Page 1
CH-9101 Herisau/Switzerland
Phone ++41 71 353 85 85
Fax ++41 71 353 89 01
Internet www.metrohm.com
E-Mail info@metrohm.com
792 Basic IC
Program «792 PC Software 1.0»
Basic IC792
Basic
Basic
BasicBasic
POWER
8.792.1003 Instructions for Use
11.04.2001 / dö
Page 2

Table of contents
Table of contents
1 Introduction
1.1 Instrument description.......................................................................................... 1
1.2 Parts and controls.................................................................................................. 3
1.3 Information on the Instructions for Use............................................................. 8
1.3.1 Organization ........................................................................................... 8
1.3.2 Notation and pictograms........................................................................ 9
1.4 Safety notes ..........................................................................................................10
1.4.1 Electrical safety..................................................................................... 10
1.4.2 General precautionary rules ................................................................. 10
2 Installation
2.1 Overview ................................................................................................................ 11
2.1.1 Flow chart ............................................................................................. 11
2.1.2 Connections in the 792 Basic IC .......................................................... 11
2.2 Setting up the instrument ................................................................................... 13
2.2.1 Packaging............................................................................................. 13
2.2.2 Check.................................................................................................... 13
2.2.3 Location ................................................................................................ 13
2.3 Attaching the accessories .................................................................................. 13
2.3.1 Connection of detector block............................................................... 13
2.3.2 Connection of syringe and aspirating tubing....................................... 14
2.3.3 Connection of the 6.5324.000 Bottle rack (option) .............................. 14
2.3.4 Connection of PEEK capillaries............................................................ 15
2.3.5 Filter unit PEEK ..................................................................................... 16
............................................................................................................
..........................................................................................................
1
11
2.4 Mains connection ................................................................................................. 17
2.4.1 Setting the mains voltage..................................................................... 17
2.4.2 Fuses .................................................................................................... 18
2.4.3 Mains cable and mains connection ..................................................... 18
2.4.4 On/off switching of the instrument ....................................................... 18
2.5 Connection to the PC ..........................................................................................19
2.5.1 Connecting cable ................................................................................. 19
2.5.2 Software installation.............................................................................. 19
2.5.3 Basic settings ....................................................................................... 20
2.6 High-pressure pump............................................................................................ 23
2.6.1 Removing the transport security screws.............................................. 23
2.6.2 Installing the pulsation dampener (option) .......................................... 23
2.6.3 Connecting the eluent bottle ................................................................ 25
2.6.4 Deaerating the pump and rinsing the pulsation dampener................. 25
2.7 Precolumns and separating columns............................................................... 28
2.7.1 General information on precolumns..................................................... 28
2.7.2 Precolumns with twin cartridge holder ................................................. 28
2.7.3 Precolumn glass cartridges with cartridge holder ............................... 30
2.7.4 IC anion precolumn SUPERSEP ..........................................................31
2.7.5 General information on separating columns........................................ 32
2.7.6 Selection of the sample loop................................................................ 32
2.7.7 Installation of the separating column without suppressor................... 32
2.7.8 Installation of the separating column with suppressor ........................ 34
792 Basic IC
I
Page 3

Table of contents
2.8 Suppressor module ............................................................................................. 35
2.8.1 General information on suppressor module........................................ 35
2.8.2 Preparation of the peristaltic pump...................................................... 35
2.8.3 Connection of supply bottles ............................................................... 38
2.8.4 Connection of the suppressor module ................................................ 39
2.9 Putting into operation ......................................................................................... 41
2.9.1 Putting into operation without suppressor........................................... 41
2.9.2 Putting into operation with suppressor ................................................ 42
3 Operating tutorial
3.1 Requirements ....................................................................................................... 45
3.2 Preparations.......................................................................................................... 46
3.3 Calibration ............................................................................................................. 47
3.4 Sample determination ......................................................................................... 54
4 Operation
4.1 Fundamentals of the operation ......................................................................... 57
...............................................................................................................
4.1.1 Starting/closing the program ............................................................... 57
4.1.2 Glossary................................................................................................ 58
4.1.3 Overview of program windows............................................................. 59
4.1.4 Main window elements......................................................................... 60
4.1.5 Icons of the main window..................................................................... 60
4.1.6 Overview of file types............................................................................ 61
4.1.7 Context sensitive menus ...................................................................... 62
4.1.8 Keyboard and mouse functions........................................................... 62
4.1.9 Help ...................................................................................................... 63
.......................................................................................
45
57
4.2 Instrument and software settings ..................................................................... 64
4.2.1 Fonts..................................................................................................... 64
4.2.2 Security system .................................................................................... 64
4.2.3 Global settings ..................................................................................... 65
4.2.4 COM port.............................................................................................. 67
4.3 Systems ................................................................................................................. 68
4.3.1 System window .................................................................................... 68
4.3.2 System file handling ............................................................................. 68
4.3.3 System functions .................................................................................. 69
Start/stop hardware and record baseline .................................... 69
Start/stop determinations............................................................. 69
Print system parameters .............................................................. 70
4.3.4 PC icon ................................................................................................. 71
4.3.5 Watch window ...................................................................................... 71
4.3.6 Instrument icon..................................................................................... 72
Menu options for instrument icon ................................................ 72
System parameters for disconnected system ............................. 72
Instrument control for connected system .................................... 73
Time program ............................................................................... 74
Configuration ................................................................................ 76
Hardware settings ........................................................................ 76
4.3.7 System state window............................................................................ 78
Status messages.......................................................................... 78
Error messages ............................................................................ 79
II
792 Basic IC
Page 4

Table of contents
4.4 Methods .................................................................................................................80
4.4.1 Method file handling ............................................................................. 80
4.4.2 Passport................................................................................................ 80
General ......................................................................................... 81
Sample.......................................................................................... 82
Column ......................................................................................... 83
Eluent ............................................................................................ 84
Comment ...................................................................................... 84
Method Log .................................................................................. 85
Data Log ....................................................................................... 86
4.4.3 Method setup........................................................................................ 87
General ......................................................................................... 87
Processing.................................................................................... 87
Math .............................................................................................. 88
4.4.4 Integration............................................................................................. 90
Setup............................................................................................. 91
Events ........................................................................................... 92
4.4.5 Calibration and quantification............................................................... 94
General information ...................................................................... 94
Notations....................................................................................... 95
External standard calibration........................................................ 96
Component table.......................................................................... 96
Peak identification ........................................................................ 98
Concentration table .................................................................... 100
Calibration curve......................................................................... 102
Update calibration ......................................................................104
Load and save calibration data.................................................. 105
Import and export calibration data ............................................. 105
Put out calibration curves ........................................................... 105
4.4.6 Report output...................................................................................... 106
Report options ............................................................................ 106
4.5 Chromatograms.................................................................................................. 118
4.5.1 Chromatogram window ...................................................................... 118
4.5.2 Chromatogram file handling............................................................... 119
Open chromatogram.................................................................. 119
Save chromatogram ................................................................... 120
Close chromatogram.................................................................. 120
Delete chromatogram................................................................. 120
Export chromatogram................................................................. 121
4.5.3 Graphical representation.................................................................... 122
Appearance ................................................................................ 122
Other graphical functions ........................................................... 126
4.5.4 Peak editor.......................................................................................... 127
Switching on/off the peak editor................................................. 127
Peak editor functions.................................................................. 127
Moving the cursor....................................................................... 128
4.5.5 Printing................................................................................................ 129
Page layout for printing .............................................................. 129
Printer settings ............................................................................ 130
Print preview ............................................................................... 130
Printing........................................................................................ 130
4.5.6 Miscellaneous functions ..................................................................... 130
Reintegration............................................................................... 130
Recalibration............................................................................... 130
Subtraction of a chromatogram ................................................. 131
Data compression ......................................................................131
Invert chromatogram .................................................................. 131
792 Basic IC
III
Page 5

Table of contents
4.6 Batch reprocessing ...........................................................................................132
4.6.1 Batch reprocessing queue file handling ............................................ 132
Open batch reprocessing queue ............................................... 132
Create new batch reprocessing queue...................................... 132
Save batch reprocessing queue ................................................ 132
4.6.2 Perform batch reprocessing............................................................... 133
Reprocess options window........................................................ 133
Merge chromatograms .............................................................. 136
4.6.3 Batch reprocessing queue editor....................................................... 137
Open batch reprocessing queue editor window ....................... 137
Batch reprocessing queue editor functions............................... 138
Print batch reprocessing queue................................................. 138
Close batch reprocessing queue editor .................................... 138
5 Notes – Maintenance – Faults
5.1 Practical notes on ion chromatography ........................................................ 139
5.1.1 Separating columns ........................................................................... 139
5.1.2 High-pressure pump .......................................................................... 140
5.1.3 Eluents ................................................................................................ 141
5.1.4 Peristaltic pump.................................................................................. 141
5.1.5 Suppressor module............................................................................ 142
5.1.6 Connections ....................................................................................... 142
...................................................
139
5.2 Maintenance and servicing .............................................................................. 143
5.2.1 General information............................................................................ 143
5.2.2 Passivation ......................................................................................... 143
5.2.3 Recycling ............................................................................................ 144
5.2.4 Shutdown............................................................................................ 144
5.2.5 Changing separating columns........................................................... 144
5.2.6 Maintenance work at the pump head ................................................ 146
5.2.7 Regeneration of the suppressor module ........................................... 150
5.2.8 Cleaning the suppressor.................................................................... 151
5.2.9 Replacing the suppressor.................................................................. 153
5.2.10 Exchanging the pump tubing............................................................. 155
5.3 Faults and malfunctions ................................................................................... 156
5.3.1 Error messages .................................................................................. 156
5.3.2 Malfunctions and their rectification .................................................... 156
5.4 Diagnostic tests / Validation / GLP ................................................................. 158
IV
792 Basic IC
Page 6

Table of contents
6 Appendix
6.1 Technical data..................................................................................................... 159
6.2 Standard equipment ..........................................................................................164
6.3 Optional accessories.........................................................................................167
6.4 Warranty and conformity .................................................................................. 176
..............................................................................................................
6.1.1 Conductivity measurement................................................................. 159
6.1.2 Conductivity detector.......................................................................... 159
6.1.3 Injection valve ..................................................................................... 160
6.1.4 High-pressure pump .......................................................................... 160
6.1.5 Peristaltic pump.................................................................................. 161
6.1.6 Suppressor module ............................................................................ 161
6.1.7 RS232 interface .................................................................................. 161
6.1.8 Mains connection ............................................................................... 162
6.1.9 Safety specifications........................................................................... 162
6.1.10 Electromagnetic compatibility (EMC)................................................. 162
6.1.11 Ambient temperature.......................................................................... 163
6.1.12 Housing............................................................................................... 163
6.3.1 Accessories for 792 Basic IC .............................................................167
6.3.2 Separating columns and precolumns................................................ 169
6.3.3 Additional devices and cables ........................................................... 175
6.4.1 Warranty.............................................................................................. 176
6.4.2 EU Declaration of conformity.............................................................. 177
6.4.3 Certificate of conformity and system validation ................................. 178
159
6.4 Index ..................................................................................................................... 179
792 Basic IC
V
Page 7
Table of contents
List of figures
Fig. 1: Front of the 792 Basic IC ................................................................................ 3
Fig. 2
Fig. 3
Fig. 4
Fig. 5
Fig. 6
Fig. 7
Fig. 8
Fig. 9
: Rear of the 792 Basic IC................................................................................. 4
: Interior of the 792 Basic IC .............................................................................6
: Connecting diagram for 792 Basic IC without suppressor.......................... 12
: Connecting diagram for 792 Basic IC with suppressor ............................... 12
: Connectors for capillaries.............................................................................15
: 6.2821.100 Filter unit PEEK .......................................................................... 16
: Setting the mains voltage ............................................................................. 18
: Connection of the pulsation dampener (option) .......................................... 24
Fig. 10
Fig. 11
Fig. 12
Fig. 13
Fig. 14
Fig. 15
Fig. 16
Fig. 17
Fig. 18
Fig. 19
: Installing precolumn cartridges .................................................................... 29
: Installation of precolumn glass cartridges with cartridge holder ................. 31
: Installation of column without suppressor.................................................... 33
: Installing pump tubings ................................................................................ 36
: Installation of column with suppressor......................................................... 37
: Connections at suppressor module ............................................................. 40
: Components of the pump head ................................................................. 147
: Replacement of the piston seal 89
: Components of inlet valve 90
: Assembling the suppressor.......................................................................
89............................................................. 147
8989
90 and outlet valve 91
9090
91 ..................................... 149
9191
153
VI
792 Basic IC
Page 8

Table of contents
List of numbered parts and controls
1111 Door to interior ....................................3,6
2222 Mains pilot lamp.....................................3
3333 Feedthrough for syringe tubing .............3
4444 Feedthrough for aspirating tubing......... 3
5555 Opening for detector cable....................4
6666 Rear panel opening ...............................4
7777 Opening for outlet capillaries.................4
8888 Knurled screw ........................................4
9999 Detachable rear panel ...........................4
10
10 Transport security screws...................... 4
1010
11
11 Mains switch ..................................... 4,18
1111
12
12 Mains connection plug .....................4,18
1212
13
13 Fuse holder ....................................... 4,18
1313
14
14 RS232 interface...................................... 4
1414
15
15 Connection for detector block ............... 4
1515
16
16 Connection for service...........................4
1616
17
17 Serial number.........................................4
1717
18
18 Inlet capillary for injector ...................6,24
1818
19
19 Mounting rail ................................ 6,33,37
1919
20
20 Column connection
2020
capillary ..............................6,29,31,33,37
21
21 Sample loop...........................................6
2121
22
22 Injection valve..........................6,24,33,37
2222
23
23 Aspirating tubing....................................6
2323
24
24 Coupling................................................. 6
2424
25
25 Syringe tubing ........................................ 6
2525
26
26 PEEK coupling ............................. 6,29,37
2626
27
27 Connection capillary .........................6,24
2727
28
28 Filter unit PEEK ..................6,16,24,36,37
2828
29
29 Connection capillary .........................6,24
2929
30
30 Connection capillary ..............................6
3030
31
31 Purge valve........................................6,24
3131
32
32 Aspirating capillary................................. 6
3232
33
33 Fastening screws...................................6
3333
34
34 Pump head......................................6,147
3434
35
35 Connection capillary .............................. 6
3535
36
36 Connection capillary .............................. 6
3636
37
37 Inlet capillary for
3737
detector block .............................. 6,33,37
38
38 Detector block.............................. 6,33,37
3838
39
39 Suppressor module ..........................6,37
3939
40
40 Tubing cartridge ...........................6,36,37
4040
41
41 Contact pressure lever.................6,36,37
4141
42
42 Holding clamp.................................. 6,37
4242
43
43 Snap-action lever .........................6,36,37
4343
44
44 Pump drive ........................................6,37
4444
45
45 Mounting pin .....................................6,37
4545
46
46 Compression fitting ......... 15,16,29,31,36
4646
47
47 Compression fitting ..............................15
4747
48
48 Capillary......................................15,16,31
4848
49
49 Connector with filter..............................16
4949
50
50 Housing for filter unit PEEK..................16
5050
51
51 Connector without filter ........................16
5151
52
52 Pulsation dampener .............................24
5252
53
53 Connection to injection valve...............24
5353
54
54 Connection to purge valve...................24
5454
55
55 Inlet capillary.........................................29
5555
56
56 Manufit housing....................................29
5656
57
57 PTFE gasket .........................................29
5757
58
58 2 Steel meshes.....................................29
5858
59
59 Precolumn cartridge.............................29
5959
60
60 Manufit pressure screw........................29
6060
61
61 Outlet capillary......................................29
6161
62
62 End fitting .............................................31
6262
63
63 Sleeve for precolumn cartridge............31
6363
64
64 Precolumn cartridge.............................31
6464
65
65 Connection piece .................................31
6565
66
66 Separating column.....................29,33,37
6666
67
67 Column holder.................................33,37
6767
68
68 Aspirating tubing for H
6868
69
69 Aspirating tubing for H
6969
70
70 Coupling ..........................................36,37
7070
71
71 Pump tubing for H
7171
72
72 Pump tubing for H
7272
73
73 Stopper................................................ 36
7373
74
74 Coupling ......................................... 36,37
7474
75
75 Suppressor inlet capillary
7575
O ................36,37
2
.............36,37
2SO4
...................36,37
2SO4
O.......................36,37
2
for eluent......................................... 37,40
76
76 Suppressor outlet capillary
7676
for eluent......................................... 37,40
77
77 Suppressor inlet capillary
7777
for H
O....................................... 36,37,40
2
792 Basic IC
VII
Page 9

Table of contents
78
78 Suppressor inlet capillary
7878
for H
79
79 Suppressor outlet capillary
7979
for H
80
80 Suppressor outlet capillary
8080
for H
81
81 Screw ................................................. 147
8181
82
82 Zircon piston ...................................... 147
8282
83
83 Spring retainer ................................... 147
8383
84
84 Spring................................................. 147
8484
85
85 Piston cartridge.................................. 147
8585
86
86 Piston guide sleeve............................147
8686
87
87 Sapphire supporting ring................... 147
8787
88
88 Piston guide sleeve............................147
8888
89
89 Piston seal .........................................147
8989
90
90 Inlet valve ....................................147,149
9090
2SO4
2
2SO4
....................................36,37,40
O ............................................37,40
.........................................37,40
91
91 Outlet valve..................................147,149
9191
92
92 Screw holder ......................................147
9292
93
93 Special tool ........................................147
9393
94
94 Special tool ........................................147
9494
95
95 Valve housing.....................................149
9595
96
96 Sealing ring ........................................149
9696
97
97 Sleeve.................................................149
9797
98
98 Sapphire sleeve .................................149
9898
99
99 Sapphire sphere.................................149
9999
100
100 Ceramic holder...................................149
100100
101
101 Seal ....................................................149
101101
102
102 Screw nut ...........................................153
102102
103
103 Connection piece...............................153
103103
104
104 Suppressor rotor ................................153
104104
105
105 Suppressor holder .............................153
105105
VIII
792 Basic IC
Page 10

1.1 Instrument description
1 Introduction
1.1 Instrument description
2.792.0020 Basic IC with suppressor module
The
system for ion chromatographic analyses. The extremely compact
housing of the 792 Basic IC contains everything needed to carry out ion
chromatography at a high quality level:
is a PC-controlled
x Injection valve
x High-pressure pump
pump with a flow range from 0.2 } 2.5 mL/min and a maximum
pressure of 25 MPa (250 bar)
x Column chamber
not only thermally stable conditions for the separation column but
also shields the system against electromagnetic interference
x Columns
separation columns for cations or organic acids – the 792 Basic IC
can accommodate them all
x Suppressor
pressure-resistant, with fully automatic regeneration, highest performance and optimal reproducibility
x Peristaltic pump
flow rate of 0.5 } 0.6 mL/min for regeneration and rinsing of the
suppressor module
x Detector
stability. The detector temperature of 40 °C varies by less than
0.01°C.
– conductivity detector with outstanding temperature
– for individual injections
– extremely low-pulsation double piston
– the perfect insulation of the housing provides
– whether anion columns with or without suppression,
– integrated Metrohm Suppressor Module (MSM),
– integrated two-channel peristaltic pump with a
792 Basic IC
All components, which come into contact with eluent and sample are
metal-free.
operation of the
The
the RS232 interface with the help of the control and evaluation program
«792 Basic IC»
tems for recording and evaluating chromatograms and modify them if
need be. Time programs can also be created in which a large number
of instrument functions can be triggered for each program step.
792 Basic IC takes place via a PC connected to
. This PC program can be used to open prepared sys-
1
Page 11

