Snorkel TB66J User Manual

OPERATOR’S
MANUAL
Part Number 0083740
May 2014
Models TB66J/TB66JRT
Replaces 0083740 March 2014

The aerial platform is not electrically insulated. Death or serious injury will result from contact with, or inadequate clearance from, an energized conductor.
Do not go closer than the minimum safe approach distance as defined by the Minimum Safe Approach Distance section in Chapter 3 – Safety.
Regard all conductors as energized.
Allow for electrical wire sag and aerial platform sway.
If the platform, booms, or any part of the aerial platform contacts a high-voltage electrical conductor, the entire machine can become electrically charged.
If that happens, remain on the machine and do not contact any other structure or object. This includes the ground, adjacent buildings, poles, and any other objects that are not part of the aerial platform.
Such contact could make your body a conductor to the other object, creating an electrical shock hazard resulting in death or serious injury.
If an aerial platform is in contact with an energized conductor the platform operator must warn ground personnel in the vicinity to stay away. Their bodies can conduct electricity creating an electrical shock hazard resulting in death or serious injury.
Do not approach or leave the aerial platform until the electricity has been turned off.
Do not attempt to operate the lower controls when the platform, booms, or any part of the aerial platform is in contact with a high-voltage electrical conductor or if there is an immediate danger of such contact.
Personnel on or near an aerial platform must be continuously aware of electrical hazards, recognizing that death or serious injury can result from contact with an energized conductor.
California
Proposition 65 Warning
Battery posts, terminals and related accessories contain lead and lead components, a chemical known to the State of California to cause cancer and birth defects or other reproductive harm. Wash hands after handling.
California
Proposition 65 Warning
Diesel and gasoline engine exhaust and some of its constituents are known by the State of California to cause cancer, birth defects and other reproductive harm.

Table of Contents
Electrical Danger............................. |
Inside Front Cover |
|
California Proposition 65................. |
Inside Front Cover |
|
Chapter 1 – Introduction |
|
|
Aerial Platform Features........................................... |
|
1 |
Options...................................................................... |
|
1 |
Operator’s Manual.................................................... |
|
1 |
Safety Alerts.............................................................. |
|
1 |
Operation.................................................................. |
|
2 |
Maintenance.............................................................. |
|
2 |
Manual of Responsibilities........................................ |
|
2 |
Additional Information............................................... |
|
2 |
Chapter 3 – Specifications |
|
|
Component Identification.......................................... |
|
3 |
Working Envelope..................................................... |
|
4 |
General Specifications.............................................. |
|
5 |
Engine Specifications................................................ |
|
6 |
Engine Oil Viscosity.................................................. |
|
8 |
Chapter 3 – Safety |
|
|
Electrocution Hazards............................................. |
|
11 |
Minimum Safe Approach Distance.......................... |
|
11 |
Prestart Inspection.................................................. |
|
12 |
Work Place Inspection and Practices...................... |
12 |
|
Operation................................................................ |
|
12 |
Tip-Over and Falling Hazards................................. |
|
13 |
Electrical System..................................................... |
|
13 |
Hydraulic System.................................................... |
|
13 |
Engine and Fuel Handling Precautions................... |
14 |
|
Placards and Decals............................................... |
|
14 |
Chapter 4 – Safety Devices |
|
|
Emergency Stop Controls....................................... |
|
15 |
Emergency Power System...................................... |
|
15 |
Emergency Lowering Knob..................................... |
|
16 |
Ground Operation Switch........................................ |
|
16 |
Platform Foot Switch............................................... |
|
16 |
Guardrails................................................................ |
|
16 |
Lanyard Anchors..................................................... |
|
16 |
Ground Fault Circuit Interrupter.............................. |
|
17 |
Tilt Alarm................................................................. |
|
17 |
Engine Protection Systems..................................... |
|
17 |
High Engine Temperature Alarm.......................... |
|
17 |
Low Oil Pressure Alarm....................................... |
|
17 |
Horn........................................................................ |
|
18 |
All Motion Alarm...................................................... |
|
18 |
Flashing Light.......................................................... |
|
18 |
Driving Lights.......................................................... |
|
18 |
Platform Work Lights............................................... |
|
18 |
Bump Guard System............................................... |
|
18 |
Chapter 5 – Gauges and Displays |
|
Hour Meter.............................................................. |
19 |
Engine Temperature Gauge.................................... |
19 |
Ammeter – Cummins, Deutz and Ford Engines...... |
19 |
Voltmeter – General Motors Engines...................... |
19 |
Engine Air Filter Gauge........................................... |
19 |
Fuel Gauge............................................................. |
19 |
Engine Oil................................................................ |
20 |
Hydraulic Fluid Filter Gauge.................................... |
20 |
Fluid Level and Temperature Gauge....................... |
20 |
Chapter 6 – Controls |
|
Battery Disconnect Switch...................................... |
21 |
Lower Controls........................................................ |
21 |
Emergency Stop Button....................................... |
21 |
Control Selector Switch........................................ |
21 |
Start Switch.......................................................... |
21 |
Ground Operation Switch..................................... |
22 |
Rotation Switch.................................................... |
22 |
Boom Elevation Switch........................................ |
22 |
Boom Extend/Retract Switch............................... |
22 |
Jib Articulation Switch.......................................... |
22 |
Boom Speed Knob .............................................. |
23 |
Platform Level Switch.......................................... |
23 |
Platform Rotation Switch...................................... |
23 |
Engine/Emergency Power Switch........................ |
23 |
Throttle Switch..................................................... |
23 |
Fuel Switch.......................................................... |
23 |
Hydraulic System Warm-up Switch...................... |
23 |
Circuit Breaker Reset Buttons................................. |
24 |
Upper Controls........................................................ |
24 |
Start Switch.......................................................... |
25 |
Emergency Stop Button....................................... |
25 |
Drive Joystick....................................................... |
25 |
Drive Range Switch............................................. |
26 |
Boom Joystick...................................................... |
26 |
Boom Extension Switch....................................... |
26 |
Jib Articulation Switch.......................................... |
26 |
Platform Level Switch.......................................... |
26 |
Platform Rotation Switch...................................... |
26 |
Boom Speed Knob............................................... |
26 |
Throttle Switch..................................................... |
26 |
Engine/Emergency Power Switch........................ |
27 |
Platform Foot Switch............................................... |
27 |
Machine/Generator Switch...................................... |
27 |
Hydraulic System Warm-up Switch......................... |
27 |
Driving and Platform Work Lights............................ |
28 |
Horn Button............................................................. |
28 |
TB66J – 0083740

