Danfoss TUB, TUBE, TCBE, TUC, TUCE Data sheet
...
Data Sheet
Thermostatic expansion valve
Type TU and TC
Thermostatic expansion valves maintain a constant superheat level at the evaporator outlet
The thermostatic expansion valves TUA/TUAE, TCAE with exchangeable orifice, TUB/TUBE/ TCBE with fixed orifice and TUC/TUCE/TCCE with fixed orifice and fixed superheat setting, are made of stainless steel and therefore especially well suited to refrigeration systems in the food industry and where aggressive environments exist. These thermostatic expansion valves have been developed and designed especially for easy and quick soldering into hermetic refrigeration systems.
The valves are offered in the following rated capacities
1. From 0.5 kW / 0.14 TR, up to 17.0 kW / 4.8 TR R407C (TU)
2. From 19.0 kW / 5.4 TR up to 28.5 kW / 8.1 TR R407C (TC)
AI308624347152en-000301

Thermostatic expansion valve, Type TU and TC
Features
•Bi-metal connections
1.Fast and easy brazing process – no wet wrap needed.
2.Braze alloys with as little as 5% Ag can be used.
•Compact, lightweight design
1.Flexible and easy integration in any system.
•Stainless steel
1.High body strength.
2.High corrosion resistance.
3.High vibration resistance
•Laser-welded power element
1.Ensures diaphragm´s structural integrity and lengthens life.
•Stainless steel capillary tube
1.Flexible lightweight capillary tube, tolerates more bending for trouble-free installation and longer life.
2.Greater resistance to vibration during operation because of low weight.
•Laser engraving
1.Durable positive valve identification; no label that peels off over time.
2.Customer-specific engraving available on request.
•Fully hermetic brazed and laser-welded design
1.Hermetic valve in accordance with EU F-gas Regulation EU 517/2014.
2.No external leakage which saves costs on maintenance and refrigerant loss.
3.Protecting the environment and climate
•Manufactured according to IATF16949
1.Quality and reliability that are second to none.
© Danfoss | Climate Solutions | 2021.03 |
AI308624347152en-000301 | 2 |

Thermostatic expansion valve, Type TU and TC
Portfolio overview
Table 1: Overview of available versions
|
Angleway |
Straightway |
||
Type |
Internal pressure equaliza |
External pressure equaliza |
Internal pressure equaliza |
External pressure equaliza |
|
tion |
tion |
tion |
tion |
|
|
|
|
|
TUB/TUBE/TCBE
Adjustable superheat
TUC/TUCE/TCCE
Non-adjustable superheat
TUA/TUAE/TCAE Adjustable superheat and exchangeable
orifice
© Danfoss | Climate Solutions | 2021.03 |
AI308624347152en-000301 | 3 |

Thermostatic expansion valve, Type TU and TC
Functions
Thermostatic expansion valves maintain a constant superheat level at the evaporator outlet. It does this by controlling the amount of refrigerant that is injected into the evaporator, taking both the evaporator load and ambient temperatures into consideration. This both optimizes the efficiency of the refrigeration system and prevents liquid refrigerant from entering the suction line, possibly causing damage to the compressor. Particularly when compared to systems that use capillary tubes, the thermostatic expansion valve will offer a significant energy saving.
