Hp 8200 User Manual

Technical Reference Guide
HP Compaq 8200 Elite Series
Business Desktop Computers
Document Part Number: 656770-001
March 2011
This document provides information on the design, architecture, function, and capabilities of the HP Compaq 8200 Elite Series Business Desktop Computers. This information may be used by engineers, technicians, administrators, or anyone needing detailed information on the products covered.
© Copyright 2011 Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P.
The information contained herein is subject to change without notice. HP is not responsible for any omissions or errors contained herein.
Microsoft, MS-DOS, Windows, Windows NT, Windows XP, Windows Vista, and Windows 7 are trademarks of Microsoft Corporation in the U.S. and other countries.
Intel, Intel Core i3/i5/i7, Pentium Dual-Core, Intel Celeron, Intel vPro, and Intel Inside are trademarks of Intel Corporation in the U.S. and in other countries.
Adobe, Acrobat, and Acrobat Reader are trademarks or registered trademarks of Adobe Systems Incorporated.
The only warranties for HP products and services are set forth in the express warranty statements accompanying such products and services. Nothing herein should be construed as constituting an additional warranty. HP shall not be liable for technical or editorial errors or omissions contained herein.
This document contains proprietary information that is protected by copyright. No part of this document may be photocopied, reproduced, or translated to another language without the prior written consent of Hewlett-Packard Company.
Technical Reference Guide
HP Compaq 8200 Elite Series Business Desktop Computers
First Edition (March 2011)
Document Part Number: 656770-001

Contents
1 Introduction
1.1 About this Guide . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1–1 1.1.1 Online Viewing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1–1 1.1.2 Hardcopy . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1–1 1.2 Additional Information Sources . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1–1 1.3 Serial Number . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1–2 1.4 Notational Conventions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1–2 1.5.1 Special Notices . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1–2 1.5.2 Values. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1–2 1.5 Common Acronyms and Abbreviations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1–3
2 System Overview
2.1 Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2–1
2.2 Features . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2–2
2.3 System Architecture . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2–4
2.3.1 Intel Processor Support . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2–6
2.3.2 Chipset . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2–6
2.3.3 Support Components . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2–7
2.3.4 System Memory . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2–7
2.3.5 Mass Storage Accomodations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2–8
2.3.6 Legacy Input/Output Interfaces . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2–8
2.3.7 Universal Serial Bus Interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2–8
2.3.8 Network Interface Controller . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2–8
2.3.9 Graphics Subsystem . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2–9
2.3.10 Audio Subsystem . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2–9
2.3.11 HP ProtectTools Embedded Security . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2–9
2.4 Specifications. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2–10
Technical Reference Guide |
www.hp.com |
iii |

Contents
3 Processor/Memory Subsystem
3.1 Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3–1
3.2 Intel Processor . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3–2
3.2.1 Intel Processor Features . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3–2
3.2.2 Processor Changing/Upgrading . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3–3
3.3 Memory Subsystem . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3–4
3.3.1 Memory Upgrading . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3–5
3.3.2 Memory Mapping and Pre-allocation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3–5
4 System Support
4.1 Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4–1
4.2 PCI Bus Overview. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4–1
4.2.1 PCI 2.3 Bus Operation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4–1
4.2.2 PCI Express Bus Operation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4–2
4.2.3 Option ROM Mapping . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4–3
4.2.4 PCI Interrupts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4–3
4.2.5 PCI Power Management Support . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4–3
4.2.6 PCI Connectors. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4–4
4.3 System Resources . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4–6
4.3.1 Interrupts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4–6
4.3.2 Direct Memory Access. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4–7
4.4 Real-Time Clock and Configuration Memory. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4–8
4.4.1 Clearing CMOS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4–8
4.4.2 Standard CMOS Locations. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4–9
4.5 System Management . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4–9
4.5.1 Security Functions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4–9
4.5.2 Power Management . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4–11
4.5.3 System Status . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4–12
4.5.4 Thermal Sensing and Cooling . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4–13
4.6 Register Map and Miscellaneous Functions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4–13
4.6.1 System I/O Map . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4–13
4.6.2 GPIO Functions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4–15
5 Input/Output Interfaces
5.1 Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5–1
5.2 SATA/eSATA Interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5–2
5.2.1 SATA Inteerface. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5–2
5.2.2 eSATA Interface. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5–3
5.3 Serial Interface. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5–4
5.4 Parallel Interface Support . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5–5
5.4.1 Standard Parallel Port Mode. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5–5
5.4.2 Enhanced Parallel Port Mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5–5
5.4.3 Extended Capabilities Port Mode. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5–5
5.4.4 Parallel Interface Connector. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5–6
5.5 Keyboard/Pointing Device Interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5–7
5.5.1 Keyboard Interface Operation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5–7
5.5.2 Pointing Device Interface Operation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5–8
iv |
www.hp.com |
Technical Reference Guide |

Contents
5.5.3 Keyboard/Pointing Device Interface Connector . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5–8
5.6 Universal Serial Bus Interface. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5–9
5.6.1 USB Connector. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5–9
5.6.2 USB Cable Data . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5–10
5.7 Audio Subsystem. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5–11
5.7.1 HD Audio Controller . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5–12
5.7.2 HD Audio Link Bus . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5–12
5.7.3 Audio Multistreaming . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5–12
5.7.4 Audio Specifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5–13
5.8 Network Interface Controller. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5–14
5.8.1 Wake-On-LAN Support . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5–15
5.8.2 Alert Standard Format Support . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5–15
5.8.3 Power Management Support . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5–15
5.8.4 NIC Connector . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5–15
5.8.5 NIC Specifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5–16
6 Integrated Graphics Subsystem
6.1 Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6–1
6.2 Functional Description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6–1
6.3 Upgrading . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6–5
6.4 Monitor Connectors. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6–5
6.5.1 Analog Monitor Connector . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6–6
6.5.2 DisplayPort Connector . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6–6
7 Power and Signal Distribution
7.1 Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7–1
7.2 Power Distribution. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7–1
7.2.1 USDT Power Distribution . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7–2
7.2.2 SFF/MT/CMT Power Distribution. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7–2
7.3 Power Control . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7–5
7.3.1 Power Button . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7–5
7.3.2 Wake Up Events. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7–7
7.4 Power Management . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7–7
7.5 Signal Distribution. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7–9
Technical Reference Guide |
www.hp.com |
v |

