Page 1

855 Robotic Titrosampler
Manual
8.855.8001EN
Page 2

Page 3

Metrohm AG
CH-9101 Herisau
Switzerland
Phone +41 71 353 85 85
Fax +41 71 353 89 01
info@metrohm.com
www.metrohm.com
855 Robotic Titrosampler
Manual
8.855.8001EN 04/2010 dm
Page 4

Teachware
Metrohm AG
CH-9101 Herisau
teachware@metrohm.com
This documentation is protected by copyright. All rights reserved.
Although all the information given in this documentation has been checked
with great care, errors cannot be entirely excluded. Should you notice any
mistakes please send us your comments using the address given above.
Page 5

■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■
Table of contents
1 Introduction 1
1.1 The 855 Robotic Titrosampler in the Titrando sys-
1.2 Instrument description ......................................................... 2
1.2.1 Model versions ........................................................................ 3
1.2.2 Instrument components .......................................................... 3
1.2.3 Intended use ........................................................................... 4
1.3 About the documentation ................................................... 4
1.3.1 Symbols and conventions ........................................................ 4
1.4 Safety instructions ................................................................ 5
1.4.1 General notes on safety ........................................................... 5
1.4.2 Electrical safety ........................................................................ 5
1.4.3 Tubing and capillary connections ............................................. 6
1.4.4 Personnel safety ...................................................................... 7
1.4.5 Flammable solvents and chemicals ........................................... 8
1.4.6 Recycling and disposal ............................................................. 8
Table of contents
tem ......................................................................................... 1
2 Overview of the instrument 9
2.1 Front and rear ....................................................................... 9
2.2 Rear panel ........................................................................... 11
2.3 Sensor connectors .............................................................. 11
2.4 Sample racks ....................................................................... 12
3 Installation 13
3.1 Setting up the instrument .................................................. 13
3.1.1 Packaging .............................................................................. 13
3.1.2 Checks .................................................................................. 13
3.1.3 Location ................................................................................ 13
3.2 Preparing the Sample Processor ....................................... 13
3.2.1 Connecting a mains cable ...................................................... 13
3.3 Connecting a computer ................................................... 14
3.4 Connecting the Swing Head .............................................. 15
3.5 Configuring the robotic arm .............................................. 16
3.6 Mounting the robotic arm ................................................. 18
3.7 Robotic arms with beaker sensor ..................................... 20
855 Robotic Titrosampler
3.8 Installing rinsing and aspiration equipment .................... 21
3.9 Guide chain for cables and tubing .................................... 24
■■■■■■■■
III
Page 6

Table of contents
■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■
3.10 Equipping the titration head ............................................. 25
3.11 Connecting the tower stirrer ............................................. 27
3.12 Connecting external pumps ............................................... 28
3.13 Connecting MSB devices ................................................... 29
3.13.1 Connecting dosing devices .................................................... 30
3.13.2 Connecting a stirrer or titration stand .................................... 31
3.13.3 Connecting a remote box ...................................................... 32
3.14 Connecting USB devices ..................................................... 33
3.14.1 Connecting a barcode reader ................................................. 33
3.15 Mounting the base plate ................................................... 34
3.16 Mounting the drip pan ....................................................... 35
3.17 Attaching the sample rack ................................................. 36
3.18 Mounting the safety shield ................................................ 37
4 Handling and maintenance 39
4.1 General ................................................................................ 39
4.2 Care ...................................................................................... 39
4.3 Quality Management and validation with Metrohm ....... 39
5 Troubleshooting 40
5.1 Sample Processor ............................................................... 40
5.2 Robotic arm ......................................................................... 40
5.3 Pump .................................................................................... 41
6 Appendix 42
6.1 Beaker sensor ..................................................................... 42
6.2 Rinsing nozzles ................................................................... 42
6.3 Remote interface ................................................................ 43
6.3.1 Pin assignment of the remote interface .................................. 44
6.4 Stirring rate ......................................................................... 45
6.5 Robotic arms ....................................................................... 46
6.5.1 Robotic arms for titration ....................................................... 46
6.5.2 Robotic arms for sample preparation ..................................... 48
6.5.3 Robotic arms for special applications ..................................... 49
■■■■■■■■
IV
7 Technical specifications 50
7.1 Measuring interface ........................................................... 50
7.1.1 Potentiometry ........................................................................ 50
7.1.2 Polarizer ................................................................................ 50
7.1.3 Temperature .......................................................................... 51
855 Robotic Titrosampler
Page 7

■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■
8 Conformity and warranty 55
Table of contents
7.2 Lift and turntable ............................................................... 51
7.3 Membrane pump(s) with valve .......................................... 52
7.4 786 Swing Head ................................................................. 52
7.5 Interfaces and connectors ................................................. 52
7.6 Mains connection ............................................................... 53
7.7 Safety specifications ........................................................... 53
7.8 Electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) ................................ 53
7.9 Ambient temperature ......................................................... 54
7.10 Reference conditions .......................................................... 54
7.11 Dimensions .......................................................................... 54
8.1 Declaration of Conformity ................................................. 55
8.2 Quality Management Principles ........................................ 56
8.3 Warranty (guarantee) ......................................................... 57
9 Accessories 58
9.1 Scope of delivery 2.855.0010 ............................................ 58
9.2 Scope of delivery 2.855.0020 ............................................ 63
9.3 Optional accessories ........................................................... 68
Index 76
855 Robotic Titrosampler
■■■■■■■■
V
Page 8

Table of figures
Table of figures
Figure 1 The Titrando system .......................................................................... 1
Figure 2 Front 855 Robotic Titrosampler ........................................................ 9
Figure 3 Rear 855 Robotic Titrosampler ........................................................ 10
Figure 4 Connector strip ............................................................................... 11
Figure 5 Sensor connectors ........................................................................... 11
Figure 6 6.2041.840 Sample rack ................................................................. 12
Figure 7 Connecting the mains cable ............................................................ 13
Figure 8 Connecting the computer ............................................................... 14
Figure 9 Connecting Swing Head .................................................................. 15
Figure 10 Robotic arms - standard model versions: ......................................... 16
Figure 11 Configuration data of the robotic arms ............................................ 17
Figure 12 Limitation screw at the robotic arm ................................................. 18
Figure 13 Mounting the robotic arm ............................................................... 19
Figure 14 Connecting a beaker sensor (for example 6.1462.150) .................... 20
Figure 15 Mounting the rinsing and aspiration tubings .................................... 22
Figure 16 Mounting the distributor ................................................................. 23
Figure 17 Guide chain - Opening chain links ................................................... 24
Figure 18 Installing the rinsing tubings and the aspiration tip .......................... 25
Figure 19 Rod stirrer 802 Stirrer ...................................................................... 27
Figure 20 Magnetic stirrer 741 Stirrer .............................................................. 27
Figure 21 Connecting the tower stirrer ............................................................ 27
Figure 22 Connecting pumps .......................................................................... 28
Figure 23 Connecting a dosing device ............................................................. 30
Figure 24 Connecting MSB stirrer .................................................................... 31
Figure 25 Rod stirrer and titration stand .......................................................... 31
Figure 26 Connecting a remote box ................................................................ 32
Figure 27 USB connectors ............................................................................... 33
Figure 28 Mounting the base plate ................................................................. 34
Figure 29 Installing the drip pan ...................................................................... 35
Figure 30 Attaching the rack ........................................................................... 36
Figure 31 Mount the safety shield ................................................................... 37
Figure 32 Beaker sensor on the tower ............................................................. 42
Figure 33 Spray nozzles - Functioning ............................................................. 43
Figure 34 Connectors of the remote box ......................................................... 43
Figure 35 Pin assignment of the remote socket and plug ................................ 44
Figure 36 Rotational speed depending on stirring rate .................................... 45
■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■
■■■■■■■■
VI
855 Robotic Titrosampler
Page 9
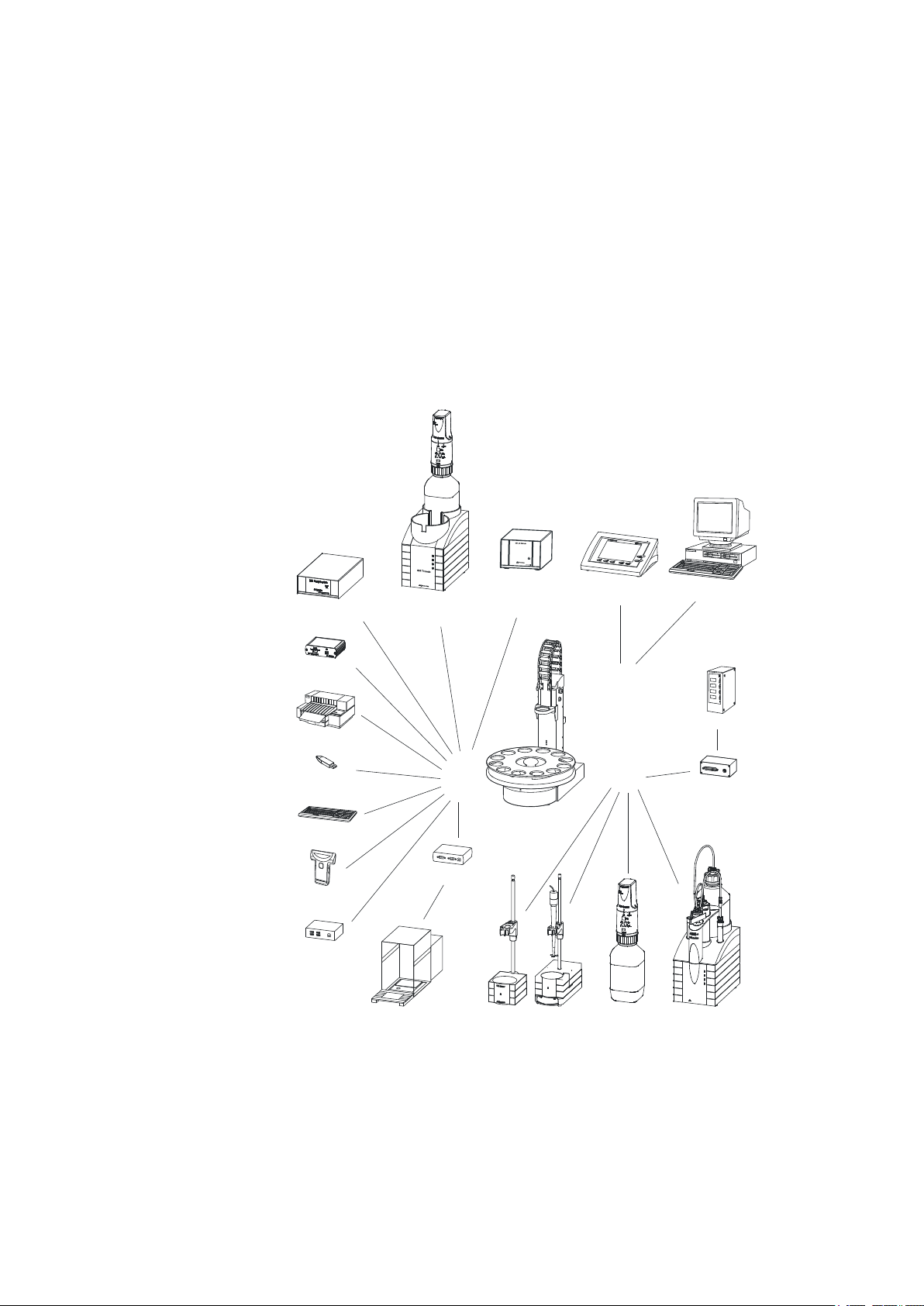
■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■
MSB
USB
Controller
PC Keyboard
Barcode
Reader
USB Hub
RS-232/USB Box
Balance
Touch Control
USB Sample Processor
Robotic Titrosampler
Printer
Bluetooth USB
Adapter
Personal Computer
Relay Box
Remote Box
Dosing Interface
USB Lab Link
Stirrer / Ti Stand Dosino Dosimat
On
Status
8
05
D
o
s
i
m
a
M
e
t
r
o
h
On
Titrando
pH Module
Conductivity Module
1 Introduction
1 Introduction
1.1 The 855 Robotic Titrosampler in the Titrando system
The 855 Robotic Titrosampler is a component of the modular Titrando system. Operation is carried out by a Touch Control with touch-sensitive screen
("Stand alone" titrator) or by a computer with a corresponding software.
A Titrando system can contain numerous, various kinds of devices. The following figure provides an overview of the peripheral devices you can connect
to the 855 Robotic Titrosampler .
855 Robotic Titrosampler
Figure 1 The Titrando system
Up to three control devices (Titrandos, Dosing Interfaces, USB Sample Processors etc.) can be controlled via USB connection by PC Control/Touch
■■■■■■■■
1
Page 10