Table of Contents
Chapter 7 – Prestart Inspection |
|
Operator’s Manual.................................................. |
29 |
Engine..................................................................... |
29 |
Oil Level............................................................... |
29 |
Coolant................................................................. |
29 |
Radiator............................................................... |
30 |
Fuel Tank............................................................. |
30 |
Fuel Line.............................................................. |
31 |
Air Filter................................................................ |
31 |
Charging System ................................................ |
31 |
Cold Weather Start Kit ........................................ |
31 |
Electrical System..................................................... |
32 |
Battery Fluid Level............................................... |
32 |
Battery Terminals................................................. |
32 |
Cables and Wiring Harness.................................... |
32 |
Hydraulic System.................................................... |
32 |
Fluid Level............................................................ |
32 |
Fluid Filter............................................................ |
33 |
Hoses, Tubes, and Fittings.................................. |
33 |
Tires and Wheels.................................................... |
33 |
Lower Control Station.............................................. |
34 |
Operating Controls............................................... |
34 |
Emergency Stop.................................................. |
34 |
Emergency Power................................................ |
34 |
Emergency Lowering.............................................. |
34 |
Level Sensor........................................................... |
35 |
Flashing Light.......................................................... |
35 |
Sandblast Protection Kit.......................................... |
36 |
Structures................................................................ |
36 |
Weldments........................................................... |
36 |
Slide Pads............................................................ |
36 |
Wire Ropes.......................................................... |
36 |
Fasteners............................................................. |
37 |
Upper Control Station.............................................. |
37 |
Guardrail System................................................. |
37 |
Lanyard Anchors.................................................. |
38 |
Operating Controls............................................... |
38 |
Emergency Stop.................................................. |
38 |
Emergency Power................................................ |
38 |
Horn..................................................................... |
39 |
Electrical Power Outlet......................................... |
39 |
All Motion Alarm...................................................... |
39 |
Air Line to Platform.................................................. |
39 |
Driving and Platform Work Lights............................ |
39 |
Tow Kit..................................................................... |
40 |
Platform Glazier Package....................................... |
40 |
Platform Control Cover............................................ |
40 |
Placards and Decals............................................... |
40 |
Prestart Inspection Checklist................................... |
47 |
Chapter 8 – Operation |
|
Cold Weather Start Up............................................ |
49 |
Engine Cold Weather Start Kit................................ |
49 |
Cummins, Kubota and Ford – Block Heater........ |
49 |
Cummins – Ether Injection................................... |
49 |
Deutz – Manifold Preheater................................. |
50 |
GM – Radiator Hose In-Line................................ |
50 |
Hydraulic System Cold Weather Warm-Up............. |
50 |
Hydraulic System Warm-up Switch...................... |
50 |
Manually Warming The Hydraulic System........... |
50 |
Preparing for Operation........................................... |
50 |
Lower Controls........................................................ |
50 |
Upper Controls........................................................ |
51 |
Boom Operation................................................... |
52 |
Driving and Steering............................................ |
52 |
Drive Speeds....................................................... |
53 |
Motion Warning Alarm.......................................... |
53 |
Four Wheel Drive.................................................... |
53 |
Gradeability............................................................. |
53 |
Percent vs. Degree of Slope................................ |
54 |
Driving on a Slope................................................ |
54 |
Calculating Percent Grade................................... |
54 |
Machine Gradeability........................................... |
55 |
All Motion Alarm...................................................... |
55 |
Four Wheel Drive.................................................... |
55 |
Electrical Power Outlet............................................ |
55 |
AC Generator.......................................................... |
55 |
Dual Fuel................................................................. |
56 |
Air Line.................................................................... |
56 |
Driving Lights.......................................................... |
56 |
Platform Work Lights............................................... |
56 |
Platform Glazier Package....................................... |
57 |
Platform Capacity................................................. |
57 |
Bump Guard System............................................... |
57 |
Chapter 9 – Stowing and Transporting |
|
Stowing................................................................... |
59 |
Transporting............................................................ |
59 |
Driving.................................................................. |
59 |
Winching.............................................................. |
60 |
Hoisting................................................................ |
60 |
Securing for Transport......................................... |
61 |
Chapter 10 – Emergency Operation |
|
Emergency Power System...................................... |
63 |
Lower Controls..................................................... |
63 |
Upper Controls..................................................... |
63 |
Emergency Lowering.............................................. |
64 |
Towing..................................................................... |
65 |
Chapter 11 – Troubleshooting |
|
Troubleshooting Chart............................................. |
67 |
Appendix A – Glossary |
|
Limited Warranty |
|
TB66J – 0083740

Chapter 1 – Introduction
Aerial Platform Features
The aerial platform is a boom-supported elevating work platform used to raise personnel, tools and materials to the workstation. The booms are raised and lowered with hydraulic cylinders. Hydraulic motors on the drive wheels provide power to move the aerial platform.
The standard machine includes the following features.
Proportional boom lift, swing and drive control
180 degree hydraulic platform rotation
360 degree continuous turntable rotation
6′ articulating jib boom
39″ x 96″ (99 cm x 243 cm) steel
500 lb (227 kg) capacity platform
Platform gravity gate
Drivable at full height
Two safety lanyard attachments
Manual lowering valve at chassis
Hydraulic oil level and temperature gauges
Tie-down/lifting lugs
Battery operated emergency power system
Engine anti-restart
High engine temperature shut down
Low oil pressure shut down
Tilt alarm
Hour meter
Ammeter – Cummins, Deutz, Ford engines
Voltmeter – GM engine
Coolant temperature gauge
Spark arrestor muffler – GM engines
Foam filled tires
Four wheel drive
Five year limited warranty
The machine may be powered with one of the following engines.
Cummins B3.3 – Diesel
Deutz F4L-1011F – Diesel
Deutz F4L-2011F – Diesel
Kubota V2403-M-T – Diesel
Ford LRG 425 – Gasoline, LPG or dual fuel
Ford LRG 423 – Gasoline, LPG or dual fuel
General Motors 2.4L – Gasoline, LPG or dual fuel
The aerial platform has been manufactured to conform to all applicable requirement of the following organizations.
Occupational Safety and Health Administration
(OSHA)
American National Standards Institute (ANSI)
Options
The following options may be provided on the machine.
Lower control cover
Platform work lights – flood lights
Flashing light
Driving lights – two headlights and two rear lights
Platform swinging gate
Side entry gravity gate
Sandblast protection kit
Cold weather start kit
Hydraulic system cold weather warm-up kit
AC generator – hydraulic powered, 110 V, 2000 W
AC generator – hydraulic powered, 220 V, 50Hz
All motion alarm
Airline to platform
Tow kit
30″ x 96 (76 cm x 244 cm) aluminum 500 lb (272 kg) capacity platform
30″ x 96″ (76 cm x 244 cm) steel 500 lb (227 kg) capacity platform
30″ x 60″ (76 cm x 152 cm) aluminum 600 lb (272 kg) capacity platform
Horn
Two wheel drive
Platform glazier package
Platform welder package
Spark arrestor muffler – Deutz engines
Dual fuel with 20 gallon gasoline tank
Tilt warning light
Flotation tires
Highway tread tires
Non-marking tires
Canadian Standards Association (CSA)
Operator’s Manual
This manual provides information for safe and proper operation of the aerial platform. Some information in this manual refers to options that may or may not be on your machine. Read and understand the information in this Operator’s Manual before operating the aerial platform on the job.
Additional copies of this manual may be ordered from Snorkel. Supply the model and manual part number from the front cover to assure that the correct manual will be supplied.
All information in this manual is based on the latest product information at the time of publication. Snorkel reserves the right to make product changes at any time without obligation.
Safety Alerts
A safety alert symbol is used throughout this manual to indicate danger, warning and caution instructions. Follow these instructions to reduce the likelihood of personal injury and property damage. The terms danger, warning
TB66J – 0083740 |
1 |