Figure 1: Angleway
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
1Thermostatic element with diaphragm
2Bulb with capillary tube
3Setting spindle for adjustment of static superheat SS
4Orifice assembly
5Filter
Figure 2: Straightway
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
1Thermostatic element with diaphragm
2Bulb with capillary tube
3Setting spindle for adjustment of static superheat SS (behind valve, not visible)
4Orifice assembly
5Filter
© Danfoss | Climate Solutions | 2021.03 |
AI308624347152en-000301 | 4 |
Thermostatic expansion valve, Type TU and TC
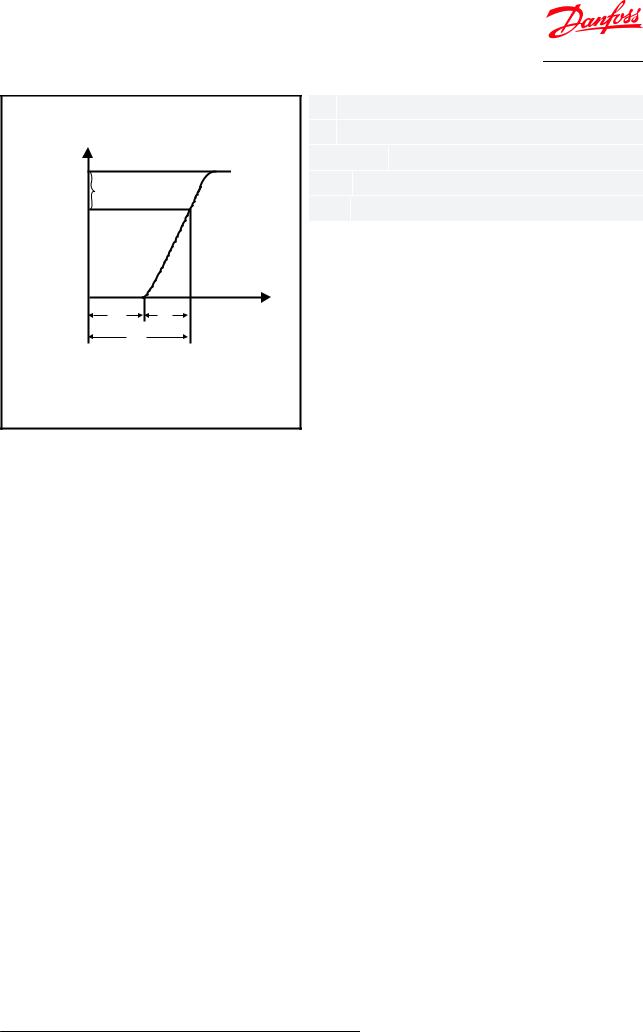
Figure 3: Superheat |
|
|
| <![if ! IE]> <![endif]>Superheat |
Q |
|
|
|
|
|
Qmax. |
|
|
min.20% |
|
|
Qnom. |
|
|
|
K |
|
SS |
OS |
|
SH |
|
SS Static superheat
OS Opening superheat
SH = SS + OS Total superheat
Qnom Rated capacity
Qmax Maximum capacity
Static superheat (SS) can be adjusted by turning the setting spindle (3), (TUB/TUBE/TCBE) Static Superheat cannot be adjusted on TUC/TUCE/TCCE.
The superheat setting is 4K for all standard valves. The opening superheat is 4K, measured from when the valve begins to open to when the valve gives its rated capacity (Qnom).
Table 2: Example
Features |
Value |
Static superheat |
SS = 4K |
Opening Superheat |
OS = 4K |
Total superheat |
SH = 4 + 4 = 8K |
|
|
Operation
Superheat
Superheat is the controlling parameter of a TXV. Superheat, measured at the evaporator outlet, is defined as the number of degrees the refrigerant vapor is heated above its saturation temperature (boiling point), at a specific pressure. Liquid entering the compressor causes serious damage. To prevent this, the TXV will maintain a certain minimum superheat. When discussing superheat in relation to TXV valve operation, the following terms are used:
Static superheat
Static superheat, SS is the superheat above which the valve will begin to open.
Opening superheat
Opening superheat, OS, is the amount of superheat above static superheat, SS, required to produce a given valve capacity.
Total superheat
Total superheat is static superheat plus opening superheat, and is what is measured at the evaporator outlet.
Subcooling
Subcooling, measured at the condenser outlet, is defined as the number of degrees a liquid refrigerant is cooled below its saturation temperature (boiling point), at a specific pressure. Subcooling is necessary to prevent flash gas forming in the liquid line. Depending on system design, various levels of subcooling may be needed. In most cases, 2 to 5K of subcooling is adequate. If flash gas forms in the liquid line, the capacity of the TXV will be greatly reduced.
© Danfoss | Climate Solutions | 2021.03 |
AI308624347152en-000301 | 5 |

Thermostatic expansion valve, Type TU and TC
Figure 4: Superheat and Subcooling
TU stainless steel technology
Figure 5: Type TU and TC
Benefits of stainless steel
The fact that the TU is an all-stainless steel expansion valve offers a number of benefits:
•Stainless steel is far more corrosionresistant than traditional valve materials.
•Stainless steel valves require no surface treatment.
•Stainless steel capillary tubes are three times stronger and twenty times more resistant to vibration than copper capillary tubes.
•Stainless steel has a greater strength- to-weight ratio, making TU valves lighter and more compact.
•Stainless steel diaphragms have greater strength and corrosion resistance for a longer life.
Danfoss precision port design
The TU thermostatic expansion valve introduces precision port design, incorporating four features that ensure superior repeatable performance over an extended valve life.
•Laser welding of the power element preserves the structural uniformity of the diaphragm, assuring consistent operation.
•A precision-machined pushrod and bushing make a practically frictionless seal with no need for a packing gland.
•The free-floating pushrod is self-aligning and eliminates binding.