1.2 Instrument description
Control. With the tiamo software the system can arbitrarily be extended with
control devices.
Updating the device software is described in the manual for PC Control/
Touch Control or in the tiamo help, respectively.
1.2 Instrument description
The 855 Robotic Titrosampler is a combined analysis instrument, unifying
the functionality of a titrator and a sample changer. It can be seamlessly
incorporated as a system component and control device into a Metrohm
Titrando system.
The 855 Robotic Titrosampler is a versatile instrument. It has been designed
exclusively for usage in factories and laboratories and thereby covers a wide
range of applications.
Thanks to the integration of high-performance USB interfaces, it can be
incorporated seamlessly into a Metrohm Titrando system. The various communication possibilities of the Titrando system (Remote Box, LIMS connection etc.) can thus all be used. Thanks to these abilities, a 855 Robotic
Titrosampler is predetermined for all kind of automation tasks in a modern
laboratory, especially for highly integrated laboratory data systems.
■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■
The user interface of the Touch Control or the tiamo™ software guarantees
comfortable operation and programming of the 855 Robotic Titrosampler . The comprehensive range of commands and the various configuration
possibilities can comfortably and efficiently be used this way. The integration
into the Titrando system also guarantees a 100% conformity of the complete
automation system according to the regulations of the FDA (Federal Drug
Administration), especially to the regulation 21 CFR part 11, electronic
records and signatures.
There are exchangeable standard sample racks available for many vessel
dimensions. Freely selectable "Special beaker" positions can be defined for
e.g. rinsing or conditioning beakers on every rack.
The equipment with a 786 Swing Head allows to process a large number of
samples in one single sample series. The robotic arms for the 786 Swing
Head make it possible to move to any given point on a sample rack. This
way the number (a maximum of 999 rack positions) and sequencing of the
samples is almost completely unlimited.
Customer-specific special racks for individual requirements can be fabricated
upon request.
■■■■■■■■
2
855 Robotic Titrosampler
Page 11
■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■
1.2.1 Model versions
The 855 Robotic Titrosampler is available in the following versions with
different components.
2.855.0010
1-Tower version
■ 1 membrane pumpe and 1 valve
■ 1 connector for an external pump
■ 1 stirrer connector (tower stirrer)
■ 1 786 Swing Head
■ 1 measuring interface
■ 3 MSB connectors for dosing devices or stirrers
■ 2 USB connectors
■ 1 controller connection
2.855.0020
1-Tower version
1 Introduction
■ 2 membrane pumps and 2 valves
■ 1 stirrer connector (tower stirrer)
■ 1 786 Swing Head
■ 1 measuring interface
■ 3 MSB connectors for dosing devices or stirrers
■ 2 USB connectors
■ 1 controller connection
1.2.2 Instrument components
The 855 Robotic Titrosampler has the following components:
■ Turntable
For sample racks with a diameter of up to 48 cm.
■ One tower with lift
With 786 Swing Head. Any robotic arm can be mounted.
■ One or two membrane pumps per tower
Instead of an integrated pump, an external pump connector is available
depending on the model version.
■ One stirrer connector on the tower
For connecting a rod stirrer (802 Stirrer) or a magnetic stirrer (741 Stirrer).
■ Sensor connectors
Four connectors for the following sensor types:
– pH or redox electrodes
– reference electrodes
– polarizable electrodes
– temperature sensors (Pt1000 or NTC)
855 Robotic Titrosampler
■■■■■■■■
3
Page 12
1.3 About the documentation
■ Controller connection
■ Two USB connectors
■ Three MSB connectors (Metrohm Serial Bus)
1.2.3 Intended use
The 855 Robotic Titrosampler is designed for usage as an automation system
in analytical laboratories. It is not suitable for usage in biochemical, biological or medical environments in its basic equipment version.
The present instrument is suitable for processing chemicals and flammable
samples. The usage of the 855 Robotic Titrosampler therefore requires that
the user has basic knowledge and experience in the handling of toxic and
caustic substances. Knowledge with respect to the application of the fire
prevention measures prescribed for laboratories is also mandatory.
■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■
For connecting a PC or Touch Control.
For connecting a printer, barcode reader or other control devices
(Titrando, Dosing Interface etc.).
For connecting dosing devices (Dosimat with exchange unit or Dosino
with dosing unit), stirrers or Remote Boxes.
1.3 About the documentation
Caution
Please read through this documentation carefully before putting the
instrument into operation. The documentation contains information and
warnings which the user must follow in order to ensure safe operation of
the instrument.
1.3.1 Symbols and conventions
The following symbols and styles are used in this documentation:
Cross-reference to figure legend
The first number refers to the figure number, the second to the instrument part in the figure.
Instruction step
Carry out these steps in the sequence shown.
Warning
■■■■■■■■
4
This symbol draws attention to a possible life hazard
or risk of injury.
855 Robotic Titrosampler
Page 13

■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■
1 Introduction
Warning
This symbol draws attention to a possible hazard due
to electrical current.
Warning
This symbol draws attention to a possible hazard due
to heat or hot instrument parts.
Warning
This symbol draws attention to a possible biological
hazard.
Caution
This symbol draws attention to a possible damage of
instruments or instrument parts.
Note
This symbol marks additional information and tips.
1.4 Safety instructions
1.4.1 General notes on safety
Warning
This instrument may only be operated in accordance with the specifications in this documentation.
This instrument has left the factory in a flawless state in terms of technical
safety. To maintain this state and ensure non-hazardous operation of the
instrument, the following instructions must be observed carefully.
1.4.2 Electrical safety
The electrical safety when working with the instrument is ensured as part of
the international standard IEC 61010.
Warning
Only personnel qualified by Metrohm are authorized to carry out service
work on electronic components.
855 Robotic Titrosampler
■■■■■■■■
5
Page 14

1.4 Safety instructions
■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■
Warning
Never open the housing of the instrument. The instrument could be damaged by this. There is also a risk of serious injury if live components are
touched.
There are no parts inside the housing which can be serviced or replaced
by the user.
Mains voltage
Warning
An incorrect mains voltage can damage the instrument.
Only operate this instrument with a mains voltage specified for it (see rear
panel of the instrument).
Protection against electrostatic charges
Warning
Electronic components are sensitive to electrostatic charges and can be
destroyed by discharges.
Always pull the mains cable out of the mains connection socket before
connecting or disconnecting electrical appliances on the rear panel of the
instrument.
1.4.3 Tubing and capillary connections
Caution
Leaks in tubing and capillary connections are a safety risk. Tighten all
connections well by hand. Avoid applying excessive force to tubing connections. Damaged tubing ends lead to leakage. Appropriate tools can
be used to loosen connections.
Check the connections regularly for leakage. If the instrument is used
mainly in unattended operation, then weekly inspections are mandatory.
■■■■■■■■
6
855 Robotic Titrosampler
Page 15

■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■
1.4.4 Personnel safety
Wear protective goggles and working clothes suitable for laboratory work
while operating the 855 Robotic Titrosampler . It is also advisable to wear
gloves when caustic liquids are used or in situations where glass vessels
could break.
Always install the safety shield supplied with the equipment before using
the instrument for the first time. Pre-installed safety shields are not
allowed to be removed.
The 855 Robotic Titrosampler may not be operated without a safety
shield!
1 Introduction
Warning
Warning
Warning
Personnel are not permitted to reach into the working area of the instrument while operations are running!
A considerable risk of injury exists for the user.
Warning
In the event of a possible blockage of a drive, the mains plug must be
pulled out of the socket immediately. Do not attempt to free jammed
sample vessels or other parts while the device is switched on. Blockages
can only be cleared when the instrument is in a voltage-free status; this
action generally involves a considerable risk of injury.
Warning
The 855 Robotic Titrosampler is not suitable for utilization in biochemical,
biological or medical environments in its basic equipment version.
855 Robotic Titrosampler
Appropriate protective measures must be implemented in the event that
potentially infectious samples or reagents are being processed.
■■■■■■■■
7
Page 16
1.4 Safety instructions
1.4.5 Flammable solvents and chemicals
Warning
All relevant safety measures are to be observed when working with flammable solvents and chemicals.
■ Set up the instrument in a well-ventilated location.
■ Keep all sources of flame far from the workplace.
■ Clean up spilled liquids and solids immediately.
■ Follow the safety instructions of the chemical manufacturer.
1.4.6 Recycling and disposal
This product is covered by European Directive 2002/96/EC, WEEE – Waste
from Electrical and Electronic Equipment.
The correct disposal of your old equipment will help to prevent negative
effects on the environment and public health.
■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■
More details about the disposal of your old equipment can be obtained from
your local authorities, from waste disposal companies or from your local
dealer.
■■■■■■■■
8
855 Robotic Titrosampler
Page 17
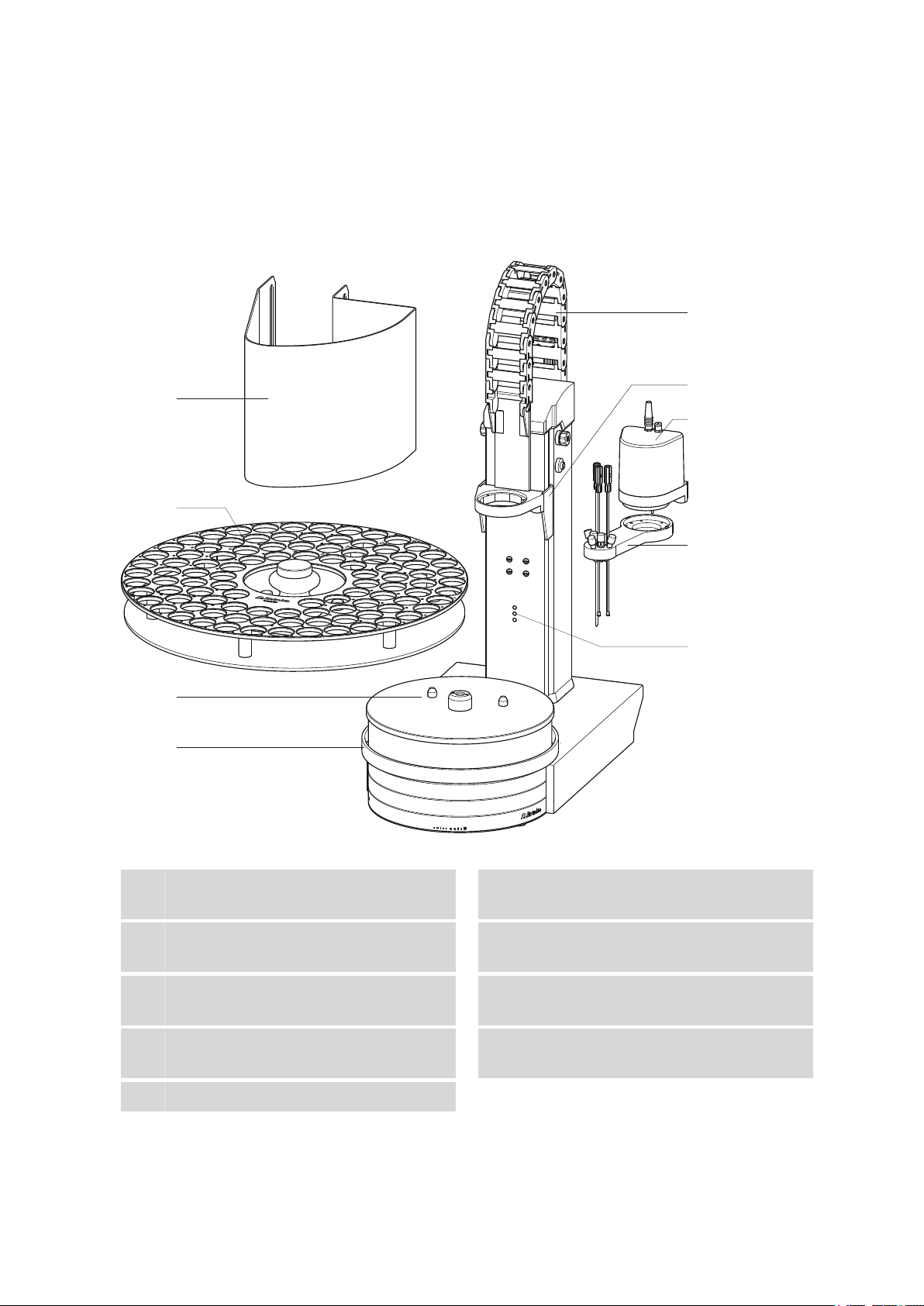
■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
2 Overview of the instrument
2.1 Front and rear
2 Overview of the instrument
Figure 2 Front 855 Robotic Titrosampler
Safety shield (6.2751.100)
1
Other models, see chap. Accessories.
Turntable
3
With guide bolts.
Guide chain
5
For cables and tubings.
786 Swing Head (2.786.0020)
7
Drive for a robotic arm.
Beaker sensor
9
855 Robotic Titrosampler
Sample rack (6.2041.800)
2
Other models, see chap. Accessories.
Assembly rail
4
For magnetic stirrer (741 Stirrer).
Lift
6
With titration head holder.
Robotic arm (6.1462.050)
8
With aspiration and dosing tips.
■■■■■■■■
9
Page 18
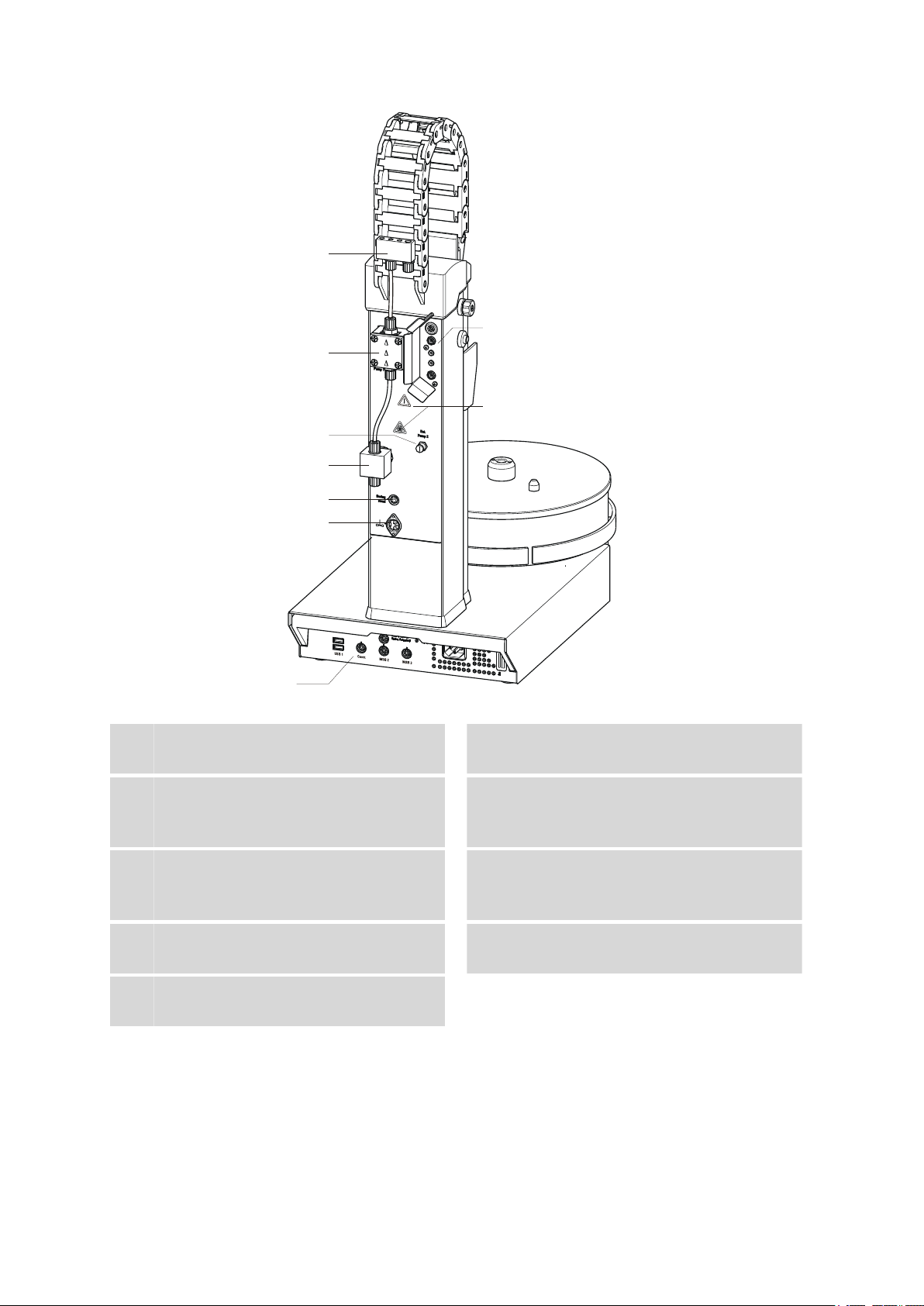
2.1 Front and rear
USB 2
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■
Figure 3 Rear 855 Robotic Titrosampler
Distributor
1
For rinsing equipment.
Pump connection
3
Pump 2. For external pumps (e. g. 722 Pump
Unit or 823 Pump Unit).
Swing Head connector
5
Mini DIN socket (9-pin).
Connector strip
7
Warning symbols
9
See chapter Safety instructions.
Membrane pump
2
Pump 1.
Pump valve
4
Stirrer connector
6
DIN socket. For rod stirrer (802 Stirrer) or
magnetic stirrer (741 Stirrer).
Measuring interface
8
With different sensor connectors.
■■■■■■■■
10
855 Robotic Titrosampler
Page 19
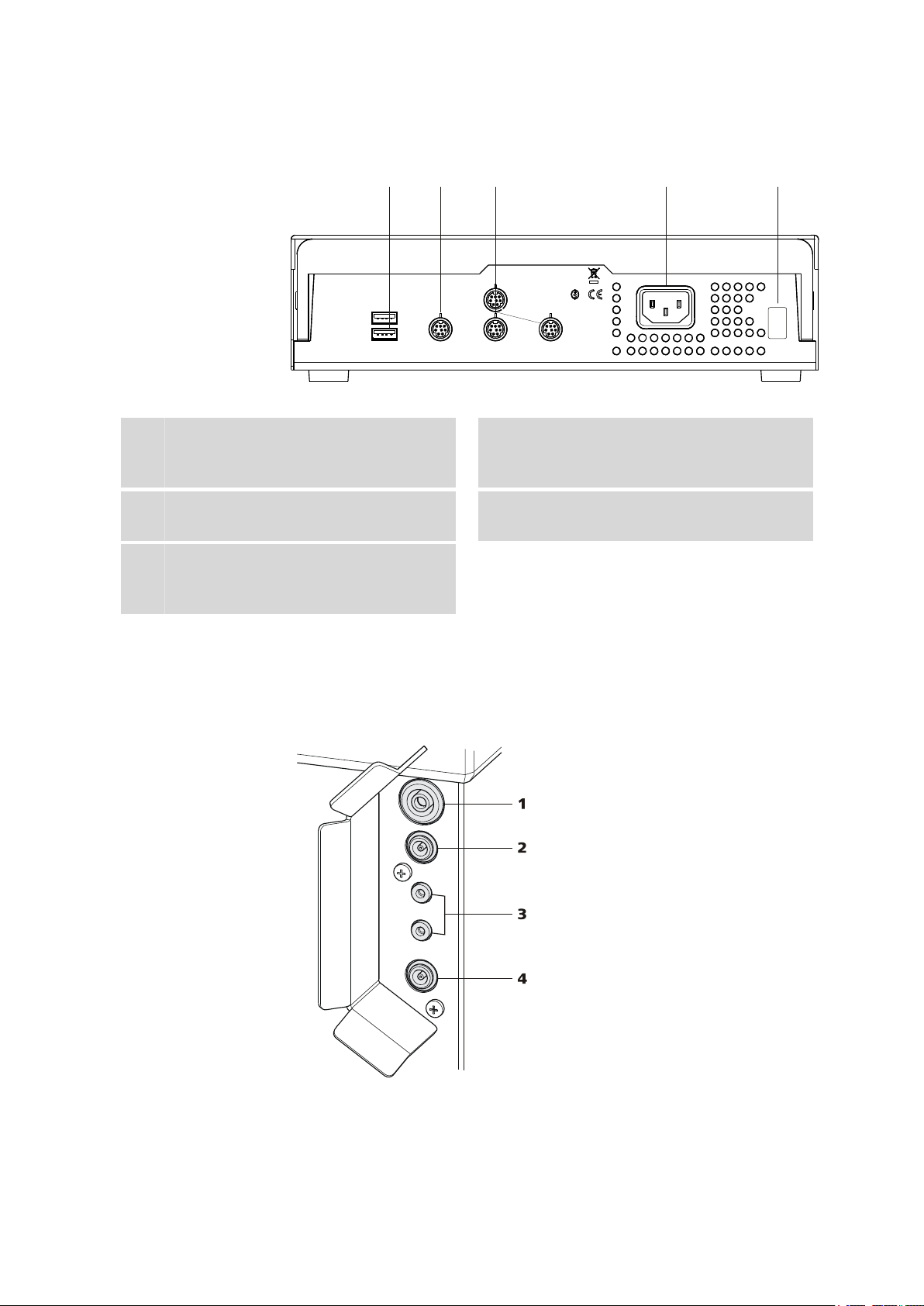
■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■
USB 2
USB 1
Contr.
MSB 1
MSB 2
MSB 3
Made by Metrohm
Herisau Switzerland
P: 115W U: 100 - 240 V f: 50 - 60 Hz
WARNING - Fire Hazard -
For continued protection replace only
with the same type and rating of fuse
Nr.
1 2 3 4 5
Ref.
Ind.
Temp.
Pol.
2.2 Rear panel
Figure 4 Connector strip
2 Overview of the instrument
USB connectors
1
MSB connector
3
For stirrers, dosing devices, Remote Box.
Type plate
5
Contains specifications concerning mains
voltage and serial number.
2.3 Sensor connectors
The connectors for electrodes and temperature sensors are located on the
rear of the tower.
Controller connector
2
For the connection to the PC or Touch Control.
Mains connection
4
Figure 5 Sensor connectors
855 Robotic Titrosampler
■■■■■■■■
11
Page 20

