica server and reestablish the replicas.
For information about resetting passwords in the master, see “Directory Services” on
page 53.
Step-by-Step Instructions
To upgrade a v10.3.9 server to v10.5, follow the instructions in this section.
1 Update your
server to v10.3.9.
3 Make adjustments as needed
after initial server setup.
2 Perform an
upgrade to v10.5
48 Chapter 4 Upgrading Mac OS X Server v10.3
Page 49

Step 1: Update your server to v10.3.9
If necessary, use Software Update to update your server to v10.3.9.
Step 2: Save all service settings
Use serveradmin or Server Admin to export all service settings for reference. Also, use
System Profiler to generate a full profile of your system. Store the exported service
settings and your server’s profile on removable media or another system.
Before upgrading create a full, bootable, tested-by-booting clone of your server as a
backup in case you need it in the future.
Step 3: Save Print service settings
Use the serveradmin settings print command to save the print settings before you
start the upgrade.
serveradmin settings print >
exported_print_settings
Also, record the names and IDs of the CUPS queues for later use.
Step 4: Perform an upgrade to v10.5
You can use the v10.5 installation disc to perform the upgrade locally on your server
computer if it has a display, keyboard, and optical drive attached.
After the upgrade is complete, the computer restarts and Server Assistant leads you
through initial server setup. Your existing settings are displayed, and you can change
them if you like.
To upgrade to v10.5 and perform initial server setup locally:
1 Make sure that DHCP or DNS servers your server depends on are running.
2 Turn on the computer and insert the installation disc into the optical drive.
3 Restart the computer while holding down the C key on the keyboard.
The computer boots from the installation disc. You can release the C key when you see
the Apple logo.
For information about restarting a headless Xserve system, see the user’s guide that
came with the system.
4 When the Installer opens, follow the onscreen instructions to proceed through each
pane, then click Continue.
Note: In the Select a Destination pane, be sure to select the disk or partition on which
v10.3.9 is installed.
During installation, progress information is displayed.
After installation is complete, the computer restarts and Server Assistant opens so you
can perform initial server setup.
Chapter 4 Upgrading Mac OS X Server v10.3 49
Page 50

5 Move through the Assistant’s panes, following the onscreen instructions.
Your existing settings are displayed in the panes, but you can change them if you like.
Enter a unique server software serial number for each server you upgrade. You’ll find
the number printed on the materials provided with the server software package. If you
have a site license, a registered owner name and organization must be entered exactly
as specified by your Apple representative.
After all setup data has been entered, Server Assistant displays a summary of the data.
6 Review the setup data, optionally clicking Go Back to change it.
7 To initiate setup of the server, click Apply.
8 When server setup is complete, click Restart Now.
Note: You may need to manually start the Mail service after upgrading the server.
To upgrade to v10.5 and perform initial server setup remotely:
1 Make sure that any DHCP or DNS servers your server depends on are running.
2 Start the computer from the installation disc.
The procedure you use depends on whether the target server has an optical drive that
can read your installation disc. If you have an installation DVD, the optical drive must
be able to read DVD discs.
If the target server has a keyboard and an optical drive that can read your installation
disc, insert the installation disc into the optical drive, then hold down the C key on the
keyboard while restarting the computer.
If the target server is an Xserve system with a built-in optical drive that can read your
installation disc, start the server using the installation disc by following the instructions
in the Xserve User’s Guide for starting from a system disc.
If the target server lacks a built-in optical drive that can read your installation disc, you
can start it in target disk mode and insert the installation disc into the optical drive on
your administrator computer. You can also use an external FireWire optical drive.
If the target server is an Xserve system, you can move its drive module to another
Xserve system that has an optical drive capable of reading your installation disc.
Instructions for using target disk mode and external optical drives are in the Quick Start
guide, Getting Started guide, or user’s guide that came with your Xserve system or
Macintosh computer.
3 On an administrator computer, navigate to /Applications/Server/ and open Server
Assistant (you don’t need to be an administrator on the local computer to use Server
Assistant), then select “Install software on a remote server.”
50 Chapter 4 Upgrading Mac OS X Server v10.3
Page 51

4 Identify the server you want to upgrade.
If it’s on the local subnet, select it in the list.
Otherwise, click “Server at IP Address” and enter an IP address in IPv4 format
(000.000.000.000).
5 When prompted for a password, enter the old administrator password.
6 Proceed by following the onscreen instructions.
7 When the Volumes pane appears, select a target disk or volume (partition) and click
Continue.
During installation, progress information is displayed.
After installation is complete, the computer restarts, and then Server Assistant opens
and displays a Welcome pane.
8 To initiate server setup, select “Set up a remote server” and click Continue.
9 In the Destination pane, put a check in the Apply column for the server you’re
upgrading, then type its preset password in the Password field and click Continue to
connect to the server.
If you don’t see the server in the list, click Add to add it or Refresh to determine
whether it’s available.
10 Move through the Assistant’s panes, following the onscreen instructions.
Your existing settings are displayed in the panes, but you can change them if you like.
You must enter a unique server software serial number for each server you upgrade.
You’ll find the number printed on the materials provided with the server software
package. If you have a site license, enter the registered owner name and organization
exactly as specified by your Apple representative.
When you use the Directory Usage pane, it’s safest to select “No change” in the server’s
directory setup. After setup is complete, you can make adjustments if necessary,
following instructions in Open Directory Administration.
You can’t enable or disable mail service or WebDAV service in the Services pane.
If either service is running when you upgrade, it will be running afterwards. If either
service is stopped when you upgrade, it will be stopped afterwards.
To enable or disable mail service or WebDAV service, use Server Admin after initial
server setup is complete.
After all setup data has been entered, Server Assistant displays a summary of the data.
11 Review the setup data, optionally clicking Go Back to change it.
12 To initiate setup of the server, click Apply.
13 When server setup is complete, click Restart Now.
Note: You may need to manually start Mail service after upgrading the server.
Chapter 4 Upgrading Mac OS X Server v10.3 51
Page 52

Step 5: Make adjustments as needed after initial server setup
Use Workgroup Manager, Server Admin, Terminal, and other applications to refine your
server’s settings and take advantage of new v10.5 features.
For an explanation of new and changed features, see the administration guide for
individual services. Following are a few suggestions of particular interest.
WebObjects
Restore httpd.conf to the previous version (httpd.conf.AppleSaved), or include the
following line in the new httpd.conf file:
Include /System/Library/WebObjects/Adaptors/Apache/apache.conf
If you didn’t install Java 1.4.2 on your v10.3.9 server, you must manually update
WebObjects application projects to use the version of the Java Virtual Machine (JVM)
included with v10.5.
To update a WebObjects project:
1 Open the project in Xcode.
2 In the Expert View for the main target’s settings, change the property value for
JAVA_VM to java.
Note: JavaMonitor and WebObjects Task Daemon (wotaskd) services are now managed
by launchd and can be accessed through Server Admin. If the server you’re upgrading
has the startup item /System/Library/StartupItems/WebObjects, you can ignore it. It’s
disabled by default and isn’t necessary for autostarting WebObjects services with
Mac OS X Server v10.5. For more information, see Web Technologies Administration and
WebObjects Deployment.
Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) Certificates
Use Server Admin to import existing SSL certificates you want to continue to use for
iChat, Open Directory, Mail, or Web services.
To import an SSL certificate:
1 Open Server Admin.
2 Select the upgraded server in the list of computers and services.
3 Click Certificates.
4 Import the certificates you want to use.
You can also create a self-signed certificate and generate a Certificate Signing Request
(CSR) to obtain an SSL certificate from a certificate authority and then install the
certificate.
5 Click Save.
6 Activate the certificates per service.
52 Chapter 4 Upgrading Mac OS X Server v10.3
Page 53

For more information about importing, creating, and activating self-signed certificates,
see iChat Service Administration, Mail Service Administration, Open Directory
Administration, and Web Technologies Administration.
Groups
If you want groups to use new v10.5 features such as nesting and stricter membership
checking, upgrade group records using Workgroup Manager.
To upgrade a group record:
1 Open Workgroup Manager.
2 Open the directory that contains the groups of interest.
3 Select one or more groups and click “Upgrade legacy group.”
4 Click Save.
Directory Services
After upgrading, you may want to convert a shared NetInfo directory to LDAP. For
details about the advantages of using LDAP and how to use Server Admin to conduct
the conversion, see Open Directory Administration.
If you want to enable Kerberos for an Open Directory master that it’s not enabled on,
use the following command, which maintains existing passwords and adds them to a
new KDC:
slapconfig -kerberize
If you have user accounts with crypt passwords and you don’t Kerberize them using the
above command, you can use Workgroup Manager to use an Open Directory password:
To use Workgroup Manager, open the application and access the directory where the
user account resides. Authenticate as the Open Directory administrator (typically
diradmin), then select a user with a crypt password. Click Advanced, choose Open
Directory from the User Password Type pop-up menu, click Basic, specify a new
password, and click Save.
For more information about slapconfig, see its man page.
LDAP ACLs
Due to a change in format, you must manually move the LDAP ACLs after the upgrade
process is finished. During the upgrade, the container or record for accesscontrols and
ACL information is made available as Read-Only.
Add custom ACLs to the new olcAccess attribute (in olcBDBConfig). You must also use
the set directive instead of the group directive.
Chapter 4 Upgrading Mac OS X Server v10.3 53
Page 54