1 Introduction
The operating software for the 792 Basic IC meets all the requirements
you could place today on a modern integration software: single or multipoint calibration, internal or external standard, selectable algorithms for
non-linear calibration, various integration modes with integration parameters and integration events, different methods for peak recognition,
peak editor, free scaling, superimposing several chromatograms, batch
reprocessing; a powerful and GLP-conform report generator with output
interfaces for monitor, printer and external databases.
792 Basic IC
2
Page 12
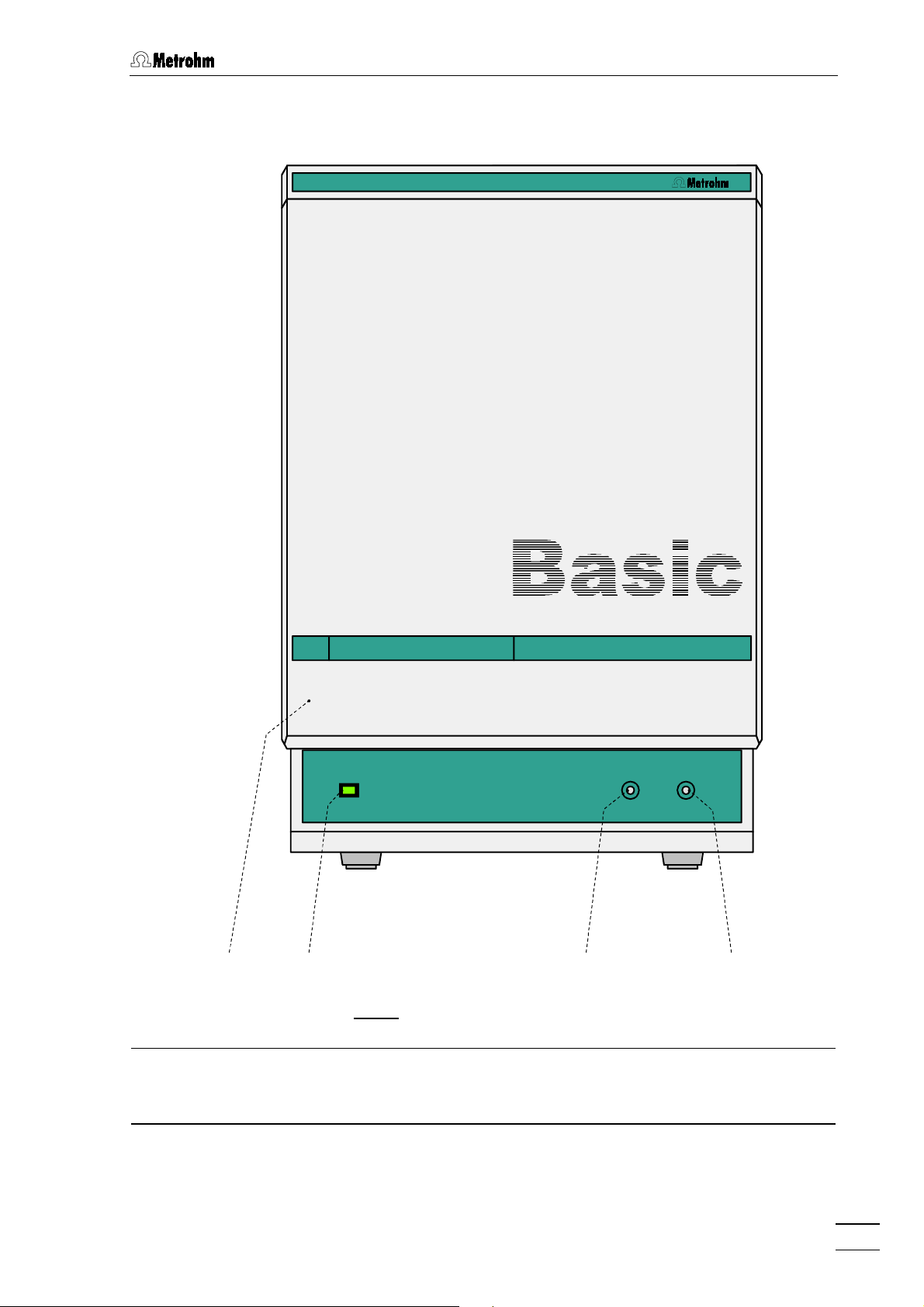
1.2 Parts and controls
1.2 Parts and controls
Basic I C792
Basic
Basic
BasicBasic
POWER
222211113
Fig. 1
: Front of the 792 Basic IC
34
33
4
44
Door to interior
1111
Mains pilot lamp
2222
lit up when instrument switched on
792 Basic IC
3333 Feedthrough for syringe tubing
for connection of the 6.2816.020 syringe
used für aspirating the sample
Feedthrough for aspirating tubing
4444
3
Page 13
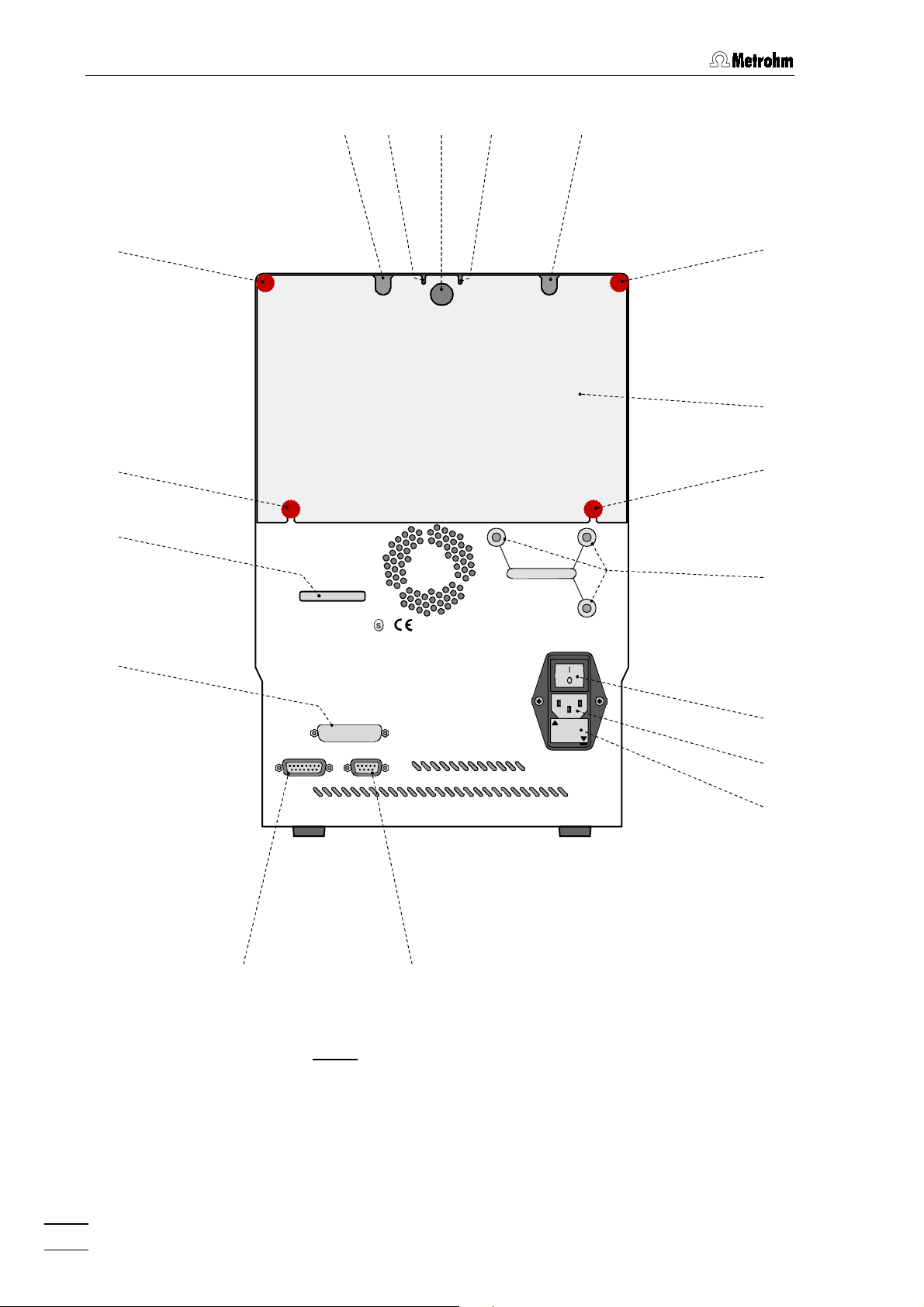
1 Introduction
8888
8888
17
17
1717
5555
Type
WARNING - Fire Hazard -
For conti nued protectio n replace only
with the sam e type and rating of fuse
66667
76
77
Waste B
Waste A
65
66
Transport security screws
5
55
8888
9999
8888
10
10
1010
16
16
1616
Service only
Detector Block
15
15 14
1515
RS 232
14
1414
: Rear of the 792 Basic IC
Fig. 2
f = 50-60 H z
S = 100 VA
Fuse
100-120V :
1,0A(T)
220-240V :
0,5A(T)
Made by Metrohm Herisau Switzerland
11
11
1111
12
12
1212
13
13
1313
792 Basic IC
4
Page 14

1.2 Parts and controls
Opening for detector cable
5555
Opening for outlet capillaries
6666
for discharge of eluent, regeneration
solution, and rinsing solution from the
inner compartment
Rear panel opening
7777
(closed with plastic stopper) for
additional supply and discharge lines to
and from the inner compartment
Knurled screw
8888
for fastening the rear panel
Detachable rear panel
9999
access to upper part of inner
compartment
10
10 Transport security screws
1010
to secure the pump head when the
instrument is transported
9999
12
12 Mains connection plug
1212
mains connection, see
13
13 Fuse holder
1313
changing the fuses, see
RS232 interface
14
14
1414
connection of the PC
15
15 Connection for detector block
1515
Connection
16
16
1616
To be used only for Metrohm Service!
Serial number
17
17
1717
section 2.4
section 2.4
Mains switch
11
11
1111
to switch instrument on and off:
I = ON 0 = OFF
792 Basic IC
5
Page 15
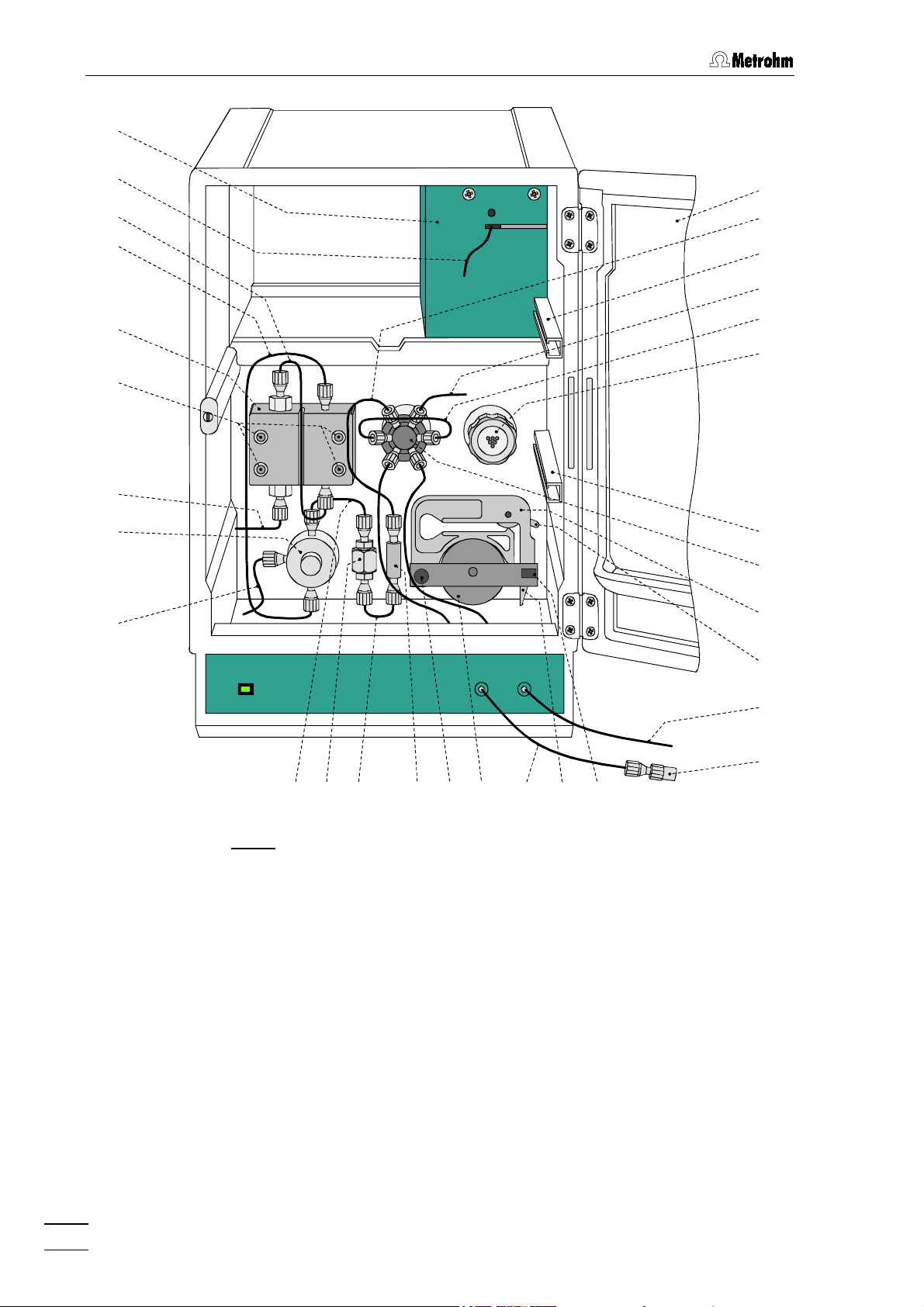
1 Introduction
38
38
3838
37
37
3737
36
36
3636
35
35
3535
34
34
3434
33
33
3333
32
32
3232
18
18
1818
19
19
1919
20
20
2020
21
21
2121
39
39
3939
1111
31
31
3131
30
30
3030
POWER
29
29
28
28 27
2929
Fig. 3: Interior of the 792 Basic IC
27
2828
2727
(with permanently attached accessories and
1.733.0110 Detector block)
26
26
2626
45
45 44
44
4545
4444
25
25
2525
43
4343
42
4243
4242
19
19
1919
22
22
2222
40
40
4040
41
41
4141
23
23
2323
24
24
2424
792 Basic IC
6
Page 16

1.2 Parts and controls
Door to interior
1111
Inlet capillary for injector
18
18
1818
PEEK capillary,
length L = 24 cm
19
19 Mounting rail
1919
for 6.2027.0X0 column holder
Column connection capillary
20
20
2020
PEEK capillary,
length L = 30 cm
Sample loop 20 PPPPL
21
21
2121
6.1825.210 PEEK sample loop
Injection valve
22
22
2222
Aspirating tubing
23
23
2323
PTFE tubing for aspirating the sample;
length L = 65 cm
Aspirating capillary
32
32
3232
Connection for 6.1834.010 aspirating
tubing
Fastening screws
33
33
3333
for pump head
Pump head (6.2824.100)
34
34
3434
35
35 Connection capillary
3535
Connection pump head – purge
valve, fixed mounting
36
36 Connection capillary
3636
in pump head, fixed mounting
37
37 Inlet capillary for detector block
3737
PEEK capillary, fixed mounting
38
38 Detector block (1.732.0110)
3838
34
34
3434
Coupling (6.2744.120)
24
24
2424
for connection of the 6.2816.020 syringe
Syringe tubing
25
25
2525
PTFE tubing for connection of the
syringe,
length L = 35 cm
26
26 PEEK coupling (6.2744.040)
2626
27
27 Connection capillary
2727
PEEK capillary,
length L = 13 cm
28
28 Filter unit PEEK (6.2821.100) 43
2828
Connection capillary
29
29
2929
PEEK capillary,
length L = 13 cm
30
30 Connection capillary
3030
PTFE capillary for connection of the
6.2816.020 syringe,
length L = 70 cm
39
39 Suppressor module
3939
40
40 Tubing cartridge (6.2755.000)
4040
41
41 Contact pressure lever
4141
42
42 Holding clamp
4242
43 Snap-action lever
4343
44
44 Pump drive
4444
44445555 Mounting pin
(inlet and outlet capillaries are not
shown)
for 6.1826.060 pump tubing
for adjusting the contact pressure
for locking the tubing cartridge into
place
for releasing the tubing cartridge
roller head with contact rollers
for attaching the tubing cartridges
Purge valve
31
31
3131
792 Basic IC
7
Page 17
1 Introduction
1.3 Information on the Instructions for Use
Please read through these Instructions for Use carefully before you put
the 792 Basic IC into operation. The Instructions for Use contain
information and warnings to which the user must pay attention in order
to assure safe operation of the instrument.
1.3.1 Organization
These
comprehensive overview of the installation, startup procedure, operation, fault rectification and technical specifications of this instrument.
The Instructions for Use are organized as follows:
To find the required information on the instruments, you will find it an
advantage to use either the
back.
8.792.1003 Instructions for Use
Section 1 Introduction
General description of instrument, parts and controls
and safety notes
Section 2 Installation
Installation of accessories and putting instrument into
operation
Section 3 Operating tutorial
Introduction to the operation using an example
Section 4 Operation
Detailed description of the operation
Section 5 Notes – Maintenance – Faults
Notes on ion chromatography, maintenance, fault rectification, diagnostic tests, validation
Section 6 Appendix
Technical data, standard equipment, options, warranty,
declarations of conformity, index
Table of contents
for the 792 Basic IC provide a
or the
Index
at the
As a supplement to the Instructions for Use, the
Monograph "Ion chromatography"
an introduction to the theoretical fundamentals and general information
on separating columns and sample pretreatment.
8.792.5003 Metrohm Monograph "Practical Ion Chromatog-
The
raphy"
tion to the basic principles of ion chromatography and also describes
22 experiments covering the whole world of ion chromatography.
The
tains all the
792 Basic IC
8
is a practical textbook, which provides an illustrative introduc-
8.732.2013 IC Applications Collection
Application Notes
on the subject of ion chromatography.
is also supplied. This provides
8.732.2003 Metrohm
is also supplied; this con-
Page 18
1.3 Information on the Instructions for Use
1.3.2 Notation and pictograms
The following notations and pictograms (symbols) are used in these Instructions for Use:
Range
SYSTEM STATE
<OK>
[ Ctrl ]
35
35
3535
Menu item, parameter or entry
value
Program window
Button
Key
Part or control of 792
Hazard
This symbol draws attention to a
possible danger to life or of injury if
the associated directions are not
followed correctly.
Warning
This symbol draws attention to
possible damage to instruments or
instrument parts if the associated
directions are not followed correctly.
792 Basic IC
Caution
This symbol marks important
information. First read the associated directions before you continue.
Comment
This symbol marks additional
information and tips.
9
Page 19
1 Introduction
1.4 Safety notes
1.4.1 Electrical safety
While electrical safety in the handling of the 792 Basic IC is assured in
the context of the specifications IEC 1010-1 (protection class 1, degree
of protection IP20), the following points should be noted:
x Mains connection
Setting of the mains voltage, checking the mains fuse and the
mains connection must be effected in accordance with the instruc-
tions in section 2.4.
x Opening the 792 Basic IC
If the 792 Basic IC is connected to the power supply, the instrument
must not be opened nor must parts be removed from it, otherwise
there is a danger of coming into contact with components which are
live. Hence, always disconnect the instrument from all voltage sources
before you open it and ensure that the mains cable is discon-
nected from mains connection 12
x Protection against static charges
Electronic components are sensitive to static charging and can be
destroyed by discharges. Before you touch any of the components
inside the 792 Basic IC, you should earth yourself and any tools you
are using by touching an earthed object (e.g. housing of the instrument or a radiator) to eliminate any static charges which exist..
12 !
1212
1.4.2 General precautionary rules
x Handling of solvents
Check all lines of the IC system periodically for possible leaks. Follow
the relevant instructions regarding the handling of flammable and/or
toxic solvents and their disposal.
792 Basic IC
10
Page 20
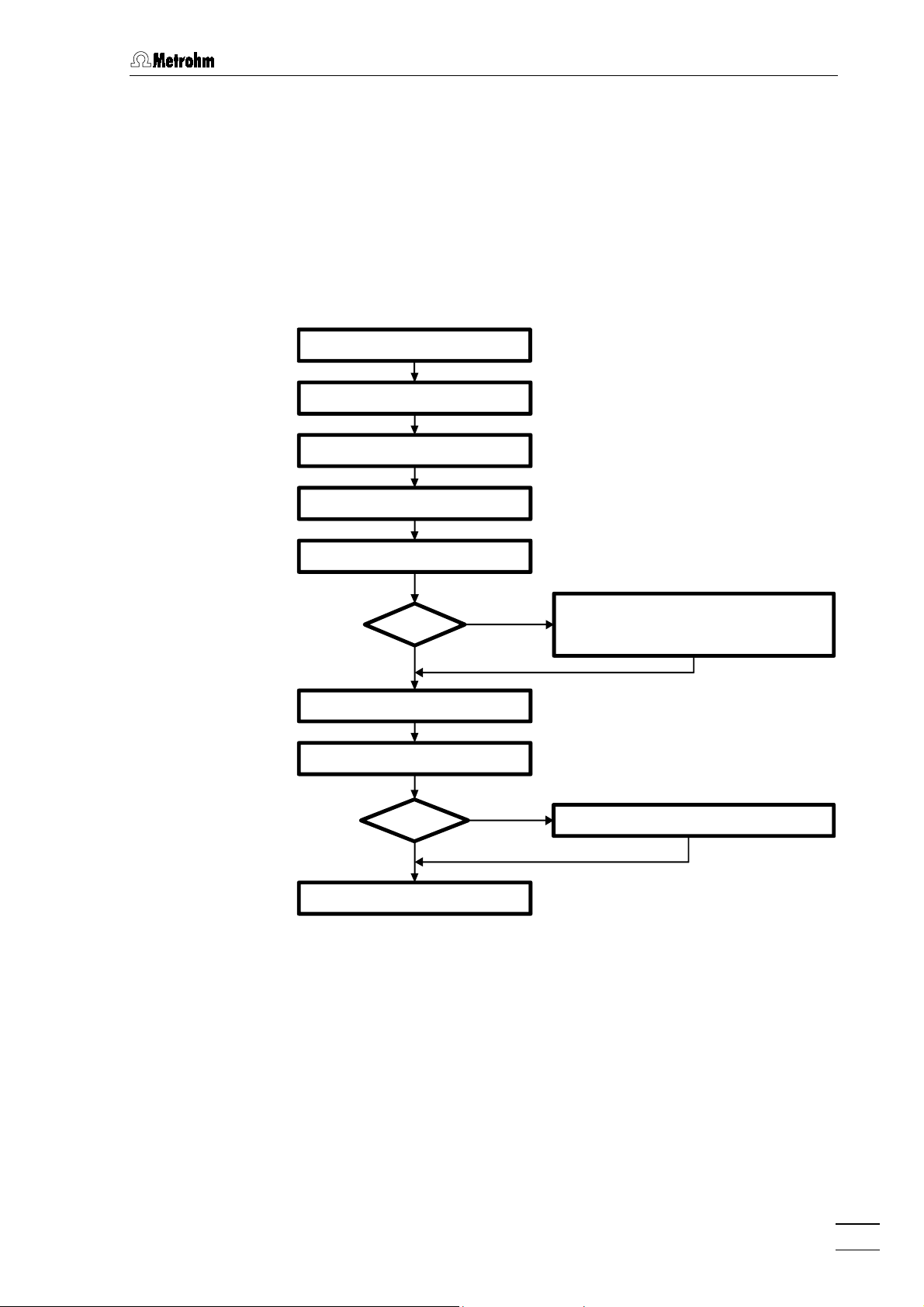
2.1 Overview
2 Installation
2.1 Overview
2.1.1 Flow chart
The following flow chart provides an overview of all installation work. You
will find more detailed information in the relevant sections.
Setting up
Setting up sect. 2.2
Setting upSetting up
Installing accessories
Installing accessories sect. 2.3
Installing accessoriesInstalling accessories
Mains connection
Mains connection sect. 2.4
Mains connectionMains connection
Connecting PC
Connecting PC sect. 2.5
Connecting PCConnecting PC
sect. 2.2
sect. 2.2sect. 2.2
sect. 2.3
sect. 2.3sect. 2.3
sect. 2.4
sect. 2.4sect. 2.4
sect. 2.5
sect. 2.5sect. 2.5
Connecting high pr. pump
Connecting high pr. pump sect 2.6
Connecting high pr. pumpConnecting high pr. pump
Precolumn
Precolumn
PrecolumnPrecolumn
No
No
NoNo
Installing sample loop
Installing sample loop sect. 2.7.6
Installing sample loopInstalling sample loop
Connecting column
Connecting column sect. 2.7.7/8
Connecting columnConnecting column
Suppressor
Suppressor Connecting suppressor module
SuppressorSuppressor
No
No
NoNo
Conditioning
Conditioning sect. 2.9
ConditioningConditioning
sect 2.6
sect 2.6sect 2.6
Yes
Yes
YesYes
sect. 2.7.6
sect. 2.7.6sect. 2.7.6
sect. 2.7.7/8
sect. 2.7.7/8sect. 2.7.7/8
Yes
Yes
YesYes
sect. 2.9
sect. 2.9sect. 2.9
Precolumn with twin cartridge holder
Precolumn with twin cartridge holder sect. 2.7.2
Precolumn with twin cartridge holderPrecolumn with twin cartridge holder
Precolumn cat. with cartr. holder
Precolumn cat. with cartr. holder sect. 2.7.3
Precolumn cat. with cartr. holderPrecolumn cat. with cartr. holder
IC anion precolumn SUPERSEP
IC anion precolumn SUPERSEP sect. 2.7.4
IC anion precolumn SUPERSEPIC anion precolumn SUPERSEP
Connecting suppressor module sect. 2.8
Connecting suppressor moduleConnecting suppressor module
sect. 2.7.2
sect. 2.7.2sect. 2.7.2
sect. 2.7.3
sect. 2.7.3sect. 2.7.3
sect. 2.7.4
sect. 2.7.4sect. 2.7.4
sect. 2.8
sect. 2.8sect. 2.8
2.1.2 Connections in the 792 Basic IC
The two following illustrations show the internal connections in the 792
Basic IC in schematic form. The meanings of the various numbered
components are given in the detailed illustrations and descriptions in
ections 2.2 – 2.9
s
792 Basic IC
.
11
Page 21
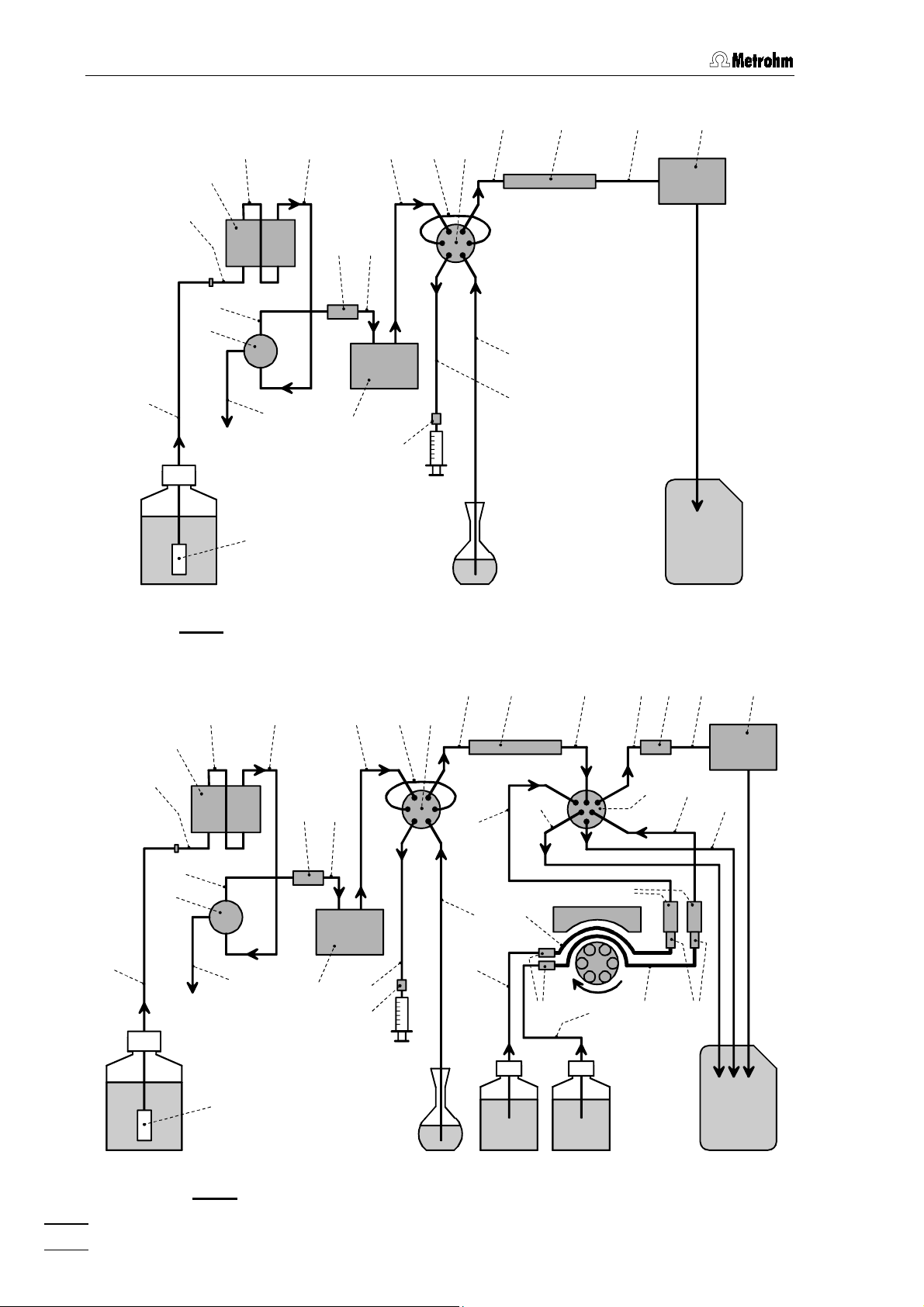
2 Installation
20
32
32
3232
31
31
3131
34
34
3434
29
29
2929
36
36 35
3636
35
3535
28
28 27
27
2828
2727
18
18 21
21 22
1818
2121
20 66
2020
22
2222
Injection valve
Column
23
23
2323
66 37
6666
37 38
3737
38
3838
Detector
6.1834.010
32
32
3232
30
30
3030
6.2821.090
Eluent
Fig. 4:
36
36 35
3636
34
34
3434
Connecting diagram for 792 Basic IC without suppressor
35
3535
28
28
2828
52
52
5252
18
18 21
1818
27
27
2727
24
24
2424
21 22
2121
22
2222
20
20 66
2020
78
78
7878
25
25
2525
Sample
66 75
6666
Column
80
80
8080
Waste
75
7575
76
76 26
26 37
7676
2626
39
39
3939
37 38
3737
Detector
77
77
7777
79
79
7979
38
3838
29
29
2929
28
28
H2O
68
68
6868
2828
72
7272
74
74
7474
31
31
3131
6.1834.010
12
30
30
3030
6.2821.090
Eluent
792 Basic IC
: Connecting diagram for 792 Basic IC with suppressor
Fig. 5
52
52
5252
25
25
2525
24
24
2424
Sample
69
69
6969
23
23
2323
71
71
7171
70
70 72
7070
H2SO
4
Waste
Page 22

