ZyXEL NBG334W Users Manual
Chapter 3 Connection Wizard
Table 11 Wizard Step 2: Basic (WEP) Security
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Next Click Next to proceed to the next screen.
Exit Click Exit to close the wizard screen without saving.
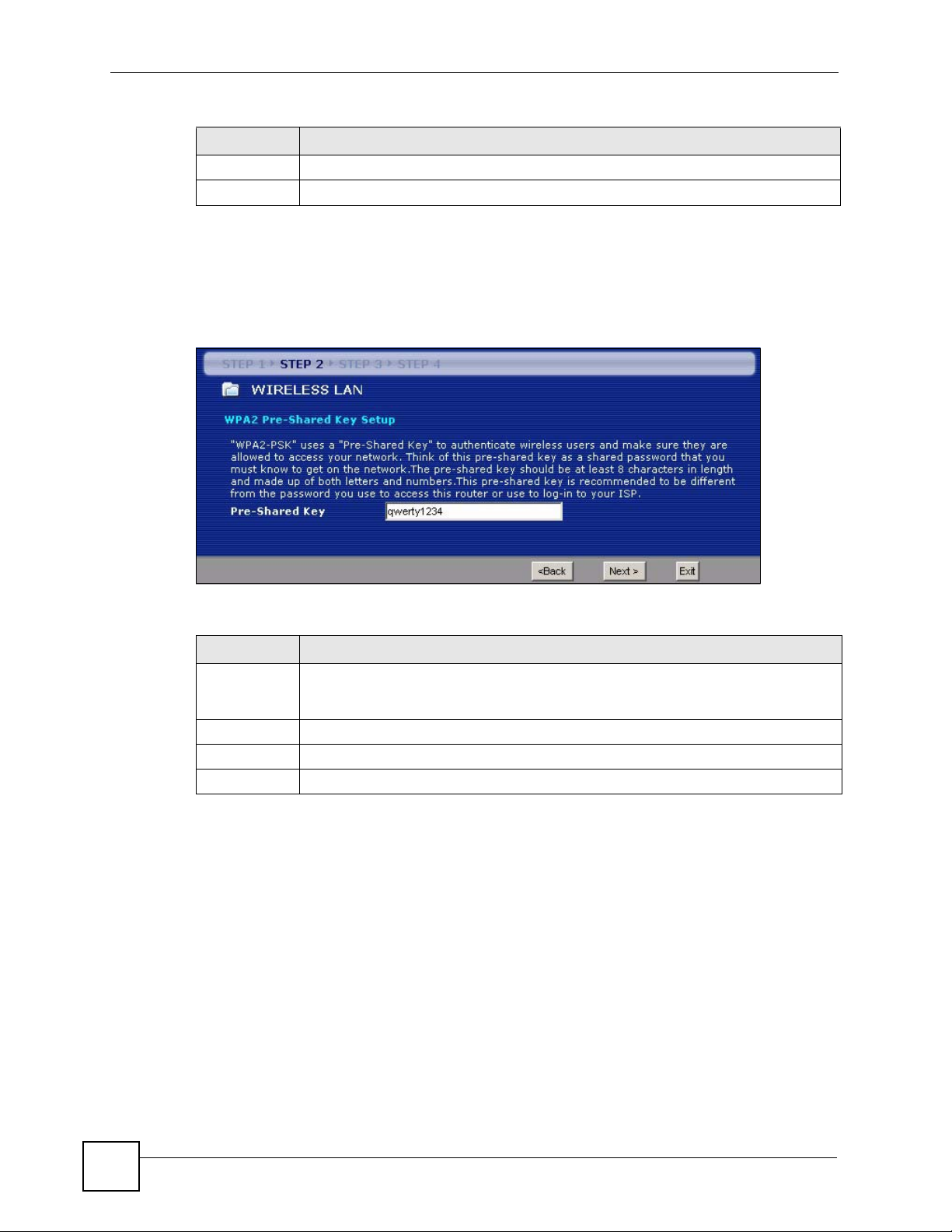
3.3.2 Extend (WPA-PSK or WPA2-PSK) Security
Choose Extend (WPA-PSK) or Extend (WPA2-PSK) security in the Wireless LAN setup
screen to set up a Pre-Shared Key.
Figure 17 Wizard Step 2: Extend (WPA-PSK or WPA2-PSK) Security
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 12 Wizard Step 2: Extend (WPA-PSK or WPA2-PSK) Security
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Pre-Shared
Key
Back Click Back to display the previous screen.
Next Click Next to proceed to the next screen.
Exit Click Exit to close the wizard screen without saving.
Type from 8 to 63 case-sensitive ASCII characters. You can set up the most secure
wireless connection by configuring WPA in the wireless LAN screens. You need to
configure an authentication server to do this.
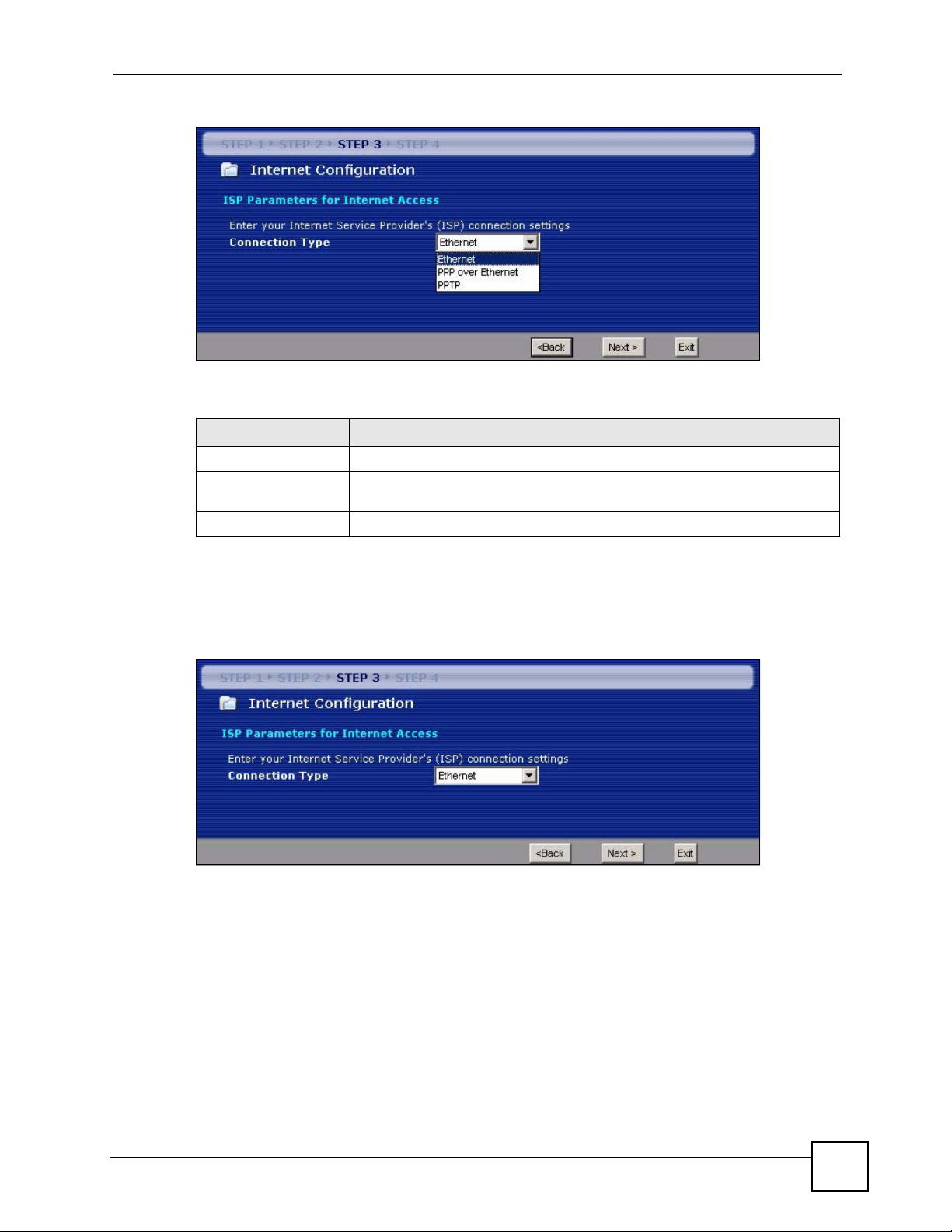
3.4 Connection Wizard: STEP 3: Internet Configuration
The NBG334W offers three Internet connection types. They are Ethernet, PPP over
Ethernet or PPTP. The wizard attempts to detect which WAN connection type you are using.