LDAP Schemas
If you update the slapd.conf file when adding schema files, run the slaptest
command. This command identifies the change for the new schema addition and
makes it persistent in the database
To run the slaptest command:
1 Back up the slapd.d directory (in /etc/openldap).
2 Run the following command to specify an alternative slapd.conf file:
slaptest -f
<path_to_slapd.conf>
-F
<path_to_slapd.d>
3 Compare the old slapd.d directory with the new directory to determine which changes
need to be made.
4 Restart
slapd.
NetBoot Images
You can reuse NetBoot images created using v10.3 following the upgrade.
To manage Netboot images, use System Image Utility, which replaces Network Image
Utility during the upgrade.
Print Service
To restore Print service settings, you must first recreate the original CUPS queues before
importing the saved settings.
In the case of printers connected directly to the server via USB, the queues are created
by CUPS when the printers are plugged in and turned on. However, for network
printers, you must add the printers using Server Admin > Print (for LPR or AppleTalk
printers) or System Preferences > Print & Fax (for all printer types).
Important: When recreating a CUPS queue, make sure you give it the same name as
the one it had before the upgrading process. If the name is not the same, Server Admin
won’t import the settings correctly.
Important: When creating the print queues using the Print & Fax pane of System
Preferences, specify Generic Postscript (Generic PPD) for any queue that enforces
quotas because there are known issues with third-party printer drivers and CUPS
quotas. For more information about this issue, see the Knowledge Base article at
http://docs.info.apple.com/article.html?artnum=303538.
After creating the print queues, import the saved settings:
serveradmin settings
exported_print_settings
54 Chapter 4 Upgrading Mac OS X Server v10.3
Page 55

DNS
When you select DNS in Server Admin for the first time after an upgrade, Server Admin
prompts you whether to upgrade.
If you click Don’t Upgrade, Server Admin leaves the DNS configuration files as they
were before the v10.5 upgrade. DNS still runs, but you can’t make DNS configuration
changes using Server Admin. If you need to make changes, you must edit the DNS
configuration files.
If you click Upgrade, Server Admin upgrades the configuration files to the v10.5 format.
After that, you can use Server Admin to make DNS configuration changes.
The Open Directory Upgrade Log
Information about upgrading the Open Directory LDAP server is stored in /Library/
Logs/slapconfig.log.
Web Service
If you’ve modified /etc/httpd/workers.properties, reapply your changes to the version
of the file that’s installed with v10.5.
Upgrading Apache Web Server to v2.2 from v1.3
When you upgrade from Mac OS X Server v10.3.9 to Mac OS X Server v10.5, the
upgrade process keeps Web service configured to run Apache v1.3.
To switch to Apache v2.2 after upgrading to Mac OS X Server v10.5, use Web service’s
Apache upgrading option in Server Admin. For more information, see “Upgrading
Apache Web Server to v2.2 from v1.3” on page 25.
Chapter 4 Upgrading Mac OS X Server v10.3 55
Page 56

56 Chapter 4 Upgrading Mac OS X Server v10.3
Page 57

5 Migrating from Mac OS X Server
v10.3
5
Use the instructions in this chapter when you need to
migrate data from a v10.3.9 server to a different computer
running v10.5.
You can migrate data from Mac OS X Server v10.3.9 computers that can’t or won’t be
upgraded to v10.5 or later. Such computers may:
 Require hard disk reformatting or replacement with a newer computer.
 Be using server hardware that doesn’t have:
 An Intel or PowerPC G5 or G4 (867 MHz or faster) processor
 At least 1 GB of RAM
 At least 20 GB of disk space available
Before You Begin
Before using the instructions in this chapter, perform initial setup of the v10.5 server
that you’ll migrate data to. For instructions, see Getting Started.
If necessary, upgrade the server whose data you’ll migrate so it’s running v10.3.9.
When the server is an Open Directory master or replica, set up the v10.5 master and
then set up the v10.5 replicas.
57
Page 58

To reestablish the master and its replicas:
1 Set up the v10.5 master.
While you’re setting up the master, client computers can’t connect to the v10.3.9 master
for Open Directory services.
In addition, clients may experience a delay while automatically finding the nearest
Open Directory replica server. You can eliminate this delay by changing the DHCP
service to use the address of an Open Directory replica server if it provides clients with
an LDAP server address.
When the v10.5 master is ready, you can change the DHCP service to use the address of
the master.
For instructions on configuring LDAP settings in DHCP service, see Network Services
Administration.
2 Change the v10.3.9 replica’s role to standalone, then set up the v10.5 server to be a
replica of the v10.5 master.
Open Directory Administration provides instructions for changing a server’s Open
Directory role to standalone and replica.
For information about resetting passwords in the master, see Step 6 on page 66.
Understanding What You Can Migrate
The information in “Step-by-Step Instructions” on page 60 describes how to reuse the
following v10.3 data with v10.5:
 Web configuration data
 Web content
 MySQL data
 Mail database
 WebMail data
 FTP configuration files
 NetBoot images
 WebObjects applications and frameworks
 Tomcat data
 JBoss applications
 AFP settings
 IP firewall configuration
 DNS configuration
 DHCP settings
 NAT settings
 Print settings
58 Chapter 5 Migrating from Mac OS X Server v10.3
Page 59

 VPN settings
 User data, including home directories
 QuickTime Streaming Server files and folders
 QTSS Publisher files and folders
 User and group accounts
Use serveradmin or Server Admin to export all service settings for reference. Store the
exported service settings on removable media or another system.
Note: One way to save service settings in Server Admin is to select the service from the
list of computers and services on the left, click Settings, and drag the button on the
bottom-right to the Desktop. Dragging this button creates a file on the Desktop
containing the service settings.
In v10.5, watchdog has been replaced by launchd. To reenable automatic hardware
restart, use the Energy Saver pane of System Preferences. To migrate settings for
services you added to /etc/watchdog.conf, create a launchd plist file and install it into /
System/Library/LaunchDaemons/. For more information about launchd, see its man
page.
Tools You Can Use
Several tools are available:
 You use Workgroup Manager to export v10.3 user and group accounts to a character-
delimited file and then import them into a v10.5 server. You can also import users
and groups using the command-line dsimport tool.
 Workgroup Manager’s import facility and the dsimport tool also let you import other
kinds of data, such as computers and computer lists.
 You use the 59_webconfigmigrator tool to migrate your web configuration.
 You use the 50_ipfwconfigmigrator tool to migrate your IP firewall configuration.
Instructions in the following sections explain when and how to use these utilities.
Chapter 5 Migrating from Mac OS X Server v10.3 59
Page 60

Step-by-Step Instructions
To move data from a Mac OS X Server v10.3.9 computer to a computer with Mac OS X
Server v10.5 installed, follow the instructions in this section.
1 Export user and
group information.
user
group
2017
Workgroup Manager
9 Test the new server.
Shared Folders
Read & Write
Engineering
Read & Write
Designs
Documents
.XML
8 Set up share points
and privileges.
Shared Folders
Read & Write
Engineering
Read & Write
Designs
Read Only
Documents
2 Create archive files of data
and user export files.
userdata.tar
database.tar
Read Only
3 Note current share
points and privileges.
Shared Folders
Read & Write
Engineering
Read & Write
Designs
Read Only
Documents
4 Copy archive files
to new server.
userdata.tar
database.tar
5 Set up home
directory
infrastructure.
6 Import user
and other data.
user
Workgroup
Manager or
dsimport tool
group
2017
7 Relocate data files
on new server.
60 Chapter 5 Migrating from Mac OS X Server v10.3
Page 61

Step 1: Export users and groups
Use Workgroup Manager to export user and group accounts from a NetInfo or LDAPv3
directory into a character-delimited file that you can import into a directory for use
with Mac OS X Server v10.5.
To export users and groups:
1 In Workgroup Manager, click Accounts, then click the globe icon below the toolbar and
choose the directory that you want to export accounts from.
2 Click the lock to authenticate as domain administrator.
3 Click the Users button to export users or click the Groups button to export groups.
4 Export user or group accounts as follows:
 To export all accounts, select all of them.
 To export one account, select it.
 To export multiple accounts, select them while holding down the Command or Shift
key.
5 Choose Server > Export.
6 Specify a name to assign to the export file and the location where you want it created.
7 Click Export.
When you export users using Workgroup Manager, password information isn’t
exported. If you want to set passwords, you can modify the export file before you
import it or you can individually set passwords after importing using the passwd
command or Workgroup Manager. For more information about setting passwords after
importing users, see User Management.
Step 2: Create archives of the following files
Save all data files that you want to reuse with Mac OS X Server v10.5. In Step 4 you’ll
move the files described below, as well as the export file created in Step 1, to the v10.5
computer.
For large amounts of data, you may want to create one or more tar archives or use
/usr/bin/mkdmg to create disk image files. You can transfer disk images and tar files
using AFP or FTP.
Note: You can also use scp -r for secure copying of files and rsync for remote file
copying. The rsync command is particularly useful where you have a large amount of
data that can be migrated before cutting over, and then updated in a small downtime
window.
Chapter 5 Migrating from Mac OS X Server v10.3 61
Page 62

To create a tar archive, use the tar command in the Terminal application. The
command’s -c flag creates an archive file in tar format. Use the -f flag to specify the
archive file name. Use the
-v (verbose) flag to view progress information as the
command executes:
tar -cvf /MyHFSVolume/Stuff.tar /MyHFSVolume/My\ Stuff
The escape character (\ in the example above) indicates a space in the name. You can
also use quotation marks to handle embedded spaces:
tar -cvf /MyHFSVolume/Stuff.tar "/MyHFSVolume/My Stuff"
Web Configuration Data
Save the following files and directories:
 /etc/httpd/httpd.conf
 /etc/httpd/httpd_macosxserver.conf
 /etc/httpd/httpd_squirrelmail.conf
 /etc/httpd/magic
 /etc/httpd/mime.types
 /etc/httpd/mime_macosxserver.types
 /etc/httpd/ssl.crt
 /etc/httpd/ssl.key
 /etc/httpd/tomcat.conf
 /etc/webperfcache/webperfcache.conf
 /Library/WebServer/
Web Content
Copy web content you want to reuse from:
 /Library/WebServer/Documents/
 /Library/WebServer/CGI-Executables/
 Any other location in which it resides
MySQL Data
Mac OS X Server v10.3.9 includes MySQL v4.0.18. Mac OS X Server v10.5 installs MySQL
v5.0.45.
To migrate MySQL databases from one computer to another, you can use the
mysqldump command to back up your data. This command has several forms
depending on the scope of data to be backed up: individual tables, single databases, or
the entire set of databases on the server.
To back up individual tables, enter:
mysqldump
62 Chapter 5 Migrating from Mac OS X Server v10.3
database tb1 [tb2 tb3
...] >
backup-file
.sql
Page 63

where
and
database
tb3
represent table names.
is the name of the database containing the listed tables and
tb1, tb2
,
To back up one or more databases, enter:
mysqldump --databases
db1 [db2 db3
...] >
backup-file
.sql
To back up all database on the system, enter:
mysqldump --all-databases >
backup-file
.sql
Additional instructions for database backup and restore can be found in the MySQL
documentation at www.mysql.org.
To back up tables or databases that require root access (for example, grant tables or
other restricted data), run mysqldump with the --user=root and -p options:
mysqldump --user=root -p --all-datagases >
backup-file
.sql
The -p option causes mysqldump to prompt for the MySQL root password before
proceeding.
Mail Database
If you want to reuse the Mail service database and store, stop Mail service if it’s running
and save the mail files. When Mail service is not running, you can copy all Mail
directories.
By default:
 The mail database resides in /var/imap/.
 The mail store resides in /var/spool/imap/. You can back up individual mail storage
folders or the entire mail store.
The ditto command-line tool is useful for backing up mail files. For more information
about ditto, see its man page.
Also, save a copy of the file /usr/bin/cyrus/bin/ctl_mboxlist so you can move it to the
v10.5 server in Step 4 on page 65. You need this file to migrate the mail database
successfully in Step 7 on page 68.
Webmail Data
If you’ve been using SquirrelMail that was installed when you installed v10.3 and you
want to continue using it after migration, make copies of the address books and
preferences stored in /var/db/squirrelmail/data/.
Chapter 5 Migrating from Mac OS X Server v10.3 63
Page 64

