Page 1

850 Professional IC
Anion – MCS – 2.850.2030
Manual
8.850.8046EN
Page 2

Page 3

Metrohm AG
CH-9101 Herisau
Switzerland
Phone +41 71 353 85 85
Fax +41 71 353 89 01
info@metrohm.com
www.metrohm.com
850 Professional IC
Anion – MCS – 2.850.2030
8.850.8046EN
Manual
06.2009 zst
Page 4

Teachware
Metrohm AG
CH-9101 Herisau
teachware@metrohm.com
This documentation is protected by copyright. All rights reserved.
Although all the information given in this documentation has been
checked with great care, errors cannot be entirely excluded. Should you
notice any mistakes please send us your comments using the address
given above.
Page 5

■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■
Table of contents
1 Introduction 1
1.1 Instrument description ......................................................... 1
1.2 Intended use ......................................................................... 5
1.3 About the documentation ................................................... 5
1.3.1 Symbols and conventions ........................................................ 5
1.4 Safety instructions ................................................................ 6
1.4.1 General notes on safety ........................................................... 6
1.4.2 Electrical safety ........................................................................ 6
1.4.3 Tubing and capillary connections ............................................. 7
1.4.4 Flammable solvents and chemicals ........................................... 8
1.4.5 Recycling and disposal ............................................................. 8
2 Installation 9
2.1 About this chapter ................................................................ 9
Table of contents
2.2 Initial installation .................................................................. 9
2.3 Flow diagram ...................................................................... 10
2.4 Setting up the instrument .................................................. 12
2.4.1 Packaging .............................................................................. 12
2.4.2 Checks .................................................................................. 12
2.4.3 Location ................................................................................ 12
2.5 Capillary connections in the IC system ............................. 13
2.6 Rear of the instrument ....................................................... 15
2.6.1 Rollers and handle ................................................................. 15
2.6.2 Positioning and connecting the detector ................................ 18
2.6.3 Transport locking screws ....................................................... 20
2.6.4 Leak sensor ........................................................................... 20
2.6.5 Drainage tubing ..................................................................... 21
2.7 Capillary and cable feed-throughs .................................... 23
2.8 Eluent ................................................................................... 26
2.8.1 Connecting eluent bottle ....................................................... 26
2.9 Eluent degasser ................................................................. 30
2.10 High pressure pump ........................................................... 31
2.10.1 Capillary connections high pressure pump/purge valve ........... 31
2.10.2 Deaerating the high pressure pump ....................................... 34
850 Professional IC – Anion – MCS
2.11 Inline filter ........................................................................... 36
2.12 Pulsation damper ............................................................... 37
2.13 Sample degasser ................................................................. 39
■■■■■■■■
III
Page 6

Table of contents
■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■
2.14 Injection valve ..................................................................... 40
2.14.1 Connecting the injection valve ............................................... 40
2.14.2 Mode of operation of the injection valve ............................... 41
2.14.3 Selecting the sample loop ...................................................... 42
2.15 Column thermostat ............................................................ 43
2.16 Metrohm Suppressor Module (MSM) ............................... 46
2.16.1 General information on the MSM .......................................... 46
2.16.2 Connecting the MSM ............................................................ 46
2.17 Peristaltic pump .................................................................. 49
2.17.1 Principle of the peristaltic pump ............................................. 49
2.17.2 Installing the peristaltic pump ................................................ 50
2.18 Metrohm CO2 suppressor (MCS) ....................................... 54
2.18.1 General information on the MCS ........................................... 54
2.18.2 Connecting MCS ................................................................... 54
2.18.3 Installing the adsorption cartridges ........................................ 55
2.19 Conductivity detector ......................................................... 57
2.20 Connecting the instrument ................................................ 60
2.20.1 Connecting the instrument to the PC ..................................... 60
2.20.2 Connecting the instrument to mains supply ........................... 60
2.21 Guard column ..................................................................... 61
2.22 Separation column ............................................................. 63
3 Start-up 65
3.1 Initial start-up ..................................................................... 65
3.2 Conditioning ........................................................................ 66
4 Operation and maintenance 68
4.1 General information ........................................................... 68
4.1.1 Care ...................................................................................... 68
4.1.2 Maintenance by Metrohm Service .......................................... 68
4.1.3 Operation .............................................................................. 69
4.1.4 Shutting down ...................................................................... 69
4.2 Capillary connections ......................................................... 69
4.2.1 Operation .............................................................................. 69
4.3 Door ..................................................................................... 70
4.4 Eluent ................................................................................... 70
4.4.1 Production ............................................................................. 70
4.4.2 Operation .............................................................................. 71
■■■■■■■■
IV
4.5 High pressure pump ........................................................... 71
4.5.1 Protection .............................................................................. 71
4.5.2 Maintenance ......................................................................... 72
850 Professional IC – Anion – MCS
Page 7

■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■
Table of contents
4.6 Inline filter ........................................................................... 82
4.6.1 Maintenance ......................................................................... 82
4.7 Inline sample preparation .................................................. 84
4.8 Rinsing the sample path .................................................... 84
4.9 Sample degasser ................................................................. 86
4.9.1 Operation .............................................................................. 86
4.10 Injection valve .................................................................... 86
4.10.1 Protection .............................................................................. 86
4.11 Metrohm Suppressor Module (MSM) ............................... 86
4.11.1 Protection .............................................................................. 86
4.11.2 Operation .............................................................................. 86
4.11.3 Maintenance ......................................................................... 87
4.12 Peristaltic pump .................................................................. 92
4.12.1 Operation .............................................................................. 92
4.12.2 Maintenance ......................................................................... 93
4.13 Metrohm CO2 suppressor (MCS) ....................................... 95
4.13.1 Replacing the CO2 adsorption cartridge ................................. 95
4.13.2 Regenerating the H2O adsorption cartridge ............................ 95
4.14 Conductivity detector ......................................................... 96
4.14.1 Maintenance ......................................................................... 96
4.15 Separation column ............................................................. 96
4.15.1 Separating efficiency .............................................................. 96
4.15.2 Protection .............................................................................. 97
4.15.3 Storage ................................................................................. 97
4.15.4 Regeneration ......................................................................... 97
4.16 Quality Management and validation with Metrohm ....... 98
5 Troubleshooting 99
5.1 Problems and their solutions ............................................. 99
6 Technical specifications 104
6.1 Reference conditions ........................................................ 104
6.2 Instrument ......................................................................... 104
6.3 Leak sensor ....................................................................... 104
6.4 Ambient conditions .......................................................... 104
6.5 Housing ............................................................................. 105
6.6 Eluent degasser ................................................................ 105
850 Professional IC – Anion – MCS
6.7 High pressure pump ......................................................... 105
6.8 Sample degasser ............................................................... 106
6.9 Injection valve ................................................................... 106
■■■■■■■■
V
Page 8

Table of contents
■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■
6.10 Column thermostat .......................................................... 107
6.11 Metrohm Suppressor Module (MSM) ............................. 107
6.12 Peristaltic pump ................................................................ 107
6.13 Metrohm CO2 suppressor (MCS) ..................................... 108
6.14 Conductivity measuring system ...................................... 108
6.15 Mains connection ............................................................. 109
6.16 Interfaces .......................................................................... 109
6.17 Safety specification .......................................................... 110
6.18 Electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) ............................. 110
6.19 Weight ............................................................................... 110
7 Conformity and warranty 111
7.1 Declaration of Conformity ............................................... 111
7.2 Quality Management Principles ...................................... 112
7.3 Warranty (guarantee) ....................................................... 113
8 Accessories 115
8.1 Scope of delivery .............................................................. 115
8.2 Optional accessories ........................................................ 126
Index 130
■■■■■■■■
VI
850 Professional IC – Anion – MCS
Page 9

■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■
Table of figures
Figure 1 Front view of the instrument ............................................................. 2
Figure 2 Flow diagram with sequential suppression ....................................... 11
Figure 3 Connection of capillaries with pressure screws ................................ 13
Figure 4 Rollers and handle ........................................................................... 15
Figure 5 Handle as MPak holder .................................................................... 17
Figure 6 Removable rear panel ...................................................................... 18
Figure 7 Connection for the leak sensor on the rear of the instrument .......... 21
Figure 8 Drainage tubing .............................................................................. 22
Figure 9 Capillary feed-throughs on the doors ............................................... 24
Figure 10 Capillary feed-throughs base tray/covering plate .............................. 25
Figure 11 Installing eluent bottle attachment .................................................. 27
Figure 12 Mounting aspiration filter ................................................................ 27
Figure 13 Installing tubing weighting and aspiration filter ............................... 28
Figure 14 Eluent aspiration tubing fully equipped. ........................................... 28
Figure 15 Eluent bottle – connected ............................................................... 29
Figure 16 Eluent degasser ............................................................................... 30
Figure 17 Capillary connections high pressure pump/purge valve .................... 32
Figure 18 High pressure pump – Connect inlet ................................................ 33
Figure 19 Deaerating the high pressure pump ................................................. 35
Figure 20 Connecting inline filter .................................................................... 37
Figure 21 Pulsation damper – Connection ....................................................... 38
Figure 22 Sample degasser ............................................................................. 39
Figure 23 Injection valve – connected ............................................................. 40
Figure 24 Injection valve – Positions ................................................................ 42
Figure 25 Column thermostat ......................................................................... 44
Figure 26 MSM – connections ........................................................................ 47
Figure 27 Peristaltic pump ............................................................................... 49
Figure 28 Installing the pump tubing .............................................................. 50
Figure 29 Install pump tubing connection with filter ....................................... 51
Figure 30 Install pump tubing connection without filter .................................. 52
Figure 31 MCS – connection ........................................................................... 54
Figure 32 Adsorption cartridge holder ............................................................. 56
Figure 33 Conductivity detector front .............................................................. 58
Figure 34 Conductivity detector rear ............................................................... 59
Figure 35 Connection detector – MCS ............................................................ 60
Figure 36 Removing piston ............................................................................. 73
Figure 37 Components of the piston cartridge ................................................ 74
Figure 38 Tool for piston seal 6.2617.010 ....................................................... 75
Figure 39 Removing the piston seal ................................................................. 76
Figure 40 Insert the piston seal into the tool ................................................... 76
Figure 41 Inserting the piston seal into the pump head ................................... 77
Figure 42 Removing valves .............................................................................. 78
Figure 43 Dismantling valve ............................................................................ 79
Figure 44 Components of the inlet valve and outlet valve ................................ 80
Figure 45 Changing the filter .......................................................................... 82
Table of figures
850 Professional IC – Anion – MCS
■■■■■■■■
VII
Page 10

Table of figures
■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■
Figure 46 MSM – Components ....................................................................... 89
Figure 47 Pump tubing connection – Changing the filter ................................. 94
VIII
■■■■■■■■
850 Professional IC – Anion – MCS
Page 11

■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■
1 Introduction
1.1 Instrument description
The instrument 850 Professional IC – Anion – MCS (2.850.2030) is
one of the model versions of the Professional IC line of instruments manufactured by the Metrohm Company. The Professional IC line of instruments is distinguished by
■ the intelligence of its components, which are able to monitor and
optimize all functions and to provide documentation according to FDA
requirements.
■ its compactness.
■ its flexibility. A suitable model version exists for every application.
Individual instruments can be converted, expanded or modified to create a different instrument as needed.
■ its transparency. All components are easily accessible and arranged in
a clear manner.
■ its safety. Chemicals and electronics are separated and a leak sensor is
integrated in the wet end.
■ its environmental compatibility.
■ low noise emission.
1 Introduction
The instrument is operated with MagIC Net software. It is connected via
a USB connection to a PC on which MagIC Net is installed. The software
automatically recognizes the instrument and checks its functional readiness. MagIC Net controls and monitors the instrument, evaluates the
measured data and administers it in a database. The operation of
MagIC Net is described in the online help or in the tutorial for MagIC Net.
850 Professional IC – Anion – MCS
■■■■■■■■
1
Page 12

1.1 Instrument description
12
2
1
8
10
4
9
5
6
7
11
3
13
■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■
Figure 1 Front view of the instrument
Eluent bottle
1
See Chapter 2.8.1.
Conductivity detector
2
See Chapter 2.19.
■■■■■■■■
2
850 Professional IC – Anion – MCS
Page 13

■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■
1 Introduction
MCS
3
See Chapter 2.18.
MSM
5
See Chapter 2.16.
Eluent degasser
7
See Chapter 2.9.
Purge valve
9
See Chapter 2.10.1.
Sample degasser
11
See Chapter 2.13. Use optional.
Column thermostat
13
See Chapter 2.15.
Peristaltic pump
4
See Chapter 2.17.
Injection valve
6
See Chapter 2.14.
High pressure pump
8
See Chapter 2.10.
Pulsation damper
10
See Chapter 2.12.
Separation column
12
See Chapter 2.22.
The instrument contains the following components:
Eluent degasser
The eluent degasser removes gas bubbles and dissolved gases from the
eluent. For degassing, the eluent flows into a vacuum chamber through a
special fluoropolymer capillary.
High pressure pump
The intelligent and low pulsation high pressure pump pumps the eluent
through the system. It is equipped with a chip on which its technical specifications and "life history" (operating hours, service data, ... ) are saved.
Inline filter
Inline filters protect the separation column securely against possible contamination from the eluent. Inline filters can however also just as well be
used for the purpose of protecting other sensitive components against
contaminations in the solutions used. The fine 2 µm material of the readily
and easily replaceable filter platelets removes particles such as bacteria
and algae from the solutions.
Pulsation damper
The pulsation damper protects the separation column from damage
caused by pressure fluctuations when switching the injection valve, and
reduces interfering pulsations during highly sensitive measurements.
Sample degasser
The sample degasser removes gas bubbles and disolved gases from the
sample. For degassing, the sample flows into a vacuum chamber through
a special fluoropolymer capillary.
850 Professional IC – Anion – MCS
■■■■■■■■
3
Page 14

1.1 Instrument description
■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■
Injection valve
The injection valve connects the eluent and sample path through rapid
and precise valve switchover. A precisely measured amount of sample
solution is injected and rinsed with eluent onto the separation column.
Column thermostat
The column thermostat controls the temperature of the column and eluent channel and thus ensures stable measuring conditions. It provides
space for 2 separation columns.
Metrohm Suppressor Module (MSM)
The MSM is used for chemical suppression during anion analysis. It is pressure-stable, robust and resistant to solvents.
Peristaltic pump
The Peristaltic pump is used for pumping sample and auxiliary solutions. It
can rotate in both directions.
Metrohm CO2 suppressor (MCS)
The MCS removes the CO2 from the eluent flow. This reduces the background conductivity, improves the detection sensitivity and minimizes the
injection and carbonate peaks.
Conductivity detector
The conductivity detector continuously measures the conductivity of the
liquid passing through and indicates these signals in digital form (DSP –
Digital Signal Processing). The conductivity detector exhibits outstanding
thermal stability and thus guarantees reproducible measuring conditions.
Separation column
The intelligent separation column is the heart of the ion chromatographic
analysis. It separates the different components corresponding to their
interactions with the column. The Metrohm analytical columns are equipped with a chip on which their technical specifications and their history
(first use / setting up, operating hours, injections, ... ) are saved.
■■■■■■■■
4
850 Professional IC – Anion – MCS
Page 15
■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■
1.2 Intended use
The instrument 850 Professional IC – Anion – MCS is used for ion
chromatographic determination of anions or polar substances with
sequential suppression:
■ Chemical suppression with the Metrohm Suppressor Module (MSM)
(see Chapter 2.16, page 46) and subsequent
■ CO
2
ter 2.18, page 54).
The use of sequential suppression reduces background conductivity to a
minimum.
If required, the instrument can also be used for the determination of cations or anions without suppression.
The present instrument is suitable for processing chemicals and flammable
samples. The usage of the 850 Professional IC – Anion – MCS therefore
requires that the user has basic knowledge and experience in the handling
of toxic and caustic substances. Knowledge with respect to the application of the fire prevention measures prescribed for laboratories is also
mandatory.
1 Introduction
suppression with the Metrohm CO2 Suppressor (MCS) (see Chap-
1.3 About the documentation
Caution
Please read through this documentation carefully before putting the
instrument into operation. The documentation contains information
and warnings which have to be followed by the user in order to ensure
safe operation of the instrument.
1.3.1 Symbols and conventions
The following symbols and styles are used in this documentation:
Cross-reference to figure legend
The first number refers to the figure number, the
second to the instrument part in the figure.
Instruction step
Carry out these steps in the sequence shown.
850 Professional IC – Anion – MCS
■■■■■■■■
5
Page 16