Contents
8 SYSTEM BIOS
8.1 Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8–1 8.2 ROM Flashing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8–2 8.2.1 Upgrading. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8–2 8.2.2 Changeable Splash Screen . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8–2 8.3 Boot Functions. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8–3 8.3.1 Boot Device Order . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8–3 8.3.2 Network Boot (F12) Support . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8–3 8.3.3 Memory Detection and Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8–4 8.3.4 Boot Error Codes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8–4 8.4 Client Management Functions. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8–6 8.4.1 System ID and ROM Type. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8–7 8.4.2 Temperature Status. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8–7 8.5 SMBIOS support . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8–7 8.6 USB Legacy Support. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8–7 8.7 Management Engine Functions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8–8
A Error Messages and Codes
A.1 Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . A–1 A.2 Beep/Powr LED Codes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . A–1 A.3 Power-On Self Test Messages. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . A–2 A.4 System Error Messages . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . A–6 A.5 Memory Error Messages . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . A–7 A.6 Keyboard Error Messages . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . A–8 A.7 Printer Error Messages . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . A–9 A.8 Video (Graphics) Error Messages . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . A–9 A.9 Diskette Drive Error Messages . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . A–10 A.10 Serial Inteface Error Messages . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . A–11 A.11 Modem Communications Error Messages . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . A–12 A.12 System Status Error Messages . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . A–13 A.13 Hard drive Error Messages . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . A–14 A.14 Hard drive Error Messages . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . A–16 A.15 Video (Graphics) Error Messages . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . A–17 A.16 Audio Error Messages. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . A–17 A.17 DVD/CD-ROM Error Messages . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . A–18 A.18 Netowrk Interface Error Messages . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . A–19 A.19 SCSI Interface Error Messages . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . A–19 A.20 Pointing Device Interface Error Messages . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . A–20
Index
vi |
www.hp.com |
Technical Reference Guide |

1
Introduction
1.1About this Guide
This guide provides technical information about HP Compaq 8200 Elite Business PC personal computers that feature the Intel® Q67 Express chipset and support select Intel Celeron®, Pentium®, Core™ i3, Core i5, and Core i7 processors. This document describes in detail the system's design and operation for programmers, engineers, technicians, and system administrators, as well as end-users wanting detailed information.
This guide primarily describes the hardware and firmware elements and primarily deal with the system board and the power supply assembly. This guide can be used either as an online document or in hardcopy form.
1.1.1 Online Viewing
Online viewing allows for quick navigating and convenient searching through the document. A color monitor will also allow the user to view the color shading used to highlight differential data. A softcopy of the latest edition of this guide is available for downloading in .pdf file format at the following URL: www.hp.com
Viewing the file requires a copy of Adobe Acrobat Reader available at no charge from Adobe Systems, Inc. at the following URL: www.adobe.com
1.1.2 Hardcopy
A hardcopy of this guide may be obtained by printing from the .pdf file. The document is designed for printing in an 8 ½ x 11-inch format.
1.2Additional Information Sources
For more information on components mentioned in this guide refer to the indicated manufacturers' documentation, which may be available at the following online sources:
■HP Corporation: www.hp.com
■Intel Corporation: www.intel.com
■Serial ATA International Organization (SATA-IO): www.serialATA.org.
■USB user group: www.usb.org
Technical Reference Guide |
www.hp.com |
1-1 |

Introduction
1.3Serial Number
The serial number is located on a sticker placed on the exterior cabinet. The serial number is also written into firmware and may be read with HP Diagnostics or Insight Manager utilities.
1.4Notational Conventions
The notational guidelines used in this guide are described in the following subsections.
1.4.1 Special Notices
The usage of warnings, cautions, and notes is described as follows:
WARNING: Text set off in this manner indicates that failure to follow directions could result in bodily harm or loss of life.
CAUTION: Text set off in this manner indicates that failure to follow directions could result in damage to equipment or loss of information.
Text set off in this manner provides information that may be helpful.
1.4.2Values
Differences between bytes and bits are indicated as follows:
MB = megabytes
Mb = megabits
1-2 |
www.hp.com |
Technical Reference Guide |

Introduction
1.5Common Acronyms and Abbreviations
Table 1-1 lists the acronyms and abbreviations used in this guide.
|
Table 1-1 |
|
Acronyms and Abbreviations |
|
|
Acronym or |
|
Abbreviation |
Description |
|
|
A |
ampere |
|
|
AC |
alternating current |
|
|
ACPI |
Advanced Configuration and Power Interface |
|
|
A/D |
analog-to-digital |
|
|
ADC |
Analog-to-digital converter |
|
|
ADD or ADD2 |
Advanced digital display (card) |
|
|
AHCI |
SATA Advanced Host controller Interface |
|
|
AMT |
Active Management Technology |
|
|
API |
application programming interface |
|
|
APIC |
Advanced Programmable Interrupt Controller |
|
|
APM |
advanced power management |
|
|
AOL |
Alert-On-LAN™ |
|
|
ASIC |
application-specific integrated circuit |
|
|
ASF |
Alert Standard Format |
|
|
AT |
1. attention (modem commands) 2. 286-based PC architecture |
|
|
ATA |
AT attachment (IDE protocol) |
|
|
ATAPI |
ATA w/packet interface extensions |
|
|
AVI |
audio-video interleaved |
|
|
AVGA |
Advanced VGA |
|
|
AWG |
American Wire Gauge (specification) |
|
|
BAT |
Basic assurance test |
|
|
BCD |
binary-coded decimal |
|
|
BIOS |
basic input/output system |
|
|
bis |
second/new revision |
|
|
BNC |
Bayonet Neill-Concelman (connector type) |
|
|
bps or b/s |
bits per second |
|
|
BSP |
Bootstrap processor |
|
|
BTO |
Built to order |
|
|
CAS |
column address strobe |
|
|
CD |
compact disk |
|
|
CD-ROM |
compact disk read-only memory |
|
|
CDS |
compact disk system |
|
|
Technical Reference Guide |
www.hp.com |
1-3 |