FTP Configuration Files
To migrate your FTP settings, save these configuration files:
In this directory Save these files
/Library/FTPServer/Configuration/ ftpaccess
ftpconversions
ftphosts
ftpgroups
ftpusers
/Library/FTPServer/Messages/ banner.txt
welcome.txt
limit.txt
AFP
Save /Library/Preferences/com.apple.AppleFileServer.plist.
NetBoot Images
You can migrate NetBoot images created using Mac OS X Server v10.3.
Save the <name>.nbi folder for each image you want to migrate, noting the path to
the folder if you want to recreate it in v10.5.
Also save the NetBoot settings. In Server Admin, select NetBoot from the list of
computers and services on the left, click Settings, and drag the button on the bottomright to the Desktop. Dragging this button creates a file on the Desktop containing the
NetBoot service settings. Save this file.
WebObjects Applications and Frameworks
Save WebObjects applications and frameworks located in:
 /Library/WebObjects/
 /System/Library/WebObjects/
Tomcat Data
Save any Tomcat servlets you want to reuse. They’re in /Library/Tomcat/webapps/.
If you’ve installed Axis independent of the version supplied with your server, save any
Simple Object Access Protocol (SOAP) services.
JBoss Applications
Save JBoss applications located in /Library/JBoss/3.2/deploy/.
IP Firewall
In the Terminal application, run this command:
sudo /System/Library/ServerSetup/MigrationExtras/50_ipfwconfigmigrator
Then, save the contents of /etc/ipfilter.
64 Chapter 5 Migrating from Mac OS X Server v10.3
Page 65

NAT
Save the contents of /etc/nat/natd.plist.
Print
Use the serveradmin settings print command to save print settings before you start
the migration process.
serveradmin settings print >
exported_print_settings
Also, record the names and IDs of the CUPS queues for later use.
VPN
Copy:
 /Library/Preferences/SystemConfiguration/com.apple.RemoteAccessServers.plist
 /Library/Keychains/System.keychain
 /etc/racoon/psk.text
If L2TP is set up and psk.text stores the IPsec shared secret, the shared secret may
also be stored in com.apple.RemoteAccessServers.plist or System.keychain.
DNS
Save the file /etc/named.conf and the directory /var/named/ and all its contents.
DHCP
In Server Admin, select the DHCP service on the left, click Settings, and drag the button
on the bottom-right to the Desktop. Dragging this button creates a file on the Desktop
containing the DHCP service settings. Save this file.
User Data
Save any user data files or folders you want to reuse, especially home directory folders.
QuickTime Streaming Server Files and Folders
Save files and folders in /Library/QuickTimeStreaming/.
QTSS Publisher Files and Folders
Save the following:
 The files and folders in /Library/Application Support/Apple/QTSS Publisher/
 The files and folders in each QTSS Publisher user’s path:
/Users/<publisher_user>/Library/Application Support/Apple/QTSS Publisher
Step 3: Note current share points and privileges
If your v10.3 server has share points and privileges you want to recreate on the v10.5
server, make a note of them. Record which share points are for home directories.
Step 4: Copy archive files to the new server
Transfer the files you saved in Steps 1 and 2 to the v10.5 server.
Chapter 5 Migrating from Mac OS X Server v10.3 65
Page 66

To transfer tar files or disk images using FTP:
1 Use Server Admin on the new server to start FTP service.
2 Set up sharing for a folder into which you’ll place files you transfer from the v10.3
computer.
3 From the v10.3 server, use FTP service to copy the tar files or disk images to the v10.5
computer.
4 On the v10.5 computer, double-click a tar file to extract its contents or double-click a
disk image to mount it.
Step 5: Set up the home directory infrastructure
Set up the destination for home directories you want to restore.
The home directory location identified in imported user accounts must match the
physical location of the restored home directories, including the share point location.
For details on how to perform the steps in the following procedure, see User
Management.
To prepare the server to store home directories:
1 Create the folder you want to serve as the home directory share point, if required.
You can use the predefined /Users folder, if you like.
2 Open Server Admin on the server where you want home directories to reside.
3 Click File Sharing to set up a share point for home directories.
If user accounts will reside in a shared Open Directory directory, create a dynamically
automounted AFP or NFS share point for the home directories. Make sure the share
point is published in the directory where the user accounts that depend on it will
reside.
4 In Workgroup Manager on the computer where you’ll import users, click Accounts, then
open the directory where you’ll import users.
If you restore home directories in locations that won’t exactly match the locations
identified in exported user records, you can define a preset that identifies the restore
location. If you identify the preset when you import users, the new location will replace
the existing location in user records.
You can also use the preset to specify other default settings you want imported users
to inherit, such as password settings, mail settings, and so forth.
Step 6: Import users and groups and other data
You can use Workgroup Manager or the dsimport tool to import users and groups and
other data:
For more information about importing by using Workgroup Manager, see User
Management.
66 Chapter 5 Migrating from Mac OS X Server v10.3
Page 67

For more information about passwords of users originally created with Mac OS X Server
v10.1.5 or earlier, see Open Directory Administration.
For more information about dsimport and a description of Workgroup Manager export
format, see Command-Line Administration.
To import users and groups using Workgroup Manager:
1 Place the export files you created in Step 1 in a location accessible from your server.
You can modify user accounts in an export file if you want to set passwords before
importing users. For instructions, see User Management.
Additionally, you can set up the preset you defined in Step 5 above so that user
passwords are validated using Open Directory authentication, and you can set up the
password validation options so users must change their passwords the next time they
log in.
For information about using Kerberos passwords, see the last step in this sequence.
2 In Workgroup Manager, click the Accounts button.
3 Click the globe icon in the toolbar to open the directory where you want to import
accounts.
4 Click the lock to authenticate as domain administrator.
5 Choose Server > Import, select the import file, and specify import options.
If you’re using a preset, make sure you specify the preset.
6 Click Import.
7 If you want groups to use new v10.5 features, upgrade groups using Workgroup
Manager.
In Workgroup Manager, open the directory containing the groups, select one or more
groups, click “Upgrade legacy group,” and click Save.
8 To create home directories for imported users, use one of the following options:
Create home directories one at a time by selecting a user account in Workgroup
Manager, clicking Home, then clicking Create Home Now.
Create all home directories by using the
-a argument of the createhomedir command.
For details, see Command-Line Administration or the man page for createhomedir.
A home directory associated with an AFP share point is created the first time a user
logs in, if it doesn’t exist already.
9 If you want to enable Kerberos for an Open Directory master that it’s not enabled on,
use the following command, which maintains existing passwords and adds them to a
new KDC.
slapconfig -kerberize
Chapter 5 Migrating from Mac OS X Server v10.3 67
Page 68

If you have user accounts with crypt passwords and you don’t Kerberize them using the
above command, you can use Workgroup Manager to use an Open Directory password.
To use Workgroup Manager, open the application and access the directory where the
user account resides. Authenticate as domain administrator, then select a user with a
crypt password. Click Advanced, choose Open Directory from the User Password Type
pop-up menu, click Basic, specify a new password, and click Save.
For more information about slapconfig, see its man page.
Step 7: Relocate saved data files
Place the files you saved from your v10.3 server in their final locations.
Web Configuration Data
To migrate web configuration data:
1 Open Server Admin.
2 Under the v10.5 server in the list of computers and services, click Web.
3 Click Stop Web if Web service is running.
4 Delete the following files:
 /etc/httpd/sites
 /etc/httpd/ssl.crt
 /etc/httpd/ssl.key
5 Copy the saved v10.3 files and directory onto the v10.5 server.
6 Open the Terminal application and with root privileges, enter the following command:
sudo /System/Library/ServerSetup/MigrationExtras/59_webconfigmigrator
A log of changes made to files is created in /Library/Logs/Migration/
webconfigmigrator.log.
The v10.3 files in /etc/httpd/ are renamed to httpd.conf.obsolete,
httpd_macosxserver.conf.obsolete, and mime_macosxserver.types.obsolete.
A new httpd.conf file and sites directory is created.
7 If you’ve modified /etc/httpd/workers.properties, reapply all your changes to the
version of the file that’s installed with server v10.5.
The v10.5 workers.properties file has a new entry for Blog service.
8 In Server Admin, start Web service.
Web Content
Copy saved web content to the following locations and anywhere else you have placed
web content on the server:
 /Library/WebServer/Documents/
 /Library/WebServer/CGI-Executables/
68 Chapter 5 Migrating from Mac OS X Server v10.3
Page 69

