Page 1

Desktop PC
User Guide
Page 2

Page 3

Contents
Chapter 1: Getting Help . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1
Thank you for purchasing our computer! . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2
Using the eMachines Web site . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2
Using Help and Support . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2
Contacting eMachines . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3
Getting help for Windows Media Center . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3
Using online help . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3
Chapter 2: Using Windows . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
Using the Windows desktop . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
Using the Start menu . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
Adding icons to the desktop . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
Identifying window items . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
Working with files and folders . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .10
Viewing drives . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
Creating folders . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
Copying and moving files and folders . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .11
Deleting files and folders . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
Searching for files . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .13
Using the Windows Search . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
Browsing for files and folders . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
Working with documents . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
Creating a new document . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
Saving a document . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
Opening a document . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
Printing a document . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
Shortcuts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
Chapter 3: Using the Internet and Faxing. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
Learning about the Internet . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .20
Setting up an Internet account . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .20
Accessing your Internet account . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
Using the World Wide Web . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .21
Connecting to a Web site . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .21
Downloading files . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .22
Using e-mail . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .22
Sending e-mail . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .22
Checking your e-mail . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .23
Using Windows Fax and Scan . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
Sending a fax . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
Setting up your cover page template . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .26
Faxing a scanned document or from programs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .27
Canceling a fax . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27
Receiving and viewing a fax . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28
Chapter 4: Playing and Creating Media Files . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
Playing music and movies . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .30
i
Page 4

Contents
Playing audio and video files . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .30
Playing optical discs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .31
Creating audio files and music li braries . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .33
Creating music files . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .33
Building a music library . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .35
Editing track information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .35
Creating music CDs and video DVDs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .36
Creating a music CD . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .36
Creating a video DVD . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .37
Creating and copying data discs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .39
Creating a data disc . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .39
Using Windows Media Center . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .40
Starting Windows Media Center . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .40
Using the Media Center remote control . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .42
Chapter 5: Networking Your Computer . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .43
Introduction to Networking . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .44
Networking terms you should know . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .44
Ethernet networking . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .44
Wired Ethernet networking . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .44
Wireless Ethernet networking . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .47
Establishing your Ethernet network connection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .49
Testing your network . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .52
Adding a printer to your network . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .52
Sharing resources . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .52
Using the network . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .54
Bluetooth networking . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .55
Chapter 6: Protecting your computer. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .57
Hardware security . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .58
Kensington lock slot . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .58
Data security . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .58
Startup and hard drive password . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .58
Windows user accounts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .58
Protecting your computer from viruses . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .59
Using Norton Internet Security . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .59
Using Windows Security Center . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .61
Security updates . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .62
Windows Update . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .62
BigFix . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .63
Chapter 7: Customizing W indows . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .65
Changing screen settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .66
Changing color depth and screen resolution . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .66
Changing the appearance of windows and backgrounds . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .67
Selecting a screen saver . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .68
Changing gadgets . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .69
ii
Page 5

www.emachines.com
Setting up multiple monitors . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 71
Changing system sounds . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .72
Changing mouse settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 73
Adding and modifying user accounts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 73
Changing power-saving settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 75
Changing the power plan . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .75
Changing accessibility settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .77
Using the Ease of Access Center . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 77
Using voice recognition . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .78
Setting up parental controls . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 78
Filtering Internet access . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .79
Scheduling computer and Internet use . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 80
Restricting game access . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 80
Restricting specific programs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 82
Creating activity reports . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 82
Notices . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .83
iii
Page 6

Contents
iv
Page 7

• Using t he eMac hines W eb sit e
• Using Help and Support
• Using online help
Chapt er 1
Getting Help
1
Page 8
Chapter 1: Ge tting Help
Thank y ou f or purc hasing our computer!
You have made an excellent decision choosing eMachines. We are sure that you will be pleased
with the outstanding quality, reliability, and performance of your new computer. Each and every
eMachines computer uses the latest technology and passes through the most stringent quality
control tests t o ensure that you are pro vided with the best pr oduct possible . Please read this manual
carefully to familiarize yourself with your computer’s software features.
eMachines stands behind our value propo sition to our customers—to prov ide be st-of - c l a ss service
and support in addition to high-quality, brand-name components at affordable prices. If you ever
have a problem, our knowledgeable , dedicated cust omer service department will prov ide you wit h
fast, considerate service.
We sincerely hope that you will receive the utmost satisfaction and enjoyment from your new
eMachines computer for years to come.
Thanks again, from all of us at eMachines.
Using t he eMachines W eb site
eMachines’ online support is av ailable 2 4hours a day, 7days a week and pr ovide s the most c urrent
drivers, product specifications, tutorials, and personalized information about your computer. Visit
the eMachines Web support site at www.emachines.com/.
Using Help and Suppor t
Your computer includes Help and Support, an easily accessible collection of help information,
troubleshooters, and automated support. Use Help and Support to answer questions about
Windows and t o help y ou quick l y disco v er and u s e t he man y features of y our eMac hine s computer.
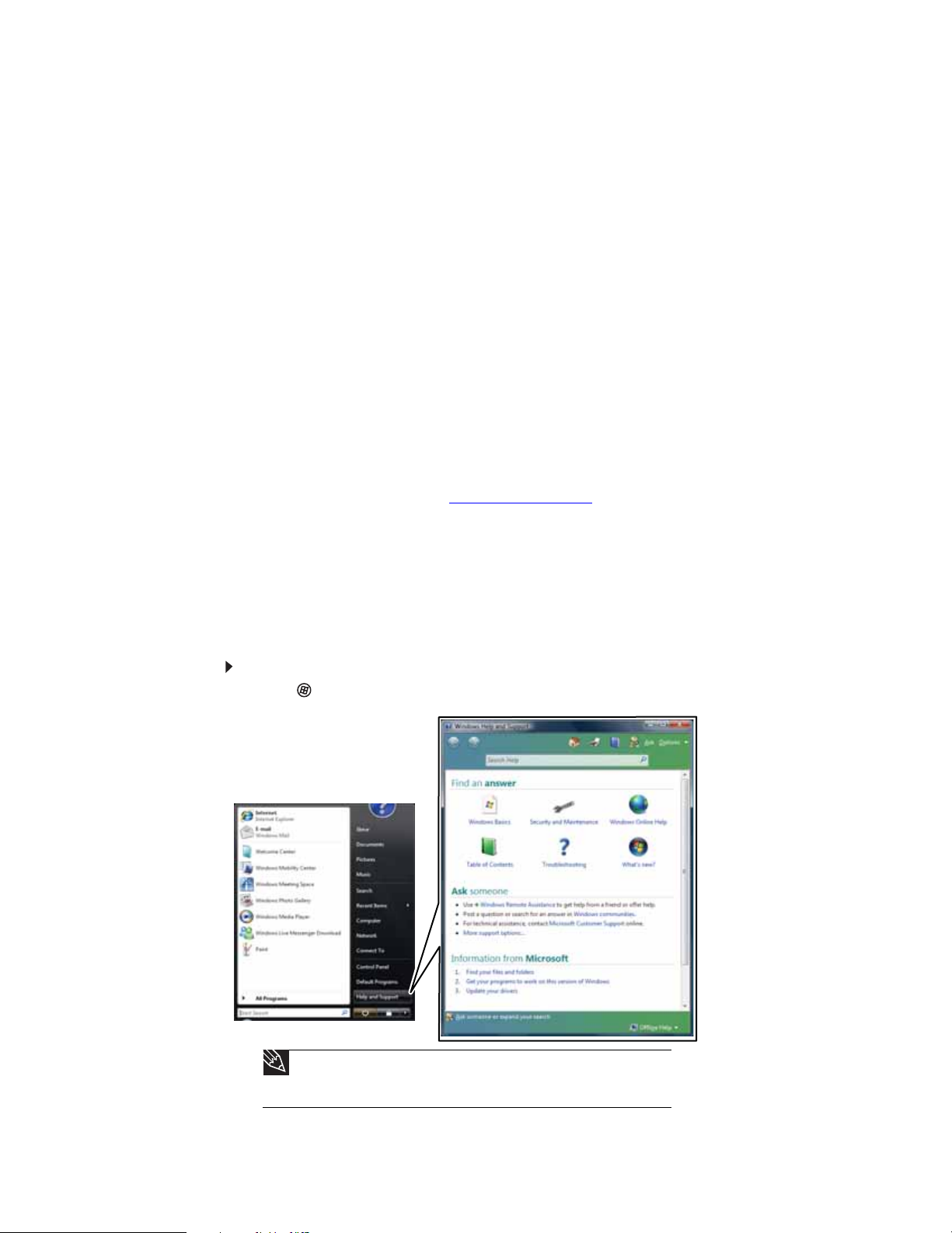
To start Help and Support:
1 Click (Start), then click Help and Support. Help and Support opens.
2
Tip
You can find help information by clicking a general topic under Find an
answer, selecting an option under Ask someone, or picking a category from
Inform atio n from Mic ros oft. You can also search for a topic.
Page 9

www.emachines.com
2 Type a word or phrase in the Search Help box located at the top of any Help and Support
screen, then p ress E
For each search, you receive a list of suggested topics. To find the answer, click the result
that most closely matches your question. Additional results may be available if the first list
does not address your question.
NTER.
Contac ting eMachine s
The label on your computer contains information that identifies your computer model and serial number.
eMachines Customer Care will need this information if you call for help.
Get ting help fo r Window s Media Cent er
If your computer is running Windows Media Center, you can access help for information on how
to use i t.
To access Media Center help:
1 Click (Start), then click Help and Support. Help and Support opens.
2 In the Help and Support window, type Windo w s Medi a Ce nte r in the Sea rch Help box,
then press E
NTER. The Media Center Help window ope ns.
-ORIf you are connected to the Internet, click Windows Online Help, then type Windows
Media Center in the Search Help For box.
Using online help
If you are connected to the Internet, many programs provide information online so you can
research a topic or learn how to perform a task while you are using the program. You can access
most online help inf or mation by selec ting a t op ic f r om a Help menu or by clicking the Help button
on the menu bar and selecting Online Support from the l ist .
Available information depends on the particular Help site to which you are taken. Many provide
FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions), a search feature, articles about their software, tutorials, and
forums where problems and issues are discussed.
3
Page 10

Chapter 1: Ge tting Help
4
Page 11

• Using the W indow s desktop
• Working with file s and f olders
• Searching f or files
• Working wit h documents
• Shortcuts
Chapt er 2
Using W indows
5
Page 12
Chapter 2: Using Windows
Using t he Window s deskt op
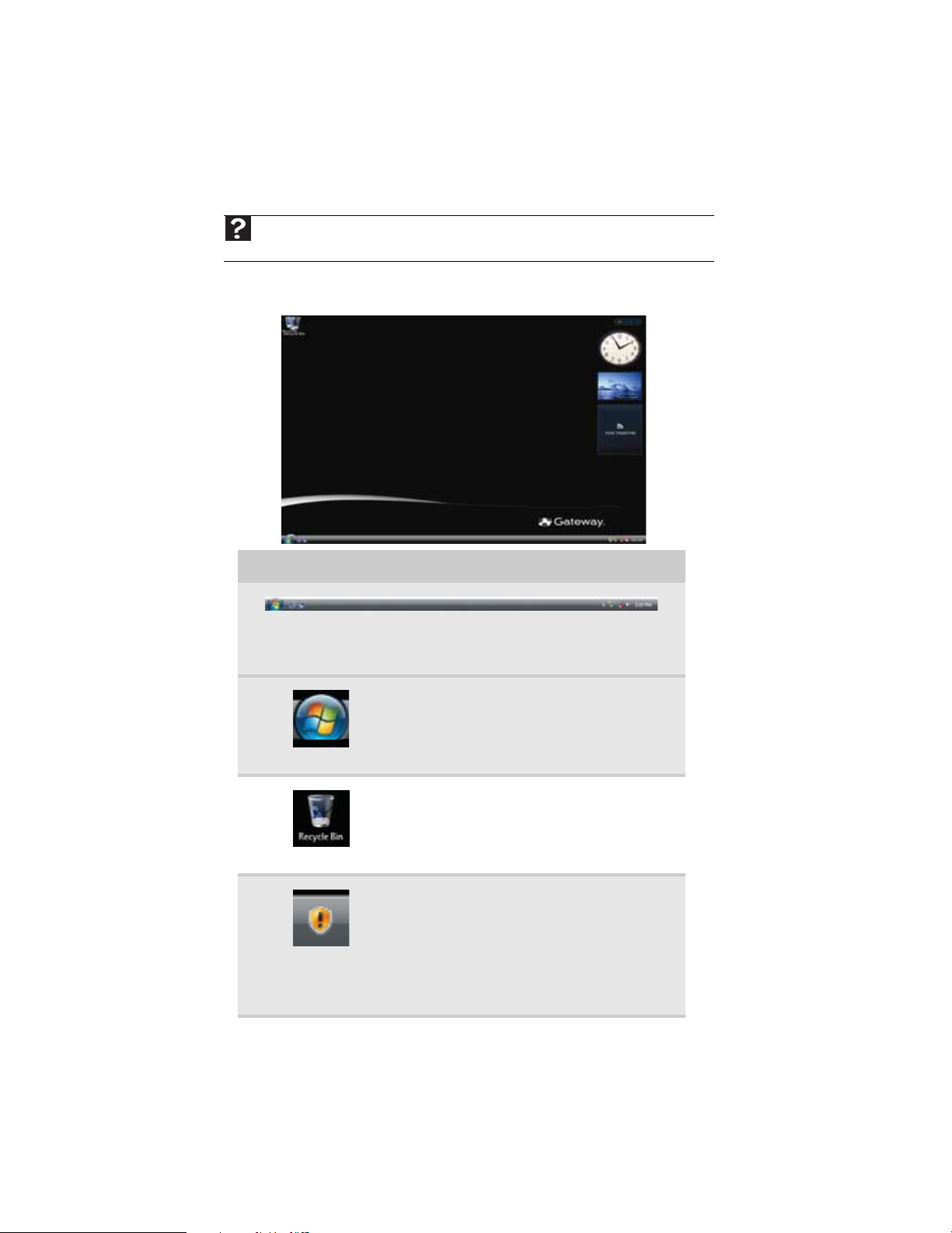
After your computer starts, the first screen you see is the Windows desktop. The desktop is like
the top of a real desk. Think of the desktop as your personalized work space where you open
.
programs and perform other tasks.
Help
For more information about the Windows desktop, click Start, then click Help and Support.
Type Wi ndo ws d esk top in the Search Help box, then press E
Your desktop may be different from this example, depending on how your computer is set up.
The desktop contains the taskbar, the Start button, and the Recycle Bin icon.
NTER.
Desktop elements Description
The taskbar is the bar at the bottom of the computer display containing the
Start button on the left and a clock on the right. Other buttons on the taskbar
represent programs that are running.
Click a program’s button on the taskbar to open the program’s window.
The Start button pro vides acces s to program s,
files, help for Windows and other programs,
and computer tools and utilities.
Click the Start button, then open a file or
program by clicking a n item on the me nu t h at
opens.
The Re cycl e B in is where files, folders, and
programs that you discarded are stored. You
must empty the Recycle Bin to permanently
delete them from your computer. For
instructions on how to use the Recycle Bin, see
“Deleting files and folders” on page12.
The Windo ws Sec urity C ente r icon may appe ar
on the taskbar near the clock. The icon
changes appea rance to not ify you when the
security settings on your computer are set
below the recommended value or when
updates are a vailable. Double-clic k this icon t o
open the Wi ndows Se curity Ce nter. For more
informatio n, see “Modifying security settings”
on page 61.
6
Page 13

