Page 1
CHAPTER 14
Wireless LAN
14.1 Overview
This chapter discusses how to configure the wireless network settings in your
NBG4615. See the appendices for more detailed information about wireless
networks.
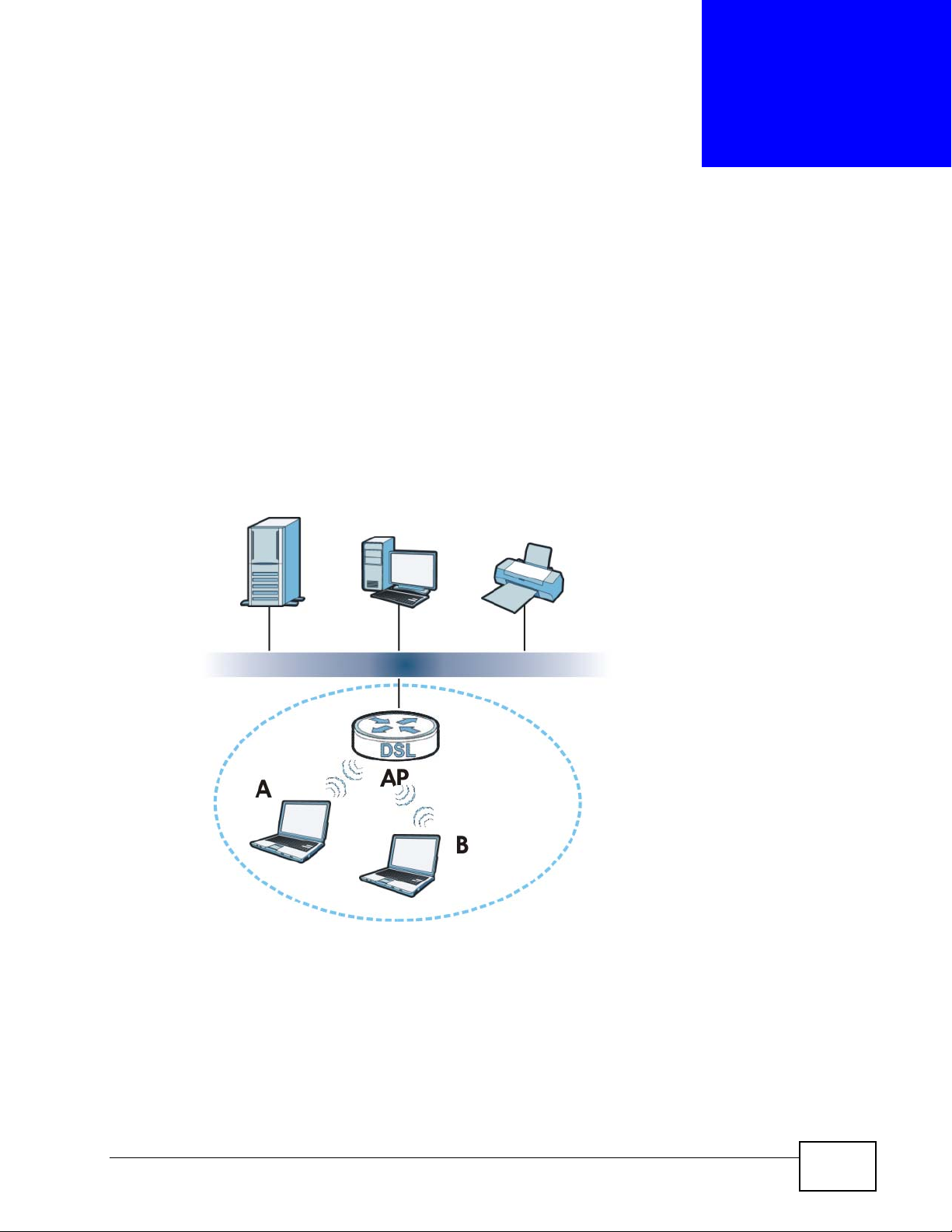
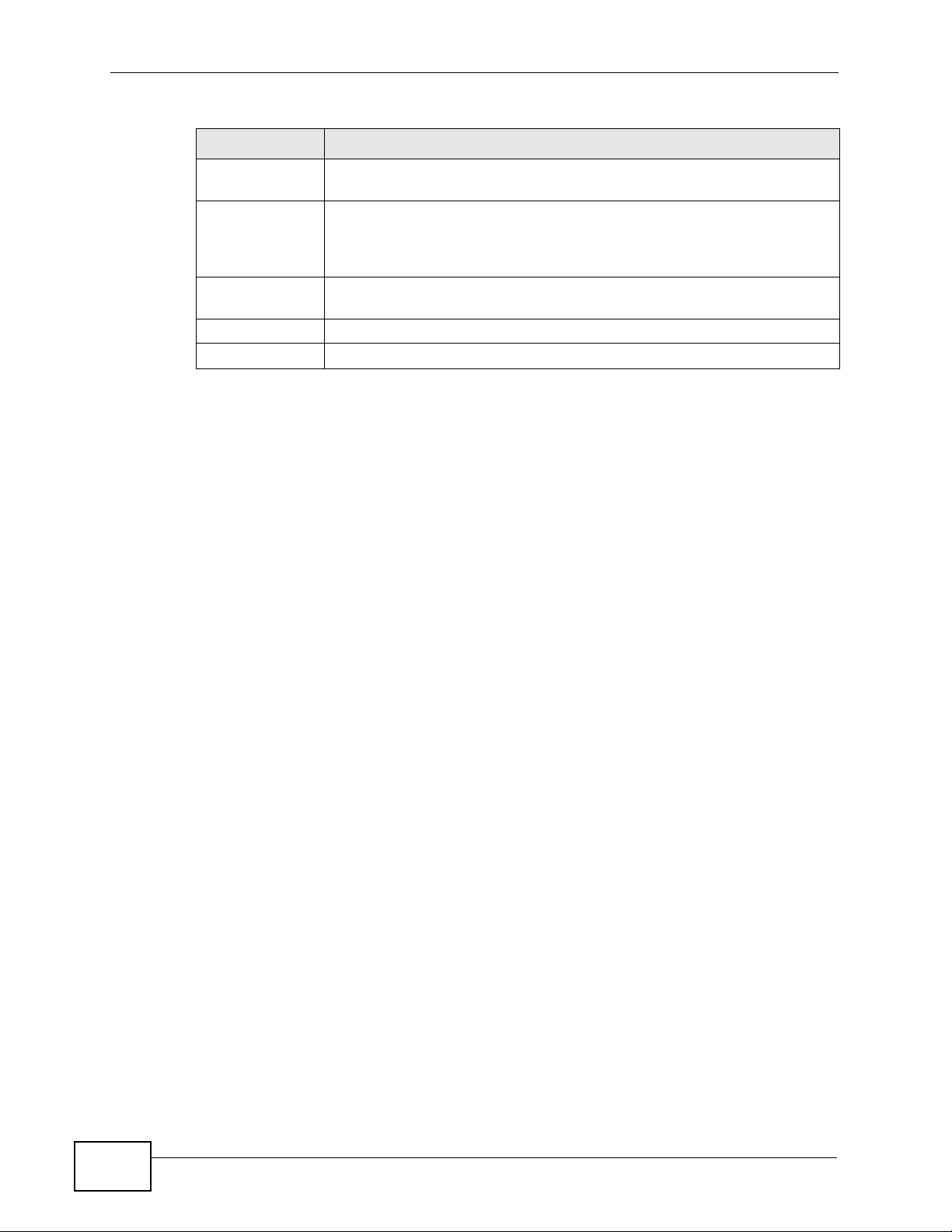
The following figure provides an example of a wireless network.
Figure 74 Example of a Wireless Network
The wireless network is the part in the blue circle. In this wireless network,
devices A and B are called wireless clients. The wireless clients use the access
point (AP) to interact with other devices (such as the printer) or with the Internet.
Your NBG4615 is the AP.
NBG4615 User’s Guide
129
Page 2

Chapter 14 Wireless LAN
14.1.1 What You Can Do
•Use the General screen to enter the SSID, enable intra-BSS traffic and select
the channel. (Section 14.2 on page 133).
•Use the Security screen to configure wireless security between the NBG4615
and the wireless clients.
•Use the MAC Filter screen to allow or deny wireless stations based on their
MAC addresses from connecting to the NBG4615 (Section 14.4 on page 139).
•Use the Advanced screen to allow intra-BSS networking and set the RTS/CTS
Threshold (Section 14.5 on page 140).
•Use the QoS screen to ensure Quality of Service (QoS) in your wireless network
(Section 14.6 on page 141).
•Use the WPS screen to quickly set up a wireless network with strong security,
without having to configure security settings manually (Section 14.7 on page
142).
•Use the WPS Station screen to add a wireless station using WPS (Section 14.8
on page 143).
•Use the Scheduling screen to set the times your wireless LAN is turned on and
off (Section 14.9 on page 144).
•Use the WDS screen to configure Wireless Distribution System on your
NBG4615 (Section 14.10 on page 146).
14.1.2 What You Should Know
Every wireless network must follow these basic guidelines.
• E very wireless client in the same wireless network must use the same SSID.
The SSID is the name of the wireless network. It stands for Service Set IDentity.
• I f two wireless networks overlap, they should use different channels.
Like radio stations or television channels, each wireless network uses a specific
channel, or frequency, to send and receive information.
• E very wireless client in the same wireless network must use securit y compatible
with the AP.
Security stops unauthorized devices from using the wireless net work. It can also
protect the information that is sent in the wireless network.
Wireless Security Overview
The following sections introduce different types of wireless s ecurity you can set up
in the wireless network.
130
NBG4615 User’s Guide
Page 3

Chapter 14 Wireless LAN
SSID
Normally , the AP acts like a beacon and regularl y broadcasts the SS ID in the area.
You can hide the SSID instead, in which case the AP does not broadcast the SS ID.
In addition, you should change the default SSID to something that is difficult to
guess.
This type of security is fairly weak, however, because there are ways for
unauthorized devices to get the SSID. In addition, unauthorized devices can still
see the information that is sent in the wireless network.
MAC Address Filter
Every wireless client has a unique identification number, called a MAC address.1 A
MAC address is usually written using twelve hexadecimal characters
example, 00A0C5000002 or 00:A0:C5:00:00:02. To get the MAC address for each
wireless client, see the appropriate User’s Guide or other documentation.
You can us e the MAC address filter to tell the AP which wireless clients are allowed
or not allowed to use the wireless network. If a wireless client is allowed to use the
wireless network, it still has to have the correct settings (SSID, channel, and
security). If a wireless client is not allowed to use the wireless network, it does not
matter if it has the correct settings.
This type of security does not protect the inf o rm at ion that is sent in the wireless
network. Furthermore, there are ways for unauthorized devices to get the MAC
address of an authorized wireless client. Then, they can use that MAC address to
use the wireless network.
2
; for
User Authentication
You can make every user log in to the wireless network before they can use it.
This is called user authentication. However, every wireless client in the wireless
network has to support IEEE 802.1x to do this.
For wireless networks, there are two typical places to store the user names and
passwords for each user.
• In the AP: this feature is called a local user database or a local database.
• In a RADIUS server: this is a server used in businesses more than in homes.
If your AP does not provide a local user database and if you do not have a RADIUS
server, you cannot set up user names and passwords for your users.
1. Some wireless devices, such as scanners, can detect wireless networks but cannot use wireless networks.
These kinds of wireless devices might not have MAC addresses.
2. Hexadecimal characters are 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, A, B, C, D, E, and F.
NBG4615 User’s Guide
131
Page 4

Chapter 14 Wireless LAN
Unauthorized devices can still see the information that is sent in the wireless
network, even if they cannot use the wireless network. Furthermore, there are
ways for unauthorized wireless users to get a valid user name and password.
Then, they can use that user name and password to use the wireless network.
Local user databases also have an additional limitation that is explained in the
next section.
Encryption
Wireless networks can use encryption to protect the informat ion that is sent in the
wireless network. Encryption is like a secret code. If you do not know the secret
code, you cannot understand the message.
The types of encryption you can choose depend on the type of user
authentication. (See page 131 for information about this.)
Table 41 Types of Encryption for Each Type of Authentication
Weakest No Security WPA
Strongest WPA2-PSK WPA2
NO AUTHENTICATION RADIUS SERVER
Static WEP
WPA-PSK
For example, if the wireless network has a RADIUS server, you can choose WPA
or WPA2. If users do not log in to the wireless network, you can choose no
encryption, Static WEP, WPA-PSK, or WPA2-PSK.
Usually, you should set up the strongest encryption that every wireless client in
the wireless network supports. For example, suppose the AP does not hav e a local
user database, and you do not have a RADIUS server. Therefore, there is no user
authentication. Suppose the wireless network has two wireless clients. Device A
only supports WEP, and device B supports WEP and WPA. Therefore, you should
set up Static WEP in the wireless network.
Note: It is recommended that wireless networks use WPA-PSK, WPA, or stronger
encryption. IEEE 802.1x and WEP encryption are better than none at all, but it
is still possible for unauthorized devices to figure out the original information
pretty quickly.
Note: It is not possible to use WPA-PSK, WPA or stronger encryption with a local user
database. In this case, it is better to set up stronger encryption with no
authentication than to set up weaker encryption with the local user database.
When you select WPA2 or WPA2-PSK in your NBG4615, you can also select an
option (WPA Compatible) to support WPA as well. In this case, if some wireless
clients support WPA and some support WPA2, you should set up WPA2-PSK or
132
NBG4615 User’s Guide
Page 5

Chapter 14 Wireless LAN
WPA2 (depending on the type of wireless network login) and select the WPA
Compatible option in the NBG4615.
Many types of encryption use a key to protect the information in the wireless
network. The longer the key, the stronger the encryption. Every wireless client in
the wireless network must have the same key.
WPS
WiFi Protected Setup (WPS) is an industry standard specification, defined by the
WiFi Alliance. WPS allows you to quickly set up a wireless network with strong
security , without having to configure secu rity settings manually. Depending on the
devices in your network, you can either press a button (on the device itself, or in
its configuration utility) or enter a PIN (Personal Identification Number) in the
devices. Then, they connect and set up a secure network by themselves. See how
to set up a secure wireless network using WPS in the Section 13.2 on page 111.
WDS
Wireless Distribution System or WDS security is used between bridged APs. It is
independent of the security between the wired networks and their respective APs.
If you do not enable WDS security, traffic between APs is not encrypted. When
WDS security is enabled, both APs must use the same pre-shared key.
14.2 General Wireless LAN Screen
Use this screen to configure the SSIDs of the wireless LAN.
Note: If you are configuring the NBG4615 from a computer connected to the wireless
LAN and you change the NBG4615’s SSID, channel or security settings, you
will lose your wireless connection when you press Apply to confirm. You must
then change the wireless settings of your computer to match the NBG4615’s
new settings.
NBG4615 User’s Guide
133
Page 6
Chapter 14 Wireless LAN
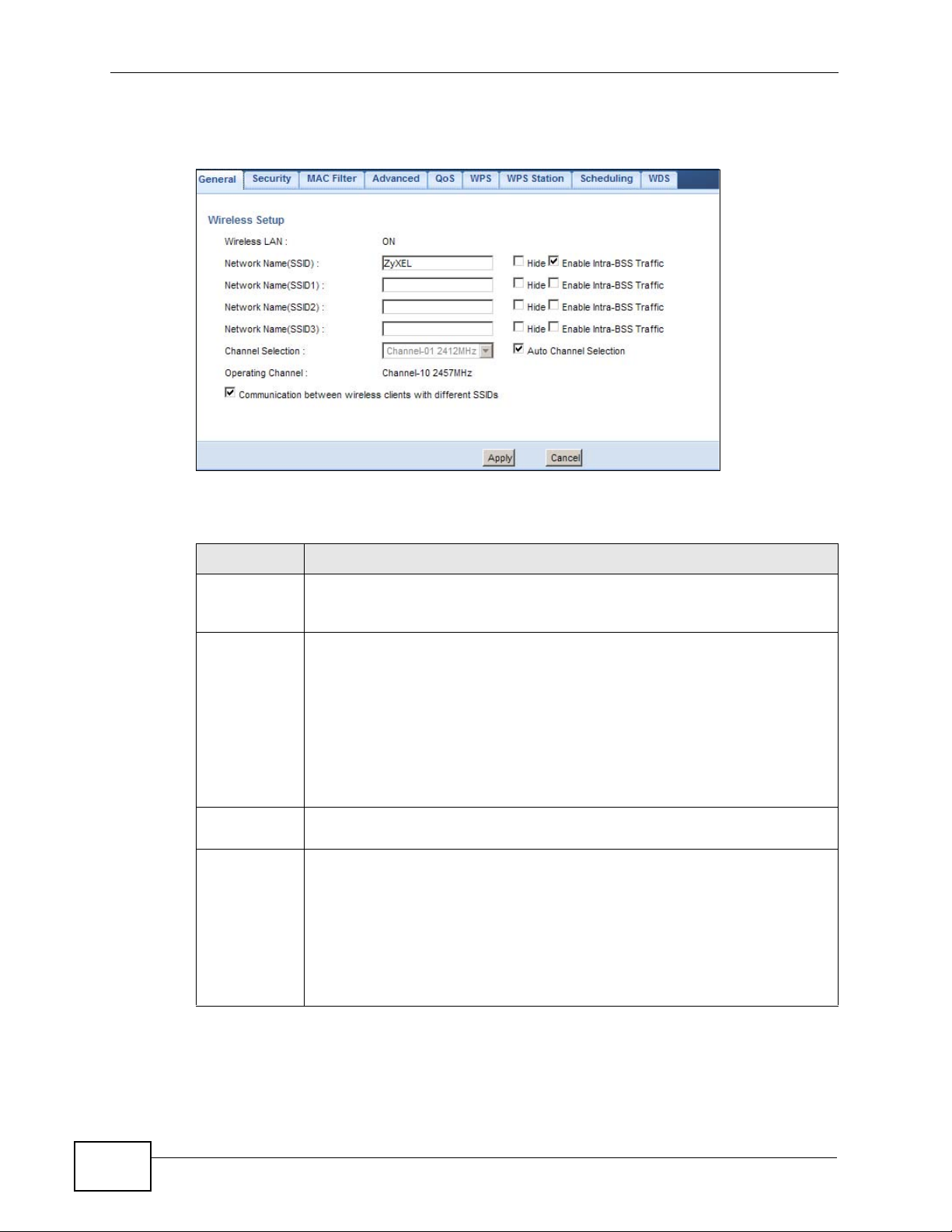
Click Network > Wireless LAN to open the General screen.
Figure 75 Network > Wireless LAN > General
The following table describes the general wireless LAN labels in this screen.
Table 42 Network > Wireless LAN > General
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Wireless LAN This shows whether the wireless LAN is ON or OFF. You can enable or
disable the wireless LAN by using the WLAN switch located on the back
panel of the NBG4615.
Network
Name(SSID)
or
Name(SSID1
~3)
Hide SSID Select this check box to hide the SSID in the outgoing beacon frame so a
Enable IntraBSS Traffic
The SSID (Service Set IDentity) identifies the Service Set with which a
wireless client is associated. Enter a descriptive name (up to 32 printable
characters found on a typical English language keyboard) for the wireless
LAN.
You can configure up to four SSIDs to enable multiple BSSs (Basic Service
Sets) on the NBG4615. This allows you to use one access point to provide
several BSSs simultaneously. You can then assign varying security types
to different SSIDs. Wireless clients can use different SSIDs to associate
with the same access point.
station cannot obtain the SSID through scanning using a site survey tool.
A Basic Service Set (BSS) exists when all communications between
wireless clients or between a wireless client and a wired network client go
through one access point (AP).
Intra-BSS traffic is traffic between wireless clients in the BS S. When IntraBSS is enabled, wireless clients can access the wired network and
communicate with each other. When Intra-BSS is disabled, wireless clients
can still access the wired network but cannot communicate with each
other.
134
NBG4615 User’s Guide
Page 7