Introduction
|
Table 1-1 (Continued) |
|
Acronyms and Abbreviations |
|
|
Acronym or |
|
Abbreviation |
Description |
|
|
CGA |
color graphics adapter |
|
|
Ch |
Channel, chapter |
|
|
cm |
centimeter |
|
|
CMC |
cache/memory controller |
|
|
CMOS |
complimentary metal-oxide semiconductor (configuration memory) |
|
|
Cntlr |
controller |
|
|
Cntrl |
control |
|
|
codec |
1. coder/decoder 2. compressor/decompressor |
|
|
CPQ |
Compaq |
|
|
CPU |
central processing unit |
|
|
CRIMM |
Continuity (blank) RIMM |
|
|
CRT |
cathode ray tube |
|
|
CSM |
1. Compaq system management 2. Compaq server management |
|
|
DAC |
digital-to-analog converter |
|
|
DC |
direct current |
|
|
DCH |
DOS compatibility hole |
|
|
DDC |
Display Data Channel |
|
|
DDR |
Double data rate (memory) |
|
|
DIMM |
dual inline memory module |
|
|
DIN |
Deutche IndustriNorm (connector type) |
|
|
DIP |
dual inline package |
|
|
DMA |
direct memory access |
|
|
DMI |
Direct Media Interface |
|
|
DP |
DisplayPort |
|
|
dpi |
dots per inch |
|
|
DRAM |
dynamic random access memory |
|
|
DRQ |
data request |
|
|
DVI |
Digital video interface |
|
|
dword |
Double word (32 bits) |
|
|
EDID |
extended display identification data |
|
|
EDO |
extended data out (RAM type) |
|
|
EEPROM |
electrically erasable PROM |
|
|
EIA |
Electronic Industry Association |
|
|
EPP |
enhanced parallel port |
|
|
1-4 |
www.hp.com |
Technical Reference Guide |

Introduction
|
Table 1-1 (Continued) |
|
Acronyms and Abbreviations |
|
|
Acronym or |
|
Abbreviation |
Description |
|
|
EIDE |
enhanced IDE |
|
|
eSATA |
external SATA |
|
|
ESCD |
Extended System Configuration Data (format) |
|
|
EV |
Environmental Variable (data) |
|
|
ExCA |
Exchangeable Card Architecture |
|
|
FDI |
Flexible Display Interface |
|
|
FIFO |
first in/first out |
|
|
FL |
flag (register) |
|
|
FM |
frequency modulation |
|
|
FPM |
fast page mode (RAM type) |
|
|
FPU |
Floating point unit (numeric or math coprocessor) |
|
|
FPS |
Frames per second |
|
|
ft |
Foot/feet |
|
|
GB |
gigabyte |
|
|
GMCH |
Graphics/memory controller hub |
|
|
GND |
ground |
|
|
GPIO |
general purpose I/O |
|
|
GPOC |
general purpose open-collector |
|
|
GART |
Graphics address re-mapping table |
|
|
GUI |
graphic user interface |
|
|
h |
hexadecimal |
|
|
HDD |
hard disk drive |
|
|
HW |
hardware |
|
|
hex |
hexadecimal |
|
|
Hz |
Hertz (cycles-per-second) |
|
|
ICH |
I/O controller hub |
|
|
IDE |
integrated drive element |
|
|
IEEE |
Institute of Electrical and Electronic Engineers |
|
|
IF |
interrupt flag |
|
|
I/F |
interface |
|
|
IGC |
integrated graphics controller |
|
|
in |
inch |
|
|
INT |
interrupt |
|
|
I/O |
input/output |
|
|
IOPS |
Input/output Operations Per Second |
|
|
Technical Reference Guide |
www.hp.com |
1-5 |

Introduction
|
Table 1-1 (Continued) |
|
Acronyms and Abbreviations |
|
|
Acronym or |
|
Abbreviation |
Description |
|
|
IrDA |
Infrared Data Association |
|
|
IRQ |
interrupt request |
|
|
ISA |
industry standard architecture |
|
|
Kb/KB |
kilobits/kilobytes (x 1024 bits/x 1024 bytes) |
|
|
Kb/s |
kilobits per second |
|
|
kg |
kilogram |
|
|
KHz |
kilohertz |
|
|
kV |
kilovolt |
|
|
lb |
pound |
|
|
LAN |
local area network |
|
|
LCD |
liquid crystal display |
|
|
LED |
light-emitting diode |
|
|
LGA |
land grid array |
|
|
LPC |
Low pin count |
|
|
LSI |
large scale integration |
|
|
LSb/LSB |
least significant bit/least significant byte |
|
|
LUN |
logical unit (SCSI) |
|
|
m |
Meter |
|
|
MMX |
multimedia extensions |
|
|
MPEG |
Motion Picture Experts Group |
|
|
MXM |
Mobile PCI eXpress Module |
|
|
ms |
millisecond |
|
|
MSb/MSB |
most significant bit/most significant byte |
|
|
mux |
multiplex |
|
|
MVA |
motion video acceleration |
|
|
MVW |
motion video window |
|
|
n |
variable parameter/value |
|
|
NIC |
network interface card/controller |
|
|
NiMH |
nickel-metal hydride |
|
|
NMI |
non-maskable interrupt |
|
|
NRZI |
Non-return-to-zero inverted |
|
|
ns |
nanosecond |
|
|
NT |
nested task flag |
|
|
NTSC |
National Television Standards Committee |
|
|
1-6 |
www.hp.com |
Technical Reference Guide |

Introduction
|
Table 1-1 (Continued) |
|
Acronyms and Abbreviations |
|
|
Acronym or |
|
Abbreviation |
Description |
|
|
NVRAM |
non-volatile random access memory |
|
|
ODD |
optical disk drive |
|
|
OS |
operating system |
|
|
PAL |
1. programmable array logic 2. phase alternating line |
|
|
PATA |
Parallel ATA |
|
|
PC |
Personal computer |
|
|
PCA |
Printed circuit assembly |
|
|
PCI |
peripheral component interconnect |
|
|
PCI-E |
PCI Express |
|
|
PCM |
pulse code modulation |
|
|
PCMCIA |
Personal Computer Memory Card International Association |
|
|
PCH |
Platform Controller Hub |
|
|
PEG |
PCI express graphics |
|
|
PFC |
Power factor correction |
|
|
PIN |
personal identification number |
|
|
PIO |
Programmed I/O |
|
|
PN |
Part number |
|
|
POST |
power-on self test |
|
|
PROM |
programmable read-only memory |
|
|
PTR |
pointer |
|
|
RAID |
Redundant array of inexpensive disks (drives) |
|
|
RAM |
random access memory |
|
|
RAS |
row address strobe |
|
|
rcvr |
receiver |
|
|
RDRAM |
(Direct) Rambus DRAM |
|
|
RGB |
red/green/blue (monitor input) |
|
|
RH |
Relative humidity |
|
|
RMS |
root mean square |
|
|
ROM |
read-only memory |
|
|
RPM |
revolutions per minute |
|
|
RTC |
real time clock |
|
|
R/W |
Read/Write |
|
|
SATA |
Serial ATA |
|
|
SCSI |
small computer system interface |
|
|
Technical Reference Guide |
www.hp.com |
1-7 |