Using the Start menu
Help
For more information about the Windows Start menu, click Start, then click Help and
Support. Type Windows Start menu in the Search Help box, then press E
You can start programs, open files, customize your system, get help, search for files and folders,
and more using the Start menu.
To u s e t he S t a rt m e nu :
Shortcut
Start➧All Programs➧
1 Click (Start) on the lower left of the Windows desktop. The Start menu opens, showing
you the first level of menu items.
www.emachines.com
NTER.
2 Click All Programs to see all programs, files, and folders in the Start menu. If you click an
item with a folder icon, the prog rams, files , and subfolders appear.
3 Click a file or program to open it.
7
Page 14
Adding icons to the de sktop
Help
For more information about the desktop icons, c lic k Start, then clic k H el p and Su ppor t. Type
desktop icons in the Search Help box, then press E
You may want to add an icon (shortcut) to the desktop for a program that you use frequently.
To add ic ons to the des ktop:
Shortcut
Start➧AllPrograms➧ right-clickprogram➧SendTo➧ Desktop (create shortcut)
1 Click (Start), then click All Programs.
2 Right-click (press the right mouse button) the program that you want to add to the desktop.
3 Click Send To, then click Desktop (create shortcut). A shortcut icon for that program
appears on the desktop.
Identifying windo w it ems
Help
For more information about windows, click Start, then click Help and Support. Type
window in the Search Help box, then press E
Chapter 2: Using Windows
NTER.
NTER.
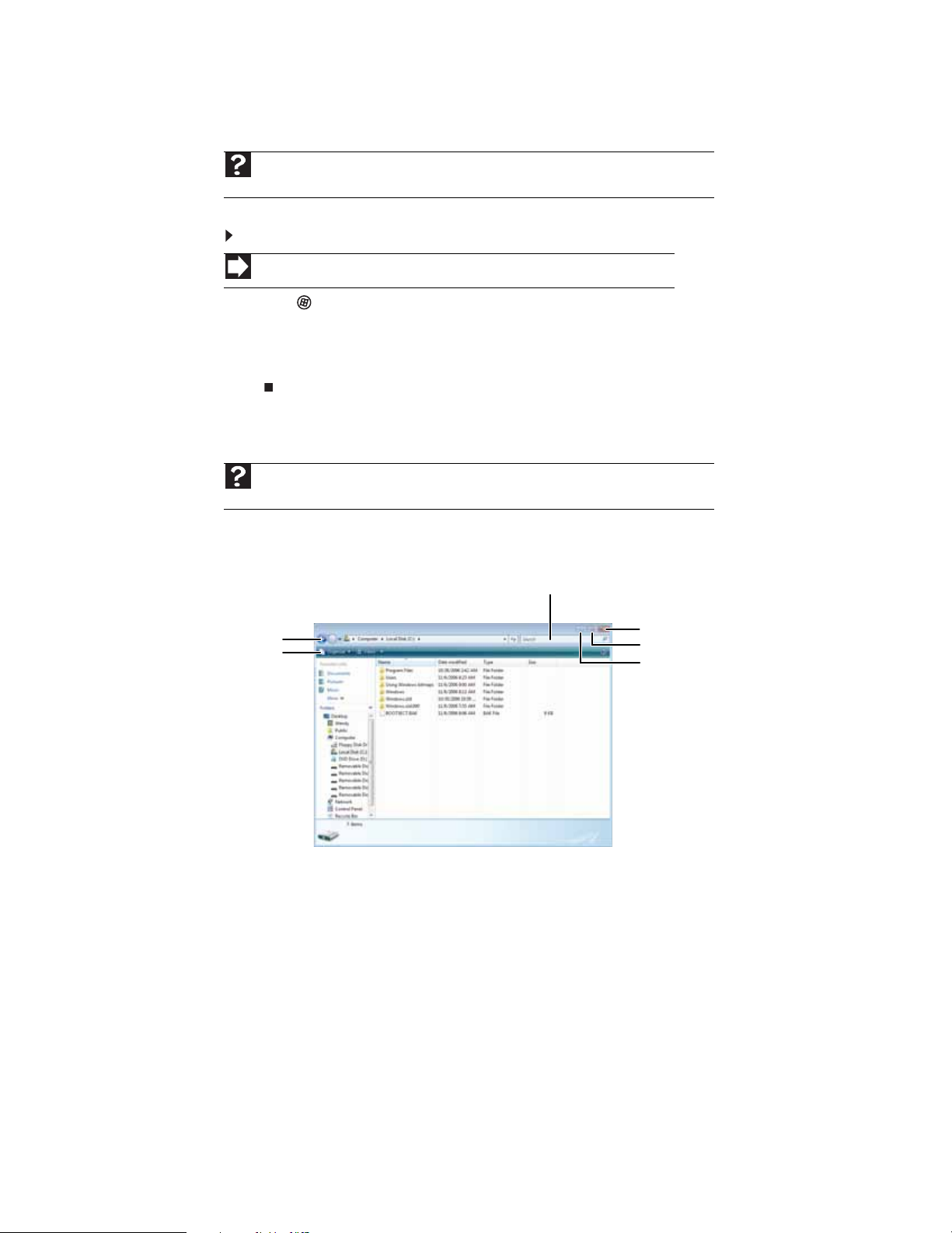
When you double-click the icon for a drive, folder , file , or program, a window opens on the desktop.
This example shows the LocalDisk (C:) window, which opens after you double-click the
Local Disk (C:)
Title bar
Menu bar
icon in the Computer win dow.
Search box
Close
Maximize
Minimize
8
Page 15
www.emachines.com
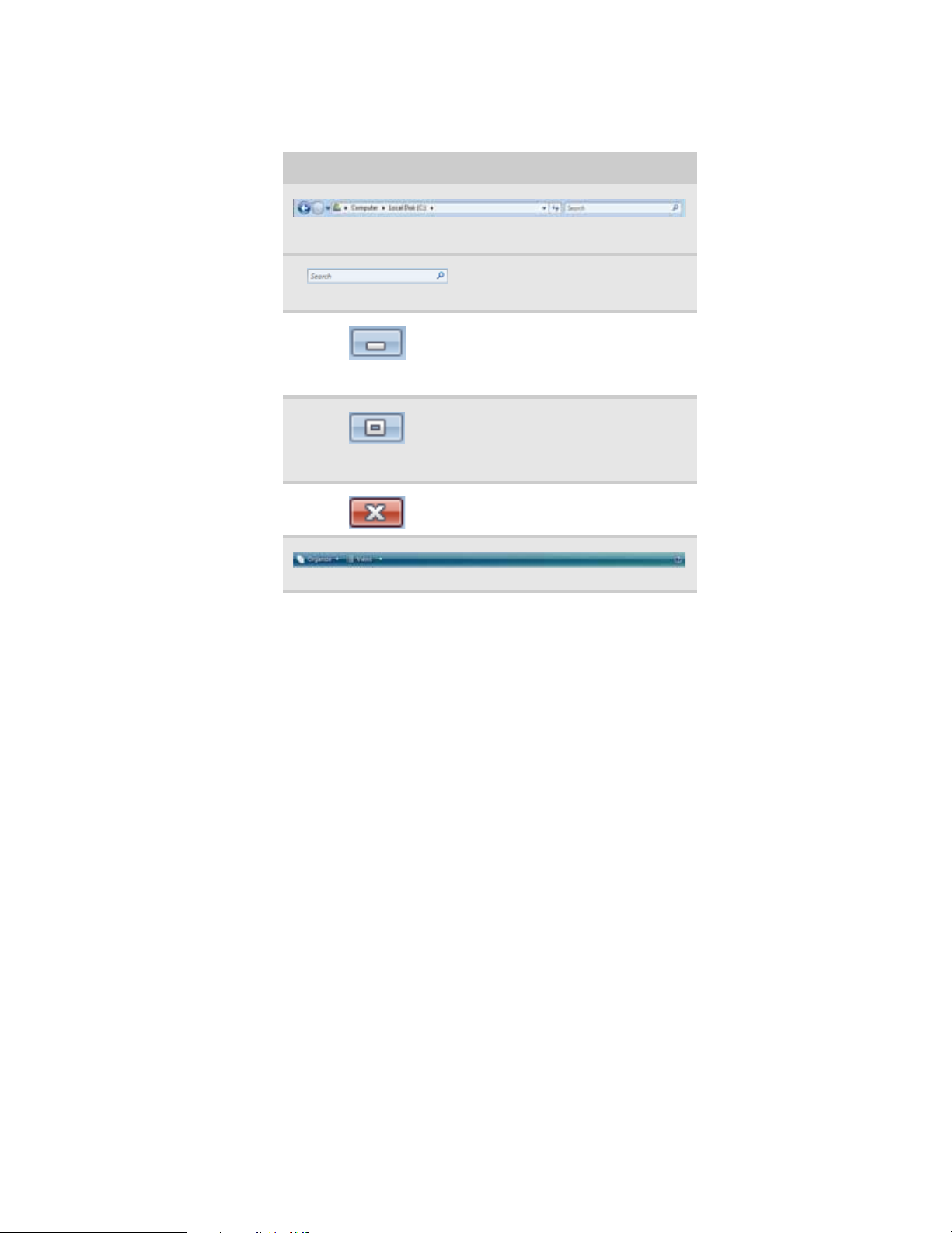
Every progr am window looks a little dif fer ent because eac h has its ow n menus, icons, and controls.
Most windows include these items:
Window item Description
The title ba r is the horizontal bar at the top of a window that shows
the window title.
The Search box lets you search for
a word or phrase in the current
window.
Clicking t he minimize bu tton r educes
the active window to a button on the
taskbar. C licking the program button
in the taskbar opens the window
again.
Clicking the maximize button
expands the ac tiv e windo w to fit t he
entire computer display. Clicking the
maximize button again restores the
window to its former size.
Clicking the close butto n closes th e
active window or program.
Clicking an item on the menu bar starts an action such as Print or Save .
9
Page 16
Chapter 2: Using Windows
Wo rking with fi les and f olders
You can organize your files and programs to suit your preferences much like you would store
information in a file cabinet. You can store these files in folders and copy, move, and delete the
information just as you would reorganize and throw away information in a file cabinet.
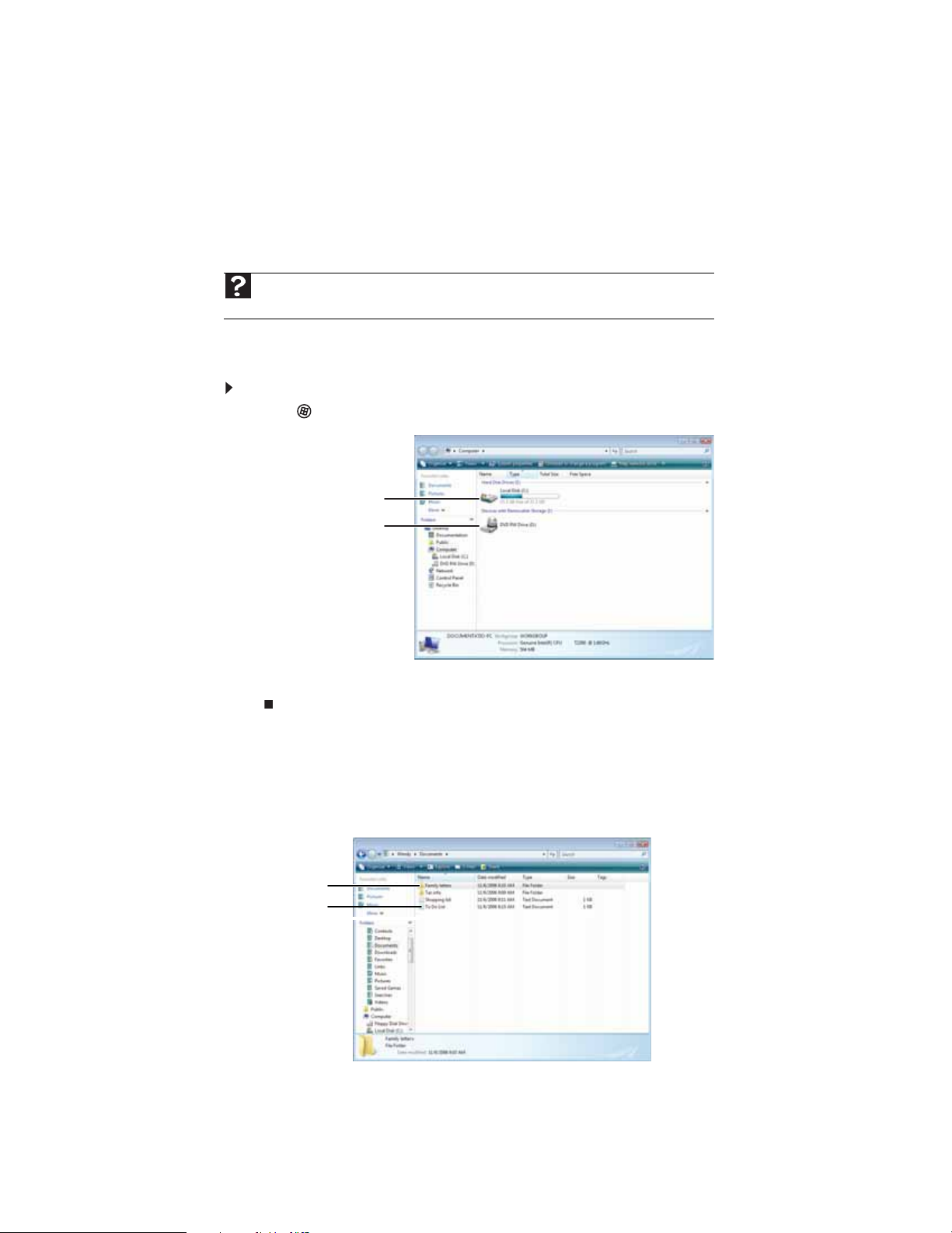
Viewing drives
Help
For more information about files and folders, click Start, then click Help and Support. Type
files and folders in the Search Help box, then press E
Drives are like file cabinets because they hold files and folders. A computer almost always has more
than one drive. Each drive has a letter, usually Local Disk(C:) for the hard drive. You may also have
more drives such as a CD or DVD drive.
To view the drives, folders, and files on your computer:
1 Click (Start), then click Computer.
Hard drive
NTER.
Creating f olders
Folders are much like the folders in a file cabinet. They can contain files and other folders.
Files are much like paper documents—letters, spreadsheets, and pictures—that you keep on your
computer. In fact, all information on a computer is stored in files.
Disc drive
2 Double-click the drive icon.
Folders
Files
10
Page 17
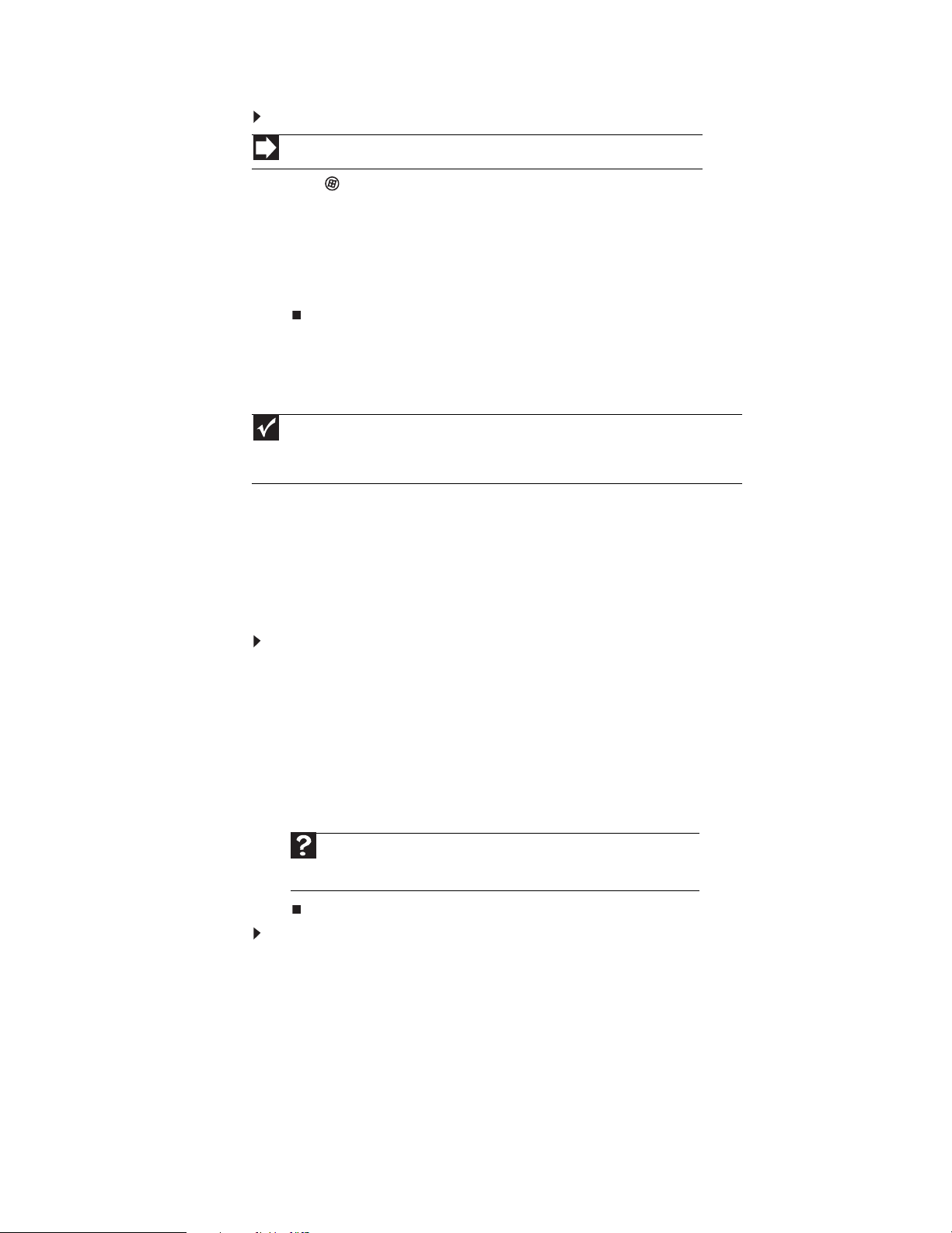
www.emachines.com
To create a folder:
Shortcut
ClickFile ➧ New ➧ Folder ➧ typename
1 Click (Start), then click Computer on the Start menu.
2 Double-click the drive where y ou w ant to put the ne w f older. Ty pically, Local Disk(C:) is your
hard drive and 3½ Floppy(A:) is your diskette drive (if installed).
3 If you want to create a new folder inside an existing folder, double-click the existing folder.
4 Click Organize, then click New Folder. The new folder is created.
5 T ype a name f or t he f older, then pre ss ENTER. The ne w folder name appears by the f older icon.
For information about renaming folders, see “Shortcuts” on page17.
Cop ying and mo ving file s and f olders
Important
The clipboard stores whatever you cut or copy until you cut or copy again. Then the clipboard
contains the new information only. Therefore, you can paste copies of a file or folder into more than
one place, but as soon as you copy or cut a different file or folder, th e original file or folder is deleted
from the cl ipb oard .
The skills you need to copy and move files are called copying, cutting, and pasting.
When you copy and paste a file or folder, you place a copy of the file or folder on the Windows
clipboard, which temporarily stores it. Then, when you decide what folder you want the copy to
go in (the destination fo ld e r), yo u paste it there.
When you cut and paste a file or folder, you remove the file or folder from its original loc ation an d
place the file or folder on the Windows clipboard. When you decide where you want the file or
folder to go, you paste it there.
To copy a file or folder to another folder:
1 Locate the file or folder you want to copy. For more information, see “Viewing drives” on
page 10 and “Searching for files” on page13.
2 Right-click (press the right mouse button) the file or folder that you want to copy. A pop-up
menu opens on the desktop.
3 Click Copy on the pop-up menu.
4 Open the destination folder.
5 With the pointer inside the destination folder, right-click.
6 Click Paste. A copy of the file or folder appears in the new location.
Help
For more info rmation about copying files and folders or moving files or
folders, click Start, then click Help and Support. Type copying files and
folders or moving files and folders in the Search He lp bo x, the n pre ss E
To move a file or folder to another folder:
NTER.
1 Locate the file or folder you want to move. For more information, see “Viewing drives” on
page 10 an d “Searching for files” on page13.
2 Right-click (press the right mouse button) the file or folder that you want to move. A pop-up
menu opens on the desktop.
3 Click Cut on the pop-up menu.
4 Open the destination folder.
11
Page 18

