ZyXEL NBG318S Users Manual
Chapter 5 Wireless LAN
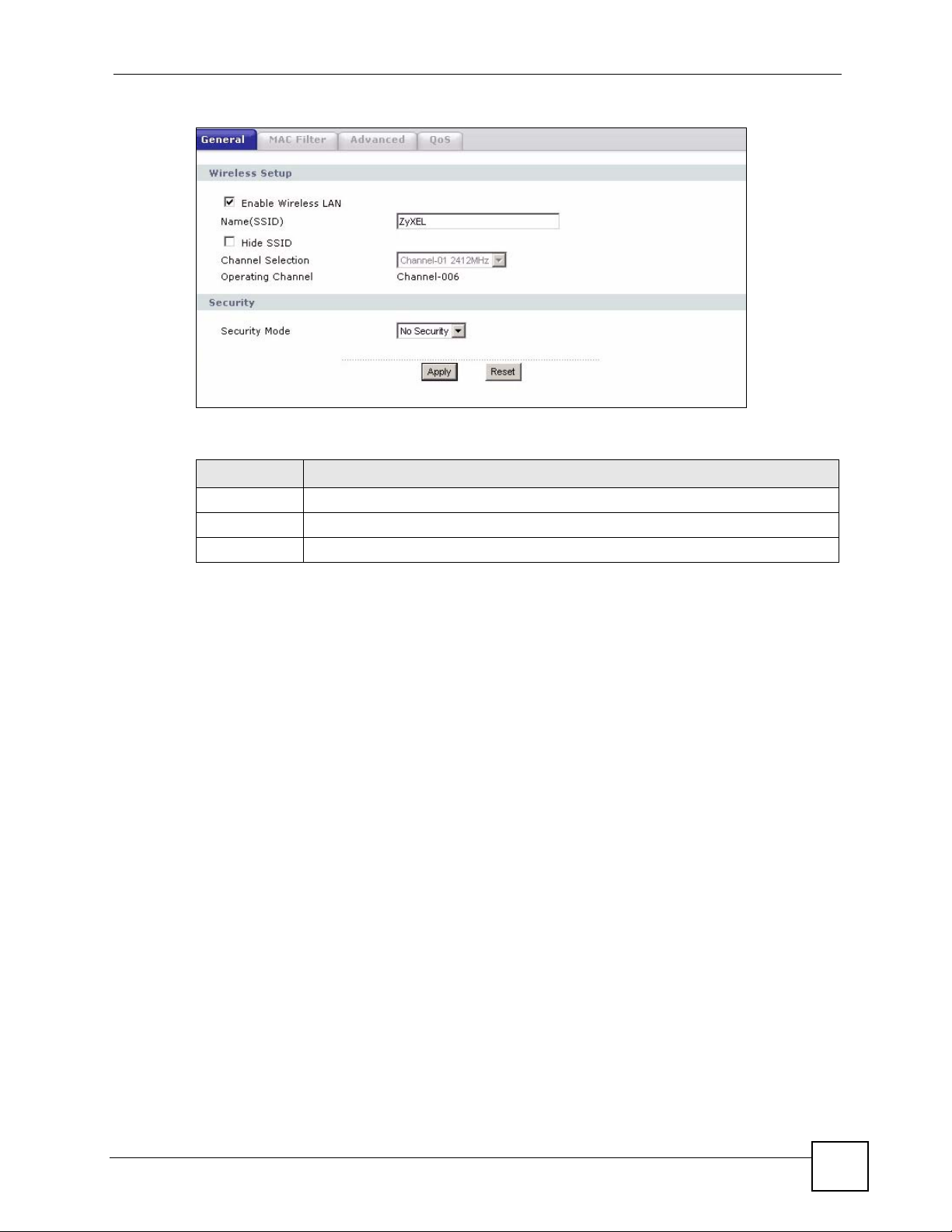
Figure 46 Network > Wireless LAN > General: No Security
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 25 Wireless No Security
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Security Mode Choose No Security from the drop-down list box.
Apply Click Apply to save your changes back to the NBG318S.
Reset Click Reset to reload the previous configuration for this screen.
5.5.2 WEP Encryption
WEP encryption scrambles the data transmitted between the wireless stations and the access
points to keep network communications private. It encrypts unicast and multicast
communications in a network. Both the wireless stations and the access points must use the
same WEP key.
Your NBG318S allows you to configure up to four 64-bit or 128-bit WEP keys but only one
key can be enabled at any one time.
In order to configure and enable WEP encryption; click Network > Wireless LAN to display
the General screen. Select Static WEP from the Security Mode list.
NBG318S User’s Guide
81
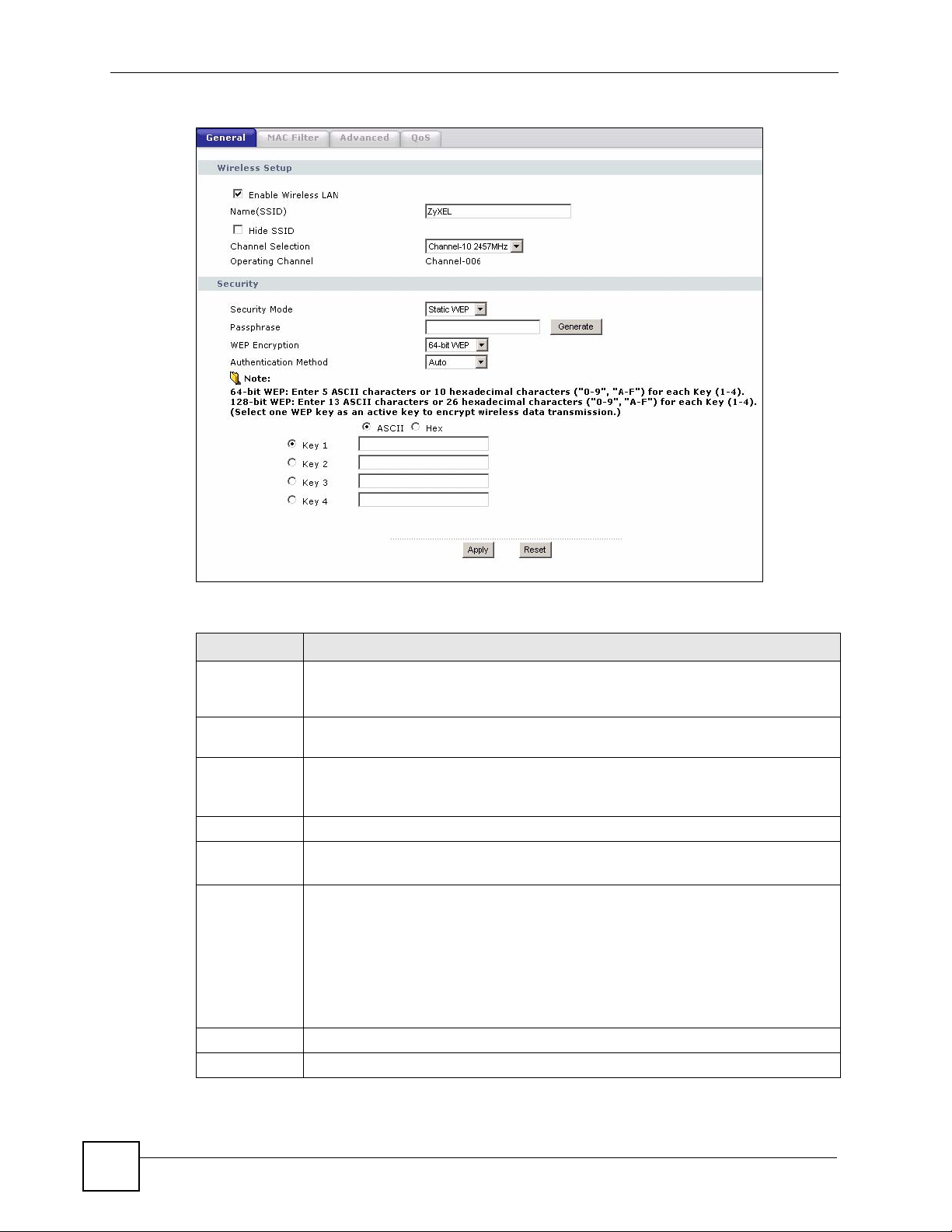
Chapter 5 Wireless LAN
Figure 47 Network > Wireless LAN > General: Static WEP
The following table describes the wireless LAN security labels in this screen.
Table 26 Network > Wireless LAN > General: Static WEP
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Passphrase Enter a passphrase (password phrase) of up to 32 printable characters and click
Generate. The NBG318S automatically generates four different WEP keys and
displays them in the Key fields below.
WEP
Encryption
Authentication
Method
ASCII Select this option in order to enter ASCII characters as WEP key.
Hex Select this option in order to enter hexadecimal characters as a WEP key.
Key 1 to Key 4 The WEP keys are used to encrypt data. Both the NBG318S and the wireless
Apply Click Apply to save your changes back to the NBG318S.
Reset Click Reset to reload the previous configuration for this screen.
Select 64-bit WEP or 128-bit WEP to enable data encryption.
This field is activated when you select 64-bit WEP or 128-bit WEP in the WEP
Encryption field.
Select Auto, Open System or Shared Key from the drop-down list box.
The preceding "0x", that identifies a hexadecimal key, is entered automatically.
stations must use the same WEP key for data transmission.
If you chose 64-bit WEP, then enter any 5 ASCII characters or 10 hexadecimal
characters ("0-9", "A-F").
If you chose 128-bit WEP, then enter 13 ASCII characters or 26 hexadecimal
characters ("0-9", "A-F").