2.2 Setting up the instrument
2.2 Setting up the instrument
2.2.1 Packaging
The 792 Basic IC is supplied together with the separately packed
accessories in special packagings containing shock-absorbing foam
linings designed to provide excellent protection. The instrument itself is
packed in an evacuated polyethylene bag to prevent the ingress of
dust. Please store all these special packagings as only they assure
transport of the instrument free from damage.
2.2.2 Check
After receipt, immediately check whether the shipment is complete and
has arrived without damage (compare with delivery note and list of
accessories in
instructions in
2.2.3 Location
section 6.2
section 6.4.1
). In the case of transport damage, see
"Warranty".
Position the instrument in the laboratory at a location convenient for operation, free from vibrations and protected against a corrosive atmosphere and contamination by chemicals.
To avoid disturbing temperature influences on the insulated column
compartment, the instrument must be protected against direct
sunlight.
2.3 Attaching the accessories
2.3.1 Connection of detector block
The metal-free
livery of the 792 Basic IC; it must be inserted in the instrument and connected up. Proceed as follows:
1 Note the cell constant
x
1.732.0110 Detector block
The cell constant
detector block. Note this value; it must subsequently be entered in the software in order to ensure that an exact display
of the conductivity is obtained (see
c = XX,X /cm
belongs to the scope of de-
is printed on the rear of the
section 2.5.3
).
792 Basic IC
2 Install detector block
x
Unscrew the four knurled screws
of the 792 Basic IC and remove rear panel (see
x
Position detector block
vided in the 792 Basic IC and push fully to the front (see
3
).
8888
from the top rear panel
Fig. 2
38
38
from the back in the space pro-
3838
).
9999
Fig.
13
Page 23

2 Installation
x
Insert the cable permanently attached to the detector block
38
38
in one of the openings
3838
the openings
x
Replace rear panel
four knurled screws
3 Connect detector block
x
Plug the gray connecting cable permanently attached to the
detector block
792 Basic IC and fasten to the instrument by tightening the
screws in the cable connector (see
4 Connect waste container
x
Lead the outlet capillary of the detector block
ciently large waste container and fix in place.
7777
of the rear panel
9999
38
38
into connection
3838
5555
and the outlet capillary in one of
9999
.
and screw to the 792 Basic IC using the
8888
.
15
15
"Detector Block" of the
1515
Fig. 2
).
38
38
to a suffi-
3838
2.3.2 Connection of syringe and aspirating tubing
22
For manual filling of the sample loop
the 6.2816.020 Syringe, the syringe tubing
23
PTFE aspirating tubing
as follows:
1 Connect syringe to syringe tubing
x
Pull syringe tubing
hand out of feedthrough
x
Mount a PEEK compression fitting
the end of the syringe tubing
(6.2744.120) to the compression fitting
x
Push 6.2816.020 Syringe (without needle) as far as it will go
into the connection of coupling
2 Install aspirating tubing
x
Pull aspirating tubing
hand out of feedthrough
23
are needed. These accessories are mounted
2323
25
25
2525
22
mounted on the injection valve,
2222
25
25
with coupling
2525
connected to injection valve
3333
as far as desired (see
46
46
(see
4646
25
25
and screw the coupling
2525
24
24
.
2424
23
23
connected to injection valve
2323
4444
as far as desired (see
section 2.3.4
46
46
.
4646
24
24
2424
22
22
2222
Fig. 3
Fig. 3
and the
by
).
) to
24
24
2424
22
22
by
2222
).
2.3.3 Connection of the 6.5324.000 Bottle rack (option)
The optional available 6.5324.000 Bottle rack for supply vessels can be
placed on top of the 792 Basic IC. The accessories include the supply
vessels for eluent (2 L), regeneration solution (1 L) and rinsing solution
(1 L).
792 Basic IC
14
Page 24
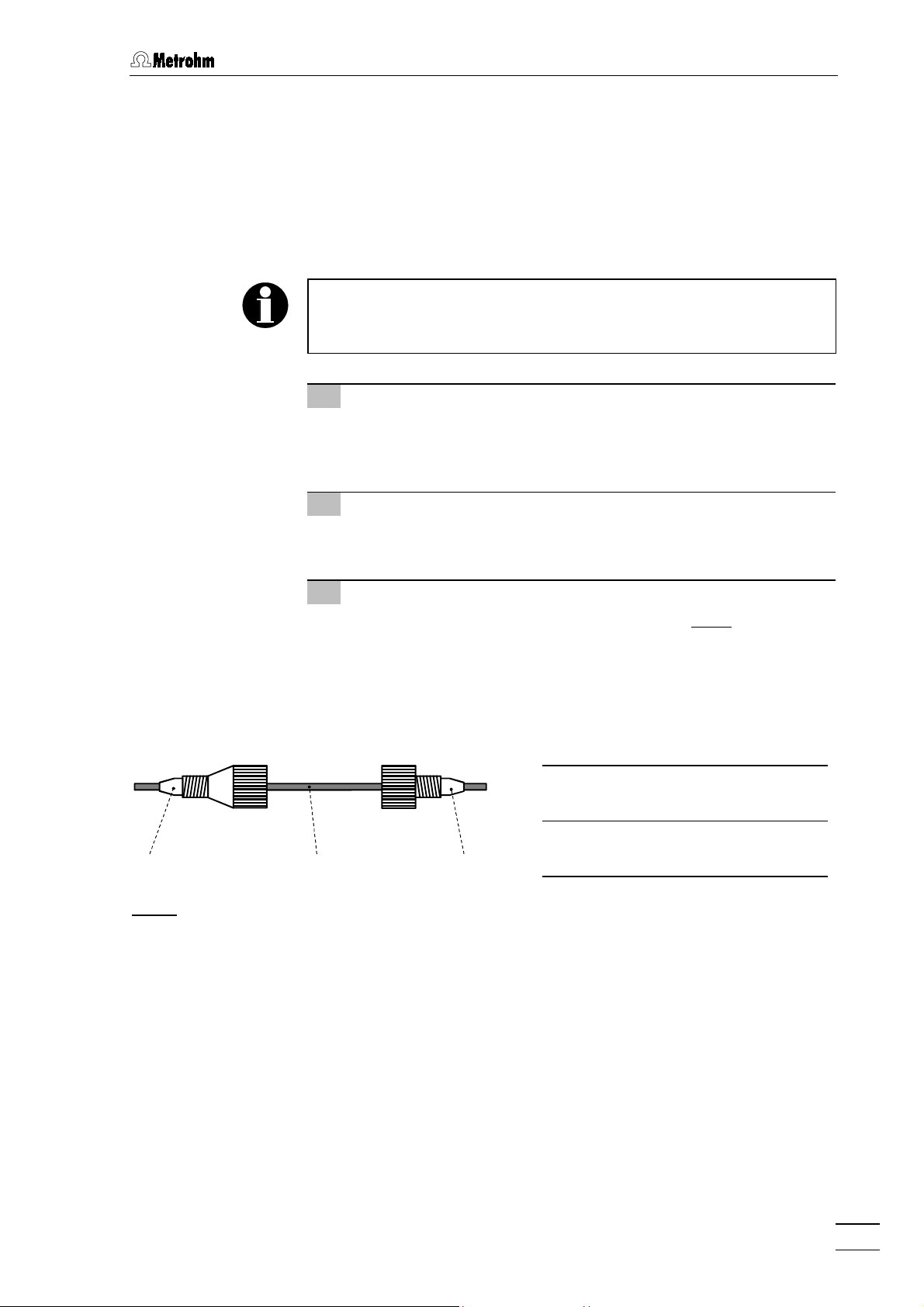
2.3 Attaching the accessories
2.3.4 Connection of PEEK capillaries
For the connections between high-pressure pump and detector block
6.1831.010 PEEK capillaries
which are connected using either
tings (long)
These PEEK connectors can also be used to connect 6.1822.010 PTFE
microcapillaries (i.d. = 0.3 mm). Proceed as follows:
Capillaries fitted with new connectors must have a perfectly flat cut
surface. To cut PEEK or PTFE capillaries it is best to use the
6.2621.080 Capillary tubing cutter.
1 Mount compression fitting
Slide a compression fitting
fitting
fastened as shown in
2 Insert capillary in connection
Push capillary end in the corresponding connection as far as it
will go (to avoid dead volume).
6.2744.070 PEEK compression fittings (short)
or
47
47
(6.2744.070) over the end of the capillary
4747
(i.d. = 0.25 mm, e.d. =
6.2744.010 PEEK compression fit-
46
46
(6.2744.010) or a compression
4646
Fig. 6
.
1
16
"
/
) are used
48
48
to be
4848
.
46
46 48
4646
Fig. 6
: Connectors for capillaries
48 47
4848
3 Tighten compression fitting
46
46
47
Tighten compression fitting
47
4747
46
46
4646
47
47
4747
48
48
4848
47
or
4646
4747
Compression fitting
(6.2744.010)
Compression fitting
(6.2744.070)
Capillary
6.1831.010 PEEK capillary or
6.1822.010 PTFE microcapillary
by hand (never use tools).
792 Basic IC
15
Page 25
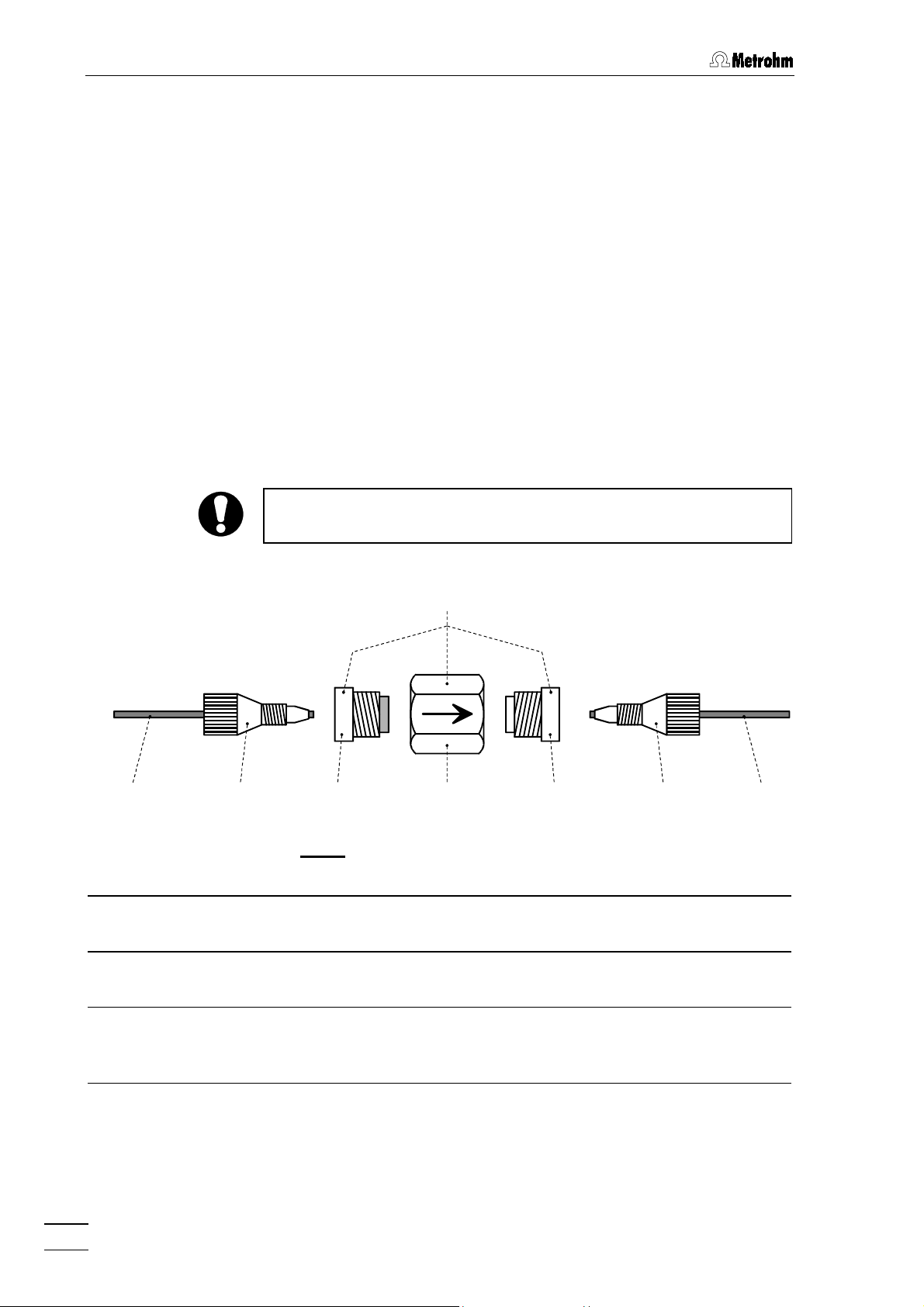
2 Installation
2.3.5 Filter unit PEEK
6.2821.100 Filter unit PEEK
One
tween the high-pressure pump and the injection valve
sic IC. This filter unit serves to avoid contamination by abrasive particles
of the piston seals.
The two other filter units PEEK supplied with the 792 Basic IC are installed between the pump tubings of the peristaltic pump and the inlet
capillaries for regeneration and rinsing solution (see
These filter units serve to protect the suppressor module from foreign
particles and bacterial growth.
28
The Filter unit PEEK
49
49
tors
For the connection of capillaries
(6.2744.010) or
filter are available as an option with the ordering number 6.2821.110
(set of 10).
(with filter) and
4949
For the connection of the filter unit, please note the flow direction
arrow printed on the housing.
28
consists of the housing
2828
51
51
(without filter) screwed into the housing
5151
47
47
(6.2744.070) must be used. New connectors
4747
28
28
2828
Fig. 7
(see
48
48
, PEEK compression fittings
4848
) is already installed be-
22
22
at the 792 Ba-
2222
section 2.8.2
50
50
and the two connec-
5050
49
49
4949
).
50
50
5050
46
46
4646
with
.
48
48 46
4848
Filter unit PEEK (6.2821.100)
28
28
2828
Compression fitting (6.2744.010)
46
46
4646
Capillary
48
48
4848
6.1831.010 PEEK capillary or
6.1822.010 PTFE microcapillary
792 Basic IC
16
46 49
4646
49 50
4949
: 6.2821.100 Filter unit PEEK
Fig. 7
50 51
5050
Connector with filter (6.2821.110)
49
49
4949
Part of 6.2821.100 Filter unit
50
Housing for filter unit
50
5050
Part of 6.2821.100 Filter unit
Connector without filter
51
51
5151
Part of 6.2821.100 Filter unit
51 46
5151
46 48
4646
48
4848
Page 26