2.4 Sample racks
■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■
Electrode connector (Ref.)
1
For connecting reference electrodes. Socket
B, 4 mm.
Temperature sensor connector
3
For connecting temperature sensors of the
Pt1000 or NTC types. Two B sockets, 2 mm.
2.4 Sample racks
A sample rack is a turntable that acts as a receptacle for sample vessels.
Various types of sample racks are available for different numbers and types
of sample vessels.
The 855 Robotic Titrosampler requires sample racks with up to a maximum
of 42 cm diameter.
Electrode connector (Ind.)
2
For connecting pH or redox electrodes with
integrated or separate reference electrode.
Socket F.
Electrode connector (Pol.)
4
For connecting polarizable electrodes, e.g.
double Pt electrodes. Socket F.
Figure 6 6.2041.840 Sample rack
Other user-defined racks can be supplied upon request and the required rack
data can be loaded and configured in the control software. Any arrangement
of rack positions is possible.
Magnet codes
Every single sample rack can be unambiguously identified by means of a
magnet code. The Sample Processor can thus recognize automatically which
rack is in place.
When replacing a rack, this should first be returned to starting position using
the Rack initialization function (see "Manual Control" in the control software). This will enable an unambiguous recognition of the rack and thus the
correct positioning of the beaker. A positioning table is assigned to each
rack type in which each rack position is defined.
■■■■■■■■
12
855 Robotic Titrosampler
Page 21
■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■
P: 115W U: 100 - 240 V f: 50 - 60 Hz
Nr.
3 Installation
3.1 Setting up the instrument
3.1.1 Packaging
The instrument is supplied in highly protective special packaging together
with the separately packed accessories. Keep this packaging, as only this
ensures safe transportation of the instrument.
3.1.2 Checks
Immediately after receipt, check whether the shipment has arrived complete
and without damage by comparing it with the delivery note.
3.1.3 Location
The instrument has been developed for operation indoors and may not be
used in explosive environments.
3 Installation
Place the instrument in a location of the laboratory suitable for operation
and free of vibrations, if possible protected from corrosive atmospheres and
contamination by chemicals.
The instrument should be protected against excessive temperature fluctuations and direct sunlight.
3.2 Preparing the Sample Processor
3.2.1 Connecting a mains cable
Warning
This instrument must not be operated except with the mains voltage
specified for it (see rear panel of the instrument).
Protect the connection sockets against moisture.
855 Robotic Titrosampler
Figure 7 Connecting the mains cable
■■■■■■■■
13
Page 22
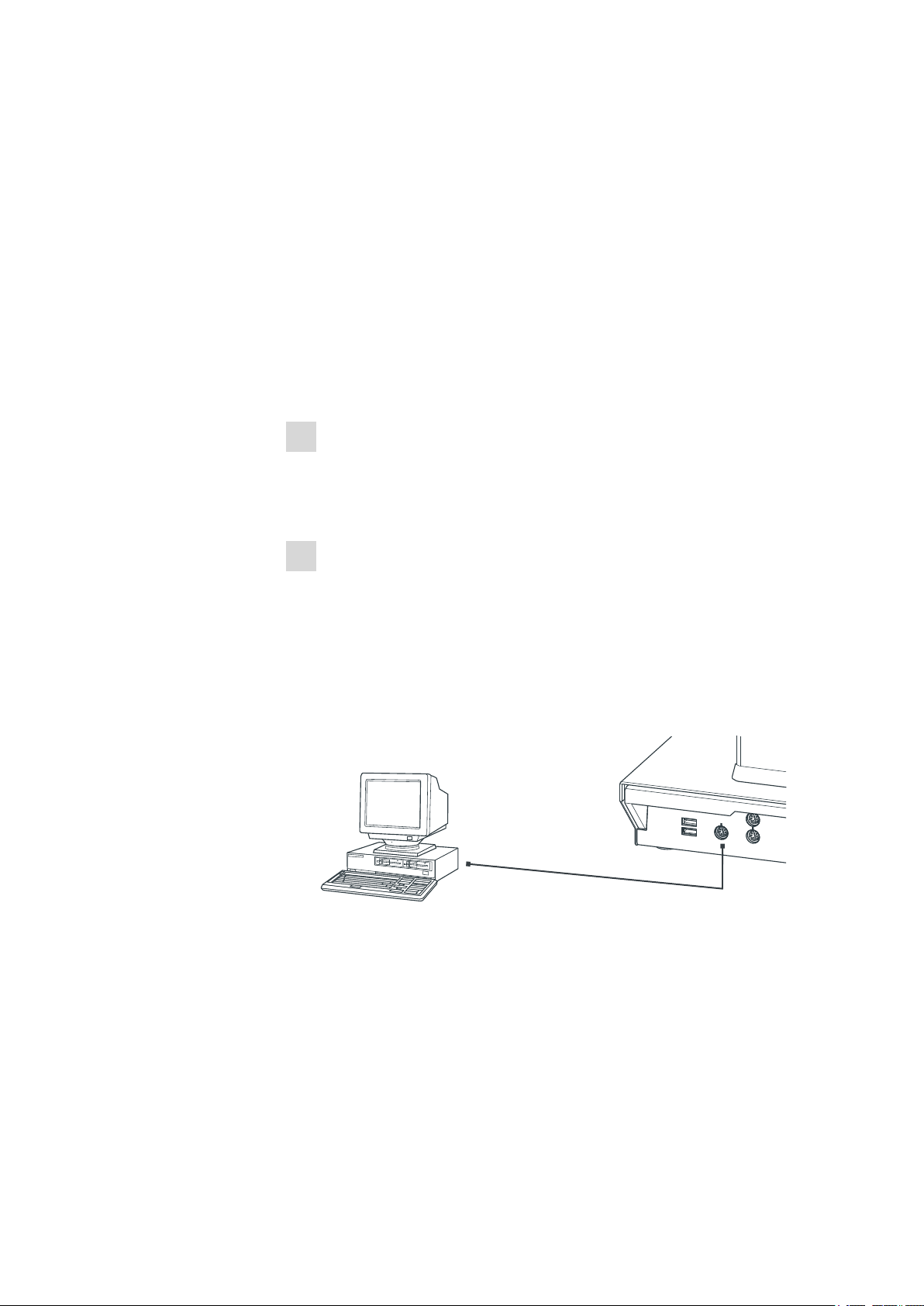
3.3 Connecting a computer
6.2151.000
USB 2
USB 1
Contr.
MSB 2
3.3 Connecting a computer
The 855 Robotic Titrosampler requires a USB connection to a computer in
order to be able to be controlled by a PC software. When a 6.2151.000
controller cable is used, the instrument can be connected directly, either to
a USB socket on a computer, to a connected USB hub or to a different
Metrohm control instrument.
Cable connection and driver installation
A driver installation is required in order to ensure that the 855 Robotic Titrosampler is recognized by the PC software. To accomplish this, you must
comply with the procedures specified. The following steps are necessary:
1
Installing the software
■ Insert the PC software installation CD and carry out the installation
program directions.
■ Exit the program if you have started it after the installation.
2
Establishing cable connections
■ Connect all peripheral devices to the instrument (see Chapter
3.13, page 29).
■ Connect the 855 Robotic Titrosampler to the mains supply if you
have not already done this.
■ Connect the instrument to your computer through a USB connector
(Type A) (see Instructions for Use for your computer). The
6.2151.000 cable is used for this purpose.
■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■
■■■■■■■■
14
Figure 8 Connecting the computer
For Windows 2000: The instrument is recognized and the driver is
installed automatically.
For Windows XP: The instrument is recognized and the installation
assistant for the driver is started automatically. Select the option "Install
software automatically" and click on [Continue]. Exit the assistant with
[Finish].
855 Robotic Titrosampler
Page 23
■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■
3 Installation
For Windows Vista: The instrument is recognized and the installation
assistant for the driver is started automatically. Select the option "Find
and install driver software". Agree to all subsequent requests. The
installation assistant will be exited automatically.
Note
The plug on the instrument end of the 6.2151.000 controller cable is
protected with an anti-pull device to prevent the cable from being pulled
out accidentally. If you wish to pull out the plug, then you must first retract
the outer plug sleeve marked with arrows.