You must configure at least one key, only one key can be activated at any one time.
The default key is key 1.
82
NBG318S User’s Guide
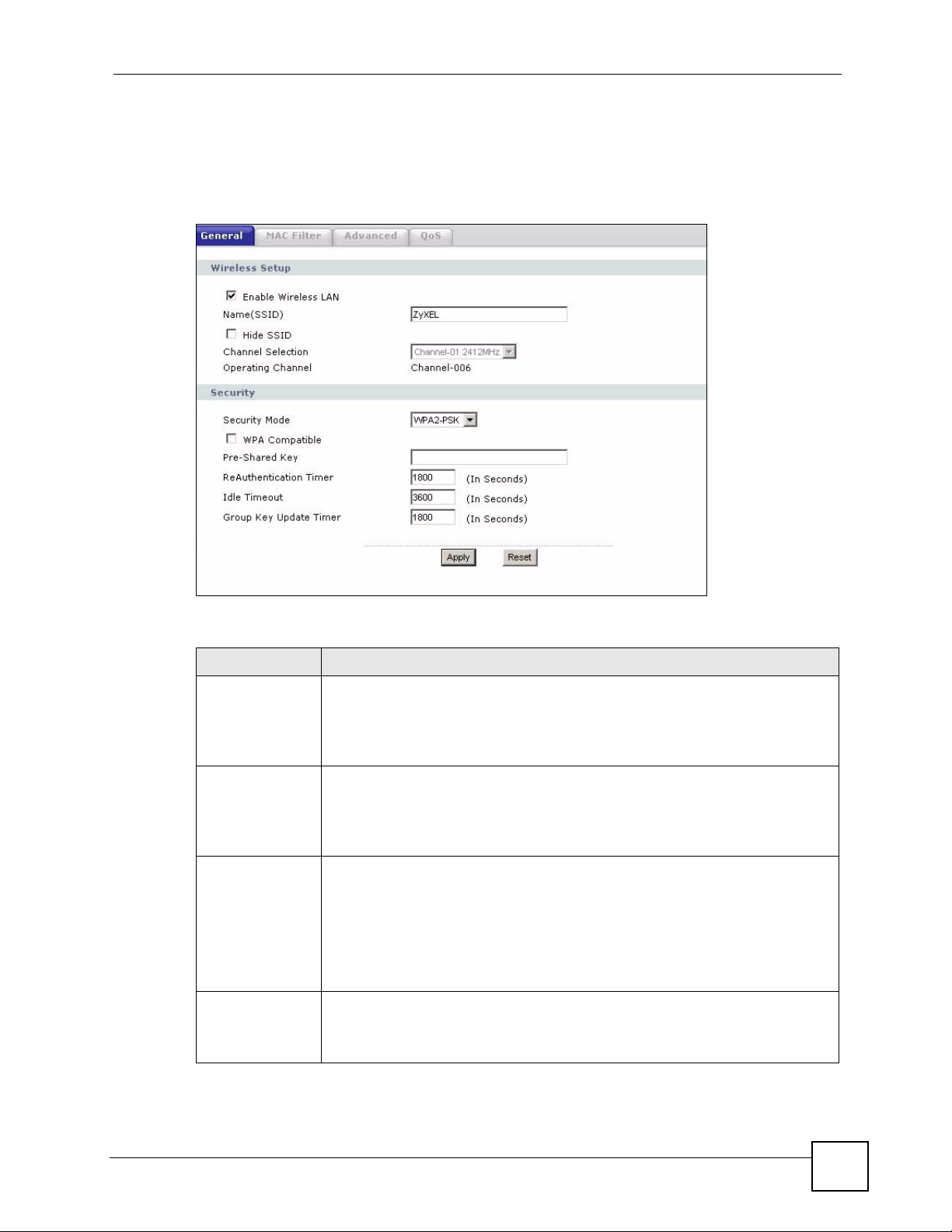
5.5.3 WPA-PSK/WPA2-PSK
Click Network > Wireless LAN to display the General screen. Select WPA-PSK or WPA2PSK from the Security Mode list.
Figure 48 Network > Wireless LAN > General: WPA-PSK/WPA2-PSK
Chapter 5 Wireless LAN
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 27 Network > Wireless LAN > General: WPA-PSK/WPA2-PSK
LABEL DESCRIPTION
WPA Compatible This check box is available only when you select WPA2-PSK or WPA2 in the
Security Mode field.
Select the check box to have both WPA2 and WPA wireless clients be able to
communicate with the NBG318S even when the NBG318S is using WPA2-PSK or
WPA2.
Pre-Shared Key The encryption mechanisms used for WPA/WPA2 and WPA-PSK/WPA2-PSK
ReAuthentication
Timer (in
seconds)
are the same. The only difference between the two is that WPA-PSK/WPA2-PSK
uses a simple common password, instead of user-specific credentials.
Type a pre-shared key from 8 to 63 case-sensitive ASCII characters (including
spaces and symbols).
Specify how often wireless stations have to resend usernames and passwords in
order to stay connected. Enter a time interval between 10 and 9999 seconds. The
default time interval is 1800 seconds (30 minutes).
Note: If wireless station authentication is done using a RADIUS
server, the reauthentication timer on the RADIUS server has
priority.
Idle Timeout The NBG318S automatically disconnects a wireless station from the wired
network after a period of inactivity. The wireless station needs to enter the
username and password again before access to the wired network is allowed. The
default time interval is 3600 seconds (or 1 hour).
NBG318S User’s Guide
83
Chapter 5 Wireless LAN
Table 27 Network > Wireless LAN > General: WPA-PSK/WPA2-PSK
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Group Key
Update Timer
Apply Click Apply to save your changes back to the NBG318S.
Reset Click Reset to reload the previous configuration for this screen.
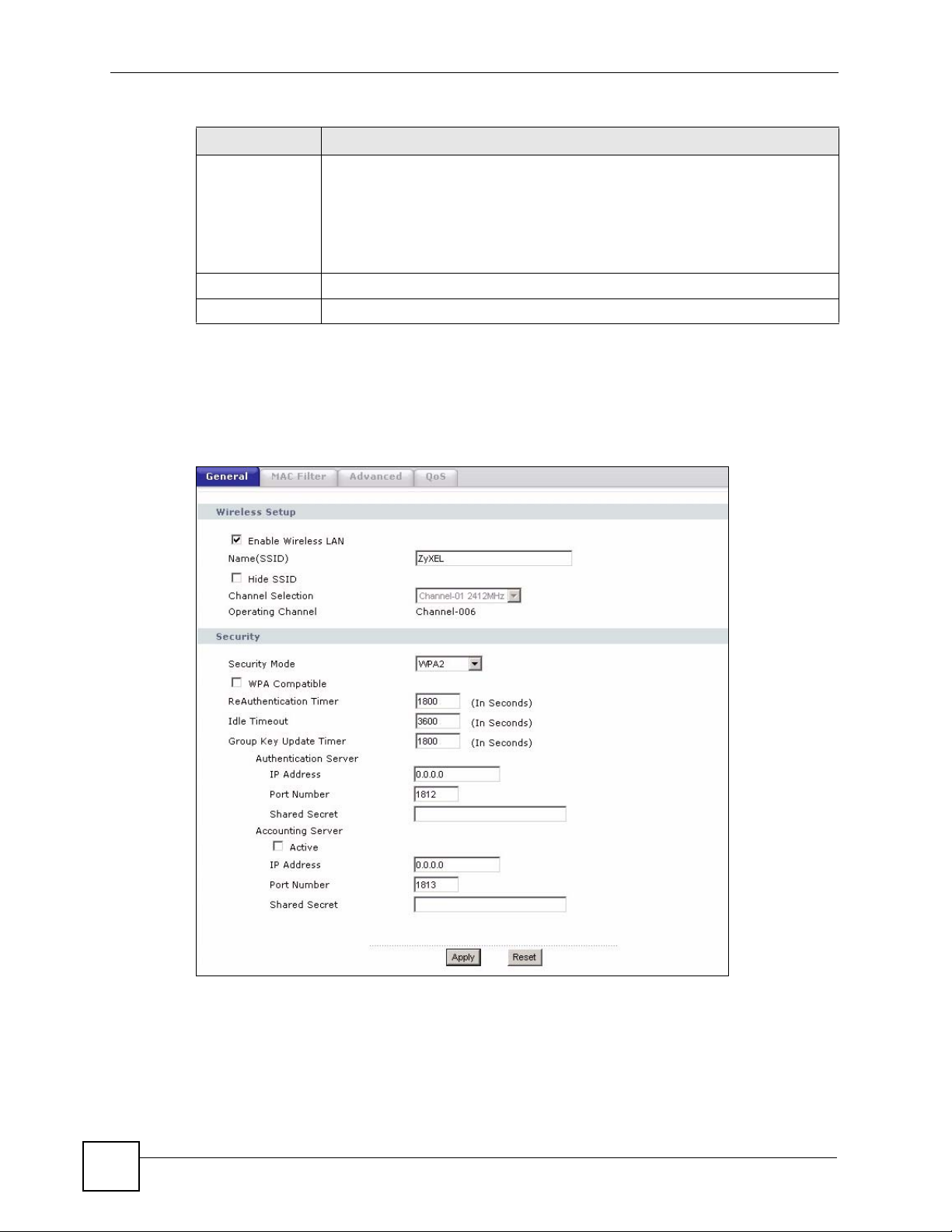
5.5.4 WPA/WPA2
Click Network > Wireless LAN to display the General screen. Select WPA or WPA2 from
the Security Mode list.