1.4 Safety instructions
■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■
Warning
This symbol draws attention to a possible life hazard
or risk of injury.
Warning
This symbol draws attention to a possible hazard due
to electrical current.
Warning
This symbol draws attention to a possible hazard due
to heat or hot instrument parts.
Warning
This symbol draws attention to a possible biological
hazard.
Caution
This symbol draws attention to a possible damage of
instruments or instrument parts.
1.4 Safety instructions
1.4.1 General notes on safety
Warning
This instrument may only be operated in accordance with the specifications in this documentation.
This instrument has left the factory in a flawless state in terms of technical
safety. To maintain this state and ensure non-hazardous operation of the
instrument, the following instructions must be observed carefully.
1.4.2 Electrical safety
The electrical safety when working with the instrument is ensured as part
of the international standard IEC 61010.
Note
This symbol marks additional information and tips.
■■■■■■■■
6
Warning
Only personnel qualified by Metrohm are authorized to carry out service
work on electronic components.
850 Professional IC – Anion – MCS
Page 17

■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■
1 Introduction
Warning
Never open the housing of the instrument. The instrument could be
damaged by this. There is also a risk of serious injury if live components
are touched.
There are no parts inside the housing which can be serviced or replaced
by the user.
Mains voltage
Warning
An incorrect mains voltage can damage the instrument.
Only operate this instrument with a mains voltage specified for it (see
rear panel of the instrument).
Protection against electrostatic charges
Warning
Electronic components are sensitive to electrostatic charges and can be
destroyed by discharges.
Always pull the mains cable out of the mains connection socket before
connecting or disconnecting electrical appliances on the rear panel of
the instrument.
1.4.3 Tubing and capillary connections
Caution
Leaks in tubing and capillary connections are a safety risk. Tighten all
connections well by hand. Avoid applying excessive force to tubing
connections. Damaged tubing ends lead to leakage. Appropriate tools
can be used to loosen connections.
Check the connections regularly for leakage. If the instrument is used
mainly in unattended operation, then weekly inspections are mandatory.
850 Professional IC – Anion – MCS
■■■■■■■■
7
Page 18
1.4 Safety instructions
1.4.4 Flammable solvents and chemicals
Warning
All relevant safety measures are to be observed when working with
flammable solvents and chemicals.
■ Set up the instrument in a well-ventilated location (e.g. laboratory
flue).
■ Keep all sources of flame far from the workplace.
■ Clean up spilled fluids and solids immediately.
■ Follow the safety instructions of the chemical manufacturer.
1.4.5 Recycling and disposal
This product is covered by European Directive 2002/96/EC, WEEE – Waste
from Electrical and Electronic Equipment.
The correct disposal of your old equipment will help to prevent negative
effects on the environment and public health.
■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■
More details about the disposal of your old equipment can be obtained
from your local authorities, from waste disposal companies or from your
local dealer.
■■■■■■■■
8
850 Professional IC – Anion – MCS
Page 19

■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■
2 Installation
2.1 About this chapter
The Installation chapter contains
■ a list of all the steps to be carried out during the initial installation (see
Chapter 2.2, page 9).
■ a schematic overview of the flow paths (see Chapter 2.3, page 10).
■ a description of the construction, connections and functionality of the
instrument.
■ step-by-step installation instructions. A part of these installation tasks
has already been carried out before delivery. They are nevertheless
described here in case they need to be carried out once again some
time in the future (e.g. after maintenance of the high pressure pump).
2 Installation
2.2 Initial installation
Note
A large number of the capillary connections are already connected at
the time the instrument is delivered.
The following steps still have to be carried out after delivery:
Setting up the instrument (see Chapter 2.4, page 12).
1
Remove handle and rollers (see Chapter 2.6.1, page 15).
2
Place the detectors in the instrument and connect them (see Chapter
3
2.6.2, page 18).
Remove transport locking screws (see Chapter 2.6.3, page 20).
4
Connect the leak sensor (see Chapter 2.6.4, page 20).
5
Connect drainage tubings (see Chapter 2.6.5, page 21).
6
Connect the eluent bottle (see Chapter 2.8.1, page 26).
7
850 Professional IC – Anion – MCS
■■■■■■■■
9
Page 20

2.3 Flow diagram
■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■
Install sample path connections.
8
■ Connect the sample degasser (if required) (see Chapter 2.13,
page 39).
■ Connect sample path connections to the injection valve (see
Chapter 2.14.2, page 41).
Installing the MSM (see Chapter 2.16, page 46) – with associated
9
peristaltic pump (see Chapter 2.17, page 49).
Connect the MCS (see Chapter 2.18.2, page 54).
10
Connect detector capillaries (see Chapter 2.19, page 57).
11
Mains connection (see Chapter 2.20, page 60).
12
Connect the instrument to the PC (see Chapter 2.20.1, page 60).
13
Initial start-up (see Chapter 3.1, page 65).
14
Install the guard column (if used) (see Chapter 2.21, page 61).
15
Install the separation column (see Chapter 2.22, page 63).
16
2.3 Flow diagram
Figure 2 Flow diagram with sequential suppression shows the flow paths
with the application of sequential suppression (MSM (2-9) and MCS
(2-10)). The arrangement of the modules in the diagram corresponds to
the front view of the instrument. Liquid containers (eluent bottle, sample
vessel, waste container, auxiliary solutions container) and guard column
(see Chapter 2.21, page 61) are not shown in the diagram. Which pressure screws, connections and couplings are used, is described in the installation chapters of the individual modules.
■■■■■■■■
10
850 Professional IC – Anion – MCS
Page 21
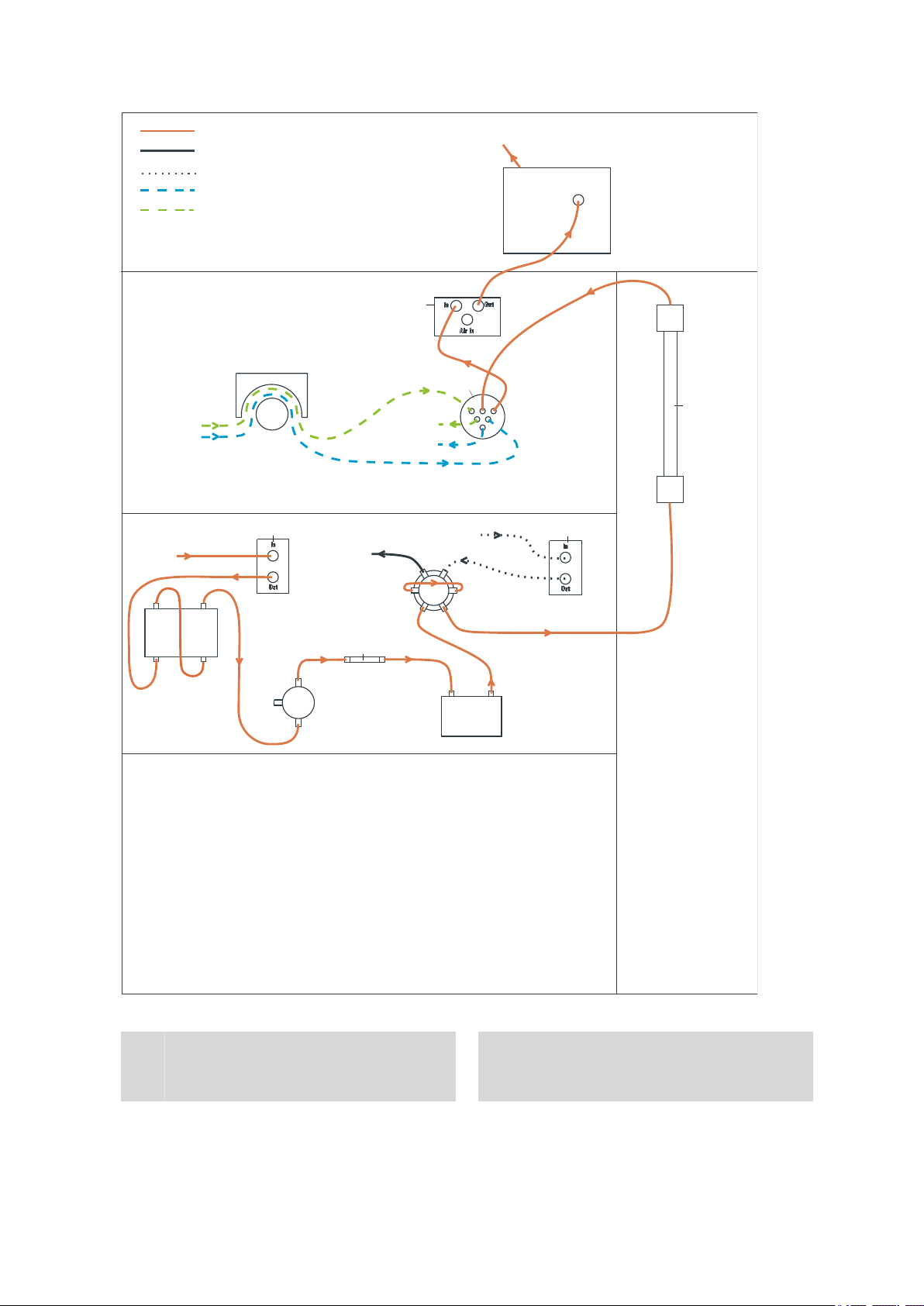
■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■
11
3
2
5
6
7
14
8
1
13
15
12
16
9
17
19
18
20
10
4
Eluent
Sample
Regeneration solution
Rinsing solution
Sample optional
2 Installation
Figure 2 Flow diagram with sequential suppression
850 Professional IC – Anion – MCS
Eluent input
1
Connection to the eluent bottle (see Chapter 2.8.1, page 26).
Eluent degasser
2
See Chapter 2.9.
■■■■■■■■
11
Page 22
2.4 Setting up the instrument
■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■
High pressure pump
3
See Chapter 2.10.
Inline filter
5
See Chapter 2.11.
Injection valve
7
See Chapter 2.14.
MSM
9
See Chapter 2.16.
Detector
11
See Chapter 2.19.
Sample input
13
Connection to the sample vessel (single vessel or sample changer).
Sample output
15
Purge valve
4
See Chapter 2.10.1.
Pulsation damper
6
See Chapter 2.12.
Separation column
8
See Chapter 2.22.
When a guard column (see Chapter 2.21,
page 61) is used, it is installed between
injection valve and separation column.
MCS
10
See Chapter 2.18.
Eluent output
12
Connection to the waste container.
Sample degasser
14
See Chapter 2.13. Use optional.
Peristaltic pump
16
See Chapter 2.17.
Regeneration solution input
17
Connection to the regeneration solution
bottle.
Rinsing solution input
19
Connection to the rinsing solution bottle.
18
20
2.4 Setting up the instrument
2.4.1 Packaging
The instrument is supplied in highly protective special packaging together
with the separately packed accessories. Keep this packaging, as only this
ensures safe transportation of the instrument.
2.4.2 Checks
Immediately after receipt, check whether the shipment has arrived complete and without damage by comparing it with the delivery note.
2.4.3 Location
The instrument has been developed for operation indoors and may not be
used in explosive environments.
Regeneration solution output
Connection to the waste container.
Rinsing solution output
Connection to the waste container.
■■■■■■■■
12
Place the instrument in a location of the laboratory which is suitable for
operation, free of vibrations, protected from corrosive atmosphere, and
contamination by chemicals.
850 Professional IC – Anion – MCS
Page 23
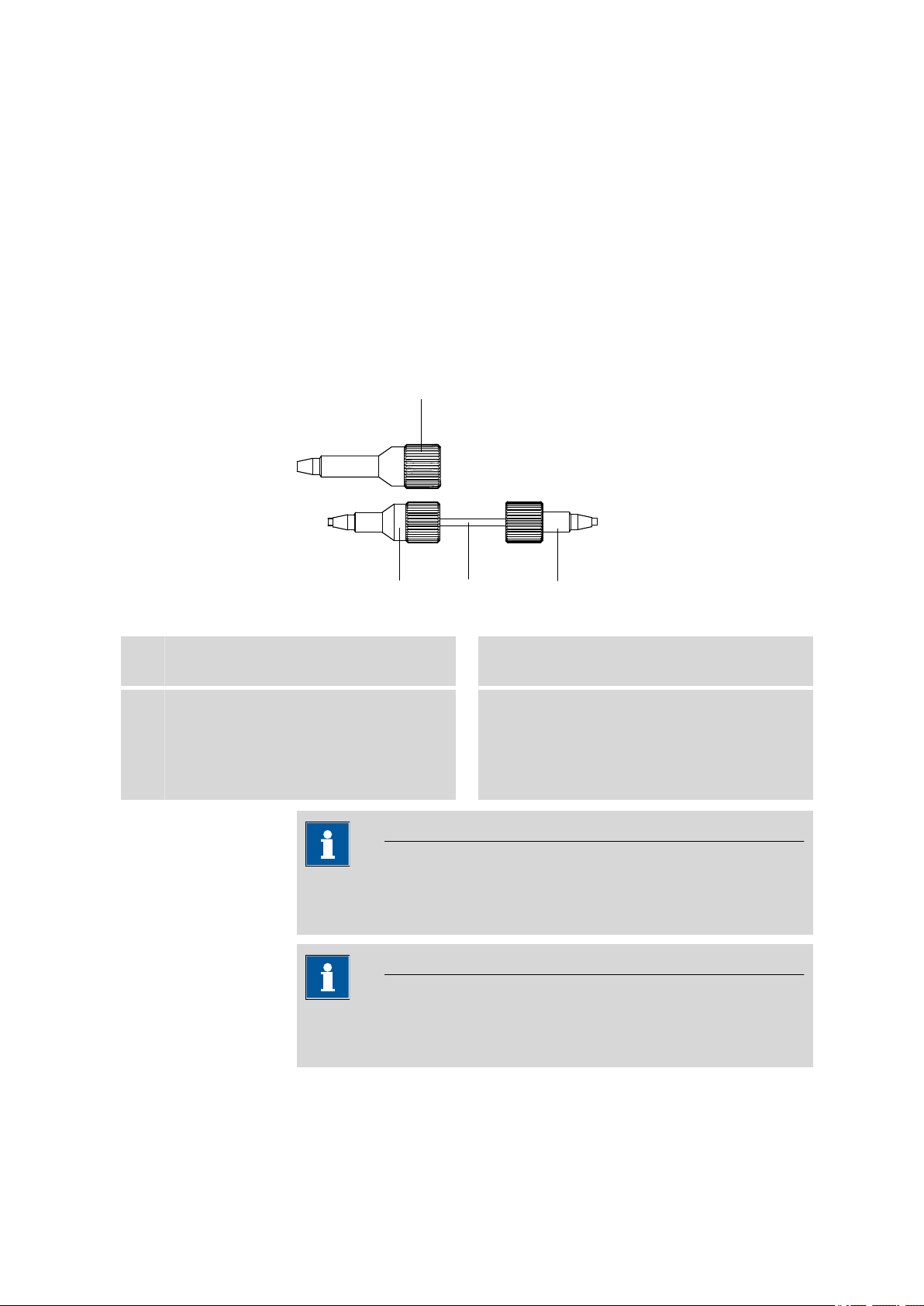
■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■
4
1
2 3
The instrument should be protected against excessive temperature fluctuations and direct sunlight.
2.5 Capillary connections in the IC system
This chapter contains general information concerning the capillary connections in the IC instruments.
Generally speaking, capillary connections between two components of an
IC instrument are made up of one connection capillary and two pressure
screws with which the capillary is connected to the respective components.
2 Installation
Figure 3
PEEK pressure screw 6.2744.014
1
Use on the injection valve.
PEEK pressure screw, short 6.2744.070
3
For use on the high pressure pump, the
purge valve, the inline filter, the pulsation
damper, the guard column and the separation column.
In order to keep the dead volume as low as possible, capillary connections should generally be as short as possible.
For an improved overview, capillary and tubing connections can be
bundled with the 6.1815.010 spiral band.
Connection of capillaries with pressure screws
Connection capillary
2
PEEK pressure screw, long 6.2744.090
4
Usage on other components. Is not used on
all instruments.
Note
Note
850 Professional IC – Anion – MCS
■■■■■■■■
13
Page 24