Chapter 1 – Introduction
and caution indicate varying degrees of personal injury or property damage that can result if the instruction is not followed.
Danger
Indicates an imminently hazardous situation which, if not avoided, will result in death or serious injury. This signal word is to be used in the most extreme situations.
Warning
Indicates a potentially hazardous situation which, if not avoided, could result in death or serious injury.
Caution
Indicates a potentially hazardous situation which, if notavoided,mayresultinminorormoderateinjury.It may also be used to alert against unsafe practices.
Notes
Notes are used to provide special information or helpful hints to assist in aerial platform operation, but do not indicate a hazardous situation.
Operation
The aerial platform has built-in safety features and has been factory tested for compliance with Snorkel specifications and industry standards. However, any personnel lifting aerial platform can be potentially dangerous in the hands of untrained or careless operators.
Warning
The potential for an accident increases when the aerial platform is operated by personnel who are not trained and authorized. Death or serious injury can result from such accidents. Read and understand the information in this manual and on the placards and decals on the machine before operating the aerial platform on the job.
Training is essential and must be performed by a qualified person.
Becomeproficientinknowledgeandactualoperation before using the aerial platform on the job.
The operator must be trained and authorized to perform any functions of the aerial platform.
Operation of the aerial platform must be within the scope of the machine specifications.
The operator bears ultimate responsibility for following all manufacturer’s instructions and warnings, regulations and safety rules of their employer and/or any state or federal law.
Maintenance
Every person who maintains, inspects, tests, or repairs the aerial platform must be qualified to do so. Following the daily prestart inspection in this Operator’s Manual will help keep the aerial platform in optimum working condition. Other maintenance functions must be performed by maintenance personnel who are qualified to work on the aerial platform.
Caution
Weldingcurrentcanbeveryintense.Damagetoelectronic components may result. Connect the ground clamp as close as possible to the area being welded. Disconnect battery cables and any microprocessors and engine control modules before welding on the machine.
If it becomes necessary to weld aerial platform components as a method of repair, take all precautions to prevent damage to electronic circuitry and devices on the machine. This includes, but may not be limited to, disconnecting battery cables and electronic devices.
Do not modify this aerial platform without prior written consentoftheSnorkelEngineeringDepartment.Modification may void the warranty, adversely affect stability, or affect the operational characteristics of the aerial platform.
Manual of Responsibilities
All owners and users of the aerial platform must read, understand, and comply with all applicable regulations. Ultimate compliance to OSHA regulations is the responsibility of the user and their employer.
ANSI publications clearly identify the responsibilities of all personnel who may be involved with the aerial platform. A reprint of the “Manual of Responsibilities for Dealers, Owners, Users, Operators, Lessors and Lessees of ANSI/SIAA92.5-2006 Boom-Supported Elevating Work Platforms” is available from Snorkel dealers or from the factory upon request.
Copies are also available from:
Scaffold Industry Association, Inc.
P.O. Box 20574
Phoenix, AZ 85036-0574 USA
Additional Information
For additional information contact your local dealer or Snorkel at:
Snorkel International P.O. Box 1160
St. Joseph, MO 64502-1160 USA 1-800-255-0317
http://www.snorkelusa.com
TB66J – 0083740
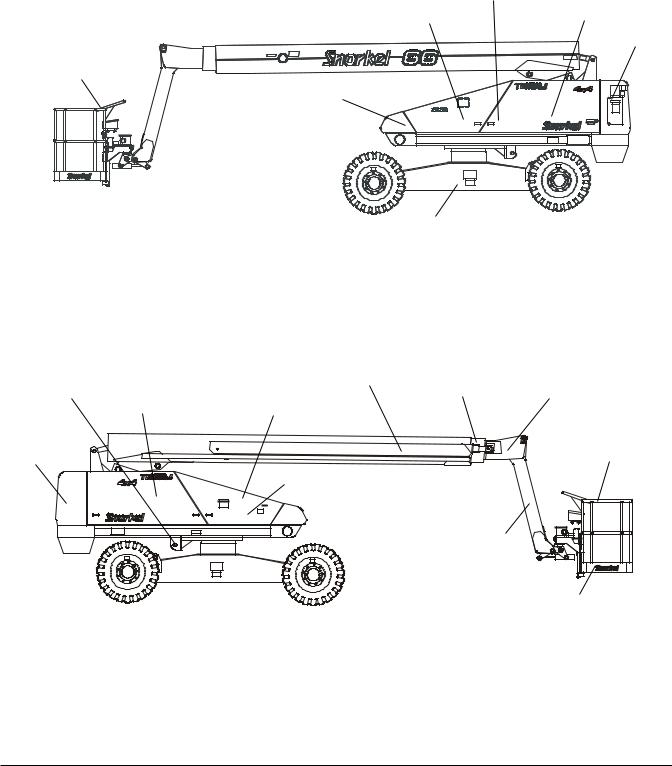
Chapter 3 – Specifications
Component Identification
Operator’s
Manual
Fuel Tank |
Wiring Box |
Lower Controls
Upper Controls
LP Fuel Tank
Chassis |
Steer Wheels |
|
Right Side
Emergency |
|
Main Boom |
Intermediate |
|
Lowering |
Hydraulic Fluid Tank |
Boom |
Tip Boom |
|
Valve |
And Filter |
Battery Disconnect Switch |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Engine |
Platform |
|
Batteries |
|
Jib Boom |
Steer Wheels |
Platform |
Foot Switch |
Left Side
TB66J – 0083740 |
3 |

Chapter 2 – Specifications
Working Envelope
Feet |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(Meters) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
70 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(21.3) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
60 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(18.3) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
50 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(15.2) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
40 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(12.2) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
30 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(9.1) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
20 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(6.1) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
10 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(3) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
5 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(1.5)60 |
50 |
40 |
30 |
20 |
10 |
0 |
10 |
(18.3) |
(15.2) |
(12.2) |
(9.1) |
(6.1) |
(3) |
|
(3) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
TB66J – 0083740 |