Figure 49 Network > Wireless LAN > General: WPA/WPA2
The Group Key Update Timer is the rate at which the AP (if using WPA-PSK/
WPA2-PSK key management) or RADIUS server (if using WPA/WPA2 key
management) sends a new group key out to all clients. The re-keying process is
the WPA/WPA2 equivalent of automatically changing the WEP key for an AP and
all stations in a WLAN on a periodic basis. Setting of the Group Key Update
Timer is also supported in WPA-PSK/WPA2-PSK mode. The default is 1800
seconds (30 minutes).
84
NBG318S User’s Guide
Chapter 5 Wireless LAN
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 28 Network > Wireless LAN > General: WPA/WPA2
LABEL DESCRIPTION
WPA Compatible This check box is available only when you select WPA2-PSK or WPA2 in the
ReAuthentication
Timer (in seconds)
Security Mode field.
Select the check box to have both WPA2 and WPA wireless clients be able to
communicate with the NBG318S even when the NBG318S is using WPA2-PSK
or WPA2.
Specify how often wireless stations have to resend usernames and passwords in
order to stay connected. Enter a time interval between 10 and 9999 seconds.
The default time interval is 1800 seconds (30 minutes).
Note: If wireless station authentication is done using a RADIUS
server, the reauthentication timer on the RADIUS server
has priority.
Idle Timeout The NBG318S automatically disconnects a wireless station from the wired
Group Key Update
Timer
Authentication Server
IP Address Enter the IP address of the external authentication server in dotted decimal
Port Number Enter the port number of the external authentication server. The default port
Shared Secret Enter a password (up to 31 alphanumeric characters) as the key to be shared
Accounting Server
Active Select Yes from the drop down list box to enable user accounting through an
IP Address Enter the IP address of the external accounting server in dotted decimal notation.
Port Number Enter the port number of the external accounting server. The default port number
Shared Secret Enter a password (up to 31 alphanumeric characters) as the key to be shared
Apply Click Apply to save your changes back to the NBG318S.
Reset Click Reset to reload the previous configuration for this screen.
network after a period of inactivity. The wireless station needs to enter the
username and password again before access to the wired network is allowed.
The default time interval is 3600 seconds (or 1 hour).
The Group Key Update Timer is the rate at which the AP (if using WPA-PSK/
WPA2-PSK key management) or RADIUS server (if using WPA/WPA2 key
management) sends a new group key out to all clients. The re-keying process is
the WPA/WPA2 equivalent of automatically changing the WEP key for an AP
and all stations in a WLAN on a periodic basis. Setting of the Group Key Update
Timer is also supported in WPA-PSK/WPA2-PSK mode. The NBG318S default
is 1800 seconds (30 minutes).
notation.
number is 1812.
You need not change this value unless your network administrator instructs you
to do so with additional information.
between the external authentication server and the NBG318S.
The key must be the same on the external authentication server and your
NBG318S. The key is not sent over the network.
external authentication server.
is 1813.
You need not change this value unless your network administrator instructs you
to do so with additional information.
between the external accounting server and the NBG318S.
The key must be the same on the external accounting server and your
NBG318S. The key is not sent over the network.
NBG318S User’s Guide
85
Chapter 5 Wireless LAN
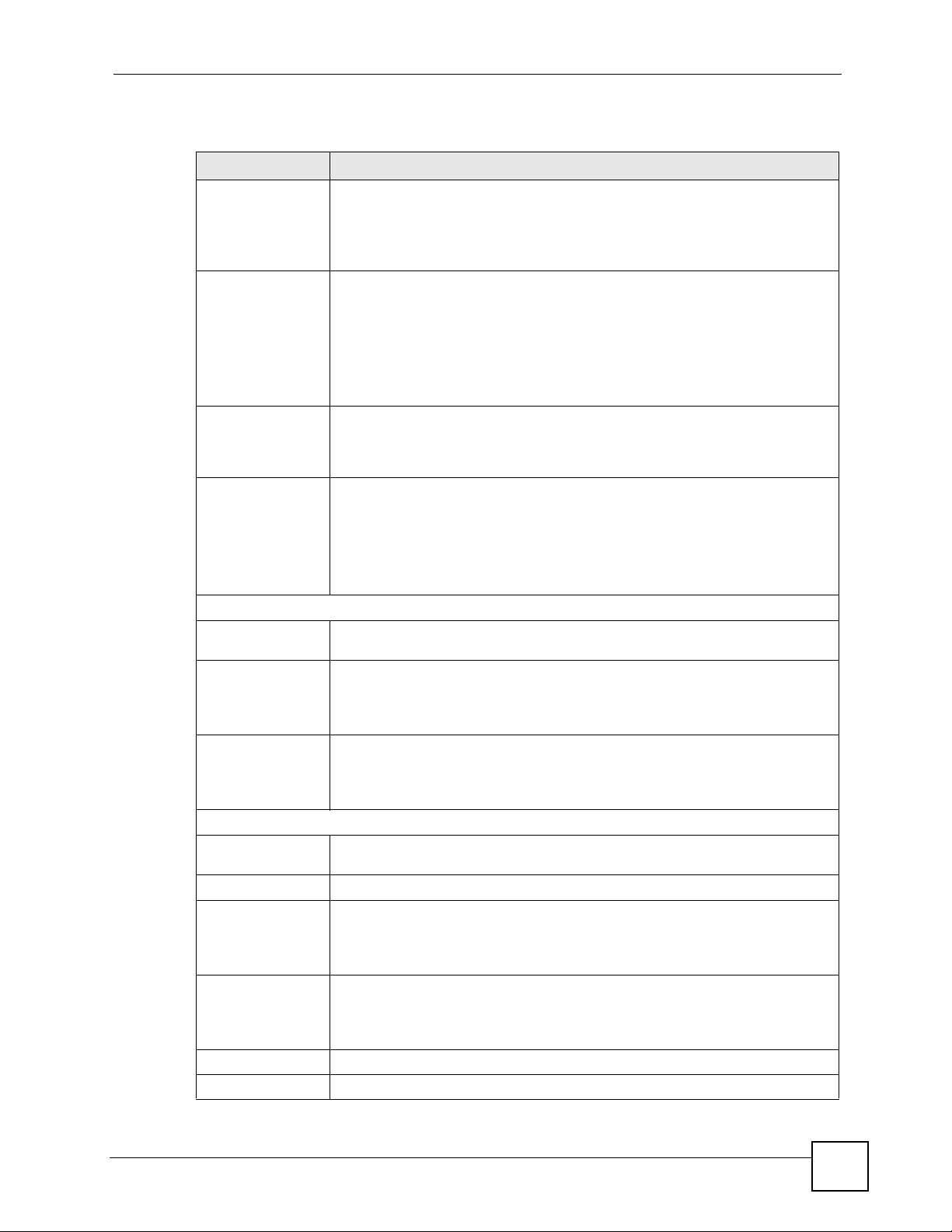
5.6 MAC Filter
The MAC filter screen allows you to configure the NBG318S to give exclusive access to up to
32 devices (Allow) or exclude up to 32 devices from accessing the NBG318S (Deny). Every
Ethernet device has a unique MAC (Media Access Control) address. The MAC address is
assigned at the factory and consists of six pairs of hexadecimal characters, for example,
00:A0:C5:00:00:02. You need to know the MAC address of the devices to configure this
screen.
To change your NBG318S’s MAC filter settings, click Network > Wireless LAN > MAC
Filter. The screen appears as shown.
Figure 50 Network > Wireless LAN > MAC Filter
86
The following table describes the labels in this menu.
Table 29 Network > Wireless LAN > MAC Filter
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Active Select Yes from the drop down list box to enable MAC address filtering.
Filter Action Define the filter action for the list of MAC addresses in the MAC Address table.
Select Deny to block access to the NBG318S, MAC addresses not listed will be
allowed to access the NBG318S
Select Allow to permit access to the NBG318S, MAC addresses not listed will be
denied access to the NBG318S.