MySQL Data
Before importing backed up MySQL data, make sure that the MySQL service is active.
You can activate the MySQL service using Server Admin or the serveradmin command.
To activate the MySQL service using the serveradmin command, enter:
serveradmin start mysql
To import database backups enter:
mysql <
backup-file
.sql
To import data into databases that require privileged access, run mysql with the --
user=root
mysql --user=root -p <
and -p options:
backup-file
.sql
The -p option causes mysql to prompt for the MySQL root password before proceeding.
Additional instructions for MySQL database backup and restoration can be found in the
MySQL documentation at www.mysql.org.
Mail Database
To migrate the mail database:
1 Make sure that v10.5 Mail service isn’t running.
Open Server Admin, then click Mail. If the Mail circle on the left side is not grayed out,
click Stop Mail at the lower left.
2 Restore the saved mail database and mail store.
By default the mail database resides in /var/imap/ and the mail store in /var/spool/
imap/.
3 Make sure the mail directories and their contents are owned by the _cyrus user and
mail group.
4 Rename the saved ctl_mboxlist file to ctl_mboxlist.old and then move it to /usr/bin/
cyrus/bin/.
If ctl_mboxlist.old is not present, the upgradedb script will fail in step 8 below.
5 In Server Admin, select Mail from the list of computers and services.
6 Click Settings, click Advanced, and click Database to indicate where you restored the
database and mail store.
7 Click Save.
8 Run the mail database upgradedb script:
sudo -u cyrusimap /System/Library/ServerSetup/SetupExtras/upgradedb
9 Run the following command to insure that the index files for all mail accounts are in
good working order:
sudo /usr/bin/cyrus/bin/reconstruct –i
Chapter 5 Migrating from Mac OS X Server v10.3 69
Page 70

10 In Server Admin, start Mail service by clicking Mail, then click Start Mail.
Webmail Data
Place saved address books and preferences in /var/db/squirrelmail/data/.
FTP Configuration Files
Copy saved FTP configuration files to:
 /Library/FTPServer/Configuration/
 /Library/FTPServer/Messages/
AFP Configuration
To migrate the AFP configuration, restore /Library/Preferences/
com.apple.AppleFileServer.plist.
NetBoot Images
Copy the <name>.nbi folder for each image you want to migrate, optionally placing it
into the location where it previously resided.
Also, restore the NetBoot settings file.
To restore NetBoot settings:
1 Open Server Admin and select NetBoot from the list of computers and services.
2 Choose Server > Import > Service Settings to import the NetBoot settings from the file
you exported earlier (see “NetBoot Images” on page 64).
3 Review the NetBoot settings to make sure they were imported correctly.
WebObjects Applications and Frameworks
To migrate WebObjects:
1 Copy saved applications to /Library/WebObjects/Applications/.
2 Copy saved frameworks to /Library/Frameworks/.
3 Add the following line to the new httpd.conf file:
Include /System/Library/WebObjects/Adaptors/Apache/apache.conf
Note: JavaMonitor and WebObjects Task Daemon (wotaskd) services are now managed
by launchd and can be accessed through Server Admin. If the server you’re upgrading
has the startup item /System/Library/StartupItems/WebObjects, you can ignore it. It’s
disabled by default and isn’t necessary for autostarting WebObjects services with
Mac OS X Server v10.5. For more information, see Web Technologies Administration and
WebObjects Deployment.
70 Chapter 5 Migrating from Mac OS X Server v10.3
Page 71

4 (Optional) If you didn’t have Java 1.4.2 installed on your v10.3 server, manually update
WebObjects application projects by opening each project in Xcode; then, in the Expert
View for the main target’s settings, change the property value for JAVA_VM to java.
These projects must be manually updated to use the version of the Java Virtual
Machine (JVM) included with Mac OS X Server v10.5.
Important: Mac OS X Server v10.5 includes WebObjects 5.4, which requires Java 1.5 to
be installed.
Tomcat Data
Restore Tomcat servlets to /Library/Tomcat/webapps/.
Place SOAP services you want to migrate in /Library/Tomcat/webapps/axis/. Mac OS X
Server v10.5 includes a version of Axis that may be newer or older than the version
you’ve been using.
JBoss Applications
JBoss does not come with Mac OS X Server v10.5. Before you can restore your JBoss
applications, install JBoss on your server.
For more information about installing and migrating JBoss applications, see the JBoss
documentation.
IP Firewall Configuration
To migrate the IP firewall configuration, restore the /etc/ipfilter folder.
Open Server Admin and click Firewall to inspect the settings and make sure they are
correct.
NAT
Restore the contents of /etc/nat/natd.plist.
You can restore the v10.5 default settings for NAT (stored in /etc/natd/natd.plist.default)
at any time by deleting the active configuration file (/etc/nat/natd.plist). The next time
NAT is accessed using Server Admin, the default configuration file is used to recreate
the active configuration file.
Note: In v10.5, the default setting of unregistered_only in /etc/nat/natd.plist.default is
true.
Chapter 5 Migrating from Mac OS X Server v10.3 71
Page 72

Print Service Settings
To restore Print service settings, you must first recreate the original CUPS queues before
importing the saved settings.
In the case of printers connected directly to the server via USB, the queues are created
by CUPS when the printers are plugged in and turned on. However, for network
printers, you must add the printers using either Server Admin > Print (for LPR or
AppleTalk printers) or System Preferences > Print & Fax (for all printer types).
Important: When recreating a CUPS queue, make sure you give it the same name as
the one it had on the older system. If the name is not the same, Server Admin won’t
import the settings correctly.
Important: When creating the print queues using the Print & Fax pane of System
Preferences, specify Generic Postscript (Generic PPD) for any queue that enforces
quotas because there are known issues with third-party printer drivers and CUPS
quotas. For more information about this issue, see the Knowledge Base article at
http://docs.info.apple.com/article.html?artnum=303538.
After creating the print queues, import the saved settings:
serveradmin settings
exported_print_settings
VPN
Restore the following:
 /Library/Preferences/SystemConfiguration/com.apple.RemoteAccessServers.plist.
 /Library/Keychains/System.keychain
 /etc/racoon/psk.text
If L2TP is set up and psk.text stores the IPsec shared secret, the shared secret may
also be stored in com.apple.RemoteAccessServers.plist or System.keychain.
Migrate the VPN MPPE Key user by using the vpnaddkeyagentuser command-line tool.
For more information about this command, see its man page.
DNS Configuration
To migrate the DNS configuration:
1 Restore the file /etc/named.conf and the directory /var/named/ and all its contents.
2 In Server Admin, select DNS from the list of computers and services.
A dialog box appears prompting you whether to upgrade:
 If you click Don’t Upgrade, Server Admin leaves the DNS configuration files as they
were before the v10.5 migration. DNS will still run, but you can’t make DNS
configuration changes using Server Admin. To make changes, you must directly edit
the DNS configuration files.
72 Chapter 5 Migrating from Mac OS X Server v10.3
Page 73

 If you click Upgrade, Server Admin upgrades the configuration files to the v10.5
format. After that, you can use Server Admin to make DNS configuration changes.
DHCP Settings
To migrate the DHCP configuration:
1 Open Server Admin and select DHCP from the list of computers and services.
2 Choose Server > Import > Service Settings to import the DHCP settings from the file
you exported earlier (see “DHCP” on page 65).
3 Inspect the Subnets and Static Maps panes of the DHCP service to make sure the
subnet and static binding settings have been imported correctly.
User Data
Restore saved user data files.
Place home directories in locations that match the locations in the imported user
records. If necessary, you can use Workgroup Manager to edit user accounts so the
locations in the account and on disk are the same.
QuickTime Streaming Server Files and Folders
Follow instructions in QuickTime Streaming and Broadcasting Administration to reuse
files and folders saved from /Library/QuickTimeStreaming/.
QTSS Publisher Files and Folders
QTSS Publisher has been removed from Mac OS X Server v10.5. However, files created
using QTSS Publisher on v10.4 should continue to work on v10.5.
Restore the QTSS Publisher files and folders on Mac OS X Server v10.5.
QTSS Publisher Media and MP3 files should be stored in:
 /Library/Application Support/Apple/ QTSS Publisher/Libraries/
 /Users/<publisher_user>/Library/Application Support/Apple/QTSS Publisher/
Libraries/
To migrate QTSS Publisher media and MP3 playlists to QTSS Web Admin:
1 Move all folders in /Library/Application Support/Apple/QTSS Publisher/Playlists/ to
/Library/QuickTimeStreaming/Playlists.
For example, you would move:
/Library/Application Support/Apple/QTSS Publisher/Playlists/my_playlist/
to
/Library/QuickTimeStreaming/Playlists/my_playlist/
2 Verify that the owner of folders and files in /Library/QuickTimeStreaming/Playlists is
qtss.
Chapter 5 Migrating from Mac OS X Server v10.3 73
Page 74

3 For media playlists, verify that the folder /Library/Application Support/Apple/QTSS
Publisher/Libraries/Media/ contains the media files listed in the .playlist files.
4 For MP3 playlists, verify that the folder /Library/Application Support/Apple/QTSS
Publisher/Libraries/MP3/ contains the media files listed in the .playlist files.
5 For every playlist, update its .config file so that paths point to the new playlist folder in
/Library/QuickTimeStreaming/Playlists.
This includes the paths defined in the pid_file, playlist_file, and sdp_file (media playlists
only) preferences.
6 Enable QTSS web-based administration using Server Admin.
7 Open Web Admin using Safari (http://<hostname>:1220) and log in.
8 Click Playlists.
You can now start manage QTSS Publisher playlists using QTSS Web Admin.
For information about using Web Admin, see QuickTime Streaming Server Darwin
Streaming Server Administrator’s Guide available at developer.apple.com/opensource/
server/streaming.
Step 8: Set up share points and privileges
Recreate the share points and privileges as required.
To create a share point and set privileges:
1 Open Server Admin and click File Sharing.
2 Click Volumes and select the volume or folder you want to share.
3 Click Share.
4 Click Permissions to set up access privileges.
5 Click Save.
New share points are shared using AFP, SMB, and FTP, but not NFS. To export a share
point using NFS, use the Protocol pane. For more information about setting up share
points, see File Services Administration.
Step 9: Test the new server
To test the new server:
1 Open Workgroup Manager and inspect user and group accounts.
2 Open Server Admin and inspect settings for services whose configuration data you
migrated.
74 Chapter 5 Migrating from Mac OS X Server v10.3
Page 75