Chapter 2 – Specifications
General Specifications
Aerial Platform |
|
|
Working height |
|
72′ (21.9 m) |
Maximum platform height |
|
66′ (20.1 m) |
Horizontal reach |
|
56′ (17.1 m) |
Main boom |
|
|
Articulation |
|
-1° to +72° |
Extension |
0 to 27′ 4″ (0 to 8.33 m) |
|
Turntable rotation |
|
360° continuous |
Turning radius, inside |
|
15′ 5″ (4.7m) |
Wheelbase |
|
10′ (3 m) |
Ground clearance |
|
13″ (33 cm) |
Maximum wheel load |
|
13,360 lbs (6060 kg) |
Maximum ground pressure |
80 psi (552 kPa) |
|
Weight, GVW |
|
|
Approximate |
26,220 lbs (11,916 kg) |
|
Stowed width |
|
7′ 11.5″ (2.4 m) |
Stowed length |
|
33′ (10 m) |
Stowed height |
|
8′ 9″ (2.7 m) |
Platform |
|
|
Dimensions |
|
|
Standard steel |
39″ x 96″ (99 cm x 243 cm) |
|
Rated work load |
|
500 lb (227 kg) |
Optional aluminum |
30″ x 60″ (76 cm x 152 cm) |
|
Rated work load |
|
600 lb (272 kg) |
Optional aluminum |
30″ x 96″ (76 cm x 244 cm) |
|
Rated work load |
|
500 lb (227 kg) |
Optional steel |
30″ x 96″ (76 cm x 244 cm) |
|
Rated work load |
|
500 lb (227 kg) |
Rotation |
|
90° CW to 80° CCW |
Maximum number of occupants |
2 people |
|
Optional AC generator |
|
125 VAC |
Optional AC generator |
|
220 VAC, 50 Hz |
Function Speed |
|
|
Turntable rotation, 360 degrees |
85 to 95 seconds |
|
Main boom |
|
|
Up |
|
40 to 50 seconds |
Down |
|
40 to 50 seconds |
Extend |
|
60 to 70 seconds |
Retract |
|
35 to 50 seconds |
Jib |
|
|
Up |
|
7 to 13 seconds |
Down |
|
7 to 13 seconds |
Platform rotation, 170 degrees |
16 to 20 seconds |
|
Drive |
|
|
High, booms stowed |
|
3.0 mph (4.8 km/h) |
Low, booms elevated |
|
1.0 mph (1.6 km/h) |
Drive System |
|
Standard |
Four-wheel drive |
Gradeability |
30% |
Optional |
Two-wheel drive |
Gradeability |
25% |
Tires |
|
Foam Fillled |
|
Highway tread,14 ply |
15″ x 19.5″ (38 cm x 50 cm) |
Bar lug, 4x4 12 ply |
15″ x 19.5″ (38 cm x 50 cm) |
Flotation, 4x4 40″ x 19-19.5″ (101.6 cm x 50 cm)
Air Fillled |
|
|
|
Flotation |
40″ x 19-19.5″ (101.6 cm x 50 cm) |
||
Electrical System |
|
|
|
Voltage |
12 V DC negative chassis ground |
||
Source |
|
12 V 550 CCA battery |
|
Fluid recommended |
|
distilled water |
|
Hydraulic System |
|
|
|
Maximum pressure |
2,500 psi (17,250 kPa) |
||
Reservoir capacity |
|
|
26.1 US gal (99 l) |
System capacity |
|
|
35 US gal (132 l) |
Maximum operating temperature |
200°F (93°C) |
||
Hydraulic fluid recommended |
|
||
Above 10°F (-12°C) Mobil DTE-13M (ISO VG32) |
|||
Below 10°F (-12°C) |
Mobil DTE-11M (ISO VG15) |
||
Engine |
|
|
|
Diesel |
|
|
Cummins B3.3 |
|
|
|
Deutz F4L-1011F |
|
|
|
Deutz F4L-2011F |
|
|
|
Kubota V2403-M-T |
Gasoline and/or LPG |
|
Ford LRG 423 |
|
|
|
|
Ford LRG 425 |
|
|
|
General Motors 2.4L |
Fuel Tank Capacity |
|
|
|
Diesel or gasoline |
|
|
40 US gal (151 l) |
LPG |
|
|
43.5 lbs (19.7 kg) |
Dual fuel gasoline |
|
|
20 US gal (76 l) |
Ambient Air Temperature Operating Range |
|||
Fahrenheit |
|
|
0°F to 110°F |
Celsius |
|
|
-18°C to 43°C |
Maximum Wind Speed |
|
|
|
Gust or steady |
|
|
28 mph (12.8 m/s) |
TB66J – 0083740 |
5 |

Chapter 2 – Specifications
Engine Specifications
Engine |
Displacement |
|
Fuel Grade |
Coolant |
Operating |
Oil |
Oil |
||
|
Temperature |
Capacity |
Grade |
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
Diesel |
|
|
|
SAE |
|
Cummins |
199 cu. in. |
|
ASTM No. 2D fuel with a mini- |
50% Water |
140°F to 212°F |
2 US gal |
15W-403 |
||
mum Cetane no. of 40.1 For op- |
|
||||||||
B3.3 |
(3.26 liter) |
|
erating temperature below 0°C |
50% Antifreeze2 |
60°C to 100°C |
(7.5 liter)3 |
API |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
(32°F) use winterized No. 2D. |
|
|
|
CH4/SG |
|
|
|
|
|
Diesel |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
DIN 51 601 (February 1986).1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
BS 2869: A1 and A2 (with A2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
refer to Deutz manual about |
|
|
2.75 US |
API: CD |
|
Deutz |
190 cu. in. |
|
sulfur content)1 |
|
172°F to 203°F |
||||
|
ASTM D 975-88: 1-D and 2-D |
Air |
gal (10.4 |
or |
|||||
F4L-1011F |
(3.11 liter) |
3 |
78°C to 95°C |
||||||
|
|
CEN EN 590 or DIN EN 590 |
|
liter) |
higher3 |
||||
|
|
|
|
NATO Code F-54 and F-75 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
For operating temperatures |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
below 0°C (32°F) use winter |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
grade diesel. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Diesel |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
DIN 51 601 (February 1986).1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
BS 2869: A1 and A2 (with A2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
refer to Deutz manual about |
|
|
2.75 US |
API: CD |
|
Deutz |
190 cu. in. |
|
sulfur content)1 |
Air |
172°F to 203°F |
||||
|
ASTM D 975-88: 1-D and 2-D |
gal (10.4 |
or |
||||||
F4L-2011F |
(3.11 liter) |
|
CEN EN 590 or DIN EN 590 |
|
78°C to 95°C |
liter) |
higher3 |
||
|
|
|
|
NATO Code F-54 and F-75 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
For operating temperatures |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
below 0°C (32°F) use winter |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
grade diesel. |
|
|
|
|
|
Kubota |
148.5 cu. in. |
|
Diesel |
50% water |
NA |
2.51 gal |
API: |
||
|
Diesel Fuel No. 2-D |
CF grade |
|||||||
V2403-M-T |
(2.43 liter) |
|
ASTM D9751 |
50% Antifreeze2 |
|
(9.5 liter) |
or higher3 |
||
Note 1: Refer to the engine manufacturers manual for specific fuel recommendations and specifications. Note 2: Refer to the engine manufacturers manual for specific coolant recommendations and specifications.
Note 3: Refer to the engine manufacturers manual for specific lubricating oil recommendations and specifications.
TB66J – 0083740