NBG318S User’s Guide
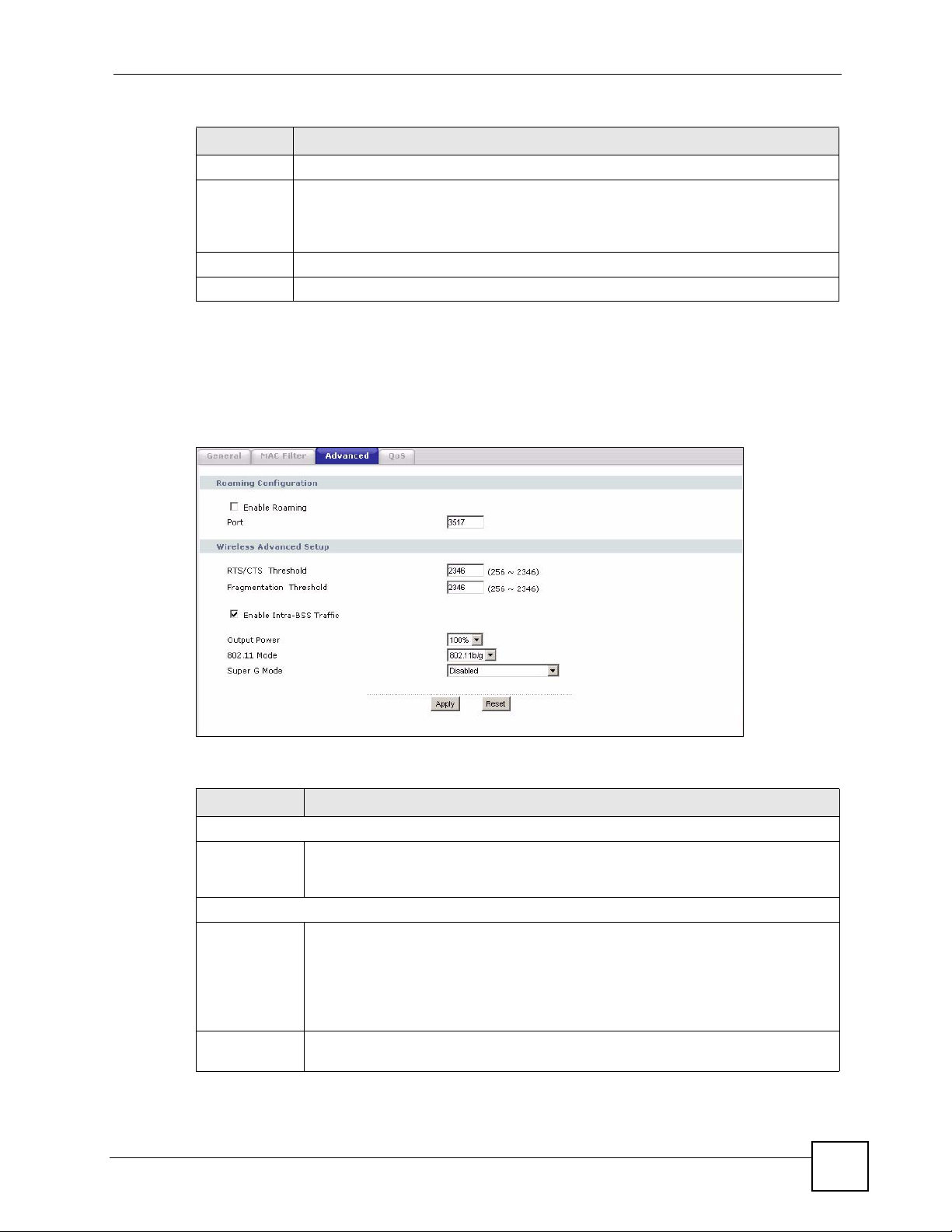
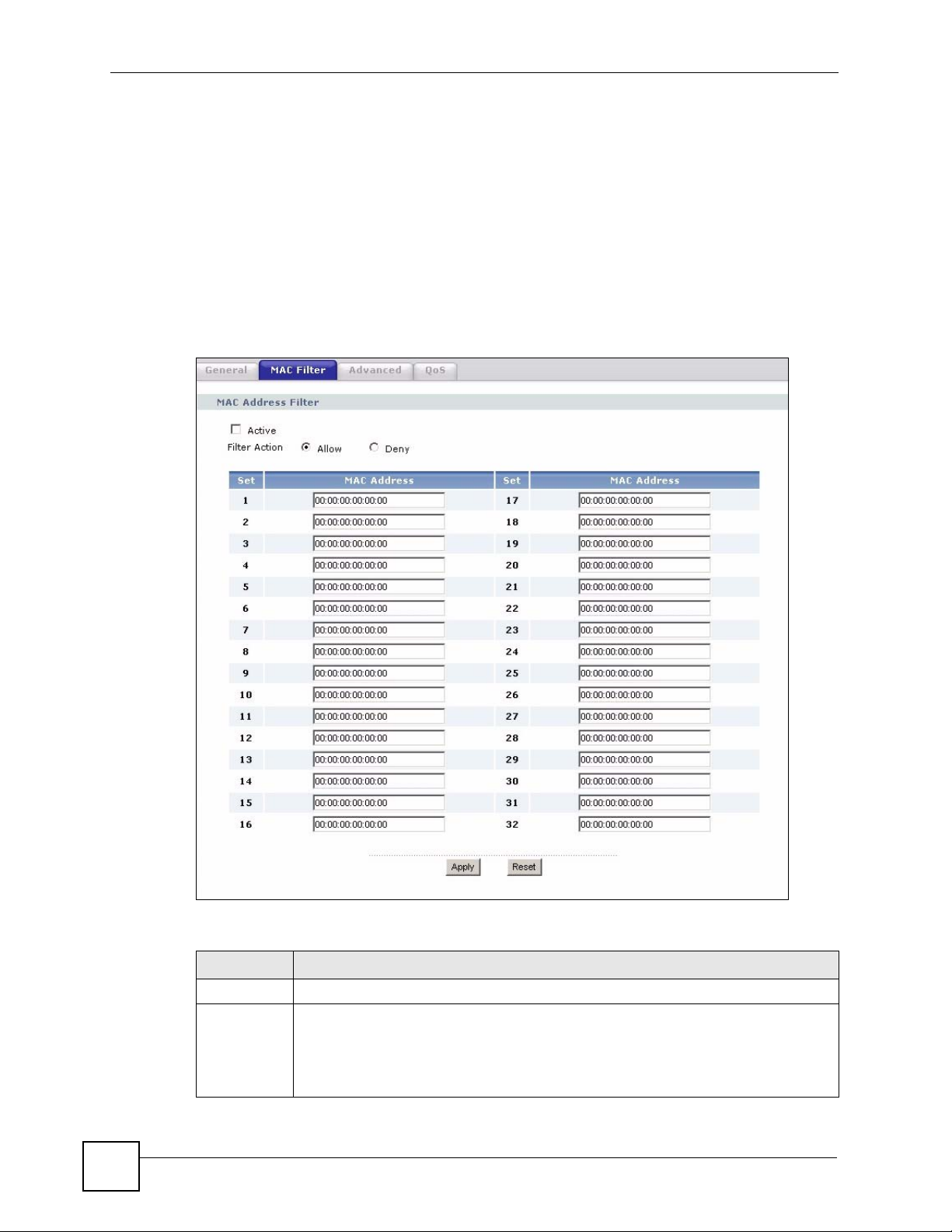
Table 29 Network > Wireless LAN > MAC Filter
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Set This is the index number of the MAC address.
MAC
Address
Apply Click Apply to save your changes back to the NBG318S.
Reset Click Reset to reload the previous configuration for this screen.
Enter the MAC addresses of the wireless station that are allowed or denied access to
the NBG318S in these address fields. Enter the MAC addresses in a valid MAC
address format, that is, six hexadecimal character pairs, for example,
12:34:56:78:9a:bc.
5.7 Wireless LAN Advanced Screen
Click Network > Wireless LAN > Advanced. The screen appears as shown.
Figure 51 Network > Wireless LAN > Advanced
Chapter 5 Wireless LAN
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 30 Network > Wireless LAN > Advanced
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Roaming Configuration
Enable
Roaming
Wireless Advanced Setup
RTS/CTS
Threshold
Fragmentation
Threshold
NBG318S User’s Guide
Select this option if your network environment has multiple APs and you want your
wireless device to be able to access the network as you move between wireless
networks.
Data with its frame size larger than this value will perform the RTS (Request To
Send)/CTS (Clear To Send) handshake.
If the RTS/CTS value is greater than the Fragmentation Threshold value, then the
RTS/CTS handshake will never occur as data frames will be fragmented before they
reach RTS/CTS size.
Enter a value between 0 and 2432.
It is the maximum data fragment size that can be sent. Enter a value between 256
and 2432.
87
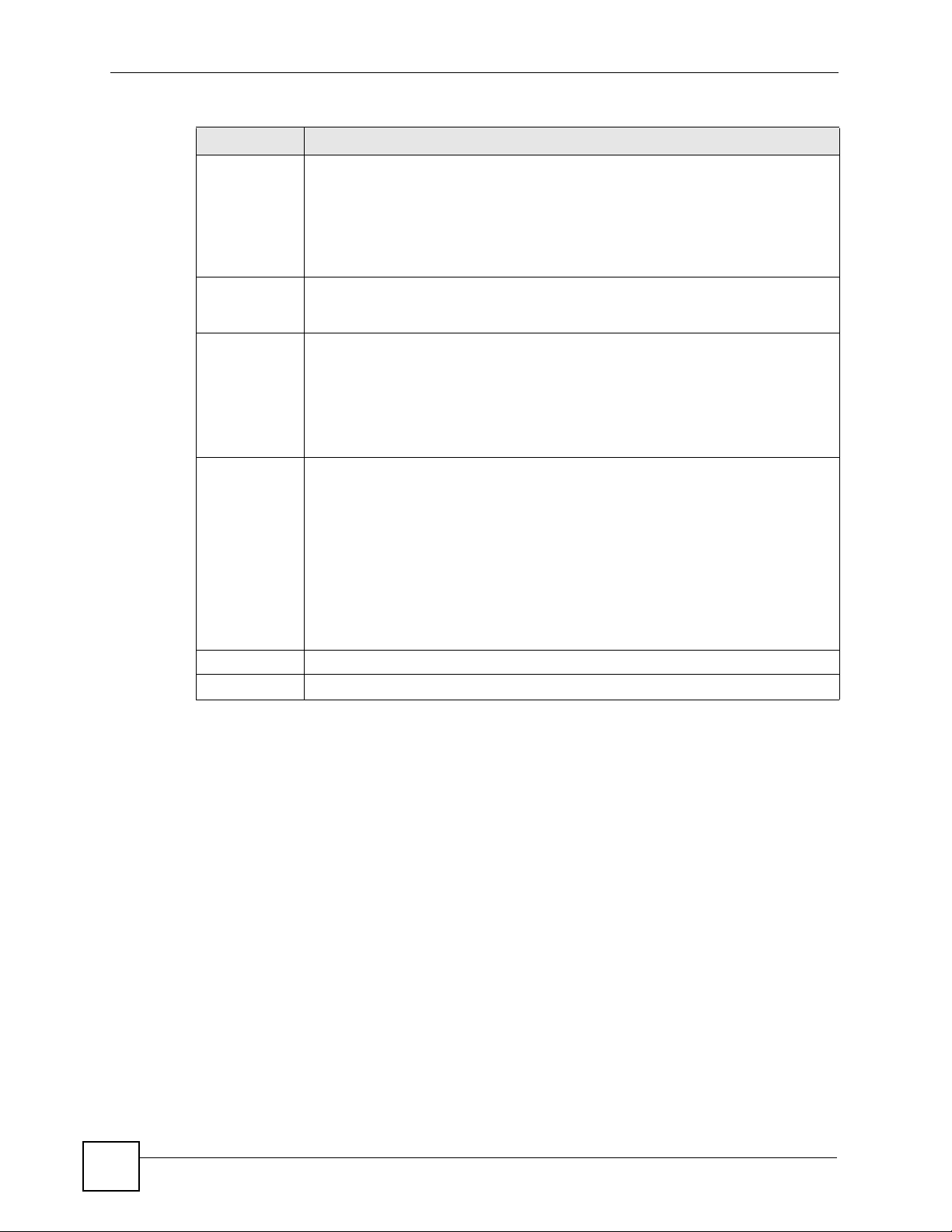
Chapter 5 Wireless LAN
Table 30 Network > Wireless LAN > Advanced
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Enable IntraBSS Traffic
Output Power Set the output power of the NBG318S in this field. If there is a high density of APs
802.11 Mode Select 802.11b to allow only IEEE 802.11b compliant WLAN devices to associate
Super G Mode Use this field to enable or disable the Super G function. Super G mode is available
Apply Click Apply to save your changes back to the NBG318S.