5 With the pointer inside the destination folder, right-click.
6 Click Paste. The file or folder you moved appears in its new location and is removed from
its old loca tion.
Deleting file s and f olders
When you throw away paper files and folders, you take them from the file cabinet and put them
in a trash can. Eventually the trash can is emptie d.
In Windows, you t hrow a wa y files and f olders by first mo ving them to t he Window s trash can, called
the Recycl e Bi n, where they remain until you decide to empty the bin.
You can recover any file in the Recycle Bin as long as the bin has not been emptied.
To delete files or folders:
1 In the Computer or Windows Explorer window, click the files or folders tha t you want to
delete . For instruc tions on ho w t o selec t multiple files and f olders, s ee “Short cuts” on page17.
If you cannot find the file you want to delete, se e “Searching for files” on page13.
2 Click Organize, then click Delete. Windows moves the files and folders to the Recycle Bin.
To recover files or folders from the Recycle Bin:
1 Double-click th e Recycle Bin icon on your Windows desktop. The Recycle Bin window opens
and lists the files and folders you have thrown away since you last emptied it.
2 Click the files or folders that you want to restore. For instructions on how to select multiple
files and folders, see “Shortcuts” on page 17.
3 Click Restore. Windows returns the deleted files or folders to their original locations.
Chapter 2: Using Windows
12
Page 19
To empty the Recycle Bin:
Caution
Emptying the Recycle Bin permanently erases any files or folders in the bin.
These files cannot be restored.
1 Double-click the Recycle Bin icon on the desktop. The Recycle Bi n window opens.
2 Click Empty the Recycle Bin. Windows asks you if you are sure that you want to empty
the bin.
3 Click Yes. Windows permanently deletes all files in the Recycle Bin.
Help
For more information about emptying the Recycle Bin, click Start, then click
Help and Support. Type emptyin g th e Recycle Bin in the Search Help box,
then press E
NTER.
Searc hing for f iles
If you are looking for a particular file or folder or a set of files or folders that have characteristics
in common, but you do not remember where they are store d on your hard drive, you can use the
Search utility.
Files and folders found using this utility can be opened, copied, cut, renamed, or deleted directly
from the list in the results window.
www.emachines.com
Using the W indow s Sear ch
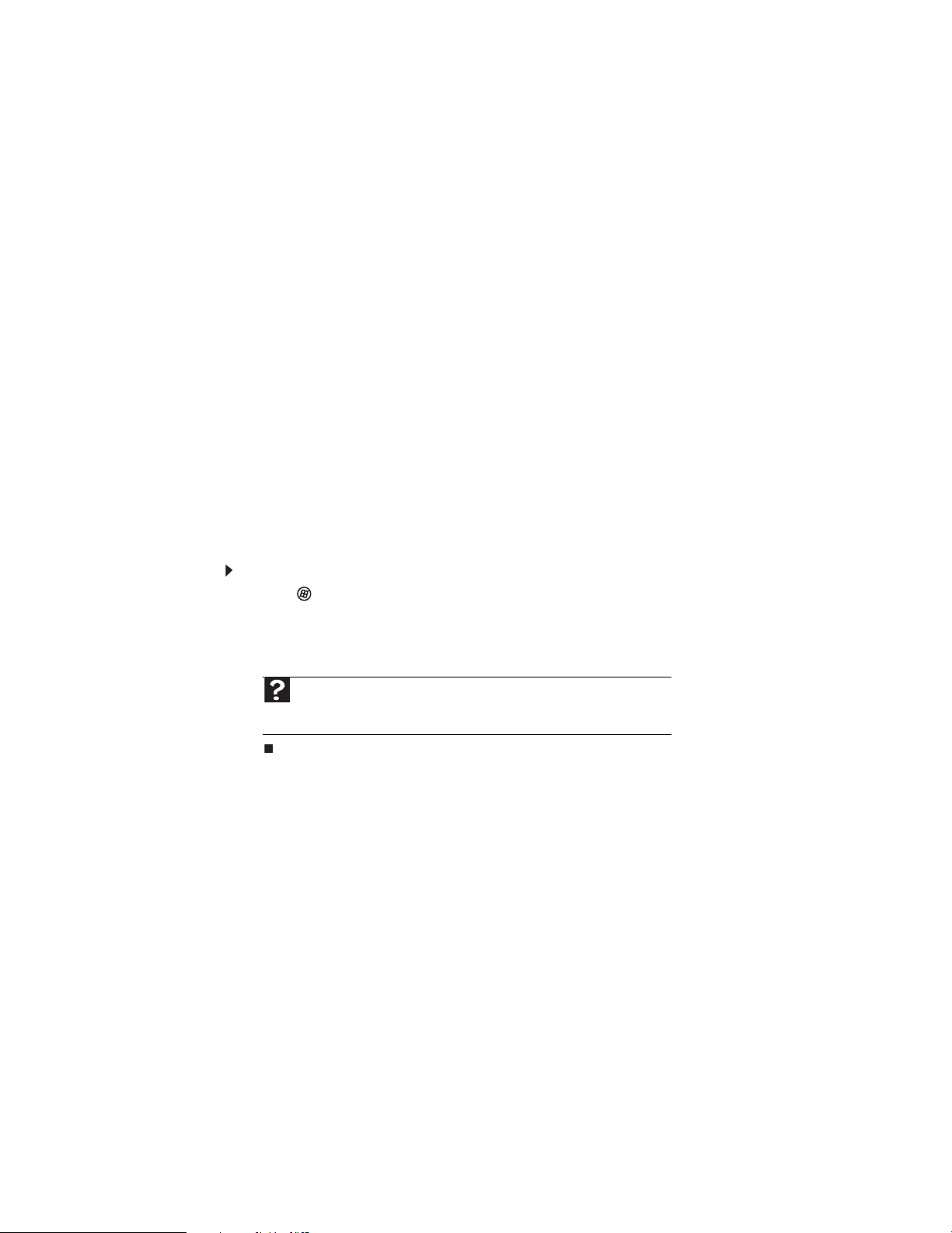
To find files and folders using the Search:
1 Click (Start), then click Search. The Search Results window opens.
2 If you want to search on your computer by file or folder name, type in all or part of the file
or folder name in the Search box in the top right of the window.
• If you type all of the name, Search will list all files and folders of that name.
• If you type part of the name, Search will list all of the file and folder names containing
the letters you typed.
3 Open a file, folder, or program by do uble -clicking the name i n the list .
Help
For more information about searching for files and folders, click Start, then
click Help and Support . T ype searching in the Search Help box, then press E
NTER.
13
Page 20
Using adv anced sea rch options
Search can find files meeting more criteria than file name. You can narrow your search by selecting
the search options that you want. You can search by the:
• Name or part of a name
• Creation date
• Modificatio n date
• File type
• Tag
• Author
• Text contained in the file
• Time period in which it was create d or modified
You can also combin e search criteria to refine sea rches.
Files and folders found using this utility can be opened, copied, cut, renamed, or deleted directly
from the list in the resul ts window.
Brow sing f or files and f olders
A file or folder that you need is rarely right on top of your Windows desktop. I t is usually on a
drive inside a folder that may be inside yet another folder, and so on.
Windows drives, folders, and files are organized in the same way as a real file cabinet in that they
may have many levels (usually many more levels than a file cabinet, in fact) . So you usually will
have to search through levels of folder s to find the file or folder that you n eed. This is cal led
browsing.
To b r ow s e f o r a f i l e:
1 Click (Start), then click Computer. The Computer win dow open s.
2 Double-click the drive or f older that y ou think contains the file or folder t hat you want t o find.
3 Continue double-clicking folders and their subfolde rs until you find the file or folder you
want.
Chapter 2: Using Windows
Help
For more information about browsing for files and folders, click Start, then
click Help and Support. Type files and folders in the Search Help box, then
press E
NTER.
14
Page 21
www.emachines.com
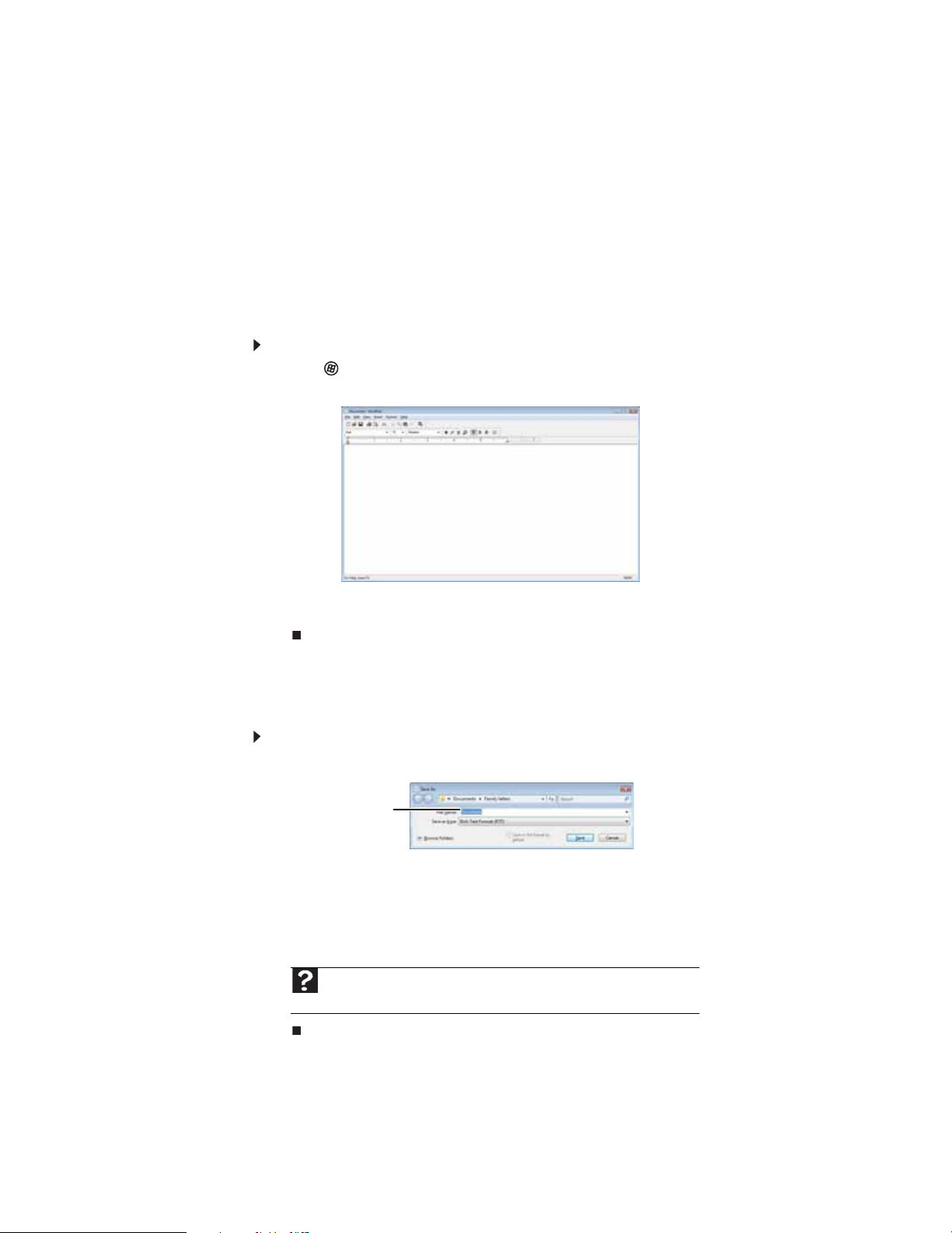
Wo rking with doc uments
Computer documents include word processing files, spreadsheet files, or other similar files. The
basic methods of creating, s aving, opening, and printing a document apply to most of these types
of files.
The following examples show how to create, save, open, and print a document using Microsoft
WordPad. Similar procedures apply to other programs such as Corel
Word, an d M icros oft E xce l.
For more information about using a program, click Help on its menu bar.
Creating a ne w doc ument
To create a new document:
1 Click (Start), All Programs, Accessories, then click WordPad. Microsof t WordPad starts
and a blank document opens.
®
WordPe rfect®, Microsoft
®
2 Begin composing your document. Use the menus and toolbar b uttons at the top of the
Sav ing a doc ument
After you create a document, you need to save it if you want to use it later.
To s a ve a do c u m e nt :
1 Click File, then click Save. The SaveAs dialog box opens.
2 Click Browse Folders to open the Folders list, then click the folder where you want to save
3 Type a new file name in the File name box.
4 Click Save.
5
wind ow to form at the d ocum ent .
File name
the file.
Help
For more information about saving documents, click Start, then click Help
and Support. Type saving in the Search Help box, then press E
NTER.
15
Page 22
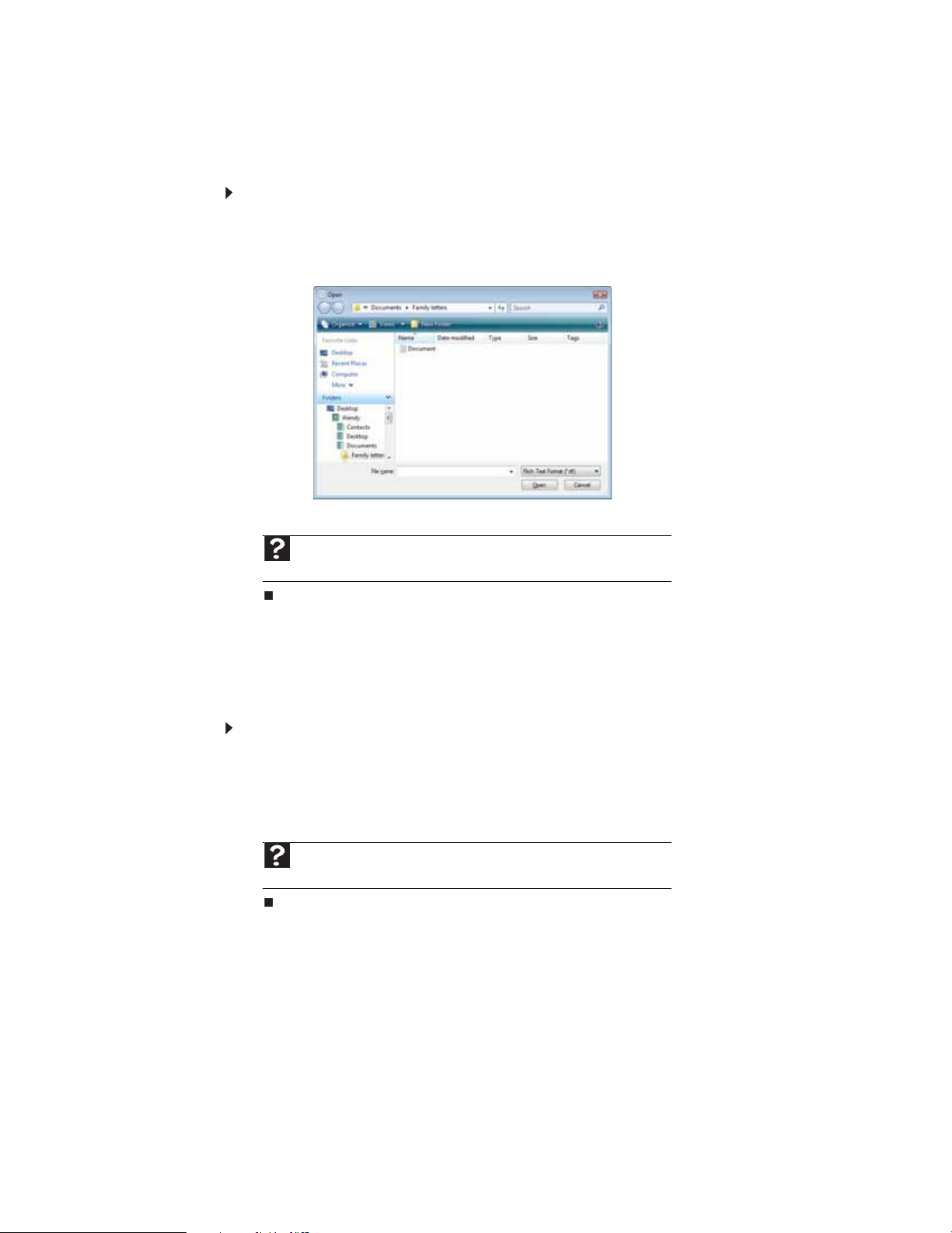
Opening a document
To view, revise, or print an existing document, first you need to open it. Open the document in
the program that it was created in.
To o p e n a d o c u me n t :
1 Start the pro gram.
2 Click File, then click Open.
3 Click Folders to op en th e Folders list, then click the folder you want to open.
Chapter 2: Using Windows
4 Double-click the document file name. The document opens.
and Support. Type opening files in the Search Help box, then press E
Printing a document
To print a document, you must have a printer connected to your computer or have access to a
network printer. For more information about installing or using your printer, see the printer
documentation.
To print a document:
1 Make s ure th at the pri nte r is tu rn ed on a nd lo ad ed with pa pe r.
2 Start the program and open the document.
3 Click File, then click Print. Th e Print dialog box opens.
4 Set the print options, then click Print. The document prints.
and Support. Type printing in the Search Help box, then press E
Help
For more information about opening documents, click Start, then click Help
Help
For more information about printing documents, click Start, then click Help
NTER.
NTER.
16
Page 23
Shortcuts
www.emachines.com
Help
For more information about Windows keyboard shortcuts, click Start, then click Help and
Support. Type Windows keyb oard sh ortcuts in the Search Help box, then press E
NTER.
The following table shows a few shortcuts that you can use in Windows and almost all programs
that run in Windows. For more information about shortcuts, see your Windows or program
documentation.
To... Do this...
Copy a file, folder, text, or
graphic
Paste a file, folder, text, or
graphic
Select multiple items in a
list or window
Select multiple adjacent
items in a list or window
Permanently delete a file
or folder
Rename a file or folder Click the file or folder, press F2, type the new
Close the acti ve window or
program
Switch to a different file,
folder, or running
program
Click the item, then press CTRL +C.
Click inside the folder or window where you
want to pas te th e o bj ect , th e n pr ess C
Click the first item, press and hold down the
CTRL key, then click each of the remaining
items.
Click the first item in the list, press and hold
down the S
the list.
Click the file or folder, then press
SHIFT +DELETE. The file or folder is
permanently deleted. The file or folder is not
stored in the Recycle Bin.
name, then press ENTER.
Press ALT +F4.
Press A
HIFT key, then click the last item in
LT +TAB.
TRL +V.
17
Page 24