2.5 Capillary connections in the IC system
Connection capillary
PEEK capillaries and PTFE capillaries are used in the IC system.
■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■
PEEK capillaries (polyetheretherketone)
PTFE capillaries (polytetrafluoroethylene)
PEEK capillaries are temperature-resistant up to 100°C, stable under pressure up to 400 bar, flexible, chemically inert and exhibit an extremely
smooth surface. They can be readily cut down to the desired length with
the capillary cutter.
Usage:
■ 6.1831.010 PEEK capillary (internal diameter of 0.25 mm) for the entire
high pressure range.
■ 6.1831.030 PEEK capillary (internal diameter of 0.75 mm) for sample
handling in the ultra trace range.
Caution
For the capillary connections between the injection valve (see Chapter
2.14, page 40) and detector (see Chapter 2.19, page 57), PEEK
capillaries with an internal diameter of 0.25 mm must be used. These
are already connected to a newly delivered instrument.
PTFE capillaries are transparent and enable visual tracing of the liquids to
be pumped. They are chemically inert, flexible and temperature-resistant
up to 80°C.
Usage:
PTFE capillaries (6.1803.0x0) are used for the low pressure range.
■ PTFE capillaries with internal diameter of 0.5 mm for sample handling.
■ PTFE capillaries with internal diameter of 0.97 mm for the sample han-
dling as for rinsing and regeneration solutions (they do not have to be
in the scope of delivery of the instrument).
Note
Capillaries must have a flawless level cut edge. For cutting PEEK capillaries only use the 6.2621.080 capillary cutter.
■■■■■■■■
14
850 Professional IC – Anion – MCS
Page 25
■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■
3
2
1
1
4
5
2.6 Rear of the instrument
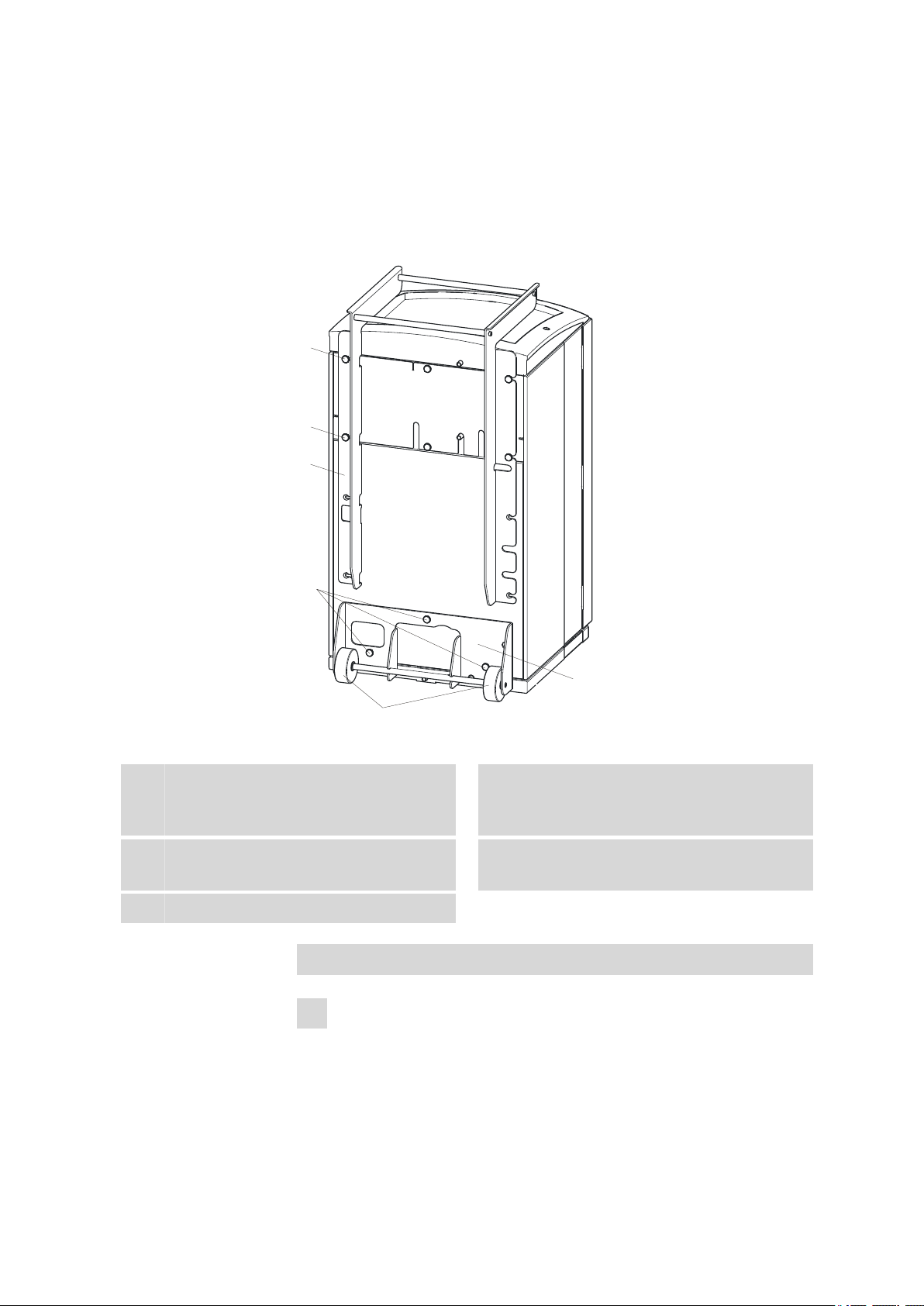
2.6.1 Rollers and handle
In order to make transport easier, the instrument is equipped with rollers
and a handle.
2 Installation
Figure 4 Rollers and handle
Knurled screws
1
For fastening the handle (4-2) and the rear
panel of the detector chamber.
Knurled screws
3
For fastening the roller holder (4-5).
Roller holder
5
2
4
Handle
Rollers
Removing handle
850 Professional IC – Anion – MCS
Loosen knurled screws (4-1) and remove handle (4-2).
1
■■■■■■■■
15
Page 26

2.6 Rear of the instrument
■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■
Removing rollers
Proceed as follows to remove the rollers:
Remove knurled screws (4-3).
1
Remove roller holder (4-5).
2
Mounting handle as MPak holder
Note
When extended, the handle (5-2) can also be used for hanging up
MPaks (eluent bags).
Move handle (5-2) upwards and screw in the knurled screws (5-1)
1
again.
■■■■■■■■
16
850 Professional IC – Anion – MCS
Page 27
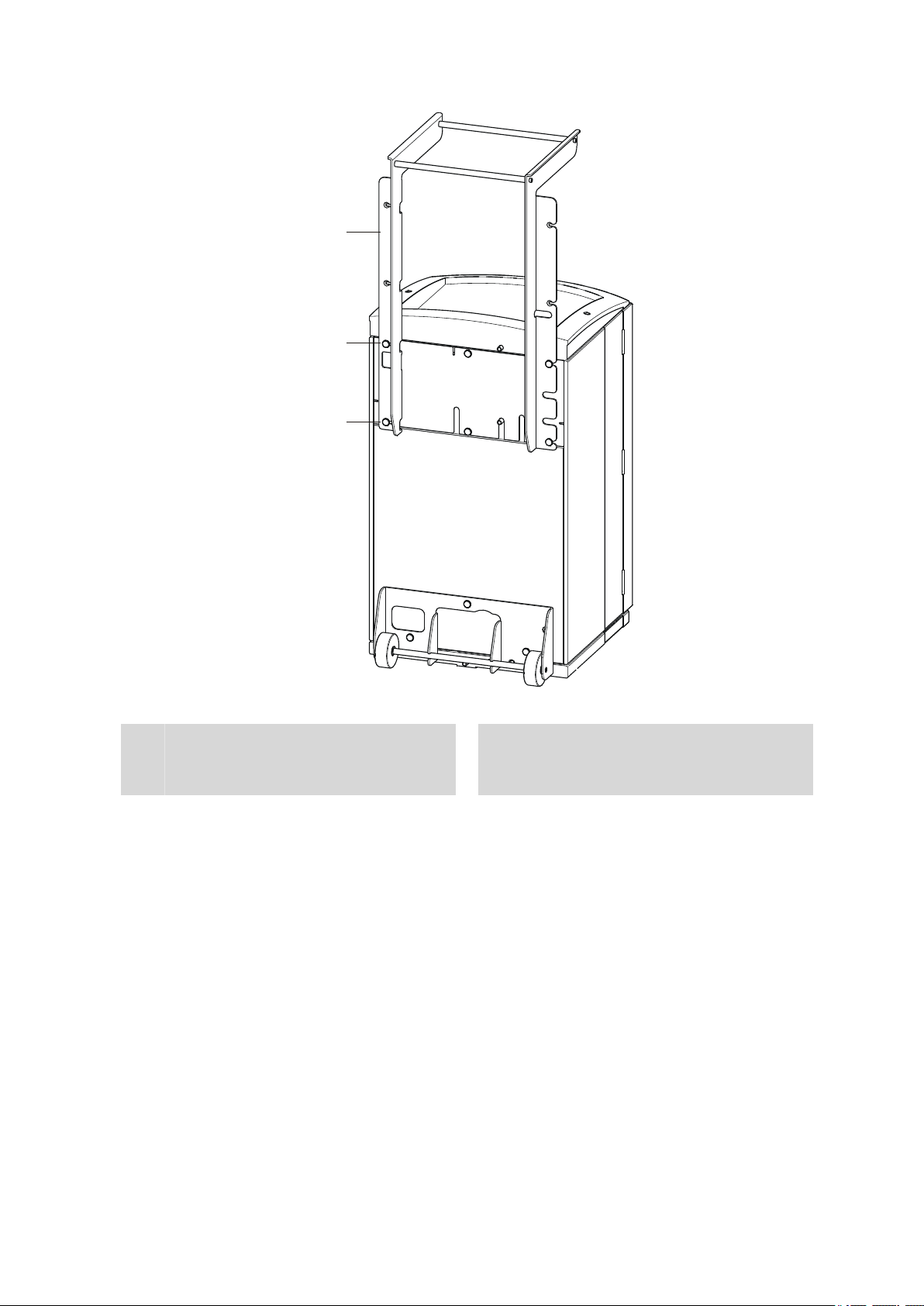
■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■
2
1
1
2 Installation
Figure 5 Handle as MPak holder
Knurled screws
1
For fastening the handle (5-2) and the rear
panel of the detector chamber.
Handle
2
Extended. As holder for MPaks (eluent bag).
850 Professional IC – Anion – MCS
■■■■■■■■
17
Page 28
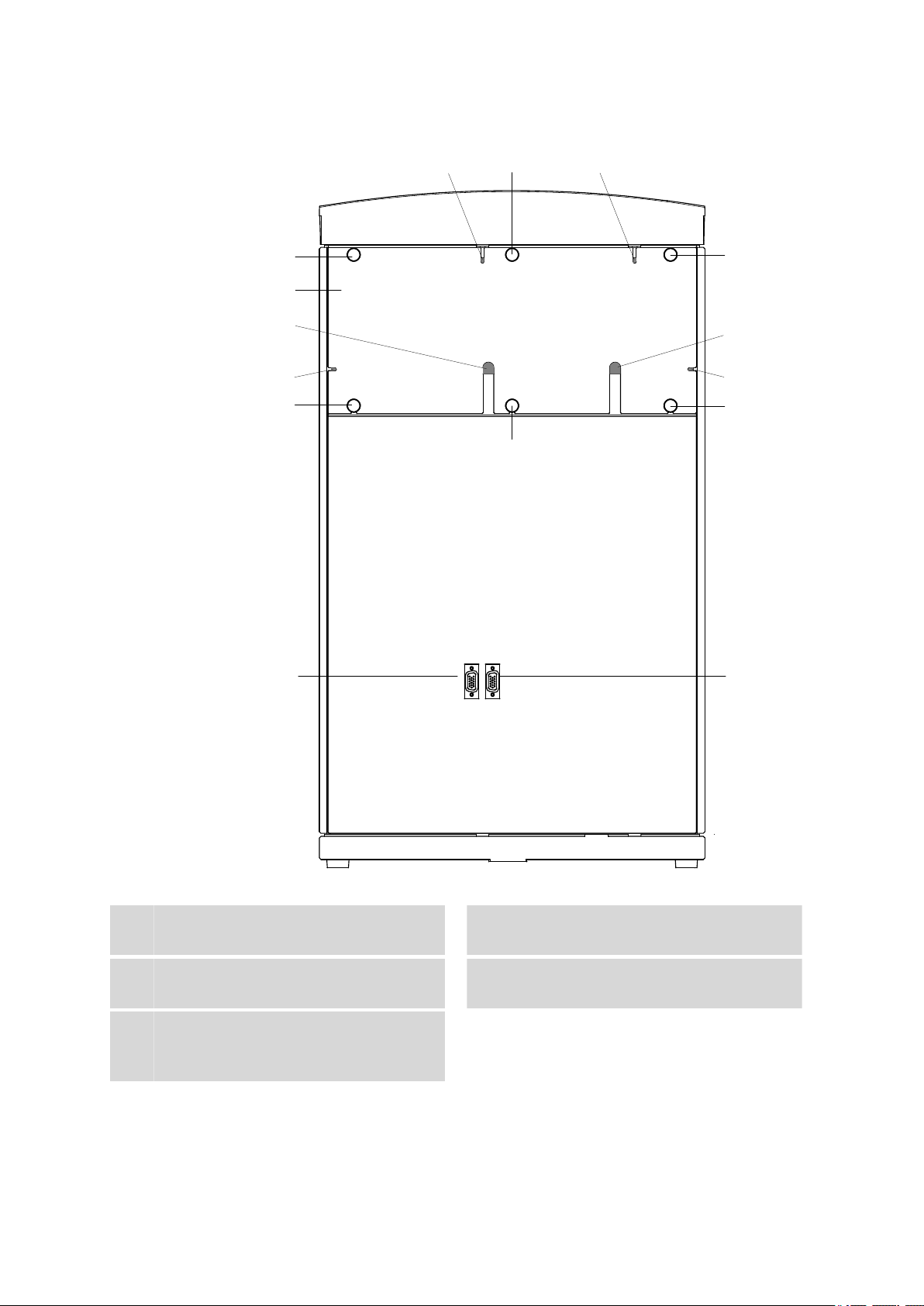
2.6 Rear of the instrument
Detector 1
Detector 2
4
4
4
4
3
3
2
1
1
1
1
1
1
5
5
2.6.2 Positioning and connecting the detector
■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■
Knurled screws
1
Figure 6 Removable rear panel
For fastening the removable rear panel.
Cable feed-throughs
3
Rear panel
2
Removable
Capillary feed-throughs
4
For feeding through detector cables.
Detector connection sockets
5
Labeled with Detector 1 and Detector 2 for
connecting Metrohm detectors.
■■■■■■■■
18
850 Professional IC – Anion – MCS
Page 29