Reset Click Reset to reload the previous configuration for this screen.
A Basic Service Set (BSS) exists when all communications between wireless clients
or between a wireless client and a wired network client go through one access point
(AP).
Intra-BSS traffic is traffic between wireless clients in the BSS. When Intra-BSS is
enabled, wireless client A and B can access the wired network and communicate
with each other. When Intra-BSS is disabled, wireless client A and B can still access
the wired network but cannot communicate with each other.
within an area, decrease the output power of the NBG318S to reduce interference
with other APs.
with the NBG318S.
Select 802.11g to allow only IEEE 802.11g compliant WLAN devices to associate
with the NBG318S.
Select 802.11b/g to allow either IEEE802.11b or IEEE802.11g compliant WLAN
devices to associate with the NBG318S. The transmission rate of your NBG318S
might be reduced.
only if you select 802.11g or 802.11b/g in the 802.11 Mode field.
Super G provides higher data transmission rates than 802.11g.
Select Disabled if your wireless clients do not support Super G.
Select Super G with Dynamic Turbo if some or all of your wireless clients support
Super G with Dynamic Turbo. Dynamic Turbo uses two channels bonded together to
achieve higher transmission rates than 802.11g or Super G without Dynamic Turbo.
Dynamic turbo is on only when all wireless devices on the network support it. The
wireless channel is automatically fixed at 6 if you select this mode.
Select Super G without Turbo if the wireless clients on your network support Super
G but do not support dynamic turbo.
5.8 Quality of Service (QoS) Screen
The QoS screen allows you to automatically give a service (such as e-mail, VoIP or FTP) a
priority level.
Click Network > Wireless LAN > QoS. The following screen appears.
88
NBG318S User’s Guide
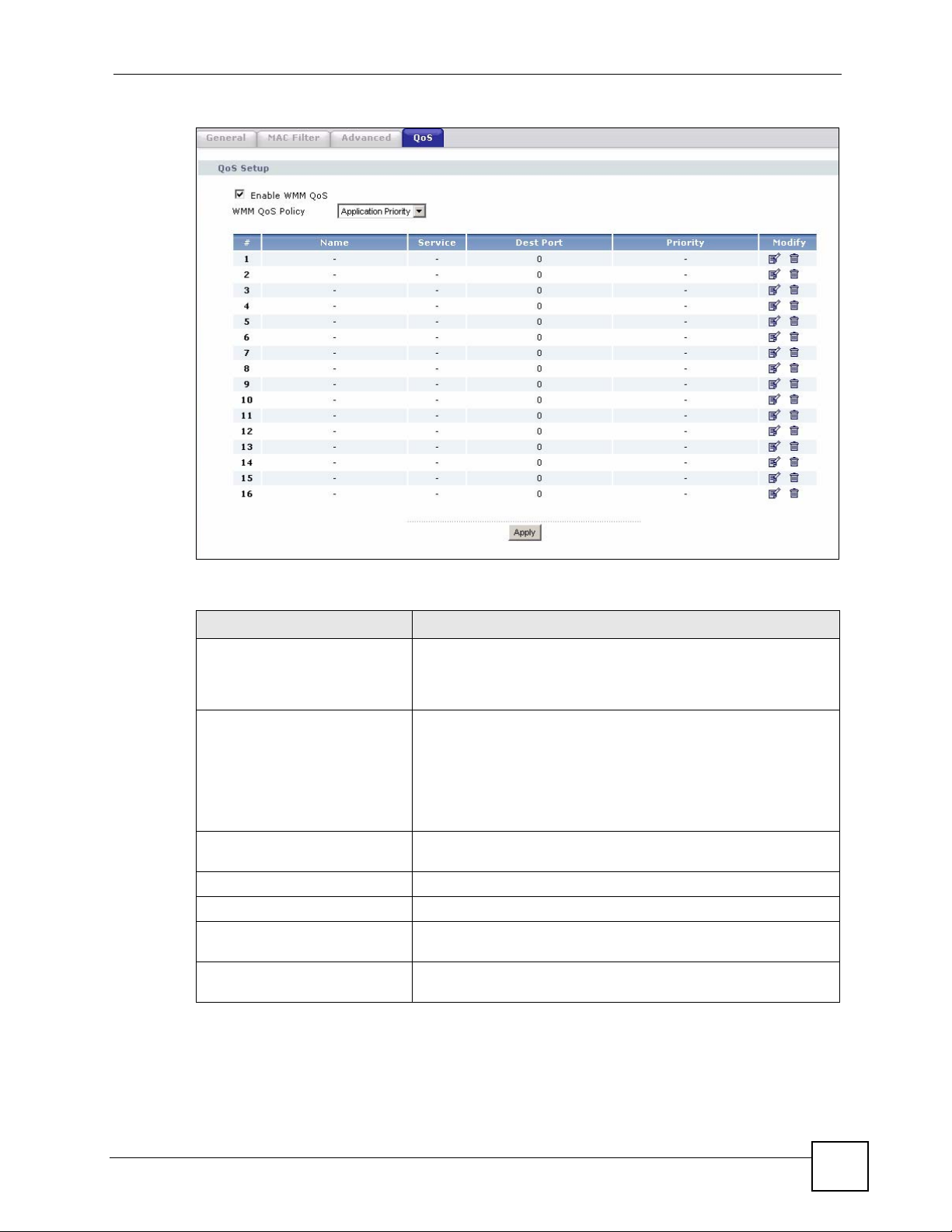
Figure 52 Network > Wireless LAN > QoS
Chapter 5 Wireless LAN
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 31 Network > Wireless LAN > QoS
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Enable WMM QoS Select this to turn on WMM QoS (Wireless MultiMedia Quality of
WMM QoS Policy Select Default to have the NBG318S automatically give a service a
# This is the number of an individual application entry.
Name This field displays a description given to an application entry.
Service This field displays either FTP, WWW, E-mail or a User Defined
Dest Port This field displays the destination port number to which the
Service). The NBG318S assigns priority to packets based on the
802.1q or DSCP information in their headers. If a packet has no
WMM information in its header, it is assigned the default priority.
priority level according to the ToS value in the IP header of packets
it sends. WMM QoS (Wifi MultiMedia Quality of Service) gives high
priority to voice and video, which makes them run more smoothly.
Select Application Priority from the drop-down list box to display a
table of application names, services, ports and priorities to which
you want to apply WMM QoS.
The table appears only if you select Application Priority in WMM
QoS Policy.
service to which you want to apply WMM QoS.
application sends traffic.
NBG318S User’s Guide
89

Chapter 5 Wireless LAN
Table 31 Network > Wireless LAN > QoS (continued)
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Priority This field displays the priority of the application.
Highest - Typically used for voice or video that should be highquality.
High - Typically used for voice or video that can be medium-quality.
Mid - Typically used for applications that do not fit into another
priority. For example, Internet surfing.
Low - Typically used for non-critical “background” applications,
such as large file transfers and print jobs that should not affect
other applications.
Modify Click the Edit icon to open the Application Priority Configuration
Apply Click Apply to save your changes to the NBG318S.
screen. Modify an existing application entry or create a application
entry in the Application Priority Configuration screen.
Click the Remove icon to delete an application entry.
5.8.1 Application Priority Configuration
Use this screen to edit a WMM QoS application entry. Click the edit icon under Modify. The
following screen displays.
Figure 53 Network > Wireless LAN > QoS: Application Priority Configuration
See Appendix F on page 271 for a list of commonly-used services and destination ports. The
following table describes the fields in this screen.
Table 32 Network > Wireless LAN > QoS: Application Priority Configuration
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Application Priority Configuration
Name Type a description of the application priority.
90
NBG318S User’s Guide
Chapter 5 Wireless LAN
Table 32 Network > Wireless LAN > QoS: Application Priority Configuration (continued)
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Service The following is a description of the applications you can prioritize with WMM
QoS. Select a service from the drop-down list box.