Chapter 2 – Specifications
Engine |
Displacement |
Fuel Grade |
Coolant |
Operating |
Oil |
Oil |
|
Temperature |
Capacity |
Grade |
|||||
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
Gasoline |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Unleaded 87 or 89 octane.1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Do not use gasoline blends with |
|
|
|
|
|
Ford |
153 cu. in. |
more than 10% ethanol by |
50% Water |
195°F to 220°F |
4.5 US qt |
API: SH |
|
volume octane index of 87 or 89. |
|||||||
LRG 425 |
(2.5 liter)3 |
50% Antifreeze3 |
91°C to 104°C |
(4.26 liter)3 |
or SJ2 |
||
|
|
LPG |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
HD-5 USA 1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
EN589 European |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Gasoline |
|
|
|
Gasoline |
|
|
|
Unleaded gasoline 85 octane |
|
|
|
API: SH |
|
Ford |
|
(motor method).1 |
|
|
|
SG only if |
|
140 cu. in. |
|
50% Water |
160°F to 190°F |
4 US qt |
SH is not |
||
LRG 423 |
(2.3 liter) |
LPG |
50% Antifreeze3 |
71°C to 88°C |
(3.8 liter) |
available2 |
|
|
|
Gas Processors Association |
|
|
|
LPG |
|
|
|
Standard 2140 |
|
|
|
||
|
|
Category: special duty propane |
|
|
|
SG or SH |
|
|
|
Gasoline |
|
|
With filter: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
1.12 US gal |
|
||
GM |
150 cu. in. |
Unleaded 87 octane1 |
50% Water |
176°F to 183°F |
(4.5 liter) |
ILSAC |
|
|
|
||||||
2.4L |
(2.4 liter) |
LPG |
50% Antifreeze5 |
80°C to 84°C |
W/o filter: |
GF-44 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
HD-51 |
|
|
1.18 US gal |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(4.25 liter) |
|
Note 1: Refer to the engine manufacturers manual for specific fuel recommendations and specifications.
Note 2: Refer to the engine manufacturers manual for specific lubricating oil recommendations and specifications. Note 3: Refer to the Ford LRG 425 Operator Handbook for specific coolant recommendations and specifications.
Note 4: API Starburst symbol on GF-4 oils reads “API Service SM.”
Note 5: Refer to the engine manufacturers manual for specific coolant recommendations and specifications.
TB66J – 0083740 |
7 |

Chapter 2 – Specifications
Engine Oil Viscosity
Cummins B3.3
Deutz F4L-1011F
Deutz F4L-2011F
Kubota V2403-M-T
S A E 15W /40
TB66J – 0083740

Chapter 2 – Specifications
Ford LRG 423
Ford LRG 425
General Motors 2.4L
°F |
-40 |
-31 -22 |
-13 |
-4 5 |
14 |
23 |
32 |
41 |
50 |
59 |
68 |
77 |
86 |
104 122 |
°F |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
°C |
-40 |
-35 -30 |
-25 |
-20 -15 |
-10 |
-5 |
0 |
5 |
10 |
15 |
20 |
25 |
30 |
40 50 |
°C |
S A E 5W /30
S A E 0W /30
Note
No straight weight oils and no specialized diesel oils are to be used in GM engines.
TB66J – 0083740 |
9 |

Chapter 2 – Specifications
10 |
TB66J – 0083740 |

Chapter 3 – Safety
Knowledge of the information in this manual, and proper training, provide a basis for safely operating the aerial platform. Know the location of all controls and how they operate to act quickly and responsibly in an emergency.
Safety devices reduce the likelihood of an accident.
Never disable, modify, or ignore any safety device.
Safety alerts in this manual indicate situations where accidents may occur.
If any malfunction, hazard or potentially unsafe condition relating to capacity, intended use, or safe operation is suspected, stop aerial platform operation and seek assistance.
The operator bears ultimate responsibility for following all manufacturer’s instructions and warnings, regulations and safety rules of their employer and/or any state or federal law.
Electrocution Hazards
The aerial platform is made of metal components and is not insulated. Regard all conductors as energized. Do not operate outside during a thunderstorm.
Minimum Safe Approach Distance
Minimum safe approach distances to energized power lines and their associated parts must be observed while operating the aerial platform.
Danger
The aerial platform is not electrically insulated. Death or serious injury will result from contact with, or inadequate clearance from, an energized conductor. Do not go closer than the minimum safe approach distance as defined by ANSI.
ANSI publications define minimum distances that must be observed when working near bus bars and energized power lines. Table 1 and Figure 3 are reprinted courtesy of Scaffold Industry Association, ANSI/SIA A92.5.
Voltage Range |
Minimum Safe Approach Distance |
|
(Phase to Phase) |
Feet |
Meters |
0 to 300V |
Avoid Contact |
|
Over 300V to 50kV |
10 |
3.05 |
Over 50kV to 200kV |
15 |
4.60 |
Over 200kV to 350Kv |
20 |
6.10 |
Over 350kV to 500kV |
25 |
7.62 |
Over 500kV to 750kV |
35 |
10.67 |
Over 750kV to 1000kV |
45 |
13.72 |
Table 1 – Minimum Safe Approach Distance
D en o tes p ro h ib ited zo n e
Figure 3 – Minimum Safe Approach Distance
TB66J – 0083740 |
11 |

Chapter 3 – Safety
Prestart Inspection
Perform a prestart inspection before each shift as described in Chapter 7. Do not use the aerial platform on the job unless you are trained and authorized to do so.
booms, or platform. Allow sufficient room and time to stop movement to avoid contact with structures or other hazards.
Always look in the direction of movement.
Work Place Inspection and Practices
Do not use the aerial platform as a ground connection when welding.
The welding ground clamp must be attached to the same structure that is being welded.
Electrical current flow can be very intense, causing serious internal damage to some components.
Inspect the area before and during aerial platform use. The following are some potential hazards that may be in the work place.
•Debris
•Slopes
•Drop-offs or holes
•Bumps and floor obstructions
•Overhead obstructions
•Unauthorized persons
•High voltage conductors
•Wind and weather conditions
•Inadequate surface and support to withstand load forces applied by the aerial platform in all operating configurations
Before using the aerial platform in any hazardous
(classified) location, make certain it is approved and of the type required by ANSI/NFPA 505 for use in that particular location.
Drive with care and at speeds compatible with the work place conditions.
Use caution when driving over rough ground, on slopes and when turning.
Do not engage in any form of horseplay or permit riders any place other than in the platform.
Secure all accessories, containers, tools, and other materials in the platform to prevent them from accidentally falling or being kicked off the platform. Remove all objects that do not belong in or on the aerial platform.
Never steady the platform by positioning it against another platform.
Warning
The potential for an accident increases when operating an aerial platform that is damaged or malfunctioning. Death or serious injury could result from such accidents. Do not operate the aerial platform if it is damaged or malfunctioning.
Do not operate the aerial platform if it is damaged or not functioning properly. Qualified maintenance personnel must correct the problem before putting the aerial platform back into service.
Know and understand the job site traffic-flow patterns and obey the flagmen, road signs and signals.
While operating the aerial platform, a good safety practice is to have qualified personnel in the immediate work area to:
•Help in case of an emergency
•Operate emergency controls as required
•Watch for loss of control by platform operator
•Warn the operator of any obstructions or hazards that may not be obvious to them
•Watch for soft terrain, sloping surfaces, drop-offs, etc. where stability could be jeopardized
•Watch for bystanders and never allow anyone to be under, or to reach through the booms while operating the aerial platform
Danger
Pinchpointsmayexistbetweenmovingcomponents. Death or serious injury will result from becoming trapped between components, buildings, structures, orotherobstacles.Makesurethereissufficientclearance around the machine before moving the chassis,
Operation
Use three points of support when entering or exiting the platform. For example, use two hands and one foot when climbing into the platform.
Never cover the platform floor grating or otherwise obstruct your view below. Make sure the area below the platform is free of personnel before lowering.
Keep both feet positioned firmly on the platform floor.
Operate the controls slowly and deliberately to avoid jerky and erratic operation.
Always stop the controls in neutral before going in the opposite direction.
Do not dismount while the aerial platform is in motion or jump off the platform.
Properly stow the aerial platform and secure it against unauthorized operation at the end of each work day, before transporting, or if it is left unattended.
12 |
TB66J – 0083740 |