Introduction
|
Table 1-1 (Continued) |
|
Acronyms and Abbreviations |
|
|
Acronym or |
|
Abbreviation |
Description |
|
|
SDR |
Singles data rate (memory) |
|
|
SDRAM |
Synchronous Dynamic RAM |
|
|
SDVO |
Serial digital video output |
|
|
SEC |
Single Edge-Connector |
|
|
SECAM |
sequential colour avec memoire (sequential color with memory) |
|
|
SF |
sign flag |
|
|
SGRAM |
Synchronous Graphics RAM |
|
|
SIMD |
Single instruction multiple data |
|
|
SIMM |
single in-line memory module |
|
|
SMART |
Self Monitor Analysis Report Technology |
|
|
SMI |
system management interrupt |
|
|
SMM |
system management mode |
|
|
SMRAM |
system management RAM |
|
|
SODIMM |
small outline DIMM |
|
|
SPD |
serial presence detect |
|
|
SPDIF |
Sony/Philips Digital Interface (IEC-958 specification) |
|
|
SPN |
Spare part number |
|
|
SPP |
standard parallel port |
|
|
SRAM |
static RAM |
|
|
SSD |
solid state disk (drive) |
|
|
SSE |
Streaming SIMD extensions |
|
|
STN |
super twist pneumatic |
|
|
SVGA |
super VGA |
|
|
SW |
software |
|
|
TAD |
telephone answering device |
|
|
TAFI |
Temperature-sensing And Fan control Integrated circuit |
|
|
TCP |
tape carrier package, transmission control protocol |
|
|
TF |
trap flag |
|
|
TFT |
thin-film transistor |
|
|
TIA |
Telecommunications Information Administration |
|
|
TPE |
twisted pair ethernet |
|
|
TPI |
track per inch |
|
|
TPM |
Trusted Platform Module |
|
|
TTL |
transistor-transistor logic |
|
|
1-8 |
www.hp.com |
Technical Reference Guide |

Introduction
|
Table 1-1 (Continued) |
|
Acronyms and Abbreviations |
|
|
Acronym or |
|
Abbreviation |
Description |
|
|
TV |
television |
|
|
TX |
transmit |
|
|
UART |
universal asynchronous receiver/transmitter |
|
|
UDMA |
Ultra DMA |
|
|
UDIMM |
unbuffered/unregistered DIMM |
|
|
UEFI |
Unified Extensible Firmware Interface |
|
|
URL |
Uniform resource locator |
|
|
us/ s |
microsecond |
|
|
USB |
Universal Serial Bus |
|
|
UTP |
unshielded twisted pair |
|
|
V |
volt |
|
|
VAC |
Volts alternating current |
|
|
VDC |
Volts direct current |
|
|
VESA |
Video Electronic Standards Association |
|
|
VGA |
video graphics adapter |
|
|
VLSI |
very large scale integration |
|
|
VRAM |
Video RAM |
|
|
W |
watt |
|
|
WOL |
Wake-On-LAN |
|
|
WRAM |
Windows RAM |
|
|
ZF |
zero flag |
|
|
ZIF |
zero insertion force (socket) |
|
|
Technical Reference Guide |
www.hp.com |
1-9 |

Introduction
1-10 |
www.hp.com |
Technical Reference Guide |

2
System Overview
2.1Introduction
The HP Compaq 8200 Elite Business PC personal computers (Figure 2-1) deliver an outstanding combination of manageability, serviceability, and compatibility for enterprise environments. Based on the the Intel Q67 Express chipset and supporting select Intel Celeron®, Pentium®, Core™ i3, Core i5, and Core i7 processors, these systems emphasize performance along with industry compatibility. All models feature a similar architecture incorporating both PCI 2.3 and PCIe 2.0 buses. All models are easily upgradeable and expandable to keep pace with the needs of the office enterprise.
HP 8200 Elite USDT |
HP 8200 Elite SFF |
HP 8200 Elite MT |
HP 8200 Elite CMT |
Figure 2-1. HP Compaq 8200 Elite Business PCs
This chapter includes the following topics:
■Features (2.2)
■System architecture (2.3)
■Specifications (2.4)
Technical Reference Guide |
www.hp.com |
2-1 |

System Overview
2.2 Features
The following standard features are included on all models unless otherwise indicated:
Intel Celeron, Intel Pentium, or Intel Core i3/i5/i7 processor (LGA1155 socket)
Independent dual monitor support:
One VGA connector
One DisplayPort (DP) connector with Multimode support
PC3-10600 and PC3-8500 DDR3 memorysupport
CAUTION: These products do not support Ultra Low voltage (1.25V) DIMM/SODIMM. Installation of ultra low voltage memory can cause damage to the system and/or memory.
Hard drive fault prediction
Ten externally-accessible USB 2.0-compliant ports (four front, six rear)
High definition (HD) audio processor with one headphone output, at least one microphone input, one line output, and one line input
Network interface controller providing 10/100/1000Base T support
Plug 'n Play compatible (with ESCD support)
PS/2 keyboard
PS/2 optical scroll mouse
HP UEFI BIOS
Management/security features including:
Flash ROM Boot Block
Diskette drive disable, boot disable, write protect
Power-on password
Administrator password
Serial port disable
Smart Cover (hood) Lock (CMT, MT, SFF only)
Smart Cover (hood) Sense
USB port disable
Intel Standard Manageability support
Intel vPro Technology support (with selected processors)
HP Virtual Safe Browser
HP ProtectTools Embedded Security
2-2 |
www.hp.com |
Technical Reference Guide |