6 Migrating from Mac OS X Server
v10.2
6
Use the instructions in this chapter when you need to
migrate data from a v10.2.8 server to a different computer
running v10.5.
You can migrate data from Mac OS X Server v10.2.8 computers that can’t or won’t be
upgraded to v10.5 or later. Such computers may:
 Require hard disk reformatting or replacement with a newer computer.
 Be using server hardware that doesn’t have:
 An Intel or PowerPC G5 or G4 (867 MHz or faster) processor
 At least 1 GB of RAM
 At least 20 GB of disk space available
Before You Begin
Before using the instructions in this chapter, perform initial setup of the v10.5 server
you’ll migrate data to. For instructions, see Getting Started.
If necessary, upgrade the server whose data you’ll migrate so it’s running v10.2.8.
Understanding What You Can Migrate
The information in “Step-by-Step Instructions” on page 77 describes how to reuse the
following v10.2 data with v10.5:
 Web configuration data
 Web content
 Mail database
 WebMail data
 FTP configuration files
 WebObjects applications and frameworks
 Tomcat data
 DNS configuration
75
Page 76

 User data, including home directories
 QuickTime Streaming Server files and directories
 User and group accounts
Use serveradmin or Server Admin to export service settings for reference. Store the
exported service settings on removable media or another system.
Note: One way to save service settings in Server Admin is to select the service from the
list of computers and services on the left, click Settings, and drag the button on the
bottom-right to the Desktop. Dragging this button creates a file on the Desktop
containing the service settings.
In v10.5, watchdog has been replaced by launchd. To reenable automatic hardware
restart, use the Energy Saver pane of System Preferences. To migrate settings for
services you added to /etc/watchdog.conf, create a launchd plist file and install it into /
System/Library/LaunchDaemons/. For more information about launchd, see its man
page.
Tools You Can Use
Several tools are available:
 You use Workgroup Manager to export v10.2 user and group accounts to a character-
delimited file, and then import them into a v10.5 server. You can also import users
and groups using the command-line dsimport tool.
 Workgroup Manager’s import facility and the dsimport tool also let you import other
kinds of data, such as computers and computer lists.
 You use the 59_webconfigmigrator tool to migrate your web configuration.
 You use the Import command in Server Admin to import service settings
Instructions in the following sections explain when and how to use these utilities.
76 Chapter 6 Migrating from Mac OS X Server v10.2
Page 77

Step-by-Step Instructions
To move data from a Mac OS X Server v10.2.8 computer to a computer with Mac OS X
Server v10.5 installed, follow the instructions in this section.
1 Export user and
group information.
user
group
2017
Workgroup Manager
9 Test the new server.
Shared Folders
Read & Write
Engineering
Read & Write
Designs
Documents
.XML
8 Set up share points
and privileges.
Shared Folders
Read & Write
Engineering
Read & Write
Designs
Read Only
Documents
2 Create archive files of data
and user export files.
userdata.tar
database.tar
Read Only
3 Note current share
points and privileges.
Shared Folders
Read & Write
Engineering
Read & Write
Designs
Read Only
Documents
4 Copy archive files
to new server.
userdata.tar
database.tar
5 Set up home
directory
infrastructure.
6 Import user
and other data.
user
Workgroup
Manager or
dsimport tool
group
2017
7 Relocate data files
on new server.
Chapter 6 Migrating from Mac OS X Server v10.2 77
Page 78

Step 1: Export users and groups
Use Workgroup Manager to export user and group accounts from a NetInfo or LDAPv3
directory into a character-delimited file that you can import into a directory for use
with Mac OS X Server v10.5.
To export users and groups:
1 In Workgroup Manager, click Accounts, then click the globe icon below the toolbar and
choose the directory that you want to export accounts from.
2 Click the lock to authenticate as domain administrator.
3 Click the Users button to export users or click the Groups button to export groups.
4 Export user or group accounts as follows:
 To export all accounts, select all of them.
 To export one account, select it.
 To export multiple accounts, select them while holding down the Command or Shift
key.
5 Choose Server > Export.
6 Specify a name to assign to the export file and the location where you want it created.
7 Click Export.
When you export users using Workgroup Manager, password information isn’t
exported. If you want to set passwords, you can modify the export file before you
import it or you can individually set passwords after importing using the passwd
command or Workgroup Manager. For more information about setting passwords after
importing users, see User Management.
Step 2: Create archives of the following files
Save all data files that you want to reuse with Mac OS X Server v10.5. In Step 4 you’ll
move the files described below, as well as the export file created in Step 1, to the v10.5
computer.
For large amounts of data, you may want to create one or more tar archives or use
/usr/bin/mkdmg to create disk image files. You can transfer disk images and tar files
using AFP or FTP.
Note: You can also use scp -r for secure copying of files and rsync for remote file
copying. The rsync command is particularly useful where you have a large amount of
data that can be migrated before cutting over, and then updated in a small downtime
window.
78 Chapter 6 Migrating from Mac OS X Server v10.2
Page 79

To create a tar archive, use the tar command in the Terminal application. The
command’s -c flag creates an archive file in tar format. Use the -f flag to specify the
archive file name. Use the
-v (verbose) flag to view progress information as the
command executes:
tar -cvf /MyHFSVolume/Stuff.tar /MyHFSVolume/My\ Stuff
The escape character (\ in the example above) indicates a space in the name. You can
also use quotation marks to handle embedded spaces:
tar -cvf /MyHFSVolume/Stuff.tar "/MyHFSVolume/My Stuff"
Web Configuration Data
Save the following files and directories:
 /etc/httpd/httpd.conf
 /etc/httpd/httpd_macosxserver.conf
 /etc/httpd/httpd_squirrelmail.conf
 /etc/httpd/magic
 /etc/httpd/mime.types
 /etc/httpd/mime_macosxserver.types
 /etc/httpd/ssl.crt
 /etc/httpd/ssl.key
 /etc/httpd/tomcat.conf
 /etc/webperfcache/webperfcache.conf
 /Library/WebServer/
Web Content
Copy web content you want to reuse from:
 /Library/WebServer/Documents/
 /Library/WebServer/CGI-Executables/
 Any other location in which it resides
Mail Database
Save the mail database if you want to reuse it. Its default location is /Library/
AppleMailServer/.
Webmail Data
If you’ve been using SquirrelMail that was installed when you installed v10.2 and you
want to continue using it after migration, make copies of the address books and
preferences stored in /var/db/squirrelmail/data/.
Chapter 6 Migrating from Mac OS X Server v10.2 79
Page 80

FTP Configuration Files
To migrate your FTP settings, save these configuration files:
In this directory Save these files
/Library/FTPServer/Configuration/ ftpaccess
ftpconversions
ftphosts
ftpgroups
ftpusers
/Library/FTPServer/Messages/ banner.txt
welcome.txt
limit.txt
WebObjects Applications and Frameworks
Save WebObjects applications and frameworks located in:
 /Library/WebObjects/
 /System/Library/WebObjects/
Tomcat Data
Save any Tomcat servlets you want to reuse. They’re in /Library/Tomcat/webapps/.
If you’ve installed Axis independent of the version supplied with your server, save any
Simple Object Access Protocol (SOAP) services.
IP Firewall
There is no direct way to migrate IP Firewall configuration information to Mac OS X
Server v10.5 because NetInfo is not supported on v10.5. You can do one of the
following:
 Manually reenter the firewall rules.
 Migrate the configuration information to a Mac OS X Server v10.3 or v10.4 system
and then migrate the firewall configuration information to v10.5.
To migrate the firewall information to a Mac OS X Server v10.3 or v10.4 system, save the
IP firewall configuration after running the following command from the Terminal
application:
nidump -r /config/IPFilters . > firewallconfig
This command writes the IP firewall configuration record stored in NetInfo to a file
named firewallconfig.
To complete the migration process, see “IP Firewall Configuration” on page 85.
80 Chapter 6 Migrating from Mac OS X Server v10.2
Page 81

DNS
Save the file /etc/named.conf and the directory /var/named/ and all its contents.
DHCP
In Server Admin, select DHCP from the list of computers and services on the left, click
Settings, and drag the button on the bottom-right to the Desktop. Dragging this
button creates a file on the Desktop containing the DHCP service settings. Save this file.
User Data
Save any user data files or folders you want to reuse, especially home directory folders.
QuickTime Streaming Server Files and Folders
Save files and folders in /Library/QuickTimeStreaming/.
For more information on migrating QTSS, see QuickTime Streaming and Broadcasting
Administration.
Step 3: Note current share points and privileges
If your v10.2 server has share points and privileges you want to recreate on the v10.5
server, make a note of them. Record which share points are for home directories.
Step 4: Copy archive files to the new server
Transfer the files you saved in Steps 1 and 2 to the v10.5 server.
To transfer tar files or disk images using FTP:
1 Use Server Admin on the new server to start FTP service.
2 Set up sharing for a folder into which you’ll place files you transfer from the v10.2
computer.
3 From the v10.2 server, use FTP service to copy the tar files or disk images to the v10.5
computer.
4 On the v10.5 server, double-click a tar file to extract its contents or double-click a disk
image to mount it.
Step 5: Set up the home directory infrastructure
Set up the destination for home directories you want to restore.
The home directory location identified in imported user accounts must match the
physical location of the restored home directories, including the share point location.
For details on how to perform the steps in the following procedure, see User
Management and File Services Administration.
Chapter 6 Migrating from Mac OS X Server v10.2 81
Page 82