■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■
Note
Up to two detectors can be positioned and connected.
Caution
The instrument must be turned off when connecting a detector.
1
Removing rear panel
■ Unscrew knurled screws (6-1) on the rear panel.
■ Remove handle if still fastened to the instrument.
■ Remove rear panel (6-2).
2
Positioning the detector
■ Put the detector through this opening and position it on the sup-
port surface intended for this purpose. Slide it right up to the
front.
3
Replacing rear panel
■ Insert the detector cable in a cable feed-through (6-3) on the rear
panel (6-2).
■ Place the detector output capillary in a suitable capillary feed-
through.
■ Replace (6-2) rear panel.
(Optionally, the handle can be remounted higher up and used as
a holder for MPaks.)
■ Tighten (6-1) knurled screws.
4
Connecting the detector
2 Installation
850 Professional IC – Anion – MCS
Note
The instrument has two detector connection sockets (6-5), Detector 1 and Detector 2. You must ensure that the selected connec-
tor corresponds to the connector entered in the MagIC Net
method.
Recommendation: Use Detector 1 as standard. In the AnCat sys-
tem with 2 detectors: Detector 1 for anions, Detector 2 for cations.
■■■■■■■■
19
Page 30

2.6 Rear of the instrument
■ Connect the detector cable to the detector connection socket
Detector 1 (6-5).
5
Conntecting detector output
Note
The detector output capillary must be free of blockages (the measuring cell is tested to 5 MPa = 50 bar backpressure).
Guide the detector output capillary into a sufficiently large waste
container and fasten it there.
2.6.3 Transport locking screws
To avoid damage to the high pressure pump and vacuum pump during
transport, the pumps are secured with transport locking screws .
Remove these transport locking screws before the initial start-up.
■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■
Removing transport locking screws
In order to avoid damage to the pumps, the transport locking screws
must be remounted each time the instrument undergoes major transport.
2.6.4 Leak sensor
The leak sensor detects escaping liquid which collects in the base tray of
the instrument.
To activate the leak sensor, the leak sensor connector plug (7-2) must be
connected, the instrument switched on and the leak sensor switched to
active in the software.
Connecting the leak sensor
Remove and keep transport locking screws.
1
Warning
■■■■■■■■
20
Plug the leak sensor connector plug (7-2) into the leak sensor con-
1
nector socket (7-1) on the rear of the instrument (see Figure 7, page
21).
850 Professional IC – Anion – MCS
Page 31

■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■
1
2
3
2 Installation
Figure 7 Connection for the leak sensor on the rear of the instrument
Leak sensor connector socket
1
Is labeled with "Leak Sensor".
Leak sensor connection cable
3
Is firmly mounted on the rear of the instrument.
Leak sensor connector plug
2
2.6.5 Drainage tubing
Fluid that escapes in the covering plate or in the detector chamber flows
through the drainage tubing into the base tray and past the leak sensor
into the waste container. This ensures that any leaks in the system will be
detected by the leak sensor.
850 Professional IC – Anion – MCS
■■■■■■■■
21
Page 32

2.6 Rear of the instrument
2
4
5
6
1
3
7
9
8
■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■
Figure 8 Drainage tubing
Drainage tubing connection
1
For draining escaped fluid from the covering
plate.
Drainage tubing connection
3
For draining escaped fluid from the detector
chamber.
Y connector 6.1807.010
5
For connecting the two drainage tubings
(8-2) and (8-4).
Drainage tubing
2
Section of the 6.1816.020 silicon tubing. For
draining escaped fluid from the covering
plate.
Drainage tubing
4
Section of the 6.1816.020 silicon tubing. For
draining escaped fluid from the detector
chamber.
Drainage tubing
6
Section of the 6.1816.020 silicon tubing.
Guides escaped fluid to the leak sensor.
■■■■■■■■
22
850 Professional IC – Anion – MCS
Page 33

■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■
2 Installation
Drainage tubing
7
Section of the 6.1816.020 silicon tubing.
Guides escaped fluid into a waste container.
Drainage tubing connection
9
For supplying escaped fluid through the connected drainage tubing to the leak sensor.
Proceed as follows to install the drainage tubing:
Installing drainage tubing
Plug drainage tubing (8-2) into the drainage tubing connection (8-1)
1
of the covering plate and shorten to required length.
Plug drainage tubing (8-4) into the drainage tubing connection (8-3)
2
of the detector chamber and shorten to required length.
Connect drainage tubing (8-2) from the covering plate and drainage
3
tubing (8-4) from the detector chamber to the Y connector (8-5).
Connect drainage tubing (8-6) to the Y connector (8-5), shorten to
4
required length and plug the other end of the drainage tubing into
the drainage tubing connection (8-9).
Plug drainage tubing (8-7) into the drainage tubing connection (8-8)
5
of the base tray and guide the other end into a waste container.
Drainage tubing connection
8
For draining escaped fluid from the base tray
through the connected drainage tubing.
2.7 Capillary and cable feed-throughs
Several openings have been integrated for feeding through capillaries and
cables. They are located on the doors (see Figure 9, page 24), on the
rear panel (see Figure 6, Page 18) or below the covering plate or above
the base tray (see Figure 10, Page 25).
850 Professional IC – Anion – MCS
■■■■■■■■
23
Page 34

2.7 Capillary and cable feed-throughs
2
1
2
1
3
4
■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■
Figure 9 Capillary feed-throughs on the doors
Luer connectors
1
For connecting a 6.2816.020 syringe. For
manual sample feeding.
PEEK pressure screws, short
3
6.2744.070
Capillary feed-through
2
Door
4
Do not feed capillaries through the Luer connectors (9-1). The capillaries
are fastened with PEEK pressure screws (9-3) from inside to the Luer connector. From outside, liquid can be aspirated or injected with a syringe.
24
■■■■■■■■
850 Professional IC – Anion – MCS
Page 35

■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■
1
2
3
4
5
6
7 8
8 7
6 5
9
10
11
12 12
11
10
9
Front
Rear
2 Installation
Figure 10 Capillary feed-throughs base tray/covering plate
Side panel (right)
1
Right panel.
Side panel (left)
3
Left panel.
Capillary feed-through
5
Upper. From front to right.
Capillary feed-through
7
Upper. From front to back.
Capillary feed-through
9
Lower. From front to right.
11
Capillary feed-through
Lower. From front to back.
Rear of the instrument
2
Front of the instrument
4
Capillary feed-through
6
Upper. From front to back.
Capillary feed-through
8
Upper. From front to left.
Capillary feed-through
10
Lower. From front to back.
12
Capillary feed-through
Lower. From front to left.
850 Professional IC – Anion – MCS
■■■■■■■■
25
Page 36

2.8 Eluent
2.8 Eluent
2.8.1 Connecting eluent bottle
The eluent is aspirated out of the eluent bottle via the eluent aspiration
tubing (11-1).
The eluent aspiration tubing is connected to the eluent degasser (see
Chapter 2.9, page 30). The tubing must be threaded through a suitable
capillary feed-through (see Chapter 2.7, page 23) of the instrument
before the other end can be equipped.
You will require the parts from the following accessories for equipping the
eluent aspiration tubing:
■ 6.1602.160 eluent bottle attachment GL 45
■ 6.2744.210 tubing adapter for aspiration filter
■ 6.2821.090 aspiration filter
To equip the eluent aspiration tubing proceed as follows:
■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■
Assembling eluent aspiration tubing
Guide the free end of the eluent aspiration tubing (11-1) out of the
1
instrument through a suitable capillary feed-through.
2
Installing the 6.1602.160 eluent bottle attachment
■ Slide tubing nipple (11-2) and O-ring (11-3) onto the eluent aspi-
ration tubing (11-1).
■ Push eluent aspiration tubing (11-1) through the bottle attach-
ment (11-4) and screw tight.
■■■■■■■■
26
850 Professional IC – Anion – MCS
Page 37

■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■
1 2
3
4
2 Installation
Figure 11 Installing eluent bottle attachment
Eluent aspiration tubing 6.1834.080
1
O-ring
3
From accessory set 6.1602.160.
3
Filter holder
1
From accessory set 6.2744.210.
Tubing nipple
2
From accessory set 6.1602.160.
Bottle attachment
4
From accessory set 6.1602.160.
Mounting aspiration filter
■ Insert filter holder (12-1) into the aspiration filter (12-2) and screw
tight.
Figure 12 Mounting aspiration filter
Aspiration filter 6.2821.090
2
850 Professional IC – Anion – MCS
■■■■■■■■
27
Page 38

2.8 Eluent
1 2
3
4
5
4
Installing tubing weighting and aspiration filter
Figure 13 Installing tubing weighting and aspiration filter
■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■
Eluent aspiration tubing 6.1834.080
1
Tubing weighting
3
From accessory set 6.2744.210.
Aspiration filter 6.2821.090
5
With filter holder from accessory set
6.2744.210.
■ Slide the tubing weighting (13-3) onto the eluent aspiration tub-
■ Slide the clamping screw (13-4) onto the eluent aspiration tubing
■ Insert eluent aspiration tubing (13-1) into the aspiration filter
■ Screw together clamping screw (13-4) and filter holder (12-1).
Eluent bottle attachment 6.1602.160
2
Clamping screw
4
From accessory set 6.2744.210.
ing (13-1).
(13-1).
(13-5). The end of the tubing must touch the base of the filter.
The end of the tubing must still touch the base of the filter.
Figure 14
■■■■■■■■
28
Eluent aspiration tubing fully equipped.
5
Mounting eluent aspiration tubing to the eluent bottle
■ Insert the eluent aspiration tubing into the eluent bottle (15-10).
850 Professional IC – Anion – MCS
Page 39

■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■
1
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
89
10
11
12
13
14
2 Installation
■ Fasten the bottle attachment (13-2) on the eluent bottle (15-10).
The aspiration filter (15-6) must rest on the base of the eluent
bottle.
6
Mounting the adsorber tube
Note
In the case of alkaline eluents and eluents with lower buffer
capacity, the eluent bottle must be equipped with a CO2 adsorber
(15-4).
■ First, place a piece of wadding (15-3), then the CO
adsorber
2
(15-4) in the large opening of the adsorber tube (15-2) and close
with the plastic cover.
■ Fasten the adsorber tube (15-2) using the SGJ clip (15-12) onto
the bottle attachment (15-11).
Eluent aspiration tubing 6.1834.080
1
For aspirating the eluent. Pre-installed.
Wadding
3
850 Professional IC – Anion – MCS
Figure 15
Eluent bottle – connected
Adsorber tube 6.1609.000
2
CO2 adsorber
4
Adsorbs CO2 from the air (e.g. Merck soda
lime with indicator, no. 6839.10).
■■■■■■■■
29
Page 40

2.9 Eluent degasser
5
6
1
3
4
■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■
Eluent
5
Filter holder
7
From accessory set 6.2744.210.
Tubing weighting
9
From accessory set 6.2744.210.
Bottle attachment 6.1602.160
11
Tubing nipple
13
2.9 Eluent degasser
Gas bubbles in the eluent lead to an unstable baseline, as high pressure
pumps can transport liquids, but not gases. The eluent therefore has to be
degassed, before it reaches the high pressure pump.
The eluent degasser removes gas bubbles and dissolved gases from the
eluent. For degassing, the eluent flows into a vacuum chamber through a
special fluoropolymer capillary.
Note
Aspiration filter 6.2821.090
6
Clamping screw
8
From accessory set 6.2744.210.
Eluent bottle 6.1608.070
10
SGJ clip 6.2023.020
12
Thread stopper
14
Eluent degasser input
1
The eluent degasser is already installed in the newly delivered instrument. The following installation instructions need not be carried out at
the time of initial installation.
Connecting the eluent degasser
Figure 16
Eluent degasser
Eluent degasser output
2
■■■■■■■■
30
850 Professional IC – Anion – MCS
Page 41

■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■
2 Installation
Tubing flare
3
With tubing nipple.
Eluent aspiration tubing 6.1834.080
5
For aspirating the eluent. The clamping
screw (16-4) is firmly mounted.
1
2
Clamping screw
4
Connection capillary 6.1834.090
6
Connection from the eluent degasser to the
high pressure pump (see Chapter 2.10, page
31). The clamping screw (16-4) is firmly
mounted.
Caution
The clamping screws (16-4) must be tightened carefully. Use the
6.2621.050 wrench for this.
■ Insert the eluent aspiration tubing (16-5) in the eluent degasser
input (16-1).
■ Carefully tighten clamping screw (16-4).
■ Insert connection capillary (16-6) (the end with the longer clamp-
ing screw (16-4)) into the eluent degasser output (16-2).
■ Carefully tighten clamping screw (16-4).
■ Connect the other end of the connection capillary (16-6) (with
the shorter clamping screw ) to the high pressure pump (see
"Connecting inlet to the high pressure pump", page 33).
2.10 High pressure pump
The intelligent and low pulsation high pressure pump pumps the eluent
through the system. It is equipped with a chip on which its technical specifications and "life history" (operating hours, service data, ... ) are saved.
The purge valve is used for deaerating (see Chapter 2.10.2, page 34)
the high pressure pump.
2.10.1 Capillary connections high pressure pump/purge valve
Note
All of the capillary connections of the high pressure pump and the
purge valve are already installed in the newly delivered instrument.
850 Professional IC – Anion – MCS
■■■■■■■■
31
Page 42

2.10 High pressure pump
10
8
9
1
2
3
4
5
6
2
7
2
2
2
11
2
12
2
13
■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■
Figure 17 Capillary connections high pressure pump/purge valve
Connection capillary
1
PEEK capillary, connects main piston and
auxiliary piston.
Outlet valve holder
3
Fastening screws
5
For fastening the pump head.
Pump head input capillary
7
PEEK capillary at the input of the pump
head.
Coupling
9
For the connection of the eluent path at the
input of the high pressure pump. Can be
ordered together with the pressure screw
(17-8) under the number 6.2744.230.
Purge valve
11
For deaerating the high pressure pump.
With rotary knob in the center and pressure
sensor.
Connection capillary
13
Connects the output of the pump head with
the purge valve.
PEEK pressure screw, short 6.2744.070
2
Pump head 6.2824.110
4
Inlet valve holder
6
Pressure screw
8
For connecting a PEEK capillary to the coupling (17-9).
Deaerating capillary
10
For aspirating the eluent when deaerating
the high pressure pump (see Chapter
2.10.2, page 34).
Connection capillary
12
For connecting the inline filter (see Chapter
2.11, page 36)
■■■■■■■■
32
850 Professional IC – Anion – MCS
Page 43

