Panasonic SBWA-520-EB, SBWA-520-EG Service manual

Table Of Contents
COVER
1 Safety Precautions PV
1.1 GENERAL GUIDELINES
1.1.1 LEAKAGE CURRENT COLD CHECK
1.1.2 LEAKAGE CURRENT HOT CHECK (See Figure 1.)
2 Handling the Lead-free Solder
2.1 About lead free solder (PbF)
3 Before Repair and Adjustment
4 Protection Circuitry
5 Connection of the Speaker Cables PV
6 Disassembly Procedure PV
6.1 Disassembly flow chart
6.2 Disassembly of the Speaker Unit and Checking of the P.C.B.s.
7 Connection of the Speaker Wiring PV
8 Block Diagram
9 Schematic Diagram
10 Printed Circuit Board
11 Wiring Connection Diagram
12 Illustration of IC ’ s, Transistors and Diodes
13 Parts Location and Replacement Parts List
13.1 Cabinet
13.1.1 Cabinet Parts Location
13.1.2 Cabinet Parts List
13.2 Electrical Parts List
13.3 Packing Materials & Accessories Parts List
13.4 Packaging

Service Manual
TOP NEXT
ORDER NO. MD0402046C2
Active Subwoofer System
●SB-WA520EB SB-WA520EG
Colour
(S)...Silver Type
Specification |
|
Active subwoofer |
|
Type |
1 way, 1 speaker system (Bass reflex) |
Woofer |
17 cm cone type |
Impedance |
4Ω |
Output sound pressure |
80 dB/W (1.0 m) |
Frequency range |
32 Hz-220 Hz (-16 dB) |
|
36 Hz-190 Hz (-10 dB) |
Dimensions (W x H x D) |
209 x 361 x 463 mm |
Mass |
11 kg |
General |
|
Power supply |
AC 230-240 V, 50 Hz (EB) |
|
AC 230 V, 50 Hz (EG) |
Power consumption |
220 W |
Power consumption in standby mode |
0.7 W |
Note :
Specifications are subject to change without notice.
Mass and dimensions are approximate.
System : SC-HT520EB |
Music Center: SA-HT520EB |
|
Satellite speakers: SB-HT520P |

|
Active Subwoofer: SB-WA520EB |
System : SC-HT520E |
Music Center: SA-HT520E |
|
Satellite speakers: SB-HT520P |
|
Active Subwoofer: SB-WA520EG |
System : SC-HT520EG |
Music Center: SA-HT520EG |
|
Satellite speakers: SB-HT520P |
|
Active Subwoofer: SB-WA520EG |
SB-HT520P-S consists of : |
|
SB-FS520P-S x 4 and SB-PC520P-S x 1 |
|
© 2004 Panasonic AVC Networks Singapore Pte. Ltd. All rights reserved. Unauthorized copying and distribution is a violation of law.
TOP NEXT
1 Safety Precautions
TOP PREVIOUS NEXT
1.1 GENERAL GUIDELINES
1.1.1 LEAKAGE CURRENT COLD CHECK
1.1.2 LEAKAGE CURRENT HOT CHECK (See Figure 1.)
TOP PREVIOUS NEXT
1.1 GENERAL GUIDELINES
TOP PREVIOUS NEXT
1.When servicing, observe the original lead dress. If a short circuit is found, replace all parts which have been overheated or damaged by the short circuit.
2.After servicing, see to it that all the protective devices such as insulation barriers, insulation papers shields are properly installed.
3.After servicing, make the following leakage current checks to prevent the customer from being exposed to shock hazards.
1.1.1 LEAKAGE CURRENT COLD CHECK
1.1.2 LEAKAGE CURRENT HOT CHECK (See Figure 1.)
TOP PREVIOUS NEXT