To prepare the server to store home directories:
1 Create the folder you want to serve as the home directory share point, if required.
You can use the predefined /Users folder, if you like.
2 Open Server Admin on the server where you want home directories to reside.
3 Click File Sharing to set up a share point for the home directories.
If user accounts will reside in a shared Open Directory directory, create a dynamically
automounted AFP or NFS share point for the home directories. Make sure the share
point is published in the directory where the user accounts that depend on it will
reside.
4 In Workgroup Manager on the computer where you’ll import users, click Accounts, then
open the directory where you’ll import users.
If you restore home directories in locations that won’t exactly match the locations
identified in exported user records, you can define a preset that identifies the restore
location. If you identify the preset when you import users, the new location will replace
the existing location in user records.
You can also use the preset to specify other default settings you want imported users
to inherit, such as password settings, mail settings, and so forth.
Step 6: Import users and groups and other data
You can use Workgroup Manager or the dsimport tool to import users and groups and
other data:
For more information about importing by using Workgroup Manager, see User
Management.
For more information about passwords of users originally created with Mac OS X Server
v10.1.5 or earlier, see Open Directory Administration.
For more information about dsimport and a description of Workgroup Manager export
format, see Command-Line Administration.
To import users and groups using Workgroup Manager:
1 Place the export files you created in Step 1 on page 78 in a location accessible from
your server.
You can modify user accounts in an export file if you want to set passwords before
importing users. For instructions, see User Management.
Additionally, you can set up the preset you defined in step 5 of Step 5 above so user
passwords are validated using Open Directory authentication and you can set up the
password validation options so users must change their passwords the next time they
log in.
2 In Workgroup Manager, click the Accounts button.
82 Chapter 6 Migrating from Mac OS X Server v10.2
Page 83

3 Click the globe icon in the toolbar to open the directory where you want to import
accounts.
4 Click the lock to authenticate as domain administrator.
5 Choose Server > Import, select the import file, and specify import options.
If you’re using a preset, make sure you specify the preset.
6 Click Import.
7 If you want groups to use new v10.5 features, upgrade groups using Workgroup
Manager.
In Workgroup Manager, open the directory containing the groups, select one or more
groups, click “Upgrade legacy group,” and click Save.
8 To create home directories for imported users, use one of the following options:
Create home directories one at a time by selecting a user account in Workgroup
Manager, clicking Home, then clicking Create Home Now.
Create all home directories by using the -a argument of the createhomedir command.
For details, see Command-Line Administration or the man page for createhomedir.
A home directory associated with an AFP share point is created the first time a user
logs in, if it doesn’t exist already.
Step 7: Relocate saved data files
Place the files you saved from your v10.2 server in their final locations.
Web Configuration Data
To migrate web configuration data:
1 Open Server Admin.
2 Under the v10.5 server in the list of computers and services, click Web.
3 Click Stop Web if Web service is running.
4 Delete the following files:
 /etc/httpd/sites
 /etc/httpd/ssl.crt
 /etc/httpd/ssl.key
5 Copy the saved v10.2 files and directory onto the v10.5 server.
6 Open the Terminal application and with root privileges, enter the following command:
/System/Library/ServerSetup/MigrationExtras/59_webconfigmigrator
A log of changes made to the files is created in /Library/Logs/Migration/
webconfigmigrator.log.
The v10.2 files in /etc/httpd/ are renamed to httpd.conf.obsolete,
httpd_macosxserver.conf.obsolete, and mime_macosxserver.types.obsolete.
Chapter 6 Migrating from Mac OS X Server v10.2 83
Page 84

A new httpd.conf file is created and a sites directory is created.
7 If you’ve modified /etc/httpd/workers.properties, reapply your changes to the version
of the file that’s installed with server v10.5.
The v10.5 workers.properties file has a new entry for Blog service.
8 In Server Admin, start Web service.
Web Content
Copy saved web content to:
 /Library/WebServer/Documents/
 /Library/WebServer/CGI-Executables/
Mail Database
To migrate the mail database:
1 Make sure that v10.5 Mail service isn’t running.
Open Server Admin, then click Mail. If the Mail circle on the left side is not grayed out,
click Stop Mail at the lower left.
2 Click Maintenance, then click Migration.
3 Place the saved database on the v10.5 server and make sure that no extra files are in
the location you select.
If you place the database in the default location (/var/imap), its location and accounts
are displayed.
Otherwise, browse for the database to identify its location and list its accounts.
4 Make sure the mail directories and their contents are owned by the _cyrus user and
mail group.
5 Make sure there is free space on the destination disk equal to the size of the mail
database.
6 Migrate a single user or all users.
To migrate mail for only one user, select the user and click Migrate User.
To migrate the entire database, click Migrate All.
7 Run the following command to insure that the index files for all mail accounts are in
good working order:
sudo /usr/bin/cyrus/bin/reconstruct –i
8 In Server Admin, start Mail service by clicking Mail, then click Start Mail.
Webmail Data
Place saved address books and preferences in /var/db/squirrelmail/data/.
FTP Configuration Files
Copy saved FTP configuration files to:
84 Chapter 6 Migrating from Mac OS X Server v10.2
Page 85

 /Library/FTPServer/Configuration/
 /Library/FTPServer/Messages/
WebObjects Applications and Frameworks
To migrate WebObjects:
1 Copy saved applications to /Library/WebObjects/Applications/.
2 Copy saved frameworks to /Library/Frameworks/.
3 Add the following line to the new httpd.conf file:
Include /System/Library/WebObjects/Adaptors/Apache/apache.conf
Note: JavaMonitor and WebObjects Task Daemon (wotaskd) services are now managed
by launchd and can be accessed through Server Admin. If the server you’re upgrading
has the startup item /System/Library/StartupItems/WebObjects, you can ignore it. It’s
disabled by default and isn’t necessary for autostarting WebObjects services with
Mac OS X Server v10.5. For more information, see Web Technologies Administration and
WebObjects Deployment.
4 (Optional) If you didn’t have Java 1.4.2 installed on your v10.2 server, manually update
WebObjects application projects by opening each project in Xcode; then, in the Expert
View for the main target’s settings, change the property value for JAVA_VM to java.
These projects must be manually updated to use the version of the Java Virtual
Machine (JVM) included with Mac OS X Server v10.5.
Important: Mac OS X Server v10.5 includes WebObjects 5.4, which requires Java 1.5 to
be installed.
Tomcat Data
Restore Tomcat servlets to /Library/Tomcat/webapps/.
Place SOAP services you want to migrate in /Library/Tomcat/webapps/axis/. Mac OS X
Server v10.5 includes a version of Axis that may be newer or older than the version
you’ve been using.
IP Firewall Configuration
To migrate the IP firewall configuration:
1 Restore the firewallconfig file on a Mac OS X Server v10.3 or v10.4 server.
2 Open Server Admin and make sure that Firewall service isn’t running.
3 Open NetInfo Manager, located in /Applications/Utilities.
4 Authenticate and go to /config.
5 Choose Directory > New SubDirectory to create a record in /config.
6 Change the name of the new record from “newdirectory” to “IPFilters” by selecting the
name property’s value and editing it.
Chapter 6 Migrating from Mac OS X Server v10.2 85
Page 86

7 In the Terminal application, run the following command from the directory where the
firewallconfig file resides:
sudo niload -r /config/IPFilters . < firewallconfig
8 Enter the following command:
sudo /System/Library/ServerSetup/MigrationExtras/50_ipfwconfigmigrator
Running this script creates a /etc/ipfilter folder with all necessary files for the migration.
9 On the Mac OS X Server v10.5 server, open Server Admin and make sure Firewall service
isn’t running.
10 Copy the /etc/ipfilter folder generated by the 50_ipfwconfigmigrator script to the
Mac OS X Server v10.5 server you want to migrate the settings to.
11 Start Firewall service on the Mac OS X Server v10.5 server.
DNS Configuration
To migrate the DNS configuration:
1 Restore the file /etc/named.conf and the directory /var/named/ and its contents.
2 In Server Admin, select DNS from the list of computers and services.
A dialog box appears prompting you whether to upgrade:
 If you click Don’t Upgrade, Server Admin leaves the DNS configuration files as they
were before the v10.5 migration. DNS will still run, but you can’t make DNS
configuration changes using Server Admin. To make changes, you must directly edit
the DNS configuration files.
 If you click Upgrade, Server Admin upgrades the configuration files to the v10.5
format. After that, you can use Server Admin to make DNS configuration changes.
DHCP Settings
To migrate the DHCP configuration:
1 Open Server Admin and select DHCP from the list of computers and services.
2 Choose Server > Import > Service Settings to import DHCP settings from the file you
exported earlier (see “DHCP” on page 81).
3 Inspect the panes of the DHCP service to make sure the DHCP settings were imported
correctly.
User Data
Restore saved user data files.
Place home directories in locations that match the locations in the imported user
records. If necessary, you can use Workgroup Manager to edit user accounts so the
locations in the account and on disk are the same.
86 Chapter 6 Migrating from Mac OS X Server v10.2
Page 87

QuickTime Streaming Server Files and Folders
Follow instructions in QuickTime Streaming and Broadcasting Administration to reuse
files and folders saved from /Library/QuickTimeStreaming/.
Step 8: Set up share points and privileges
Recreate the share points and privileges as required.
To create a share point and set privileges:
1 Open Server Admin and click File Sharing.
2 Click Volumes and select the volume or folder you want to share.
3 Click Share.
4 Click Permissions to set up access privileges.
5 Click Save.
New share points are shared using AFP, SMB, and FTP, but not NFS. To export a share
point using NFS, use the Protocol pane. For more information about setting up share
points, see File Services Administration.
Step 9: Test the new server
To test the new server:
1 Open Workgroup Manager and inspect user and group accounts.
2 Open Server Admin and inspect settings for services whose configuration data you
migrated.
Chapter 6 Migrating from Mac OS X Server v10.2 87
Page 88