Chapter 14 Wireless LAN
Table 42 Network > Wireless LAN > General (continued)
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Channel
Selection
Auto Channel
Selection
Operating
Channel
Communicati
on between
wireless
clients with
different
SSIDs
Apply Click Apply to save your changes back to the NBG4615.
Cancel Click Cancel to reload the previous configuration for this screen.
Set the operating frequency/channel depending on your particular region.
Select a channel from the drop-down list box. The options vary depending
on the frequency band and the country you are in.
Refer to the Connection Wizard chapter for more inform ation on channels.
This option is only available if Auto Channel Selection is disabled.
Select this check box for the NBG4615 to automatically choose the
channel with the least interference. Deselect this check box if you wish to
manually select the channel using the Channel Section field.
This displays the channel the NBG4615 is currently using.
Select the check box to allow communication between wireless clients of
different SSIDs. Do not select the check box if you do not want to enable
this function.
See the rest of this chapter for information on the other labels in this screen.
14.3 Wireless Security Screen
Use this screen to select the wireless security mode for each SSID. Click Network
> Wireless LAN > Security to open the Security screen. The screen varies
depending on what you select in the Security Mode field.
14.3.1 No Security
Select No Security to allow wireless clients to communicate with the access
points without any data encryption.
NBG4615 User’s Guide
135
Page 8
Chapter 14 Wireless LAN
Note: If you do not enable any wireless security on your NBG4615, your network is
accessible to any wireless networking device that is within range.
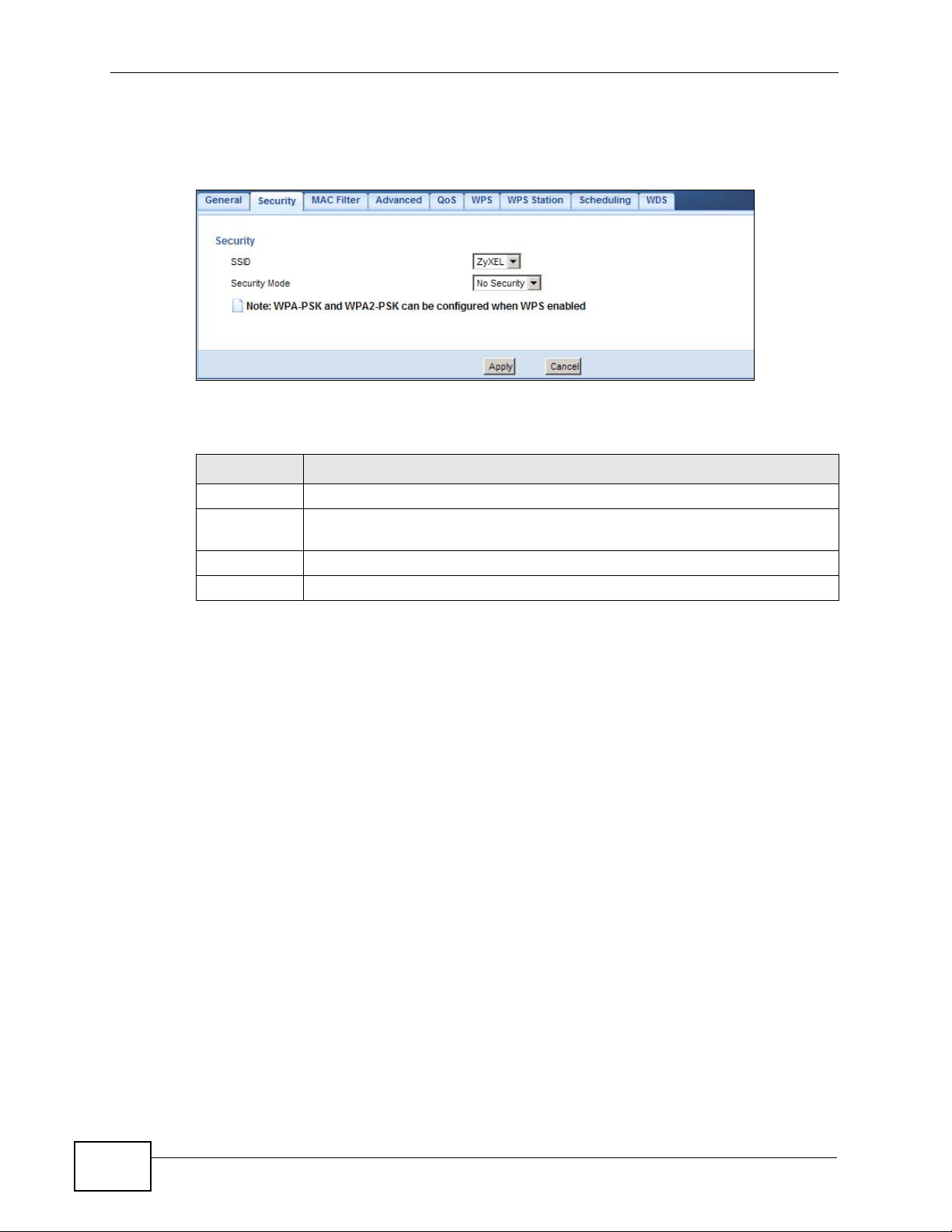
Figure 76 Network > Wireless LAN > Security: No Security
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 43 Network > Wireless LAN > Security: No Security
LABEL DESCRIPTION
SSID Select the SSID for which you want to configure the security.
Security
Mode
Apply Click Apply to save your changes back to the NBG4615.
Cancel Click Cancel to reload the previous configuration for this screen.
Choose No Security from the drop-down list box.
14.3.2 WEP Encryption
WEP encryption scrambles the data transmitted bet ween the wireless stations and
the access points to keep network communications private. It encrypts unicast
and multicast communications in a network. Both the wireless stations and the
access points must use the same WEP key.
Your NBG4615 allows you to configure up to four 64-bit or 128-bit WEP keys but
only one key can be enabled at any one time.
136
NBG4615 User’s Guide
Page 9
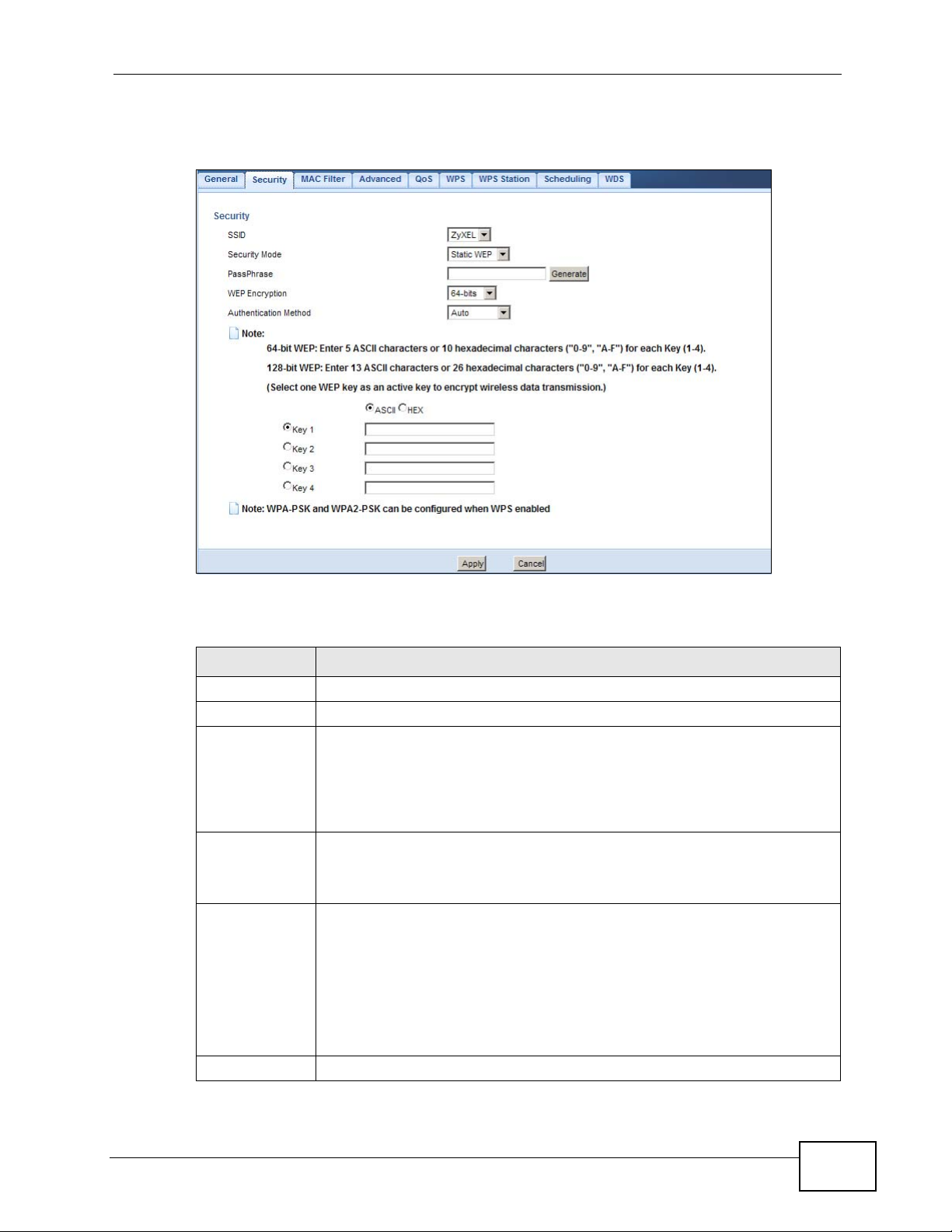
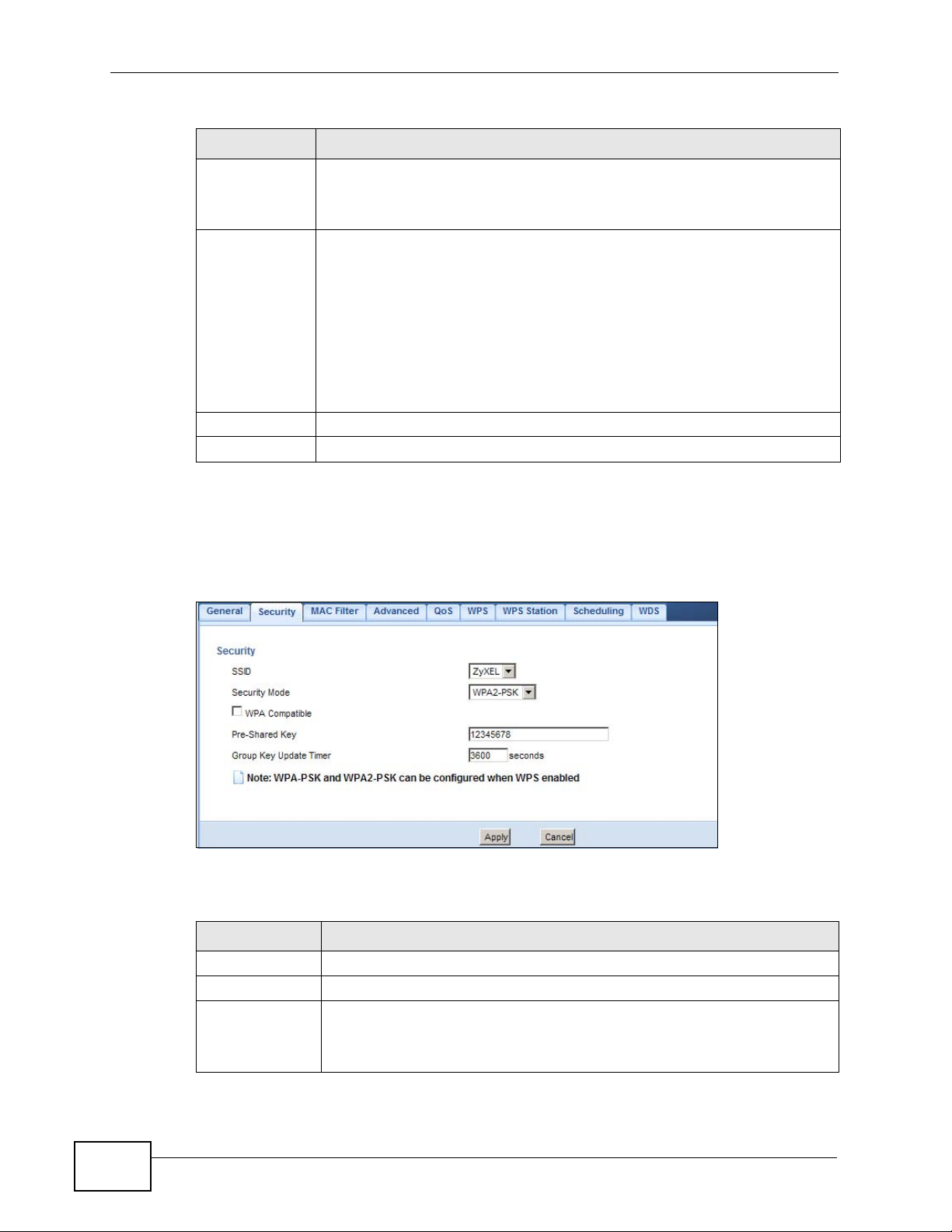
Select Static WEP from the Security Mode list.
Figure 77 Network > Wireless LAN > Security: Static WEP
Chapter 14 Wireless LAN
The following table describes the wireless LAN security labels in this screen.
Table 44 Network > Wireless LAN > Security: Static WEP
LABEL DESCRIPTION
SSID Select the SSID for which you want to configure the security.
Security Mode Select Static WEP to enable data encryption.
PassPhrase Enter a Passphrase (up to 26 printable characters) and click Generate.
A passphrase functions like a password. In WEP security mode, it is
further converted by the NBG4615 into a complicated string that is
referred to as the “key”. This key is requested from all devices wishing to
connect to a wireless network.
WEP
Encryption
Authentication
Method
ASCII Select this option in order to enter ASCII characters as WEP key.
Select 64-bits or 128-bits.
This dictates the length of the security key that the network is going to
use.
Select Auto or Shared Key from the drop-down list box.
This field specifies whether the wireless clients have to provide the WEP
key to login to the wireless client. Keep this setting at Auto unless you
want to force a key verification before communication between the
wireless client and the NBG4615 occurs.
Select Shared Key to force the clients to provide the WEP key prior to
communication.
NBG4615 User’s Guide
137
Page 10
Chapter 14 Wireless LAN
Table 44 Network > Wireless LAN > Security: Static WEP (continued)
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Hex Select this option in order to enter hexadecimal characters as a WEP key.
The preceding "0x", that identifies a hexadecimal key, is entered
automatically.
Key 1 to Key 4 The WEP keys are used to encrypt data. Both the NBG4615 and the
wireless stations must use the same WEP key for data transmission.
If you chose 64-bit WEP, then enter any 5 ASCII characters or 10
hexadecimal characters ("0-9", "A-F").
If you chose 128-bit WEP, then enter 13 ASCII characters or 26
hexadecimal characters ("0-9", "A-F").
You must configure at least one key, only one key can be activated at
any one time. The default key is key 1.
Apply Click Apply to save your changes back to the NBG4615.
Cancel Click Cancel to reload the previous configuration for this screen.
14.3.3 WPA-PSK/WPA2-PSK
Select WPA-PSK or WPA2-PSK from the Security Mode list.
Figure 78 Network > Wireless LAN > Security: WPA-PSK/WPA2-PSK
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 45 Network > Wireless LAN > Security: WPA-PSK/WPA2-PSK
LABEL DESCRIPTION
SSID Select the SSID for which you want to configure the security.
Security Mode Select WPA-PSK or WPA2-PSK to enable data encryption.
WPA
Compatible
This field appears when you choos e WPA2-PSK as the Security Mode.
Check this field to allow wireless devices using WPA-PSK security
mode to connect to your NBG4615.
138
NBG4615 User’s Guide
Page 11
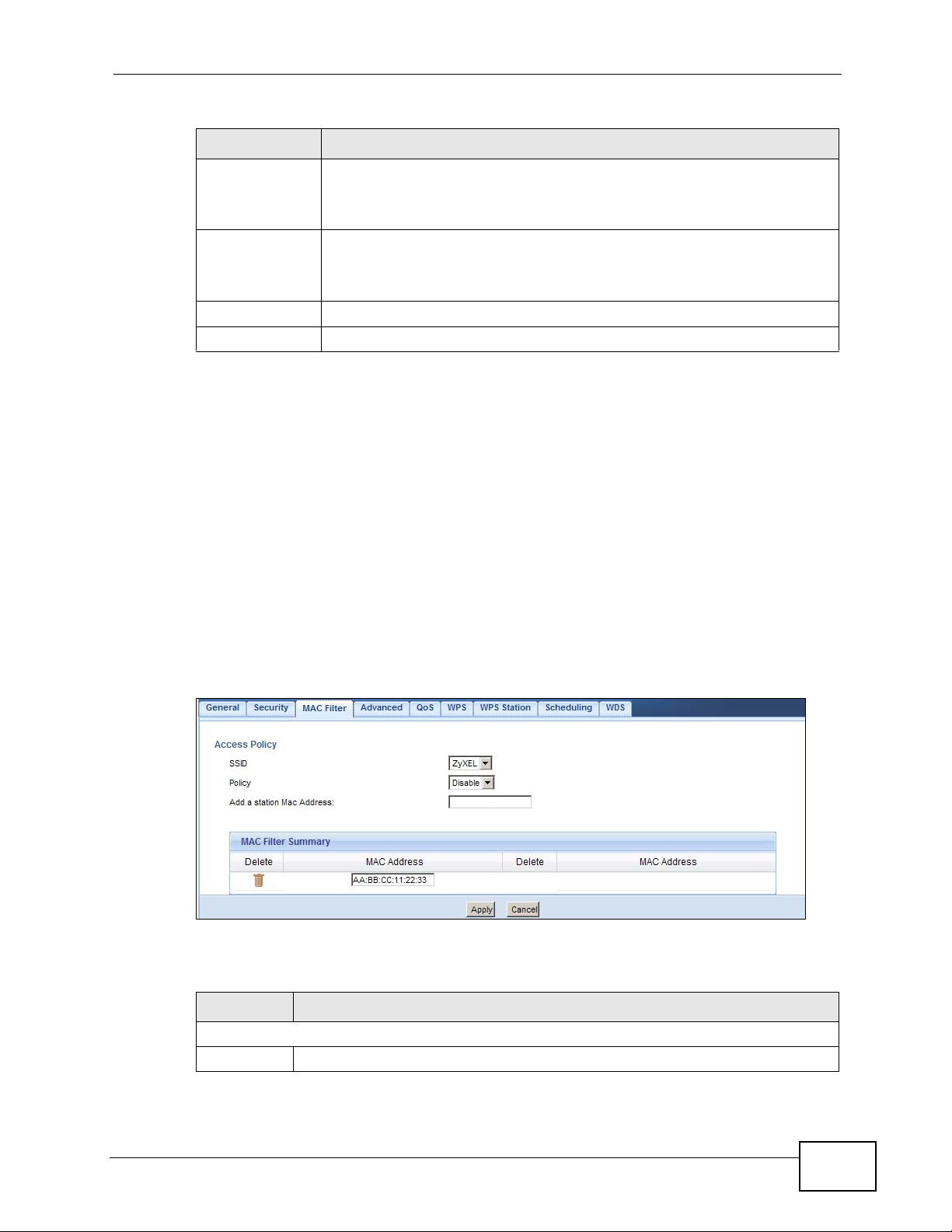
Table 45 Network > Wireless LAN > Security: WPA-PSK/WPA2-PSK (continued)
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Pre-Shared Key WPA-PSK/WPA2-PSK uses a simple common password for
authentication.
Type a pre-shared key from 8 to 63 case-sensitive keyboard characters.
Group Key
Update Timer
Apply Click Apply to save your changes back to the NBG4615.
Cancel Click Cancel to reload the previous configuration for this screen.
The Group Key Update Timer is the r ate at which the AP sends a new
group key out to all clients.
The default is 3600 seconds (60 minutes).
14.4 MAC Filter
The MAC filter screen allows you to configure the NBG4615 to give exclusive
access to devices (Allow) or exclude devices from accessing the NBG4615 (Deny).
Every Ethernet device has a unique MAC (Media Access Control) address. The MAC
address is assigned at the factory and consists of six pairs of hexadecimal
characters, for example, 00:A0:C5:00:00:02. You need to know the MAC address
of the devices to configure this screen.
Chapter 14 Wireless LAN
To change your NBG4615’s MAC filter settings, click Network > Wireless LAN >
MAC Filter. The screen appears as shown.
Figure 79 Network > Wireless LAN > MAC Filter
The following table describes the labels in this menu.
Table 46 Network > Wireless LAN > MAC Filter
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Access Policy
SSID Select the SSID for which you want to configure MAC filtering.
NBG4615 User’s Guide
139
Page 12
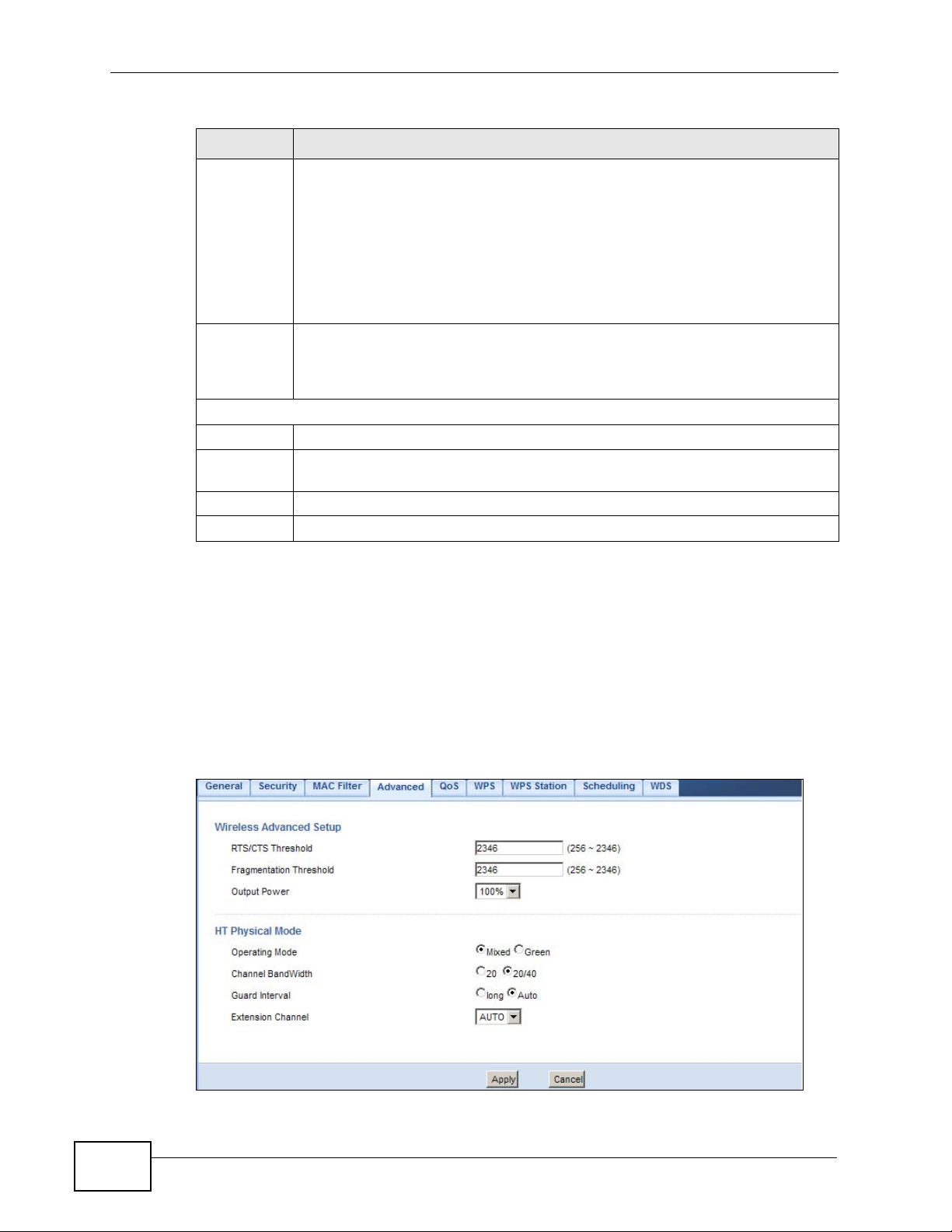
Chapter 14 Wireless LAN
Table 46 Network > Wireless LAN > MAC Filter (continued)
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Policy Define the filter action for the list of MAC addresses in the MAC Address
Add a
station Mac
Address
MAC Filter Summary
Delete Click the delete icon to remove the MAC address from the list.
MAC
Address
Apply Click Apply to save your changes back to the NBG4615.
Cancel Click Cancel to reload the previous configuration for this screen.
table.
Select Disable to deactivate the MAC filtering rule you configure below.
Select Allow to permit access to the NBG4615, MAC addresses not listed
will be denied access to the NBG4615.
Select Reject to block access to the NBG4615, MAC addresses not listed
will be allowed to access the NBG4615
Enter the MAC addresses of the wireless station that are allowed or denied
access to the NBG4615 in these address fields. Enter the MAC addresses in
a valid MAC address format, that is, six hexadecimal character pairs, for
example, 12:34:56:78:9a:bc. Click Add.
This is the MAC address of the wireless station that are allowed or denied
access to the NBG4615.
14.5 Wireless LAN Advanced Screen
Use this screen to allow wireless advanced features, such as the output power,
RTS/CTS Threshold and high-throughput physical mode settings.
Click Network > Wireless LAN > Advanced. The screen appears as shown.
Figure 80 Network > Wireless LAN > Advanced
140
NBG4615 User’s Guide
Page 13
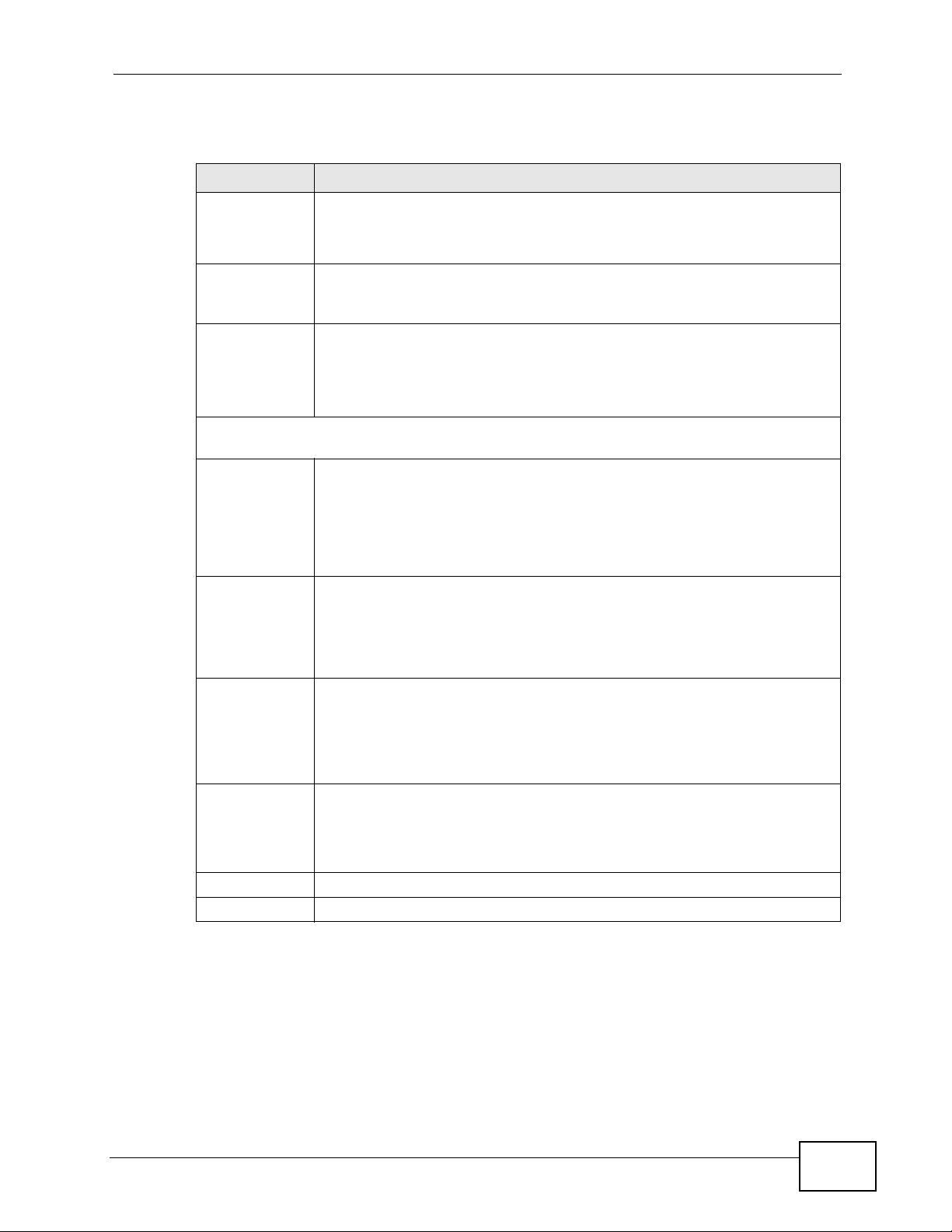
Chapter 14 Wireless LAN
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 47 Network > Wireless LAN > Advanced
LABEL DESCRIPTION
RTS/CTS
Threshold
Fragmentation
Threshold
Output Power Set the output power of the NBG4615 in this field. If there is a high
HT (High Throughput) Physical Mode - Use the fields below to configure the 802.11
wireless environment of your NBG4615.
Operating
Mode
Data with its frame size larger than this value will perform the RTS
(Request To Send)/CTS (Clear To Send) handshake.
Enter a value between 256 and 2432.
The threshold (number of bytes) for the fragmentation boundary for
directed messages. It is the maximum data fragment size that can be
sent. Enter an even number between 256 and 2346.