• E-Mail
Electronic mail consists of messages sent through a computer network to
specific groups or individuals. Here are some default ports for e-mail:
POP3 - port 110
IMAP - port 143
SMTP - port 25
HTTP - port 80
•FTP
File Transfer Protocol enables fast transfer of files, including large files that it
may not be possible to send via e-mail. FTP uses port number 21.
•WWW
The World Wide Web is an Internet system to distribute graphical, hyperlinked information, based on Hyper Text Transfer Protocol (HTTP) - a client/
server protocol for the World Wide Web. The Web is not synonymous with the
Internet; rather, it is just one service on the Internet. Other services on the
Internet include Internet Relay Chat and Newsgroups. The Web is accessed
through use of a browser.
•User-Defined
User-defined services are user specific services configured using known ports
and applications.
Dest Port This displays the port the selected service uses. Type a port number in the
field provided if you want to use a different port to the default port.
Priority Select a priority from the drop-down list box.
Apply Click Apply to save your changes back to the NBG318S.
Cancel Click Cancel to return to the previous screen.
NBG318S User’s Guide
91

Chapter 5 Wireless LAN
92
NBG318S User’s Guide

CHAPTER 6
WAN
This chapter describes how to configure WAN settings.
6.1 WAN Overview
See the chapter about the connection wizard for more information on the fields in the WAN
screens.
6.2 WAN MAC Address
The MAC address screen allows users to configure the WAN port's MAC address by either
using the factory default or cloning the MAC address from a computer on your LAN. Choose
Factory Default to select the factory assigned default MAC Address.
Otherwise, click Clone the computer's MAC address - IP Address and enter the IP address
of the computer on the LAN whose MAC you are cloning. Once it is successfully configured,
the address will be copied to the rom file (ZyNOS configuration file). It will not change unless
you change the setting or upload a different ROM file.
MAC address prior to hooking up the WAN Port.
6.3 Multicast
Traditionally, IP packets are transmitted in one of either two ways - Unicast (1 sender - 1
recipient) or Broadcast (1 sender - everybody on the network). Multicast delivers IP packets to
a group of hosts on the network - not everybody and not just 1.
IGMP (Internet Group Multicast Protocol) is a network-layer protocol used to establish
membership in a Multicast group - it is not used to carry user data. IGMP version 2 (RFC
2236) is an improvement over version 1 (RFC 1112) but IGMP version 1 is still in wide use. If
you would like to read more detailed information about interoperability between IGMP
version 2 and version 1, please see sections 4 and 5 of RFC 2236. The class D IP address is
used to identify host groups and can be in the range 224.0.0.0 to 239.255.255.255. The address
224.0.0.0 is not assigned to any group and is used by IP multicast computers. The address
224.0.0.1 is used for query messages and is assigned to the permanent group of all IP hosts
(including gateways). All hosts must join the 224.0.0.1 group in order to participate in IGMP.
The address 224.0.0.2 is assigned to the multicast routers group.
It is recommended that you clone the
NBG318S User’s Guide
93
Chapter 6 WAN
The NBG318S supports both IGMP version 1 (IGMP-v1) and IGMP version 2 (IGMP-v2).
At start up, the NBG318S queries all directly connected networks to gather group
membership. After that, the NBG318S periodically updates this information. IP multicasting
can be enabled/disabled on the NBG318S LAN and/or WAN interfaces in the web
configurator (LAN; WAN). Select None to disable IP multicasting on these interfaces.
6.4 Internet Connection
Use this screen to change your NBG318S’s Internet access settings. Click Network > WAN.
The screen differs according to the encapsulation you choose.
6.4.1 Ethernet Encapsulation
This screen displays when you select Ethernet encapsulation.
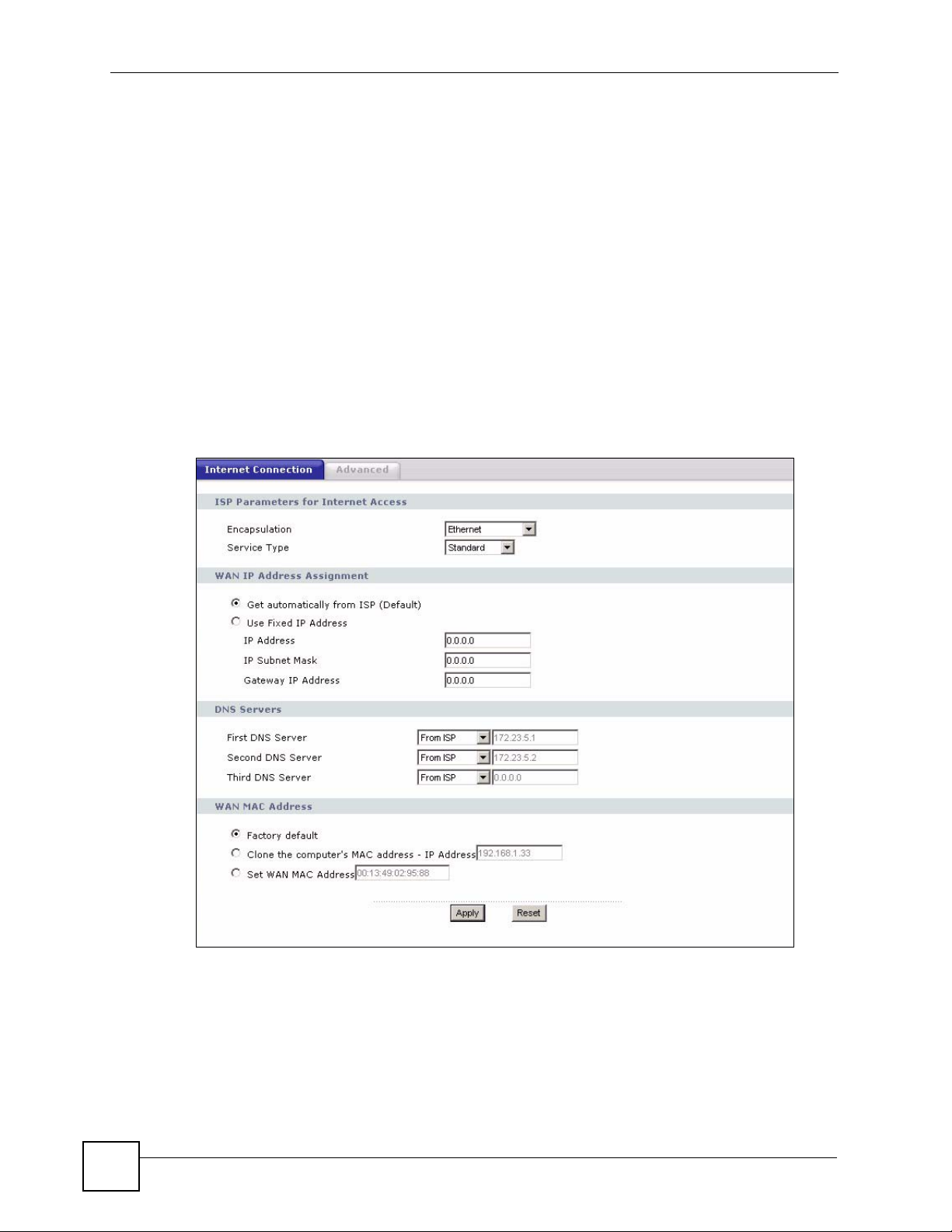
Figure 54 Network > WAN > Internet Connection: Ethernet Encapsulation
94
NBG318S User’s Guide
Chapter 6 WAN
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 33 Network > WAN > Internet Connection: Ethernet Encapsulation
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Encapsulation You must choose the Ethernet option when the WAN port is used as a regular
Service Type Choose from Standard, RR-Telstra (RoadRunner Telstra authentication
User Name Type the user name given to you by your ISP.
Password Type the password associated with the user name above.
Retype to Confirm Type your password again to make sure that you have entered is correctly.
Login Server IP
Address
Login Server
(Telia Login only)
Relogin
Every(min) (Telia
Login only)
WAN IP Address Assignment
Get automatically
from ISP
Use Fixed IP
Address
IP Address Enter your WAN IP address in this field if you selected Use Fixed IP Address.
IP Subnet
Mask
Gateway IP
Address
DNS Servers
First DNS Server
Second DNS
Server
Third DNS Server
WAN MAC
Address
Factory default Select Factory default to use the factory assigned default MAC Address.
Clone the
computer’s MAC
address
Ethernet.
method), RR-Manager (Roadrunner Manager authentication method), RR-
Toshiba (Roadrunner Toshiba authentication method) or Telia Login.
The following fields do not appear with the Standard service type.
Type the authentication server IP address here if your ISP gave you one.
This field is not available for Telia Login.
Type the domain name of the Telia login server, for example login1.telia.com.
The Telia server logs the NBG318S out if the NBG318S does not log in
periodically. Type the number of minutes from 1 to 59 (30 default) for the
NBG318S to wait between logins.
Select this option If your ISP did not assign you a fixed IP address. This is the
default selection.
Select this option If the ISP assigned a fixed IP address.
Enter the IP Subnet Mask in this field.
Enter a Gateway IP Address (if your ISP gave you one) in this field.
Select From ISP if your ISP dynamically assigns DNS server information (and the
NBG318S's WAN IP address). The field to the right displays the (read-only) DNS
server IP address that the ISP assigns.
Select User-Defined if you have the IP address of a DNS server. Enter the DNS
server's IP address in the field to the right. If you chose User-Defined, but leave
the IP address set to 0.0.0.0, User-Defined changes to None after you click
Apply. If you set a second choice to User-Defined, and enter the same IP
address, the second User-Defined changes to None after you click Apply.