■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■
5
1
2
3
4
2 Installation
Note
The eluent aspiration tubing is already installed in the newly delivered
instrument. The following installation instructions need not be carried
out at the time of initial installation.
Connecting inlet to the high pressure pump
Figure 18 High pressure pump – Connect inlet
Pressure screw
1
For connecting the coupling (18-2) to the
pump head input capillary (17-7).
Can be ordered together with the coupling
under the number 6.2744.230.
Clamping screw
3
Backup ring
5
1
Connecting coupling
Fasten the coupling (18-2) with a pressure screw (18-1) on the pump
head input capillary (17-7).
2
Connecting eluent aspiration tubing
Coupling 6.2744.230
2
For connecting the eluent aspiration tubing
(18-4) to the input of the high pressure
pump.
Eluent aspiration tubing
4
Eluent aspiration tubing 6.1834.080 or
6.1834.090.
Caution
The clamping screws must be tightened carefully. To tighten, grip
the coupling (18-2) with the 6.2739.000 key and grip the clamping screw (18-3) with the 6.2621.050 wrench.
■ Plug the eluent aspiration tubing (18-4) into the coupling (18-2).
■ Tighten clamping screw (18-3).
850 Professional IC – Anion – MCS
■■■■■■■■
33
Page 44

2.10 High pressure pump
2.10.2 Deaerating the high pressure pump
The high pressure pump will only operate perfectly if the pump head contains no more air bubbles. Therefore it must be deaerated during initial
start-up and after every change of eluent.
Caution
The high pressure pump must not be deaerated before the initial startup (see Chapter 3.1, page 65).
Deaerate the high pressure pump as follows (see Figure 19, page 35):
■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■
■■■■■■■■
34
850 Professional IC – Anion – MCS
Page 45

■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■
5
1
2
6
7
5
3
4
5
2 Installation
Deaerating the high pressure pump
The instrument must be connected to the PC and switched on to deaerate
the high pressure pump.
Syringe 10 mL 6.2816.020
1
For aspirating the eluent.
Purging needle 6.2816.040
3
PEEK pressure screws, short
5
6.2744.070
Purge valve rotary knob
7
Figure 19 Deaerating the high pressure pump
Luer connector
2
On purging needle.
Deaerating capillary
4
Purge valve
6
1
Connecting the purging needle
■ Push the end of the purging needle (19-3) over the end of the
deaerating capillary (19-4) on the purge valve.
2
Connecting the syringe
■ Insert syringe (19-1) in the Luer connector (19-2) of the purging
needle (see Figure 19, page 35).
3
Opening purge valve
■ Open the rotary knob (19-7) by approx. ½ rotation counterclock-
wise.
850 Professional IC – Anion – MCS
■■■■■■■■
35
Page 46

2.11 Inline filter
■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■
4
Setting the flow rate
■ Start MagIC Net (if not yet started).
■ Ensure that the eluent aspiration tubing is immersed sufficiently in
the eluent.
■ Let the high pressure pump run.
5
Aspirating eluent
■ Aspirate with the syringe (19-1) until bubble-free eluent flows into
the syringe.
6
Completing deaerating
■ Turn off high pressure pump.
■ Close rotary knob (19-7).
■ Remove syringe (19-1) from the Luer connector (19-2).
■ Pull the purging needle (19-3) out of the deaerating capillary
(19-4).
2.11 Inline filter
Between the purge valve and the pulsation damper the 6.2821.120 inline
filter is installed as protection against particles.
Inline filters protect the separation column securely against possible contamination from the eluent. Inline filters can however also just as well be
used for the purpose of protecting the suppressor against contaminations
in the regeneration or rinsing solutions. The fine 2 µm material of the
readily and easily replaceable filter platelets removes particles such as bacteria and algae from the solutions.
The inline filter is already installed in the newly delivered instrument.
The following installation instructions need not be carried out at the
time of initial installation.
Note
■■■■■■■■
36
850 Professional IC – Anion – MCS
Page 47

■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■
2 3
2 4
1
Installing the inline filter
Observe the flow direction marked on the filter housing for the connection of the inline filter.
Figure 20 Connecting inline filter
2 Installation
Caution
Connection capillary
1
Connects the purge valve with the inline filter
Inline filter 6.2821.120
3
Protects against particles.
Screw on the connection capillary running from the purge valve with
1
a 6.2744.070 pressure screw to the input side of the inline filters.
Screw on the connection capillary running to the pulsation damper
2
with a 6.2744.070 pressure screw to the output side of the inline filter.
2.12 Pulsation damper
Note
PEEK pressure screws, short
2
6.2744.070
Connection capillary
4
Connects the inline filter with the pulsation
damper.
The pulsation damper is already installed in the newly delivered instrument.
Caution
The pulsation damper is maintenance-free and may not be opened.
850 Professional IC – Anion – MCS
■■■■■■■■
37
Page 48

2.12 Pulsation damper
3
4
5
2
3
6
1
2
■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■
The pulsation damper protects the separation column from damage
caused by pressure fluctuations when switching the injection valve, and
reduces interfering pulsations during highly sensitive measurements. In
order to ensure these functionalities, it must be connected between the
high pressure pump (see Chapter 2.10, page 31) and injection valve (see
Chapter 2.14, page 40).
The pulsation damper can be operated in both directions.
Figure 21 Pulsation damper – Connection
Connection capillary
1
Connection to the inline filter.
PEEK pressure screws, short
3
6.2744.070
Pulsation damper 6.2620.150
5
Fastening screws
2
Holder for pulsation damper
4
Connection capillary
6
Connection to the injection valve.
■■■■■■■■
38
850 Professional IC – Anion – MCS
Page 49

■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■
1
2
3
4
2.13 Sample degasser
The sample degasser removes gas bubbles and disolved gases from the
sample. For degassing, the sample flows into a vacuum chamber through
a special fluoropolymer capillary.
Gas bubbles in the sample lead to poor reproducibility, as the quantity of
sample in the sample loop would not always be the same. Samples (containing gas) should therefore be degassed before injection. For this the
sample is sucked through a degasser chamber before injection, whereby
any gas bubbles are automatically removed.
Note
When using the sample degasser, the rinsing time extends by at least 2
minutes.
2 Installation
Figure 22
Sample degasser input
1
PEEK pressure screw, long 6.2744.090
3
Sample degasser
2
4
Sample degasser output
Connection capillaries 6.1803.040
Connecting the sample degasser
Remove and keep 6.2744.220 thread stoppers from the input and
1
output of the sample degasser.
Connect the end of the 6.1803.040 sample aspirating capillary con-
2
nected to the injection valve with a long PEEK pressure screw (22-3)
to the output of the sample degasser (22-2).
Connect 6.1803.040 connection capillary with a long PEEK pressure
3
screw (22-3) to the input of the sample degasser (22-1).
850 Professional IC – Anion – MCS
■■■■■■■■
39
Page 50

2.14 Injection valve
1
2
3
4
5
6
2
4
5
7
7
Guide the other end of the connection capillary out of the instrument
4
through a capillary feed-through.
Caution
If the sample degasser is not used, the input and output must be
sealed with the 6.2744.220 thread stoppers.
2.14 Injection valve
The injection valve connects the eluent and sample path. Through rapid
and precise valve switchover a precise amount of sample solution defined
by the size of the sample loop is injected and rinsed with eluent onto the
separation column.
2.14.1 Connecting the injection valve
The injection valve has six connectors: two for the sample path (connectors 1 and 2), two for the eluent path (connectors 4 and 5) and two for
the sample loop (connectors 3 and 6).
■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■
Injection valve
1
Note
The capillaries of the eluent path and the sample path and the sample
loop are already installed in the newly delivered instrument.
Figure 23
Injection valve – connected
Sample loop
2
Connected to connectors 3 and 6.
■■■■■■■■
40
850 Professional IC – Anion – MCS
Page 51

■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■
2 Installation
Connection capillary
3
Connected to connector 4. Carries eluent to
the injection valve.
Connection capillary
5
Connected to connector 1. Carries sample to
the injection valve.
PEEK pressure screw 6.2744.010
7
Replacing the sample loop
The sample loop can be replaced, depending on requirements. For additional information concerning selection of the appropriate sample loop,
see Chapter 2.14.3, page 42.
Use only 6.2744.010 PEEK pressure screws for connecting capillaries
and sample loop to the injection valve.
1
Removing existing sample loop
■ Loosen 6.2744.010 pressure screws at connector 3 and connec-
■ Remove sample loop.
2
Mounting new sample loop
■ Fasten one end of the sample loop (23-2) with a 6.2744.010
■ Fasten the other end of the sample loop (23-2) with a second
Connection capillary (column inlet
4
capillary)
Connected to connector 5. Carries eluent to
the separation column.
Connection capillary
6
Connected to connector 2. Carries sample to
the waste container.
Note
tor 6.
PEEK pressure screw (23-7) to connector 3.
6.2744.010 PEEK pressure screw (23-7) to connector 6.
2.14.2 Mode of operation of the injection valve
The injection valve (see Figure 24, page 42) can adopt two valve positions - FILL and INJECT. Switching back and forth between the two valve
positions determines whether the sample path or the eluent path is guided through the sample loop. The following figure provides a schematic
display of the flow paths of the two valve positions.
850 Professional IC – Anion – MCS
■■■■■■■■
41
Page 52

2.14 Injection valve
12
4 5
3 6
12
4 5
3 6
1
2
4
3
5
4
3
1
2
A B
Figure 24 Injection valve – Positions
■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■
Position FILL
A
Eluent input
1
Capillary coming from the high pressure
pump.
Sample input
3
Sample aspirating capillary.
Sample loop
5
Position A In the position FILL, the sample solution flows
Position B In the position INJECT, the eluent flows through
Position INJECT
B
Eluent output
2
Capillary to the column.
Sample output
4
Capillary to waste container.
through the sample loop to the waste container.
The eluent flows directly to the separation column at the same time.
the sample loop to the separation column. If
sample solution is to be found in the sample
loop at the time of the valve switchover, then
this will be conveyed along with the eluent, thus
making its way to the separation column. The
flow in the sample path is either stopped or the
sample flows directly to the waste container.
2.14.3 Selecting the sample loop
The amount of sample solution injected depends on the volume of the
sample loop. The choice is made on the basis of the application. The following sample loops are normally used:
Cation determination
■■■■■■■■
42
Anion determination with suppression 20 µL
Anion determination without suppression 100 µL
10 µL
850 Professional IC – Anion – MCS
Page 53

■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■
2.15 Column thermostat
The column thermostat controls the temperature of the column and eluent channel and thus ensures stable measuring conditions. It provides
space for 2 separation columns.
2 Installation
850 Professional IC – Anion – MCS
■■■■■■■■
43
Page 54

2.15 Column thermostat
1
3
2
1
1
1
1
2
■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■
Capillary feed-throughs
1
For guiding the capillaries in and out.
Column holder
3
For fastening the columns.
With column recognition.
Figure 25 Column thermostat
Capillary recesses
2
For controlling the temperature of the eluent.
Preheating capillary already pre-installed.
The column thermostat contains two column holders (25-3) equipped
with chip recognition. The separation columns can be clicked into the column holder with the chip.
■■■■■■■■
44
850 Professional IC – Anion – MCS
Page 55

■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■
2 Installation
Note
The column input capillary is already threaded into the capillary recesses
of the column thermostat at the time the instrument is first delivered.
The following installation instructions need not be carried out at the
time of initial installation.
Threading capillaries
Introduce column input capillary into the column thermostat via a
1
suitable capillary feed-through (25-1).
Slide the column input capillary from below into the outer of the two
2
capillary recesses (25-2). Slide it through under the holder plate until
it emerges again at the top.
Carefully bend the column input capillary downward and slide from
3
from above to below through the inner capillary recess until it
emerges at the lower edge of the holder plate.
4
Note
The columns (guard column and separation column) may only be
installed after the initial start-up (see Chapter 3.1, page 65).
■ Before initial start-up:
Fasten the 6.2744.040 coupling with a 6.2744.010 pressure
screw to the end of the column input capillary.
■ After initial start-up:
Fasten the guard column (if used) or the separation column with a
6.2744.010 pressure screw to the end of the column input capillary.
850 Professional IC – Anion – MCS
■■■■■■■■
45
Page 56

2.16 Metrohm Suppressor Module (MSM)
2.16 Metrohm Suppressor Module (MSM)
2.16.1 General information on the MSM
The MSM is used for chemical suppression during anion analysis. It is pressure-stable, robust and resistant to solvents. It consists of 3 suppressor
units in total, which are used for suppression, regenerated with sulfuric
acid or rinsed with ultra pure water in rotation.
Suppression reaction in the MSM
When using a carbonate eluent, the following reaction (amongst others)
occur in the MSM:
-H+
R-SO
+ NaHCO3/Na2CO3➙ R-SO
3
2.16.2 Connecting the MSM
Caution
-Na+
+ H2O + CO
3
■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■
2
To protect the MSM against foreign particles or bacterial growth, a
6.2744.180 pump tubing connection with filter (29-3) must be mounted between the peristaltic pump and the input capillaries of the MSM.
The three inputs and outputs of the suppressor units numbered 1..3 on
the MSM each have 2 fixed mounted PTFE capillaries (see Figure 26, page
47).
■■■■■■■■
46
850 Professional IC – Anion – MCS
Page 57

■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■
1
3
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
2
1
2 Installation
Figure 26 MSM – connections
Union nut
1
Eluent input capillary
3
Labeled with Eluent.
Rinsing solution input capillary
5
Labeled with H2O.
Regeneration solution output capillary
7
Labeled with Waste.
MSM connecting piece 6.2832.010
2
Eluent output capillary
4
Labeled with Detector.
Rinsing solution output capillary
6
Labeled with Waste.
Regeneration solution input capillary
8
Labeled with H2SO4.
The PTFE capillaries firmly mounted on the MSM are connected to the
other components of the IC system as follows:
Caution
As the PTFE capillaries are very soft, the pressure screws should not be
overtightened.
Flattened capillaries must be shortened with the help of a 6.2621.080
capillary cutter.
850 Professional IC – Anion – MCS
■■■■■■■■
47
Page 58

2.16 Metrohm Suppressor Module (MSM)
Connecting the capillaries of the MSM
1
2
3
4
5
6
■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■
Connecting the eluent input capillary
■ Fasten the end of the input capillary labeled with Eluent with a
6.2744.070 short PEEK pressure screw to the output of the column.
Connecting the eluent output capillary
■ Fasten the end of the output capillary labeled with Detector with
a 6.2744.090 long PEEK pressure screw to the input of the MCS
(insofar as an MCS is being used).
OR
Connect the end of the output capillary labeled with Detector and
the detector input capillary with a 6.2744.040 coupling and two
6.2744.070 short pressure screws.
Connecting the rinsing solution input capillary
■ Fasten the end of the input capillary labeled with H2O with a
6.2744.070 short PEEK pressure screw to the pump tubing connection of the pump tubing which carries the rinsing solution.
Connecting the rinsing solution output capillary
■ Guide the end of the output capillary labeled with Waste into a
sufficiently large waste container and fasten it there.
Connecting the regeneration solution input capillary
■ Fasten the end of the input capillary labeled with H2SO4 with a
6.2744.070 short PEEK pressure screw to the pump tubing connection of the pump tubing which carries the regeneration solution.
Connecting the regeneration solution output capillary
■ Guide the end of the output capillary labeled with Waste into a
sufficiently large waste container and fasten it there.
■■■■■■■■
48
The rinsing and regeneration solutions are pumped with a peristaltic pump
(see Chapter 2.17, page 49).
850 Professional IC – Anion – MCS
Page 59