Chapter 2: Using Windows
18
Page 25

Using t he Internet and F axing
• Learning about t he Inter net
• Setting up an Int ernet account
• Using the Wor ld WideWeb
• Using e-mail
• Using Window s F ax and Scan
• Sending a fax
• Receiv ing and vie wing a fax
Chapt er 3
19
Page 26

Chapter 3: Using the Internet and Faxing
Lear ning about the Inter net
The Internet is a worldw ide netw ork of comput ers link ed t oget her to pr ov ide inf orm ation t o people
everywhere. The two most popular services on the Internet are e-mail and the World Wide Web.
You can access this network by connecting yo ur computer to a telephone, DSL (Digital Subscriber
Line), or cable television line and signing up with an Internet service provider(IS P).
Internet Servers
store information so other computers can
access it from the Internet.
You r c o m p u t er
connects to the Internet
through an ISP.
If you want to access the Internet you need:
ISP Servers
let you connect to t he Internet
and access your e-mail
messages.
• A modem—a device that connects your computer to other computers or servers using a
telephone, D SL, or cable tele v ision line. Your computer may have a built -in dial-up telephone
modem. Cable and DSL modems connect to your computer through an Ethernet jack and
provide a faster connection speed than a standard telephone modem.
• An Internet service provider—a company that provides access to the Internet through an
ISPserver . When you connec t t o an ISP, the ISPserver lets y ou ac ces s th e Int erne t and y our e-mai l
messages. Check your telephone book for a list of Internet service provid ers available locally.
• A Web browser—a program that displays information from the World Wide Web. Microsoft
Internet Explorer was included with your computer. For more information, see “Using the
World Wide Web” on page 21.
• An e-mail program—a pro gram that le ts you create, send, and receive e-mail mes s age s over
the Internet. Microsoft Outlook or Outlook Express was included with your computer. For
more informat ion, see “Using e-mail” on page 22.
Set ting up an Interne t account
Before y ou can view t he information on the W orld Wide W eb, you need to s et up an Internet a ccount
with an Internet service provider (ISP). To set up an ISP service or to transfer an existing account
to this computer, contact the ISP directly.
Dial-up Internet connections are those using a telephone system to connect to the Internet. This
may include ordinary analog telephone lines, ISDN connections, and in some cases ADSL over PPP,
or other technologies. Because dial-up connections are designed to be temporary connections to
the Internet, dial-up charges (with both your telephone company and Internet service provider)
often increase the longer you connect to the Internet. To minimize the cost for dial-up Internet
service, we suggest that you only connect to the Internet during your e-mail and Web browsing
session, then disconnect when you are finished. Your Internet service provider can provid e
instructions on how to connect to and disconnect from the Internet.
Cable and DSL modems, a connection known as broadband, use your cable television or special
telephone lines to connect to your ISP and access the Internet. In many instances, broadband is
considered an always-connected service. With this type of service, your cost is the same regardless
of the amount of time you use your Internet connect ion.
20
Page 27
www.emachines.com
Acces sing your In ter net account
Help
For general information about using Internet accounts, click Start, then click Help
and Support. Type ISP in the Search Hel p box, then press E
The method you use to access your Internet account varies from ISP to ISP. Contact your ISP for
the correct procedure.
Using t he WorldWideWeb
The World Wide Web is a multimedia window to the Internet that gives you access to millions of
information sou rces.
Information on the Web comes to you on Web p ages , which are electronic documents that you
view using a Web page display program called a browser. You can use any of the commercially
available Web browsers, like Microsoft Internet Explorer or Netscape Navigator.
Web pages can contain tex t, animations, mus ic, and other multimedia featur es. A group of related
Web pages is called a Web site. You can acce s s We b site s t o shop, tr ack in v es tments, read th e new s,
download programs, and much more.
You can explore a Web site or visit other Web sites by clicking areas on a Web page called links
or hyperlinks. A link may be colored or underlined text, a picture, or an animated image. You can
identify a link by moving the mouse pointer over it. If the pointer changes to a hand, the item is
a link.
To learn more about using the Web browser features, click Help in the menu b ar.
NTER.
Connec ting to a W ebsite
After you set up an account with an Internet service provider (ISP), you can access the many
information sources on the World Wide Web.
To connect to a Web site:
1 Connect to your Internet account.
2 Depending on the method you use to connect to your Internet account, you may need to
start your Web browser. Cl ick (Start), then click Internet. Your default Web browser
opens showing an opening page or welcome screen.
3 To go to a different Web site, type the address (called a URL for “Univ ersal R e source L ocat or”)
in the browser address bar (for example www.emachines.com), then click GO on the
browser address bar.
- OR On the current Web page, click a link to a Web site.
Help
For more info rmation about connecting to a Web site, click Start, then click
Help and Support. Type connecting to a Web site in the Search Help box,
then press E
The Web browser locates the server computer on the Internet, downloads (transfers) data
to your computer, and displays the page on the site that you requeste d.
Sometimes Web pages displa y slowl y. The speed that a Web page displays on your sc reen depends
on the complexity of the Web page and other Internet conditions. Additionally, the speed of your
connection will determine how fast Web pages display.
NTER.
21
Page 28

Downloading files
download. For more information, see “Protecting your computer from viruses” on page59.
Downloading is the process of transferring files from a computer on the Internet to your computer.
To download files or programs from a Web site:
1 Connect to your Internet account.
2 In the address bar, type the address of the Web site that contains the file or program you
3 Create or locate the folder where you want to store the file on your computer. For more
4 Click the link on the Web page for the file that you want to download.
5 Follow the on-screen instructions for saving the file in the folder that you want. A copy of
6 Open the folder that yo u created.
7 Install or v ie w the downloaded file b y double-cl ic king it . If applic abl e , follow the instruc tions
Chapter 3: Using the Internet and Faxing
Caution
To protect your computer against viruses, make sure that you scan the files you
want to down load , th en p ress ENTER.
- OR Click a l i nk on a Web p ag e to navi ga te to t he Web s ite c on ta in in g th e fi l e th a t yo u wa nt to
download.
information, see “Working with files and folders” on page 10.
the file is downloaded to your computer. The time that it takes to transfer the file to your
computer depends on file size and Internet conditions.
provided on the Web site to run or install the program.
Help
For more information about downloading files, click Start, then click Help and
Support. Type downloading files in the Search Help box, then click E
Using e-mail
E-mail (electronic mail) lets you send messages to anyone who has an Internet connection and
e-mail address. E-mail is usually a free service of your Internet account.
The Internet never closes, so you can send e-mail messages at any time. Your e-mail messages
arrive at most e-mail addresses in minutes.
An e -mail address consists of a user name, the @symbol, and the Internet domain name of the
Internet ser vice p rovider (ISP) or comp any tha t “h osts ” tha t user. Your e-mail add ress is assigne d
when you sign up f or an account w ith an ISP. For example, a pers on with an account with Hotmail
mig ht h ave an e -m ai l ad dress that is s imi lar to th is on e:
Sending e-mail
To send e-mail using Windows Mail:
1 Connect to your Internet service provider.
2 Click (Start), then click E-mail. Your default e-mail program opens.
3 Click Create Mail.
4 Type the e- mail address of the recipient you want to send e -mail to in the To box.
NTER.
jdoe@hotmail.com
User name Internet domain name
22
Page 29

5 Type the subject of your e-mail in the Subject box.
6 Type the e-mail message.
e-mail. For more information, see the help for your e-mail program.
7 When finished, click Send. Your e-mail is sent over the Internet to the e-mail address you
specified.
Checkin g your e-mail
Help
For general information about using e-mail, clic k Start, then clic k Help and Support.
Type e-mail in the Search Help box, then press E
To check yo ur e-mail using Windows Mail:
1 Connect to your Internet service provider.
2 Click (Start), then click E-Mail. Your default e-mail program opens.
3 Click Send/Receive.
4 Double-click the message you want to read.
www.emachines.com
Tip
Most e-mail programs let you attach files, such as photographs, to your
NTER.
Tip
To protect your computer from viruses, check any e-mail attachments using
antivirus software. For m ore information, see “Protecting your computer from
viruses” on p age 59.
For more information about managing and organizing your e-mail messages, see the onl ine help
in your e- mail pro gram.
Using W indow s Fax and Scan
Windows Fax and Scan comes pre-installed with Windows Vista Business, Enterprise, or Ultimate
Editions. Windows automatically detects the optional built-in fax modem. You can connect your
computer to one local fax modem, although you can connect to multiple fax servers or devices
on a network. If you are not sure whether your computer has a built-in fax mod em, check the
hardware information that came with your computer. If you have an external fax modem, fol low
the manufacturer's instructi ons for attaching it to your computer. M ake sure that the modem is
turned on before proc eeding.
Y our fax cov er page, on which you can include all requir ed informati on, is set up when you prepar e
to send the firs t fax from th is c omp uter.
Y ou cannot send or receiv e a fa x using a cable or DSL modem by f ollow ing these inst ructions. Man y
Internet services exist that let you send or receive faxes using a broadband connection.
Your dial-up modem cable must be installed before you can send and receive fa xes. You cannot
use your standard te lephone modem to connect to the Internet while sending and receiving faxe s.
Sending a f ax
Windows Fax and Scan lets you send and receive faxes using your dial-up modem.
To s e n d a f a x:
1 Click (Start), All Programs, then click Windows Fax and Scan. Windows Fax and Scan
opens.
2 If Windows Fax and Scan is in Scan view, click Fax in the lower left corner of the window.
23
Page 30

Chapter 3: Using the Internet and Faxing
3 If you have never sent a fax on this computer before, click New Fax on the toolbar. The Fax
Setup window opens.
4 Click the type of connection you will be using (fax modem or fax server). The Choose a
modem name screen opens.
5 T ype the name of the f ax modem in the dialog box, then clic k Next. The Choose how to receive
faxes screen opens.
6 Click how you want to receive faxes, then click Unblock when the The Security Alert window
opens. The New Fax wind ow op ens .
24
Page 31

www.emachines.com
7 Create your f ax, then open the Cov er Page menu by clicking the arrow and selecting a cov er
page from the list . The Sender Info rmatio n dialog box opens.
8 Type your information in the spaces provided, then click OK. The New Fax dialog box opens.
9 To enter optional dialing rule information, click Dialing Rule and select a rule f rom the menu.
If you have not set up a dialing rule, select New Rule from the menu. The Location
Information dialog box opens.
10 Type your location in formation, then click OK. The Dialing Rules dialog box opens.
25
Page 32

Chapter 3: Using the Internet and Faxing
11 Highlight your location, then click Edit. The Edit Locat ion dialog box opens.
12 Complete the location inf ormatio n, then clic k OK. Y ou are returned to the Dialing Rules dialog
box.
13 Click OK. The New Fax dialog box opens.
14 Enter, scan, or attach the fax information you want to send, then click Send.
Setting up your co ve r page templat e
Y ou can create your o wn cov er page template that y ou can use in place of the cover page templates
that Windows Fax and Scan provides for you. To create a cover page template, you use the Fax
Cover Page Editor. On this te mplate, you insert information fields that automatically import values
you enter in both the Send Fax Wizard and the Fax Con figuration Wizard when you send your fax.
To set up your fax cover page template:
1 Click (Start), All Programs, then click Windows Fax and Scan. Windows Fax and Scan
opens.
2 If Windows Fax and Scan is in Scan view, click Fax in the lower left corner of the window.
26
Page 33

www.emachines.com
3 Click Tools, Cover Pages, then click New. The Fa x Cover Pag e Edito r opens.
• If you want to include fields that are imported from the Send Fax Wizard or the Fax
Configuration Wizard (such as To or From), add them to the page by using the Insert
menu, then move them t o the appropriate place on your template. You can also use the
Insert menu to include information that is automatically calcul ated (such as number of
pages or date and time sent).
• If you want to inc lude te xt t hat alw a y s appears on your co ve r page (such as a le tt erhead
or address), draw a box using the text box tool, type your text inside of it, then move
the box to the appropriate place on your template.
• If you want to include a logo that appears on your cover page, copy it to the Windows
clipboard, then paste it into the Cover Page Editor and move it to the appropriate place
on yo ur te mp late.
4 To save you r co ver p a g e te mp l a te, cl ic k File, then click Save. The Sa ve As dialog box opens
with your personal cover pages folder already in the Save in list.
5 Type the new cover page template name, then click Save.
Faxing a s canned docu ment or fr om progr ams
To fax a scanned document or to fax directly from programs:
1 Scan the document using the program for your scanner, or ope n your document in the
program it was cre ated in.
2 Click File, then click Print. Th e Print dialog box opens.
3 Click the arr ow b utto n to op en the Name list, then click the Fax printer.
4 Click Print. The Send Fax Wizard opens.
5 Complet e the wizar d by following the instru ctions in “Sending a fax” on page 23, or “Faxing
a scanned document or from programs” on page27.
Canceling a f ax
You can cancel a fax that you have set up to send at a time in the future.
To cancel a fax that has not been sent:
1 Click (Start), All Programs, then click Windows Fax and Scan. Windows Fax and Scan
opens.
2 If Windows Fax and Scan is in Scan view, click Fax in the lower left corner of the window.
3 Click Outbox, then rig ht-cl ick the fax you wa nt to can cel .
27
Page 34

Chapter 3: Using the Internet and Faxing
4 Click Delete to cancel the fax.
5 Click Yes.
Rece iv ing and v ie wing a f ax
To r e c e iv e a n d vi e w a f a x:
1 Click (Start), All Programs, then click Windows Fax and Scan. Windows Fax and Scan
opens.
2 If Windows Fax and Scan is in Scan view, click Fax in the lower left corner of the window.
3 To view a fax, click Inbox, then double-click the fax you want to vie w. The fax viewer opens,
where you can view and print the fax.
28
Page 35

Chapt er 4
Pla ying and Cr eating
• Pla ying music and mo v ies
• Creating audio file s and music libr aries
• Creating music CDs and video DVDs
• Creating and copy ing data disc s
• Using Windo ws Media C enter
Media Fi les
29
Page 36