2.4 Mains connection
2.4 Mains connection
Follow the instructions below for connecting to the power supply. If
the instrument is operated with a mains voltage set wrongly and/or
wrong mains fuse, there is a danger of fire!
2.4.1 Setting the mains voltage
Before switching on the 792 Basic IC for the first time, check that the
mains voltage set on the instrument (see
mains voltage. If this is not
on the instrument as follows:
1 Disconnect mains cable
Disconnect mains cable from mains connection plug
792 Basic IC.
the case, you must reset the mains voltage
Fig. 8
) matches the local
12
12
1212
of the
2 Remove fuse holder
13
Using a screwdriver, loosen fuse holder
12
connection plug
3 Check and change fuse if necessary
Carefully take the fuse installed for the desired mains voltage out
of fuse holder
fuse in the fuse holder is marked by the white arrow imprinted
next to the mains voltage range):
100}}}}120 V 1.0 A (slow-blow)
220}}}}240 V 0.5 A (slow-blow)
4 Insert fuse
Change fuse if necessary and reinsert in fuse holder
5 Install fuse holder
Depending on the desired mains voltage, insert fuse holder
the 792 Basic IC so that the corresponding mains voltage range
can be read normally and the adjacent white arrow points to the
white bar imprinted below the fuse holder (see
12
and take out completely.
1212
13
13
and check its specifications (the position of the
1313
13
below the mains
1313
Metrohm No. U.600.0016
Metrohm No. U.600.0013
13
13
1313
Fig. 8
).
.
13
13
in
1313
792 Basic IC
17
Page 27
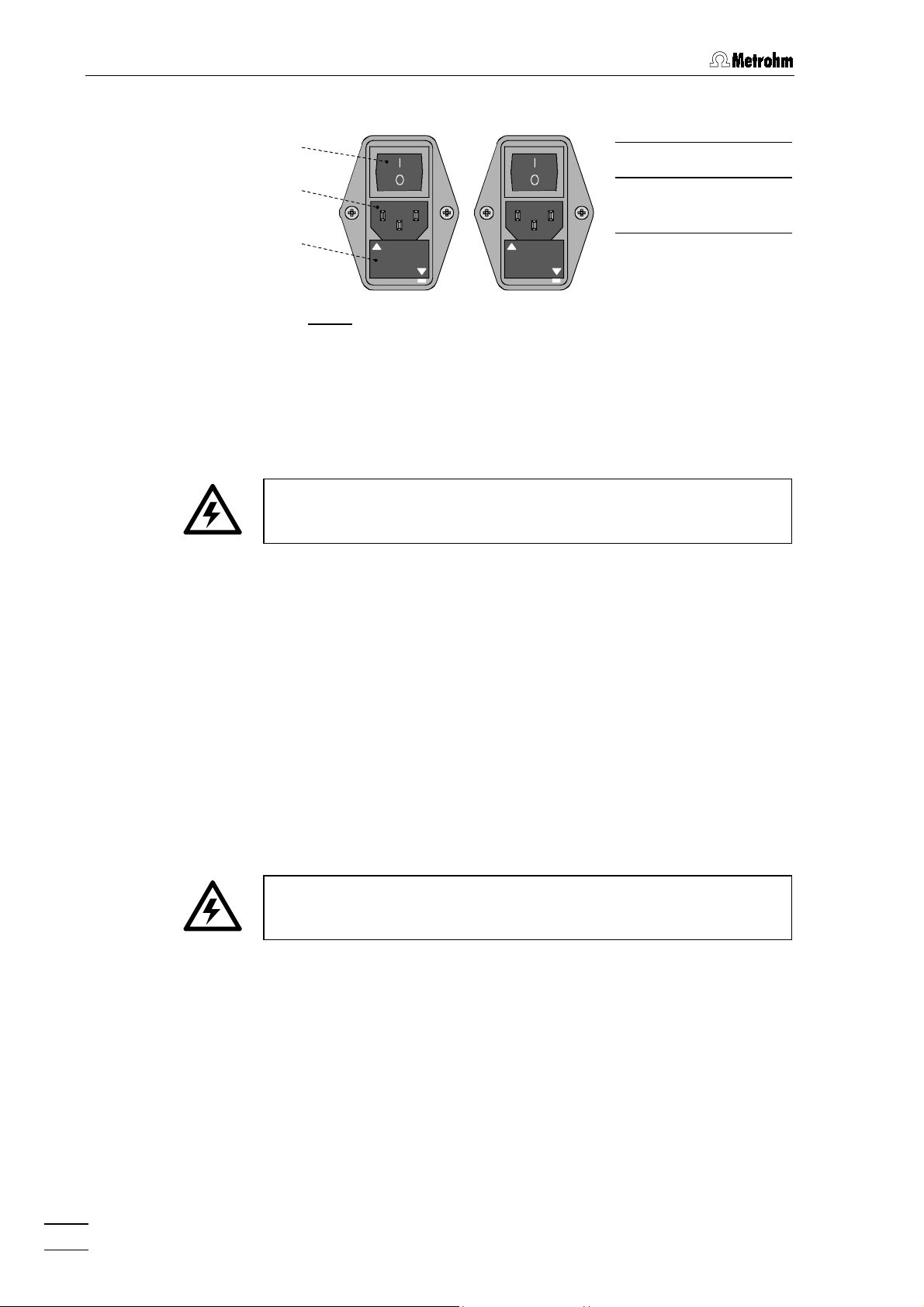
2 Installation
2.4.2 Fuses
100 – 120 V
Mains switch
11
11
1111
Mains connec-
12
12
1212
11
11
1111
12
12
1212
220 – 240 V
tion plug
220
240 V
100
----
120 V
----
13
13 Fuse holder
1313
13
13
1313
220
----
240 V
100
120 V
----
Fig. 8
: Setting the mains voltage
One of the two fuses 1 A/slow-blow for 100}120 V or 0.5 A/slow-blow
13
for 220}240 V is installed in fuse holder
13
of the 792 Basic IC as
1313
standard.
Ensure that the instrument is never put into operation with fuses of
another type, otherwise there is danger of fire!
For checking or changing fuses, process as described in
2.4.3 Mains cable and mains connection
Mains cable
The instrument is supplied with one of three mains cables
x
6.2122.020 with plug SEV 12 (Switzerland, })
x
6.2122.040 with plug CEE(7), VII (Germany, })
x
6.2133.070 with plug NEMA 5-15 (USA, })
which are three-cored and fitted with a plug with an earthing pin. If a different plug has to be fitted, the yellow/green lead (IEC standard) must
be connected to protective earth (protection class 1).
Any break in the earthing inside or outside the instrument can make it
a hazard!
Mains connection
Plug the mains cable into mains connection plug
Fig. 8
(see
).
section 2.4.1
12
12
of the 792 Basic IC
1212
.
2.4.4 On/off switching of the instrument
The 792 Basic IC is switched on and off using mains switch
the instrument is switched on, the mains pilot lamp
792 Basic IC
18
2222
lights up.
11
11
. When
1111
Page 28

2.5 Connection to the PC
2.5 Connection to the PC
2.5.1 Connecting cable
Always switch off 792 Basic IC and PC before you connect the two
instruments with the 6.2134.100 Cable.
14
Connect the RS232 interface
COM ports at the PC using the 6.2134.100 Cable (9 pin/9 pin). If only a
25-pin COM interface is available on the PC then the optionally available 6.2125.110 Cable (9 pin/25 pin) or a commercially available
adapter must be used.
2.5.2 Software installation
14
at the 792 Basic IC to one of the serial
1414
The PC program
«792 Basic IC 1.0»
is required for the operation of
the 792 Basic IC; this is contained on the 6.6045.003 CD included in the
accessories. This program runs under Windows 95, Windows 98, Windows NT and Windows 2000 operating systems and is installed as follows:
1 Install program
x
Insert 6.6045.003 Installation CD into CD drive.
x
Select
<Start>
installation CD and click on
x
Click on "
792
and
Run
. Browse for the
<OK>
.
setup.exe
file on the
" and follow the instructions given in the setup
program.
The software package will be installed in the desired direc-
tory. In addition to the program files, the following folders are
installed:
Data
Folder for storage of chromatogram files
Devices
Methods
Reports
Systems
*.chw
) and batch reprocessing files (
(
Folder for storage of device files (
Folder for storage of method files (
Folder for storage of report files (
*.wmf
and graphic files (
)
Folder with subfolders with system files
*.smt
).
(
*.dev
*.mtw
*.txt
*.bar
)
)
)
)
792 Basic IC
2 Registrierung
x
Please send us your 8.792.8007 Registration card as soon as
possible. Only registered users will get updated program versions at a special price.
19
Page 29
2 Installation
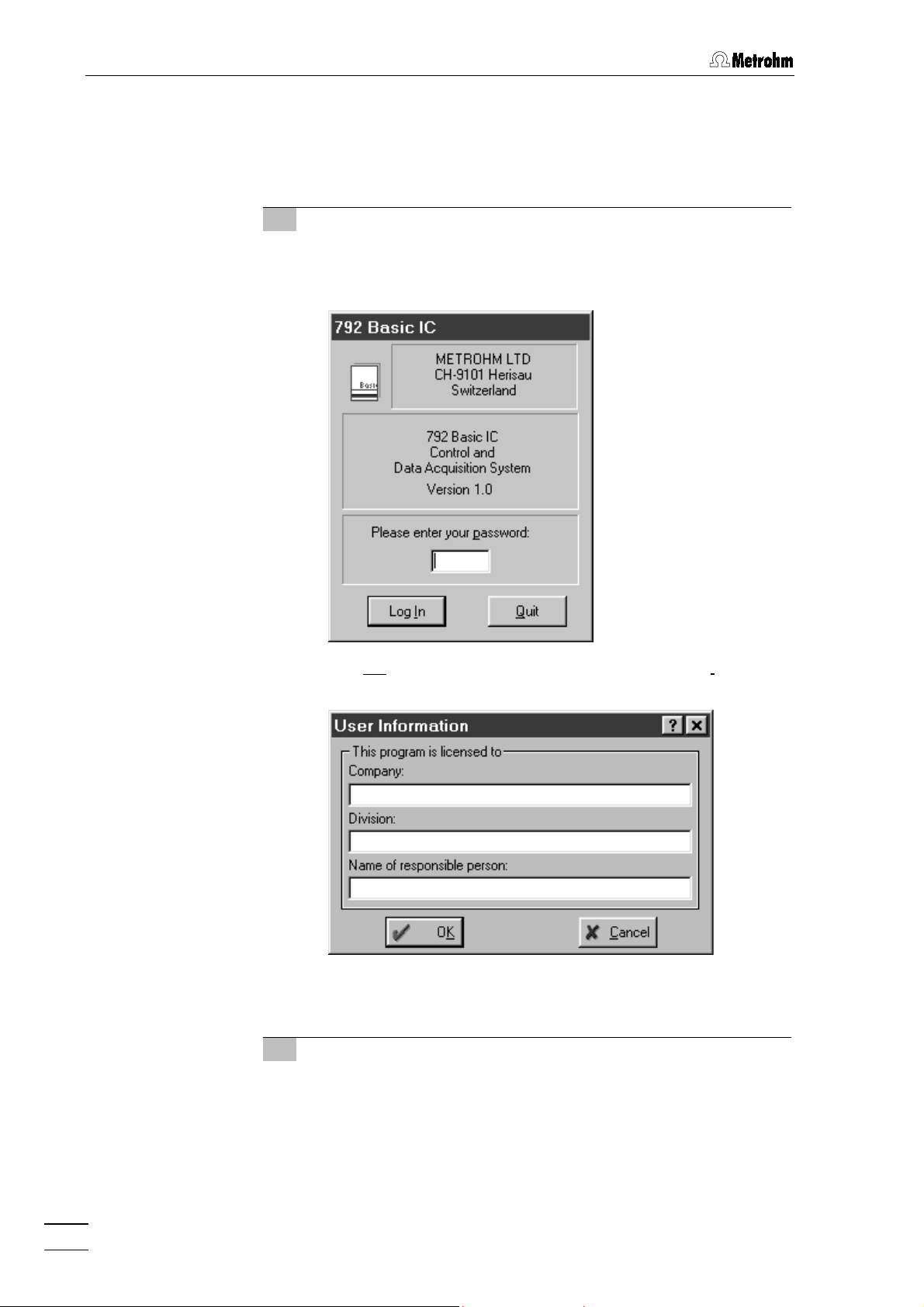
2.5.3 Basic settings
When the program is started for the first time several basic settings
must be made for the 792 Basic IC. Proceed as follows:
1 Start program
x
Double-click the software icon to start the program. The
program window with the opening picture is opened and the
Log In window appears on the screen:
x
Do not
enter any password here, just click on
<Log In>
following window appears:
x
Enter company, division and name and click on
<OK>
window appears only one time after software installation.
2 COM port settings
This step must only be carried out if a different COM interface
from COM1 is used for connection to the 792 Basic IC.
x
Click on
Options / 792 Basic IC:COM1
to open the
Links
. The
. This
window:
792 Basic IC
20
Page 30
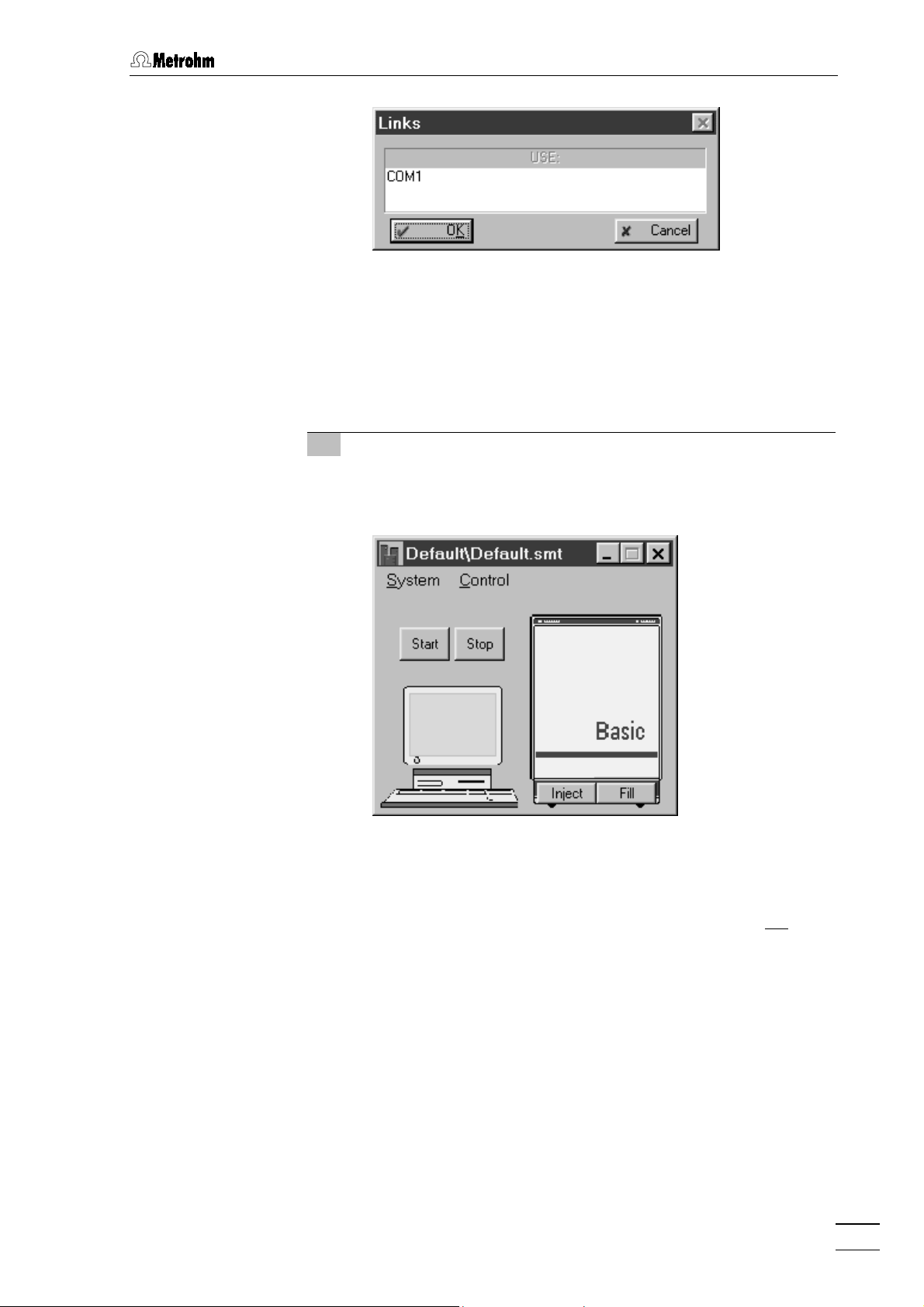
2.5 Connection to the PC
x
Click on
Change
COM1
menu item to open a window listing all available COM
ports at the PC.
x
Select the desired COM port to which the 792 Basic IC has
been connected and click on
x
Close the
Links
3 Open a system
x
Click on
folder
<Open>
File / Open / System
Default
. Select the system file
. The corresponding system window is opened:
using the right mouse button and select the
<OK>
. The window is closed.
window by clicking on
<OK>
.
in the main window. Open the
Default.smt
and click on
792 Basic IC
x
If the connection between PC and 792 Basic IC is working the
message
'#####' not found! Create?
create the configuration file
x
If the connection between PC and Personal IC does not
then the message
COM# ]]
Hardware settings file for 792 unit with serial number
will appear. Click
#####.792
Detection of hardware failed[792 Basic IC [
appears in the
SYSTEM STATE
<Yes>
in order to
for this instrument.
window. In this case
check whether the instrument has been switched on, whether
the connection cable is connected up properly and whether
the COM interface has been set correctly (see point 2). Then
repeat point 3.
work
21
Page 31

2 Installation
4 Hardware settings
Of the general hardware settings only the input of the cell constant
is described. Standard settings can normally be used for all other
parameters.
x
Click the 792 icon using the right mouse button and select
the
Hardware
item. The
Hardware settings
window is opened:
In the
Cell constant
field enter the cell constant which is
x
printed on the 1.732.0110 Detector block (see
x
Click on
<OK>
to close the window and save the settings.
section 2.3.1
).
792 Basic IC
22
Page 32

2.6 High-pressure pump
2.6 High-pressure pump
In order to avoid damage to the pump it must never be operated dry.
Each time that the pump is switched on always first check that the
eluent supply has been connected up correctly and that sufficient
eluent is present in the eluent bottle.
2.6.1 Removing the transport security screws
In order to prevent the pump drive from being damaged during trans-
10
port the pump head is fitted with three transport security screws
Fig. 2
). These transport security screws must be removed before the
high-pressure pump is started up. Also remove the red sticker attached
34
to the pump head
In order to avoid damage to the pump head these three security
screws should be attached to the pump head each time that it is to be
transported.
34
3434
.
10
1010
(see
2.6.2 Installing the pulsation dampener (option)
To protect the column material of sensitive separating columns (e.g.
methacrylate-based columns) against pressure drops caused by the injector, the use of the optional
recommended. It has to be installed between the high-pressure pump
and the injection valve of the 792 Basic IC as follows (see
1 Install pulsation dampener
x
Position the pulsation dampener
Basic IC on the base.
2 Connection to the pump
x
Unscrew PEEK capillary
54
connection
3 Connection to injection valve
x
Unscrew PEEK capillary
connection
The pulsation dampener is filled with isopropanol and must be rinsed
with eluent before connection to a separating column (see section
2.6.4).
54
of the pulsation dampener
5454
53
53
of the pulsation dampener
5353
6.2620.150 Pulsation dampener MF
52
52
in the interior of the 792
5252
27
27
of coupling
2727
18
18
of coupling
1818
Fig. 9
26
26
and attach it to
2626
52
52
.
5252
26
26
and attach it to
2626
52
52
.
5252
is
):
792 Basic IC
The 6.2620.150 Pulsation dampener can be operated in both directions.
23
Page 33

2 Installation
18
18
1818
29
29
2929
31
31
3131
POWER
28
28 27
2828
Fig. 9
: Connection of the pulsation dampener (option)
Inlet capillary for injector
18
18
1818
PEEK capillary,
length L = 24 cm
22
22 Injection valve 52
2222
27
27 Connection capillary
2727
PEEK capillary,
length L = 13 cm
28
28 Filter unit PEEK (6.2821.100) 54
2828
29
29 Connection capillary
2929
PEEK capillary,
length L = 13 cm
27 54
2727
31
31 Purge valve
3131
52 Pulsation dampener (6.2620.150)
5252
53
53 Connection to injection valve
5353
54 Connection to purge valve
5454
54 22
5454
53
53
5353
52
52
5252
22
2222
792 Basic IC
24
Page 34