System Overview
Table 2-1 shows the differences in features between the different PC series based on form factor.
Table 2-1
Feature Differences by Form Factor
|
USDT |
SFF |
MT |
CMT |
|
|
|
|
|
Thermal Design Power (TPD) |
65 W |
95 W |
95 W |
95 W |
(processor) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
# and type of memory sockets |
2 DDR3 |
4 DDR3 |
4 DDR3 |
4 DDR3 |
|
SODIMMs |
UDIMMs |
UDIMMs |
UDIMMs |
|
|
|
|
|
Serial ports |
0 |
1 std., |
1 std., |
1 std., |
|
|
1 opt. [1] |
1 opt. [1] |
1 opt. [1] |
|
|
|
|
|
Parallel ports |
0 |
optional |
optional |
optional |
|
|
|
|
|
Drive bays: |
|
|
|
|
Externally accessible |
1 [9] |
1 - 5.25” |
2 - 5.25” [7] |
3 - 5.25” [7] |
Internal |
|
1 - 3.50” |
1 - 3.50” |
|
1- 2.50” |
1 - 3.50” |
2 - 3.50” [8] |
3 - 3.50” [8] |
|
|
|
|
|
|
# of SATA/eSATA drives |
2 |
3/1 |
4 |
5 |
supported: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
MXM 3.0 slot? |
Yes |
No |
No |
No |
|
|
|
|
|
PCIe slots: |
|
(all low profile) |
(all full height) |
(all full height) |
2.0 x16 (graphics) |
|
1 [2] |
1 [4] |
1 [4] |
2.0 x4 (x16 connector) |
|
1 [2] |
1 [5] |
1 [5] |
2.0 x1 connector |
|
1 [3] |
1 [6] |
1 [6] |
1.2 Mini Card |
1 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
|
|
|
|
|
PCI 2.3 32-bit 5-V slot, |
|
1 |
1 full-height |
3 full-height |
25-watt maximum |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Power Supply Unit: |
|
|
|
|
Module type |
external |
internal |
internal |
internal |
Power rating |
135- or180-watt |
240-watt |
320-watt |
320-watt |
NOTES:
[1]2nd serial port requires optional cable/bracket assembly.
[2]Low-profile, 25 W maximum.
[3]Low profile, 10-watt maximum
[4]Full-length;
75-watt maximum if PCIe x4 slot is not populated, 35-watt maximum if PCIe x4 slot is populated
[5]35-watt maximum
[6]Half-height, half-length, 10-watt maximum
[7]3.5” devices supported with adapters
[8]2.5” solid state drives supprted with adapter brackets
[9]Slimline bay
Technical Reference Guide |
www.hp.com |
2-3 |
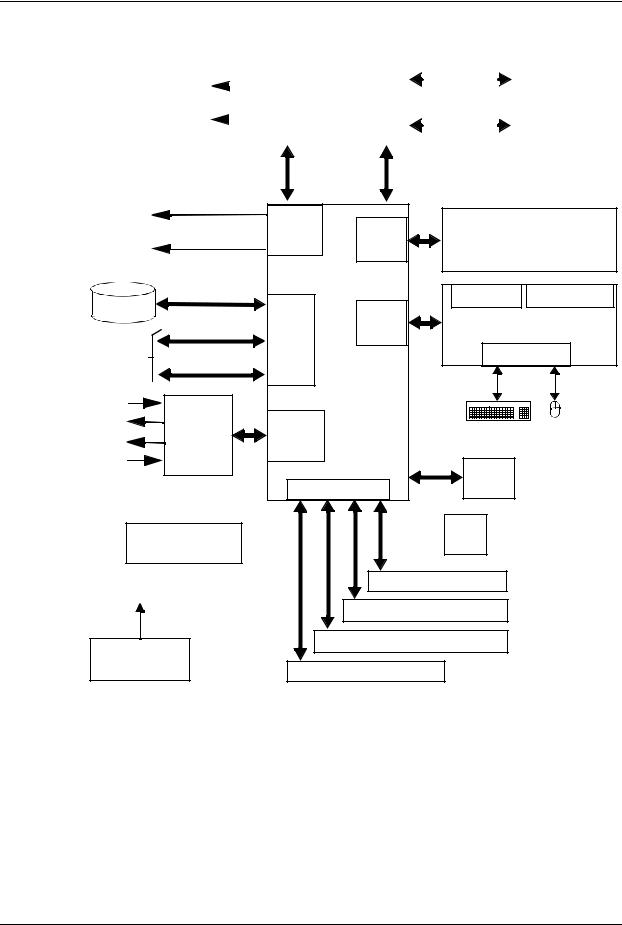
System Overview
2.3System Architecture
The systems covered in this guide feature an architecture based on the Intel Celeron, Pentium and Intel Core i3/i5/17 processors and the Intel Q67 Express Platform Controller Hub (PCH) shown in Figure 2-2. All systems covered in this guide include the following key components:
■Intel Pentium processor or Intel Core i3/i5/i7 processor
■Intel Q67 Express PCH-DO chipset
■Super I/O (SIO) controller supporting PS/2 keyboard and mouse peripherals
■ALC261 audio controller supporting line in, line out, microphone in, and headphones out
■Intel 82579LM GbE network interface controller
■HP ProtectTools Embedded Security
The Q67 Express PCH provides a major portion of system functionality. Designed to complement 2nd generation Intel Core processors, the Q67 Express PCH communicates with the processor through the Flexible Display Interface (FDI) and the Direct Media Interface (DMI). All systems include a serial ATA (SATA) hard drive in the standard configuration.
Table 2-2 lists the differences between models by form factor.
Table 2-2.
Architectural Differences by Form Factor
Function |
USDT |
SFF |
MT |
CMT |
|
|
|
|
|
# and type of memory sockets |
2 SODIMMs |
4 UDIMMs |
4 UDIMMs |
4 UDIMMs |
|
|
|
|
|
Maximum amount |
8 GB |
16 GB |
16 GB |
16 GB |
of memory supported |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
MXM 3.0 slot |
1 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
|
|
|
|
|
PCIe 2.0 x16 graphics slot |
0 |
1 [1] |
1 |
1 |
|
|
|
|
|
PCIe 2.0 x4 slot (x16 connector) |
0 |
1 |
1 |
1 |
|
|
|
|
|
PCIe 2.0 x1 slot |
0 |
1 [1] |
1 |
1 |
|
|
|
|
|
PCIe Mini Card 1.2 slot |
1 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
|
|
|
|
|
PCI 2.3 slot |
0 |
1 [1] |
1 |
3 |
|
|
|
|
|
SATA interface: |
|
|
|
|
SATA 3.0 |
2 |
2 |
2 |
2 |
SATA 2.0 |
0 |
1 |
1 |
2 |
eSATA [2] |
0 |
1 |
1 |
1 |
|
|
|
|
|
Notes:
[1]Low-profile slot.
[2]Operates as SATA 2.0 internally, SATA 1.0 as eSATA
2-4 |
www.hp.com |
Technical Reference Guide |
System Overview
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1066/1333 MHz |
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Ch A DDR3 |
||||
PCIe 2.0 |
|
|
|
|
|
Intel |
|
|
|
|
|
SDRAM |
x16 slot (PEG) [1] |
|
|
|
|
Display |
Mem. |
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
I/F |
Processor |
Cntlr. |
1066/1333 MHz |
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
MXM 3.0 [2] |
|
|
|
|
Ch B DDR3 |
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
SDRAM |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
FDI |
DMI |
Analog |
VGA |
|
|
|
USB 2.0 |
|
Monitor |
|
Graphics |
USB |
|
||
Digital |
DisplayPort |
Cntlr. |
(6 rear ports, 4 front ports, |
|||
|
I/F |
|
4 internal ports in CMT/MT/SFF, |
|||
|
|
|
||||
Monitor |
|
|
|
|
2 internal ports in USDT) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
SATA |
SATA |
|
LPC |
|
Serial I/F [3] |
Parallel I/F [4] |
Hard Drive |
|
|
|
SIO Controller |
||
Additional |
SATA |
SATA |
I/F |
|
||
|
|
|
||||
|
I/F [1] |
Q67 |
|
|
|
|
SATA |
|
Express |
|
Kybd-Mouse I/F |
||
Devices |
SATA/eSATA |
|
|
|
|
|
PCH-D0 |
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
||
Line In |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Line Out |
ALC261 |
|
|
|
Keyboard |
Mouse |
Phones Out |
Audio |
Audio I/F |
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|||
Subsystem |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Mic In |
|
|
LCI |
|
|
|
|
|
|
NIC |
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
PCI Cntlr. |
|
I/F |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
HP ProtectTools |
|
|
|
BIOS |
|
|
Embedded Security |
|
|
|
|
|
|
System board |
|
PCI 2.3 slot [5] |
|
|||
|
PCIe 2.0 x1 slot [4] |
|
||||
12 VDC [1] |
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
||
19.5 VDC [2] |
|
PCIe 2.0 x4 slot (x16 conn.) [4] |
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|||
Power Supply |
PCIe MiniCard Slot 1.2 [2] |
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|||
Notes:
[1]CMT, MT, SFF only
[2]USDT only
[3]2 in CMT, MT, and SFF
[4]1 in CMT, MT, and SFF only
[5]3 in CMT, 1 in MT and SFF
Figure 2-2. HP Compaq 8200 Elite Business PC Architecture, Block diagram
Technical Reference Guide |
www.hp.com |
2-5 |