Chapter 4: Playing an d Creating Media Files
Pla ying mu sic and movie s
Pla ying aud io and video f iles
WindowsMedia Player can play several types of audio and video files, including WAV, MIDI, MP3,
AU, AVI, and MPEG formats. For more information about using WindowsMedia Playe r, click Help.
To play a file using Windows Media Player:
Shortcut
Start➧Computer ➧ find the file ➧ double-click the file
1 Click (Start), All Programs, then click Windows Media Player. WindowsMedia Player
opens.
2 Click Library, then doub le-click the media file you want to play.
30
Media libraryPlayback controls
Page 37

www.emachines.com
3 Click one of the following to control playback:
• Shuffle randomizes the playback order of the files in th e playlist.
• Repeat starts playing the list over again after it reaches the end.
• Stop stops playba ck and rewinds the current file to the beginning.
• Rewind qu ickly rewinds the curre nt file (when you click and hold it) or skips to the
• Pause/Play al ternately pauses and res umes playback.
• Fast forward quickly fa s t forwards the current file (when you c l ick and hold it) or skips
• Volume adjusts the volume.
Pla ying optical dis cs
Optical discs are flat dis c s that u s e a la se r t o read and wr ite data. CDs, DVDs, HD-DVDs, and Blu-ray
Discs are all optical discs.
Important
Some music CDs have copy protection softwa re. You may not be able to play these
CDs on your computer.
Help
For more information about playing optical discs, click Start, then click Help and
Support. Type playing discs in the Search Help box, then press E
Repeat
Shuffle Stop
previous file in the playlist (when you click it).
to the next file in the playlist (when you click it).
Rewind
Fast forward Volume
Pause/Play
NTER.
Mute
Pla ying an optical d isc using Wind ows Med ia Pla yer
Use WindowsMediaPlayer to listen to CDs or watch movies on DVDs, HD-DVDs, or Blu-ray Discs.
For more information about using Windows MediaPlayer, click Help.
To play an optical disc:
Shortcut
Insert disc➧Wind ows Media P layer automatical ly plays
1 Make sure that the speakers are turned on or h eadphones are plugged in and that the
volume is turned up.
2 Insert an optical disc into the optical disc drive.
31
Page 38

Chapter 4: Playing an d Creating Media Files
3 If a dialog box opens and asks you what you want the computer to do with the disc, click
Play. WindowsMedia Player opens and begins playing the disc.
If Windows Media Player does not open automatically, click (Start), All Programs, then
click Windows Media Player. Windows Media Player opens.
Playback controls
4 If the disc is not already playing , click (play) .
Playlist
Video screen
32
Page 39

www.emachines.com
5 Click one of the following to control playback:
Repeat
Shuffle Stop
Rewind
Fast forward Volume
Pause/Play
Mute
• Shuffle randomizes the playback order of the files on the disc.
• Repeat starts playing the list over again after it reaches the end.
• Stop stops playba ck and rewinds the current file to the beginning.
• Rewind qu ickly rewinds the curre nt file (when you click and hold it) or skips to the
previous file on the disc (when you cl ick it).
• Pause/Play al ternately pauses and res umes playback.
• Fast forward quickly fa s t forwards the current file (when you c l ick and hold it) or skips
to the next file on the disc (when you click it).
• Volume adjusts the volume.
Creating a udio files and mu sic libraries
Creating music f iles
Help
For more information about making or playing an audio recording, click Start, then
click Help and Support. Type recordin g audio or ripping in the Search Help box,
then press E
NTER.
You can create several types of audio files for your listening enjoyment, including WAV, MP3, and
WMA files.
Recording audio files
Sound recorder is a simple Windows program that lets you record and play audio files. For
information about playing audio files, see “Playing audio and video files” on page30.
To record an audio file:
Shortcut
Start➧All Programs➧ Accessories➧Sound Recorder
1 Plug a microphone into one of the microphone jacks on your compute r. For the location of
the microphone jacks, see your computer’s Referenc e G ui d e.
2 Click (Start), All Programs, Accessories, then click Sound Recorder. The
SoundRecorder opens.
3 Click Start Recording, th en speak or make other sounds into the microphone.
33
Page 40

Chapter 4: Playing an d Creating Media Files
4 When you finish recording, click Stop Recording. The Save As dialog box opens.
5 Type a name for the recording, specify the file type and location where you want to save
the recordin g, then click Save. The recording is saved.
Creating WMA and MP3 music files
Important
Some music CDs have copy protection softwa re. You cannot copy tracks from
copy-protected CDs.
Using Windows Media Player, you can copy the tracks from a musicCD to your computer’s hard
drive as WMA or MP3 files. WMA and MP3 are methods f or digit ally compr essin g high-fidel ity music
into compact files without noticeably sacrificing quality. WMA files end in the file extension WMA,
and MP3 files end in the file extension MP3.
To create WMA or MP3 files:
1 Click (Start), All Programs, then click Windows Media Player. Windows Media Player
opens.
2 Right-click th e Rip tab, click Format, then click Windows Media Audio or mp3 to se lect
the format you want for your music files.
3 Insert a music CD into your optical disc drive.
4 Click the Rip tab. The Rip screen opens.
5 Click to clear the check box for any track you do not want to record, then click Start Rip.
Windows Media Player records the tracks to your hard drive. A progress bar appears next
to each track as it is recorded.
34
Tip
For more information about ripping music from CDs, click the Rip ta b, then
click Help with Ripping.
Page 41

Building a music libr ary
Use Windows Media Player to build a music library. You can organize your musi c tracks (individual
MP3 or WMA audio files) by categories, find a track quickly by sorting, and add information to a
music file.
You can add music tracks to your music library by:
• Creating MP3 or WMA files—When you create MP3 or WMA files from the tracks on your
music CD, Windows Media Player automatically adds these files to your music librar y.
• Dragging and Dropping—Drag and drop files from Windows Explorer or your des ktop t o the
music library.
Caution
During the download pr oces s, WMA and MP3 fil es may becom e corrupt. If y ou
are having trouble playing a downloaded file, try downloading the file again.
• Downloading files fr om the Internet—When y ou are connect ed to the Interne t, WMA and MP3
files that you d ownload are automatically added to your music library.
Editing track in for mation
After you add a WMA or MP3 file to your m usic library, you can edit the track’s tags
(informationalfields).
To edit trac k information:
1 Click (Start), All Programs, then click Windows Media Player. WindowsMedia Player
opens.
2 Click the Library tab .
3 Right-click the track or album you want to edit, then click Advanced Tag Editor. The
Advanced Tag Editor dialog box opens.
www.emachines.com
4 Enter track informati on such as Title, Artist, Album, and Genre, then click OK. The new
track information appears in the Windows Media Player library.
35
Page 42

Chapter 4: Playing an d Creating Media Files
Creating mu sic CDs and video D VDs
Creating a music CD
Important
We recommen d th at y ou do not u se y our com put er for other tasks while cr eat ing CDs
or DVDs.
If you record copyrighted material on a CD or DVD, you need permission from the copyright
owner . Oth erwise, you m ay be v iolatin g copyrig ht law and be subjec t t o payment of damage s
and other remedies. If you are uncertain about your rights, contact your legal advisor
Creating a music CD using W indows Media Play er
To create a music CD using Windows Media Player:
1 Click (Start), All Programs, then click Windows Media Player. WindowsMedia Player
opens.
2 Insert a blank, writable CD into you r recordable disc drive.
Important
Make sur e that you use a writable CD for creating music CDs. Most car stereos
will not play DVDs.
3 Click the Burn tab, the n click and drag songs that you want to burn to CD from the Library
to the Burn List .
36
Library Burn List
4 Click Start Burn. The music is recorded onto the blank CD.
Page 43

Creating a v ideo DVD
Creating a video DVD using W indows D VD Mak er
If your computer has Windows Vista Home Premium or Windows Vista Ultimate Edition, you can
create video DV Ds using Windows DVD Maker.
To create a video DVD using Windows DVD Maker:
creating CDs or DVDs.
If you record copyrighted material on a CD or DVD, you need permission from the
copyright owner. Otherwise, you may be violating copyright law and be subject to
payment of damages and other remedie s. If you are uncertain about your rights,
contact your legal advisor.
1 Insert a blank, writeable DVD into your recordable optical disc drive.
2 Click (Start), All Programs, then click Windows DVD Maker. The Windows DVD Maker
introduction window opens.
www.emachines.com
Important
We recommend that you do not use your computer for other tasks while
3 Click Choose Photos and Videos. The main screen opens.
37
Page 44

Chapter 4: Playing an d Creating Media Files
4 Click Add items. The Add Items to DVD dialog box opens.
5 Find and select the videos you want to add to the video DV D, then click Add. The videos are
added to the video list, and a graphic in the lower left corner of t he window show s y ou how
much disc capacity will be used.
38
6 Click Next. The Ready to burn disc dialog box opens.
Page 45

www.emachines.com
7 Click any of the following options to customize your video disc:
• Preview shows how your DVD’s opening menu will look using the current settings.
• Menu text changes the disc title, font, and button names.
• Customize menu changes the menu fonts, background and foreground videos, audio
track, and button styles.
• Slide show creates a slide show from photo files.
8 Click Burn. You r DVD is re corded.
Creating and cop ying data dis cs
You can burn two types of data discs:
• Live File System writes files immedi ately to the recordable disc, mak ing it a one -step
process like copying files to a flash drive. The resulting disc is compatible with WindowsXP
and later versions of Windows .
• Mastered cop ies fi le s to a te mp o rar y fol de r b efo re you tel l t he co mp u ter to b ur n t he fi les
to the disc. Although this is a slower process than Live File System, the resulting disc is
compatible with all operating systems.
The following instructions show you how to burn a disc using the Mastered format, which can be
read by all personal computers, regardless of the operating system installed.
Help
For information about burning a disc using the Live File System format, click Start,
then click Help and Support. Type live file system in the Search Help box, then
pressE
NTER.
Creating a data disc
To c r e a te a d a t a d is c :
1 Insert a blank, writable optical disc into your optical disc drive. The Autoplay dialog box
opens.
2 Click Burn files to disc. Th e Prepare this blank disc dialog box opens.
3 Type the title of the disc, then click Show formatting op tions.
4 Click Mastered, then click Next. An empty folder opens.
5 Open the f o lder that contains the f iles you want to burn t o disc, then click and drag the files
to the empty disc folder.
6 Click Burn to disc. The files are burned to the disc.
39
Page 46

Chapter 4: Playing an d Creating Media Files
Using W indow s Media Cent er
If your computer has Windows Vista Home Premium or Windows Vista Ultimate Edition, you can
use Window s Media Center to w atch TV , v ideos, and movi es, listen to musi c, and view photo s. Media
Center is a simplified, streamlined interface that is ideally suited for playing and managing media
files.
Because the remote control is an optional accessory, most instructions in this section assume you
are using a mouse to navigate the Media Center menus.
Starting Windo ws Media C enter
To start Windows Media Center:
1 Click (Start), All Programs, then click Windows Media Center.
- OR Press the Start butto n on th e re mo te c ont rol .
The first time you start Windows Media Center, the Welcome screen opens.
2 For the easiest setup, click Express setup, then click OK. The Windows Media Center’s main
screen opens.
40
Page 47

www.emachines.com
3 Use the remote control navigation buttons to select a Media Center menu option, then
pressOK.
• TV + Movies lets y ou play TV programs y ou hav e recorded, play a D VD or Blu-ray mov ie ,
or set up your TV tuner card (if installed).
• Online Media lets you play online games.
• Tasks lets you set up your displa y and media types, shut down or resta rt your computer ,
burn an optical disc (CD or DVD), and synchronize with another digital media devi ce (such
as an MP3 player).
• Pictures + Videos lets you view individual pictures, pictures in a slideshow, or select
movies from your video library.
• Music lets you select songs f rom your music library, se t up and u se your FM radio tuner
card (if installed), and play music playlists.
4 To exit Windows Media Center, click the X in the u pper-right co rner o f the screen .
41
Page 48

Chapter 4: Playing an d Creating Media Files
Using the Me dia Cent er remot e control
With Media Center mode active, you can use the optional remote control to play all of your media
files fr om ac ro s s t he r oom. (T he re mot e control, if inc luded wit h y our comput er, may look differ ent
from th at s hown belo w.)
Sho rtcu t bu tto ns
Audio/Video (A/V) control buttons
Numeric keypad/data entry buttons
Sta rt b utto n
Power b u tton
Transport buttons
Navigation buttons
42
Button(s) Functions
Shortcut buttons Give you direct access to Media Center features.
Start button Opens the Media Center’s main menu.
Audio/Video (A/V) control
buttons
Numeric keypad/data entry
buttons
Power bu tto n Puts the Media Center computer in Sleep mode (reduced power) .
Transport buttons Let you control the playback of media files and optical discs.
Navigation buttons Let you move the cursor around the Guide and menus, make selections,
Lets you c ontrol v olume lev els, v olum e mute , c hannel selec tions, an d the
movie menu.
Lets you en te r nu m be rs an d ch ar acte rs fro m t he rem ote co nt ro l.
navigate back to the previous screen, change the screen display aspect
ratio, and get more information. Press the OK button to make a selection.
Page 49

Networking Y our C omput er
• Introduc tion to Ne tworking
• Ethernet ne tworking
• Bluetoot h networking
Chapt er 5
43
Page 50

Chapter 5: Networking Your Computer
Introduc tion to Ne tworking
Networking t erms y ou should know
DHCP—Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) lets a router temporarily assign an IP address
to a computer on the network.
IP address—Internet Protoc ol (IP) address is a number that un iquely identifies a computer on the
network.
LAN—A local area network (LAN) is a computer network covering a local area, like a home or office.
Wired and wireless E thernet are common methods of creating a LAN.
PAN—A personal are a network (PAN) is a computer network used for communication among
computer devices (i ncluding cellular telephones, personal digital assistants, and printers) close to
one person. A wireless personal area netw ork (WPAN) is made pos sible with Bluet ooth. Th e primary
purpose of a WPAN is to replace USB or Firewire cables.
Subnet mask—Subnet mask is a number that identifies what subnetwork the computer is located
on. This number will be the same on all computers on a home network.
WAN—A wide area network (WAN) is a computer network that covers a broad geographical area.
The largest and most well-known example of a WAN is the Internet.
Ether net netw orking
Wir ed Ether net netw orking
An wired Ethernet network consists of two or more computers connected together through an
Ethernet cable. This connection type is commonly used in offices around the world and can be
used to build computer networks in the home.
Ethernet, F ast Ethernet, or Gigabit Ethernet
Important
Check local code requirements before installing Ethernet cable or other wiring in your home or office. Your
municipality may require you to obtain a permit and hire a licensed installer.
Ethernet is available at three different speeds. Standard Ethernet runs at 10 Mbps, Fast Ethernet
runs at 100Mbps, and Gigabit Ethernet runs at 1000 Mbps. Most home networks are built using
Standard or Fast Ethernet components. Business networks are typically built using Fast or Gigabit
Ethernet comp onents.
To create a wired Ethernet network, you or your electrician must install special Ethernet cables in
your home or office.
Using a router
The most common way t o set up a w ired Ethernet netw ork is Dyna mic Host Control Pr otocol (DHCP)
using a router. A DHCP network configuration uses a router to automatically assign IP addresses
to each computer or network device. For information on setting up a router, see the router’s
documentation.
44
Example router-bas ed Ethernet network
The following is an example of a wired Ethernet network. The network is made up of a router, a
cable or DSL modem, y our comput ers, and cables connecting eac h of thes e components. The r outer
is the central control point for the network.
Tip
To add the ability to access a wireless Ethernet network to your wired Ethernet network, connect an access point
to the router or use a router that has a built-in access point.
Page 51

www.emachines.com
Attached to the router are all of your computers or Ethernet-ready devices. Also connected to the
router is a cable or DSL modem that provides access to the Internet.
Cable/DSL
modem
Router
Equipment you need for a rout er-based Ethernet network
Important
For best results, all Ethernet components shou ld be either stan dard Ethernet (10 Mbps), Fast Ethernet (100 Mbps or
10/100) , or Gigabit Ethernet (1000 Mbps or 10/100/1000). A mixture of components rated at different speeds will result
in your network running at the speed of the slowest rated component.
For a wired Ethernet network you need:
• Two or more computers with Ethernet jacks
• One router
• One broadband Internet connection (optional)
• Ethernet cables connecting all of the network equipment
When buying your route r, be sure the model includes everyth ing your network needs, including:
• Internet security fe atures, such as a firewall, to protect your network from unwanted
intruders
• 4-port switch to eliminate the need for additional network hardware
• DHCP server/dynamic IP address assignment to automatically configure network and IP
addresses
Determining if an E thernet card is already in stalled on your computer
To determine if an Ethernet card is already installed on your computer:
1 Click (Start), then click Control Panel. The Cont rol Pane l wind ow opens .
2 Click System and Maintenance, then click System.
3 Click Device Manager from the task list on the left. The Device Manager wi ndow ope ns.
4 Click the plus (+) in front of Network adapters. The Ethernet device installed in your
computer is listed. If one is not listed, you must install one.
45
Page 52