2.6 High-pressure pump
2.6.3 Connecting the eluent bottle
To connect the eluent bottle with the high-pressure pump, insert the
supplied 6.1834.010 aspirating tubing (i.d. = 1.5 mm, e.d. = 2.5 mm,
5555
length = 2.5 m) into one of the openings
Basic IC. Pull the aspirating tubing sufficiently far into the interior of the
792 Basic IC and push at least 5 mm of it onto aspirating capillary
Fig. 3
(see
) of the high-pressure pump (it may be necessary to use emery paper). Screw on the 6.2821.090 aspirating filter at the other end of
the aspirating tubing and insert it into the eluent bottle.
7777
or
in the interior of the 792
32
32
3232
Only degassed (with N
, He or vacuum) and microfiltered (0.45 Pm
2
filter) eluents should be used!
Care must be taken that the eluent used is freely miscible with any
solvent remaining in the pump head (the pump head leaves the
factory filled with either isopropanol or methanol/water). If this is not
the case then the pump must first be rinsed with a solvent which is
miscible with both the previous eluent and the following eluent (e.g.
acetone).
2.6.4 Deaerating the pump and rinsing the pulsation dampener
The first time that it is started up the high-pressure pump must be
deaerated. Proceed as follows:
1 Prepare for deaeration
31
x
Open the rotary knob on purge valve
the counterclockwise direction (see
x
Mount a PEEK compression fitting
30
the end of capillary
the compression fitting
x
Push 6.2816.020 Syringe (without needle) into the connection
24
on coupling
24
2424
30
and screw coupling
3030
46
46
.
4646
until the stop is reached.
31
by approx. ½ turn in
3131
Fig. 3
).
46
46
4646
section 2.3.4
(see
24
24
2424
(6.2744.120) to
) to
792 Basic IC
2 Open system
x
Start the «792 Basic IC» PC program, if it has not been already been started (see
x
Select
folder
<Open>
File / Open / System
Default
. The corresponding system window is opened:
section 2.5.3
in the main window and open the
. Select the system file
).
Default.smt
and click on
25
Page 35

2 Installation
3 Set flow rate to 2 mL/min
x
Double-click the 792 icon in the system window to open the
window for manual control of the 792 Basic IC (see below).
x
Set the flow rate to
x
Click to
<Send to unit>
2 mL/min
to send this value to the 792 Basic IC.
in the
Flow
field.
792 Basic IC
26
Page 36

2.6 High-pressure pump
4 Deaerate pump
x
Make sure that the 6.1834.010 aspirating tubing for the highpressure pump has been immersed into the eluent.
x
Click the
<On>
button for
IC pump
to switch on the high-
pressure pump.
x
Use the syringe connected to the purge valve 31 to aspirate
air until eluent flows into the syringe.
x
Click the
<Off>
button for
IC pump
to switch off the high-
pressure pump.
31
x
Close the rotary knob on purge valve
clockwise direction (see
x
Remove the syringe from coupling
Fig. 3
).
31
by turning it in a
3131
24
24
.
2424
5 Rinse pulsation dampener (if present)
20
x
Place a beaker beneath the column connection capillary
x
Click the
<On>
button for
IC pump
to switch on the high-
pressure pump and rinse the pulsation dampener
52
52
5252
20
2020
filled
.
with isopropanol for ca. 10 min with eluent.
x
Click the
<Off>
button for
IC pump
to switch off the high-
pressure pump.
6 Reduce flow rate
x
Reset the original flow rate under
x
<Send to unit>
Click
Flow
(e.g.
0.2 mL/min
).
to send this value to the 792 Basic IC.
792 Basic IC
27
Page 37

2 Installation
2.7 Precolumns and separating columns
2.7.1 General information on precolumns
The use of easily exchangeable precolumns protects the separating
columns and prolongs their lifetime. The precolumns available from
Metrohm (see
cartridges, which are used together with the 6.2821.050 Twin cartridge
holder or the 6.2828.110 Precolumn cartridge holder.
New IC precolumns are normally filled with solution and sealed at both
ends. Before the precolumn is installed in the system, it must be
ensured that this solution is freely miscible with the eluent used
(check manufacturer's specifications).
section 6.3.2
) are either real precolumns or precolumn
2.7.2 Precolumns with twin cartridge holder
The 6.1005.020, 6.1005.040, 6.1005.050, 6.1007.010 and 6.1010.010
Precolumn cartridges are installed in the 6.2821.050 Twin cartridge
holder as follows (see
1 Install cartridge
x
Insert inlet capillary
in Manufit housing
x
Insert outlet capillary
tridge in Manufit pressure screw
x
Remove end caps from the precolumn cartridge
mesh
tridge).
x
Fit the two capillary end pieces onto the precolumn cartridge
59
59
(comply with the flow direction if specified on the column).
5959
x
Screw Manufit pressure screw
firmly together.
2 Connect precolumn
x
Cut inlet capillary
desired length and mount a compression fitting
tion 2.5
x
Connect inlet capillary
column connection capillary
valve or directly to connection "4“ of injection valve A.
x
Shorten outlet capillary
mount a compression fitting
Fig. 10
58
58
and gaskets
5858
).
):
55
55
with end piece for precolumn cartridge
5555
56
56
.
5656
61
61
with end piece for precolumn car-
6161
57
57
are already inserted in the car-
5757
60
60
6060
55
55
of the assembled precolumn to the
5555
55
55
either using the Coupling
5555
20
20
2020
61
61
of the precolumn to ca. 5 cm and
6161
46
46
4646
60
60
.
6060
59
59
(the steel
5959
56
(see
26
26
26 26
56
5656
to the
and Manufit housing
46
46
4646
mounted on the injection
section 2.5
(see
).
sec-
792 Basic IC
28
Page 38

2.7 Precolumns and separating columns
46
46
4646
61
61
6161
60
60
6060
57
57
5757
58
58
5858
3 Rinse the precolumn
61
61
.
6161
Column
x
Place a beaker beneath outlet capillary
x
Switch on 709 IC Pump, rinse precolumn for ca. 10 min with
eluent and then switch off 709 IC Pump.
20
20 Column connection capillary of
2020
injector
26
26 PEEK coupling (6.2744.120)
2626
Compression fitting (6.2620.000)
46
46
4646
Inlet capillary
55
55
5555
Manufit housing
56
56
5656
59
59
5959
58
58
5858
57
57
5757
56
56
5656
55
55
5555
46
46
4646
26
26
2626
46
46
4646
PTFE gasket (6.2821.010)
57
57
5757
2 Steel meshes (6.2821.020)
58
58
5858
Precolumn cartridge
59
59
5959
Manufit pressure screw
60
60
6060
61
61 Outlet capillary
6161
20
20
2020
Injector
Fig. 10
792 Basic IC
: Installing precolumn cartridges
29
Page 39

2 Installation
2.7.3 Precolumn glass cartridges with cartridge holder
The precolumn glass cartridge METROSEP Anion Dual 1 (6.1006.030)
is inserted in the 6.2828.110 Precolumn cartridge holder as follows (see
Fig. 11
):
1 Insert cartridge
x
Remove end fittings
x
Insert precolumn cartridge
tion of the column cartridge on sleeve, the column cartridge
should always be operated in the same flow direction).
x
Screw both end fittings
x
Tighten both end fittings
screwdriver (½ ¼ turn).
2 Connect precolumn
x
Provide the column connection capillary
injection valve with a PEEK compression fitting
tion 2.3.4
) and screw it tightly onto end fitting
side of the precolumn.
x
Screw connection piece
of the precolumn.
62
62
from sleeve
6262
64
64
in sleeve
6464
62
62
loosely to sleeve
6262
62
62
first by hand, then firmly using a
6262
65
65
to end fitting
6565
63
63
.
6363
63
63
(mark flow direc-
6363
63
63
6363
20
20
mounted on the
2020
62
62
on the other end
6262
by hand.
46
46
(see
4646
62
62
on the inlet
6262
sec-
3 Rinse precolumn
x
Place a beaker beneath the outlet capillary of the precolumn.
x
Open software window for manual system control.
x
If necessary, modify
inserted separating column and click on
send this value to the 792 Basic IC.
x
Switch on high-pressure pump (
rinse precolumn with eluent for ca. 10 min.
x
Switch off high-pressure pump by clicking
Flow rate
to the value suited for the
<Send to unit>
IC pump
) by clicking
<Off>
<On>
.
to
and
792 Basic IC
30
Page 40

2.7 Precolumns and separating columns
20
2020
4620
4646
63
62
62
6262
63
6363
64
64
6464
62
62
6262
65
6546
6565
Fig. 11
20
20 Column connection capillary
2020
from injector
Compression fitting (6.2744.010)
46
46
4646
PEEK capillary (6.1831.010)
48
48
4848
End fitting
62
62
6262
: Installation of precolumn glass cartridges with cartridge holder
Sleeve for precolumn cartridge
63
63
6363
64
64 Precolumn cartridge (6.1006.030)
6464
65
65 Connection piece
6565
for connection precolumn – column
2.7.4 IC anion precolumn SUPERSEP
The 6.1009.010 IC Anion Precolumn SUPERSEP has two connections
for PEEK capillaries and is installed as follows:
1 Connect precolumn
x
Remove end caps from the precolumn.
x
Fit PEEK compression fitting
20
20
lary
2020
x
Screw precolumn to column connection capillary
x
Cut a piece from the 6.1831.010 PEEK capillary as short as
possible and fit with PEEK compression fittings
tion 2.3.4
x
Fasten the prepared capillary to the other end of the precolumn.
(see
).
section 2.3.4
).
46
46
to column connection capil-
4646
20
20
.
2020
46
46
(see
4646
sec-
792 Basic IC
2 Rinse precolumn
x
Place a beaker beneath the outlet capillary of the precolumn.
x
Open software window for manual system control.
x
If necessary, modify
inserted separating column and click on
send this value to the 792 Basic IC.
x
Switch on high-pressure pump (
rinse precolumn with eluent for ca. 10 min.
x
Switch off high-pressure pump by clicking
Flow rate
to the value suited for the
<Send to unit>
IC pump
) by clicking
<Off>
<On>
.
to
and
31
Page 41

2 Installation
2.7.5 General information on separating columns
New IC separating columns are normally filled with solution and
sealed at both ends. Before the column is installed in the system, it
must be ensured that this solution is freely miscible with the eluent
used (check manufacturer's specifications).
The IC separating columns and precolumns currently available from
Metrohm are listed in
mation leaflet is provided with each column. You will find additional information concerning these columns in the 8.732.2003 Metrohm Monograph «Ion chromatography» and in special «Application Bulletins»,
which are available on request free of charge from your local Metrohm
agency.
When you install the column, always ensure that this is inserted
correctly in accordance with the flow direction shown (arrow must
point upwards
).
section 6.3.2
. A test chromatogram and an infor-
2.7.6 Selection of the sample loop
Selection of the sample loop depends on the separating column used.
Normally, the following sample loops are used:
Cation columns 10 PL
Anion columns with suppressor 20 PL
Anion columns without suppressor 100 PL
In the 792 Basic IC, the
stalled. If desired, the built-in sample loop can be replaced by one of
the sample loops available as an option (see
6.1825.210 sample loop (20 PPPPL, PEEK)
section 6.3.1
).
is in-
2.7.7 Installation of the separating column without suppressor
For operation of the 792 Basic IC 792 without suppressor module, the
IC separating column is installed as follows (see
1 Connect column to injector
66
).
20
20
2020
66
6666
x
Remove end caps from column
x without precolumn:
Screw inlet end of separating column
to column connection capillary
x with precolumn in twin cartridge holder:
Screw inlet end of separating column
to outlet capillary
section 2.7.2
in
x with precolumn in cartridge holder:
Screw inlet end of separating column
to the precolumn fixed in the cartridge holder as described in
section 2.7.3
(see
(see
61
61
of the twin cartridge holder as described
6161
Fig. 10
Fig. 11
).
Fig. 12
.
66
66
6666
mounted on the injector.
66
66
6666
66
66
6666
):
(note flow direction)
(note flow direction)
(note flow direction)
792 Basic IC
32
Page 42

2.7 Precolumns and separating columns
x with IC anion precolumn SUPERSEP:
66
Screw inlet end of separating column
to the precolumn installed as described in
2 Rinse column
x
Place a beaker beneath the column outlet.
x
Open software window for manual system control.
x
If necessary, modify
inserted separating column and click on
send this value to the 792 Basic IC.
x
Switch on high-pressure pump (
rinse column with eluent for ca. 10 min.
x
Switch off high-pressure pump by clicking
3 Connect column to detector block
x
Screw outlet end of separating column
37
37
permanently mounted on the detector block
3737
Flow rate
to the value suited for the
66
6666
IC pump
(note flow direction)
section 2.7.4
<Send to unit>
) by clicking
<Off>
.
66
66
to the inlet capillary
6666
38
38
3838
.
to
<On>
.
and
4 Fix column
x
Insert one or two column holders
or 6.2027.050) in the mounting rails
column
66
66
in the column holder
6666
38
38
3838
37
37
3737
67
67
6767
19
19
1919
22
22
2222
66
66
6666
19
19
1919
67
67
6767
67
67
(6.2027.030, 6.2027.040
6767
19
19
and fasten separating
1919
67
67
.
6767
19
19 Mounting rail
1919
67
for column holder
20
20 Column connection
2020
capillary
Connection injection
22
22
valve
separating column
Injection valve
22
22
2222
Inlet capillary for
37
37
3737
detector block
PEEK capillary, fixed
mounting
38
38 Detector block
3838
(1.733.0110)
66
66 Separating column
6666
2222
–
67
6767
66
66
6666
Fig. 12
792 Basic IC
20
20
2020
: Installation of column without suppressor
67
67 Column holder
6767
(6.2027.0X0)
33
Page 43

2 Installation
2.7.8 Installation of the separating column with suppressor
For operation of the 792 Basic IC with suppressor module, the IC separating column is first connected to the injector or precolumn. The connection to the suppressor module and the detector block is described
section 2.8
in
1 Connect column to injector
2 Rinse column
.
66
x
Remove end caps from column
x
Screw inlet end of separating column
to column connection capillary
precolumn (procedure see
x
Place a beaker beneath the column outlet.
x
Open software window for manual system control.
x
If necessary, modify
Flow rate
inserted separating column and click on
66
.
6666
66
66
(note flow direction)
6666
20
20
or to the already installed
2020
section 2.7.7
).
to the value suited for the
<Send to unit>
send this value to the 792 Basic IC.
x
Switch on high-pressure pump (
IC pump
) by clicking
rinse column with eluent for ca. 10 min.
x
Switch off high-pressure pump by clicking
<Off>
..
to
<On>
and
3 Fix column
67
x
Insert one or two column holders
or 6.2027.050) in the mounting rails
66
column
66
in the column holder
6666
67
(6.2027.030, 6.2027.040
6767
19
19
and fasten separating
1919
67
67
.
6767
792 Basic IC
34
Page 44

2.8 Suppressor module
2.8 Suppressor module
2.8.1 General information on suppressor module
Metrohm Suppressor Module MSM
The
stalled in the 2.792.0020 Basic IC comprises a total of 3 suppressor
units which are in turn used for suppression, regenerated with sulfuric
acid and rinsed with water. To record every new chromatogram under
comparable conditions, work is normally carried out with freshly regenerated suppressor. Switching is either automatic together with the valve
switching or manual.
for chemical suppression in-
The suppressor units must never be regenerated with H
same flow direction used for the eluent. You should thus always install
2SO4
in the
the inlet and outlet capillaries as described in section 2.8.4 according
to the scheme shown in Fig. 15.
For operation of the suppressor module, the
pump
built into the 2.792.0020 Basic IC is used which conveys the regeneration solution (normally
tion (normally
dist. H
20 mmol/L H
O
) to the suppressor units (flow rate of
2
two-channel peristaltic
) and the rinsing solu-
2SO4
0.5 mL/min).
The three inlets and outlets numbered 1...3 on the suppressor module
each have 2 permanently mounted PTFE capillaries, which must be
connected as described in
section 2.8.4
(see
Fig. 14
and
Fig. 15
).
To avoid contamination of the suppressor module by foreign particles
or bacterial growth, the two
tion 2.3.5
) supplied with the 2.792.0020 Basic IC must be installed be-
6.2821.100 Filter units PEEK
(see
tween the peristaltic pump and the inlet capillaries of the suppressor
module.
The suppressor module must never
be switched in the dry state as
there is a danger of blocking. Before every switching operation of the
suppressor module, the three suppressor units must have been
rinsed for at least ½ h with eluent, regeneration and rinsing solution.
sec-
2.8.2 Preparation of the peristaltic pump
Before start-up the accessories for the 2-channel peristaltic pump built
into the 792 Basic IC must be mounted according to
as follows:
1 Attach pump tubings
x
Loosen both tubing cartridges
44
44
from the holding clamp
4444
43
43
lever
792 Basic IC
and remove from mounting pin
4343
Fig. 13
40
40
mounted above pump drive
4040
42
42
by pressing down snap-action
4242
45
45
(see
4545
. Proceed
Fig. 14
).
35
Page 45

2 Installation
41
x
Press contact pressure lever
41
on both tubing cartridges
4141
down as far as it will go.
71
x
Insert the pump tubings
71
7171
the tubing cartridges as shown in
73
stopper
73
must click into the corresponding holder on the
7373
and
72
72
(6.1826.060) into each of
7272
Fig. 13
. The white-yellow
left-hand side of the tubing cartridge.
45
x
Place the tubing cartridges on mounting pin
down on the right-hand side until snap-action lever
42
into position on holding clamp
42
. Take care that no kinks are
4242
45
and press
4545
43
43
4343
clicks
formed in the pump tubing.
2 Install Filter units PEEK
74
71
71
7171
74
(6.2744.110) to the outlet end of the two
7474
72
72
and
7272
.
28
28
28 28
section 2.3.5
(see
) to the other
x
Mount a coupling
pump tubings
x
Attach a filter unit PEEK
end of this coupling (note flow direction!).
68/69
68/69 70
68/6968/69
70 71/72
46 28
4646
71/72 73
7070
71/7271/72
73 40
7373
40 41
4040
41 73
4141
73 74
4346
7373
4343
74 77/78
28 46
7474
2828
46
4646
77/7843
77/7877/78
Fig. 13
28
28
Filter unit PEEK (6.2821.100)
2828
Tubing cartridge
40
40
4040
Contact pressure lever
41
41
4141
43
43 Snap-action lever 73
4343
PEEK compression fitting
46
46
4646
(6.2744.010)
68
68 Aspirating tubing for H
6868
69
69 Aspirating tubing for H
6969
792 Basic IC
36
: Installing pump tubings
70
O 77
2
78
2SO4
70 Coupling (6.2744.030)
7070
71
71 Pump tubing (6.1826.060) for H2SO4
7171
72
72 Pump tubing (6.1826.060) for H2O
7272
73 Stopper (white-yellow)
7373
74
74 Coupling (6.2744.110)
7474
77 Suppressor inlet capillary for H2O
7777
78 Suppressor inlet capillary for
7878
H
2SO4
Page 46

2.8 Suppressor module
80
80
8080
79
79
7979
69
69
6969
68
68
6868
22
22
2222
20
20
2020
37
37
3737
38
38
3838
75
75
7575
26
26
2626
19
19
1919
67
67
6767
76
76
7676
66
66
6666
39
39
3939
19
19
1919
67
67
6767
40
40
4040
77
77
7777
78
78
7878
70
70
7070
70
70
7070
45
45
4545
28 28
2828
Fig. 14: Installation of column with suppressor
Mounting rail
19
19
1919
67
for column holder
Column connection capillary
20
20
2020
PEEK capillary (6.1831.010; 30 cm)
Injection valve
22
22
2222
67
6767
74
7428
7474
28
2828
74
74
7474
66
66
6666
67
67 Column holder (6.2027.0X0)
6767
68
68 Aspirating tubing for H2O
6868
44
44
4444
71
7171
Separating column
6.1803.020 PTFE tubing
72
7271
7272
41
41
4141
42
42
4242
43
43
4343
PEEK coupling (6.2744.040)
26
26
2626
Filter unit PEEK (6.2821.100)
28
28
2828
37
37 Inlet capillary to detector block
3737
(fixed mounting)
38
38 Detector block (1.733.0110) 72
3838
792 Basic IC
69
69 Aspirating tubing for H2SO4
6969
6.1803.020 PTFE tubing
70
70 Coupling (6.2744.030)
7070
71
71 Pump tubing (6.1826.060) for H
7171
72 Pump tubing (6.1826.060) for H
7272
2SO4
O
2
37
Page 47