If the wizard does not detect a connection type, you must select one from the drop-down list
box. Check with your ISP to make sure you use the correct type.
This wizard screen varies according to the connection type that you select.
50
NBG334W User’s Guide
Chapter 3 Connection Wizard
Figure 18 Wizard Step 3: ISP Parameters.
The following table describes the labels in this screen,
Table 13 Wizard Step 3: ISP Parameters
CONNECTION TYPE DESCRIPTION
Ethernet Select the Ethernet option when the WAN port is used as a regular Ethernet.
PPPoE
PPTP Select the PPTP option for a dial-up connection.
Select the PPP over Ethernet option for a dial-up connection. If your ISP
gave you a an IP address and/or subnet mask, then select PPTP.
3.4.1 Ethernet Connection
Choose Ethernet when the WAN port is used as a regular Ethernet.
Figure 19 Wizard Step 3: Ethernet Connection
3.4.2 PPPoE Connection
Point-to-Point Protocol over Ethernet (PPPoE) functions as a dial-up connection. PPPoE is an
IETF (Internet Engineering Task Force) standard specifying how a host personal computer
interacts with a broadband modem (for example DSL, cable, wireless, etc.) to achieve access
to high-speed data networks.
For the service provider, PPPoE offers an access and authentication method that works with
existing access control systems (for instance, RADIUS).
NBG334W User’s Guide
51
Chapter 3 Connection Wizard
One of the benefits of PPPoE is the ability to let end users access one of multiple network
services, a function known as dynamic service selection. This enables the service provider to
easily create and offer new IP services for specific users.
Operationally, PPPoE saves significant effort for both the subscriber and the ISP/carrier, as it
requires no specific configuration of the broadband modem at the subscriber’s site.
By implementing PPPoE directly on the NBG334W (rather than individual computers), the
computers on the LAN do not need PPPoE software installed, since the NBG334W does that
part of the task. Furthermore, with NAT, all of the LAN's computers will have Internet access.
Refer to the appendix for more information on PPPoE.
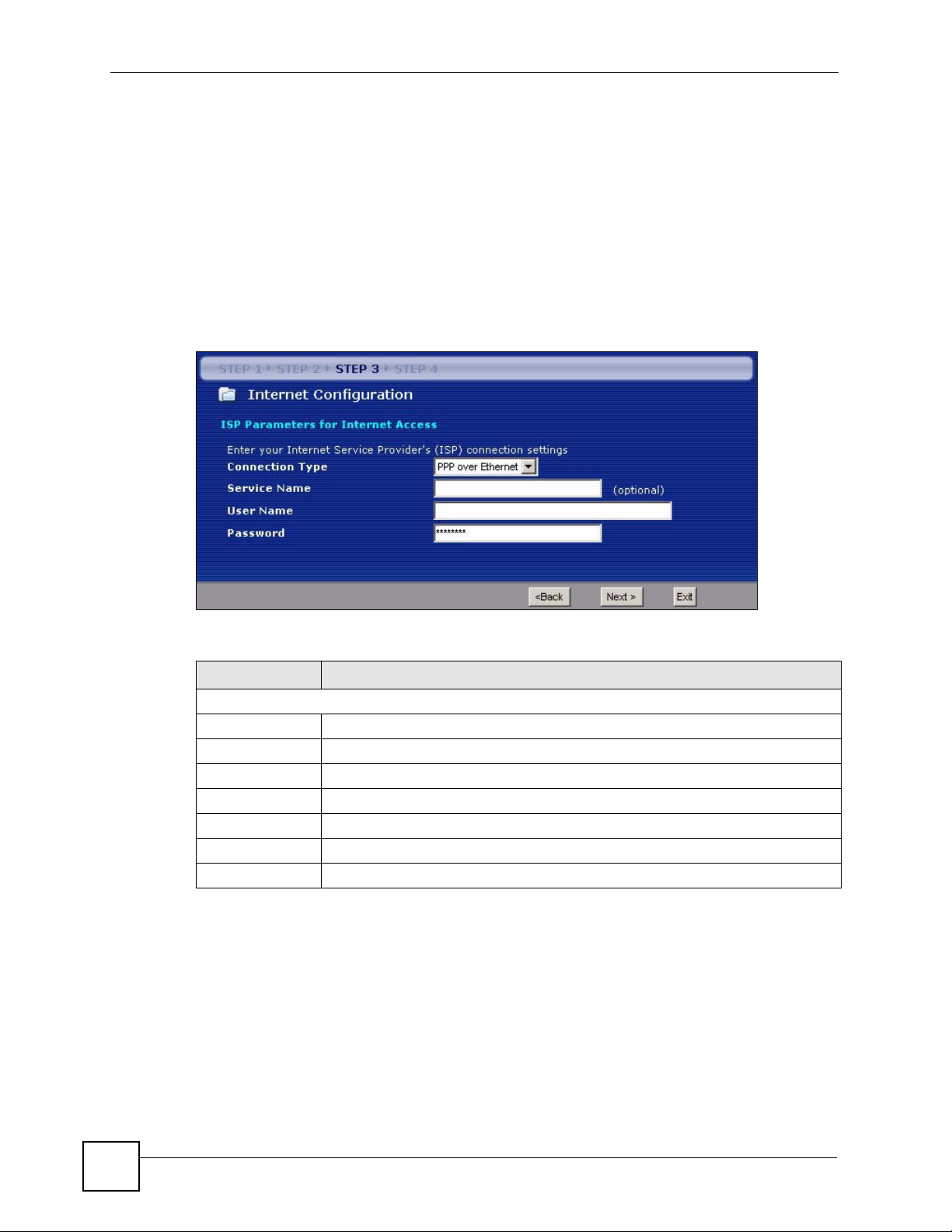
Figure 20 Wizard Step 3: PPPoE Connection
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 14 Wizard Step 3: PPPoE Connection
LABEL DESCRIPTION
ISP Parameter for Internet Access
Connection Type
Service Name Type the name of your service provider.
User Name Type the user name given to you by your ISP.
Password Type the password associated with the user name above.
Back Click Back to return to the previous screen.
Next Click Next to continue.
Exit Click Exit to close the wizard screen without saving.
Select the PPP over Ethernet option for a dial-up connection.
3.4.3 PPTP Connection
Point-to-Point Tunneling Protocol (PPTP) is a network protocol that enables transfers of data
from a remote client to a private server, creating a Virtual Private Network (VPN) using TCP/
IP-based networks.
PPTP supports on-demand, multi-protocol, and virtual private networking over public
networks, such as the Internet.
52
Refer to the appendix for more information on PPTP.
NBG334W User’s Guide
Chapter 3 Connection Wizard
" The NBG334W supports one PPTP server connection at any given time.