Chapter 5: Networking Your Computer
Setting up wired Ethern et network hardw are
Making sure your broadband connection works
Important
If you do not have a broadband connection already installed, make the necessary arrangements with your ISP. Be
sure to find out how soon after the installation the line will be activated.
Broadband Internet settings differ from ISP to ISP. Before you begin setting up your network, you should contact your ISP
for any specific instructions they have fo r setting up a network.
Before you change anything about you r home setup, make sure that your broadband connection
is working correctly. To test the connection, log onto the Internet using your current setup. If the
connection is not working, contact your Internet service provider.
Installing Ethernet cards and drivers
After you ha v e det ermined the ty pe of Ethernet y ou are u sing for your netw ork, y ou need to install
Ethernet cards and drivers on the computers that do not have Ethernet already installed. Use the
documentation that comes w ith y our Et herne t car ds f or i nstruc tions on installing t he car d and an y
required drivers.
Plug your Ethernet cable into your comp uter’s jack and the router or the cable or DSL modem at
this point, if you have not already done so.
Connecting network cables
We recommend using category 5 (Cat 5), unshielded, twisted-pair cable (about 1/4-inch diameter
with a thin outer-jacket, containin g ei ght color-coded wires), and equipment compatible with this
type of cable. This type of cable is equipped with RJ-45 connectors (like a large telephone jack
connector, but with eight pins) on each end.
Cat 5 cables are available in two different types; straight-through cables, used to connect
computers to a router, and crossover cables, used to connect two computers.
T o det er mine whic h type of cable y ou ha v e, hold both ends of the cable with the connectors fac ing
away from you and with the spring clip on the bottom. For straight-through cable, the wires on
both co nn ector s a re a tta che d to cop pe r p in s i n th e sa me ord er (sa me co lor s, le ft to rig ht ) . Fo r a
crossover cable, the wires on each connector are attached to the copper pins in a different order
(different colors, left to right).
Setting up a network using a router
If you are setting up a network for more than two computers and you wi ll be connecting your
network to a high-speed Broadband Internet connection (cable or DSL modem), we recommend
the use of a router. A router lets you access the Internet connection from any network computer.
The router can assign IP addresses to the computers on the network and can provide firewall
protection for your network as well.
46
Page 53

www.emachines.com
In addition to a router, you need a straight-through cable for each computer you want to connect
to the net wor k.
Cable/DSL
modem
Router
WAN por t
To set up a network using a router:
1 Plug one end of the power adapter into the AC connector on the router and the other end
into a grounded, 110V electrical outlet.
2 Tu r n o n y our com put ers .
3 Plug one end of a straight-through network cable into any numbered port on the router
(except the W AN port). The WAN port is used t o connect the r outer t o the DS L or cable modem
and is identified by a label or a switch. Plug the other end of the cable into the network
jack on the computer. As each computer is connected to the rout er, the corresponding green
indicator should light on the front of the router, indicating a good connection.
4 Repeat Step3 for each computer on the network.
5 For an Internet connection, plug a straight-through cable into the WAN port on the router
and the other end into the Ethernet jack on the DSL or cable modem.
Wir eless Et hernet ne tworking
Wireless Ethernet networking is the latest advance in computer communication. With a wireless
home network, you can set up your computer wherever you like.
A wireless Ethernet network uses radio waves to communicate. Typically, a wireless Ethernet
network is made up of an access point, a cable or DSL modem (for Internet access), and your
wirel ess c om pu ters .
47
Page 54

Chapter 5: Networking Your Computer
Wireless Ethernet standards
Current wireless Ethernet standards include the following:
• 802.11a — 54Mbps
• 802.11b — 11Mbps
• 802.11g — 54Mbps
• 802.11n — 540Mbps
Speed is not the only issue if you decide to use equipment with different sta nda rds. Compatibility
can also be an issue . Take the f ollo wing in t o consider ation when y ou pur c has e wir ele ss equipment :
Access point Wireless cards supported
802.11a 802.11a only
802.11b 802.11b only
802.11g 802.11b and 802.11g
802.11n 802.11b, 802.11g, and 802.11n
Using an access point
An access point is a small el ectronic dev ice that serv es as the ce ntral contro l point for y our netw ork.
You connect your modem to the access point, set up a network connection, then browse the
Internet, send e-mail, share files and folders with other networked computers, and access other
devices, like a printer or scanner.
Cable or DSL modem
Access point
Equipment you need f or an access point -based netw ork
Tip
When you buy your access point, make sure it has:
• IEEE 802.11n support. 802.11n is the fastest method for wireless communications. 802.11n is compatible with the older
IEEE 802.11g and IEEE802.11b formats but not with the competing IEEE802.11a format. Make sure that you get the
correct format that matches your computer.
• DHCP server/dynamic IP address assignment capability that makes it easier to set up and access your network.
• Internet security features like a firewall to keep intruders out of your network.
• Wireless secu rity features like SecureEasySetup™ or 128-b it WEP encryption.
For a wireless Ethernet network you need:
• Your Gateway computer with wireless networking installed
• A broadband Internet connection (optional)
• An access point
48
Page 55

www.emachines.com
Determining if a wireless Ethernet device is already installed on your computer
To determine if an Ethernet card is already installed on your computer:
1 Click Start, then click Control Panel. The Contro l Panel window op ens.
2 Click System and Maintenance, then click System.
3 Click Device Manager from the task list on the left. The Device Manager wi ndow ope ns.
4 Click the plus (+) in front of Network adapters. The wireless Ethernet device installed in
your computer is listed. If one is not listed, you must install one.
Setting up wireless Ethernet netw ork hardware
Making sure your broadband connection works
Important
If you do not have a broadband connection already installed, make the necessary arrangements with your ISP. Be
sure to find out how soon after the installation the line will be activated.
Broadband Internet settings differ from ISP to ISP. Before you begin setting up your network, you should contact your ISP
for any specific instructions they have fo r setting up a network.
Before you change anything about you r home setup, make sure that your broadband connection
is working correctly. To test the connection, log onto the Internet using your current setup. If the
connection is not working, contact your Internet service provider.
Installing wireless cards and drivers
After you have determined the type of wireless equipment you are using for your network, you
need to install wir eless c ards and dri vers on t he computers that do not ha ve t hem alread y installed.
To order wireless Ethernet PCI or PC cards, visit the Accessories Store at www.emachines.com
Use the documentation t hat come s w ith your wireless cards for i nstruc tions on install ing the car ds
and any required drive rs.
.
Setting up your access point
A wireless Etherne t network sends and recei v es inf ormation thr ough radio wa v es. T his means that
another computer outside your network can intercept the radio waves and take control of your
network.
If you do not set up sec urity f or y our netw ork, a hac ker can gain access to your Internet connection
to send spam e-mail and to your hard drive to download viruses or view your personal data, like
credit card numbers, Social Security numbers, and personal online banking information.
Check your access point documentation for information about installing the access point and
setting network securit y.
Establishing y our Etherne t netw ork connec tion
Naming the computers and the workgroup
Important
You must give each computer on the network a unique Computer Name and the same Workgroup Name.
Make sure th at you have set up your router (wired network) or access point (wireless network) .
If you are setting up a wired network, make sure that you have connected the network cabling.
To identify this computer on the network:
1 Click Start, then click Control Panel. The Contro l Panel window op ens.
2 Click System and Maintenance. The System and Maintenance window opens.
3 Click System, then click Change Settings in the Computer Name, Domain and
Workg ro up se tti ng s area. The System Prop erties dialog box opens.
4 Click Change.
49
Page 56

Chapter 5: Networking Your Computer
5 If your computer does not already have a name, type a unique computer name in the
Computer name box. This name identifies the computer to other users on the network.
Use a computer name of up to 15 characters with no blank spaces . Each computer name
must be unique on your network. All-numeric computer name s are not allowed. Names mu st
contain some letters.
6 Type a name for your workgroup in the Workgroup b ox. Use a workgroup name of up to
15 c harac ters w ith no blank spaces. The work group name mu st be the s ame for al l computers
in your network workgroup, and the name must be different than any computer name on
you r ne two rk .
7 Click OK. When you are prompted to restart your computer, click Restart Now.
Configuring the T CP/IP prot ocol
A networking protocol is a language computers use to talk to each other. One of several available
protocols must be se t up on each computer you plan to u se on your network. We recommend you
use the Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol (TCP/IP), which is widely accepted and
compatible for local area networks (LANs), as well as for Internet communications.
When networking is set up in Windows Vi sta™, TCP/IP is automatically installed as the default
protocol.
Using a DHCP server
In order to us e t he TCP/IP protocol on a computer wit h a router or acces s point router, the pr ot ocol
must be set to “Obtain an IP address from a DHCP server.” This is typically preset when you receive
your computer.
Configuring your router
After you have named your computers and set up TCP/IP on them, you can configure your route r
using your Web browser. For instructions, see your router’s documentation.
Connectin g to a wireless Ether net network
Important
Each computer on your network needs a unique Computer Name. All the computers on your network need the same
Workgroup Name. You may have already named your computer and workgroup the first time you turned on your computer.
Connecting to your network
Help
For more inf orma tion about connec ting t o y our net work, c lic k Start, then click Help and Support. Type t he f ollowing
in the Search Help box, then press E
• Connect to an available network
• Man ually add a wireless Ethernet network
• Connecting to wireless Ethernet network.
After you have named your computer and workgr oup, you need to set up the network connection
on your computer.
NTER.
50
Page 57

www.emachines.com
To connect to your wireless Ethernet network:
1 Click (Start), then click Network. The Network window opens .
2 Click Network and Sharing Center. The Network and Sharing Center win dow ope ns.
3 Click Connect to a network on the left of the window. The Con nect to a n etw ork dialog
box opens.
51
Page 58

4 Click a network, then click Connect.
If you can see the network name , but you cannot connect t o it, your network is u sing security .
Right-click on the network, then click Properties. Modify the security settings to match the
settings you set on your access po int.
Wireless security
For information on wireless security, refer to the documentation that came with your access point.
Help
For more information about wireless network security methods, click Start, then click Help and Support. Type
wireless network secu rity methods in the Searc h Help box, then press E
T esting y our netw ork
Now that your home network is set up, log onto one of your computers and access a favorite
Inte rnet Web si te.
If you are unable to connect to the Internet:
• Click Start, Control Panel, Network and Internet, then click Network and Sharing
Center. Select Diagnose and Repair on the left of the window. Take any actions suggested.
• If you are using a wired Ethernet network, check all physical cable connections.
• Make sure that your router or access point is plugged in and compare the status lights on
the fro nt of the rou ter or ac cess po int wi th th e p atte rns de scrib ed in the rou ter or acc ess
point documentation.
• Temporarily turn off any firewall software on your desktop computer.
• Turn off all of the devices, then power them back on.
• Refer to your router’s or access point’s troubleshooting information.
• Contact your Internet service provider.
Chapter 5: Networking Your Computer
NTER.
Adding a print er to y our ne twork
Instead of plugging a printer into each of you r computers, you can add a printer to your network.
To add a printer to the network, do one of the following:
• Connect your printer to your networked computer, then share the printer. For information
about sharing printers, see “Sharing drives and printers” on page 52.
• Connect your printe r to your router or access point if the router or access point includes a
USB or parallel port. For more information, see the instructions that came with your router
or access point.
• Use a printer that has built-in networking.
• Use a pr int ser ver.
Sharing re sour ces
With a network, you can share your Internet connection, drives, and printers.
Sharing driv es and printers
With a network, y ou can share drive s (f or ex ample hard dri v es and D VD driv es) and pr inters among
the computers connected to the network.
Important
To share a printer among the network computers, each computer must have the shared printer’s drivers installed.
Follow the instructions included with your printer to install th e printer drivers on each computer.
52
Page 59

www.emachines.com
Aft er the driv e s and pr inte rs on eac h netw ork co mput er are share d, yo u can acce ss t hem a s thoug h
they were attached directly to your computer. Then you can:
• View a network drive
• Open and copy files store d on other network computers
• Print documents on network printers
Sharing drives or folders
To share drives or folders:
1 Click (Start), then click Computer.
2 Right-click the drive or folder that you want to share, then click Share. The Properties dialog
box opens.
If you share a drive, the entire contents of that drive will be available to everyone on your
network. If you share a folder, only the contents of that folder will be available to everyone
on the network.
3 Click the Sharing tab.
Click Share.
- OR If Share is grayed out, click Advanced Sharing to set sha ri ng for th is dr ive o r fo ld er.
4 Click OK, then click Close.
Un-sharing drives and folders
To un-share drives or folders:
1 Click (Start), then click Computer.
2 Right-click th e drive or folder that you want to un-share, th en click Share.
3 Click Advanced Sharing, then click Share this folder (or drive) to uncheck the box.
4 Click Apply, the n click OK.
53
Page 60

Sharing printers
To s h a re p r i nt e rs :
1 Click (Start), then click Control Panel. The Cont rol Pane l wi nd ow o pe ns.
2 Under Hardware and Sound, click Printer The Printers window opens.
3 Right-click the name and ico n of the p rinter you want to share, then click Sharing on the
4 On the Sharing tab, click Share this printer, then click OK.
Using the network
After the drives and printers on each network computer are shared, you can:
• View sha red d rives a nd fold er s
• Map a network drive
• Open and copy files store d on other network computers
• Print documents on network printers
Viewing shared drives and folders
Help box, then press E
Chapter 5: Networking Your Computer
menu.
Help
For more inf ormation about work gr oups, clic k Start, then click Help and Sup por t. T ype workgroups in the Search
NTER.
To view shared drives and folders:
1 Click (Start), then click Network. The Network wind ow opens.
2 If no drives or folders are displayed, click the option bar under the menu bar, then click Turn
on network discover and file sharing.
3 Double-click the name of the computer containing the drive or folder you want to view. All
shared drives and folders are listed.
Creating a shortcut to a netw ork driv e
After a shortcut is created on a computer for a drive or folder on another computer, the contents
of the drive or folder can be accessed as if the drive were attached directly to the computer.
For example, a shortcut is created on computer 2 to the Documents folder on computer 1. To access
the Documents folder on computer 1 from computer 2, double-click the shortcut icon.
To map a network drive:
1 Locate the drive or folder by completing the steps in “Viewing shared drives and folders”
on page 54.
2 Right-click the drive or folder, then click Create Shortcut. A shortcut is created for the drive
or folder and the icon for the shortcut is placed on your desktop.
3 Click × to close the window.
Opening files across the network
To open files across the network:
1 Start the p rogram for the file you wan t to open .
2 Click File, then click Open.
3 Browse to the network drive that contains the file you want to open.
4 Double-click the folder containing the file, then double-click the file.
54
Page 61

www.emachines.com
Copying files across the network
To copy files across the network:
1 Click (Start), then click Computer. The Computer window opens.
2 Browse to the network drive that contains the file you want to copy.
3 Browse to the file you want to copy.
4 Right-click the file, then click Copy.
5 Right-click the folder where you want to copy the file to, then click Paste.
Printing files across the network
Important
Before you can print a file across the network, you must install the driver for the printer o n the computer you are
sending the file from. You can obtain the printer driver and installation instructions from the CD that shipped with your
prin ter o r fro m the m a nu factu rer ’s We b si te.
To print files across the network:
1 Open the file you want to print, then click Print.
2 Click the arr ow b utto n to op en the pri nte r na me li st , th en c li ck th e n etw or k pr in ter.
3 Click Print.
Bluet ooth netw orking
You can use Bluetooth to communicate with other Bluetooth-enabled devices. These devices may
include printers, MP3 play ers, cellular telephones, and other computers. Bluet ooth lets y ou transfer
information between these devices without the use of a USB or Firewire cable. To access a
Bluet o oth-enabled device, you must inst al l the devic e, then conne ct to the Bl ue tooth pers on al area
network.
Important
Your notebook may have a Bluetooth radio built-in. If you are using a desktop computer or if your notebook does
not have built-in Bluetooth, you can purchase a Bluetooth adapter to connect to a USB port on your computer.
To install a Bluetooth enabled device:
1 Turn on your Bluetooth radio and the Bluetooth devi ce.
2 Click (Start), Control Panel, then click Hardware and Sound.
3 Click Bluetooth Devices.
4 Click Add, then follow th e on-screen instructions.
To install a Bluetooth printer:
1 Turn on your Bluetooth radio and the Bluetooth printer.
2 Click (Start), Control Panel, then click Hardware and Sound.
3 Click Add a printer.
4 Click Add a network, wireless, or Bluet ooth pri nter, click Next, then fo llow the on-sc reen
instructions.
To connect to a Bluetooth personal area network:
1 Turn on your Bluetooth radio and the Bluetooth devi ce.
2 Click (Start), Control Panel, then click Network and Internet.
3 Click Network and Sharing Center.
4 Click Manage Network Connections. The Network Connections window opens.
55
Page 62

Chapter 5: Networking Your Computer
5 Under Personal Area Network, click Bluetooth Network Connection.
6 On the toolbar, click View Bluetooth network devices. The Bluetooth Personal Area
Network Devices dialog box opens.
7 Under Bl uetooth devices, click that device you want to connect to, then click Connect.
Help
For more information about Bluetooth, click Start, then click Help and Support. Type Bluetooth in the Search
Help box, then press E
NTER.
56
Page 63

Pr otec ting your comput er
• Hardware security
• Data security
• Security updat es
Chapt er 6
57
Page 64