■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■
6
4
3
5
7
2.17 Peristaltic pump
2.17.1 Principle of the peristaltic pump
The Peristaltic pump is used for pumping sample and auxiliary solutions. It
can rotate in both directions.
The peristaltic pump pumps liquids according to the principle of displacement. The pump tubing is clamped between the rollers (27-3) and the
tubing cartridge (27-5). During operation, the peristaltic pump drive
rotates the roller hub (27-2), so that the rollers (27-3) push the liquid forward in the pump tubing.
2 Installation
Figure 27
Knurled screw in the mounting pin
1
Rollers
3
Tubing cartridges 6.2755.000
5
Snap-action lever
7
850 Professional IC – Anion – MCS
Peristaltic pump
Roller hub
2
Cartridge holder
4
Contact pressure lever
6
■■■■■■■■
49
Page 60

2.17 Peristaltic pump
6.2744.160
1
6.2744.180
2 3 4 5 6 7 8 1
9 10 3
6 7 8
2.17.2 Installing the peristaltic pump
Figure 28 Installing the pump tubing
■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■
PEEK pressure screws, short
1
(6.2744.070)
Stopper
3
The colors of the stopper indicate the inner
diameter of the pump tubing.
Contact pressure lever
5
Adapter
7
Pump tubing (6.1826.xx0)
9
2
4
6
8
10
Mount the pump tubing as follows:
1
Removing the tubing cartridge
Release the tubing cartridge from the cartridge holder by pressing
the snap-action lever and unhooking from the mounting pins (27-1).
2
Connecting the aspiration side
Place a 6.2744.034 tubing olive (28-2) on the aspiration side of the
pump tubing.
Tubing olive (6.2744.034)
Tubing cartridge (6.2755.000)
Union nut
Tubing olive
Either with filter holder (6.2744.180) or
without filter holder (6.2744.160).
Snap-action lever
■■■■■■■■
50
850 Professional IC – Anion – MCS
Page 61

■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■
1
2
3
3
Connecting the pressure side
Note
Depending on the use of the peristaltic pump, on the pressure side
you can either connect:
■ Case A: a 6.2744.180 pump tubing connection with filter
(see Figure 29, page 51) or
■ Case B: a 6.2744.160 pump tubing connection without filter
(see Figure 30, page 52).
For pumping the auxiliary solutions to the MSM or to the SPM, a
6.2744.180 pump tubing connection with filter must be used.
Case A: 6.2744.180 pump tubing connection with filter:
2 Installation
Union nut
1
Tubing olive with filter holder
3
Figure 29
■ Slide union nut (29-1) onto the pump tubing.
■ Select a suitable adapter (29-2) and slide it onto the pump tubing.
Install pump tubing connection with filter
Adapter
2
The type of adapter depends on the pump tubing (see Table 1,
page 52).
■ Place the tubing olive with filter holder (29-3) onto the pump tub-
ing.
■ Screw the union nut (29-1) onto the tubing olive (29-3).
or
Case B: 6.2744.160 pump tubing connection without filter:
850 Professional IC – Anion – MCS
■■■■■■■■
51
Page 62

2.17 Peristaltic pump
1
2
3
■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■
Figure 30 Install pump tubing connection without filter
1
3
Union nut
Tubing olive
Adapter
2
■ Slide union nut (30-1) onto the pump tubing.
■ Select a suitable adapter (30-2) and slide it onto the pump tubing.
The type of adapter depends on the pump tubing (see Table 1,
page 52).
■ Place the tubing olive (30-3) onto the pump tubing.
■ Screw the union nut (30-1) onto the tubing olive (30-3).
4
Inserting the pump tubing
■ Press the contact pressure lever all the way down.
■ Place the pump tubing in the tubing cartridge. The stoppers
(28-3) must snap into the corresponding holders of the tubing
cartridge.
5
Inserting the tubing cartridge
■ Hang the tubing cartridge in the mounting pin and press in the
cartridge holder until the snap-action lever snaps in.
6
Connecting the capillaries
■ Screw the respective capillaries tightly to the two tubing olives
with PEEK pressure screws (28-1).
■■■■■■■■
52
Table 1 Pump tubings and suitable adapters
Pump tubing Adapter
6.1826.020 (blue/blue)
6.1826.310 (orange/green)
6.1826.320 (orange/yellow)
6.1826.330 (orange/white)
850 Professional IC – Anion – MCS
Page 63

■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■
2 Installation
Pump tubing Adapter
6.1826.340 (black/black)
6.1826.360 (white/white)
6.1826.380 (gray/gray)
6.1826.390 (yellow/yellow)
Set flow rate
The contact pressure of the tubing cartridge must be adjusted in order to
regulate the flow rate. Proceed as follows:
Set the contact pressure
■ Fully loosen the contact pressure lever (28-5), i.e. press it all the
1
way down.
■ Switch on the peristaltic pump.
■ Raise the contact pressure lever one step at a time until liquid
flows.
■ When liquid starts flowing, raise the contact pressure lever by an
additional 2 ratchet increments.
The contact pressure is now set optimally.
The delivery rate depends not only on the correct contact pressure
but also on the interior diameter of the pump tubing and the rotational speed of the drive.
Note
Pump tubings are consumable material. The service life of the pump
tubings depends on the contact pressure amongst other factors.
850 Professional IC – Anion – MCS
■■■■■■■■
53
Page 64

2.18 Metrohm CO2 suppressor (MCS)
1
2
3
4 4
5 5
6
7
2.18 Metrohm CO2 suppressor (MCS)
2.18.1 General information on the MCS
The MCS removes the CO2 from the eluent flow. This reduces the background conductivity, improves the detection sensitivity and minimizes the
injection and carbonate peaks.
The MCS is used for removing CO2 from the eluent flow before detection.
CO2 can reach the eluent flow through the sample itself or arise through
the suppression reaction in the MSM.
The CO2 peak is effectively minimized through connection of the MCS
between the MSM and detector. The principle is based on the gas permeability of the fluoropolymer membrane inside the degassing cell of the
MCS. The eluent is guided through a capillary with a fluoropolymer membrane inside the degassing cell. A vacuum is generated in the degassing
cell via a pump. At the same time, the pump sucks CO2-free air (CO2 is
removed by a CO2 adsorption cartridge (32-4)) through the degassing cell.
The pressure and concentration difference in the degassing cell in comparison to the inside of the capillary now causes the CO2 to diffuse out of the
eluent flow.
■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■
2.18.2 Connecting MCS
The MCS is connected between the MSM (see Chapter 2.16, page 46)
and detector.
Figure 31
MCS input
1
Connection to the MSM.
MCS – connection
MCS output
2
Connection to the detector.
■■■■■■■■
54
850 Professional IC – Anion – MCS
Page 65

■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■
2 Installation
Aspirating capillary
3
For aspirating air low in CO2 (as a result of
CO2 adsorption cartridge (32-4)).
Capillary connection
5
Luer coupling 6.2744.120
7
Mounted on the air aspirating capillary with
pressure screw 6.2744.070.
Connecting the MCS
1
Connecting the MSM
Connect the eluent output capillary (labeled with Detector) using a
6.2744.090 long PEEK pressure screw (31-4) to the MCS inlet (31-1).
2
Connecting the detector
Connect the detector input capillary (33-3) using a long PEEK pressure screw 6.2744.090 (31-4) to the MCS output (31-2).
PEEK pressure screw, long 6.2744.090
4
Pressure screw, short 6.2744.070
6
Mounted on the air aspirating capillary.
Caution
If the MCS is not used, the input and output should be sealed with
6.2744.220 stoppers.
2.18.3 Installing the adsorption cartridges
For effective CO2 removal, the air sucked through the degassing cell
should be as low in CO2 as possible. To achieve this, the air is aspirated
through a 6.2837.000 CO2 adsorption cartridge (32-4).
Moisture can block the CO2 adsorption cartridge. In order to prevent this,
a 6.2837.010 H2O adsorption cartridge (32-7) is connected upstream.
850 Professional IC – Anion – MCS
■■■■■■■■
55
Page 66

2.18 Metrohm CO2 suppressor (MCS)
9
3
8 7
3
1
2 3
3
4
5
6
■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■
Figure 32 Adsorption cartridge holder
PEEK pressure screw, short 6.2744.070
1
Clips
3
For fastening the adsorption cartridges.
Adapter 6.1808.190
5
For connecting the H2O adsorption cartridge
and CO2 adsorption cartridge.
H2O adsorption cartridge 6.2837.010
7
For removing the H2O from the aspirated air.
Filled with bead desiccant.
MCS aspirating capillary
9
Connection to the MCS. Corresponds to
(31-3).
Luer coupling 6.2744.120
2
CO2 adsorption cartridge 6.2837.000
4
For removing the CO2 from the aspirated air.
3-layer filled, blue-brown-gray.
PVC tubing
6
For connecting the H2O adsorption cartridge
and CO2 adsorption cartridge.
Adsorption cartridge holder
8
6.2057.080
Installing the adsorption cartridges
1
Preparing the adsorption cartridge holder
Push the 4 clips (32-3) into the slot of the adsorption cartridge
holder (32-8).
■■■■■■■■
56
850 Professional IC – Anion – MCS
Page 67

■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■
2
Removing the caps
■ Remove the two locking caps at the tip of the two cartridges.
■ In the case of the H
O adsorption cartridge, replace the round
2
sealing cap on the larger end with the star-shaped sealing cap.
3
Connecting the CO2 adsorption cartridge
■ Insert the CO
adsorption cartridge into the coupling (32-2) on
2
the end of the MCS aspirating capillary .
■ Click the CO
adsorption cartridge into the two lower clips (32-3)
2
of the adsorption cartridge holder (32-8).
4
Connecting the PVC tubing
■ Insert the adapter (32-5) into the CO
■ Fasten the PVC tubing (32-6) on the adapter (32-5).
5
Connecting the H2O adsorption cartridge
■ Place the H
■ Click the H
O adsorption cartridge into the PVC tubing (32-6).
2
O adsorption cartridge into the two upper clips (32-3)
2
adsorption cartridge.
2
of the adsorption cartridge holder (32-8).
6
Placing the adsorption cartridge holder in the instrument
■ Place the adsorption cartridge holder with cartridges into the
detector chamber of the instrument.
2 Installation
2.19 Conductivity detector
The conductivity detector continuously measures the conductivity of the
liquid passing through and indicates these signals in digital form (DSP –
Digital Signal Processing). The conductivity detector exhibits outstanding
thermal stability and thus guarantees reproducible measuring conditions.
850 Professional IC – Anion – MCS
■■■■■■■■
57
Page 68

2.19 Conductivity detector
2
1
3
■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■
Figure 33 Conductivity detector front
IC detector 1.850.9010
1
Detector input capillary
3
Permanently installed.
Opening for temperature sensor
2
■■■■■■■■
58
850 Professional IC – Anion – MCS
Page 69

■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■
3
2
2 Installation
Figure 34 Conductivity detector rear
Detector cable
1
With mounted plug.
Type plate
3
With serial number.
Detector output capillary
2
Permanently installed.
Note
In order to prevent unnecessary peak widening after separation, the
connection between the outlet of the separation column and the inlet
in the detector should be kept as short as possible.
Connecting the detector input capillary to the MCS
■ Fasten the detector input capillary (35-1) using a 2.2744.090 long
1
PEEK pressure screw (35-2) on the output of the MCS (35-3).
850 Professional IC – Anion – MCS
■■■■■■■■
59
Page 70

2.20 Connecting the instrument
3 2
1
■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■
Figure 35 Connection detector – MCS
Detector input capillary
1
MCS output
3
Pressure screw, long 6.2744.090
2
2.20 Connecting the instrument
2.20.1 Connecting the instrument to the PC
Note
The instrument must be turned off when connecting the PC.
1
Connecting the USB cable
Connect the PC connection socket of the instrument to a USB connector of the computer via the 6.2151.020 USB cable.
2.20.2 Connecting the instrument to mains supply
Warning
■■■■■■■■
60
The power supply unit must not get wet. Protect it against the direct
effect of liquids.
Mains cable
Which mains cable is supplied depends on the location:
■ 6.2122.020 with plug SEV 12 (Switzerland, …)
■ 6.2122.040 with plug CEE(7), VII (Germany, …)
■ 6.2122.070 with plug NEMA 5-15 (USA, …)
850 Professional IC – Anion – MCS
Page 71

■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■
The mains cable is three-core and provided with a plug with grounding. If
another plug has to be mounted, the yellow/green conductor (IEC standard) must be connected to the protective ground (protection class I).
1
Connecting the mains cable
■ Plug the mains cable into the mains connection socket .
■ Connect the mains cable to the mains supply.
2
Switching the instrument on and off
Switch the instrument on and off with the mains switch .
After switching on, the LED on the front of the instrument flashes
while a system test is carried out and the connection to the software
is established. Once the system test is complete and the connection
to the software has been established, the LED lights up continuously.
2.21 Guard column
The use of guard columns serves for protecting the separation column and
increasing their service life considerably. The guard columns available from
Metrohm represent either actual guard columns or are so-called guard
column cartridges which are used together with a cartridge holder. The
installation of a guard column cartridge in the associated holder is described in the information sheet of the guard columns.
2 Installation
Note
Information regarding which guard column is suitable for your separation column can be found in the Metrohm IC Column Program
(which is available from your Metrohm agent), the information sheet
provided along with your separation column, the product information
on the separation column at http://www.metrohm.com (product area
Ion Chromatography), or obtained directly from your agent.
Caution
New guard columns are filled with solution and are sealed on both
sides with stoppers or caps, respectively. Before using the guard column, you need to ensure that this solution is miscible with the eluents
used (observe manufacturer's data).
850 Professional IC – Anion – MCS
■■■■■■■■
61
Page 72

2.21 Guard column
■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■
Note
The guard column may only be installed after the initial start-up (see
Chapter 3.1, page 65) of the instrument. Until then, use the
6.2744.040 coupling instead of the guard and separation column.
Connecting and rinsing the guard column
1
Connecting the guard column
Caution
When inserting the guard column, always ensure that it is inserted
correctly corresponding to the flow direction (if indicated).
■ Remove locking caps and/or stoppers from the guard column.
■ Fasten the lower end of the guard column with a 6.2744.070
short PEEK pressure screw to the column input capillary .
■ Fasten the connection capillary (3.4224.240) enclosed with the
guard column to the upper end of the guard column with a
6.2744.070 short PEEK pressure screw.
Guard columns are also available which can be screwed with the
upper end directly onto the separation column.
2
Rinsing the guard column
■ Place beaker under the outlet capillary of the guard column.
■ Start the high pressure pump and rinse the guard column approx.
5 minutes with eluent. Set the flow according to the corresponding column information sheet.
■ Switch off the high pressure pump again.
■■■■■■■■
62
850 Professional IC – Anion – MCS
Page 73

■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■
2.22 Separation column
The intelligent separation column (iColumn) is the heart of the ion chromatographic analysis. It separates the different components corresponding to their interactions with the column. Metrohm analytical columns are
equipped with a chip on which their technical specifications and their history (first use / setting up, operating hours, injections, ... ) are saved.
Note
Information regarding which separation column is suitable for your
application can be found in the Metrohm IC Column Program, the
product information for your separation column at http://
www.metrohm.com in the product area ion chromatography, or
obtained directly from your agent.
Caution
2 Installation
New separation columns are filled with solution and are sealed on both
sides with stoppers. Before using the column, you need to ensure that
this solution is miscible with the eluents used (observe manufacturer's
data).
You can find the separation columns and guard columns currently available from Metrohm in the Metrohm IC Column Program, or in the Internet
at http://www.metrohm.com in the product area Ion Chromatography. A
test chromatogram and an information sheet are provided along with
each column. You can request detailed information on special IC applications in the corresponding "Application Bulletins" or "Application
Notes", available in the Internet at http://www.metrohm.com in the
Applications area or via the Metrohm agent responsible free of charge.
Note
The separation column may only be installed after the initial start-up
(see Chapter 3.1, page 65) of the instrument. Until then, use the
6.2744.040 coupling instead of the guard and separation column.
850 Professional IC – Anion – MCS
■■■■■■■■
63
Page 74