density of APs in an area, decrease the output power of the NBG4615 to
reduce interference with other APs. Select one of the following 100%,
90%, 75%, 50%, 25% or 10%. See the product specifications for
more information on your NBG4615’s output power.
Choose this according to the wireless mode(s) used in your network.
Mixed - Select this if the wireless clients in your network use different
wireless modes (for example, IEEE 802.11b/g and IEEE 802.1n modes)
Green - Select this if the wireless clients in your network uses only one
type of wireless mode (for example, IEEEE 802.11 n only)
Channel
Bandwidth
Guard Interval Select Auto to increase data throughput. However, this may make data
Extension
Channel
Apply Click Apply to save your changes back to the NBG4615.
Cancel Click Cancel to reload the previous configuration for this screen.
Select the channel bandwidth you want to use for your wireless network.
It is recommended that you select 20/40 (20/40 MHz).
Select 20 MHz if you want to lessen radio interference with other
wireless devices in your neighborhood.
transfer more prone to errors.
Select Long to prioritize data integrity. This may be because your
wireless network is busy and congested or the NBG4615 is located in an
environment prone to radio interference.
This is set to Auto by default.
If you select 20/40 as your Channel Bandwidth, the extension
channel enables the NBG4615 to get higher data throughput. This also
lowers radio interference and traffic.
14.6 Quality of Service (QoS) Screen
The QoS screen allows you to automatically give a service (such as VoIP and
video) a priority level.
NBG4615 User’s Guide
141
Page 14
Chapter 14 Wireless LAN
Click Network > Wireless LAN > QoS. The following screen appears.
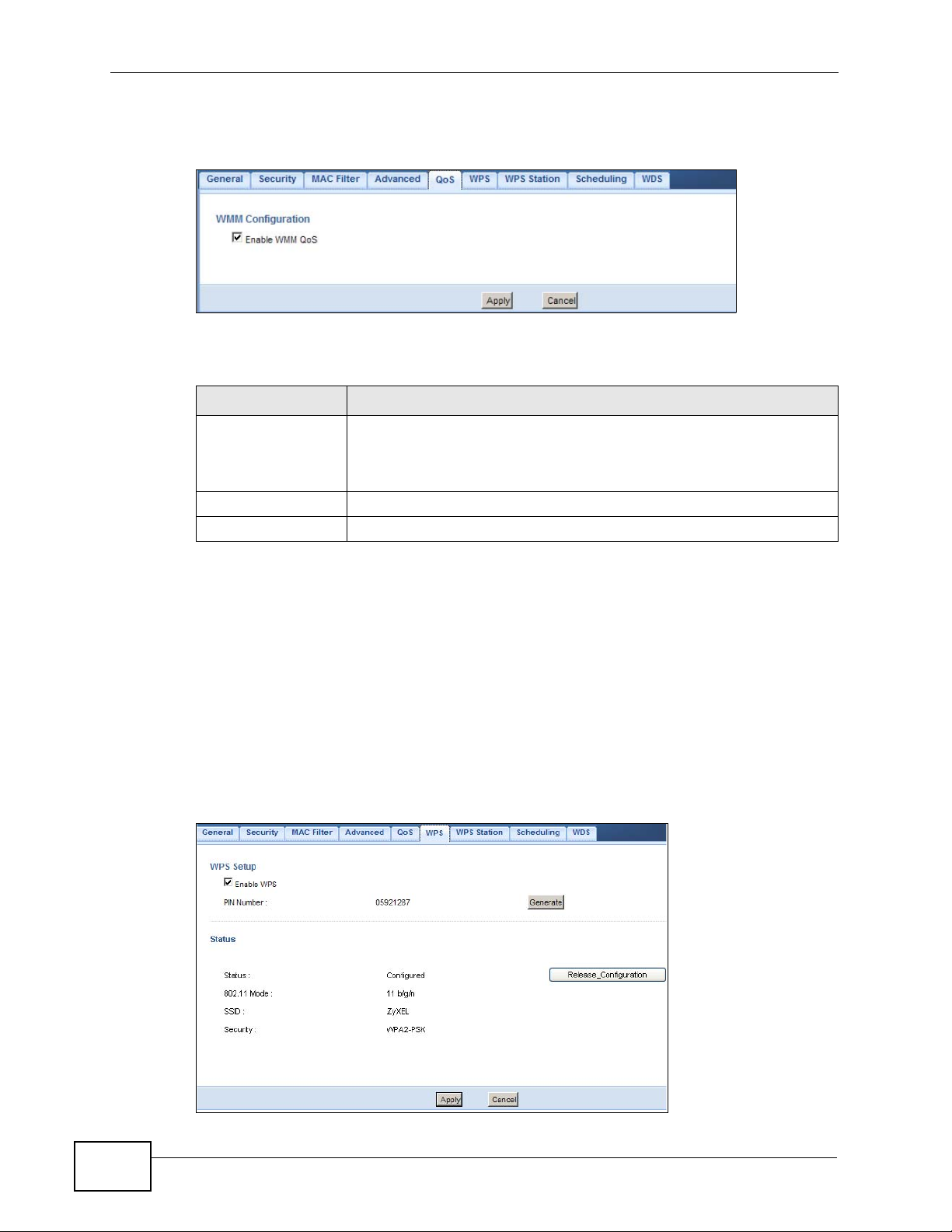
Figure 81 Network > Wireless LAN > QoS
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 48 Network > Wireless LAN > QoS
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Enable WMM QoS Check this to have the NBG4615 automatically give a service a
Apply Click Apply to save your changes to the NBG4615.
Cancel Click Cancel to reload the previous configuration for this screen.
priority level according to the ToS value in the IP header of packets
it sends. WMM QoS (Wifi MultiMedia Quality of Service) gives high
priority to voice and video, which makes them run more smoothly.
14.7 WPS Screen
Use this screen to enable/disable WPS, view or generate a new PIN number and
check current WPS status. To open this screen, click Network > Wireless LAN >
WPS tab.
Note: With WPS, wireless clients can only connect to the wireless network using the
first SSID on the NBG4615.
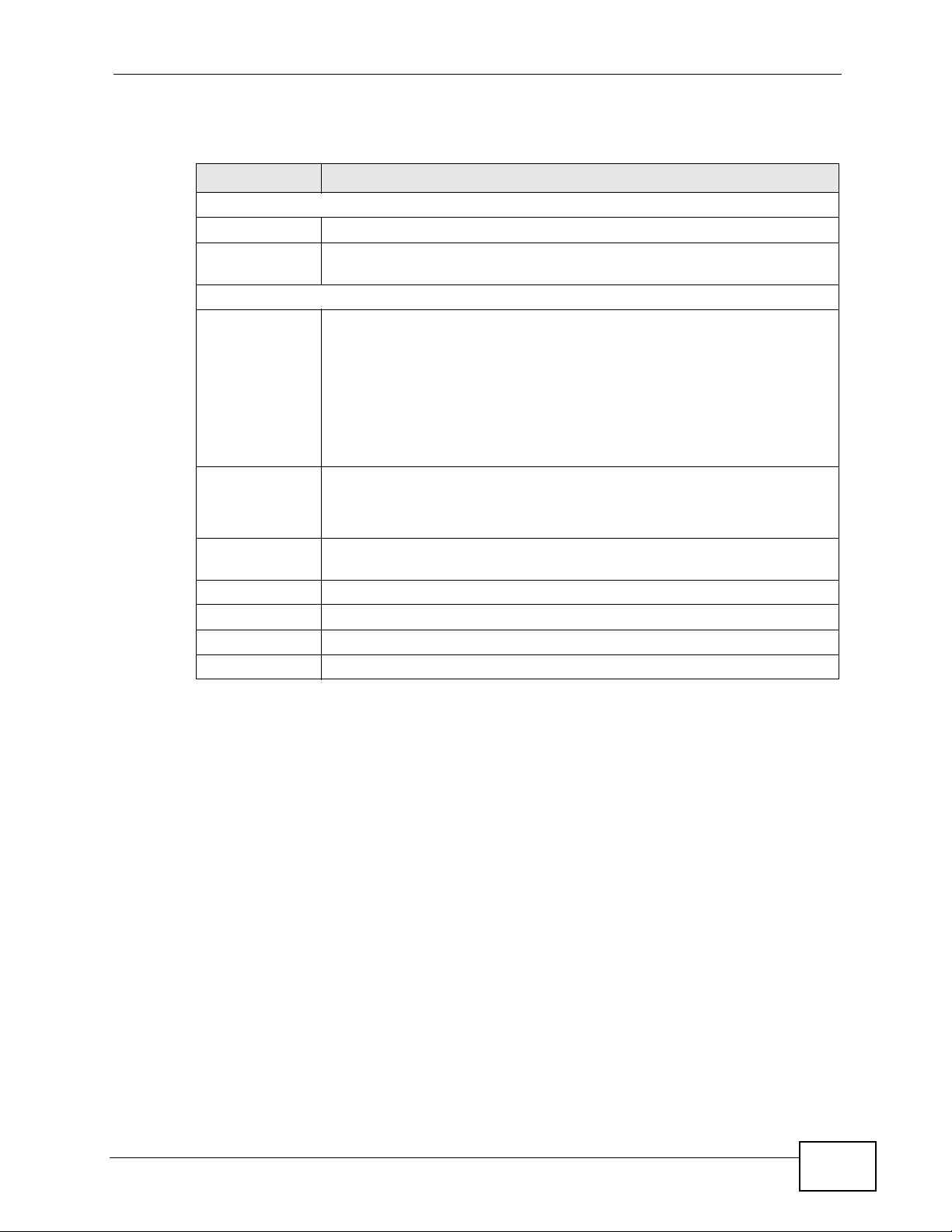
Figure 82 Network > Wireless LAN > WPS
142
NBG4615 User’s Guide
Page 15
Chapter 14 Wireless LAN
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 49 Network > Wireless LAN > WPS
LABEL DESCRIPTION
WPS Setup
Enable WPS Select this to enable the WPS feature.
PIN Number This displays a PIN number last time system generated. Click Generate
to generate a new PIN number.
Status
Status This displays Configured when the NBG4615 has connected to a
wireless network using WPS or when Enable WPS is selected and
wireless or wireless security settings have been changed. The current
wireless and wireless security settings also appear in the screen.
This displays Unconfigured if WPS is disabled and there are no
wireless or wireless security changes on the NBG4615 or you click
Release_Configuration to remove the configured wireless and
wireless security settings.
Release
Configuration
802.11 Mode This is the 802.11 mode used. Only compliant WLAN devices can
SSID This is the name of the wireless network (the NBG4615’s first SSID).
Security This is the type of wireless security employed by the network.
Apply Click Apply to save your changes back to the NBG4615.
Cancel Click Cancel to reload the previous configuration for this screen.
This button is only available when the WPS status displays Configured.
Click this button to remove all configured wireless and wireless security
settings for WPS connections on the NBG4615.
associate with the NBG4615.
14.8 WPS Station Screen
Use this screen when you want to add a wireless station using WPS. To open this
screen, click Network > Wireless LAN > WPS Station tab.
NBG4615 User’s Guide
143
Page 16
Chapter 14 Wireless LAN
Note: After you click Push Button on this screen, you have to press a similar button
in the wireless station utility within 2 minutes. To add the second wireless
station, you have to press these buttons on both device and the wireless station
again after the first 2 minutes.
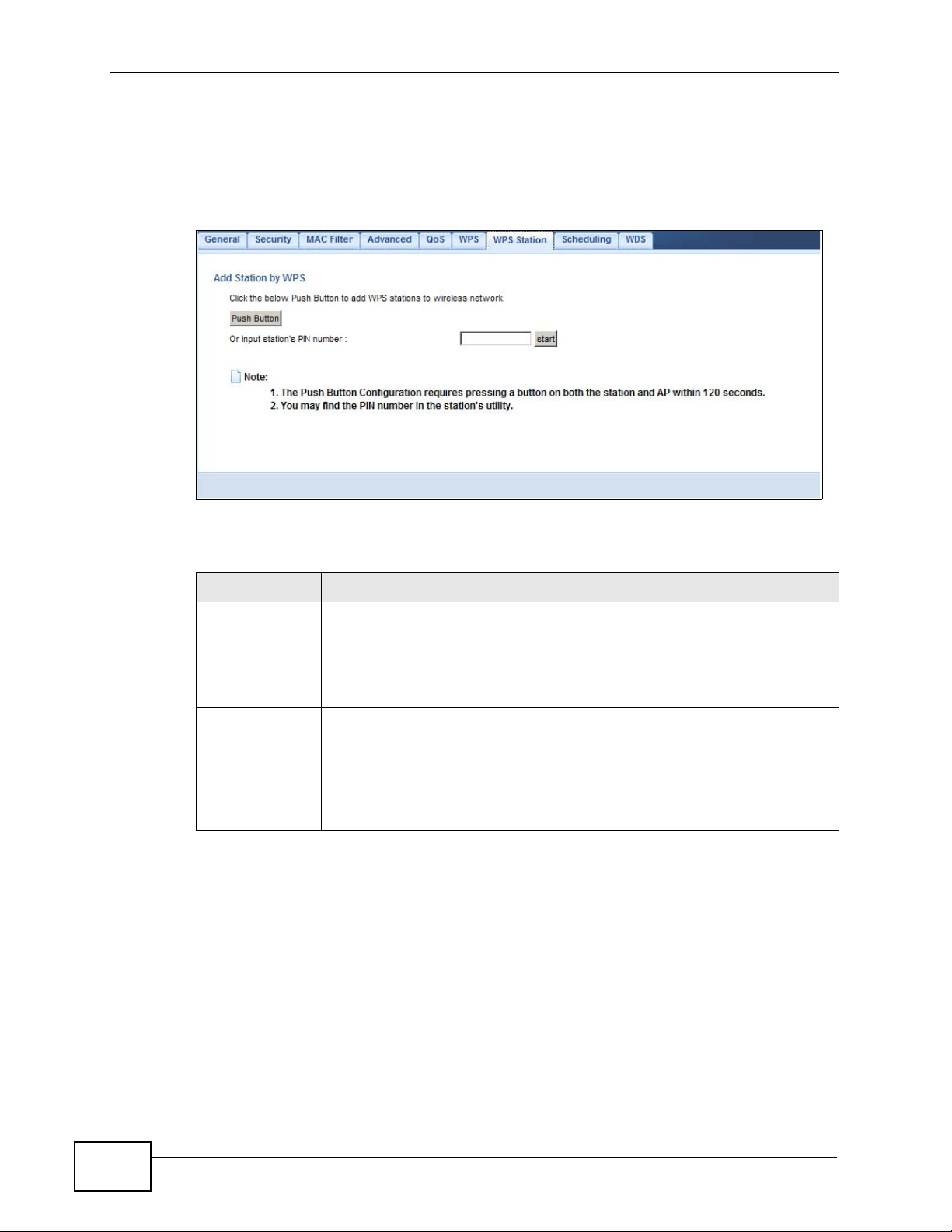
Figure 83 Network > Wireless LAN > WPS Station
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 50 Network > Wireless LAN > WPS Station
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Push Button Use this button when you use the PBC (Push Button Configuration)
method to configure wireless stations’s wireless settings. See Section
4.3.1 on page 32.
Click this to start WPS-aware wireless station scanning and the wireless
security information synchronization.
Or input
station’s PIN
number
Use this button when you use the PIN Configuration method to
configure wireless station’s wireless settings. See Section 4.3.2 on page
33.
Type the same PIN number generated in the wireless station’s utility.
Then click Start to associate to each other and perform the wireless
security information synchronization.
14.9 Scheduling Screen
Use this screen to set the times your wireless LAN is turned on and off. Wireless
LAN scheduling is disabled by default. The wireless LAN can be scheduled to turn
144
NBG4615 User’s Guide
Page 17
Chapter 14 Wireless LAN
on or off on certain days and at certain times. To open this screen, click Network
> Wireless LAN > Scheduling tab.
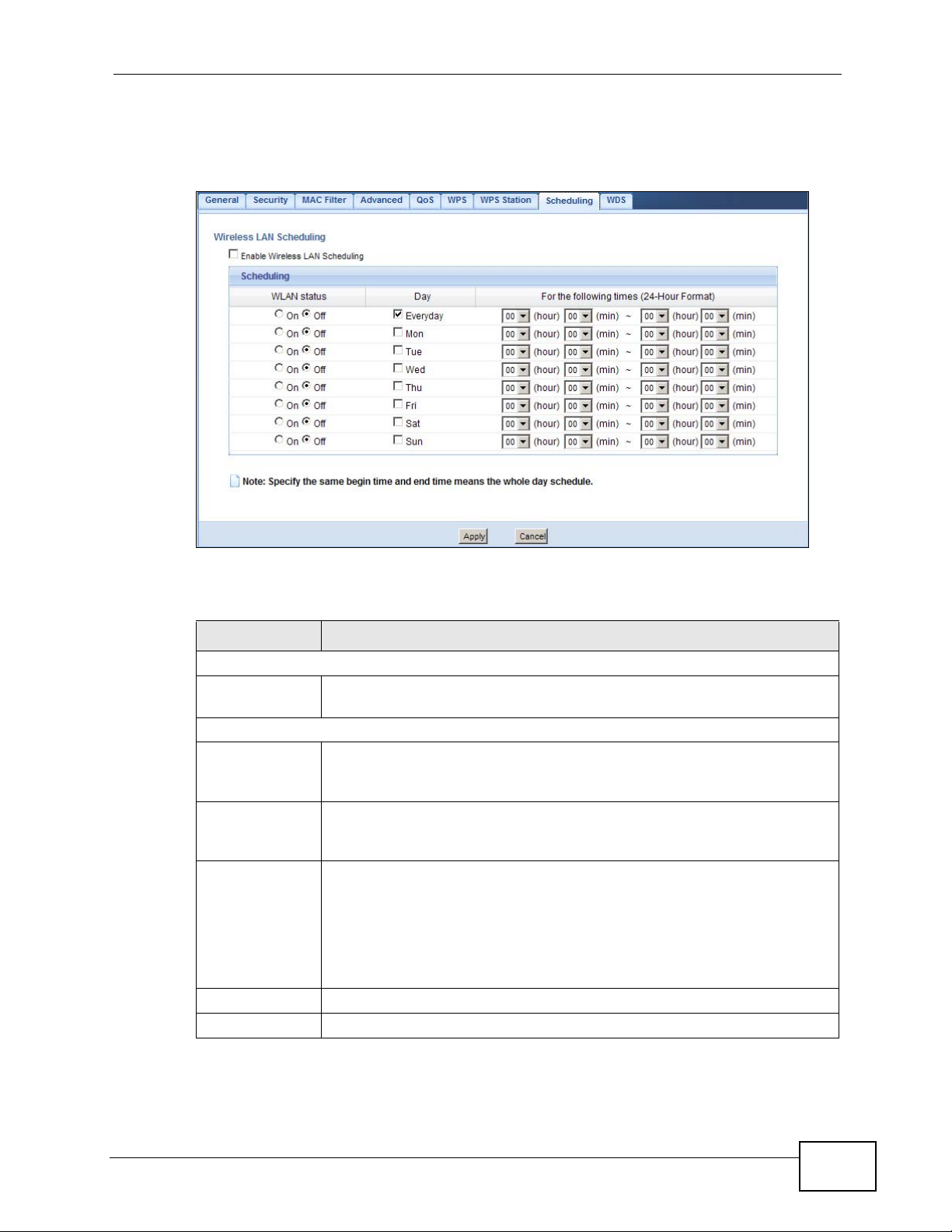
Figure 84 Network > Wireless LAN > Scheduling
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 51 Network > Wireless LAN > Scheduling
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Wireless LAN Scheduling
Enable Wireless
LAN Scheduling
Scheduling
WLAN Status Select On or Off to specify whether the Wireless LAN is turned on or off.
Day Select Everyday or the specific days to turn the Wireless LAN on or off.
For the
following times
(24-Hour
Format)
Apply Click Apply to save your changes back to the NBG4615.
Cancel Click Cancel to reload the previous configuration for this screen.
Select this to enable Wireless LAN scheduling.
This field works in conjunction with the Day and For the following
times fields.
If you select Everyday you can not select any specific days. This field
works in conjunction with the For the following times field.
Select a begin time using the first set of hour and minute (min) drop
down boxes and select an end time using the second set of hour and
minute (min) drop down boxes. If you have chosen On earlier for the
WLAN Status the Wireless LAN will turn on between the two times you
enter in these fields. If you have chosen Off earlier for the WLAN Status
the Wireless LAN will turn off between the two times you enter in these
fields.
NBG4615 User’s Guide
145
Page 18
Chapter 14 Wireless LAN
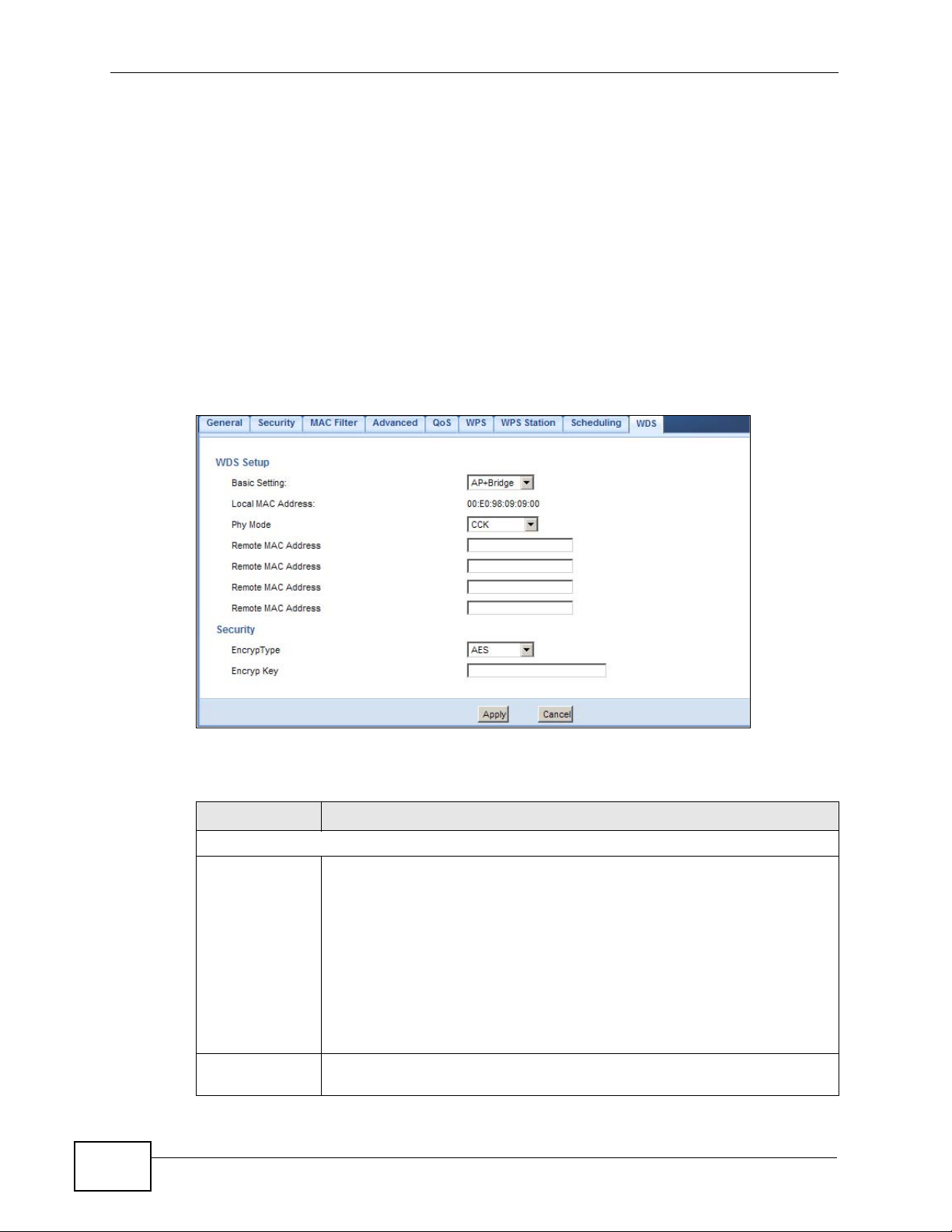
14.10 WDS Screen
A Wireless Distribution System (WDS) is a wireless connection between two or
more APs. Use this screen to set the operating mode of your NBG4615 to AP +
Bridge or Bridge and establish wireless links with other APs. You need to know
the MAC address of the peer device, which also must be in bridge mode.
Note: You must enable the same wireless security settings on the NBG4615 and on
all wireless clients that you want to associate with it.
Click Network > Wir eless LAN > WDS tab. The foll owing screen opens with the
Basic Setting set to Disabled, and Security Mode set to No Security.
Figure 85 Network > Wireless LAN > WDS
146
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 52 Network > Wireless LAN > WDS
LABEL DESCRIPTION
WDS Setup
Basic Settings Select the operating mode for your NBG4615.
• Disable - The NBG4615 works as an access point only and cannot
establish wireless links with other APs.
The NBG4615 functions as a bridge and access point
Local MAC
Address
• AP + Bridge -
simultaneously.
• Bridge - The NBG4615 acts as a wireless network bridge and
establishes wireless links with other APs.
You need to know the MAC address of the peer device, which also must
be in bridge mode. The NBG4615 can establish up to five wireless links
with other APs.
This is the MAC address of your NBG4615.
NBG4615 User’s Guide
Page 19
Chapter 14 Wireless LAN
Table 52 Network > Wireless LAN > WDS (continued)
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Phy Mode Select the Phy mode you want the NBG4615 to use. This dictates the
maximum size of packets during data transmission.
This field is not available when you select Disable in the Basic Setting
field.
Remote MAC
Address
Security
EncrypType Select whether to use WEP, TKIP or AES encryption for your WDS
EncrypKey The Encryp Key is used to encrypt data. Peers must use the same key
Apply Click Apply to save your changes to NBG4615.
Cancel Click Cancel to reload the previous configuration for this screen.
This is the MAC address of the peer device that your NBG4615 wants to
make a bridge connection with.
You can connect to up to 4 peer devices.
connection in this field.
Otherwise, select No Security.
for data transmission.
NBG4615 User’s Guide
147
Page 20