1.1.1 LEAKAGE CURRENT COLD CHECK
TOP PREVIOUS NEXT
1.Unplug the AC cord and connect a jumper between the two prongs on the plug.
2.Measure the resistance value, with an ohmmeter, between the jumpered AC plug and each exposed metallic cabinet part on the equipment such as screwheads, connectors, control shafts,
etc. When the exposed metallic part has a return path to the chassis,the reading should be between 1MΩ and 5.2Ω.
When the exposed metal does not have a return path to the chassis, the reading must be
 .
.
Fig. 1
TOP PREVIOUS NEXT
1.1.2 LEAKAGE CURRENT HOT CHECK (See
Figure 1.)
TOP PREVIOUS NEXT
1.Plug the AC cord directly into the AC outlet. Do not use an isolation transformer for this check.
2.Connect a 1.5kΩ, 10 watts resistor, in parallel with a 0.15μF capacitors, between each exposed metallic part on the set and a good earth ground such as a water pipe, as shown in Figure 1.
3.Use an AC voltmeter, with 1000 ohms/volt or more sensitivity, to measure the potential across the resistor.
4.Check each exposed metallic part, and measure the voltage at each point.
5.Reverse the AC plug in the AC outlet and repeat each of the above measurements.
6.The potential at any point should not exceed 0.75 volts RMS. A leakage current tester (Simpson Model 229 or equivalent) may be used to make the hot checks, leakage current must not exceed 1/2 milliamp. In case a measurement is outsideof the limits specified, there is a possibility of a shock hazard, and the equipment should be repaired and rechecked before it is returned to the customer.
TOP PREVIOUS NEXT
2 Handling the Lead-free Solder
TOP PREVIOUS NEXT
2.1 About lead free solder (PbF)
TOP PREVIOUS NEXT
2.1 About lead free solder (PbF)
TOP PREVIOUS NEXT
Distinction of PbF P.C.B. :
P.C.B.s (manufactured) using lead free solder will have a PbF stamp on the P.C.B.
Caution:
● Pb free solder has a higher melting point that standard solder; Typically the melting point is 50 - 70°F (30 - 40°C) higher.
Please use a high temperature soldering iron. In case of the soldering iron with temperaturecontrol, please set it to 700 ± 20°F (370 ± 10°C).
●Pb free solder will tend to splash when heated too high (about 1100°F/600°C).
●When soldering or unsoldering, please completely remove all of the solder on the pins or solder area, and be sure to heat the soldering points with the Pb free solder until it melts enough.
TOP PREVIOUS NEXT
3 Before Repair and Adjustment
TOP PREVIOUS NEXT
Disconnect AC power, discharge Power Supply Capacitors C546, C547, C548, C549 through a 10 Ω, 1 W resistor to ground.
DO NOT SHORT-CIRCUIT DIRECTLY (with a screwdriver blade, for instance), as this may destroy solid state devices.
After repairs are completed, restore power gradually using a variac, to avoid overcurrent.
Current consumption at AC 230-240V, 50Hz in NO SIGNAL mode should be ~250 mA (EB).
Current consumption at AC 230V, 50Hz in NO SIGNAL mode should be ~250 mA (EG).
TOP PREVIOUS NEXT
4 Protection Circuitry
TOP PREVIOUS NEXT
The protection circuitry may have operated if either of the following conditions are noticed:
●No sound is heard when the power is turned on.
●Sound stops during a performance.
The function of this circuitry is to prevent circuitry damage if, for example, the positive and negative speaker connection wires are
“shorted”, or if speaker systems with an impedance less than the indicated rated impedance of the amplifier are used.
If this occurs, follow the procedure outlines below:
1.Turn off the power.
2.Determine the cause of the problem and correct it.
3.Turn on the power once again after one minute.
Note :
When the protection circuitry functions, the unit will not operate unless the power is first turned off and then on again.
TOP PREVIOUS NEXT