2.22 Separation column
■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■
Connecting and rinsing the separation column
1
Connecting the separation column
Caution
When using the columns, always ensure that these are correctly
inserted corresponding to the flow direction indicated.
■ Remove stoppers from the separation column.
■ Connect the lower end of the separation column with a
6.2744.070 short PEEK pressure screw to the outlet capillary of
the guard column (if used), or to the column input capillary .
2
Rinsing the separation column
■ Place beaker under the outlet end of the separation column.
■ Set the flow rate of the high pressure pump to the value suitable
for the separation column selected.
■ Start the high pressure pump and rinse the separation column
approx. 10 minutes with eluent.
■ Switch off the high pressure pump again.
3
Mounting the separation column
■ Hang separation column with chip into the column holder.
Note
The iColumns are equipped with a chip on which their operating data is
saved. The chip has to be hooked into the chip holder provided for this
so that the column recognition can function.
■■■■■■■■
64
850 Professional IC – Anion – MCS
Page 75

■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■
3 Start-up
The chapter Start-up is divided into 2 sections:
Initial start-up The initial start-up is carried out during the ini-
Conditioning Conditioning is carried out as a final installation
3.1 Initial start-up
The initial start-up is carried out during the initial installation. The entire
system is flushed before guard column and separation column are installed.
3 Start-up
tial installation.
step and each time after the system is started.
Caution
The separation column and guard column may not be installed for the
initial start-up.
Make sure that the 6.2744.040 coupling is being used instead of the
columns.
Perform the following steps during the initial start-up:
1
Preparing the software
■ Start the PC program MagIC Net.
■ Open the Equilibration tab in MagIC Net.
■ Select (or create) a suitable method.
2
Preparing the instrument
■ Ensure that the eluent aspiration tubing is immersed in the eluent
and that there is enough eluent in the eluent bottle.
■ Switch on the instrument.
3
Deaerating the high pressure pump
■ Deaerate the high pressure pump(s) via the purge valve (see
Chapter 2.10.2, page 34).
850 Professional IC – Anion – MCS
■■■■■■■■
65
Page 76

3.2 Conditioning
4
Setting the contact pressure of the peristaltic pump
This work step needs to be performed only if a peristaltic pump is
being used.
■ If peristaltic pumps are used, set the contact pressure (see "Set
5
Rinsing the instrument without columns
■ Rinse the instrument (without columns) with eluent for 5 minutes.
The instrument is now prepared for the installation of the columns (see
Chapter 2.21, page 61).
3.2 Conditioning
■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■
Note
flow rate", page 53).
After the installation and after switching on the instrument, the system
must be conditioned with eluent until a stable baseline is reached.
Note
After a change of eluent (see Chapter 4.4.2.3, page 71), the conditioning time can lengthen considerably.
Conditioning the system
1
Preparing the software
Caution
Ensure that the flow set is not higher than the flow permissible for
the corresponding column (see column information sheet and chip
data set).
■ Start the PC program MagIC Net.
■ Open the Equilibration tab in MagIC Net.
■ Select (or create) a suitable method.
■■■■■■■■
66
850 Professional IC – Anion – MCS
Page 77

■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■
2
Preparing the instrument
■ Ensure that the column is correctly mounted in accordance with
the flow direction indicated on the label (arrow must point in the
direction of flow).
■ Ensure that the eluent aspiration tubing is immersed in the eluent
and that there is enough eluent in the eluent bottle.
3
Checking leak-tightness
■ In MagIC Net, start the equilibration.
■ Check all capillaries and their connections from the high pressure
pump to the detector block for signs of liquid escaping. If eluent
escapes anywhere, tighten the corresponding pressure screw or
loosen the connection, check the end of the capillary, shorten it
with a capillary cutter if necessary, and restore the connection.
4
Conditioning the system
Rinse the system with eluent until the required stability of the baseline is attained (normally 30 minutes).
3 Start-up
The instrument is now ready for measuring samples.
850 Professional IC – Anion – MCS
■■■■■■■■
67
Page 78

4.1 General information
4 Operation and maintenance
4.1 General information
4.1.1 Care
Warning
The instrument housing must not be opened by untrained personnel.
The instrument requires appropriate care. Excess contamination of the
instrument may result in functional disruptions and a reduction in the service life of the sturdy mechanics and electronics.
Caution
■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■
Although this is extensively prevented by design measures, the mains
plug should be unplugged immediately if aggressive media has penetrated the inside of the instrument, so as to avoid serious damage to the
instrument electronics. In such cases, the Metrohm Service must be
informed.
On the rear of the instrument, the drainage tubings must be mounted and
the leak sensor must be plugged in and activated as protection against
escaping liquids.
Spillages of chemicals and solvents should be cleaned up immediately. In
particular, the plug connections on the rear panel of the instrument (especially the mains plug) should be protected from contamination.
4.1.2 Maintenance by Metrohm Service
Maintenance of the instrument is best carried out as part of an annual
service, which is performed by specialist personnel of the Metrohm company. If working frequently with caustic and corrosive chemicals, a shorter
maintenance interval is recommended. The Metrohm service department
offers every form of technical advice for maintenance and service of all
Metrohm instruments.
■■■■■■■■
68
850 Professional IC – Anion – MCS
Page 79

■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■
4.1.3 Operation
In order to avoid disturbing temperature influences, the entire system
including the eluent bottle must be protected against direct sunlight.
4.1.4 Shutting down
If the instrument is shut down for a longer period, the entire IC system
(without separation column) must be rinsed salt-free with methanol/ultra
pure water (1:4), in order to prevent eluent salts from forming crystals
which may cause subsequent damage.
Guard column and separation column are excluded from the eluent path
for rinsing. The connection capillaries are directly connected to one
another with a 6.2744.040 coupling. Rinsing is carried out with methanol/
ultra pure water (1:4) until the conductivity drops below 10 µS/cm.
4 Operation and maintenance
Caution
Rinse with eluent for at least 15 minutes at starting up again and before
connecting the guard column and separation column.
4.2 Capillary connections
4.2.1 Operation
All connections between injection valve (see Chapter 2.14, page 40), separation column (see Chapter 2.22, page 63) and detector (see Chapter
2.19, page 57) must be as short as possible, have a low dead volume and
be completely leak-tight. The PEEK capillary after the detector must be
free of blockages (the measuring cell is tested to 5 MPa = 50 bar backpressure). Only use PEEK capillaries with an internal diameter of 0.25 mm
in the high pressure range between the high pressure pump (see Chapter
2.10, page 31) and the detector.
850 Professional IC – Anion – MCS
■■■■■■■■
69
Page 80

4.3 Door
4.3 Door
4.4 Eluent
4.4.1 Production
The chemicals used for the production of eluents should have a degree of
purity of at least "p.a.". Only ultra pure water (resistance > 18.2 MΩ*cm)
may be used for dilution (this generally applies for reagents which are
used in ion chromatography).
■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■
Caution
The door is made of PMMA (polymethylmetacrylate). It must never be
cleaned with abrasive media or solvents.
Caution
Never use the door as a handle.
Newly produced eluents should always be microfiltered (filter 0.45 µm).
Caution
Only microfiltered (filter 0.45 µm) eluents may be used.
The composition of the eluent has a crucial effect on the chromatographic
analysis:
Concentration An increase in the concentration generally leads
to shorter retention times and faster separation,
but also to higher background conductivity.
pH pH changes result in shifts in the dissociation
equilibria and hence changes in the retention
times.
Organic solvents The addition of an organic solvent (e.g. metha-
nol, acetone, acetonitrile) to aqueous eluents
generally accelerates lipophilic ions.
■■■■■■■■
70
850 Professional IC – Anion – MCS
Page 81

■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■
4.4.2 Operation
4.4.2.1 Supply bottle
The supply bottle with the eluent must be connected as indicated in Chapter 2.8.1, Page 26. This is above all important for eluents with volatile sol-
vents (e.g. acetone).
Moreover, condensation must also be prevented in the eluent bottle. Drop
formation can change the concentration ratio in the eluent.
4.4.2.2 Aspiration filter
To protect the IC system against foreign particles, we recommend aspirating the eluents via a 6.2821.090 aspiration filter (12-2). This aspiration filter must be replaced should it show signs of yellow discoloration (but no
later than every 3 months).
In the case of very sensitive measurements, the eluent should be stirred
constantly with a magnetic stirrer.
4 Operation and maintenance
4.4.2.3
Changing the eluent
When changing the eluent, it must be ensured that no precipitates can
occur. Solutions following one another in direct succession must therefore
be miscible. If the system has to be rinsed organically, several solvents
with rising or falling lipophilia must be used.
4.5 High pressure pump
4.5.1 Protection
Caution
The pump head is filled ex works with methanol/ultra pure water. It
must be ensured that the eluent used is freely miscible with the solvent
remaining in the pump head.
To protect the high pressure pump against foreign particles, we recommend that the eluent undergoes a microfiltration (filter 0.45 µm) before
being aspirated via a 6.2821.090 aspiration filter (see "Assembling eluent
aspiration tubing", page 26).
850 Professional IC – Anion – MCS
Salt crystals between the piston and seal cause abrasion particles which
can find their way into the eluent. These lead to contaminated valves, a
rise in pressure and in extreme cases scratched pistons. It is therefore
essential to ensure that no precipitates can occur (see Chapter 4.4.2.3,
page 71).
■■■■■■■■
71
Page 82

4.5 High pressure pump
In order to spare the pump seals, the pump should not be operated dry.
Therefore ensure that the eluent supply is correctly connected and that
there is enough eluent in the eluent bottle each time before turning on
the pump.
4.5.2 Maintenance
Maintenance work on the high pressure pump may not be carried out
unless the instrument is switched off.
Pump head maintenance
An unstable baseline (pulsation, flow fluctuations) is in many cases the
result of contaminated valves (42-2), (42-3) or defective, leaking piston
seals on the high pressure pump. Proceed as follows for cleaning contaminated valves and/or replacing worn parts such as pistons, piston seal and
valves:
■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■
Caution
Caution
This maintenance work should be carried out at least once a year.
Removing the pump head
Turn off high pressure pump and wait until pressure is released.
1
Loosen the pressure screw on the inlet valve holder (17-2) and
2
unscrew the coupling (17-9), the pump head input capillary (17-7)
and the eluent aspiration tubing from the pump head.
Unscrew the pump head output capillary (17-13) from the pump
3
head.
Remove pump head from the pump housing by loosening the 4 fas-
4
tening screws (17-5) using the 6.2621.030 hexagon key. The main
piston is on the left (viewed from the front), and the auxiliary piston
is on the right.
■■■■■■■■
72
850 Professional IC – Anion – MCS
Page 83

■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■
2
1
4 Operation and maintenance
Cleaning/replacing the zirconium oxide piston
Clean one piston after the other as follows:
1
Removing the piston cartridge from the pump head
Loosen the piston cartridge with a wrench and unscrew from the
pump head by hand.
1
Pump head
Figure 36 Removing piston
Piston
2
2
Dismantle the piston
Caution
On the inside of the piston cartridge there is a taut spring than can
jump out of the piston cartridge if suddenly loosing tension.
When opening the piston cartridge, hold pressure towards the
spring and unscrew carefully.
■ Loosen the screw of the piston cartridge with a wrench and
unscrew carefully by hand and by holding pressure towards the
taut spring.
■ Remove the zirconium oxide piston and lay on a tissue.
■ Remove the spring retainer, spring and the inner plastic sleeve
from the piston cartridge and lay by.
850 Professional IC – Anion – MCS
■■■■■■■■
73
Page 84

4.5 High pressure pump
1 2
3
4
5 6
7
8
■ Remove the backup ring from the pump head and lay to the other
parts.
Figure 37 Components of the piston cartridge
■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■
Piston cartridge screw
1
Zirconium oxide piston with piston
3
shaft
Order number: 6.2824.070.
Spring
5
Order number: 6.2824.060.
Piston cartridge
7
3
4
Retaining washer
2
Spring retainer
4
Inner plastic sleeve
6
Protects from metallic abrasion.
Backup ring
8
Cleaning the components of the piston
■ Clean zirconium oxide pistons contaminated by abrasion or
deposits with pure abrasive cleaning powder, rinse particle free
with ultra pure water and dry.
Replace highly contaminated or scratched zirconium oxide pistons
(spare part: 6.2824.070 zirconium oxide piston).
■ Rinse the other parts of the piston and dry with a lint-free cloth.
Assembling the piston
■ Insert the inner plastic sleeve, spring and spring retainer into the
piston cartridge.
■ Slide the zirconium oxide piston carefully into the piston cartridge
until its tip emerges from the small opening of the piston cartridge.
■ Attach screw and tighten by hand.
■■■■■■■■
74
Replacing the piston seal
The 6.2617.010 special tool (see Figure 38, page 75) is necessary in
order to remove the piston seal from the pump head. It consists of two
850 Professional IC – Anion – MCS
Page 85

■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■
2
1
4 Operation and maintenance
parts: a tip for removing the old piston seal and a sleeve for inserting the
new piston seal.
Figure 38 Tool for piston seal 6.2617.010
Pin
1
Pin for removing the old piston seal.
Sleeve
2
Sleeve for inserting the new piston seal.
Caution
Screwing the 6.2617.010 special tool for the piston seal into the piston
seal destroys this completely!
1
Removing the piston seal
Caution
Avoid touching the sealing surface in the pump head (17-4) with
the tool.
Screw the special tool for the piston seal (38-1) with the narrow side
just as far into the piston seal as the same can be removed.
850 Professional IC – Anion – MCS
■■■■■■■■
75
Page 86

4.5 High pressure pump
1
2
1
2
■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■
Figure 39 Removing the piston seal
Piston seal
1
2
Tool for piston seal 6.2617.010
1
Sleeve for inserting the new piston seal.
Tool for piston seal
2
Pin of the tool.
Inserting the new piston seal into the tool
Insert the new piston seal tightly by hand into the recess of the
sleeve of the tool for the piston seal (38-2). The sealing springs must
be visible from the outside.
Figure 40 Insert the piston seal into the tool
Piston seal
2
Order number: 6.2741.020
■■■■■■■■
76
3
Inserting the new piston seal into the pump head
Guide the sleeve of the tool for the piston seal (38-2) with inserted
piston seal into the pump head and press the seal with the wide end
of the tool for the piston seal (38-1) into the pump head recess.
850 Professional IC – Anion – MCS
Page 87

■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■
1
2
4 Operation and maintenance
Figure 41 Inserting the piston seal into the pump head
4
Replacing the piston cartridge
Screw the assembled piston cartridge back into the pump head and
tighten, first by hand, then additionally by approx. 15° with a
wrench.
Cleaning the inlet valve and outlet valve
1
Removing valves
■ Unscrew the connection capillary for the auxiliary piston (17-1)
from the outlet valve holder.
■ Unscrew the holders for the inlet and outlet valves and remove
valves.
850 Professional IC – Anion – MCS
■■■■■■■■
77
Page 88