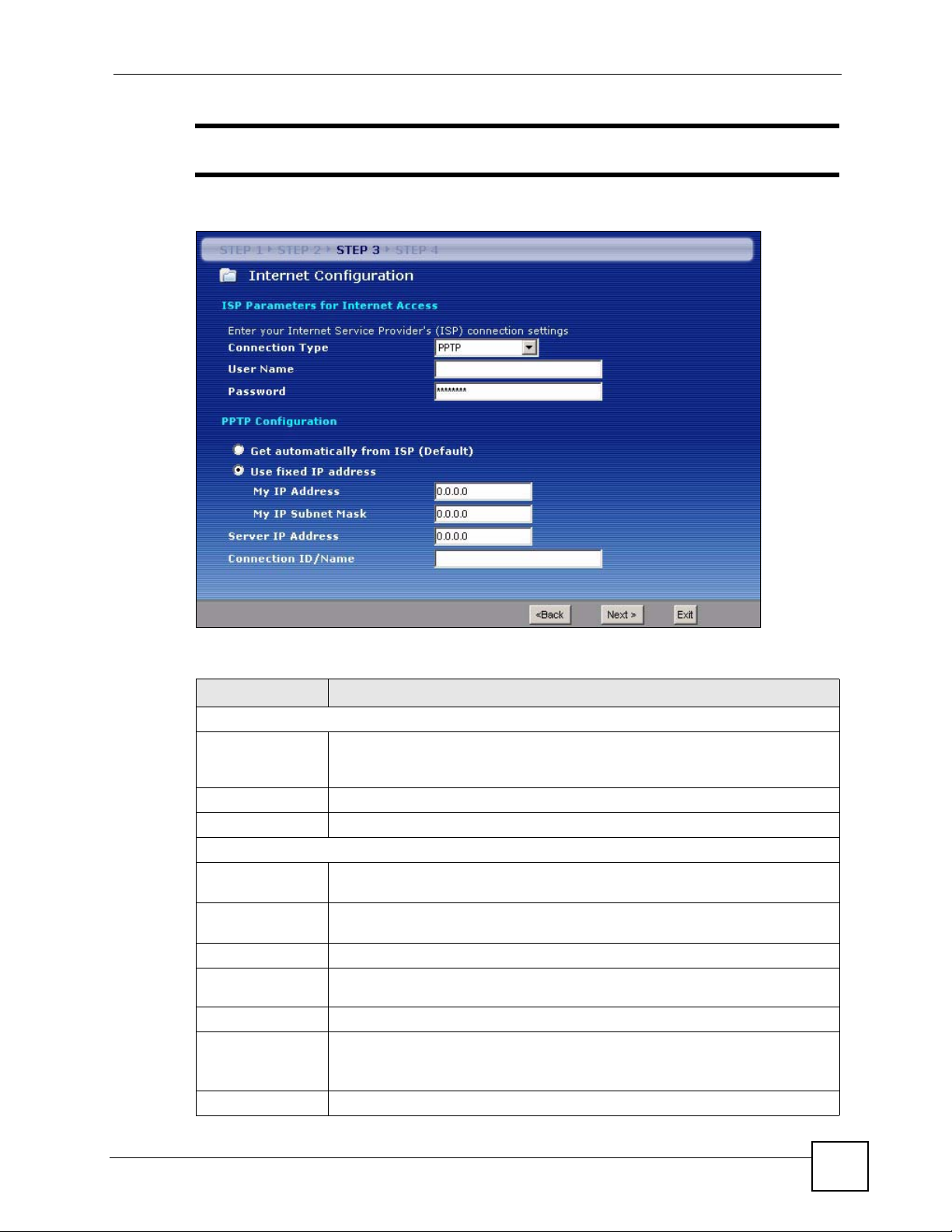
Figure 21 Wizard Step 3: PPTP Connection
The following table describes the fields in this screen
Table 15 Wizard Step 3: PPTP Connection
LABEL DESCRIPTION
ISP Parameters for Internet Access
Connection Type Select PPTP from the drop-down list box. To configure a PPTP client, you must
User Name Type the user name given to you by your ISP.
Password Type the password associated with the User Name above.
PPTP Configuration
Get automatically
from ISP
Use fixed IP
address
My IP Address Type the (static) IP address assigned to you by your ISP.
My IP Subnet
Mask
Server IP Address Type the IP address of the PPTP server.
Connection ID/
Name
Back Click Back to return to the previous screen.
configure the User Name and Password fields for a PPP connection and the
PPTP parameters for a PPTP connection.
Select this radio button if your ISP did not assign you a fixed IP address.
Select this radio button, provided by your ISP to give the NBG334W a fixed,
unique IP address.
Type the subnet mask assigned to you by your ISP (if given).
Enter the connection ID or connection name in this field. It must follow the "c:id"
and "n:name" format. For example, C:12 or N:My ISP.
This field is optional and depends on the requirements of your ISP.
NBG334W User’s Guide
53
Chapter 3 Connection Wizard
Table 15 Wizard Step 3: PPTP Connection
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Next Click Next to continue.
Exit Click Exit to close the wizard screen without saving.
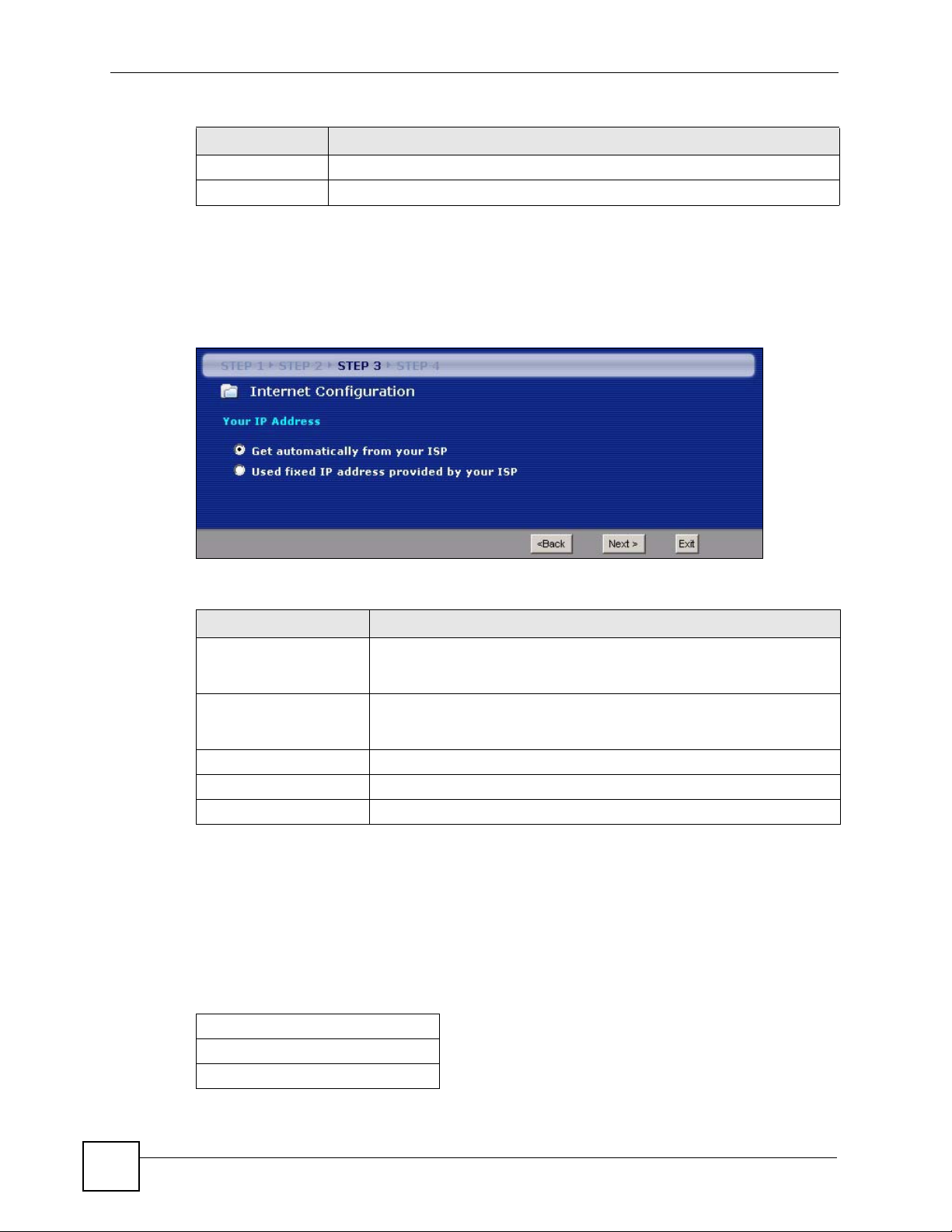
3.4.4 Your IP Address
The following wizard screen allows you to assign a fixed IP address or give the NBG334W an
automatically assigned IP address depending on your ISP.