Chapter 14 Wireless LAN
148
NBG4615 User’s Guide
Page 21

CHAPTER 15
IPv6
15.1 Overview
IPv6 (Internet Protocol version 6), is designed to enhance IP address size and
features. The increase in IPv6 address size to 128 bits (from the 32-bit IPv4
address) allows up to 3.4 x 1038 IP addresses.
• See Appendix G on page 325 for more information on IPv6.
15.1.1 What You Need to Know
IPv6 Addressing
The 128-bit IPv6 address is written as eight 16-bit hexadecimal blocks separated
by colons (:). This is an example IPv6 address
2001:0db8:1a2b:0015:0000:0000:1a2f:0000.
IPv6 addresses can be abbreviated in two ways:
• Leading zeros in a block can be omitted. So
2001:0db8:1a2b:0015:0000:0000:1a2f:0000 can be written as
2001:db8:1a2b:15:0:0:1a2f:0.
• Any number of consecutive blocks of zeros can b e replaced by a do uble colon. A
double colon can only appear once in an IPv6 address. So
2001:0db8:0000:0000:1a2f:0000:0000:0015 can be written as
2001:0db8::1a2f:0000:0000:0015, 2001:0db8:0000:0000:1a2f::0015,
2001:db8::1a2f:0:0:15 or 2001:db8:0:0:1a2f::15.
IPv6 Prefix and Prefix Length
Similar to an IPv4 subnet mask, IPv6 uses an address prefix to represent the
network address. An IPv6 prefix length specifies how many most significant bits
(start from the left) in the address compose the network address. The prefix
length is written as “/x” where x is a number. For example,
2001:db8:1a2b:15::1a2f:0/32
means that the first 32 bits (2001:db8) is the subnet prefix.
NBG4615 User’s Guide
149
Page 22
Chapter 15 IPv6
15.2 The IPv6 Screen
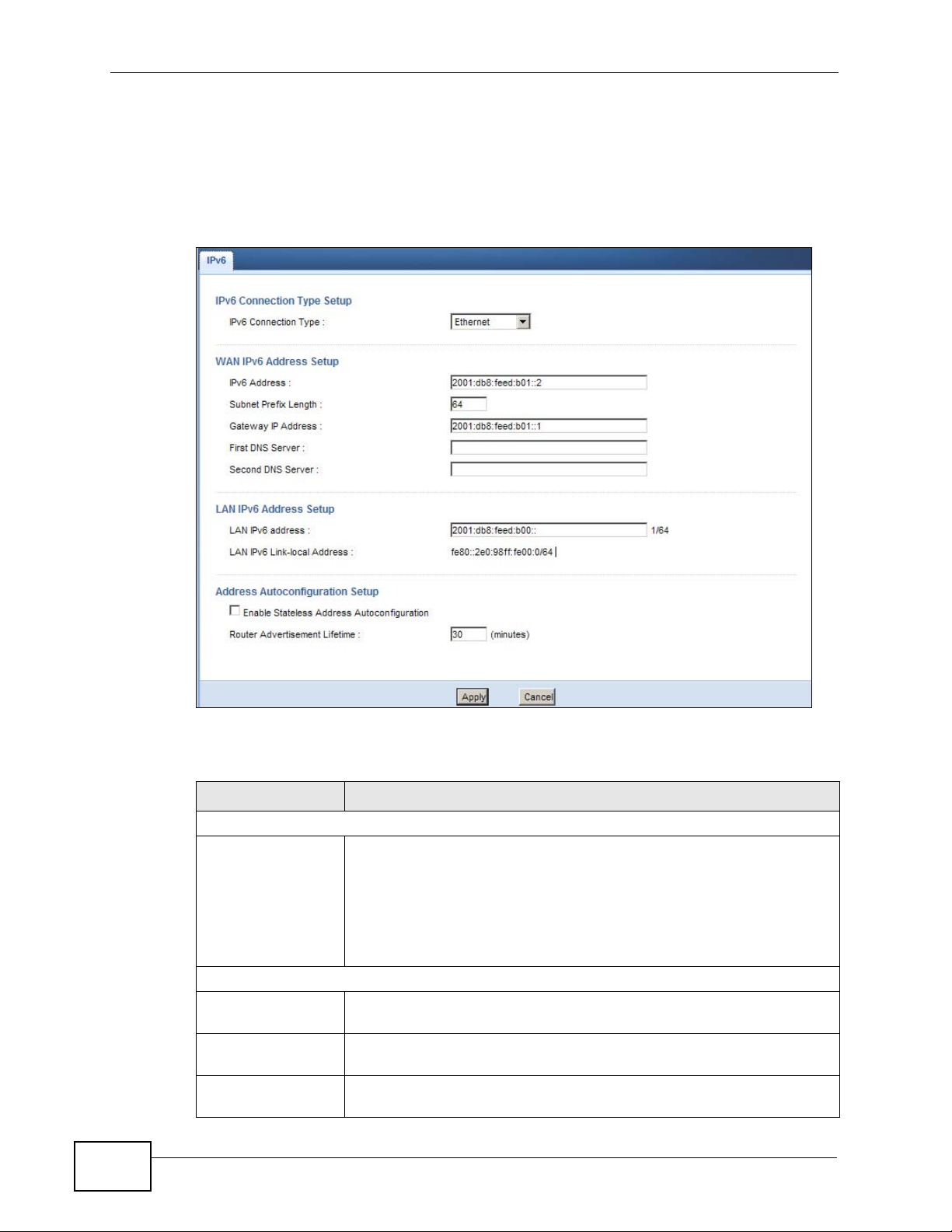
Click Network > IPv6 to open the IPv6 screen. Use this screen to configure the
IPv6 settings for your NBG4615.
Figure 86 Network > IPv6
150
The following table describes the fields in this screen.
Table 53 Network > IPv6
LABEL DESCRIPTION
IPv6 Connection Type Setup
IPv6 Connection
Type
WAN IPv6 Address Setup
IPv6 Address Enter the static IPv6 address provided by your ISP using colon (:)
Subnet Prefix
Length
Gateway IP
Address
Select the IPv6 connection type:
• Ethernet: Select this if your ISP provides you a static IPv6
address. You need to enter the IPv6 information below according
to what your ISP provided.
• Link-local only: Use this connection mode for the NBG4615 to
communicate with other IPv6 devices on the LAN side. You do not
need to configure the settings below if you choose this mode.
hexadecimal notation.
Enter the bit number of the IPv6 subnet mask provided by your ISP.
Enter the IPv6 address of the default outgoing gateway using a colon
(:) hexadecimal notation.
NBG4615 User’s Guide
Page 23
Chapter 15 IPv6
Table 53 Network > IPv6 (continued)
LABEL DESCRIPTION
First DNS Server Enter the primary DNS server's IP address in this field.
Second DNS
Server
LAN IPv6 Address Setup
LAN IPv6 address Enter a valid IPv6 address for the LAN using colon (:) hexadecimal
LAN IPv6 Link-local
Address
Address Autoconfiguration Setup
Enable Stateless
Address
Autoconfiguration
Router
Advertisement
Lifetime
Apply Click Apply to save your changes back to the NBG4615.
Cancel Click Cancel to reload the previous configuration for this screen.
Enter the secondary DNS server's IP address in this field.
notation.
This shows the IPv6 link-local address that the NBG4615 generates
automatically.
Select the checkbox to enable Stateless Address Autoconfiguration
on the NBG4615.
If this function is enabled, IP addresses are not generated by a DHCP
server. They are formed by combining network prefixes with an
interface identifier, which are derived from embedded IEEE
Identifiers.
Specify the lifetime of the router advertisement.
Router advertisement is a response to a router solicitation or a
periodical multicast advertisement from a router to advertise its
presence and other parameters, such as IPv6 prefix and DNS
information.
NBG4615 User’s Guide
151
Page 24

Chapter 15 IPv6
152
NBG4615 User’s Guide
Page 25
CHAPTER 16
WAN
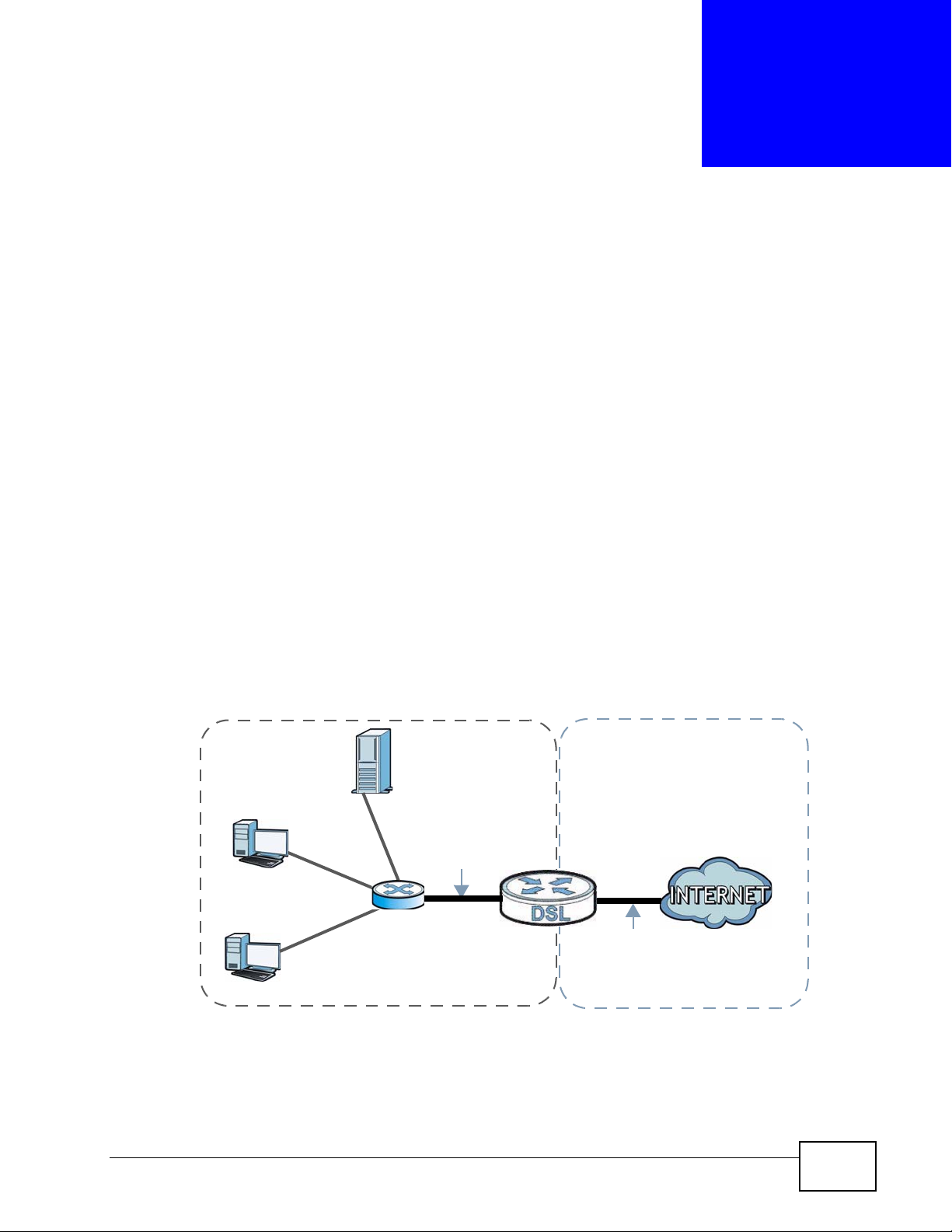
16.1 Overview
This chapter discusses the NBG4615’s WAN screens. Use these screens to
configure your NBG4615 for Internet access.
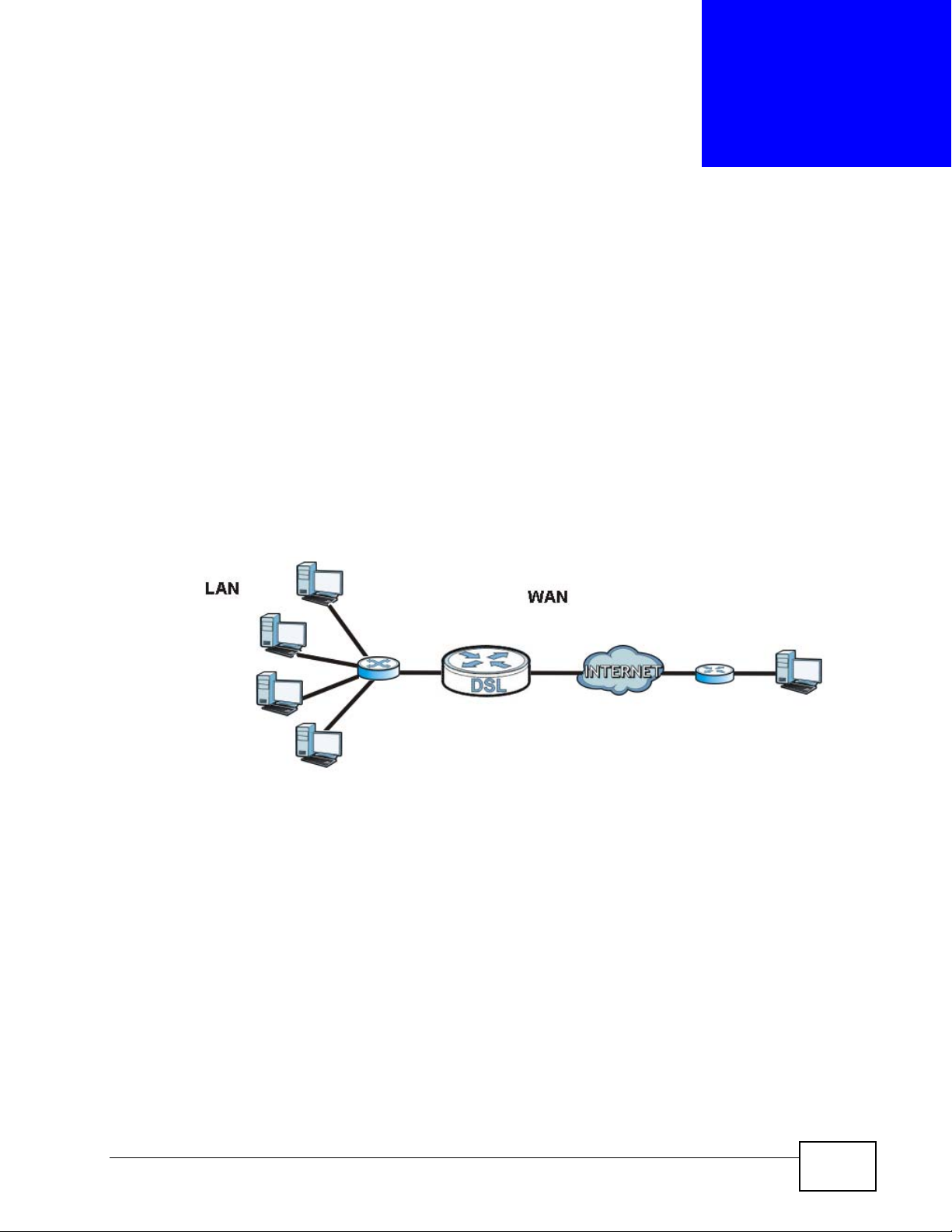
A WAN (Wide Area Network) connection is an outside connection to another
network or the Internet. It connects your private networks such as a LAN (Local
Area Network) and other networks, so that a computer in one location can
communicate with computers in other locations.
Figure 87 LAN and WAN
16.2 What You Can Do
•Use the Internet Connection screen to enter your ISP information and set
how the computer acquires its IP, DNS and WAN MAC addresses (Section 16.4
on page 156).
•Use the Advanced screen to enable multicasting, configure Windows
networking and bridge (Section 16.5 on page 166).
•Use IGMP Snooping screen to enable IGMP snooping in the LAN ports (Section
16.6 on page 167).
NBG4615 User’s Guide
153
Page 26