Select None if you do not want to configure DNS servers. If you do not configure
a DNS server, you must know the IP address of a computer in order to access it.
The MAC address section allows users to configure the WAN port's MAC address
by either using the NBG318S’s MAC address, copying the MAC address from a
computer on your LAN or manually entering a MAC address.
Select Clone the computer's MAC address - IP Address and enter the IP
address of the computer on the LAN whose MAC you are cloning. Once it is
successfully configured, the address will be copied to the rom file (ZyNOS
configuration file). It will not change unless you change the setting or upload a
different ROM file.
NBG318S User’s Guide
95
Chapter 6 WAN
Table 33 Network > WAN > Internet Connection: Ethernet Encapsulation
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Set WAN MAC
Address
Apply Click Apply to save your changes back to the NBG318S.
Reset Click Reset to begin configuring this screen afresh.
Select this option and enter the MAC address you want to use.
6.4.2 PPPoE Encapsulation
The NBG318S supports PPPoE (Point-to-Point Protocol over Ethernet). PPPoE is an IETF
standard (RFC 2516) specifying how a personal computer (PC) interacts with a broadband
modem (DSL, cable, wireless, etc.) connection. The PPP over Ethernet option is for a dialup connection using PPPoE.
For the service provider, PPPoE offers an access and authentication method that works with
existing access control systems (for example Radius).
One of the benefits of PPPoE is the ability to let you access one of multiple network services,
a function known as dynamic service selection. This enables the service provider to easily
create and offer new IP services for individuals.
Operationally, PPPoE saves significant effort for both you and the ISP or carrier, as it requires
no specific configuration of the broadband modem at the customer site.
By implementing PPPoE directly on the NBG318S (rather than individual computers), the
computers on the LAN do not need PPPoE software installed, since the NBG318S does that
part of the task. Furthermore, with NAT, all of the LANs’ computers will have access.
This screen displays when you select PPPoE encapsulation.
96
NBG318S User’s Guide

Figure 55 Network > WAN > Internet Connection: PPPoE Encapsulation
Chapter 6 WAN
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 34 Network > WAN > Internet Connection: PPPoE Encapsulation
LABEL DESCRIPTION
ISP Parameters for Internet Access
Encapsulation The PPP over Ethernet choice is for a dial-up connection using PPPoE. The
Service Name Type the PPPoE service name provided to you. PPPoE uses a service name to
User Name Type the user name given to you by your ISP.
Password Type the password associated with the user name above.
NBG318S User’s Guide
NBG318S supports PPPoE (Point-to-Point Protocol over Ethernet). PPPoE is an
IETF Draft standard (RFC 2516) specifying how a personal computer (PC)
interacts with a broadband modem (i.e. xDSL, cable, wireless, etc.) connection.
Operationally, PPPoE saves significant effort for both the end user and ISP/carrier,
as it requires no specific configuration of the broadband modem at the customer
site. By implementing PPPoE directly on the router rather than individual
computers, the computers on the LAN do not need PPPoE software installed, since
the router does that part of the task. Further, with NAT, all of the LAN's computers
will have access.
identify and reach the PPPoE server.
97

Chapter 6 WAN
Table 34 Network > WAN > Internet Connection: PPPoE Encapsulation
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Retype to
Confirm
Nailed-Up
Connection
Idle Timeout This value specifies the time in seconds that elapses before the router
WAN IP Address Assignment
Get automatically
from ISP
Use Fixed IP
Address
DNS Servers
First DNS Server
Second DNS
Server
Third DNS Server
WAN MAC
Address
Factory default Select Factory default to use the factory assigned default MAC Address.
Clone the
computer’s MAC
address
Set WAN MAC
Address
Apply Click Apply to save your changes back to the NBG318S.
Reset Click Reset to begin configuring this screen afresh.
My WAN IP
Address
Remote IP
Address
Remote IP
Subnet Mask
Type your password again to make sure that you have entered is correctly.
Select Nailed-Up Connection if you do not want the connection to time out.
automatically disconnects from the PPPoE server.
Select this option If your ISP did not assign you a fixed IP address. This is the
default selection.
Select this option If the ISP assigned a fixed IP address.
Enter your WAN IP address in this field if you selected Use Fixed IP Address.
Enter the remote IP address (if your ISP gave you one) in this field.
Enter the remote IP subnet mask in this field.
Select From ISP if your ISP dynamically assigns DNS server information (and the
NBG318S's WAN IP address). The field to the right displays the (read-only) DNS
server IP address that the ISP assigns.
Select User-Defined if you have the IP address of a DNS server. Enter the DNS
server's IP address in the field to the right. If you chose User-Defined, but leave
the IP address set to 0.0.0.0, User-Defined changes to None after you click
Apply. If you set a second choice to User-Defined, and enter the same IP
address, the second User-Defined changes to None after you click Apply.
Select None if you do not want to configure DNS servers. If you do not configure a
DNS server, you must know the IP address of a computer in order to access it.
The MAC address section allows users to configure the WAN port's MAC address
by using the NBG318S’s MAC address, copying the MAC address from a computer
on your LAN or manually entering a MAC address.
Select Clone the computer's MAC address - IP Address and enter the IP
address of the computer on the LAN whose MAC you are cloning. Once it is
successfully configured, the address will be copied to the rom file (ZyNOS
configuration file). It will not change unless you change the setting or upload a
different ROM file.
Select this option and enter the MAC address you want to use.
6.4.3 PPTP Encapsulation
Point-to-Point Tunneling Protocol (PPTP) is a network protocol that enables secure transfer of
data from a remote client to a private server, creating a Virtual Private Network (VPN) using
TCP/IP-based networks.
98
NBG318S User’s Guide
Chapter 6 WAN
PPTP supports on-demand, multi-protocol and virtual private networking over public
networks, such as the Internet.
This screen displays when you select PPTP encapsulation.
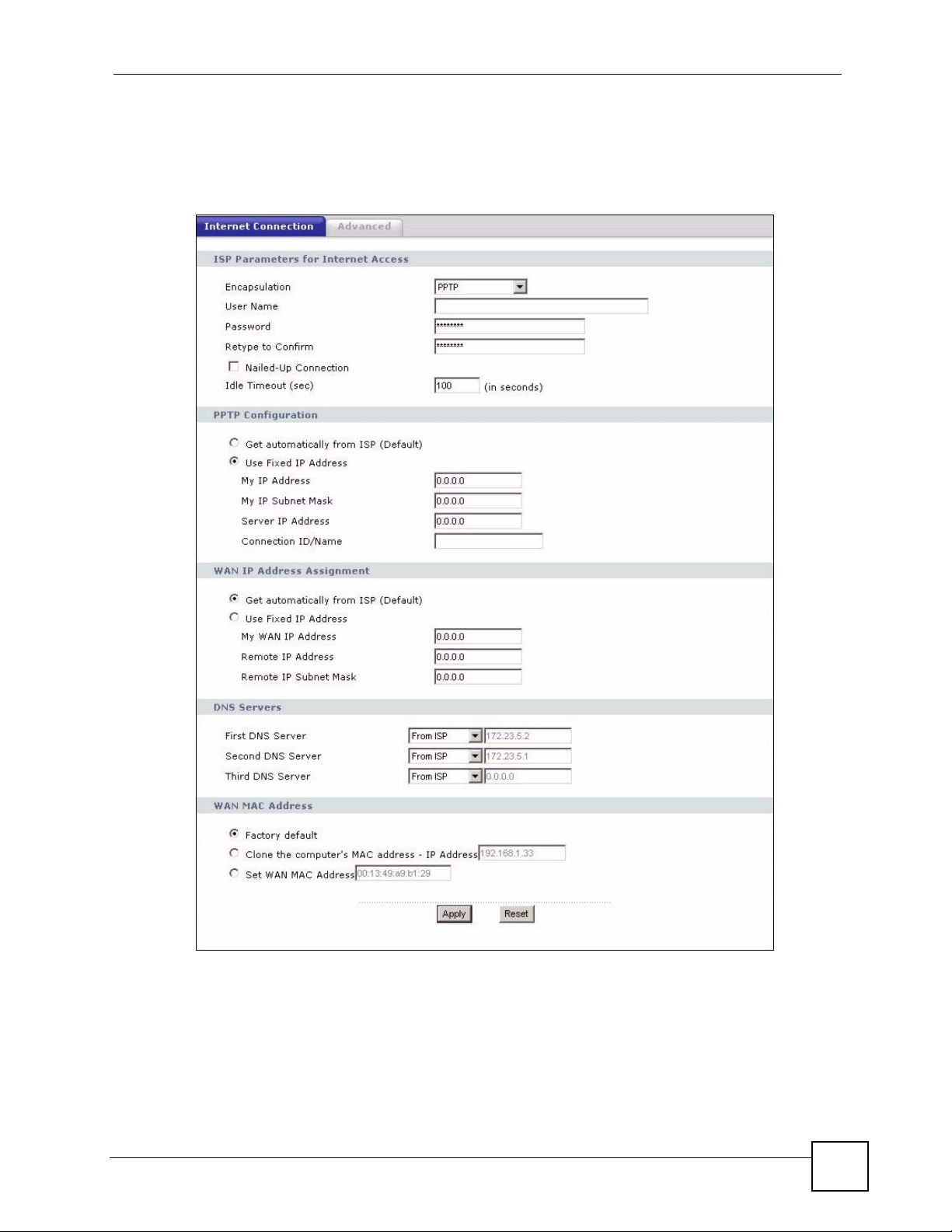
Figure 56 Network > WAN > Internet Connection: PPTP Encapsulation
NBG318S User’s Guide
99
Chapter 6 WAN
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 35 Network > WAN > Internet Connection: PPTP Encapsulation
LABEL DESCRIPTION
ISP Parameters for Internet Access
Encapsulation Point-to-Point Tunneling Protocol (PPTP) is a network protocol that enables
User Name Type the user name given to you by your ISP.