Figure 22 Wizard Step 3: Your IP Address
The following table describes the labels in this screen
Table 16 Wizard Step 3: Your IP Address
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Get automatically from
your ISP
Use fixed IP address
provided by your ISP
Back Click Back to return to the previous screen.
Next Click Next to continue.
Exit Click Exit to close the wizard screen without saving.
Select this option If your ISP did not assign you a fixed IP address. This is
the default selection. If you choose this option, skip directly to section
3.4.9.
Select this option if you were given IP address and/or DNS server settings
by the ISP. The fixed IP address should be in the same subnet as your
broadband modem or router.
3.4.5 WAN IP Address Assignment
Every computer on the Internet must have a unique IP address. If your networks are isolated
from the Internet, for instance, only between your two branch offices, you can assign any IP
addresses to the hosts without problems. However, the Internet Assigned Numbers Authority
(IANA) has reserved the following three blocks of IP addresses specifically for private
networks.
Table 17 Private IP Address Ranges
10.0.0.0 - 10.255.255.255
172.16.0.0 - 172.31.255.255
192.168.0.0 - 192.168.255.255
54
NBG334W User’s Guide

Chapter 3 Connection Wizard
You can obtain your IP address from the IANA, from an ISP or have it assigned by a private
network. If you belong to a small organization and your Internet access is through an ISP, the
ISP can provide you with the Internet addresses for your local networks. On the other hand, if
you are part of a much larger organization, you should consult your network administrator for
the appropriate IP addresses.
" Regardless of your particular situation, do not create an arbitrary IP address;
always follow the guidelines above. For more information on address
assignment, please refer to RFC 1597, Address Allocation for Private Internets
and RFC 1466, Guidelines for Management of IP Address Space.
3.4.6 IP Address and Subnet Mask
Similar to the way houses on a street share a common street name, so too do computers on a
LAN share one common network number.
Where you obtain your network number depends on your particular situation. If the ISP or
your network administrator assigns you a block of registered IP addresses, follow their
instructions in selecting the IP addresses and the subnet mask.
If the ISP did not explicitly give you an IP network number, then most likely you have a single
user account and the ISP will assign you a dynamic IP address when the connection is
established. The Internet Assigned Number Authority (IANA) reserved this block of addresses
specifically for private use; please do not use any other number unless you are told otherwise.
Let's say you select 192.168.1.0 as the network number; which covers 254 individual
addresses, from 192.168.1.1 to 192.168.1.254 (zero and 255 are reserved). In other words, the
first three numbers specify the network number while the last number identifies an individual
computer on that network.
Once you have decided on the network number, pick an IP address that is easy to remember,
for instance, 192.168.1.1, for your NBG334W, but make sure that no other device on your
network is using that IP address.
The subnet mask specifies the network number portion of an IP address. Your NBG334W will
compute the subnet mask automatically based on the IP address that you entered. You don't
need to change the subnet mask computed by the NBG334W unless you are instructed to do
otherwise.
3.4.7 DNS Server Address Assignment
Use DNS (Domain Name System) to map a domain name to its corresponding IP address and
vice versa, for instance, the IP address of www.zyxel.com is 204.217.0.2. The DNS server is
extremely important because without it, you must know the IP address of a computer before
you can access it.
The NBG334W can get the DNS server addresses in the following ways.
1 The ISP tells you the DNS server addresses, usually in the form of an information sheet,
when you sign up. If your ISP gives you DNS server addresses, enter them in the DNS
Server fields in the Wizard and/or WAN > Internet Connection screen.
NBG334W User’s Guide
55
Chapter 3 Connection Wizard
2 If the ISP did not give you DNS server information, leave the DNS Server fields set to
0.0.0.0 in the Wizard screen and/or set to From ISP in the WAN > Internet
Connection screen for the ISP to dynamically assign the DNS server IP addresses.
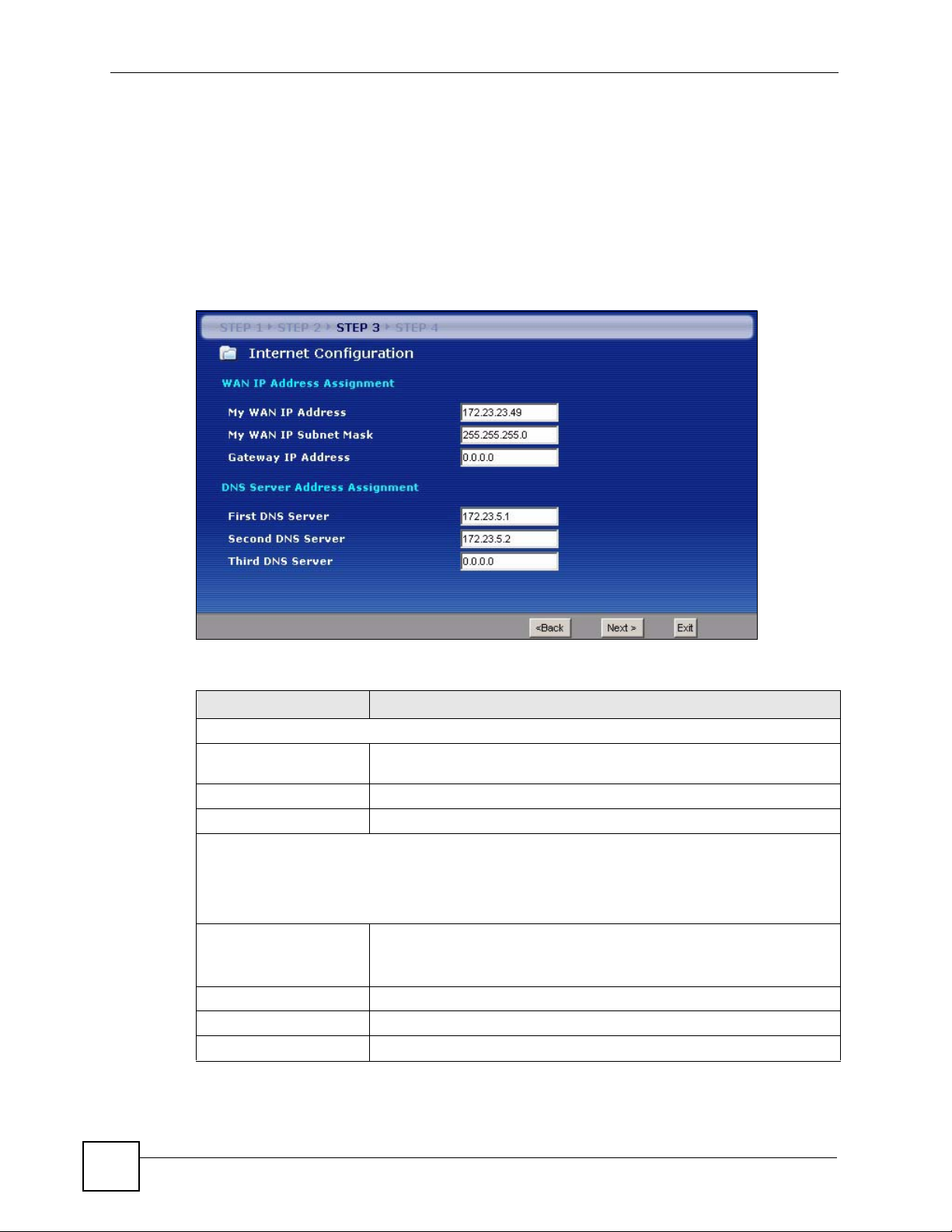
3.4.8 WAN IP and DNS Server Address Assignment
The following wizard screen allows you to assign a fixed WAN IP address and DNS server
addresses.