88 Chapter 6 Migrating from Mac OS X Server v10.2
Page 89

7 Migrating to Mac OS X Server
from Windows NT
7
This chapter contains instructions for transferring data and
settings from a Windows NT server to a computer running
Mac OS X Server v10.5.
This chapter includes the following sections:
 “Before You Begin” on page 89 describes the prerequisite tasks you must perform
before you start the migration process.
 “Understanding What You Can Migrate” on page 90 describes what you can migrate
from a Windows NT server to a Mac OS X Server v10.5 computer.
 “Tools You Can Use” on page 96 describes the tools you can use to migrate a
Windows NT server to a Mac OS X Server v10.5 computer.
 “Step-by-Step Instructions” on page 97 tells you how to transfer user, group, and
computer records from a Windows NT primary domain controller (PDC) to a
Mac OS X Server PDC. It also tells you how to set up home directories and roaming
user profiles on Mac OS X Server for Windows users.
This section also describes how to set up shared folders on Mac OS X Server and
copy shared folders and files to them from Windows NT network folders.
In addition, this section explains how to set up Mac OS X Server print queues for
Windows access and how to add them as printers on client Windows computers.
For additional information on setting up and managing services for Windows users, see
File Services Administration. It also describes how to manage user, group, and computer
records for Windows clients.
Note: Because Apple periodically releases new versions and updates to its software,
images shown in this book may be different from what you see on your screen.
Before You Begin
Before using the instructions in this chapter, perform initial setup of the Mac OS X
Server v10.5 server that you’ll migrate data to. For instructions, see Getting Started.
89
Page 90

Understanding What You Can Migrate
The instructions in “Step-by-Step Instructions” on page 97 describe how to reuse the
following data from a Windows NT server with a Mac OS X Server PDC:
 User and group accounts
 Records for computers that are members of the NT domain
 Users’ personal files from My Documents folders and home directory folders
 Roaming user profiles
To migrate user, group, and computer records, you must have a Mac OS X Server
system that is or can be an Open Directory master.
Migrated users have the same home directory path after migration as before. During
migration, each user’s home directory path is copied to their Mac OS X Server user
account. Users should be able to continue using their same home directories unless the
home directories were on the Windows NT PDC server, which must be taken out of
service after migration.
If users have home directories on the Windows NT PDC server, they’ll need to
temporarily copy their home directory files to another location before you migrate their
records to the Mac OS X Server PDC.
These users can copy their home directory files to their My Documents folders if their
client computers have sufficient disk space for all copied files. Alternatively, the users
can copy their files to a network folder that’s not located on the PDC server.
You’ll need to set up new home directories for these users on the Mac OS X Server PDC
or a member server. After you migrate the users, they’ll be able to copy files to their
new home directories.
What Migrated Users Can Do
When you migrate users, groups, and computers from a Windows NT server to
Mac OS X Server, the Mac OS X Server computer becomes a PDC. Migrated users can
then do the following:
 Log in to the new PDC’s domain using the same user names, passwords, and
workstations as before.
 Have their roaming profiles stored and retrieved on a Mac OS X Server system.
 Use network home directories located on a Mac OS X Server system.
 Remain members of the same group.
 Access the contents of network folders that you copy to Mac OS X Server share
points.
 Use print queues that you set up on Mac OS X Server and add as printers to users’
Windows workstations.
90 Chapter 7 Migrating to Mac OS X Server from Windows NT
Page 91

Other users for whom you set up Mac OS X Server accounts can also use these services.
In addition, Mac OS X Server can provide Windows Internet Naming Service (WINS) and
Windows domain browsing across subnets for migrated and new Windows users.
Mac OS X Server can provide additional services to Windows, Mac OS X, and UNIX
users, including Mail, Web, Blog, iChat (Jabber), VPN, DHCP, DNS, and NAT. For details,
see the Mac OS X Server setup and administration guides described in the Preface.
By providing these services, Mac OS X Server can replace Windows NT servers in small
workgroups.
For example, you may be administering several Windows NT servers acquired over the
years to support domain login and shared network folders. By today’s standards, your
older servers are probably slow and have small storage capacities.
It’s possible to migrate user accounts from multiple Windows NT domain controllers to
one Mac OS X Server system. The same Mac OS X Server system can also host shared
network folders for Windows users.
If you prefer to isolate user accounts on a dedicated Mac OS X Server system, the
shared folders can reside on another Mac OS X Server system.
While serving users of Windows workstations, Mac OS X Server can also serve users of
Mac OS X computers. A user account on the server can be used to log in from a
Mac OS X computer as well as a Windows workstation. A user who logs in on both
platforms can have the same home directory no matter where he or she logs in.
Note: Log in and log on mean the same thing. Log on is commonly used in the
Windows environment and log in is commonly used in the Mac OS X environment.
Planning Your Migration
Before you begin migrating accounts and services from a Windows NT server to
Mac OS X Server, you need to plan for the following:
 Migrating users, groups, and computers to a Mac OS X Server PDC
 Providing home directories and roaming user profiles
 Migrating Windows file service
 Providing Windows access to print service
 Configuring DNS
Chapter 7 Migrating to Mac OS X Server from Windows NT 91
Page 92

Migrating Users, Groups, and Computers to a Mac OS X Server PDC
Mac OS X Server includes a command-line tool, ntdomainmigration.sh, that:
 Sets up Mac OS X Server as a PDC.
 Extracts user and group information and uses it to create Mac OS X Server user and
group accounts.
 Extracts computer information and uses it to add Windows computers to the
Mac OS X Server Windows Computers list, making them members of the Mac OS X
Server PDC domain.
Important: Due to a known issue, the Windows NT Domain Migration script
(NTdomainmigration.sh) does not migrate group information. As a workaround,
manually create the group information on the Mac OS X Server acting as a PDC.
The migrated user and group accounts are stored in the server’s LDAP directory with
the migrated computer records and other information. The PDC has access to this
directory information because you migrate to a server that is an Open Directory master,
which hosts an LDAP directory.
The LDAP directory can remain efficient with up to 200,000 records. If the server has
sufficient hard disk space to store all the records.
The PDC also uses the Open Directory master’s Password server to authenticate users
when they log in to the Windows domain. The Password server can validate passwords
using the NTLMv2, NTLMv1, LAN Manager, and many other authentication methods.
The Open Directory master can also have a Kerberos Key Distribution Center (KDC). The
PDC function doesn’t use Kerberos to authenticate users for Windows services, but mail
and other services can be configured to use Kerberos to authenticate Windows
workstation users who have accounts in the LDAP directory. For additional information
on directory and authentication services, see Open Directory Administration.
If you want to provide failover and backup for the new PDC and you have additional
Mac OS X Server systems, you can make one or more of them backup domain
controllers (BDCs). The PDC and BDCs have synchronized copies of directory and
authentication data, and they share client requests for this data. If the PDC becomes
unavailable, clients fail over to a BDC until the PDC becomes available.
For more information and instructions on setting up a BDC, see Open Directory
Administration.
If you have Mac OS X Server systems that are neither PDCs nor BDCs, you can set them
up to provide additional Windows services as members of the Mac OS X Server
Windows domain. As a Windows domain member, Mac OS X Server’s Windows services
use the domain controller for user identification and authentication.
92 Chapter 7 Migrating to Mac OS X Server from Windows NT
Page 93

When setting up Mac OS X Server as a PDC, make sure your network doesn’t have
another PDC with the same domain name. The network can have multiple Open
Directory masters, but only one PDC.
Providing Home Directories and Roaming User Profiles
Migrated users can continue using their existing home directories unless the home
directories are located on the Windows NT server that you’re taking out of service. If
some users have home directories on the Windows NT server that’s going out of
service, you can migrate their home directories to Mac OS X Server. You can also
migrate other users’ home directories to Mac OS X Server.
Before you migrate home directories from the Windows NT server, users must copy
their files temporarily to another location such as their My Documents folder or a
network folder. After you set up Mac OS X Server home directories, users can then copy
their files to their new home directories.
When a user with a Mac OS X Server home directory logs in to the Mac OS X Server
PDC’s Windows domain, Windows maps the home directory to a network drive. If the
same user logs in to a Mac OS X client computer, Mac OS X automatically mounts the
same home directory. The user has the same network home directory whether logging
in to a Windows computer or a Mac OS X computer.
A Mac OS X Server home directory is located in a share point, which is a folder, hard
disk, hard disk partition, or other volume that can be accessed over the network. A
home directory share point can be on the same server as the PDC or it can be on a
Mac OS X Server domain member. Settings in the user account specify the home
directory location and the drive letter for the Windows mapped drive. You can manage
share points and home directory settings with Workgroup Manager.
Mac OS X Server also stores a user profile for each Windows user who logs in and out
of the PDC. These are roaming profiles. Each user has the same profile when he or she
logs in to the PDC from any Windows workstation on the network. A user profile stores
a Windows user’s preference settings (screen saver, colors, backgrounds, event sounds,
web cookies, and so on), favorites, My Documents folder, and more in a share point on
a Mac OS X Server system.
Normally the PDC server stores users’ roaming profile data, but you can have another
Mac OS X Server system store the user profile data for any users. If you have only one
Mac OS X Server system, it can be the PDC as well as hosting home directories and
roaming user profiles.
Providing File Service
Whether you migrate users, groups, and computers to a Mac OS X Server PDC, you can
set up Mac OS X Server to replace the file service that Windows NT servers currently
provide to Windows users.
Chapter 7 Migrating to Mac OS X Server from Windows NT 93
Page 94

Windows users can
map network drives
to Mac OS X Server
User accounts defined on Mac OS X Server can be used to authenticate access to
shared network folders via the Windows standard protocol for file service, Server
Message Block. Windows users access shared folders on Mac OS X Server by using
normal procedures such as mapping a network drive.
User accounts in the Mac OS X Server PDC (the server’s LDAP directory) can be used to
access the PDC server’s shared folders, if any. The PDC user accounts can also be used
to access shared folders on servers that are members of the Windows domain. In
addition, user accounts defined in a server’s local directory domain can be used to
access shared folders on that server.
Shared folders reside in Mac OS X Server share points. Windows users can map network
drives to share points on Mac OS X Server in the same way they map network drives to
network folders on Windows NT servers.
share points
You can set up share points for the exclusive or nonexclusive use of Windows users.
For example, you can set up a share point where Windows and Mac OS X users save
shared graphics or word processing files that can be used on either platform.
Conversely, you can set up a share point for SMB access only to provide a single point
of access for your Windows users and let them take advantage of both opportunistic
file locking (oplocks) and strict file locking.
In general, file locking prevents multiple clients from modifying the same information
at the same time. A client locks the file or part of the file to gain exclusive access.
Opportunistic locking grants exclusive access but also allows a client to cache its
changes locally (on the client computer) for improved performance.
Important: Do not enable opportunistic locking, also known as oplocks, for a share
point that’s using any protocol other than SMB.
You can control users’ access to folders and files stored in Mac OS X Server share points
by setting standard UNIX permissions (read, read and write, write, none) for owner,
group, and everyone. For more flexible control, you can use access control lists (ACLs).
For additional information on share points and permissions, see File Services
Administration.
94 Chapter 7 Migrating to Mac OS X Server from Windows NT
Page 95