Chapter 6: Protecting y our computer
Hardware security
Although you may be able t o replace your comput er with a call to your insurance agent, you cannot
replace the information stored on your computer. Take steps to prevent theft of your computer.
K ensington loc k slot
The first step in computer security is preventing your computer from being stolen.
Attach a cable lock to t he K ensingt on lock slot on y our comput er, then wrap the lock’ s cable around
the leg of a desk or table. You can buy a cable lock at most electronics store s and many department
stores.
For the location of the Kensington lock slot, see your Reference G uid e.
Data security
The second s tep in co mputer securi ty is keep ing your d ata safe and secure.
Startup and har d driv e pas sw ord
Use a startup and hard drive password to keep other people from using your computer. You have
to enter your password when you turn on your computer or access your files.
These passwords are set in your computer’s BIOS setup utility. Use a password that you can
remember but that would be hard for someone else to guess.
Tip
For instructions on creating a startup and hard drive password, see your computer’s
Referenc e G ui d e. Make sure that you use a password you can remember. The password
feature is very secure, and you cannot bypass it. If you forget your password, you will have
to return your computer to eMachines so we can reset it.
Windo ws us er accounts
Windows lets you set up a user account for each person who uses your computer. When you set
up user accounts, Windows sets up a Documents folder for each account. You can assign a
password to each account so only the account owner can access files in the Documents folder.
When you set up a user account, you can also limit the programs that a user can install or run.
58
Help
For more information about Windows user account s, click Start, then click Help and
Support. Type user accounts in the Search Help box, then press E
NTER.
Page 65

www.emachines.com
Prot ecting y our comput er f rom v iru ses
A virus is a program that attaches itself to a file on a computer, then spreads from one computer
to another. Viruses can damage data or cause your computer to malfunction. Some viruses go
undetected for a period of time because they are activated on a certain date.
Protect your computer from a virus by:
• Subscribing to N orton In ternet Securit y for regul ar virus a nd spyware p rotection u pdates.
• Using Norto n Intern et Securi ty to check files an d progra ms tha t are a ttached to e-m ail
messa ges or down lo ad ed from the In tern et.
• Checking all programs fo r viruses before installing them.
• Disabling macros on suspicious Microsoft Word and Excel files. These programs will warn
you if a document that you are opening contains a macro that might have a virus.
• Making sure that the Windows Security C enter is configured t o pr o v ide you w ith t he highest
level of protection.
Tip
For more information about modifying security settings, see “Modifying security
settings” on page 61.
Help
For more information about protecting your computer against viruses, click Start,
then click Help and Support. Type viruses in the Search Help box, then press E
NTER.
Using Norton Internet Security
Norton Internet Security helps protect your computer from viruses, spyware, and i dentity theft.
T o learn mor e about the s e f eat ure s, inc luding how t o s chedule s y stem scans and security updates,
click Learn More on the right side of the screen. For additional help and technical support, click
Help & Support in the upper right corner of the screen. The Help & Support screen opens.
59
Page 66

Chapter 6: Protecting y our computer
Removing viruses and spyware
To scan for and remove viruses and spyware:
1 Click (Start), All Programs, Norton Internet Secu rity, then click Norton I nternet
Security. Norton Internet Security op ens.
2 On the left si de of the windo w , clic k Scan Now. Norton Internet Security scans your computer
for vir use s and spyw are and remo ve s any that it f inds. When the sca n is finished, a summary
of fixed problems appears.
Updating your virus and spyware definitions
You should update your virus definitions frequently so Norton Internet Security can recognize the
latest threats.
To update your virus and spyware definitions:
1 Make s ure th at yo u a re c on ne cted to th e In tern et .
2 Click (Start), All Programs, Norton Internet Secu rity, then click Norton I nternet
Security. Norton Internet Security op ens.
60
Page 67

3 On the left side of the window, click Run Liv eUpdate . Y our comput er downloads and installs
the latest virus definitions.
Important
To update Norton Internet Security after the 60-day subscription period ends,
you must extend your subscription.
Using W indows Se curity C ente r
www.emachines.com
Windows Security Center helps protect your computer throu gh:
• A firewall
• Automatic Windows updates
• Third party virus protectio n software
• Security options in Internet Explorer
Modifying security settings
To modify security settings:
1 Click (Start), Control Panel, then Click Security.
2 Click Security Center. The Windows Security Center dialog box opens.
61
Page 68

3 Click:
• Windows Update to run Windows Update or modify the Windows Update settings.
• Window s Fir ewall to prevent outsiders from accessing the information on your
computer.
• Window s Defe nder to scan your computer for malicious or unwanted software that
may have been placed on your computer either fr om an Internet w eb sit e or from other
programs that you have installed.
• Internet Options to prevent certain prog rams from running on your computer that
might be found on Web sites.
Help
For more information about Windows Security Center, click Start, then
click Help and Support. Type secu rity cente r in the Search Help box, then pr ess
E
NTER.
For more informat ion a bo ut the Wind ows Securit y Center, click Get help about Security Center.
Secur ity updates
To keep your computer secure, you need to ke ep Windows and your computer’s system software
up to date.
Chapter 6: Protecting y our computer
Windo ws Updat e
If a hacker finds a way to bypass the security features built into Windows, Microsoft creates a
high-priority Windows update to fix the problem. You should update Windows regularly to keep
your computer secu re.
To u p d at e Wi n d ow s :
1 Click (Start), Control Panel, then click Security.
2 Click Security Center. The Windows Security Center dialog box opens.
3 Click Windows Update. Windows checks the Microsoft Web site to see if any updates are
available.
62
Page 69

www.emachines.com
4 Click:
• Install Updates to download and install updates on your computer. These updates
include security updates.
• Install Extras to download additional Windows software for your computer.
Help
For more information about Windows Update, click Start, then
click Help andSupport. Type Windows update in the Search box, th en press
E
NTER.
Scheduling automatic updates
Use the Windows Security Center to schedule automatic updates. Windows can ro utinely c hec k for
the latest updates for your computer and install them automatically.
To schedule automatic updates:
1 Click (Start), Control Panel, then click Security.
2 Click Security Center. The Windows Security Center dialog box opens.
3 Click Windows Update.
4 Click Change Settings. The Change Setti ngs dialog box opens.
BigFix
5 Make your changes to the schedule settings, then click OK.
Your computer may include BigFix. BigFix monitors your computer for problems and conflicts. It
automatically gathers information about the latest bugs, security alerts, and updates from BigFix
sites on the Internet. Whenever BigFix detects a problem, it alerts you by flashing the blue taskbar
icon. To fix the problem, click on that icon to open BigFix.
63
Page 70

Chapter 6: Protecting y our computer
64
Page 71

Chapt er 7
C ust omizing W indows
• Changing screen settings
• Changing s yst em sounds
• Changing mouse settings
• Adding and modifying us er accounts
• Changing pow er -sa ving se ttings
• Changing accessibility set tings
• Setting up par ental controls
65
Page 72

Chapter 7:
Changing s cr een set tings
Adjusting the color depth and screen area ar e two of t he most basic display set ting s you ma y need
to change. You can also adjust settings such as the screen background and screen saver.
Changing color dept h and sc reen re solution
Color depth and screen resolution are two of the most basic monitor settings you may need to
change to suit your needs.
Color depth is the number of colors your computer uses to display images on your monitor. Most
images look best displayed with the maximum number of colors available. If the color in your
images seems “false” or “jump y,” especiall y af t er y ou ha v e pla yed a game or run a video-intensive
program, check the color depth setti ng and return it to the highest color setting, if necessary.
Screen resol uti on is the number of pixels (individual colored dots) your computer uses to display
images on your monitor. The higher the resolution, the more information and scr een components
(such as icons and menu bars) can be displayed on the monitor.
Help
For more information about adjusting the screen, click Start, then click Help and
Support. Type adjusting monitor sett ings in the Searc h Help box, the n press E
To change the color depth or screen resolution:
1 Click (Start), Control Panel, then under Appearance and Pers onalization, c lic k Adjust
Screen Resolution. The Display Settings dialog box opens.
NTER.
66
2 To change the color depth, click the Colors list, then click the color depth you want.
• Low (8-bit) = 256 colors
• Medium (16-bit) = 65,500 colors
• Highest (32-bit) = 16,700,000 colors
3 To change the screen resolution, drag the Resolution slider to the size yo u prefer.
4 Click Apply. If the new se ttings do not look right, click No. If the new set tings make the screen
illegible and you cannot click No, th e se tti ngs ret ur n to the ir previ ous val ue s a fter severa l
seconds.
5 Click OK, then click Yes to save you r ch an ges .
Page 73

www.emachines.com
Changing the ap pearance of wind ows and bac k grounds
You can change the appearance of Windows desktop items, such as the colors of windows and
dialog boxes and the color and design of the desktop background.
To change window colors an d effects:
1 Click (Start), Cont rol Panel, then under Appearance and Personalization, click
Customize colors. The Window Color and Appearance dialog box opens.
2 Click one of the color choices and adju st the Color intensity slider, then click OK. Your new
color settings are ap plied.
3 For even more color adjustment options, such as color schemes, shading effects, and screen
fon t s , c l i c k (Start), Control Panel, then under Appearance and Personalization, click
Change the color scheme. Change the setting you want, then click OK.
To change the Windows desktop background:
1 Click (Start), Control Panel, then under Appearance and P ersonalization, c lick Change
desktop background. The Choose a desktop background dialog box opens.
2 Click t he Picture Location list, then click the location where you w ant to look f or back ground
images. If the loc ation you w ant is not in t he list, c lick Browse and locate the drive and f older .
3 Click the picture or color you want to use for the background, then click OK.
67
Page 74

Selecting a sc reen sa ver
Caution
If you are using a monitor (not a flat-panel display), an image may get burned in on
your monitor screen if you leave your computer on for long periods of time without using
it. You should use a screen saver which constantly changes its image to avoid this damage.
Flat panel displays cannot be damaged with image burn-in.
Y ou can use a sc r een sa ver to keep others from view ing y our s cr een while y ou are a w a y f r om y our
computer. Windows supplies a variety of screen savers that you can choose from, and many more
are available from the Internet and as commercial products.
To select a screen saver:
1 Click (Start), Cont rol Panel, Appearance and Personalization, then click Change
screen saver. The Screen Saver Settings dialog box opens.
Chapter 7:
2 Click the Screen saver list, then click the screen saver you want to use. An example of the
screen saver plays on the preview screen.
• To change the settings for the screen saver, click Settings, change the settings, then
click OK.
Important
If the Settings button is not available, yo u c ann ot customize the screen save r
you se le cted .
• To see a full-screen preview of the screen saver, click Preview.
• To change the length of computer inactivity time that passes before the screen saver
starts, change the number of minutes in the Wait box.
3 Click OK. Your screen saver changes are applied.
Help
For more information about selecting a screen saver, click Start, then click
Help and Support. Type screen savers in the Search Help box, then pre ss E
NTER.
68
Page 75

Changing gadgets
Gadgets are constantly running mini-programs that are visible on your Wi ndows desktop. They
can be moved, removed, resized, and configured according to your preference. Although you can
position them anywhere on your desktop, gadgets are usually visi ble on the right edge of your
screen in the Sidebar.
Gadgets can include:
• Clocks and timers
• News feeds, weather forecasts, and stock tickers
• Slide shows and puzzles
• Calendars and contact lists
• Sticky notes
To a d d a ga d g e t:
1 Click the + at the top of the Sidebar, or right-click in an empty area of the Sidebar and click
www.emachines.com
Add Gadgets. The gadget selection window opens.
2 Click the gadget you want, then drag it to the Sideba r.
Tip
To shop online for more gadgets, click Get more gadgets online.
To delete a gadget, right-click the gadget, then click Close Gadget.
To configure a gadget:
1 In the Sidebar, right -clic k the gadget, then c lick Options. The gadget’s configurati on window
opens.
2 Make the changes you want, then click OK. Your changes are saved.
69
Page 76

Chapter 7:
Using a gadge t’s control pane l
Some gadgets have built-in control panels that you can use to control their behavior.
To use a gadget’s control panel:
1 In the Sidebar, hold the mouse pointer over the gadget. The gadget’s built-in control panel
appears on the gadget. (Slideshow gadget shown)
2 Click the control you want to operate.
Config uring the gadget Side bar
You can change the appearance and behavior of the Sidebar.
To change Sidebar properties:
1 Right-click in an empty area of the Sidebar, then click Properties. The Windows Sidebar
Properties dialog box opens.
70
You can change:
• Whether the Sidebar starts each time Windows starts
• Whether the Sidebar is always on top of other windows (always visible)
• The side o f the screen the sid ebar a ppear s on
• The monitor that the sidebar appears on (if you have multiple monitors)
Page 77

Setting up multiple monitors
Important
The dialog boxes shown in this section are for demonstrativ e purposes only and may
not represent the screens on your computer.
If your computer’s video card supports additional monitors (it must have two vid eo ports), you
can connect an additional monitor or projector to your computer.
You can use the second monitor or projector as a duplicate of the primary display, or as an
extension to roughly double the size of your Windows desktop. Use the additional desktop space
to accommodate additional windows.
To use a projector or additi onal monitor:
1 Turn off your computer.
2 Plug the projector or m onitor cable into the secondary monitor port on your computer. For
the location of the monitor port on your computer, see the setup poster or your Reference
Guide.
3 Plug the pr oje ctor ’s or m oni tor ’s pow er co rd i nto an AC power o utle t, th en turn it on .
4 Turn on your computer. Windows recognizes the new hardware and searches for its driver.
You may need to install the driver from the disc supplied by the manufacture r or download
the driver from the ma nufacturer’s Web site.
5 After the driver is installed, click (Start), Control Panel, Appearan ce and
Personalization, Personalization, then click Display Settings. The Display Settings dialog
box opens.
www.emachines.com
Shortcut
Right-click an empty space on the desktop ➧ Personalize ➧
Display Settings.
6 Right-click the second monitor icon (labeled 2) , click Attached, then click Apply.
7 Adjust properties such as Resolution or C olor Qual ity if necessa ry.
Tip
To help identify your multiple monitors in t he Display Setting s dialog box, c lic k
Identify Monitors. A la rge number appears on the screen of each monitor.
8 T o use the second monitor or projec tor as a “mir ror” (duplicate) of the primary monitor (both
monitors have the same content), click to deselect the check box for Extend my Wind ows
desk top o nto t his mon itor.
71
Page 78

Chapter 7:
9 To use the second monitor or projector as an extension of your desktop (increasing the size
of your Windows desktop), click to select the check box for Extend my Windows desktop
onto t h i s m o n i tor. You can click and drag the “2” monitor icon to position it the same way
the physical monitor is arranged on your desk.
10 Click OK.
Changing s yst em sounds
You can change the sounds that play for system events, such as Windows startup and shut down,
logging on and logging off, window maximizing and minimizing, and error messages.
To change system sounds:
1 Click (Start), Control Panel, Hardware and Sound, then under Sound, click Change
system sounds. The Sound dialog box opens.
2 Click the Sound Scheme list, then click the sound scheme you want.
- OR Click an event in the Program list, then click the Sounds list and click the sound file you
want associated with the event. If you do not see the sound file in the Sounds lis t, click
Browse and find the file in the appropriate folder.
3 To test a sound you have selected, click Test.
4 Click OK to save your changes.
72
Page 79

www.emachines.com
Changing mouse settings
Help
For more inf ormation about mou se setting s, clic k Start, then click Help and Support.
Type m ouse settings in the Search Help box, then press E
You can adjust the double-click speed, pointer speed, left-hand or right-hand configuration, and
other mouse settings.
To change your mouse settings:
Shortcut
Start➧Contro l Pa ne l ➧H ard wa re a n d S o un d ➧ Mouse
1 Click (Start), Control Panel, then under Hardware and Sound, clic k Mouse. T he Mouse
Properties dialog box opens.
NTER.
2 Change the settings yo u want. You can:
• Switch the left and right buttons
• Change the double-click speed
• Change the pointer appearance and speed
• Change the mouse wheel actions
3 Click OK to save your changes.
Adding and modifying u ser accounts
You can create and customize a user account for each person who uses your computer. You can
also change between user accounts without turning off your computer.
User account tips
• If you want to create an account for so meone, but you do not want that user to have full
access to your computer, be sure to make that account limited. Remember that limited
accounts may not be able to install some older programs.
• Files creat ed in one account are not acce ssible f rom other ac counts unless the files are st ored
in the Shared Documents folder. The Shared Documents f older is a cces sib le f rom all accounts
on that computer and from other computers on the network.
73
Page 80

Chapter 7:
To add, delete, or modify user accounts:
1 Click (Start), Control Panel, then un der User Acco unts an d Family Sa fety, click Add
or remove user acco unts.
• To create a new account, click Create a new account, then follow the on-screen
instructions to finish the setup.
• To c hange an account, clic k t he account name , t hen clic k the option y ou want to change.
• To delete an account, click the account name, then click Delete the account and confirm
the deletion of related files. T he account is deleted. (Y ou cannot delete t he administrator
account.)
Help
For more information about user accounts, click Start, then click Help and
Support. Type user accounts in the Search Help box, then press E
NTER.
To switch between user accounts:
1 Save any open documents that are being worked on in your current account.
2 Click (Start) , click the arrow next to the lock icon, then click Switch Us er or Log Off.
• Switc h U s e r opens the account selection screen but does not log off the current user,
and any programs that were running for the previous user continue to run.
• Log Off logs off the current use r, then opens the account selection screen.
Caution
If you click Log Off, any programs that were running may be closed, and
unsaved document changes may be lost.
3 Click the user acco unt that you want to use.
74
Page 81

www.emachines.com
Changing po wer - sav ing set tings
Changing the po wer plan
Power plans (groups of power settings) let you change power saving options such as when the
monitor or hard drive is automatically turned off. You can select one of the defined power plans
or crea te a cus tom po wer p lan.
Help
For more in forma tio n a bou t p owe r pl an s, click Start, then click Help and Support.
Type power plan or power management in the Search Help box, then press E
To change the power plan:
Shortcut
Start➧Contro l Pa ne l ➧Sy st em a n d M a i nte n a n c e ➧Po we r O p ti o n s
1 Click (Start), Control Panel, Hardware and Sound, then under Power O pt io ns , click
Change power-saving settings. The Select a power plan dialog box opens.
NTER.
2 Click a power plan (default plans shown):
• Balanced uses several energy-saving features while maintaining reasonable
performance and convenience.
• Powe r sa ver maximizes energy savings but reduces performance and conve nience.
• High performance maximizes performance but reduces energy savings.
3 To change a power plan, click Change plan settings, change the settings you want, then
click Save changes.
75
Page 82