Chapter 16 WAN
16.3 What You Need To Know
The information in this section can help you configure the screens for your WAN
connection, as well as enable/disable some advanced features of your NBG4615.
16.3.1 Configuring Your Internet Connection
Encapsulation Method
Encapsulation is used to include data from an upper layer protocol into a lower
layer protocol. To set up a WAN connection to the Internet, you need to use the
same encapsulation method used by your ISP (Internet Service Provider). If your
ISP offers a dial-up Internet connection using PPPoE (PPP over Ethernet) or PPTP
(Point-to-Point Tunneling Protocol), they should also provide a username and
password (and service name) for user authentication.
WAN IP Address
The WAN IP address is an IP address for the NBG4615, which makes it accessible
from an outside network. It is used by the NBG4615 to communicate with other
devices in other networks. It can be static (fixed) or dynamically assigned by the
ISP each time the NBG4615 tries to access the Internet.
If your ISP assigns you a static WAN IP address, they should also assign you the
subnet mask and DNS server IP address(es) (and a gateway IP add ress if you use
the Ethernet or ENET ENCAP encapsulation method).
DNS Server Address Assignment
Use Domain Name System (DNS) to map a domain name to its corresponding IP
address and vice versa, for instance, the IP address of www.zyxel.com is
204.217.0.2. The DNS server is extremely important because without it, you must
know the IP address of a computer before you can access it.
The NBG4615 can get the DNS server addresses in the following ways.
1 The ISP tell s you the DNS server addresses, usually in the form of an information
sheet, when you sign up. If your ISP gives you DNS server addresses, manually
enter them in the DNS server fields.
154
2 If your ISP dynamically assigns the DNS server IP addresses (along with the
NBG4615’s WAN IP address), set the DNS server fields to get the DNS server
address from the ISP.
NBG4615 User’s Guide
Page 27
WAN MAC Address
The MAC address screen allows users to configure the WAN port's MAC address by
either using the factory default or cloning the MAC address from a computer on
your LAN. Choose Factory Default to select the factory assigned default MAC
Address.
Otherwise, click Clone the computer's MAC address - IP Address and enter
the IP address of the computer on the LAN whose MAC you are cloning. Once it is
successfully configured, the address will be copied to configuration file. It is
recommended that you clone the MAC address prior to hooking up the WAN Port.
16.3.2 Multicast
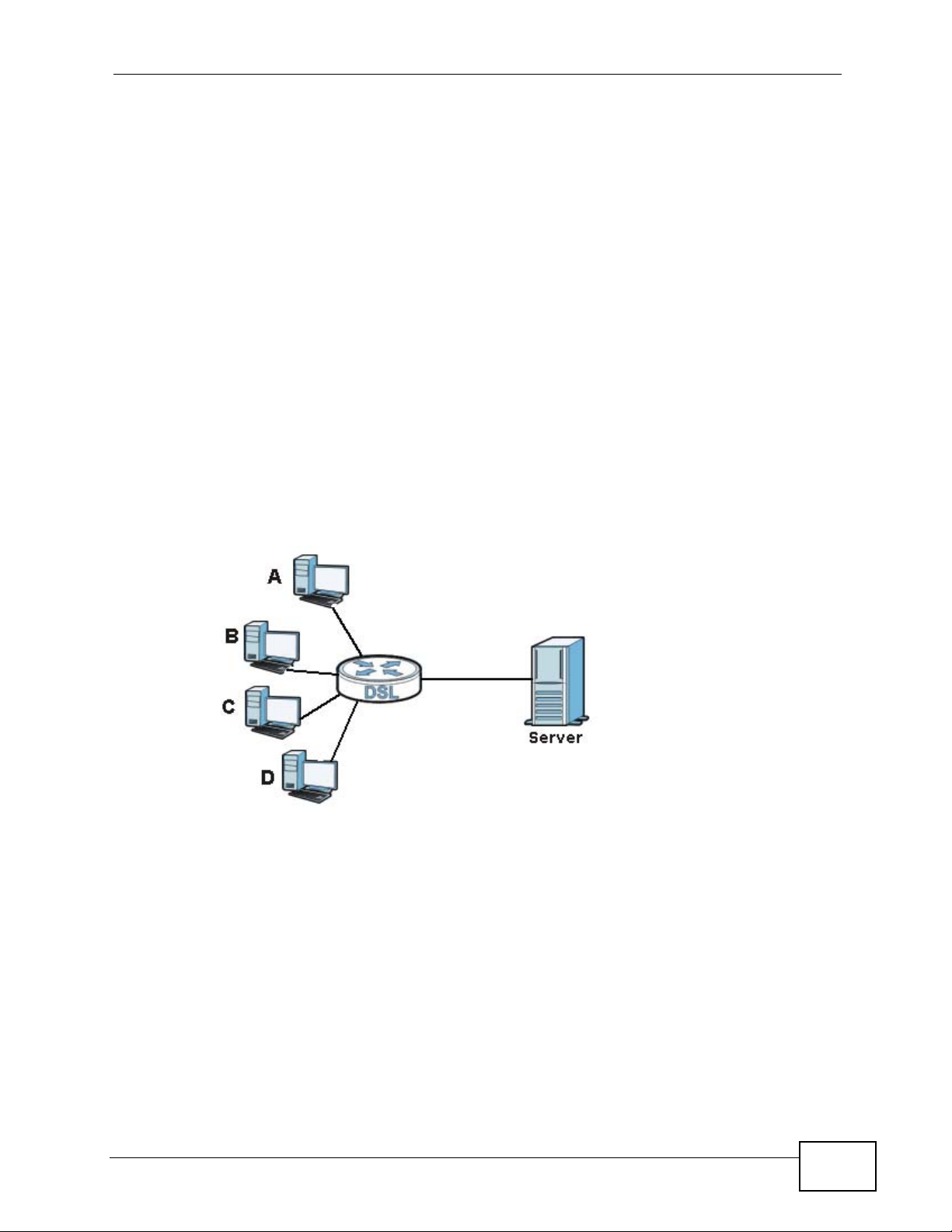
Traditionally, IP packets are transmitted in one of either two ways - Unicast (1
sender - 1 recipient) or Broadcast (1 sender - everybody on the network).
Multicast delivers IP packets to a group of hosts on the network - not everybody
and not just 1.
Chapter 16 WAN
Figure 88 Multicast Example
In the multicast example above, systems A and D comprise one multicast group.
In multicasting, the server only needs to send one data stream and this is
delivered to systems A and D.
IGMP (Internet Group Multicast Protocol) is a network-layer protocol used to
establish membership in a multicast group - it is not used to carry user data. The
NBG4615 supports both IGMP version 1 (IGMP-v1) and IGMP version 2 (IGMP-
v2).
At start up, the NBG4615 queries all directly connected networks to gather group
membership. After that, the NBG4615 periodically updates this information. IP
multicasting can be enabled/disabled on the NBG4615 LAN and/or W AN interfaces
NBG4615 User’s Guide
155
Page 28
Chapter 16 WAN
in the Web Configurator (LAN; WAN). Select None to disable IP multicasting on
these interfaces.
16.4 Internet Connection
Use this screen to change your NBG4615’s Internet access settings. Click WAN
from the Configuration menu. The screen differs according to the encapsulation
you choose.
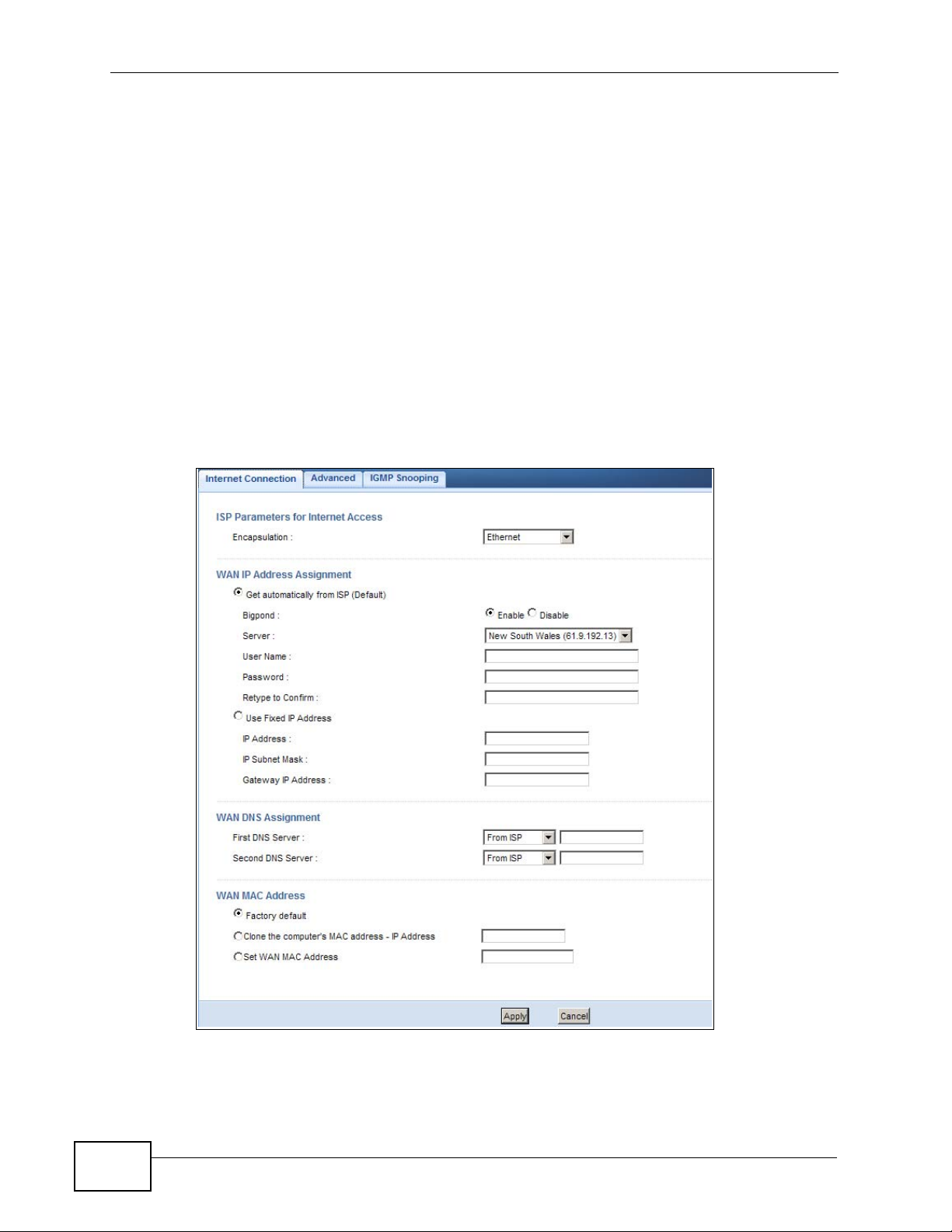
16.4.1 Ethernet Encapsulation
This screen displays when you select Ethernet encapsulation.
Figure 89 Network > WAN > Internet Connection: Ethernet Encapsulation
156
NBG4615 User’s Guide
Page 29
Chapter 16 WAN
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 54 Network > WAN > Internet Connection: Ethernet Encapsulation
LABEL DESCRIPTION
ISP Parameters for Internet Access
Encapsulation You must choose the Ethernet option when the WAN port is used as a
regular Ethernet.
WAN IP Address Assignment
Get
automatically
from ISP
(Default)
Bigpond Select Enable if you subscribe to Internet service from BigPond in
Server Type the IP address of the BigPond server.
User Name Type the user name given to you by your ISP. You can use
Password Type the password associated with the user name above. Use up to 64
Retype to
Confirm
Use Fixed IP
Address
IP Address Enter your WAN IP address in this field if you selected Use Fixed IP
IP Subnet
Mask
Gateway IP
Address
WAN DNS Assignment
First DNS Server
Second DNS
Server
Select this option If your ISP did not assign y ou a fixed IP address. This
is the default selection.
Australia. Then configure the fields below with the information
provided.
alphanumeric and -_@$./ characters, and it can be up to 31 characters
long.
ASCII characters except [, ] and ?. This field can be blank.
Type your password again for confirmation.
Select this option If the ISP assigned a fixed IP address.
Address.
Enter the IP Subnet Mask in this field.
Enter a Gateway IP Address (if your ISP gave you one) in this field.
Select From ISP if your ISP dynamically assigns DNS server
information (and the NBG4615's WAN IP address). The field to the right
displays the (read-only) DNS server IP address that the ISP assigns.
Select User-Defined if you have the IP address of a DNS server. Enter
the DNS server's IP address in the field to the right. If you chose User-
Defined, but leave the IP address set to 0.0.0.0, User-Defined
changes to None after you click Apply. If you set a second choice to
User-Defined, and enter the same IP address, the second UserDefined changes to None after you click Apply.
WAN MAC
Address
NBG4615 User’s Guide
Select None if you do not want to configure DNS servers. If you do not
configure a DNS server, you must know the IP address of a computer in
order to access it.
The MAC address section allows users to configure the WAN port's MAC
address by either using the NBG4615’s MAC address, copying the MAC
address from a computer on your LAN or manually entering a MAC
address.
157
Page 30
Chapter 16 WAN
T able 54 Network > WAN > Internet Connection: Ethernet Encapsulation (continued)
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Factory default Select Factory default to use the factory assigned default MAC
Address.
Clone the
computer’s MAC
address - IP
Address
Set WAN MAC
Address
Apply Click Apply to save your changes back to the NBG4615.
Cancel Click Cancel to begin configuring this screen afresh.
Select Clone the computer's MAC address - IP Address and enter
the IP address of the computer on the LAN whose MAC you are cloning.
Select this option and enter the MAC address you want to use.
16.4.2 PPPoE Encapsulation
The NBG4615 supports PPPoE (Point -to-Point Protocol over Ethernet). PPPoE is an
IETF standard (RFC 2516) specifying how a personal computer (PC) inter acts with
a broadband modem (DSL, cable, wireless, etc.) connection. The PPP over
Ethernet option is for a dial-up connection using PPPoE.
For the service provider, PPPoE offers an access and authentication method that
works with existing access control systems (for example Radius).
One of the benefits of PPPoE is the ability to let you access one of multiple network
services, a function known as dynamic servic e selection. This enables the service
provider to easily create and offer new IP services for individuals.
Operationally, PPPoE saves significant effort for both y ou and the ISP or carri er, as
it requires no specific configuration of the broadband modem at the customer site .
By implementing PPPoE directly on the NBG4615 (rather than individual
computers), the computers on the LAN do not need PPPoE software installed,
since the NBG4615 does that part of the task. Furthermore, with NAT, all of the
LANs’ computers will have access.
158
NBG4615 User’s Guide
Page 31

Chapter 16 WAN
This screen displays when you select PPPoE encapsulation.
Figure 90 Network > WAN > Internet Connection: PPPoE Encapsulation
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 55 Network > WAN > Internet Connection: PPPoE Encapsulation
LABEL DESCRIPTION
ISP Parameters for Internet Access
Encapsulation Select PPP over Ethernet if you connect to your Internet via dial-up.
User Name Type the user name given to you by your ISP.
Password Type the password associated with the user name above.
Retype to
Confirm
MTU Size Enter the Maximum Transmission Unit (MTU) or the largest packet size
Nailed-Up
Connection
Idle Timeout
(sec)
WAN IP Address Assignment
NBG4615 User’s Guide
Type your password again to make sure that you have entered is
correctly.
per frame that your NBG4615 can receive and process.
Select Nailed-Up Connection if you do no t want the connection to time
out.
This value specifies the time in minutes that elapses before the router
automatically disconnects from the PPPoE server.
159
Page 32

Chapter 16 WAN
Table 55 Network > WAN > Internet Connection: PPPoE Encapsulation (continued)
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Get
automatically
from ISP
Use Fixed IP
Address
WAN DNS Assignment
First DNS
Server
Second DNS
Server
My WAN IP
Address
Select this option If your ISP did not assign you a fixed IP address. This
is the default selection.
Select this option If the ISP assigned a fixed IP address.
Enter your WAN IP address in this field if you selected Use Fixed IP
Address.
Select From ISP if y our ISP dynamically assigns DNS server information
(and the NBG4615's WAN IP address). The field to the right displays the
(read-only) DNS server IP address that the ISP assigns.
Select User-Defined if you have the IP address of a DNS server. Enter
the DNS server's IP address in the field to the right. If you chose User-
Defined, but leave the IP address set to 0.0.0.0, User-Defined
changes to None after you click Apply. If you set a second choice to
User-Defined, and enter the same IP address, the second UserDefined changes to None after you click Apply.
Select None if you do not want to configure DNS servers. If you do not
configure a DNS server, you must know the IP address of a computer in
order to access it.
WAN MAC
Address
Factory default Select Factory default to use the factory assigned default MAC
Clone the
computer’s
MAC address IP Address
Set WAN MAC
Address
Apply Click Apply to save your changes back to the NBG4615.
Cancel Click Cancel to begin configuring this screen afresh.
The MAC address section allows users to configure the WAN port's MAC
address by using the NBG4615’s MAC address, copying the MAC address
from a computer on your LAN or manually entering a MAC address.
Address.
Select Clone the computer's MAC address - IP Address and enter
the IP address of the computer on the LAN whose MAC you are cloning.
Select this option and enter the MAC address you want to use.
16.4.3 PPTP Encapsulation
Point-to-P oint Tunneling Protocol (PPTP) is a network protocol that enables secure
transfer of data from a remote client to a private server, creating a Virtual Private
Network (VPN) using TCP/IP-based networks.
160
PPTP supports on-demand, multi-protocol and virtual private networking over
public networks, such as the Internet.
NBG4615 User’s Guide
Page 33

Chapter 16 WAN
This screen displays when you select PPTP encapsulation.
Figure 91 Network > WAN > Internet Connection: PPTP Encapsulation
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 56 Network > WAN > Internet Connection: PPTP Encapsulation
LABEL DESCRIPTION
ISP Parameters for Internet Access
Connection Type To configure a PPTP client, you must configure the User Name and
User Name Type the user name given to you by your ISP.
Password Type the password associated with the User Name above.
Retype to Confirm Type your password again to make sure that you have entered is
NBG4615 User’s Guide
Password fields for a PPP connection and the PPTP parameters for
a PPTP connection.
correctly.
161
Page 34

Chapter 16 WAN
Table 56 Network > WAN > Internet Connection: PPTP Encapsulation (continued)
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Nailed-up
Connection
Idle Timeout This value specifies the time in minutes that elapses before the
PPTP Configuration
Server IP Address Type the IP address of the PPTP server.
Get automatically
from ISP
Use Fixed IP
Address
WAN IP Address Assignment
Get automatically
from ISP
Use Fixed IP
Address
WAN DNS Assignment
First DNS Server
Second DNS Server
Select Nailed-Up Connection if you do not want the connection to
time out.
NBG4615 automatically disconnects from the PPTP server.
Select this option If your ISP did not assign you a fixed IP address.
This is the default selection.
Select this option If the ISP assigned a fixed IP address.
IP Address Enter your WAN IP address in this field if you selected Use Fixed IP
Address.
IP Subnet Mask Your NBG4615 will automatically calculate the subnet mask based
on the IP address that you assign. Unless you are implementing
subnetting, use the subnet mask computed by the NBG4615.
Gateway IP
Address
My WAN IP
Address
Enter a Gateway IP Address (if your ISP gave you one) in this
field.
Select this to get your WAN IP address from your ISP.
Select this option If the ISP assigned a fixed IP address.
Enter your WAN IP address in this field if you selected Use Fixed IP
Address.
Select From ISP if your ISP dynamically assigns DNS server
information (and the NBG4615's WAN IP address). The field to the
right displays the (read-only) DNS server IP address that the ISP
assigns.
162
Select User-Defined if you have the IP address of a DNS server.
Enter the DNS server's IP address in the field to the right. If you
chose User-Defined, but leave the IP address set to 0.0.0.0, User-
Defined changes to None after you click Apply. If you set a second
choice to User-Defined, and enter the same IP address, the
second User-Defined changes to None after you click Apply.
Select None if you do not want to configure DNS servers. If you do
not configure a DNS server, you must know the IP address of a
computer in order to access it.
WAN MAC Address The MAC address section allows users to configure the WAN port's
MAC address by either using the NBG4615’s MAC address, copying
the MAC address from a computer on your LAN or manually entering
a MAC address.
Factory default Select Factory default to use the factory assigned default MAC
Address.
NBG4615 User’s Guide
Page 35

Table 56 Network > WAN > Internet Connection: PPTP Encapsulation (continued)
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Clone the
computer’s MAC
address - IP
Address
Set WAN MAC
Address
Apply Click Apply to save your changes back to the NBG4615.
Cancel Click Cancel to begin configuring this screen afresh.
Select Clone the computer's MAC address - IP Address and
enter the IP address of the computer on the LAN whose MAC you
are cloning.
Select this option and enter the MAC address you want to use.
16.4.4 L2TP Encapsulation
The Layer 2 Tunneling Protocol (L2TP) works at layer 2 (the data link layer) to
tunnel network traffic between two peer devices over another network (like the
Internet).
Chapter 16 WAN
NBG4615 User’s Guide
163
Page 36

Chapter 16 WAN
This screen displays when you select L2TP encapsulation.
Figure 92 Network > WAN > Internet Connection: L2TP Encapsulation
164
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 57 Network > WAN > Internet Connection: L2TP Encapsulation
LABEL DESCRIPTION
ISP Parameters for Internet Access
Connection Type To configure a L2TP client, you must configure the User Name and
Password fields for a layer-2 connection and the L2TP parameters
for an L2TP connection.
User Name Type the user name given to you by your ISP.
Password Type the password associated with the User Name above.
Retype to Confirm Type your password again to make sure that you have entered is
correctly.
L2TP Configuration
Server IP Address Type the IP address of the L2TP server.
NBG4615 User’s Guide
Page 37

Chapter 16 WAN
Table 57 Network > WAN > Internet Connection: L2TP Encapsulation (continued)
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Get automatically
from ISP
Use Fixed IP
Address
IP Address Enter your WAN IP address in this field if you selected Use Fixed IP
IP Subnet Mask Your NBG4615 will automatically calculate the subnet mask based
Gateway IP
Address
WAN IP Address Assignment
Get automatically
from ISP
Use Fixed IP
Address
My WAN IP
Address
WAN DNS Assignment
First DNS Server
Second DNS Server
Select this option If your ISP did not assign you a fixed IP address.
This is the default selection.
Select this option If the ISP assigned a fixed IP address.
Address.
on the IP address that you assign. Unless you are implementing
subnetting, use the subnet mask computed by the NBG4615.
Enter a Gateway IP Address (if your ISP gave you one) in this
field.
Select this to get your WAN IP address from your ISP.
Select this option If the ISP assigned a fixed IP address.
Enter your WAN IP address in this field if you selected Use Fixed IP
Address.
Select From ISP if your ISP dynamically assigns DNS server
information (and the NBG4615's WAN IP address). The field to the
right displays the (read-only) DNS server IP address that the ISP
assigns.
Select User-Defined if you have the IP address of a DNS server.
Enter the DNS server's IP address in the field to the right. If you
chose User-Defined, but leave the IP address set to 0.0.0.0, User-
Defined changes to None after you click Apply. If you set a second
choice to User-Defined, and enter the same IP address, the
second User-Defined changes to None after you click Apply.
Select None if you do not want to configure DNS servers. If you do
not configure a DNS server, you must know the IP address of a
computer in order to access it.
WAN MAC Address The MAC address section allows users to configure the WAN port's
MAC address by either using the NBG4615’s MAC address, copying
the MAC address from a computer on your LAN or manually entering
a MAC address.
Factory default Select Factory default to use the factory assigned default MAC
Address.
Clone the
computer’s MAC
address - IP
Address
Set WAN MAC
Address
Apply Click Apply to save your changes back to the NBG4615.
Reset Click Reset to begin configuring this screen afresh.
Select Clone the computer's MAC address - IP Address and
enter the IP address of the computer on the LAN whose MAC you
are cloning.
Select this option and enter the MAC address you want to use.
NBG4615 User’s Guide
165
Page 38

Chapter 16 WAN
16.5 Advanced WAN Screen
Use this screen to enable Multicast and enable Auto-bridge.
Note: The categories shown in this screen are independent of each other.
To change your NBG4615’s advanced WAN settings, click Network > WAN >
Advanced. The screen appears as shown.
Figure 93 Network > WAN > Advanced
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 58 Network > WAN > Advanced
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Multicast Setup
Multicast Select IGMPv1/v2 to enable multicasting. This applies to traffic
routed from the WAN to the LAN.
Select None to disable this feature. This may cause incoming tr affic
to be dropped or sent to all connected network devices.
Auto-Subnet Configuration
None Select this option to have the NBG4615 do nothing when it gets a
WAN IP address in the range of 192.168.x.y (where x and y are
from zero to nine) or in the same subnet as the LAN IP address.
Enable Auto-bridge
mode
Enable Auto-IPChange mode
Select this option to have the NBG4615 switch to bridge mode
automatically when the NBG4615 gets a WAN IP address in the
range of 192.168.x.y (where x and y are from zero to nine) no
matter what the LAN IP address is.
Select this option to have the NBG4615 change its LAN IP address
to 10.0.0.1 or 192.168.1.1 accordingly when the NBG4615 gets a
dynamic WAN IP address in the same subnet as the LAN IP address
192.168.1.1 or 10.0.0.1.
The NAT, DHCP server and firewall functions on the NBG4615 are
still available in this mode.
166
NBG4615 User’s Guide
Page 39

Table 58 Network > WAN > Advanced (continued)
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Apply Click Apply to save your changes back to the NBG4615.
Cancel Click Cancel to begin configuring this screen afresh.
16.6 IGMP Snooping Screen
Use this screen to enable IGMP snooping if you have LAN users that subscribe to
multicast services.
IGMP (Internet Group Multicast Protocol) is a network-layer protocol used to
establish membership in a multicast group - it is not used to carry user data.
Click Network > WAN > IGMP Snooping. The screen appears as shown.
Figure 94 Network > WAN > IGMP Snooping
Chapter 16 WAN
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 59 Network > WAN > IGMP Snooping
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Enable IGMP
Snooping
Apply Click Apply to save your changes back to the NBG4615.
Cancel Click Cancel to begin configuring this screen afresh.
NBG4615 User’s Guide
Select this option to have the NBG4615 use IGMP snooping.
Check the LAN port/s to which IGMP snooping applies.
167
Page 40

Chapter 16 WAN
168
NBG4615 User’s Guide
Page 41
CHAPTER 17
LAN
17.1 Overview
This chapter describes how to configure LAN settings.
A Local Area Network (LAN) is a shared communication system to which many
computers are attached. A LAN is a computer network limited to the immediate
area, usually the same building or floor of a building. The LAN screens can help
you configure a LAN DHCP server, manage IP addresses, and partition your
physical network into logical networks.
Figure 95 LAN Example
The LAN screens can help you manage IP addresses.
17.2 What You Can Do
•Use the IP screen to change the IP address for your (Section 17.4 on page
171).
•Use the IP Alias screen to have the NBG4615 apply IP alias to create LAN
subnets (Section 17.5 on page 172).
NBG4615 User’s Guide
169
Page 42

Chapter 17 LAN
17.3 What You Need To Know
The actual physical connection determines whether the NBG4615 ports are LAN or
WAN ports. There are two separate IP networks, one inside the LAN network and
the other outside the WAN network as shown next.
Figure 96 LAN and WAN IP Addresses
The LAN parameters of the NBG4615 are preset in the factory with the following
values:
• IP address of 192.168.1.1 with subnet mask of 255.255.255.0 (24 bits)
• DHCP server enabled with 32 client IP addresses starting from 192.168.1.33.
These parameters should work for the majority of installations. If your ISP gives
you explicit DNS server address(es), read the embedded Web Configurator help
regarding what fields need to be configured.
17.3.1 IP Pool Setup
The NBG4615 is pre-configured with a pool of 32 IP addresses starting from
192.168.1.33 to 192.168.1.64. This configuration leaves 31 IP addresses
(excluding the NBG4615 itself) in the lower range (192.168.1.2 to 192.168.1.32)
for other server computers, for instance, servers for mail, FTP, TFTP, web, etc.,
that you may have.
17.3.2 LAN TCP/IP
170
The NBG4615 has built-in DHCP server capability that assigns IP addresses and
DNS servers to systems that support DHCP client capability.
NBG4615 User’s Guide
Page 43

17.3.3 IP Alias
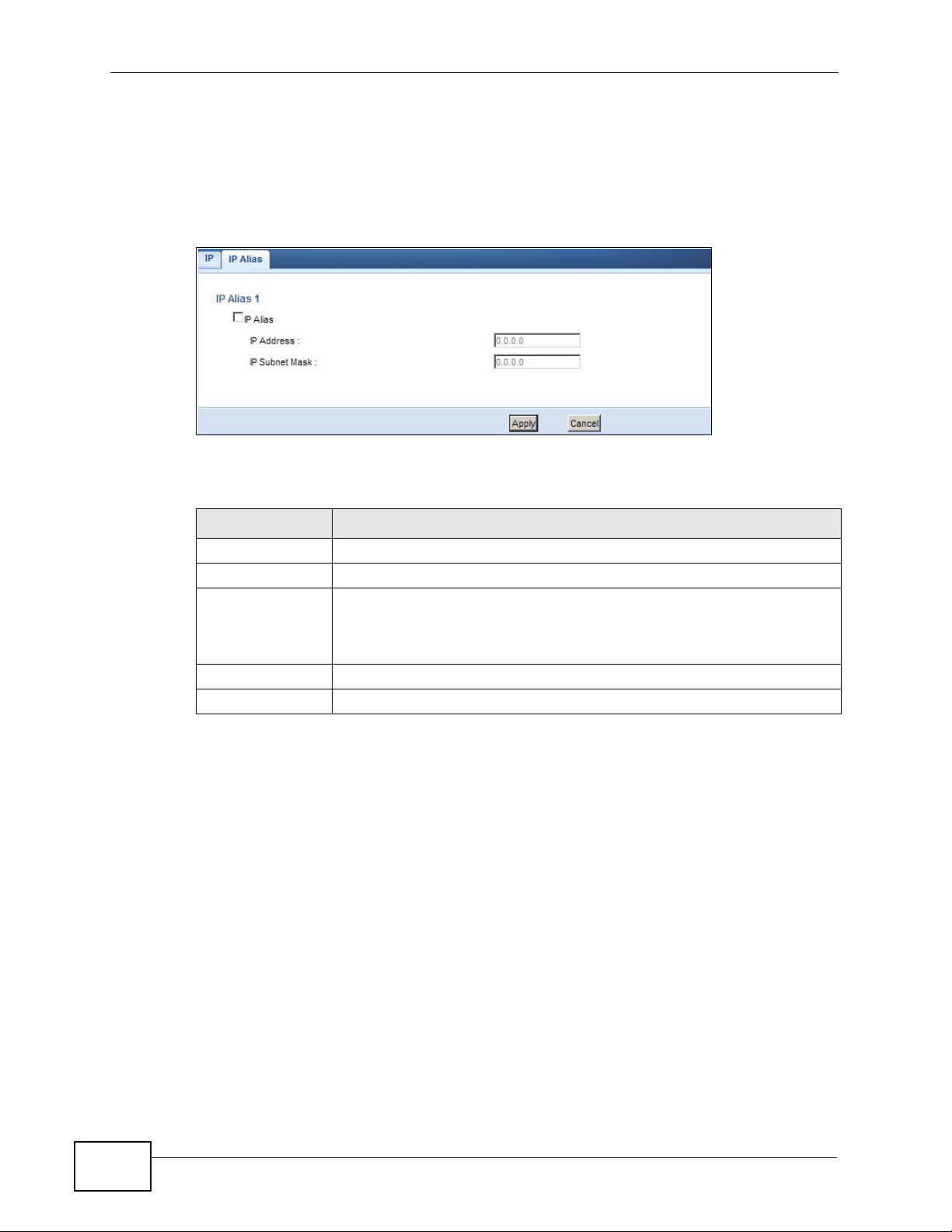
17.4 LAN IP Screen
Use this screen to change the IP address for your NBG4615. Click Network >
LAN > IP.
Figure 97 Network > LAN > IP
Chapter 17 LAN
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 60 Network > LAN > IP
LABEL DESCRIPTION
IP Address Type the IP address of your NBG4615 in dotted decimal notation.
IP Subnet Mask The subnet mask specifies the network number portion of an IP
address. Your NBG4615 will automatically calculate the subnet mask
based on the IP address that you assign. Unless you are implementing
subnetting, use the subnet mask computed by the NBG4615.
Apply Click Apply to save your changes back to the NBG4615.
Cancel Click Cancel to begin configuring this screen afresh.
NBG4615 User’s Guide
171
Page 44
Chapter 17 LAN
17.5 IP Alias Screen
Use this screen to have the NBG4615 apply IP alias to create LAN subnets. Click
LAN > IP Alias.
Figure 98 Network > LAN > IP Alias
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 61 Network > LAN > IP Alias
LABEL DESCRIPTION
IP Alias Check this to enable IP alias.
IP Address Type the IP alias address of your NBG4615 in dotted decimal notation.
IP Subnet Mask The subnet mask specifies the network number portion of an IP
address. Your NBG4615 will automatically calculate the subnet mask
based on the IP address that you assign. Unless you are implementing
subnetting, use the subnet mask computed by the NBG4615.
Apply Click Apply to save your changes back to the NBG4615.
Cancel Click Cancel to begin configuring this screen afresh.
172
NBG4615 User’s Guide
Page 45