2 Installation
39
39 Suppressor module 74
3939
40
40 Tubing cartridge (6.2755.000)
4040
71/72
for pump tubings
41
41 Contact pressure lever
4141
for adjusting the contact pressure
42
42 Holding clamp
4242
71/72
71/7271/72
74
7474
75
75 Suppressor inlet capillary for
7575
76
76 Suppressor outlet capillary for
7676
77
77 Suppressor inlet capillary for
7777
for locking the tubing cartridge into
place
43
43 Snap-action lever
4343
for releasing the tubing cartridge
44
44 Pump drive
4444
Roller head with contact rollers
45
45 Mounting pin
4545
for attaching the tubing cartridge
78
78 Suppressor inlet capillary for
7878
79
79 Suppressor outlet capillary for H
7979
80
80 Suppressor outlet capillary for
8080
2.8.3 Connection of supply bottles
The supply lines for the regeneration and rinsing solution between the
storage bottles and the peristaltic pump are installed as follows:
Coupling (6.2744.110)
eluent
eluent
O
H
2
2SO4
2SO4
H
H
O
2
1 Prepare supply bottle for H2SO4
x
Prepare regeneration solution suited for the desired application and separating column (normally 20 mmol/L H
x
Fill regeneration solution into supply bottle and label the
bottle.
2 Connect aspirating tubing for H2SO4
69
x
Prepare aspirating tubing
69
: Cut a piece of the 6.1803.020
6969
PTFE tubing to the required length (normally ca. 120 cm).
69
x
Insert one end of the aspirating tubing
69
6969
tion solution storage bottle and tighten it so that the tubing is
firmly held.
69
x
Insert the free end of aspirating tubing
openings
5555
of the 792 Basic IC (
see Fig. 2
69
6969
ciently far into the interior.
70
71
71
7171
70
70
7070
70
(6.2744.030) to the inlet end of the rear
7070
.
69
69
and screw this compression fitting on to
6969
Fig. 14
(see
).
x
Mount a coupling
pump tubing
x
Mount a 6.2744.010 Compression fitting at the end of the
aspirating tubing
the coupling
).
2SO4
into the regenera-
into one of the
) and pull it suffi-
3 Prepare supply bottle for H2O
x
Prepare rinsing solution suited for the desired application and
separating column (normally dist. H
x
Fill rinsing solution into a supply bottle and label the bottle.
792 Basic IC
38
O).
2
Page 48

2.8 Suppressor module
4 Connect aspirating tubing for H2O
68
x
Prepare aspirating tubing
68
: Cut a piece of the 6.1803.020
6868
PTFE tubing to the required length (normally ca. 120 cm).
68
x
Insert one end of the aspirating tubing
68
into the rinsing
6868
solution storage bottle and tighten it so that the tubing is
firmly held.
68
x
Insert the free end of aspirating tubing
openings
5555
of the 792 Basic IC (
see Fig. 2
68
into one of the
6868
) and pull it suffi-
ciently far into the interior.
70
72
72
7272
70
70
7070
70
(6.2744.030) to the inlet end of the front
7070
.
68
68
and screw this compression fitting on to
6868
Fig. 14
(see
).
x
Mount a coupling
pump tubing
x
Mount a 6.2744.010 Compression fitting at the end of the
aspirating tubing
the coupling
2.8.4 Connection of the suppressor module
The three inlets and outlets numbered 1...3 on the suppressor module
39
39
each have 2 permanently mounted PTFE capillaries, which must be
3939
connected as follows (see
Fig. 14
1 Inlet capillary for eluent
75
x
Screw inlet capillary
39
module
39
to outlet end of separating column
39 39
75
7575
6.2744.010 Compression fitting.
2 Outlet capillary for eluent
x
Screw outlet capillary
39
sor module
39
to coupling
3939
sion fitting.
37
x
Screw inlet capillary
26
coupling
26
2626
.
37
3737
3 Inlet capillary for H2SO4
78
x
Attach inlet capillary
39
module
unit PEEK
39
using a 6.2744.010 Compression fitting to the filter
3939
28
28
2828
connected to the rear pump tubing
78
7878
Fig. 15
and
marked with "Eluent" of suppressor
76
76
marked with "Detector" of suppres-
7676
26
26
2626
of detector block
marked with "H
):
66
66
using a
6666
using a 6.2744.010 Compres-
38
38
to other end of
3838
" of suppressor
2SO4
71
71
.
7171
792 Basic IC
4 Outlet capillary for H2SO4
80
x
Pull outlet capillary
39
module
39
from below through one of the openings
3939
80
marked with "Waste" of the suppressor
8080
the inner compartment of the 792 Basic IC.
80
x
Lead outlet capillary
80
to a sufficiently large waste container
80 80
and fix it in place.
6666
out of
39
Page 49

2 Installation
H2SO
Waste
Fig. 15
Eluent
4
78
7878
80
80
8080
2
Waste
75
75
7575
79
79
7979
76
7678
7676
1
3
77
77
7777
Detector
H2O
: Connections at suppressor module
5 Inlet capillary for H2O
x
Attach inlet capillary
39
module
unit PEEK
39
using a 6.2744.010 Compression fitting to the filter
3939
28
28
connected to the front pump tubing
2828
Suppressor inlet capil-
75
75
7575
lary for eluent
76
76 Suppressor outlet
7676
capillary for eluent
77
77 Suppressor inlet capil-
7777
lary for H
78
78 Suppressor inlet capil-
7878
lary for H
79
79 Suppressor outlet
7979
capillary for H
80
80 Suppressor outlet
8080
capillary for H
77
77
marked with "H
7777
O" of suppressor
2
O
2
2SO4
O
2
2SO4
72
72
7272
.
6 Outlet capillary for H2O
79
x
Pull outlet capillary
39
module
39
from below through one of the openings
3939
79
marked with "Waste" of the suppressor
7979
the inner compartment of the 792 Basic IC.
79
x
Lead outlet capillary
79
to a sufficiently large waste container
79 79
and fix it in place.
7 Fasten capillaries to the side walls
x
If necessary, the two aspirating tubings
fixed in the required position in the interior with the help of a
Y.107.0150 self-adhesive strap.
x
If necessary, the two outlet capillaries
in the required position in the interior with the help of a
Y.107.0150 self-adhesive strap.
79
79
7979
68
68
6868
and
and
80
80
8080
69
69
6969
6666
out of
can be
can be fixed
792 Basic IC
40
Page 50

2.9 Putting into operation
2.9 Putting into operation
2.9.1 Putting into operation without suppressor
Before sample solutions can be injected at the
792 Basic IC
(without
use of the suppressor), the entire system must be tested for leaks and
then conditioned with eluent until the baseline is stable. Proceed as follows:
1 System öffnen
x
Start the «792 Basic IC» PC program, if it has not already
<Open>
section 2.5.3
in the main window. Select the sys-
.
).
anionsupp.smt
)
been started (see
x
Select
File / Open / System
tem file suited for the inserted column (e.g.
and click on
2 Open control window
x
Double-click the 792 icon in the system window. The control
window for manual control of the 792 Basic IC appears, which
indicates conductivity, pressure and current system parameters.
792 Basic IC
3 Start system
x
Make sure, that the aspirating tubing 6.1834.010 for the highpressure pump is immersed in the eluent.
x
Select
Startup hardware (Measure baseline)
menu in the system window. The high-pressure pump is
started, at the same time, a chromatogram window is opened
where the baseline is recorded continuously.
from the
Control
41
Page 51

2 Installation
4 Check for leaks
x
Check all capillaries and their connections between the highpressure pump and the detector block for escaping liquid. If
eluent escapes anywhere, the appropriate compression fitting
must be tightened further or changed.
5 Condition system
x
Rinse the system with eluent until the desired stability of the
baseline is reached (normally 30}60 min; if the eluent is
changed, the establishment of the ion exchanger equilibrium
on the separating column can take longer).
x
The instrument is now ready for sample determinations using
the selected system.
2.9.2 Putting into operation with suppressor
Before sample solutions can be injected at the
792 Basic IC
(with use
of the suppressor), the entire system must be tested for leaks and then
conditioned with eluent until the baseline is stable. At the same time,
the suppressor module must be conditioned. Proceed as follows:
1 Open system "Prep MSM.smt"
x
Start the «792 Basic IC» PC program, if it has not already
been started (see
x
Select
Suppressed anion
Click on
File / Open / System
<Open>
section 2.5.3
).
in the main window. Open the folder
and select the system file
.
Prep MSM.smt
.
2 Open control window
x
Double-click the 792 icon in the system window. The control
window for manual control of the 792 Basic IC appears, which
indicates conductivity, pressure and current system parameters.
792 Basic IC
42
Page 52

2.9 Putting into operation
3 Start system
x
Make sure, that the aspirating tubing 6.1834.010 for the highpressure pump is immersed in the eluent.
x
Select
Startup determination
from the
Control
menu in the system window. The high-pressure pump and the peristaltic
pump are started, at the same time, a chromatogram window
is opened where the baseline is recorded continuously. The
suppressor module is automatically switched to the next position every 20 min and conditioned in this way.
4 Set contact pressure for pump tubings
x
Press contact pressure lever
41
on both tubing cartridges
4141
40
40
4040
41
upwards until regeneration and rinsing solution just start to be
drawn in.
41
x
Then press contact pressure lever
41
upwards until it clicks
4141
once more to obtain optimal contact pressure.
5 Check for leaks
x
Check all capillaries and their connections in the 792 Basic IC
for escaping liquid. If eluent escapes anywhere, the appropriate compression fitting must be tightened further or changed.
6 Condition system
x
Rinse the system with eluent until the desired stability of the
baseline is reached (normally 30}60 min; if the eluent is
changed, the establishment of the ion exchanger equilibrium
on the separating column can take longer). After this time the
suppressor module is sufficiently conditioned too.
x
The instrument is now ready for sample determinations using
the selected system.
Pump tubings are consumable material with a lifetime, which depends
on the contact pressure. This is why the tubing cartridges should be
raised completely by loosening snap-action lever on the right-hand
side if the pump is to remain switched off for a considerable length of
time (the set contact pressure remains unchanged).
792 Basic IC
43
Page 53

2 Installation
792 Basic IC
44
Page 54

3.1 Requirements
3 Operating tutorial
This section introduces you to the operation of the 792 Basic IC by
means of a brief operating tutorial which describes the basic operating steps needed for the recording of an ion chromatogram using one
of the system files supplied.
The determination of the anionic content of a drinking water sample
with the METROSEP Anion Dual 1 column is used as an illustrative
example. Please note that the steps and parameter settings described
apply only to this example. If you use a different separating column
and system file, the procedures described in the tutorial must be
modified appropriately.
For further explanations of the operation, please refer to section 4.
3.1 Requirements
For the determination of anions in drinking water described in this tutorial, the following instruments, accessories and solutions are required:
x 2.792.0020 Basic IC
with suppressor module
x 6.1825.210 Sample loop (20 PPPPL, PEEK)
already integrated in the 792 Basic IC
x 6.5325.000 Starter Kit
incl. the following accessories:
6.1006.020 IC Column cartridge
6.2828.100 Glass cartridge holder (150 mm)
6.2620.150 Pulsation dampener
METROSEP Anion Dual 1 (150 mm)
792 Basic IC
x Eluent
2.4 mmol/L NaHCO
in dist. H
Flow: 0.5 mL/min
x Standard
Standard solution with 0.5 mg/L fluoride, 5 mg/L chloride, 5 mg/L
nitrite, 10 mg/L bromide, 10 mg/L nitrate, 10 mg/L phosphate and
10 mg/L sulfate (in dist. H
/ 2.5 mmol/L Na2CO3/ 2 % Acetone
3
O
2
O)
2
45
Page 55

3 Operating tutorial
3.2 Preparations
Before you start this brief tutorial, the entire IC system must be correctly
installed as described in
points for the installation are described once again (for details, see the
sections mentioned).
1 Install 792 Basic IC
Setting up instrument
section 2.
In what follows, the most important
section 2.2
Installing and connecting detector block
Mounting syringe and aspirating tubing
Mains connection
Connection to PC
2 Prepare eluent
Preparing eluent:
2.4 mmol/L NaHCO
2 % Acetone in dist. H
Microfiltering and degassing eluent
/ 2.5 mmol/L Na2CO3/
3
O
2
3 Install high-pressure pump
Removing transport security screws
Mounting pulsation dampener
Installing eluent supply
Degassing pump
section 2.3.1
section 2.3.2
section 2.4
section 2.5
section 5.1.3
section 2.6.1
section 2.6.2
section 2.6.3
section 2.6.4
4 Connecting separating column
Connecting IC cation column
Conditioning system
792 Basic IC
46
section 2.7.7
section 2.9.1
Page 56

3.3 Calibration
3.3 Calibration
After the complete IC system has been installed as described in
tion 3.2
, the first calibration can be started. A standard solution is re-
sec-
quired for this; it should contain the substances to be determined in
approximately the same concentrations in which they can be expected
in the sample.
In our example of drinking water determination using the METROSEP
Anion Dual 1 column a 20 PL sample loop is used; this is filled with the
following standard solution:
0.5 mg/L fluoride
5 mg/L chloride and nitrite
10 mg/L bromide, nitrate, phosphate and sulfate
Please note that all program displays refer to the condition in which the
system
this tutorial at a later date and the system
Asupp.smt
is loaded for the first time. If you want to work through
Asupp.smt
has been altered in
the meantime then differences with respect to the program display and
the parameter values may occur.
In the description of the calibration procedure, it is assumed that the PC
and 792 Basic IC are not in operation and that the system must first be
conditioned again. If this is not the case (e.g. if you start the tutorial
immediately after conditioning) then you can skip steps 1 to 5.
1 Switch on 792 Basic IC
Switch on 792 Basic IC with mains switch
the instrument. After the instrument has been switched on the
mains pilot lamp
2222
lights up.
2 Switch on PC
Switch on PC and start «792 Basic IC» program.
3 Open system "
Select
File / Open / System
system file
<Open>
on
4 Start system "
Select
Start determination
Asupp.smt
Asupp.smt
.
Asupp.smt
"
in the folder
"
window. The high-pressure pump is started, at the same
time, a chromatogram window opens where the baseline is
recorded continuously.
11
11
on the rear of
1111
in the main window. Select the
of the
Suppressed anion
Control
menu in the system
and click
792 Basic IC
5 Condition system "
Rinse IC system with eluent until the desired stability of the
baseline is achieved (at least 1 h).
Asupp.smt
"
47
Page 57

3 Operating tutorial
6 Start determination
Click on
tion
of the
<Start>
Control
in the system window or select
menu. A chromatogram window opens
Start determina-
where the baseline is recorded continuously. The status bar
of this window shows the message
Measure(Baseline)
, beside
this running time, analysis time, absolute conductivity and
number of measuring points per second are displayed. The
message
STATE
window.
Waiting for INJECT [792COM#]
appears in the
SYSTEM
7 Enter information for determination
Enter the desired information concerning the sample in the
automatically opened
bration level
to 0 and confirm with
Edit sample description
<OK>
.
window. Set
Cali-
8 Condition system
Let the system run for several minutes. If the system has
already been conditioned then a stable conductivity value of
approx. 16 PS/cm will be obtained after a few minutes.
Double-click the chromatogram or select
View all
of the
View
menu. The sensitivity is set automatically so that all measuring points are visible.
This function is only available if the integration has been
started. In the present example the integration only starts
after a delay period
Delay = 3.3 min
.
Select the desired sensitivity using the cursor keys <Ï> or
<Ð>. In the chromatogram window the following display is
seen, for example:
792 Basic IC
48
Page 58

3.3 Calibration
9 Switch injection valve to "FILL" position
Click on the
button of the 792 icon in the system
window to switch the injection valve to the "FILL" position. At
the same time, the suppressor module is switched to the next
position.
10 Fill sample loop
23
Immerse the aspirating tubing
Using the syringe fixed to syringe tubing
23
in the standard solution.
2323
25
25
, siphon in ca.
2525
1 mL standard solution.
11 Switch injection valve to "INJECT" position
Click on the
button of the 792 icon in the system
window to switch the injection valve to the "INJECT" position.
At the same time, the data recording is started automatically.
The status bar of the chromatogram window shows the mes-
Measure
sage
INJECT done [792COM#]
When the analysis time of 16 min set in the method has
SYSTEM STATE
, the
window shows the message
.
expired, the recorded chromatogram is automatically evaluated and stored. The chromatogram window then closes.
12 Open chromatogram
Click on
dow. Select the chromatogram file
click on
<OK>
File / Open / Chromatogram
or
*.chw
in the main win-
just recorded and
. The chromatogram window is opened where
the found peaks are numbered and the baselines are drawn
in.
792 Basic IC
49
Page 59

3 Operating tutorial
13 Modify integration parameters
Click on
or select
Integration
from the
the main window to open the integration parameters window.
If required (e.g. if the fluoride peak is not detected), change
<Apply>
Delay
before starting peak integration.
Integration parameters
. The
the time delay
Click on
and the chromatogram is reintegrated.
Method
menu in
window is opened
792 Basic IC
50
Page 60
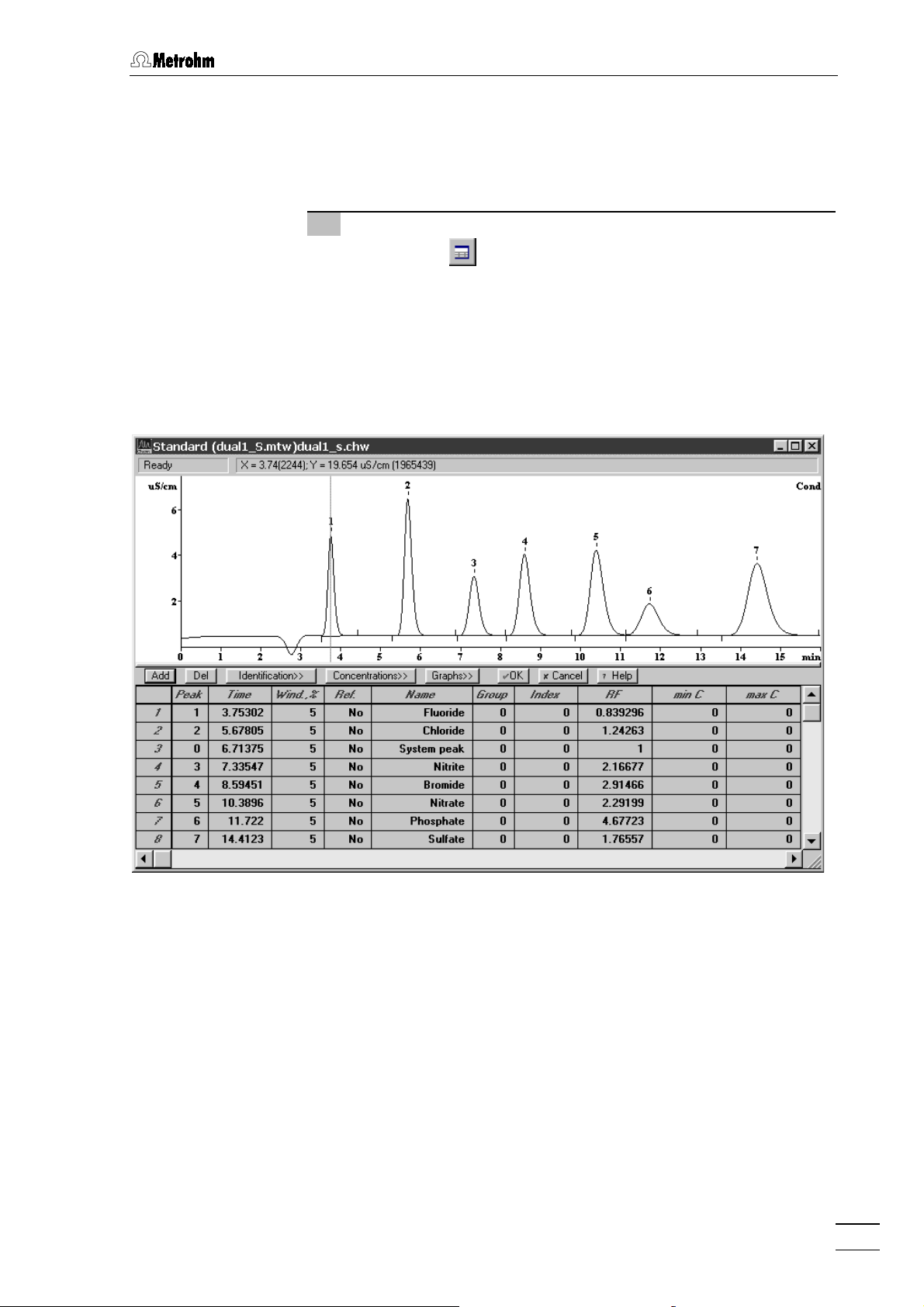
3.3 Calibration
Repeat this procedure for all other integration parameters
until the result satisfies your expectations. Click on
<Apply>
for
each parameter change.
Close the
Integration parameters
window with
<OK>
.
14 Modify peak allocation
Click on
Method
or select
menu. The prepared table for the components fluo-
Calibration / Components
from the
ride, chloride, nitrite, bromide, nitrate, phosphate and sulfate
is displayed below the chromatogram. For all peaks, which
could be allocated unambiguously to a component this table
Peak
contains the peak number in the
Time
tion time in the
column. In the chromatogram itself, this
column and the reten-
retention time is indicated by the cursor (vertical line).
792 Basic IC
If the
Peak
column contains a 0 the peak must be manually
allocated to a component. In this case, insert the peak num-
Peak
ber from the chromatogram into the
Time
the
field on this row with the mouse. The corresponding
column and click
retention time is then inserted automatically as the new time
for this component.
For each correctly allocated peak, click on the retention time
Time
in the
column. This time is automatically shown in the
chromatogram by the cursor. If the retention time is not located in the area of the middle of the peak, then the value in
Time
the
column should be adapted accordingly. This is done
by clicking on the chromatogram and moving the cursor with
the aid of the cursor keys <Í> and <Î> to the middle of
the peak and reading off the corresponding retention time in
51
Page 61

3 Operating tutorial
the status line. Enter this value (rounded off if necessary) into
Time
the
column. The optimized table could, for example,
then appear as follows:
15 Start calibration
Click the
<Concentrations>
button in the component window.
Click on
<Calibrate>
. The following window appears:
792 Basic IC
52
Page 62