4.5 High pressure pump
1
2
3
4
■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■
Figure 42 Removing valves
Outlet valve holder
1
Inlet valve
3
Order number: 6.2824.170
Outlet valve
2
Order number: 6.2824.160
Inlet valve holder
4
2
Cleaning undissected valve
Clean contaminated or blocked valves initially without dismantling
them completely.
■ Rinse the valve in eluent flow and counterflow direction using a
spray bottle filled with ultra pure water, RBS solution or acetone.
■ The rinsing effect is further increased through a short treatment
(lasting for a maximum of 20 s) in an ultrasonic bath.
Note
Longer lasting ultrasonic baths can damage the ruby ball of the
valve.
Only if this cleaning is useless, dismantle the valves separately and
clean the components.
3
Dismantling valve
Dismantle every valve separately.
■■■■■■■■
78
Note
For dismantling the valve the 6.2617.020 tool for valve cartridges
is required.
850 Professional IC – Anion – MCS
Page 89

■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■
1
3
4
2
4 Operation and maintenance
■ Place the valve with the seal faced downwards above the recess
in the holder.
■ Push the valve components out of the valve housing using the
needle of the tool.
Figure 43 Dismantling valve
Needle
1
For pushing the valve components out of
the valve housing.
Holder
3
The components of the valve are collected in the recess of the
holder.
The components of the valve are very small. In order not to lose
them, put the components into a dish.
■ The inlet valve and the outlet valve consist of the same, just differ-
Valve
2
Recess
4
For collecting the valve components.
Note
ently arranged components (see Figure 44, page 80).
850 Professional IC – Anion – MCS
■■■■■■■■
79
Page 90

4.5 High pressure pump
1
2
3
5
6
7
8
9
10
9
8
7
10
5
4
6
■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■
Figure 44 Components of the inlet valve and outlet valve
Inlet valve 6.2824.170
1
Inlet valve housing
3
Sealing ring (black)
5
Sapphire sleeve
7
The shiny side must point to ruby ball.
Ceramic holder for ruby ball
9
4
Clean the components of the valve
Outlet valve 6.2824.160
2
Outlet valve housing
4
Sleeve
6
Ruby ball
8
Seal
10
The larger opening must point outwards.
Rinse the valve components with ultra pure water and/or acetone
and dry with a lint-free cloth.
5
Reassemble the valve
Reassemble valve components according to figure 44, page 80.
■ Insert the seal with the larger opening faced downwards into the
recess of the tool.
■ Lay the other valve components above another in the correct
sequence (see Figure 44, page 80).
■■■■■■■■
80
850 Professional IC – Anion – MCS
Page 91

■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■
4 Operation and maintenance
■ Place the valve housing over the stacked components and hold it
tightly.
■ By tilting the tool, the valve components slide into the valve hous-
ing.
■ Press the seal by hand well on the valve housing.
6
Checking the flow direction
Rinse the valve in the direction of the arrow on the valve housing and
check wether liquid is escaping on the other end.
If this is not the case, the valve has to be dismantled again and be
assembled correctly (see Figure 44, page 80).
7
Inserting the valves back into the pump head
Caution
If by mistake, the inlet valve is mounted instead of the outlet valve,
an extreme pressure builds up within the working cylinder, which
can destroy the piston seal!
When inserting the valves, please take into account that the liquid
is being pumped through the pump head from bottom to top.
■ Insert the inlet valve into the inlet valve holder the way the seal is
visible.
■ Screw the inlet valve holder into the bottom of the pump head
and tighten with a wrench (42-4).
■ Insert the outlet valve into the outlet valve holder the way the seal
is visible.
■ Screw the outlet valve holder into the top of the pump head and
tighten with a wrench (42-1).
850 Professional IC – Anion – MCS
■■■■■■■■
81
Page 92

4.6 Inline filter
1 2 3
4
1
5
5
■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■
Mounting the pump head
Note
To prevent the pump head from being positioned the wrong way, it is
provided with different bore hole depths for the fastening bolts, i. e. a
fastening bolt is longer than all others. The bore hole with the greatest
depth must therefore be assigned to the longest bolt. If this is not the
case, the pump will not function perfectly.
1
Mount the pump head on the pump again using the four fastening
screws (17-5). Firmly tighten the screws with the 6.2621.030 hexagon key.
Screw connection capillaries (17-1), (17-7) and (17-13) onto the
2
pump head again.
4.6 Inline filter
4.6.1 Maintenance
The 6.2821.120 inline filters comprise the filter housing (45-2), the filter
screw (45-4) and the flter (45-3). New filters (45-3) are available under
the order number 6.2821.130 (10 items).
The 6.2821.130 filters (20-3) should be changed every 3 months (more
frequently at higher backpressure).
Figure 45
1
3
Changing the filter
PEEK pressure screws, short
6.2744.070
6.2821.130 filter
Packaging contains 10 items.
Filter housing
2
Housing of the inline filter. Part of the
6.2821.120 accessories.
Filter screw
4
Screw of the inline filter. Part of the
6.2821.120 accessories.
■■■■■■■■
82
Connection capillaries
5
850 Professional IC – Anion – MCS
Page 93

■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■
4 Operation and maintenance
Changing the filter
The flow must be stopped before changing the filter.
1
Removing the inline filter
■ Unscrew the pressure screws (45-1) from the inline filter.
2
Unscrewing the filter screw
■ Screw the filter screw (45-4) out of the filter housing (45-2) with
the aid of two 6.2621.000 adjustable wrenches.
3
Inserting the filter
■ Remove the old filter (45-3) with tweezers.
■ Place the new filter (45-3) flat in the filter housing with tweezers
(45-2).
4
Mounting filter screw
■ Screw the filter screw (45-4) back into the filter housing (45-2)
and tighten by hand. Then additionally tighten slightly with two
6.2621.000 adjustable wrenches.
5
Remounting the inline filter
■ Screw the pressure screws (45-1) back onto the inline filter.
6
Rinsing the inline filter
■ Dismantle the guard column (if present) and the separation col-
umn and replace with a 6.2744.040 coupling.
■ Rinse the instrument with eluent.
850 Professional IC – Anion – MCS
■■■■■■■■
83
Page 94

4.7 Inline sample preparation
4.7 Inline sample preparation
To protect the separation column (see Chapter 2.22, Page 63) against foreign particles which can affect the separating efficiency, we recommend
that all samples undergo a microfiltration (filter 0.45 µm). The ultrafiltration cell can be used for filtration (see documentation on the IC Equip-
ment for Ultrafiltration).
Samples containing significant amounts of gas should be degassed. The
sample degasser (see Chapter 2.13, Page 39) (if available) is used for
degassing.
Matrix-loaded samples (e.g. blood, oil) should be prepared for the measurement by means of dialysis (see documentation on the IC Equipment for
Dialysis).
If the concentration of the sample is too high, it should be diluted before
feeding (see documentation on the IC Equipment for Sample Dilution).
For the sample preparation methods Neutralization (replacement of e.g.
Na+ with H+) and cation exchange (replacement of e.g. heavy metals
with H+), a sample preparation module (SPM) is used.
■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■
4.8 Rinsing the sample path
Before a new sample can be measured, the sample path must be rinsed
with it so that the measuring result is not falsified by the previous sample
(Sample carry-over).
In the case of automated sample feeding, the rinsing time should be at
least 3 times the transfer time. The transfer time is the time required by
the sample to flow from the sample vessel to the end of the sample loop.
Ascertaining the transfer time
The transfer time depends on the pump capacity of the peristaltic pump,
the total capillary volume and the volume of the gas removed by the sample degasser (if used) - in other words the amount of gas in the sample.
1
Emptying the sample path
Pump air through the sample path (pump tubing, tubing connections, capillary in the degasser, sample loop) for several minutes until
all liquid is displaced by the air.
■■■■■■■■
84
850 Professional IC – Anion – MCS
Page 95

■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■
4 Operation and maintenance
2
Aspirating the sample and measuring time
Aspirate a sample typical for the later application and use a stop
watch to measure the time required by the sample to travel from the
sample vessel to the end of the sample loop.
The time measured corresponds to the "transfer time". The rinsing
time should be at least 3 times the transfer time.
Checking the rinsing time
It is possible to determine whether the rinsing time is adequate via a direct
measurement of the sample carry-over. Proceed as follows:
1
Preparing two samples
■ Sample A: A typical sample for the application.
■ Sample B: Ultra pure water.
2
Determining "Sample A"
Let "Sample A" pass through the sample path for the duration of the
rinsing time, then inject and measure.
3
Determining "Sample B"
Let "Sample B" pass through the sample path for the duration of the
rinsing time, then inject and measure.
4
Calculating sample carry-over
The degree of the sample carry-over corresponds to the ratio of the
peak areas of the measurement for sample B to the measurement for
sample A. The lower the ratio, the lower the sample carry-over. This
ratio can be altered by varying the rinsing time – thus allowing the
rinsing time required for the application to be ascertained.
850 Professional IC – Anion – MCS
■■■■■■■■
85
Page 96

4.9 Sample degasser
4.9 Sample degasser
4.9.1 Operation
If you are working with sample degassing, the longer "transfer time" (see
Ascertaining the transfer time, page 84) means that it is also necessary to
rinse for longer (with the subsequent sample). The rinsing time should be
at least 3 times the "transfer time" so as to minimize the carry-over
effects. The "transfer time" itself depends on the pump capacity, total
capillary volume and volume of gas removed (i.e. the amount of gas in the
sample).
Note
When using the sample degasser, the rinsing time extends by at least 2
minutes.
■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■
4.10 Injection valve
4.10.1 Protection
To prevent contamination of the injection valve, a 6.2821.120 inline filter
(see Chapter 2.11, page 36) should be mounted between the high pressure pump and the pulsation damper.
4.11 Metrohm Suppressor Module (MSM)
4.11.1 Protection
To protect the MSM against foreign particles or bacterial growth, a pump
tubing connection with filter must be mounted between the peristaltic
pump (see Chapter 2.17, page 49) and the input capillaries of the MSM
(see Figure 29, page 51).
4.11.2 Operation
Note
The suppressor units must never be regenerated in the same flow direction in which the eluent is pumped. Therefore always mount the input
and output capillaries according to diagram outlined in Figure 26, Page
47.
■■■■■■■■
86
The MSM consists of 3 suppressor units, which are used for suppression,
regenerated with sulfuric acid or rinsed with ultra pure water in rotation.
850 Professional IC – Anion – MCS
Page 97

■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■
In order to record every new chromatogram under comparable conditions, you should normally work with a freshly regenerated suppressor.
The MSM must never be switched over in a dry state, as there is a risk
of jamming. If the MSM is in a dry state, the MSM must be rinsed for at
least 5 minutes before it may be switched over.
In the case of reduced capacity or high backpressure, the MSM must be
regenerated (see Chapter 4.11.3.1, page 87), cleaned (see Chapter
4.11.3.2, page 88) or replaced (see Chapter 4.11.3.3, page 91).
4.11.3 Maintenance
4 Operation and maintenance
Caution
Caution
4.11.3.1
Regenerating the MSM
If the suppressor units are loaded for a longer period with certain heavy
metals (e.g. iron) or organic impurities, these can no longer be completely
removed with the regeneration solution (50 mmol/L H2SO4) normally used.
The capacity of the suppressor units is consequently affected, which can
result in reduced phosphate sensitivity in less serious cases and a significant rise in the baseline in more serious cases. If such capacity problems
occur at one or more positions, the suppressor units must be regenerated:
Regenerating the MSM
Regenerate the MSM as follows:
1
Disconnecting the MSM from the IC system
■ Disconnect the MSM from the separation column and detector.
2
Regenerating the MSM
Caution
850 Professional IC – Anion – MCS
The pump tubing made of PVC must not be used for rinsing with
solutions containing organic solvents. In this case, other pump
tubing must be used for rinsing.
■■■■■■■■
87
Page 98

4.11 Metrohm Suppressor Module (MSM)
3
■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■
Note
The high pressure pump can be used for regeneration. For this,
remove the guard column and separation column and connect the
capillary directly to the MSM (regenerate in opposite direction).
■ Rinse the 3 suppressor units with the following solutions for
about 15 minutes each:
– Contamination with heavy metals:
1 mol/L H2SO4 + 0.1 mol/L oxalic acid
– Contamination with organic cationic complexing
agents:
0.1 mol/L H2SO4 / 0.1 mol/L oxalic acid / acetone 5%
– Severe contamination with organic substances:
0.2 mol/L H2SO4 / acetone≥ 20%
Connecting the MSM to the IC system
■ Reconnect the MSM to the IC system. If the capacity problems
remain, MSM rotor A must be replaced (see Chapter 4.11.3.3,
page 91).
4.11.3.2 Cleaning the MSM
It may be necessary to clean the MSM in the following cases:
■ Increased backpressure onto the output capillaries of the MSM.
■ Blockage of the MSM which cannot be eliminated (solutions can no
longer be pumped through the MSM).
■ Jamming of the MSM which cannot be eliminated (MSM can no longer
be switched over).
■■■■■■■■
88
850 Professional IC – Anion – MCS
Page 99

■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■
1
2
3 4
5
Figure 46 MSM – Components
4 Operation and maintenance
Union nut
1
MSM rotor A 6.2832.000
3
Slot in the MSM housing
5
MSM connecting piece 6.2832.010
2
MSM housing
4
Cleaning the MSM
Clean the MSM as follows:
1
Disconnecting the MSM from the IC system
■ Switch off the instrument.
■ Disconnect the MSM from the separation column, peristaltic
pump and detector.
2
Dismantling the MSM
■ Unscrew union nut (46-1) from the MSM housing (46-4).
■ Pull MSM connecting piece (46-2) and MSM rotor A (46-3) out of
the MSM housing (46-4). The MSM connecting piece and MSM
rotor A normally stick to one another - if this is not the case: Take
a sharp object, insert into the slot (46-5) in the MSM housing,
and pull out MSM rotor A (46-3) in this way.
■ Detach the MSM connecting piece (46-2) from MSM rotor A
(46-3).
3
Cleaning the supply and discharge lines
■ Connect in turn each of the 6 capillary tubings fastened on the
MSM connecting piece (46-2) on the high pressure pump (see
Chapter 2.10, page 31) and pump through ultra pure water.
850 Professional IC – Anion – MCS
■■■■■■■■
89
Page 100

4.11 Metrohm Suppressor Module (MSM)
4
5
6
7
8
■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■
■ Check whether solution emerges at the MSM connecting piece
(46-2). If one of the supply or discharge lines remained blocked,
the SPM connecting piece (46-2) must be replaced (order number
6.2832.010).
Cleaning the MSM rotor A
■ Clean sealing surface of the MSM rotor A (46-3) with ethanol
using a lint-free cloth.
Inserting the MSM rotor A
Caution
An incorrectly inserted MSM rotor A (46-3) can be destroyed
during start-up.
■ Insert the MSM rotor A (46-3) into the MSM housing (46-4) in
such a way that the tubing connections on the rear of MSM rotor
A fit into the corresponding recesses inside the MSM housing and
one of the three holes of the MSM rotor A is visible from below in
the slot of the MSM housing (46-5).
■ If the MSM rotor A (46-3) is correctly inserted, its sealing area will
be approx. 4 mm within the MSM housing (46-4). If this is not the
case, MSM rotor A must be moved into the right position from
below using a sharp object (e.g. screwdriver).
Cleaning the MSM connecting piece
■ Clean sealing surface of the MSM connecting piece (46-2) with
ethanol using a lint-free cloth.
Inserting the MSM connecting piece
■ Insert the MSM conencting piece (46-2) into the MSM housing
(46-4) in such a way that the connector 1 is on top and the three
pins of the MSM connecting piece fit into the corresponding
recesses on the MSM housing (46-4).
Connecting and conditioning the MSM
■ Reconnect the MSM to the IC system.
■ Before switching the MSM over for the first time, rinse the three
suppressor units with solution for 5 minutes.
■■■■■■■■
90
850 Professional IC – Anion – MCS
 Loading...
Loading...