System Overview
2.3.1 Intel Processor Support
The models covered in this guide can each support an Intel Celeron, Pentium, Core i3, Core i5, or Core i7 processor. These processors are backward-compatible with software written for earlier x86 microprocessors and include streaming SIMD extensions (SSE, SSE2, and SSE3) for enhancing 3D graphics and speech processing performance. Intel processors with vPro Technology include hardware-based tools that allow corporate IT organizations to remotely manage and protect systems.
The system board includes a zero-insertion-force (ZIF) H2 socket (LGA1155) designed for mounting an LGA1155-type processor package.
CAUTION: The CMT, MT, and SFF form factors can support a processor with a TPD rating of up to 95 watts. The USDT form factor can support a processor rated up to 65 watts. Exceeding these limits can result in system damage and loss of data.
These systems use processor sockets that support 2nd generation Intel Core i3, Core i5, and Core i7 processors and are not compatible with earlier generations of those processors.
The processor heatsink/fan assembly mounting differs between form factors. Always use the same assembly or one of the same type when replacing the processor. Refer to the applicable Maintenance & Service Guide for detailed removal and replacement procedures of the heatsink/fan assembly and the processor.
2.3.2Chipset
The Intel Q67 Express PCH-D0 is a single component that provides the following functions:
■PCI 2.3 bus controller
■PCIe bus controller
■LPC bus controller
■SMBus interface
■SATA interface
■HD audio interface
■RTC/CMOS function
■IRQ controller
■Serial Peripheral Device
■Power management logic
■USB 1.1/2.0 controllers supporting 14 ports
■Gigabit Ethernet controller
2-6 |
www.hp.com |
Technical Reference Guide |

System Overview
2.3.3 Support Components
Input/output functions not provided by the chipset are handled by other support components. Some of these components also provide “housekeeping” and various other functions as well. Table 2-3 shows the functions provided by the support components.
Table 2-3
Support Component Functions
Component Name |
Function |
|
|
Nuvoton SIO11 Controller |
Keyboard and pointing device I/F |
|
Serial I/F (COM1and COM2) [1] |
|
Parallel I/F (LPT1, LPT2, or LPT3) [2] |
|
PCI reset generation |
|
Interrupt (IRQ) serializer |
|
Power button and front panel LED logic |
|
GPIO ports |
|
Processor over temperature monitoring |
|
Fan control and monitoring |
|
Power supply voltage monitoring |
|
SMBus and Low Pin Count (LPC) bus I/F |
|
|
Intel 82579 LOM Network |
10/100/1000 Fast Ethernet network interface controller. |
Interface Controller |
|
|
|
ALC261 HD Audio Codec |
Audio mixer |
|
Two digital-to-analog stereo converters |
|
Two analog-to-digital stereo converters |
|
Analog I/O |
|
Supports stereo (two-channel) audio streams |
NOTE:
[1]COM2 requires external bracket/cable assembly.
[2]Requires external bracket/cable assembly.
2.3.4System Memory
These systems implement a dual-channel Double Data Rate (DDR3) memory architecture. All models support DDR3 1333-MHz (PC3-10600) and 1066-MHz (PC3-8500) memory modules. The CMT, MT, and SFF form factors provide four UDIMM sockets and support a maximum of 16 gigabytes of memory. The USDT form factor provides two SODIMM sockets and supports up to eight gigabytes of memory.
Technical Reference Guide |
www.hp.com |
2-7 |