Providing Print Service
Mac OS X Server Print service helps you set up a managed printing environment on
your network. You can share PostScript-compatible printers by setting up print queues
for them on a server. When a user prints to a shared queue, the print job waits on the
server until the printer is available or until established scheduling criteria are met.
For example, you can:
 Hold a job for printing at a later time
 Limit the number of pages individual users can print on specific printers
 Keep logs summarizing printer use
Mac OS X Server can make print queues available to Windows users via the standard
Windows protocol for printer sharing, SMB. Printing to a Mac OS X Server print queue is
like printing to any network printer in Windows.
Installing a printer on a Windows computer requires computer administrator privileges.
Users logged in using PDC user accounts can’t install printers unless they’re members
of the local Administrators group (or the local Power Users group in Windows 2000).
To control the number of pages each user prints, you establish print quotas. A print
quota sets how many pages a user can print during a specified time period. A user who
reaches the print quota can’t print again until the quota period ends. For each user,
you set either a single quota that covers all print queues or individual quotas for each
print queue.
Configuring DNS
Some services of Mac OS X Server require or are easier to use with a properly
configured DNS. In particular, Kerberos authentication requires a properly configured
DNS.
Although Mac OS X Server doesn’t use Kerberos to authenticate Windows users for
domain login or print service, Mac OS X Server can use Kerberos to authenticate
Windows users for other services. For example, Mac OS X Server can use Kerberos to
authenticate Mac OS X users for login and file service.
If you expect Mac OS X Server to provide services to Mac OS X users as well as
Windows users, make sure your network’s DNS is configured to resolve the server’s
name to its IP address and to resolve a reverse-lookup of the server’s IP address to the
server’s name.
Chapter 7 Migrating to Mac OS X Server from Windows NT 95
Page 96

DNS can also be used as a fallback mechanism for name resolution by Windows
workstations. Windows workstations initially try to discover the PDC via NetBIOS, so
DNS is not required for Mac OS X Server to provide a PDC or other services to Windows
users. However, Windows clients will fall back to DNS name resolution if they can’t
discover a server name via NetBIOS. As a result, having DNS properly configured and
enabled can be beneficial to Windows users.
Your DNS may be provided by Mac OS X Server or another server on your network.
If you have an independent Internet service provider (ISP), it can also provide DNS.
For information on configuring DNS in Mac OS X Server, see Network Services
Administration.
Tools You Can Use
This section describes the tools you can use for migrating to Mac OS X Server v10.5
from Windows NT.
Tools for Migrating Users, Groups, and Computers
To migrate users, groups, and computers, you use:
 Server Admin, to make Mac OS X Server an Open Directory master and configure
WINS service
 The ntdomainmigration.sh command-line tool, to set up Mac OS X Server as a PDC
and migrate user and computer information to it from the NT server
Important: Due to a known issue, the Windows NT Domain Migration script
(NTdomainmigration.sh) does not migrate Group information. As a workaround,
manually create the group information on the Mac OS X Server acting as a PDC.
 Workgroup Manager, to edit migrated user and group accounts, set up network
home directories, and configure roaming user profiles
 Windows Explorer, to copy users’ files to their new home directories
Tools for Migrating the File Service
To migrate file service, you use:
 Workgroup Manager, to create share points and shared folders, and to set ACLs and
UNIX privileges for them
 Windows Explorer, to copy shared files and map network drives to Mac OS X Server
share points
96 Chapter 7 Migrating to Mac OS X Server from Windows NT
Page 97

Tools for Providing Windows Access to Print Service
To provide Windows access to print service, you can use:
 Server Admin, to configure print queues for Windows access and print quota
enforcement
 The Add Printer wizard on each Windows workstation, to add print queues as
printers
 Workgroup Manager, to set print quotas for users (optional)
Step-by-Step Instructions
This section describes how to migrate to Mac OS X Server v10.5 from Windows NT.
 “Migrating Users, Groups, and Computers” on page 97
 “Migrating Windows File Service” on page 108
 “Providing Windows Access to Print Service” on page 111
Migrating Users, Groups, and Computers
Use the instructions in this section to transfer user and group accounts, computer
records, and users’ personal files from a Windows NT PDC to a Mac OS X Server PDC.
Important: Due to a known issue, the Windows NT Domain Migration script
(NTdomainmigration.sh) does not migrate Group information. As a workaround,
manually create the group information on the Mac OS X Server acting as a PDC
(Primary Domain Controller).
Chapter 7 Migrating to Mac OS X Server from Windows NT 97
Page 98

The following diagram summarizes the steps for migrating users, groups, and
computers. The diagram is followed by detailed instructions.
1 Set up an Open
Directory master.
3 Migrate user, group,
and computer records.
4 Set up the home
directory infrastructure.
5 Transfer
login scripts.
2 Have users copy files from
old home directories.
Windows
NT server
Mac OS X
Server
6 Have users transfer files to
new home directories.
Windows clients
7 Have users log out to
save profile settings.
Step 1: Set up an Open Directory master
You can set up an Open Directory master during initial server setup that follows the
installation of Mac OS X Server. If Mac OS X Server is already installed, you can use
Server Admin to set up an Open Directory master.
When you set up an Open Directory master, Kerberos starts only if the server is
configured to use a DNS service that resolves the server’s fully qualified DNS name and
resolves a reverse-lookup of the server’s IP address.
Mac OS X Server doesn’t use Kerberos authentication for Windows services, but can use
Kerberos for other services. If you expect Mac OS X Server to provide services to
Mac OS X users as well as Windows users, configure it so that Kerberos is running.
98 Chapter 7 Migrating to Mac OS X Server from Windows NT
Page 99

To make Mac OS X Server an Open Directory master:
1 If Mac OS X Server will use an existing DNS service, configure your network’s DNS
service to resolve the server’s name and IP address and to resolve a reverse-lookup of
the server’s IP address to the server’s name.
2 Install the Mac OS X Server v10.5 software if it isn’t installed yet.
For installation instructions, see Getting Started.
If the Mac OS X Server software is already installed, go to step 4.
3 During the initial server setup that follows installation, use advanced server
configuration to create an Open Directory master using the following information, but
don’t create a Windows PDC and don’t set SMB file service to start automatically:
 In the TCP/IP Settings pane, enter the IP addresses of one or more DNS servers that
are configured to resolve the new server’s name and IP address.
If no DNS server is configured to resolve the new server’s name and IP address, don’t
enter any DNS server address.
 In the Directory Usage pane, choose Open Directory Master from the “Set directory
usage to” pop-up menu. Do not select Enable Windows Primary Domain Controller.
The server will become a PDC in Step 3, “Migrate users, groups, and computers to
Mac OS X Server” on page 100.
 In the Services pane, leave Windows file service turned off.
You can turn on other services in this pane. If you don’t turn on services now, you
can turn them on later using Server Admin.
4 If Mac OS X Server will provide its own DNS service, use the following to set it up and
configure the server’s Network preferences to use it.
 For instructions on setting up the server’s DNS service, see Network Services
Administration.
 In the Network pane of System Preferences, make sure the server’s IP address is the
first address in the DNS Servers field for the primary network interface. For
instructions, open System Preferences, choose Help > System Preferences Help, and
search for “changing network settings”.
5 Use Server Admin to confirm that the server is an Open Directory master and
determine whether Kerberos is running.
Open Server Admin, connect to the server, select Open Directory in the list of
computers and services, click Overview, and verify the following.
 If Open Directory’s Overview pane doesn’t say the server is an Open Directory
master, click Settings, click General, and choose Open Directory Master from the Role
pop-up menu. For detailed instructions, see Open Directory Administration.
Chapter 7 Migrating to Mac OS X Server from Windows NT 99
Page 100

 If the Overview pane says Kerberos is stopped, start it. Click Settings, click General,
then click Kerberize and authenticate when prompted. For detailed instructions on
starting Kerberos after setting up an Open Directory master, see Open Directory
Administration.
Kerberos won’t start if the server isn’t configured to use a DNS server that resolves
the server’s fully qualified DNS name and resolves a reverse-lookup of the server’s IP
address.
6 Use Server Admin to do the following to make sure the authentication methods use by
Windows services—NTLMv1, NTLMv2, and optionally LAN Manager—are enabled.
With Open Directory selected for the PDC server in Server Admin’s list of computers
and services, click Settings, click Policy, then click Authentication. Make sure “NTLMv1
and NTLMv2” is selected. Select other authentication methods needed by services and
users of the server.
Step 2: Have users copy files from old home directories
Tell users who have home directories on the Windows NT server that’s going out of
service that they need to copy files from their home directories to their My Documents
folders or a network folder that’s staying in service. Later, these users can copy their
files to their new Mac OS X Server home directories.
Users who have home directories on Windows servers that are staying in service don’t
need to copy their home directory files anywhere. After you migrate these users to
Mac OS X Server, they can access their home directories as before.
Step 3: Migrate users, groups, and computers to Mac OS X Server
Use the
ntdomainmigration.sh command-line tool to migrate user, group, and
computer information from the NT server.
For migrated user and groups, the tool creates user accounts and group accounts in
the LDAP directory of Mac OS X Server.
For migrated computers, the tool creates computer records and adds them to the
Windows Computers computer list in the LDAP directory.
In addition, the tool sets up Mac OS X Server as a PDC and starts Windows services.
To use ntdomainmigration.sh, you must know the NT server’s Windows domain, the
name and password of an NT domain administrator, and the name and password of an
LDAP directory administrator. If your network has an existing WINS server, you must
also know its IP address or DNS name.
When you run
ntdomainmigration.sh, it outputs information about migrated users,
groups, and computers. You can save this information if you want to keep a log of the
migration.
100 Chapter 7 Migrating to Mac OS X Server from Windows NT
 Loading...
Loading...