Registering and configuring the instrument in the PC software
The instrument must be registered in the configuration of your PC software.
Once that has been done, you can then configure it according to your
requirements. Proceed as follows:
1
Setting up the instrument
■ Start up the PC software.
The instrument is recognized automatically. The configuration dialog for the instrument is displayed.
■ Make configuration settings for the instrument and its connectors.
More detailed information concerning the configuration of the instument can be found in the documentation for the respective PC software.
3.4 Connecting the Swing Head
Take care to ensure that the Swing Head is connected before the instrument
is started up. Check the connection cable.
The connection socket (Mini DIN) for the Swing Head drive is each located
on the rear of the tower next to the stirrer connector.
Figure 9 Connecting Swing Head
855 Robotic Titrosampler
■■■■■■■■
15
Page 24
3.5 Configuring the robotic arm
321
4 5
If the Swing Head is not connected, connect it as follows:
1
Plug in the cable
■ Guide the connection cable of the Swing Head through the guide
chain of the tower (see Chapter 3.9, page 24).
■ Plug the Mini DIN plug into the socket 'Swing Head'.
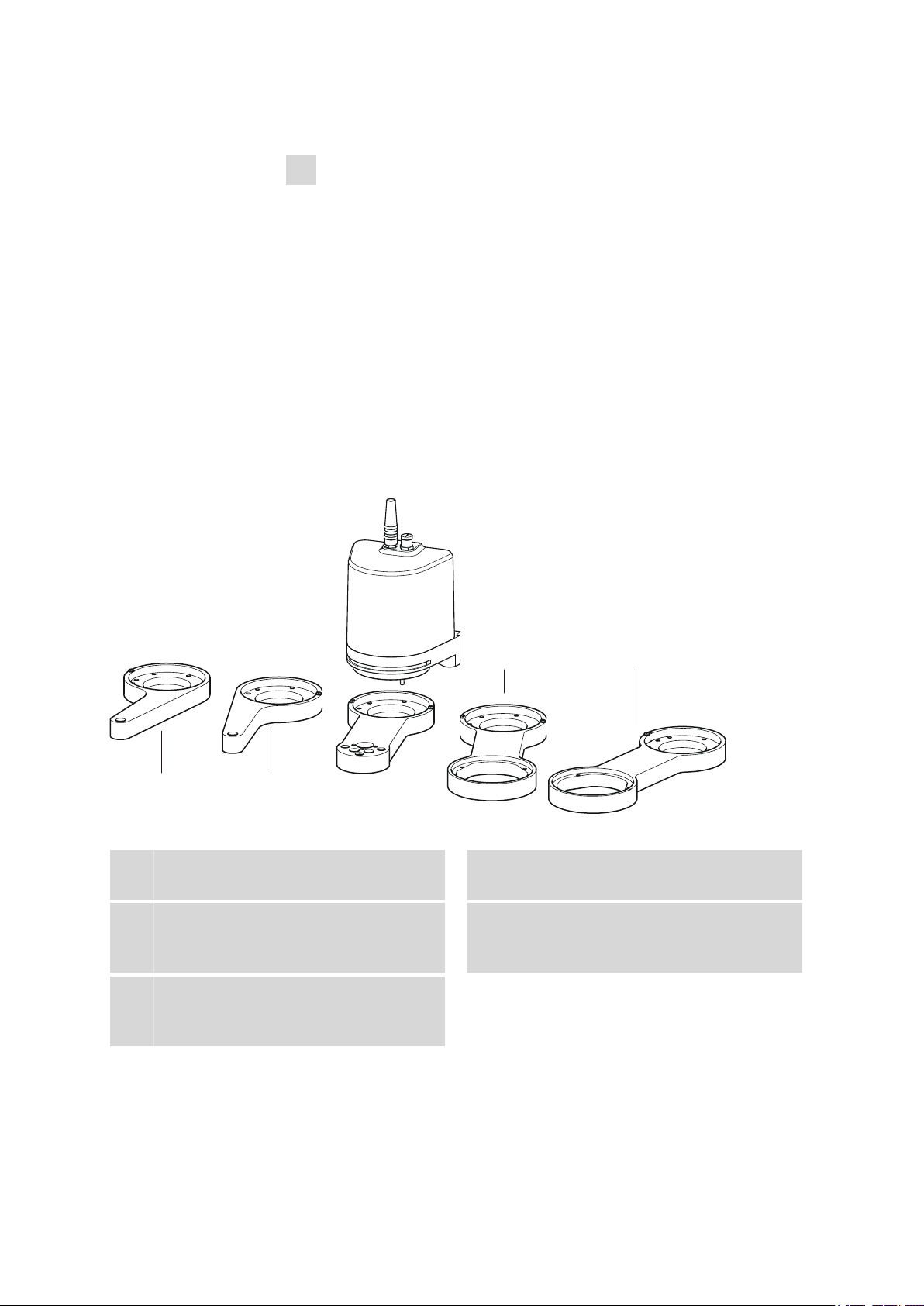
3.5 Configuring the robotic arm
A variety of differently constructed robotic arms is available for enabling a
wide range of applications. They differ from one another in their geometric
sizes, e.g. swing radius or maximum permissible swing angle. The configuration data must be entered in the Sample Processor or in the control
software prior to the assembly of the robotic arm. The data required
is engraved on the underside of the robotic arm. Examples of the most
common robotic arms are shown in the illustration below.
■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■
Figure 10 Robotic arms - standard model versions:
Transfer robotic arm (6.1462.030)
1
For sample transfer, left-swinging.
Titration robotic arm (6.1462.050)
3
With titration head, left-/right-swinging *).
Macro robotic arm (6.1462.070)
5
With holder for a 6.1458.XXX titration head
insert, right-swinging.
*) can be mounted in two ways
■■■■■■■■
16
Transfer robotic arm (6.1462.040)
2
For sample transfer, right-swinging.
Macro robotic arm (6.1462.060)
4
With holder for a 6.1458.XXX titration head
insert, left-swinging.
855 Robotic Titrosampler
Page 25
■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■
2
3
4
5
1
3 Installation
Note
A detailed list of the available robotic arms, along with the necessary
configuration data, can be found in Chapter Robotic arms, page 46ff.
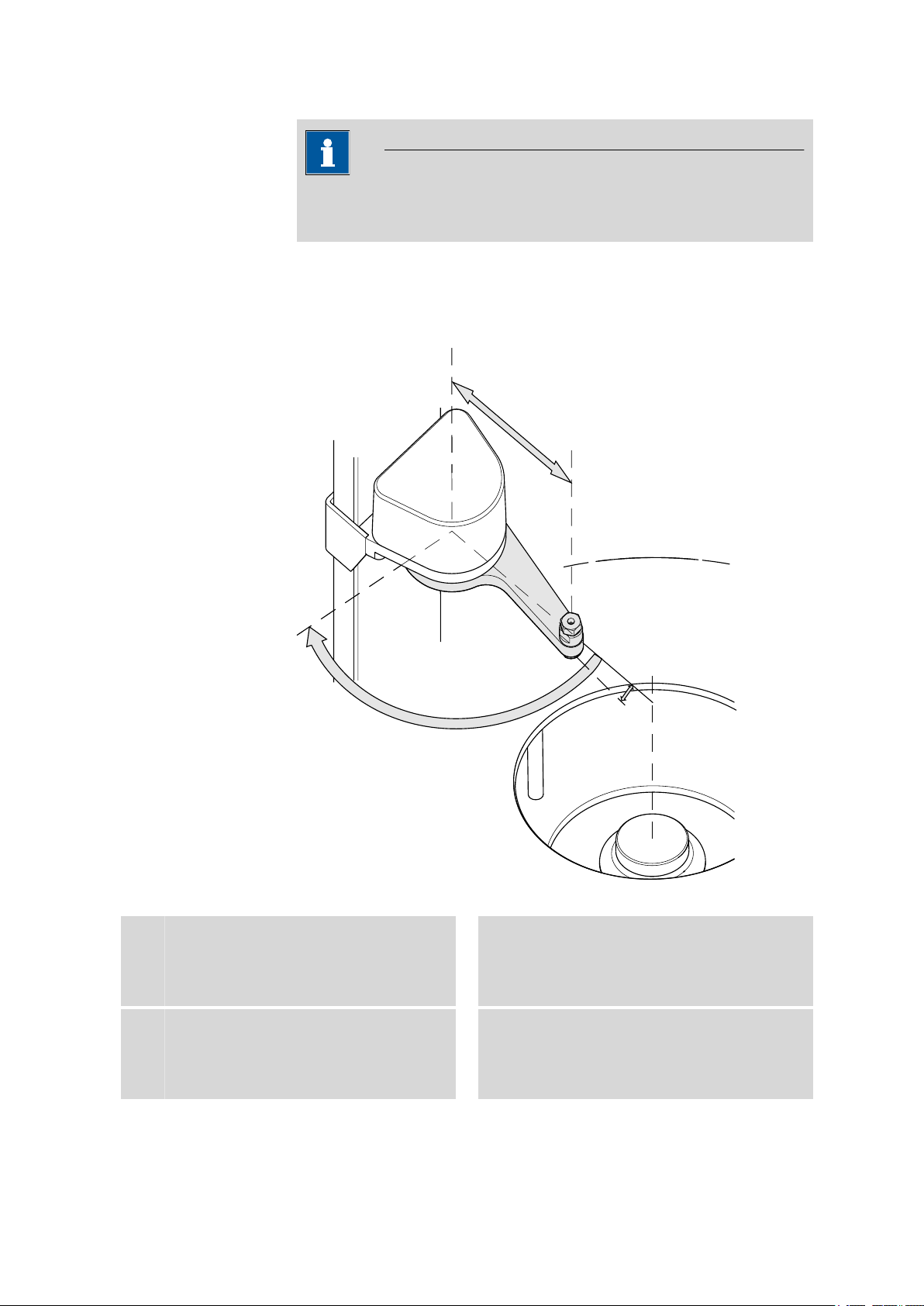
The following figure illustrates the most important configuration data that
needs to be set in the control software to ensure correct usage of a robotic
arm (left-swinging, here).
Figure 11 Configuration data of the robotic arms
Swing axis
1
This runs through the middle of the Swing
Head drive.
Source axis
3
This runs from the swing axis to the midpoint
of the sample rack and marks the initial position of the robotic arm.
855 Robotic Titrosampler
Swing radius
2
This is determined by the length of the robotic
arm. The radius runs from the axis of rotation
to the midpoint of the tip of the robotic arm.
Swing offset
4
This determines the 0° position of the robotic
arm.
■■■■■■■■
17
Page 26
3.6 Mounting the robotic arm
1
2
Max. swing angle
5
This stands for the swing range that the
robotic arm can reach. The range runs from
the source axis to the maximum possible
robotic arm position.
Swing direction
Left-swinging (swing direction +) or right-swinging (swing direction –)
model versions are available as different types of robotic arms. Left-swinging
means swinging from the initial position (pointing towards the middle of the
rack) outwards to the left.
In the case of a Sample Processor with two towers, a right-swinging robotic
arm must be mounted on Tower 1, a left-swinging robotic arm on Tower 2.
If the alignment is incorrect, the two robotic arms could possibly come into
contact with one another, resulting in damage to the drives.
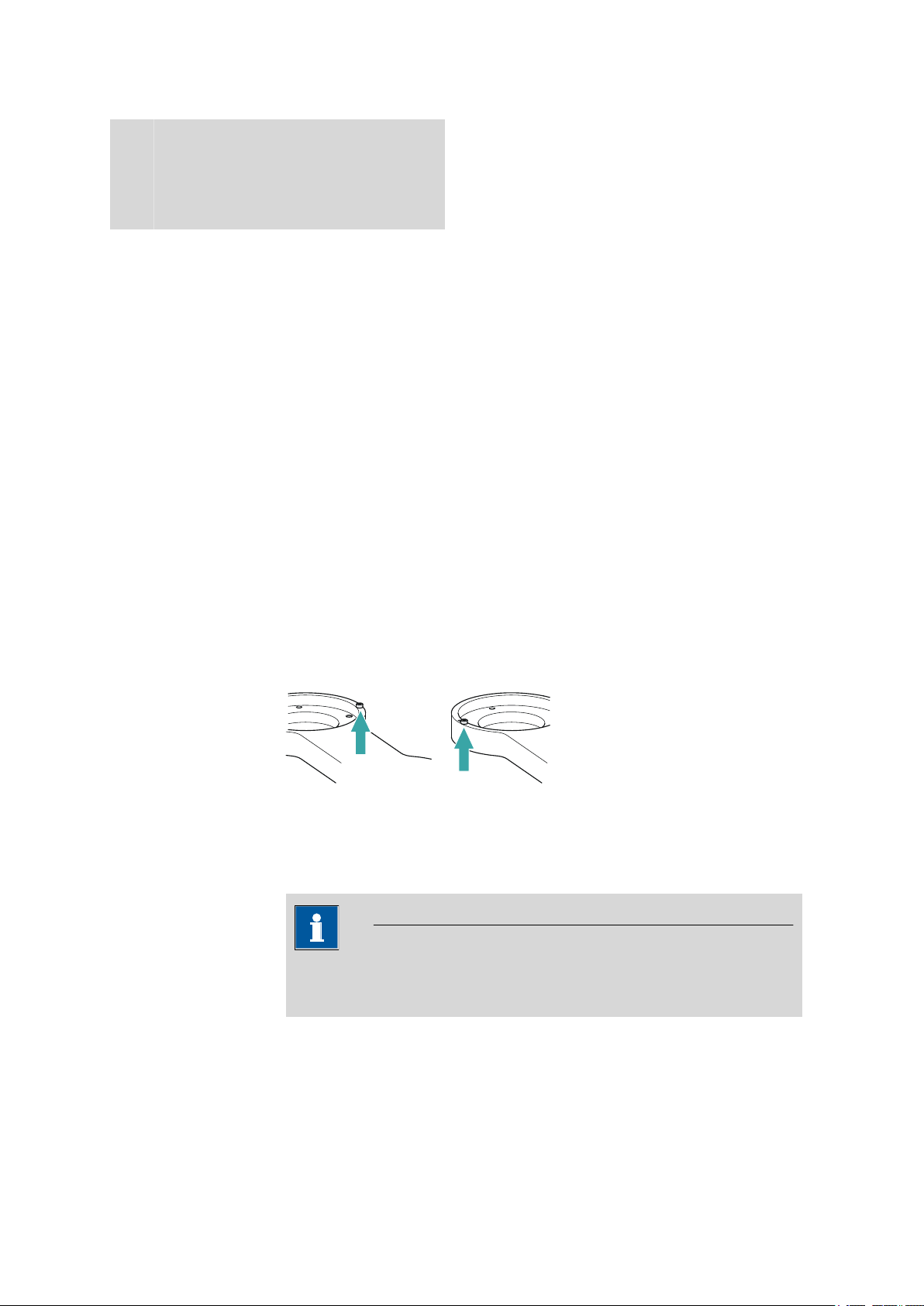
3.6 Mounting the robotic arm
■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■
Depending on the model, robotic arms can be mounted as either rightswinging or left-swinging. The position of the limitation screw of the robotic
arm must be taken into account during assembly. The limitation screw must
face the tower of the Sample Processor during the mounting of the robotic
arm. The following illustration shows on the left the position of the limitation
screw at a right-swinging robotic arm (Position 1) and on the right with a
left-swinging robotic arm (Position 2).
Figure 12 Limitation screw at the robotic arm
For robotic arms which can be mounted in two different ways (e.g.
6.1462.050), the limitation screw can be fitted in accordance with the
required assembly direction (see above).
Note
The configuration data of a robotic arm must be configured in the control
software before it is mounted (see Chapter 3.5, page 16).
18
■■■■■■■■
855 Robotic Titrosampler
Page 27