System Overview
2.3.5 Mass Storage Accommodations
All models support at least two mass storage devices, with one being externally accessible for removable media. The storage device accommodations are as follows:
CMT: six bays total; three 5.25-inch externally accessible, three 3.5-inch internal
MT: five bays total; two 5.25-inch externally accessible, one 3.5-inch externally acessible, two 3.5-inch internal
SFF: three bays total; one 5.25-inch externally accessible, one 3.5-inch externally accessible, one 3.5-inch internal
USDT: two bays total; one 5.25-inch externally accessible (for slimline optical disk drive), one 2.5-inch internal
These systems may be preconfigured or upgraded with a SATA hard drive and one removable media drive such as a CD-ROM drive.
2.3.6 Legacy Input/Output Interfaces
PS/2 Port
All systems provide two PS/2 ports at the rear of the chassis for connection of a keyboard and mouse.
Serial port
The CMT, MT, and SFF form factors provide a serial port at the rear of the chassis and support a second serial port option. The serial interface is RS-232-C/16550-compatible and supports standard baud rates up to 115,200 as well as two high-speed baud rates of 230K and 460K.
Parallel port
The CMT, MT, and SFF form factors support a parallel port option.
2.3.7 Universal Serial Bus Interface
All models provide ten externally accessible Universal Serial Bus (USB) ports. Four ports are provided at the front of the unit, six ports are provided on the rear panel. Accessible through a header on the system board are two USB ports in the USDT form factor and four USB ports in the CMT, MT, and SFF form factors. These systems support a media card reader module that connects to the internal header. USB 1.1 and 2.0 functionality is available on all ports.
BIOS Setup allows for the disabling of USB ports individually or in groups. In order to secure the system against a physical attack, ports may be disabled even if there is nothing physically connected to them, such as the two front ports for the media card reader module when the module is not present.
2.3.8 Network Interface Controller
All models feature an Intel 82579 gigabit (GbE) Network Interface Controller (NIC) integrated on the system board. The controller provides automatic selection of 10BASE-T, 100BASE-TX, or 1000BASE-T operation with a local area network and includes power-down, wake-up, Alert-On-LAN (AOL), and AMT features. An RJ-45 connector with status LEDs is provided on the rear panel.
2-8 |
www.hp.com |
Technical Reference Guide |

System Overview
2.3.9 Graphics Subsystem
In the standard configuration, these systems use the integrated graphics controller (IGC) of the Intel processor. Intel Celeron, Pentium, Core i3, and most Core i5 and Core i7 processors feaure the HD Graphics 2000 IGC while select Core i5 and Core i7 processor feature the HD Graphics 3000 IGC.
The Intel HD Graphics 2000 uses six execution units providing high-performance 2D and casual 3D capabilities. The Intel HD Graphics 3000 uses 12 execution units providing high-performance 3D capabilities without the need for a separate graphics card.
All systems include a legacy analog video (VGA) connector and a DisplayPort connector and support dual monitor operation. The DisplayPort includes a multimode feature that allows a VGA, DVI, or HDMI adapter to be connected to the DisplayPort.
For upgrading the graphics controller, the CMT, MT, and SFF form factors provide a PCIe 2.0 x16 graphics slot while the USDT form factor provides an MXM 3.0 slot.
2.3.10 Audio Subsystem
These systems use the integrated High Definition audio controller of the chipset and the Realtek ADL261 High Definition audio codec. HD audio provides enhanced audio performance with higher sampling rates, refined signal interfaces, and audio processors with increased signal-to-noise ratio. The audio line input jack can be re-configured as a microphone input, and multi-streaming is supported. These systems include a 1.5-watt output amplifier driving an internal speaker, which can be muted with the F10 BIOS control. All models include a front panel accessible stereo microphone input jack (re-taskable as a Line-In input) and a headphone output audio jack.
2.3.11 HP ProtectTools Embedded Security
HP ProtectTools Embedded Security is a hardware/software solution providing file and folder encrypytion service that integrates with the operating system. The software component—the HP ProtectTools Embedded Security Manager (preinstalled), controls the basic operation of the hardware component—the Trusted Platform Module (TPM) security chip. These components are compliant with the Trusted Computing Group (TCG) security standards organization.
HP ProtectTools Embedded Security includes the following features:
■Enhanced Windows operating system files and folder encryption
■Enhanced email encryption—built-in authentication for Outlook, Outlook Express, Lotus Notes, Eudora
■Strengthens defense against hacking, system attacks, denial of service and network attacks
■“Embedded smart card” functionality
■Strengthens authentication with LANs, WANs.
■Works with/enhances third-party security solutions
HP ProtectTools Embedded Security Manager is acecssed through a Windows Control Panel applet. The management functions are accessible through established protocols such as DMI, SNMP, or WEBEM.
Technical Reference Guide |
www.hp.com |
2-9 |

System Overview
2.4 Specifications
This section includes the environmental, electrical, and physical specifications for the systems covered in this guide. Where provided, metric statistics are given in parenthesis. Specifications are subject to change without notice.
Table 2-4
Environmental Specifications (Factory Configuration)
Parameter |
Operating |
Non-operating |
Ambient Air Temperature 50o to 95o F (10o to 35o C, max. rate of change < 10 C/Hr)
-22o to 140o F (-30o to 60o C, max. rate of change < 20 C/Hr)
Shock (w/o damage) |
5 Gs [1] |
20 Gs [1] |
|
|
|
Vibration |
0.000215 G2/Hz, 10-300 Hz |
0.0005 G2/Hz, 10-500 Hz |
|
|
|
Humidity |
10-90% Rh @ 28o C max. |
5-95% Rh @ 38.7o C max. |
|
wet bulb temperature |
wet bulb temperature |
|
|
|
Maximum Altitude |
10,000 ft (3048 m) [2] |
30,000 ft (9144 m) [2] |
NOTE:
[1]Peak input acceleration during an 11 ms half-sine shock pulse.
[2]Maximum rate of change: 1500 ft/min.
|
Table 2-5 |
Power Supply Electrical Specifications |
|
|
|
Parameter |
Value |
|
|
Input Line Voltage: |
|
Nominal: |
100–240 VAC |
Maximum |
90–264 VAC |
|
|
Input Line Frequency Range: |
|
Nominal |
50–60 Hz |
Maximum |
47–63 Hz |
|
|
Maximum Continuous Power: |
|
USDT |
135 / 180 W |
SFF |
240 W |
MT |
320 W |
CMT |
320 W |
|
|
2-10 |
www.hp.com |
Technical Reference Guide |