Figure 23 Wizard Step 3: WAN IP and DNS Server Addresses
The following table describes the labels in this screen
Table 18 Wizard Step 3: WAN IP and DNS Server Addresses
LABEL DESCRIPTION
WAN IP Address Assignment
My WAN IP Address Enter your WAN IP address in this field. The WAN IP address should be in
the same subnet as your DSL/Cable modem or router.
My WAN IP Subnet Mask Enter the IP subnet mask in this field.
Gateway IP Address Enter the gateway IP address in this field.
System DNS Server Address Assignment (if applicable)
DNS (Domain Name System) is for mapping a domain name to its corresponding IP address and vice
versa. The DNS server is extremely important because without it, you must know the IP address of a
computer before you can access it. The NBG334W uses a system DNS server (in the order you specify
here) to resolve domain names for DDNS and the time server.
First DNS Server
Second DNS Server
Third DNS Server
Back Click Back to return to the previous screen.
Next Click Next to continue.
Exit Click Exit to close the wizard screen without saving.
Enter the DNS server's IP address in the fields provided.
If you do not configure a system DNS server, you must use IP addresses
when configuring DDNS and the time server.
56
NBG334W User’s Guide
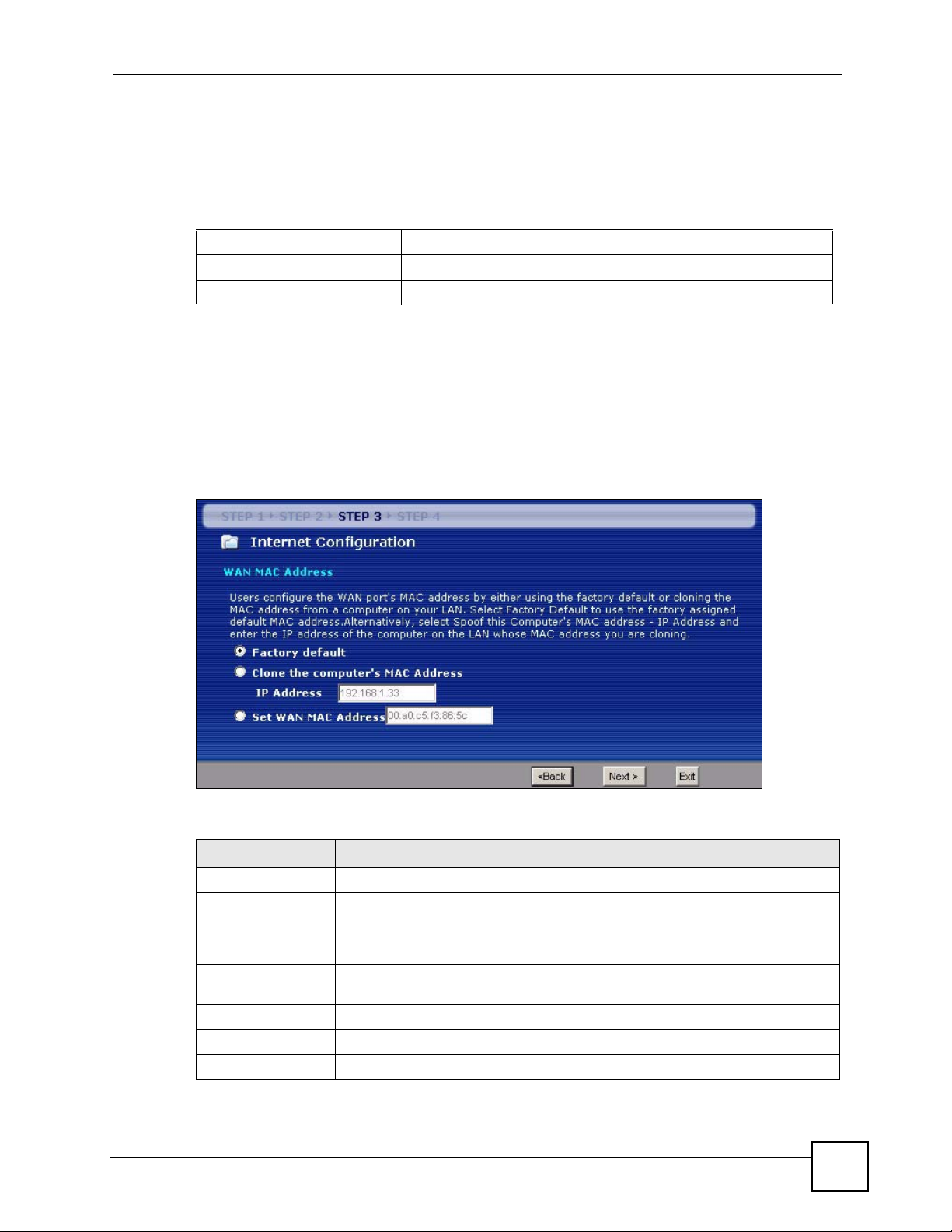
3.4.9 WAN MAC Address
Every Ethernet device has a unique MAC (Media Access Control) address. The MAC address
is assigned at the factory and consists of six pairs of hexadecimal characters, for example,
00:A0:C5:00:00:02.
Table 19 Example of Network Properties for LAN Servers with Fixed IP Addresses
Choose an IP address 192.168.1.2-192.168.1.32; 192.168.1.65-192.168.1.254.
Subnet mask 255.255.255.0
Gateway (or default route) 192.168.1.1(NBG334W LAN IP)
This screen allows users to configure the WAN port's MAC address by either using the
NBG334W’s MAC address, copying the MAC address from a computer on your LAN or
manually entering a MAC address. Once it is successfully configured, the address will be
copied to the "rom" file (ZyNOS configuration file). It will not change unless you change the
setting or upload a different "rom" file. It is advisable to clone the MAC address from a
computer on your LAN even if your ISP does not presently require MAC address
authentication.
Figure 24 Wizard Step 3: WAN MAC Address
Chapter 3 Connection Wizard
The following table describes the fields in this screen.
Table 20 Wizard Step 3: WAN MAC Address
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Factory Default Select Factory Default to use the factory assigned default MAC address.
Clone the
computer’s MAC
address
Set WAN MAC
Address
Back Click Back to return to the previous screen.
Next Click Next to continue.
Exit Click Exit to close the wizard screen without saving.
NBG334W User’s Guide
Select this option and enter the IP address of the computer on the LAN whose
MAC you are cloning. It is advisable to clone the MAC address from a computer
on your LAN even if your ISP does not presently require MAC address
authentication.
Select this option and enter the MAC address you want to use.