5 Connection of the Speaker Cables
TOP PREVIOUS NEXT
●Be sure to connect speaker cables before connecting the AC power supply cord.
●The load impedance of any speaker used with this unit must be 4Ω.
●Be sure to connect the cable from the right speaker to the right terminal and the cable from the left speaker to the left terminal.
1.Strip off the outer covering, and twist the center conductor. Make sure the bare ends of the wires are not unravelled. (If they are, twist them tight again.)
2.Insert the wire to the rear panel of the unit and close the lever.
Notes :
●To prevent damage to circuitry, never short-circuit positive (+) and negative (-) speaker wires.
●Be sure to connect only positive (red) wires to positive (+) terminals and negative (black) wires to negative (-) terminals.
TOP PREVIOUS NEXT
6 Disassembly Procedure
TOP PREVIOUS NEXT
“ATTENTION SERVICER”
Some chassis components may have sharp edges.
Be careful when disassembling and servicing.
1.This section describes procedures for checking the operation of the major printed circuit boards and replacing the main components.
2.For reassembly after operation checks or replacement, reverse the respective procedures.
Special reassembly procedures are described only when required.
3.Select items from the following index when checks or replacement are required.
Contents
●Disassembly of the Speaker Unit
●Main Component Replacement Procedures
6.1 Disassembly flow chart
6.2 Disassembly of the Speaker Unit and Checking of the P.C.B.s.
TOP PREVIOUS NEXT
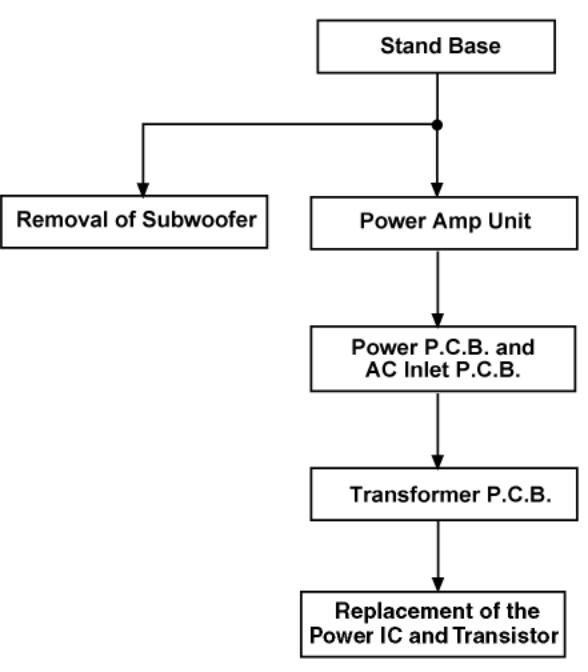
6.1 Disassembly flow chart
TOP PREVIOUS NEXT
The following chart is the procedure for disassembling the casing and inside parts for internal inspection when carrying out the servicing.
To assemble the unit, reverse the steps shown in the chart below.
TOP PREVIOUS NEXT
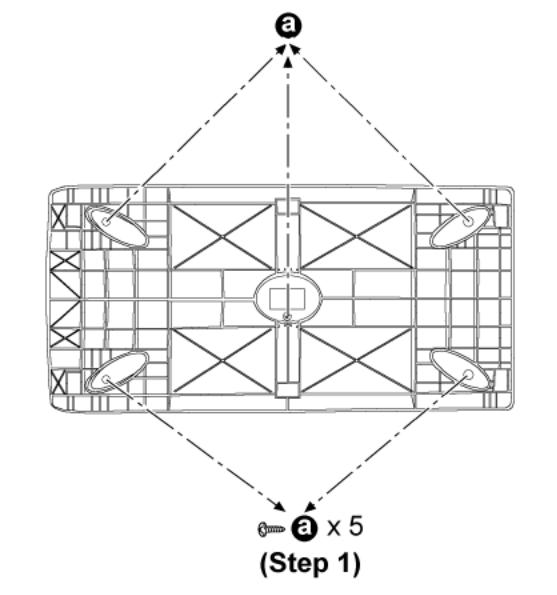
6.2 Disassembly of the Speaker Unit and Checking of the P.C.B.s.
TOP PREVIOUS NEXT
Step 1: Remove all the screws.
Step 2: Remove the stand base.

Step 3: Remove all the screws from the bottom of the speaker unit.
Step 4: Remove the screws from the rear panel’s speaker unit guide.
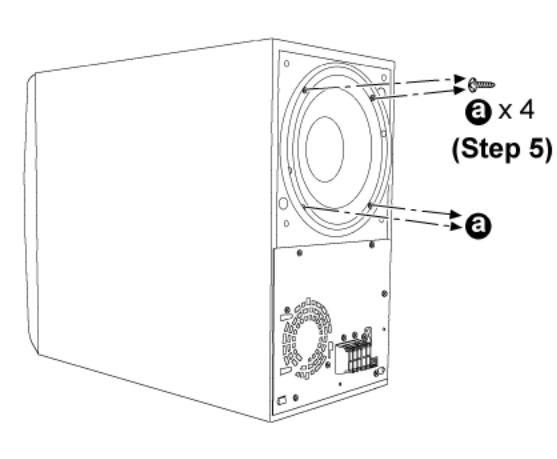
Step 5: Remove the screws from the subwoofer.
● Disassembly of Power Amp unit.

Step 6: Remove 2 screws from the Power Amp unit.
 Loading...
Loading...