Chapter 7:
4 T o change ad vance d power s etti ngs, clic k Change plan settings, Change advanced power
settings.
5 Change the settings you want, then click OK.
You can change:
• Power-down times for your hard drive, wireless network adapter, USB devices, and
processor
• Power management settings for your d isplay, processor, and expansion cards
• Behavior of your computer’s power button
6 Click Save changes.
7 To create a new power plan, on the left side of the Select a po wer plan window click Create
a power plan, then follow the on-screen instructions.
76
Page 83

www.emachines.com
Changing acce ssibility s ettings
Your computer can be a powerful tool, but it may be less useful to you if items on the screen are
difficult to see, or if the mouse is difficu lt to control. Windows has several tools that help you use
it more easily.
Using the Ease of Access Center
Use the Ease of Acc ess Center to change several system display settings.
To use the Ease of Access Center:
1 Click (Start), Control Panel, Ease of Access, then click Ease of Access Center. The Ease
of Access Center opens.
2 In the Quic k a cce ss to com mo n too ls section, click one of the following options to make
some of the most common accessibility changes to Windows:
• Start Magnifier provides a close-up view of the area near your mouse pointer.
• Start On-Screen Keyboard displays a keyboard on the screen. You can p ress keys on
the on-screen keyboard by clicking them with your mouse.
• Start Narrator reads on-screen text and describes graphics.
• Set up High Contrast changes the Windows color scheme to use high-contrast colors.
You can also use the Ease of Access Cente r to:
• Use the computer without a display, mouse, or keyboard
• Make the computer display easier to see
• Make th e m o use an d keybo ard e as ie r t o us e
• Use text or visual alternatives for soun ds
77
Page 84

Using v oice recognition
You can attach a microph one to your computer and configure Windows to create typed text from
you r voi ce.
To set up voice recognition:
1 Click (Start), Control Panel, Ease of Access, then click Speech Recognition Options.
The Speech Recognition Options window opens.
Chapter 7:
2 Click one of the following settings to start setting up speech recognition:
• Start Speech Recognition turns on speech recognition. With an attached microphone,
you can then control your computer using voice commands.
• Set up microphone configures your attache d microphone to work correctly with
speech recognition.
• Take Speech Tutorial helps you learn how to use speech recognition.
• Train your computer to better understand you helps you create several voice
samples that your computer can use to bette r recognize the words you speak.
• Open the Speech Reference Card lets yo u view and print a list of common voice
commands.
3 If you want to con figure your computer’s settings for re ading aloud on-screen text, click
Text to Speech on th e le ft of the wi ndo w.
Set ting up parental controls
You can use parental controls to:
• Control and monitor the Internet activi ty of your children
• Block inappropriate games and programs
• Schedule the times your children can use the computer
• Print activity reports that contain a detailed history of computer use
To use parental controls most effectively, you should set up a separate user account for each of
your children. For information on setting up user accounts, see “Adding and modifying user
accounts” on page 73.
78
Important
You must be logged in to an administrator account to set up parental controls. You
cannot set up parental controls for an administrator user account.
Page 85

Filter ing Inter net access
You can specify the type of Internet content that can be accessed by a user.
To set up Internet filtering:
1 Click (Start), Control Panel, then under User Accounts and Family Safety, click Set
up parenta l controls for any user. The Parental Controls dialog box opens.
2 Click the user account to set up restrictions for. The User Cont rol s dialog box opens.
www.emachines.com
3 Click On, enforce current settings, then click Windows Vista Web Filter. The Web
Restrictions dialog box opens.
4 Spe cify the sett in gs yo u wa nt to use for thi s use r, the n cl ick OK. The settings are saved.
79
Page 86

Chapter 7:
Scheduling computer and I ntern et us e
To schedule the times a user can access the Internet:
1 Click (Start), Control Panel, then under User Accounts and Family Safety, click Set
up parenta l controls for any user. The Parental Controls dialog box opens.
2 Click the user account to schedule for, then click Time limits. The Time Restrict ion s dialog
box opens.
3 Click inside the grid to set when the user can access the computer. Blocked hours are blue,
and allowed hours are white.
Restricting game access
You can restrict games by game ratings, or you can specify the games which are not al lowed.
To restrict games by game ratings:
1 Click (Start), Control Panel, then under User Accounts and Family Safety, click Set
up parenta l controls for any user. The Parental Controls dialog box opens.
2 Click the user account to set up restrictions for, then click Games. The Game Controls dialog
box opens.
80
Page 87

www.emachines.com
3 Click Set game ratings. The Game Restrictions dialog box opens.
4 Click the level of games you want allowed, then click OK. The sett ings are saved.
To restrict specific games:
1 Click (Start), Control Panel, then under User Accounts and Family Safety, click Set
up parenta l controls for any user. The Parental Controls dialog box opens.
2 Click the user account to set up restrictions for, then click Games. The Game Controls dialog
box opens.
3 Click Block or Allow specific games. The Game Overrides dialog box opens.
81
Page 88

4 Click the level of access you want for each game listed, then click OK. If the game you want
to restrict access to is not shown on the list, see “Res tricting specific programs” on page82.
Re stricting spec ific pr ograms
To restrict specific programs:
1 Click (Start), Control Panel, then under User Accounts and Family Safety, click Set
up parenta l controls for any user. The Parental Controls dialog box opens.
2 Click the user account to set up restrictions for, then click Allow and block specific
programs. The Application Restrictions dialog box opens.
Chapter 7:
3 Click [User name] can only use the programs I allow , c lick the checkbo x f or each program
you want to allow access to, then click OK.
Tip
Click Check All, then click to uncheck the checkboxes of the programs you
want to restrict access to.
Creating acti vity reports
To create a report of a user’s computer and Internet use:
1 Click (Start), Control Panel, then under User Accounts and Family Safety, click Set
up parenta l controls for any user. The Parental Controls dialog box opens.
2 Click the user account to create a report for, then click View activity re ports. The activity
report is displayed.
The activity report includes such information as:
• Top 10 Web sites visited
• Most recent 10 Web sites blocked
• File downloads
• Applications run
• Logo n t i mes
82
Page 89

Notices
www.emachines.com
Copyrig ht © 2007 Gateway, Inc.
All Rights Reserved
7565 Ir vi ne Ce nte r D rive
Irvine, CA 92618USA
All Rights Reserved
This publication is protecte d by copyright and all rights are reserved. No part of it may be
reproduced or transmitted by any m eans or in any form, without prior consent in writing from
Gateway.
The inf orm ation in this manual has been car eful ly c hec k ed a nd is be lie v ed t o be a cc urat e . How e v er,
changes are made periodically. These changes are incorporated in newer publication editions.
Gateway may improve and/or change products described in this publication at any time. Due to
continuing system improvements, Gateway is not responsible for inaccurate information which
may appear in this manual. For the latest product updates, consult the Gateway Web site at
www.gateway.com
incidental, or consequential damages resulting from any defect or omission in this manual, even
if advised of the possibility of such damages.
In the interest of continued product development, Gateway reserves the right to make
improvements in this manual and the products it describes at any time, without notices or
obligation.
. In no event will Ga teway be liable for direct, indirect, s pecial, exempla ry,
T radem ark acknow ledgments
Gateway, eMachines, and the Black-and-White Spot Design are trademarks or registered
trademarks of Gateway, Inc. in the U.S. and other countries. Intel, Intel Inside logo, and Pentium
are registered trademarks and MMX is a trademark of Intel Corporation. Microsoft, MS, MS-DOS,
and Windows are trademarks or regist er ed trademarks of Micro sof t Corp oration. All other produc t
names mentioned herein are used for identification purposes only, and may be the trademarks
or registered trademarks of their respective co mpanies.
83
Page 90

Chapter 7:
84
Page 91

Index
A
access point
setting up
using 48
accessibility
high contrast color scheme
Magnifier 77
Narrator 77
on-screen keyboard 77
settings 77
accessing
shared drives
shared files 54
shared folders 54
accounts
Internet
ISP 20
user 73
Windows user 58
adding
user account s
address
e-mail
Web 21
AU file
playing
audio
playing
recording file 33
audio CD
adding tracks to library 35
editing track information 35
playing 31
AVI file
playing
49
77
54
20
73
22
30
30
30
B
background
changing Windows
BigFix 63
Bluetooth network 55
installing device 55
installing printer 55
personal area netw ork 55
Blu-ray Disc
playing
broadband Int ernet connect ion
browser
Web
browsing for files and folders 14
31
20, 46, 49
20, 21
67
C
cable modem 20, 44, 46
CD
adding tracks to library 35
creating audio 36
creating data 39
editing track information 35
playing musi c 31
clipboard 11
close button 9
closing
program
window 9, 17
color
changing scheme 67
depth 66
high contrast scheme 77
computers
naming
configuring
router
TCP/IP protocol 50
connecting
to Internet 21
to Web site 21
connections
monitor (VGA)
projector 71
VGA 71
copying
files across netwo rk 55
files and folders 11, 17
text and graphics 17
creating
data disc
desktop icon 8
desktop shortcut 8
document 15
folder 10
MP3 file 34
music file 34
video DVD 37
WMA file 34
customizing 65
cutting
files and folders 11
9, 17
49
50
71
39
D
deleting files and folders 6, 12, 17
desktop
adding icon
adding shortcut 8
adjusting settings 66
changing background 67
changing color scheme 67
extending 71
selecting screen saver 68
using 6
8
using Start menu 7
DHCP 44, 50
disconnecting from Internet 20
display
using screen saver 68
documentation
eMachines Web site 2
help 2
Help and Support 2
online help 3
documents
creating 15
opening 16
printing 16
saving 15
downloadin g files 22
drivers
updating
drives
mapping ne twork
sharing 53
un-sharing 53
viewing contents 10
viewing files and folders 10
DSL modem 20, 44, 46
DVD
creating data
creating video 37
playing 31
Dynamic Host Configuration
Protocol
2
54
39
50
E
Ease of Access Center 77
editing
music track inform ation
eMachines
contact info rmation
Web address 2
Web site 2
e-mail
address
checking for messages 23
sending 22
using 20, 22
Ethernet netw ork
See wired Ethernet network
See wi reless Eth ernet netwo rk
22
35
3
F
Fast Ethernet 44
faxes
canceling 27
receiving and viewing 27
sending 23, 27
85
Page 92

Index
sending from program 27
sending scanned image 27
setting up cover page
template
files
copying
cutting 11
deleting 6, 12, 17
downloading 22
finding 13, 14
moving 11
opening 7
opening shared 54
pasting 11, 17
recovering 12
renaming 17
searching for 13, 14
sharing 53
un-sharing 53
viewing list 10
finding
files and folders
folders
copying
creating 10
cutting 11
deleting 6, 12, 17
finding 13, 14
moving 11
opening 10
pasting 11, 17
recovering 12
renaming 17
searching for 13, 14
sharing 53
un-sharing 53
viewing list 10
11, 17
13, 14
11, 17
G
gadgets
adding
changing 69
configuring 69
configuring Sidebar 70
using cont rol pane l 70
game access
restricting
Gateway
model number
serial number 3
Gigabit Ethernet 44
69
80
3
H
HD-DVD
playing
help
Media Center
31
3
27
online 3
using 2
Help and Support 2
starting 2
hyperlinks 21
I
Internet
account
connecting to 21
downloadin g files 22
filtering 79
requirements to access 20
using 20
Internet Explorer 20
Internet service provider (ISP) 20
connecting to 21
disconnecting from 20
setting up account 20
IP address 44
entering 50
ISP
See Internet service provider
20
K
Kensington lock slot 58
keyboard
on-screen
shortcuts 17
77
L
labels
model number
serial number 3
LAN 44
LCD panel
using screen saver
links 21
local area network (L AN) 44
lock slot
Kensington 58
3
68
M
maintenance
virus protection
mapping netw ork drives 54
maximize button 9
Media Center
See Windows Media C enter
Media Player
See Windows Media P layer
menu bar
messages
checking e-mail
9
59
23
sending e-mail 22
MIDI file
playing
minimize button 9
model number 3
modem
cable 20, 44, 46
dial-up 20
DSL 20, 44, 46
monitor
color quality
controls 66
screen resolution 71
setting up m ultiple 71
using screen saver 68
mouse
changing settings 73
using Magnifier 77
moving
files
folders 11
MP3 file
creating
editing track information 35
playing 30
MPEG file
See MP3 file
multimedia
playing audio CD
playing DVD 31
recording audio 33
using Windows Medi a Player
music library
building
editing 35
music tracks
copying 34
creating CD 36
30
71
11
34
31
30
35
N
name
computer 49
workgroup 49
naming
computers
workgroup 49
Narrator 77
network
Bluetooth
testing 52
using 54
wired Ethernet 44
wireless Ethernet 47
Norton Internet Security
scanning for viruses
49
55
60
86
Page 93

www.emachines.com
starting 60
updating 60
O
online help 2, 3
opening
documents
16
files 7
files across network 54
folders 10
programs 7
optical disc
creating data
39
playing 31
Outlook 20
Outlook Express 20
P
PAN 44
parental controls
activity repo rts
blocking specific games 81
game ratings 80
Internet filt ering 79
restricting game access 80,
81
restricting programs 82
scheduling comput er use 80
scheduling Internet access 80
setting up 78
time limits,setting 80
password
hard drive 58
startup 58
pasting
files and folders
text and graphics 17
personal ar ea network (P AN) 44
playing
audio CD
audio file 30
Blu-ray Disc 31
DVD 31
HD-DVD 31
multimedia files 30
music CD 31
video files 30
Windows Media Player file 30
power
changing plans 75
plans 75
schemes 75
printer
adding Bluetooth
sharing 54
printing
82
11, 17
31
55
documents
16
files across netwo rk 55
programs
closing 17
opening 7
restricting 82
projector
color quality
71
connecting 71
screen resolution 71
R
recording
audio file 33
CD tracks 34
recovering files and folders 12
Recycle Bin 6
deleting file s and folders 12
emptying 13
recovering files and folders
12
remote control
Windows Medi a Center 42
removing files and fo lders 6, 12,
13, 17
renaming files and folders 17
resolution
changing screen
66
restoring file s and fold ers 12
router
configuring
50
example netwo rk 44
setting up 46, 47
using 44
S
saving
documents 15
scheduling
computer use 80
screen
adjusting settings 66
resolution 71
saver 68
screen saver
changing
Search utility 13
searching
for files and folders
security
BigFix
data 58
hardware 58
lock slot 58
Norton Internet Security 59
68
13, 14
63
password 58
user accounts 58
virus protection 59
Windows Security Cen ter 61
Windows Update 62
wireless Ethernet 52
serial number 3
Shared Document s folder 73
sharing
drives
53
folders 53
printer 54
shortcuts
adding to desktop
8
closing programs 17
closing windows 17
copying 17
deleting files and folders 17
keyboard 17
pasting 17
renaming files and folde rs 17
selecting adjacent items in
17
list
selecting items in li st 17
switching between files,
folders, or programs
17
Sidebar
configuring
70
gadgets 70
software
See programs
sound
changing system
72
scheme 72
Sound Recorder
recording audio
33
speech recognition 78
Start button 6
Start menu 7
starting programs 7
subnet mask 44
entering 50
support
using 2
system identification label 3
T
taskbar 6
TCP/IP protocol
configuring 50
telephone
canceling fax 27
installing Windows Fax and
Scan
receiving and viewing faxes
23
87
Page 94

Index
27
sending fax 27
sending fax from p rogram 27
sending scanned image fax
27
setting up fax cover page
template
testing networ k 52
text to speech 78
title bar 9
transferring
files from In ternet
27
22
U
un-sharing
drives
folders 53
updating
device drivers
Norton Internet Security 60
Windows 62
user account s
adding in Windows
deleting 73
switching in Windows 73
53
2
73
V
VGA port 71
video
playing
viewing
shared drives
shared folders 54
virus
protecting ag ainst
removing 59
voice recognition 78
30
54
59
W
WAN 44
WAV file
playing 30
Web browser 20, 21
Web page 21
Web site 21
connecting to 21
downloadin g files 22
eMachines 2
wide area network (WAN) 44
window 8
changing colors 67
close button 9
closing 9, 17
maximize button 9
menu bar 9
minimize button 9
title bar 9
Windows
changing background 67
clipboard 11
Search utility 13
user account s 58
Windows DVD Maker 37
Windows Fax and Scan 23
Windows Medi a Center 40
help 3
starting 40
Windows Medi a Player
building mus ic library
creating MP3 34
creating music files 34
creating WMA files 34
editing tack info rmation 35
playing audio CD 31
playing audio file 30
playing Blu -ray Disc 31
playing DVD 31
playing HD-DVD 31
playing opt ical disc 31
viewing video file 30
Windows Security C enter
6
icon
using 59
Windows Updat e 62
wired Ethernet network 44
equipment needed 45
example 44
installing card s 46
installing drivers 46
setting up 46
wireless Ethernet network 47
connecting to 50
equipment needed 48
installing card s 49
installing drivers 49
security 52
setting up 49
WMA file
creating
editing track information 35
playing 30
Wordpad 15
workgroup
naming
World Wide Web (WWW) 21
downloadin g files 22
34
49
35
88
Page 95

Page 96

MAN ECOOPER USR GDE R2 10/07
 Loading...
Loading...