■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■
1
2
3
3 Installation
Mounting the robotic arm
The mounting of a robotic arm on the Swing Head is described here, taking
as an example a 6.1462.070 robotic arm for titration and a 6.1458.040
titration head insert. Initialize the Sample Processor before performing the
mounting sequence.
After the initialization of the Sample Processor, the drive disc of the Swing
Head is positioned as though the robotic arm were located in the outermost
position.
Figure 13 Mounting the robotic arm
Mount the robotic arm as follows:
Place the 6.1458.040 titration head insert in the opening of the robotic
1
arm and screw tight with the supplied screws.
Hold the robotic arm in such a way that the opening faces to the right.
2
While doing so, rotate the robotic arm outwards as far as possible,
i.e. towards the tower - see above. Slip the robotic arm from below
over the guide pins of the drive disc of the Swing Head.
Note
Take care to ensure that you do not twist the drive disc, thus causing
pressure against the drive.
855 Robotic Titrosampler
■■■■■■■■
19
Page 28

3.7 Robotic arms with beaker sensor
6.1462.150
1
2
3
Screw the robotic arm to the Swing Head tightly with the screws and
3
washers provided.
3.7 Robotic arms with beaker sensor
For safety reasons, the presence of a beaker on the sample rack of a Sample
Processor can be detected. Some robotic arm model versions are therefore
equipped with a beaker sensor.
■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■
Figure 14 Connecting a beaker sensor (for example 6.1462.150)
Plug of the connection cable
1
Beaker sensor
3
Contact sensor in accordance with the Piezo
principle
A robotic arm with beaker sensor is mounted as described on page 18. The
Connection socket on the 786 Swing
2
Head
connection of the sensor cable must take place while the instrument is
switched off.
The beaker sensor is automatically recognized when switching on the instru-
■■■■■■■■
20
ment.
855 Robotic Titrosampler
Page 29

■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■
Functioning of the beaker sensor
If the beaker sensor of the robotic arm is activated, then the lift of the Sample
Processor will move automatically into its work position after a MOVE command. The presence of the sample vessel is checked by the robotic arm
setting down on top of it.
No separate LIFT command is required in such cases.
Note
The work position of the lift must be configured in such a way that the
robotic arm is in place on the sample vessel. The robotic arm must bend
very slightly while doing so, so that the Piezo sensor will generate a signal.
3.8 Installing rinsing and aspiration equipment
Various tubings are necessary for rinsing the electrode and the dosing tips
as well as for aspirating the sample solution after the titration. First, mount
the tubings on the distributor.
3 Installation
Mounting the rinsing and aspiration tubings
Install the tubings as follows:
855 Robotic Titrosampler
■■■■■■■■
21
Page 30

3.8 Installing rinsing and aspiration equipment
6.1805.510
6.1805.060
6.1808.170
6.1812.000
1
2
3
4
Figure 15 Mounting the rinsing and aspiration tubings
1
Mount the rinsing tubings
■ Manually tighten the three 6.1805.060 FEP tubings (60 cm) in
the M6 bore holes of the distributor. Place the tubings into the guide
chain (see Chapter 3.9, page 24).
These are the feed lines for the spray nozzles.
2
Mount the aspiration tubing
■ Manually tighten the 6.1805.510 FEP aspiration tubing (60 cm)
in the M8 bore hole of the distributor.
3
Mount the feed line for the rinsing liquid
■ Remove the union nut of the left-hand connector of the distributor
and guide it over the end of a 6.1812.000 PTFE tubing. You may
have to extend the tubing end in order to be able to better mount
the tubing, see note below. Pull the end of the tubing over the
connection nipple of the distributor and fasten in place with the
union nut.
The tubing leads to the rinsing pump (Pump 1) and can be cut to
the correct length.
■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■
■■■■■■■■
22
855 Robotic Titrosampler
Page 31

■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■
6.1808.170
1
2
3 Installation
Note
The opening of the tubing may need to be widened with a sharp
object (e.g. with a Phillips screwdriver).
A piece of sandpaper may be used to get a better grip on the tubing.
Do not extend the tubing end before having slid the union nut onto
the tubing.
4
Mount the outlet tubing
■ Remove the union nut of the right-hand connector of the distributor
and guide it over the end of the 6.1812.000 PTFE tubing. Pull
the end of the tubing over the connection nipple of the distributor
and fasten in place with the union nut.
The tubing leads to the aspiration pump (Pump 2) and can be cut
to the correct length.
Mounting the distributor
Figure 16 Mounting the distributor
Proceed as follows:
1
Remove a chain link
■ Remove the clip of the third chain link of the guide chain. Pry out
the clip with a screwdriver on both sides of the chain link, as shown
in the preceding illustration.
2
Insert the distributor
■ Apply strong pressure to insert the 6.1808.170 distributor (with
the tubing connected) into the open chain link.
855 Robotic Titrosampler
■■■■■■■■
23
Page 32

3.9 Guide chain for cables and tubing
3
Fix the rinsing tubings
■ Place the rinsing tubings into the guide chain.
3.9 Guide chain for cables and tubing
Tubings and cables can be placed into the guide chain.
You can open the individual chain links with a screwdriver as follows.
1
Open the guide chain
■ Insert a screwdriver into the groove located on the side of a chain
link.
■ Loosen the clip with a forceful leverage movement.
■ Pull the clip out of the chain by hand.
■ Repeat the above actions for each chain link.
■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■
■■■■■■■■
24
Figure 17 Guide chain - Opening chain links
2
Insert into the guide chain
■ Place the required tubings or cables into the guide chain.
3
Close the guide chain
■ Close the clip for each chain link again by hand and apply forceful
pressure to snap them into place.
855 Robotic Titrosampler
Page 33

■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■
1
2
3
6.1805.060
6.1805.510
6.1543.170
Caution
Take care to ensure when mounting tubing and cables that there is no
traction on the drives while moving the lift or swiveling the robotic arm.
This could lead to overloading of and possible damage to the drive.
Remove the clips of the two lowest chain links when you install the rinsing
and aspiration tubing.
3.10 Equipping the titration head
Mounting the aspiration and rinsing tubings
3 Installation
855 Robotic Titrosampler
Figure 18 Installing the rinsing tubings and the aspiration tip
Proceed as follows:
1
Connect the rinsing nozzles
■ Connect the three rinsing tubings that are already connected to the
Tower 2 distributor to the rinsing nozzles already mounted on the
titration head.
■■■■■■■■
25
Page 34

3.10 Equipping the titration head
1
2
3
4
1.802.0010
6.1909.050
6.2104.030
6.1236.020
6.0229.100
6.1805.120
■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■
2
Insert the aspiration tip
■ Insert the 6.1543.170 aspiration tip into the opening left on the
front of the titration head.
3
Connect the aspiration tubing
■ Connect the 6.1805.510 aspiration tubing already connected to the
distributor with the aspiration tip.
Inserting the stirrer and the electrode, connecting the dosing tubings
■■■■■■■■
26
The equipment of the titration head is completed as follows:
1
Insert the rod stirrer
■ Insert the rod stirrer (802 Stirrer) into the rear opening of the titra-
tion head (at the arrow).
■ Insert the cable into the guide chain.
855 Robotic Titrosampler
Page 35

■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■
2
Mount the stirring propeller
■ Fasten the 6.1909.050 stirring propeller to the rod stirrer from
below.
3
Insert the electrode
■ Insert the electrode (e.g. a 6.0229.100 Solvotrode) with a
6.1236.020 SGJ sleeve into the titration head.
4
Connect the dosing tubings
■ Connect two dosing tubings (e.g 6.1805.120) to the pre-mounted
dosing tips on the titration head.
3.11 Connecting the tower stirrer
A DIN socket for connecting a rod stirrer (802 Stirrer) or a magnetic stirrer
(741 Stirrer) is located on the rear side of the tower.
3 Installation
Figure 19 Rod stirrer 802 Stirrer
Figure 20 Magnetic stirrer 741 Stirrer
Take care to observe correct orientation of the contact pins when plugging
in the stirrer connection cable. The rib on the outside of the plug must match
the reference mark (on the left) on the socket.
Figure 21 Connecting the tower stirrer
855 Robotic Titrosampler
■■■■■■■■
27
Page 36

3.12 Connecting external pumps
Note
If an MSB stirrer is connected to the MSB1 socket, then the stirrer connector at tower 1 cannot be used, because both sockets are controlled
internally via MSB1.
3.12 Connecting external pumps
If no integrated pump or a Sample Processor model version without pumps
is used, up to two external pumps per tower can be connected.
The 843 Pump Station (as model version with membrane pumps or with
peristaltic pumps) has two pump drives and is connected to two sockets of
the Sample Processor via the 6.2141.300 connection cable (double cable
with two plugs). The 772 Pump Unit (peristaltic pump) and the 823
Membrane Pump Unit (membrane pump) have a firmly mounted connection cable with a single plug.
■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■
Connecting pumps
Figure 22 Connecting pumps
Connect external pumps as follows:
1
Connect the connection cable
■ Plug each of the two threaded plugs of the connection cable into
one of the connection sockets Ext. pump 1 or Ext. pump 2 on
the rear of a tower of the Sample Processor.
Correct alignment of the 3 contact pins must be observed.
■ Tighten the knurled screw at the front end of the plug by hand in
clockwise direction. This will secure the plug.
With an 843 Pump Station, connect the other end of the cable (9-pin
2
D-Sub plug) to the socket Remote 1 of the pump.
■■■■■■■■
28
855 Robotic Titrosampler
Page 37

■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■
3.13 Connecting MSB devices
In order to connect MSB devices, e.g.stirrers or dosing devices, Metrohm
instruments are equipped with up a maximum of four connectors at what
is referred to as the Metrohm Serial Bus (MSB). Various kinds of peripheral
devices can be connected in sequence (in series, as a "daisy chain") at a single
MSB connector (8-pin Mini DIN socket) and controlled simultaneously by the
respective control instrument. In addition to the connection cable, stirrers
and the remote box are each equipped with their own MSB socket for this
purpose.
The following illustration provides an overview of the devices that can be
connected to an MSB socket, along with a number of different cabling variations.
The question of which peripheral devices are supported depends on the
control instrument.
Note
3 Installation
When connecting MSB devices together, the following must be observed:
■ Only one device of the same type can be used at a single MSB con-
nector at one time.
■ Type 700 Dosino and 685 Dosimat dosing devices cannot be connec-
ted together with other MSB instruments on a shared connector. These
dosing devices must be connected separately.
Caution
Exit the control software before you plug MSB instruments in. The control
instrument recognizes when it is switched on which instrument is connected at which MSB connector. The operating unit or the control
software enters the connected MSB devices into the system configuration
(Device manager).
MSB connections can be extended with the 6.2151.010 cable. The length
of the connection must not exceed a maximum of 15 m.
855 Robotic Titrosampler
■■■■■■■■
29
Page 38

3.13 Connecting MSB devices
USB 1
Contr.
MSB 2
MSB 3
T.2400.102
3.13.1 Connecting dosing devices
Three dosing devices can be connected to the instrument.
The types of dosing devices that are supported are:
■ 800 Dosino
■ 700 Dosino
■ 805 Dosimat
■ 685 Dosimat
Warning
If a Dosino is connected to the 855 Robotic Titrosampler then the connection cable must be equipped with a T.2400.102 ferrite core. The ferrite
core reduces any interference voltages that may occur and thus ensures
compliance with strict EMC standards pursuant to applicable technical
norms, see Chapter "Technical Data".
Proceed as follows:
1
Mounting ferrite core
Fasten a T.2400.102 ferrite core to the Dosino connection cable near
to the plug.
2
Connect a dosing device
■ Exit the control software.
■ Connect the connection cable to one of the sockets marked with
MSB on the rear of the control instrument.
■ Start the control software.
■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■
■■■■■■■■
30
Figure 23 Connecting a dosing device
855 Robotic Titrosampler
Page 39

■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■
USB 1
Contr.
MSB 2
MSB 3
3.13.2 Connecting a stirrer or titration stand
You can use a magnetic stirrer 801 Stirrer or 803 Ti Stand (stirring "from
below") or the 804 Ti Stand with a rod stirrer 802 Stirrer (stirring "from
above").
Connect a stirrer or a titration stand as follows:
1
Connect a stirrer or titration stand
■ Exit the control software.
■ Connect the connection cable of the magnetic stirrer or of the titra-
tion stand to one of the sockets marked with MSB on the rear of
the control instrument.
■ If desired, connect the rod stirrer to the stirrer socket (with stirrer
symbol) of the titration stand.
■ Start the control software.
3 Installation
Figure 24 Connecting MSB stirrer
Figure 25 Rod stirrer and titration stand
855 Robotic Titrosampler
■■■■■■■■
31
Page 40

3.13 Connecting MSB devices
USB 1
Contr.
MSB 2
MSB 3
Note
If an MSB stirrer ist connected to the MSB1socket, then the stirrer connector at Tower 1 cannot be used, because both sockets are controlled
internally via MSB1. This also applies to the MSB2 socket and the stirrer
connector on Tower 2 for 2-tower models of USB Sample Processors.
3.13.3 Connecting a remote box
Instruments that are controlled via remote lines and/or which send control
signals via remote lines can be connected using the 6.2148.010 remote box.
In addition to Metrohm, other instrument manufacturers also use similar
connectors that make it possible to connect different instruments together.
These interfaces are also frequently given the designations "TTL Logic", "I/O
Control" or "Relay Control" and generally have a signal level of 5 volts.
Control signals are understood to be electrical line statuses or brief
(> 200 ms) electrical pulses which display the operational state of an instrument or which trigger or report an event. Sequences on a variety of
instruments can thus be coordinated in a single complex automation system.
No exchange of data is possible, however.
■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■
Proceed as follows:
1
Connect a remote box
■ Exit the control software.
■ Connect the remote box connection cable to one of the sockets
marked with MSB on the rear of the control instrument.
■ Start the control software.
Figure 26 Connecting a remote box
You can, for example, connect an 849 Level Control Box (fill level monitor
in a waste canister) or a 731 Relay Box (switch box for 230/110 volt alternating current sockets and low-voltage direct current outlets). The remote
box also has an MSB socket at which a further MSB instrument, e.g. a dosing
device or a stirrer, can be connected.
You will find precise information concerning the pin assignment of the
interface on the remote box in the appendix (see Chapter 6.3, page 43).
■■■■■■■■
32
855 Robotic Titrosampler
Page 41

■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■
USB 2
USB 1
3.14 Connecting USB devices
Two USB connectors (Type A sockets) are available for connecting devices
with USB interfaces. The 855 Robotic Titrosampler functions then as a USB
hub (distributor). If you wish to connect more than two USB devices, you
can also use an additional commercially available USB hub.
Note
When a USB device is connected, the control instrument recognizes which
device is connected. The control software automatically enters a connected USB device into the system configuration (Device manager).
3.14.1 Connecting a barcode reader
A barcode reader is used as an input aid for entering text and numbers. You
can connect a barcode reader to a USB interface.
3 Installation
Connect a barcode reader as follows:
1
Connecting the cable
■ Plug the USB plug (Type A) of the barcode reader into one of the
USB sockets on the rear side of the instrument.
Figure 27 USB connectors
2
Configuring the barcode reader in the control software
■ Configure the barcode reader in the configuration part of the con-
trol software as described in the online Software Help.
855 Robotic Titrosampler
Settings of the barcode reader
The barcode reader requires certain basic settings. You will find directions
in the Instructions for Use as to how you can program the barcode reader.
■■■■■■■■
33
Page 42

3.15 Mounting the base plate
6.2001.070
1
2
3
4
5
6
Switch the barcode reader to programming mode and make the following
settings:
■ Select the keyboard layout for the desired country (USA, Germany,
1
France, Spain, Switzerland (German)). This setting must match the
setting in the control software.
■ Make sure that the Ctrl characters (ASCII 00 to 31) are allowed to
be sent.
■ Adjust the settings so that the ASCII character 02 (STX or Ctrl B) is
sent as the first character as "Preamble" or "Prefix Code".
■ Adjust the settings so that the ASCII character 04 (EOT or Ctrl D) is
sent as the last character as "Postamble" or "Record Suffix" or "Postfix Code".
■ Exit programming mode.
3.15 Mounting the base plate
If it is needed by an application that a determination is not carried out on
the sample rack but in an external measuring cell, a stand plate can be
mounted. It can be placed on the left or on the right of a tower of the 855
Robotic Titrosampler . Any accessories parts can be placed on the support
rod of the stand plate.
■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■
Mounting the base plate
Figure 28 Mounting the base plate
■■■■■■■■
34
855 Robotic Titrosampler
Page 43