57
Chapter 3 Connection Wizard
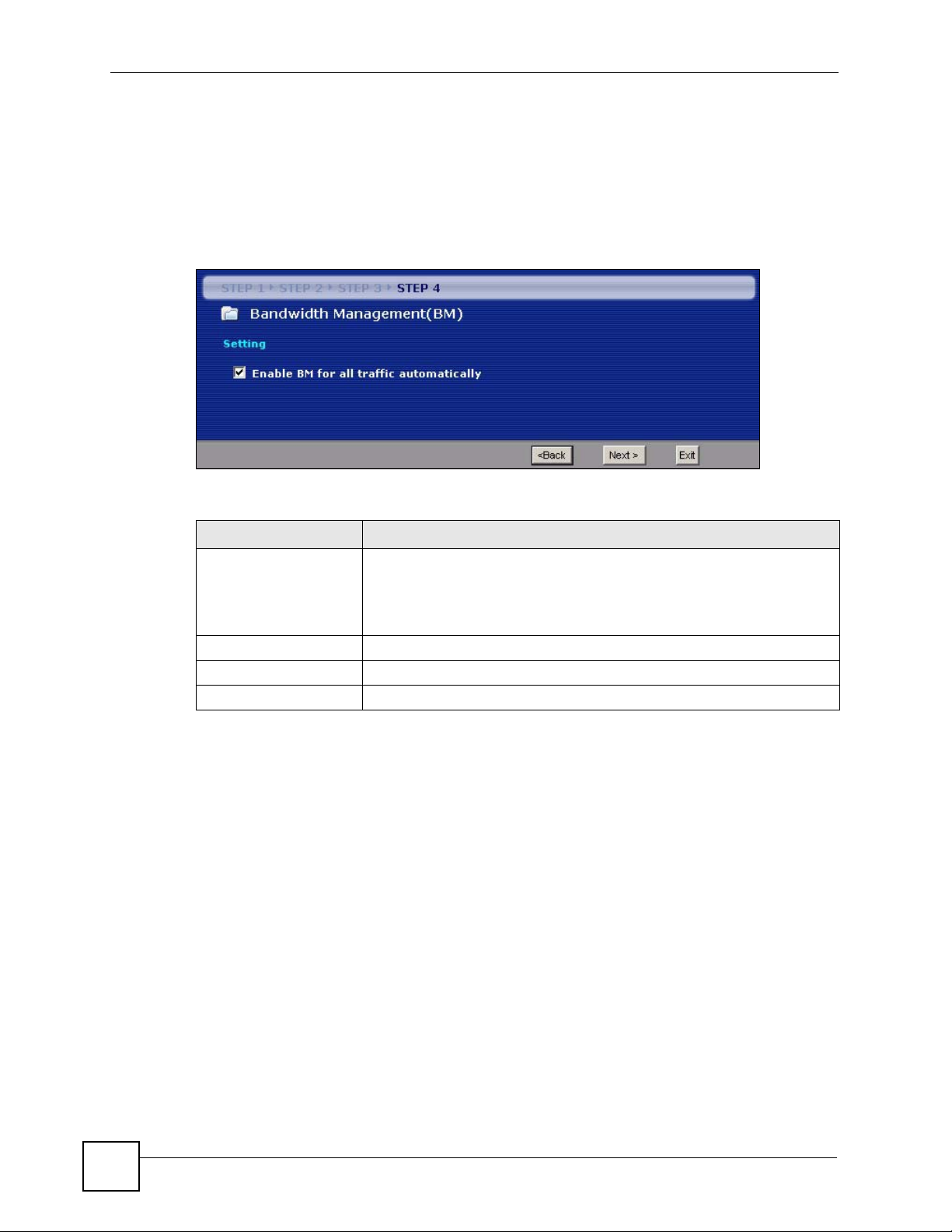
3.5 Connection Wizard: STEP 4: Bandwidth management
Bandwidth management allows you to control the amount of bandwidth going out through the
NBG334W’s WAN, LAN or WLAN port and prioritize the distribution of the bandwidth
according to the traffic type. This helps keep one service from using all of the available
bandwidth and shutting out other users.
Figure 25 Wizard Step 4: Bandwidth Management
The following fields describe the label in this screen.
Table 21 Wizard Step 4: Bandwidth Management
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Enable BM for all traffic
automatically
Back Click Back to return to the previous screen.
Next Click Next to continue.
Exit Click Exit to close the wizard screen without saving.
Select the check box to have the NBG334W apply bandwidth management
to traffic going out through the NBG334W’s WAN, LAN, HomePlug AV or
WLAN port. Bandwidth is allocated according to the traffic type
automatically. Real-time packets, such as VoIP traffic always get higher
priority.
3.6 Connection Wizard Complete
Click Apply to save your configuration.
58
NBG334W User’s Guide
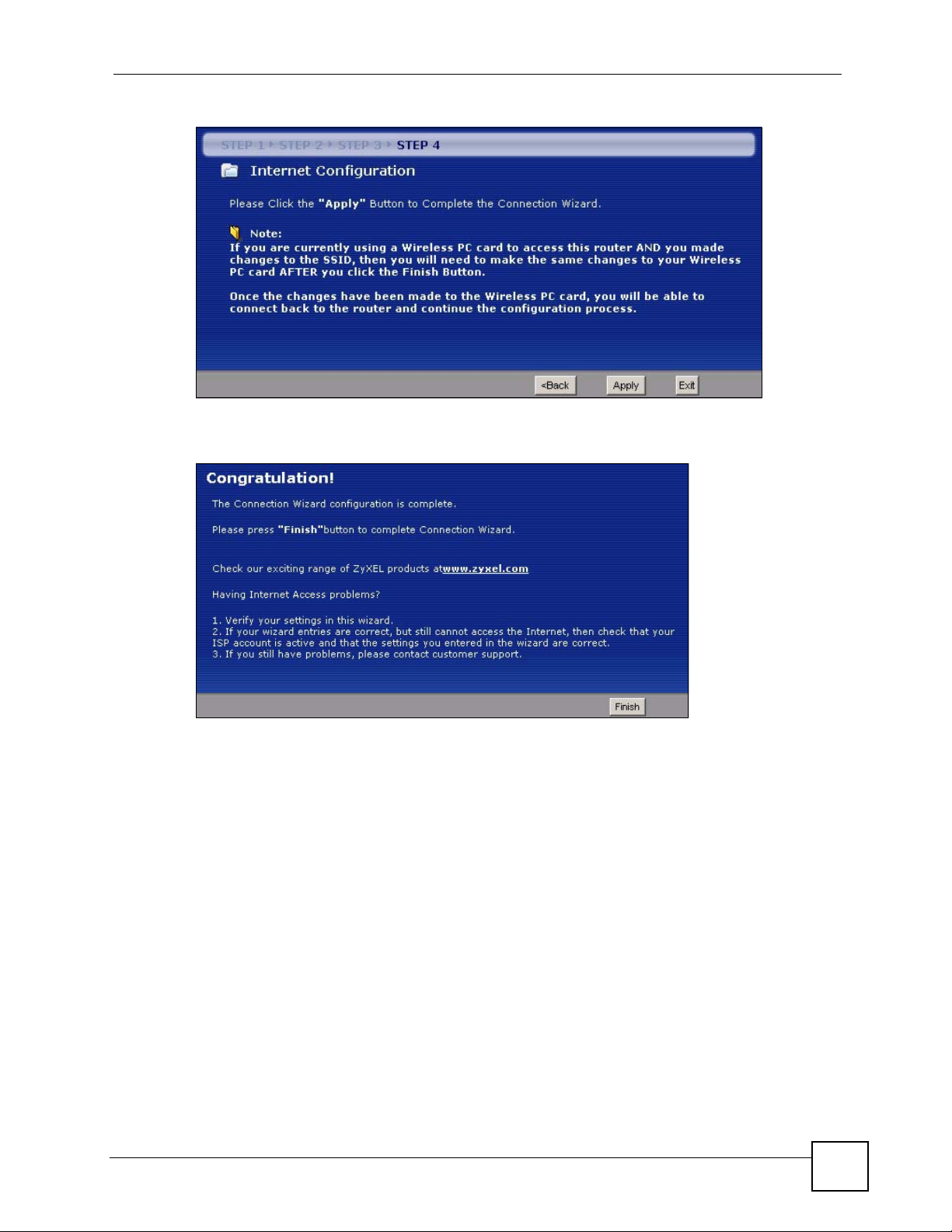
Chapter 3 Connection Wizard
Figure 26 Connection Wizard Save
Follow the on-screen instructions and click Finish to complete the wizard setup.
Figure 27 Connection Wizard Complete
Well done! You have successfully set up your NBG334W to operate on your network and
access the Internet.
NBG334W User’s Guide
59

Chapter 3 Connection Wizard
60
NBG334W User’s Guide
CHAPTER 4
AP Mode
This chapter discusses how to configure settings while your NBG334W is set to AP Mode.
Many screens that are available in Router Mode are not available in AP Mode.
" See Chapter 6 on page 89 for an example of setting up a wireless network in
AP mode.