•The precision-machined cone and orifice accurately meter refrigerant under all operating conditions.
High quality
The TU is manufactured on fully automated, process-monitored production lines. Cellularized computer-monitored technology ensures uniform high quality and that, when delivered, every valve meets Danfoss quality standards and customer specifications. Cellularized production also makes possible simultaneous production of large and small quantities of standard and custom version valves.
Advanced technology - fast and easy installation
The TU stainless steel thermostatic expansion valve has significant installation advantages because it is a valve
© Danfoss | Climate Solutions | 2021.03 |
AI308624347152en-000301 | 6 |

Thermostatic expansion valve, Type TU and TC
designed specifically for soldering. The TU can be installed in less than half the time required for traditional brassbodied valves. The valve connections are made of copper and stainless steel bi-metal which makes installation easy, reliable, and fast.
Figure 6: TUAE
No need for a wet cloth
Bi-metal has a very low thermal conductivity, actually only 10% that of copper, so heat applied during soldering remains largely in the copper layer of the connection tube, instead of being conducted to the valve body. External cooling is unnecessary. The result is less energy consumption and better solder quality. At the same time, the diaphragm's structural integrity is preserved.
© Danfoss | Climate Solutions | 2021.03 |
AI308624347152en-000301 | 7 |
Thermostatic expansion valve, Type TU and TC
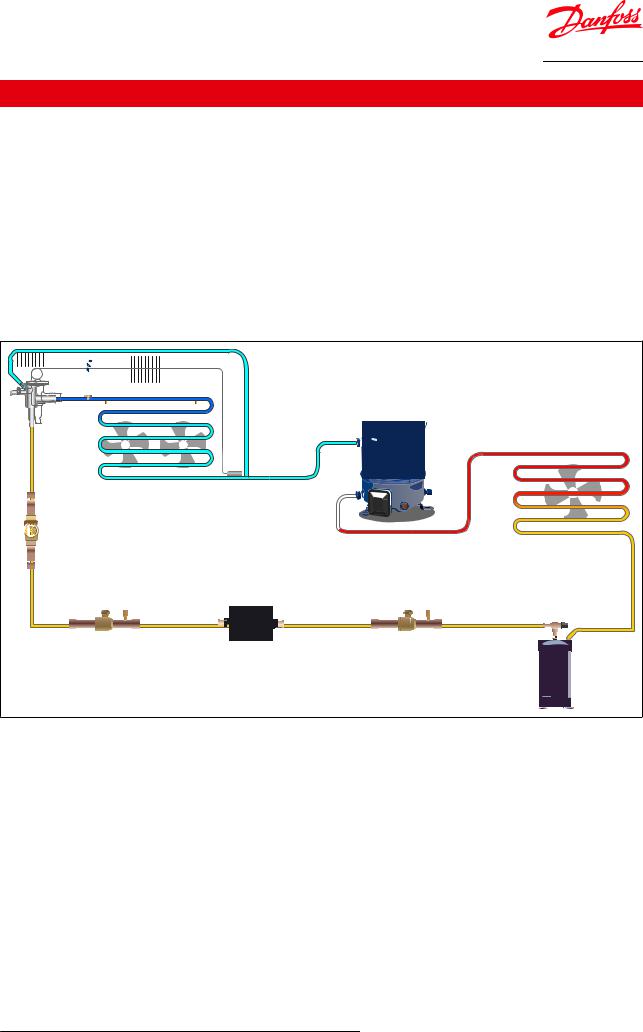
Applications
Thermostatic expansion valves regulate the amount of refrigerant that is injected into the evaporator. It does this to keep a constant superheat level at the outlet of the evaporator, thereby preventing liquid refrigerant from entering the suction line and possibly causing damage to the compressor.
Typical applications for TU and TC valves are:
•Conventional refrigeration systems
•Heat pump systems
•Air conditioning systems
•Specialty refrigeration appliances
•Liquid chillers
•Ice machines
•Transport refrigeration
Figure 7: Application Diagram
Available charges
Universal charge
This is the standard charge, used in most applications. It is characterized by a very large operational evaporating temperature range, with only small variations in static superheat across the temperature range. It is available in two temperature ranges. One for normal (-40°C to +10°C / -40°F to 50°F) and one for low (-60 to -25°C / -76°F to -13°F) temperature applications.