■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■
1
2
Proceed as follows:
Insert the enclosed countersunk screw from below into the opening on
1
the very back of the base plate.
Place the washer (flat side upwards) over the countersunk screw and
2
tighten the support rod with the countersunk screw. The necessary
hexagon key is enclosed with the 855 Robotic Titrosampler .
Hang the base plate to the assembly rail of the turntable with the hold-
3
ing clamps. Slide the whole stand plate as near to the tower as possible.
Fix the holding clamps with a hexagon key to the assembly rail.
Note
Before the stand plate is fixed to the tower, e.g. a magnetic stirrer
or a measuring cell can be mounted on the support rod.
3 Installation
Guide the bracing from above over the support rod.
4
Loosen the screw for fastening the bracing on the rear panel of the
5
tower (see figure) and fix the bracing with the enclosed hexagon screw.
Fix the bracing to the support rod with a hexagon key, see figure.
6
3.16 Mounting the drip pan
Serious damage to the instrument or a danger to the user can occur if
chemicals or liquid samples are spilled. The use of the drip pan (6.2711.060)
is recommended in order to avoid such incidents.
Mounting the drip pan
855 Robotic Titrosampler
Figure 29 Installing the drip pan
■■■■■■■■
35
Page 44

3.17 Attaching the sample rack
1
2
Install the drip pan as follows:
Fasten the tubing enclosed to the drainage nipple on the drip pan and
1
then guide the free end of the tubing into a waste container.
Place the drip pan on the assembly rail of the turntable as shown in the
2
figure.
3.17 Attaching the sample rack
■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■
Figure 30 Attaching the rack
The easiest way to put a sample rack into position is when the turntable is
in the initial position.
If the instrument is switched off, then the turntable can be rotated manually
into position. Both of the turntable guide bolts must be positioned so that
they are pointing towards the tower.
Put the rack into place as follows:
Carefully center the rack on the turntable. The guide bolts on the turn-
1
table must engage with the openings in the bottom of the rack. Tip:
hold the rack in such a way that the printed Metrohm logo is legible
horizontally.
Screw the fixing screw in the handle tight by turning it clockwise.
2
36
■■■■■■■■
Carry out the [Rack Reset] function in the manual operation of the
3
control software.
855 Robotic Titrosampler
Page 45

■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■
1
2
3
The rack is moved into starting position. The magnet code of the rack
is read by the instrument during this process. The white arrow in figure
30 indicates the position of the magnet holder. The six-digit magnet
code is used to identify the rack type. The sample positions and any
special positions on the rack are defined along with the rack type.
3.18 Mounting the safety shield
Warning
It is imperative that the safety shield be installed before the first time the
855 Robotic Titrosampler is used. The device is not permitted to be operated without a safety shield.
3 Installation
855 Robotic Titrosampler
Figure 31 Mount the safety shield
Proceed as follows:
Loosen the knurled screws on both sides of the tower.
1
Move the safety shield into position, starting from the top. Observe
2
the corresponding illustration.
Fix the safety shield in place with the knurled screws.
3
■■■■■■■■
37
Page 46

3.18 Mounting the safety shield
■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■
Note
You can adjust the vertical position of the safety shield at any time
by loosening the screws. Take care to ensure that is not possible to
reach into the working area of the lift while the instrument is in
operation.
■■■■■■■■
38
855 Robotic Titrosampler
Page 47

■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■
4 Handling and maintenance
4.1 General
The 855 Robotic Titrosampler requires appropriate care. Excess contamination of the instrument may result in functional disruptions and a reduction
in the service life of the sturdy mechanics and electronics of the instrument.
Severe contamination can also have an influence on the measured results.
Regular cleaning of exposed parts can prevent this to a large extent.
Spilled chemicals and solvents must be removed immediately. In particular,
the mains plug should be protected from contamination.
4.2 Care
■ Check all tubing connections regularly for leaks.
■ Flush out the tubing connections from time to time. The tubing must be
replaced after prolonged usage.
4 Handling and maintenance
4.3 Quality Management and validation with Metrohm
Quality Management
Metrohm offers you comprehensive support in implementing quality management measures for instruments and software. Further information on
this can be found in the brochure «Quality Management with
Metrohm» available from your local Metrohm agent.
Maintenance
Electronic and mechanical functional groups in Metrohm instruments can
and should be checked as part of regular maintenance by specialist personnel from Metrohm. Please ask your local Metrohm agent regarding the
precise terms and conditions involved in concluding a corresponding maintenance agreement.
Note
You can find information on the subjects of quality management, validation and maintenance as well as an overview of the documents currently
available at www.metrohm.com/com/ under Support.
855 Robotic Titrosampler
■■■■■■■■
39
Page 48

5.1 Sample Processor
5 Troubleshooting
5.1 Sample Processor
Problem Cause Remedy
■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■
The instrument is not
recognized by the
control software.
Sample Processor – No USB
connection available.
Sample Processor – Power
supply of the instrument is
missing.
1. Correctly plug in the USB connection cable
on both ends.
2. Restart the control software or switch the
Touch Control off and on again.
1. Plug in the mains cable on the instrument.
2. Restart the control software or switch the
Touch Control off and on again.
5.2 Robotic arm
Problem Cause Remedy
The robotic arm
moves all the way
outward and buzzes.
Sample Processor – The
Swing Head is not correctly
configured.
Sample Processor – Robotic
arm is wrongly mounted.
In the control software under "Configuration" (or under "Device manager" for Touch
Control), enter the correct value for the Swing
offset.
Disconnect the mains plug and dismount the
robotic arm. Check the configuration of the
robotic arm and mount it correctly if necessary
(left-swinging ⇔ right-swinging).
The Swing Head
either misses the
rack positions totally
or is inaccurate
■■■■■■■■
40
Sample Processor – The
Swing Head is not correctly
configured.
Sample Processor – The
axial distance is not correctly configured.
Sample Processor – The
wrong rack table is being
used.
In the control software under "Configuration" (or under "Device manager" for Touch
Control), enter the correct values for the Swing
radius, Swing offset etc.
In the control software under "Configuration" (or under "Device manager" for Touch
Control), enter the correct value for the Axial
distance.
Initialize the rack using the function Initialize
rack in the "Manual control".
855 Robotic Titrosampler
Page 49

■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■
Problem Cause Remedy
5 Troubleshooting
Swing Head – The Swing
Contact the Metrohm Service.
Head drive is defective.
5.3 Pump
Problem Cause Remedy
The pump is leaking.
Sample Processor – A tubing
connection is leaking.
Canister – There is too much
pressure on the pump valve.
Check the tubing connections especially
between the distributor an the pump and seal
tightly.
■ Ensure that the canisters are not placed on
a higher level than the pump.
■ Check the fill level of the canisters.
855 Robotic Titrosampler
■■■■■■■■
41
Page 50

6.1 Beaker sensor
6 Appendix
6.1 Beaker sensor
Every tower of a Sample Processor is equipped with a beaker sensor detecting the availability of a sample vessel in front of the tower. An infrared sensor
identifies devices of various materials if they are located in a correct position
in the front of the tower. In the rack configuration of the control device or
the control software, the setting 'Beaker sensor' Tower must be selected.
The beaker test is carried out whenever a rack position is moved to in a
method run.
■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■
Figure 32 Beaker sensor on the tower
The beaker sensor on the tower can only be used with single-row sample
racks.
6.2 Rinsing nozzles
Using rinsing nozzles is very effective in order to rinse sample vessels (with
sensors and buret tips) efficiently. Rinsing nozzles are available in two model
versions:
■ 6.2740.020 spray nozzle
For the fine-spraying of the rinsing solution. The nozzle has a small ball
at the opening. The distribution (but also the backpressure) of the rinsing
liquid is clearly higher than the one of a rinsing nozzle.
■ 6.2740.030 rinsing nozzle
The rinsing liquid is applied as a fine jet for optimal removal of layers on
electrodes and on titration accessories.
■■■■■■■■
42
855 Robotic Titrosampler
Page 51

■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■
1
2
3
6 Appendix
Figure 33 Spray nozzles - Functioning
The height of the nozzles can be adjusted in the titration head in order to
reach an optimal rinsing effect.
6.3 Remote interface
The 6.2148.010 remote box allows devices to be controlled which cannot
be connected directly to the MSB interface of the Titrosampler .
Figure 34 Connectors of the remote box
Cable
1
For connecting the Titrosampler .
Remote connector
3
For connecting devices with a remote interface.
MSB connector
2
Metrohm Serial Bus. For connecting external
dosing devices or stirrers.
855 Robotic Titrosampler
■■■■■■■■
43
Page 52

6.3 Remote interface
13
1
14
25
1
13
14
25
+5 V
t
p
t
p
6.3.1 Pin assignment of the remote interface
Figure 35 Pin assignment of the remote socket and plug
The above presentation of the pin assignment of a Metrohm remote interface applies not only for the remote box, but also for all Metrohm devices
with 25-pin D-Sub remote connection.
Inputs
approx. 50 kΩ Pull-up
tp >20 ms
■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■
active = low, inactive = high
The input lines can be scanned with the SCAN command.
Outputs
Open Collector
tp >200 ms
active = low, inactive = high
IC = 20 mA, V
CEO
= 40 V
+5 V: maximum load = 20 mA
The output lines can be set with the CONTROL command.
Table 1 Inputs and outputs of the remote interface
Assigment Pin No. Assigment Pin No.
Input 0 21 Output 0 5
Input 1 9 Output 1 18
Input 2 22 Output 2 4
Input 3 10 Output 3 17
Input 4 23 Output 4 3
Input 5 11 Output 5 16
Input 6 24 Output 6 1
44
■■■■■■■■
855 Robotic Titrosampler
Page 53

■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■
2000
1500
1000
500
-15 -10 -5 0 5 10 15
r/min
Assigment Pin No. Assigment Pin No.
Input 7 12 Output 7 2
0 volts / GND 14 Output 8 6
+5 volts 15 Output 9 7
0 volts / GND 25 Output 10 8
Output 11 13
Output 12 19
Output 13 20
6.4 Stirring rate
The stirring rate can be adjusted in steps of –15 to +15.
The approximate rotational speed can be calculated with the following formula:
6 Appendix
Rotational speed/min (r/min) = 125 · stirring rate
Example:
Stirring rate set: 8
Rotational speed in rpm = 125 · 8 = 1000
Figure 36 Rotational speed depending on stirring rate
855 Robotic Titrosampler
■■■■■■■■
45
Page 54

6.5 Robotic arms
6.1462.050
6.1462.060
6.1462.070
6.1462.260
■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■
6.5 Robotic arms
6.5.1 Robotic arms for titration
Table 2 Configuration data of the titration robotic arms
Type 6.1462.050 6.1462.060 6.1462.070 6.1462.260
Swing direction +/– + – +
Swing offset 0° –8° –8° –8°
Max. swing angle 84° 73° 73° 105°
Swing radius 110 mm 127 mm 127 mm 110 mm
6.1462.050
Robotic arm with titration head, left or right-swinging
For titration in 75 mL sample vessels and larger.
The arm can be equipped with two microelectrodes, one propeller stirrer
and three spray nozzles. Two buret tips with anti-diffusion valve and one
aspiration tip with connections for M6 tubing are already retracted into the
arm.
Material: PP
6.1462.060
Robotic arm with holder for a titration head, left-swinging
The arm can be modified to create the desired titration robotic arm by means
of the installation of a titration head 6.1458.xxx.
Material: PP
6.1462.070
Robotic arm with holder for a titration head, right-swinging
■■■■■■■■
46
The arm can be modified to create the desired titration robotic arm by means
of the installation of a titration head 6.1458.xxx.
Material: PP
855 Robotic Titrosampler
Page 55

■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■
6.1462.150
6.1462.160
6.1462.170
6 Appendix
6.1462.260
Robotic arm with holder for a titration head, left-swinging, external
The arm can be modified to create the desired titration robotic arm by means
of the installation of a titration head 6.1458.xxx. The cutout permits movement to external positions near the rack, e.g. an external rinsing station.
Material: PVC
Table 3 Configuration data of the robotic arms with beaker sensor
Type 6.1462.150 6.1462.160 6.1462.170
Swing direction +/– + –
Swing offset 0° –8° –8°
Max. swing angle 84° 73° 73°
Swing radius 110 mm 127 mm 127 mm
6.1462.150
Robotic arm with titration head and beaker sensor, left or rightswinging
For titration in 75 mL sample vessels and larger.
The arm can be equipped with two microelectrodes, one propeller stirrer
and three spray nozzles. Two buret tips with anti-diffusion valve and one
aspiration tip with connections for M6 tubing are already retracted into the
arm.
Material: PP
6.1462.160
Robotic arm with holder for a titration head and beaker sensor,
left-swinging
The arm can be modified to create the desired titration robotic arm by means
of the installation of a titration head 6.1458.xxx.
855 Robotic Titrosampler
Material: PP
■■■■■■■■
47
Page 56

6.5 Robotic arms
6.1462.030
6.1462.040
6.1462.090
6.1462.240
■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■
6.1462.170
Robotic arm with holder for a titration head and beaker sensor,
right-swinging
The arm can be modified to create the desired titration robotic arm by means
of the installation of a titration head 6.1458.xxx.
Material: PP
6.5.2 Robotic arms for sample preparation
Table 4 Configuration data of the robotic arms for sample preparation
Type 6.1462.030 6.1462.040 6.1462.090 6.1462.240
Swing direction + – – –
Swing offset 8° 8° 8° –8.6°
Max. swing angle 117° 117° 117° 122°
Swing radius 112 mm 112 mm 112 mm 149.8 mm
6.1462.030
Robotic arm with transfer head, left-swinging
Robotic arm for fully automated pipetting or dilution of liquid samples with
Sample Processor Systems.
Material: PP
6.1462.040
Robotic arm with transfer head, right-swinging
Robotic arm for fully automated pipetting or dilution of liquid samples with
Sample Processor Systems.
Material: PP
6.1462.090
Robotic arm with Luer lock adapter, right-swinging
For the connection of hollow needles with Luer lock connection. Suitable
for the transfer of samples from sealed vials with septum seal.
Material: PP
6.1462.240
Robotic arm with transfer head, bent, right-swinging
■■■■■■■■
48
The transfer head can, when equipped with 6.1808.220 adapter, be used
as a holder for various tools with Luer connection on multirow racks.
855 Robotic Titrosampler
Page 57