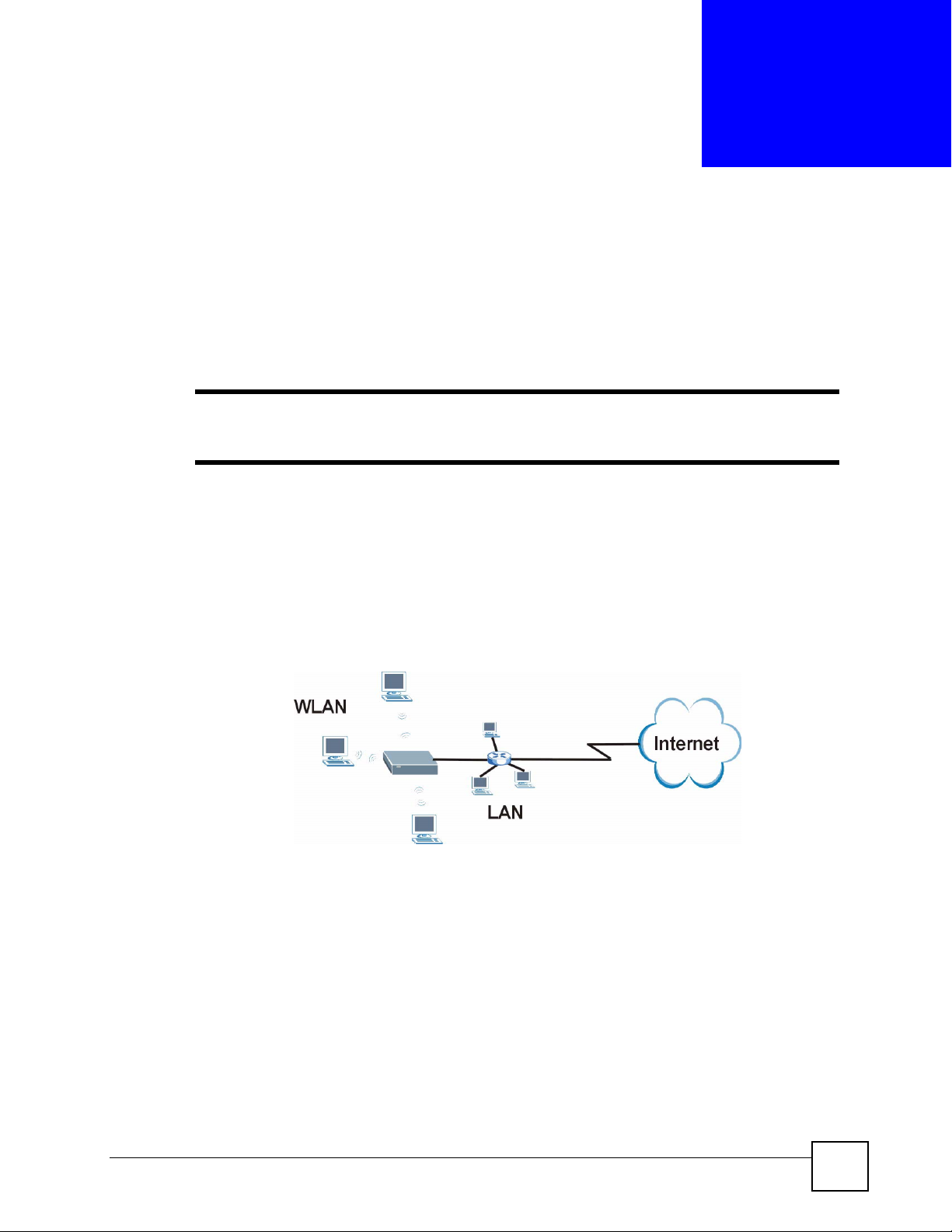
4.1 AP Mode Overview
Use your NBG334W as an AP if you already have a router or gateway on your network. In this
mode your device bridges a wired network (LAN) and wireless LAN (WLAN) in the same
subnet. See the figure below for an example.
Figure 28 Wireless Internet Access in AP Mode
4.2 Setting your NBG334W to AP Mode
1 Log into the web configurator if you haven’t already. See the Quick start Guide for
instructions on how to do this.
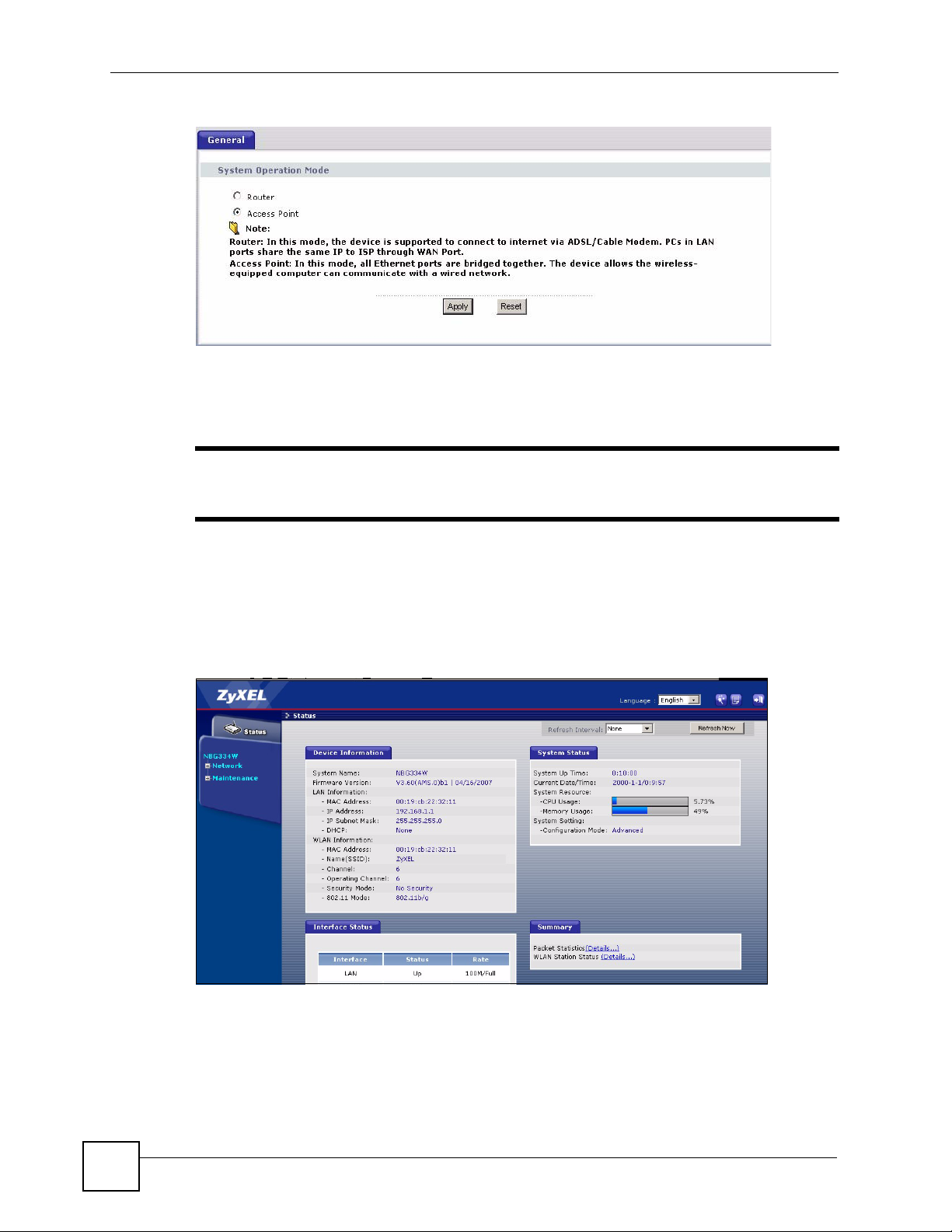
2 To set your NBG334W to AP Mode, go to Maintenance > Sys OP Mode > General
and select Access Point.