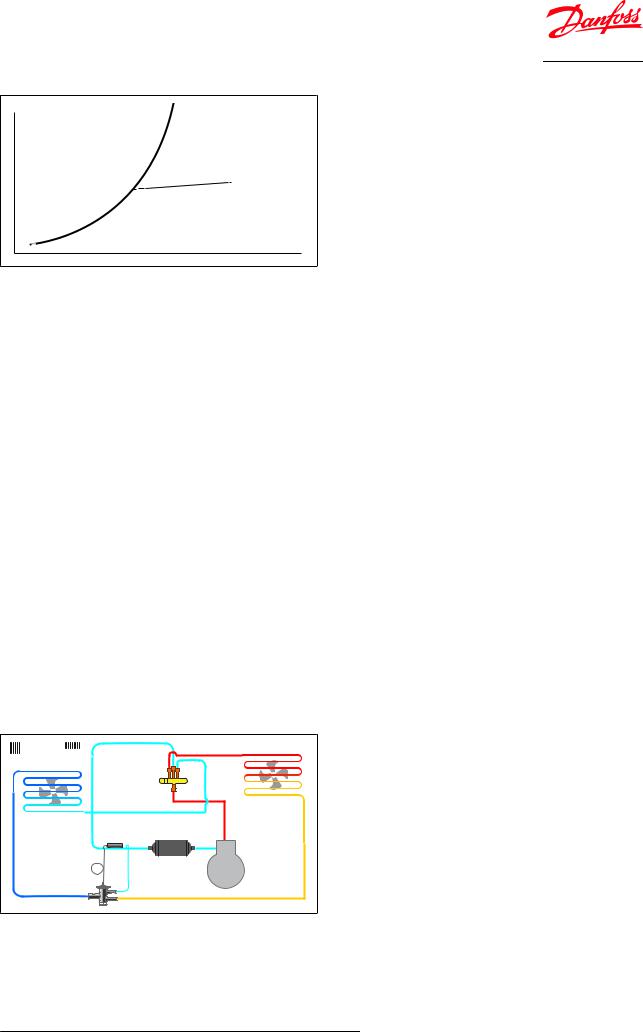
MOP charge (MOP = Maximum Operating Pressure)
The MOP charge is used to protect the compressor motor against overload during start-up. A valve with MOP charge will throttle liquid injection into the evaporator and thus prevent the evaporating pressure from rising above the specified MOP point. Above the MOP point, any increase in sensor temperature results in only minimal additional opening of the expansion valve. A number of different MOP points are available
© Danfoss | Climate Solutions | 2021.03 |
AI308624347152en-000301 | 8 |
Thermostatic expansion valve, Type TU and TC
Figure 8: MOP = Maximum Operating Pressure
<![if ! IE]><![endif]>
NOTE:
The MOP point will change if the factory superheat setting of the expansion valve is changed. If the setting is reduced, the MOP point will go up and vice versa.
MAH charge
The Danfoss Marinite Anti-Hunt (MAH) charge can be used in dynamic systems, often A/C systems. Here it reduces valve hunting during evaporator load changes, thereby helping to maintain stable system superheat and improve system performance.
F-charge
The F-charge is designed for refrigeration systems where low total superheat is required. Valves with this charge are delivered with an optimized low static superheat setting which allows for installation with no or minimal field adjustment. The F-charge also includes the Danfoss MAH function, as described above.
Ice charge
The ice charge is designed with an optimized static superheat characteristic, which allows for optimal function, particularly in Ice cubers, where low superheat is required in order to fully utilize the entire evaporator coil.
Milk charge
The milk charge is designed for use in milk cooling tanks where a limitation of the suction pressure is required, but where an MOP valve would suffer from charge migration.
Bi-flow
Bi-flow function is sometimes used in systems with 4-way reversing valves where hot gas defrosts, or heating cycles are required. Only externally equalized TU valves with orifices X to 8 and externally equalized TC valves with orifices 1 and 2 – without MOP charges, can be used in bi-flow mode. When used in reverse direction, the rated valve capacity will be reduced by up to 15%. Valves for bi-flow operation should be installed so that the normal refrigerant flow is towards the main evaporator
Figure 9: Bi-flow
|
|
| <![if ! IE]> <![endif]> |
STF |
|
4-way valve |
|
<![if ! IE]> <![endif]> |
| <![if ! IE]> <![endif]> |
|
|
<![if ! IE]> <![endif]> |
|
DML / DCL |
|
Filter drier |
|
|
Sizing example
How to select a TU or TC thermostatic expansion valve.
Example: Refrigerant: R134a
Cooling capacity: 3KW
Evaporating temperature: -10 °C
© Danfoss | Climate Solutions | 2021.03 |
AI308624347152en-000301 | 9 |
 Loading...
Loading...