Chapter 3 – Safety
Tip-Over and Falling Hazards
Operate the aerial platform only on a firm, flat, level surface capable of withstanding all load forces imposed by the aerial platform in all operating conditions. Refer to theGeneralSpecificationschartforthemaximumwheel load and ground pressure. Raise the booms only when the aerial platform is on level ground.
Danger
The aerial platform can tip over if it becomes unstable. Death or serious injury will result from a tip-over accident. Do not drive or position the aerial platform for elevated use near any drop-off, hole, slope, soft or uneven ground, or other tip-over hazard.
All platform occupants must wear a fall restraint device connected to a lanyard anchor point.
It is best not to transfer from the platform to another structure or from the structure to the platform, unless that is the safest way to do the job. Judge each situation separately taking the work environment into account. If it is necessary to transfer from the platform to another structure the following guidelines apply:
1.Where possible, place the platform over a roof or walking structure to do the transfer.
2.Transfer your anchorage from one structure to the other before stepping across.
3.Remember that you might be transferring to a structure where personal fall arrest is required.
4.Use the platform entrance, do not climb over or through the guardrails.
Do not operate the aerial platform in windy or gusty conditions. Do not add anything to the aerial platform that will increase the wind loading such as billboards, banners, flags, etc.
Never operate the aerial platform without all parts of the guardrail system in place and the gate closed. Make sure that all protective guards, cowlings and doors are securely fastened.
Do not exceed the platform capacity as indicated on the platform rating placard on the platform. Do not carry loads that extend beyond the platform guardrails without prior written consent from Snorkel.
Do not operate the aerial platform from trucks, trailers, railway cars, floating vessels, scaffolds or similar equipment unless the application is approved in writing by Snorkel.
Do not use the aerial platform as a crane, hoist, jack or for any purpose other than to position personnel, tools and materials.
Do not climb on the guardrails or use ladders, planks or other devices to extend or increase the work position from the platform.
Take care to prevent rope, electrical cords, and hoses, etc., from becoming caught in or on the aerial platform.
If the platform or booms becomes caught on an adjacent structure or other obstacle and is prevented from normal motion, reverse the control to free the platform.
If control reversal does not free the platform, evacuate the platform before attempting to free it.
Electrical System
Charge the batteries in a well-ventilated area free of flame, sparks or other hazards that might cause fire or explosion.
Do not operate any of the aerial platform functions while the battery charger is plugged in.
Warning
Batteries give off hydrogen and oxygen that can combine explosively. Death or serious injury could result from a chemical explosion. Do not smoke or permit open flames or sparks when checking the batteries.
Battery acid can damage the skin and eyes. Serious infection or reaction can result if medical treatment is not given immediately. Wear face and eye protection when working near the batteries.
Batteries contain sulfuric acid that can damage your eyes or skin on contact.
Wear a face shield, rubber gloves, and protective clothing when working around batteries.
If acid contacts your eyes, flush immediately with clear water and get medical attention.
If acid contacts your skin, wash off immediately with clear water.
Hydraulic System
Thehydraulicsystemcontainshoseswithhydraulicfluid under pressure.
Danger
Hydraulic fluid escaping under pressure can have enough force to inject fluid into the flesh. Serious infection or reaction will result if medical treatment is not given immediately. In case of injury by escaping hydraulic fluid, seek medical attention at once.
TB66J – 0083740 |
13 |

Chapter 3 – Safety
Do not place your hand or any part of your body in front of escaping hydraulic fluid. Use a piece of cardboard or wood to search for hydraulic leaks.
Engine and Fuel Handling Precautions
Refer to the engine manufacturer’s Operator’s Manual for complete information on safe engine operation, maintenance and specifications.
Danger
Engine exhaust contains carbon monoxide, a poisonous gas that is invisible and odorless. Breathing engine exhaust fumes will cause death or serious illness. Do not run the engine in an enclosed area or indoors without adequate ventilation.
Operate dual fuel machines on LPG fuel when indoors to reduce exhaust fumes and carbon monoxide.
Be careful not to run the diesel fuel tank empty. Bleed the fuel system if air enters the lines between the tank and the injection pump.
Allow the engine to return to idle before shutting the engine off.
Do not smoke or permit open flames while fueling or near fueling operations.
Never remove the fuel cap or fill the fuel tank while the engine is running or hot. Never allow fuel to spill on hot machine components.
Maintain control of the fuel filler nozzle when filling the tank. Spilled fuel is a potential fire hazard.
Do not overfill the fuel tank. Allow room for expansion.
Clean up spilled fuel immediately.
Tighten the fuel tank cap securely. If the fuel cap is lost, replace it with an approved cap from Snorkel. Use of a non-approved cap without proper venting may result in pressurization of the tank.
Never use fuel for cleaning purposes.
For diesel engines, use the correct fuel grade for the operating season.
Caution
Engine coolant escaping under pressure may cause serious burns. Shut the engine off and let it cool before removing the radiator cap.
Let the engine and radiator cool before adding coolant.
Placards and Decals
The aerial platform is equipped with placards and decals that provide instruction for operation and accident prevention. Do not operate the aerial platform if any placards or decals are missing or not legible.
14 |
TB66J – 0083740 |

Chapter 4 – Safety Devices
This aerial work platform is manufactured with safety devices, placards, and decals to reduce the likelihood of an accident.
For the safety of all personnel, do not disable, modify, or ignore any safety device.
Safety devices are included in the daily prestart inspection.
Warning
The potential for an accident increases when safety devices do not function properly. Death or serious injury could result from such accidents. Do not alter, disable, or override any safety device.
If any safety devices are defective, remove the aerial platformfromserviceuntilqualifiedmaintenancepersonnel can make repairs.
Emergency Stop Controls
There is an emergency stop control at the lower and upper controls.
At the lower controls, the emergency stop button is a two-position push button (refer to Figure 4.1).
Emergency |
|
Engine/Emergency |
Stop Button |
|
Power Switch |
Ground Operation
Switch
Figure 4.1 – Lower Controls
Push the emergency stop button inward to disconnect power to all control circuits.
Pull the button outward to restore power.
On older machines the emergency stop is a twoposition toggle switch with a red safety guard.
Push the guard down over the toggle switch to disconnect power to all control circuits. Lift the guard and push the switch up to restore power.
Note
The lower controls override the upper controls. If the upper control emergency stop button is engaged, the lower controls can still be used to operate the aerial platform.
At the upper controls, the emergency stop is a two-posi- tion push button (refer to Figure 4.2).
Engine/Emergency
Emergency Power Switch
Stop Button
Figure 4.2 – Upper Controls
Push the emergency stop button inward to disconnect power to the upper control circuits.
Pull the button outward to restore power.
Emergency Power System
The emergency power system includes a back-up pump, motor, and battery. Use this system to operate the boom and turntable functions to lower the platform if the main power system fails due to engine or pump failure.
Caution
The emergency power system is for emergency lowering and stowing only. The length of time the pump can be operated depends on the capacity of the battery. Do not use this system for normal operation.
Hold the engine/emergency power switch (refer to Figure 4.1 and 4.2) downward to activate the emergency power system.
Release the switch to disengage the emergency power system.
The length of time the pump can be operated depends on the capacity of the battery.
TB66J – 0083740 |
15 |