NBG334W User’s Guide
61
Chapter 4 AP Mode
Figure 29 Maintenance > Sys OP Mode > General
3 A pop-up appears providing information on this mode. Click OK in the pop-up message
window. (See Section 22.2 on page 200 for more information on the pop-up.) Click
Apply. Your NBG334W is now in AP Mode.
" You do not have to log in again or restart your device when you change
modes.
4.3 The Status Screen in AP Mode
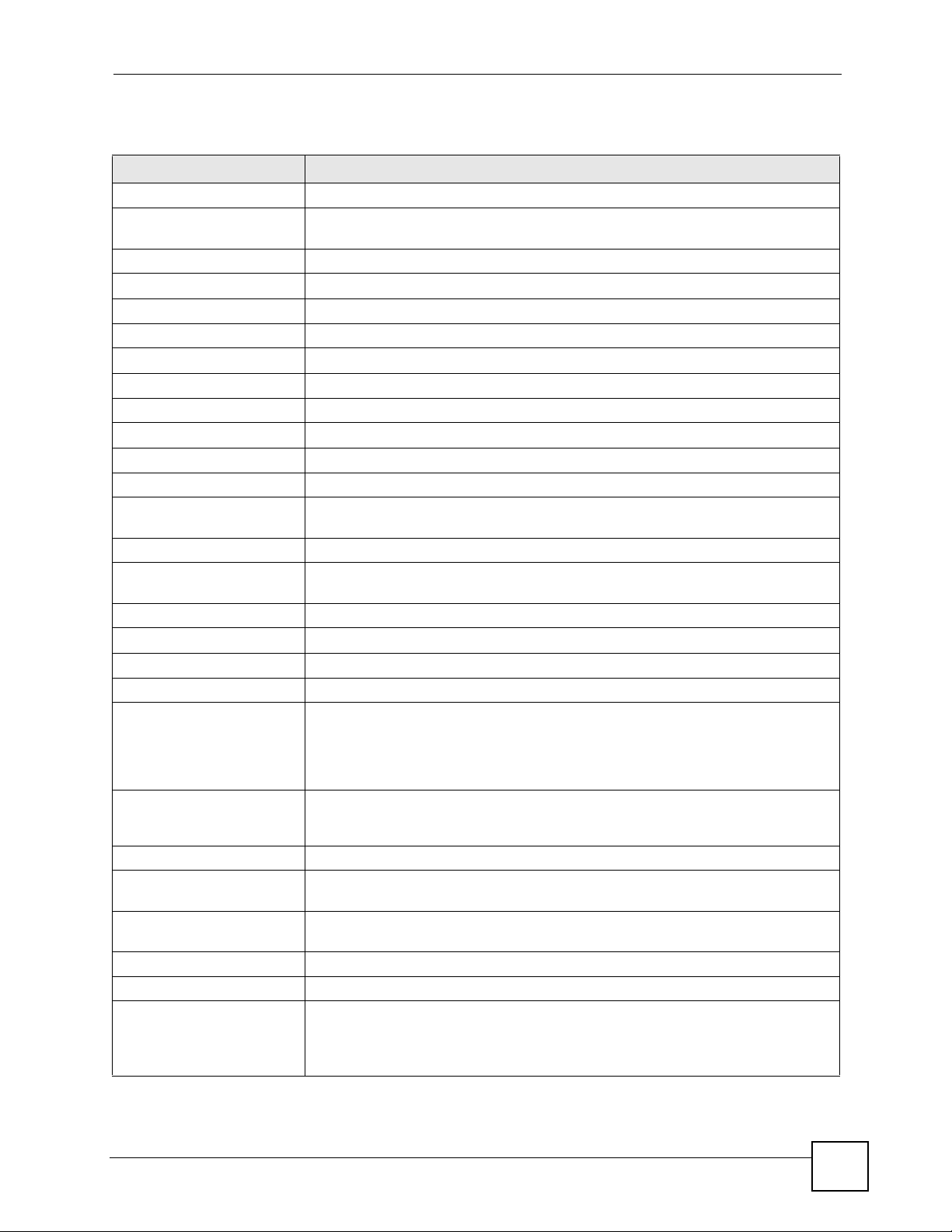
Click on Status. The screen below shows the status screen in AP Mode.
Figure 30 Status: AP Mode
62
NBG334W User’s Guide
Chapter 4 AP Mode
The following table describes the labels shown in the Status screen.
Table 22 Web Configurator Status Screen
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Device Information
System Name This is the System Name you enter in the Maintenance > System > General
screen. It is for identification purposes.
Firmware Version This is the firmware version and the date created.
LAN Information
- MAC Address This shows the LAN Ethernet adapter MAC Address of your device.
- IP Address This shows the LAN port’s IP address.
- IP Subnet Mask This shows the LAN port’s subnet mask.
- DHCP This shows the LAN port’s DHCP role - Client or None.
WLAN Information
- MAC Address This shows the wireless adapter MAC Address of your device.
- Name (SSID) This shows a descriptive name used to identify the NBG334W in the wireless LAN.
- Channel This shows the channel number which you select manually.
- Operating Channel This shows the channel number which the NBG334W is currently using over the
wireless LAN.
- Security Mode This shows the level of wireless security the NBG334W is using.
- 802.11 Mode This shows the IEEE 802.11 standard that the NBG334W supports. Wireless clients
must support the same standard in order to be able to connect to the NBG334W
System Status
System Uptime This is the total time the NBG334W has been on.
Current Date/Time This field displays your NBG334W’s present date and time.
System Resource
- CPU Usage This displays what percentage of the NBG334W’s processing ability is currently
used. When this percentage is close to 100%, the NBG334W is running at full load,
and the throughput is not going to improve anymore. If you want some applications to
have more throughput, you should turn off other applications (for example, using
bandwidth management.
- Memory Usage This shows what percentage of the heap memory the NBG334W is using. Heap
memory refers to the memory that is not used by ZyNOS (ZyXEL Network Operating
System) and is thus available for running processes like NAT and the firewall.
System Setting
- Configuration Mode This shows whether the advanced screens of each feature are turned on
(Advanced) or not (Basic).
- System Operation Mode This shows whether the system is configured to connect to the Internet in Router
Mode or Access Point Mode.
Interface Status
Interface This displays the NBG334W port types. The port types are: LAN and WLAN.
Status For the LAN port, this field displays Down (line is down) or Up (line is up or
connected).
For the WLAN, it displays Up when the WLAN is enabled or Down when the WLAN
is disabled.
NBG334W User’s Guide
63

Chapter 4 AP Mode
Table 22 Web Configurator Status Screen (continued)
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Rate For the LAN ports, this displays the port speed and duplex setting or N/A when the
line is disconnected.
For the WLAN, it displays the maximum transmission rate when the WLAN is
enabled and N/A when the WLAN is disabled.
Summary
Any IP Table Use this screen to view details of IP addresses assigned to devices not in the same
subnet as the NBG334W.
Packet Statistics Use this screen to view port status and packet specific statistics.
WLAN Station Status Use this screen to view the wireless stations that are currently associated to the
NBG334W.
4.3.1 Navigation Panel
Use the menu in the navigation panel to configure NBG334W features in AP Mode.
The following screen and table show the features you can configure in AP Mode.
Figure 31 Menu: AP Mode
64
The following table describes the sub-menus.
Table 23 Screens Summary
LINK TAB FUNCTION
Status This screen shows the NBG334W’s general device, system and
interface status information. Use this screen to access the wizard,
and summary statistics tables.
Network
Wireless
LAN
General Use this screen to configure wireless LAN.
MAC Filter Use the MAC filter screen to configure the NBG334W to block
access to devices or block the devices from accessing the
NBG334W.
Advanced This screen allows you to configure advanced wireless settings.
QoS Use this screen to configure Wi-Fi Multimedia Quality of Service
(WMM QoS). WMM QoS allows you to prioritize wireless traffic
according to the delivery requirements of individual services.
NBG334W User’s Guide
 Loading...
Loading...