CHAPTER 18
DHCP Server
18.1 Overview
DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol, RFC 2131 and RFC 2132) allows
individual clients to obtain TCP/IP configuration at start-up from a server. You can
configure the NBG4615’s LAN as a DHCP server or disable it. When configured as a
server, the NBG4615 provides the TCP/IP configuration for the clients. If DHCP
service is disabled, you must have another DHCP server on your LAN, or else the
computer must be manually configured.
18.1.1 What You Can Do
•Use the General screen to enable the DHCP server (Section 18.2 on page 174).
•Use the Advanced screen to assign IP addresses on the LAN to specific
individual computers based on their MAC Addresses (Section 18.3 on page 175).
18.1.2 What You Need To Know
The following terms and concepts may help as you read through this chapter.
MAC Addresses
Every Ethernet device has a unique MAC (Media Access Control) address. The MAC
address is assigned at the factory and consists of six pairs of hexadecimal
characters, for example, 00:A0:C5:00:00:02. Find out the MAC addresses of your
network devices if you intend to add them to the DHCP Client List screen.
NBG4615 User’s Guide
173
Page 46

Chapter 18 DHCP Server
18.2 General
Use this screen to enable the DHCP server. Click Network > DHCP Server. The
following screen displays.
Figure 99 Network > DHCP Server > General
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 62 Network > DHCP Server > General
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Enable DHCP
Server
IP Pool Starting
Address
Pool Size This field specifies the size, or count of the IP address pool for LAN.
Apply Click Apply to save your changes back to the NBG4615.
Cancel Click Cancel to begin configuring this screen afresh.
Select the checkbox to enable DHCP for LAN.
DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol, RFC 2131 and RFC
2132) allows individual clients (computers) to obtain TCP/IP
configuration at startup from a server. Leave the Enable DHCP
Server check box selected unless your ISP instructs you to do
otherwise. Clear it to disable the NBG4615 acting as a DHCP server .
When configured as a server, the NBG4615 provides TCP/IP
configuration for the clients. If not, DHCP service is disabled and
you must have another DHCP server on your LAN, or else the
computers must be manually configured. When set as a server, fill in
the following four fields.
This field specifies the first of the contiguous addresses in the IP
address pool for LAN.
174
NBG4615 User’s Guide
Page 47

18.3 Advanced
This screen allows you to assign IP addresses on the LAN to specific individual
computers based on their MAC addresses. You can also use this screen to
configure the DNS server information that the NBG4615 sends to the DHCP
clients.
To change your NBG4615’s static DHCP settings, click Network > DHCP Server
> Advanced. The following screen displays.
Figure 100 Network > DHCP Server > Advanced
Chapter 18 DHCP Server
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 63 Network > DHCP Server > Advanced
LABEL DESCRIPTION
LAN Static DHCP Table
# This is the index number of the static IP table entry (row).
MAC Address Type the MAC address (with colons) of a computer on your LAN.
IP Address Type the LAN IP address of a computer on your LAN.
DNS Server
DNS Servers
Assigned by
DHCP Server
NBG4615 User’s Guide
The NBG4615 passes a DNS (Domain Name System) server IP
address (in the order you specify here) to the DHCP clients. The
NBG4615 only passes this information to the LAN DHCP clients when
you select the Enable DHCP Server check box. When you clear the
Enable DHCP Server check box, DHCP service is disabled and you
must have another DHCP sever on your LAN, or else the computers
must have their DNS server addresses manually configured.
175
Page 48
Chapter 18 DHCP Server
Table 63 Network > DHCP Server > Advanced (continued)
LABEL DESCRIPTION
First DNS Server
Second DNS
Server
Select From ISP if your ISP dynamically assigns DNS server
information (and the NBG4615's WAN IP address). The field to the
right displays the (read-only) DNS server IP address that the ISP
assigns.
Select User-Defined if you have the IP address of a DNS server.
Enter the DNS server's IP address in the field to the right. If you chose
User-Defined, but leave the IP address set to 0.0.0.0, User-Defined
changes to None after you click Apply. If you set a second choice to
User-Defined, and enter the same IP address, the second UserDefined changes to None after you click Apply.
Select DNS Relay to have the NBG4615 act as a DNS proxy. The
NBG4615's LAN IP address displays in the field to the right (readonly). The NBG4615 tells the DHCP clients on the LAN that the
NBG4615 itself is the DNS server. When a computer on the LAN sends
a DNS query to the NBG4615, the NBG4615 forwards the query to the
NBG4615's system DNS server (configured in the WAN > Internet
Connection screen) and relays the response back to the computer.
You can only select DNS Relay for one of the three servers; if you
select DNS Relay for a second or third DNS server, that choice
changes to None after you click Apply.
Select None if you do not want to configure DNS servers. If you do
not configure a DNS server, you must know the IP address of a
computer in order to access it.
Apply Click Apply to save your changes back to the NBG4615.
Cancel Click Cancel to begin configuring this screen afresh.
176
NBG4615 User’s Guide
Page 49
CHAPTER 19
A: 192.168.1.33
B: 192.168.1.34
C: 192.168.1.35
IP address
192.168.1.1
WANLAN
assigned by ISP
FTP, Telnet, SNMP
Port 80
Ports 21 to 25
NAT
19.1 Overview
NAT (Network Address Translation - NAT, RFC 1631) is the translation of the IP
address of a host in a packet. For example, the source address of an outgoing
packet, used within one network is changed to a different IP address known within
another network.
The figure below is a simple illustration of a NAT network. You want to assi gn ports
21-25 to one FTP, Telnet and SMTP server (A in the example), port 80 to another
(B in the example) and assign a default server IP address of 192.168.1.35 to a
third (C in the example).
You assign the LAN IP addresses to the devices (A to D) connected to your
NBG4615. The ISP assigns the WAN IP address. The NAT network appears as a
single host on the Internet. All traf fic coming from A to D going out to the Internet
use the IP address of the NBG4615, which is 192.168.1.1.
Figure 101 NAT Example
NBG4615 User’s Guide
This chapter discusses how to configure NAT on the NBG4615.
177
Page 50

Chapter 19 NAT
Note: You must create a firewall rule in addition to setting up NAT, to allow traffic from
the WAN to be forwarded through the NBG4615.
19.1.1 What You Can Do
•Use the General screen to enable NA T and set a default server (Section 19.2 on
page 180).
•Use the Application screen to change your NBG4615’s port forwarding settings
(Section 19.3 on page 181).
•Use the Advanced screen to change your NBG4615’s trigger port settings
(Section 19.5.3 on page 185).
19.1.2 What You Need To Know
The following terms and concepts may help as you read through this chapter.
Inside/Outside
This denotes where a host is located relative to the NBG4615, for example, the
computers of your subscribers are the inside hosts, while the web servers on the
Internet are the outside hosts.
Global/Local
This denotes the IP address of a host in a packet as the packet tr a v erses a router,
for example, the local address refers to the IP address of a host when the packet
is in the local network, while the global address refers to the IP address of the
host when the same packet is traveling in the WAN side.
Note: Inside/outside refers to the location of a host, while global/local refers to the IP
address of a host used in a packet.
An inside local address (ILA) is the IP address of an inside host in a packet when
the packet is still in the local network, while an inside global address (IGA) is the
IP address of the same inside host when the packet is on the WAN side. The
following table summarizes this information.
Table 64 NAT Definitions
ITEM DESCRIPTION
178
Inside This refers to the host on the LAN.
Outside This refers to the host on the WAN.
NBG4615 User’s Guide
Page 51

Chapter 19 NAT
Table 64 NAT Definitions (continued)
ITEM DESCRIPTION
Local This refers to the packet address (source
or destination) as the packet travels on
the LAN.
Global This refers to the packet address (source
or destination) as the packet travels on
the WAN.
Note: NAT never changes the IP address (either local or global) of an outside host.
What NAT Does
In the simplest form, NA T changes the source IP address in a pack et received from
a subscriber (the inside local address) to another (the inside global address)
before forwarding the packet to the WAN side. When the response comes back,
NAT translates the destination address (the inside global address) back to the
inside local address before forwarding it to the original inside host. Note that the
IP address (either local or global) of an outside host is never changed.
The global IP addresses for the inside hosts can be either static or dynamically
assigned by the ISP. In addition, you can designate servers, for example, a web
server and a telnet server, on your local network and make them accessible to the
outside world. If you do not define any servers , NAT offers the additional benefit
of firewall protection. With no servers defined, your NBG4615 filters out all
incoming inquiries, thus preventing intruders from probing your network. For
more information on IP address translation, refer to RFC 1631, The IP Network
Address Translator (NAT).
How NAT Works
Each packet has two addresses – a source address and a destination address. For
outgoing packets, the ILA (Inside Local Address) i s the source address on the LAN,
and the IGA (Inside Global Address) is the source address on the WAN. For
incoming packets, the ILA is the destination address on the LAN, and the IGA is
the destination address on the WAN. NAT maps private (local) IP addresses to
globally unique ones required for communication with hosts on other networks. It
replaces the original IP source address in each packet and then forwards it to the
Internet. The NBG4615 keeps track of the orig inal addresses and port numbers so
NBG4615 User’s Guide
179
Page 52

Chapter 19 NAT
incoming reply packets can have their original values restored. The following
figure illustrates this.
Figure 102 How NAT Works
19.2 General
Use this screen to enable NAT and set a default server. Click Network > NAT to
open the General screen.
Figure 103 Network > NAT > General
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 65 Network > NAT > General
LABEL DESCRIPTION
NAT Setup
Enable Network
Address
Translation
Network Address Translation (NAT) allows the translation of an Internet
protocol address used within one network (for example a private IP
address used in a local network) to a different IP address known within
another network (for example a public IP address used on the Internet).
180
Select the check box to enable NAT.
NBG4615 User’s Guide
Page 53

Table 65 Network > NAT > General (continued)
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Default Server Setup
Server IP
Address
Apply Click Apply to save your changes back to the NBG4615.
Cancel Click Cancel to begin configuring this screen afresh.
In addition to the servers for specified services, NAT supports a default
server. A default server receives packets from ports that are not
specified in the Application screen.
If you do not assign a Default Server IP address, the NBG4615
discards all packets received for ports that are not specified in the
Application screen or remote management.
19.3 Application
Port forwarding allows you to define the local servers to which the incoming
services will be forwarded. To change your NBG4615’s port forwarding settings,
click Network > NAT > Application. The screen appears as shown.
Chapter 19 NAT
Note: If you do not assign a Default Server IP address in t he NAT > General screen,
the NBG4615 discards all packets received for ports that are not specified in
this screen or remote management.
Refe r to Appendix F on page 321 for port numbers commonly us ed for p a rt ic ular
services.
Figure 104 Network > NAT > Application
NBG4615 User’s Guide
181
Page 54

Chapter 19 NAT
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 66 Network > NAT > Application
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Add Application Rule
Active Select the check box to enable this rule and the requested service can
Service Name Type a name (of up to 31 printable characters) to identify this rule in
Port Enter the start and end port(s) to be forwarded.
Server IP
Address
Application Rules Summary
# This is the number of an individual port forwarding server entry.
Active This icon is turned on when the rule is enabled.
Name This field displays a name to identify this rule.
Port This field displays the port number(s).
Server IP
Address
Modify Click the Edit icon to display and modify an existing rule setting in the
be forwarded to the host with a specified internal IP address.
Clear the checkbox to disallow forwarding of these ports to an inside
server without having to delete the entry.
the first field next to Service Name. Otherwise, select a predefined
service in the second field next to Service Name. The predefined
service name and port number(s) will display in the Service Name and
Port fields.
Type the inside IP address of the server that receives packets from the
port(s) specified in the Port field.
This field displays the inside IP address of the server.
fields under Add Application Rule.
Click the Remove icon to delete a rule.
Apply Click Apply to save your changes back to the NBG4615.
Cancel Click Cancel to begin configuring this screen afresh.
182
NBG4615 User’s Guide
Page 55

19.4 Advanced
To change your NBG4615’s trigger port settings, click Network > NAT >
Advanced. The screen appears as shown.
Note: Only one LAN computer can use a trigger port (range) at a time.
Figure 105 Network > NAT > Advanced
Chapter 19 NAT
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 67 Network > NAT > Advanced
LABEL DESCRIPTION
# This is the rule index number (read-only).
Name Type a unique name (up to 15 char acters) for identification purposes. All
characters are permitted - including spaces.
Incoming Incoming is a port (or a range of ports) that a server on the WAN uses
when it sends out a particular service. The NBG4615 forwards the traffic
with this port (or range of ports) to the client computer on the LAN that
requested the service.
Port Type a port number or the starting port number in a range of port
numbers.
End Port Type a port number or the ending port number in a range of port
numbers.
Trigger The trigger port is a port (or a range of ports) that causes (or triggers)
the NBG4615 to record the IP address of the LAN computer that sent
the traffic to a server on the WAN.
Port Type a port number or the starting port number in a range of port
numbers.
NBG4615 User’s Guide
183
Page 56
Chapter 19 NAT
Table 67 Network > NAT > Advanced (continued)
LABEL DESCRIPTION
End Port Type a port number or the ending port number in a range of port
numbers.
Apply Click Apply to save your changes back to the NBG4615.
Cancel Click Cancel to begin configuring this screen afresh.
19.5 Technical Reference
The following section contains additional technical information about the NBG4615
features described in this chapter.
19.5.1 NATPort Forwarding: Services and Port Numbers
A port forwarding set is a list of inside (behind NAT on the LAN) servers, for
example, web or FTP, that you can make accessible to the outside world even
though NAT mak es your whole inside network appear as a single machine to the
outside world.
Use the Application screen to forward incoming service requests to the server(s)
on your local network. You may enter a single port number or a range of port
numbers to be forwarded, and the local IP address of the desired server. The port
number identifies a service; for example, web service is on port 80 and FTP on
port 21. In some cases, such as for unknown services or where one server can
support more than one service (for example both FTP and web service), it might
be better to specify a range of port numbers.
In addition to the servers for specified services, NAT supports a default server. A
service request that does not have a server explicitly designated for it is forwarded
to the default server. If the default is not defined, the service request is simply
discarded.
Note: Many residential broadband ISP accounts do not allow you to run any server
processes (such as a Web or FTP server) from your location. Your ISP may
periodically check for servers and may suspend your account if it discovers any
active services at your location. If you are unsure, refer to your ISP.
19.5.2 NAT Port Forwarding Example
Let's say you want to assign ports 21-25 to one FTP , Telnet and SMTP server (A in
the example), port 80 to another (B in the example) and assign a default server IP
address of 192.168.1.35 to a third (C in the example). You assign the LAN IP
184
NBG4615 User’s Guide
Page 57
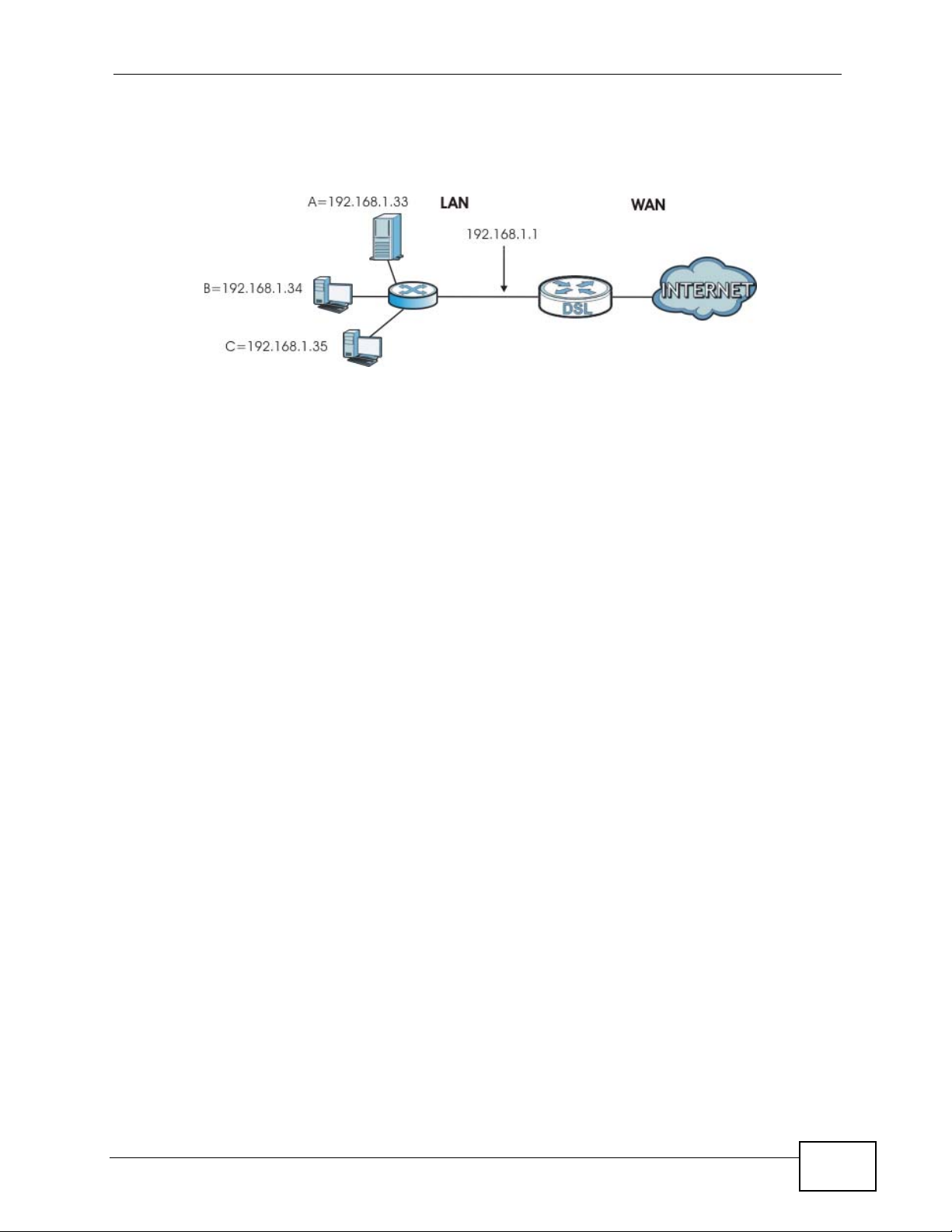
addresses and the ISP assigns the WAN IP address. The NAT network appears as a
single host on the Internet.
Figure 106 Multiple Servers Behind NAT Example
19.5.3 Trigger Port Forwarding
Some services use a dedicated range of ports on the client side and a dedicated
range of ports on the server side. With regular port forwarding you set a
forwarding port in NAT to forward a service (coming in from the server on the
WAN) to the IP address of a computer on the client side (LAN). The problem is
that port forwarding only forwards a service to a single LAN IP address. In order to
use the same service on a different LAN computer, you have to manually replace
the LAN computer's IP address in the forwarding port with another LAN
computer's IP address.
Chapter 19 NAT
Trigger port forwarding solves this problem by all owi ng c o m p ut ers o n the LAN to
dynamically take turns using the service. The NBG4615 records the IP address of
a LAN computer that sends traffic to the WAN to request a service with a specific
port number and protocol (a "trigger" port). When the NBG4615's WAN port
receives a response with a specific port number and protocol ("incoming" port),
the NBG4615 forwards the traffic to the LAN IP address of the computer that sent
the request. After that computer’s connection for that service closes, another
computer on the LAN can use the service in the same manner. This way you do not
need to configure a new IP address each time you want a different LAN computer
to use the application.
NBG4615 User’s Guide
185
Page 58

Chapter 19 NAT
19.5.4 Trigger Port Forwarding Example
The following is an example of trigger port forwarding.
Figure 107 Trigger Port Forwarding Process: Example
1 Jane requests a file from the Real Audio server (port 7070).
2 P ort 7070 is a “trigger” port and causes the NBG4615 to record Jane’ s computer IP
address. The NBG4615 associates Jane's computer IP address with the "incoming"
port range of 6970-7170.
3 The Real Audio server responds using a port number ranging between 6970-7170.
4 The NBG4615 forwards the traffic to Jane’s computer IP address.
5 Only Jane can connect to the Real Audio server until the connection is closed or
times out. The NBG4615 times out in three minutes with UDP (User Datagram
Protocol), or two hours with TCP/IP (Transfer Control Protocol/Internet Protocol).
19.5.5 Two Points To Remember About Trigger Ports
1 Trigger events only happen on data that is going coming from inside the NBG4615
and going to the outside.
2 If an application needs a continuous data stream, that port (r ange) will be ti ed up
so that another computer on the LAN can’t trigger it.
186
NBG4615 User’s Guide
Page 59

CHAPTER 20
DDNS
20.1 Overview
DDNS services let you use a domain name with a dynamic IP address.
20.1.1 What You Need To Know
The following terms and concepts may help as you read through this chapter.
What is DDNS?
DDNS, or Dynamic DNS, allows you to update your current dynamic IP address
with one or many dynamic DNS services so that anyone can contact you (in
NetMeeting, CU-SeeMe, etc.). You can also access your FTP server or Web site on
your own computer using a domain name (for instance myhost.dhs.org, where
myhost is a name of your choice) that will never change instead of using an IP
address that changes each time you reconnect. Your friends or relatives will
always be able to call you even if they don't know your IP address.
DynDNS Wildcard
Enabling the wildcard feature for your host causes *.yourhost.dyndns.org to be
aliased to the same IP address as yourhost.dyndns.org. This feature is useful if
you want to be able to use, for example, www.yourhost.dyndns. org and still reach
your hostname.
Note: If you have a private WAN IP address, then yo u cannot use Dynamic DNS. You
must have a public WAN IP address.
NBG4615 User’s Guide
187
Page 60

Chapter 20 DDNS
20.2 General
T o change your NBG4615’ s DDNS, click Network > DDNS. The screen appears as
shown.
Figure 108 Dynamic DNS
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 68 Dynamic DNS
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Dynamic DNS Setup
Enable Dynamic
DNS
Service Provider Select the name of your Dynamic DNS service provider.
Host Name Enter a host names in the field provided. You can specify up to two
User Name Enter your user name.
Password Enter the password assigned to you.
Apply Click Apply to save your changes back to the NBG4615.
Cancel Click Cancel to begin configuring this screen afresh.
Select this check box to use dynamic DNS.
host names in the field separated by a comma (",").
188
NBG4615 User’s Guide
Page 61