System Overview
Table 2-6
Physical Specifications
Parameter |
USDT |
SFF [2] |
MT |
CMT [3] |
|
|
|
|
|
Height |
2.60 in |
3.95 in |
14.5 in |
17.63 in |
|
(6.60 cm) |
(10.03 cm) |
(36.8 cm) |
(44.8 cm) |
|
|
|
|
|
Width |
9.90 in |
13.3 in |
6.88 in |
7.0 in |
|
(25.15 cm) |
(33.78 cm) |
(17.5 cm) |
(17.8 cm) |
|
|
|
|
|
Depth |
10.0 in |
14.9 in |
16.31 in |
17.5 in |
|
(25.40 cm) |
(37.85 cm) |
(41.1) |
(44.5 cm) |
|
|
|
|
|
Weight [1] |
7.0 lb |
16.72 lb |
23.8 lb |
26.2 lb |
|
(3.18 kg) |
(7.6 kg) |
(10.8 kg |
(11.5 kg) |
NOTES:
[1]System configured with 1 hard drive, 1 optical media drive, and no PCI cards.
[2]Desktop (horizontal) configuration.
[3]Minitower configuration. For desktop configuration, swap Height and Width dimensions.
Technical Reference Guide |
www.hp.com |
2-11 |

System Overview
2-12 |
www.hp.com |
Technical Reference Guide |
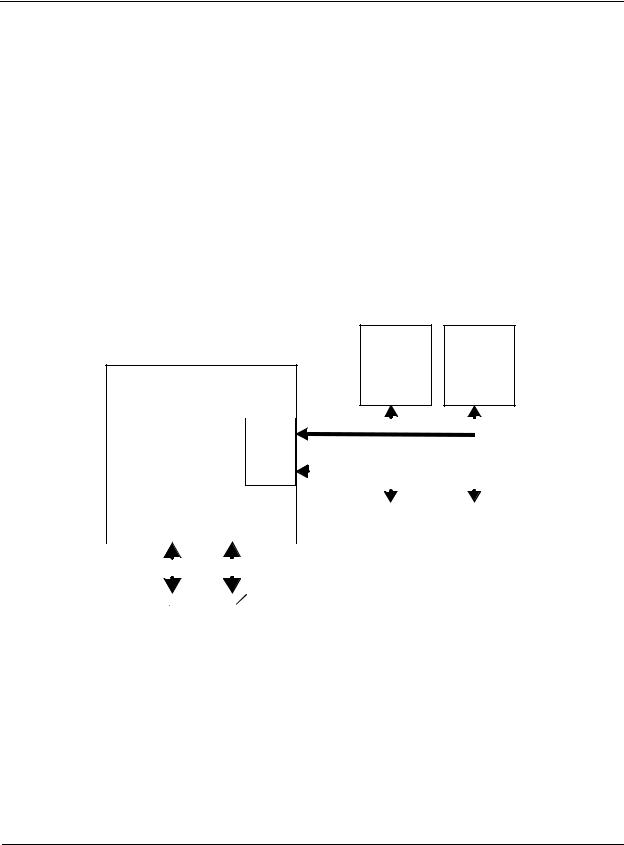
3
Processor/Memory Subsystem
3.1Introduction
This systems provide an LGA 1155 (H2) socket supporting an Intel Celeron, Pentium Dual-Core, Core i3, Core i5, or Core i7 processor. These processors include an integrated dual-channel DDR3 memory controller (Figure 3-1) and support PC3-8500 and PC3-10600 memory modules. This chapter describes the processor/memory subsystem.
XMM1 XMM2
DIMM
or DIMM [2] SODIMM [1]
Intel |
DDR3 |
|
Channel B |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
||
SDRAM |
|
Channel A |
|
|||
Processor |
|
|
||||
Cntlr |
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
DIMM |
|
DIMM [2] |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
or |
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
FDI |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
DMI |
|
|
SODIMM [1] |
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
XMM3 |
|
XMM4 |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
PCH |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
NOTES:
[1]USDT uses SODIMM sockets
[2]CMT, MT, and SFF only
Figure 3-1. Processor/Memory Subsystem Architecture
This chapter includes the following topics:
■Intel processor(3.2)
■Memory subsystem (3.3)
Technical Reference Guide |
www.hp.com |
3-1 |

Processor/Memory Subsystem
3.2Intel Processor
These systems support an Intel Celeron, Pentium Dual-Core, Core i3, Core i5, or Core i7 processor that mounts in a zero-insertion force LGA1155 (H2) socket.
3.2.1 Intel Processor Features
Table 3-1 provides the specifications of processors supported by these systems.
Table 3-1
Specifications of Supported Intel Processors
|
|
|
CPU |
L3 |
|
|
Intel |
|
# Cores / |
Clock Rate |
Cache |
Graphics |
|
Series |
Model |
Threads |
Base / Turbo |
Size |
Controller |
TDP |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Core i7 |
2600K |
4 / 8 |
3.4 / 3.8 GHz |
8 MB |
HD 3000 |
95 W |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2600 |
|
|
|
HD 2000 |
|
|
2600S |
|
2.8 / 3.8 GHz |
|
|
65 W |
Core i5 |
2500K |
4 / 4 |
3.3 / 3.7 GHz |
6 MB |
HD 3000 |
95 W |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2500 |
|
3.3 / 3.7 GHz |
|
HD 2000 |
|
|
2500S |
|
2.7 / 3.7 GHz |
|
|
65 W |
|
2500T |
|
2.3 / 3.3 GHz |
|
|
45 W |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2400 |
|
3.1 / 3.4 GHz |
|
|
95 W |
|
2400S |
|
2.5 / 3.3 GHz |
|
|
65 W |
|
2300 |
|
2.8 / 3.1 GHz |
|
|
95 W |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2390T |
2 / 4 |
2.7 / 3.5 GHz |
3 MB |
|
35 W |
Core i3 |
2120 |
2 / 4 |
3.3 / na GHz |
3 MB |
HD 2000 |
65 W |
|
2105 |
|
3.1 / na GHz |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2100 |
|
3.1 / na GHz |
|
|
|
|
2100T |
|
2.5 / na GHz |
|
|
35 W |
Pentium |
G850 |
2 / 2 |
2.9 / na GHz |
|
|
65 W |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
G840 |
|
2.8 / na GHz |
|
|
|
|
G620 |
|
2.6 / na GHz |
|
|
|
|
G620T |
|
2.2 / na GHz |
|
|
35 W |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
These processors include an integrated memory controller that supports 1333-MHz dual-channel DDR3 memory.
3-2 |
www.hp.com |
Technical Reference Guide |
 Loading...
Loading...