3.3 Calibration
Confirm
Click on
Level 1
<OK>
in the
<OK>
with
Concentrations
.
16 Display calibration curves
Click on
Select the desired component in the
<Graphs>
in the
Components
the calibration curve should be displayed (e.g. for
window.
window.
Component
field for which
chloride
).
792 Basic IC
Close the
Close the
clicking on
Component - chloride
Components
<OK>
window below the chromatogram by
.
window with
17 Save chromatogram and method
Close the chromatogram window. A window appears with the
message
Click on
already exists. Overwrite?
Click on
dual1_S.mtw was modified. Save changes?
Click on
Changes in *.chw. Modified: Calibration. Save changes?
<Yes>
. A window appears with the message
.
<Yes>
. A window appears with the message
<Yes>
.
<OK>
.
.
*.chw
Method
.
53
Page 63

3 Operating tutorial
3.4 Sample determination
Following the calibration of the IC system as described in
the first sample solution can be injected.
1 Start determination
Click on
<Start>
or select
Start determination
of the
menu in the system window. An empty chromatogram window opens where the baseline is recorded continuously. The
message
STATE
Initialisation [792 COM#]
window. Then the
appears in the
Edit sample description
SYSTEM
window is
opened automatically.
2 Enter information for determination
Enter the desired information concerning the sample in the
Edit sample description
libration level
to 0 and confirm with
window and confirm with
<OK>
.
<OK>
section 3.3
Control
. Set
Ca-
3 Switch injection valve to "FILL" position
Click on the
button of the 792 icon in the system
window to switch the injection valve to the "FILL" position. At
the same time, the suppressor module is switched to the next
position.
4 Fill sample loop
23
Immerse the aspirating tubing
23
in the vessel containing the
2323
drinking water sample.
25
Using the syringe fixed to the syringe tubing
25
, siphon in ca.
2525
1 mL drinking water.
792 Basic IC
54
Page 64

3.4 Sample determination
5 Switch injection valve to "INJECT" position
Click on the
button of the 792 icon in the system
window to switch the injection valve to the "INJECT" position.
At the same time, the data recording is started automatically.
The status bar of the chromatogram window shows the mes-
Measure
sage
INJECT done [792COM#]
When the analysis time of 16 min set in the method has
SYSTEM STATE
, the
window shows the message
.
expired data recording is automatically stopped and the
chromatogram is integrated and evaluated. In the chromatogram window the peaks which have been found are numbered and the baseline drawn. In the
the message
Finished [792COM#]
appears. It is now possible
SYSTEM STATE
window
to record further samples with the same system.
At the end of the determination, the chromatogram window is
closed and the chromatogram is saved automatically. The file
name is generated automatically and contains date and time
in a coded form:
st
1
numeral: Alphabetical code for year
(e.g. j = 1999, k = 2000, l = 2001, etc.)
nd
numeral: Code for month
2
(1...9 = Jan....Sept., a...c = Oct....Dec.)
rd+4th
3
5
numeral: Day (01 ... 31)
th
- 8th numeral: Time (hh:mm)
6 Open chromatogram
Click on
File / Open / Chromatogram
or
dow. Select the chromatogram file
<OK>
click on
. The chromatogram window is opened where
the found peaks are numbered and the baselines are drawn
in.
in the main win-
*.chw
just recorded and
792 Basic IC
55
Page 65

3 Operating tutorial
7 Report output
Click on
main window. The
or select
Report Options
Make report
of the
Process
menu in the
window appears.
Under
Report destination
for report output.
Under
Items to report
elements for the report output.
Click on
target.
8 Print report
Click on
window. The standard printing window is opened where
printer, printing range and number of copies can be selected.
After confirmation with
chromatogram are printed out.
<Report>
or select
, switch on the desired target option
More items to report
and
, click all desired
to start the report output to the selected
Print
of the
<OK>
the results including the
File
menu in the main
792 Basic IC
56
Page 66

4.1 Fundamentals of the operation
4 Operation
This section describes the most important points concerning the
operation of the 792 Basic IC. For further details, please refer to the
on-line help in the PC program, which can provide you with the
required information rapidly and conveniently from any place in the
program.
4.1 Fundamentals of the operation
4.1.1 Starting/closing the program
Start the «792 Basic IC» program
Start the program
Double-click this icon or the
Basic IC 1.0» program. The Login window appears:
Enter your password and click on
Metro792.exe
<Log In>
file to start the «792
.
792 Basic IC
After software installation, the program can be
started without entering a
tion of users, see section 4.2.2.
Close the «792 Basic IC» program
792 BASIC IC / File / Exit
Exit the «792 Basic IC» program.
The program is also quit by clicking on
of the main window
792 BASIC IC
Password
.
. For the defini-
in the upper right part
57
Page 67

4 Operation
4.1.2 Glossary
System
The term “system“ is used to describe the combination of
settings, time program
processing method
and
, which have been
optimized for the specific separating column and the determination to
be carried out with it. A system is used to start single determinations or
determinations with the help of a sample queue.
instrument
Systems are stored as
system files
*.smt
(
) in the
Systems
directory.
Method
A method contains all information necessary for
tegration, peak evaluation
quantification
and
data acquisition, in-
. It can be considered
as the chromatogram template, i.e. chromatogram without raw data.
Methods are stored as
method files
*.mtw
(
) in the
Methods
directory.
Each system is linked to a method. This method is called
method
and is opened automatically at the start of a new determina-
tion.
Chromatogram
A chromatogram is a graphic plot of the elution curve (signal vs. time)
recorded following a chromatographic separation on a separating column.
Chromatograms are stored as
chromatogram files
*.chw
(
directory. As well as the measuring data, the chromatogram files also
contain the method parameters and system settings, which have been
used for data recording, data processing and remote control.
processing
) in the
Data
Determination
In order to carry out a determination a suitable
system
must be se-
lected for the separating problem. The result of the determination is a
chromatogram
, in which the measuring data and results of the deter-
mination are stored.
Calibration
Calibration is used to describe the method of determining the relationship between the peak height or peak area found for one component
and its concentration in the sample. The result of the calibration is a
calibration function
(calibration curve), which shows the relationship
between the amount of sample and the evaluated quantity.
The determination of the calibration function with reference solutions
can be carried out as a
one-point
or as a
multiple-point calibration
The calibration method that is mainly used in ion chromatography is the
external standard calibration
internal standard
an
(relative calibration) or
(absolute calibration); calibrations with
tabulated calibrations
are also possible.
.
792 Basic IC
58
Page 68

4.1 Fundamentals of the operation
Integration
Integration is to be understood as being the method for determining the
peak area and peak height with the aid of approximate baselines. The
integration algorithm included in the program is influenced by the
gration parameters
events
, which are defined in the method. In addition, the integration
and the optionally programmable
can be manually corrected later with the aid of the
peak editor
integration
inte-
.
Batch reprocessing
Batch reprocessing is understood to be the subsequent reprocessing
of a series of chromatograms, which have been loaded in a batch reprocessing queue. During reprocessing with a selected method the settings for calibration, integration, passport, appearance and report can
be altered at will.
4.1.3 Overview of program windows
The «792 Basic IC» program consists of different windows whose functionality is linked together. The different windows are:
792 BASIC IC
CHROMATOGRAM
SYSTEM
SYSTEM STATE
WATCH WINDOW
Main program window for file administration,
printing, opening of systems, methods and
chromatograms, login and user rights, optional
settings and window handling.
Window for graphic plot of running or recorded
chromatograms.
Window for loaded system with possibility for
manual control of the 792 Basic IC.
Window for display of status messages for the
connected system.
Window for display of conductivity and pressure.
792 Basic IC
QUEUE EDITOR
Window for edition of batch reprocessing
queues.
59
Page 69

4 Operation
4.1.4 Main window elements
The elements of the main window
tool bar and the status bar, indicating prompts and logged-in user.
Menu bar
Toolbar
Status bar
Prompts, information
4.1.5 Icons of the main window
The following icons are displayed in the
792 BASIC IC
Logged-in user
792 BASIC IC
are the menu bar, the
main window:
Open chromatogram
Save chromatogram
Open last batch reprocessing file
Report settings
Print preview
Print report
Passport
General method settings
Integration parameters
Component table
Cascade all opened chromatogram windows
Vertical tiling of open chromatogram windows
Horizontal tiling of open chromatogram windows
Appearance of the chromatogram window
792 Basic IC
60
Page 70

4.1 Fundamentals of the operation
Enable/disable peak editor mode
View whole chromatogram
Help
Lock system
Opened system
4.1.6 Overview of file types
The following file types are produced by the «792 Basic IC» software:
*.bar
*.cal
*.chw
*.mtw
*.rtt
Batch reprocessing file
This binary file contains data of the batch reprocessing
queue. The
*.bar
file is stored automatically in the
Data
fol-
der.
Calibration file
This binary file contains calibration data, which can be exported with
tion
. The
Methods
Chromatogram file
792 BASIC IC / Method / Calibration / Export calibra-
*.cal
file is stored automatically in the
folder.
This binary file contains chromatogram, system and
*.chw
method data of a determination. The
Data
automatically in the
Method
folder.
file is stored
This binary file contains the data acquisition method linked
*.mtw
to a system. The
Methods
folder.
Report template
This ASCII file contains a report template. The
file is stored automatically in the
*.rtt
file is
stored in the program folder.
792 Basic IC
*.smt
*.dev
System file
This ASCII file contains the system settings. The
stored automatically in the
Device file
Systems
folder.
This ASCII file contains drivers for devices. The
stored in the
Devices
folder.
*.stm
*.dev
file is
file is
61
Page 71

4 Operation
4.1.7 Context sensitive menus
Some of the menu functions of the program windows are also accessible by clicking on the desired window or item and pressing the
mouse button
. The pop up windows have different contents and func-
right
tions depending on the selected active window or item type.
4.1.8 Keyboard and mouse functions
mouse
The
functions such as the selection of menu items and fields. It can additionally be used for magnifying a section of a chromatogram (
ing
). To
cursor to the upper left corner of the square to zoom, press the left
mouse button and drag the cursor to the lower right corner of the rectangle. After releasing of the left mouse button the selected region will
be zoomed full-screen. If the cursor is active in the peak editor mode
then it can be moved by pressing down the right-hand mouse key.
keyboard
The
dow, as described below.
can be used to carry out the normal program operating
zoom
a portion of the plot it is necessary to place the mouse
can also be used to scale a chromatogram in the win-
zoom-
Keyboard quick reference
Cursor is inactive:
[ up ] Increases sensitivity on the Y axis.
[ down ] Reduces sensitivity on the Y axis.
[ right ] Expands a chromatogram on the X axis.
[ left ] Shrinks a chromatogram on the X axis.
[ Ctrl ] + [ Home ] Autoscale procedure on the X axis (shows all
on X).
[ Ctrl ] + [ End ] Autoscale procedure on the Y axis (shows all
on Y).
1
[ PageUp ] Shifts a chromatogram on
/10 part of a screen
upwards.
1
[ PageDown ] Shifts a chromatogram on
/10 part of a screen
downwards.
[ Shift ] + [ up ] Increases a distance between channels of a
chromatogram.
[ Shift ] + [ down ] Reduces a distance between channels of a
chromatogram.
[ 0 (Zero) ] Adjusts a zero on the last point of a chroma-
togram (running chromatogram) or its lowest
level (finished run).
792 Basic IC
62
Page 72

4.1 Fundamentals of the operation
Only part of the chromatogram is on screen:
[ Ctrl ] + [ right ] Moves one window right (without change of
scale on X and Y axes).
[ Ctrl ] + [ left ] Moves one window left (without change of
scale on X and Y axes).
[ Home ] Shows the beginning of a chromatogram (with-
out change of scale on X and Y).
[ End ] Shows the end of a chromatogram (without
change of scale on X and Y).
[ 0 (Zero) ] Adjusts a zero on the lowest level in the win-
dow.
Cursor is active:
[ 0 (Zero) ] Adjust a zero in site of the cursor.
[ right ] Moves cursor left to right.
4.1.9 Help
[ Shift ] + [ right ] Quickly moves cursor left to right.
[ left ] Moves cursor right to left.
[ Shift ] + [ left ] Quickly moves cursor right to left.
[ Home ] Moves cursor to beginning of a window.
[ End ] Moves cursor to end of a window.
[ Shift ] + [ End ] Sets the beginning of a window in site of the
cursor.
[ Shift ] + [ Home ] Sets the end of a window in site of the cursor.
By clicking on , by clicking on , by selecting the
Contents
menu item, or by pressing the [ F1 ] key you can get on-line
Help /
help on the current topic anywhere in the program.
792 Basic IC
Green texts
Violet texts
Blue texts
can be clicked to jump to a different Help topic.
identify the dialog item, parameter or button in
the corresponding window.
identify titles and important information.
63
Page 73

4 Operation
4.2 Instrument and software settings
4.2.1 Fonts
792 BASIC IC / Options / Fonts
This option allows the selection of fonts used by the system.
Font for dialog...
Font for reports...
Font for tables...
Font for plots...
Save fonts configuration
4.2.2 Security system
The «792 Basic IC» program has a security system based on the list of
users. Every user has his unique password and one of the following access levels:
Selection of font used for dialog boxes.
Default setting:
MS Sans Serif / Standard / 8 pt.
Selection of font used for report output to the
screen or printer.
Default setting:
Courier New / Standard / 10 pt.
Selection of font used for data presentation in
tables on the screen.
Default setting:
MS Sans Serif / Bold / 8 pt.
Selection of font used for labels on chroma-
togram plots and calibration curves.
Default setting:
Times New Roman / Bold / 10 pt.
Save chosen font configuration.
Novice
Restricted access to program functions. Allows
only start and stop of determinations using existing system and method files and manual
control of the 792 Basic IC. Modifications of
system, method and data files are not allowed.
Master
Access to all program functions with few excep-
Administrator
tions: the user cannot set
Hardware settings
and security system.
Global preferences
Access to all program functions.
,
It is recommended to make user lists and enter passwords as a first action after system installation. Therefore, select the menu item
IC / Options / Security
and click on
entering a password. The
Security options
<Log In>
in the Log In window without
window appears:
792 BASIC
792 Basic IC
64
Page 74

4.2 Instrument and software settings
Enter user name, password and access level for all users. Don't forget
to make one of the users an
Administrator
open again. At the end, click on
<OK>
, otherwise this window will not
.
After configuration of the security system the program prompts for the
password every time the system starts. This user name stamps all
methods, chromatograms and reports. It is possible at any time to
change the user with the menu item
792 BASIC IC / Options / Lock system
.
4.2.3 Global settings
792 BASIC IC / Options / Global preferences
This window is used for
global program settings
.
792 Basic IC
This window is only accessible for users with
access level.
Administrator
65
Page 75

4 Operation
Data file overwrite
Never
Chromatogram files cannot be overwritten. A
Ask
Always
If method changed
Don't ask to save
Ask to save
Overwrite without asking
If disk method is newer
Chromatogram files are always overwritten
Overwriting of chromatogram files:
Saving of method files:
The method file is not saved automatically. It
modified chromatogram is saved as a new file
with the file name number raised by 1.
The user is asked if the chromatogram should
be overwritten.
without confirmation.
File
Save / Method
can be saved only with
/
The user is asked if the method should be
saved.
Method files are overwritten without confirmation.
Overwriting of method files:
.
Ask to overwrite
Overwrite without asking
Opening chromatograms
Ignore last data directory
GLP On
OK, Apply buttons mean
If this option is enabled, the following parame-
Save object to file
The user is asked if the method should be
overwritten.
Method files are overwritten without confirmation.
Opening of chromatograms:
If this option is enabled, the default data direc-
Data
tory
is opened.
ters are automatically set:
Data file overwrite = Never
If method changed = Don't ask to save
If disk method is newer = Ask to overwrite
If this option is enabled, the
<Apply>
button in
system settings windows is replaced by the
<Save>
the
button. The system settings are saved if
<Save>
or
<OK>
button is clicked.
Chromatogram units
Flow
Pressure
Print via print spooler
Units for chromatograms:
Unit for flow rate:
Unit for pressure:
PPPPL/min
MPa, psi, bar, atm
mL/min
,
Switch on/off printing via print spooler. Switch
off this option if you use a GDI printer.
792 Basic IC
66
Page 76

4.2 Instrument and software settings
Measuring priority
<Default colors>
4.2.4 COM port
792 BASIC IC / Options / 792 Basic IC:COM1
This menu item opens the
terface) selection and settings.
Setting the priority of program execution.
time
means that the «792 Basic IC» program
has the highest priority,
normal
means that all
real-
active programs have the same priority.
Default colors for chromatographic windows
(details see
Links
section 4.5.3
).
window for COM port (serial RS232 in-
COM1
If
is clicked with the right mouse button, the following menu items
appear:
Put on desktop
Change
Possibility for changing the COM port (default
Possibility for setting COM port parameters for
recording data transfer (details see on-line
help).
COM1
setting:
). The following window is
opened, where the interface can be changed
by clicking on the desired COM port.
792 Basic IC
67
Page 77

4 Operation
w
4.3 Systems
The term “System“ describes the combination of
time program
a specific separating column and the determination to be carried out
with it. A system is used to start single determinations. Systems are
stored as
system files
4.3.1 System window
A system window is opened with
the selection of the desired system file. It contains icons for PC,
window
a determination.
Start/Stop buttons
Watch windo
(screen) and
processing method
and
*.smt
) in the
(
792 Basic IC
instrument settings
which has been optimized for
Systems
792 BASIC IC / File / Open / System
directory.
Watch
, and two buttons to
start
and
792 Basic IC
and
stop
,
PC
4.3.2 System file handling
The following menu items are used for opening, changing, saving and
closing of systems:
792 BASIC IC / File / Open / System
Load an existing system file (
the corresponding system window.
The directory and name of the opened system file are displayed in the
title bar of the system window. A star (
cates that the system settings have been changed since the last saving.
SYSTEM / System / Change
Load a new system and open automatically the system window.
SYSTEM / System / Save
Save the current system settings in a system file (
directory.
*.smt
) from the
*
) at the end of the name indi-
Systems
directory and open
*.smt
) in the
Systems
SYSTEM / System / Close
Close the selected system.
792 Basic IC
68
Page 78

4.3 Systems
4.3.3 System functions
Start/stop hardware and record baseline
SYSTEM / Control / Startup hardware (Measure Baseline)
Starting the hardware
startup values
, starting of the high-pressure pump and starting of the
at the 792 Basic IC includes sending of
peristaltic pump.
System
At the same time, the
recording of the measurement signal
the method defined for the system is started. Independently of the set
chromatogram
Duration
, the measurement signal is recorded until a new
determination is started. Alternatively the baseline recording can be
stopped by clicking the
icon of the chromatogram window. In this
case, the user is asked if the recorded baseline should be saved or not.
SYSTEM / Control / Shutdown hardware
High-pressure pump and peristaltic pump at the 792 Basic IC are immediately stopped. A running determination is also stopped.
Start/stop determinations
SYSTEM / Control / Start determination
Start determination
start command, the
using the settings of the selected system. At this
System startup values
are set at the 792 Basic IC.
The high-pressure pump and the peristaltic pump are started if they are
not already running. The time program is started immediately; the data
recording is started after switching the injection valve to the "Inject"
position.
using
At each start of a determination, the
Edit sample description
window is
opened automatically. This window can be used for entering information concerning the sample:
792 Basic IC
69
Page 79

4 Operation
Ident
User defined identifier (title) for the chroma-
togram to be displayed in the title bar of the
chromatogram window and in the
open
window.
Chromatogram
Calibration level
Info 1 / Info 2
Volume
Dilution
Vial number
Amount
Injected volume in PL.
Dilution of the sample.
Sample amount. If this value is different for the
Calibration level (0 = sample; 1}n = calibra-
Sample description.
Autosampler vial position to take sample from.
Internal standard amount
Date/time when...
Date and time of sample collection (the default
tion solutions).
calibration run (c) and the sample run (s), the
component concentrations of the sample are
calculated as follows:
C
•
c
Amount
C
=
s
Amount
/
s
c
Concentration of the internal standard compo-
nent for relative concentration calculations.
values are equal to the date and time when the
chromatogram starts).
SYSTEM / Control / Stop determination
Stop running determination
. Data acquisition and time program are
terminated immediately. The recorded chromatogram is saved automatically if the
Processing
tab is enabled.
Save chromatogram after the run
option on the
Alternatively the determination can be stopped by clicking the
of the chromatogram window. In this case, the user is asked always if
the determination should be saved or not.
Print system parameters
SYSTEM / System / Print parameter
A report of the system parameters including the time program is created and opened using the «Microsoft Word» program. The
opened can be printed, saved and exported into other programs. The
system report includes the name of the method linked to the system,
the configuration settings for the 792 Basic IC, the system startup values and the time program (incl.
exists and is switched on (
ENABLED
Remote configuration
).
), if such a program
Passport /
icon
*.rtf
file
792 Basic IC
70
Page 80

4.3 Systems
4.3.4 PC icon
The PC icon is one of the components of the system window. If the system is connected and this icon is clicked with the right mouse button,
the following menu items appear:
Open
Load the processing method linked to the system
and open an empty chromatogram window.
Setup
Open PC setup window for selection of processing
method:
Processing method
Connected data source
Directory and name of the method file (
*.mtw
)
linked to the system.
The method file can be selected with
and opened with
<show>
.
<choose>
Display of data source for main measurement
channel (read only).
4.3.5 Watch window
The watch window icon is one of the components of the
dow. If the system is connected and this icon is clicked with the right
mouse button, the following menu item appears:
Open
Open the
792 Basic IC
WATCH WINDOW
tivity and pressure:
SYSTEM
win-
for live display of conduc-
71
Page 81