CHAPTER 21
Static Route
21.1 Overview
This chapter shows you how to configure static routes for your NBG4615.
Each remote node specifies only the network to which the gateway is directly
connected, and the NBG4615 has no knowledge of the networks beyond. For
instance, the NBG4615 knows about network N2 in the following figure through
remote node Router 1. However, the NBG4615 is unable to route a packet to
network N3 because it doesn't know that there is a route through the same
remote node Router 1 (via gateway Router 2). The static routes are for you to tell
the NBG4615 about the networks beyond the remote nodes.
Figure 109 Example of Static Routing Topology
NBG4615 User’s Guide
189
Page 62

Chapter 21 Static Route
21.2 IP Static Route Screen
Click Network > Static Route to open the IP Static Route screen.
Figure 110 Network > Static Route
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 69 Network > Static Route
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Static Routing Settings
Route Name Enter a the name that describes or identifies this route.
Destination IP
Address
IP Subnet
Netmask
Gateway IP
Address
Metric Assign a number to identify the route.
Interface Select the interface through which the traffic is routed.
Add Rule Click this to add the IP static route.
Application Rules Summary
No. This is the number of an individual static route.
Active The rules are always on and this is indicated by the icon.
Name This is the name that describes or identifies this route.
Destination This parameter specifies the IP network address of the final destination.
Gateway This is the IP address of the gateway. The gateway is a router or switch
Metric This is the number assigned to the route.
Enter the IP network address of the final destination.
This is the subnet to which the route’s final destination belongs.
Enter the IP address of the gateway.
Routing is always based on network number.
on the same network segment as the device's LAN or WAN port. The
gateway helps forward packets to their destinations.
190
NBG4615 User’s Guide
Page 63

Chapter 21 Static Route
Table 69 Network > Static Route (continued)
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Delete Click the Delete icon to remove a static route from the NBG4615. A
window displays asking you to confirm that you want to delete the route.
Cancel Click Cancel to begin configuring this screen afresh.
NBG4615 User’s Guide
191
Page 64

Chapter 21 Static Route
192
NBG4615 User’s Guide
Page 65

CHAPTER 22
RIP
22.1 Overview
Routing Information Protocol (RIP) is an interior or intra-domain routing protocol
that uses distance-vector routing algorithms. RIP is used on the Internet and is
common in the NetWare environment as a method for exchanging routing
information between routers.
22.2 RIP Screen
Use this screen to enable RIPv1 or RIPv2, which are LAN broadcast protocols. Click
Network > RIP. The screen appears as shown.
Figure 111 Network > RIP
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 70 Network > RIP
LABEL DESCRIPTION
RIP Select the RIPv1 or RIPv2 you want the NBG4615 to use.
Otherwise select None.
Apply Click Apply to save your changes back to the NBG4615.
Cancel Click Cancel to begin configuring this screen afresh.
NBG4615 User’s Guide
193
Page 66

Chapter 22 RIP
194
NBG4615 User’s Guide
Page 67

CHAPTER 23
WAN
LAN
3
4
1
2
A
Firewall
23.1 Overview
Use these screens to enable and configure the firewall that protects your NBG4615
and your LAN from unwanted or malicious traffic.
Enable the firewall to protect your LAN computers from at tacks by hack ers on t he
Internet and control access between the LAN and WAN. By default the firewall:
• allows traffic that originates from your LAN computers to go to all of the
networks.
• blocks traffic that originates on the other networks from going to the LAN.
The following figure illustrates the default firewall action. User A can initiate an IM
(Instant Messaging) sess ion from the LAN to the WAN (1). Return traffic for this
session is also allowed (2). However other traffic initiated from the W AN is blocked
(3 and 4).
Figure 112 Default Firewall Action
23.1.1 What You Can Do
•Use the General screen to enable or disable the NBG4615’s firewall (Section
23.2 on page 198).
NBG4615 User’s Guide
195
Page 68

Chapter 23 Firewall
•Use the Services screen enable service blocking, enter/delete/modify the
services you want to block and the date/time you want to block them (Section
23.3 on page 198).
23.1.2 What You Need To Know
The following terms and concepts may help as you read through this chapter.
What is a Firewall?
Originally, the term “firewall” referred to a construction technique designed to
prevent the spread of fire from one room to another. The networking term
"firewall" is a system or group of systems that enforces an access-control policy
between two networks. It may also be defined as a mechanism used to protect a
trusted network from a network that is not trusted. Of course, firewalls cannot
solve every security problem. A firewall is one of the mechanisms used to
establish a network security perimeter in support of a network security policy. It
should never be the only mechanism or method employed. For a firewall to guard
effectively, you must design and deploy it appropriately. This requires integrating
the firewall into a broad information-security policy. In addition, specific policies
must be implemented within the firewall itself.
Stateful Inspection Firewall
Stateful inspection firewalls restrict access by screening data packets against
defined access rules. They make access control decisions based on IP address and
protocol. They also "inspect" the session data to assure the integrity of the
connection and to adapt to dynamic protocols. These firewalls generally provide
the best speed and transparency; however, they may lack the gr anular application
level access control or caching that some proxies support. Firewalls, of one type or
another, have become an integral part of standard security solutions for
enterprises.
About the NBG4615 Firewall
The NBG4615’s firewall feature physically separates the LAN and the WAN and
acts as a secure gateway for all data passing between the networks.
It is a stateful inspection firewall and is designed to protect against Denial of
Service attacks when activated (click the General tab under Firewall and then
click the Enable Firewall check box). The NBG4615's purpose is to allow a
private Local Area Network (LAN) to be securely connected to the Internet. The
NBG4615 can be used to prevent theft, destruction and modification of data, as
well as log events, which may be important to the security of your network.
196
NBG4615 User’s Guide
Page 69

Chapter 23 Firewall
The NBG4615 is installed between the LAN and a broadband modem connecting to
the Internet. This allows it to act as a secure gateway for all data passing between
the Internet and the LAN.
The NBG4615 has one Ethernet WAN port and four Ethernet LAN ports, which are
used to physically separate the network into two areas.The WAN (Wide Area
Network) port attaches to the broadband (cable or DSL) modem to the Internet.
The LAN (Local Area Network) port attaches to a network of computers, which
needs security from the outside world. These computers will have access to
Internet services such as e-mail, FTP and the World Wide W eb . However, "inbound
access" is not allowed (by default) unless the remote host is authorized to use a
specific service.
Guidelines For Enhancing Security With Your Firewall
1 Change the default password via Web Configurator.
2 Think about access control before you connect to the network in any way,
including attaching a modem to the port.
3 Limit who can access your router.
4 Don't enable any local service (such as NTP) that you don't use. Any enabled
service could present a potential security risk. A determined hacker might be able
to find creative ways to misuse the enabled services to access the firewall or the
network.
5 For local services that are enabled, protect against misuse. Protect by configuring
the services to communicate only with specific peers, and protect by configuring
rules to block packets for the services at specific interfaces.
6 Protect against IP spoofing by making sure the firewall is active.
7 Keep the firewall in a secured (locked) room.
NBG4615 User’s Guide
197
Page 70

Chapter 23 Firewall
23.2 General
Use this screen to enable or disable the NBG4615’s firewall, and set up firewall
logs. Click Security > Firewall to open the General screen.
Figure 113 Security > Firewall > General l
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 71 Security > Firewall > General
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Enable Firewall Select this check box to activate the firewall. The NBG4615 performs
Apply Click Apply to save the settings.
Cancel Click Cancel to start configuring this screen again.
access control and protects against Denial of Service (DoS) attacks
when the firewall is activated.
23.3 Services
If an outside user attempts to probe an unsupported port on your NBG4615, an
ICMP response packet is automatically returned. This allows the outside user to
know the NBG4615 exists. Use this screen to prevent the ICMP response packet
from being sent. This keeps outsiders from discovering your NBG4615 when
unsupported ports are probed.
You can also use this screen to enable service blocking, enter/delete/modify the
services you want to block and the date/time you want to block them.
198
NBG4615 User’s Guide
Page 71
Chapter 23 Firewall
Click Security > Firewall > Services. The screen appears as shown next.
Figure 114 Security > Firewall > Services l
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 72 Security > Firewall > Services
LABEL DESCRIPTION
LABEL DESCRIPTION
ICMP Internet Control Message Protocol is a message control and error-
reporting protocol between a host server and a gateway to the Internet.
ICMP uses Internet Protocol (IP) datagrams, but the messages are
processed by the TCP/IP software and directly apparent to the
application user.
Respond to Ping onThe NBG4615 will not respond to any incoming Ping requests when
Disable is selected. Select WAN to reply to incoming WAN Ping
requests.
Apply Click Apply to save the settings.
Enable Firewall Rule
Enable Firewall
Rule
Apply Click Apply to save the settings.
Add Firewall Rule
Service Name Enter a name that identifies or describes the firewall rule.
Select this check box to activate the firewall rules that you define (see
Add Firewall Rule below).
NBG4615 User’s Guide
199
Page 72

Chapter 23 Firewall
Table 72 Security > Firewall > Services (continued)
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Dest IP Address Enter the IP address of the computer to which traffic for the application
Source IP
Address
Protocol Select the protocol (ALL,TCP, UDP or BOTH) used to transport the
Dest Port Range Enter the port number/range of the destination that define the traffic
Source Port
Range
Add Rule Click Add to save the firewall rule.
Firewall Rule
# This is your firewall rule number . The ordering of your rules is important
Service Name This is a name that identifies or describes the firewall rule.
Dest IP This is the IP address of the computer to which traffic for the application
Source IP This is the IP address of the computer from which traffic for the
Protocol This is the protocol (ALL,TCP, UDP or BOTH) used to transport the
Dest Port Range This is the port number/range of the destination that define the traffic
Source Port
Range
Action Drop - Traffic matching the conditions of the firewall rule are stopped.
Delete Click Delete to remove the firewall rule.
Cancel Click Cancel to start configuring this screen again.
or service is entering.
The NBG4615 applies the firewall rule to traffic initiating from this
computer.
Enter the IP address of the computer that initializes traffic for the
application or service.
The NBG4615 applies the firewall rule to traffic initiating from this
computer.
packets for which you want to apply the firewall rule.
type, for example TCP port 80 defines web traffic.
Enter the port number/range of the source that define the traffic type,
for example TCP port 80 defines web traffic.
as rules are applied in turn.
or service is entering.
application or service is initialized.
packets for which you want to apply the firewall rule.
type, for example TCP port 80 defines web traffic.
This is the port number/r a nge of the source that define the traffic type,
for example TCP port 80 defines web traffic.
200
See Appendix F on page 321 for commonly used services and port numbers.
NBG4615 User’s Guide
Page 73

CHAPTER 24
Content Filtering
24.1 Overview
This chapter provides a brief overview of content filtering using the embedded
web GUI.
Internet content filtering allows you to create and enforce Internet access policies
tailored to your needs. Content filtering is the ability to block certain web features
or specific URL keywords.
24.1.1 What You Need To Know
The following terms and concepts may help as you read through this chapter.
Content Filtering Profiles
Content filtering allows you to block certain web features, such as cookies, and/or
block access to specific web sites. For example, you can configure one policy that
blocks John Doe’s access to arts and entertainment web pages.
A content filtering profile conveniently stores your custom settings for the
following features.
Keyword Blocking URL Checking
The NBG4615 checks the URL’s domain name (or IP address) and file path
separately when performing keyword blocking.
The URL’s domain name or IP address is the characters that come before the first
slash in the URL. For example, with the URL www.zyxel.com.tw/news/
pressroom.php, the domain name is www.zyxel.com.tw.
The file path is the characters that come after the first slash in the URL. For
example, with the URL www.zyxel.com.tw/news/pressroom.php
news/pressroom.php
.
, the file path is
NBG4615 User’s Guide
201
Page 74

Chapter 24 Content Filtering
Since the NBG4615 checks the URL’s domain name (or IP address) and file path
separately, it will not find items that go across the two. For example, with the URL
www.zyxel.com.tw/news/pressroom.php
domain name (www.zyxel.com.tw)
(news/pressroom.php
) but it would not find “tw/news”.
24.2 Content Filter
Use this screen to restrict web features, add keywords for blocking and designate
a trusted computer. Click Security > Content Filter to open the Content Filter
screen.
Figure 115 Security > Content Filter
, the NBG4615 would find “tw” in the
. It would also find “news” in the file path
202
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 73 Security > Content Filter
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Trusted IP Setup To enable this feature, type an IP address of any one of the computers
in your network that you want to have as a trusted computer. This
allows the trusted computer to have full access to all features that are
configured to be blocked by content filtering.
Leave this field blank to have no trusted computers.
Restrict Web
Features
Select the box(es) to restrict a feature. When you download a page
containing a restricted feature, that part of the web page will appear
blank or grayed out.
NBG4615 User’s Guide
Page 75

Chapter 24 Content Filtering
Table 73 Security > Content Filter (continued)
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Enable URL
Keyword
Blocking
Keyword Type a keyword in this field. You may use any character (up to 64
Keyword List This list displays the keywords already added.
Add Click Add after you have typed a keyword.
Delete Highlight a keyword in the lower box and click Delete to remove it.
Clear All Click this button to remove all of the listed keywords.
Apply Click Apply to save your changes.
Cancel Click Cancel to begin configuring this screen afresh
The NBG4615 can block Web sites with URLs that contain certain
keywords in the domain name or IP address. For example, if the
keyword "bad" was enabled, all sites containing this keyword in the
domain name or IP address will be blocked, e.g., URL http://
www.website.com/bad.html would be blocked. Select this check box to
enable this feature.
characters). Wildcards are not allowed. You can also enter a numerical
IP address.
Repeat this procedure to add other keywords. Up to 64 keywords are
allowed.
When you try to access a web page containing a keyword, you will get
a message telling you that the content filter is blocking this request.
The keyword disappears from the text box after you click Apply.
24.3 Technical Reference
The following section contains additional technical information about the NBG4615
features described in this chapter.
24.3.1 Customizing Keyword Blocking URL Checking
You can use command s to set how much of a websi te’s URL the content filter is to
check for keyword blocking. See the appendices for information on how to access
and use the command interpreter.
Domain Name or IP Address URL Checking
By default, the NBG4615 checks the URL’s domain name or IP address when
performing keyword blocking.
This means that the NBG4615 checks the characters that come before the first
slash in the URL.
For example, with the URL www.zyxel.com.tw/news/pressroom.php
filtering only searches for keywords within www.zyxel.com.tw
.
, content
NBG4615 User’s Guide
203
Page 76

Chapter 24 Content Filtering
Full Path URL Checking
Full path URL checking has the NBG4615 check the characters that come before
the last slash in the URL.
For example, with the URL www.zyxel.com.tw/news/pressroom.php
checking searches for keywords within www.zyxel.com.tw/news/
Use the ip urlfilter customize actionFlags 6 [disable | enable]
command to extend (or not extend) the keyword blocking search to include the
URL's full path.
, full path URL
.
File Name URL Checking
Filename URL checking has the NBG4615 check all of the characters in the URL.
For example, filename URL checking searches for keywords within the URL
www.zyxel.com.tw/news/pressroom.php
Use the ip urlfilter customize actionFlags 8 [disable | enable]
command to extend (or not extend) the keyword blocking search to include the
URL's complete filename.
.
204
NBG4615 User’s Guide
Page 77

CHAPTER 25
A
B
-> VOIP
-> FTP
-> HTTP
-> Chat, Email
Bandwidth Management
25.1 Overview
This chapter contains information about configuring bandwidth management and
editing rules.
ZyXEL’s Bandwidth Management allows you to specify bandwidth management
rules based on an application.
In the figure below, uplink tr affic goes from t he LAN device ( A) to the W AN device
(B). Bandwidth management is applied before sending the packets out to the
WAN. Downlink traffic comes back f rom the WAN device (B) to the LAN device (A).
Bandwidth management is applied before sending the traffic out to LAN.
Figure 116 Bandwidth Management Example
You can allocate specific amounts of bandwidth capacity (bandwidth budgets) to
individual applications (like VoIP, Web, FTP, and E-mail for example).
25.2 What You Can Do
•Use the General screen to enable bandwidth management and assign
bandwidth values (Section 25.4 on page 206).
•Use the Advanced screen to configure bandwidth managements rule for the
pre-defined services and applications (Sectio n 25.5 on page 207).
NBG4615 User’s Guide
205
Page 78

Chapter 25 Bandwidth Management
•Use the Monitor screen to view the amount of network bandwidth that
applications running in the network are using (Section 25.6 on page 211).
25.3 What You Need To Know
The sum of the bandwidth allotments that apply to the WAN interface (LAN to
WAN, WLAN to WAN) must be less than or equal to the Upstream Bandwidth
that you configure in the Bandwidth Management Advanced screen (Section
25.5 on page 207).
The sum of the bandwidth allotments that apply to the LAN interface (WAN to
LAN, WAN to WLAN) must be less than or equal to the Downstream Bandwidth
that you configure in the Bandwidth Management Advanced screen Section
25.5 on page 207.
25.4 General Screen
Use this screen to have the NBG4615 apply bandwidth management.
Click Management > Bandwidth MGMT to open the bandwidth management
General screen.
Figure 117 Management > Bandwidth Management > General
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 74 Management > Bandwidth Management > General
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Enable
Bandwidth
Management
This field allows you to have NBG4615 apply bandwidth management.
Enable bandwidth management to give traffic that matches a
bandwidth rule priority over traffic that does not match a bandwidth
rule.
206
Enabling bandwidth management also allows you to control the
maximum or minimum amounts of bandwidth that can be used by
traffic that matches a bandwidth rule.
NBG4615 User’s Guide
Page 79

Table 74 Management > Bandwidth Management > General (continued)
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Apply Click Apply to save your customized settings.
Cancel Click Cancel to begin configuring this screen afresh.
25.5 Advanced Screen
Use this screen to configure bandwidth management rules for the pre-defined
services or applications.
You can also use this screen to configure bandwidth management rule for other
services or applications that are not on the pre-defined list of NBG4615.
Additionally, you can define the source and destination IP addresses and port for a
service or application.
Note: The two tables shown in this screen can be configure d and applied at the same
time.
Chapter 25 Bandwidth Management
NBG4615 User’s Guide
207
Page 80

Chapter 25 Bandwidth Management
Click Management > Bandwidth Management > Advanced to open the
bandwidth management Advanced screen.
Figure 118 Management > Bandwidth Management > Advanced
208
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 75 Management > Bandwidth Management > Advanced
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Management Bandwidth
Upstream
Bandwidth
Downstream
Bandwidth
Application List Use this table to allocate specific amounts of bandwidth based on a pre-
Select the total amount of bandwidth (from 64 Kilobits to 32 Megabits)
that you want to dedicate to uplink traffic.
This is traffic from LAN/WLAN to WAN.
Select the total amount of bandwidth (from 64 Kilobits to 32 Megabits)
that you want to dedicate to uplink traffic.
This is traffic from WAN to LAN/WLAN.
defined service.
NBG4615 User’s Guide
Page 81
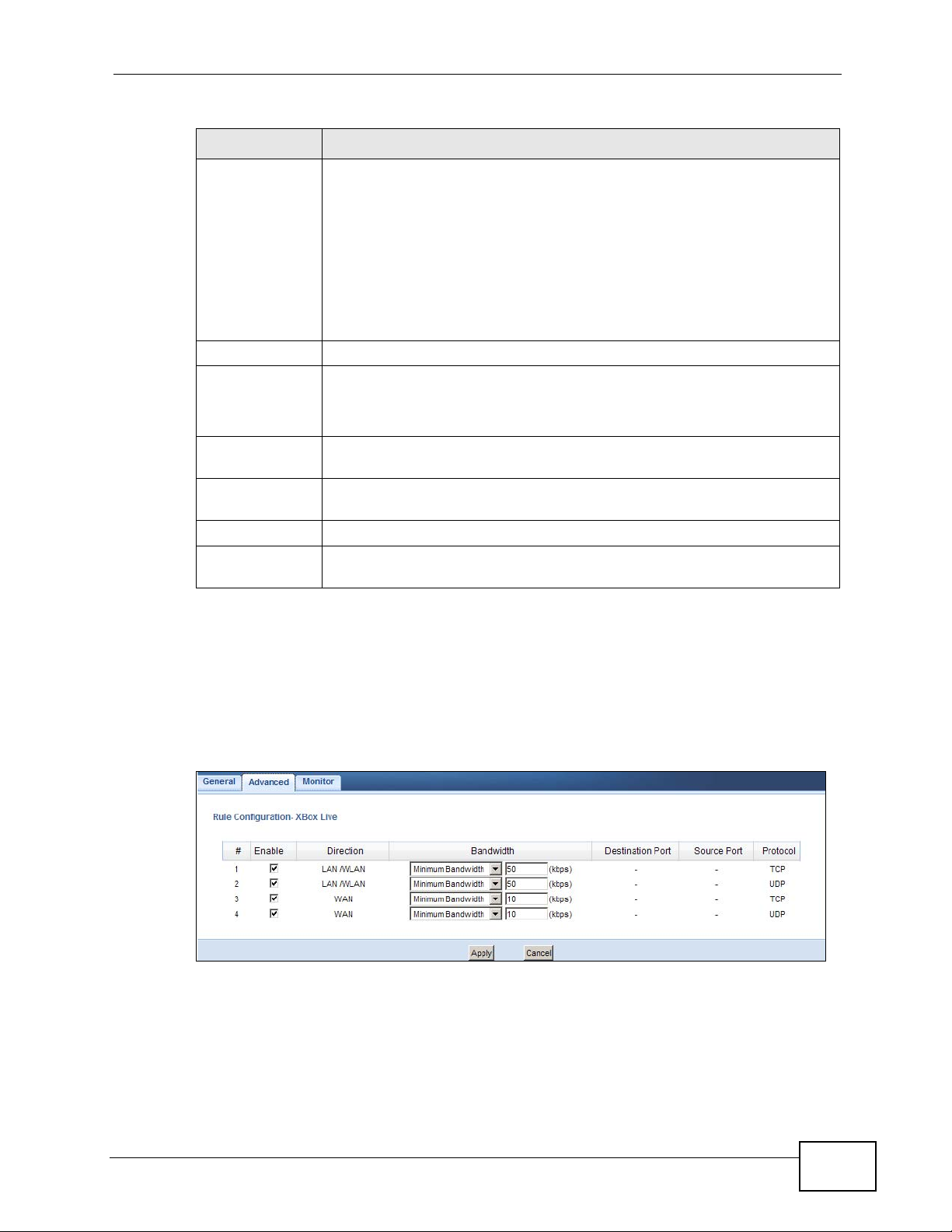
Chapter 25 Bandwidth Management
Table 75 Management > Bandwidth Management > Advanced (continued)
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Priority Select a priority from the drop down list box. Choose High, Mid or
Low.
• High - Select this for voice traffic or video that is especially sensitive
to jitter (jitter is the variations in delay).
• Mid - Select this for "excellent effort" or better than best effort and
would include important business traffic that can tolerate some
delay.
• Low - Select this for non-critical "background" traffic such as bulk
transfers that are allowed but that should not affect other
applications and users.
Category This is the category where a service belongs.
Service This is the name of the service.
Select the check box to have the NBG4615 apply this bandwidth
management rule.
Advanced
Setting
User-defined
Service
# This is the number of an individual bandwidth management rule.
Enable Select this check box to have the NBG4615 apply this bandwidth
Click the Edit icon to open the Rule Configuration screen where you
can modify the rule.
Use this table to allocate specific amounts of bandwidth to specific
applications or services you specify.
management rule.
25.5.1 Rule Configuration: Application Rule Configuration
If you want to edit a bandwidth management rule for a pre-defined service or
application, click the Edit icon in the Application List table of the Advanced
screen. The following screen displays.
Figure 119 Bandwidth Management Rule Configuration: Application List
NBG4615 User’s Guide
209
Page 82

Chapter 25 Bandwidth Management
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 76 Bandwidth Management Rule Configuration: Application List
LABEL DESCRIPTION
This is the port number of the destination that define the traffic type,
for example TCP port 80 defines web traffic.
See Appendix F on page 321 for some common services and port
numbers.
This is the port number of the source that define the traffic type, for
example TCP port 80 defines web tr affic.
See Appendix F on page 321 for some common services and port
numbers.
25.5.2 Rule Configuration: User Defined Service Rule
Configuration
If you want to edit a bandwidth management rule for other applications or
services, click the Edit icon in the User-defined Service table of the Advanced
screen. The following screen displays.
Figure 120 Bandwidth Management Rule Configuration: User-defined Service
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 77 Bandwidth Management Rule Configuration: User-defined Service
LABEL DESCRIPTION
BW Budget Select Maximum Bandwidth or Minimum Bandwidth and
specify the maximum or minimum bandwidth allowed for the rule
in kilobits per second.
Destination Address
Start
Enter the starting IP address of the destination computer.
The NBG4615 applies bandwidth management to the service or
application that is entering this computer.
210
NBG4615 User’s Guide
Page 83