■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■
6.1462.250
6.1462.080
Material: PP
6.5.3 Robotic arms for special applications
Table 5 Configuration data of the special robotic arms
Type 6.1462.250 6.1462.080
6 Appendix
Swing direction + +
Swing offset 0° 8°
Max. swing angle 115.5° 117°
Swing radius 110 mm 112 mm
6.1462.250
Robotic arm as holder for a Polytron, left-swinging
The robotic arm makes it possible to use the Polytron for sample preparation
on multirow sample racks. It contains one retracted buret tip for adding
solvents and three spray nozzles for cleaning.
Material: PP
6.1462.080
Robotic arm DIS-COVER, left-swinging
Robotic arm for placing and removing sample vessel covers (75 and 250 mL)
covers 6.2037.050 und 6.2037.060) on the sample rack of a Robotic Sample
Processor.
Material: PP
855 Robotic Titrosampler
■■■■■■■■
49
Page 58

7.1 Measuring interface
7 Technical specifications
7.1 Measuring interface
The 855 Robotic Titrosampler has one galvanically isolated measuring interface.
The measuring cycle is 100 ms for all measuring modes.
7.1.1 Potentiometry
One high-ohm measuring input (Ind.) for pH, redox or ISE electrodes and
one reference measuring input (Ref.) for a separate reference electrode.
■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■
Input resistance
Offset current
Measuring mode
Measuring
range
Resolution
Measuring accuracy
7.1.2 Polarizer
Measuring mode
Ipol
Polarization current
Measuring
range
Resolution
Measuring
accuracy
>1· 10 12Ω
<1· 10
-20…+20 pH
0.001 pH
0.1 mV
±0.003 pH
±0.2 mV
(±1 digit, without sensor error, under reference conditions)
A measuring input (Pol.) for a polarizable electrode.
Determination with adjustable polarization current.
–125.0…+125.0 µA (in increments of 2.5 µA)
–125…–121 µA / +121…+125 µA: non-guaranteed values, dependent
on reference voltage +2.5 V
-1200…+1200 mV
0.1 mV
±0.2 mV
(±1 digit, without sensor error, under reference conditions)
-12
A (under reference conditions)
Measuring mode
Upol
Polarization
voltage
■■■■■■■■
50
Determination with adjustable polarization voltage
-1250…+1250 mV (in increments of 25 mV)
855 Robotic Titrosampler
Page 59

■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■
–1250…–1210 mV / +1210…+1250 mV: non-guaranteed values,
dependent on reference voltage +2.5 V
Measuring
range
Resolution
-120…+120 µA
0.1 µA
7.1.3 Temperature
One measuring input (Temp.) for a temperature sensor, Pt 1000 or NTC.
Automatic temperature compensation for NTC sensors R (25 °C) and B value
can be configured.
Measuring range
Pt 1000
NTC
Resolution
PT 1000
NTC
–150…+250 °C
–5…+250 °C
(R (25 °C) = 30'000Ω and B (25/50) = 4100 K )
0.1 °C
0.1 °C
7 Technical specifications
Measuring accuracy
PT 1000
NTC
± 0.2 °C
(Applies for measuring range 20…+150°C; ±1 digit; without sensor error,
under reference conditions)
±0.6 °C
(Applies for measuring range +10…+40°C; ±1 digit; without sensor error,
under reference conditions)
7.2 Lift and turntable
Stroke path
Maximum lift load
Lift rate
Shift rate
235 mm
approx. 30 N / 3 kg
adjustable, 5…25 mm/s
adjustable, 3...20 angle degrees/sec
855 Robotic Titrosampler
■■■■■■■■
51
Page 60

7.3 Membrane pump(s) with valve
7.3 Membrane pump(s) with valve
■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■
Delivery rate
> 450 mL/min
Pressure height 2 m
7.4 786 Swing Head
Maximum load
Swing rate
Beaker sensor connector
Approx. 15 N
10...55 degrees/s
Socket with M8 thread
7.5 Interfaces and connectors
Controller connection
MSB connectors
MSB1…MSB3
USB connectors
1/2
USB Upstream Port (9-pin Mini DIN socket) for connecting a computer
for controlling of the instrument.
Three 9-pin Mini DIN sockets for connecting dosing devices (Dosino/
Dosimat), stirrers, etc.
Two USB Downstream Ports (Type A sockets), each 500 mA, for connecting Metrohm instruments or USB peripheral devices of other manufacturers.
Stirrer connector
Stirring rate
Pump connectors
Swing Head connector
DIN socket
Rod stirrer 722/802: 180…3000 rpm
Magnetic stirrer 741: 180...2600 rpm
adjustable in 15 steps each in both shift directions
Two sockets with M8 thread for 772 Pump Unit, 823 Membrane Pump
Unit or 843 Pump Station
U= 16 ± 1 V, I=≤ 0.8 A
9-pin Mini DIN socket
■■■■■■■■
52
855 Robotic Titrosampler
Page 61

■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■
7.6 Mains connection
7 Technical specifications
Voltage
Frequency
Power consump-
100…240 V
50…60 Hz
115 W
tion
Fuse
2.0 ATH
7.7 Safety specifications
Design and testing
Safety instructions
According to EN/IEC/UL 61010-1, CSA-C22.2 No. 61010-1, EN/IEC
61010-2-081, protection class Ⅰ
This document contains safety instructions which have to be followed by
the user in order to ensure safe operation of the instrument.
7.8 Electromagnetic compatibility (EMC)
Emission
Standards fulfilled
■ EN/IEC 61326-1
■ EN/IEC 61000-6-3
■ EN 55022 / CISPR 22
■ EN/IEC 61000-3-2
■ EN/IEC 61000-3-3
Immunity
Standards fulfilled
■ EN/IEC 61326-1
■ EN/IEC 61000-6-2
■ EN/IEC 61000-4-2
■ EN/IEC 61000-4-3
■ EN/IEC 61000-4-4
■ EN/IEC 61000-4-5
■ EN/IEC 61000-4-6
■ EN/IEC 61000-4-8
■ EN/IEC 61000-4-11
■ EN/IEC 61000-4-14
■ NAMUR
855 Robotic Titrosampler
■■■■■■■■
53
Page 62

7.9 Ambient temperature
7.9 Ambient temperature
■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■
Nominal function
range
Storage
Transport
5…45 °C
Humidity < 80 %
–20…60 °C
–40…60 °C
7.10 Reference conditions
Ambient temperature
Relative humidity
25 °C (±3 °C)
≤ 60 %
7.11 Dimensions
Width
Height
Depth
Weight (without
accessories)
0.28 m
0.73 m
0.53 m
1.855.0010: 15.5 kg
1.855.0020: 16.4 kg
Material
Housing
Metal housing, surface-treated
■■■■■■■■
54
855 Robotic Titrosampler
Page 63

■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■
8 Conformity and warranty
8.1 Declaration of Conformity
This is to certify the conformity to the standard specifications for electrical
appliances and accessories, as well as to the standard specifications for
security and to system validation issued by the manufacturing company.
8 Conformity and warranty
Name of commodity
Electromagnetic compatibility
855 Robotic Titrosampler
Sample changer with built-in titrator for the automation of batch processing of larger sample series in analytical laboratories.
This instrument has been built and has undergone final type testing according to the standards:
Emission: EN/IEC 61326-1: 2002, EN/IEC 61000-6-3: 2001,
EN 55022 / CISPR 22: 2003,
EN/IEC 61000-3-2: 2000,
EN/IEC 61000-3-3: 2001
Immunity: EN/IEC 61326-1: 2002, EN/IEC 61000-6-2: 2001,
EN/IEC 61000-4-2: 2001,
EN/IEC 61000-4-3: 2002,
EN/IEC 61000-4-4: 2004,
EN/IEC 61000-4-5: 2001,
EN/IEC 61000-4-6: 2001,
EN/IEC 61000-4-8: 2001,
EN/IEC 61000-4-11: 2004,
EN/IEC 61000-4-14: 2004, NAMUR: 2004
Safety specifications
855 Robotic Titrosampler
EN/IEC 61010-1: 2001, UL 61010-1: 2004, CSA-C22.2 No. 61010-1: 2004,
EN/IEC 61010-2-081: 2003, protection class I
This instrument meets the requirements of the CE mark as contained in the
EU directives 2006/95/EC (LVD), 2004/108/EC (EMC). It fulfils the following
specifications:
EN 61326-1 Electrical equipment for measurement, control and
laboratory use – EMC requirements
EN 61010-1 Safety requirements for electrical equipment for
measurement, control and laboratory use
■■■■■■■■
55
Page 64

8.2 Quality Management Principles
■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■
EN 61010-2-081 Particular requirements for automatic and semi-
automatic laboratory equipment for analysis and
other purposes
Manufacturer
Metrohm Ltd., CH-9101 Herisau/Switzerland
Metrohm Ltd. is holder of the SQS certificate ISO 9001:2000 Quality management system for development, production and sales of instruments and
accessories for ion analysis.
Herisau, 20 February, 2009
D. Strohm
Vice President, Head of R&D
8.2 Quality Management Principles
Metrohm Ltd. holds the ISO 9001:2000 Certificate, registration number
10872-02, issued by SQS (Swiss Association for Quality and Management
Systems). Internal and external audits are carried out periodically to assure
that the standards defined by Metrohm’s QM Manual are maintained.
A. Dellenbach
Head of Quality Management
The steps involved in the design, manufacture and servicing of instruments
are fully documented and the resulting reports are archived for ten years.
The development of software for PCs and instruments is also duly documented and the documents and source codes are archived. Both remain the
possession of Metrohm. A non-disclosure agreement may be asked to be
provided by those requiring access to them.
The implementation of the ISO 9001:2000 quality management system is
described in Metrohm’s QM Manual, which comprises detailed instructions
on the following fields of activity:
Instrument development
The organization of the instrument design, its planning and the intermediate
controls are fully documented and traceable. Laboratory testing accompanies all phases of instrument development.
Software development
Software development occurs in terms of the software life cycle. Tests are
performed to detect programming errors and to assess the program’s functionality in a laboratory environment.
■■■■■■■■
56
855 Robotic Titrosampler
Page 65

■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■
8 Conformity and warranty
Components
All components used in the Metrohm instruments have to satisfy the quality
standards that are defined and implemented for our products. Suppliers of
components are audited by Metrohm as the need arises.
Manufacture
The measures put into practice in the production of our instruments guarantee a constant quality standard. Production planning and manufacturing
procedures, maintenance of production means and testing of components,
intermediate and finished products are prescribed.
Customer support and service
Customer support involves all phases of instrument acquisition and use by
the customer, i.e. consulting to define the adequate equipment for the analytical problem at hand, delivery of the equipment, user manuals, training,
after-sales service and processing of customer complaints. The Metrohm
service organization is equipped to support customers in implementing
standards such as GLP, GMP, ISO 900X, in performing Operational Qualification and Performance Verification of the system components or in carrying
out the System Validation for the quantitative determination of a substance
in a given matrix.
8.3 Warranty (guarantee)
Metrohm guarantees that the deliveries and services it provides are free from
material, design or manufacturing errors. The warranty period is 36 months
from the day of delivery; for day and night operation it is 18 months. The
warranty remains valid on condition that the service is provided by an
authorized Metrohm service organization.
Glass breakage is excluded from the warranty for electrodes and other
glassware. The warranty for the accuracy corresponds to the technical specifications given in this manual. For components from third parties that make
up a considerable part of our instrument, the manufacturer's warranty provisions apply. Warranty claims cannot be pursued if the Customer has not
complied with the obligations to make payment on time.
During the warranty period Metrohm undertakes, at its own choice, to either
repair at its own premises, free of charge, any instruments that can be shown
to be faulty or to replace them. Transport costs are to the Customer's
account.
Faults arising from circumstances that are not the responsibility of Metrohm,
such as improper storage or improper use, etc. are expressly excluded from
the warranty.
855 Robotic Titrosampler
■■■■■■■■
57
Page 66

9.1 Scope of delivery 2.855.0010
9 Accessories
Note
Subject to change without notice.
9.1 Scope of delivery 2.855.0010
Qty. Order no. Description
1 1.855.0010 855 Robotic Titrosampler
2 6.1236.020 Sleeve with SGJ 14/12 mm
Sleeve with SGJ 14/12 mm and O-ring.
Material: PP
■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■
1 6.1621.000 Container 10 L
As rinsing or waste container in automated systems.
Material: PE
Width (mm): 265
Height (mm): 400
Volume (mL): 10000
■■■■■■■■
58
855 Robotic Titrosampler
Page 67

■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■
Qty. Order no. Description
3 6.1805.060 FEP tubing / M6 / 60 cm
With light and kink protection
Material: FEP
Inner diameter (mm): 2
Length (mm): 600
1 6.1805.120 FEP tubing / M6 / 100 cm
With light and kink protection
Material: FEP
Inner diameter (mm): 2
Length (mm): 1000
9 Accessories
1 6.1812.000 PTFE tubing 4/6 mm, 4m
Material: PTFE
Outer diameter (mm): 6
Inner diameter (mm): 4
1 6.1828.000 PVDF connection nipple
For 6.1621.000 container
Material: PVDF
855 Robotic Titrosampler
■■■■■■■■
59
Page 68

9.1 Scope of delivery 2.855.0010
Qty. Order no. Description
1 6.2053.000 Cable clip
Cable clip for fastening cables and tubes
1 6.2103.130 Adapter red 2 mm plug / 4 mm socket
For connecting plug B (4 mm) to 2 mm socket.
■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■
1 6.2103.140 Adapter black 2 mm plug / B socket 4 mm
For connecting plug B (4 mm) to 2 mm socket.
1 6.2151.000 Cable USB A – mini-DIN 8-pin
Controller cable
Length (m): 1.8
■■■■■■■■
60
855 Robotic Titrosampler
Page 69

■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■
Qty. Order no. Description
1 6.2621.030 Hexagon key 4 mm
Length (mm): 73
1 6.2621.070 Hexagon key 5 mm
5 mm.
Length (mm): 80
9 Accessories
1 6.2621.130 Hexagon key 2 mm
2 mm.
1 6.2621.140 Hexagon key 2.5 mm
855 Robotic Titrosampler
■■■■■■■■
61
Page 70

9.1 Scope of delivery 2.855.0010
Qty. Order no. Description
3 6.2740.020 Spray nozzle
For the fine-spraying of the rinsing solution
Material: ETFE
Outer diameter (mm): 10
Length (mm): 47
1 6.2751.100 Splash protection
Splash protection for Sample Processors with 786 Swing Head
■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■
4 T.240.0102 Ferrite cores
Anti-interference adapters
1 6.2122.0x0 Mains cable with C13 line socket IEC-60320-
C13
Cable plug according to customer requirements.
Switzerland: Type SEV 12
6.2122.020
Germany, …: Type CEE(7), VII
6.2122.040
USA, …: Type NEMA/ASA
6.2122.070
1 8.855.8001EN Manual 855 Robotic Titrosampler
■■■■■■■■
62
855 Robotic Titrosampler
Page 71

■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■
9.2 Scope of delivery 2.855.0020
Qty. Order no. Description
1 1.855.0020 855 Robotic Titrosampler
2 6.1236.020 Sleeve with SGJ 14/12 mm
Sleeve with SGJ 14/12 mm and O-ring.
Material: PP
1 6.1543.170 Aspiration tip / M8 thread
9 Accessories
Aspiration tip to Sample Processors
Material: PTFE
Length (mm): 198
2 6.1621.000 Container 10 L
As rinsing or waste container in automated systems.
Material: PE
Width (mm): 265
Height (mm): 400
Volume (mL): 10000
855 Robotic Titrosampler
■■■■■■■■
63
Page 72