4 Operation
The colors of the watch window fields can be
changed by clicking the fields with the right mouse
button and selecting the menu item
Choose color / ...
.
4.3.6 Instrument icon
Menu options for instrument icon
System
disconnected
System connected
Injection valve in
INJECT
"
" position
System connected
Injection valve in
FILL
"
" position
The instrument icon for the 792 Basic IC is one of the components of
SYSTEM
the
window. If the system is connected, the icon contains two
buttons for manual control of the injection valve:
<Inject>
<Fill>
Switch injection valve to "INJECT" position.
Switch injection valve to "FILL" position.
If the system is connected and the 792 icon is clicked with the right
mouse button, the following menu appears:
Open
Open the
Hardware
Diagnostics
Open the
Open the
system settings
window.
hardware settings
diagnostics
window.
window.
System parameters for disconnected system
A double-click on the instrument icon or selection of the
item using the right mouse button opens the system settings window.
Initial
For a disconnected system, the
tab is displayed.
Open
menu
792 Basic IC
72
Page 82

4.3 Systems
Flow, mL/min
Startup value for flow rate of the high-pressure
pump.
Pressure max, MPa
Entry range:
0.20
Startup value for maximum pressure limit for
2.50 mL/min
...
high-pressure pump.
0.0
25.0 MPa
...
Pressure min, MPa
Entry range:
Startup value for minimum pressure limit for
high-pressure pump.
0.0
25.0 MPa
Entry range:
...
Instrument control for connected system
A double-click on the instrument icon or selection of the
item using the right mouse button opens the system settings window.
For a connected system, the
Control
tab is displayed. It allows manual
control of the 792 Basic IC functions and setting of startup values to be
sent to the instrument. This tab shows the current measurement values
for conductivity and pressure.
Open
menu
792 Basic IC
Conductivity, PPPPS/cm
Pressure, MPa
Actual values
Flow, mL/min
Pressure max, MPa
Pressure min, MPa
Live display of measured pressure.
Display of actual values
Live display of measured conductivity.
The color settings for this two fields can be
changed by clicking the fields with the right
mouse button and selecting the menu item
Choose color / ...
.
Display of flow rate of the high-pressure pump.
Display of maximum pressure limit for high-
pressure pump.
Display of minimum pressure limit for high-
pressure pump.
73
Page 83

4 Operation
Valve
Injection valve
<Inject>
<Fill>
Switch injection valve to "INJECT" position.
Switch injection valve to "FILL" position
Suppressor
<Step>
IC pump
<On>
<Off>
Peristaltic
<On>
<Off>
System startup values
Flow, mL/min
Pressure max, MPa
Pressure min, MPa
Suppressor module
Switch the suppressor module to the next posi-
High-pressure pump
Start high-pressure pump.
Stop high-pressure pump.
Peristaltic pump
Start peristaltic pump.
Stop peristaltic pump.
tion. The time since the last switching of the
suppressor module is displayed in the field be-
<Step>
side the
button.
The system startup values are sent and applied
to the 792 Basic IC each time the system is
connected, a determination is started, or the
values are sent manually with
<Send to unit>
.
Startup value for flow rate of the high-pressure
pump.
Entry range:
0.20
2.50 mL/min
...
Startup value for maximum pressure limit for
high-pressure pump. This limit is controlled
even without connection to the PC.
0.0
25.0 MPa
Entry range:
...
Startup value for minimum pressure limit for
high-pressure pump. This limit is controlled
even without connection to the PC.
0.0
25.0 MPa
Entry range:
...
Time program
On the
Program
tab of the system settings window a user-defined time
program for instrument control can be entered. This program is started
automatically at the moment the determination is started. The time program contains program steps including time, program instruction and
parameter.
792 Basic IC
74
Page 84

4.3 Systems
Time (1st column)
Time at which program instruction is applied.
Entry range:
0.0 ... 999.9 min
If no time is entered, the program instruction is
applied together with the last instruction with
time entry.
Command (2nd column)
Parameter (3rd column)
ENABLED
Program instruction (see
structions
).
Parameter for program instruction (see
program instructions
Enable program start (a disabled program is
List of program in-
List of
).
not started).
<Add>
Add new program instruction.
<Delete>
<Verify>
Delete selected program instruction.
Test the time program (error messages are dis-
played if program is faulty).
List of program instructions
The following program instructions can be added to the time program
on the
Program
subpage:
Instruction Parameter entry Meaning
Valve Inject, Fill
Switch
injection valve
"FILL" position.
ICPump on, off
Flow 0.2 ... 2.5 mL/min
Switch on or
pump
Set
.
flow rate
pump to the desired value.
Pmax
0.0 ... 25.0 MPa
maximum pressure limit
Set
high-pressure pump to the desired
value.
Pmin
0.0 ... 25.0 MPa
minimum pressure limit
Set
high-pressure pump to the desired
value.
Program
END, RESET
The
END
program, especially if the program time
should be longer than the chromatogram duration. Additional steps after
this flag are not allowed. The
is used to reset the parameters to the
system startup values.
to "INJECT" or
off
high-pressure
the
of the high-pressure
for the
for the
flag can be used to end a
RESET
flag
792 Basic IC
Suppressor
Peristaltic on, off
Switch
position
Switch on or
suppressor module
.
off
peristaltic pump
the
to the next
.
75
Page 85

4 Operation
Configuration
Configuration
The
tab in the system settings window contains configura-
tion settings for the 792 Basic IC.
Method
Suppressor
Use peristaltic pump
Polarity
Selection of the method with or without sup-
Suppressor module:
Autostep with
Selection of the polarity of the output signal:
pressor:
With MSM
Without MSM
method with suppressor
method without suppressor
Automatic switching to the next position each
time the injection valve is switched either to the
Fill
or to the
Inject
position.
If this option is disabled, the peristaltic pump is
not switched on automatically at the start of a
determination or with
+
positive polarity (for anions)
–
negative polarity (for cations)
Startup hardware
.
Hardware settings
Selection of the
Hardware
menu item using the right mouse button
opens the hardware settings window consisting of the two tabs
and
Alarm stops
.
ware
Hardware
This tab of the hardware settings window defines general parameters
which are set automatically at power on of the instrument.
792 Basic IC
76
Hard-
Page 86

4.3 Systems
Flow correction
Cell constant
Cell constant of the conductivity cell for correct
Factor for correction of the difference between
displayed and actual flow rate of the highpressure pump.
0.9
1.09
Range:
...
The flow correction is determined by measurement of the actual flow rate with the aid of a
measuring cylinder as follows:
Flow correction
=
Displayed flow rate
Measured flow rate
display of the absolute conductivity. Enter the
cell constant printed on the detector block into
this field.
0.1
99.9 /cm
Range:
...
For a precise determination of the cell constant,
pump a calibration solution of known conductivity through the IC system, observe the displayed conductivity and change the cell constant until the correct conductivity value is
displayed.
792 Basic IC
<Break times>
Possibility for changing the break times for in-
jection valve
pressor
.
Valve
and suppressor module
Sup-
These values should only be changed after
consulting the Metrohm Service.
Alarm stops
Alarm stops
The
tab of the hardware settings window defines the events
for which the 792 Basic IC is stopped immediately. At an alarm stop,
high-pressure pump and peristaltic pump are stopped immediately; the
running determination and the active sample queue are also stopped.
77
Page 87

4 Operation
Event
Events for alarm stop:
Pump stop
Hardware error
Pump stopped because pressure limits are ex-
ceeded.
Hardware error detected at the 792 Basic IC
(high-pressure pump, injection valve, or sup-
Power on
pressor not working correctly).
Temporary power failure at the 792 Basic IC.
4.3.7 System state window
SYSTEM STATE
The
opened. It shows status and error messages for this system. Messages
concerning the 792 Basic IC hardware are followed by
messages concerning the loaded system are followed by
(name of subfolder containing the system file).
Status messages
Checking on-line
On-line
UploadStartupValues
Initialization
Ready
Starting
Running
window is automatically opened if a system is
[792 Basic IC]
["folder"]
Checking connection between PC and 792 Basic IC.
Connection between PC and 792 Basic IC ok.
System startup values have been loaded to the 792
Basic IC.
Hardware or system initialization.
System is ready for starting a new determination.
Starting program or chromatogram data acquisition.
Running program or chromatogram data acquisition.
,
Running program
(xxx min left)
Waiting for INJECT
Running time program
(in brackets: time left).
Waiting for "INJECT" to start program and/or
chromatogram data acquisition.
INJECT done
Injection valve has been switched to the "INJECT"
position.
Finished
SHUTDOWN
792 Basic IC
78
Determination has been finished.
792 Basic IC hardware is shutdown
Page 88

4.3 Systems
Error messages
Detection of hardware failed
E1
E2
E200
E237
E238
E240
E258
E295
E296
E298
Bad connection between PC and 792 Basic IC or
instrument switched off (check connecting cable or
switch on instrument).
Program checksum wrong (call Metrohm service).
RAM faulty (call Metrohm service).
Invalid instrument adjustment (call Metrohm service).
Storage of configuration values failed (repeat last
action; if error reappears, call Metrohm service).
Storage of instrument number failed (repeat last
action; if error reappears, call Metrohm service).
EEPROM faulty (call Metrohm service).
Storage of setup values failed (repeat last action; if
error reappears, call Metrohm service).
Storage of memory values failed (repeat last action; if
error reappears, call Metrohm service).
Instrument stopped (restart instrument; if error
reappears, call Metrohm service).
Storage of flow correction value failed (repeat last
action; if error reappears, call Metrohm service).
E299
E300
E301
E302
E303
Storage of break time values failed (repeat last action;
if error reappears, call Metrohm service).
High-pressure pump faulty (restart pump; if error
reappears, call Metrohm service).
Injection valve blocked (check injection valve; if error
reappears, call Metrohm service).
Suppressor module blocked (check suppressor; if
error reappears, call Metrohm service).
Storage of maintenance information failed (repeat last
action; if error reappears, call Metrohm service).
792 Basic IC
79
Page 89

4 Operation
4.4 Methods
A method contains all information necessary for
tegration, peak evaluation
as the chromatogram template, i.e. chromatogram without raw data.
Methods are stored as
prepared, write-protected methods are copied to this directory at program installation.
Each system is linked to a method. This method is called
method
and is opened automatically at the start of a new determina-
tion.
4.4.1 Method file handling
The following menu items are used for opening and saving of methods:
SYSTEM / PC icon / Open
By clicking this menu item or by double-clicking the PC icon in the system window, the method file (
from the
window is opened.
The name of the method is displayed in the title bar of the system window. A star (
been changed since the last saving.
Methods
*
) at the end of the name indicates that the method has
data acquisition, in-
quantification
and
method files
*.mtw
(
. It can be considered
) in the
Methods
directory. 35
processing
*.mtw
) belonging to the system is loaded
directory. At the same time, an empty chromatogram
792 BASIC IC / File / Save / Method
Save the method of the current chromatogram in a method file (
Methods
the
4.4.2 Passport
792 BASIC IC / Method / Passport
This menu item opens the
tual description of the chromatographic run and consists of the following tabs:
directory.
General
Sample
Column
Eluent
Comment
Method Log
General information on determination.
Sample information.
Passport
window that includes a detailed tex-
Column information.
Eluent information.
User comments on chromatogram.
GLP log with date/time stamp for method.
*.mtw
) in
Data Log
792 Basic IC
80
GLP log with date/time stamp for chromatogram.
Page 90

4.4 Methods
General
General
Tab
of the passport with general description of the method and
determination.
Ident
User defined identifier (title) for the chroma-
togram to be displayed in the title bar of the
Chromatogram
Duration
chromatogram window and in the
open
window.
Duration of the chromatogram in minutes. You
can modify this value when the chromatogram
is running.
METHOD
Path and file name of the
method
used for
data acquisition (read-only).
DATA
Path and file name of the current
Date/time
togram
Date and time of the chromatogram start (read-
(read-only).
chroma-
only).
Last update
Date and time of the last chromatogram modifi-
cation and saving (read-only).
Calibration level
If the current run is used for calibration, the
calibration level is a positive integer, otherwise
it equals zero. You can modify this value when
the chromatogram is running.
User
Name of the current user. It is taken from the
list of users, in accordance with the password
entered at the program starting.
Detector
Name of the detector (read-only).
792 Basic IC
Run
Number of the current run starting from the very
first one. All runs are automatically numbered
by the system.
81
Page 91

4 Operation
Batch
Sample
Tab
To reset the Run
The
Analysis number
number press [Ctrl] [F8].
window is opened where
the run number for the next run can be
modified to the desired value.
X/Y: total number of started sample queues /
current analysis number in the sample queue
(read-only).
Sample
of the passport with sample information.
Info 1
First sample description (max. 256 characters).
Info 2
Second sample description (max. 256 charac-
ters).
Volume
Dilution
Vial number
Amount
Injected volume in PL.
Dilution of the sample.
Autosampler vial position to take sample from.
Sample amount. If this value is different for the
calibration run (c) and the sample run (s), the
component concentrations of the sample are
calculated as follows:
Internal standard amount
C
•
c
Amount
C
=
s
Concentration of the internal standard compo-
Amount
/
s
c
nent for relative concentration calculations.
Date/time when...
Date and time of sample collection (the default
values are equal to the date and time when the
chromatogram starts).
792 Basic IC
82
Page 92

4.4 Methods
Column
Column
Tab
of passport with column information.
Number
ID
Length
Packing material
Serial number of column (max. 256 characters).
Internal diameter of the column in mm.
Length of the column in mm. This parameter is
used to calculate
Linear flow
.
Column
Particle size
Column description (max. 256 characters).
Particle size of the column in Pm. This value is
used for the calculation of reduced theoretical
Reduced TP height.
Logarithmic index, Capacity factor
. It is calculated by the system in accor-
Void volume
plate height
Void volume for the column in %. Used to cal-
culate
ear flow
dance with the settings defined on
/ Math
.
Precolumn
ID
Length
Internal diameter of the precolumn in mm.
Length of the precolumn in mm (set length to 0
if no precolumn is used).
Lin-
and
Method setup
792 Basic IC
83
Page 93

4 Operation
Eluent
Eluent
Tab
of passport with eluent information.
Eluent A
Description of eluent composition (max. 256
characters).
Eluent B
Description of eluent composition (max. 256
characters).
Eluent C
Description of eluent composition (max. 256
characters).
Flow
Flow rate of the high-pressure pump in mL/min.
The flow rate is used to recalculate the time axis
into volumetric units. The system startup value
for the flow rate is entered automatically into
this field at the start of a determination.
Pressure
Pressure in MPa. The measured value for the
pressure is entered automatically into this field
at the start of a determination.
Temp.
Temperature in °C. Here you can enter the
temperature of the column’s thermostat or the
ambient temperature.
Comment
Comment
Tab
of passport for entry of free-text user comments into the
chromatogram description. Use this feature to enter any additional information about the chromatogram not included in other sections of the
method.
792 Basic IC
84
Page 94

4.4 Methods
Method Log
Method Log
Tab
Log
displays all automatically produced GLP messages concerning
of passport with GLP Log for the method. The
Method
modifications made on a method. In addition to these messages, freetext user comments can be entered. All this entries are stamped automatically with date and time of the entry.
792 Basic IC
<Add new>
<Clear>
Add a new GLP comment. Text can be entered
New comment
in the
logged-in user are automatically added.
window, date/time and
Clear all GLP messages and add a new GLP
comment. Text can be entered in the
ment
window, date/time and logged-in user are
New com-
automatically added.
85
Page 95

4 Operation
Data Log
Data Log
Tab
of passport with GLP Log for the recorded chromatogram.
Here a GLP message is automatically produced for every modification
made on a recorded chromatogram. In addition to these messages,
free-text user comments can be entered. All this entries are stamped
automatically with date and time of the entry and cannot be cleared.
<Add new>
Add a new GLP comment. Text can be entered
New comment
in the
logged-in user are automatically added.
window, date/time and
792 Basic IC
86
Page 96

4.4 Methods
4.4.3 Method setup
792 BASIC IC / Method / Method setup
This menu item opens the
common parameters for data acquisition and evaluation of the method
and consists of the following tabs:
Method setup
window that includes the most
General
Processing
General information on determination.
Set actions that are performed when the chromatogram finishes.
Math
Parameters that are used for various types of calculations.
General
General
Tab
method and determination. This tab is identical to the
Method / Passport
with
Method setup
of
(see
window with general description of the
General
section 4.4.2
).
Processing
Tab
Processing
Method setup
of
window for definition of actions that are
performed during the run or when the chromatogram finishes. Automatic post-run data processing is especially useful for chromatographic
systems that include an autosampler.
tab called
792 Basic IC
Save chromatogram after the run
If checked, autosaving of the chromatogram
will be performed on data acquisition ending.
while running every ... min
Save the chromatogram during the run for data
0
safety at the time interval set (if
is set, the
chromatogram is not saved during the run).
Show all
If checked, scales on X and Y axes will be
automatically chosen so that the recorded
chromatogram fits the window.
87
Page 97

4 Operation
Make report
Close window
Chromatogram directory
If checked, report auto-printing will be per-
Math
Tab
Math
Method setup
of
ous types of calculations.
formed on data acquisition ending.
If checked, the window is closed automatically
after the run (or sample queue) is finished.
Directory where the current chromatogram is
saved. Use the
<Browse>
button to select a new
directory.
window with parameters that are used for vari-
Parameter
Formula
Selection of
Formula set
Theoretical plates
Resolution
Asymmetry
Selection of
Custom formulae
calculation parameter
Formula setting by customer (
or according either to
US Pharmacopoeia
or
European Pharmacopoeia
.
:
Custom formulae
)
Selection of calculation formula for number of
theoretical plates if
lae
is set.
Formula set
Custom formu-
=
Selection of calculation formula for resolution if
Formula set
Custom formulae
=
is set.
Selection of calculation formula for asymmetry if
Formula set
lation parameter selected for
rameter = Formula set
Custom formulae
=
calculation formula
the following settings are
is set.
for the calcu-
Parameter
. With
Pa-
possible:
Formula setting by customer.
792 Basic IC
88
Page 98

4.4 Methods
European Pharmacopoeia
US Pharmacopoeia
Void time/volume
Calculation method
None
Manual entry in the
1st component
1st peak
From void volume %
The first detected peak is used as a void time
Formula setting according to European Pharmacopoeia.
Formula setting according to US Pharmaco-
poeia.
Calculation of
void time/void volume
:
Selection of the method for void time calcula-
tion:
Void time
field.
The peak corresponding to the first component
is selected as a void time marker and its retention time replaces the previous value of the void
time. If the first component is not identified, the
expected retention time is used.
marker for the run and its retention time is
stored in the
Void time
field.
For the calculation of the void time, the % value
entered in the
Void volume
field is multiplied by
the ratio of empty column volume and eluent
flow rate.
Void volume
Void time
Index
Interpolation
Internal
External
Void volume in mL and % of column volume.
The % value can be entered manually if
tion method =
From void volume %
is set.
Calcula-
Void time in s. This value can be entered
manually if
Calculation method = None
Calculation of
Retention index
:
is set.
Use of linear or logarithmic interpolation scale
for retention index calculation.
The index scale is constructed on the basis of
the current chromatogram. All components
used for index scale calibration should be present in the current sample.
The index scale is constructed based on an-
other standard chromatogram.
792 Basic IC
89
Page 99

4 Operation
4.4.4 Integration
792 BASIC IC / Method / Integration
This menu item opens the
parameters and events for peak integration and consists of the following two tabs:
Setup
Integration parameters.
Integration parameters
window that contains
Events
Integration events.
The «792 Basic IC» software includes a built-in automatic integration
algorithm to detect peaks on the chromatographic curve and to evaluate them using calculated baselines. The integration procedure is tuned
Setup
by the integration parameters on the
Events
events on the
tab. Integration events have higher priority than in-
tab and the integration
tegration parameters. The integration can be modified manually using
the peak editor (see
section 4.5.4
).
The built-in integrator algorithm is based on the use of the first derivative (slope). In order to decide whether the slope at some point is significant, the first derivative value is divided by the baseline noise and
the result is compared with a threshold value called “
Slope
”. The
threshold values for the upslope and down slope differ.
The baseline and the start and end points are determined for each
peak. For separated peaks, the baseline consists of a straight line between the start point and the end point. For overlapping neighboring
peaks, a common baseline is normally constructed; this connects the
start point of the first peak with the end point of the last peak. The
peaks are separated from one another by dropping a perpendicular line
from the lowest point (valley) between the peaks to the common baseline. Alternatively, the baseline can also be drawn directly between the
valleys of the peaks with the event
events for baseline).
Enable valley-to-valley
Merged peaks
(see integration
Peak apex
Single
peak
792 Basic IC
90
Valley point
Drop line
Peak start
Baseline
Peak end
Page 100

4.4 Methods
Setup
Tab
Setup
Integration parameters
of
window with integration parameters.
The two most important of these parameters for peak recognition are
Width
and
Slope
.
If the signal-to-noise ratio of the chromatogram is high enough (e.g.
100:1 or higher), the integration algorithm is not too sensitive to
changes in integration parameters. On the contrary, if the baseline
noise is high, careful tuning of these parameters may be needed.
Number of peaks
Delay
Time delay before starting peak detection
Number of peaks detected (read-only).
(in min).
Width
Entry range:
Peak width
0}}}}1440 min
(at the baseline, in s).
This parameter is used for setting baseline start
and end points. If this value is too low, excessive narrow peaks are detected from the baseline noise. If it is too large, several adjacent
peaks or baseline drift can be integrated as a
single peak. For an optimal evaluation, it is recommended to enter the width of the narrowest
peak on the chromatogram (normally 2}10 s).
Slope
Entry range:
Threshold for peak recognition
0.1}}}}480 s
The value of the first derivation (slope) of the
curve is divided by the baseline noise (which is
estimated using a special algorithm) and the
result is compared with the
value. Reasonable range of
Slope
Slope
0.5...25.
Entry range:
0.1}}}}400
.
threshold
parameter is
792 Basic IC
91
 Loading...
Loading...