Chapter 25 Bandwidth Management
Table 77 Bandwidth Management Rule Configuration: User-defined Service
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Destination Address
End
Destination Port This is the port number of the destination that define the traffic
Source Address Start Enter the starting IP address of the computer that initializes
Source Address End Enter the ending IP address of the computer that initializes tr affic
Source Port This is the port number of the source that define the traffic type,
Protocol Select the protocol (TCP, UDP, BOTH) for which the bandwidth
Enter the ending IP address of the destination computer.
The NBG4615 applies bandwidth management to the service or
application that is entering this computer.
type, for example TCP port 80 defines web traffic.
traffic for the application or service.
The NBG4615 applies bandwidth management to traffic initiating
from this computer.
for the application or service.
The NBG4615 applies bandwidth management to traffic initiating
from this computer.
for example TCP port 80 defines web traffic.
management rule applies.
If you select BOTH, enter the protocol for which the bandwidth
management rule applies. For example, ICMP for ping traffic.
Apply Click Apply to save your customized settings.
Cancel Click Cancel to exit this screen without saving.
See Appendix F on page 321 for commonly used services and port numbers.
25.6 Monitor Screen
Use this screen to view the amount of network bandwidth that applications
running in the network are using.
The bandwidth is measured in kilobits per second (kbps).
NBG4615 User’s Guide
211
Page 84

Chapter 25 Bandwidth Management
The monitor shows what kinds of applications are running in the network, the
maximum kbps that each application can use, as well as the percentage of
bandwidth it is using.
Figure 121 Management > Bandwidth Management > Monitor
25.6.1 Predefined Bandwidth Management Services
The following is a description of some services that you can select and to which
you can apply media bandwidth management in the Management > Bandwidth
Management > Advanced screen.
Table 78 Media Bandwidth Management Setup: Services
SERVICE DESCRIPTION
FTP File Transfer Program enables fast transfer of files, including large files
that may not be possible by e-mail.
WWW The World Wide Web (WWW) is an Internet system to distribute
graphical, hyper-linked information, based on Hyper Text Transfer
Protocol (HTTP) - a client/server protocol for the World Wide Web. The
Web is not synonymous with the Internet; rather, it is just one service
on the Internet. Other services on the Internet include Internet Relay
Chat and Newsgroups. The Web is accessed through use of a browser.
E-Mail Electronic mail consists of messages sent through a computer network
to specific groups or individuals. Here are some default ports for e-mail:
VoIP (SIP) Sending voice signals over the Internet is called Voice over IP or VoIP.
Session Initiated Protocol (SIP) is an internationally recognized
standard for implementing VoIP. SIP is an application-layer control
(signaling) protocol that handles the setting up, altering and tearing
down of voice and multimedia sessions over the Internet.
212
SIP is transported primarily over UDP but can also be transported over
TCP.
NBG4615 User’s Guide
Page 85

Chapter 25 Bandwidth Management
Table 78 Media Bandwidth Management Setup: Services (continued)
SERVICE DESCRIPTION
BitTorrent BitTorrent is a free P2P (peer-to-peer) sharing tool allowing you to
distribute large software and media files. BitTorrent requires you to
search for a file with a searching engine yourself. It distributes files by
corporation and trading, that is, the client downloads the file in small
pieces and share the pieces with other peers to get other half of the file.
Gaming Online gaming services lets you play multiplayer games on the Internet
via broadband technology. As of this writing, your NBG4615 supports
Xbox, Playstation, Battlenet and MSN Game Zone.
NBG4615 User’s Guide
213
Page 86

Chapter 25 Bandwidth Management
214
NBG4615 User’s Guide
Page 87

CHAPTER 26
Remote Management
26.1 Overview
This chapter provides information on the Remote Management screens.
Remote Management allows you to manage your NBG4615 from a remote lo cation
through the following interfaces:
•LAN and WAN
•LAN only
•WAN only
Note: The NBG4615 is managed using the Web Configurator.
26.2 What You Need to Know
Remote management over LAN or WAN will not work when:
1 The IP address in the Secured Client IP Address field (Section 26.3 on page
216) does not match the client IP address. If i t does not match, the NBG4615 wi ll
disconnect the session immediately.
2 There is already another remote management session. You may only have one
remote management session running at one time.
3 There is a firewall rule that blocks it.
26.2.1 Remote Management and NAT
When NAT is enabled:
• Use the NBG4615’s WAN IP address when configuring from the WAN.
• Use the NBG4615’s LAN IP address when configuring from the LAN.
NBG4615 User’s Guide
215
Page 88

Chapter 26 Remote Management
26.2.2 System Timeout
There is a default system management idle timeout of five minutes (three
hundred seconds). The NBG4615 automatically logs you out if the management
session remains idle for longer than this timeout period. The management session
does not time out when a statistics screen is polling. You can change the timeout
period in the System screen
26.3 WWW Screen
To change your NBG4615’s remote management settings, click Management >
Remote Management > WWW.
Figure 122 Management > Remote Management > WWW
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 79 Management > Remote Management > WWW
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Server Port You may change the server port number for a service if needed,
however you must use the same port number in order to use th at
service for remote management.
Server Access Select the interface(s) through which a computer may access the
NBG4615 using this service.
Secured Client IP
Address
Apply Click Apply to save your customized settings and exit this screen.
Cancel Click Cancel to begin configuring this screen afresh.
Select All to allow all computes to access the NBG4615.
Otherwise, check Selected and specify the IP address of the
computer that can access the NBG4615.
216
NBG4615 User’s Guide
Page 89

CHAPTER 27
Universal Plug-and-Play (UPnP)
27.1 Overview
This chapter introduces the UPnP feature in the web configurator.
Universal Plug and Play (UPnP) is a distributed, open networking standard that
uses TCP/IP for simple peer-to-peer network connectivity between devices. A
UPnP device can dynamically join a network, obtain an IP address, convey its
capabilities and learn about other devices on the network. In turn, a device can
leave a network smoothly and automatically when it is no longer in use.
27.2 What You Need to Know
UPnP hardware is identified as an icon in the Network Connections folder
(Windows XP). Each UPnP compatible device installed on your network will appear
as a separate icon. Selecting the icon of a UPnP device will allow you to access the
information and properties of that device.
27.2.1 NAT Traversal
UPnP NAT traversal automates the process of allowing an application to operate
through NAT. UPnP network devices can automatically configure network
addressing, announce their presence in the network to other UPnP devices and
enable exchange of simple product and service descriptions. NAT traversal allows
the following:
• Dynamic port mapping
• Learning public IP addresses
• Assigning lease times to mappings
Windows Messenger is an example of an application that supports NAT traversal
and UPnP.
See the NAT chapter for more information on NAT.
NBG4615 User’s Guide
217
Page 90

Chapter 27 Universal Plug-and-Play (UPnP)
27.2.2 Cautions with UPnP
The automated nature of NAT traversal applications in establishing their own
services and opening firewall ports may present network security issues. Network
information and configuration may also be obt ained and modified by users in some
network environments.
When a UPnP device joins a network, it announces its presence with a multicast
message. For security reasons, the NBG4615 allows multicast messages on the
LAN only.
All UPnP-enabled devices may communicate freely with each other without
additional configuration. Disable UPnP if this is not your intention.
27.3 UPnP Screen
Use this screen to enable UPnP on your NBG4615.
Click Management > UPnP to display the screen shown next.
Figure 123 Management > UPnP
The following table describes the fields in this screen.
Table 80 Management > UPnP
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Enable the Universal Plug
and Play (UPnP) Feature
Apply Click Apply to save the setting to the NBG4615.
Cancel Click Cancel to return to the previously saved settings.
Select this check box to activate UPnP. Be aware that anyone
could use a UPnP application to open the web configurator's
login screen without entering the NBG4615's IP address
(although you must still enter the password to access the web
configurator).
218
NBG4615 User’s Guide
Page 91
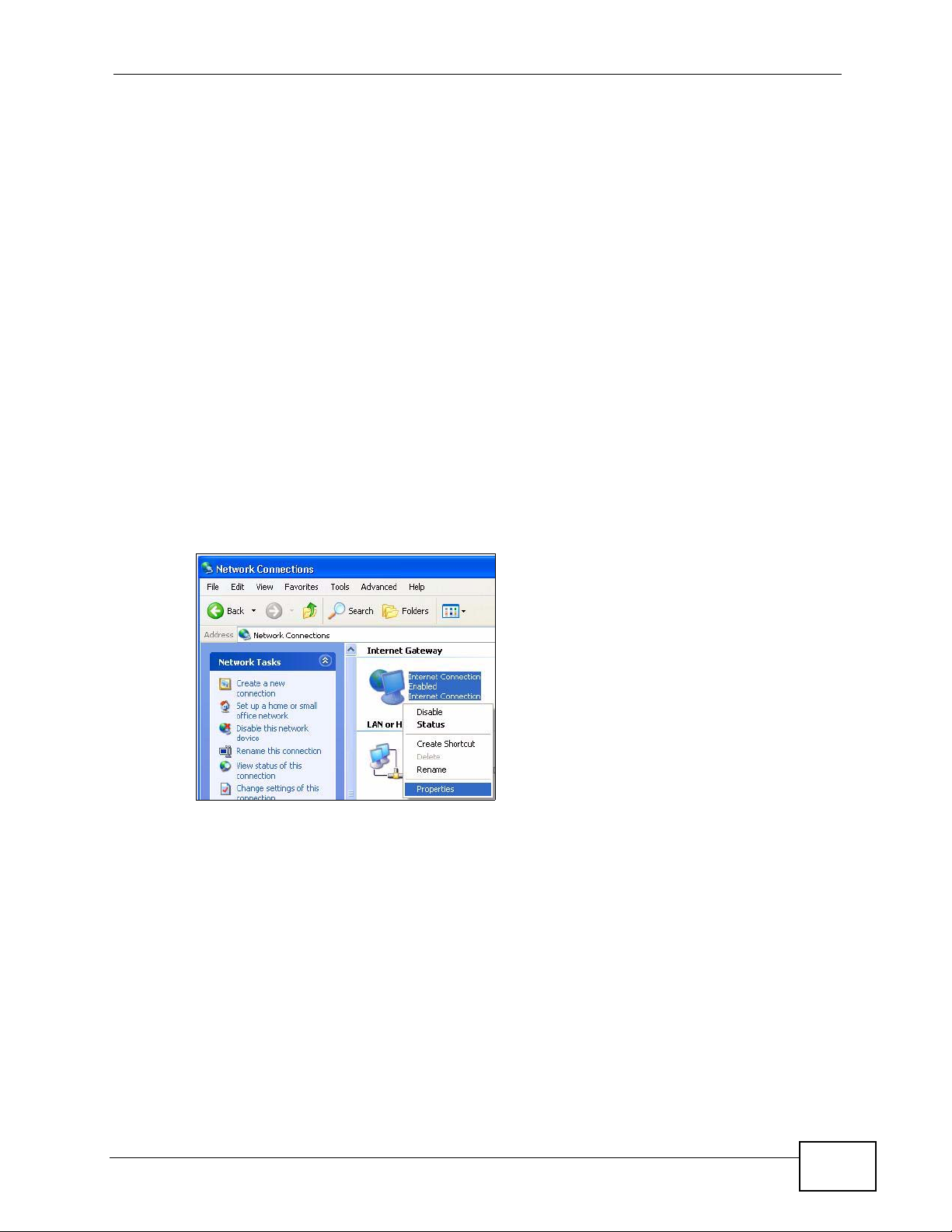
Chapter 27 Universal Plug-and-Play (UPnP)
27.4 Technical Reference
The sections show examples of using UPnP.
27.4.1 Using UPnP in Windows XP Example
This section shows you how to use the UPnP feature in Windows XP. You must
already have UPnP installed in Windows XP and UPnP activated on the NBG4615.
Make sure the computer is connected to a LAN port of the NBG4615 . Turn on your
computer and the NBG4615.
27.4.1.1 Auto-discover Your UPnP-enabled Network Device
1 Click start and Control Panel. Double-click Network Connections. An icon
displays under Internet Gateway.
2 Right-click the icon and select Properties.
Figure 124 Network Connections
NBG4615 User’s Guide
219
Page 92
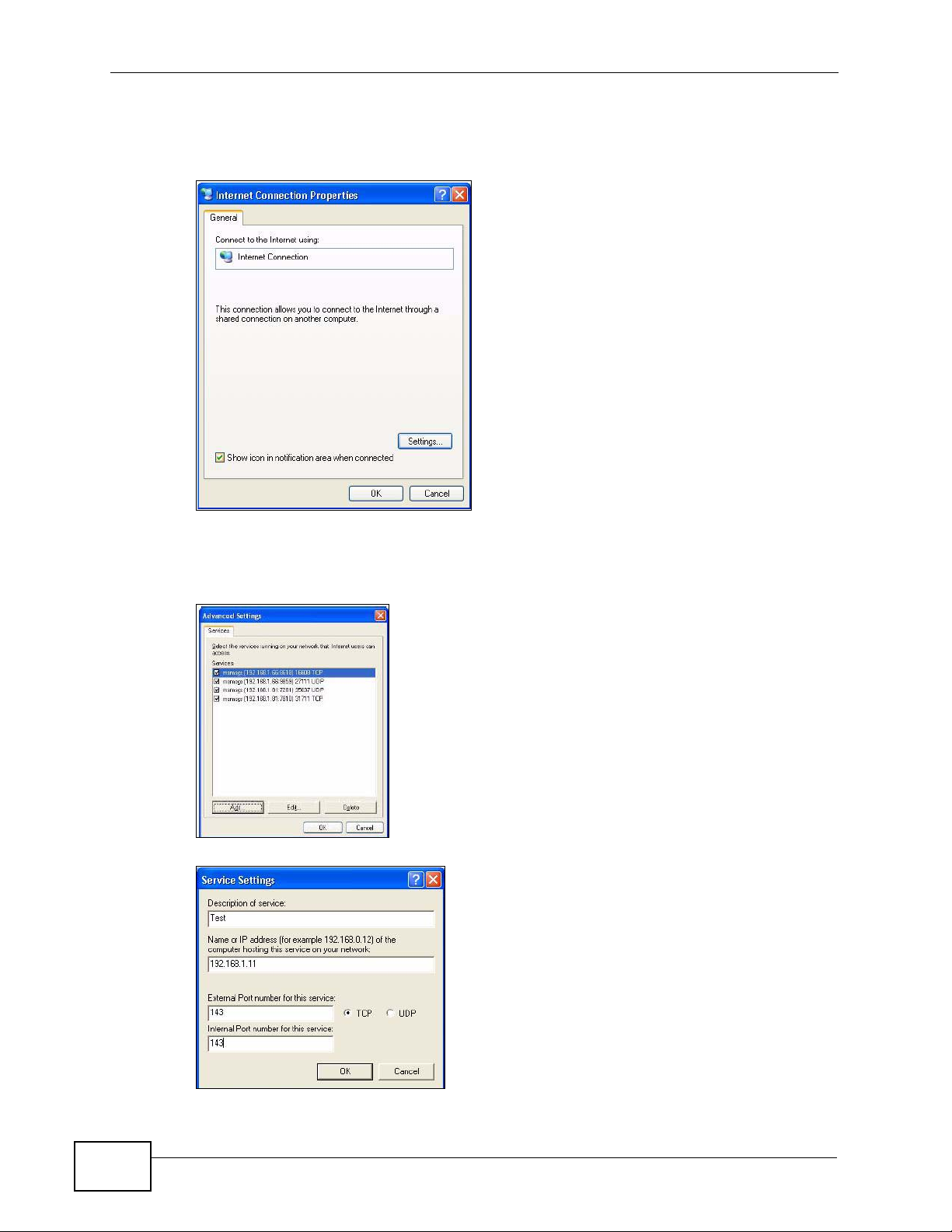
Chapter 27 Universal Plug-and-Play (UPnP)
3 In the Internet Connection Properties window, click Settings to see the port
mappings there were automatically created.
Figure 125 Internet Connection Properties
4 You may edit or delete the port mappings or click Add to manually add port
mappings.
Figure 126 Internet Connection Properties: Advanced Settings
Figure 127 Internet Connection Properties: Advanced Settings: Add
220
NBG4615 User’s Guide
Page 93

Chapter 27 Universal Plug-and-Play (UPnP)
Note: When the UPnP-enabled device is disconnected from your computer, all port
mappings will be deleted automatically.
5 Select Show icon in notification area when connected option and click OK.
An icon displays in the system tray.
Figure 128 System Tray Icon
6 Double-click on the icon to display your current Internet connection status.
Figure 129 Internet Connection Status
27.4.2 Web Configurator Easy Access
With UPnP, you can access the web-based configurator on the NBG4615 without
finding out the IP address of the NBG4615 first. This comes helpful if you do not
know the IP address of the NBG4615.
Follow the steps below to access the web configurator.
1 Click Start and then Control Panel.
2 Double-click Network Connections.
NBG4615 User’s Guide
221
Page 94

Chapter 27 Universal Plug-and-Play (UPnP)
3 Select My Network Places under Other Places.
Figure 130 Network Connections
4 An icon with the description for each UPnP-enabled device displays under Local
Network.
5 Right-click on the icon for your NBG4615 and select Invoke. The web configurator
login screen displays.
Figure 131 Network Connections: My Network Places
222
NBG4615 User’s Guide
Page 95

Chapter 27 Universal Plug-and-Play (UPnP)
6 Right-click on the icon for your NBG4615 and select Properties. A properties
window displays with basic information about the NBG4615.
Figure 132 Network Connections: My Network Places: Properties: Example
NBG4615 User’s Guide
223
Page 96

Chapter 27 Universal Plug-and-Play (UPnP)
224
NBG4615 User’s Guide
Page 97

CHAPTER 28
Maintenance
28.1 Overview
This chapter provides information on the Maintenance screens.
28.2 What You Can Do
•Use the General screen to set the timeout period of the management session
(Section 28.3 on page 226).
•Use the Password screen to change your NBG4615’s system password (Section
28.4 on page 226).
•Use the Time screen to change your NBG4615’ s time and d ate (Section 28.5 on
page 228).
•Use the Firmware Upgrade screen to upload firmware to your NBG4615
(Section 28.6 on page 230).
•Use the Backup/Restore screen to view information related to factory
defaults, backup configuration, and restoring configuration (Section 28.8 on
page 233).
•Use the Reset/Restart screen to reboot the NBG4615 without turning the
power off (Section 28.8 on page 233).
•Use the Sys OP Mode screen to select how you want to use your NBG4615
(Section 28.10 on page 236).
NBG4615 User’s Guide
225
Page 98

Chapter 28 Maintenance
28.3 General Screen
Use this screen to set the management session timeout period. Click
Maintenance > General. The following screen displays.
Figure 133 Maintenance > General
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 81 Maintenance > General
LABEL DESCRIPTION
System Setup
System Name System Name is a unique name to identify the NBG4615 in an
Ethernet network.
Domain Name Enter the domain name you want to give to the NBG4615.
Administrator
Inactivity Timer
Apply Click Apply to save your changes back to the NBG4615.
Cancel Click Cancel to begin configuring this screen afresh.
T ype how many minutes a management session can be left idle before
the session times out. The default is 5 minutes. After it times out you
have to log in with your password again. Very long idle timeouts may
have security risks. A value of "0" means a management session never
times out, no matter how long it has been left idle (not
recommended).
28.4 Password Screen
It is strongly recommended that you change your NBG4615's password.
If you forget your NBG4615's password (or IP address), you will need to reset the
device. See Section 28.8 on page 233 for details.
226
NBG4615 User’s Guide
Page 99

Chapter 28 Maintenance
Click Maintenance > Password. The screen appears as shown.
Figure 134 Maintenance > Password
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 82 Maintenance > Password
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Password Setup Change your NBG4615’s password (recommended) using the fields as
shown.
Old Password Type the default password or the existing password you use to access
the system in this field.
New Password Type your new system password (up to 30 characters). Note that as
you type a password, the screen displays an asterisk (*) for each
character you type.
Retype to Confirm Type the new password again in this field.
Apply Click Apply to save your changes back to the NBG4615.
Cancel Click Cancel to begin configuring this screen afresh.
NBG4615 User’s Guide
227
Page 100
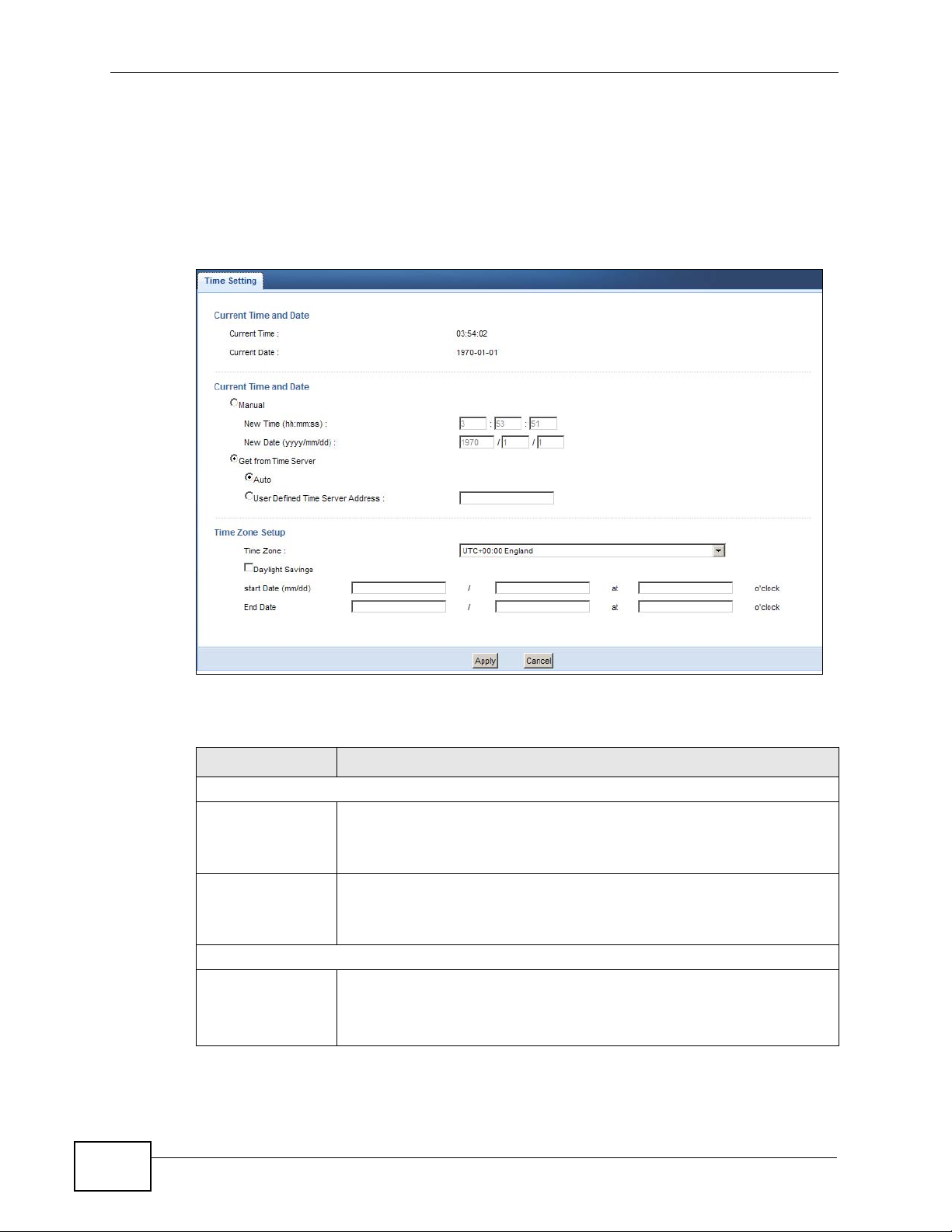
Chapter 28 Maintenance
28.5 Time Setting Screen
Use this screen to configure the NBG4615’s time based on your local time zone. To
change your NBG4615’s time and date, click Maintenance > Time. The screen
appears as shown.
Figure 135 Maintenance > Time
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 83 Maintenance > Time
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Current Time and Date
Current Time This field displays the time of your NBG4615.
Each time you reload this page, the NBG4615 synchronizes the time
with the time server.
Current Date This field displays the date of your NBG4615.
Each time you reload this page, the NBG4615 synchronizes the date
with the time server.
Current Time and Date
Manual Select this radio button to enter the time and date manually. If you
configure a new time and date, Time Zone and Daylight Saving at the
same time, the new time and date you entered has priority and the
Time Zone and Daylight Saving settings do not affect it.
228
NBG4615 User’s Guide
 Loading...
Loading...