9.2 Scope of delivery 2.855.0020
Qty. Order no. Description
3 6.1805.060 FEP tubing / M6 / 60 cm
With light and kink protection
Material: FEP
Inner diameter (mm): 2
Length (mm): 600
1 6.1805.120 FEP tubing / M6 / 100 cm
With light and kink protection
Material: FEP
Inner diameter (mm): 2
Length (mm): 1000
■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■
1 6.1805.510 PTFE tubing / M8 / 60 cm
With kink protection
Material: PTFE
Inner diameter (mm): 3
Length (mm): 600
■■■■■■■■
64
855 Robotic Titrosampler
Page 73

■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■
Qty. Order no. Description
2 6.1812.000 PTFE tubing 4/6 mm, 4m
Material: PTFE
Outer diameter (mm): 6
Inner diameter (mm): 4
2 6.1828.000 PVDF connection nipple
For 6.1621.000 container
Material: PVDF
1 6.2053.000 Cable clip
9 Accessories
Cable clip for fastening cables and tubes
1 6.2103.130 Adapter red 2 mm plug / 4 mm socket
For connecting plug B (4 mm) to 2 mm socket.
855 Robotic Titrosampler
■■■■■■■■
65
Page 74

9.2 Scope of delivery 2.855.0020
Qty. Order no. Description
1 6.2103.140 Adapter black 2 mm plug / B socket 4 mm
For connecting plug B (4 mm) to 2 mm socket.
1 6.2151.000 Cable USB A – mini-DIN 8-pin
Controller cable
Length (m): 1.8
■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■
1 6.2621.030 Hexagon key 4 mm
Length (mm): 73
1 6.2621.070 Hexagon key 5 mm
5 mm.
Length (mm): 80
■■■■■■■■
66
855 Robotic Titrosampler
Page 75

■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■
Qty. Order no. Description
1 6.2621.130 Hexagon key 2 mm
2 mm.
1 6.2621.140 Hexagon key 2.5 mm
9 Accessories
3 6.2740.020 Spray nozzle
For the fine-spraying of the rinsing solution
Material: ETFE
Outer diameter (mm): 10
Length (mm): 47
1 6.2751.100 Splash protection
Splash protection for Sample Processors with 786 Swing Head
855 Robotic Titrosampler
■■■■■■■■
67
Page 76

9.3 Optional accessories
Qty. Order no. Description
4 T.240.0102 Ferrite cores
Anti-interference adapters
1 6.2122.0x0 Mains cable with C13 line socket IEC-60320-
C13
Cable plug according to customer requirements.
Switzerland: Type SEV 12
6.2122.020
Germany, …: Type CEE(7), VII
6.2122.040
USA, …: Type NEMA/ASA
6.2122.070
1 8.855.8001EN Manual 855 Robotic Titrosampler
9.3 Optional accessories
■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■
Qty. Order no. Description
1 2.802.0020 802 Stirrer
Rod stirrer for sample changer and Sample Processor. With 6.1909.020
Propeller stirrer 104 mm and fixed cable.
■■■■■■■■
68
855 Robotic Titrosampler
Page 77

■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■
Qty. Order no. Description
1 2.849.0010 849 Level Control
Additional equipment for Sample Processors for monitoring the filling
level of rinsing or waste canisters via Remote. Prevents pumps from
running dry and/or canisters from overflowing and is suitable for use
with aqueous solutions, solvents and suspensions.
1 6.1462.030 Robotic arm with transfer head for 786
Swing Head, left swinging
Transfer robotic arm for liquid handling purposes
Material: PP (black)
1 6.1462.040 Robotic arm with transfer head for 786
Swing Head, right swinging
9 Accessories
Transfer robotic arm for liquid handling purposes
Material: PP (black)
1 6.1462.050 Robotic arm with titration head for 786
Swing Head, left or right swinging
Titration head for Swing Head
Material: PP (black)
1 6.1462.060 Robotic arm with holder for titration head,
left swinging
Titration head holder to 786 Swing Head
Material: PP (black)
1 6.1462.070 Robotic arm with holder for titration head,
right swinging
Titration head holder to 786 Swing Head
Material: PP (black)
855 Robotic Titrosampler
■■■■■■■■
69
Page 78

9.3 Optional accessories
Qty. Order no. Description
1 6.1462.090 Robotic arm with Luer-Lock adapter for 786
Swing Head, right swinging
Transfer robotic arm for liquid handling
Material: PP (black)
1 6.1462.150 Robotic arm with titration head and beaker
sensor for 786 Swing Head, left or right
swinging
Titration head with beaker sensor for 786 Swing Head, 2 x M10, 1 x
SGJ 14.5, 2 x buret tip
Material: PP (black)
■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■
1 6.1462.160 Robotic arm with holder for titration head
and sensor for 786 Swing Head, left swinging
Titration head holder with beaker sensor for 786 Swing Head
Material: PP (black)
■■■■■■■■
70
855 Robotic Titrosampler
Page 79

■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■
Qty. Order no. Description
1 6.1462.170 Robotic arm with holder for titration head
and sensor for 786 Swing Head, right swinging
Titration head holder with beaker sensor for 786 Swing Head
Material: PP (black)
1 6.1909.010 Stirring propeller / 96 mm
Propeller stirrer, length from lower edge of SGJ: 96 mm. For use with
beakers with 722, 802 Rod Stirrer
Material: PP
9 Accessories
1 6.1909.020 Stirring propeller / 104 mm
Propeller stirrer, length from lower edge of SGJ: 104 mm. For use with
beakers with 722, 802 Rod Stirrer
Material: PP
1 6.1909.030 Stirring propeller / 104 mm
Propeller stirrer with PP shaft, PVDF tip. Length from the SGJ: 104 mm.
For KF applications with 722, 802 Rod Stirrer
Material: PP
855 Robotic Titrosampler
■■■■■■■■
71
Page 80

9.3 Optional accessories
Qty. Order no. Description
1 6.1909.040 Stirring propeller / 102 mm
Propeller stirrer, length from lower edge of SGJ: 102 mm. For titration
vessels with SGJ 14/15 and 722, 802 Rod Stirrer
Material: ETFE
1 6.1909.050 Propeller for 120 mL beaker (6.1459.300)
Propeller for 802 Stirrer when this is used with sample racks for 120
mL beakers (6.1459.300)
Material: ETFE
Length (mm): 111
■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■
1 6.2041.400 Sample rack 126 x 11 mL
Sample rack for 126 x 11 mL samples, multi-row
Material: PVC
Outer diameter (mm): 420
Hole diameter (mm): 16 / 65
1 6.2041.410 Sample rack 141 x 11 mL
Sample rack for 141 x 11 mL samples, multi-row
Material: PVC
Outer diameter (mm): 420
Hole diameter (mm): 16 / 70
■■■■■■■■
72
855 Robotic Titrosampler
Page 81

■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■
Qty. Order no. Description
1 6.2041.430 Sample rack 127 x 11 mL
Sample rack for 127 x 11 mL samples with 2 rinsing beakers
Material: PVC
Outer diameter (mm): 420
Hole diameter (mm): 17 / 68
1 6.2041.440 Sample rack 148 x 11 mL
Sample rack for 148 x 11 mL samples with 3 rinsing beakers
Material: PVC
Outer diameter (mm): 420
Hole diameter (mm): 17 / 68
1 6.2041.450 Sample rack 56 x 11 mL + 56 x 50 mL
Sample rack 56 x 11 mL + 56 x 50 mL
Material: PVC
Outer diameter (mm): 420
Hole diameter (mm): 29 / 17
9 Accessories
1 6.2041.710 Sample rack 160 x 6 mL
Sample rack 160 x 6 mL vials
Material: PVC
Outer diameter (mm): 420
Hole diameter (mm): 22
1 6.2041.800 Sample rack 100 x 75 mL
Sample rack for 100 x 75 mL samples, multi-row
Material: PVC
Outer diameter (mm): 480
Hole diameter (mm): 35
1 6.2041.810 Sample rack 34 x 150 mL
Sample rack for 34 x 150 mL samples, multi-row
Material: PVC
Outer diameter (mm): 480
Hole diameter (mm): 55
855 Robotic Titrosampler
■■■■■■■■
73
Page 82

9.3 Optional accessories
Qty. Order no. Description
1 6.2041.820 Sample rack 28 x 250 mL
Sample rack for 28 x 250 mL samples (6.1432.320), multi-row
Material: PVC
Outer diameter (mm): 480
Hole diameter (mm): 65
1 6.2041.830 Sample rack 28 x 200 mL
Sample rack for 28 x 200 mL samples (6.1459.310), multi-row
Material: PVC
Outer diameter (mm): 480
Hole diameter (mm): 55
1 6.2041.840 Sample rack 59 x 120 mL
Sample rack for 59x120 mL samples (6.1459.300), multi-row
Material: PVC
Outer diameter (mm): 480
Hole diameter (mm): 42
■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■
1 6.2041.850 Sample rack 59 x 120 mL, PP
Sample rack for 59x120 mL samples (6.1459.300), multi-row
Material: PP
Outer diameter (mm): 480
Hole diameter (mm): 42
1 6.2041.900 Sample rack insert 54 x 75 mL for water bath
Insert for waterbath rack 54 x 75 mL
Outer diameter (mm): 480
Hole diameter (mm): 35
■■■■■■■■
74
855 Robotic Titrosampler
Page 83

■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■
Qty. Order no. Description
1 6.2141.300 Remote cable 843 Pump Station to Sample
Processor
Remote cable for the direct connection of the 843 Pump Station to the
pump connectors of the Sample Processors
1 6.2148.010 Remote Box MSB
Additional remote interface for the connection of devices that can be
controlled via remote lines. With permanently attached cable.
1 6.2840.000 Water bath for Robotic Sample Processors
and Robotic Titrosampler
9 Accessories
Water bath rack for Robotic Sample Processors and Titrosampler.
Material: PVC
1 6.2841.010 External washing station for Robotic Swing
arm with titration head 6.1458.040
The external washing station can be mounted on the side of the
Robotic Sample Processor tower and allows the external cleaning of
the titration equipment while other actions can be carried out on the
sample rack.
Material: PP
Material 2: PVC
1 6.6050.500 Titrando-PC-Control-Software 6.0
PC software for controlling Titrandos, USB Sample Processors, 846
Dosing Interface, 847 USB Lab Link. Simple and intuitive user guidance.
Method and data compatible with Touch Control. With freely progammable favorites for fast method access. Compliant with 21 CFR
Part 11. Standard dialog languages English and German; one further
language can be retrofitted. Including hardware dongle. The
6.2151.000 Cable is required for connecting the Titrando to a PC.
855 Robotic Titrosampler
■■■■■■■■
75
Page 84

Index
Index
■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■
Numbers/Symbols
685 Dosimat ............................ 30
700 Dosino .............................. 30
741 Stirrer ................................ 27
800 Dosino .............................. 30
801 Stirrer ................................ 31
802 Stirrer ................................ 27
803 Ti Stand ............................. 31
804 Ti Stand ............................. 31
805 Dosimat ............................ 30
A
Aspiration equipment ............... 21
B
Beaker sensor ..................... 20, 47
C
Computer
connecting ......................... 14
Connecting
Computer ........................... 14
Dosing devices ................... 30
MSB devices ....................... 29
Remote box ........................ 32
Stirrer or titration stand ...... 31
Connector
MSB ..................................... 4
Connectors .............................. 11
Controller cable 6.2151.000 ..... 14
Controller connector ................ 11
D
Device software
Update ................................. 2
DIS-COVER ............................... 49
Distributor ................................ 23
Dosing devices
Connecting ........................ 30
Drip pan ................................... 35
Drive disc ................................. 19
Driver
Installing ............................ 14
E
Electrode
Mounting ........................... 26
Electrode connector
pH electrode ...................... 12
Polarizable electrode .......... 12
Redox electrode ................. 12
Reference electrode ............ 12
Electrostatic charge .................... 6
F
Ferrite core
Mounting ........................... 30
G
GLP .......................................... 39
Guarantee ................................ 57
Guide chain .............................. 24
Guide pins ................................ 19
I
Installation
Driver ................................. 14
Installing
Pump ................................. 28
L
Left-swinging. .......................... 16
Limitation screw ....................... 18
Luer lock adapter ..................... 48
M
Magnet code ........................... 12
Magnetic stirrer
Connecting ........................ 31
Mounting ........................... 27
Mains connection ..................... 11
Mains voltage ............................. 6
Maintenance ............................ 39
Max. swing angle ..................... 18
Metrohm Serial Bus MSB, see also
"MSB" ...................................... 29
Model versions ........................... 3
Mounting
Drip pan ............................. 35
Rinsing equipment .............. 21
MSB
Connecting devices ............ 29
MSB connector ..................... 4, 11
P
Pins .......................................... 44
Polytron ................................... 49
Propeller stirrer ......................... 27
Pump
Installing ............................ 28
Q
Quality Management ................ 39
R
Rack ......................................... 12
Rack code ................................ 12
Rear panel ................................ 11
Remote
Input .................................. 44
Interface ............................. 44
Output ............................... 44
Remote box
Connecting ........................ 32
Pin assignment ................... 44
Right-swinging.. ....................... 16
Rinsing equipment .................... 21
Robotic arm
Beaker sensor ............... 20, 47
Bent ................................... 48
Configuration data
......................... 17, 46, 48, 49
Configuring ........................ 16
Left-swinging ..................... 18
Luer lock adapter ................ 48
Model versions ............. 16, 46
Mounting ..................... 18, 19
Right-swinging ................... 18
Titration head ..................... 46
Transfer head ..................... 48
Robotic arms
Model versions ................... 48
Rod stirrer ................................ 27
S
Safety instructions ...................... 5
Sample preparation .................. 48
Sample rack ............................. 12
Sensor connector
pH electrode ...................... 12
Polarizable electrode .......... 12
Redox electrode ................. 12
Reference electrode ............ 12
Temperature sensor ............ 12
Serial number ........................... 11
Service ....................................... 5
Service Agreement ................... 39
Stirrer
Connecting .................. 27, 31
Mounting ........................... 26
Stirring rate .............................. 45
■■■■■■■■
76
855 Robotic Titrosampler
Page 85

■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■
Index
Swing axis ................................ 17
Swing direction ........................ 18
Swing Head
Connect ............................. 15
Connection ........................ 15
Swing offset ............................. 17
Swing radius ............................ 17
T
Titration head ........................... 46
Equipping ........................... 25
Titration stand .......................... 31
Connecting ........................ 31
Tower stirrer ............................. 27
Transfer head ........................... 48
Type plate ................................ 11
U
Update
Device software .................... 2
USB connectors ........................ 11
V
Validation ................................. 39
W
Warranty .................................. 57
Windows .................................. 14
855 Robotic Titrosampler
■■■■■■■■
77
 Loading...
Loading...