Password Type the password associated with the User Name above.
Retype to Confirm Type your password again to make sure that you have entered is correctly.
Nailed-up Connection Select Nailed-Up Connection if you do not want the connection to time out.
Idle Timeout This value specifies the time in seconds that elapses before the NBG318S
PPTP Configuration
Get automatically from
ISP
Use Fixed IP Address Select this option If the ISP assigned a fixed IP address.
WAN IP Address Assignment
Get automatically from
ISP
Use Fixed IP Address Select this option If the ISP assigned a fixed IP address.
DNS Servers
secure transfer of data from a remote client to a private server, creating a
Virtual Private Network (VPN) using TCP/IP-based networks. PPTP supports
on-demand, multi-protocol, and virtual private networking over public
networks, such as the Internet. The NBG318S supports only one PPTP server
connection at any given time.
To configure a PPTP client, you must configure the User Name and
Password fields for a PPP connection and the PPTP parameters for a PPTP
connection.
automatically disconnects from the PPTP server.
Select this option If your ISP did not assign you a fixed IP address. This is the
default selection.
My IP Address Type the (static) IP address assigned to you by your ISP.
My IP Subnet
Mask
Server IP Address Type the IP address of the PPTP server.
Connection ID/
Name
My WAN IP
Address
Remote IP
Address
Remote IP Subnet
Mask
Your NBG318S will automatically calculate the subnet mask based on the IP
address that you assign. Unless you are implementing subnetting, use the
subnet mask computed by the NBG318S.
Type your identification name for the PPTP server.
Select this option If your ISP did not assign you a fixed IP address. This is the
default selection.
Enter your WAN IP address in this field if you selected Use Fixed IP
Address.
Enter the remote IP address (if your ISP gave you one) in this field.
Enter the remote IP subnet mask in this field.
100
NBG318S User’s Guide
Chapter 6 WAN
Table 35 Network > WAN > Internet Connection: PPTP Encapsulation
LABEL DESCRIPTION
First DNS Server
Second DNS Server
Third DNS Server
WAN MAC Address The MAC address section allows users to configure the WAN port's MAC
Factory default Select Factory default to use the factory assigned default MAC Address.
Clone the computer’s
MAC address
Set WAN MAC
Address
Apply Click Apply to save your changes back to the NBG318S.
Reset Click Reset to begin configuring this screen afresh.
Select From ISP if your ISP dynamically assigns DNS server information (and
the NBG318S's WAN IP address). The field to the right displays the (readonly) DNS server IP address that the ISP assigns.
Select User-Defined if you have the IP address of a DNS server. Enter the
DNS server's IP address in the field to the right. If you chose User-Defined,
but leave the IP address set to 0.0.0.0, User-Defined changes to None after
you click Apply. If you set a second choice to User-Defined, and enter the
same IP address, the second User-Defined changes to None after you click
Apply.
Select None if you do not want to configure DNS servers. If you do not
configure a DNS server, you must know the IP address of a computer in order
to access it.
address by either using the NBG318S’s MAC address, copying the MAC
address from a computer on your LAN or manually entering a MAC address.
Select Clone the computer's MAC address - IP Address and enter the IP
address of the computer on the LAN whose MAC you are cloning. Once it is
successfully configured, the address will be copied to the rom file (ZyNOS
configuration file). It will not change unless you change the setting or upload a
different ROM file.
Select this option and enter the MAC address you want to use.
6.5 Advanced WAN Screen
To change your NBG318S’s advanced WAN settings, click Network > WAN > Advanced.
The screen appears as shown.
Figure 57 Network > WAN > Advanced
NBG318S User’s Guide
101
Chapter 6 WAN
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 36 WAN > Advanced
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Multicast Setup
Multicast Select IGMP V-1, IGMP V-2 or None. IGMP (Internet Group Multicast
Windows Networking (NetBIOS over TCP/IP): NetBIOS (Network Basic Input/Output System) are TCP
or UDP broadcast packets that enable a computer to connect to and communicate with a LAN. For
some dial-up services such as PPPoE or PPTP, NetBIOS packets cause unwanted calls. However it
may sometimes be necessary to allow NetBIOS packets to pass through to the WAN in order to find a
computer on the WAN.
Allow between LAN
and WAN
Allow Trigger Dial Select this option to allow NetBIOS packets to initiate calls.
Apply Click Apply to save your changes back to the NBG318S.
Reset Click Reset to begin configuring this screen afresh.
Protocol) is a network-layer protocol used to establish membership in a
Multicast group - it is not used to carry user data. IGMP version 2 (RFC 2236)
is an improvement over version 1 (RFC 1112) but IGMP version 1 is still in
wide use. If you would like to read more detailed information about
interoperability between IGMP version 2 and version 1, please see sections 4
and 5 of RFC 2236.
Select this check box to forward NetBIOS packets from the LAN to the WAN
and from the WAN to the LAN. If your firewall is enabled with the default
policy set to block WAN to LAN traffic, you also need to enable the default
WAN to LAN firewall rule that forwards NetBIOS traffic.
Clear this check box to block all NetBIOS packets going from the LAN to the
WAN and from the WAN to the LAN.
102
NBG318S User’s Guide

CHAPTER 7
LAN
This chapter describes how to configure LAN settings.
7.1 LAN Overview
A Local Area Network (LAN) is a shared communication system to which many computers
are attached. A LAN is a computer network limited to the immediate area, usually the same
building or floor of a building. The LAN screens can help you configure a LAN DHCP server,
manage IP addresses, and partition your physical network into logical networks.
7.1.1 IP Pool Setup
The NBG318S is pre-configured with a pool of 32 IP addresses starting from 192.168.1.33 to
192.168.1.64. This configuration leaves 31 IP addresses (excluding the NBG318S itself) in the
lower range (192.168.1.2 to 192.168.1.32) for other server computers, for instance, servers for
mail, FTP, TFTP, web, etc., that you may have.
7.1.2 System DNS Servers
Refer to the IP address and subnet mask section in the Connection Wizard chapter.
7.2 LAN TCP/IP
The NBG318S has built-in DHCP server capability that assigns IP addresses and DNS servers
to systems that support DHCP client capability.
7.2.1 Factory LAN Defaults
The LAN parameters of the NBG318S are preset in the factory with the following values:
• IP address of 192.168.1.1 with subnet mask of 255.255.255.0 (24 bits)
• DHCP server enabled with 32 client IP addresses starting from 192.168.1.33.
These parameters should work for the majority of installations. If your ISP gives you explicit
DNS server address(es), read the embedded web configurator help regarding what fields need
to be configured.
NBG318S User’s Guide
103

Chapter 7 LAN
7.2.2 IP Address and Subnet Mask
Refer to the IP address and subnet mask section in the Connection Wizard chapter for this
information.
7.2.3 Multicast
Traditionally, IP packets are transmitted in one of either two ways - Unicast (1 sender - 1
recipient) or Broadcast (1 sender - everybody on the network). Multicast delivers IP packets to
a group of hosts on the network - not everybody and not just 1.
IGMP (Internet Group Multicast Protocol) is a network-layer protocol used to establish
membership in a Multicast group - it is not used to carry user data. IGMP version 2 (RFC
2236) is an improvement over version 1 (RFC 1112) but IGMP version 1 is still in wide use. If
you would like to read more detailed information about interoperability between IGMP
version 2 and version 1, please see sections 4 and 5 of RFC 2236. The class D IP address is
used to identify host groups and can be in the range 224.0.0.0 to 239.255.255.255. The address
224.0.0.0 is not assigned to any group and is used by IP multicast computers. The address
224.0.0.1 is used for query messages and is assigned to the permanent group of all IP hosts
(including gateways). All hosts must join the 224.0.0.1 group in order to participate in IGMP.
The address 224.0.0.2 is assigned to the multicast routers group.
The NBG318S supports both IGMP version 1 (IGMP-v1) and IGMP version 2 (IGMP-v2).
At start up, the NBG318S queries all directly connected networks to gather group
membership. After that, the NBG318S periodically updates this information. IP multicasting
can be enabled/disabled on the NBG318S LAN and/or WAN interfaces in the web
configurator (LAN; WAN). Select None to disable IP multicasting on these interfaces.
7.2.4 Any IP
Traditionally, you must set the IP addresses and the subnet masks of a computer and the
NBG318S to be in the same subnet to allow the computer to access the Internet (through the
NBG318S). In cases where your computer is required to use a static IP address in another
network, you may need to manually configure the network settings of the computer every time
you want to access the Internet via the NBG318S.
With the Any IP feature and NAT enabled, the NBG318S allows a computer to access the
Internet without changing the network settings (such as IP address and subnet mask) of the
computer, when the IP addresses of the computer and the NBG318S are not in the same
subnet. Whether a computer is set to use a dynamic or static (fixed) IP address, you can simply
connect the computer to the NBG318S and access the Internet.
The following figure depicts a scenario where a computer is set to use a static private IP
address in the corporate environment. In a residential house where a NBG318S is installed,
you can still use the computer to access the Internet without changing the network settings,
even when the IP addresses of the computer and the NBG318S are not in the same subnet.
104
NBG318S User’s Guide
 Loading...
Loading...