Chapter 4 – Safety Devices
Emergency Lowering Knob
The emergency lowering knob may be used to lower the booms if the engine will not start and the emergency power system will not work.
The knob is on the base end of the main boom lift cylinder (refer to Figure 4.3) under the left side of the turntable.
Emergency
Lowering Knob
Guardrails
The guardrails (refer to Figure 4.5) help protect personnel from falling off the platform.
The guardrail system includes:
A top rail
A mid rail
A gravity gate or optional swinging gate
Optional side entry gravity gate
Toeboards around the sides of the platform.
The gravity gate(s) allow for access to the platform and close automatically after entering or exiting the platform. After entering the platform check to make sure the gates are fully lowered and even with the mid rail.
The optional swinging gate (refer to Figure 4.5) allows for access to the platform. The gate must be securely latched except when personnel are entering or leaving the platform.
Figure 4.3 – Emergency Lowering Knob
Ground Operation Switch
The ground operation switch (refer to Figure 4.1) prevents boom and platform movement if a control switch on the lower control panel is accidentally moved.
Hold the switch up to operate the machine from the lower controls.
Platform Foot Switch
Step down on the platform foot switch (refer to Figure 4.4) to activate the upper controls.
|
Top Rail |
Lanyard |
Gravity |
Anchors |
Gate |
|
Mid Rail |
Platform Foot |
|
Switch |
|
|
Toeboard |
Figure 4.4 – Platform
The foot switch must be engaged and a control must be moved to operate the boom, drive and/or platform from the upper controls.
Figure 4.5 – Platform Swing Gate
Lanyard Anchors
Two lanyard anchors for fall restraint anchorage are provided below the upper controls at the front of the platform (refer to Figure 4.4).
Note
The lanyard anchors are not designed for lifting or tying the machine down.
All personnel in the platform must connect their fall restraint device to a lanyard anchor before raising the platform.
Attach only one fall restraint device to each lanyard anchor.
Do not use the aerial platform for personal fall arrest anchorage.
16 |
TB66J – 0083740 |

Chapter 4 – Safety Devices
Ground Fault Circuit Interrupter
Theelectricalpoweroutletattheplatform(refertoFigure 4.6) contains a ground fault circuit interrupter (GFCI) to provide protection for personnel.
Electrical
 Power Outlet
Power Outlet
Figure 4.6 – Electrical Outlet
Tilt Alarm
If the aerial platform chassis is out of level more than fivedegreeswhenthemainboomisraisedorextended, an alarm will sound. The tilt alarm is located under the upper control panel.
Danger
The aerial platform can tip over if it becomes unstable. Death or serious injury will result from a tip-over accident. Do not drive or position the aerial platform for elevated use near any drop-off, hole, slope, soft or uneven ground, or other tip-over hazard.
Completely retract and lower the main boom and then drive to a level surface when the tilt alarm sounds.
The tilt alarm is for added protection and does not justify operating on anything other than firm, flat, level surfaces.
Engine Protection Systems
A constant alarm will sound to warn against high engine temperature or low oil pressure.
The engine will shut-down
if the operating temperature exceeds a preset level
or if the oil pressure is too low for safe operation.
An engine temperature gauge is on the lower control panel (refer to Figure 4.7).
Engine
Temperature
Gauge
Figure 4.7 – Lower Control Panel
High Engine Temperature Alarm
If the coolant in a Cummins or GM engine exceeds the engine operating temperature an alarm will sound and the engine will shut off.
If the oil in a Deutz engine exceeds 230°F (110°C) an alarm will sound and the engine will shut off. Any time there is no alternator current being produced, an alarm will sound and the engine will shut off. This prevents high engine temperature if the fan belt breaks.
Do not restart the engine until the condition that caused the overheating has been corrected.
Low Oil Pressure Alarm
The low oil pressure alarm sounds when the engine oil pressure is near the lower limit for safe engine operation. If the alarm sounds, lower the platform to the ground and then turn the engine off.
If the engine oil pressure falls below a safe operating value the engine will shut off.
The engine can be restarted with low oil pressure, but it will only run for a few seconds before it shuts off again.
Do not restart the engine until the condition that caused the low oil pressure has been corrected.
TB66J – 0083740 |
17 |

Chapter 4 – Safety Devices
Horn
An optional horn may be used to warn personnel on the ground. The horn button is on the right side of the upper control box.
The horn is operational when the emergency stop button and the start switches are both on, at the lower and the upper controls.
All Motion Alarm
An optional all motion alarm may be provided on the machine. The alarm sounds, in short beeps, anytime the machine functions are being operated. The alarm is used to warn personnel in the work area to stand clear.
Flashing Light
An optional amber flashing light may be located on the top of the boom near the base end (refer to Figure 4.8). The flashing light warns personnel that the aerial platform is in the area.
Flashing Light
Figure 4.8 – Flashing Light
The light flashes at about one flash per second when the engine is running.
Driving Lights
The optional headlights and blinking tail lights may be used to help improve visibility while driving the aerial platform and help others see it too.
The headlights are located on the top of the front cowling.
The tail lights are mounted on the sides of the rear cowling.
Do not use the driving lights to drive on public roadways.
Platform Work Lights
The optional platform work lights may be used to help improve visibility while working aloft in dimly lit areas.
The platform work lights are located on the top rail of the platform, one on each side of the upper control panel (refer to Figure 4.9).
Do not use the platform work lights to drive on public roadways.
Light Switch
Figure 4.9 – Platform Work Lights
Bump Guard System
The optional bump guard system is a spring mounted padded railing below the platform. There are two infrared lights mounted along the bottom of the platform next to two infrared sensitive switches. The lights shine on reflectors on the bump guard system and are reflected back to the switches.
If the bump guard comes into contact with a stationary object, the bump guard moves and one or both of the light beams is broken, immediately stopping all platform movement.
18 |
TB66J – 0083740 |

Chapter 5 – Gauges and Displays
The aerial platform is equipped with several gauges to monitor the condition of the machine before and during operation.
Hour Meter
The hour meter is located on the wiring box on the left side of the lower controls (refer to Figure 5.1). It measures the accumulated engine operating time.
Hour
Meter
Figure 5.1 – Wiring Box
Engine Temperature Gauge
The temperature gauge is located on the lower control panel (refer to Figure 5.2).
Machines with Kubota engines do not have an engine temperature gauge.
Engine |
Temperature |
Gauge |
Ammeter – Cummins, Deutz, |
and Ford Engines |
Voltmeter – General Motors Engines |
Figure 5.2 – Lower Controls
The gauge on liquid cooled engines shows the temperature of the water and antifreeze mixture in the engine block.
The gauge on air cooled engines shows the temperature of the engine oil as the oil leaves the filter.
Ammeter – Cummins, Deutz and Ford
Engines
Theammeterislocatedonthelowercontrolpanel(refer toFigure5.2).Theammeterdisplaysthelevelofcurrent flow from the alternator to the batteries.
After the engine has been running for a few minutes under normal operating conditions, the ammeter gauge indicator should read “0.”
Machines with Kubota engines do not have an engine ammeter gauge.
Voltmeter – General Motors Engines
The voltmeter is located on the engine gauge panel above the lower controls. The voltmeter displays battery voltage.
After the engine has been running for a few minutes under normal operating condition, the voltmeter should indicate between 12.5 and 14 volts.
Engine Air Filter Gauge
The air filter gauge (refer to Figure 5.3) is located on the engine gauge panel above the lower controls.
Air Filter
Gauge
Reset Button
Figure 5.3 – Air Filter Gauge
The air filter gauge measures the air pressure between the intake manifold and the air filter.
The yellow indicator disk inside the sight glass stays at its highest level when the engine is turned off.
When the yellow indicator disk reaches the red area, it’s time to change the filter element.
Afterchangingthefilter,presstheresetbuttontoreset the indicator disk to the bottom of the sight glass.
Fuel Gauge
The fuel gauge is located on top of the diesel or gasoline tank (refer to Figure 5.4).Access the gauge by opening the door on the right side of the chassis.
TB66J – 0083740 |
19 |

Chapter 5 – Gauges and Displays
Fuel Gauge
Figure 5.4 – Fuel Tank
Read the fuel gauge at the line in the clear plastic window.
The gauge indicates the fuel tank level in fractions of a full tank.
Note
Do not run a diesel fuel tank empty. Air in the fuel line makes the engine hard to start.
LPG tanks have a fuel gauge that has two scales. One scale measures the fuel level when the tank is mounted vertical and the other is used when the tank is mounted horizontal (refer to Figure 5.5).
Horizontal Scale
Figure 5.5 – LPG Tank
The LPG tank is mounted horizontally behind the rear cowling door on the right side of the machine.
Read the horizontal scale to determine the fuel level.
Engine Oil
The engine oil level is measured with a dipstick. The dipstick is the only way to accurately determine the engine oil level. The engine oil level should always be between the add and full marks on the dipstick.
Hydraulic Fluid Filter Gauge
Thefluidfiltergauge(refertoFigure5.6)islocatedonthe return line filter on the top of the reservoir.The reservoir is behind the door on the left side of the turntable.
During high pump flow situations, the gauge indicates the condition of the filter.
When the needle on the gauge is in the red zone, its time to change the filter.
Filter Gauge
Figure 5.6 – Hydraulic Fluid Filter Gauge
Fluid Level and Temperature Gauge
A sight gauge on the right side of the hydraulic reservoir displays the level and temperature of the hydraulic fluid (refer to Figure 5.7).The reservoir is behind the door on the left side of the machine.
Onlyreadthefluidlevelwhentheaerialplatformisinthe stowed position, booms completely down and retracted. Otherwise, the cylinders act as large reservoirs for hydraulic fluid making the level appear too low.
The fluid should be between the minimum and maximum lines.
If the temperature rises above 200°F (93°C) stop machine operation and let the fluid cool before resuming operation.
Fluid Level and
Temperature Gauge
Figure 5.7 – Hydraulic Fluid Filter Gauge
20 |
TB66J – 0083740 |

Chapter 6 – Controls
Danger
Pinch points may exist between moving components. Death or serious injury can result from being trappedbetweencomponents,buildings,structures, or other obstacles. Make sure all personnel stand clear while operating the aerial platform.
Controls to position the platform are located on the lower control panel on the turntable and on the upper control panel in the platform.
Controls to drive the aerial platform are located on the upper control panel only.
Battery Disconnect Switch
The battery disconnect is located behind the door on the left side of the turntable above the batteries (refer to Figure 6.1).
Battery Disconnect Switch
Figure 6.1 – Battery Disconnect Switch
The battery disconnect removes electrical power from all electrically controlled functions when in the off position.
Place the switch in the on position to electrically connect the battery to the electrical system.
Caution
Only authorized personnel should operate the aerial platform. Unqualified personnel may cause injury to coworkers or property damage. Lock the battery disconnect switch in the off position before leaving the aerial platform unattended.
Turn the battery disconnect switch off to prevent unauthorized use of the aerial platform.
Lower Controls
Thelowercontrols(refertoFigure6.2)arelocatedonthe right side of the turntable. Boom and platform functions can be operated from the lower controls.
The following are located on the lower control panel.
•Emergency stop button
•Control selector switch
•Start switch
•Ground operation switch
•Rotation switch
•Boom elevation switch
•Boom extend/retract switch
•Jib articulation switch
•Boom speed knob
•Platform level switch
•Platform rotation switch
•Engine/emergency power switch
•Throttle switch
•Fuel switch (dual fuel machines)
Emergency Stop Button
The emergency stop button (refer to Figure 6.2) is a two-position, red push button.
Push the button inward to disconnect power to all control circuits.
Pull the button outward to restore power.
On older machines, the emergency stop is a two-position toggle switch with a red safety guard.
Push the guard down over the toggle switch to disconnect power to all control circuits
Lift the guard and push the toggle switch up to restore power.
Control Selector Switch
Use the control selector switch (refer to Figure 6.2) to select between the lower control and upper control operation.
Push the switch upward to operate the aerial platform from the upper controls.
Push the switch downward to operate the aerial platform from the lower controls.
Start Switch
The start switch (refer to Figure 6.2) works like an automobile ignition switch.
Hold the switch in the start position until the engine starts, then release it to on.
If the engine dies, the switch must be turned to off before it can be turned back to start.
An alarm sounds, when the switch is turned on, to warn others that the machine engine is being started.
TB66J – 0083740 |
21 |

Chapter 6 – Controls
Boom Elevation |
|
|
Switch |
Control Selector |
|
|
|
|
|
Switch |
|
Boom Extend/Retract |
|
Boom Speed |
|
Knob |
|
Switch |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Emergency Stop Button |
Platform Rotation |
|
Engine/Emergency |
Switch |
|
|
|
Power Switch |
|
|
|
|
Platform Level Switch |
|
Ground Operation |
|
|
Switch |
Rotation Switch |
|
Start Switch |
|
|
|
Throttle Switch |
|
Circuit Breaker Reset Button |
|
|
|
|
Jib Articulation Switch |
|
Figure 6.2 – Lower Controls
Note
On some machines it may be necessary to pause about three seconds in the on position before going to start so the starter can engage.
If the platform is to stay in a particular position for a long time, turn the start switch to off to shut off the engine and save fuel.
Ground Operation Switch
Thegroundoperationswitch(refertoFigure6.2)isused to operate the machine from the lower controls. The switch is spring returned to the off position.
Hold the ground operation switch upward continually to operate the machine from the lower controls.
The engine speed increases when the switch is held upward.
Rotation Switch
The rotation switch (refer to Figure 6.2) is used to rotate the turntable in a clockwise or counterclockwise direction. The switch is spring returned to the center off position.
Hold the switch to the right to rotate the turntable counterclockwise.
Hold the switch to the left to rotate the turntable clockwise.
Boom Elevation Switch
The boom elevation switch (refer to Figure 6.2) is used to raise or lower the main boom. The switch is spring returned to the center off position.
Hold the switch up to raise the main boom.
Hold the switch down to lower the main boom.
Boom Extend/Retract Switch
The boom extend/retract switch (refer to Figure 6.2) is used to extend or retract the booms. The switch is spring returned to the center off position.
Hold the switch to the left to extend the tip boom.
Hold the switch to the right to retract the tip boom.
Jib Articulation Switch
The jib switch (refer to Figure 6.2) is used to raise or lower the jib. The switch is spring returned to the center off position.
Hold the switch up to raise the jib.
Hold the switch down to lower the jib.
22 |
TB66J – 0083740 |
 Loading...
Loading...